Mid-Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic volcanism and tectonic evolution of the Qilian Mountain
-
摘要:
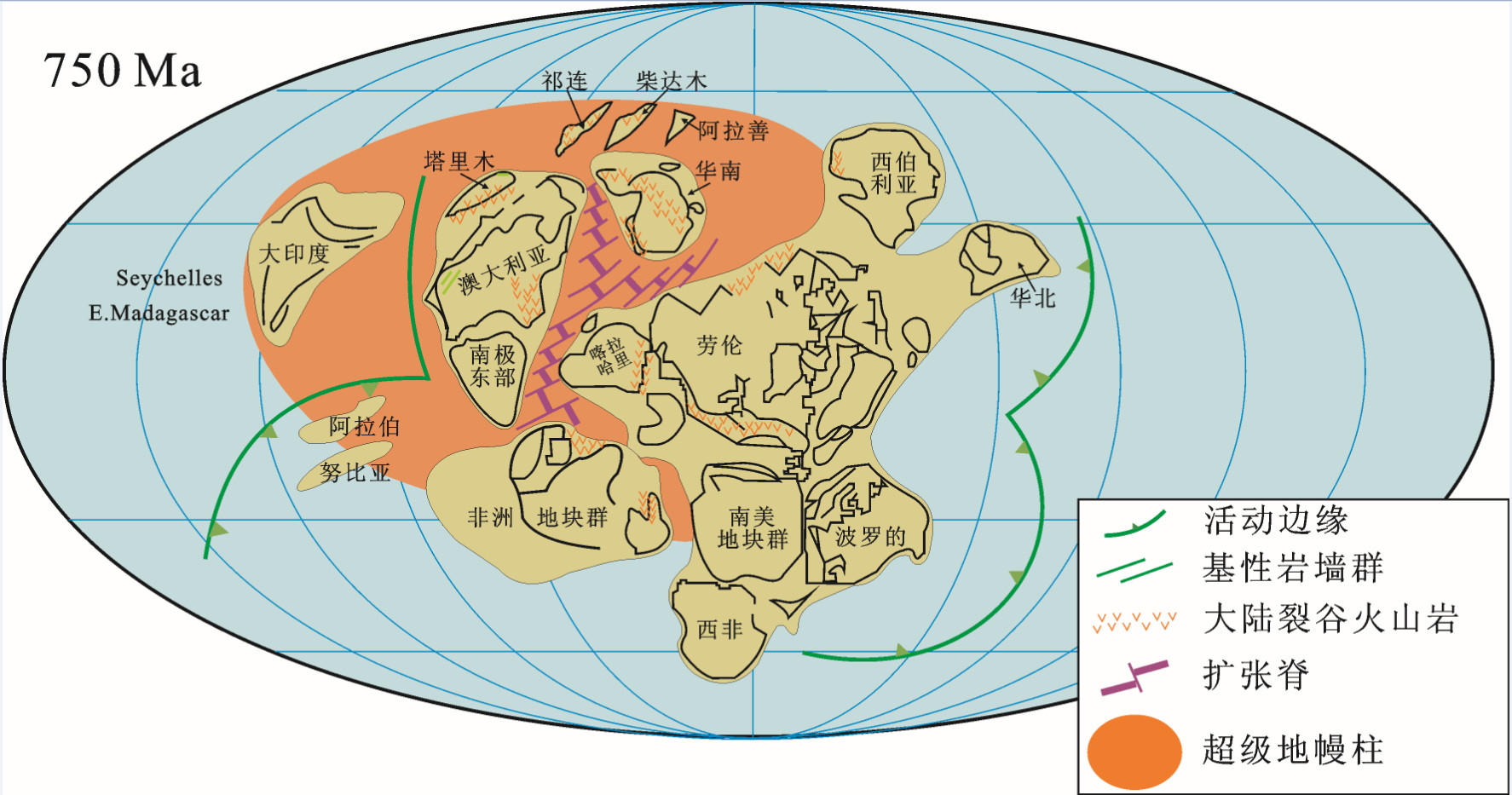
祁连山地区的新元古代中-晚期至早古生代火山作用显示系统地时、空变化,其乃是祁连山构造演化的火山响应。随着祁连山构造演化从Rodinia超大陆裂谷化-裂解,经早古生代大洋打开、扩张、洋壳俯冲和弧后伸展,直至洋盆闭合、弧-陆碰撞和陆-陆碰撞,火山作用也逐渐从裂谷和大陆溢流玄武质喷发,经大洋中脊型、岛弧和弧后盆地火山活动,转变为碰撞后裂谷式喷发。850~604 Ma的大陆裂谷和大陆溢流熔岩主要分布于祁连和柴达木陆块。从大约550 Ma至446 Ma,在北祁连和南祁连洋-沟-弧-盆系中广泛发育大洋中脊型、岛弧和弧后盆地型熔岩。与此同时,在祁连陆块中部,发育约522~442 Ma的陆内裂谷火山作用。早古生代洋盆于奥陶纪末(约446 Ma)闭合。随后,从约445 Ma至约428 Ma,于祁连陆块北缘发育碰撞后火山活动。此种时-空变异对形成祁连山的深部地球动力学过程提供了重要约束。该过程包括:(1)地幔柱或超级地幔柱上涌,导致Rodinia超大陆发生裂谷化、裂解、早古生代大洋打开、扩张、俯冲,并伴随岛弧形成;(2)俯冲的大洋板片回转,致使弧后伸展,进而形成弧后盆地;(3)洋盆闭合、板片断离,继而发生软流圈上涌,诱发碰撞后火山活动。晚志留世至早泥盆世(420~400 Ma),先期俯冲的地壳物质折返,发生强烈的造山活动。400 Ma后,山体垮塌、岩石圈伸展,相应发生碰撞后花岗质侵入活动。
Abstract:Mid-Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic volcanism in the Qilian Mountain area, which shows systematic variations in space and time, seems to have been the volcanic response to the tectonic evolution of the Qilian Mountain. The volcanism gradually changed from rift-related and continental flood basaltic through MORB-type and island-arc and back-arc to post collisional rift-related eruptions along with the tectonic evolution of the Qilian Mountain shifting from rifting and break up of Rodinia through opening and spreading of the Early Paleozoic oceans, subduction of the oceanic slabs and back-arc extension and ocean closure to arc-continent and continent-continent collision. The continental rift-related and flood lavas with ages of 850-604 Ma are distributed mainly on the Qilian and Qaidam Blocks. The widespread MORB-type and "island-arc-backarc"-type lavas were generated from about 550 to 446 Ma in both the North Qilian and the South Qilian ocean-trench-arc-basin systems. In the meantime, the intracontinental rift related volcanism occurred in the central Qilian Block between about 522 and 442 Ma. The Early Paleozoic oceanic basins were closed at the end of Ordovician (about 446 Ma). Subsequent post-collisional volcanism occurred on the northern margin of the Qilian Block from about 445 to 428 Ma. Such spatial-temporal variations provide important constraints on the geodynamic processes that evolved at the depth to form the Qilian Mountain. These processes involved (1) upwelling of mantle plumes or a mantle superplume and subsequent rifting and break-up of Rodinia and subsequent opening, spreading and subduction of Early Paleozoic oceans followed by island-arc formation, (2) roll-back of the subducted oceanic slabs followed by back-arc extension and back-arc basin formation, (3) ocean closure and slab break-off followed by upwelling of asthenosphere and post-collisional volcanism. Intensive orogenic activities occurred in the Late Silurian and Early Devonian (about 420 to about 400 Ma) in response to the exhumation of the subducted crustal materials. Mountain collapse and lithosphere extension happened and formed post-collisional granitic intrusions at < 400 Ma.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
锗(Ge)是一种典型的稀散元素,其地壳丰度为1.5×10-6,主要富集在煤和铅锌矿床中。统计结果显示,闪锌矿是铅锌矿床中Ge的主要载体矿物,但不同类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量存在差异。除热液脉型和浅成热液型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量较高(可达2500×10-6)外,其他主要类型(如喷流沉积型,SEDEX;火山块状硫化物型,VMS;密西西比河谷型,MVT,等)铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的平均含量通常 < 300×10-6。本次发现贵州贵定竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的显著超常富集现象,现报道如下。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
在细致深入的矿床学和矿物学研究基础上,利用激光剥蚀等离子质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)对竹林沟锌矿床主要金属矿物闪锌矿进行原位微量元素组成分析。统计闪锌矿中Ge等元素的富集特征,结合相关分析和以往研究成果,揭示竹林沟锌矿床中Ge的超常富集机制。
3. 研究结果(Results)
竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量为592×10-6~1100×10-6(平均764×10-6,表 1),锌矿石中Ge的平均品位97.9×10-6。闪锌矿LA-ICP-MS微区原位Ge含量分析资料显示,扬子板块及其周缘地区MVT铅锌矿床,如牛角塘、会泽、毛坪、富乐等,其闪锌矿中Ge的含量均 < 652×10-6,即便富乐矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量最高,但其平均含量也仅为191×10-6,明显比竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)低。
表 1 竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿部分元素含量(10-6)Table 1. The part elemental contents of sphalerite from the Zhulingou Zn deposit(10-6)
与世界上主要类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿LA-ICP-MS微区原位Ge含量分析资料相比,竹林沟矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量比SEDEX(Ge含量通常 < 50×10-6)、VMS(Ge含量多数 < 100×10-6)和MVT(Ge含量n×10-6~n×102×10-6,Ge平均含量 < 300×10-6)等闪锌矿中Ge的含量高出一个数量级。竹林沟矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量与法国Noailhac-Saint Salvy热液脉型Zn-Ge-Ag-Pb-Cd矿床(Ge平均含量750×10-6)和玻利维亚Porco浅成热液型Ag-Zn-Pb-Sn-Ge矿床(n×102×10-6~2500×10-6)等少数类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)相当。
可见,竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量比目前已知扬子板块及其周缘地区MVT矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)都高,且明显高出全球主要类型(除岩浆热液型和热液脉型外)铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)一个数量级,具有显著超常富集特征(接近Ge地壳丰度的1000倍)。
初步分析显示,竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Zn与Ga和Cd之间具有正相关关系;相反,Fe与Ga和Cd之间均具有负相关关系,这表明该矿床闪锌矿中Ga和Cd很可能不是直接替代Zn而是替代Fe,与笔者前期认识基本一致。然而,不难发现该矿床闪锌矿中Zn与Ge之间呈一定的负相关关系,但Fe和Ge之间则呈一定的正相关关系,进一步地Zn与Fe之间具有显著的负相关关系,且Zn与Fe+Ge之间负相关性更显著(图 1)。目前,闪锌矿中主要有六种Ge替代Zn的方式:(1)2Cu++Cu2++Ge4+↔4Zn2+;(2)Ge2+↔Zn2+;(3)2Ag++Ge4+↔3Zn2+;(4)2Cu++Ge4+↔3Zn2+;(5)□(晶体空位)+Ge4+↔2Zn2+;(6)nCu+Ge↔(n+1)Zn。可见,这六种替代方式均不能解释竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿Zn和Fe+Ge之间的强烈负相关关系。因此,笔者推测该矿床中Ge很可能是与Fe一起共同替代Zn进入闪锌矿晶格(Fe+Ge↔2Zn),是一种新的Ge替代方式。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中显著超常富集锗,锗的富集程度接近1000倍,且锗与铁一起共同替代锌进入闪锌矿晶格,是一种新的锗替代方式。初步估算竹林沟锌矿床锗金属储量超过400 t,而竹林沟锌矿床外围还有半边街等锌矿床,初步预测研究区锗资源量可能达到超大型规模(>1000 t),一个新的国家级乃至世界级锗资源基地曙光已现。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgments)
感谢科技部、国家自然科学基金委、云南省科技厅和云南大学对本项目的支持。
致谢: 审稿专家对论文提出了宝贵修改意见, 在此致以诚挚的谢意! -
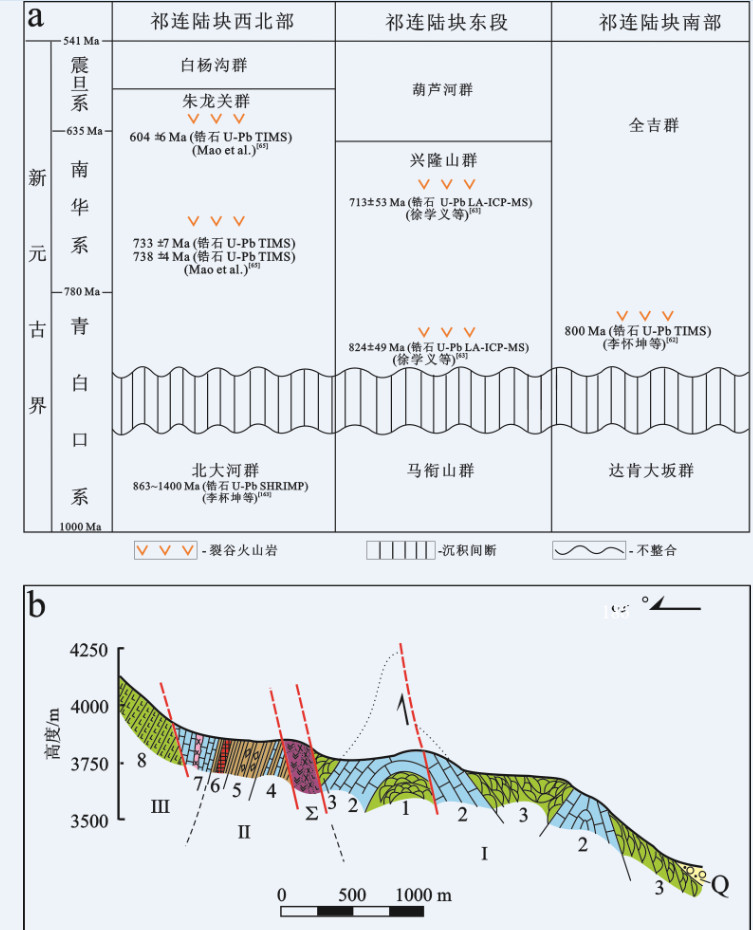
图 5 a—祁连山地区祁连陆块中新元古界地层划分和对比; b—肃南县熬油沟朱龙关群剖面(据文献[116]修编)
Ⅰ—龙关群下部岩系: 1—枕状辉石玄武岩; 2—含石英白云岩及白云岩; 3—枕状辉石玄武岩(有辉绿岩脉侵入); Ⅱ—朱龙关群中部岩系: 4—砂泥质板岩夹灰岩; 5—含砾(有火山岩砾)泥质板岩; 6—硅质板岩夹菱铁矿-赤铁矿层。Ⅲ―朱龙关群上部岩系: 7—含石英白云岩(有辉长岩脉侵入); 8—辉石玄武岩。Q—第四系; Ʃ—熬油沟蛇绿岩岩片(由被肢解的蛇纹岩、辉长岩、块状玄武岩和枕状玄武岩构成)
Figure 5. a-Stratigraphic division and correlation of Neoproterozoic strata in the Qilian Block from the Qilian Mountain; b-Geological section of the Zhulongguan Group from Aoyougou area of Sunan County (modified after reference [116])
Ⅰ-The lower part of the Zhulongguan Group: 1-Pillow pyroxene-basalt; 2-Quartz-bearing dolomite and dolomite; 3-Pillow pyroxene-basalt into which diabase veins intruded.Ⅱ-The middle part of the Zhulongguan Group: 4-Sand-argillaceous slate with limestone; 5-Gravel-bearing argillaceous slate (with gravels of volcanic rock); 6-Siliceous slate with siderite-hematite bed.Ⅲ-The upper part of the Zhulongguan Group: 7-Quartz-bearing dolomite into which gabbro veins intruded; 8-Pyroxene-basalt. Q-Quaternary sediments; Ʃ-Aoyougou ophiolite slice (consisting of dismembered serpentinite, gabbro, and massive and pillow-like basalts)
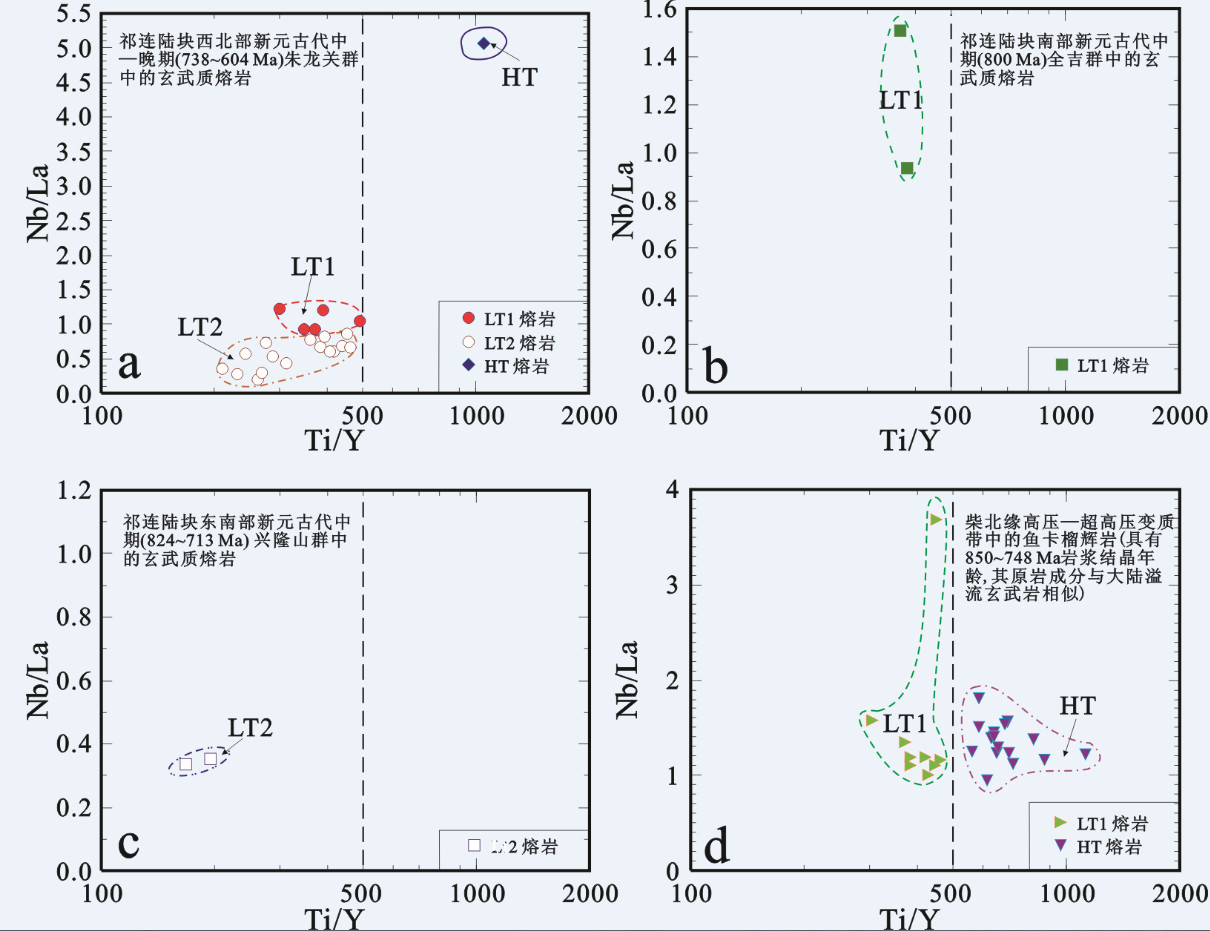
图 6 a—祁连陆块西北部朱龙关群玄武质熔岩, b—祁连陆块南部全吉群玄武质熔岩, c—祁连陆块东部兴隆山群玄武质熔岩和d—柴达木陆块北缘高压—超高压变质带中鱼卡榴辉岩(原岩与大陆溢流玄武岩相似)的Ti/Y–Nb/La分类图解(数据来源: (a): [19, 69, 116]; (b): [62]; (c): [63]; (d): [46, 51])
Figure 6. Classification of Mid-Late Neoproterozoic rift-related basaltic lavas of a-Zhulongguan Group in the northwestern Qilian Block, b-Quanji Group in the southern Qilian Block, c-Xinglongshan Group in the southeastern Qilian Block, and d-Yuka eclogites (protoliths similar to continental flood basalts) in the HPM-UHPM belt from northern margin of the Qaidam Block in terms of Ti/Y versus Nb/La (Data sources: (a): [19, 69, 116]; (b): [62]; (c): [63]; (d): [46, 51])
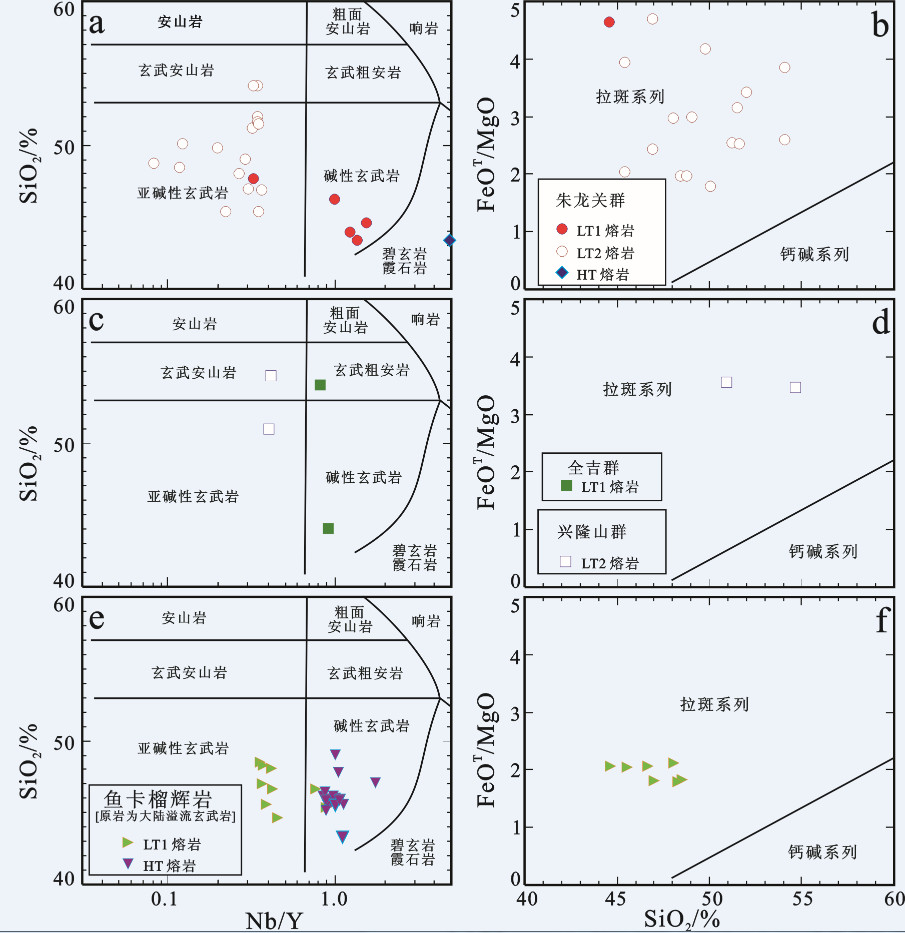
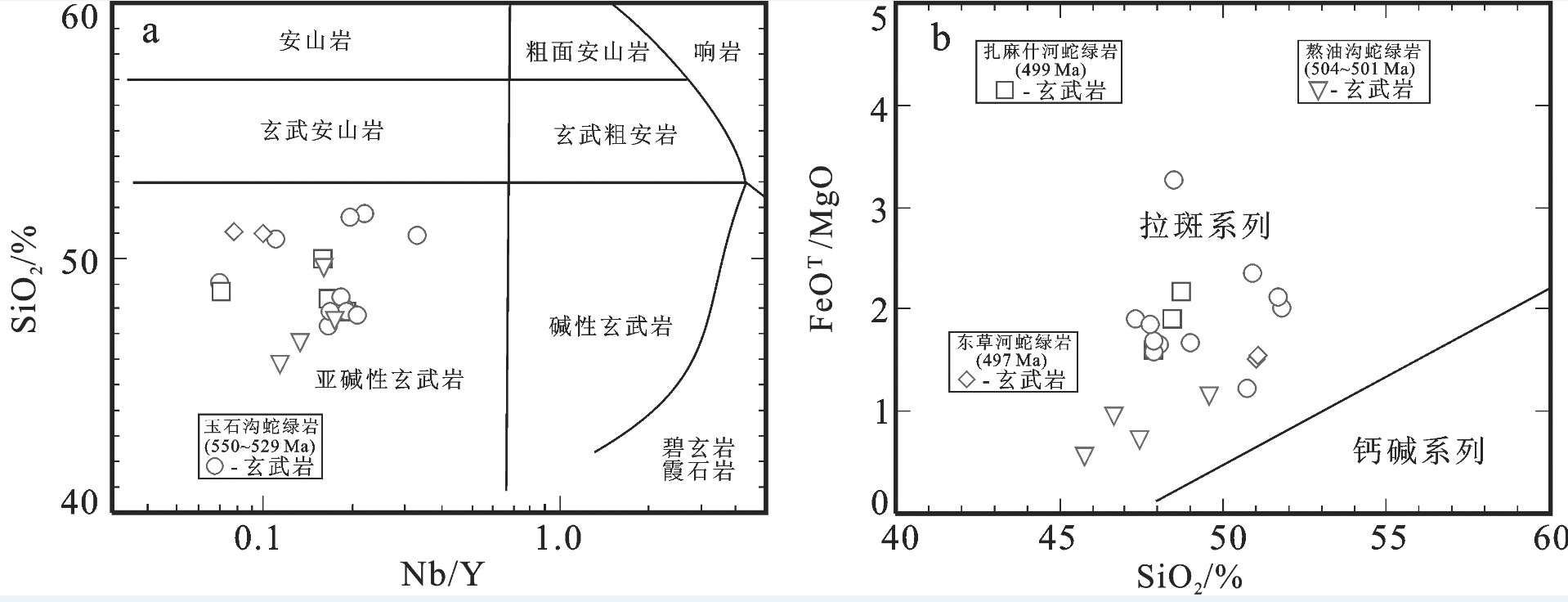
图 7 祁连山新元古代中—晚期裂谷玄武质熔岩a, c, e—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(据[154])和b, d, f—FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(据[155])
图 7‒b, d, f分别适用于图 7‒a, c, e中的亚碱性火山岩;数据来源同图 6
Figure 7. a, c, e-SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagrams (after reference [154]) and b, d, f-FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagrams (after freference [155]) for Mid-Late Neoproterozoic rift-related basaltic lavas from the Qilian Mountain
Fig. 7‒b, d, f show the sub-alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig. 7‒a, c, e respectively; Data sources as for Fig. 6
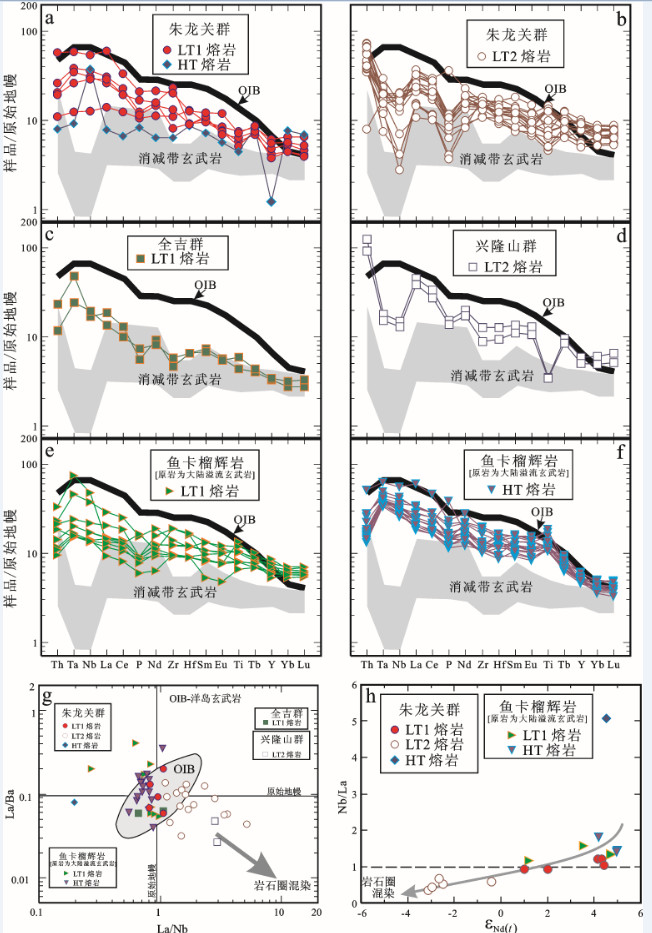
图 8 a, b—祁连陆块西北部朱龙关群, c—祁连陆块南部全吉群, d—祁连陆块南部兴龙山群新元古代中晚期玄武质熔岩, e, f—柴达木陆块北缘高压-超高压变质带中鱼卡榴辉岩(原岩与大陆溢流玄武岩相似)的不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图; g—朱龙关群、全吉群、兴龙山群新元古代中晚期裂谷玄武质熔岩和鱼卡榴辉岩(原岩与大陆溢流玄武岩相似)的La/ Ba-La/Nb图解; h—朱龙关群新元古代中晚期裂谷玄武质熔岩和鱼卡榴辉岩(原岩与大陆溢流玄武岩相似)的Nb/La-ɛNd(t)图解
图 8-a~f中, 洋岛玄武岩(OIB)据[156]; 图中阴影区表示消减带玄武岩的成分范围, 其上限和下限分别由高-K玄武岩和低-K玄武岩的平均值(据[157])限定; 图 8-g中, 岩石圈混染效应导致成分点向高La/Nb和低La/Ba方向迁移; 洋岛玄武岩(OIB)的成分范围据[158, 159]数据来源同图 6
Figure 8. Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace-element spider diagrams for Mid-Late Neoproterozoic basaltic lavas of a, b-Zhulongguan Group in the northwestern Qilian Block, c-Quanji Group in the southern Qilian Block, d-Xinglongshan Group in the southeastern Qilian Block, and e, f-Yuka eclogites (protoliths similar to continental flood basalts) in the HPM-UHPM belt from northern margin of the Qaidam Block; g-La/Ba versus La/Nb plots for Mid-Late Neoproterozoic rift-related basaltic lavas of Zhulongguan Group, Quanji Group, Xinglongshan Group and Yuka eclogites (protoliths similar to continental flood basalts); h-Nb/La versus ɛNd(t) diagram for Mid-Late Neoproterozoic rift-related basaltic lavas of Zhulongguan Group and Yuka eclogites (protoliths similar to continental flood basalts)
In Fig. 8-a-f, patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB) are from [156]. The shaded area shows the range for subduction-zone basalts, with the lower and upper limits being defined by"average"low-K and high-K basalts, respectively (after [157]). In Fig. 8-g, the dispersion to higher La/ Nb and lower La/Ba may represent the effects of lithospheric contamination. Field for oceanic island basalts (OIB) after reference [158, 159]; data sources as for Fig. 6
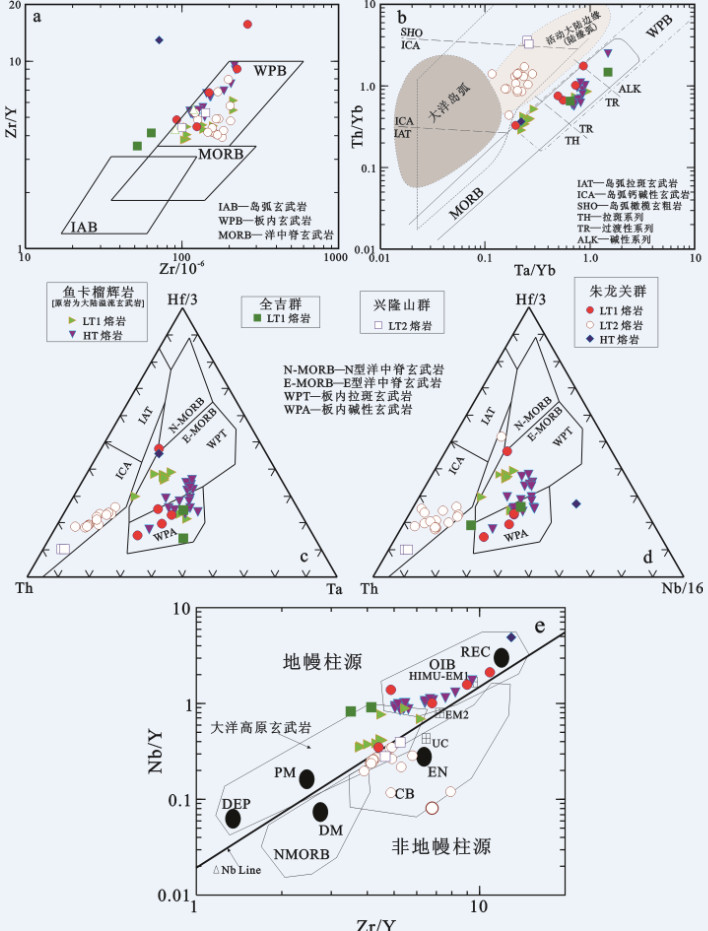
图 9 祁连山新元古代中—晚期裂谷玄武质熔岩形成的构造环境判别图解a—Zr/Y-Zr图解(据[160]); b—Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图解(据[161]); c—Hf/3‒Th‒Ta图解(据[162]); d—Hf/3‒Th‒Nb/16图解(据[162]); e—祁连山新元古代中-晚期裂谷玄武质熔岩的Zr/Y-Nb/Y图解(据[167])
缩写符: UC—上部陆壳; CB—受到大陆壳或/和大陆岩石圈混染的大陆玄武岩; PM—原始地幔; DM—浅部亏损地幔; HIMU—高-µ(U/Pb)源; EM1和EM2富集地幔源; OIB—洋岛玄武岩; DEP—深部亏损地幔; EN—富集组分; REC—再循环组分数据来源同图 6
Figure 9. Tectonic setting of Mid-Late Neoproterozoic rift-related basaltic lavas from the Qilian Mountain a-Zr/Y versus Zr diagram (after [160]); b-Th/Yb versus Ta/Yb diagram (after [161]); c-Hf/3‒Th‒Ta diagram (after [162]); d-Hf/3‒Th‒Nb/16 diagram (after reference [162]); e-Zr/Y versus Nb/Y diagram (after reference [167]) for Mid-Late Neoproterozoic riftrelated basaltic lavas from the Qilian Mountain
Abbreviations: UC-Upper continental crust; CB-Contaminated (by continental crust or/and subcontinental lithosphere) basalts; PM-Primitive mantle; DM-Shallow depleted mantle; HIMU-High-µ(U/Pb) source; EM1 and EM2-Enriched mantle sources; OIB-Oceanic island basalt; DEP-Deep depleted mantle; EN-Enriched component; REC-Recycled component Data sources as for Fig. 6
图 11 北祁连山仰冲的新元古代晚期—寒武纪洋壳(蛇绿岩)残片中玄武岩的a—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(据[154])和b—FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(据[155])
图 11-b适用于图 11-a中的亚碱性火山岩;数据来源: [14, 16-18, 66, 67, 69, 70, 81]
Figure 11. a−SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagrams (after reference [154]) and b−FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagrams (after reference [155]) for basalts in the obducted slices of Late Neoproterozoic−Cambrian ocean−crust (ophiolites) from the North Qilian Mountain
Fig. 11-b shows the sub−alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig. 11-a; Data sources: [14, 16-18, 66, 67, 69, 70, 81]
图 12 北祁连山仰冲的新元古代晚期—寒武纪洋壳(蛇绿岩)残片中玄武岩的不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图
洋岛玄武岩(OIB)、E型洋脊玄武岩(E−MORB)和N型洋脊玄武岩(N−MORB)据[156]数据来源同图 11
Figure 12. Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace−element spider diagrams for basalts in the obducted slices of Late Neoproterozoic−Cambrian ocean−crust (ophiolites) from the North Qilian Mountain
Patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB), E−type mid−ocean ridge basalts (E−MORB) and N−type mid−ocean ridge basalts (N−MORB) after reference [156] Data sources as for Fig. 11
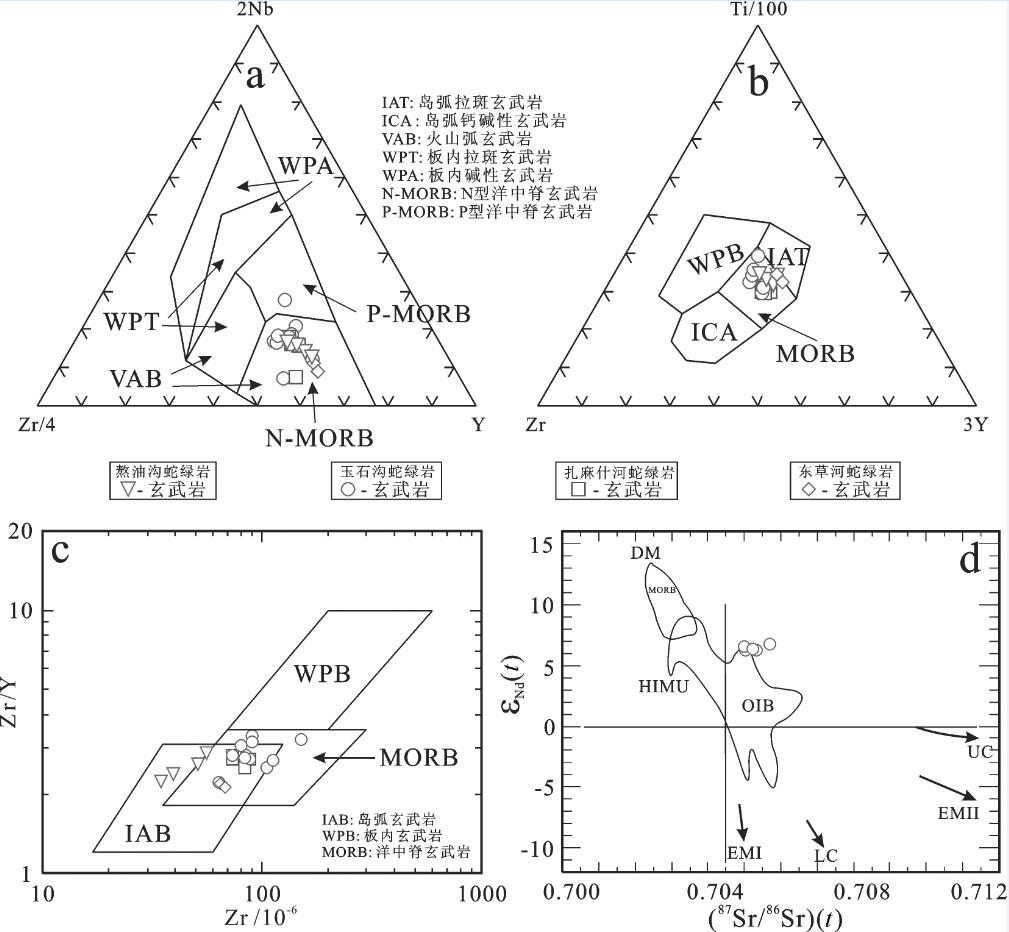
图 13 北祁连山仰冲的新元古代晚期—寒武纪洋壳(蛇绿岩)残片中玄武岩的构造环境判别图解
a—2Nb−Zr/4−Y图解(据[183]); b—Ti/100‒Zr‒3Y图解(据[184]); c—Zr/Y-Zr图解(据[160]); d—玉石沟蛇绿岩中玄武岩的εNd(t)-87Sr/86Sr(t)图解(据[185]) UC—上地壳; LC—下地壳; EMⅠ和EMⅡ—富集地幔源Ⅰ和Ⅱ; HIMU—高μ地幔源; DM—亏损地幔源数据来源同图 11
Figure 13. Tectonic setting of basalts in the obducted slices of Late Neoproterozoic−Cambrian ocean−crust (ophiolites) from the North Qilian Mountain
a−2Nb−Zr/4−Y diagram (after reference [183]); b−Ti/100−Zr−3Y diagram (after reference [184]); c−Zr/Y vesus Zr diagram (after reference [160]); d−εNd(t) versus 87Sr/86Sr(t) diagram for the basalts in the Yushigou ophiolite (after reference [185]) UC-Upper crust; LC−Lower crust; EMⅠand EMⅡ-Enriched mantleⅠandⅡsources; HIMU-High−µmantle source; DM−Depleted mantle source Data sources as for Fig. 11
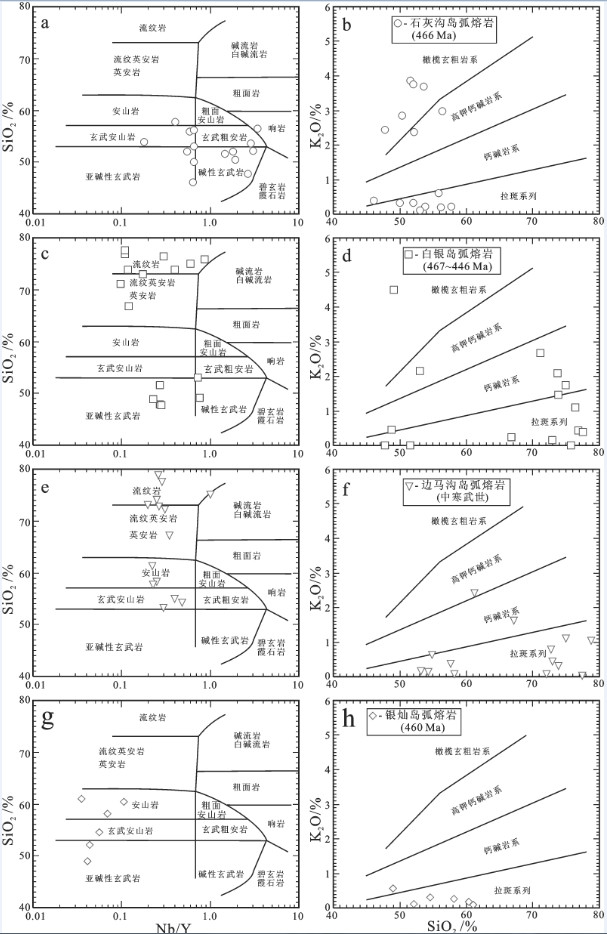
图 14 北祁连山中寒武世—奥陶纪弧火山岩的a, c, e, g—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(据[154])和b, d, f, h—K2O-SiO2图解(据[190])数据来源: (a, b): [13, 14, 16, 17, 20]; (c, d): [14, 16, 17, 72]; (e, f); [19, 20, 191]; (g, h): [76]
Figure 14. a, c, e, g−SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagrams (after reference [154]) and b, d, f, h−K2O versus SiO2 diagrams (after reference [190]) for Middle Cambrian-Ordovician arc−related volcanic rocks from the North Qilian Mountain Data sources: (a, b): [13, 14, 16, 17, 20]; (c, d): [14, 16, 17, 72]; (e, f): [19, 20, 191; (g, h): [76]
图 15 北祁连山中寒武世—奥陶纪弧火山岩的a, c, e, g—不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图和b, d, f, h—Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图解(据[161])
图中阴影区表示弧亚碱性玄武岩的成分范围, 其下限和上限分别由低‒K玄武岩和高‒K玄武岩的平均值(据[157])限定数据来源同图 14
Figure 15. a, c, e, g−Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace−element spider diagrams and b, d, f, h−Th/ Yb versus Ta/Yb diagrams (after reference [161]) for Middle Cambrian−Ordovician arc−related volcanic rocks from the North Qilian Mountain
The shaded area shows the range for arc sub−alkaline basalts, with the lower and upper limits being defined by"average"low−K and high−K basalts, respectively (after reference [157]) Data sources as for Fig. 14
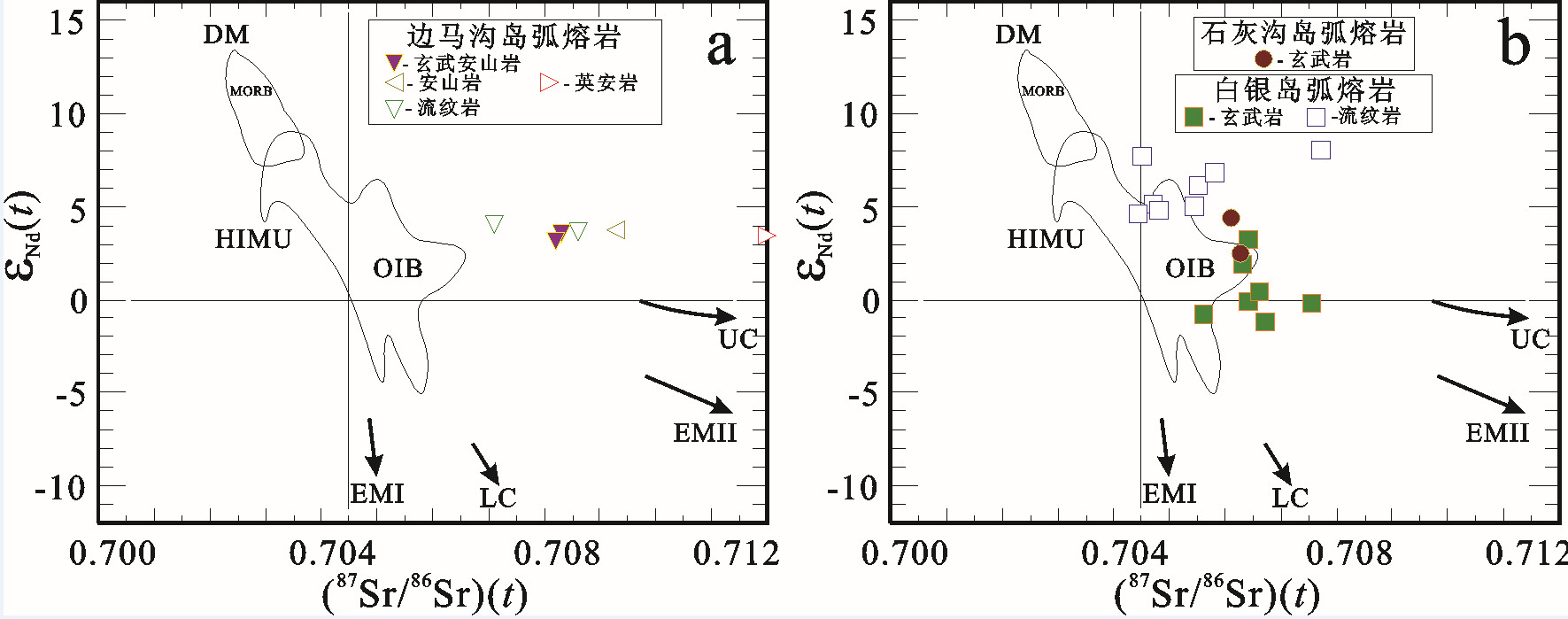
图 16 a, b—北祁连山中寒武世—奥陶纪弧火山岩的εNd(t)-87Sr/86Sr(t)图解(据[185])
UC—上地壳; LC—下地壳; EMⅠ和EMⅡ—富集地幔源Ⅰ和Ⅱ; HIMU—高μ地幔源; DM—亏损地幔源数据来源同图 14
Figure 16. a, b−Plots ofεNd(t) versus 87Sr/86Sr(t) for Middle Cambrian−Ordovician arc−related volcanic rocks from the North Qilian Mountain (diagram after [185])
UC-Upper crust; LC−Lower crust; EMⅠand EMⅡ-Enriched mantleⅠandⅡsources; HIMU-High−μmantle source; DM−Depleted mantle source Data sources as for Fig. 14
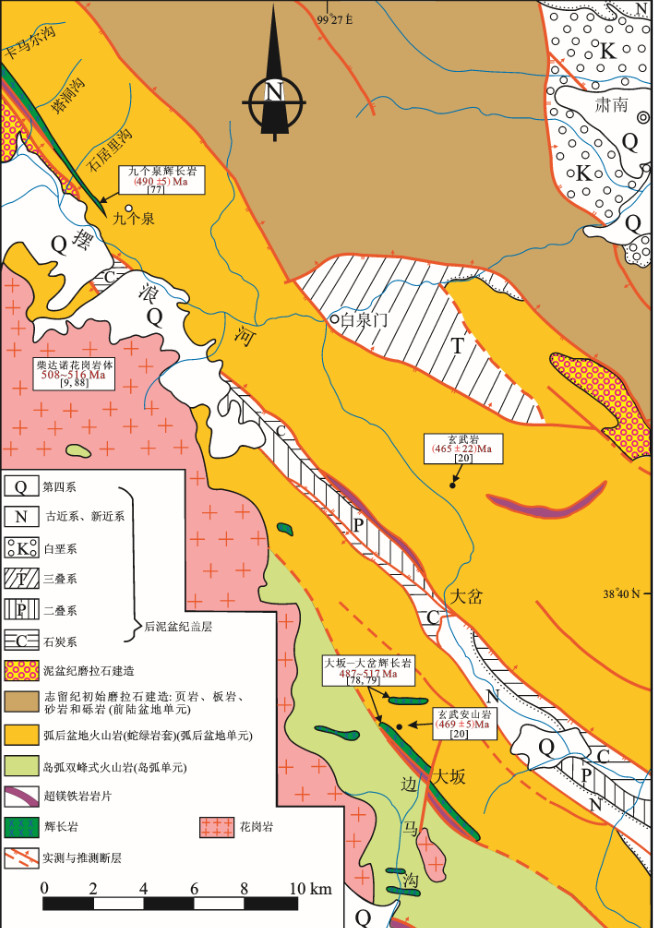
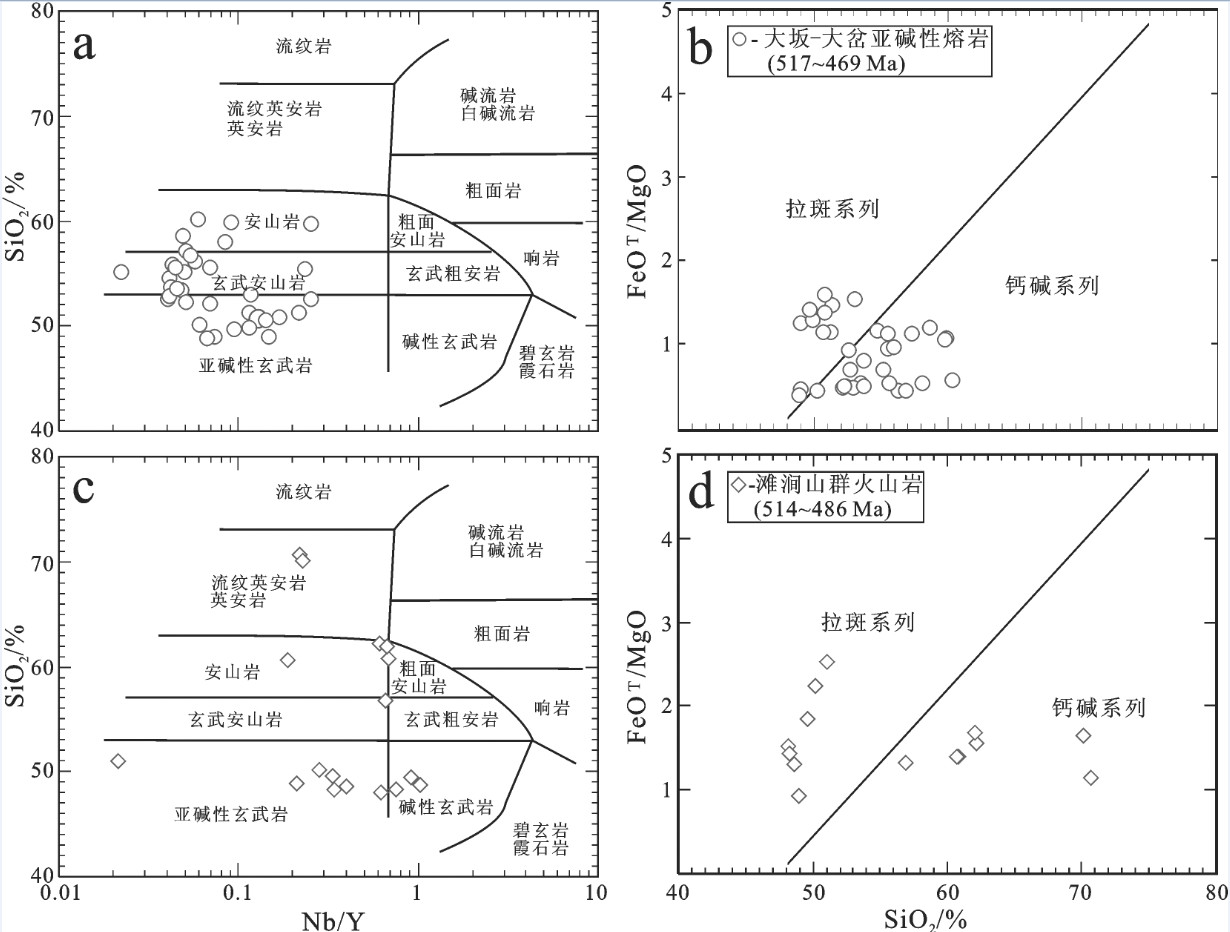
图 18 a, b—北祁连山大坂—大岔地区火山岩(517~469 Ma)和c, d—柴北缘滩涧山群火山岩(514~486 Ma)的SiO2-Nb/Y图解(图解据[154])和FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(图解据[155])
图b, d分别适用于图a, c中的亚碱性火山岩; 数据来源: (a, b): [16-19, 78, 79, 192]; (c, d): [57, 58]
Figure 18. SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagrams (after reference [154]) and FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagrams (after reference [155]) for a, b−Volcanic rocks (517-469 Ma) in the Daban−Dacha area of the North Qilian Mountain and c, d−Tanjianshan Group volcanic rocks (514-486 Ma) from the North Qaidam
Fig. 18−b, d show the sub−alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig 18−a, c; Data sources: (a, b): [16-19, 78, 79, 192]; (c, d): [57, 58]
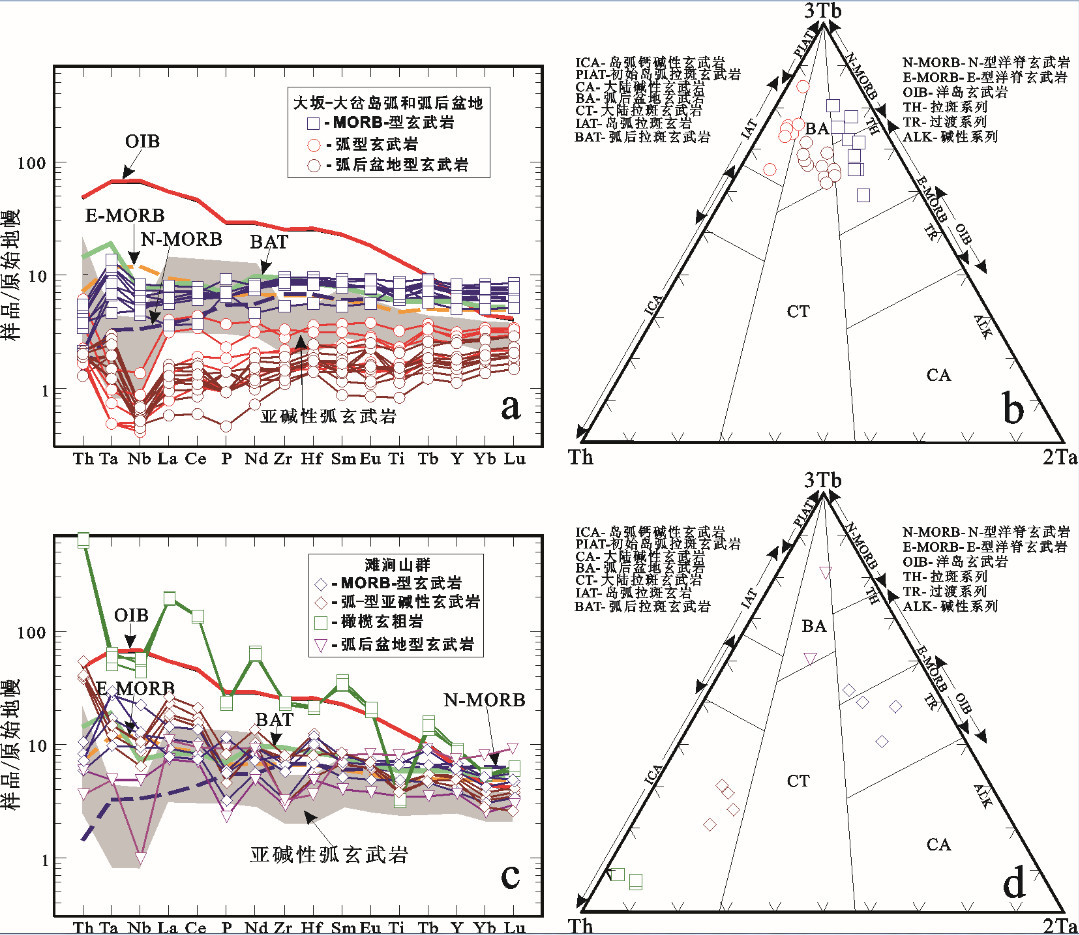
图 19 北祁连山大坂—大岔地区火山岩(517~469 Ma)和柴北缘滩涧山群火山岩(514~486 Ma)的a, c—不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图和b, d—3Tb-Th-2Ta图解(据[193])
洋岛玄武岩(OIB)、E型洋脊玄武岩(E-MORB)和N型洋脊玄武岩(N-MORB)据[156]; 弧后拉斑玄武岩(BAT)据[194]数据来源同图 18
Figure 19. a, c-Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace-element spider diagrams and b, d-3Tb-Th-2Ta diagrams (after reference [193]) for the volcanic rocks (517~469 Ma) in the Daban-Dacha area of the North Qilian Mountain and the Tanjianshan Group volcanic rocks (514~486 Ma) from the North Qaidam
Patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB), E-type mid-ocean ridge basalts (E-MORB) and N-type mid-ocean ridge basalts (N-MORB) after reference [156]. Patterns for back-arc tholeiites (BAT) after reference [194] Data sources as for Fig. 18
图 20 北祁连山弧后盆地火山岩(490~449 Ma)的a, c, e—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(图解据[154])和b, d, f—FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(图解据[155])
图b, d, f分别适用于图a, c, e中的亚碱性火山岩; 数据来源: (a, b): [16-20, 77, 191]; (c, d): [16-20, 195]; (e, f): [16-18]
Figure 20. a, c, e-SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagrams (after Winchester and Floyd, 1977) and b, d, f-FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagrams (after Miyashiro, 1975) for the volcanic rocks (490-449 Ma) in the back-arc basins from the North Qilian Mountain
b, d, f show the sub-alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig. 20 a, c, e Data sources: (a, b): [16-20, 77, 191]; (c, d): [16-20, 195]; (e, f): [16-18]
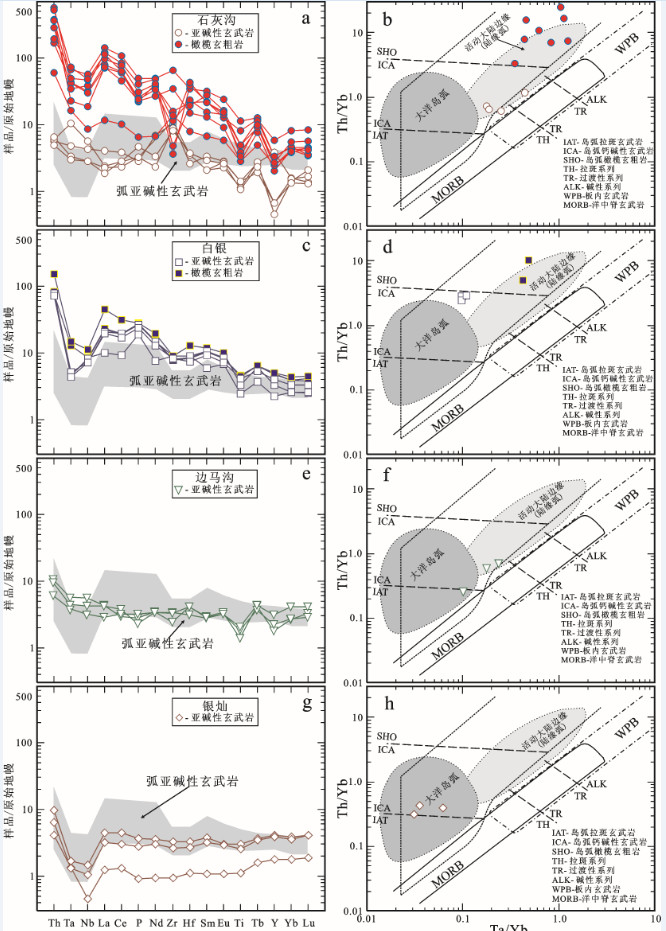
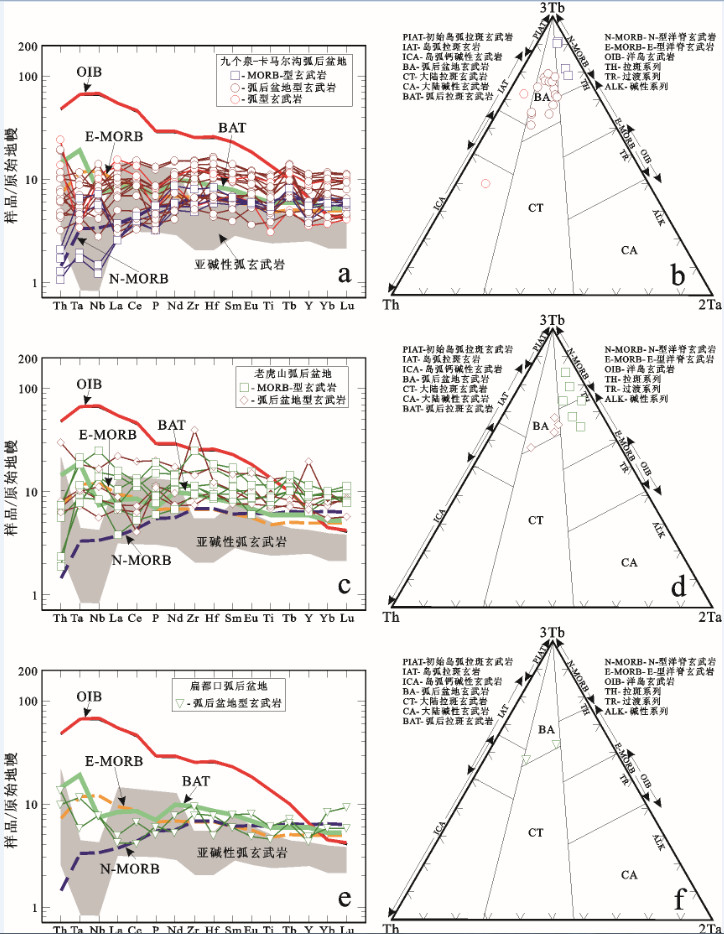
图 21 北祁连山弧后盆地玄武质熔岩(490~449 Ma)的a, c, e—不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图和b, d, f—3Tb−Th−2Ta图解(据[193])
洋岛玄武岩(OIB)、E型洋脊玄武岩(E−MORB)和N型洋脊玄武岩(N−MORB)据[156]; 弧后拉斑玄武岩(BAT)据[194]数据来源同图 20
Figure 21. a, c, e−Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace−element spider diagrams and b, d, f−3Tb−Th−2Ta diagrams (after reference [193]) for the basaltic lavas (490−449 Ma) in the Back−arc basins from the North Qilian Mountain
Patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB), E−type mid−ocean ridge basalts (E−MORB) and N−type mid−ocean ridge basalts (N−MORB) after reference [156]. Patterns for back−arc tholeiites (BAT) after reference [194] Data sources as for Fig. 20
图 22 北祁连山大坂—大岔地区玻安岩的a—MgO-SiO2图解, b—TiO2−SiO2图解, c—Ni−Cr图解和d—REE球粒陨石(据[201])标准化蛛网图; e和f—老虎山和九个泉—卡马尔沟弧后盆地中玄武岩的εNd(t)-87Sr/86Sr(t)图解, 图解据[185]
北祁连山大坂—大岔地区玻安岩的a—MgO-SiO2图解, b—TiO2−SiO2图解, c—Ni−Cr图解和d—REE球粒陨石(据[201])标准化蛛网图; e和f—老虎山和九个泉—卡马尔沟弧后盆地中玄武岩的εNd(t)-87Sr/86Sr(t)图解, 图解据[185]
Figure 22. a−MgO versus SiO2 diagram, b−TiO2 versus SiO2 diagram, c−Ni versus Cr diagram and d−Chondrite (after reference [201]) normalized spider diagram for the boninites in the Daban−Dacha area from the North Qilian Mountain; e and f−Plots ofεNd(t) versus 87Sr/86Sr(t) for the basalts in the Laohushan and the Jiugequan−Kamargou back−arc basins (diagrams after [185])
UC-Upper crust; LC−Lower crust; EMⅠand EMⅡ-Enriched mantleⅠandⅡsources; HIMU-High−µmantle source; DM−Depleted mantle source Data sources as for Fig. 18 and Fig. 20
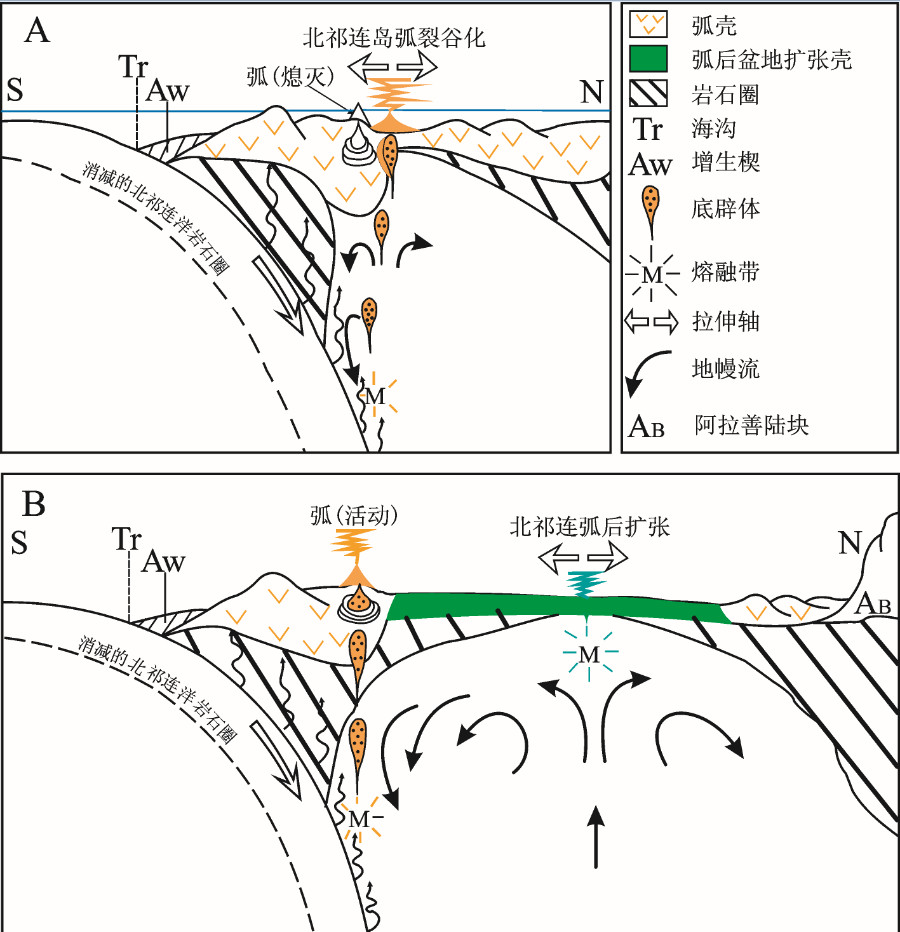
图 23 北祁连山弧后盆地构造演化示意图(显示地幔对流方式和熔体产生过程的变化, 据[20]修编)
A—早期的岛弧裂谷化没有扰乱地幔中岛弧岩浆生成的正常过程, 悬浮的底辟体克服周围地幔由于消减板片俯冲引起的下沉而上升, 产生岛弧熔体, 这些熔体从岛弧转向附近的裂谷区; B—弧后海底扩张体制的建立反映弧后盆地扩张脊之下地幔的上隆, 从而导致近于绝热状态的柱状地幔发生减压熔融, 这一过程和正常洋中脊处发生的作用相似。随着底辟体克服周围下沉的地幔流上升, 继续产生岛弧岩浆, 但是, 此时弧后拉伸轴已与岛弧火山前峰分离, 从而发育正常岩浆弧
Figure 23. Schematic representation of tectonics showing changing patterns of mantle convection and processes of melt generation associated with the evolving back-arc basin now preserved in the North Qilian Mountain (modified after reference [20])
A-Early island-arc rifting did not disturb normal processes of arc magmagenesis in the mantle. Arc melts resulted from the rise of buoyant diapirs at a rate that allowed these to overcome the ambient mantle down flow induced by the subducting slab. These melts were diverted from the arc to the nearby rift axis; B-Establishment of a seafloor-spreading regime reflects establishment of a zone of mantle upwelling beneath the spreading ridge in the back-arc basin, resulting in decompression melting of a nearly adiabatic mantle column indistinguishable from that of normal mid-ocean ridges. Arc magmas continued to be generated and to diapirically ascend against ambient downward mantle flow, but the separation of the extension axis and the arc volcanic front allowed development of a normal magmatic arc
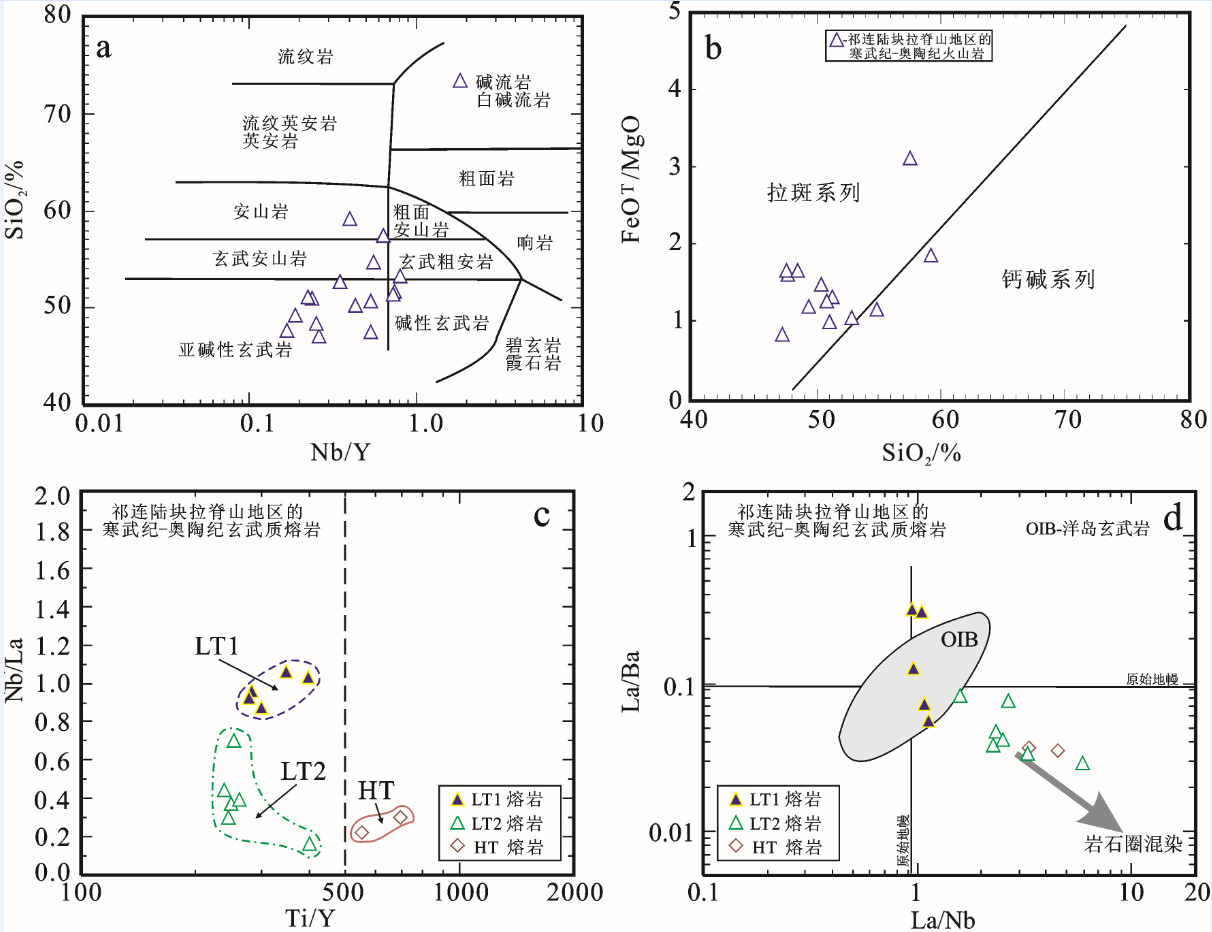
图 24 祁连陆块拉脊山地区寒武纪—奥陶纪火山岩的a—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(图解据[154])和b—FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(图解据[155]); 祁连陆块拉脊山地区寒武纪-奥陶纪玄武质熔岩的c—Nb/La-Ti/Y图解和d—La/Ba-La/Nb图解
图 24‒b适用于图 24‒a中的亚碱性火山岩数据来源: [14, 206]
Figure 24. a-SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagram (after reference [154]) and b-FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagram (after reference [155]) for Cambrian to Ordovician volcanic rocks in the Lajishan area of the Qilian Block; c-Nb/La versus Ti/Y diagram and d-La/Ba versus La/Nb diagram for Cambrian to Ordovician basaltic lavas in the Lajishan area of the Qilian Block
Fig. 24 b shows the sub-alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig. 24-a Data sources: references [14, 206]
图 25 a, b—连陆块拉脊山地区寒武纪—奥陶纪玄武质熔岩的不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图; 祁连陆块拉脊山地区寒武纪—奥陶纪裂谷玄武质熔岩形成的构造环境判别图解: c—Zr/Y-Zr diagram (图解据[160]); d—Ce/Yb-Ta/ Yb图解(图解据[161]); e—3Tb‒Th‒2Ta图解(图解据[193])
图 25-a, b中, 洋岛玄武岩(OIB)据[156]; 图中阴影区表示消减带玄武岩的成分范围, 其上限和下限分别由高-K玄武岩和低-K玄武岩的平均值(据[157])限定数据来源同图 24
Figure 25. a, b-Primitive mantle (after reference [156]) normalized incompatible trace-element spider diagrams for Cambrian to Ordovician basaltic lavas in the Lajishan area of the Qilian Block. Tectonic setting of Cambrian to Ordovician rift-related basaltic lavas in the Lajishan area of the Qilian Block. c-Zr/Y versus Zr diagram (after reference [160]); d-Ce/Yb versus Ta/Yb diagram (after reference [161]); e-3Tb‒Th‒2Ta diagram (after reference [193])
In Fig. 25-a, b, the patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB) are after reference [156]; the shaded area shows the range for subduction-zone basalts, with the lower and upper limits being defined by"average"low-K and high-K basalts, respectively (after reference [193]) Data sources as for Fig. 24
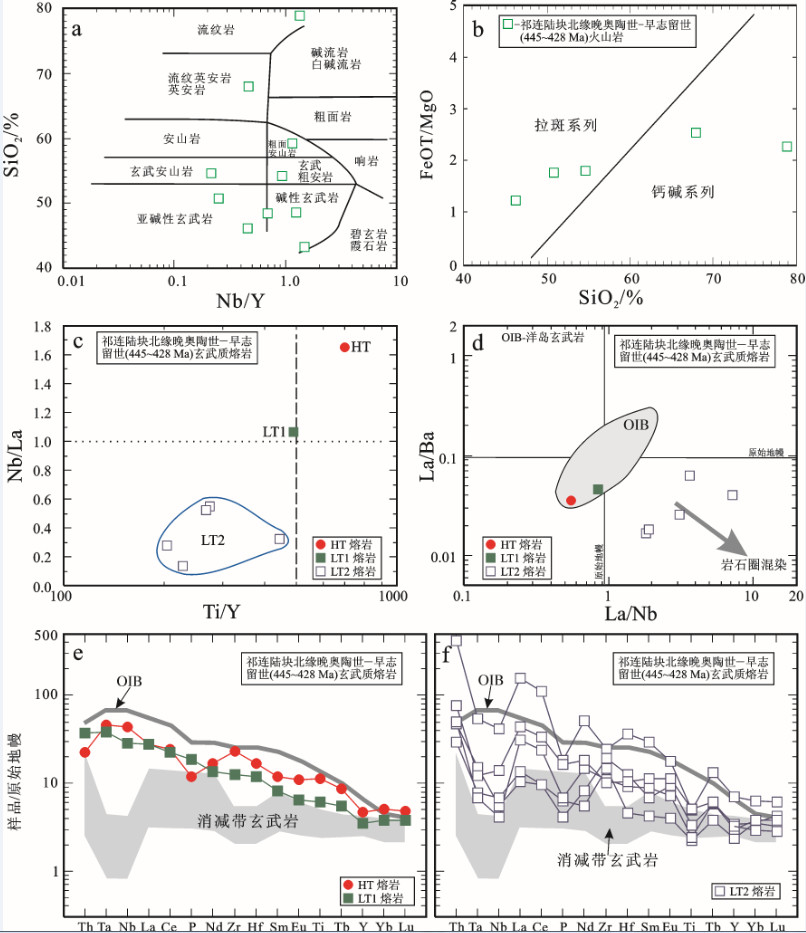
图 26 祁连陆块北缘晚奥陶世—早志留世(445~428 Ma)火山岩的a—SiO2-Nb/Y图解(图解据[154])和b—FeOT/MgO-SiO2图解(图解据[155]); 祁连陆块北缘晚奥陶世—早志留世(445~428 Ma)玄武质熔岩的c—Nb/La-Ti/Y图解, d—La/Ba-La/Nb图解, 和e, f—不相容微量元素原始地幔(据[156])标准化蛛网图
图 26‒b适用于图 26‒a中的亚碱性火山岩; 图 26‒d中, 岩石圈混染效应导致成分点向高La/Nb和低La/Ba方向迁移; 洋岛玄武岩(OIB)的成分范围据[158, 159]; 图 26‒e, f中, 洋岛玄武岩(OIB)据Sun & McDonough (1989);图中阴影区表示消减带玄武岩的成分范围, 其上限和下限分别由高-K玄武岩和低-K玄武岩的平均值(据[157])限定数据来源: [16, 17]
Figure 26. a-SiO2 versus Nb/Y diagram (after reference [154]) and b-FeOT/MgO versus SiO2 diagram (after reference [155]) for Late Ordovician-Early Silurian (445-428 Ma) volcanic rocks on the northern margin of the Qilian Block; c-Nb/La versus Ti/Y diagram, (d-La/Ba versus La/Nb diagram; and e, f-Primitive mantle (after [156]) normalized incompatible trace-element spider diagrams for Late Ordovician-Early Silurian (445-428 Ma) basaltic lavas on the northern margin of the Qilian Block
Fig. 26-b shows the sub-alkaline volcanic rocks as plotted in Fig. 26-a. In Fig. 26-d, the dispersion to higher La/Nb and lower La/Ba ratios may represent the effects of lithospheric contamination. Field for oceanic island basalts (OIB) is after references [158, 159]. Patterns for oceanic island basalts (OIB) are from reference [156]. In Fig. 26-e, f, the shaded area shows the range for subduction-zone basalts, with the lower and upper limits being defined by"average"low-K and high-K basalts, respectively (after reference [157]) Data sources: references [16, 17]
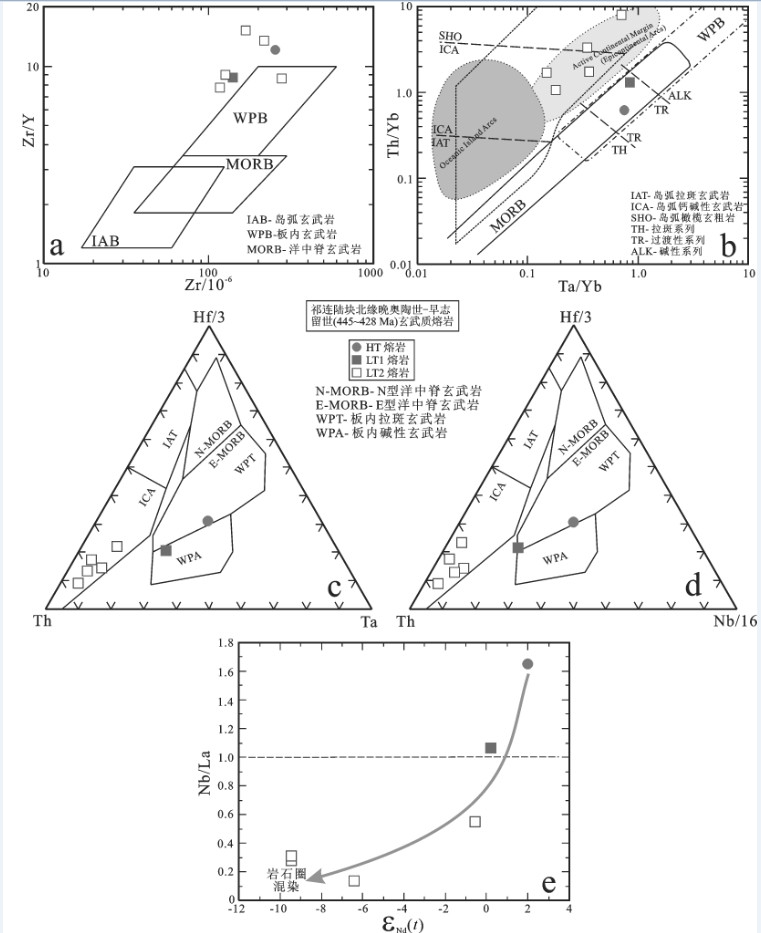
图 27 祁连陆块北缘晚奥陶世—早志留世(445~428 Ma)玄武质熔岩形成的构造环境判别图解
a—Zr/Y-Zr图解(据[160]); b—Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图解(据[161]); c—Hf/3‒Th‒Ta图解(据[162]); d—Hf/3‒Th‒Nb/16图解(据[162]); e—祁连陆块北缘晚奥陶世—早志留世(445~428 Ma)玄武质熔岩的Nb/La-εNd(t)图解数据来源同图 26
Figure 27. Tectonic setting of Late Ordovician-Early Silurian (445-428 Ma) basaltic lavas on the northern margin of the Qilian Block
a-Zr/Y versus Zr diagram (after reference [160]); b-Th/Yb versus Ta/Yb diagram (after reference [161]); c-Hf/3‒Th‒Ta diagram (after reference [162]); d-Hf/3‒Th‒Nb/16 diagram (after reference [162]); e-Nb/La versus εNd(t) diagram for Late Ordovician-Early Silurian (445-428 Ma) basaltic lavas on the northern margin of the Qilian Block Data sources as for Fig. 26
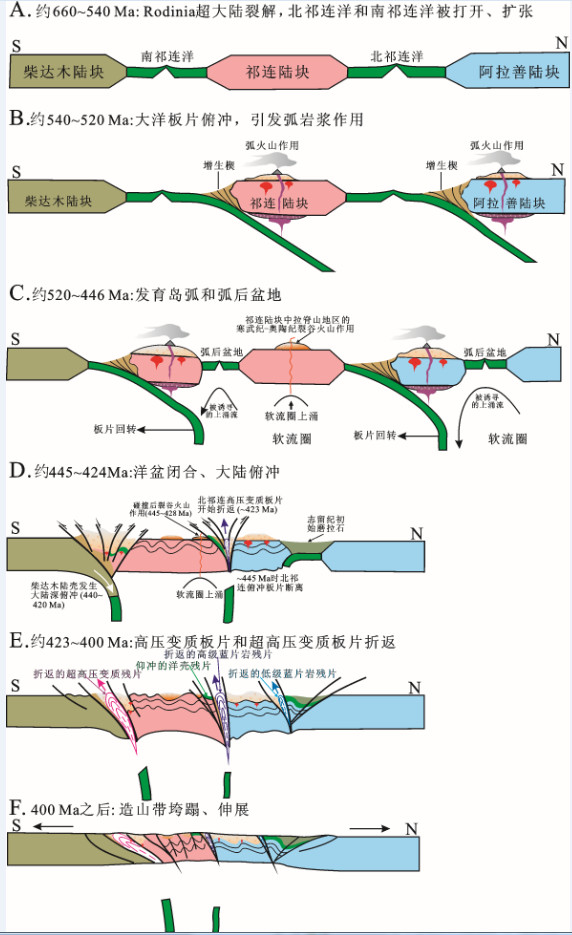
图 28 祁连山新元古代—古生代构造岩浆演化阶段示意图
A—新元古代, Rodinia超大陆裂解导致全球性早古生代大洋(包括北祁连洋和南祁连洋)打开;B—早古生代大洋岩石圈以低角度向北俯冲-消减, 导致弧火山作用;C—大约自早寒武世(约520 Ma)起, 北祁连和南祁连大洋板片回转, 相伴发生软流圈上涌, 导致弧后岩石圈伸展和弧后盆地火山作用;与此同时(525~442 Ma), 包括拉脊山和化隆地区在内的祁连陆块的中部, 则是处于陆内裂谷环境;D—北祁连洋和南祁连洋的最终闭合分别发生于445 Ma和441 Ma;大约在445 Ma, 北祁连大洋板片断离, 诱使软流圈上涌, 导致在祁连陆块北缘发生445~428 Ma的碰撞后裂谷火山活动;大约自440 Ma始, 柴达木大陆岩石圈开始深俯冲;E—大约自423 Ma始, 俯冲的北祁连洋壳开始折返;大约在420~400 Ma, 南祁连板片断离, 致使俯冲的南祁连板片折返, 形成柴北缘高压-超高压变质带;F—晚泥盆世, 祁连造山系开始垮塌;在大约400~370 Ma期间, 连续的岩石圈伸展和拆沉, 致使发生地壳熔融和强烈的岩浆活动, 形成许多碰撞后花岗质侵入体
Figure 28. Sketch map showing the stages of Qilian Mountain Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic tectonomagmatic evolution
A-The global Early Paleozoic Ocean, including the North Qilian Ocean and the South Qilian Ocean, was opened in the Neoproterozoic as the consequence of breakup of supercontinent Rodinia. B-Carton, showing the north-dipping, low-angle subduction of the Early Paleozoic oceanic lithosphere, which resulted in the arc volcanism. C-Carton: illustrating the back-arc lithospheric extension and back-arc basin volcanism in both North Qilian and South Qilian back-arc basins that occurred as a result of upwelling of asthenosphere accompanied by roll-back of the North Qilian and South Qilian oceanic slabs since early Cambrian (about 520 Ma). In the meantime (525-442 Ma), the central part of the Qilian Block, including the Lajishan and the Hualong areas, was in an intracontinental rift-related setting. D-The final closure of the North Qilian Ocean and the South Qilian Ocean took place at 445 Ma and 441 Ma, respectively. The break-off of the North Qilian oceanic slab at about 445 Ma induced an upwelling of asthenosphere, which gave rise to the 445-428 Ma post-collisional rift-related volcanism on the north margin of the Qilian Block. At about 440 Ma, the Qaidam continental deep subduction started. E-At about 423 Ma, the subduced North Qilian oceanic crust started to exhume. The subducted South Qilian slab started to exhume, forming the North Qaidam HPM-UHPM belt, as a result of South Qilian slab break off at 420-400 Ma. F-In the late Devonian, the Qilian orogenic system started to collapse; continuous lithosphere extension and delamination resulted in crust melting and strong magmatic activity and formed a number of post-collisional granitic intrusions with the ages of 400-370 Ma
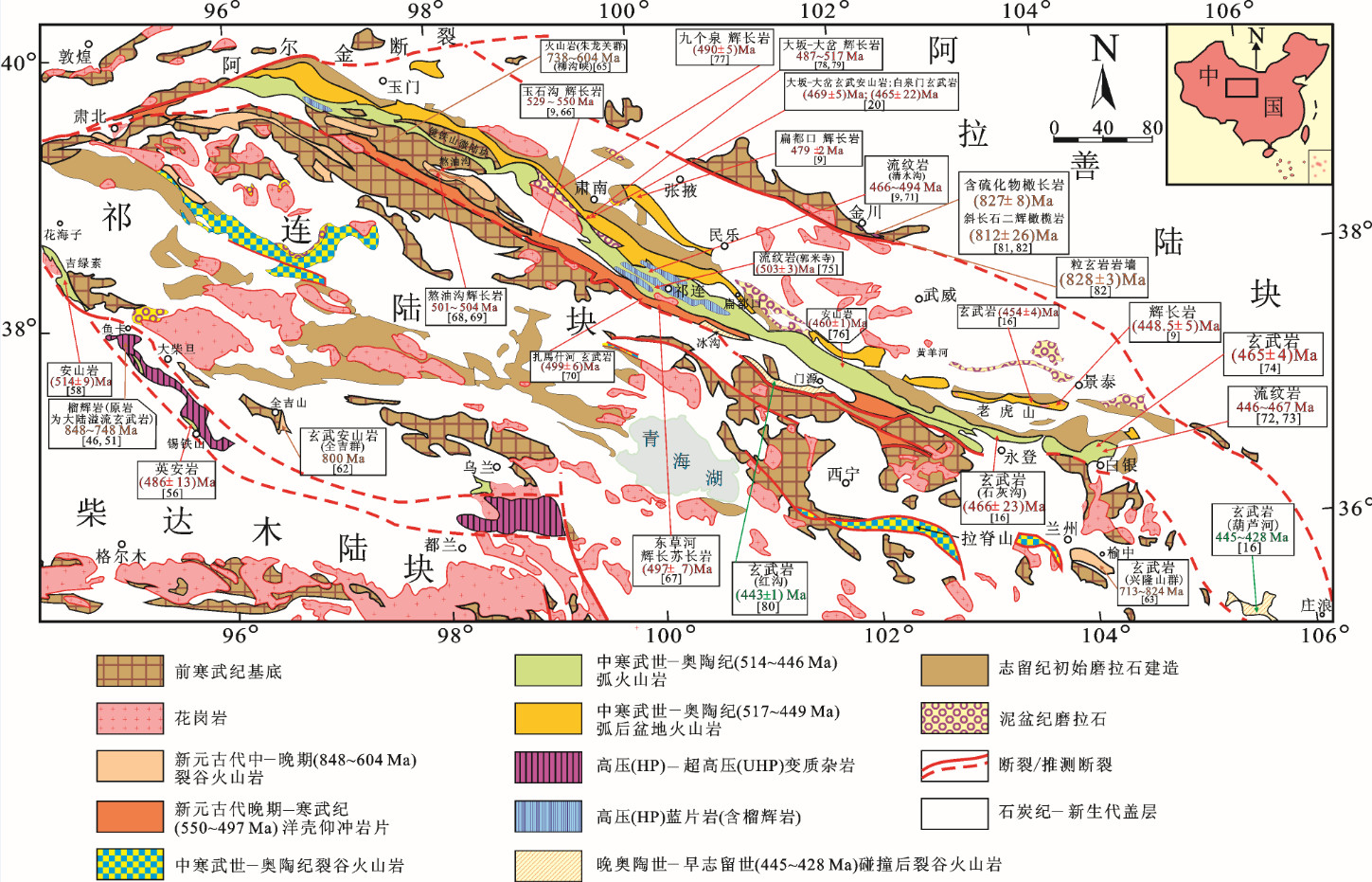
表 1 祁连山新元古代—早古生代火山岩、蛇绿岩和超镁铁质岩的年龄数据
Table 1 Compiled age data of Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic volcanic rocks, ophiolites and ultramafic rocks in the Qilian Mountain

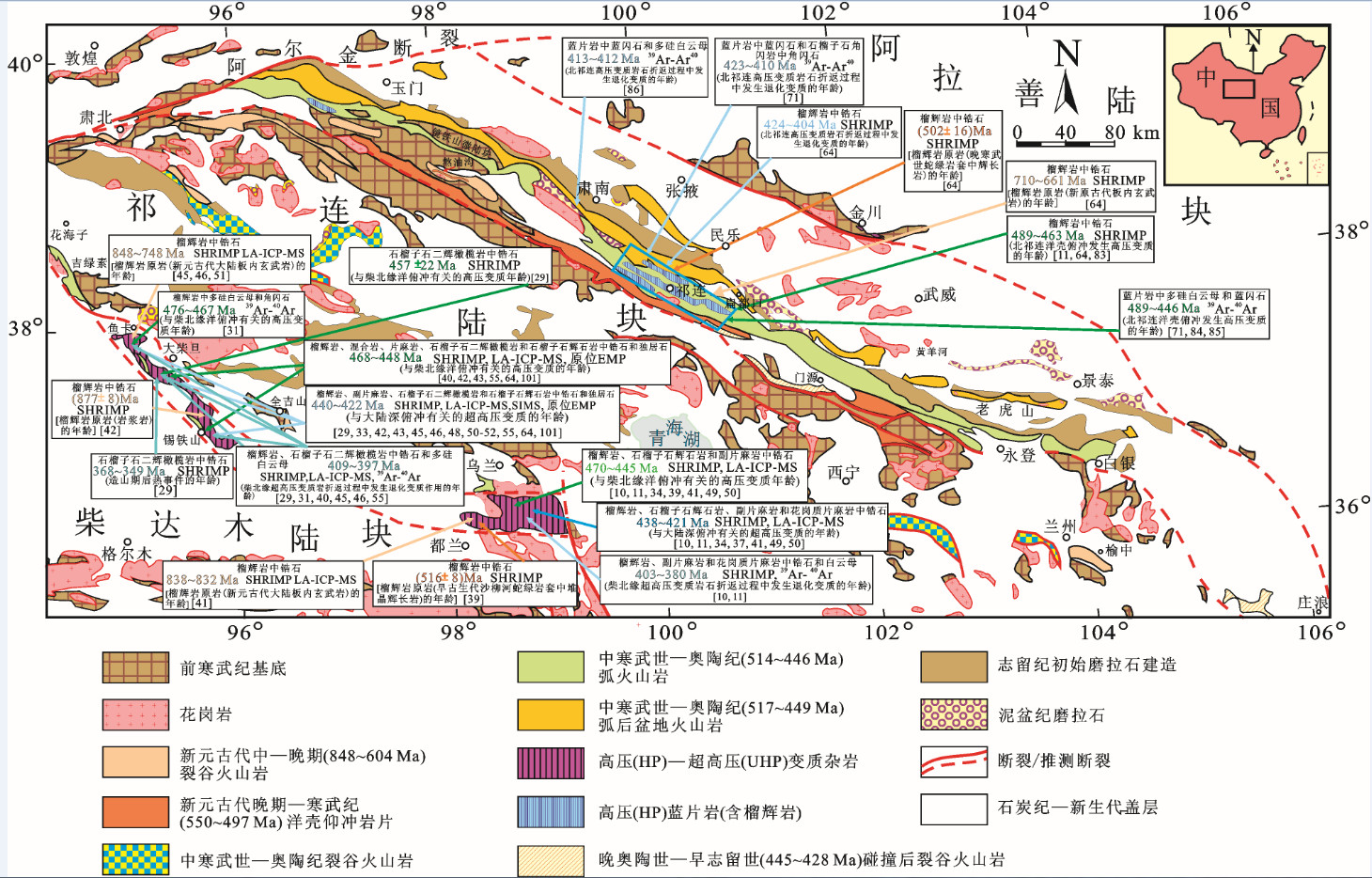
表 2 北祁连山高压变质带中高压变质岩石的年龄数据
Table 2 Compiled age data of HPM rocks in the HPM belt from the North Qilian Mountains

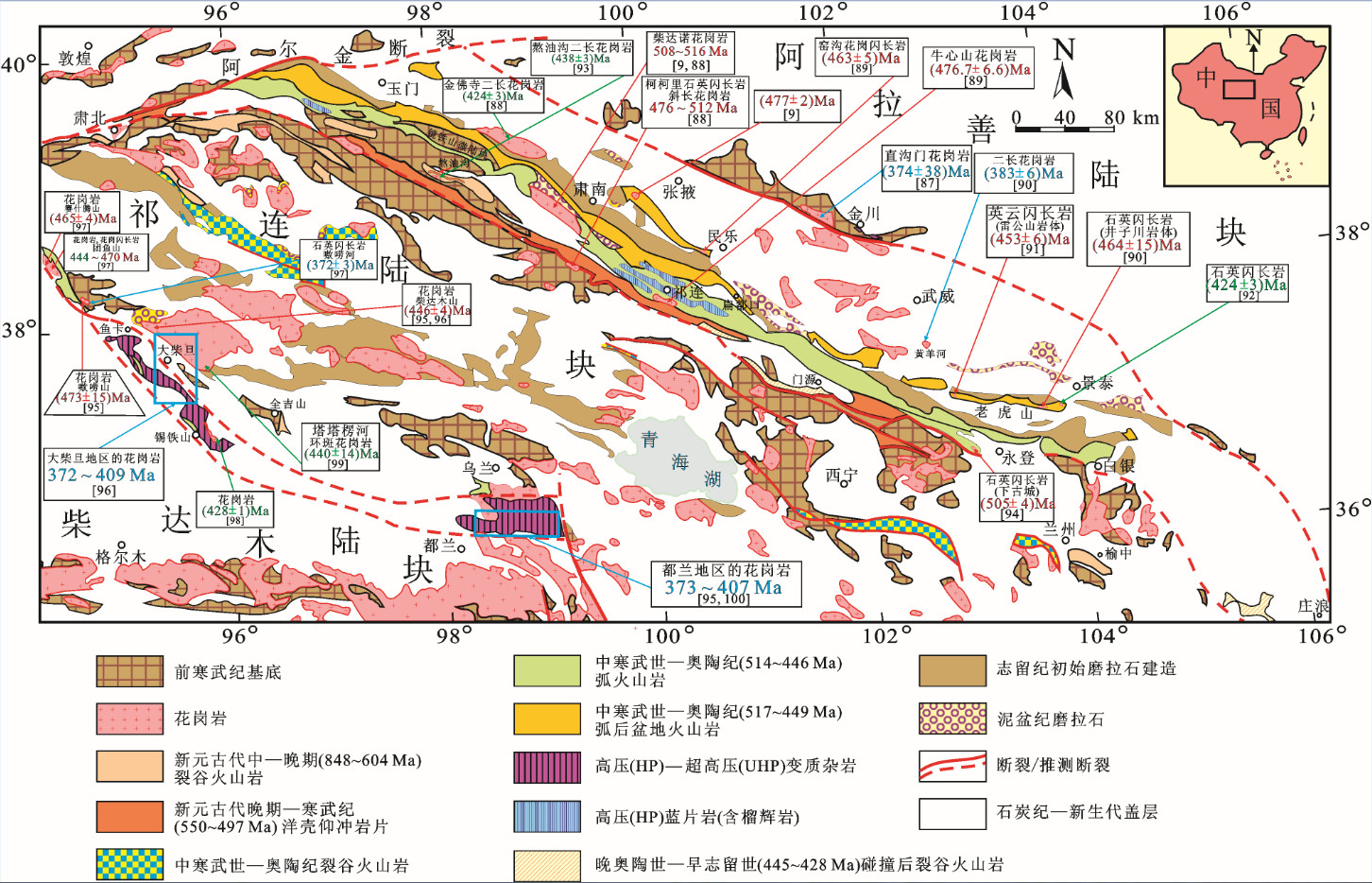
表 3 祁连山古生代花岗岩类年龄数据
Table 3 Compiled age data on Paleozoic granites in the Qilian Mountain

表 4 柴北缘高压、超高压变质带中高压、超高压变质岩石的年龄数据
Table 4 Compiled age data on HPM−UHPM rocks of the Northern Qaidam HPM−UHPM belt

-
[1] Santosh M, Zhao G.Supercontinent dynamics[J].Gondwana Res., 2009, 15:225-227. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.01.008
[2] Santosh M.A synopsis of recent conceptual models on supercontinent tectonics in relation to mantle dynamics, life evolution and surface environment[J].J.Geodyn., 2010, 50(3-4):116-133. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2010.04.002
[3] Yoshida M, Santosh M.Supercontinent, mantle dynamics and plate tectonics:A perspective based on conceptual vs.numerical models[J].Earth Sci.Rev., 2011, 105:1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.12.002
[4] Santosh M, Maruyama S, Yamamoto S.The making and breaking of supercontinents:Some speculations based on superplumes, super downwelling and the role of tectosphere[J].Gondwana Res., 2009, 15:324-341. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.11.004
[5] 姜春发, 王宗起, 李锦轶, 等.中央造山带开合构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. Jiang Chunfa, Wang Zongqi, Li Jinyi, et al.Opening Closing Tectonics of Central Orogenic Belt[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000(in Chinese).
[6] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Song S G, et al.Subduction of continental crust in the early palaeozoic North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, NW China:evidence from the discovery of coesite in the belt[J].Acta Geol.Sin.Engl.Ed., 2002, 76:63-68. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1976215819&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Zhang J X, et al.Early Palaeozoic North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt on the north-eastern Tibetan plateau and a paired subduction model[J].Terra Nova, 2002, 14:397-404. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00438.x
[8] Xu Z Q, Yang J S, Wu C L, et al.Timing and mechanism of formation and exhumation of the Northern Qaidam ultrahighpressure metamorphic belt[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2006, 28:160-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.016
[9] Song S G, Niu Y L, Su L, et al.Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China[J].Gondwana Res., 2013, 23:1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004
[10] Song S G, Niu Y L, Su L, et al.Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continental collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and recycling:The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J].Earth Sci.Rev., 2014, 129:59-84. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010
[11] Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L, et al.Evolution from oceanic subduction to continental collision:a case study of the Northern Tibetan Plateau inferred from geochemical and geochronological data[J].J.Petrol., 2006, 47:435-455. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2102249420&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] Gehrels G E, Yin A, Wang X F.Detrital-zircon geochronology of the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J].Geol.Soc.Am.Bull., 2003, 115(7):881-896. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2003)115 & lt; 0881:DGOTNT & gt; 2.0.CO; 2
[13] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 彭礼贵, 等.北祁连山石灰沟奥陶纪岛弧火山岩系岩浆性质的确定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1991, 10(1):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199101000.htm Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Peng Ligui, et al.Determination of nature of Ordovician island-arc volcanic series at Shihuigou area from Northern Qilian Mountains[J].Acta Petrol.Mineral., 1991, 10(1):1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199101000.htm
[14] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 任有祥, 等.祁连、秦岭山系海相火山岩[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1991.Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Ren Youxiang, et al.Marine Volcanic Rocks from Qilian and Qinling Mountains[M].Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press, 1991(in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.北祁连山构造-火山岩浆演化动力学[J].西北地质科学, 1995, 16(1):1-28. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi.Dynamics of tectono-volcanomagmatic evolution from North Qilian Mountains, China[J].Northwest Geoscience, 1995, 16(1):1-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.北祁连山海相火山岩岩石成因[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi.Petrogenesis of Marine Volcanic Rocks from Northern Qilian Mountains[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1996(in Chinese).
[17] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 任有祥, 等.祁连山及邻区火山作用与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Ren Youxiang, et al.Volcanism and mineralization in Qilian Mountains and its adjacent area[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1998(in Chinese).
[18] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.北祁连山早古生代洋脊-洋岛和弧后盆地火山作用[J].地质学报, 1998, 72(4):301-312. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi.Early Paleozoic mid-ocean ridge-ocean island and back-arc basin volcanism in the North Qilian Mountains[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 1998, 72(4):301-312(in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 任有祥, 等.北祁连山构造-火山岩浆-成矿动力学[M].北京:中国大地出版社, 2001. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Ren Youxiang, et al.Tectonics-Volcanic Magmatism-Mineralization Dynamics of North Qilian Mountains[M].Beijing:China Land Press, ,2001(in Chinese).
[20] Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Xu X Y.Magmagenesis in the Ordovician backarc basins of the Northern Qilian Mountains, China[J].Geol.Soc.Am.Bull., 2003, 115:1510-1522. doi: 10.1130/B25269.1
[21] 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 张建新, 等.北祁连走廊南山加里东俯冲杂岩增生地体及其动力学[J].地质学报, 1994, 68(1):1-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199401000.htm Xu Zhiqin, Xu Huifen, Zhang Jianxin, et al.The Zhoulangnanshan Caledonian subduction complex in the Northern Qilian Mountains and its dynamics[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 1994, 68(1):1-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199401000.htm
[22] 冯益民, 何世平.祁连山大地构造与造山作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996. Feng Yimin, He Shiping.Geotectonics and Orogeny of the Qilian Mountains[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1996(in Chinese).
[23] 杨建军, 朱红, 邓晋福, 等.柴达木北缘石榴石橄榄岩的发现及其意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1994, 13:97-105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW402.000.htm Yang Jianjun, Zhu Hong, Deng Jinfu, et al.Discovery of garnetperidotite at the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin and its significance[J].Acta Petrol.Mineral., 1994, 13:97-105(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW402.000.htm
[24] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Li H B, et al.Discovery of eclogite at northern margin of Qaidam basin, NW China[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 1998, 43:1755-1760. doi: 10.1007/BF02883981
[25] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Song S G, et al.Brunel, M.Discovery of coesite in the North Qaidam Early Palaeozoic ultrahigh pressure (UHP) metamorphic belt, NW China[J].C.R.Acad.Sci.ⅡFascicule Sci.Terre Planets, 2001, 333:719-724. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2012021382&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] Song S G, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al.Metamorphic evolution of coesite-bearing UHP terrane in the North Qaidam, northern Tibet, NW China[J].J.Metamorph.Geol., 2003, 21:631-644. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00469.x
[27] Song S G, Yang J S, Liou J G, et al.Petrology, geochemistry and isotopic ages of eclogites in the Dulan UHPM terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China[J].Lithos, 2003, 70(3-4):195-211. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(03)00099-9
[28] Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L.Ultra-deep origin of garnet peridotite from the North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau, NW China[J].American Mineral., 2004, 89:1330-1336. doi: 10.2138/am-2004-8-922
[29] Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L, et al.Geochronology of diamondbearing zircons from garnet-peridotite in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, North Tibetan Plateau:a record of complex histories associated with continental collision[J].Earth.Planet.Sci.Lett., 2005, 234:99-118. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.036
[30] 宋述光, 牛耀龄, 张立飞, 等.大陆造山运动:从大洋俯冲到大陆俯冲、碰撞、折返的时限——以北祁连山、柴北缘为例[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9):2067-2077. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200909003.htm Song Shuguang, Niu Yaoling, Zhang Lifei, et al.Time constraints on orogenesis from oceanic subduction to continental subduction, collision, and exhumation:An example from North Qilian and North Qaidam HP-UHP belts[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2009, 25(9):2067-2077(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200909003.htm
[31] Zhang J X, Yang J S, Mattinson C G, et al.Two constrasting eclogite cooling histories, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China:Petrological and isotopic constraints[J].Lithos, 2005, 84:51-76. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.02.002
[32] 张贵宾, 宋述光, 张立飞, 等.柴北缘超高压变质带沙柳河蛇绿岩型地慢橄榄岩及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21:1049-1058. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504002.htm Zhang Guibin, Song Shuguang, Zhang Lifei, et al.Ophiolite-type mantle peridotite from Shaliuhe, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China and its tectonic implications[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2005, 21:1049-1058(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504002.htm
[33] 马旭东, 陈丹玲.柴达木盆地北缘超高压变质岩的围岩长英质片麻岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年[J].地质通报, 2006, 25:99-103. Ma Xudong, and Chen Danling.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of quartz-feldspathic gneisses:the country rocks of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin, Northwest China[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2006, 25:99-103(in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Mattinson C G, Wooden J L, Liou J G, et al.Age and duration of eclogite-facies metamorphism, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China[J].American J.Sci., 2006, 306:683-711. doi: 10.2475/09.2006.01
[35] Mattinson C G, Wooden J L, Liou J G, et al.Geochronology and tectonic significance of Middle Proterozoic granitic orthogneiss, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, Western China[J].Mineral.Petrol., 2006, 88:227-241. doi: 10.1007/s00710-006-0149-1
[36] Mattinson C G, Menold C A, Zhang J X, et al.High-and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the North Qaidam and South Altyn Terranes, western China[J].Int.Geol.Rev., 2007, 49:969-995. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.11.969
[37] Mattinson C G, Wooden J L, Zhang J X, et al.Paragneiss zircon geochronology and trace element geochemistry, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.12.007
[38] Zhang J X, Yang J S, Meng F C, et al.U-Pb isotopic studies of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam Mountains, western China:new evidence for an early Paleozoic HP-UHPmetamorphic belt[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2006, 28:143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.017
[39] Zhang G B, Song S G, Zhang L F, et al.The subducted oceanic crust within continental-type UHP metamorphic belt in the North Qaidam, NW China:Evidence from petrology, geochemistry and geochronology[J].Lithos, 2008, 104:99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.001
[40] Zhang J X, Mattinson C G, Meng F C, et al.Polyphase tectonothermal history recorded in granulitized gneisses from the North Qaidam HP/UHP metamorphic terrane, Western China:evidence fromzircon U-Pb geochronology[J].Geol.Soc.Am.Bull., 2008, 120:732-749. doi: 10.1130/B26093.1
[41] Zhang J X, Mattinson C G, Yu S Y, et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology of coesite-bearing eclogites from the southern Dulan area of the North Qaidam UHP terrane, northwestern China:spatially and temporally extensive UHP metamorphism during continental subduction[J].J.Metamorph.Geol., 2010, 28:955-978. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2010.28.issue-9
[42] Zhang C, Zhang L F, Roermund H V, et al.Petrology and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the eclogite in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam HP-UHP metamorphic belt, Western China[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2011, 42:752-767. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.002
[43] Zhang C, Van Roermund H, Zhang L F, et al.A polyphase metamorphic evolution for the Xitieshan paragneiss of the north Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt, western China:In-situ EMP monazite-and U-Pb zircon SHRIMP dating[J].Lithos, 2012, 136:27-45. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2035436047&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[44] 张贵宾, 张立飞, 宋述光.柴北缘超高压变质带:从大洋到大陆的深俯冲过程[J].高校地质学报, 2012, 18:28-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201201005.htm Zhang Guibin, Zhang Lifei, Song Shuguang.An overview of the tectonic evolution of North Qaidam UHPM belt:from oceanic subduction to continental collision[J].Geol.J.China Univ., 2012, 18:28-40(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201201005.htm
[45] Chen D L, Sun Y, Liu L.In situ LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites in the Yukahe area, northern margin of the Qaidam basin[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 2007, 37(Supp.):279-287.
[46] Chen D L, Liu L, Sun Y, et al.Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:259-272. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.12.001
[47] Chen N S, Gong S L, Sun M, et al.Precambrian evolution of the Quanji Block, northeastern margin of Tibet:insights from zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotope compositions[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:367-376. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.004
[48] 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良.柴北缘鱼卡河榴辉岩围岩的变质时代及其地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(1):108-116. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60005-0 Chen Danling, Sun Yong, Liu Liang.The metamorphic ages of the country rock of the Yukahe eclogites in the North Qaidam and its geological significance[J].Earth Sci.Front., 2007, 14(1):108-116(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60005-0
[49] 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良.柴北缘野马滩超高压榴辉岩中副片麻岩夹层的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(5):1059-1067. Chen Danling, Sun Yong, Liu Liang.Zircon U-Pb dating of paragneiss interbed in the UHP eclogite from Yematan area, the North Qaidam UHP terrane, NW China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2008, 24(5):1059-1067(in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良, 等.柴北缘野马滩超高压地体的成因——年代学研究结果的约束[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(4):631-638. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200904030.htm Chen Danling, Sun Yong, Liu Liang, et al.Formation mechanism of the Yematan UHP terrane, the North Qaidam:constrains from zircon U-Pb dating[J].J.Northwest Univ.(Natur.Sci.Ed.), 2009, 39(4):631-638(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200904030.htm
[51] Song S G, Su Li, Li X H, et al.Tracing the 850-Ma continental flood basalts from a piece of subducted continental crust in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J].Precambrian Res., 2010, 183:805-816. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.09.008
[52] 宋述光, 张聪, 李献华, 等.柴北缘超高压带中锡铁山榴辉岩的变质时代[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(4):1191-1197. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201104027.htm Song Shuguang, Zhang Cong, Li Xianhua, et al.HP/UHP metamorphic time of eclogite in the Xitieshan terrane, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2011, 27(4):1191-1197(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201104027.htm
[53] Song S G, Su L, Li X H, et al.Grenville-age orogenesis in the Qaidam-Qilian block:the link between South China and Tarim[J].Precambrian Res., 2012, 220:9-22. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926812001799
[54] Liu X C, Wu Y B, Gao S, et al.First record and timing of UHP metamorphism from zircon in the Xitieshan terrane:implications for the evolution of the entire North Qaidam metamorphic belt[J].Am.Mineral., 2012, 97:1083-1093. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.4048
[55] Zhang J X, Mattinson G G, Meng F C, et al.U-Pb geochronology of paragneisses and metabasite in the Xitieshan area, north Qaidam Mountains, western China:Constraints on the exhumation of HP/UHP metamorphic rocks[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:245-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.08.008
[56] 赵风清, 郭进京, 李怀坤.青海锡铁山地区滩间山群的地质特征及同位素年代学[J].地质通报, 2003, 22:28-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200301004.htm Zhao Fengqing, Guo Jinjing, Li Huaikun.Geological characteristics and isotopic age of Tanjianshan Group along northern margin of Qaidam basin[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2003, 22:28-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200301004.htm
[57] 王惠初, 陆松年, 袁桂邦, 等.柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群的构造属性及形成时代[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(7):487-493. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200307004.htm Wang Huichu, Lu Songnian, Yuan Guibang.et al.Tectonic setting and age of the Tanjianshan Group on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2003, 22(7):487-493(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200307004.htm
[58] 史仁灯, 杨经绥, 吴才来, 等.柴达木北缘超高压变质带中的岛弧火山岩[J].地质学报, 2004, 78:52-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200401007.htm Shi Rendeng, Yang Jingsui, Wu Cailai, et al.Island arc volcanic rocks in the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2004, 78:52-64(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200401007.htm
[59] Liu L, Che Z C, Luo J H, et al.Determination of eclogite in the west segment of Altun mountains and its geological significance[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 1996, 41:1458-1488.
[60] Zhang J X, Zhang Z M, Xu, Z.Q., et al.Petrology and geochrology of eclogite from the western segment of the Altyn Tagh, northwestern China[J].Lithos, 2001, 56:187-206. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00052-9
[61] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 等.阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J].地质学报, 1999, 73:193-205. doi: 10.1111/acgs.1999.73.issue-2 Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Zhang Jianxin, et al.A comparison between the tectonic units on the two sides of the Altyn Tagh sinistral strike-slip fault and the mechanism of lithospheric shearing[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 1999, 73:193-205(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/acgs.1999.73.issue-2
[62] 李怀坤, 陆松年, 王惠初, 等.青海柴北缘新元古代超大陆裂解的地质记录——全吉群[J].地质调查与研究, 2003, 26(1):27-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200301005.htm Li Huaikun, Lu Songnian, Wang Huichu, et al.Geological records of break-up of Neoproterozoic supercontinent from northern margin of the Qaidam Block, Qinghai Province[J].Geol.Sur.Res., 2003, 26(1):27-37(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200301005.htm
[63] 徐学义, 王洪亮, 陈隽璐, 等.中祁连东段兴隆山群基性火山岩错石U-Pb定年及岩石成因研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):827-840. Xu Xueyi, Wang Hongliang, Chen Junlu, et al.Zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of Xinglongshan Group basic volcanic rocks at eastern segment of Middle Qilian Mts[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2008, 24(4):827-840(in Chinese with English abstract).
[64] Zhang J X, Meng F C, Wan Y S.A cold Early Paleozoic subduction zone in the North Qilian Mountains, NW China:petrological and U-Pb geochronological constraints[J].J.Metamor.Geol., 2007, 25:285-304. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2007.25.issue-3
[65] Mao J W, Zhang Z C, Yang J M.Dating of single-grain zircon for Precambrican strata in western part of from North Qilian Mountains[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 1997, 42:1414-1417.
[66] 史仁灯, 杨经绥, 吴才来, 等.北祁连玉石沟蛇绿岩形成于晚震旦世的SHRIMP年龄证据[J].地质学报, 2004, 78:649-657. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200400001108.htm Shi Rendeng, Yang Jingsui, Wu Cailai, et al.First SHRIMP dating for the formation of the Late Sinian Yushigou ophiolite, North Qilian Mountains[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2004, 78:649-657((in Chinese with English abstract). http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200400001108.htm
[67] Tseng C Y, Yang H J, Yang H Y, et al.The Dongcaohe ophiolite from the North Qilian Mountains:a fossil oceanic crust of the Paleo-Qilian ocean[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2007, 52:2390-2401. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0300-3
[68] 相振群, 陆松年, 李怀坤, 等.北祁连西段熬油沟辉长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].地质通报, 2007, 26:1686-1691. Xiang Zhenqun, Lu Songnian, Li Huaikun, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb zircom age of gabbro in Aoyougou in the western segment of the North Qilian Mountains, China and its geological implications[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2007, 26:1686-1691(in Chinese with English abstract).
[69] 夏小洪, 孙楠, 宋述光, 等.北祁连西段熬油沟-二只哈拉达坂蛇绿岩的形成环境和时代[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(5):757-769. Xia Xiaohong, Sun Nan, Song Shuguang, et al.Age and tectonic setting of the Aoyougou-Erzhihaladaban ophiolite in the Western North Qilian Mountains, NW China[J].Acta Sci.Natura.Univ.Pekin., 2012, 48(5):757-769(in Chinese with English abstract).
[70] 武鹏, 李向民, 徐学义, 等.北祁连山扎麻什地区东沟蛇绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(6):896-906. Wupeng, Li Xiangmin, Xu Xueyi, et al.LA-ICP-MS zircon UPb dating and geochemical characteristics of Donggou ophiolites in Zamashi area of northern Qilian Mountains[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2012, 31(6):896-906(in Chinese with English abstract).
[71] 张建新, 许志琴, 陈文, 等.北祁连中段俯冲-增生杂岩/火山弧的时代探讨[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1997, 16:112-119. Zhang Jianxin, Xu Zhiqin, Chen Wen, et al.A tentative discussion on the ages of the subduction-accretionary complex/volcanic arcs in the middle sector of North Qilian Mountains[J].Acta Petrol.Minerl., 1997, 16:112-119(in Chinese with English abstract).
[72] Wang C Y, Zhang Q, Qian Q, et al.Geochemistry of the Early Paleozoic Baiyin volcanic rocks (NW China):implications for the tectonic evolution of the North Qilian Orogenic Belt[J].J.Geol., 2005, 113:83-94. doi: 10.1086/425970
[73] 何世平, 王洪亮, 陈隽璐, 等.甘肃白银矿田变酸性火山岩锆石LA-ICP-MS测年——白银式块状硫化物矿床形成时代新证据[J].矿床地质, 2006, 25:401-411. He Shipin, Wang Hongliang, Chen Junlu, et al.A LA-ICP-MS U-Pb chronological study of zircons from meta-acdic volcanics in Baiyin orefield, Gansu Province:new evidence for metallogenic age of Baiyin type massive sulfide deposits[J].Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25:401-411(in Chinese with English abstract).
[74] Li李向民, 马中平, 孙吉明, 等.甘肃白银矿田基性火山岩的LAICP-MS同位素年代学[J].地质通报, 2009, 28:901-906. Xiangmin, Ma Zhongping, Sun Jiming, et al.A LA-ICP-MS chronological study of basic volcanics in Baiyin orefield, Gansu, China[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2009, 28:901-906(in Chinese with English abstract).
[75] 余吉远, 李向民, 马中平, 等.青海省祁连县清水沟-白柳沟矿田含矿火山岩系年代学研究[J].地球科学进展, 2010, 25(1):55-60. Yu Jiyuan, Li Xiangmin, Ma Zhongping, et al.Chronological study of mata-acidic volcanics in Qingshuigou-Bailiugou orefield, Qilian County of Qinghai Province[J].Advance Earth Sci., 2010, 25(1):55-60(in Chinese with English abstract).
[76] 余吉远, 李向民, 马中平, 等.北祁连构造带冷龙岭地区火山岩地球化学特征及年代学[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(4):6-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201004003.htm Yu Jiyuan, Li Xiangmin, Ma Zhongping, et al.2010.Geochemical characters and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Lenglongling volcanic rocks from the North Qilian tectonic belt[J].Geol.Sci.Technol.Inform., 2010, 29(4):6-13(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201004003.htm
[77] Xia X H, and Song S G.Forming age and tectono-petrogenesis of the Jiugequan ophiolite in the North Qilian Mountains, NW China[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2010, 55:1899-1907. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3207-3
[78] Xia X H, Song S G, Niu Y L.Tholeiite-Boninite terrane in the North Qilian suture zone:Implications for subduction initiation and back-arc basin development[J].Chem.Geol., 2012, 328:259-277. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.12.001
[79] 孟繁聪, 张建新, 郭春满, 等.大岔大坂MOR型和SSZ型蛇绿岩对北祁连洋演化的制约[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(5):453-466. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201005000.htm Meng Fancong, Zhang Jianxin, Guo Chunman, et al.Constraints on the evolution of the North Qilian ocean basin:MOR-type and SSZ-type ophiolites from Dachadaban[J].Acta Petrol.Mineral., 2010, 29(5):453-466(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201005000.htm
[80] 王国强, 李向民, 徐学义, 等.青海门源地区红沟铜矿床含矿基性火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(7):1060-1065. Wang Guoqiang, Li Xiangmin, Xu Xueyi.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of zircons from basic volcanic rocks in the Honggou copper polymetallic deposit, Menyuan area, Qinghai[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2011, 30(7):1060-1065(in Chinese with English abstract).
[81] Li X H, Su L, Song B, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion and its geological significance[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2004, 49:420-422. doi: 10.1007/BF02900329
[82] Li X H, Su L, Chung S L, et al.Formation of the Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion and the world's third largest Ni-Cu sulfide deposit:associated with the similar to 825 Ma south China mantle plume?[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Seosystems, 2005, 6:Q11004, doi: 10.1029/2005GC001006.
[83] Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L, et al.Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP ages of eclogites from the North Qilian Mountains, NW China and their tectonic implication[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2004, 49:848-852. doi: 10.1007/BF02889759
[84] Liou J G, Wang X, Coleman R G.Blueschists in major suture zones of China[J].Tectonics, 1989, 8:609-619. doi: 10.1029/TC008i003p00609
[85] Liu Y J, Neubauer F, Takasu A, et al.40Ar/39Ar ages of blueschist facies politic schists from Qingshuigou in the Northern Qilian Mountains, western China[J].Island Arc, 2006, 15:187-198. doi: 10.1111/iar.2006.15.issue-1
[86] Lin Y H, Zhang L F, Ji J Q, et al.40Ar/39Ar age of Jiugequan lawsonite-blueschists in northern Qilian Mountains and its petrologic significance[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2010, 55:2021-2027. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3239-8
[87] 胡能高, 许安东, 杨家喜.龙首山直沟门岩体特征及构造环境[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2005, 27:5-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200502004.htm Hu Nenggao, Xu Andong, Yang Jiaxi.Characteristics and ctectonic environment of Zhigoumen pluton in Longshoushan area[J].J.Earth Sci.Environ., 2005, 27:5-11(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200502004.htm
[88] 吴才来, 徐学义, 高前明, 等.北祁连早古生花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26:1027-1044. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201004004.htm Wu Cailai, Xu Xueyi, Gao Qianming, et al.Early Palaeozoic granitoid magmatism and tectonic evolution in North Qilian, NW China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2010, 26:1027-1044(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201004004.htm
[89] 吴才来, 姚尚志, 杨经绥, 等.北祁连洋早古生代双向俯冲的花岗岩证据[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1197-1208. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060602&flag=1 Wu Cailai, Yao Shangzhi, Yang Jingsui.et al.Doubel subduction of the Early Paleozoic North Qilian oceanic plate:evidence from granites in the central segment of North Qilian, NW China[J].Geology in China, 2006, 33(6):1197-1208(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060602&flag=1
[90] 吴才来, 杨经绥, 杨宏仪, 等.北祁连东部两类I型花岗岩定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(3):425-432. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200502019.htm Wu Cailai, Yang Jingsui, Yang Hongyi.2004 Two types of I-type granite dating and geological significance from North Qilian, NW China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2004, 20(3):425-432(in Chinese with Enmglish abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200502019.htm
[91] Tseng C Y, Yang H J, Yang H Y, et al.Continuity of the North Qilian and North Qinling orogenic belts, Central Orogenic System of China:evidence from newly discovered Paleozoic adakitic rocks[J].Gondwana Res., 2009, 16:285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.04.003
[92] Qian钱青, 王岳明, 李惠民, 等.甘肃老虎山闪长岩的地球化学特征及其成因[J].岩石学报, 1998, 14:520-528. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB804.009.htm Qing, Wang Yueming, Li Huimin, et al.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of diorites from Laohushan, Gasu Province[J].Acta Petrl.Sin., 1998, 14:520-28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB804.009.htm
[93] Chen Y X, Song S G, Xia X H.Petrogenesis of Aoyougou highsilica adakite in the western sector of Noth Qilian Mountains, NW China:evidence for decompression melting of oceanic slab[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 2012, 57:2072-2085. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2048690001&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[94] 秦海鹏, 吴才来, 王次松, 等.北祁连下古城花岗岩体LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石化学特征[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(10):1832-1842. Qin Haipeng, Wu Cailai, Wang Cisong, et al.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb characteristical of Xiagucheng granite in North Qilian[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2014, 88(10):1832-1842(in Chinese with English abstract).
[95] 吴才来, 杨经绥, 许志琴等.柴达木盆地北缘古生代超高压带中花岗质岩浆作用[J].地质学报, 2004, 78(5):658-674. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200405009.htm Wu Cailai, Yang Jingsui, Xu Zhiqin, et al.2004.Granitic magmatism on the Early Paleozoic UHP belt of Northern Qaidam, NW China.Acta Geol.Sin.78(5):658-674.(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200405009.htm
[96] Wu吴才来, 郜源红, 吴锁平, 等.柴达木盆地北缘大柴旦地区古生代花岗岩错石SHRIMP定年[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(8):1861-1875. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200708007.htm Cailai, Gao Yuanhong, Wu Suoping, et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granites from the Daqaidam area in the north margin of Qaidam basin, NW China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2007, 23(8):1861-1875(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200708007.htm
[97] Wu C L, Wooden J L, Robinson P T., et al.Geochemistry and zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granitoids from the west segment in the North Qaidam[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 2009, 52:1771-1790. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0147-3
[98] 孟繁聪, 张建新, 杨经绥.柴北缘锡铁山早古生代H P/U H P变质作用后的构造热事件:花岗岩和片麻岩的同位素与岩石地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(1):45-56. Meng Fancong, Zhang Jianxin, Yang Jingsui.Tectono-thermal event of post-HP/UHP metamorphism in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam Mountains, western China:isotopic and geochemical evidence of granite and gneiss[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2005, 21(1):45-56(in Chinese with English abstract).
[99] 卢欣祥, 孙延贵, 张雪亭, 等.柴达木盆地北缘塔塔楞环斑花岗岩的SHRIMP年龄[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(5):626-634. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200705005.htm Lu Xinxiang, Sun Yangui, Zhang Xueting, et al.The SHRIMP age of Tatalin rapakivi granite at the north margin of Qaidam basin[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2007, 81(5):626-634(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200705005.htm
[100] Wu C L, Gao Y H, Li Z L, et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granites from Dulan and the chronological framework of the North Qaidam UHP belt, NW China[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 2014.57(12):2945-2965. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4958-5
[101] Xiong Q, Zheng J P, Griffin W L, et al.Zircons in the Shenglikou ultrahigh-pressure garnet peridotite massif and its country rocks from the north qaidam terrane (western China):Meso-Neoproterozoic crust-mantle coupling and early Paleozoic convergent plate-margin processes[J].Precambrian Res., 2011, 187, 33-57. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.02.003
[102] 赵国春.华北克拉通基底主要构造单元变质作用演化及其若干问题讨论[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25:1772-1792. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200908006.htm Zhao Guochun.Metamorphic evolution of major tectonic units in the basement of the North China Craton:key issues and discussion[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2009, 25:1772-1792(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200908006.htm
[103] Zhai M G, Santosh M.The early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton:a synoptic overview[J].Gondwana Res., 2011, 20, 6-25. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.005
[104] 修群业, 于海峰, 李铨, 等.龙首山岩群成岩时代探讨[J].地质学报, 2004, 78:366-373. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200403009.htm Xiu Qunye, Yu Haifeng, Li Quan, et al.Discussion on the petrogenic time of Longshoushan Group, Gansu Province[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2004, 78:366-373(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200403009.htm
[105] 宁夏地质矿产局.宁夏区域地质志.中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990. NBGMR (Ningxia Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources).Regional Geology of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region.Geological Memoirs of Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1990(in Chinese).
[106] 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等.内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质基底阿拉善群的再厘定[J].中国地质, 2006, 33:138-145. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060115&flag=1 Geng Yuansheng, Wang Xinshe, Shen Qihan, et al.Redefinition of the Alxa Group-complex (Precambrian metamorphic basement) in the Alxa area, Inner Mongolia[J].Geology in China, 2006, 33:138-145(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060115&flag=1
[107] 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等.内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质岩系形成时代的初步研究[J].中国地质, 2007, 34:251-261. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070206&flag=1 Geng Yuansheng, Wang Xinshe, Shen Qihan, et al.Chronology of the Precambrian metamorphic series in the Alxa area, Inner Mogolia[J].Geology in China, 2007, 34:251-261(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070206&flag=1
[108] Tung K A, Yang H Y, Liu D Y.SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons from the Longshoushan Group and its tectonic significance[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2007, 52:1414-1425. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0189-x
[109] 万渝生, 许志琴, 杨经绥.祁连山带及邻区前寒武纪深变质基底的时代和组成[J].地质学报, 2001, 75:375-384. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200104011.htm Wan Yusheng, Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui.Ages and compositions of the Precambrian highgrade basement of the Qilian terrance and its adjacent areas[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2001, 75:375-384(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200104011.htm
[110] 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等.阿拉善地区新元古代晋宁期变形花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J].矿物岩石学杂志, 2002, 21:412-420. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200204012.htm Geng Yuansheng, Wang Xinshe, Shen Qihan, et al.The discovery of Neoproterozoic Jinningian deformed granites in Alax area and its significance[J].Mineral.Petrogi.Acta, 2002, 21:412-420(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200204012.htm
[111] Dan W, Li X H, Guo J, Liu, et al.Paleoproterozoic evolution of the eastern Alxa Block, westernmost North China:evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb dating and Hf-O isotopes[J].Gondwana Res., 2012, 21:838-864. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.004
[112] 陆松年.青藏高原北部前寒武纪地质初探[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002. Lu Songnian.Preliminary Study of Precambrian Geology in the North Tibet-Qinghai Plateau[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2002(in Chinese).
[113] Wang Q Y, Pan Y M, Chen N S, et al.Proterozoic polymetamorphism in the Quanji Block, northwestern China:evidence from microtextures, garnet compositions and monazite CHIME ages[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 34:686-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.008
[114] 郭进京, 赵凤清, 李怀坤.中祁连东段晋宁期碰撞型花岗岩及其地质意义[J].地球学报, 1999, 20:10-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB901.001.htm Guo Jinjing, Zhao Fengqing, Li Huaikun.Jinningian collisional granite belt in the eastern sector of the Central Qilian Massif and its implication[J].Acta Geosci.Sin., 1999, 20:10-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB901.001.htm
[115] Tung K A, Yang H J, Yang H Y, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the zircons from the Precambrian basement of the Qilian Block and its geological significances[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2007, 52:2687-2701. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0356-0
[116] Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Zhao J T, et al.Determination of properties of Proterozoic continental flood basalts of western part from North Qilian Mountains[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 1999, 42:506-514. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2404552665&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[117] Darby B J, Gehrels G.Detrital zircon reference for the North China block[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2006, 26:637-648. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.12.005
[118] 王惠初, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 等.柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡河岩群的地质特征和时代[J].地质通报, 2004, 23:314-321. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200404002.htm Wang Huichu, Yuan Guibang, Xin Houtian.Geological characteristic and age of the Iqe River Group-complex on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2004, 23:314-321(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200404002.htm
[119] 高振家, 王务严, 彭昌文, 等.新疆震旦系[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆人民出版社, 1985. Gao Zhenjia, Wang Wuyan, Peng Changwen, et al.Sinian System in Xinjiang, China[M].Urumqi:Xinjiang People's Publishing House, 1985(in Chinese with English abstract).
[120] 高振家, 陈晋镳, 陆松年, 等.新疆北部前寒武系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993. Gaozhenjia, Chenjinbiao, Lu Songnian, et al.The Precambrian Geology in Northern Xinjiang[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1993(in Chinese with English abstract).
[121] 高振家, 陈克强.新疆的南华系及我国南华系的几个地质问题——纪念恩师王曰伦先生诞辰一百年[J].地质调查与研究, 2003, 26(1):8-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200301002.htm Gao Zhenjia, Chen Keqiang.The Nanhua System of Xinjiang and some geological issues of Nanhua System in China[J].Geological Survey and Research, 2003, 26(1):8-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200301002.htm
[122] Xu B, Jian H, Zou H, et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Neoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the Tarim Block of northwestern China:implications for the breakup of Rodinia supercontinent and Neoproterozoic glaciations[J].Precambrian Res., 2005, 136:107-23. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.09.007
[123] 姜常义, 吴文奎, 李良辰, 等.南天山东段显生宙构造演化[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001. Jiang Changyi, Wu Wenkui, Li Liangchen, et al.The Phanerozoic Tectonic Evolution in Eastern Segment of South Tianshan[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2001(in Chinese).
[124] 夏林圻, 张国伟, 夏祖春, 等.天山古生代洋盆开启、闭合时限的岩石学约束——来自震旦纪、石炭纪火山岩的证据[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(2):55-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200202001.htm Xia Linqi, Zhang Guowei, Xia Zuchun, et al.Constraints on the timing of opening and closing of the Tianshan Paleozoic oceanic basin:evidence from Sinian and Carboniferous volcanic rocks[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(2):55-2(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200202001.htm
[125] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等.天山岩浆作用[M].北京:中国大地出版社, 2007. Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi, et al.2007.Magmatism in the Tianshan[M].Beijing:China Land Press, 2007(in Chinese).
[126] Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Xu X Y, et al.Mid-late-Neoproterozoic riftrelated volcanic rocks in China:Geological records of rifting and break-up of Rodinia[J].Geosci.Front., 2012, 3:375-399. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.004
[127] 王飞, 王博, 舒良树.塔里木西北缘阿克苏地区大陆拉斑玄武岩对新元古代裂解事件的制约[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(2):547-558. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201002018.htm Wangfei, Wangbo, Shuliangshu.Continental tholeiitic basalt of the Akesu area (NW China) and its implication for the Neoproterozoic rifting in the north Tarim[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2010, 26(2):547-558(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201002018.htm
[128] 朱杰辰, 孙文鹏.新疆天山地区震旦系同位素地质研究[J].新疆地质, 1987, 5(1):55-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI198701005.htm Zhujiechen, Sunwenpeng.Geochronology study of Sinian system for Tianshan region, Xinjiang[J].Xinjiang Geol., 1987, 5(1):55-61(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI198701005.htm
[129] Xu B, Xiao S H, Zou H B, et al.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age constraints on Neoproterozoic Qurugtagh diamictites in NW China[J].Precambrian Res., 2009, 168:247-258. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.10.008
[130] 朱杰辰, 孙文鹏.中天山变质岩系的成岩时代及演化探讨[J].新疆地质, 1986, 4(4):47-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI198604003.htm Zhujiechen, Sunwenpeng.Approach of deagenetic age and evolution of metamorphic rocks of middle Tianshan[J].Xinjiang Geol., 1986, 4(4):47-52(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI198604003.htm
[131] Chen Y, Xu B, Zhan S, et al.First mid-Neoproterozoic paleomagnetic results from the Tarim Basin (NW China) and their geodynamic implications[J].Precambrian Res., 2004, 133:271-281. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.05.002
[132] Zhang C L, Li Z X, Li X H, Ye, et al.Neoproterozoic mafic dyke swarms at the northern margin of the Tarim Block, NW China:age, geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.02.003
[133] Zhu W B, Zheng B H, Shu L S, et al.Geochemistry and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Korla mafic dykes:constrains on the Neoproterozoic continental breakup in the Tarim Block, northwest China[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2011, 42:791-804. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.018
[134] 李曰俊, 贾承造, 胡世玲, 等.塔里木盆地瓦基里塔格辉长岩40Ar/39Ar年龄及其意义[J].岩石学报, 1999, 15:594-599. Liyuejun, Jiachengzao, Hushiling, et al.The 40Ar/39Ar isotopic age of Wajilitag gabbro in Tarim basin and its geological significance[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1999, 15:594-599(in Chinese with English abstract).
[135] Zhang C L, Li X H, Li Z X, et al.Neoproterozoic ultramaficmafic-carbonatite complex and granitoids in Quruqtagh of northeastern Tarim Block, western China:geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[J].Precambrian Res., 2007, 152:149-169. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.11.003
[136] Zhang C L, Yang D S, Wang H Y, et al.Neoproterozoic maficultramafic layered intrusion in Quruqtagh of northeastern Tarim Block, NW China:two phases of mafic igneous activity with different mantle sources[J].Gondwana Res., 2011, 19:177-190. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.03.012
[137] Guo ZJ, Yin A, Bobinson A, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of deep-drill-core samples from the basement of the central Tarim basin[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2005, 25:45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.016
[138] Zhang C L, Yang D S, Wang H Y, et al.Neoproterozoic mafic dykes and basalts in the southern margin of Tarim, northwest China:age, geochemistry and geodynamic implications[J].Acta Geol.Sin., 2010, 84:549-562. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2010.84.issue-3
[139] 王剑.华南新元古代裂谷盆地演化-兼论与Rodinia解体的关系[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. Wangjian.Neoproterozoic Rifting History of South China:Significance to Rodinia Breakup[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000(in Chinese with English abstract).
[140] Wang J, Li Z X.History of Neoproterozoic rift basins in South China:implications for Rodinia break-up[J].Precambrian Res., 2003, 122:141-158. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00209-7
[141] 李献华, 周汉文, 李正祥, 等.川西新元古代双峰式火山岩成因的微量元素和Sm-Nd同位素制约及其大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 2002, 37(3):264-276. Li Xianhua, Zhouhanwen, Lizhengxiang, et al.Petrogenesis of Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanics in western Sichuan and its tectonic implications:geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic constraints[J].Chin.J.Geol., 2002, 37(3):264-276(in Chinese with English abstract).
[142] Li X H, Li Z X, Zhou H, et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and Nd isotopic study of Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the Kangdian Rift of South China:implications for the initial rifting of Rodinia[J].Precambrian Res., 2002, 113:135-154. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00207-8
[143] Li X H, Li Z X, Sinclair J A, et al.Revisiting the "Yanbian Terrane":implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the western Yangtze Block, South China[J].Precambrian Res., 2006, 151:14-30. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.07.009
[144] Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, Lo, et al.Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China:constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J].Precambrian Res., 2009, 174:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004
[145] Ye M F, Li X H, Li W X, et al.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronological and whole-rock geochemical evidence for an early Neoproterozoic Sibaaoan magmatic arc along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block[J].Gondwana Res., 2007, 12:144-156. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.09.001
[146] 高林志, 杨明桂, 丁孝忠, 等.华南双桥山群及河上镇群凝灰岩中的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄——对江南新元古代造山带地质演化的制约[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(10):1744-1758. Gaolinzhi, Yangminggui, Dingxiaozhong, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of tuff in the Shuangqiaoshan and Heshangzhen groups in South China:constraints on the evolution of the Jiangnan Neoproterozoic Orogenic Belt[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2008, 27(10):1744-1758(in Chinese with English abstract).
[147] 高林志, 戴传固, 刘燕学, 等.黔东南-桂北地区四堡群凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(9):1259-1267. Gaolinzhi, Daichuangu, Liuyanxue, et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of tuff bed of the Sibao Group in southern Guizhounorthern Guangxi area, China and its stratigraphic implication[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2010, 29(29):1259-1267(inChinese with English abstract).
[148] 高林志, 陈峻, 丁孝忠, 等.湘东北岳阳地区冷家溪群及板溪群凝灰岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄——对武陵运动的制约[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(9):1001-1008. Gaolinzhi, Chenjun, Dingxiaozhong, et al.Zircon SHRIMP UPb dating of the tuff bed of Lengjiaxi and Banxi groups, northeastern Hunan:constraints on the Wuling Movement[J].Geol.Bull.China, 2011, 30(9):1001-1008(in Chinese with English abstract).
[149] 周金城, 王孝磊, 邱检生.江南造山带新元古代构造-岩浆演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014. Zhoujinchen, Wangxiaolei X L, Qiu J S.Neoproterozoic Tectono-Magmatic Evolution of the Jiangnan Orogen[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2014(in Chinese).
[150] Qiu Y M, Gao S, McNaughton N J, et al.First evidence of > 3.2 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of South China and its implications for Archean crustal evolution and Phanerozoic tectonics[J].Geology, 2000, 28:11-14. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)028 & lt; 0011:FEOGCC & gt; 2.0.CO; 2
[151] Li X H.Timing of the Cathaysia block formation:constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology[J].Episodes, 1997, 20:188-192. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279909961_Timing_of_the_Cathaysia_Block_formation_Constraints_from_SHRIMP_U-Pb_zircon_geochronology
[152] Li Z X, Li X H.Formation of the 1300 km-wide intracontinental orogen and post-orogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:a flat-slab subduction model[J].Geology, 2007, 35:179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[153] 甘肃省地质矿产局.甘肃省区域地质志.中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989. GBGMR (Gansu Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources).Regional Geology of Gansu Province.Geological Memoirs of Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1989(in Chinese).
[154] Winchester J A, Floyd P A.Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chem.Geol., 1977, 20:325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[155] Miyashiro A.Classification, characteristics and origin of ophiolites[J].J.Geol., 1975, 83:249-281. doi: 10.1086/628085
[156] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J (eds.).Magmatism in the Ocean Basins[D].Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:pp.313-346. http://www.oalib.com/references/7915584
[157] Tatsumi Y, Eggins S M.Subduction Zone Magmatism[M].Cambridge:Blackwell Science, 1995.
[158] Fitton J G.Coupled molybdenum and niobium depletion in continental basalts[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1995, 136:715-721. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(95)00171-8
[159] Fitton J G, James D, Leeman W P.Basic magmatism associated with the late Cenozoic extension in the western United States:compositional variations in space and time[J].J.Geophys.Res., 1991, 96:13693-13711. doi: 10.1029/91JB00372
[160] Pearce J A.and Norry M J.Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J].Contrib.Mineral.Petrol., 1979, 69, 33-47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192
[161] Pearce, J A.Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorps R S (ed.).Andesites.New York:JohnWiley and Sons, 1982:525-548.
[162] Wood D A.The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of British Tertialy volcanic province[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1980, 50:11-30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
[163] 李怀坤, 陆松年, 相振群, 等.北祁连山西段北大河岩群碎屑锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究[J].地质论评, 2007, 53:132-140. Li Huaikun, Lu Songnian, Xiang Zhenqun, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb geochronological research on detrital zircons from the Beidahe complex-Group in the western segment of the North Qilian Mountains, Northwest China[J].Geol.Rev., 2007, 53:132-140(in Chinese with English abstract).
[164] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等.利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):77-89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200701010.htm Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi, et al.The discrimination between continental basalt and island arc basalt based on geochemical method[J].Acta Petrol.Mineral.2007, 26(1):77-89(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200701010.htm
[165] Xia L Q.The geochemical criteria to distinguish continental basalts from arc related ones[J].Earth Sci.Rev., 2014, 139:195-212. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.006
[166] Condie K C, Incompatible element ratios in oceanic basalts and komatites:tracking deep mantle sources and continental growth rates with time[J].Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2003, 4(1):1005. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1667967001&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[167] Condie K C.High field strength element ratios in Archean basalts:a window to evolving sources of mantle plumes?[J].Lithos, 2005, 79:491-504. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.09.014
[168] Zhao J X, McCulloch M T, Korsch R J.Characterisation of a plume-related approximately 800 Ma magmatic event and its implications for basin formation in central-southern Australia[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1994, 121:349-367. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90077-9
[169] Wingate M T D, Campbell I H, Compston W, et al.Ion microprobe U-Pb ages for Neoproterozoic basaltic magmatism in south-central Australia and implications for the breakup of Rodinia[J].Precambrian Res., 1998, 87:135-159. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(97)00072-7
[170] Radhakrishna T, Mathew J.Late Precambrian (850-800 Ma) palaeo-magnetic pole for the south Indian shield from the Harohalli alkaline dykes:geotectonic implications for Gondwana reconstructions[J].Precambrian Res., 1996, 80:77-87. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(96)00006-X
[171] Frimmel H E, Zartman R, Späth E.The Richtersveld igneous complex, South Africa:U-Pb zircon and geochemical evidence for the beginning of Neoproterozoic continental breakup[J].J.Geol., 2001, 109:493-508. doi: 10.1086/320795
[172] Stein M, Goldstein S L.From plume head to continental lithosphere in the Arabiane Nubian shield[J].Nature, 1996, 382:773-778. doi: 10.1038/382773a0
[173] Teklay M, Kröner A.Mezger, K.Enrichment from plume interaction in the generation of Neoproterozoic arc rocks in northern Eritrea:implications for crustal accretion in the southern Arabiane-Nubian Shield[J].Chem.Geol., 2002, 184:167-184. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00359-X
[174] Su Q, Golberg S A, Fullagar P D.Precise U-Pb zircon ages of Neoproterozoic plutons in the southern Appalachian Blue Ridge and their implications for the initial rifting of Laurentia[J].Precambrian Res., 1994, 68:81-95. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(94)90066-3
[175] Aleinikoff J N, Zartman R E, Walter M.et al.U-Pb ages of metarhyolites of the Catoctin and Mount Rogers formations Central and Southern Appalachians:evidence for two pulses of Lapetan rifting[J].Am.J.Sci., 1995, 295:428-454. doi: 10.2475/ajs.295.4.428
[176] Fetter A H, Goldberg S A.Age and geochemical characteristics of bimodal magmatism in the Neoproterozoic Grandfather Mountain Rift Basin[J].J.Geol., 1995, 103:313-326. doi: 10.1086/629749
[177] Li Z X, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, et al.Assembly, configuration, and breakup history of Rodinia:a synthesis[J].Precambrian Res., 2008, 168:179-210.
[178] Li Z X, Zhang L, Powell C M.Positions of the East Asian cratons in the Neoproterozoic supercontinent Rodinia[J].Australian J.Earth Sci., 1996, 43:593-604. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728281
[179] Evins L Z, Jourdan F, Phillips D.The Cambrian Kalkarindji Large Igneous Province:extend and characteristics based on new 40Ar/39Ar and geochemical data[J].Lithos, 2009, 110:294-304. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.01.014
[180] 冯益民, 何世平.北祁连蛇绿岩的地质地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊):125-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB5S1.009.htm Feng Yimin, He Shiping.Research for geology and geochemistry of several ophiolites in the North Qilian Mountains, China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 1995, 11(Supp.):125-146(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB5S1.009.htm
[181] Hou Q Y, Zhao Z D, Zhang H F, et al.Indian Ocean-MORBtype isotopic signature of Yushigou Ophiolite in north Qilian Mountains and its implications[J].Sci.China.(Ser.D), 2006, 49(6):561-572. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-0561-8
[182] 张聪, 张立飞, 张贵宾, 等.柴北缘锡铁山一带榴辉岩的岩石学特征及其退变PT轨迹[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25:2247-2259. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200909017.htm Zhang Cong, Zhang Lifei, Zhang Guibin, et al.Petrology and calculation of retrograde PT path of eclogites from Xitieshan, North Qaidam, China[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 2009, 25:2247-2259(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200909017.htm
[183] Meschede M.A method of discriminating between different type of mid-ocean ridge basalt and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J].Chem.Geol., 1986, 56:207-218. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(86)90004-5
[184] Pearce J A.and Cann J R.Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1973, 19, 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
[185] Zindler A, Hart S R.Chemical geodynamics[J].Annu.Rev.Earth Planet.Sci., 1986, 14:493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[186] Yogodzinski G M, Naumann T R, Smith E I, et al.Crustal assimilation by alkalic basalt, and the evolution of a mafic volcanic field in the central Great Basin, south-central Nevada[J].J.Geophys.Res., 1996, 101:17425-17445. doi: 10.1029/96JB00816
[187] Gehrels G, Kapp P, DeCelles P, et al.Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen[J].Tectonics, 2011, 30:TC5016-TC. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2097103166&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[188] Sengör A M C.The cimmeride orogenic system and the tectonics of Eurasia[J].Geol.Soc.Am.Special paper, 1984, 195;82 pp.
[189] Metcalfe I.Gondwanaland dispersion, Asian accretion and evolution of Eastern Tethys[J].Australian J.Earth Sci., 1996, 43(6):605-623. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728282
[190] Peccerillo A.and Taylor S R.Geochemistry of Eocene calc alkaline volcanic rocks from Kastamonu area, North Turkey[J].Contrib.Miner.Petrol., 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
[191] 张旗, 孙晓猛, 周德进, 等.北祁连蛇绿岩的特征、形成环境及其构造意义[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12:366-393. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ704.008.htm Zhang Qi, Sun Xiaomeng, Zhou Dejin, et al.The characteristics of North Qilian ophiolites, forming settings and their tectonic significance[J].Advance in Earth Sci., 1997, 12:366-393(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ704.008.htm
[192] Zhang Q, Chen Y, Zhou D J, et al.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Dacha-Daban ophiolite in North Qilian area[J].Sci.China (Ser.D), 1998, 41:277-281. doi: 10.1007/BF02973116
[193] Cabanis P B, Thiéblemont D.La discrimination des tholéiites continentals et des basalts arrière-arc.Proposition d'un nouveau diagramme, le triangle Th-3Tb-2Ta[J].Bull.Soc.Géol.Fr., 1988, IV (6):927-935.
[194] Holm P E.The geochemical fingerprints of different tectonomagmatic environments using hygromagmatophile element abundances of tholeiitic basalts and basaltic andesites[J].Chem.Geol., 1985, 51:303-323. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90139-1
[195] 张旗, 王岳明, 钱青, 等.甘肃景泰县老虎山地区蛇绿岩及其上覆岩系中枕状熔岩的地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 1997, 13(1):92-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB701.007.htm Zhang Qi, Wang Yuemin, Qian Qin, et al.Geochemical characteritics of pillow lavas in ophiolite and its overlying rock sequence in the Laohushan area from Jingtai county, Gansu province[J].Acta Petrol.Sin., 1997, 13(1):92-99(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB701.007.htm
[196] 周德进, 陈雨, 张旗, 等.北祁连山南侧阿拉斯加型岩体的发现及地质意义[J].地质科学, 1997, 32:122-127. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199701014.htm Zhou Dejin, Chen Yu, Zhang Qi, et al.The finding of Alaskatype mafic-ultramafic complex from Qilian County and constraints on Qilian Mountain tectonic evolusion[J].Sci.Geol.Sin., 1997, 32:122-127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199701014.htm
[197] Gehrels G E, Yin A.Magmatic history of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].J.Geophys.Res., 2003, 108(B9):2423. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2007004781&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[198] Yin A, Manning C E, Lovera O, et al.Early Paleozoic tectonic and thermomechanical evolution of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks in the Northern Tibetan Plateau, Northwest China[J].Int.Geol.Rev., 2007, 49:681-716. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.8.681
[199] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yong Y, et al.Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the Qilian Shan, NW China[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2009, 35:323-333. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.001
[200] 左国朝, 刘寄陈.北祁连山早古生代大地构造演化[J].地质科学, 1987, 63:14-24. Zuo Guochao, Liu Jichen.1987.The evolution of tectonics of Early Paleozoic in North Qilian Range.China[J].Sci.Geol.Sin., 1987, 63:14-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
[201] Boynton W V.Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements:Meteorite Studies[C]//Henderson P (ed.).Rare Earth Element Geochemistry, 1984:63-114.
[202] Crawford A J, Beccaluva L, Serri G.Tectono-magmatic evolution of the west Philippine-Mariana region and the origin of boninites[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1981, 54:346-356. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(81)90016-9
[203] Wu H Q, Feng Y M, Song S G.Metamorphism and deformation of blueschist belts and their tectonic implications, North Qilian Mountains, China[J].J.Metamor.Geol., 1993, 11:523-36. doi: 10.1111/jmg.1993.11.issue-4
[204] 宋述光.北祁连山俯冲杂岩带的构造演化[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12:351-365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ704.007.htm Song Shuguang.Tectonic evolution of subductive complex belts in the North Qilian Mountains[J].Advance in Earth Siences, 1997, 12:351-365(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ704.007.htm
[205] 赖绍聪, 邓晋福, 赵海玲.柴达木北缘奥陶纪火山作用与构造机制[J].西安地质学院学报, 1996, 18:9-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX603.001.htm Lai Shaocong, Deng Jinfu, Zhao Hailing.Volcanism and tectonic setting during Ordovician period on north margin of Qaidam[J].J.Xi'an College Geol., 1996, 18:9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX603.001.htm
[206] 邱家骧, 曾广策, 王思源, 等.拉脊山早古生代海相火山岩与成矿[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996. Qiu Jiaxiang, Zeng Guangce, Wang Siyuan, et al.Early Paleozoic marine volcanic rocks and mineralization in Laji Mountains[M].Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press, 1996(in Chinese with English abstract).
[207] Weaver B L, Tarney J.Empirical approach to estimating the composition of the continental crust[J].Nature, 1984, 310:575-577. doi: 10.1038/310575a0
[208] Wedepohl K H.The composition of the continental crust[J].Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta, 1995, 59:1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
[209] Campbell I H.Identification of ancient mantle plumes[A].In:Ernst, R.E., Buchan, K.L.(Eds.), Mantle Plumes:Their Identification Through Times[D].Geol.Soc.Am.Spec.Pap., 2001, 352:5-21. doi: 10.1130/0-8137-2352-3
[210] Ernst R E, Buchan K L, Campbell I H.Frontiers in large igneous province research[J].Lithos, 2005, 79:271-297. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.09.004
[211] Condie K C.Mantle Plumes and Their Record in Earth History[M].Oxford.UK:Cambridge University Press, 2001.
[212] Kieffer B, Arndt N, Lapierre H, et al.Flood and shield basalts from Ethiopia:magmas from the African superswell[J].J.Petrol., 2004, 45:793-834. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egg112
[213] Saunders A D, Storey M, Kent R W, et al.Consequences of plume-lithosphere interactions[C]//Storey B C, Alabaster T, Pankhurst R J (eds.).Magmatism and the Causes of Continental Breakup.Geological Society of London Special Publication, London, 1992, 68:41-60.
[214] 任纪舜, 姜春发, 张振坤.中国大地构造及其演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980. Ren Jishun, Jiang Chunfa, Zhang Zhenkun.Geotectonics and Evolution of China[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1980(in Chinese).
[215] Meert J G.A synopsis of events related to the assembly of eastern Gondwana[J].Tectonophysics, 2003, 362:1-40. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00629-7
[216] Torsvik T H.The Rodinia jigsaw puzzle[J].Science, 2003, 300:1379-1381. doi: 10.1126/science.1083469
[217] Wilson M.Igneous Petrogenesis[M].London:Unwin Hyman, 1989.
[218] 张照伟, 李文渊, 王亚磊, 等.南祁连化隆地区镁铁-超镁铁质侵入岩地质、地球化学特征与铜镍成矿[J].地质学报, 2015, 89:632-644. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12452 Zhang Zhaowei, Li Wenyuan, Wang Yalei, et al.Geological and geochemical characteristics of mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Hualong area, southern Qilian Mountains and its Ni-Cu mineralization[J].Acta.Geol.Sin., 2015, 89:632-644(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12452
[219] 青海省地质矿产局.青海省区域地质志.中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报[M].北京:地质出版社, 1991. QBGMR (Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources).Regional Geology of Qinghai Province.Geological Memoirs of Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1991(in Chinese).
[220] Wortel M J R, Spakman W.Subduction and slab detachment in the Mediterranean-Carpathian region[J].Science, 2000, 290:1910-1917. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5498.1910
[221] Doglioni C, Carminati E, Cuffaro M, et al.Subduction kinematics and dynamic constraints[J].Earth Sci.Rev., 2007, 83:125-175. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.04.001
[222] 许志琴, 张建新, 许惠芬, 等.中国主要大陆山链韧性剪切带及动力学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1997. Xu Zhiqin, Zhang Jianxin, Xu Huifen, et al.Ductile Shear Zones in the Main Continental Mountain Chains of China and Their Dynamics[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1997(in Chinese with English abstract).
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 程涌,周家喜,孙国涛,黄智龙. 贵州半边街锗锌矿床锗的富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2024(01): 43-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何叶,周高明,钟华,程涌,岳正鹏,刘和松,周家喜. 云南毛坪铅锌矿床新发现Ⅵ号矿带硫化物稀散元素富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2023(10): 2985-3001 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄亮,周家喜,孙载波,熊波,龙天祥,王晓林,吴嘉林. 滇西漕涧地区发现流纹岩型铌矿化. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2022(01): 185-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨昌华,周家喜,罗开,姜永果,李晓红,杨丰铭,陶永林. 云南省兰坪-思茅盆地发现钴超常富集矿化点. 大地构造与成矿学. 2022(06): 1167-1169 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨德智,周家喜,孔志岗,吴越,黄智龙,金中国. 闪锌矿矿物结构对Ge超常富集的制约:以贵州竹林沟Ge-Zn矿床为例. 大地构造与成矿学. 2022(06): 1120-1136 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 罗开,周家喜,徐畅,贺康建,王永彬,孙国涛. 四川乌斯河大型锗铅锌矿床锗超常富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2021(09): 2761-2777 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周家喜,杨德智,余杰,周祖虎,罗开,徐阳东. 贵州黄丝背斜地区实现大型共(伴)生锗矿床找矿突破. 矿物学报. 2020(06): 772 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: