Geochemical characteristics and geochronology of porphyroid biotite monzogranite from the Reshui Mo polymetallic deposit, East Kunlun Mountains
-
摘要:
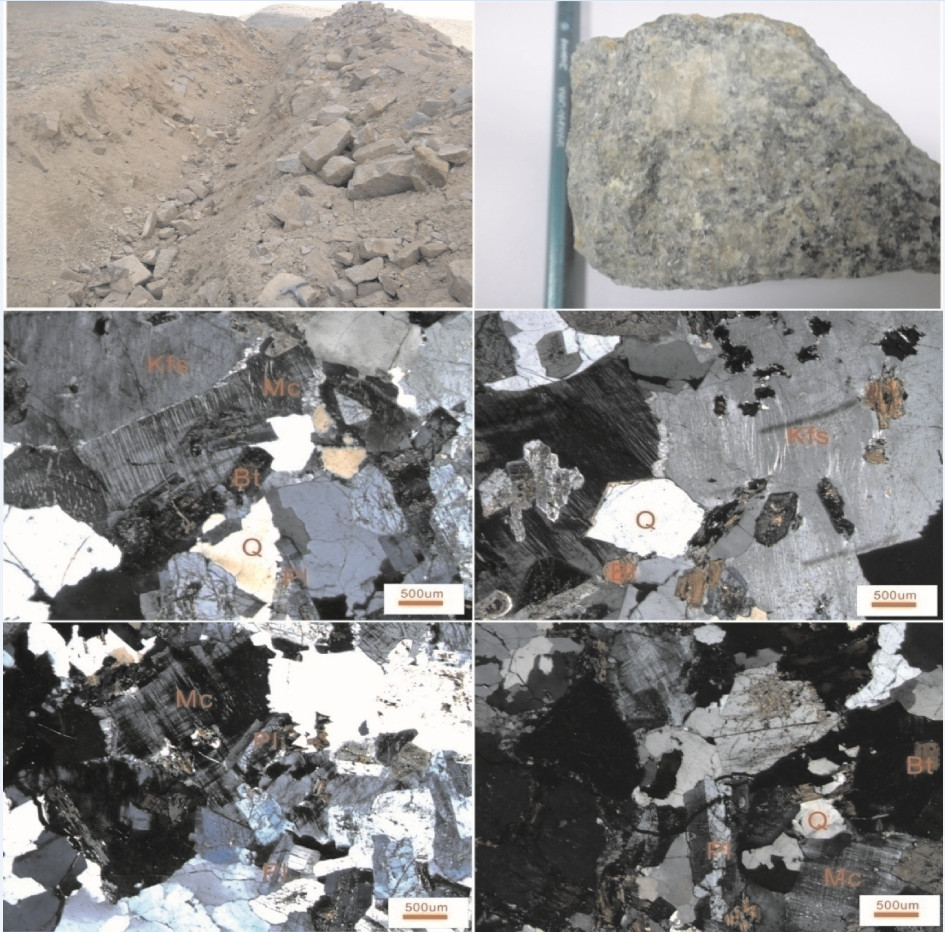
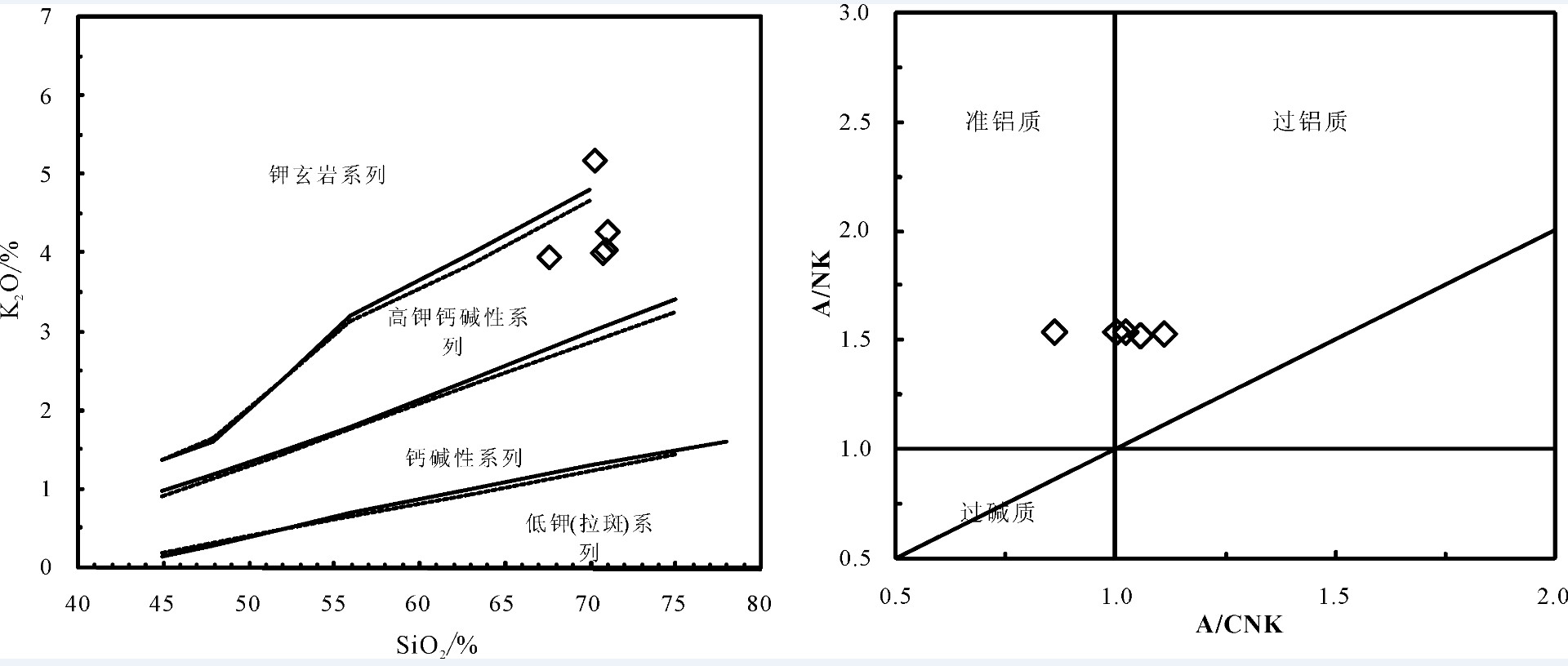
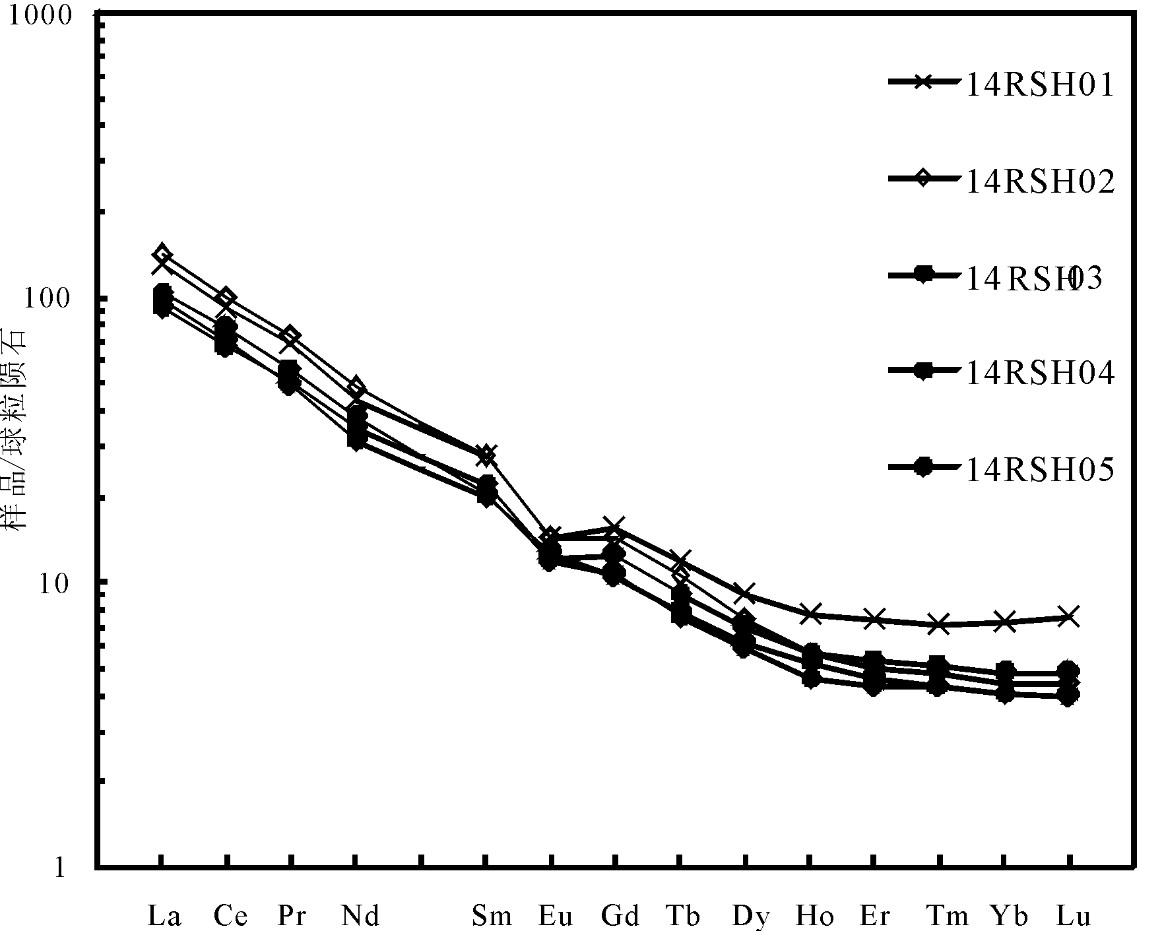
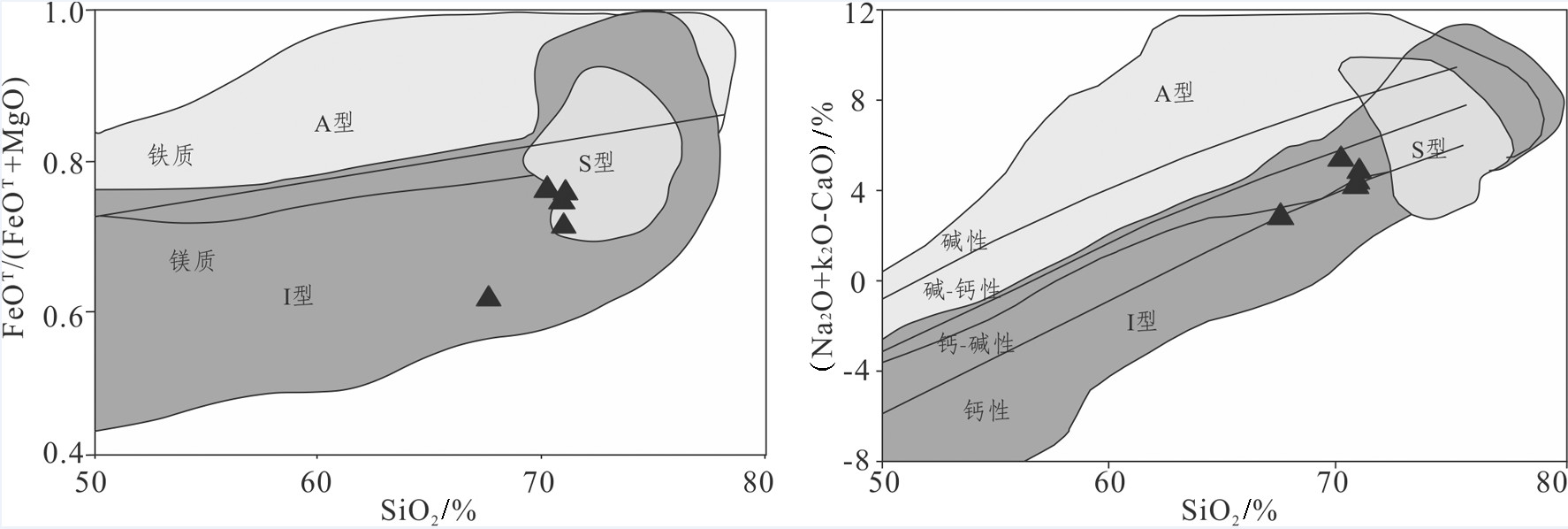
热水钼矿区处于东昆仑造山带东段,大地构造位置位于北昆仑岩浆弧,区内侵入岩较发育,其中与热水钼多金属矿密切相关的矿化似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩岩相学及地球化学数据显示,SiO2含量在67.64%~71.09%,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为0.86~1.11,为准铝质到过铝质,K2O/Na2O值1.35~2.32,里特曼指数为1.73~1.99,属于高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩。岩石总体上富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、U、K、Pb等,明显亏损高场强元素Ta、Nb、Ce等,贫P、Ti。稀土元素总量(ΣREE)为94.27×10-6~127.44×10-6,平均为110.92×10-6,稀土元素配分曲线呈右倾型,具有较明显的轻稀土富集、重稀土亏损的特征,弱到中等程度的负铕异常。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(230.9±1.4)Ma,形成于印支期,钼多金属矿与这一时期岩浆活动密切相关。综合分析表明,似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩形成构造体制转换阶段,在热水地区具有寻找斑岩型矿床潜力。
-
关键词:
- 似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 /
- 地球化学 /
- 锆石U-Pb定年 /
- 热水钼矿区
Abstract:The Reshui Mo polymetallic deposit is located at the North Kunlun magmatic arc, where lots of intrusive rocks occur. Geochemical data reveal that the porphyroid biotite monzogranite from East Kunlun is rich in silicon (67.64%-71.09%), Al2O3 (13.8%-14.57%), Na2O(2.23%-3.02%), and K2O(3.95%-5.18%), with ratios of K2O/Na2O being 1.35-2.32 and A/CNK being 0.86-1.11, 1.01 on average, suggesting that the granite should belong to high potassic calc-alkaline and I type granite. The porphyroid biotite monzogranite is intensively depleted in HFSE (Ta, Nb, mCe), enriched in LILE (Rb, Th, U, K, Pb), and poor in P, Ti. The total rare earth elements (ΣREE) are 94.27×10-6-127.44×10-6, with an average of 110.92×10-6. The rare earth element distribution curve shows the right-inclined type, and has characteristics of obvious enrichment of light rare earth and depletion of heavy rare earth elements. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating shows that the formation age of the rock is (230.9±1.4) Ma, belonging to Indosinian stage. The molybdenum polymetallic deposit is closely related to the magmatic activity during this period. Based on tectonic history and the structure environment in combination with the geochemical characteristics, the authors hold that the porphyritic biotite monzonitic granite of the Reshui deposit was formed at the structural transformation stage, and Rershui area has potential for finding porphyry deposits.
-
1. 前言
太行山存在重力梯度带是华北克拉通最显著的地质特征之一,该梯度带两侧的地貌、大地热流值、地壳厚度和岩石圈厚度存在明显的差异,造成这种差异的原因是华北岩石圈减薄存在时空不均一性[1]。沿该重力梯度带北东向发育大量的晚中生代侵入-火山岩带,特别是在太行山北段。前人对这些侵入岩开展了大量的年代学和地球化学研究[2-3],取得了重要进展。同时在太行山中北段探明存在多个中小型矽卡岩铜多金属矿[4-5]和石湖大型金矿床[6]。近几年在该地区新探明了木吉村大型斑岩型铜(钼)矿[7]和安妥岭大型斑岩型钼矿[8],暗示太行山北段具有很大的找矿潜力。区域地质工作显示,赤瓦屋岩体是太行山北段南部典型的杂岩体[9],前人虽然对该岩体开展过一些锆石测年工作,但多限于岩体边缘相石英闪长岩的研究[10-13],最近的找矿工作新类型铜钨矿体主要集中于岩体中心相斑状花岗闪长岩。因此,本文对赤瓦屋岩体不同岩相开展详细的锆石U-Pb 测年工作,结合区域含矿岩体的年代学资料,以期对太行山北段中生代金属矿床的成矿规律有更明确的认识。
2. 区域地质
研究表明,太行山北段的构造演化大致经历了3 个主要阶段,分别为太古宙变质基底形成阶段、元古宙至古生代稳定发展阶段和中生代活化阶段[14]。阜平杂岩是华北克拉通太古宙变质结晶基底的一部分,现今表现为NE向展布的穹隆状构造,主要岩性为黑云斜长片麻岩、角闪斜长片麻岩、浅粒岩夹斜长角闪岩,该套岩石地层单元普遍遭受强烈区域变质及混合岩化作用[15]。除了阜平杂岩以外,还发育一系列元古宙—侏罗纪沉积地层。岩浆岩是太行山北段中生代活化阶段的产物,沿太行山重力梯度带呈NNE向展布(图 1-a),其分布受东、西两侧分布的NNE 向紫荆关断裂和乌龙沟断裂带控制[5],由NNE向分布的多个岩基(体)和髫髻山组火山岩组成,由北向南依次发育大河南、王安镇岩基和麻棚、赤瓦屋岩体(图 1-b),这些岩体为中酸性高钾钙碱性花岗质岩石[2]。其中王安镇岩基周缘探明了多个斑岩-矽卡岩型多金属矿床,新发现的木吉村大型斑岩铜钼矿和安妥岭大型斑岩型钼矿分别位于该岩基的南缘和北缘;在麻棚岩体西侧1~4 km探明了太行山地区最大的金矿——石湖金矿(图 1-b)。
赤瓦屋岩体位于太行山北段北东向岩浆带的南端,该岩体平面上呈近圆状,直径约5 km,面积约63 km2。根据前人资料和本次野外地质考察,该岩体由不同岩相组成(图 2),自岩体中部向外呈同心圆状展布: 中心相为斑状花岗闪长岩,中粗粒斑状结构,向外过渡为细中粒花岗闪长岩; 边缘相为细粒石英闪长岩(图 3)。不同岩相的黑云母和角闪石含量不同[9],边缘相的黑云母和角闪石含量分别为15%和10%,过渡相分别为10%和5%~10%,中心相角闪石少见,黑云母含量为5%,由边部向内部暗色矿物逐渐减少,暗示岩浆9 演化程度越来越高。除此以外,还发育大量的南北向花岗闪长斑岩脉。
此次野外观察可见,大小为2~10 m的黑色闪长质包体呈椭圆体和透镜状普遍发育于花岗闪长岩中,与寄主岩体边缘清楚。前人对太行山北段岩体开展过成矿潜力评价,赤瓦屋岩体的岩浆分异指数(DI)为75.04,轻重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)均较高,为20.2,黑云母MgO为12.80%~14.28%,石英Ti 含量为17×10-6,全岩的氧同位素为8.89%,暗示赤瓦屋岩体具有较大的成矿潜力[9]。早期资料显示该岩体有铜矿化,最近地勘队发现中心相斑状花岗闪长岩中发育铜钨多金属矿化,可见早阶段NE 向石英黄铁矿白钨矿脉和晚阶段SN 向黄铜矿脉,辉钼矿呈细脉浸染状产于岩体中,多与黄铜矿、黄铁矿共生。
3. 样品采集与测试方法
本次测年工作采集4 个不同岩性的样品,分别为石英闪长岩(CWW14)、花岗闪长岩(CWW2)、斑状花岗闪长岩(CWW12) 和花岗闪长斑岩脉(CWW1),具体采样位置见图 2。将测年样品破碎后,经常规重力和磁选方法分选出锆石,在双目镜下挑纯。将待测锆石颗粒置于环氧树脂中制靶,然后磨至一半用于后期测试。锆石阴极发光在中国地质科学院地质研究所离子探针室HITACHIS3000-N型扫描电子显微镜上完成。在透射光、反射光显微镜观察及阴极发光研究的基础上,选择合适的锆石颗粒进行锆石U-Pb定年测试。
LA-MC-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 定年测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,定年分析所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICPMS及与之配套的Newwave UP 213 激光剥蚀系统。所用激光剥蚀斑束直径为25 μm,频率为10 Hz,能量密度约为2.5 J/cm2,以He 为载气。信号较小的207Pb、206P、204Pb(+204Hg)、202Hg 用离子计数器(multi-ion-counters)接收,208Pb、232Th、238U信号用法拉第杯接收,实现了所有目标同位素信号的同时接收,并且不同质量数的峰基本上都是平坦的,可以获得高精度的数据。均匀锆石颗粒207Pb/206Pb、206Pb/238U、207Pb/235U的测试精度(2σ )均为2%左右,对锆石标准样品的定年精度和准确度在1%(2σ )左右。LA-MC-ICPMS 激光剥蚀采样采用单点剥蚀的方式,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1 调试仪器,使之达到最优状态,锆石U-Pb 定年以锆石GJ-1 为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M257(U: 923×10-6; Th: 439×10-6; Th/U:0.475)[16]为外标进行校正。测试过程中每测定5~7个样品前后重复测定2 个锆石标准样品,对样品进行校正,并测量一个锆石标准Plesovice,观察仪器的状态以保证测试精确度。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal 程序,测量过程中绝大多数分析点206Pb/204Pb>1000,未进行普通铅校正,204Pb 由离子计数器检测,204Pb 含量异常高的分析点可能受包体等普通Pb 的影响,在计算时予以剔除,锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot 3.0 程序获得。样品分析过程中,Plesovice 标样作为未知样品的分析结果为(337.3±1.1)Ma(n=5,2σ),对应的年龄推荐值为(337.13±0.37)Ma(2σ)[17],两者在误差范围内完全一致,测试数据精度较好。
4. 分析结果
赤瓦屋不同岩相花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb 分析测试结果见表 1,锆石U-Pb 谐和图见图 4。由图 4可知,石英闪长岩样品CWW14 锆石多呈长柱状,长为80~250 μm,宽为40~120 μm。本文对石英闪长岩中15 颗锆石进行年代学测试,Th 和U含量分别为100×10-6~306×10-6和150×10-6~347×10-6,其Th/U为0.4~1.5(表 1),谐和年龄为(134±1)Ma,MSWD=3.4; 加权平均年龄为(134±2)Ma,MSWD=0.62(图 4-a)。
表 1 太行山北段赤瓦屋铜钨矿区不同岩相的花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄测年结果Table 1. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb data of different petrofacies of granitoids in Chiwawu area,Northern Taihang Mountain
花岗闪长岩样品CWW2 锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长20~320 μm,宽40~120 μm。本文分析了花岗闪长岩中23 颗锆石,Th 和U 含量分别为59.2×10-6~197×10-6 和105×10-6~289×10-6,其Th/U 为0.4~1.0(表 1),谐和年龄为(133±1)Ma,MSWD=2.3; 加权平均年龄为(133±2)Ma,MSWD=0.37(图 4-b)。
斑状花岗闪长岩样品CWW12锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长120~500 μm,宽80~100 μm。本文分析了斑状花岗长岩中12 粒锆石,Th 和U含量分别为88.6×10-6~492×10-6和227×10-6~596×10-6,其Th/U为0.3~0.8(表 1),谐和年龄为(131±2)Ma,MSWD=2.6; 加权平均年龄为(132±4)Ma,MSWD=0.68(图 4-c)。
花岗闪长斑岩脉样品CWW1锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长200~360 μm,宽10~100 μm。本文分析了斑状花岗长岩中28 粒锆石,Th和U含量分别为45.6×10-6~1303×10-6和83.1×10-6~775×10-6,其Th/U比值为0.4~1.7(表 1),谐和年龄为(128 ±1)Ma,MSWD=6.2; 加权平均年龄为(128±1)Ma,MSWD=2.4(图 4-d)。
5. 讨论
5.1 赤瓦屋岩体时代
赤瓦屋岩体位于太行山北段中生代岩浆带的南部(图 1-b),其形成时代受到高度关注。喻学惠等[5]提出该岩体由同心环状的不同岩相带(石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和斑状花岗闪长岩)组成,全岩Rb-Sr 等时线年龄为135.2 Ma;刘阳等[10] 利用SHRIMP测年获得该岩体北部和西部边缘相石英闪长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄分别为(134.0±5.3)Ma 和(139.8±3.1)Ma;李林林等[12]获得该岩体西部边缘相石英闪长岩的LA-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 年龄为(126.4±2.4) Ma。该岩体北部边缘相花岗闪长岩和闪长岩包体的LA-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 年龄分别为(130±1.0) Ma和(128.2±1.5) Ma[13]。
如前文所述,赤瓦屋岩体除边缘相石英闪长岩外,还存在过渡相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期酸性岩脉,已有的锆石U-Pb 测年工作主要集中于边缘相[10, 12-13]。本文获得赤瓦屋岩体边缘相石英闪长岩、边缘相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期花岗闪长岩岩脉的锆石LAICPMS谐和年龄分别为(134 ±1)Ma、(133±1)Ma、(131±2)Ma和(128±1)Ma,其中本次边缘相的锆石U-Pb 年龄与前人获得的锆石U-Pb 年龄在误差范围内基本一致,表明本次测年数据是可靠的。本文测年数据表明,赤瓦屋岩体不同岩相体形成时代(134~131 Ma)在识差范围内基本一致,暗示岩浆经历了快速侵位、快速冷却结晶的地质过程,类似于邻区的麻棚岩体[12]。据野外实地观察,赤瓦屋岩体形成时代(134~131 Ma)略早于花岗闪长斑岩脉(128Ma),这些与地质穿插关系观察一致。因此,赤瓦屋杂岩体形成于早白垩世,与太行山北段岩基和岩体的时代基本一致(见下文讨论)。
5.2 两期岩浆-成矿事件
由图 1-a 可知,NE向太行山北段岩浆带位于重力梯度带附近,其侵入岩的年龄一直受到高度关注,该带已有的晚中生代岩浆岩锆石U-Pb 年龄数据见表 2。由表 2 可知,太行山北段大河南岩基的石英二长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为127 Ma[18];王安镇岩基中酸性岩浆和包体形成于132~126 Ma,东南部辉石闪长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为138 Ma[3, 18-19];赤瓦屋岩体中酸性岩和包体形成于132~126 Ma[10, 12-13];麻棚中酸性岩体和包体形成于131~124 Ma[6, 10, 12, 20]。除此之外,木吉村斑岩铜矿含矿岩体-闪长玢岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为144.7 Ma[7]和144.1 Ma[21],石湖金矿区石英闪长岩脉的锆石U-Pb 年龄为130 Ma[6]。由此可见,太行山北段晚中生代侵入岩存在2 期岩浆事件,分别为144~138 Ma和132~124 Ma,其中以第二期岩浆事件形成大面积的中酸性岩基和岩体为显著特征,而第一期岩浆事件形成的侵入岩规模相对较小,主要有集中分布于王安镇岩基东南部的辉石闪长岩和木吉村与斑岩铜矿成矿密切相关的闪长玢岩。最近研究表明:木吉村斑岩铜矿区的闪长玢岩是髫髻山火山旋回晚阶段次火山岩相的产物[7],最新测年资料显示,太行山北段和燕山东部北东向发育的髫髻山组火山岩形成于晚侏罗世—早白垩世(151~131 Ma)[22],这些火山岩可能是太行山北段第一期岩浆事件的产物。
表 2 太行山北段晚中生代侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年龄Table 2. Compilation of isotopic ages for important Late Mesozoic intrusions in Northern Taihang Mountain
太行山北段与晚中生代岩浆事件密切相关的成矿作用存在2 期矿化事件,第一期主要为与髫髻山组火山作用相关的斑岩铜钼多金属矿床,如木吉村大型斑岩铜钼矿(图 1-b),其辉钼矿Re-Os 模式年龄为(138.5±1.9) ~(142.7±2.0) Ma[21],5 个辉钼矿Re-Os 样品等时线年龄为(142.5±1.4) Ma[7];在其南侧10 km处的中型大湾斑岩型锌钼矿(图 1-b)的辉钼矿Re-Os模式年龄为(144.4 ± 7.4) Ma[23]。位于大河南与王安镇岩基之间大型安妥岭斑岩钼矿(图 1-b)的5 个辉钼矿Re-Os 样品等时线年龄为(147.3±3.7) Ma[8]或(147.8 ± 0.95) Ma[24]。
在第二期王安镇岩基周围发现了多个铜金矿床,如在木吉村矿区北侧的浮图峪矿田发现60 余处铜矿床(或矿点)(图 1-b),金矿床和矿点更是星罗棋布,遍及全区[5],这些铜矿多为矽卡岩铜铁矿[4]。目前还缺少对这些中小型矽卡岩铜矿成矿时代的精确测年数据,根据含矿岩体的年龄推测,它们可能为第二期的产物。本次野外实地观察发现,赤瓦屋地区早阶段钨矿和晚阶段铜矿呈脉状产于岩体内部相的斑状花岗闪长岩中((131 ±2)Ma),暗示钨铜矿化形成时代不早于131 Ma,赤瓦屋铜钨矿化是第二期成矿事件的产物。另外,在麻棚岩体南缘探明了与岩体密切相关的石英脉状金矿(石湖大型金矿)、隐爆角砾岩型银矿和斑岩钼矿[20],石湖金矿区石英闪长岩脉的锆石U-Pb 年龄为130 Ma,石湖金矿热液钾长石K-Ar 年龄为132~120 Ma[6],麻棚岩体周缘金银钼矿是第二期成矿事件的产物。由此可见,太行山北段晚中生代至少存在两期岩浆-成矿事件,具有较大的找矿潜力。与第一期斑岩型铜钼矿床相比,第二期成矿事件具有成矿类型多样性,晚中生代两期成矿事件特征类似于华南地区[25]。
6. 结论
(1)赤瓦屋岩体边缘相石英闪长岩、过渡相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期花岗闪长岩岩脉形成时代分别为(134 ± 1) Ma、(133 ±1) Ma、(131 ±2) Ma和(128 ±1) Ma,这些数据表明该岩体形成于早白垩世。
(2)太行山北段晚中生代存在两期岩浆-成矿事件,具有较大的找矿潜力。
致谢: 感谢项目组成员在野外的协助,西北大学大陆重点实验室以及中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心国土资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室工作人员在实验及测试上的指导与支持,在此一并感谢。 -
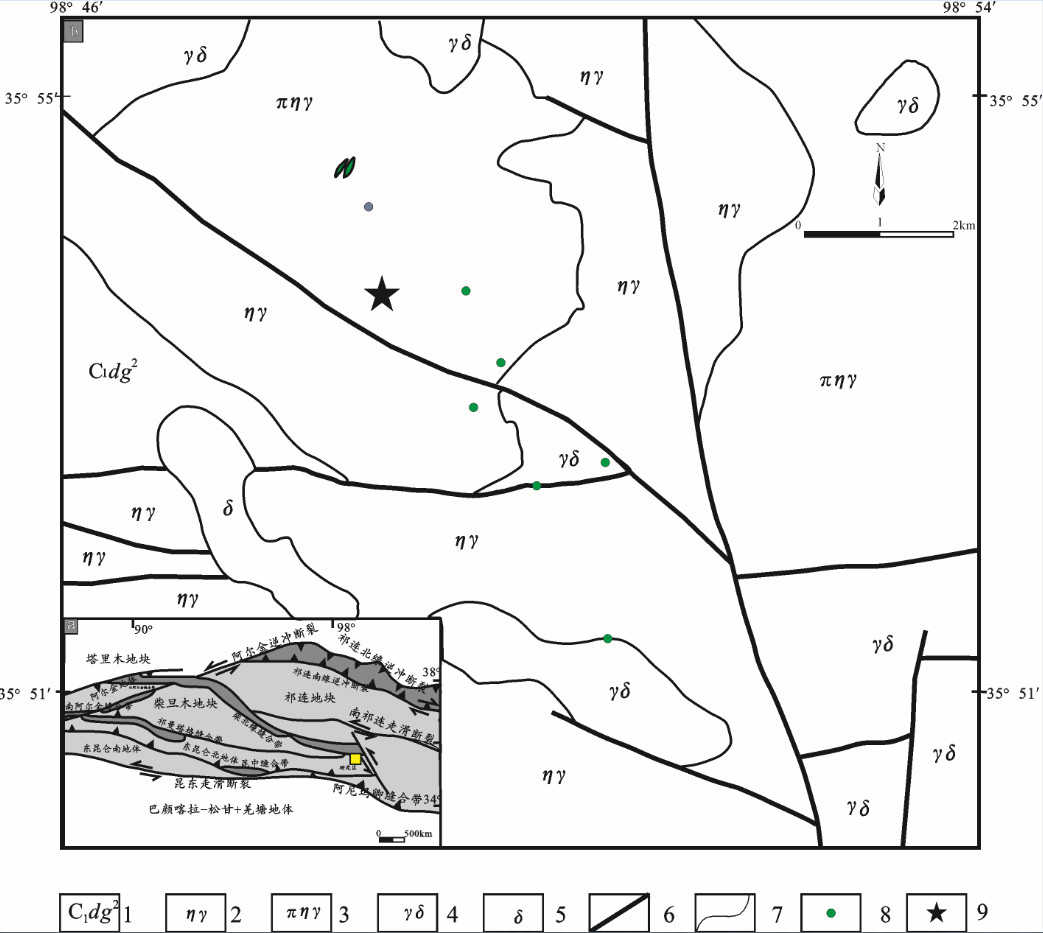
图 1 热水钼多金属矿地质简图(图a据[36, 37]修改)
1—石炭系酸性熔岩组:浅肉红色流纹岩及灰绿色薄层粉砂岩,细砂岩夹灰岩;2—灰白—肉红色二长花岗岩;3—灰白—肉红色似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;4—灰白色花岗闪长岩;5—灰绿色闪长岩、角闪闪长岩;6—断层;7—地质界线;8—铜矿化点;9—采样位置
Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Reshui Mo polymetallic ore district
1-Carboniferous acidic lava group: light red rhyolite and celadon thin layer siltstone, fine sandstone with limestone; 2-Grayish white-red monzonitic granite; 3-Grayish white and red porphyritic monzonitic granite; 4-Grayish white granodiorite; 5-Diorite, hornblende diorite; 6-Fault; 7-Geological boundary; 8-Copper mineralized site; 9-Sampling location
图 4 似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩稀土元素配分模式图(球粒陨石标准化值据[42])
Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of porphyroid biotite monzogranite
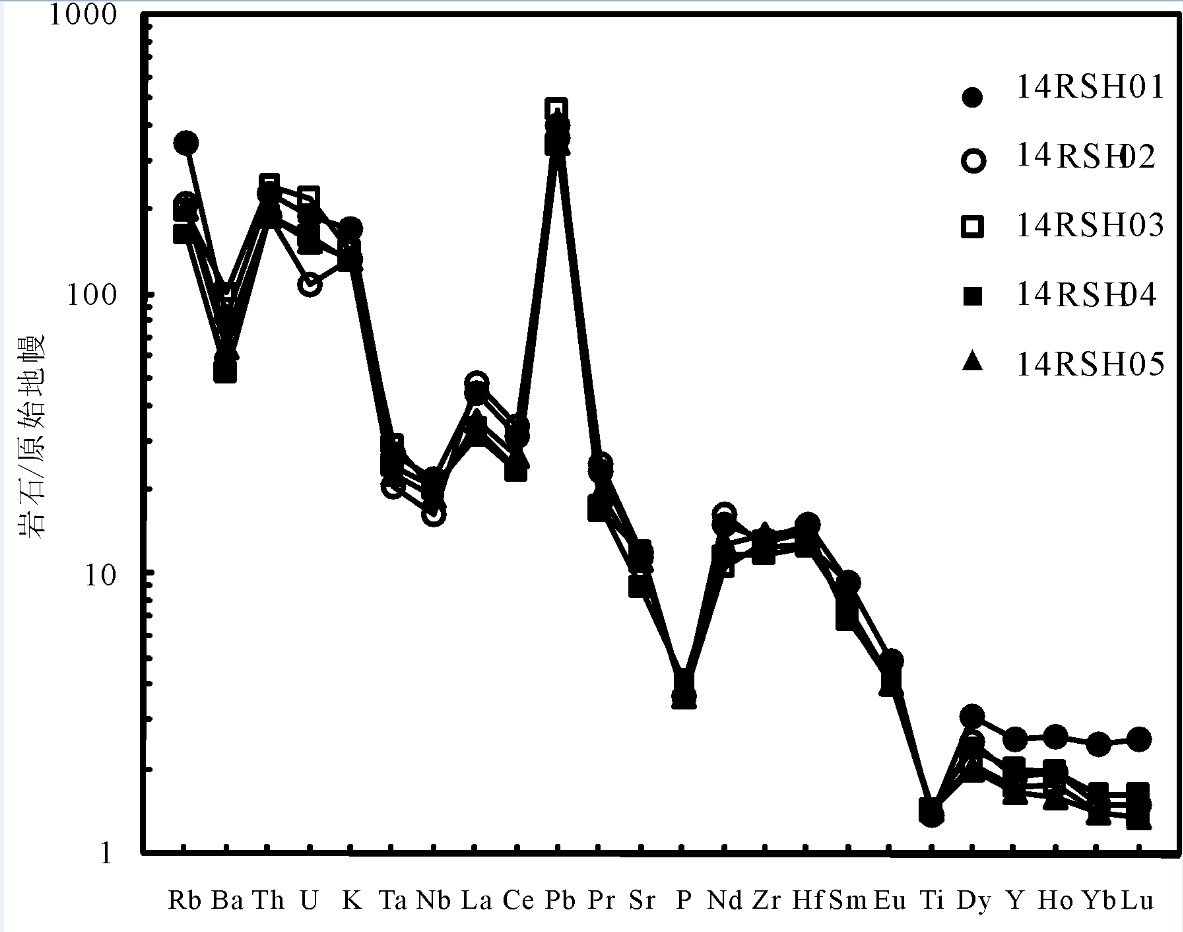
图 5 似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩微量元素蛛网图(原始地幔标准化值据[43])
Figure 5. Primitive mantle-mormoalized trace elemet spirder diagrams of porphyroid biotite monzogranite
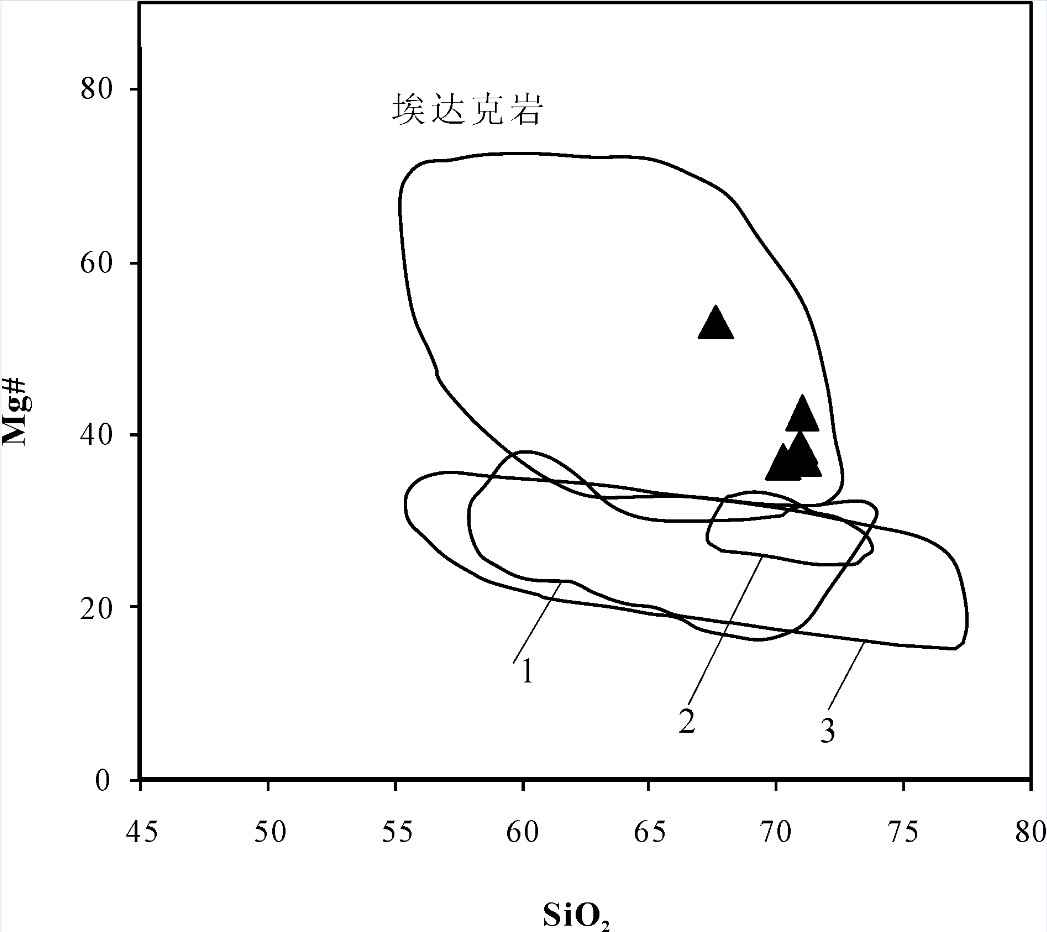
图 9 似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩SiO2-Mg#图
1—压力7 kbar,温度:825~950℃环境下纯地壳的局部熔融(据文献[59]);2—压力7~13 kbar,温度:825~950℃环境下纯地壳的局部熔融(据文献[60]);3—压力8~16 kbar,温度1000~1050℃环境下纯地壳的局部熔融(据文献[56])
Figure 9. Porphyroid biotite monzogranite of SiO2-Mg# diagram
1-Pure crustal partial melt at 7kbar and 825~950℃(after reference [59]); 1-Pure crustal partial melt at 7~13 kbar and 825~950℃(after reference [60]; 3-Pure crustal partial melt at 8~16kbar and 1000~1050℃(after reference [56])
表 1 热水似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩主量元素(%)
Table 1 Major elements (%) of porphyroid biotite monzogranite

表 2 热水似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩微量元素(10-6)和稀土元素(10-6)
Table 2 Trace elements (10-6) and REE (10-6) of porphyroid biotite monzogranite

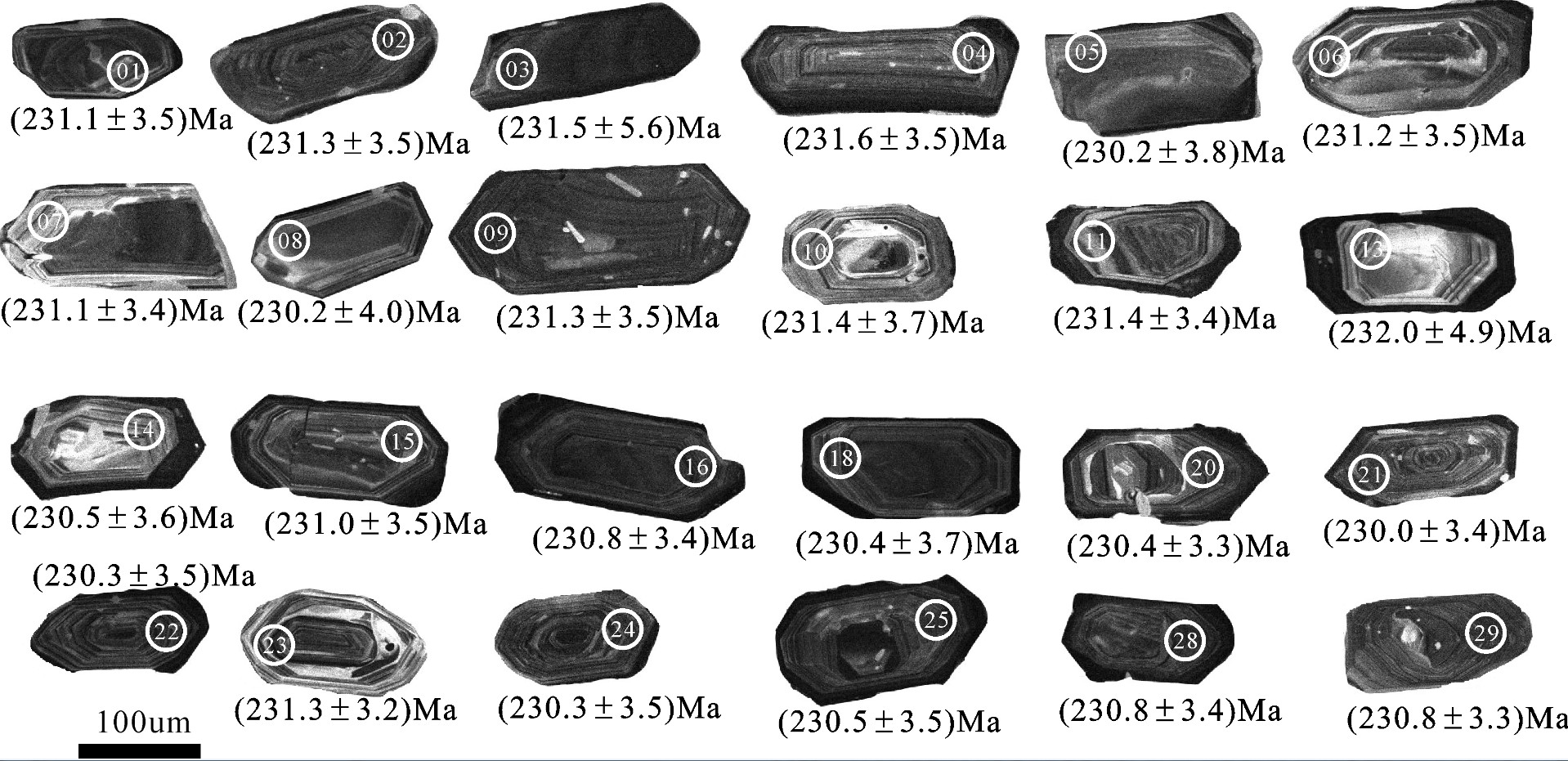
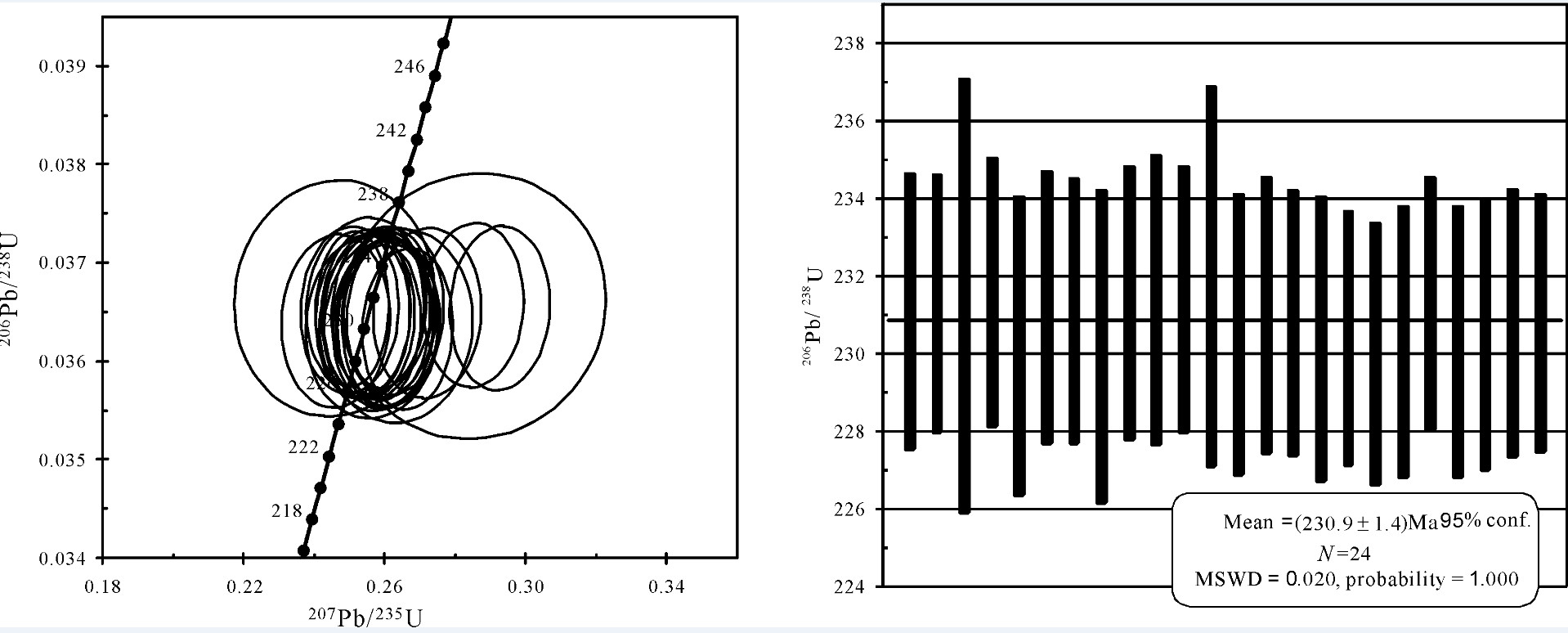
表 3 似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试结果
Table 3 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotope analytical results of porphyroid biotite monzogranite

表 4 热水地区印支期含矿岩体(矿床)年龄及测试方法
Table 4 Age of Indosinian ore-beariang rock mass and testing method

-
[1] 袁万明, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等.东昆仑印支期区域构造背景的花岗岩记录[J].地质论评, 2000, 46(2):203-211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200002012.htm Yuan Wanming, Mo Xuanxue, Yu Xuehu, et al.The record of Indosinian tectonic setting from the granotoid of Eastern Kulun Mountains[J].Geological Review, 2000, 46(2):203-211(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200002012.htm
[2] 姜春发.中央造山带几个重要地质问题及其研究进展(代序)[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(8):453-455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2002Z2000.htm Jiang Chunfa.Several important geological problems of central orogenic belt and its research progress[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(8):453-455(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2002Z2000.htm
[3] 刘成东.东昆仑造山带东段花岗岩岩浆混合作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008. Liu Chengdong.East Section of East Kunlun Orogenic Belt Granite Magma Mingling[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] 杜玉良, 贾群子, 韩生福.青海东昆仑成矿带中生代构造-岩浆-成矿作用及铜金多金属找矿研究[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(4):69-75. Du Yuliang, Jia Qunzi, Han Shengfu.Mesozoic tectonomagmatic-mineralization and copper-gold polymetallic ore prospecting research in east Kunlun Metallogenic Belt in Qinghai[J].Northwestern Geology, 2012, 45(4):69-75(in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] 丰成友, 李东生, 吴正寿, 等.东昆仑祁漫塔格成矿带矿床类型、时空分布及多金属成矿作用[J].西北地质, 2010, 43(4):10-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201004004.htm Feng Chengyou, Li Dongsheng, Wu Zhengshou, et al.Major types, time-space distribution and metallogeneses of polymetallic deposits in the Qimantag Metallogenic Belt, Eastern Kunlun area[J].Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4):10-17(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201004004.htm
[6] 丰成友, 赵一鸣, 李大新, 等.青海西部祁漫塔格地区矽卡岩型铁铜多金属矿床的矽卡岩类型和矿物学特征[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(7):1108-1115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201107005.htm Feng Chengyou, Zhao Yiming, Li Daxin, et al.Skarn types and mineralogical characteristics of the Fe-Cu-polymetallic skarn deposits in the Qimantag area, Western Qinghai Province[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(7):1108-1115(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201107005.htm
[7] 伍跃中, 乔耿彪, 陈登辉.东昆仑祁漫塔格地区构造岩浆作用与成矿关系初步探讨[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 25(2):232-241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201102009.htm Wu Yuezhong, Qiao Gengbiao, Chen Denghui.A preliminary study on relationship between tectonic magmatism and mineralization in Qimantag area, Eastern Kunlun Mountains[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(2):232-241(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201102009.htm
[8] 武明德.青海省东昆仑燕山期斑岩型矿床成矿潜力研究[D].中国地质大学(北京), 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1014125461.htm Wu Mingde.Ore Potential of the Yanshanian Porphyry Deposit, East Kunun of Qinghai Province[D].China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1014125461.htm
[9] 许长坤, 刘世宝, 赵子基, 等.青海省东昆仑成矿带铁矿成矿规律与找矿方向研究[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(10):1621-1636. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201210007.htm Xu Changkun, Liu Shibao, Zhao Ziji, et al.Metallogenic law and prospect direction of iron deposists in the East Kunlun Metallogenic Belt in Qinghai[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(10):1621-1636(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201210007.htm
[10] 赵财胜.青海东昆仑造山带金、银成矿作用[D].长春:吉林大学, 2004. http://www.oalib.com/references/19182596 Zhao Caisheng.Gold, Silver Metallogeny in Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/references/19182596
[11] 赵俊伟.青海东昆仑造山带造山型金矿床成矿系列研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2008. http://www.oalib.com/references/18449192 Zhao Junwei.Study on Orogenic Gold Mettallogenic Series in Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/references/18449192
[12] 张文秦.青海省东昆仑地区火成岩的岩石-地球化学基本特征及含矿性研究[D].中国地质大学(北京), 2003. Zhang Wenqin.The East Kunlun Area of Igneous Rock-Geochemical Characteristics and Ore Research, Qinghai Province[D].China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2003(in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] 张德全, 丰成友, 李大新, 等.柴北缘-东昆仑地区的造山型金矿床[J].矿床地质, 2001, 20(2):137-146. Zhang Dequan, Feng Chengyou, Li Daxin, et al.Orogenic gold deposits in the North Qaidam and East Kunlun Orogen, West China[J].Mineral Deposits, 2001, 20(2):137-146(in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] 胡正国, 刘继庆, 钱壮志, 等.东昆仑区域成矿规律初步研究[J].黄金科学技术, 1998, 6(5):6-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ8Z1.001.htm Hu Zhengguo, Liu Jiqing, Qian Zhuangzhi, et al.A study of the regional metallogenetic regularity in East Kunlun Mountain[J].Gold Science and Technology, 1998, 6(5):6-13(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ8Z1.001.htm
[15] 罗照华, 柯珊, 曹永清, 等.东昆仑印支晚期幔源岩浆活动[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(6):292-297. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200206002.htm Luo Zhaohua, Ke Shan, Cao Yongqing, et al Late Indosinian mantle-derived magmatism in the East Kunlun[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(6):292-297(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200206002.htm
[16] 王松, 丰成友, 李世金, 等.青海祁漫塔格卡尔却卡铜多金属矿区花岗闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(1):74-84. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090105&flag=1 Wang Song, Feng Chengyou, Li Shijin, et al.Zircon SHRIMP UPb dating of granodiorite in the Kaerqueka polymetallic ore deposist, Qimantag Mountain, Qinghai Province, and its geological implications[J].Geology in China, 2009, 36(1):74-84(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090105&flag=1
[17] 苏旭亮, 赵永亮, 赵闯, 等.东昆仑祁漫塔格克停哈尔斑岩型铜钼矿找矿突破思路及找矿模型[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(6):2048-2062. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140619&flag=1 Su Xuliang, Zhao Yongliang, Zhao Chuang, et al.Prospecting thinking and model for the Ketinghaer porphyry copper molybdenum deposit in the East Kunlun Mountains[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(6):2048-2062(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140619&flag=1
[18] 刘建楠, 丰成友, 亓锋, 等.青海都兰县下得波利铜钼矿区锆石UPb测年及流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):679-690. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202026.htm Liu Jiannan, Feng Chengyou, Qi Feng, et al.SIMS zircon U-Pb dating and fluid inclusion studies of Xiadeboli Cu-Mo ore district in Dulan County, Qinghai Province, China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2):679-690.(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202026.htm
[19] 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等.青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩:年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):665-678. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202025.htm Feng Chengyou, Wang Song, Li Guocheng, et al.Middle to Late Triassic granitoids in the Qimantag area, Qinghai Province, China:Chronology, geochemistry and metallogenic significances[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2):665-678(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202025.htm
[20] 姜常义, 凌锦兰, 周伟, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木镁铁质-超镁铁质岩体岩石成因与拉张型岛弧背景[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(4):1117-1136. Jiang Changyi, Lin Jinlan, Zhou Wei, et al.Petrogenesis of the Xiarihamu Nibearing layered mafic-ultramafic intrusion, East Kunlun:Implications for its extensional island arc environment[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(4):1117-1136(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] 杨延乾, 李碧乐, 许庆林, 等.东昆仑埃坑德勒斯特二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].西北地质, 2013, 46(1):56-62. Yang Yanqian, Li Bile, Xu Qinglin, et al.Zircon U-Pb ages and its geological significance of the monzonitic granite in the Aikengdelesite, Eastern Kunlun[J].Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(1):56-62(in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] 奚仁刚, 校培喜, 伍跃中, 等.东昆仑肯德可克铁矿区二长花岗岩组成、年龄及地质意义[J].西北地质, 2010, 43(4):195-202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201004029.htm Xi Rengang, Xiao Peixi, Wu Yuezhong, et al.The geological significances, composition and age of the monzonitic granite in Kendekeke Iron Mine[J].Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4):195-202(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201004029.htm
[23] 奥琮, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等.青海夏日哈木矿区中泥盆世闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].西北地质, 2014, 47(1):96-106. Ao Cong, Sun Fengyue, Li Bile, et al.Geochemistry, Zircon UPb dating and geological significance of diorite porphyrite in Xiarihamu Deposit, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai[J].Northwestern Geology, 2014, 47(1):96-106(in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 杨延乾, 李碧乐, 许庆林, 等.东昆仑埃坑德勒斯特二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].西北地质, 2013, 46(1):56-62. Yang Yanqian, Li Bile, Xu Qinglin, et al.Zircon U-Pb ages and its geological significance of the monzonitic granite in the Aikengdelesite, Eastern Kunlun[J].Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(01):56-62(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] 高永宝, 李文渊, 马晓光, 等.东昆仑尕林格铁矿床成因年代学及Hf同位素制约[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(2):36-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201202008.htm Gao Yongbao, Li Wenyuan, Ma Xiaoguang, et al.Genesis, geoehronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the magmatic rocks in Galinge iron deposit, Eastern Kunlun[J].Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences)2012, 48(2):36-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201202008.htm
[26] 赵财胜, 杨富全, 代军治.青海东昆仑肯德可克钴铋金矿床成矿年龄及意义[J].矿床地质, 2006, (S1):427-430. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2006S1113.htm Zhao Caisheng, Yang Fuquan, Dai Junzhi.Metallogenic age of the Kendekeke Co, Bi, Au deposit in East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, and its significance[J].Mineral Deposits, 2006, (S1):427-430(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2006S1113.htm
[27] 肖晔, 丰成友, 刘建楠, 等.青海肯德可克铁多金属矿区年代学及硫同位素特征[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(01):177-186. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201301016.htm Xiao Ye, Feng Chegyou, Liu Jiannan, et al.LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and sulfur isotope characteristics of Kendekeke Fe-polymetallic deposit, Qinghai Province[J].Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(01):177-186(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201301016.htm
[28] 丰成友, 王雪萍, 舒晓峰, 等.青海祁漫塔格虎头崖铅锌多金属矿区年代学研究及地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6):1806-1817. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201106014.htm Feng Chengyou, Wang Xueping, Shu Xiaofeng, et al.Isotopic chronology of the Hutouya skarn lead-zinc polymetailic ore district in Qimantag area of Qinghai Province and its geological significance[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(6):1806-1817(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201106014.htm
[29] 李世金, 孙丰月, 丰成友, 等.青海东昆仑鸭子沟多金属矿的成矿年代学研究[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):949-955. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200807015.htm Li Shijin, Sun Fengyue, Feng Chengyou, et al.Geochronological study on Yazigou polymetallic deposit in Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province[J].Acta Geological Sinica, 2008, 82(7):949-955(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200807015.htm
[30] 南卡俄吾, 贾群子, 李文渊, 等.青海东昆仑哈西亚图铁多金属矿区石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2014, (6):841-849. Namhka Norbu, Jia Qunuzi, Li Wenyuan, et al.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of quartz diorite from the Haxiyatu iron-polymetallic ore district in Eastern Kunlun[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, (6):841-849(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] 孔会磊, 李金超, 栗亚芝, 等.青海东昆仑东段按纳格闪长岩地球化学及锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(6):11-17. Kong Huilei, Li Jinchao, Li Yanzhi, et al.Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of annage diorite in the Eastern Section from East Kunlun in Qinghai Province[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(6):11-17(in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 何书跃, 李东生, 李良林, 等.青海东昆仑鸭子沟斑岩型铜(钼)矿区辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(2):236-242. He Shuyue, Li Dongsheng, Li Lianglin, et al.Re-Os age of molybdenite from the Yazigou copper (molybdenum) mineralized area in Eastern Kunlun of Qinghai Province, and its geological significance[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(2):236-242(in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 宋忠宝, 张雨莲, 陈向阳, 等.东昆仑哈日扎含矿花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(1):157-168. Song Zhongbao, Zhang Yulian, Chen Xiangyang, et al.Geochemical characteristics of Harizha granite diorite-porphyry in East Kunlun and their geological implications[J].Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(1):157-168(in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] 许庆林.青海东昆仑造山带斑岩型矿床成矿作用研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2014. Xu Qinglin.Study on Metallogenesis of Porphyry Deposits in Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 殷鸿福, 张克信.中央造山带的演化及其特点[J].地球科学, 1998, 23(5):437-442. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX805.000.htm Yin Hongfu, Zhang Kexin.The evolution of the central orogenic belt and its characteristics[J].Journal of Earth Science, 1998, 23(5):437-442(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX805.000.htm
[36] Song Shuguang, Niu Yaoling, Su Li, et al.Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling:The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 129(1):59-84. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2075328050&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[37] 许志琴, 姜枚, 杨经绥.青藏高原北部隆升的深部构造物理作用:以"格尔木-唐古拉山"地质及地球物理综合剖面为例[J].地质学报, 1996, 70(3):195-206. Xu Zhiqin, Jiang Mei, Yang Jingsui.Tectonophysical process at depth for the uplife of the Northern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau:illustrated by the geological and geophysical comprehensive profile from Golmud to the Tanggula Mountains, Qinghai Province China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 1996, 70(3):195-206(in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yuan Honglin, Gao Shan, Dai Mengning, et al.Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1/2):100-118. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2001772043&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[39] Ludwig K R.Mathematical-statistical treatment of data and errors for 230Th/U geochronology[J].Reviews in Mineralogy &Geochemistry, 2003, 52(1)631-656. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2011085792&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[40] Rickwood Peter C.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J].Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
[41] Peccerillo Angelo, Taylor S R.Geochemistry of Eocene calcalkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
[42] Boynton W V.Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements:meteoric studies[J].Rare Earth Element Geochemistry, 1984:63-114. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2245266537&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[43] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[44] 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei.Zircon genetic mineralogy research and interpretation of U-Pb age restriction[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604(in Chinese).
[45] Yang Shuiyuan, Jiang Shaoyong, Jiang Yaohui, et al.Geochemical, zircon U-Pb dating and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the age and petrogenesis of an Early Cretaceous volcanic-intrusive complex at Xiangshan, Southeast China[J].Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 58(11):21-48. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2095157687&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[46] Claesson S, Vetrin V, Bayanova T, et al.U-Pb zircon ages from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola Peninsula, Russia:A record of geological evolution from the Archaean to The Palaeozoic[J].Lithos, 2000, 51(1):95-108. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2038728224&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[47] 李文良, 夏锐, 卿敏, 等.应用辉钼矿Re-Os定年技术研究青海什多龙矽卡岩型钼铅锌矿床的地球动力学背景[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(06):900-907. Li Wenliang, Xia Rui, Qing Min, et al.Re-Os molybdenite ages of the shenduolong skarn Mo-Pb-Zn deposit and geodynamic framework, Qinghai Province[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(06):900-907(in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Xia Rui, Wang Changming, Qing Min, et al.Molybdenite Re-Os, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of the Shuangqing Fe-Pb-Zn-Cu skarn deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66:114-131. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.024
[49] 孙延贵, 张国伟, 郑健康, 等.柴达木地块东南缘岩浆弧(带)形成的动力学背景[J].华南地质与矿产, 2001, (04):16-21. Sun Yangui, Zhang Guowei, Zheng Jiankang, et al.Analysis of dynamic backgrounds of magmatic arc in the southeastern margin of Qaidam massif[J].Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2001, (04):16-21(in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] Frost B Ronald, Barnes Calvin G, Collins William J, et al.A geochemical classification for granitic rocks[J].Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(11):2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
[51] Pitcher Wallace Spencer.Granites and yet more granites forty years on[J].Geologische Rundschau, 1987, 76(76):51-79.
[52] Pearce Julian A, Harris Nigel B W, Tindle Andrew G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J].Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[53] Petford Nick, Atherton Michael.Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust:the Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru[J].Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(6):1491-1521. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491
[54] Defant Marc J, Mmond Mark S.Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J].Nature, 1990, 347(6294):662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[55] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境:火山岩约束[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):534-546. Zhu Dicheng, Pan Guitang, Mo Xuanxue, et al.Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting in middle-northern Gangdese:New insights from volcanic rocks[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(3):534-546(in Chinese with English abstract).
[56] Rapp Robert P, Watson E.Bruce.Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J].Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[57] Barth Matthias G, Nough William F, Rudnick Roberta L.Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J].Chemical Geology, 2000, 165(99):197-213. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1988215475&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[58] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[59] Sisson T W, Ratajeski K, Hankins W B, et al.Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources[J].Contributions to Mineralogy&Petrology, 2005, 148(6):635-661. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2053396208&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[60] Douce Alberto E, Patiño, Johnston A.Dana.Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system:implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites[J].Contributions to Mineralogy&Petrology, 1991, 107(2):202-218. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1966564764&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[61] Roberts Malcolm P., Clemens John D.Origin of high-potassium, talc-alkaline, I-type granitoids[J].Geology, 1993, 21(9):825. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2
[62] 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等.东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):403-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htm Mo Xuanxue, Luo Zhaohua, Deng Jinfu, et al.Granite and crustal growth orogenic belt of East Kunlun[J].Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3):403-414(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htm
[63] 熊富浩.东昆仑造山带东段古特提斯域花岗岩类时空分布、岩石成因及其地质意义[D].中国地质大学(武汉), 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10491-1014340842.htm Xiong Fuhao.Spatial-temporal Pattern, Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of Paleo-Tethyan Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt (Eastern Segment)[D].China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10491-1014340842.htm
[64] 郭正府, 邓晋福, 许志琴, 等.青藏东昆仑晚古生代末-中生代中酸性火成岩与陆内造山过程[J].现代地质, 1998, 12(3):344-352. Guo Zhengfu, Deng Jinfu, Xu Zhiiqin, et al.Late Palaeozoicmesozoic intracontinental orogenic process and iniermedate-acidic igneous rocks from the Eastern Kunlun Mountains of Northwestern China[J].Geoscience, 1998, 12(3):344-352(in Chinese with English abstract).
[65] 孙延贵.西秦岭-东昆仑造山带的衔接转换与共和坳拉谷[D].西安:西北大学, 2004. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10697-2004104020.htm Sun Yangui.Gonghe Aulaeogen and Conjugate and Transfer between the West Qinling and East Kunlun orogens[D].Xi'an:Northwest University, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10697-2004104020.htm
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 孙杨,谢远云,迟云平,康春国,吴鹏. 大兴安岭东麓龙江县白土山组地层特征:化学风化、沉积循环、源-汇体系和沉积环境. 山地学报. 2022(01): 14-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 仲米山,吕东霖,王岐,张化南,敖光,吴子杰,杨运来,王艺龙,谭超. 大兴安岭中段索伦地区林西组岩石地球化学特征与沉积构造环境. 中国地质调查. 2022(05): 89-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张海华,李晓海,张健,郑月娟,陈树旺,张德军,苏飞,卞雄飞,孙雷. 松辽盆地北部上二叠统林西组古生物年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 现代地质. 2021(02): 568-578 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张健,张海华,陈树旺,郑月娟,张德军,苏飞,黄欣. 松辽盆地北部上二叠统林西组地球化学特征及地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2020(02): 518-530 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张德军,张健,郑月娟,陈树旺,苏飞,黄欣,张海华,甄甄. 内蒙古自治区兴安盟突泉盆地TD-2井晚二叠世孢粉的发现及其油气地质意义. 中国地质. 2020(03): 798-809 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 邢作昌,张忠涛,林畅松,张博,洪方浩,张正涛. 珠江口盆地荔湾凹陷上渐新统—早中新统物源特征及其对沉积充填的影响. 中国地质. 2020(05): 1577-1588 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 陈兴,彭成龙,陈建书,吴开彬,张德明,王文明,龚桂源,邓贵标,骆珊. 右江盆地中三叠世碎屑岩地球化学特征及其物源分析∶以贵州册亨地区为例. 高校地质学报. 2020(06): 639-655 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: