The origin of the mantle peridotite from ophiolitite in northeast Jiangxi and its geological implications
-
摘要:
赣东北蛇绿岩作为华南少有的前寒武纪蛇绿岩长期都是华南大地构造研究中的热点。该蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩以方辉橄榄岩为主,稀土总量为0.83×10-6~2.62×10-6,远低于原始地幔的含量,而MgO含量高于原始地幔。稀土元素表现为LREE相对富集,微量元素表现为大离子亲石元素(LILE)富集,高场强元素Nb明显亏损的特征,这表明赣东北地幔橄榄岩具有亏损地幔源区特征,同时也有不同程度的俯冲带流体的交代特征。HREE模拟的部分熔融程度为10%~30%;同时,赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩中同时包含Cr#>60和Cr# < 60两种不同成因的铬尖晶石,说明其经历了MOR(mid-ocean ridge)和SSZ(supra-subduction zone)两种构造环境。结合前人资料,笔者推测赣东北蛇绿岩早先可能形成于洋中脊环境(约1060 Ma),随后在洋内俯冲作用下(约970 Ma),位于俯冲带上部的地幔橄榄岩受到了来自俯冲带的流体/熔体的交代,经历了SSZ环境的改造。
Abstract:The ophiolite in northeast Jiangxi is one of rare Precambrian ophiolites in Jiangnan orogenic belt and also a hot topic for the tectonics of South China. The mantle peridotite mainly consists of harzburgite. Compared with primitive mantle, the peridotites have lower total REE values varying from 0.83×10-6 to 2.62×10-6 and higher MgO content. On the chondrite-normalized REE patterns, the rocks display enriched LREE patterns. When normalized to primitive mantle, all samples show variable enrichment of LILEs and are characterized by significant Nb negative anomalies. These features imply a depleted mantle source, which was overlapped by fluid alteration in a subduction zone. On the HREE patterns, the calculation shows that the harzburgites exhibit the residues of 10%-30% partial melting of the mantle source. Meanwhile, the spinels from mantle peridotites in northeast Jiangxi can be divided into two types which are Cr#>60 and Cr# < 60 in the light of their chemical compositions. It is thus concluded that the spinels are of characteristics of both MOR and SSZ setting. In combination with previous researches, the authors infer that ophiolites in northeast Jiangxi originated in a MOR setting at ca. 1060 Ma, and was modified by melts and fluids in a SSZ mantle wedge at ca. 970 Ma.
-
Keywords:
- mantle peridotite /
- spinel /
- ophiolite in northeast Jiangxi MOR /
- SSZ /
-
造山带中的蛇绿岩可以为大洋岩石圈的岩浆事件、变质事件、构造作用以及古洋盆演化的过程提供重要的信息[1]。赣东北蛇绿岩位于江南造山带东段(图 1-a),是华南目前公认的少数前寒武纪蛇绿岩之一[2],蕴含了有关江南造山带乃至华南前寒武纪大地构造演化的重要信息,一直以来都是华南前寒武纪研究的热点而备受关注[3-14]。
前人对赣东北蛇绿岩的形成环境的研究,多集中在火山岩的地球化学和同位素方面,且较为一致的认为其为SSZ型蛇绿岩,形成于岛弧环境或弧后盆地环境中[6, 12, 15-17]。而对于蛇绿岩中的地幔橄榄岩的研究工作,尚比较薄弱。蛇绿岩中的橄榄岩可为地幔熔融过程,岩石-流/熔体反应提供重要的信息,进而为蛇绿岩形成的构造背景的研究提供重要线索[18]。
本文对赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩进行了系统研究,为赣东北蛇绿岩的性质和演化过程提供了新的制约。
1. 区域地质概况
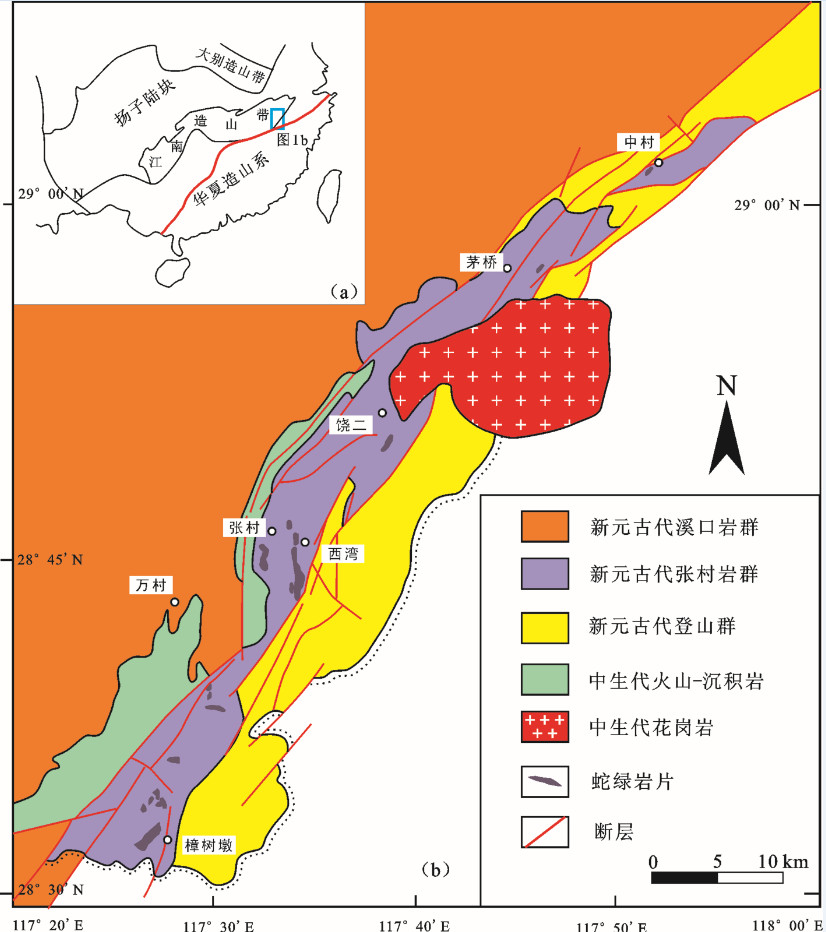
赣东北断裂带是扬子东南缘一条重要的地体构造边界,即江南东段九岭地体和怀玉地体的分界线[8, 19-21]。沿该断裂带广泛分布中—新元古代基性-超基性岩块,构成NNE向展布的赣东北蛇绿岩带。赣东北蛇绿岩带南起弋阳樟树墩,北至德兴中村,全长约80 km,呈NNE方向展布(图 1-b)。它们由一系列基性-超基性岩块组成,包括樟树墩、西湾、饶二和茅桥等超基性岩块,构造侵位在张村岩群浅变质火山-沉积岩中[4, 12, 15]。赣东北蛇绿岩的原始层序已经被构造肢解,岩性复杂,主要岩石类型为变质橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩、辉石岩、辉绿岩、闪长岩、浅色花岗岩、玄武岩和硅质岩[5]。地幔橄榄岩出露面积最大,普遍强烈蛇纹石化。辉长岩和辉绿岩规模较小。浅色花岗岩出露在西湾变质橄榄岩中,呈团块状散布,出露面积很小。这些浅色花岗岩可分为2类:一类为俯冲型的钠长花岗岩,年龄约为970Ma[9, 14];另一类为代表仰冲型的黑云母花岗岩,年龄约为880 Ma[13]。变质火山岩主要为变质玄武岩和细碧岩[17]。与赣东北蛇绿岩套共生的沉积岩则出现大量的白云质大理岩和条带状大理岩,是典型的深海沉积岩[7]。在西湾变质橄榄岩与千枚岩之间的断层接触带上,前人还报道见有高压变质岩,由蓝闪石片岩、硬玉钠长石片岩与千枚岩混杂组成,并获得高压变质矿物(蓝闪石/青铝闪石)K-Ar年龄为866 Ma左右[8]。赣东北蛇绿岩内的这些岩石单元普遍经历了低绿片岩相变质,并强烈地构造变形, 与围岩呈明显的构造接触,在接触带上存在明显的挤压破碎带。
2. 分析方法
在详细野外观察基础上,系统采集樟树墩和西湾等地地幔橄榄岩样品,显微镜下开展详细岩相学研究,选择较为新鲜的样品进行全岩地球化学分析。全岩主量分析在南京地质矿产研究所实验室完成,主量元素用原子荧光光谱仪(AFS-2202a)分析,微量元素采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ELMENT2)分析,分析精度相对误差符合DZ/T0130-2006行业标准。分析结果见表 1。
表 1 赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩主量(%)、微量和稀土元素(10-6)组成Table 1. Major (%), trace and rare earth (10-6) elements compositions of the mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi 表 2 赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩全岩CIPW标准矿物计算的矿物成分Table 2. Mineral composition of the mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi ophiolites calculated by CIPW method
表 2 赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩全岩CIPW标准矿物计算的矿物成分Table 2. Mineral composition of the mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi ophiolites calculated by CIPW method
选择代表性矿物进行电子探针成分分析及背散射图像分析(BSE)。所有分析均在中国冶金地质总局山东测试中心用JOEL JXA 8230型电子探针完成。选用15 kV加速电压,20 nA电子束电流,5µm电子束直径。标准样品选用硬玉(Si、Na)、橄榄石(Mg)、铁铝榴石(Fe、Al)、透辉石(Ca)、钾长石(K)、氧化铬(Cr)、金红石(Ti)、硅化镍(Ni)、金属钴(Co)、蔷薇辉石(Mn)、磷灰石(P)。Ni、Co、F、Mn的测试时间为30 s,其他的元素的测试时间为10 s。详细的分析误差及分析方法见[22]。分析结果见表 3。
表 3 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩中尖晶石电子探针分析结果(%)Table 3. Electron microprobe analyses of spinel in mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi ophiolites
3. 岩石地球化学特征
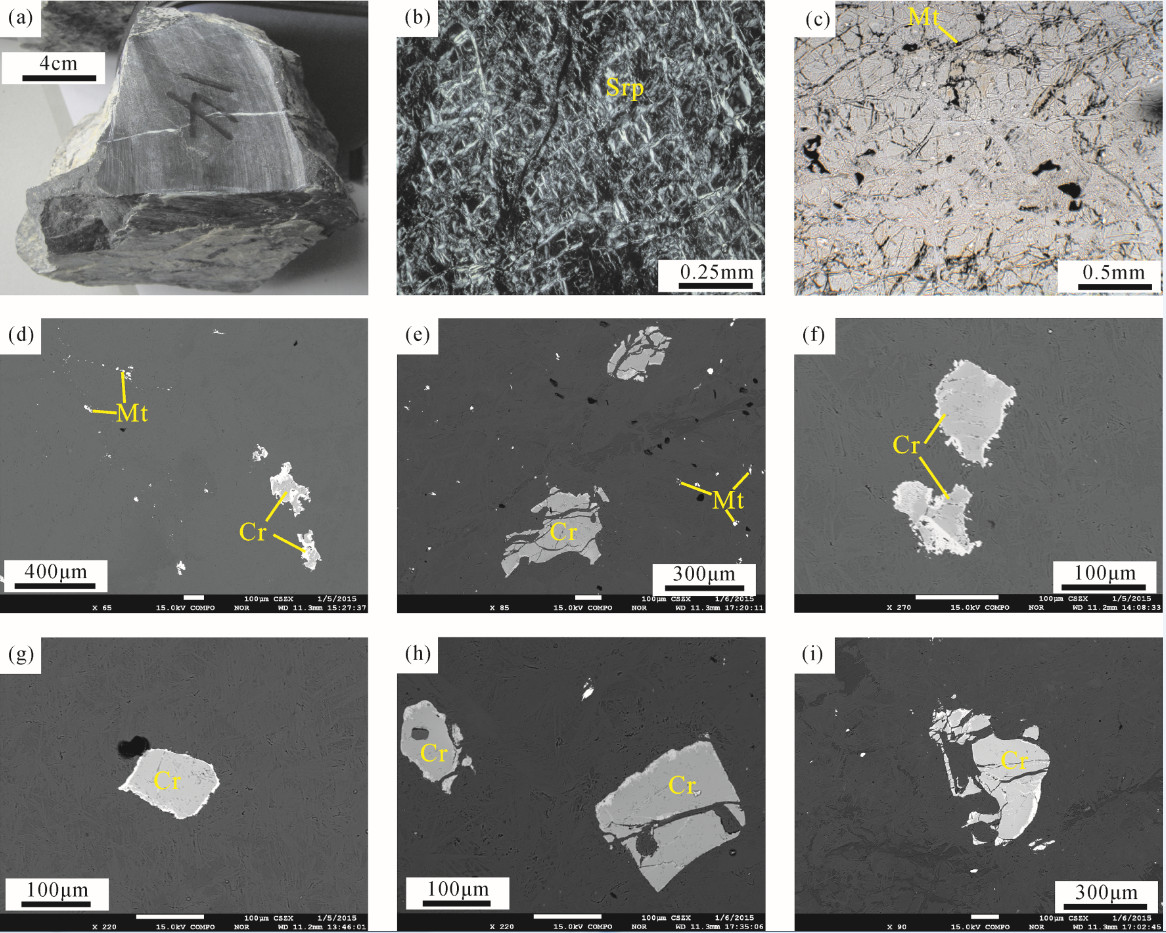
赣东北蛇绿岩中的地幔橄榄岩呈灰黑色,块状构造,强烈蛇纹石化成蛇纹岩(图 2-a)。矿物组成主要有蛇纹石、碳酸盐类、尖晶石及少量磁铁矿。蛇纹石多为叶蛇纹石,呈叶片状(图 2-b),仍保留有橄榄石假象,含量约为70%;碳酸盐矿物主要为菱镁矿,约占15%;尖晶石镜下仅在矿物边缘微透光,呈现红褐色、黄褐色色调,具不等粒粒状结构,发育不规则网脉状裂纹,粒径0~1.5 mm,约占10%;磁铁矿及其他不透明矿物约占5%(图 2-c)。
![]() 图 2 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩照片和背散射图像a—蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩手标本;b—蛇纹岩主要由叶蛇纹石组成;c—蛇纹石化过程形成的磁铁矿条带;d~i—蛇纹岩中自形和半自形的铬尖晶石;Srp—蛇纹石;Cr—铬尖晶石;Mt—磁铁矿Figure 2. Photographs and back-scattered electron (BSE) images of the peridotites from the northeast Jiangxi ophiolitesa-Hand specimen of the serpentinized harzburgite; b-Serpentinite mainly composed of serpentine; c-Magnetite band formed during serpentinization; d-i-Euhedral Cr–spinel and subhedral Cr–spinel within serpentinite; Srp-Serpentine; Cr-Chrome spinel; Mt-Magnetite
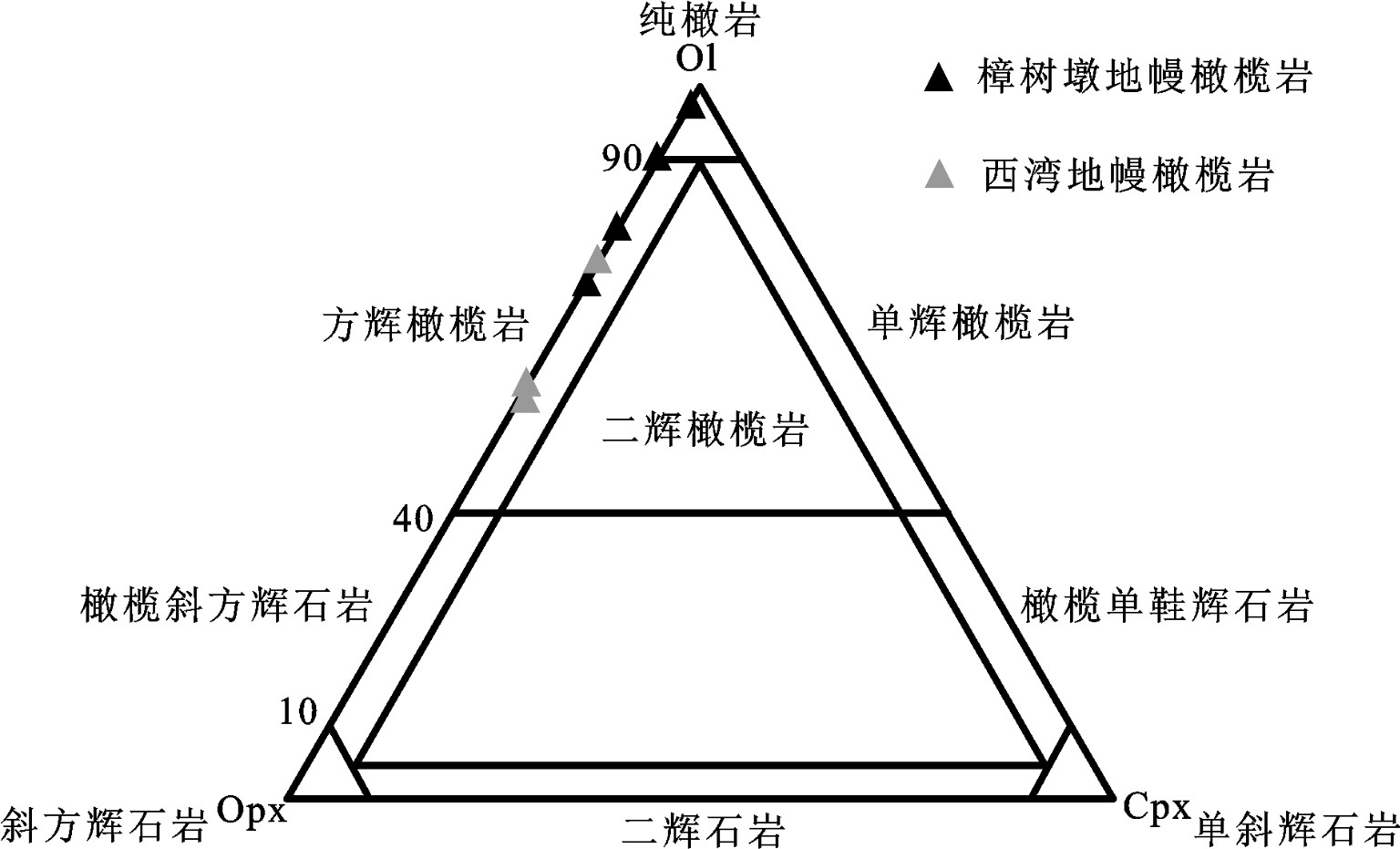
图 2 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩照片和背散射图像a—蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩手标本;b—蛇纹岩主要由叶蛇纹石组成;c—蛇纹石化过程形成的磁铁矿条带;d~i—蛇纹岩中自形和半自形的铬尖晶石;Srp—蛇纹石;Cr—铬尖晶石;Mt—磁铁矿Figure 2. Photographs and back-scattered electron (BSE) images of the peridotites from the northeast Jiangxi ophiolitesa-Hand specimen of the serpentinized harzburgite; b-Serpentinite mainly composed of serpentine; c-Magnetite band formed during serpentinization; d-i-Euhedral Cr–spinel and subhedral Cr–spinel within serpentinite; Srp-Serpentine; Cr-Chrome spinel; Mt-Magnetite尽管岩石受到了一定的蚀变,但对于这种蛇纹石化的岩石进行CIPW标准矿物的计算仍然可以帮助我们判断原岩的矿物组成。从CIPW标准矿物计算结果中可以看出,赣东北蛇绿岩中蛇纹石化的地幔橄榄岩的原岩除一个样品落在纯橄岩区域外,大多为方辉橄榄岩(图 3)。
樟树墩和西湾蛇蛇纹石化地幔橄榄岩强烈亏损易容元素Al2O3(0.60%~1.71%)、CaO(0.04%~1.09%)、Na2O( < 0.04%)和TiO2(0.01%~0.03%),含量均明显低于原始地幔的平均值[23]。过渡元素Ni和Cr富集,Ni为1600×10-6~1990×10-6,Cr为1030×10-6~1510×10-6,Mg#值较高(变化于91~94)(表 1),反映了地幔残留岩石的特征。
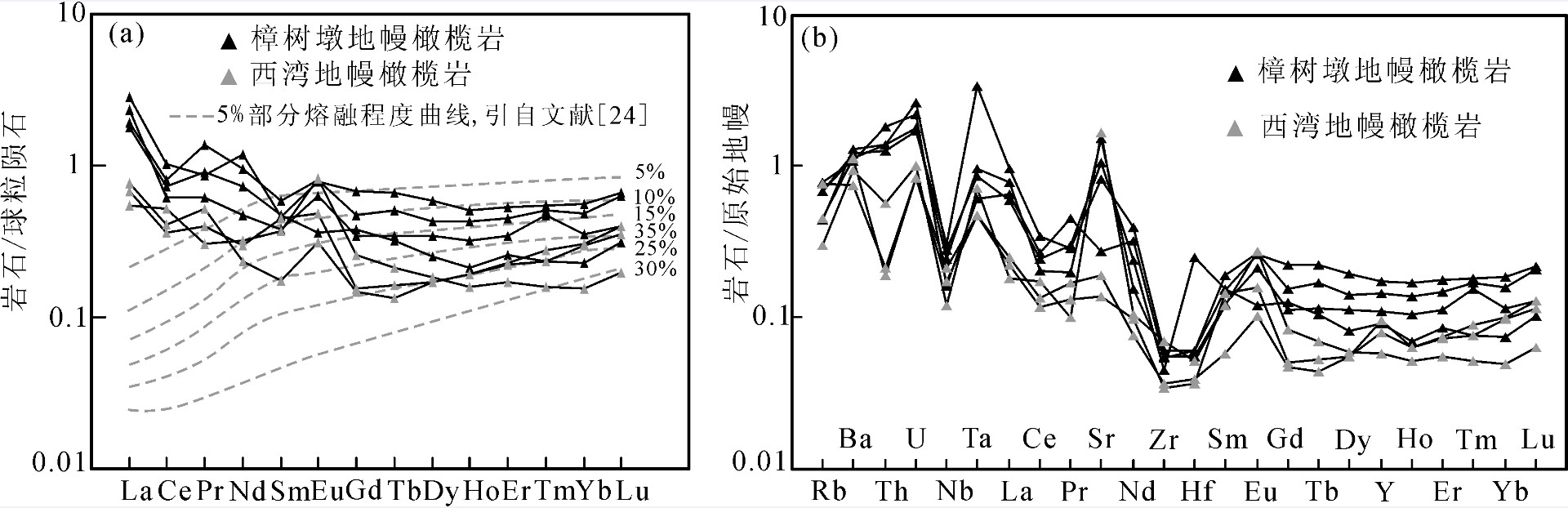
赣东北地幔橄榄岩REE丰度较低,∑REE为0.83×10-6~2.62×10-6,远低于原始地幔(∑REE=7.430×10-6)和亏损地幔(∑REE=4.245×10-6),指示了地幔橄榄岩岩石经历了较高程度的部分熔融作用。LREE/HREE=3.29~5.31,(La/Yb)N和(La/Sm)N分别变化于3.75~13.14和2.44~10.22。虽然REE含量略有变化,但分布模式却较为一致。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素图解中(图 4-a),表现出略呈“U”型的配分型式。LREE均富集,富集程度略有差异。研究表明,地幔橄榄岩的LREE在蛇纹石化的过程中保持稳定,LREE的富集主要受流体/熔体与地幔橄榄岩之间的反应控制[24-25]。樟树墩和西湾地幔橄榄岩的LREE相对富集的特征,表明岩石受到了后期流体/熔体的改造。Niu [24]对采自现代洋脊的深海橄榄岩的研究显示,地幔橄榄岩的全岩HREE含量主要受岩石中单斜辉石含量的控制,而在后期蛇纹石化及地幔交代作用中基本保持稳定,认为可以用HREE来定量模拟地幔橄榄岩的部分熔融程度。樟树墩和西湾地幔橄榄岩利用HREE模拟的部分熔融程度为10%~30%(图 4-a)。
在地幔橄榄岩微量元素原始地幔标准化图中(图 4-b),显示一个向右倾斜的特征。其中大离子亲石元素(LILE)富集,指示俯冲带流体作用;高场强元素Nb明显亏损,可能是受到了后期分异熔体交代作用造成的[26]。总体显示后期流体/熔体的交代改造特点。
4. 矿物化学成分
在地幔橄榄岩中,尖晶石是一种非常重要的副矿物,虽然含量较低,但它非常稳定,在后期地质作用过程中,不容易发生蚀变,因此可以作为其寄主岩石地幔橄榄岩的成因指示剂[27-29]。在高度蛇纹石化蚀变的样品中,尖晶石具有氧化边,因此,本项研究中分析的都是尖晶石新鲜的核部。
镜下观察显示,在樟树墩和西湾地幔橄榄岩中的尖晶石出现在蛇纹石化的橄榄石颗粒之间(图 2-d、e)。大多数尖晶石颗粒在50~100μm,在矿物边缘的亮度与中心明显不一致,形成一圈氧化边(图 2-f、g)。在薄片中,还见到磁铁矿围绕蛇纹石化的橄榄石边缘分布(图 2-f~i)。从所有尖晶石的分析结果(表 3)可以看出,尖晶石具有高的Cr2O3、FeO和Al2O3含量,MgO含量变化大,但Na2O、K2O、NiO、SiO2和TiO2含量低。CaO和K2O含量大部分在检出限以下。所有测试结果表明,这些原生尖晶石为铬尖晶石,Cr#值(100×Cr/(Cr+Al))在52~70。这种变化可能是由于岩浆抽取或后期的蚀变导致[30]。从尖晶石表面结构分析,在地幔橄榄岩就位前,发生过部分熔融事件。
5. 讨论
5.1 地幔橄榄岩成因
赣东北地幔橄榄岩中易熔元素和稀土总量远低于原始地幔的含量,而MgO含量高于原始地幔,表明该地幔橄榄岩为一套高亏损的原始地幔熔融残留物。从稀土元素配分模式来看,赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩配分模式基本相似,均表现为略具“U”型,LREE相对富集,微量元素中Cr和Ni含量较高。大离子亲石元素富集,高场强元素Nb明显亏损,表明赣东北地幔橄榄岩既具有亏损地幔源区的特征,也有不同程度的俯冲带流体的交代特征。
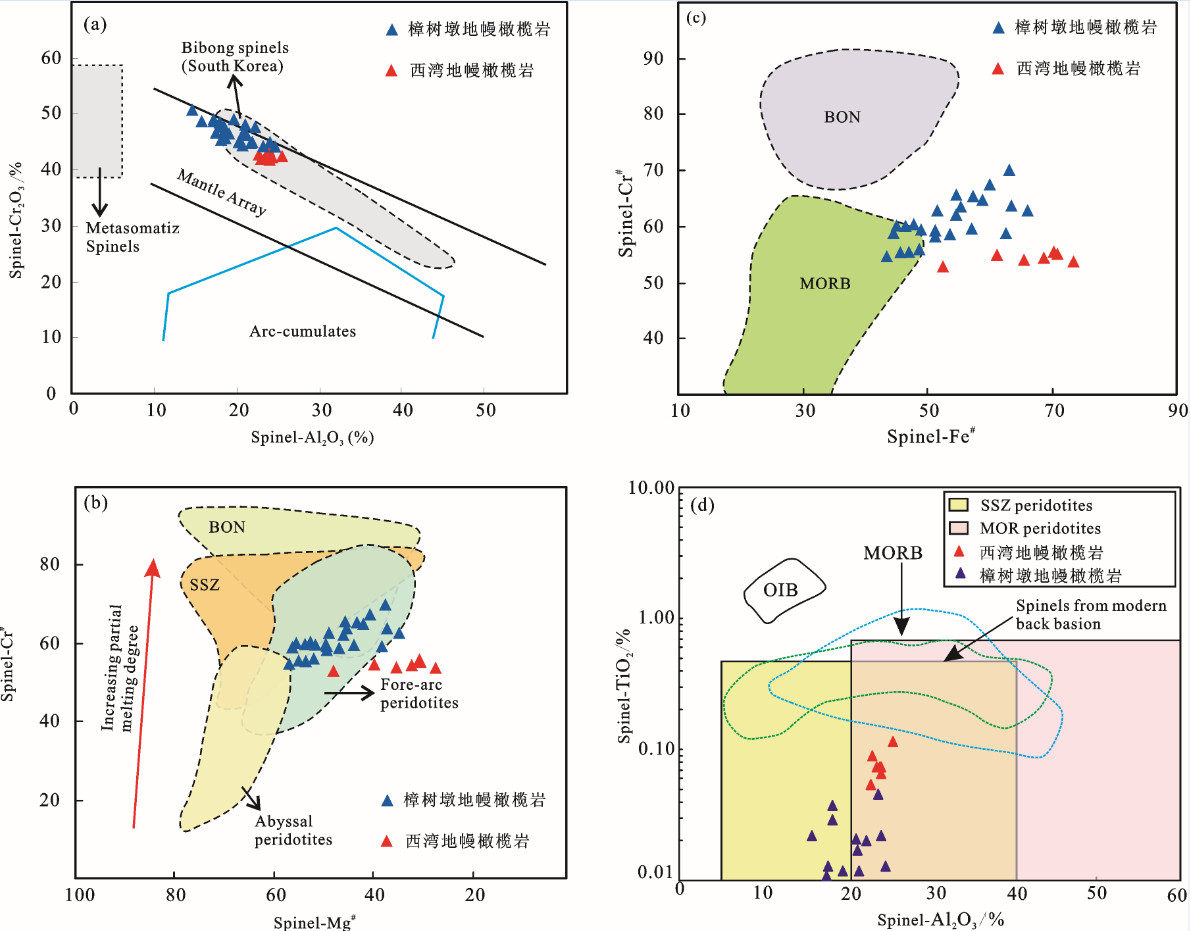
同时,我们的研究表明,地幔橄榄中的尖晶石属于Cr尖晶石。Cr尖晶石在蛇绿岩的研究中,是一种比较稳定的标型矿物,它在一般的后期蚀变中不会改变成分[30, 34-36]。含Cr尖晶石的地幔橄榄岩在部分熔融过程中,Cr尖晶石是部分熔融程度的标型矿物[27, 37]。随着部分熔融程度的增加,Cr尖晶石的Cr#值会随之增高[38]。从赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩的尖晶石化学成分看,在Al2O3-Cr2O3图解中(图 5-a),所有测试点位于地幔演化区域内,和韩国地区Bibong蛇绿岩相当[30]。随着Cr#的增加,Fe2+#[TFe2+/(Mg+TFe2+)]也随之增加,部分落入MORB区域,暗示着其与大洋洋中脊之间的成因联系(图 5-b)。在Mg#-Cr#的图解中,两者基本呈负相关关系,除个别点落入深海地幔橄榄岩之外,几乎所有测试点位于弧前地幔橄榄岩的区域(图 5-c)。除了Cr#值之外,尖晶石中TiO2也可作为地幔橄榄岩形成的构造环境的指示剂[35]。从表 3可以看到,赣东北地幔橄榄岩铬尖晶石TiO2含量较低,变化于0~0.115%,平均为0.03%,小于0.1%。在TiO2-Al2O3关系图中(图 5-d),一部分尖晶石落入大洋洋中脊(MOR)地幔橄榄岩区,一部分尖晶石落入SSZ型地幔橄榄岩区,显示了该区地幔橄榄岩成因上具有同时具有MOR和SSZ地幔橄榄岩的特点。
5.2 构造意义
自蛇绿岩的概念提出以来,对于蛇绿岩的成因及构造环境有了较多的研究,其中以Pearce et al.[39]将蛇绿岩分为MOR型和SSZ型最为经典和适用。随着研究的不断深入,研究发现在造山带中出露的蛇绿岩产出环境往往很复杂,并非具单一的某种形式[27]。但地幔橄榄岩仍然是一个重要的判别标志。MOR型蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩一般为二辉橄榄岩型[40],副矿物尖晶石Cr#值低于60[27];SSZ型蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩为方辉橄榄岩,尖晶石Cr#值较高,常大于60[32]。
而对于在一个地幔橄榄岩中同时出现Cr#值大于60和Cr#值小于60的尖晶石,有学者认为是与地幔橄榄岩的部分熔融程度、原岩亏损程度及岩浆性质有关[41];也有人认为是地幔岩在形成过程中经历了从洋中脊到岛弧环境的变化所致[42];Liu et al.[43]则认为这可能是在MOR和SSZ环境分别形成低Cr#和高Cr#的地幔橄榄岩,由于后期构造运动而使两者结合在一起。同时越来越多的学者证明同一蛇绿岩可以同时存在俯冲带上和深海橄榄岩2种不同特征,反映蛇绿岩在不同构造环境下经历多期演化[44-51]。
赣东北地幔橄榄岩中尖晶石Cr#值变化于52~70,表明其具有复杂的熔融历史,其形成过程可能经历了2种构造环境的转变。最近对赣东北蛇绿岩樟树墩辉长岩的研究表明,赣东北蛇绿岩可能为形成于1061 Ma的初始裂解的洋中脊环境[52],形成具有MOR性质的低熔橄榄岩(尖晶石Cr#值小于60);同时样品具有弧前地幔橄榄岩的特征(图 5-c),表明赣东北一带可能曾发生洋内俯冲作用,这也得到了赣东北蛇绿岩西湾约970 Ma的埃达克质斜长花岗岩的证据支持[12, 14, 53],俯冲作用使早先形成的MOR型低熔橄榄岩进入岛弧环境。由于流体的作用,处于岛弧之下的地幔楔可以发生较高程度的熔融,从而形成含高Cr#值尖晶石的SSZ型橄榄岩。
6. 结论
(1)赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩以方辉橄榄岩为主,稀土总量远低于原始地幔的含量,而MgO含量高于原始地幔。LREE和LILE相对富集,高场强元素Nb明显亏损,表明赣东北地幔橄榄岩具有亏损地幔源区特征,同时也有不同程度的俯冲带流体的交代特征。HREE模拟的部分熔融程度为10%~30%。
(2)赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩中尖晶石可分为Cr#值大于60和小于60两种不同成因类型,说明其可能经历了MOR和SSZ两种构造环境。
(3)推测赣东北蛇绿岩早先可能形成于洋中脊环境(约1060 Ma),随后在洋内俯冲作用下(约970Ma),位于俯冲带上部的地幔橄榄岩受到了来自俯冲带的流体/熔体的交代,经历了SSZ环境的改造。
致谢: 野外工作得到了东华理工大学余达淦教授和林子瑜教授的精心指导,电子探针实验得到了中国冶金地质总局山东测试中心林培军工程师的热情帮助,文稿修改中审稿专家给予了宝贵修改意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢! -
图 2 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩照片和背散射图像
a—蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩手标本;b—蛇纹岩主要由叶蛇纹石组成;c—蛇纹石化过程形成的磁铁矿条带;d~i—蛇纹岩中自形和半自形的铬尖晶石;Srp—蛇纹石;Cr—铬尖晶石;Mt—磁铁矿
Figure 2. Photographs and back-scattered electron (BSE) images of the peridotites from the northeast Jiangxi ophiolites
a-Hand specimen of the serpentinized harzburgite; b-Serpentinite mainly composed of serpentine; c-Magnetite band formed during serpentinization; d-i-Euhedral Cr–spinel and subhedral Cr–spinel within serpentinite; Srp-Serpentine; Cr-Chrome spinel; Mt-Magnetite
图 5 赣东北地幔橄榄岩铬尖晶石特征图解
a—Cr2O3-Al2O3图解(据文献[31]);b—Cr#-Mg#图解(据文献[33]);c—Cr#-Fe#图解(据文献[28, 32]);d—TiO2-Al2O3图解(据文献[33])
Figure 5. Plot of chromian spinels on discrimination diagrams
a-Al2O3 versus Cr2O3 (wt.%) diagram (after rererence[31]); b-Mg/(Mg+Fe2+) versus Cr/(Cr+Al) diagram (after rererence[33]); c-TFe2+/(Mg+TFe2+) versus Cr/(Cr+Al) diagram (after rererence[28, 32]); d-Al2O3 versus TiO2 (wt.%) diagram (after rererence[33])
表 1 赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩主量(%)、微量和稀土元素(10-6)组成
Table 1 Major (%), trace and rare earth (10-6) elements compositions of the mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi

表 2 赣东北蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩全岩CIPW标准矿物计算的矿物成分
Table 2 Mineral composition of the mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi ophiolites calculated by CIPW method

表 3 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩中尖晶石电子探针分析结果(%)
Table 3 Electron microprobe analyses of spinel in mantle peridotites from northeast Jiangxi ophiolites

-
[1] Bezard R, Hébert R, Wang C, et al.Petrology and geochemistry of the Xiugugabu ophiolitic massif, western Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, Tibet[J].Lithos, 2011, 125(1):347-367. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1996635867&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] Zhang Qi, Wang Yan and Liu Dunyi.A brief review of ophiolites in China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32:308-324. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.012
[3] 白文吉, 甘启高, 杨经绥, 等.江南古陆东南缘蛇绿岩完整层序剖面的发现和基本特征[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1986, 5(4):289-299. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW198604000.htm Bai Wenji, Gan Qingao, Yang Jingsui, et al.Discovery of wellreserved ophiolite and its basical characters in southeastern margin of the Jiangnan ancient continent[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogical, 1986, 5(4):289-299(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW198604000.htm
[4] 徐备, 乔广生.赣东北晚元古代蛇绿岩套的Sm-Nd同位素年龄及原始构造环境[J].南京大学学报(地球科学), 1989, (3):108-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199202002.htm Xu Bei, Qiao Guangsheng.Sm-Nd isotopic age of the late Proterozoic ophiolite suite in NE Jiangxi province and its primary tectonic environment[J].Journal of Nanjing University (Earth Sciences), 1989, (3):108-114(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199202002.htm
[5] Zhou G Q.The discovery and significance of the northeastern Jiangxi Province ophiolite (NEJXO), its metamorphic peridotite and associated high-temperature high-pressure metamorphic rocks[J].Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Science, 1989, 3:237-247. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(89)90028-7
[6] 邢凤鸣, 徐祥, 陈江峰, 等.赣东北元古代蛇绿岩Sm-Nd同位素年龄及地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1992, 11(2):120-124. Xing Fengming, Xu Xiang, Chen Jiangfeng, et al.Sm-Nd isotopic age of proterozoic ophiolites in northeastern Jiangxi and its geological significance[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogical, 1992, 11(2):120-124(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Zou H B, Zhou X M and Zhou G Q.Two types of ophiolites:one associated with lenticular chromite and the other without[J].Geology and Exploration, 1992, 28(4):30-46.
[8] Shu L S, Zhou G Q, Shi Y S, et al.Study on the high-pressure metamorphic blueschist and its Late Proterozoic age in the eastern Jiangnan belt[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1994, 39:1200-1204. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JXTW199414012.htm
[9] 李献华, 周国庆, 赵建新.赣东北蛇绿岩的离子探针锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].地球化学, 1994, 23(2):125-131. Li Xianhua, Zhou Guoqing, Zhao Jianxin, et al.SHRIMP ion probe zircon age of the NE Jiangxi Ophiolite and its tectonic implications[J].Geochimica, 1994, 23:125-131(in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] 赵崇贺, 何科昭, 莫宣学.赣东北深断裂带蛇绿混杂岩中含晚古生代放射虫硅质岩的发现及其意义[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(23):2161-2163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199523013.htm Zhao Chonghe, He Kezhao, Mo Xuanxue, et al.Discovery of late Palaeozoic radiolarian-bearing chert in ophiolitic complexes of the rift zone, northeast Jiangxi, and the significance[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(23):2161-2163(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199523013.htm
[11] 何科昭, 赵崇贺, 邰道乾, 等.赣东北蛇绿混杂岩带中多处发现含晚古生代放射虫硅质岩[J].现代地质, 1996, 10(3):303-307. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ603.001.htm He Kezhao, Zhao Chonghe, Tai Daoqian, et al.Discovery of late Palaeozoic radiolarian silicolite in many places in northeastern Jiangxi ophiolitic mélange belt[J].Geoscience, 1996, 10(3):303-307(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ603.001.htm
[12] Li X H, Zhao J X, McCulloch M T, et al.Geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic study of Neoproterozoic ophiolites from southeastern China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Precambrian Research, 1997, 81:129-144. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(96)00032-0
[13] Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X, et al.Obduction-type granites within the NE Jiangxi Ophiolite:Implications for the final amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J].Gondwana Research, 2008, 13(3):288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.12.010
[14] Gao J, Reiner K, Long L L, et al.Adakitic signature formed by fractional crystallization:An interpretation for the Neo-Proterozoic meta-plagiogranites of the NE Jiangxi ophiolitic mélange belt, South China[J].Lithos, 2009, 110:277-293. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.01.009
[15] Chen, J F, Foland K A, Xing F M, et al.Magmatism along the southeast margin of the Yangtze and Cathysia block of China[J].Geology, 1991, 19, 815-818. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0815:MATSMO>2.3.CO;2
[16] Zhou G Q and Zhao J X.Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of the NE Jiangxi ophiolite (NEJXO), SE Margin of the Yangtze craton, South China[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1991, 36:1374-1379. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=171507405&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] 赵建新, 李献华, McCulloch M T, 等.皖南和赣东北蛇绿岩成因及其大地构造意义元素和Sm-Nd同位素制约[J].地球化学, 1995, 24(4):311-326. Zhao Jianxin, Li Xianhua, McCulloch M T, et al.Petrogenesis of ophiolites from South Anhui and Northeast Jiangxi, and their tectonic implications:chemical and Sm-Nd isotopic constraints[J].Geochimca, 1995, 24:311-326(in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Dai J, Wang C, Hébert R, et al.Petrology and geochemistry of peridotites in the Zhongba ophiolite, Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone:Implications for the Early Cretaceous intra-oceanic subduction zone within the Neo-Tethys[J].Chemical Geology, 2011, 288(3-4):133-148. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.07.011
[19] 汪新, 马瑞士.怀玉山蛇绿混杂岩及古陆碰撞缝合线的确定[J].南京大学学报(地球科学版), 1989, 1-2:72-81. Wang Xin and Ma Ruishi.Confirmation of Huaiyu mountain ohpiolitic mélange and tectonic suture line[J].Journal of Nanjing University (Earth Sciences), 1989, 1-2:72-81(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Shu L S, Faure M, Jiang S Y, et al.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age, litho-and biostratigraphic analyses of the Huaiyu Domain in South China:Evidence for a Neoproterozoic orogen, not Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic collision[J].Episodes, 2006, 29:244-252. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2259475724&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[21] Shu L S, Faure M, Yu J H, et al.Geochronological and geochemical features of the Cathaysia block (South China):New evidence for the Neoproterozoic breakup of Rodinia[J].Precambrian Research, 2011, 187:263-276. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.03.003
[22] Liu X C, Xiong X L, Audétat A, et al.Partitioning of Cu between mafic minerals, Fe-Ti oxides and intermediate to felsic melts[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 151:86-102. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.12.010
[23] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt:Implication for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J (eds.).Magmatism in the Ocean Basin.Geology Society London Special Publication, 1989, 42:528-548.
[24] Niu Y L.Bulk-rock major and trace element compositions of abyssal peridotites:Implications for mantle melting, melt extraction and post-melting processes beneath mid-ocean ridges[J].Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45(12):2423-2458. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egh068
[25] Paulick H, Bach W, Godard M, et al.Geochemistry of abyssal peridotites (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 15 degrees 20'N, ODP Leg 209):Implications for fluid/rock interaction in slow spreading environments[J].Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(3/4):.
[26] Bodinier J I, Dautria J M and Morten L.Evolution of LILEenriched small melt fractions in the lithospherie mantle:A case study from the Easten African Rift[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 153:67-83. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00167-2
[27] Dick HJB and Bullen T.Chromian spinel as a petrogenetic indicator in abyssal and Alpine-type peridotites and spatially associated lavas[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1984, 86(1):54-76. doi: 10.1007/BF00373711
[28] Barnes S J and Roeder P L.The range of spinel compositions in terrestrial mafic and ultramafic rocks[J].Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(12):2279-2302. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.12.2279
[29] Ahmed H A, Arai S, Yaser M, et al.Spinel composition as a petrogenetic indicator of the mantle section in the Neoproterozoic Bou Azzer ophiolite, Anti-Atlas, Morocco[J].Precambrian Research, 2005, 138(3-4):225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.05.004
[30] Oh C W, Rajesh V J, Seo J, et al.Spinel compositions and tectonic relevance of the Bibong ultramafic bodies in the Hongseong collision belt, South Korea[J].Lithos, 2010, 117, 198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.02.015
[31] Franz L and Wirth R.Spinel inclusions in olivine of peridotite xenoliths from TUBAF seamount (Bismark Archipelago/Papua New Guinea):evidence for the thermal and tectonic evolution of the oceanic lithosphere[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 140, 283-295. doi: 10.1007/s004100000188
[32] Arai S.Characterization of spinel peridotites by olivine-spinel compositional relationships:review and interpretation.Chemical Geology, 1994, 113, 191-204. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90066-3
[33] Kamenetsky V S, Crawford A J, Meffre S.Factors controlling chemistry of magmatic spinel:an empirical study of associated olivine, Cr-spinel and melt inclusions from primitive rocks[J].Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(4), 655-671. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.4.655
[34] Ahmed A H, Arai S, Attia A K.Petrological characteristics of podiform chromitites and associated peridotites of the Pan African Proterozoic ophiolite complexes of Egypt[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36(1), 72-84. doi: 10.1007/s001260050287
[35] Ahmed A H, Arai S, Abdel-Aziz Y M, et al.Spinel composition as a petrogenetic indicator of the mantle section in the Neoproterozoic Bou Azzer ophiolite, Anti-Atlas, Morocco[J].Precambrian Research, 2005, 138, 225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.05.004
[36] Hellebrand E, Snow J E, Mühe R.Mantle melting beneath Gakkel Ridge (Arctic Ocean):abyssal peridotite spinel compositions[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 182:227-235. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00291-1
[37] Hellebrand E, Show J E, Dick H J B.Coupled major and trace elements as indicators of the extent of melting in the mid-oceanridge peridotites[J].Nature, 2001, 410:677-681. doi: 10.1038/35070546
[38] Ohara Y, Ishi T.Peridotites from the southern Mariana fore-arc:heterogeneous fluid supply in mantle wedge[J].Island Arc, 1998, 7, 541-558. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1738.1998.00209.x
[39] Pearce J A, Lippard S J, and Roberts S.Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[C]//Kokelaar B P, Howells M F (eds.).Marginal Basin Geology.Geological Society of London Special Publication 16:London, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1984:77-94.
[40] 邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 周肃, 等.青藏高原西部蛇绿岩类型:岩石学与地球化学证据[J].地学前缘, 2005, 12(2):277-291. Qiu Ruizhao, Deng Jinfu, Zhou Su, et al.Ophiolite types in western Qinghai-Tibetan plateau:Evidences from petrology and geochemistry[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(2):277-291(in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Zhou M F, Robinson P T, Malpas J, et al.Melt/mantle interaction and melt evolution in the Sartohay high-Al chromite deposits of the Dalabute ophiolite (NW China)[J].Journal of Asian Eartht Sciences, 2001(19):517-553. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2024663793&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[42] Arai S and Matsukage K.Petrology of a chromitite micropod from Hess Deep, equatorial Pacific:A comparison between abyssal and alpine-type podifrom chromitites[J].Lithos, 1998, 43:1-14. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00003-6
[43] Liu C Z, Wu F Y, Chu Z Y, et al.Preservation of ancient Os isotope signatures in the Yungbwa ohpiolite (southwestern Tibet) after subduction modification[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.08.010
[44] Choi S H, Shervais J W and Mukasa S B.Supra-subduction and abyssal mantle peridotites of the Coast Range ophiolite, California[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 156(5):551-576. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0300-6
[45] 徐向珍, 杨经绥, 郭国林, 等.雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段普兰蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩的岩石学研究[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(11):3179-3196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111003.htm Xu Xiangzhen, Yang Jingsui, Guo Guolin, et al.Lithological research on the Purang mantle perdotite in western Yarlung Zangbo suture zone in Tibet[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(11):3179-3196(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111003.htm
[46] 李源, 杨经绥, 刘钊, 等.西藏雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段巴尔地幔橄榄岩成因及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 27(11):3239-3254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111007.htm Li Yuan, Yang Jingsui, Liu Zhao, et al.The origins of Baer ophiolitic peridotite and its implication in the Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, southern Tibet.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(11):3239-3254(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111007.htm
[47] 王泽利, 刘建国, 李旭平, 等.西藏普兰超镁铁岩体东部铬尖晶石矿物学特征及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2012, 58(6):1038-1045. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201206005.htm Wang Zeli, Liu Jianguo, Li Xuping, et al.Mineralogy of spinel in the Eastern Purang ultramafic rocks, Xizang (Tibet) and its geological implication[J].Geological Review, 2012, 58(6):1038-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201206005.htm
[48] 周文达, 杨经绥, 赵军红, 等.西藏雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段普兰蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩矿物学研究和成因探讨[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(8):2185-2203. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201410071016.htm Zhou Wenda, Yang Jingsui, Zhao Junhong, et al.Mineralogical study and the origin discussion of Purang ophiolite peridotites, western part of YarlungZangbo Suture Zone (YZSZ), Southern Tibet[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(8):2185-2203(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201410071016.htm
[49] 冯光英, 杨经绥, 熊发挥, 等.雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩带西段错不扎地幔橄榄岩组成特征及岩石成因[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1337-1353. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150512&flag=1 Feng Guangying, Yang Jingsui, Xiong Fahui, et al.Petrology, geochemistry and genesis of the Cuobuzha peridotite in the western Yarlung Zangbo suture zone[J].Geology in China, 2015, 42(5):1337-1353(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150512&flag=1
[50] 周文达, 杨经绥, 赵军红, 等.西藏雅江缝合带西段普兰蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩成因:一种新认识[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1354-1378. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150513&flag=1 Zhou Wenda, Yang Jingsui, Zhao Junhong, et al.Petrogenesis of peridotites from the Purang ophiolite in the western part of Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, southern Tibet:A new perspective[J].Geology in China, 2015, 42(5):1354-1378(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150513&flag=1
[51] 田亚洲, 杨经绥.新疆西准噶尔达拉布特蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩成因[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1379-1403. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150514&flag=1 Tian Yazhou, Yang Jingsui.The genesis of peridotite in Darbute ohiolite within West Junggar basin, Xinjiang[J].Geology in China, 2015, 42(5):1379-1403(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150514&flag=1
[52] 王存智, 邢光福, 余明刚, 等.赣东北蛇绿岩形成时代及构造环境:樟树墩辉长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学约束[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(3):309-321. Wang Cunzhi, Xing Guangfu, Yu Minggang, et al.Timing and tectonic setting of the NE Jiangxi ophiolite:Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, Hf isotope and geochemistry of the Zhangshudun gabbro[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralgica, 2015, 34(3):309-321(in Chinese with English abstract).
[53] Li W X, Li X H.Adakitic granites within the NE Jiangxi ophiolites, South China:geochemical and Nd isotopic evidence[J].Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00206-1
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 张银国,陈建文,龚建明,梁杰,廖晶,王建强,杨长清,赵青芳,孙晶,杨传胜,雷宝华,袁勇. 青岛海洋地质研究所45年来海域油气资源调查进展. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(03): 1-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱清波,王存智,靳国栋,赵希林,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿构造混杂岩露头解剖及其对华南新元古代洋盆演化的启示. 地质通报. 2022(Z1): 388-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 谭满堂,龙文国,魏运许,邓新,田洋,王晶,金巍,徐大良,徐扬,黄皓. 湘东北仓溪岩群锆石U-Pb年龄及新元古代弧盆系演化. 华南地质. 2022(01): 120-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾庆友,林忠良,谢芳军,吴忠如,潘世语. 江西石坞金矿玄武岩地球化学特征及构造意义. 有色金属(矿山部分). 2021(04): 92-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱清波,靳国栋,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿混杂岩带1:50000专题地质图数据库. 中国地质. 2021(S2): 66-77 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 任雪斌,李学森. 赣东北樟树墩-西湾蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩和玄武岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 四川地质学报. 2020(03): 364-370 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘婷,郑有业,王朋冲,杨伟光,郭统军. 豆荚状铬铁矿床成矿地球化学指标对比和成矿作用讨论. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2019(01): 176-183+194 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘婷,郑有业,郭统军. 大中型豆荚状铬铁矿床地球化学特征研究. 地质科技情报. 2019(02): 217-225 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郑涛,黄德志,崔建军,徐益龙,周炜鉴. 皖南伏川SSZ型蛇绿岩的地球化学特征与构造意义. 矿物学报. 2019(03): 281-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 兰锐,徐梦婧. 中国造山带地幔橄榄岩的研究现状. 内蒙古石油化工. 2018(10): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: