Geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of Early Jurassic Quemo Co Formation inWoruoshan area, north Qiangtang basin
-
摘要:
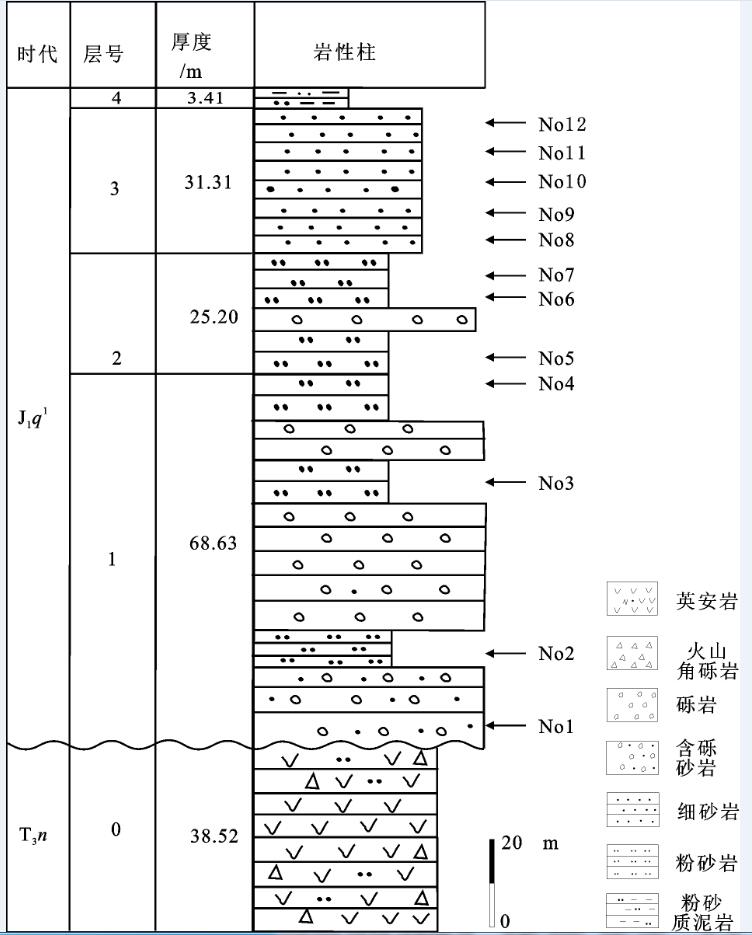
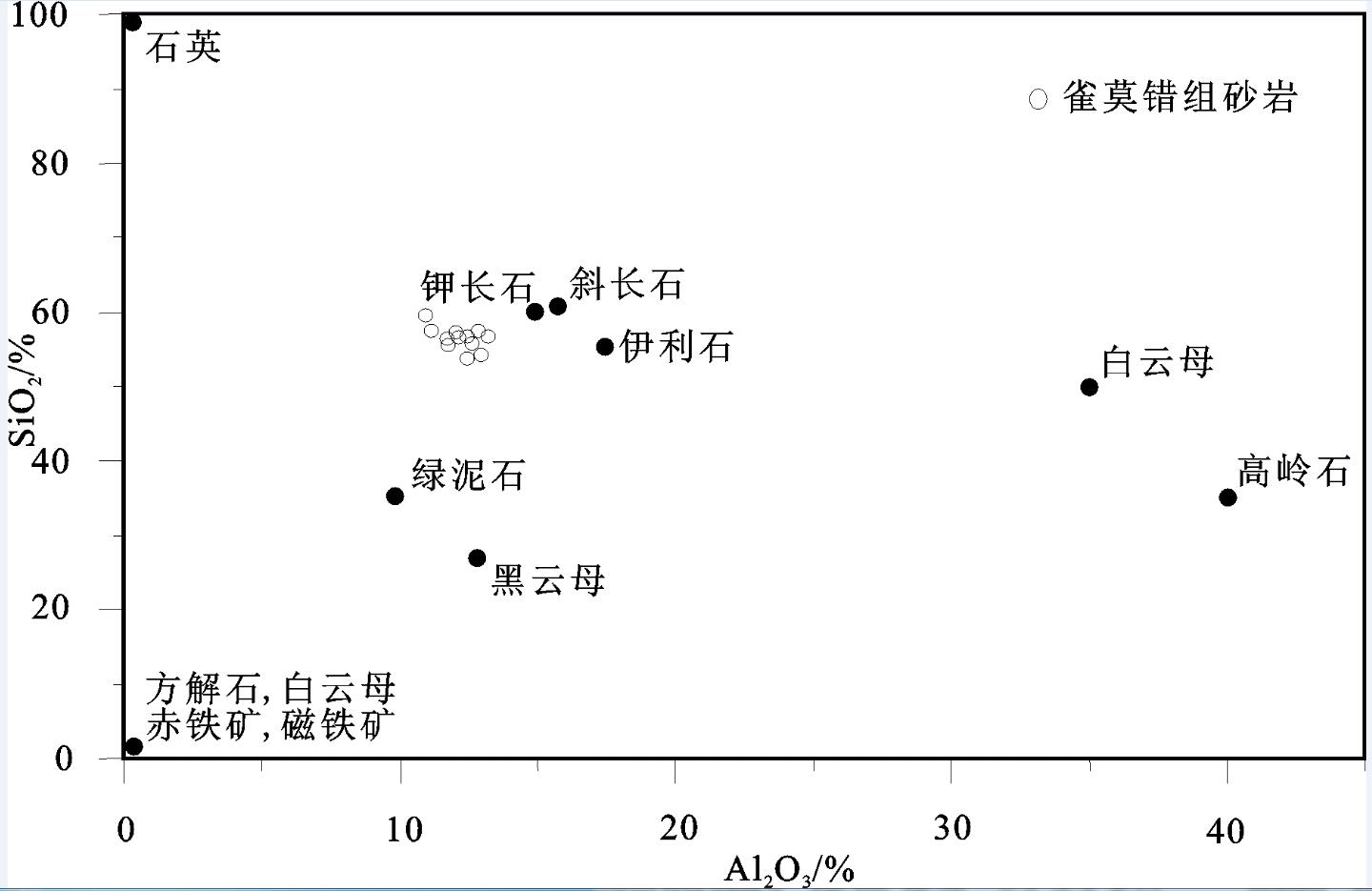
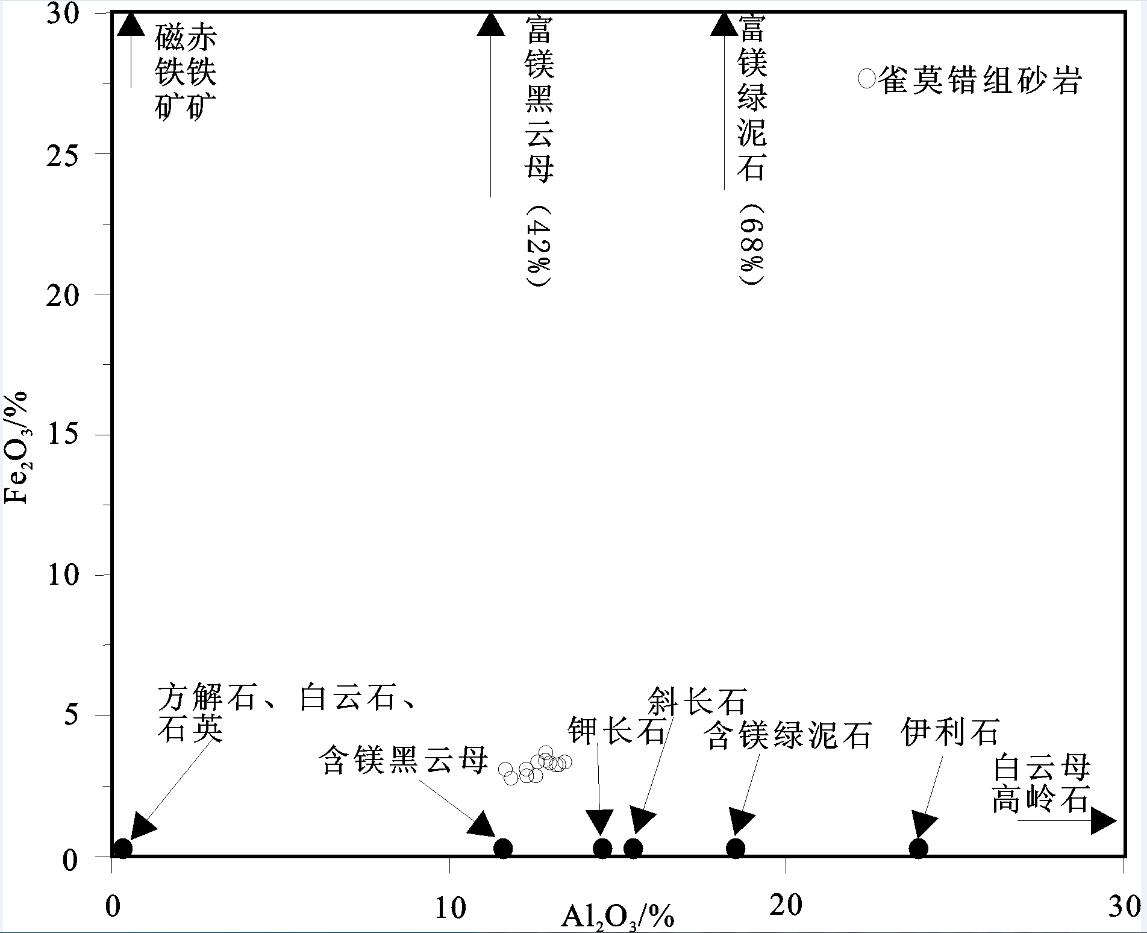
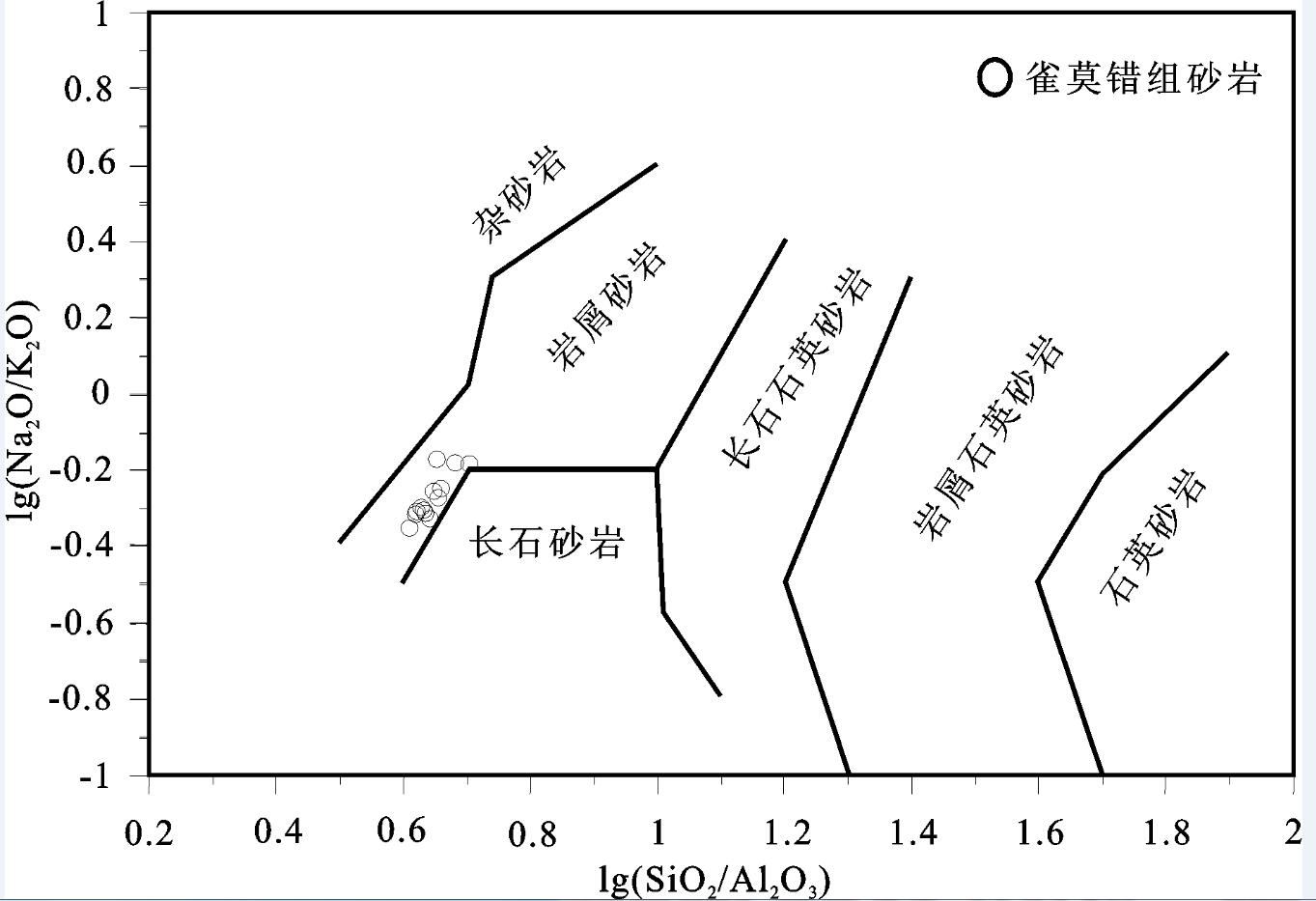
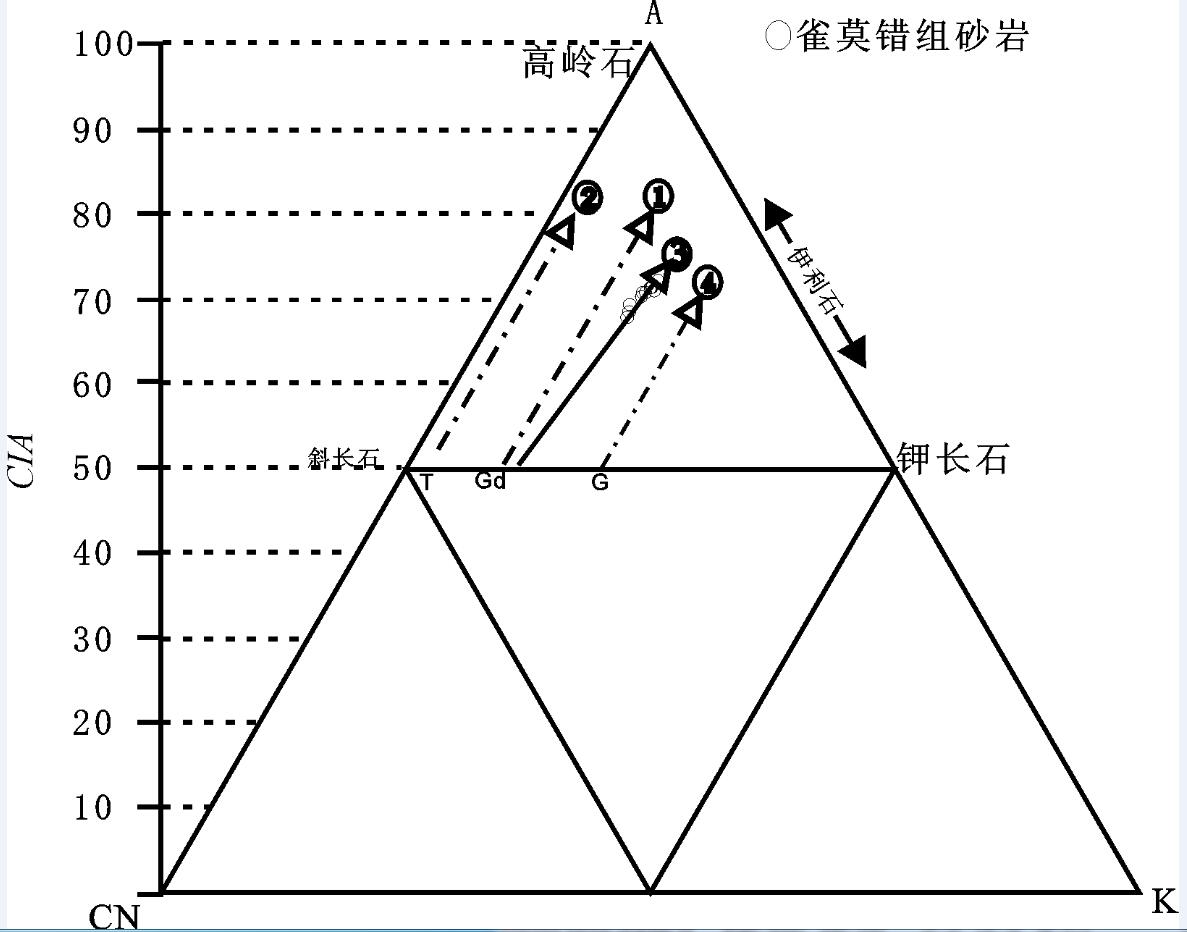
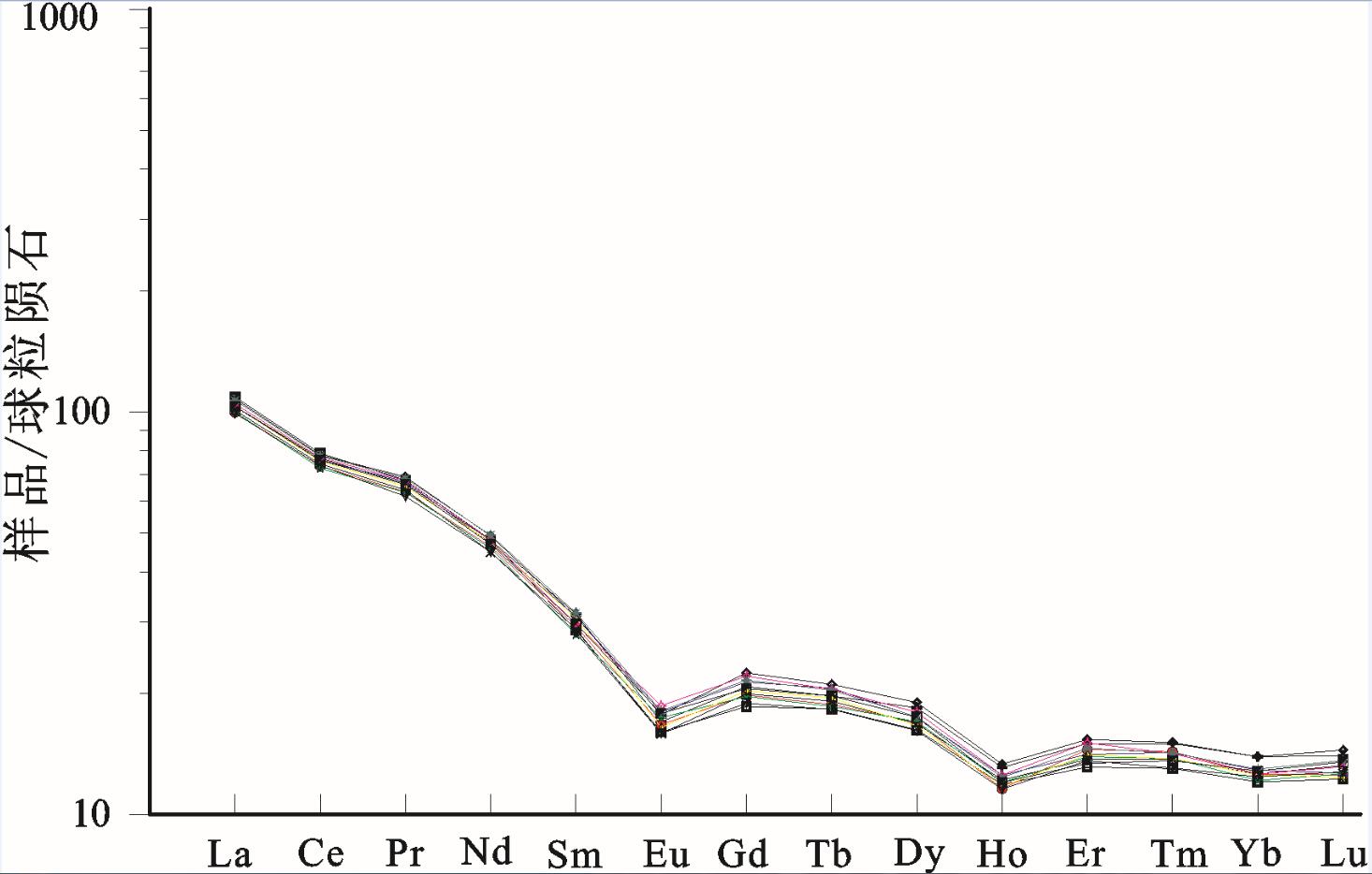
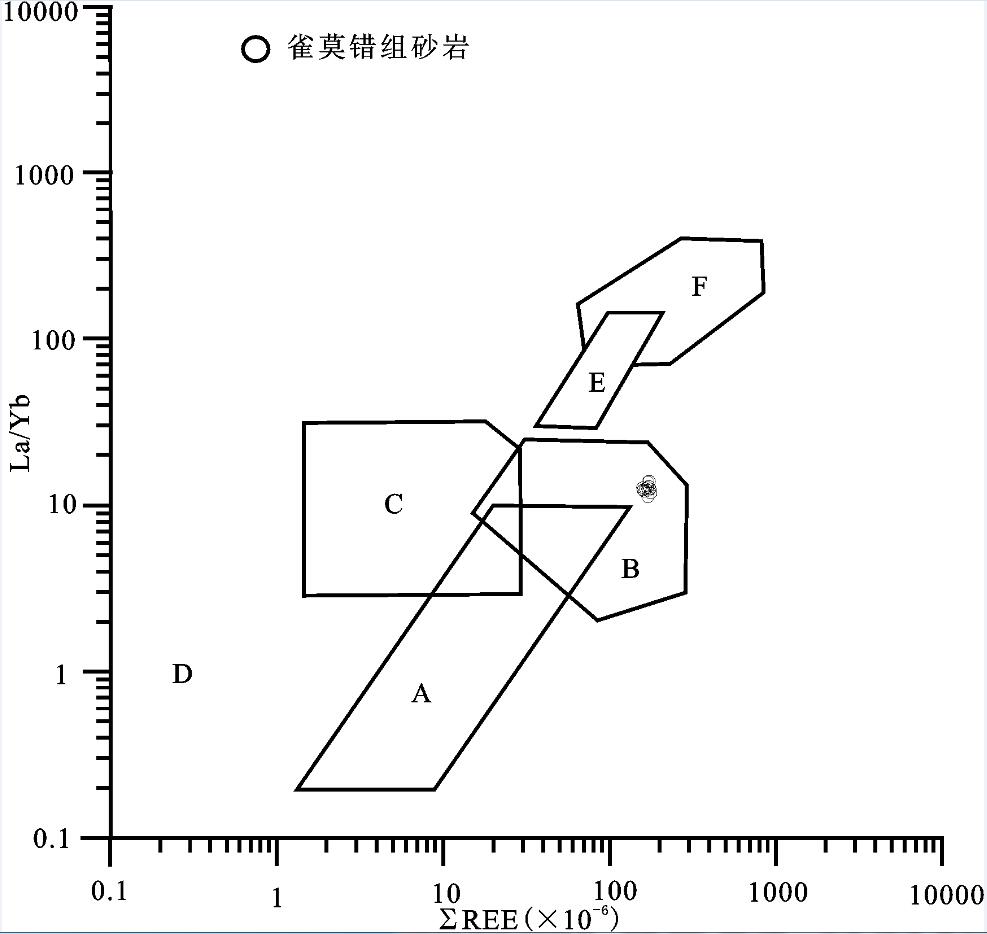
出露于羌塘盆地沃若山地区的雀莫错组砂岩是北羌塘盆地早侏罗世的沉积物,对研究早侏罗世沉积盆地的演化特征具有重要的意义。通过对其地球化学特征的分析研究,结果表明该组砂岩为被动大陆边缘裂陷期的沉积产物,岩性主要为岩屑砂岩,岩石矿物成分主要在钾长石、斜长石、伊利石、绿泥石以及石英之间变化。化学风化作用指标(CIW)、化学蚀变作用指标(CIA)和A-CN-K图解,反映该组砂岩的碎屑成分受到了强烈的风化环境,并在风化过程中发生钾交代作用,长石发生伊利石化。化学组分指标(ICV)表明岩石碎屑为近源的第一次旋回沉积物,受沉积分选和再循环作用影响不大;A-CN-K图解还反映出砂岩碎屑源岩中斜长石含量高于钾长石含量,主要在花岗岩和花岗闪长岩之间变化;稀土元素特征表明该组砂岩具有同源性,其成分主要受源区岩石成分控制,为酸性火山岩类。
Abstract:Early Jurassic Quemo Co Formation is very important for studying the sedimentary evolution form the late Triassic to the early Jurassic in Qiangtang basin. Geochemistry and provenance characteristics of sandstones in the Quemo Co Formation of Woruo Mmountain area were studied by analyzing the selected major element and trace element compositions. The results suggest that the sandstone deposited in the chasmic stage of the passive continental margin. The sandstones are the lithic sandstone which mainly consist of K-feldspar, plagioclase, illite, chlorite and quartz. The chemical index of weathering (CIW), the chemical index of alteration (CIA) parameters and the A-CN-K plot of the sandstones suggest that weathering of the elastic constituents has been intense in the area, the elastic constituents of sandstones underwent K-metasomatisim during weathering processes, illite replaced feldspar and perhaps the original kaolinite in the feldspar. The index of compositional variability (ICV) suggests that some sandstones contain first cycle materials The A-CN-K diagram indicates that a high average plagioclase-to-K-feldspar ratio in the provenance, varying from granodiorite to granite. The REE characteristics suggest only one source of acid igneous rock for the sandstones in this area.
-
Keywords:
- sandstone /
- element geochemistry /
- REE /
- provenance /
- north Qiangtang basin
-
致谢: 成都地质调查中心杨哲超、罗红民等同志在藏北无人区给予积极合作与十分宝贵的后勤保障; 在文章的撰写中, 与杜佰伟高级工程师开展了有益的交流与讨论;同时,审稿专家对论文提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此一并致以衷心的感谢!
-
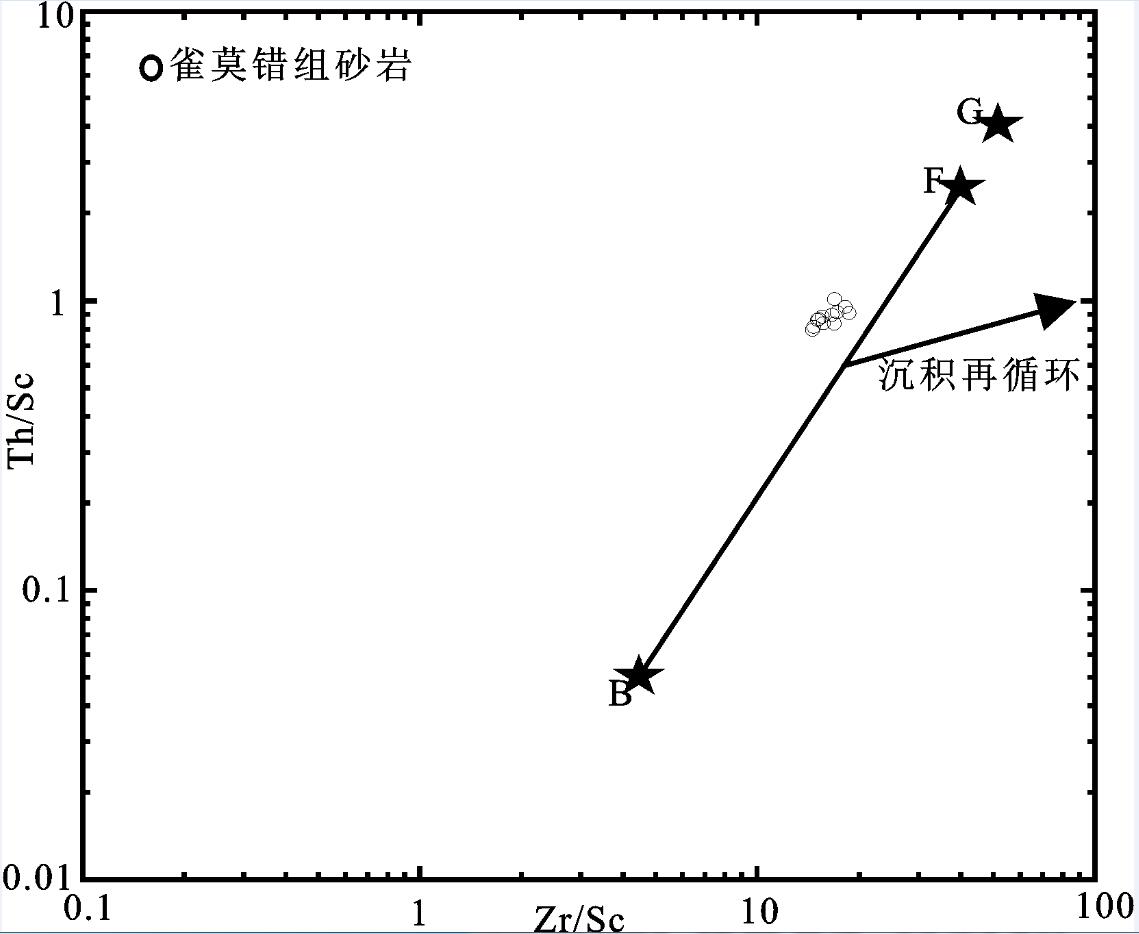
图 7 沃若山地区雀莫错组砂岩Zr/Sc-Th/Sc图解(据McLemian等修改)[24]
B—玄武岩,F—长英质岩石,G—花岗岩
Figure 7. Zr/Sc versus Th/Sc diagram of the sandstones in Quemo Co Formation of Woruo Mountain, Qiangtang Basin
B-Basalt; F-Felsic rock; G-Granite
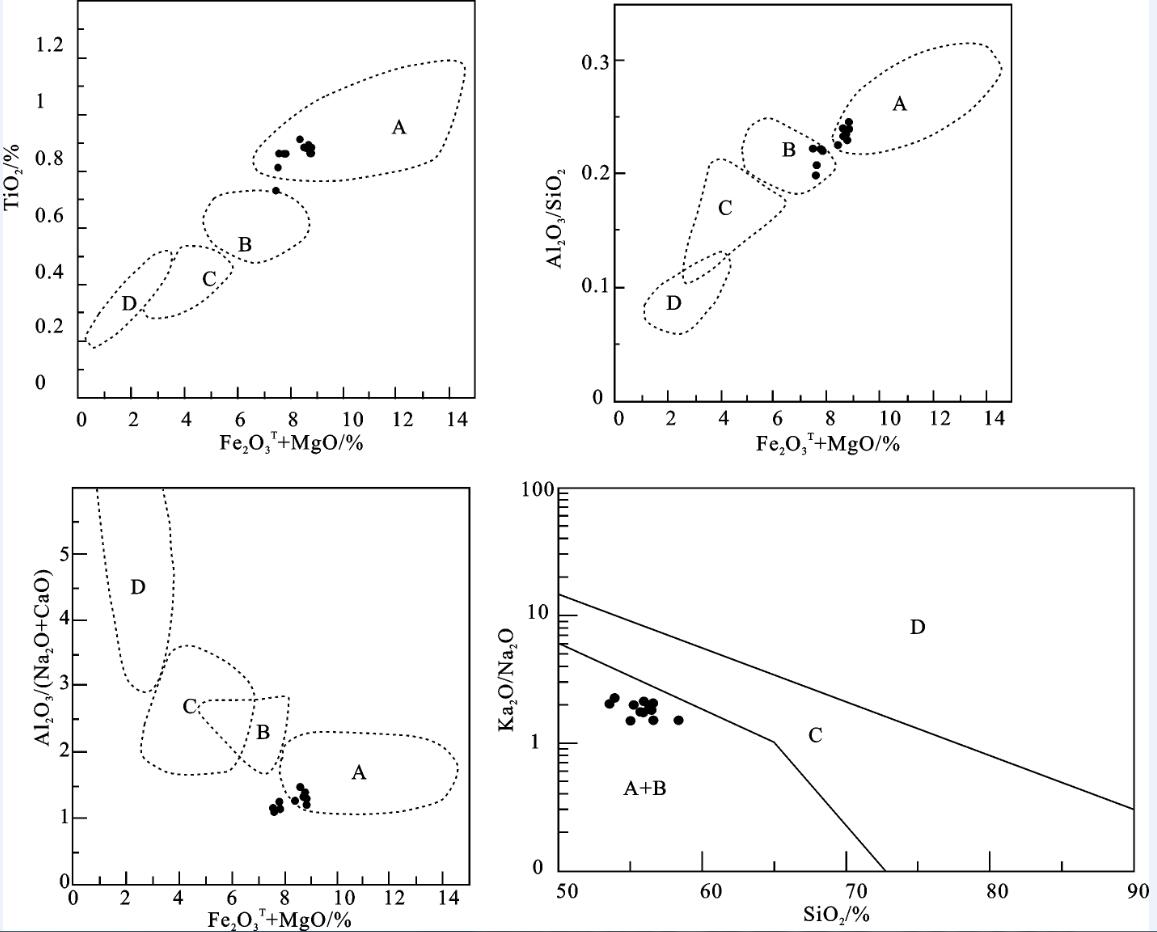
图 10 羌塘盆地沃若山地区雀莫错组砂岩主量元素构造背景判别图
A—大洋岛弧; B—大陆岛弧; C—活动大陆边缘; D—被动大陆边缘
Figure 10. Major element composition of sandstones for tectonic setting discrimination in the Quemo Co Formation of Woruo Mountain, Qiangtang Basin
A-Oceanic island arc; B-Continental island arc; C-Active continental margin; D-Passive continental margin
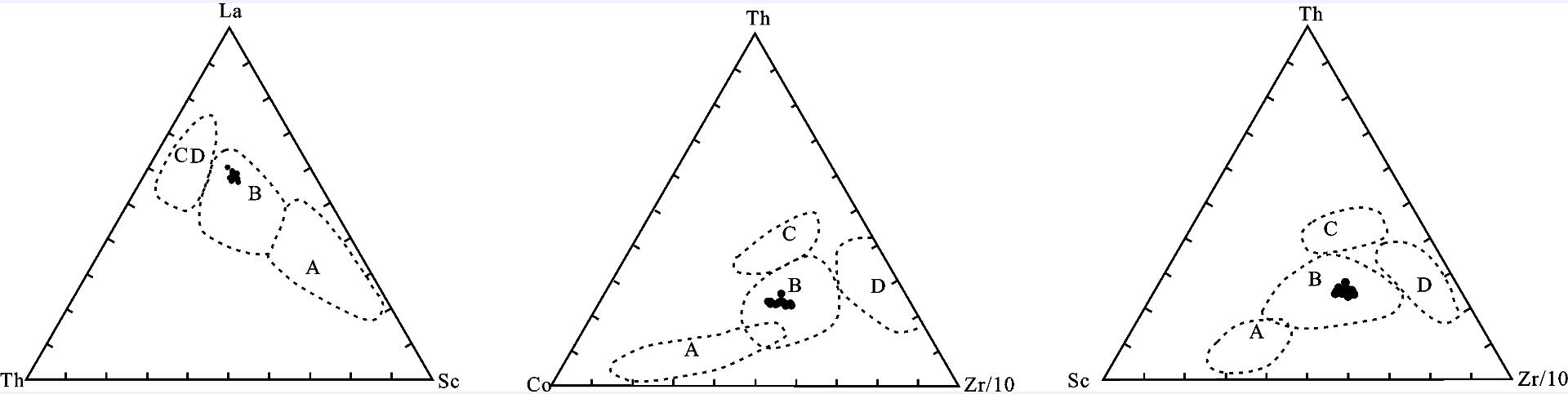
图 11 沃若山地区雀莫错组La-Th-Sc、Co-Th-Zr/10、Sc-Th-Zr/10构造背景判别图解[27]
A—大洋岛弧;B—大陆岛弧;C—活动大陆边缘;D—被动大陆边缘
Figure 11. Tectonic setting discrimination plots of La-Th-Sc, Co-Th-Zr/10, Sc-Th-Zr/10 of the Quemo Co Formation of Woruo Mountain, Qiangtang Basin
A-Oceanic island arc; B-Continental island arc; C-Active continental margin; D-Passive continental margin
表 1 沃若山地区雀莫错组(J1q)主量元素测试结果(%)
Table 1 Major elements (wt.%) data of the Woruo Mountain area in Qiangtang basin, northern Tibet

表 2 沃若山地区雀莫错组(J1q)微量元素测试结果(10-6)
Table 2 Trace elements (10-6) data of the Woruo Mountain area in Qiangtang basin, northern Tibet

-
[1] McLennan S M, Taylor S H, McCulloch M T, et al.Geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic composition of deep-sea turbidites:Crustal evolution and plate tectonic associations[J].Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta, 1990, 54(7):2015-2050. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90269-Q
[2] McLennan S M, Taylor S H.Sedimentary rock and crustal evolution:Tectonic setting and secular trends[J].J Geol., 1991, 99(1):1-21. doi: 10.1086/629470
[3] 胡元邦, 侯中健, 邓江红, 等.滇西昌宁更戛乡下泥盆统向阳寺组硅质岩地球化学特征及构造环境探讨[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(2):650-661. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201602024.htm Hu Yuanbang, Hou Zhongjian, Deng Jianghong, et al.Geochemical characteristics and tectonic environment discussion of chert from the Lower Devonian Xiangyangsi Formation in Gengga, Changning, Western Yunnan[J].Geology in China, 2016, 43(2):650-661(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201602024.htm
[4] 付修根, 王剑, 吴滔, 等.羌塘盆地胜利河地区雀莫错组地层及其古环境[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(5):1305-1312. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201005009.htm Fu Xiugen, Wang Jian, Wu Tao, et al.Stratigraphy and paleoenvironment of the Quemo Co Formation in Shengli River area, northern Tibet[J].Geology in China, 2010, 37(5):1305-1312(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201005009.htm
[5] 曾胜强, 王剑, 冯兴雷, 等.北羌塘盆地沃若山地区中-下侏罗统雀莫错组一段沉积环境分析[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(1):162-172. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201401/48842938.html Zeng Shengqiang, Wang Jian, Feng Xinglei, et al.A sedimentary environment analysis of the first member of the Quemo Co Formation in Woruo Mountain area of the North Qiangtang Basin[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(1):162-172(in Chinese with English abstract).. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201401/48842938.html
[6] 王建坡, 赵兵.羌塘雁石坪中侏罗统雀莫错组地层及沉积环境[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2004, 24(3):43-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200403006.htm Wang Jianpo, Zhao Bing.Stratigraphy and sedimentary environments of the Qoimaco Formation in the Yanshiping region, Qiangtang[J].Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2004, 24(3):43-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200403006.htm
[7] 谭富文, 王剑, 王小龙, 等.羌塘盆地雁石坪地区中-晚侏罗世碳、氧同位素特征与沉积环境分析[J].地球学报, 2004, 26(2):119-126. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DQXB200402003.htm Tan Fuwen, Wang Jian, Wang Xiaolong, et al.Analysis of carbon and oxygen isotope composition and sedimentary environment of the Yanshiping area of the Qiangtang basin in Middle-Late Jurassic[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2004, 26(2):119-126(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DQXB200402003.htm
[8] 李勇, 王成善, 伊海生, 等.青藏高原中侏罗世-早白垩世羌塘复合型前陆盆地充填模式[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(1):20-27. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/cjxb200101003.htm Li Yong, Wang Chengshan, Yi Haisheng, et al.Fill models of the Qiangtang composite foreland basin in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(1):20-27(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/cjxb200101003.htm
[9] 王剑, 付修根, 陈文西, 等.北羌塘沃若山地区火山岩年代学及区域地球化学对比——对晚三叠世火山-沉积事件的启示[J].中国科学(D辑), 2008, 38(1):33-43. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1599117080&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Wang Jian, Fu Xiugen, Chen Wenxi, et al.Chronology and geochemistry of the volcanic rocks in Woruo Mountain region, Northern Qiangtang depression:Implications to the Late Triassic volcanic-sedimentary events[J].Science in China (Series D), 2008, 38(1):33-43(in Chinese). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1599117080&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等.青藏高原大地构造特征与盆地演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:23-25. Zhao Zhengzhang, Li Yongtie, Ye Hefei, et al.Tectonic Characteristics and Basin Evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2001:23-25(in Chinese).
[11] 王剑, 谭富文, 李亚林, 等.青藏高原重点沉积盆地油气资源潜力分析[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004:34-88. Wang Jian, Tan Fuwen, Li Yalin, et al.The Potential of the Oil and Gas Resources in Major Sedimentary Basin on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2004:34-88(in Chinese).
[12] Cullers R L.The controls on the major and trace element variation of shale, silt stones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age from up lifted continental blocks in Colorado to platform sedimentin Kansas, USA[J].Geochimica et Cosmochim Acta, 1994, 58:4955-4972. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90224-0
[13] Pettijohn F J, Potter P E, Siever R.Sand and Sandstone[M].New York:Stringer-Verlag, 1972:618.
[14] Fedo C M, Young G M, Nesbitt H W.Paleoclimatic control on the composition of the Paleoproterozoic Serpent Formation, Huronian Supergroup, Canada:a greenhouse to icehouse t ansition[J].Precambrian Research, 1997, 86:210-223. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2064469025&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sandstones and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology, 1995, 23:921-924. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2
[16] Harnois L.The CIW index:A new chemical index of weathering[J].Sedimentary Geology, 1988, 55:319-322. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(88)90137-6
[17] Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major elemental chemistry of lutites[J].Nature, 1982, 199:715-717. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/31969588_Early_Proterozoic_climates_and_plate_motions_inferred_from_major_element_chemistry_of_lutites._Nature_(London)
[18] Van de Kamp P C, Leake B E.Petrography and geochemistry of feldspathic and mafic sediments of the northeastern Pacific margin[J].Trans.R.Soc.Edinburgh Earth Sci., 1985, 76:411-449. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300010646
[19] Cox R, Low D R, Cullers R L.The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J].Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta, 1995, 59:2919-2940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
[20] Johnsson M J.Tectonic assembly of east central Alaska:Evidence from Cretaceous Tertiary sandstones of the Kandik River terrane[J].Geol.Soc.Amer.Bull., 2000, 112:1023-1042. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1023:TAOEAE>2.0.CO;2
[21] Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continental Crust:It's Composition and Evolution[M].Oxford:Blackwell, 1985.
[22] Allegre C T.Quantitative modes of trace planet[J].Earth Plant.Sci.Lett., 1978, 38(1):1-25. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1
[23] 赵振华.微量元素地球化学原理[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:56-187. Zhao Zhenhua.Trace Element Geochemical Principle[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1997:56-187(in Chinese).
[24] McLennan S M.A geochemical approach to sedimentary provenance[C]//GSA.GSA Abstracts with Programs.Boulder:GSA, 1991, 23(5):108.
[25] Bhatia M R.Composition and classification of Paleozoic flysch mudrocks of eastern Australia:Implications in provenance and tectonic setting interpretation[J].Sediment Geol., 1984, 41(2/4):249-268. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2046972872&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] Roser B P, Korsch R J.Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio[J].J.Geol., 1986, 94:635-650. doi: 10.1086/629071
[27] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W.Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J].Comtrib.Mineral Petrol., 1986., 92(2):181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292
[28] Bhatia M R, Taylor S R.Trace-element geochemistry and sedimentary provinces:A study from the Tasman Geosyncline, Australia[J].Chem.Geol., 1981, 33(1/2):115-125. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2002972402&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] Bhatia M R.Rare earth element geochemistry of Austrilian Paleozonic grawacks mudrocks, provenance and tectonic control[J].Sed.Geol., 1985, 45-52. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1982291435&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[30] 高长林, 叶得燎, 黄泽光, 等.塔里木库鲁克塔格古原洋与地幔柱[J].石油实验地质, 2004, 26(2):161-168. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/sysd200402007.htm Gao Changlin, Ye Deliao, Huang Zeguang, et al.Kuruktag Urocean rift and mantle plume in the Tarim Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(2):161-168(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/sysd200402007.htm
[31] 高长林, 秦德余, 吉让寿, 等.扬子板块北部古被动大陆边缘的地球化学特征[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1991, (4):330-338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199104004.htm Gao Changlin, Qin Deyu, Ji Rangshou, et al.Geoehemieal characteristics of ancient passive continental margin of the northern Yangtze Plate[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 1991, (4):330-338(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199104004.htm
[32] 马文璞.被动大陆边缘性质.中国区域地质, 1986, (3):239-248. Ma Wenpu.Geology of passive continental margins[J].Reigonal Geology of China, 1986, (3):239-248(in Chinese with English abstract).



 下载:
下载: