A study of structure and activity characteristics of the northern segment of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault in Beijing plain area
-
摘要:
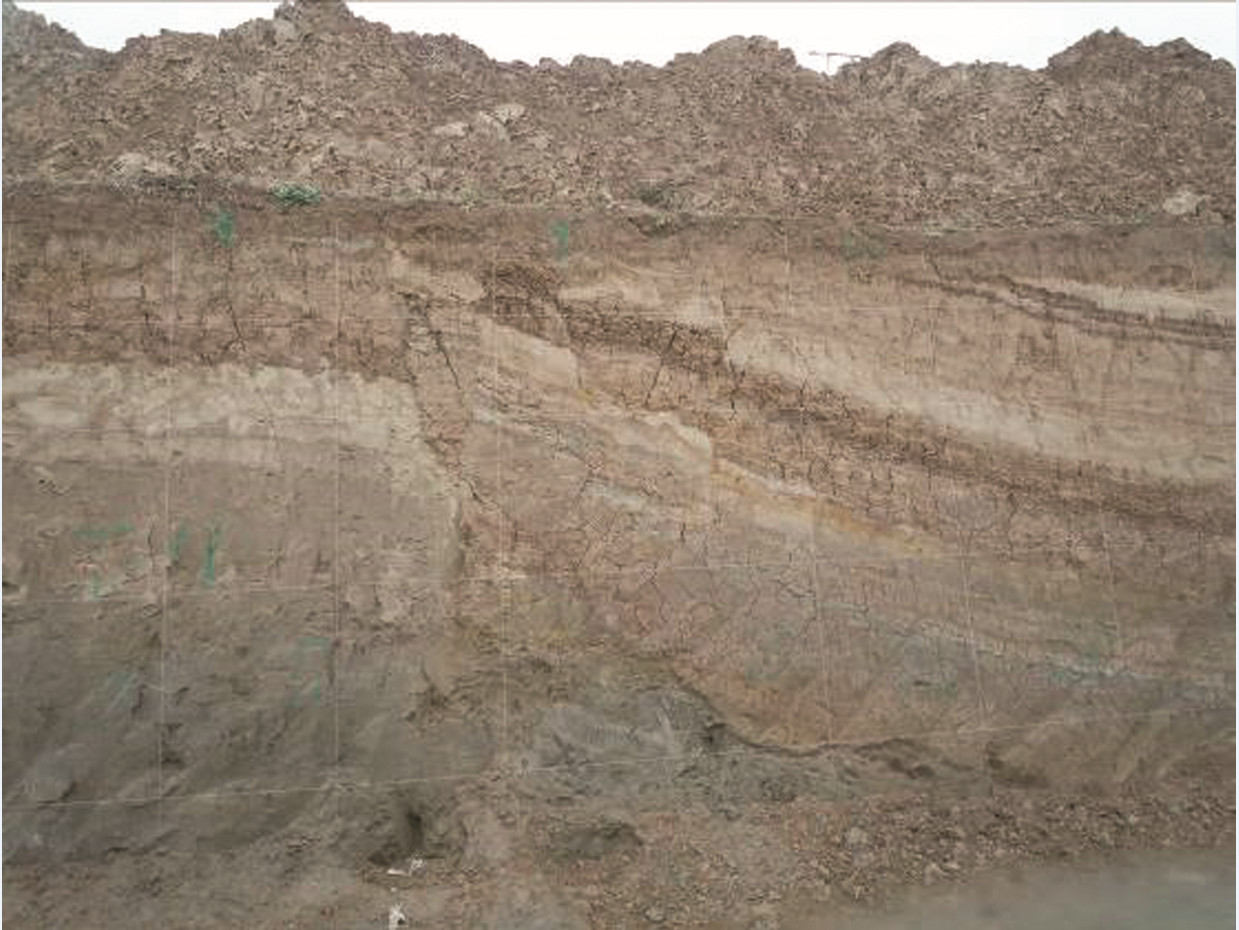
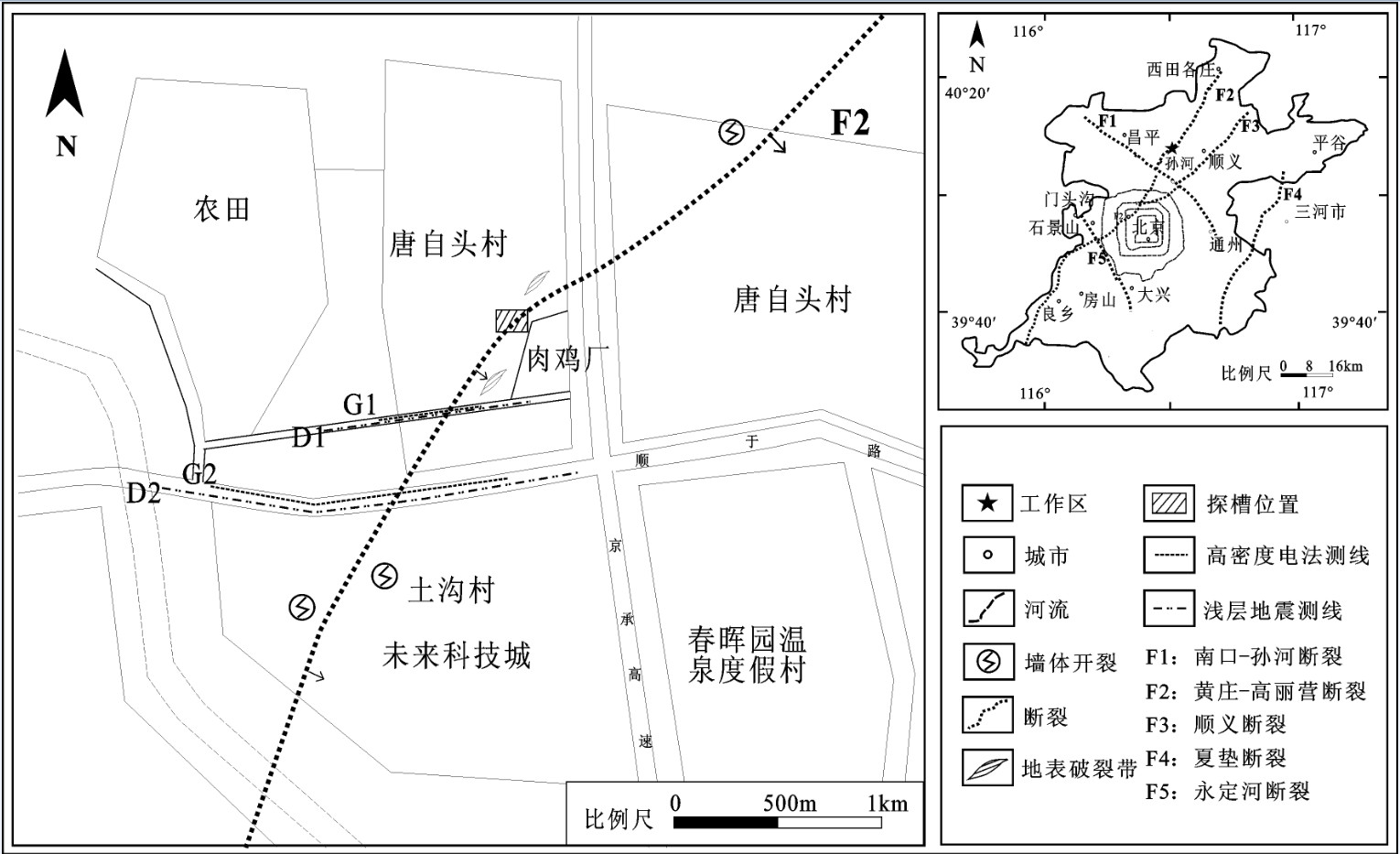
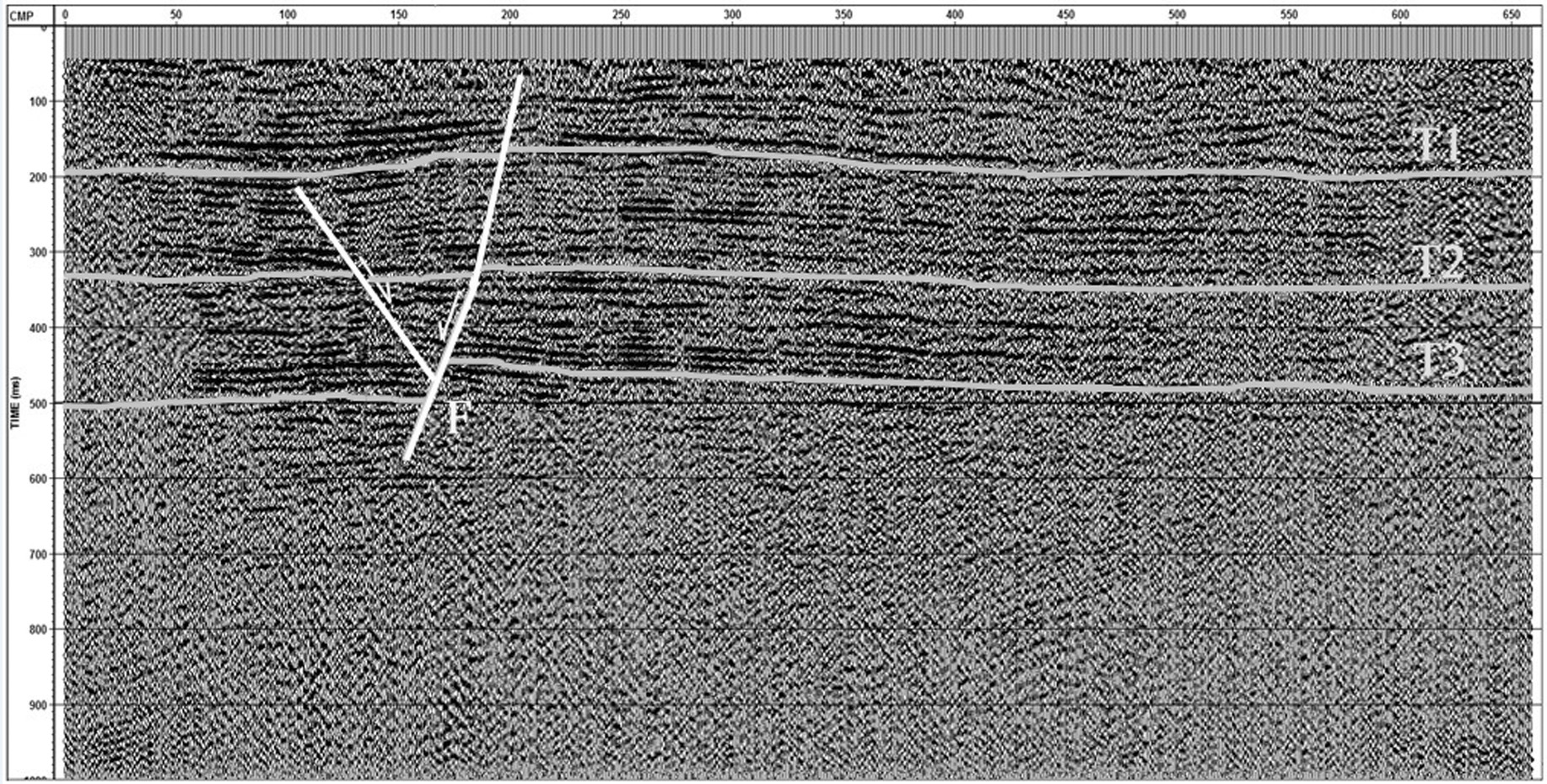
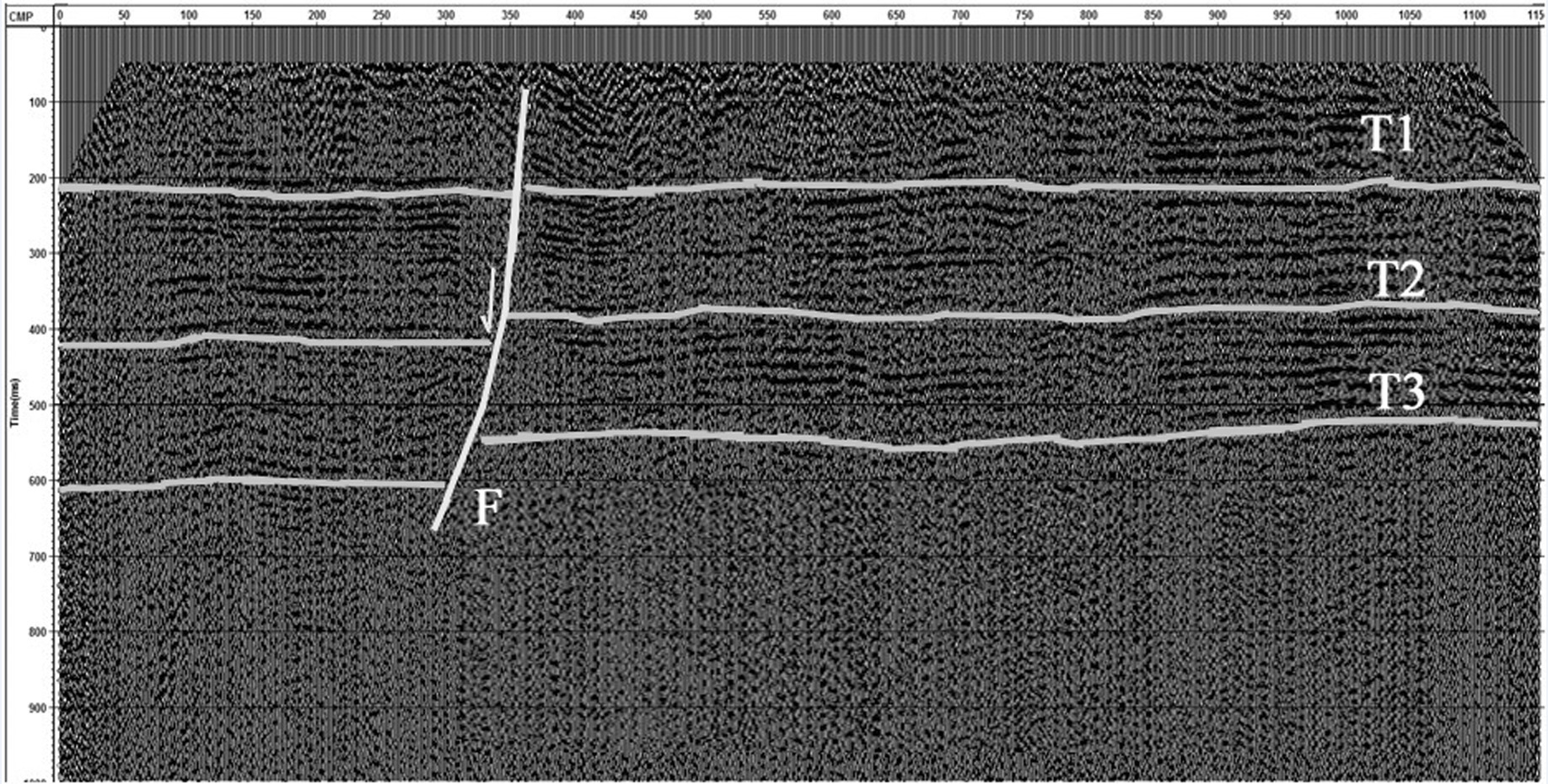
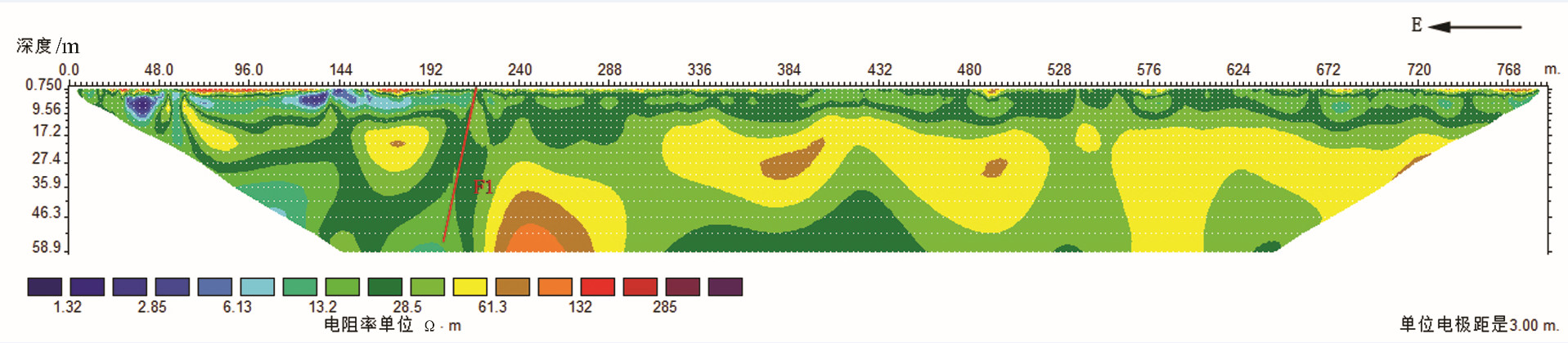
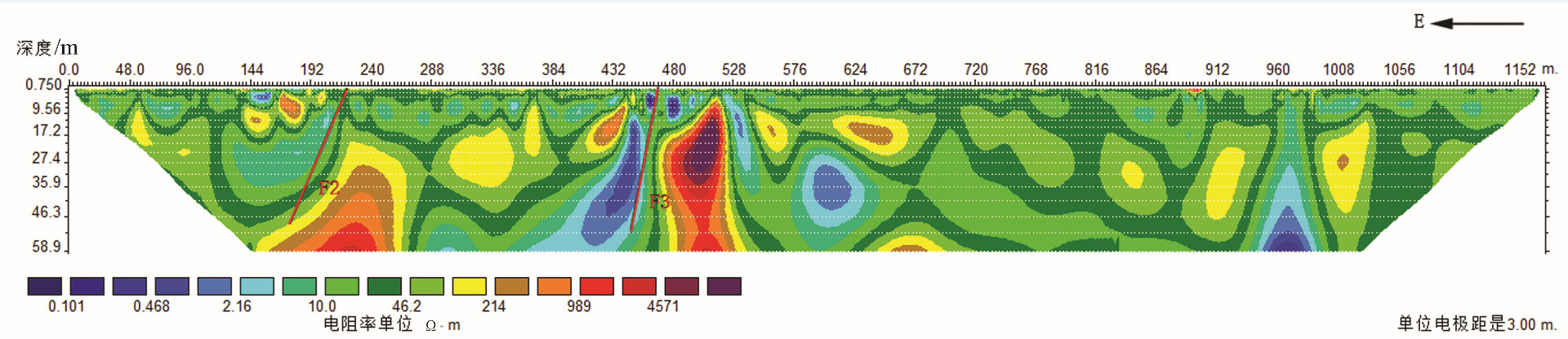
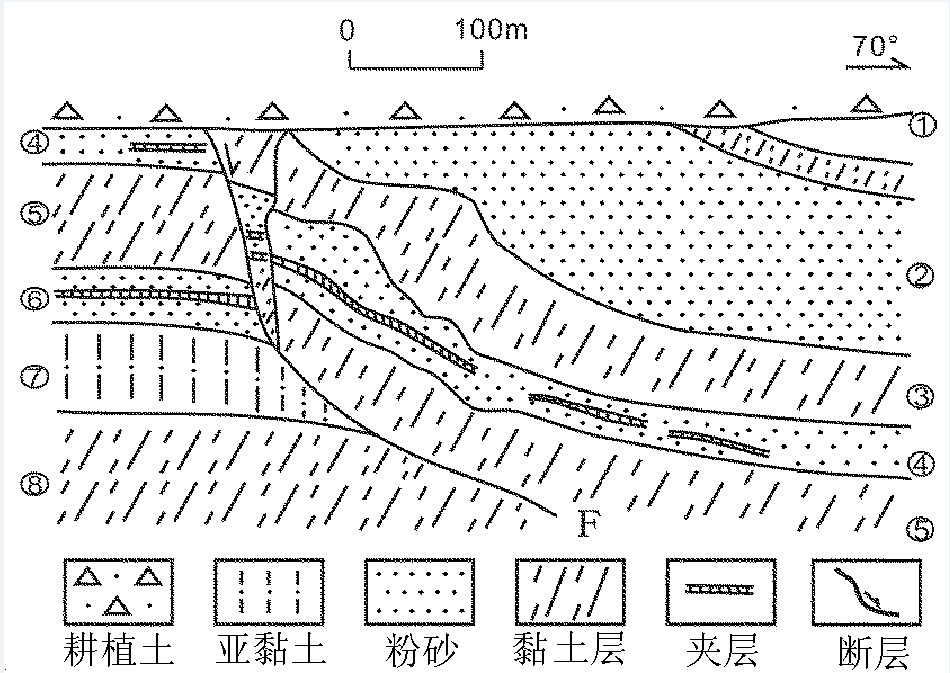
黄庄-高丽营断裂是横穿北京市城区的一条规模较大的隐伏深大活动断裂,是北京凹陷和西山隆起的分界构造。本次研究工作区选在黄庄-高丽营断裂北段昌平未来科技城一带,对目标断裂先后开展了地震勘探、高密度电阻率法勘探以及槽探3种方法组合对其结构与活动性进行综合分析研究,查明了目标断裂的结构及其活动性。研究表明,黄庄-高丽营断裂由主断裂和次级断裂组成的断裂带,断裂带内次级断层也较为发育。断裂带在基岩中表现为阶梯状断层,向上延伸至第四系内部,形成“Y”字形断层组合。该断裂在全新世以来断裂活动明显,物探解译结果的上断点以及探槽中的现象均已达到地表。由此可见,本次工作所采用的3种物探方法组合,对探测城市隐伏断裂并探究其活动性,具有明显的效果,对减轻城市地震灾害实际应用评估具有十分重要的意义。
Abstract:Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault is a relatively large buried active fault across Beijing urban area. It is the tectonic belt of Beijing depression and Xishan uplift. The study area is located in the Future Science and Technology City in Changping. In this paper, the authors analyzed the structure and activity of the fault with the methods of shallow seismic exploration, high density resistivity method and trench profile. The results show that Huangzhuang-Gaoliyang fault is a fault zone that consists of the major fault and secondary faults. The fault belt in bedrock is mainly manifested as step fault and extends up to Quaternary, being a "Y" fault combination. Research shows that this fault has been strongly active since Holocene. Thus, the combination of three methods of shallow seismic exploration, high-density electrical and trenches is significant for detecting the buried fault in the city and exploring its activity, and it is also very important in applying practical assessment to reducing urban seismic hazard.
-
1. 引言
遥感地质找矿是遥感信息获取、含矿信息提取以及含矿信息成矿分析与应用的过程, 近年来, 被广泛应用于地质、矿产资源及相关环境的调查中(刘燕君等, 1993; 朱振海, 1994; 郭德方, 1995; Sabins, 1999; Everett et al., 2002; 廖崇高等, 2002; 连长云等, 2005; 刘颖璠等, 2012; 钱建平等, 2012; 谭克龙等, 2012; 杜小弟等, 2015)。航空高光谱是当前遥感的前沿技术, 通过高光谱成像所获取的地球表面的图像包含光谱维信息融合为一体, 即“图谱合一” (束炯等, 2006), 具有波段数多, 波带窄, 对地物能定量分析等优点, 是20世纪末期以来遥感领域最大的技术进展(Campbell et al., 2011)。航空高光谱遥感技术相对于星载高光谱遥感技术, 可以获取高空间分辨率的高光谱遥感数据, 因而对微小地物具有更强的识别能力(刘德长等, 2015)。通过高光谱矿物填图, 可以大面积、快速提取蚀变矿物(Clack et al., 1990)。王润生等(2010)系统总结了高光谱矿物填图技术流程、工作方法和技术体系。中国国土资源航空物探遥感中心在新疆土屋东—三岔口地区, 应用HyMap航空成像光谱数据填绘出了白云母、绿泥石、绿帘石、绿泥石和绿帘石组合、高岭石、蒙脱石、透辉石、透闪石、蛇纹石、褐铁矿、方解石等矿物或矿物组合种类(王润生等, 2011)。
本文以新疆卡拉塔格地区获取的HyMap航空高光谱数据、地面准同步定标数据、地面高光谱数据为例, 提取并筛选了基于HyMap航空高光谱影像的成矿有利蚀变信息, 在此基础上对红山铜金矿床航空-地面高光谱提取的蚀变信息进行了综合剖析, 并结合矿区地质背景, 建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型, 圈定了2处找矿有利地段。
2. 研究区地质概况
研究区大地构造位于东天山吐哈盆地南缘、大南湖—头苏泉晚古生代岛弧带(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 新疆卡拉塔格地区地质矿产图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中—上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿Figure 1. Geological map of Kalatag area in Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit
图 1 新疆卡拉塔格地区地质矿产图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中—上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿Figure 1. Geological map of Kalatag area in Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit区内地层整体呈北西向产出, 由中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组(O2Hd)、中—上志留统红柳峡组(S2-3h)、下泥盆统大南湖组(D1d)、上石炭统脐山组(C2qs)、中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组(P2a)、上二叠统库莱组(P3k)、下侏罗统三工河组(J1s)、全新统(Qh)组成。
该区经历了多期次的构造变动, 区域构造形成类型多样、特征复杂, 褶皱、断裂和火山机构发育, 区域性的断裂构造控制着该区火山岩和侵入岩的展布, 次级断裂控制着矿化蚀变带的分布, 更次一级构造裂隙带控制着矿化体的产出。主要发育北西、北北西和北东东向三组断裂构造, 其中北西向断裂为该区主要控矿构造, 同火山断裂发育, 含矿火山热液沿断裂活动强烈。
区内火山活动强烈, 火山岩分布广泛。岩石类型以中基性火山岩为主, 中酸性火山岩次之, 从奥陶系至二叠系均有出露, 其中奥陶系最为发育, 其次为泥盆系、石炭系, 二叠系局部出现。侵入岩较为发育, 主要为一套古生代侵入体, 包括中酸性闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗岩等侵入岩, 中部为与铜金矿化直接相关的中生代中酸性火山机构, 主要由石英斑岩、钠长斑岩、英安岩、英安斑岩、安山玢岩、闪长玢岩和火山角砾集块岩等岩性构成。其中志留纪侵入岩由老到新依次为英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、二长花岗岩、花岗斑岩。该区经受了区域埋深变质作用, 变质程度较弱, 主要变质矿物为绿泥石、钠长石、葡萄石、石英、阳起石、方解石、绿帘石。
区内已知矿床自北西向南东依次产出有:红山铜金矿床→梅岭铜锌金矿床→红石铜金矿床→红海铜锌金矿床。
3. 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法用于寻找铜金矿床的原理
3.1 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法的依据
不同矿床类型由于岩石岩性和蚀变矿物不同, 它们的光谱特征有明显的差异(姚佛军, 2006)。铜金矿床属于内生金属矿床, 这类矿床与地表蚀变密切相关, 可以利用航空高光谱遥感影像进行蚀变矿物提取, 结合地表岩石光谱测试分析, 应用HyMap航空成像光谱仪和美国ASD公司的FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪对不同类型矿床的光谱特征进行测量, 分析其不同类型矿床的光谱特征, 进行蚀变矿物遥感信息提取, 开展高光谱遥感地空综合预测研究, 进而指导找矿。
3.2 蚀变矿物诊断性光谱特征分析
岩矿的光谱包含有一系列特征吸收谱带。每一个特征谱带或谱带组合与岩矿内部微粒的物质属性存在一定的对应关系(Povarennykh, 1978)。在短波红外光谱区域, 褐铁矿、黄钾铁矾、白云母、绿泥石等具有可以识别的诊断性光谱特征, 特征吸收波段的深度与岩石中这些矿物的含量密切相关(刘圣伟, 2006)。矿物诊断性光谱吸收包括金属阳离子在可见光区域的电子过程以及阴离子基团在近红外区域的振动过程。蚀变矿物的可见光−近红外范围内几种官能团主要包括Fe2+、Fe3+、Al−OH、Mg−OH、OH-、CO32-。
一般阴离子诊断谱带位于2000~2500 nm光谱区域。而Fe2+、Fe3+和Mn2+诊断谱带一般位于400~1200 nm光谱区域(甘甫平等, 2003)。所以根据400~1100 nm光谱区间的Fe吸收谱带和2000~2500 nm羟基和碳酸根谱带将矿物分为含铁矿物、含羟基矿物和含碳酸根矿物以及其他矿物(甘甫平, 2003)。褐铁矿的光谱吸收谷是矿物光谱分析、遥感铁染异常提取常用的波段。其中Fe3+离子的特征吸收谷位主要在600~800 nm, 中心位置在700 nm左右, Fe2+离子的特征吸收谷位主要在900~1500 nm, 中心位置在1200 nm左右; 白云母的诊断性光谱特征是Al−OH键在2180~2230 nm之间的尖锐而深的吸收特征, 以及在2340 nm和2440 nm附近的较弱Al−OH特征, Clark et al.(1990)在高光谱分辨率下, 检测到白云母矿物在2200 nm附近的吸收波段随Al含量的增加向长波方向的移动; 绿泥石的光谱具有Fe−OH和Mg−OH的诊断性吸收特征, 波长位置分别为2235~2255 nm和2320~2360 nm, 这些吸收特征的波长随着绿泥石中铁离子含量的增加而增大。
4. HyMap航空高光谱数据获取及处理
综合考虑仪器参数、成图精度的要求、研究区自然地理、地形起伏、野外工作条件等因素, 进行飞行方案的最优设计(表 1)。将HyMap成像光谱仪搭载在Y−12飞机上, 利用国外引进的HyMap航空高光谱遥感测量系统、地面ASD光谱测量系统。采集高光谱分辨率的HyMap航空高光谱遥感数据、地面准同步的地物光谱定标数据。具体获取过程分为3个步骤:首先对HyMap成像光谱仪进行实验室定标, 保证其性能指标达到项目要求, 以获取优质的高光谱影像数据; 其次进行HyMap仪器的安装和测试, 按照仪器安装规范方法, 将HyMap安装在Y−12飞机上, 保证机下的摄影窗口满足数据获取要求, 按照航空成像光谱数据获取规范进行地面测试; 最后为HyMap航空高光谱数据获取和初步质量检查。
表 1 HyMap航空成像光谱仪主要技术参数Table 1. Main technical parameters of HyMap aviation imaging spectroradiometer
在此基础上, 开展HyMap航空高光谱遥感数据辐射定标、大气校正光谱反演、几何校正和地理编码等数据处理工作。通过此项研究, 为高光谱遥感地空综合预测铜金矿床的技术方法研究和应用提供可靠的数据基础。
5. 地面高光谱数据获取及处理
地面光谱测量采用美国ASD公司生产的FieldSpec Pro FR地面光谱测量仪(表 2)。利用该仪器开展了地面光谱准同步定标。在HyMap高光谱数据获取过程中, 准同步布设黑白布定标场和明暗地物定标场, 利用FieldSpec Pro FR地面光谱测量仪进行光谱定标数据获取(图 2,图 3), 并基于经验线性模型法, 对高光谱影像进行大气校正和光谱比对分析。
表 2 FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪主要技术参数Table 2. Main technical parameters of FieldSpec Pro FR spectrometer
同时开展了典型铜金矿床地表蚀变围岩和其他相关的岩石地物的光谱测量, 完成了4条贯穿地层走向的成矿有利地质单元光谱测量和4条典型矿床光谱测量。共完成光谱测量点287个, 光谱测量曲线2870条。测量完成后, 开展了各岩石类型的岩矿光谱数据处理、光谱库建立、光谱特征分析等研究工作, 研究及分析结果为航空高光谱蚀变矿物信息提取、地面光谱验证、铜金矿床围岩蚀变信息筛选等提供重要的地面光谱信息支持。
地面高光谱数据处理采用ViewSpec Pro软件, 利用ViewSpec Pro软件挑选符合要求的地面岩矿光谱曲线, 并将这些曲线转换为txt格式的文件。由于受到太阳位置、角度条件、大气条件、地形影响及传感器本身性能的影响, 传感器所记录的数据与目标的光谱反射率或光谱辐射亮度值并不一致。需先将传感器记录的原始辐射值(DN值)转化为地物反射率(李志忠等, 2015)。
6. 蚀变矿物信息提取处理方法及分布特征
目前基于高光谱遥感影像数据提取矿物的处理方法可以分为2类: (1)通过像元光谱与矿物标准光谱曲线的匹配实现识别和量化目标矿物; (2)提取矿物光谱特征吸收波段参数作为识别和量化指标(卢燕, 2014)。前者在处理过程中光谱数据信息可能由于重定标而部分丢失。且基于单幅图像统计参数的处理方法难以做到无缝衔接, 该方法也涉及大量的运算。本次研究区蚀变矿物提取主要基于第2种方法。该方法利用ENVI软件, 基于可编程实现的特征提取处理通道, 该通道中脚本设计是基于提取光谱参数, 首先对影像光谱数据进行均值标准化、去连续统、卷积平滑等数据预处理, 在进行特征深度、特征面积、特征宽度、极小值波长、比值、算术和逻辑运算等特征参数提取。同时利用多个诊断性特征来标记或约束特定的矿物, 提取矿物的分布和相对含量, 并增强矿物识别的精度。
根据矿物光谱特征吸收波段参数的蚀变矿物提取方法, 在研究区提取了褐铁矿−黄钾铁矾、白云母−蒙脱石、绿泥石−绿帘石−碳酸盐、叶腊石等蚀变矿物或组合(图 4), 其中褐铁矿−黄钾铁矾、白云母−蒙脱石、绿泥石−绿帘石−碳酸盐等蚀变矿物组合在全区范围内分布, 且呈团块状、条带状及星散状。叶腊石则仅在研究区北东部呈星点状分布, 蚀变不明显, 对于指导找矿意义不大(黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置)。
![]() 图 4 新疆卡拉塔格地区HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物丰度图a—褐铁矿-黄钾铁矾; b—白云母-蒙脱石; c—绿泥石、绿帘石、碳酸盐; d—叶腊石, 黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置Figure 4. HyMap aviation hyperspectral alteration mineral abundance map of Kalatag area in Xinjianga-Limonite-jarosite; b-Muscovite-montmorillonite; c-Chlorite, epidote, carbonate; d-Pyrophyllite, yellow circle indicates pyrophyllite distribution position
图 4 新疆卡拉塔格地区HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物丰度图a—褐铁矿-黄钾铁矾; b—白云母-蒙脱石; c—绿泥石、绿帘石、碳酸盐; d—叶腊石, 黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置Figure 4. HyMap aviation hyperspectral alteration mineral abundance map of Kalatag area in Xinjianga-Limonite-jarosite; b-Muscovite-montmorillonite; c-Chlorite, epidote, carbonate; d-Pyrophyllite, yellow circle indicates pyrophyllite distribution position7. 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的建立与找矿有利地段优选
7.1 矿区地质特征
红山铜金矿床是高硫型−浅成低温热液型矿床(董承维, 2013)。矿床产于陆相蚀变酸性火山穹窿及其通道中, 该次火山机构受近东西与北西向两组断裂控制, 且主要控岩控矿构造为北西向断裂。铜矿体受北西向断裂及其次级构造破碎带控制, 为浸染状辉铜矿化和黄铜矿化。金矿化主要与酸性次火山岩中的细粒黄铁矿有关(王瑞军等, 2014) (图 5)。
![]() 图 5 红山铜金矿区地质图(据王京彬, 2006)1—第四系残坡积物、风积物; 2—英安岩、英安斑岩、安山岩; 3—蚀变英安岩; 4—流纹斑岩、石英斑岩、霏细斑岩; 5—花岗岩; 6—花岗闪长岩脉; 7—闪长玢岩脉; 8—氧化带矿体; 9—推测断层; 10—片理化带; 11—金矿体; 12—铜矿体Figure 5. Geological map of the Hongshan Cu-Au deposit (after Wang, 2006)1-quaternary debris slope sediments, aeolian; 2-dacite, British Ann porphyry, andesite; 3-alteration dacite; 4-rhyolitic porphyry and quartz porphyry, faye fine porphyry; 5-granite; 6-granite diorite vein; 7-diorite Bin dike; 8-oxidation zone ore body; 9-speculation fault; 10-piece of physics and chemistry; 11-gold ore body; 12-copper ore body
图 5 红山铜金矿区地质图(据王京彬, 2006)1—第四系残坡积物、风积物; 2—英安岩、英安斑岩、安山岩; 3—蚀变英安岩; 4—流纹斑岩、石英斑岩、霏细斑岩; 5—花岗岩; 6—花岗闪长岩脉; 7—闪长玢岩脉; 8—氧化带矿体; 9—推测断层; 10—片理化带; 11—金矿体; 12—铜矿体Figure 5. Geological map of the Hongshan Cu-Au deposit (after Wang, 2006)1-quaternary debris slope sediments, aeolian; 2-dacite, British Ann porphyry, andesite; 3-alteration dacite; 4-rhyolitic porphyry and quartz porphyry, faye fine porphyry; 5-granite; 6-granite diorite vein; 7-diorite Bin dike; 8-oxidation zone ore body; 9-speculation fault; 10-piece of physics and chemistry; 11-gold ore body; 12-copper ore body矿区地表发育黄钾铁钒化、绢云母化、硅化、褐铁矿化、黄铁矿化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、青磐岩化。近矿蚀变以火山岩酸淋滤带蚀变体的黄钾铁矾化−明矾石化−高岭土化−石膏和中性斑岩体的绢云母化−硅化为显著特征, 远矿蚀变为青磐岩化(许英霞等, 2008)。矿区中心为泥化、硫酸盐带, 向北为硅化−伊利石化−绢云母化−褐铁矿化带。具有找矿标志的矿化蚀变为:硅化−绢云母化、伊利石化、褐铁矿化、硅化、高岭土化−明矾石化等。
红山铜金矿床矿化以铜、金矿为主, 赋矿岩性主要为流纹岩、英安岩、安山玢岩、闪长玢岩、火山角砾岩。矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿、蓝铜矿、闪锌矿、磁铁矿、赤铁矿、黄钾铁钒等。脉石矿物为石英、斜长石、绢云母、绿泥石等。矿石呈稠密浸染状、细脉状、角砾状构造(许英霞, 2010)。
7.2 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的建立
充分研究区域成矿有利的构造、地层、岩浆岩条件、变质条件的基础上, 结合区域控矿因素、矿床、矿化蚀变特征, 进行航空高光谱蚀变矿物分布特征分析及评价。本文截取了研究区内红山铜金矿床及外围基于HyMap航空高光谱遥感影像的蚀变矿物分布图(图 6), 图中显示红山铜金矿床中心位置处于开采状态, 呈黑白相间且颜色突变的色调, 影纹粗糙且不均匀, 矿床外围呈灰黑色、灰绿色色调, 影纹粗糙。与矿床有关的航空高光谱蚀变矿物组合主要为褐铁矿+黄钾铁钒、绢云母+蒙脱石等, 呈大面积的团块状分布。在矿床外围分布着呈星散状、星点状的绿泥石+绿帘石蚀变矿物组合, 该组蚀变为铜金矿床外围主要发育的蚀变组合, 对于寻找该类型矿床有一定的指示作用。
在红山铜金矿区收集了具体的剖线采样和光谱数据, 图 7为红山铜金矿区的地质光谱综合剖面, 出露的地层为中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组, 岩性主要为英安岩、片理化带、流纹斑岩、花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、构造蚀变岩以及铜金矿化体等。蚀变矿物主要有褐铁矿、黄钾铁钒、绢云母、石膏、高岭石、明矾石及方解石等。通过样品采集和光谱测试结果, 研究与该区铜金矿关系密切的几种赋矿岩性的光谱曲线, 分别为构造蚀变岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗岩、流纹斑岩、蚀变英安岩、及铜金矿化体。
![]() 图 7 红山铜金矿区剖线地面高光谱蚀变矿物分布图1—英安岩; 2—片理化带; 3—流纹斑岩; 4—花岗岩; 5—花岗闪长岩; 6—断裂构造; 7—地面光谱样采样点; 8—地面光谱测试点编号; 9—褐铁矿; 10—黄钾铁矾; 11—绢云母; 12—石膏; 13—高岭石; 14—明矾石; 15—方解石Figure 7. Surface hyperspectral alteration mineral distribution along geological section in the Hongshan copper gold orefield1-Dacite; 2-Schistosity zone; 3-Rhyolitic porphyry; 4-Granite; 5-Granite diorite; 6-Fracture structure; 7-Surface spectrum sampling site; 8-Serial number of spectrum test point; 9-Limonite; 10-Jarosite; 11-Sericite; 12-Gypsum; 13-Kaolinite; 14-Alunite; 15-Calcite
图 7 红山铜金矿区剖线地面高光谱蚀变矿物分布图1—英安岩; 2—片理化带; 3—流纹斑岩; 4—花岗岩; 5—花岗闪长岩; 6—断裂构造; 7—地面光谱样采样点; 8—地面光谱测试点编号; 9—褐铁矿; 10—黄钾铁矾; 11—绢云母; 12—石膏; 13—高岭石; 14—明矾石; 15—方解石Figure 7. Surface hyperspectral alteration mineral distribution along geological section in the Hongshan copper gold orefield1-Dacite; 2-Schistosity zone; 3-Rhyolitic porphyry; 4-Granite; 5-Granite diorite; 6-Fracture structure; 7-Surface spectrum sampling site; 8-Serial number of spectrum test point; 9-Limonite; 10-Jarosite; 11-Sericite; 12-Gypsum; 13-Kaolinite; 14-Alunite; 15-Calcite经研究分析发现:红山铜金矿床及外围不同岩性地面光谱特征各不相同, 各类岩性具体曲线(图 8)特征如下:
![]() 图 8 红山铜金矿床及外围各岩性光谱曲线对比图a—构造蚀变岩; b—花岗闪长岩; c—花岗岩; d—流纹斑岩; e—蚀变英安岩; f—铜金矿化体Figure 8. Comparison diagram of various lithology spectral curves from the Hongshan copper gold deposit and peripheral areasa-Tectonic altered rock; b-Granodiorite; c-Granite; d-Rhyolitic porphyry; e-Altered dacite; f-Copper gold mineralization body
图 8 红山铜金矿床及外围各岩性光谱曲线对比图a—构造蚀变岩; b—花岗闪长岩; c—花岗岩; d—流纹斑岩; e—蚀变英安岩; f—铜金矿化体Figure 8. Comparison diagram of various lithology spectral curves from the Hongshan copper gold deposit and peripheral areasa-Tectonic altered rock; b-Granodiorite; c-Granite; d-Rhyolitic porphyry; e-Altered dacite; f-Copper gold mineralization body构造蚀变岩(图 8-a)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的Fe3+特征吸收可能为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱吸收峰为发育弱绢云母化所致, 2260 nm处的较强吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化所致。故构造蚀变岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁矾+绢云母。
花岗闪长岩(图 8-b)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处较强的对称吸收峰为岩石发育褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处较强的吸收峰, 及右肩2250 nm处较弱次级吸收峰, 是Al−OH的特征吸收, 为明矾石化所致; 2350 nm处强的主吸收峰, 左肩2250 nm处较强的次级吸收峰, 是Mg−OH的特征吸收, 为绿泥石化所致。故其蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+明矾石+绿泥石。
花岗岩(图 8-c)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 910 nm处较弱的Fe3+特征吸收峰为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为绢云母化引起, 其右肩2250 nm处的较弱吸收峰可能为明矾石化所致; 2265 nm处的较弱吸收峰可能为黄钾铁矾化所致; 2330 nm处可见较强吸收峰, 是CO32-的特征吸收峰, 为岩石发育碳酸盐化所致, 故花岗岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁矾+绢云母+明矾石+方解石。
流纹斑岩(图 8-d)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的较强吸收峰为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的强Al−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育绢云母化所致; 2265 nm处的弱Fe−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化所致, 故流纹斑岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁钒+绢云母。
蚀变英安岩(图 8-e)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的弱吸收峰为弱褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为绢云母化引起; 2350 nm处的较强主吸收峰及其左肩2250 nm处的较强次级吸收峰, 是Mg−OH的特征吸收峰, 为绿泥石化所致; 2330 nm处的较强主吸收峰以及1880 nm、2060 nm、2170 nm处较弱次级吸收峰, 是CO32-的特征吸收峰, 为岩石发育碳酸盐化所致; 1836 nm、1935 nm、2213 nm、2270 nm处可见多处较强吸收峰, 为岩石发育石膏所致。故蚀变英安岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+绢云母+绿泥石+方解石+石膏。
铜金矿化体(图 8-f)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的较强Fe3+特征吸收为岩石发育褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育绢云母化; 2265 nm处的弱Fe−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化; 1540 nm、1835 nm、1920 nm、2000 nm、2165 nm、2208 nm、2250 nm、2329 nm、2374 nm、2385 nm处可见多处较强吸收峰, 可能为岩石发育黝帘石化所致。故铜金矿化体蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+绢云母+黄钾铁钒+黝帘石。
根据航空高光谱和地面高光谱蚀变矿物或组合的类型和分布特征, 结合红山铜金矿床的地质特征, 进行典型矿床航空−地面高光谱综合剖析, 最终建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型(表 3)。
表 3 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型Table 3. Hyperspectral remote sensing air comprehensive prospecting model for the Hongshan copper gold deposit
7.3 铜金矿床找矿有利地段优选
在建立红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的基础上, 结合地质、野外调查验证等多源地学信息, 运用高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法, 优选了2处与已知矿床航空−地面高光谱向类似的找矿有利地段, 分别为I−1和I−2(图 9)。
![]() 图 9 新疆卡拉塔格地区找矿有利地段优选图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中-上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿; 23—高光谱找矿有利地段Figure 9. Favorable ore-prospecting optimization segments in Kalatag area of Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit; 23-Hyperspectral favorable ore-prospecting segments
图 9 新疆卡拉塔格地区找矿有利地段优选图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中-上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿; 23—高光谱找矿有利地段Figure 9. Favorable ore-prospecting optimization segments in Kalatag area of Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit; 23-Hyperspectral favorable ore-prospecting segmentsI−1找矿有利地段分布在玉带铜金矿点北西侧一带, 呈北北西向展布, 面积约5.2 km2。区内分布的地层为中−上志留统红柳峡组(S2-3h)火山岩, 近东西向断裂构造发育, 区内多发育褐铁矿化、硅化、绿帘石化等蚀变。微量元素分析23个, 化学分析显示钛含量最高达0.23×10-2, 金红石含量最高达0.38×10-2。为铜、金、钛等元素多金属找矿有利地段(图 10)。
I−2找矿有利地段分布在东二区南东侧, 呈近东西向展布, 面积约6.8 km2。区内分布的地层为中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组(O2Hd)火山岩, 北东东向断裂构造发育, 花岗闪长岩体呈近东西向展布, 区内多发育硅化、褐铁矿化、赤铁矿化、绿帘石化、孔雀石化等蚀变。微量元素分析15个, 化学分析显示钛元素含量最高达0.21×10-2, 金红石含量最高达0.35×10-2, 且区内已有红山铜金矿床分布, 为铜、金、钛等元素多金属找矿有利地段(图 11)。
8. 结论
(1) 新疆东天山卡拉塔格铜金多金属矿床集中, 地表具有指示意义的蚀变矿物分布较为典型, 适合利用高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法在该区寻找铜金及多金属矿床, 故该方法为寻找铜金矿床的有效技术方法。
(2) 在运用HyMap航空成像光谱仪和FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪进行高光谱数据获取和处理的基础上, 结合HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物提取效果分析, 最终开展典型矿床航空−地面高光谱综合剖析研究, 建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型, 并综合地质、野外调查验证等多源地学信息, 圈定了I−1和I−2等两处找矿有利地段。
(3) 与常规的地质、区域化探等地质矿产勘查方法相比, 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法具有低成本、快速高效的优势。但由于各类矿床的找矿标志和高光谱异常信息多种多样, 从而造成蚀变异常信息的多解性, 加上利用高光谱地空综合预测方法开展多金属矿产资源调查研究还比较少, 需要今后继续完善成熟。
致谢: 感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵修改意见! -
[1] 徐明才, 高景华, 刘建勋, 等.应用于城市活断层调查的地震方法技术[J].中国地震, 2005, 21(1):17-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD200501001.htm Xu Mingcai, Gao Jinghua, Liu Jianxun, et al.Application of the seismic method to detecting active faults[J].Earthquake Research in China, 2005, 21(1):17-23(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD200501001.htm
[2] 高文学, 马瑾.首都圈地震地质环境与地震灾害[M].北京:地震出版社, 1993. Gao Wenxue, Ma Jin.Seismo-Geological Background and Earthquake Hazard in Beijing Area[M].Beijing:Seismological Press, 1993(in Chinese).
[3] 徐锡伟, 吴为民, 张先康, 等.华北地区地壳最新构造变动与地震[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002. Xu Xiwei, Wu Weimin, Zhang Xiankang, et al.The Earth's Crust Tectonism and Earthquake in The Capital Area[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2002(in Chinese).
[4] 焦青, 邱泽华.北京平原区主要活动断裂研究进展[C]//地壳构造与地壳应力文集, 2006, 18:72-84. Jiao Qing, Qiu Zehua.Research Progress of Major Active Faults in Beijing Plain Area[C]//Crust Structure and Crust Stress Corpus.2006, 18:72-84(in Chinese).
[5] 北京市地质调查研究院.北京市多参数立体地质调查成果报告[D].2007. Beijing Institute of Geological Survey.Multiparameters 3-dimensional geological survey report in Beijing[D].2007(in Chinese).
[6] 车兆宏, 范燕.北京黄庄-高丽营断层、八宝山断层现今活动追踪研究[J].地震, 2008, 51(5):1503-1510. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200303013.htm Che Zhaohong, Fan Yan.Tracing study of fault activity of the Beijing Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault and Babaoshan fault in recent time[J].Earthquake, 2008, 51(5):1503-1510(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200303013.htm
[7] 车兆宏.首都圈断层活动性研究[J].华北地震科学, 1993, 11(2):23-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD199302002.htm Che Zhaohong.A study of the fault activity in the capital circle[J].North China Earthquake Sciences, 1993, 11(2):23-34(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD199302002.htm
[8] 贾三满, 郭萌.从高丽营探槽分析黄庄-高丽营断裂与地裂缝的关系[J].城市地质, 2007, 2(4):24-28. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CSDZ200704007.htm Jia Sanman, Guo Meng.The relation bewteen Hunagzhung-Gaoliying fualt and by Gaoliying trench and earth fissure[J].Urban Geology, 2007, 2(4):24-28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CSDZ200704007.htm
[9] 尹功明, 卢演俦, 魏兰英, 等.北京高丽营断层时间年代学研究[J].地震地质, 2002, 24(1):101-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200201009.htm Yin Gongming, Lu Yanchou, Wei Lanying, et al.Chronological study of faulting events of Gaoliying fault, Beijing[J].Seismology and Geology, 2002, 24(1):101-110(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200201009.htm
[10] 向宏发, 方仲景, 张晚霞, 等.北京平原区隐伏断裂晚第四纪活动性的初步研究[J].地震学报, 1993, 15(5):385-388. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB199303018.htm Xiang Hongfa, Fang Zhongjing, Zhang Wanxia, et al.Preliminary study of late Quaternary activities of concealed fractures in Beijing plain[J].Acta Seismologica Sinica, 1993, 15(5):385-388(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB199303018.htm
[11] 张杰坤, 万志清, 陈奇, 等.北京地区北东向主要活动断裂的地震工程效应评价[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1992, 3(2):16-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH199202002.htm Zhang Jiekun, Wan Zhiqing, Chen Qi, et al.Assessment of the seismic engineering effect of the main active faults along NE direction in Beijing district[J].The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1992, 3(2):16-25(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH199202002.htm
[12] 徐杰, 汪良谋, 方仲景, 等.北京八宝山断裂和黄庄-高丽营断裂构造活动性的初步分析[J].华北地震科学, 1992, 10(3):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200504011.htm Xu Jie, Wang Liangmou, Fang Zhongjing, et al.Preliminary analysis of the tectonic activities of Babaoshan and Huangzhuang-Gaoliying faults in Beijing area[J].North China Earthquake Sciences, 1992, 10(3):1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200504011.htm
[13] 江娃利, 候治华, 等.北京平原主要活动断裂全新世活动定量研究及未来地震危险性预测[C]地壳构造与地壳应力文集, 2000(13). Jiang Wali, Hou Zhihua, et al.Quantitative Study of Holocene Activity of Main Active Faults in the Beijing Plain and Prediction of Future Seismic Danger[C]//Crust Structure and Crust Stress Corpus, 2006(13)(in Chinese).
[14] 马文涛, 唐文榜, 徐锡伟等.北京市黄庄-高丽营隐伏断裂立水桥段浅层活动特征的地震探测[J].物探与化探, 2005, 29(6):503-505. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/WTYH200506006.htm Ma Wentao, Tang Wenbang, Xu Xiwei, et al.Seismic exploration of shallow deformation along Lishuiqiao section of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying active fault in Beijing urban area.[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(6):503-505(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/WTYH200506006.htm
[15] 马文涛, 徐锡伟, 郝书俭, 等.北京市立水桥附近黄庄-高丽营隐伏断裂的浅层地震勘探[J].地震地质, 2004, 26(4):698-705. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZDZ200404014.htm Ma Wentao, Xu Xiwei, Hao Shujian, et al.Shallow seismic exploration for Huang Zhuang-Gaoliying buried fault in the vicinity of Lishuiqiao, Beijing[J].Seismology and Geology, 2004, 26(4):698-705(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZDZ200404014.htm
[16] 白凌燕, 张磊, 蔡向民, 等.磁性地层年代对北京平原顺义断裂第四纪活动性的约束[J].现代地质, 2014(6):1234-1242. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201406013.htm Bai Lingyan, Zhang Lei, Cai Xiangmin, et al.Quaternary magnetostratigraphic time framework constraints on activity characteristics of the Shunyi fault, Beijing plain[J].Geoscience, 2014(6):1234-1242(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201406013.htm
[17] 张磊, 白凌燕, 蔡向民, 等.北京南口-孙河断裂北西段综合物探剖面定位及其活动性研究[J].现代地质, 2014(1):234-242. http://www.doc88.com/p-1364322356185.html Zhang Lei, Bai Lingyan, Cai Xiangmin, et al.Study on the positon of the north west section of the Nankou-Sunhe fault in Beijing and its activity[J].Geoscience, 2014(1):234-242(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.doc88.com/p-1364322356185.html
[18] 张磊, 白凌燕, 蔡向民, 等.北京平原南口-孙河断裂带北西段活动性分析[J].中国地质, 2014(3):902-911 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140317&flag=1 Zhang Lei, Bai Lingyan, Cai Xiangmin, et al.An analysis of the activity of the northwest part of Nankou-Sunhe fault[J].Geology in China, 2014(3):902-911(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140317&flag=1
[19] 刘保金, 胡平, 孟勇奇, 等.北京地区地壳精细结构的深地震反射剖面探测研究[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(9):2264-2272. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200909012.htm Liu Baojin, Hu Ping, Meng Yongqi, et al.Research on fine crustal structure using deep seismic reflection profile in Beijing region[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(9):2264-2272(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200909012.htm
[20] 高战武, 陈棋福, 黄金莉, 等.北京地区主要活动断裂深部速度结构特征及强震构造分析[J].震灾防御技术, 2010, 55(3):271-280. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY201003000.htm Gao Zhanwu, Chen Qifu, Huang Jinli, et al.Velocity structure beneath the active faults in Beijing area and their seismo-tectonic characteristics[J].Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2010, 5(3):271-280(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY201003000.htm
[21] 向宏发, 方仲景, 贾三发, 等.隐伏断裂研究及其工程应用——以北京平原区为例[M], 北京:地震出版社, 1994:1-97. Xiang Hongfa, Fang Zhongjing, Jia Sanfa, et al.Study of the Buried Fault and its Application to Engineering Project——a Case Study of the Beijing[M].Seismological Press, 1994:1-97(in chinese).
[22] 向宏发.隐伏活动构造探测研究的若干问题讨论[J].地震地质, 2003, 25(3):460-466. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200303010.htm Xiang Hongfa.Some problems in the exploration and research of buried active fault[J].Seismology and Geology, 2003, 25(3):460-466(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200303010.htm
[23] 马文涛, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 等.首都圈地区的地震活动性与断裂的关系[J].地震地质, 2004, 26(2):293-304. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200402010.htm Ma Wentao, Xu Xiwei, Yu Guihua, et al.The relationship between seismic activity and fault activity in Beijing region[J].Seismology and Geology, 2004, 26(2):293-304(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200402010.htm
[24] 胡平, 刘宝金, 白立新, 等.奥林匹克公园隐伏断裂综合探测[J].地球物理学报, 2010, 53(6):1486-1494. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201101003214.htm Hu Ping, Liu Baojin, Bai Lixin, et al.Synthetic exploration of the buried faults in Olympic park area[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(6):1486-1494(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201101003214.htm
[25] 常旭, 李林新, 刘伊克, 等.北京断陷黄庄-高丽营断层伪随机可控源地震剖面[J].地球物理学报, 2003, 23(3):97-103. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DQWX200805025.htm Chang Xu, Li Linxin, Liu Yinke, et al.Seismic profile of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault in Beijing by Mini-sosie method[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2003, 23(3):97-103(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DQWX200805025.htm
[26] 白登海, 王立凤, 孙洁, 等.福州八一水库尚干断裂的高密度电法和瞬变电磁法试验探测[J].地震地质, 2003, 23(3):97-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204010.htm Bai Denghai, Wang Lifeng, Sun Jie, et al.DC and Tem test sounding for the Bayi ShuiKu-Shang Gan fault in Fuzhou city, Fujian Provice, China[J].Seismology and Geology, 2003, 23(3):97-103(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204010.htm
[27] 刘万恩.高密度电法探测基岩起伏和隐伏断裂中的应用[J].上海地质, 2007, 13(3):51-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD200703013.htm Liu Wanen.The application of exploring bedrock relief and embedded fracture via high-density resistivity method[J].Shanghai Geology, 2007, 13(3):51-53(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD200703013.htm
[28] 葛鸣, 邢立杰, 罗福忠, 等.高密度电法在和田隐伏断层探测中的应用[J].中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(12):62-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201412019.htm Ge Ming, Xing Lijie, Luo Fuzhong, et al.application of high density electric method in hidden fault prospecting, Hetian, Xinjiang[J].Coal Geology of China.2014, 26(12):62-65(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201412019.htm
[29] 池跃龙, 张亭, 王星捷.高密度电法在探测隐伏断裂带中的应用[J].城市地质, 2014(3):44-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ201403012.htm Chi Yuelong, Zhang Ting, Wang Xingjie.The Application of the high-density electrical method in detecting the underground faults[J].Urban Geology, 2014(3):44-46(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ201403012.htm
[30] 刘艳春, 高树义, 庄明芳, 等.高密度电法在探测隐伏断裂中的应用[J].山西建筑, 2014, 40(30):89-91. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX201430046.htm Liu Yanchun, Gao Shuyi, Zhuang Mingfang, et al.Application of high-density resistivity method on detecting buried fault[J].Shanxi Architecture, 2014, 40(30):89-91(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX201430046.htm
[31] 侯治华, 钟南才, 郝彦军, 等.应用高密度电法探测北京南口-孙河隐伏断裂[J].防灾科技学院学报, 2011, 13(1):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201102013.htm Hou Yehua, Zhong Nancai, Hao Yanjun, et al.Detecting Nankou-Sunhe buried faulty by high density resistivity method[J].Journal of Institute of Disaster-prevention Science and Technology, 2011, 13(1):1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201102013.htm
[32] 玄月, 王金萍, 冯军, 等.高密度电法在隐伏断裂探测中的应用[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2011, 31(2):56-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201102013.htm Xuan Yue, Wang Jinping, Feng Jun, et al.Application of highdensity resistivity method to buried fault exploration[J].Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics.2011, 31(2):56-59(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201102013.htm
[33] 江娃利, 侯治华, 谢新生.北京平原南口-孙河断裂带昌平旧县探槽古地震事件研究[J].中国科学(D辑), 2001, 6(31):501-509. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/JDXK200106008.htm Jiang Wali, Hou Zhihua, Xie Xinsheng.Research on paleoearthquakes in Jiuxian trenches across Nankou-Sunhe fault zone in Changping Country of Beijing plain[J].Scisence in China (Series D).2001, 6(31):501-509(in Chinese). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/JDXK200106008.htm
[34] 赵勇, 蔡向民, 王继明, 等.北京平原构造断块划分及微断块第四纪活动性探讨[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(6):1876-1884. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150615&flag=1 Zhao Yong, Cai Xiang-min, Wang Ji-min, et al.The division of "small blocks" of structure in Beijing plain and a discussion on the activity of micro block in Quaternary period[J].Geology in China, 2015, 42(6):1876-1884(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150615&flag=1
[35] 华伟, 陈廷东, 季红军, 等.高邮凹陷真武断裂带断层活动及演化规律[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(3):605-611. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120304&flag=1 Hua Wei, Chen Tingdong, Ji Hongjun, et al.Fault activity and evolution of the Zhenwu fault zone in Gaoyou sag[J].Geology in China, 2012, 39(3):605-611(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120304&flag=1
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 南燕云,李亦纲,刘亢,裴跟弟,宋键. 邯东断裂浅部特征及第四纪活动性分析. 震灾防御技术. 2024(02): 262-275 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵勇,李瑞杰,杨誉博,王纯君,杨吉龙,王强,李莉. 上新世以来北京平原NBT1孔记录的地层沉积及构造指示. 地质学报. 2023(02): 553-564 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 牛文治,何付兵,刘振华,崔玉斌,白凌燕,王安国,张悦泽,曹萌萌,周捷铭. 北京南苑-通县断裂北东段结构特征及第四纪活动性研究. 地质力学学报. 2023(06): 879-887 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 徐吉祥,张晓亮,李潇,王继明,薛爱民,舒律. 地表浅部地震勘探方法在城市隐伏活动断裂调查中的应用. 城市地质. 2022(01): 79-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘旭东,张世民,晏云翔,李林元,计昊旻,赵俊香. 基于浅层地震勘探与钻孔联合地质剖面探测的苏北盆地倪湖庄-七里墩断裂研究. 震灾防御技术. 2022(01): 11-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郭莉,刘旭东,高学泉,尤世娜,周瑜琨,白凌燕. 北京市平原区黄庄-高丽营断裂北段土壤气汞地球化学特征. 城市地质. 2022(02): 128-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王超群,贾丽云,胡道功,马秀敏,顾静超,丁莹莹,曹新文,夏蒙蒙,吴环环. 海南岛北部马袅—铺前断裂东段活动性与地壳稳定性评价. 中国地质. 2021(02): 618-631 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 张晓亮,张磊,王志辉,白凌燕,蔡向民,张敬江,刘振华,张悦泽,倪敬波. 基于磁性地层和沉积地层特征对北京市南口—孙河断裂活动性评估. 中国地质. 2020(03): 868-878 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 刘元章,刘凯,刘久荣,王树芳,王丽亚,崔一娇,王旭,孙赵爽. 基于地热钻孔资料探讨北京黄庄-高丽营断裂的构造活动特征. 地震工程学报. 2019(06): 1521-1528 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 田苗壮,王荣,赵龙,罗勇,王新惠,孔祥如,齐鸣欢,沙特. 高密度电法在北京宋庄地裂缝中的应用. 上海国土资源. 2017(03): 90-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: