Major and trace element migration and metallogenic processes of the Xinshuijing U-Th deposit in the Longshoushan metallogenic belt, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
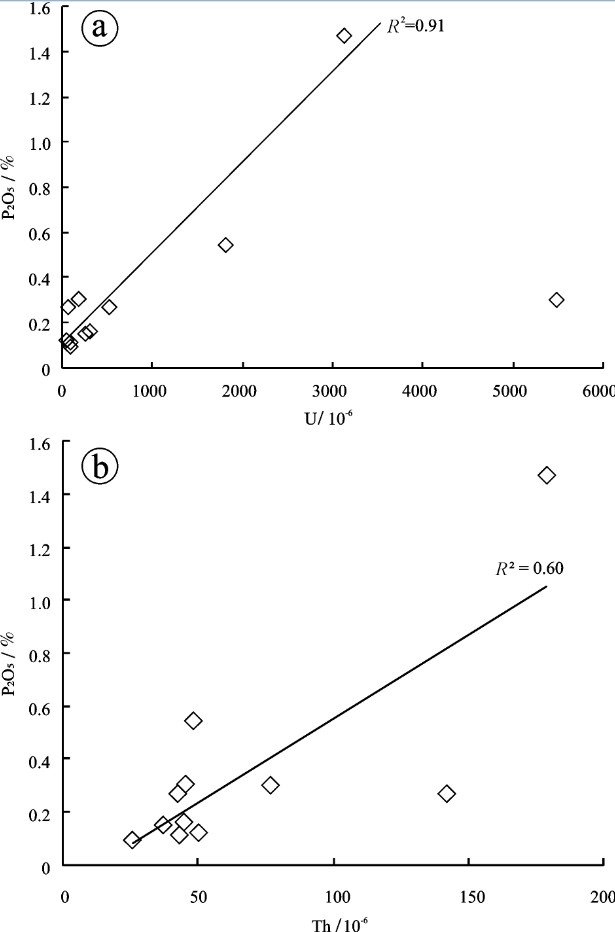
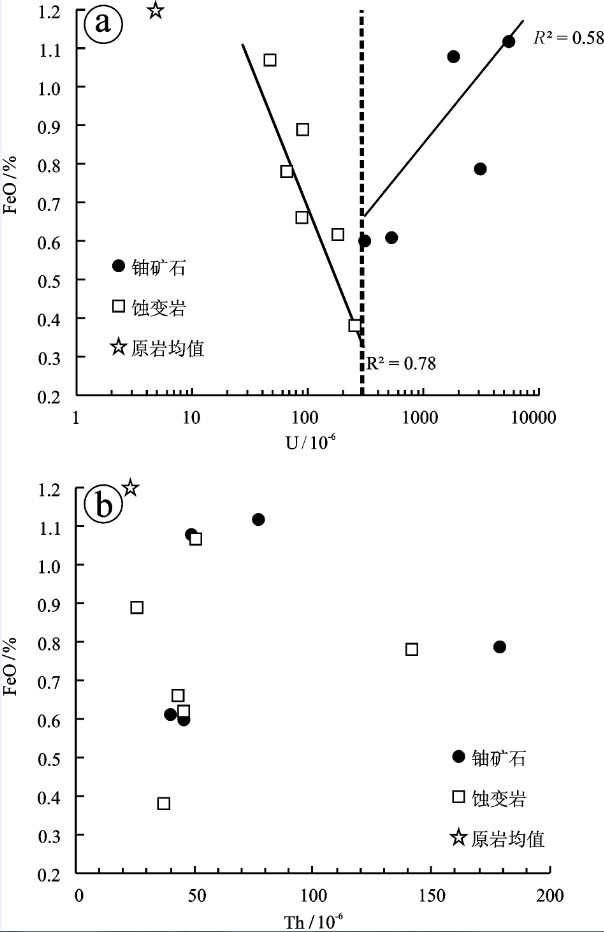
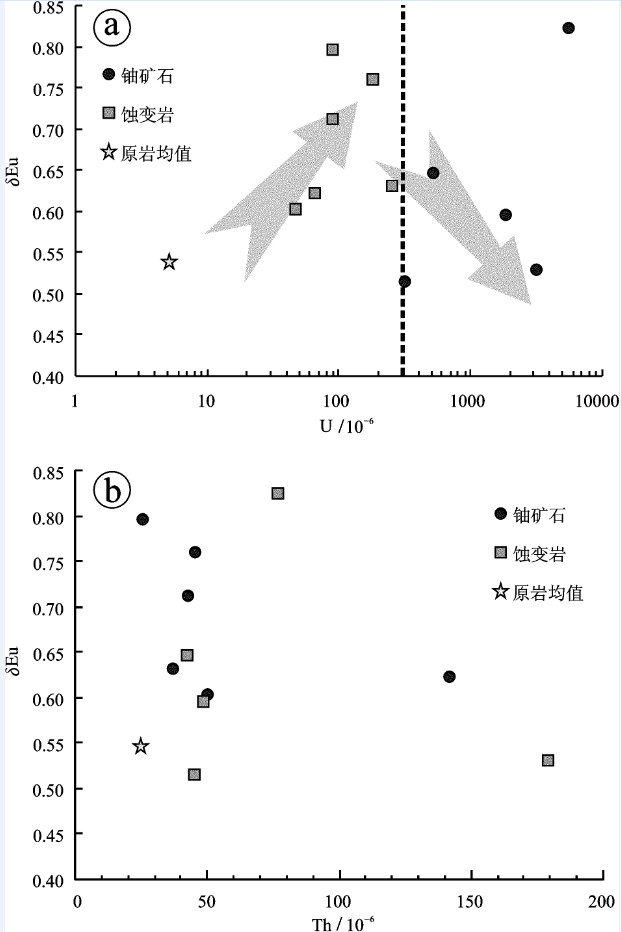
新水井铀(钍)矿床位于甘肃省龙首山成矿带,是碱交代型铀矿床的典型代表,其矿体完全产于钠交代蚀变花岗岩中,成矿过程可划分为钠交代蚀变、铀钍矿化和成矿后3个主要阶段。文章对该矿床花岗岩原岩、蚀变岩及矿石开展了系统主微量元素分析,采用Grant等浓度线法探讨了钠交代蚀变和铀钍矿化阶段的元素迁移规律,结果表明:钠交代蚀变阶段为富含Na、Ca、过渡族元素(Sc、V、Cr、Co、Ni)、U、Th及CO2、H2O等挥发分的复杂流体,钠交代过程中原岩中的大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba)和部分轻稀土元素(LREE)不同程度带出;而铀钍成矿阶段成矿流体则富集重稀土元素(HREE)、U、Th、PO43-等成分,CO2等挥发分大量逸出。结合前人研究,认为新水井矿床成矿流体可能来自地幔流体和大气降水热液的混合;等挥发分CO2的逸出是新水井矿床最重要的矿质沉淀机制,导致了铀钍矿物和磷酸盐矿物(磷灰石)的共沉淀,而磷灰石的沉淀又促进了以磷酸盐形式搬运的Th元素的沉淀。
Abstract:The Xinshuijing U-Th deposit in the Longshoushan metallogenic belt of Gansu Province is a typical alkali metasomatic U-Th deposit hosted in albitite. The ore-forming processes can be divided into three major mineralization stages, i.e., Nametasomatism, U-Th mineralization and post-ore stage. In this paper, the authors systematically analyzed major and trace elements in less-altered granite, albitite and ore of the Xinshuijing deposit, and discussed the element transportation using the isocon diagram proposed by Grant. During the Na-metasomatism stage, Na, Ca, Sc, V, Cr, Co, Ni, U, Th and CO2, H2O were enriched, while large ion lithophile elements and some of the light rare earth elements were depleted. The ore-forming fluids of the U-Th mineralization stage were rich in heavy rare earth elements, U, Th, PO43-, with volatile components (CO2, H2O, F, etc) abundantly escaped. Combined with former studies, the authors hold that the ore-forming fluid was the mixture between the mantle fluid and meteoric water. Vapor escape and the oxygen fugacity decrease seem to have been the major mineralization mechanism, which induced coprecipitation of U-Th minerals and apatite. Th transported in the form of compound phosphate was further precipitated after apatite formation.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
甘肃省高台县大青山地区地处阿拉善地块龙首山基底杂岩带,位于酒东盆地马营凹陷东段山前沉积盆地北缘(图 1a)。区内主要出露有古元古界—新太古界龙首山岩群、中元古界蓟县系墩子沟群、海西期侵入岩、侏罗系龙凤山组和白垩系庙沟组(图 1b)。
为实现研究区金属资源和油气资源的综合调查,中国地质调查局发展研究中心联合甘肃省地调院、探矿工程所、吉林大学在前期“甘肃省高台县臭泥墩—西小口子地区三幅1∶5万矿产远景调查”项目基础上,通过开展专题地质填图、矿产综合信息预测、智能找矿预测等工作,部署实施钻孔ZK1201,以期实现找矿突破。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
利用研究区地质调查、磁法、激电测深、化探数据和无人机影像等资料,开展综合信息解译。采用卷积和孪生网络神经网络模型对区内典型金属矿床成矿作用特征标志、油气赋矿层位进行深度学习,提出工程验证建议。钻探验证所采用钻机为汽车钻,整机包括车底盘、动力系统、液压系统、操控系统等。
3. 结果(Results)
在综合研究和智能预测的基础上,布设的ZK1201孔在钻穿早二叠世花岗闪长岩(图 1c)后,钻遇地层,续钻至393.8 m后终孔(图 1c)。此次工作共钻遇中侏罗统龙凤山组地层220 m,共发现14层油层(总厚145 m,单层最大厚度28 m,最小厚度1.4 m)。钻孔含油性由上部砾岩(油斑级以下)向下部砂岩(富含油或饱含油)逐渐增多,其中高角度裂缝普遍见可流动原油(图 1d~g)。经国家地质实验测试中心分析,原油中饱和烃、芳烃含量分别占32.4%和34.6%,为高品质轻质原油。原油中正构烷烃分布完整,主峰碳数、奇偶优势及甾烷和藿烷分布都指示其陆相烃源岩来源。
野外地质调查发现,白垩系庙沟组近水平发育,与下伏侏罗系龙凤山组呈角度不整合接触。庙沟组主要由厚层暗色泥岩组成,并发育薄层暗色粉砂质泥岩,可能为区域烃源岩层。初步判断成熟的烃源岩排出的油气沿角度不整合运移至侏罗系砂砾岩和砂岩储层后,被逆冲推覆花岗岩体封闭,形成构造-岩性油气藏(图 1h)。
研究发现区域内沉积盆地最南缘边界处在祁连山北缘断裂之下,最北缘处在龙首山断裂的下盘,南北跨度约80 km。区域内沉积地层较厚,其中侏罗系龙凤山组厚约2100 m,白垩系庙沟组厚约900 m,说明研究区具有较大的成藏潜力。此次油气藏的发现,预示着大青山地区具有完整的油气成藏系统,显示出良好油气勘探前景。建议进一步加强油气基础地质调查研究工作。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)在大青山地区花岗岩逆冲推覆体之下的中生代沉积地层中发现原油,所发现的高品质轻质原油,具陆相烃源岩来源特征。
(2)研究区具有良好的油气勘探前景,建议进一步加强油气地质调查研究工作。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
感谢甘肃省地质调查院董国强,北京探矿工程研究所渠洪杰、谭春亮以及国家实验测试中心沈斌在野外工作和样品测试过程中的协助。
致谢: 野外采样工作得到了西安蓝天铀业公司韦力高级工程师、张武康工程师、陈晓斌工程师的帮助, 论文成文过程中, 与林锦荣、李月湘研究员及胡志华工程师开展了有益探讨, 审稿专家对论文提出了宝贵修改意见, 谨此致谢! -
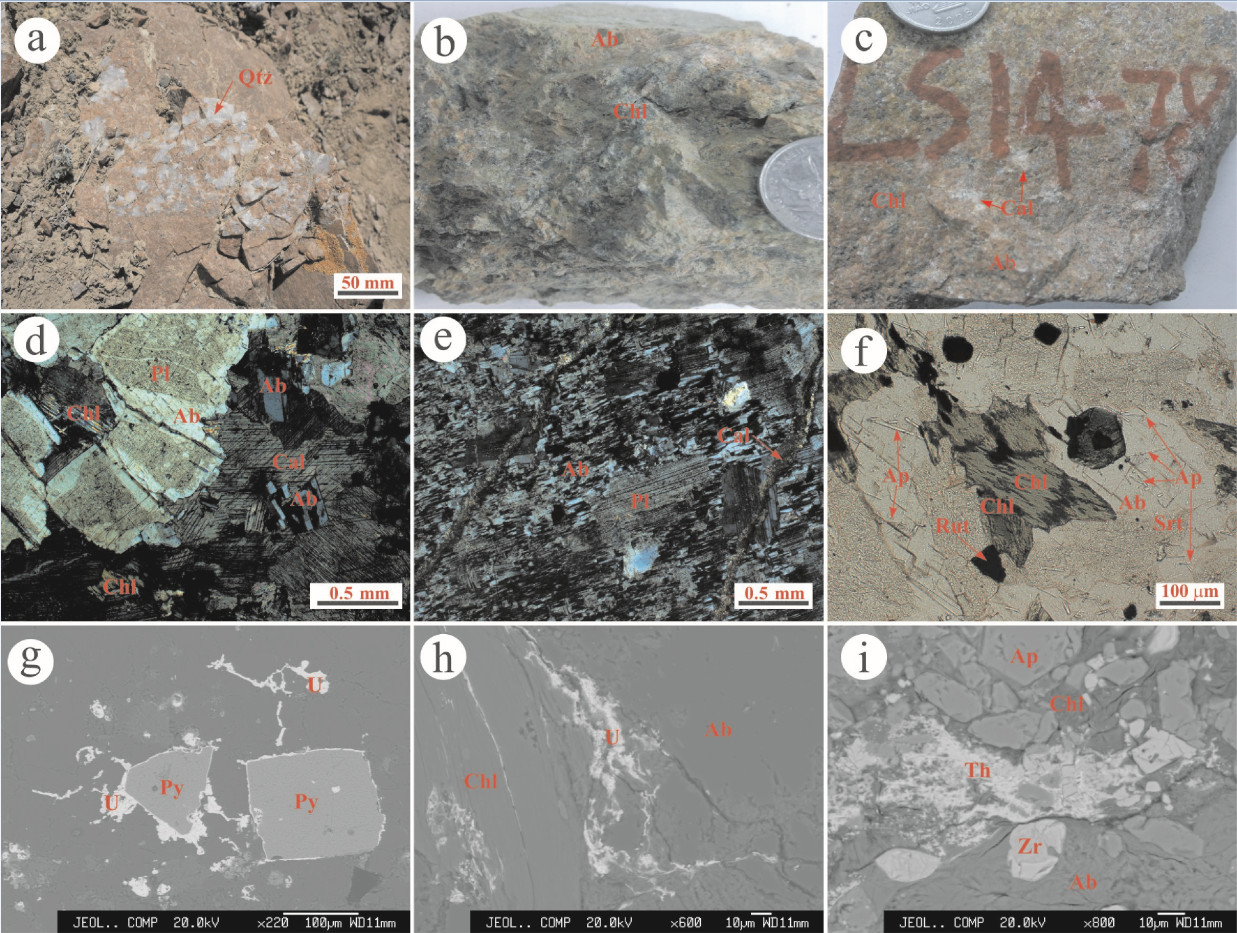
图 3 新水井矿床手标本及镜下显微照片
a—钠交代蚀变岩中的“排硅”现象,溶解的石英后期再沉淀于钠交代蚀变岩局部;b—新水井矿石照片(U含量为522×10-6),全岩蚀变,主要矿物包括钠长石(铁染呈红色)、绿泥石;c—新水井矿床碱交代蚀变岩,主要组成矿物包括钠长石、雪花状方解石、绿泥石、赤铁矿等;d—赤铁矿絮状充填的钠长石边部为新生细粒钠长石沿边部交代(左上),方解石、绿泥石和少量细粒新生钠长石充填于溶蚀矿物(可能主要为石英)而形成的空洞之中(右下);e—棋盘格状钠长石交代斜长石,后者呈交代残余孤岛,后期方解石脉穿切钠长石;f—绿泥石交代黑云母,与针柱状磷灰石、金红石共生;g—沥青铀矿包裹黄铁矿颗粒产出;h—沥青铀矿呈细脉状沿绿泥石解理和外侧裂隙产出;i—含钍矿物(化学成分接近水氟碳钙钍矿)与磷灰石、绿泥石、锆石沿裂隙充填
Figure 3. Photographs showing ore fabrics and mineral assemblages of the Xinshuijing deposit.
a-dequartzification of the albitite; b-ore sample with U content of 522×10-6; c-typical albitite; d-albite replaced and surrounded plagioclase (upper left), and minor fine-grained albite intergrown with calcite and chlorite filled in the void formed by quartz (or other minerals) dissolution; e-chessboard-shaped albite replaced plagioclase and was cut by the late-stage calcite veins; f-biotite was replaced into chlorite, accompanied by rutile formation and abundant occurrence of rod-like apatite; g-pitchblende surrounding pyrite; h-pitchblende filled in the fractures and cleavage of chlorite; i-Pitchblende and pyrite filling the fractures of albite
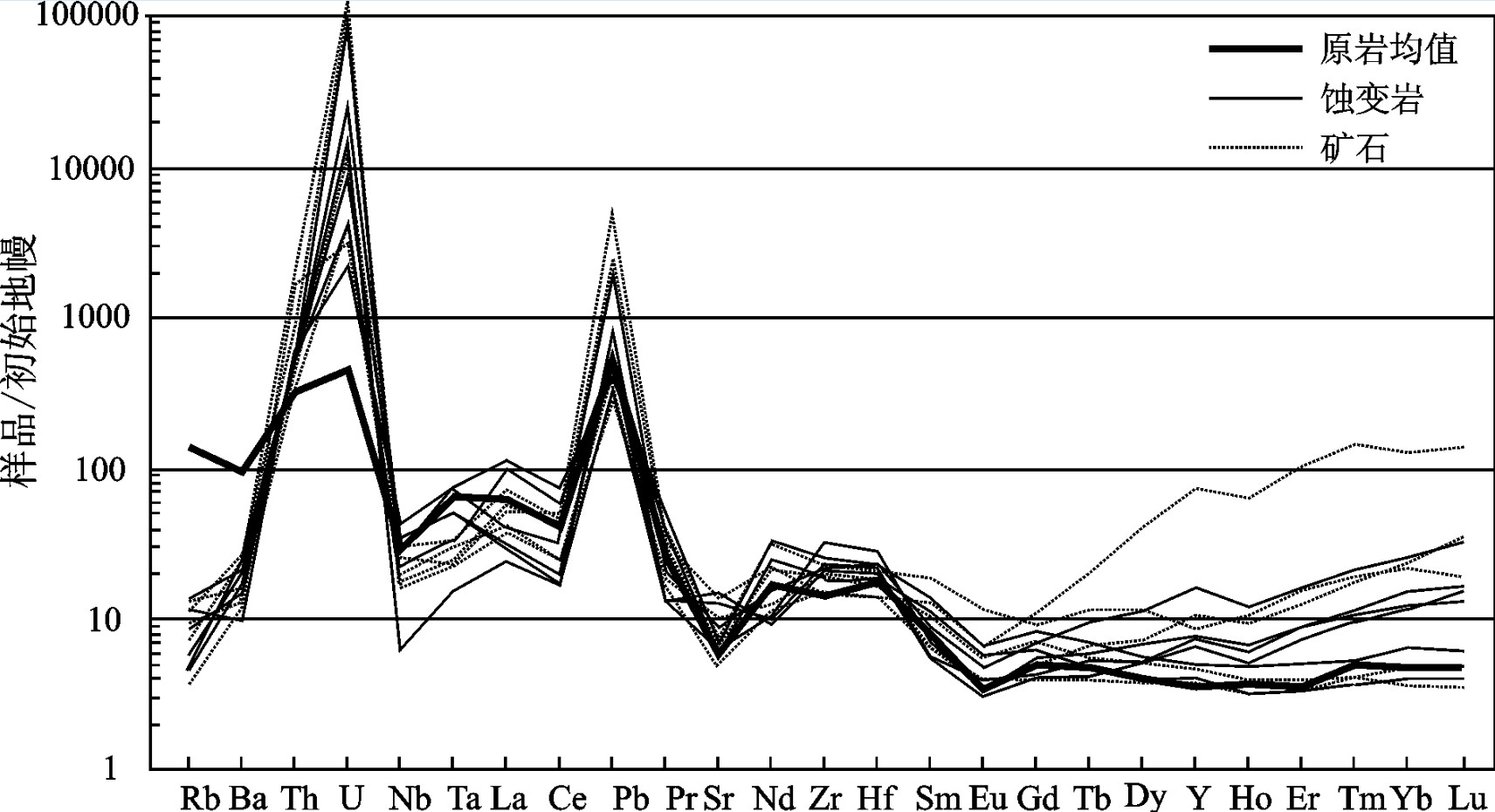
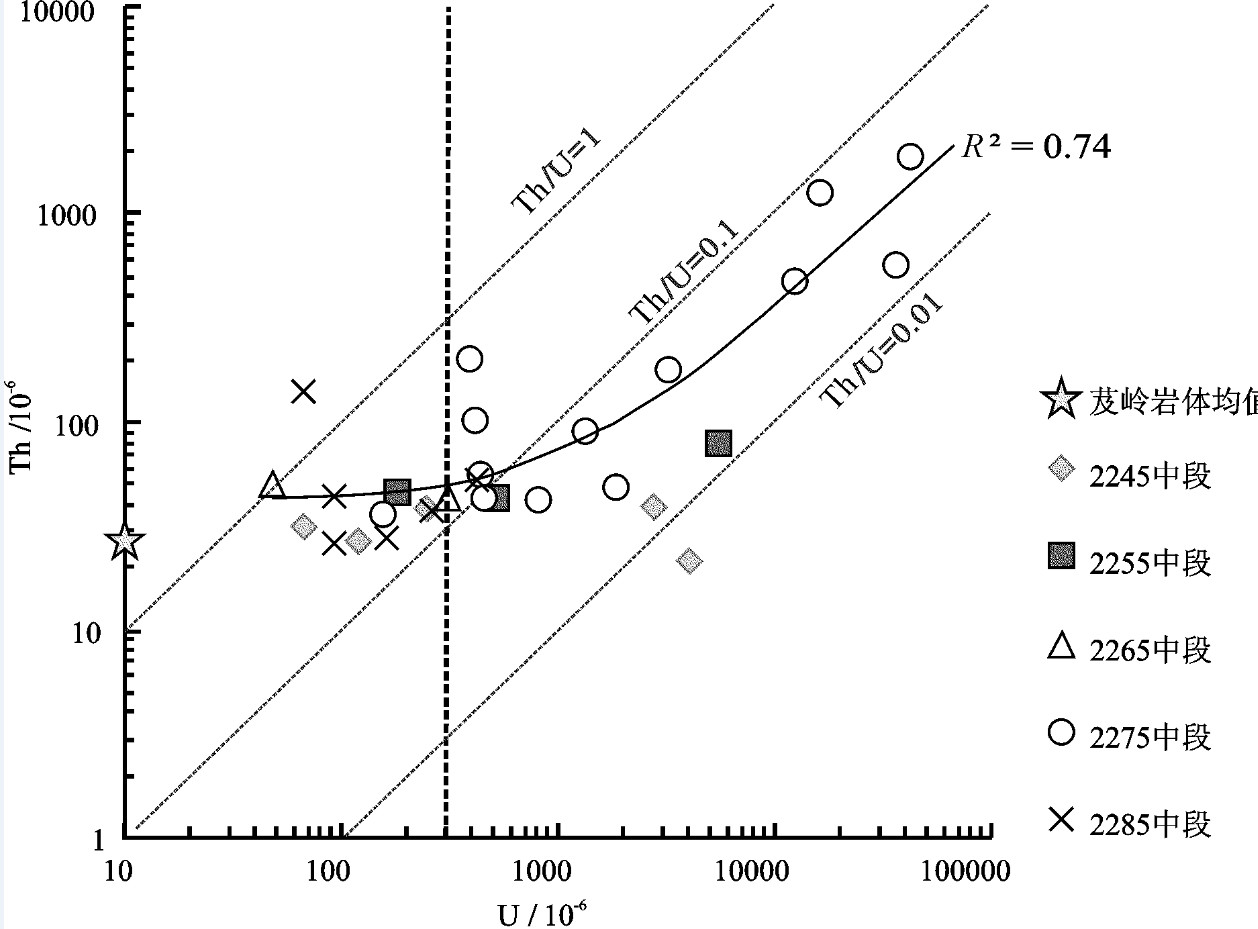
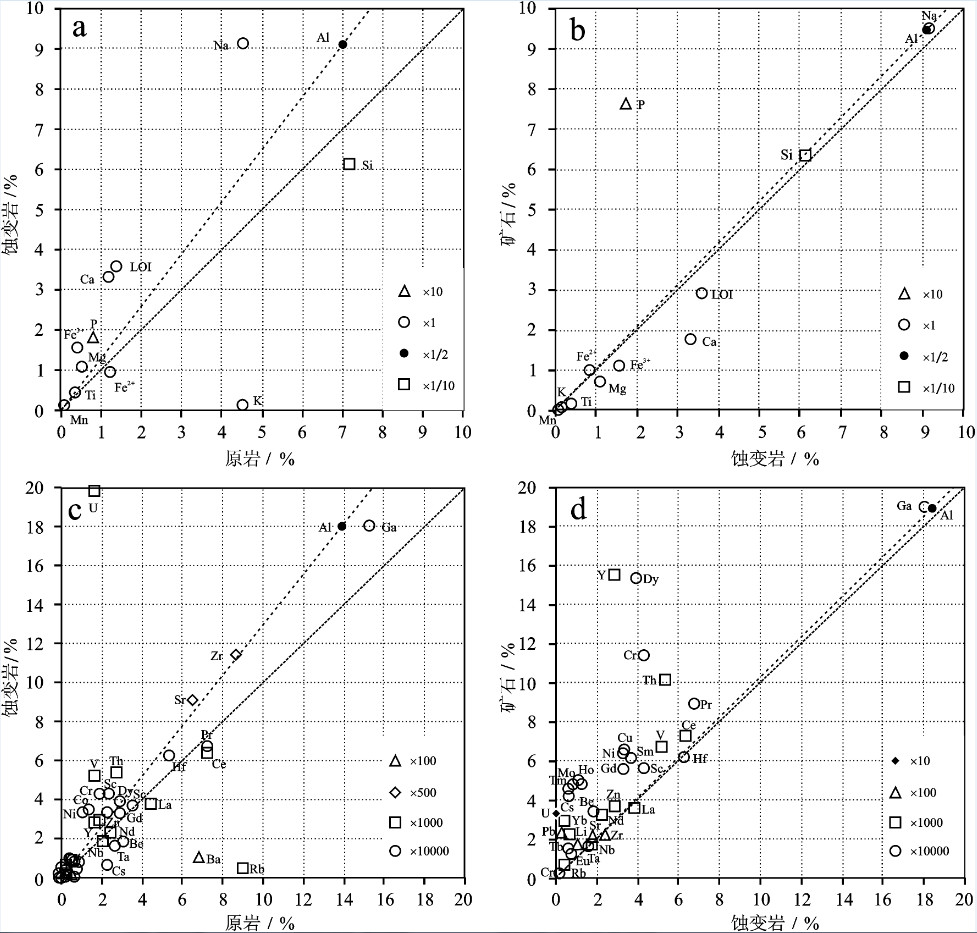
图 6 钠交代蚀变和铀钍成矿作用过程中元素变异图解
a—钠交代蚀变岩相对原岩的主量元素变异图(原点与Al元素间虚线为无元素带入带出的等质量线, 位于此线上部元素在蚀变过程中得到富集, 下部则被贫化。图中斜率为1虚线为蚀变后总质量不变条件下的等质量线, 后图同); b—铀矿石相对蚀变岩的主量元素变异图; c—钠交代蚀变岩相对原岩的稀土和微量元素变异图; d—铀矿石相对蚀变岩的稀土和微量元素变异图
Figure 6. Isocon diagram showing element enrichment and depletion during Na-metasomatism and U (Th) mineralization
a-Major element variation diagram during Na-metasomatism stage; b-Major element variation diagram in the U (Th) mineralization stage; c-Trace element variation diagram in Na-metasomatism stage; d-Trace element variation diagram in the U (Th) mineralization stage. Note that the line between the original point and Al point marks the isocon with no element enrichment or depletion. Those plotted above the line were enriched, while below depleted
表 1 新水井矿床主微量元素分析样品
Table 1 Sample description for major and trace element analyses in the Xinshuijing deposit

表 2 新水井矿床蚀变岩、矿石及花岗岩原岩主量元素含量(%)
Table 2 Major element content (%) of the albitite, ore and less-altered granite samples in the Xinshuijing deposit

表 3 新水井矿床蚀变岩、矿石及花岗岩原岩稀土及微量元素含量(10-6)
Table 3 Rare earth and trace element content (10-6) of albitite, ore and less-altered granite in the Xinshuijing deposit

-
[1] Cuney M.The extreme diversity of uranium deposits[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2009, 44:3-9. doi: 10.1007/s00126-008-0223-1
[2] Cuney M, Emetz A, Mercadier J, et al.Uranium deposits associated with Na-metasomatism from central Ukraine:A review of some of the major deposits and genetic constraints[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 44:82-106. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.007
[3] Dolníček Z, René M, Hermannová S, et al.Origin of the Okrouhlá Radouň episyenite-hosted uranium deposit, Bohemian Massif, Czech Republic:fluid inclusion and stable isotope constraints[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2014, DOI10.1007/s00126-013-0500-5. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2062788183&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] Polito P A, Kyser T K, Stanley C.The Proterozoic, albitite-hosted, Valhalla uranium deposit, Queensland, Australia:A description of the alteration assemblage associated with uranium mineralization in diamond drill hole V39[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2009, 44:11-40. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0162-2
[5] 王驹, 杜乐天.早元古代连山关铀矿床的地质地球化学特征[J].铀矿地质, 1988, 4(6):321-331. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198806000.htm Wang Ju, Du Letian.Geological and geochemical features of the Early Proterozoic Lianshanguan uranium deposit, Liaoning Province, northeast China[J].Uranium Geology, 1988, 4(6):321-331(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198806000.htm
[6] 王凤岗, 范洪海, 何德宝, 等.赣南河草坑铀矿田蚀变特征[J].铀矿地质, 2009, 25(3):150-158. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200903003.htm Wang Fenggang, Fan Honghai, He Debao, et al.The alteration characteristic in Hecaokeng uranium ore field in southern Jiangxi Province[J].Uranium Geology, 2009, 25(3):150-158(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200903003.htm
[7] 邓平, 凌洪飞, 沈渭州, 等.粤北石土岭铀矿床碱交代作用成因探讨[J].地质论评, 2005, 51(5):557-565. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200505011.htm Deng Ping, Ling Hongfei, Shen Weizhou, et al.A discussion on alkali metasomatism in Shituling uranium deposit, northern Guangdong Province[J].Geological Review, 2005, 51(5):557-565(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200505011.htm
[8] 吴俊奇, 闵茂中, 翟建平, 等.华南诸广山复式岩体中段花岗岩的碱交代蚀变[J].岩石学报, 1998, 14(1):90-98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB801.008.htm Wu Junqi, Min Maozhong, Zhai Jianping, et al.Alkali metasomatic alteration of the granite in middle Chuguang Mountain, South China[J].Acta Petrologic Sinica, 1998, 14(1):90-98(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB801.008.htm
[9] 王青山.龙首山钠交代岩型铀矿地球化学特征及其控矿因素[J].甘肃地质, 2008, 17(1):23-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200801007.htm Wang Qinshan.Geochemical features and ore-control factors of soda metasomatite type uranium deposits in Longshoushan[J].Gansu Geology, 2008, 17(1):23-29(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200801007.htm
[10] 赵如意, 陈云杰, 武彬, 等.甘肃龙首山芨岭地区钠交代型铀矿成矿模式研究[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(1):67-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201301009.htm Zhao Ruyi, Chen Yunjie, Wu Bin, et al.A metallogenic model of the sodic metasomatic type uranium ore deposit in the Jiling area of Longshoushan, Gansu Province[J].Geology and Exploration, 2013, 49(1):67-74(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201301009.htm
[11] 陈云杰, 赵如意, 武彬.甘肃龙首山地区芨岭铀矿床隐爆角砾岩发现及成因探讨[J].地质与勘探, 2012, 48(6):1101-1108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201206007.htm Chen Yunjie, Zhao Ruyi, Wu Bin.Discovery of cryptoexplosive breccias in the Jiling uranium deposit of the Longshoushan area, Gansu Province and their genesis[J].Geology and Exploration, 2012, 48(6):1101-1108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201206007.htm
[12] 陈云杰, 傅成铭, 王刚, 等.花岗岩型热液铀矿床C、O同位素研究——以甘肃省龙首山芨岭矿区为例[J].地质与勘探, 2014, 50(4):641-648. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201404004.htm Chen Yunjie, Fu Chengming, Wang Gang, et al.Carbon and oxygen isotopes in granite-type hydrothermal uranium deposits:A case study of the Jiling uranium ore field in Longshou Shan, Gansu Province[J].Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(4):641-648(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201404004.htm
[13] 陈云杰, 王伟, 王刚, 等.甘肃省龙首山地区芨岭铀矿区蚀变特征分析[J].矿产与地质, 2015, 29(2):144-151. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201502002.htm Chen Yunjie, Wang Wei, Wang Gang, et al.Characteristics of alteration in Jiling uranium mining area in Longshoushan area of Gansu[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2015, 29(2):144-151(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201502002.htm
[14] 杜乐天.烃碱流体地球化学原理——重论热液作用与岩浆作用[M].北京:科学出版社, 1996:1-229. Du Letian.Geochemical Principles of HACONS——Re-Discuss Hydrothermalism and Magmatism[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1996:1-229(in Chinese).
[15] 杜乐天.中国热液铀矿基本成矿规律和一般热液成矿学[M].北京:原子能出版社, 2001:1-307. Du Letian.Basic Metallogenic Regularity of Uranium Deposit in China and Common Hydrothermal Metallogeny[M].Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 2001:1-307(in Chinese).
[16] Cathelineau M.The hydrothermal alkali metasomatism effects on granitic rocks:Quartz dissolution and related subsolidus changes[J].Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27:945-965. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.4.945
[17] Recio C, Fallick A E, Ugidos J M, et al.Characterization of multiple fluid-granite interaction processes in the episynites of Avila-Béjar, Central Iberian Massif, Spain[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 143:127-144. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00106-X
[18] Alexandre P.Mineralogy and geochemistry of the sodium metasomatism-related uranium occurrence of Aricheng South, Guyana[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2010, 45:351-367. doi: 10.1007/s00126-010-0278-7
[19] Turpin L, Leroy J L, Sheppard S M F.Isotopic systematic (O, H, C, Sr, Nd) of superimposed barren and U-bearing hydrothermal systems in a Hercynian granite, Massif Central, France[J].Chemical Geology, 1990, 88:85-98. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90105-G
[20] 王承花.龙首山成矿带成矿规律及找矿方向[J].甘肃科技, 2010, 26(10):39-44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSKJ201010017.htm Wang Chenghua.Metallogenic regularity and potential prospecting area in the Longshoushan metallogenic belt[J].Gansu Science and Technology, 2010, 26(10):39-44(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSKJ201010017.htm
[21] 黄净白, 黄世杰.中国铀资源区域成矿特征[J].铀矿地质, 2005, 21(5):129-138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200503001.htm Huang Jinbai, Huang Shijie.Metallogenic characteristics of uranium resources in China[J].Uranium Geology, 2005, 21(5):129-138(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200503001.htm
[22] 魏正宇, 张树明, 刘金枝, 等.甘肃龙首山碱交代型铀矿床绿泥石特征及意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(3):517-526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201403010.htm Wei Zhengyu, Zhang Shuming, Liu Jinzhi, et al.Characteristics and significance of chlorite in the Longshoushan alkali-metasomatic type uranium deposit[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2014, 33(3):517-526(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201403010.htm
[23] 汤中立.华北古陆西南边缘(龙首山-祁连山)成矿系统及成矿构造动力学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000:1-393. Tang Zhongli.Mineralization Systems and Dynamic Metallogeny in the Southwestern Margin (Longshoushan-Qilianshan) of the North China Craton[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000:1-393(in Chinese).
[24] 修群业, 陆松年, 于海峰, 等.龙首山岩群主体划归古元古代的同位素年龄证据[J].前寒武纪研究进展, 2002, 25(2):93-96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200202004.htm Xiu Qunye, Lu Songnian, Yu Haifeng, et al.The isotopic evidence for main Longshoushan Group contributing to Paleoproterozoic[J].Progress in Precambrian Research, 2002, 25(2):93-96(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200202004.htm
[25] 修群业, 于海峰, 李铨, 等.龙首山群成岩时代探讨[J].地质学报, 2004, 78(3):366-373. Xiu Qunye, Yu Haifeng, Li Quan, et al.Discussion on the petrogenic time of Longshoushan Group, Gansu Province[J].2004, 78(3):366-373(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] 陆松年.青藏高原北部前寒武纪地质初探[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002, 41-43. Lu Songnian.Preliminary Study on Pre-Cambrian Geology in Northern Part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2002:41-43(in Chinese).
[27] 夏明哲, 夏昭德, 卢荣辉, 等.龙首山地块的归属问题:来自地壳结构和中-新元古代地层的证据[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(2):132-136. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XAGX201102006.htm Xia Mingzhe, Xia Zhaode, Lu Ronghui, et al.Attribution of Longshoushan Terrane:Evidence from the crustal structures and Mesoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic Strata[J].Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(2):132-136(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XAGX201102006.htm
[28] 李文渊.龙首山地区的震旦系[J].西北地质, 1991, 12(2):1-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI199102000.htm Li Wenyuan.Sinian strata in the Longshoushan area[J].Northwestern China Geology, 1991, 12(2):1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI199102000.htm
[29] 谢从瑞, 校培喜, 杨忠智, 等.甘肃龙首山地区韩母山群研究的新进展[J].地层学杂志, 2013, 37(1):54-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201301010.htm Xie Congrui, Xiao Peixi, Yang Zhongzhi, et al.Progress in the studying of the Hanmushan Group in the Longshou Moutains of Gansu Province[J].Journal of Stratigraphy, 2013, 37(1):54-57(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201301010.htm
[30] 校培喜, 由伟丰, 曹轩铎, 等.甘肃中西部龙首山一带"韩母山群"的重新厘定[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(8):1228-1232. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201108007.htm Xiao Peixi, You Weifeng, Cao Xuanduo, et al.Redefining of the Hanmushan Group in Longshoushan, central-western Gansu Province[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(8):1228-1232(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201108007.htm
[31] 宫江华, 张建新, 于胜尧.阿拉善地块南缘龙首山东段"龙首山岩群"的再厘定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1):1-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201301002.htm Gong Jianghua, Zhang Jianxin, Yu Shengyao.Redefinition of the Longshoushan Group outcropped in the eastern segment of Longshoushan on the southern margin of Alxa Block:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb dating results[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(1):1-22(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201301002.htm
[32] 汤中立, 李文渊.金川铜镍硫化物(含铂)矿床成矿模式及地质对比[M].北京:地质出版社, 1995:1-204. Tang Zhongli, Li Wenyuan.Metallogenic Model and Geological Comparison of the Jinchuan Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposit[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1995:1-204(in Chinese).
[33] 赵亚云, 张树明, 汤琳, 等.龙首山中段加里东期花岗岩浆作用与铀成矿作用研究述评[J].甘肃地质, 2015, 24(2):71-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ201502013.htm Zhao Yayun, Zhang Shuming, Tang Ling, et al.Caledonian granitic magmatism and U mineralization in Middle Longshoushan[J].Gansu Geology, 2015, 24(2):71-78(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ201502013.htm
[34] 辛存林, 马维云, 安国堡, 等.甘肃龙首山207铀矿床成矿地质特征及其成矿机制探讨[J].地质学报, 2013, 87(4):577-590. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201304012.htm Xin Cunlin, Ma Weiyun, An Guobao, et al.Geological characteristics and mineralization mechanism of the No.207 uranium deposit in Longshoushan, Gansu Province[J].Acta Geological Sinica, 2013, 87(4):577-590(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201304012.htm
[35] 辛存林, 安国堡, 孙现辉, 等.龙首山成矿带207铀矿床矿化特征和外围铀成矿潜力分析[J].地质科技情报, 2013, 32(3):125-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201303021.htm Xin Cunlin, An Guobao, Sun Xianhui, et al.Mineralization characteristics of uranium deposit No.207 in Longshoushan metallogenic belt and the metallogenic potential of its peripheral area[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(3):125-134(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201303021.htm
[36] 陈云杰, 赵如意, 李涛.甘肃省金边寺铀矿床铀矿化特征及成矿条件分析[J].甘肃地质, 2011, 20(3):46-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ201103007.htm Chen Yunjie, Zhao Ruyi, Li Tao.Characteristics of uranium mineralization and metallogenic conditions of Jinbiansi deposit[J].Gansu Geology, 2011, 20(3):46-50(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ201103007.htm
[37] Norrish K, Hutton J T.An accurate X-ray spectrographic method for the analysis of a range of geological samples[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1969, 33(4):431-454. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(69)90126-4
[38] Qu Xiaoming, Hou Zengqian, Li Yigang.Melt components derived from a subducted slab in late Orogenic ore-bearing porphyries in the Gangdese copper belt, southern Tibeatan Plateau[J].Lithos, 2004, 74:131-148. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.01.003
[39] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic study of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J (eds.).Magmatism in Oceanic Basins.Geological Society of London, Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345. http://www.oalib.com/references/19053661
[40] Grant J A.The isocon diagram——a simple solution to Gresens' equation for metasomatic alteration[J].Economic Geology, 1986, 81:1976-1982. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.81.8.1976
[41] 安芳, 朱永峰.新疆图拉苏盆地京希-伊尔曼德金矿地质和地球化学特征研究[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(08):2275-2286. An Fang, Zhu Yongfeng.Geology and geochemistry of Jingxi-Yelmand gold deposit in Tulasu basin.North Tianshan, Xinjiang[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(08):2275-2286(in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] 宓奎峰, 柳振江, 李春风, 等.内蒙古乌努格图山大型铜钼矿床元素迁移及成矿过程探讨[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(4):1270-1287. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140419&flag=1 Mi Kuifeng, Liu Zhenjiang, Li Chunfeng, et al.Metallogenic processes and migration of ore-forming elements in the Wunugetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(4):1270-1287(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140419&flag=1
[33] Barns T M.Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, 3rd edtion[M].JohnWiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1997.
[44] 凌洪飞.论花岗岩型铀矿床热液来源——来自氧逸度条件的制约[J].地质论评, 2011.57(2):193-206. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201102005.htm Ling Hongfei.Origin of hydrothermal fluids of granite-type uranium deposits:Constraints from redox conditions[J].Geological Review, 2011.57(2):193-206(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201102005.htm
[45] Nieto F.Chemical composition of metapelitic chlorite:X-Ray diffraction and optical property approach[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 1997, 9:829-841. doi: 10.1127/ejm/9/4/0829
[46] Battaglia S.Applying X-Ray geothermometer diffraction to a chlorite[J].Clay and Clay Minerals, 1999, 47(1):54-63. doi: 10.1346/CCMN
[47] 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等.不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(9):2085-2108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200709009.htm Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Fan Hongrui, et al.Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(9):2085-2108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200709009.htm
[48] 陈衍景, 李诺.大陆内部浆控高温热液矿床成矿流体性质及其与岛弧区同类矿床的差异[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(10):2477-2508. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200910016.htm Chen Yanjing, Li Nuo.Nature of ore-forming fluids of intracontinental intrusion-related hypothermal deposits and its difference from those in island arcs[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(10):2477-2508(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200910016.htm
[49] Zhong Jun, Chen Yanjing, Pirajno F, et al.Geology, geochronology, fluid inclusion and H-O isotope geochemistry of the Luoboling porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Zijinshan orefield, Fujian Province, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 57:61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.004
[50] Zhong Jun, Chen Yanjing, Pirajno F.Geology, geochemistry and tectonic settings of the molybdenum deposits in South China:A review[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, submitted. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2341516606&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[51] 武新丽, 毛景文, 周振华, 等.大兴安岭中南段布敦化铜矿床S-Pb同位素特征及成矿指示[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(6):1812-1829. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201401016.htm Wu Xinli, Mao Jingwen, Zhou Zhenhua, et al.H-O-S-Pb isotopic components of the Budunhua Cu deposit in the middlesouth part of the Da Hinggan Moutains and their implications for the ore-forming process.Geology in China, 2012, 39(6):1812-1829(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201401016.htm
[52] 刘军, 武广, 王峰, 等.黑龙江省岔路口斑岩钼矿床流体包裹体和稳定同位素特征[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(4):1231-1251. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201304022.htm Liu Jun, Wu Guang, Wang Feng, et al.Fluid inclusions and stable isotope characteristics of the Chalukou porphyry Mo deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J].Geology in China, 2013, 40(4):1231-1251(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201304022.htm
[53] Rosenbaum J M, Zindler A, Rubenstone J L.Mantle fluids:Evidence from fluid inclusions[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60:3229-3252. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00167-6
[54] 刘丛强, 黄智龙, 李和平, 等.地幔流体及其成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2001, 8(4):231-243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200104000.htm Liu Congqiang, Huang Zhilong, Li Heping, et al.The geofluid in the mantle and its role in ore-forming processes[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(4):231-243(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200104000.htm
[55] 姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 凌洪飞.地幔流体与铀成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(2):491-499. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200402026.htm Jiang Yaohui, Jiang Shaoyong, Ling Hongfei.Mantle-derived fluids and uranium mineralization[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(2):491-499(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200402026.htm
[56] 温志坚, 杜乐天, 刘正义.相山铀矿田磷灰石与富矿形成的关系[J].铀矿地质, 1999, 4:26-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ904.004.htm Wen Zhijian, Du Letian, Liu Zhengyi.Relation between francolite and metallogenesis of high-grade uranium ores in Xiangshan uranium orefield[J].Uranium Geology, 1999, 4:26-33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ904.004.htm
[57] 王正其, 李子颖.幔源铀成矿作用探讨[J].地质论评, 2007, 53(5):608-615. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200705005.htm Wang Zhengqi, Li Ziying.Discussion on mantle-derived uranium mineralization[J].Geological Review, 2007, 53(5):608-615(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200705005.htm
[58] Rich R A, Holland H, Petersen U.Hydrothermal Uranium Deposits[M].Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1977:1-264.
[59] Hu Ruizhong, Burnard P G, Bi Xianwu, et al.Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi province, China:Evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 266:86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.017
[60] Boyle R W.Geochemical prospecting for thorium and uraium deposits[M].Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, 1982:1-530.
[61] Chen Yanjing, Zhao Yongchao. Geochemical characteristics and evolution of REE in the Early Precambrian sediments: evidences from the southern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Episodes, 1997, 20(2): 109-116. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/ExternalResource-kwys200403012%5e7.aspx




 下载:
下载: