An integrated ore prospecting model for the Mwamola gold deposit, Tanzania
-
摘要:
坦桑尼亚Mwamola金矿位于坦桑尼亚环维多利亚湖区域的太古宙卡哈马(Kahama)绿岩带,是典型的铁建造(BIF)型金矿,为一大型隐伏矿床,因此建立Mwamola金矿床综合找矿模式,对寻找同类型矿床具有重要意义。太古宙卡哈马绿岩带是坦桑尼亚重要的成矿带,已发现金矿床和矿点多处,Mwamola金矿是代表性矿床之一,矿体呈层状、似层状,受地层和剪切带双重控制,矿化作用局限于条带状铁建造地层和岩性单元。地面高精度磁测高强度负异常能有效地识别控矿地层-条带状含铁建造带或矿化带,激发极化测深显示的“低阻高极化”异常可对条带状含铁建造和金矿体进行空间定位。岩石地球化学测量表明矿体上Au、As、Sb具强富集特性,且Au与As、Sb具有明显的相关性。本文根据地质、地球物理和地球化学信息,建立了Mwamola金矿地质、物化探综合找矿模式,提出了一套有效的找矿方法组合,为该绿岩带铁建造型金矿的勘查和评价提供指导。
Abstract:Located along Kahama Archean greenstone belt around Victoria Lake area in Tanzania, the Mwamola gold deposit is a concealed large iron formation (BIF) type gold deposit closely related to the banded iron formation. The establishment of an oreprospecting model is very important in the search for the same type of deposits. The Mwamola gold deposit is the representative one among many gold deposits in the Archean Kahama greenstone belt of Tanzania. Orebodies are commonly stratiform and stratoid in form, controlled jointly by shear zone and strata, and mineralization is confined to the banded iron formation stratigraphic and lithologic units. The△T negative anomalies of ground high-precision magnetic survey can be used as a geophysical prospecting indicator because they can accurately identify ore-controlling strata (banded iron formation) or ore-bearing faults. The induced polarization depth measurement shows that "low resistance and high polarization" anomaly characteristics can serve as an indicator for the spatial orientation of the banded iron formation and gold orebody. The rock geochemical survey shows that Au, As, Sb have the feature of strong enrichment, and Au and As, Sb have significant correlation. Combined with geological, geophysical, geochemical prospecting information, the authors built a model of the Mwamola gold deposit, and establiehed a set of optimum combination prospecting methods and processes. The results obtained by the authors can play a certain guiding role in the exploration and evaluation of the greenstone belt banded iron form (BIF) type gold deposits.
-
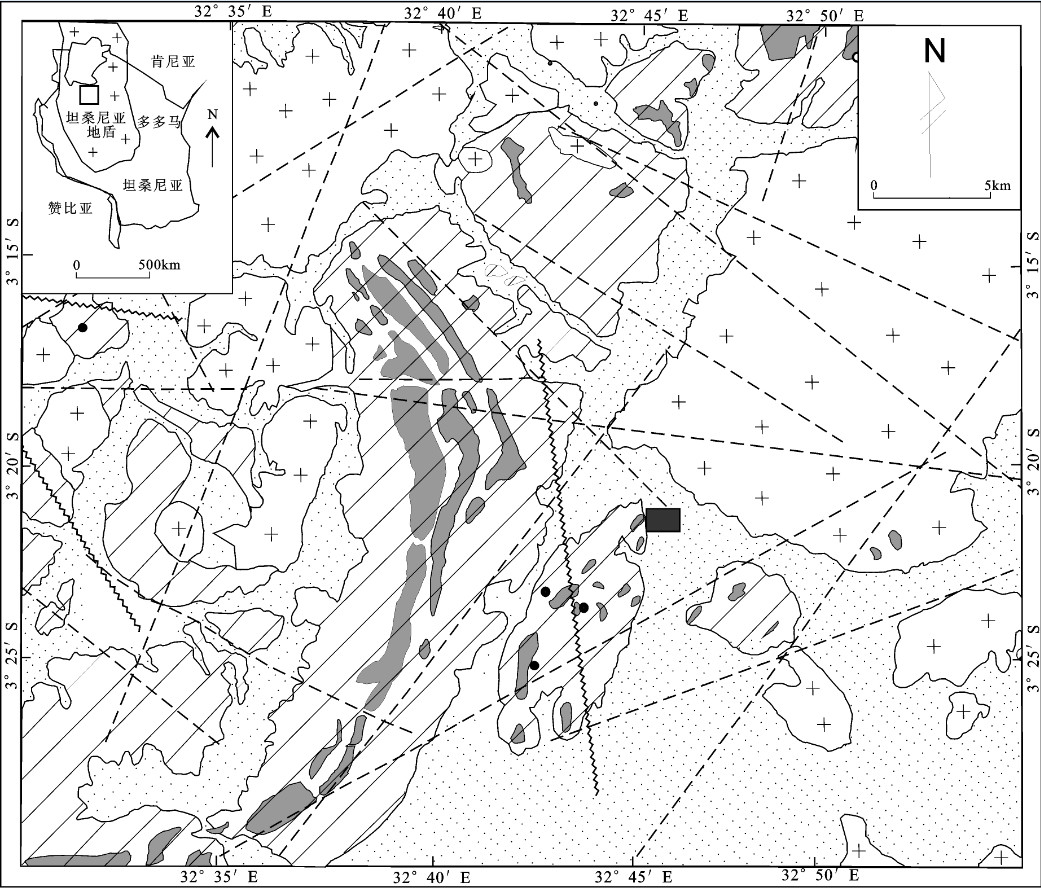
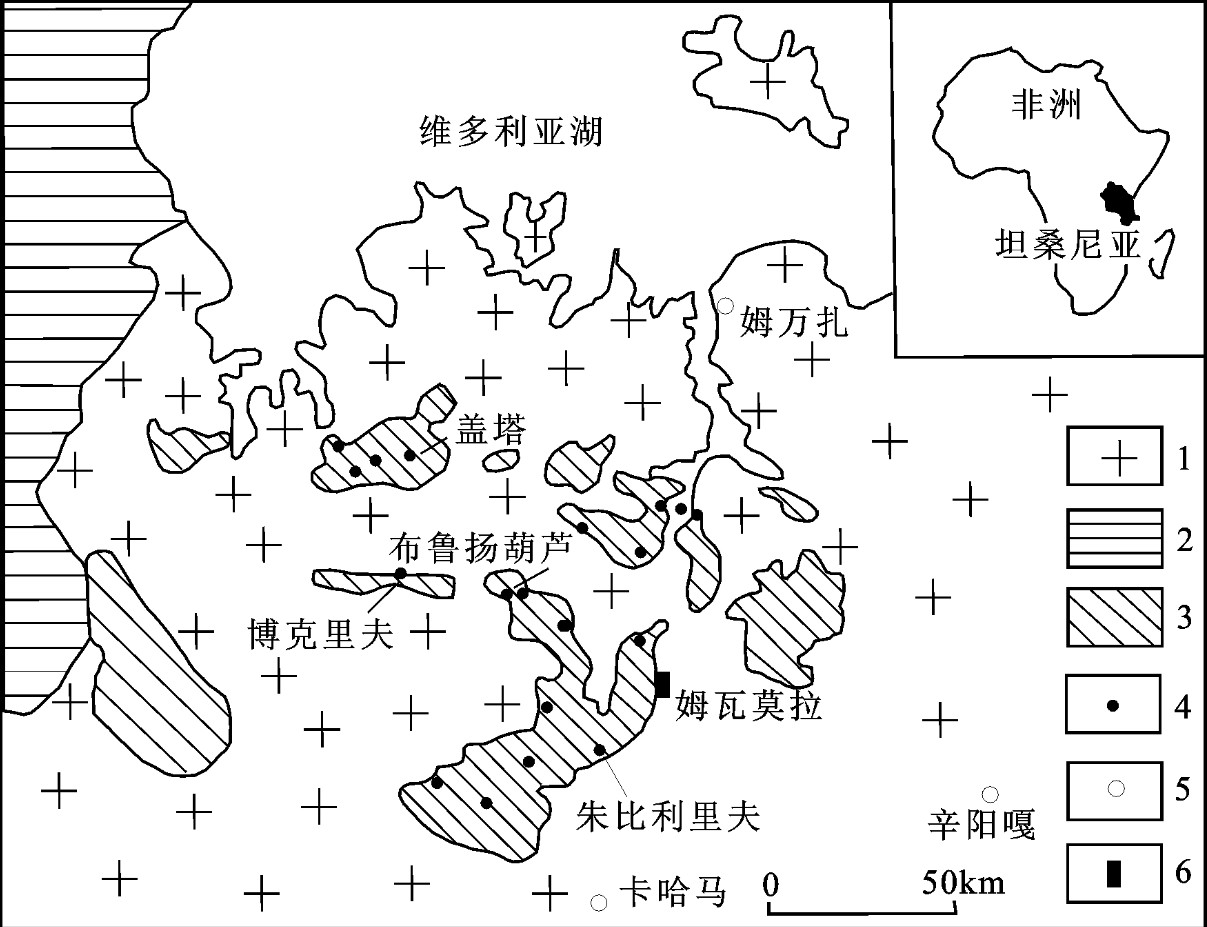
太古宙卡哈马绿岩带为坦桑尼亚环维多利亚湖区域八大绿岩带之一,长约100 km,是坦桑尼亚重要的成矿带之一,带上分布有盖塔(Geita)、朱比利里夫(Jubilee Reef)等大型、特大型金矿床和众多金矿(化)点,具有很大的找矿前景;姆瓦莫拉(Mwamola)金矿是中国河南省地质矿产勘查开发局第二地质矿产调查院在坦桑尼亚发现的大型金矿床,属典型的铁建造(BIF)型金矿床,矿体与条带状含铁建造密切相关,已探明(332+333)金金属资源量34 t,为扩大矿床规模,目前仍在矿区深部和外围继续勘查;该金矿位于维多利亚湖(Lake Victoria)南部的姆万扎(Mwanza)和卡哈马(Kahama)地区之间(图 1)。科研方面,沈保丰等对条带状含铁建造(BIF)的形成时代、形成过程以及BIF中的金的成矿作用,进行了深入研究[1-3];Borg等对BIF型金矿床的地质特征、成矿时代及成因开展了较多的探讨[4-5],普遍认为该类型金矿床受地层和剪切带双重控制,矿化作用局限于条带状铁建造(BIF)地层和岩性单元,但对成因模式(同生或后生)存在分歧;李水平等对该类型金矿床的岩(矿)石磁参数特征、南半球低磁纬度区磁异常特征进行了探讨[6-7],然而,至今尚缺乏对该铁建造型金矿的找矿模式研究。
地物化综合找矿模式的建立在矿产勘查及资源预测评价中十分重要,以地质、物化探方法为基础,建立找矿模型或准找矿模式,可在矿产勘查中选择有效地物化探技术方法,对异常做出正确合理的解释,提高找矿效率[8-13]。本文根据姆瓦莫拉(Mwamola)金矿床的成矿地质条件、地球物理和地球化学等多源找矿信息,进行了综合分析研究,构建了BIF型金矿床的地质、物化探综合找矿模式,确立了一套找矿方法组合和流程,对在卡哈马绿岩带和其它绿岩带上寻找同类型金矿具有一定的指导意义。
1. 区域地质背景
坦桑尼亚大地构造位于坦桑尼亚地盾核心部位,其国土面积的约70%由前寒武纪岩石组成。该地盾形态大体呈椭圆形太古代克拉通地块,分布在该国北部;由若干条太古界绿岩带和规模巨大的太古宙(部分元古宙)花岗岩体组成,是太古宙绿岩带型金矿的主要成矿物质来源。
区域上出露地层主要为:(1)多多马(Dodoma)系,由花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗片麻岩和混合岩组成;(2)尼安萨系(Nyanzian),由变质火山岩、沉积岩和花岗岩组成的典型绿岩带组合;(3)卡维隆多(Kavirondian)系,由沉积岩组成的层序,已被花岗岩侵入(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 姆瓦莫拉金矿区及外围地质简图1—第四纪及沼泽性黑土; 2—绿岩带(以太古界尼安萨群岩层为主,夹条带状含铁建造); 3—花岗质岩石(无法确定时代); 4—金矿床; 5—金矿点; 6—断层; 7—剪切带; 8—地质界线; 9—Mwamola金矿; 10—矿区区域位置Figure 2. Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its peripheryFig. 2 Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its periphery (From geological map of Karumwa area, sheet 47/1-2, in the geological division, department of lands and mines, Dodoma in Tanzania) 1-Quaternary and swampy black soil; 2-Greenstone belts (mainly Nyanzian rock layer, interlayer banded iron formations); 3-Granitoids (unable to determine the age); 4-Gold deposit; 5-Au ore spot; 6-Fault; 7-Shear zone; 8-Geological boundary; 9-Mwamola gold deposit; 10-Location of ore district
图 2 姆瓦莫拉金矿区及外围地质简图1—第四纪及沼泽性黑土; 2—绿岩带(以太古界尼安萨群岩层为主,夹条带状含铁建造); 3—花岗质岩石(无法确定时代); 4—金矿床; 5—金矿点; 6—断层; 7—剪切带; 8—地质界线; 9—Mwamola金矿; 10—矿区区域位置Figure 2. Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its peripheryFig. 2 Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its periphery (From geological map of Karumwa area, sheet 47/1-2, in the geological division, department of lands and mines, Dodoma in Tanzania) 1-Quaternary and swampy black soil; 2-Greenstone belts (mainly Nyanzian rock layer, interlayer banded iron formations); 3-Granitoids (unable to determine the age); 4-Gold deposit; 5-Au ore spot; 6-Fault; 7-Shear zone; 8-Geological boundary; 9-Mwamola gold deposit; 10-Location of ore district20世纪70年代末,前联邦德国对坦桑尼亚整个国土面积进行了1:12.5万低分辨率航空磁测和部分地区(约占国土面积的15%)1:5万高分辩率航空磁测。1:5万航磁资料显示,Mwamola地区磁场强度高,梯度大,Mwamola金矿区处在NE、NW走向,呈弧形展布的条带状强磁异常带上[7]。
2. 地质信息
2.1 地层
姆瓦莫拉金矿位于坦桑尼亚维多利亚湖南部太古宙花岗岩-绿岩地体中的卡哈马绿岩带的东北端,矿区地层比较简单,地表被沼泽性黑土和第四系松散残坡积物覆盖,仅在局部见花岗岩风化形成的砂质黏土。通过钻探查明,其下为尼安萨系(群)变质火山-沉积岩,主要为浅变质长英质凝灰岩、变酸性凝灰岩、变凝灰质砂岩,变基性凝灰岩及条带状含铁建造(磁铁石英岩)。尼安萨系(群)是矿区主要含矿层位,BIF金矿体严格受该层位控制,尼安萨系(群)出露地区可作为有利的找矿远景区。
2.2 构造
区域构造以褶皱构造为主,这些褶皱经历了多次叠加改造。矿区主要控矿构造为受倒转背斜控制的尼安萨群上、下段界面上的层间滑动剪切破碎带。褶皱有构造变形期形成的复式背斜和与后期剪切作用有关的小型横褶皱,后者为沿密集剪切面滑动产生的。褶皱紧闭,背斜轴面近SN走向,西倾,向南倾伏,M1、M2矿脉即处于此倒转背斜的两翼。褶皱层间的剪切破碎带是主要的控矿构造,如磁铁石英岩条带中的“皱纹状构造”、燧石条带角砾拉伸形成的“石香肠构造”、“交错脉状构造”、“脉状穿插构造”、“网脉状构造”等。以横褶皱切过早期纵向等斜褶皱轴部的地段矿化较强。
从矿体产出部位及赋矿围岩看,Mwamola金矿同时受层间破碎剪切带及条带状含铁建造岩层控制,呈现明显的岩性-构造双重控矿特征。
2.3 岩浆岩
多期次火山-岩浆侵入活动,生成了区内种类繁多超基性-酸性岩浆岩。其中中太古代后期到新太古代早期,广泛分布的花岗质火山沉积变质岩和尼安萨群深源镁铁质超基性、基性火山岩、变质玄武岩与金矿化密切相关。
2.4 矿体分布特征
M1-Ⅰ和M2-Ⅰ金矿体主要赋存在中酸性-中基性火山沉积岩和酸性火山碎屑岩层间剪切破碎带偏中基性火山岩一侧。金矿化普遍发育于磁铁石英岩、条带状含磁铁绿泥千枚岩和凝灰岩,尤其是上述岩层的接触部位或层间碎裂岩中。矿体受层间剪切带及条带状铁建造岩层控制,形态简单,成层状、似层状展布,沿走向、倾向上基本连续。
M1-Ⅰ金矿体产状与M1矿脉(倒转背斜西翼)基本一致,总体走向8°,倾向278°,倾角75°。矿体围岩主要是条带状磁铁石英岩、凝灰质砂岩和变质凝灰岩。矿体平均厚度2.68 m,最大厚度22.87 m,金平均含量4.73×10-6。
M2-Ⅰ金矿体产状与M2矿脉(倒转背斜东翼)基本一致,总体走向8°,倾向278°,倾角83°。矿体平均厚度1.25 m,金平均含量3.92×10-6。
2.5 矿石结构构造及矿物组合
矿石以原生矿为主。原生矿以自形—半自形粒状结构、他形粒状结构和碎裂结构为主,条带状、块状、浸染状、细脉状、脉状穿插构造,主要金属矿物为自然金、黄铁矿、毒砂、磁黄铁矿、磁铁矿、黄铜矿;脉石矿物有石英、长石、绢云母、绿泥石、碳酸盐矿物;氧化矿石多见交代残余结构,蜂窝状和块状构造为主,以褐铁矿、赤铁矿、高岭石、石膏和黏土矿物常见。
2.6 蚀变类型及分带
矿区含矿围岩蚀变主要有硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化,金属矿化有黄铁矿化、毒砂化、磁黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化、铅锌矿化。其中硅化、绿泥石化、黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化与金矿化关系最为密切。
热液活动受断裂构造带控制,热液蚀变从断裂带中心向两侧,强度逐渐减弱,具一定分带性。根据矿化、蚀变强度及蚀变矿物组合可划分出上、下两段。上段蚀变带主要分布在中基性岩层中,其蚀变、矿化强度从剪切破碎带中心向边缘逐渐减弱,由主矿层向外依次出现稠密浸染状黄铁矿化矿层、稀疏浸染状黄铁矿化矿层、细脉状黄铁矿化矿层、星点状黄铁矿化矿层,最后为不含矿的的磁铁石英岩、基性凝灰岩等,主矿层矿化蚀变带厚度多约10 m。而下段蚀变带主要分布于在中酸性火山碎屑岩一侧,主要为绢云母化、磁黄铁矿化、黄铁矿化和铅锌矿化,未发现金矿化。
3. 地球物理信息
3.1 磁测异常
3.1.1 岩(矿)石磁性特征
岩(矿)石物性标本取自岩心,磁性测定使用SM-30磁化率仪(捷克生产),测定结果(表 1)表明:金矿石和条带状含铁建造均具强磁性,与围岩磁性差异明显。由于BIF金矿体与含铁建造密切相关,因此利用地面磁测即可达到间接发现BIF型金矿之目的。
表 1 姆瓦莫拉金矿岩(矿)石磁化率特征Table 1. Statistics of magnetic susceptibility parameters of rocks in the Mwamola gold deposit
3.1.2 磁异常特征
1:1万地面高精度磁测,测网密度为100 m×20 m,测线方向东西,测量设备为国产WCZ-1型质子磁力仪,数据处理采用MAGS3.0系统。
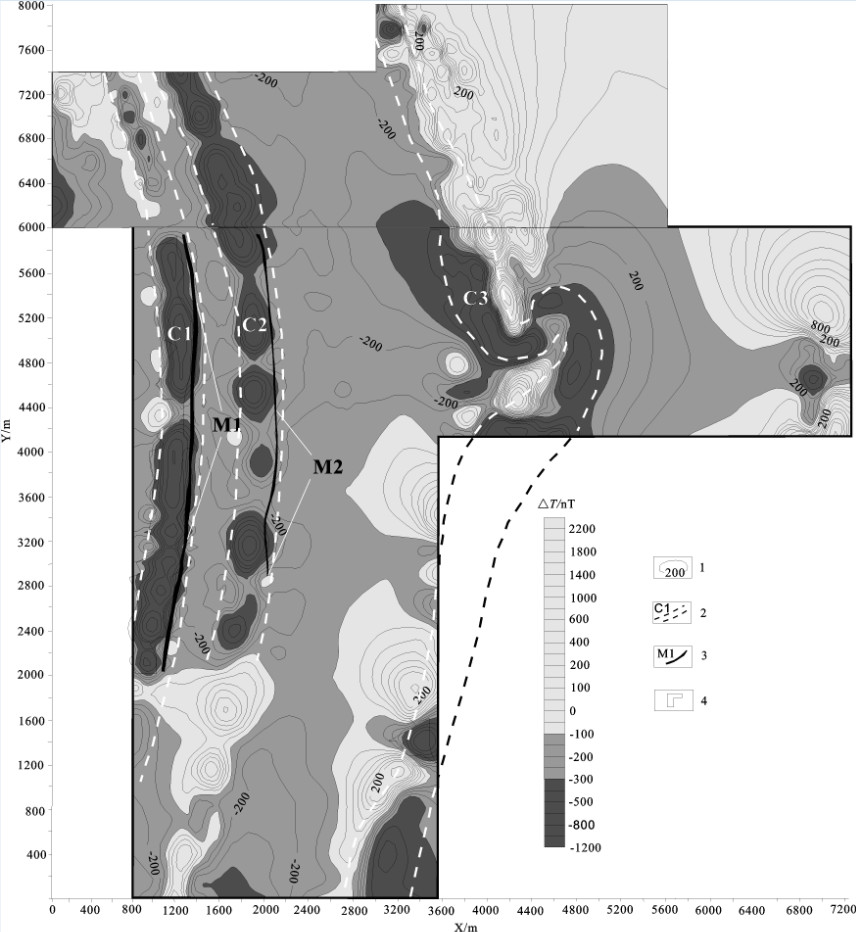
经数据处理成图(图 3),测区内圈出了3条近南北向、呈弧形带状分布的△T磁异常带(C1、C2、C3),磁异常带强度高,规模大,南北两端均未封闭,磁异常主要由含铁建造产生。其中C1、C2磁异常区已证实存在含金矿脉,探明(332+333)金金属资源量34 t;C3磁异常带上只施工了2个验证孔,也见到了工业矿体。C1、C2负磁异常带上的两条金矿脉(M1、M2)呈近南北向分布,处在负磁异常向背景场过渡的梯度带上,矿脉稳定,延续性好。两矿脉近乎平行,其长度、形态、延伸方向、均与各自对应的负磁异常带一致,表明了条带状含铁建造对金矿脉的控制作用。
3.1.3 2.5维人机交互正演拟合
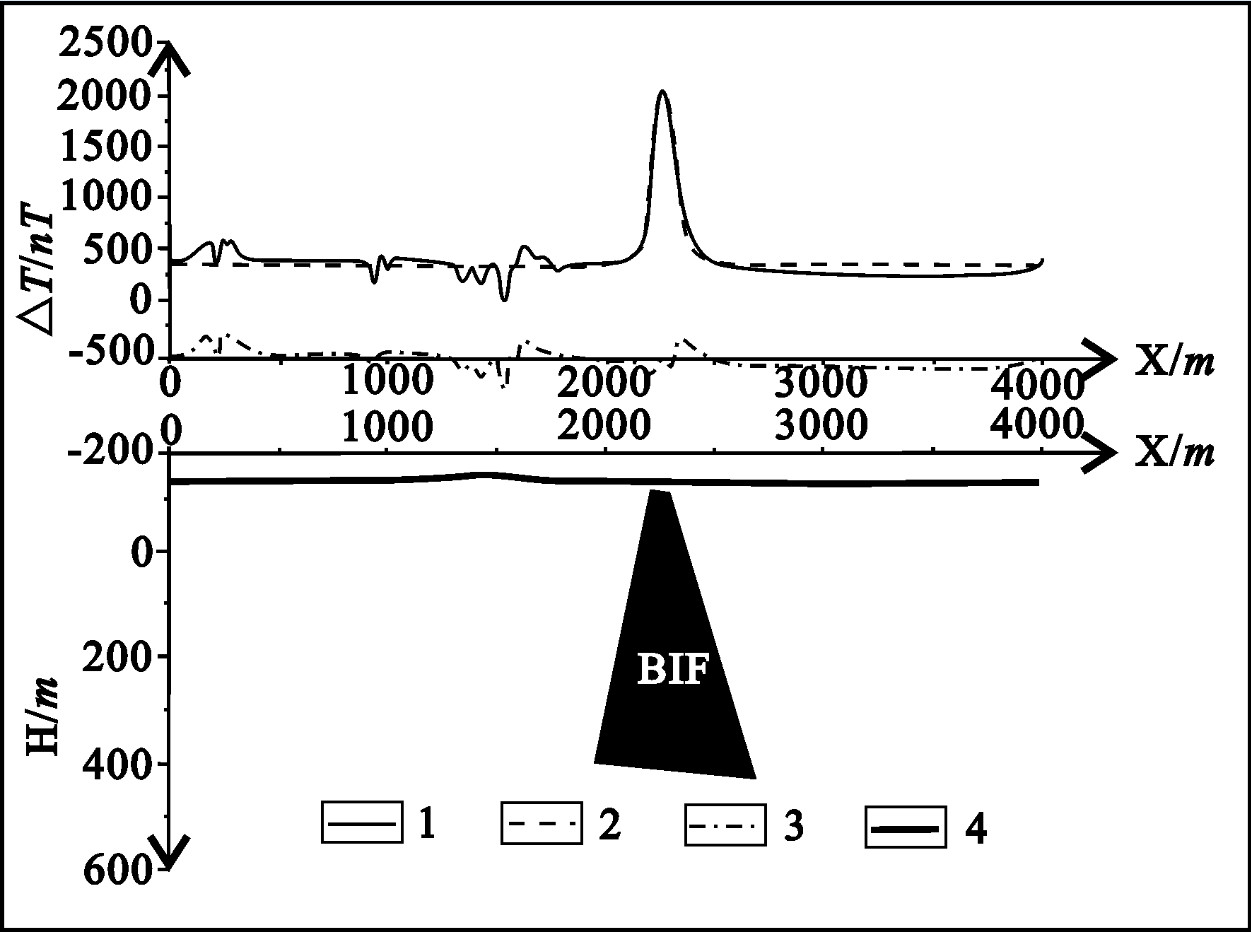
在C1磁异常带布置了精测剖面,对其中一剖面的化极异常进行了2.5维人机交互正演拟合[11](图 4),正演拟合计算磁参数采用:有效磁化强度28000×10-3A/m,有效磁化倾角-30°。可见计算曲线与实测曲线拟合度较好,获得的磁性地质体(BIF)对应实测高值异常,说明异常由条带状含铁建造引起[14],表明人机交互正演计算可有效的对隐伏条带状含铁建造(控、赋矿围岩)进行空间定位,为找矿工程部署提供依据。
3.1.4 磁异常剖面
从14勘探线M1矿脉地质-磁异常综合剖面可见,M1矿脉对应明显的△T负磁异常,异常值高、梯度较陡、范围较宽,表明条带状含铁建造具有较强磁性和规模,磁异常经化磁极处理后,南半球ΔT正、负异常整体发生了互换,ΔT异常与化极异常二者构成了倒相180°的关系[15],ΔT化极异常极大值与含铁建造中心位置相对应,而金矿体则位于ΔT化极异常曲线的梯度带偏BIF一侧;化极异常曲线两翼基本对称,表明条带状含铁建造与矿体的产状较陡且具有一定延深。高磁异常是条带状含铁建造和金矿脉的共同反映。
3.2 激电异常
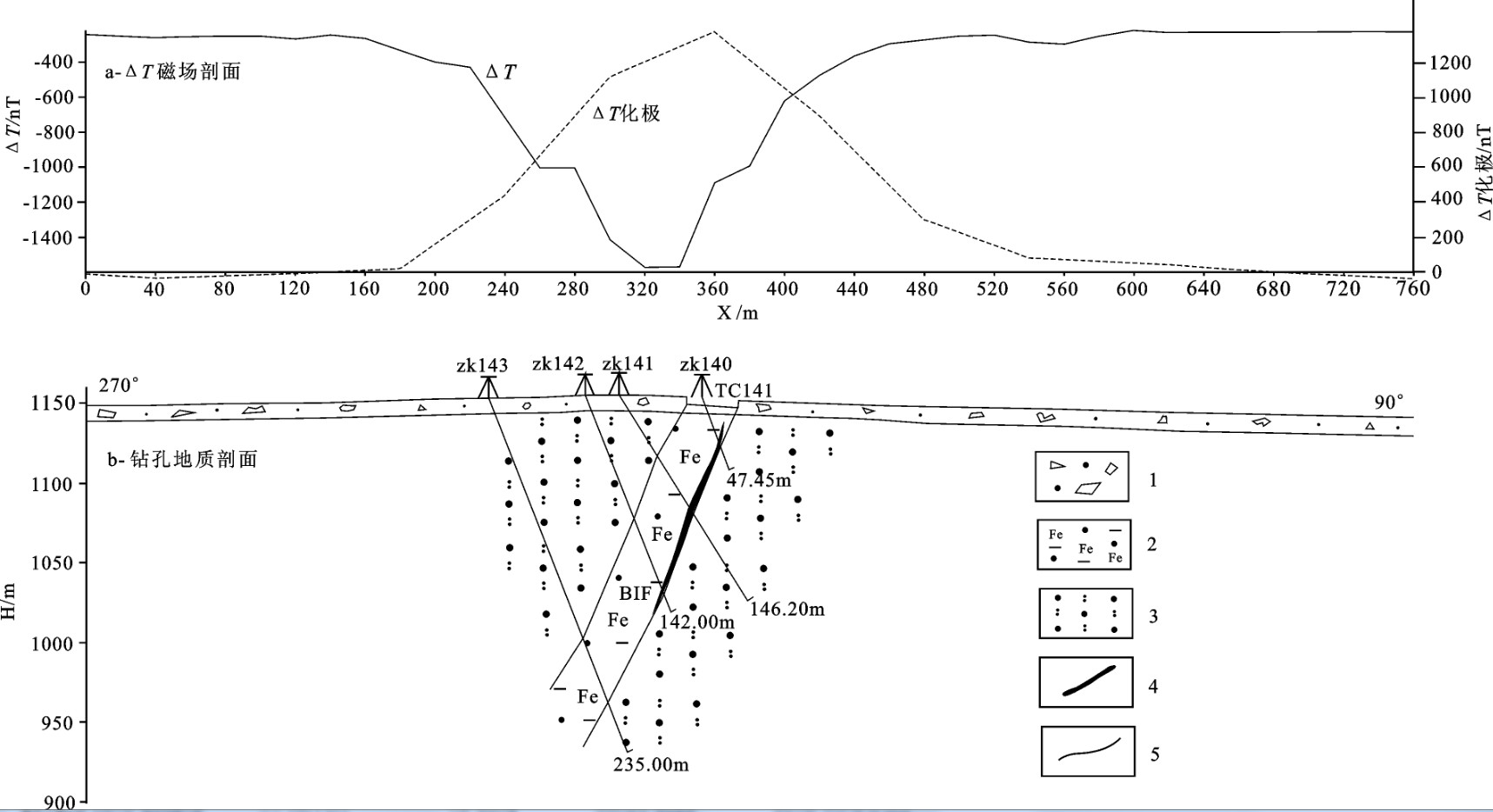
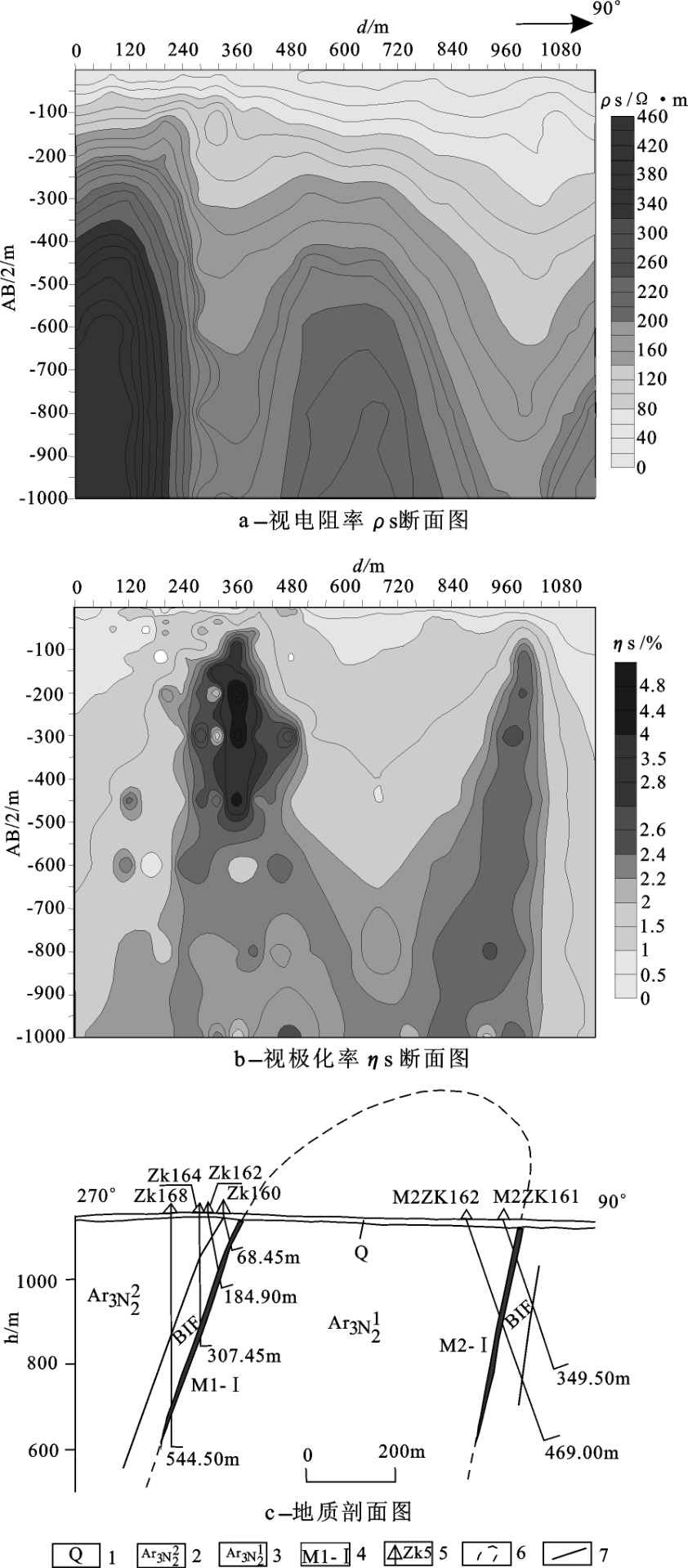
根据激电异常能够发现并圈定地下含金属或金属硫化物的地质体[16]。矿区内含铁建造和金矿体均含有磁铁矿和黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿等金属硫化物。大功率时间域对称四极激电测深拟断面图显示(图 6),视电阻率等值线(a)在240~400点和960~1000点呈“低阻”下凹,而同一位置的视极化率等值线(b)则呈现“高极化”上凸,这一特征与含铁建造构成的倒转背斜的两翼形态相一致,同时也说明BIF和金矿体具有低阻、高极化电性特征[17]。表明激电测深可以对BIF和金矿体进行空间定位。
![]() 图 6 16勘探线地质-激电异常综合剖面1—第四系松散残坡积物和沼泽黑土;2—新太古界上Nyanzian群上段;3—新太古界上Nyanzian群下段;4—金矿体及编号;5—钻孔及编号;6—推测背斜构造;7—地质界线Figure 6. The profile along line 16 for geological-geophysical survey of the Mwamola gold deposit1-Residual sediments and swampy black soil; 2-Ar3N22―NeoArchean Upper Nyanzian Group; 3-Ar3N21―Lower segment of NeoArchean Nyanzian Group; 4-Gold orebody and its serial number; 5-Drill hole and its serial number; 6-Inferred anticline structure; 7-Geological boundary
图 6 16勘探线地质-激电异常综合剖面1—第四系松散残坡积物和沼泽黑土;2—新太古界上Nyanzian群上段;3—新太古界上Nyanzian群下段;4—金矿体及编号;5—钻孔及编号;6—推测背斜构造;7—地质界线Figure 6. The profile along line 16 for geological-geophysical survey of the Mwamola gold deposit1-Residual sediments and swampy black soil; 2-Ar3N22―NeoArchean Upper Nyanzian Group; 3-Ar3N21―Lower segment of NeoArchean Nyanzian Group; 4-Gold orebody and its serial number; 5-Drill hole and its serial number; 6-Inferred anticline structure; 7-Geological boundary4. 地球化学信息
4.1 地球化学参数特征
矿区无基岩出露,在M1矿化带钻孔内开展了岩石化学测量,分析元素有Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、W、Sn、Mo、As、Sb、B、Cr、Hg、Bi,分别统计计算了各类岩石中元素的平均含量、变异系数及浓集克拉克值(表 2),结果表明其元素的分布特征,受成矿作用控制明显,从地层围岩到控矿构造带,元素呈规律性递增富集。矿区内变质凝灰岩、变凝灰质砂岩中金的平均含量最低,标准离差<350,变异系数<2;条带状磁铁石英岩和金矿(化)带中金的平均含量最高,标准离差>3000,变异系数>2.5;在各地层单元中,条带状磁铁石英岩Au、As呈强富集,Sb为中等富集。说明矿区成矿有利层位为条带状磁铁石英岩。
表 2 岩石地球化学特征Table 2. Geochemical characteristics of rocks
4.2 元素的R型聚类分析
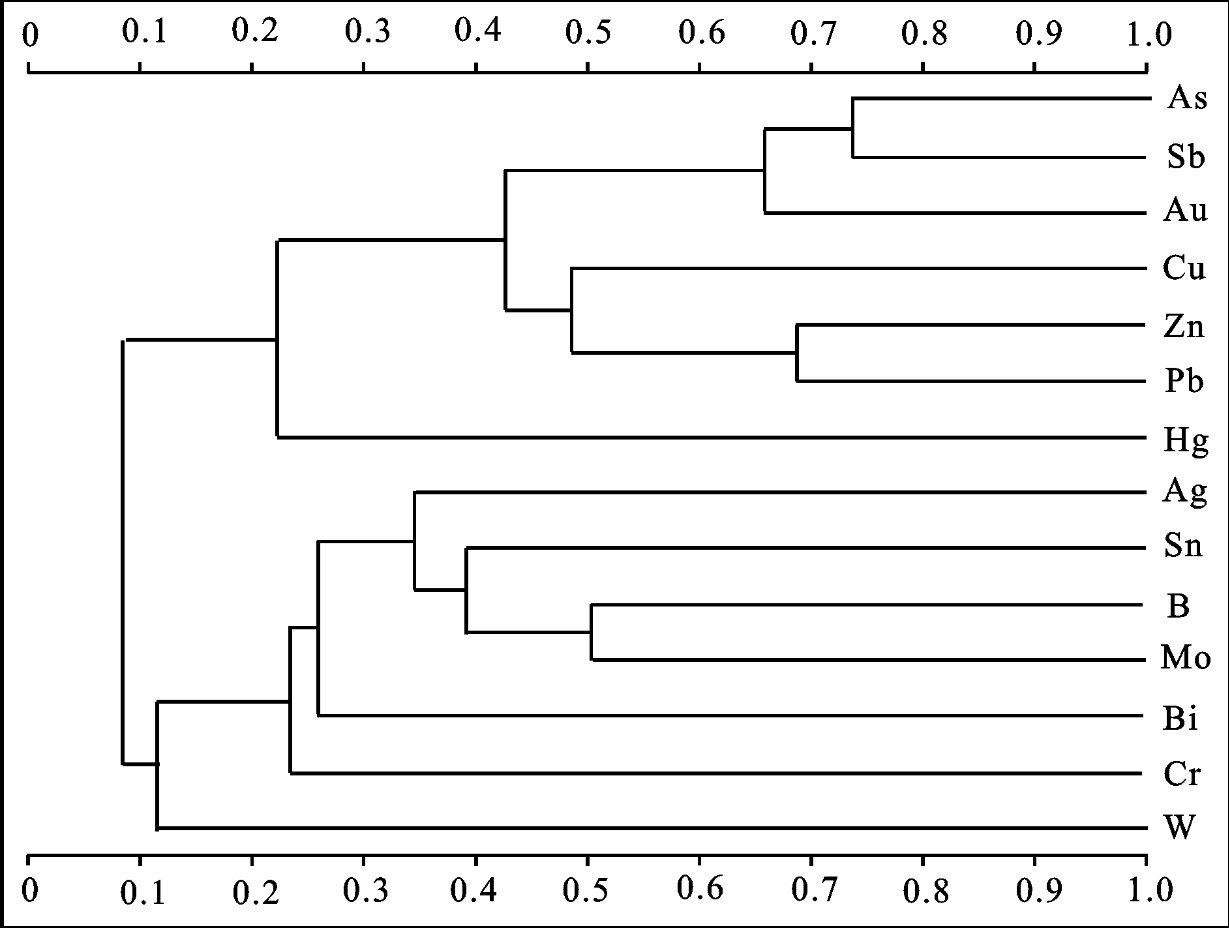
从岩石样品选择与BIF(条带状磁铁石英岩)有关的样品,对元素的相关性进行R型聚类分析(表 3、图 7),可以看出,区内Au与As、Sb具有显著的相关性,其次为Ag、Zn、Pb等。As、Sb对发现金矿体具有较好的指示作用。
表 3 矿化带岩石样品R型聚类结果Table 3. R type cluster tree of rocks in the mineralized belt
4.3 元素地球化学异常特征
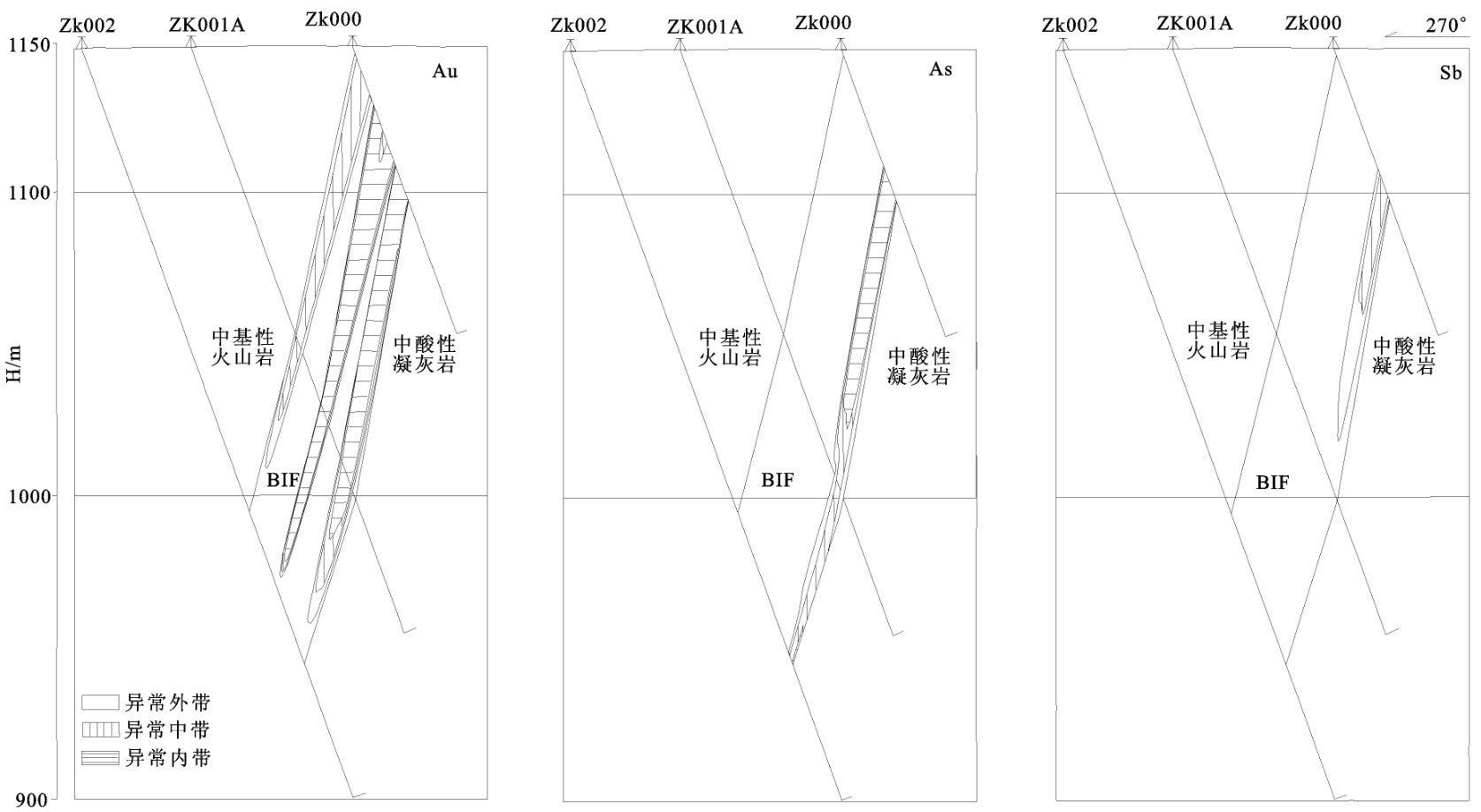
00勘探线钻孔地球化学测量结果(图 8),Au、As、Sb异常与BIF矿化带(或金矿体)的吻合度高,Au、As、Sb异常呈带状、帚状。Au异常不连续,受地层分布控制;As异常有向深部延伸态势;Sb异常规模相对较小,近矿体分布。上述特征说明金、砷、锑元素对在该地区寻找金矿有重要指示作用,也说明该区金矿化严格受地层控制。
4.4 元素垂直变化特征
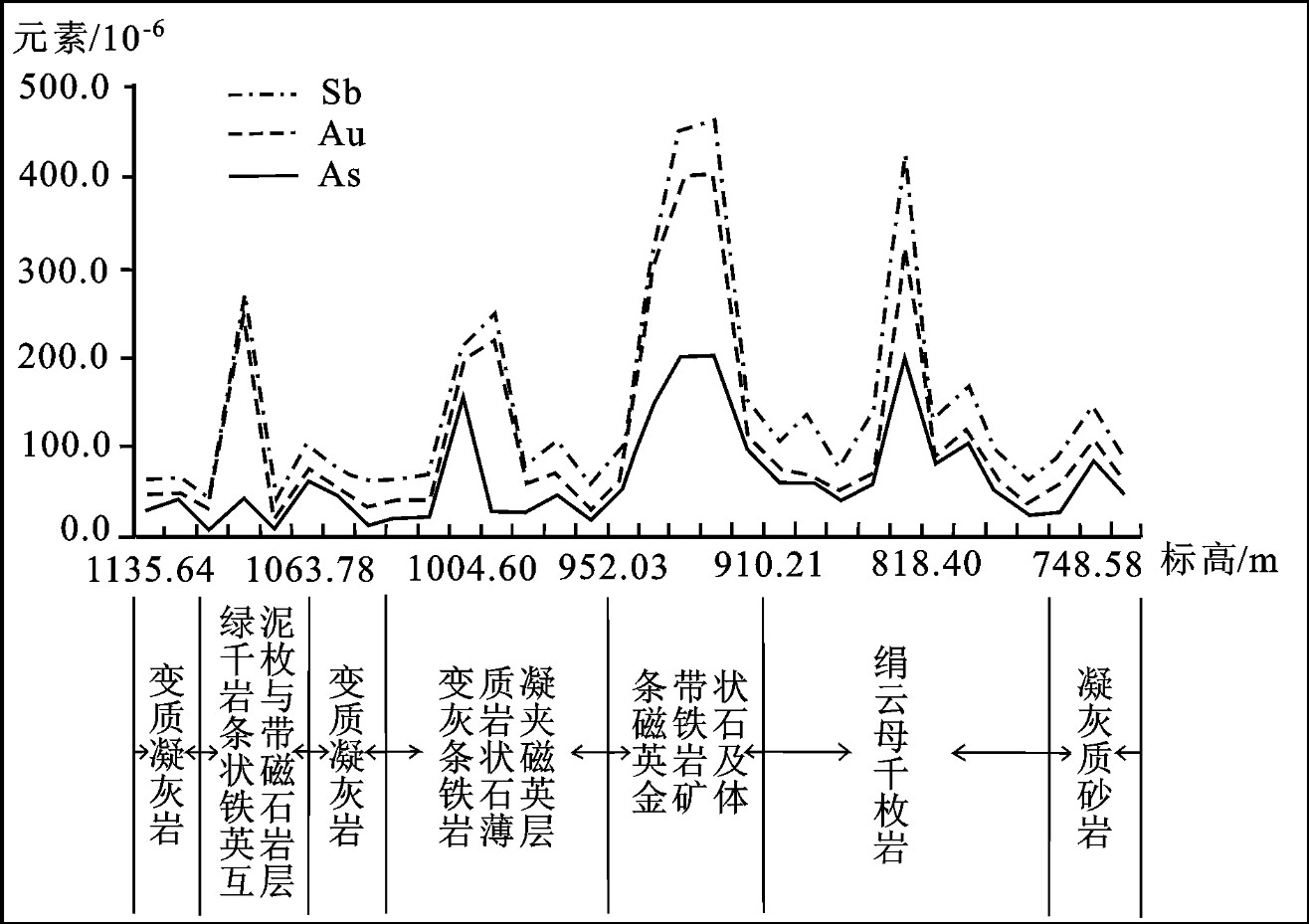
从钻孔(ZK034)中主要金属元素Au、As、Sb含量随深度变化曲线(图 9)可以看出,3种元素含量变化同步,与岩性变化明显相关。900~950 m处是含铁建造和金矿体,Au、As、Sb为极大值,且变化规律非常一致,表明Au、As、Sb是指示赋矿围岩和金矿体的主要元素组合异常。
5. 综合找矿模式
根据矿床地质特征、地球物理、地球化学异常信息,建立了姆瓦莫拉金矿床地、物、化综合找矿模式(表 4)。
表 4 姆瓦莫拉金矿综合找矿模式Table 4. Integrated ore-prospecting model for the Mwamola gold deposit
(1)其地质找矿标志:
① 姆瓦莫拉金矿床产在条带状含铁建造中,尤其是含铁建造层与酸性火山沉积岩层的接触部位。
② 主要控矿构造是褶皱层间剪切破碎带。尤以控矿构造内具有皱纹状、石香肠、网脉状构造特征碎裂岩、角砾岩、糜棱岩是矿化富集部位。
③ 矿体围岩蚀变主要为硅化、绿泥石化,金属矿化主要为黄铁矿化、磁黄铁矿化,其中硅化、绿泥石化、黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化与金矿化最为密切。
(2)地球物理找矿标志:
① 磁法找矿标志:金矿石、赋矿围岩-条带状含铁建造与围岩磁性差异明显,含铁建造上出现宽度窄、幅值高、梯度大的负磁异常,金矿(化)体则位于高磁异常与背景异常的过渡带。
② 电法找矿标志:金矿体和含铁建造呈现高极化率、低电阻率异常;激电测深可以对含铁建造和金矿体进行空间定位。
(3)地球化学找矿标志:矿体上方有明显的Au、As、Sb异常,且含铁建造分布区内大于200×10-9的金异常区可能指示金矿(化)体的存在。
6. 找矿方法组合
姆瓦莫拉金矿地处季节性沼泽区,覆盖层厚度大,采用高效的地面高精度磁测探测隐伏的条带状含铁建造,是金矿普查-详查首选的物探方法。在矿(化)体上布置激电测深剖面,可对矿体进行空间定位,为部署探矿工程提供依据。因此,高精度磁测和激发极化法是姆瓦莫拉金矿区有效地物探方法组合。物探找矿工作程序为:(1)在成矿有利地区,开展面积性(1:1万)地面高精度磁测和精测剖面测量,发现圈定条带状含铁建造,通过数据处理和地质解释研究其分布特性;(2)在地电条件满足地段,开展激电测深,对含铁建造和金矿体进行定位,指导工程验证。
致谢: 感谢审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵修改意见! -
图 2 姆瓦莫拉金矿区及外围地质简图
1—第四纪及沼泽性黑土; 2—绿岩带(以太古界尼安萨群岩层为主,夹条带状含铁建造); 3—花岗质岩石(无法确定时代); 4—金矿床; 5—金矿点; 6—断层; 7—剪切带; 8—地质界线; 9—Mwamola金矿; 10—矿区区域位置
Figure 2. Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its periphery
Fig. 2 Geological map of the Mwamola gold deposit and its periphery (From geological map of Karumwa area, sheet 47/1-2, in the geological division, department of lands and mines, Dodoma in Tanzania) 1-Quaternary and swampy black soil; 2-Greenstone belts (mainly Nyanzian rock layer, interlayer banded iron formations); 3-Granitoids (unable to determine the age); 4-Gold deposit; 5-Au ore spot; 6-Fault; 7-Shear zone; 8-Geological boundary; 9-Mwamola gold deposit; 10-Location of ore district
图 6 16勘探线地质-激电异常综合剖面
1—第四系松散残坡积物和沼泽黑土;2—新太古界上Nyanzian群上段;3—新太古界上Nyanzian群下段;4—金矿体及编号;5—钻孔及编号;6—推测背斜构造;7—地质界线
Figure 6. The profile along line 16 for geological-geophysical survey of the Mwamola gold deposit
1-Residual sediments and swampy black soil; 2-Ar3N22―NeoArchean Upper Nyanzian Group; 3-Ar3N21―Lower segment of NeoArchean Nyanzian Group; 4-Gold orebody and its serial number; 5-Drill hole and its serial number; 6-Inferred anticline structure; 7-Geological boundary
表 1 姆瓦莫拉金矿岩(矿)石磁化率特征
Table 1 Statistics of magnetic susceptibility parameters of rocks in the Mwamola gold deposit

表 2 岩石地球化学特征
Table 2 Geochemical characteristics of rocks

表 3 矿化带岩石样品R型聚类结果
Table 3 R type cluster tree of rocks in the mineralized belt

表 4 姆瓦莫拉金矿综合找矿模式
Table 4 Integrated ore-prospecting model for the Mwamola gold deposit

-
[1] 沈保丰, 李上森, 骆辉.前寒武纪条带状铁建造(BIF)中金的成矿作用[J].国外前寒武纪地质, 1988, (1):1-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-qhwj198801000.htm Shen Baofeng, Li Shangsen, Luo Hui.Precambrian banded iron formation (BIF) gold mineralization[J].International Precambrian Geology, 1988, (1):1-34(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-qhwj198801000.htm
[2] 李碧乐, 霍亮, 李永胜.条带状铁建造(BIFs)研究的几个问题[J].矿物学报, 2007, 27(2):205-210. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2269398295&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Li Bile, Huo Liang, Li Yongsheng.Several problems involved in the study of banded iron formations (BIFs)[J].Acta Minalogica Sinica, 2007, 27(2):205-210(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2269398295&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 王长乐, 张连昌, 刘利, 等.条带状铁建造(BIF)的形成时代及其研究方法[J].地质科学, 2014, 49(4):1201-1215. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/article/cpfdtotal-dzdq201501005062.htm Wang Changle, Zhang Lianchang, Liu Li, et al.The formation era of BIF and its research methods[J].Chinese Journal of Geology, 2014, 49(4):1201-1215(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/article/cpfdtotal-dzdq201501005062.htm
[4] Borg G, 等.坦桑尼亚盖塔和朱比利里夫太古代条带状铁建造中金矿床的成因探讨[J].吴礼道译.国外火山地质, 1992, 33(1):32-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GWHD199201005.htm Borg G, et al.Discussion the cause of Archean article banded iron formation the gold deposit in Geita and Jubilee Reef, Tanzania[J]Wu Lidao (Trans.).International Volcanology, 1992, 33(1):32-43(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GWHD199201005.htm
[5] 杨东潮, 白德胜, 曹琼.坦桑尼亚太古宙绿岩带中的BIF型金矿床的勘查标志——以Maheiga金矿为例[J].黄金科学技术, 2013, 21(4):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201304002.htm Yang Dongchao, Bai Desheng, Cao Qiong.The BIF gold exploration criteria in greenstone belt of archaean, Tanzania:Taking Maheiga gold mine for example[J].Gold Science and Technology, 2013, 21(4):1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201304002.htm
[6] 李水平, 杨东朝, 程华, 等.坦桑尼亚条带状含铁建造磁化率参数统计特征及其应用[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(4):784-790. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201304024.htm Li Shuiping, Yang Dongchao, Cheng Hua, et al.Demographic characteristics and its application of magnetic susceptibility parameters of banded iron formation (BIF) in Tanzania[J].Geology and Prospecting, 2013, 49(4):784-790(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201304024.htm
[7] 李水平, 王建光, 白德胜, 等.坦桑尼亚Maheiga金矿地球物理特征及找矿标志[J].地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(5):2395-2400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201405060.htm Li Shuiping, WangJianguang, Bai Desheng, et al.Geophysical characteristics and prospecting indicators of the Maheiga gold deposit in Tanzannia[J].Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(5):2395-2400(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201405060.htm
[8] 龚鹏, 胡小梅, 李娟, 等.建立地质-地球化学找矿模型——以西藏甲玛铜多金属矿床为例[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(10):1601-1612. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDKJ200309010.htm Gong Peng, Hu Xiaomei, Li Juan et al.The construction of the geological and geochemical prospecting model:A case study of the Jiama copper-polymetallic deposit in Tibet[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(10):1601-1612(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDKJ200309010.htm
[9] 肖克炎.试论综合找矿模型[J].地质与勘探, 1994, 30(1):41-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT401.009.htm Xiao Keyan.Preliminary study of compreensive information prospecting model[J].Geology and Prospecting, 1994, 30(1):41-45(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT401.009.htm
[10] 杨立德.地质·物探·化探找矿模型[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):741-742. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200906031.htm Yang Lide.Geological, geophysical, geochemical prospecting model[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(6):741-742(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200906031.htm
[11] 李艳军, 魏俊浩, 李欢, 等.义敦岛弧带夏塞银铅锌矿床地质、物化探特征及综合找矿模型[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(5):1636-1649. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140518&journal_id=geochina Li Yanjun, Wei Junhao, Li Huan, et al.Geological, geophysical and geochemical characteristics and comprehensive prospecting model of the Xiasai Ag-Pb-Zn deposit in the Yindun Island Arc[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(5):1636-1649(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140518&journal_id=geochina
[12] 方向, 唐菊兴, 李彦波, 等.西藏多龙矿集区拿若铜(金)矿床成矿元素空间分布规律及地球化学勘查模型[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(3):936-950. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140319&journal_id=geochina Fang Xiang, Tang Juxing, Li Yanbo, et al.Metallogenic element spatial distribution of the Naruo copper (gold) deposit in the Duolong ore concentration area of Tibet and its geochemical exploration model[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(3):936-950(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140319&journal_id=geochina
[13] 杨剑, 王绪本, 王永华, 等.电、磁综合方法在云南北衙铁金矿勘查中的应用[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(2):602-610. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140221&journal_id=geochina Yang Jian, Wang Xuben, Wang Yonghua, et al.The application of integrated geophysical methods of magnetic survey and AMT to the exploration of the Beiya gold deposit[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(2):602-610(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140221&journal_id=geochina
[14] 刘天佑.磁法勘探软件手册MAGS3.0使用说明[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2009:60-62. Liu Tianyou.Magnetic prospecting so Ftware Manual MAGS3.0 Directions for Use[M].Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press, 2009:60-62(in Chinese).
[15] 李水平.低磁纬度地区△T异常处理解释方法在坦桑尼亚某地区金矿预查中的应用[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):657-659. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/WTYH200906011.htm Li Shuiping.The Application of the approaches to the interpretation of magnetic△T anomalies in the low magnetic latitude area to gold deposit for Tanzania[J].Geophysical and geochemical exploration, 2009, 33(6):657-659(in Chinese with English abstract). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/WTYH200906011.htm
[16] 李赛赛, 魏刚锋, 崔敏利.陕西勉县王家沟金矿区物化探勘查技术应用及找矿预测[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(2):474-485. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120218&journal_id=geochina Li Saisai, Wei Gangfeng Cui Minli.The application of geophysical and geochemical exploration and metallogenic prediction in the Wangjiagou gold ore district of Mianxian County, Shaanxi Province[J].Geology in China, 2012, 39(2):474-485(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120218&journal_id=geochina
[17] 李水平, 白德胜, 程华, 等.坦桑尼亚某金矿的磁力、激电异常特征[J].物探与化探, 2012, 36(5):737-740. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201205006.htm Li Shuiping, Bai Desheng, Cheng Hua, et al.Magnetic and induced polarization anomaly characteristics of a gold ore deposit in Tanzania[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(5):737-740(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201205006.htm
-
期刊类型引用(30)
1. 司建涛,白德胜,祁东,孙进,张明礼,梁永安,邵江波,姚明高. 坦桑尼亚恩泽加地区覆盖区选区评价及综合找矿方法研究. 矿产与地质. 2024(01): 119-125+153 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 司建涛,赵志强,张明礼,孟有杰,孙进,董岘证. 坦桑尼亚尼昂华莱地区条带状铁建造型金矿床地质特征及勘查方向研究. 黄金. 2024(04): 80-85+95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 藏瑞秋,王昆,王见荥. 激电中梯测量在大红山金多金属矿区的找矿应用. 地质找矿论丛. 2024(04): 544-551 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 海连富,陶瑞,张晓军,刘安璐,刘金科,魏俊浩,白金鹤,李海峰. 宁夏卫宁北山地区金场子金矿区找矿模型及成矿预测. 地质科技通报. 2023(02): 19-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘莎,艾国梁. 湖南清水塘铅锌矿区物化探异常特征. 地质学刊. 2023(01): 91-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 司建涛,张明礼,白德胜,邵江波,郭鑫,孙进,张晓丽. 坦桑尼亚恩泽加绿岩带隐伏金矿床综合找矿模型. 地质与勘探. 2023(03): 678-690 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 彭俊,白德胜,祁东,梁永安,楚明春. 坦桑尼亚维多利亚湖金矿田典型金矿床成矿特征与矿床成因. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1377-1389 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张参辉,李水平,白德胜,程华,曹杰,张爱玲,孙进,赵华奇. 时间域激电法在浅覆盖区萤石矿勘查中的应用——以河南省方城县铁炉萤石矿床为例. 地质与勘探. 2022(02): 369-380 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王进寿,潘彤,薛万文,李鹏,安永尉,田永革,雷晓清,余福承. 青海省柴北缘成矿带区域成矿规律综述. 矿床地质. 2022(05): 917-938 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王明明,罗清威,张克川,李新超. 坦桑尼亚穆索马-马拉绿岩带型金矿遥感、物探、地质综合找矿研究. 地质与勘探. 2022(05): 1117-1127 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 梁成,马林霄,陈德稳,席鹏,秦磊. 坦桑尼亚索罗瓦金矿地质特征及找矿远景. 矿产勘查. 2021(01): 2-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 白德胜,李水平,纵瑞,程华,齐勇攀,张爱玲,孙进,赵华奇. 豫西董家埝构造蚀变岩型银矿物化探异常特征及找矿模型. 地质与勘探. 2021(02): 241-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 邵江波,袁杨森,王滑冰,张超,张明礼,孟有杰,梁永安,陈璐璐. 综合物探方法在坦桑尼亚西嘎山地区金矿勘查中的应用. 地球物理学进展. 2021(02): 644-653 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 白德胜,李水平,赵志强,袁杨森,程华,张爱玲. 坦桑尼亚环维多利亚湖地区金矿勘查地球物理方法应用研究. 地球物理学进展. 2021(03): 1029-1045 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 郭景会,张明礼,沈芳. 坦桑尼亚穆索马-马拉绿岩带塔拉尼金矿床地质特征及找矿潜力分析. 地质找矿论丛. 2021(04): 516-525 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 郭景会,白德胜,张超,彭俊,黄达,姚明高,陈景伟. 坦桑尼亚克拉通太古代绿岩带造山型金矿床地质特征及成因. 世界地质. 2021(04): 816-829 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 孟有杰,袁杨森,李水平,邵江波. 综合物化探方法在坦桑尼亚卡尹泽金矿区勘查中的应用. 矿产勘查. 2020(02): 328-334 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 齐勇攀,李水平,荆鹏. 时间域激电法在坦桑尼亚尼亚斯罗利金矿勘查中的应用. 矿产勘查. 2020(06): 1270-1276 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 程华,李水平,张爱玲,荆鹏,齐勇攀,孙进. 坦桑尼亚环维多利亚湖地区航磁异常特征及金矿床类型勘查地域划分. 地球物理学进展. 2020(05): 1933-1944 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 邵江波,王滑冰,都鹏飞,孙进,吴昊,张艳飞,郭鑫. 综合地球物理方法在坦桑尼亚卢帕金矿田东缘Twiga金矿勘查中的应用. 矿产勘查. 2020(11): 2522-2529 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 李水平,司建涛,程华,毛金彪,曹杰,孙进,张勇,高福利. 时间域激电测深在坦桑尼亚金矿床勘查中的应用例析. 地球物理学进展. 2019(02): 588-595 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 荆鹏,李水平,曹杰,齐勇攀,张爱玲,邵江波. 音频大地电磁测深在坦桑尼亚金矿勘查中的应用. 矿产勘查. 2019(09): 2355-2361 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 张克川,罗清威,义爱文,秦德雨,权成,杨继兵. 坦桑尼亚PL7184金矿床矿石特征与金的赋存状态. 黄金科学技术. 2019(06): 826-834 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 袁杨森,李水平,程华,卫建征,刘正好,曹杰,邵江波,赵华奇. 坦桑尼亚凯巴卡瑞地区构造蚀变岩型金矿航磁异常特征与找矿意义. 地球物理学进展. 2019(06): 2361-2368 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. Quanjiang Zhang,Yingping Liu,Mingyou He,Jun Bai,Wei Xu,Cong Zhao. Ore prospecting model and targets for the Dashuigou tellurium deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Acta Geochimica. 2018(04): 578-591 .  必应学术
必应学术
26. 李水平,袁杨森,程华,刘振超,刘正好,孟有杰,谢彦军,赵华奇. 坦桑尼亚西嘎山一带铁建造型金矿床航磁异常特征及找矿意义. 地球物理学进展. 2018(03): 1051-1058 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 张克川,义爱文,杨继兵,祝少辉,秦德雨. 坦桑尼亚芒果金矿成矿地质特征及金赋存状态研究. 矿产勘查. 2018(04): 761-765 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 曹杰,李水平,刘正好,司建涛,梁永安,高福利. 坦桑尼亚恩泽加地区辉长岩地球物理特征及构造意义. 物探与化探. 2018(05): 946-951 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 程华,李水平,刘振超,孙进,张勇,谢彦军,宋永利. 近场源三极激电法在坦桑尼亚铁建造型金矿床中的应用. 矿产勘查. 2018(10): 2015-2020 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 李水平,彭俊,荆鹏,张爱玲,邵江波,赵华奇. 微磁测量在坦桑尼亚构造蚀变岩型金矿床上的应用研究. 地球物理学进展. 2017(05): 2021-2028 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: