An analysis of the groundwater flow system based on environmental isotopes in Turpan basin
-
摘要:
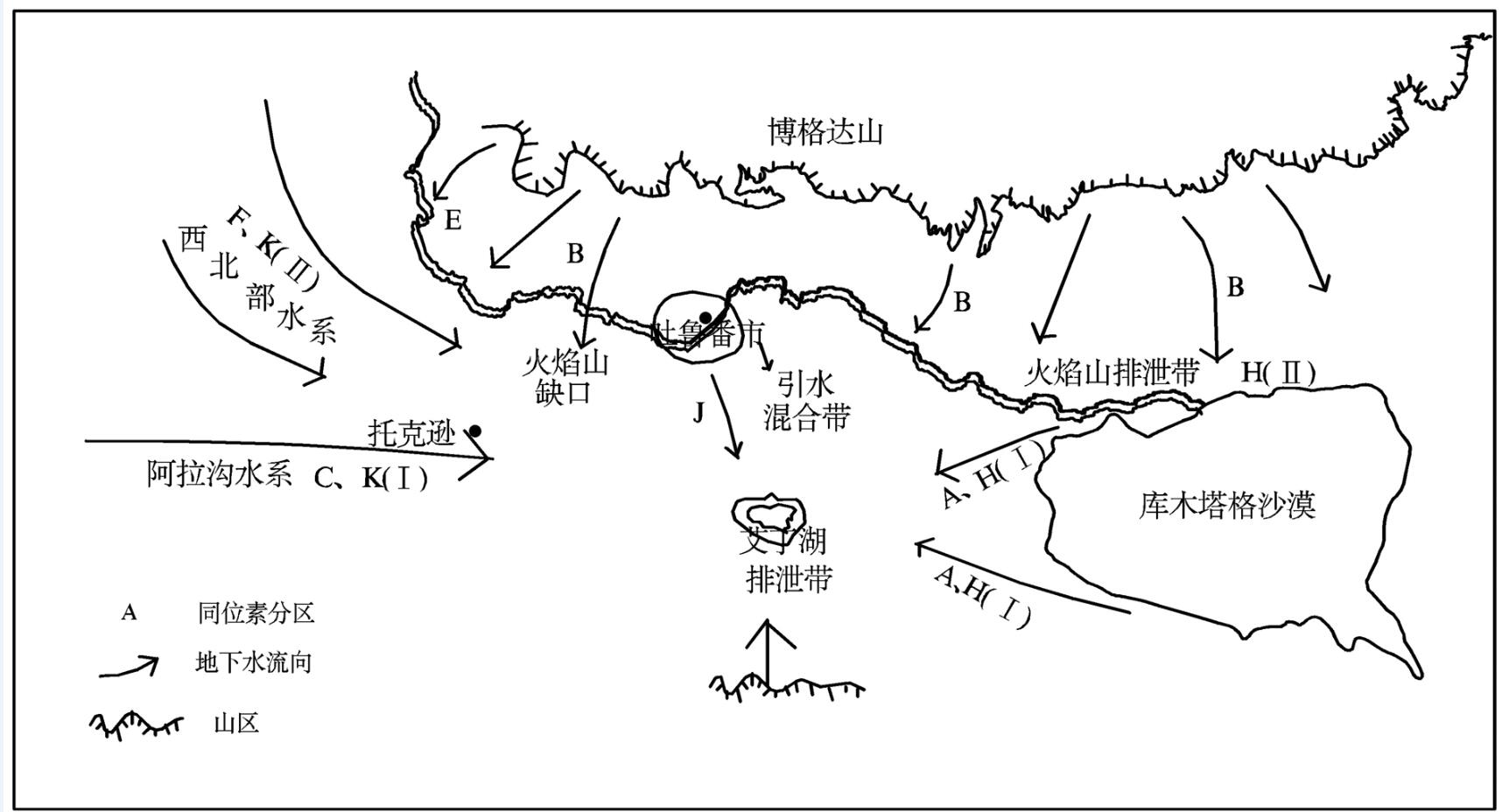
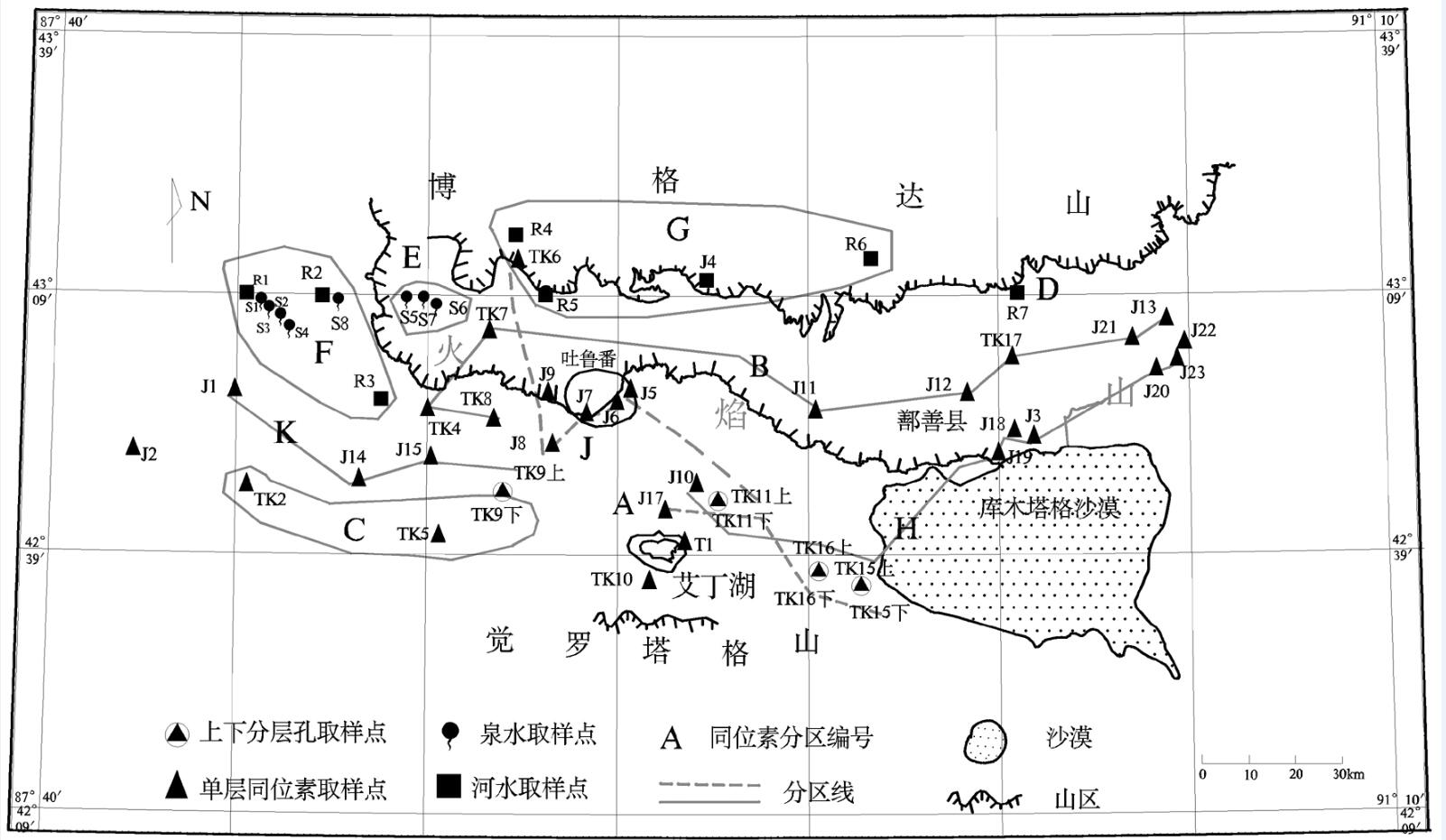
吐鲁番盆地是中国重要的煤炭基地之一,研究盆地地下水流系统对于区域水资源评价具有重要意义。通过在野外开展取样工作,首先根据取样点井深的不同,将所有样点分为4组,结合当地水文地质条件、同位素值的高程效应以及取样点位置,将同位素值以及位置相近的点归为同一个水流系统。经分析,在火焰山以北存在一个相同型式的地下水流动系统,而在火焰山以南随着山区坎尔其水库的修建,水利工程设施的不断完善和农业灌溉制度的改革,存在多级地下水流动系统,其形成条件主要受自然和人类活动影响。其中同位素和TDS值都较高的T1点曾是艾丁湖湖面的边缘,当时湖水水位浅,同位素蒸发效应明显。同时,火焰山地下基岩存在缺口,存在北盆地向南盆地的地下水补给。
Abstract:Turpan basin is an important coal base in China, and studying the regional groundwater flow system is of great significance for regional water resources research. The well depths of the sampling points are mainly concentrated in more than 100 meters and less than 30 meters. All the samples can be divided into four groups based on the well depth, and in combination with the elevation effect of the isotope value and the locations of the sampling points, the nearby points are grouped into the same water system. An analysis shows that the north of the volcanic rocks belongs to the same type of groundwater flow system, while the water system in the south of the volcanic rock exhibits features of multistage flow system because of the reservoir building, the continuous improvement of the water conservancy facilities and the reformation of agricultural irrigation system; its forming condition is mainly influenced by natural and human activities. The isotope and TDS values of T1 point are higher, so it might have been the edge of the Aydingkol Lake, and the lake water level was shallow and isotope evaporation effect was obvious at that time. At the same time, loopholes were existent in the bedrock, the groundwater could flow from the north to the south of the basin.
-
Keywords:
- Turpan basin /
- isotope /
- flow system /
- surface water
-
-
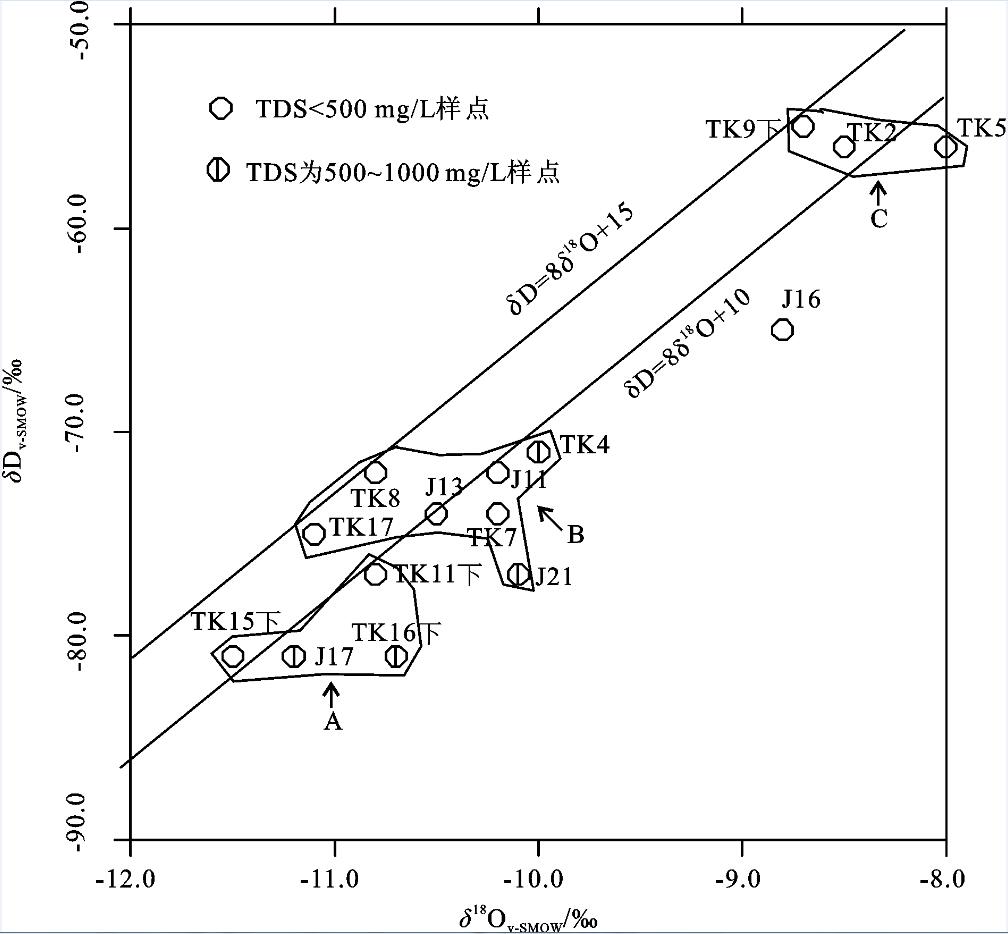
表 1 井深大于100 m样点的稳定同位素数据(‰,V-SMOW)
Table 1 The isotope data of samples with well depth more than 100 meters (‰, V-SMOW)

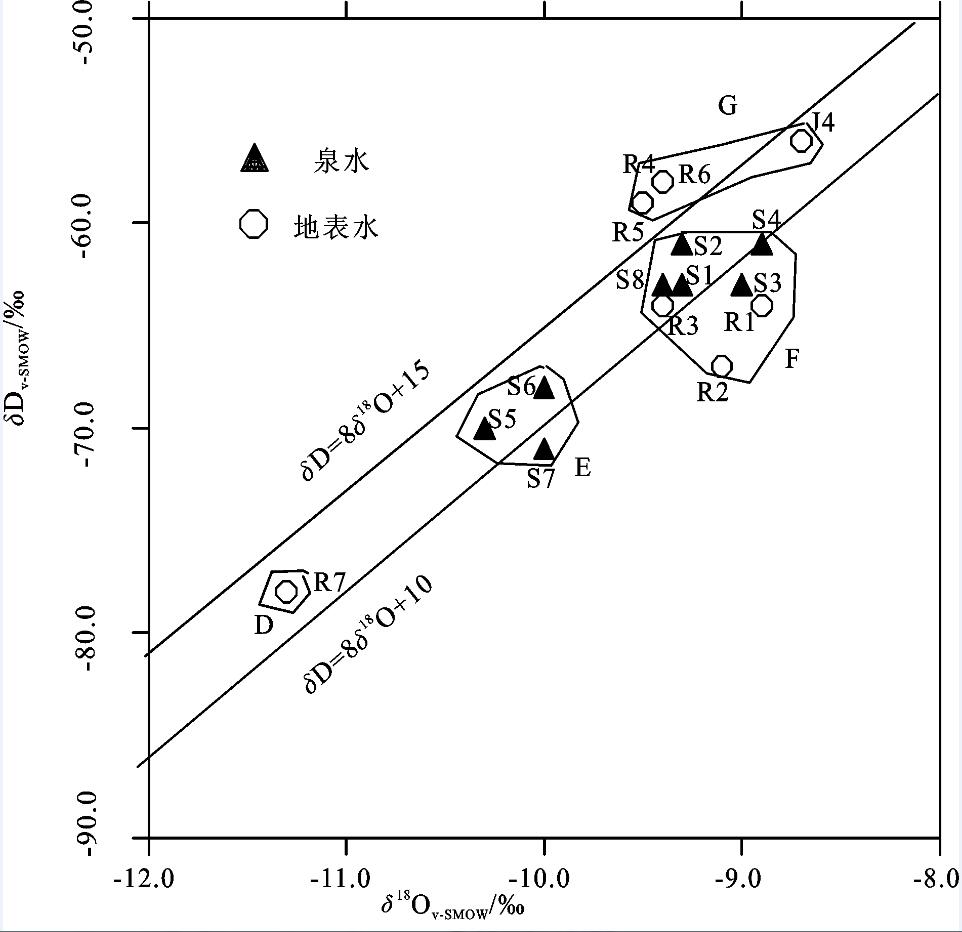
表 2 地表水和泉水的稳定同位素数据(‰,V-SMOW)
Table 2 The isotope data of spring and surface water samples (‰, V-SMOW)

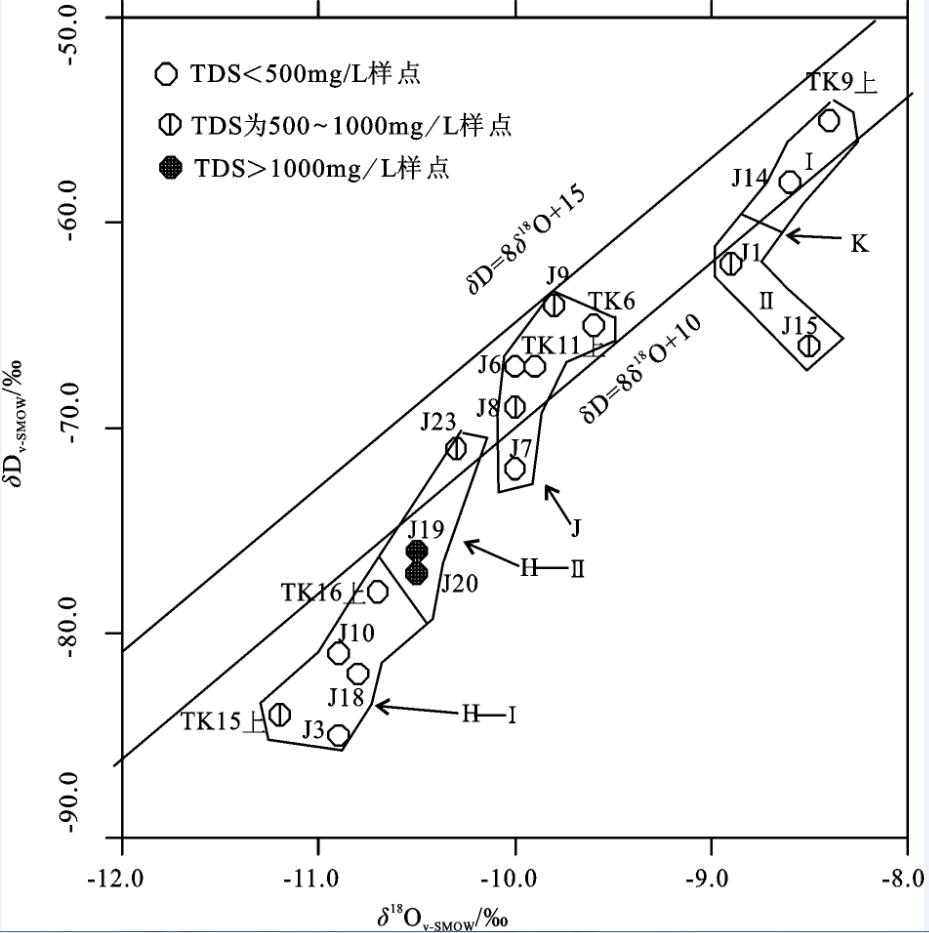
表 3 井深0~30 m样点的稳定同位素数据(‰,V-SMOW)
Table 3 The isotope data of samples with well depth 0-30 meters (‰, V-SMOW)

-
[1] 胡卫忠.吐鲁番盆地水资源开发与水环境保护[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 1998, 9(2):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB802.004.htm Hu Weizhong.Water resources and environmental protection in Turpan Basin[J].Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 1998, 9(2):27-32(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB802.004.htm
[2] Ian Cartwright, Tamie R Weaver, Craig T Simmons, et al.Physical hydrogeology and environmental isotopes to constrain the age, origins, and stability of a low-salinity groundwater lens formed by periodic river recharge Murray Basin, Australia[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 380(1/2):203-221. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2090194232&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] James M Thomas, Duane P Moser, Jenny C Fisher, et al.Using water chemistry, isotopes and microbiology to evaluate groundwater sources, flow paths and geochemical reactions in the Death Valley Flow System, USA[J].Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2013, 7:842-845. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.033
[4] 陈宗宇, 刘君, 杨湘奎, 等.松嫩平原地下水流动模式的环境同位素标记[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(6):94-101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006013.htm Chen Zongyu, Liu Jun, Yang Xiangkui, et al.The environmental isotope markers of groundwater flow patterns of the Song-Nen Plain[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(6):94-101(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006013.htm
[5] 武倩倩, 任加国, 许模.新疆叶尔羌河流域地下水同位素特征及其补给来源分析[J].中国地质, 2008, 35(2):331-336. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200802020.htm Wu Qianqian, Ren Jiaguo, Xu Mo.Isotope features and supply sources of groundwater in the Yarkant River drainage area, Xinjiang[J].Geology in China, 2008, 35(2):331-336(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200802020.htm
[6] 郝爱兵.吐鲁番盆地东部地下水运动特征及水资源开发利用规划研究[D].北京:中国地质科学院, 1993. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ylrq201309010 Hao Aibing.The Research of Groundwater Movement and the Exploitation and Utilization Planning of Water Resources in the East of Turpan Basin[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1993(in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ylrq201309010
[7] 李亚民, 王英男, 徐旭, 等.奎屯河流域南洼地地下水补给特征分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 2008, 35(4):31-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200804012.htm Li Yamin, Wang Yingnan, Xu Xu, et al.Characteristics of groundwater rechargement of Nanwadi in Kuitun River Basin[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2008, 35(4):31-33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200804012.htm
[8] 殷秀兰, 李文鹏, 王俊桃, 等.新疆柴窝堡盆地地下水化学及稳定同位素研究[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(3):439-448. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201003013.htm Yin Xiulan, Li Wenpeng, Wang Juntao, et al.Hydro-chemical and isotopic research in Chaiwopu Basin, Urumqi River catchment[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(3):439-448(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201003013.htm
[9] Freeze R A, Cherry J A.Ground Water[M].Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1979:269-273.
[10] Todd D K, Mays LW.Groundwater Hydrology[M].America John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2005:589.
[11] 王永兴, 李新.吐鲁番盆地水资源持续利用研究[J].干旱期资源与环境, 1997, 11(3):9-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ199702011.htm Wang Yongxing, Li Xin.Studies on sustainable utilization of water resources in the Turpan Basin[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 1997, 11(3):9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ199702011.htm
[12] 王瑞久.水文地质学的概念模型[J].水文地质工程地质, 1985, 12(4):25-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198504007.htm Wang Ruijiu.Conceptional hydrogeological model[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1985, 12(4):25-28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198504007.htm
[13] 李文鹏, 焦培新, 赵忠贤.塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地地下水化学及环境同位素水文地质研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 1995, (4):22-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG504.009.htm Li Wenpeng, Jiao Peixin, Zhao Zhongxian.The hydrology geological research of groundwater chemical and environmental isotope in the hinterland of Taklamakan desert[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1995, (4):22-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG504.009.htm
[14] Edmunds W M.Contribution of isotopic and nuclear tracers to study of groundwaters//Aggarwal P K, Gat J R, Froehlich K F O, (eds.).Isotopes in the Water Cycle:Past, Present and Future of a Developing Science.IEA, Netherland, 2005:171-192.



 下载:
下载: