Late Mesozoic sedimentary-volcanic filling record in Yungang basin and its tectonic implications
-
摘要:
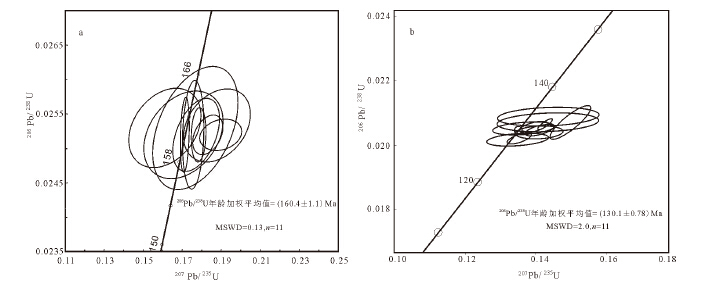
利用凝灰岩夹层及安山岩的锆石U-Pb同位素测年,对云岗盆地晚中生代地层充填序列的关键时限进行了限定。结合地层接触关系、安山岩的地球化学特征,分析了重点地质界面的构造意义。取得了以下主要认识:(1)早中侏罗世,盆地为一套湖进序列的连续沉积,以大同组含煤地层为代表,暗示着区域拉张的构造背景;(2)盆地整体缺失了晚侏罗世(160.4±1.1)Ma至早白垩世(130.1±0.7)Ma的沉积地层,其发生的动力学背景可能与古太平洋、西伯利亚、特提斯同时向东亚大陆汇聚产生的远程效应有关;(3)旧高山安山岩形成于早白垩世(130.1±0.7)Ma大陆板内裂谷的构造背景,与华北克拉通破坏的动力学背景紧密相关。研究成果对旧高山安山岩时代归属提出了新的认识,并不归属于上侏罗统髫髻山组,而相当于下白垩统张家口组。
Abstract:Based on regional stratigraphic correlation and using zircon dating method of tuff layer and andesite rocks in the Late Mesozoic stratigraphic sequence, the authors defined the key time of the sedimentary-fill record. According to the formation contact relationship and the geochemical characteristics of the andesite, the authors also analyzed the tectonic significance of the key geological interface. Some conclusions have been reached:(1) During the Early-Middle Jurassic, the sedimentary sequence was characterized by a suite of lake transgression sequence with the coal-bearing strata of Datong Formation, indicating the tectonic setting of the regional extension; (2) These strata had no sedimentary record from Late Jurassic (160.4±1.1 Ma) to Early Cretaceous (130.1±0.7 Ma), which was dynamically associated with far field effects produced by synchronous convergences toward the east Asia continent of different plates (Siberia, Paleo-Pacific, Tethys); (3) The andesite of Jiugaoshan was developed in the tectonic setting of the continental rift during the Early Cretaceous, which might have been associated with the destruction of the North China Craton. The andesite age of Jiugaoshan was defined in the study. It does not belong to the Tiaojiashan Formation, but corresponds to the Zhangjiakou Formation in Yanshan area.
-
Keywords:
- Yungang basin /
- Jiugaoshan /
- Late Mesozoic /
- tuffaceous carbonate /
- andesite /
- zircon U-Pb isotopic age
-
1. 引言
在资源枯竭、经济发展和环境保护的三重压力下,寻找并开发利用新型清洁能源是关系国计民生和社会可持续发展的紧迫任务。推动绿色发展,构建清洁、安全、高效的能源体系已成为时代的要求。地热资源作为清洁能源的重要组成部分被寄予厚望。
天津市地热资源条件优越,地热开发利用水平一直处于全国前列。天津地热勘查研究工作开始于20世纪70年代,李四光同志主导的天津地热会战掀起了全国地热勘查研究的第一个春天,并发现了新近系和奥陶系两个热储。80年代以来,在市政府和原地矿部的支持以及联合国开发计划署的援助下,地热勘查开始向深部基岩热储发展,先后完成王兰庄、山岭子、塘沽地区三个地热田的勘查工作。自此之后,天津的地热研究与开发工作一直处于中国前列。先后发现地热田8个,已发现两大类6个热储,即孔隙型热储(新近系明化镇组、馆陶组热储和古近系东营组)和裂隙溶隙型热储(奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储),3000 m以浅年可开采地热流体为7606×104 m3。其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储是天津地热开发的主力储层。随着开发强度不断增大,部分地区开采潜力已达极限(天津地热勘查开发设计院, 2000;Wang, 2008;王继革等,2013)。
随着钻探技术的不断进步和清洁能源需求的持续增长,向地球深部进军,探测深部地热资源、开辟深部热储第二空间、增加可开采资源量,成为保障天津地区地热可持续开发的有效途径之一。为此,2017年以来,中国地质调查局在天津东丽湖地区部署了深部地热探测工作,并在主力储层下部探获雾迷山组二段高产能新储层。本文主要介绍天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储探测和高产能地热井参数研究取得的新成果、新进展。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 地热地质背景
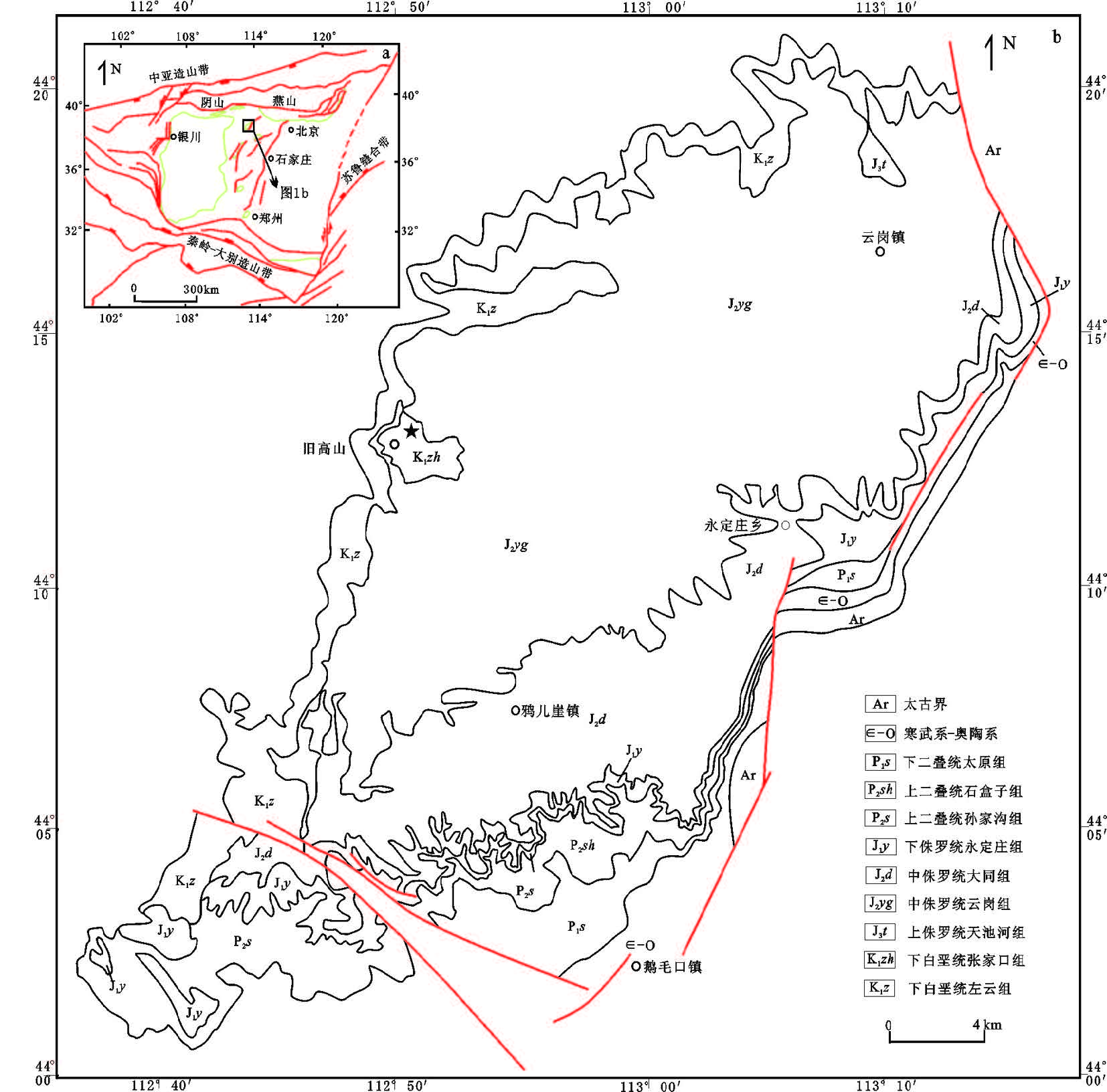
天津市地处Ⅰ级构造单元华北地台北缘,以宁河—宝坻断裂为界分为北部山区和南部平原区。其中,南部平原区属Ⅱ级构造单元华北断坳区,是中、新生代断陷、坳陷盆地。区内Ⅲ级构造单元包括一隆两坳即沧县隆起、冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷。隆起和坳陷及其间分布的诸多Ⅳ级构造单元凸起、凹陷的延伸方向和较大断裂的走向均呈北北东(NNE)向,形成雁行式相间排列的构造格局(陈墨香, 1988)(图 1)。
宝坻—宁河断裂以南为天津南部平原区,总面积8700 km2,地热资源条件优越。发育有王兰庄、山岭子、滨海、武清、潘庄—芦台、宁河—汉沽、万家码头和周良庄等8个地热田,年可开采地热流体7606×104 m3(图 2)。各地热田均位于华北断坳范围内,地面均为第四系松散沉积物覆盖,厚度可达数百米。其下是巨厚的新生界陆相碎屑岩沉积,是一套半胶结的砂岩和泥岩地层,沉积厚度在沧县隆起相对较薄,在冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷沉积较厚,最大厚度可达近万米。在新生界的巨大不整合覆盖之下,主要是古生界和中上元古界的基底地层,在坳陷中还有局部中生界分布。区内地热资源主要赋存于两大类6个储层中:一类为孔隙型热储,包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组和古近系东营组热储;一类为裂隙溶隙型热储,包括奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组热储(张百鸣等, 2006; Wang, 2008)(图 3)。
东丽湖地区位于天津市东部,隶属于天津市东丽区,位于Ⅳ级构造单元潘庄凸起上,发育有著名的山岭子地热田。依据研究区内地热井的钻探资料,揭露的地层从新到老为:新生界(第四系和新近系)、古生界(奥陶系和寒武系)、中新元古界(青白口系和蓟县系)(表 1)。区内已发现新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、奥陶系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段4个热储。其中,雾迷山组三、四段为当前主力储层,沧县隆起上钻孔揭露顶板埋深为1752~2016 m,揭露厚度为480~1032 m,单井出水量为70~120 m3/h,最大可达204 m3/h,出水温度为88~102℃,孔隙度1%~5.8%,渗透率5.52×10-14 m2,水化学类型为Cl · HCO3·SO4-Na或Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na型,总矿化度为1670~2200 mg/L,总硬度为120~240 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值为7.3~8.4(林黎等, 2007; 王继革等, 2013)。从区域地质资料看(高昌,2003;赵苏民等, 2006),区内雾迷山组厚度约3500 m,岩石组合为一套富镁碳酸盐岩,岩性主要为白云岩。燧石条带白云岩、硅质白云岩夹2~5层棕红、紫红色泥岩和页岩,可作为雾迷山组三、四段和一、二段的分界线。从岩性组合的相似性可以推测,雾迷山组一、二段可作为未来深部热储探测的重要方向,也是本次研究的重点。
表 1 天津东丽湖地区综合地层简表Table 1. The simplified table of geological strata in Donglihu area, Tianjin
2.2 开发利用现状
天津地热资源开发利用水平在全国居于较高地位,也是全国中低温地热直接利用规模最大的城市,是全国第一批“中国温泉之都”。自20世纪30年代以来,经过80多年的发展,天津地热资源开发利用从浅到深、从无序到有序、从粗放到精细,逐渐形成了规模化、产业化,在中国地热勘查开发利用史上具有举足轻重的作用。截至2017年,天津市共有地热开采井466眼,年开采总量为5181.08×104 m3,其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段约占开采总量的54%。地热资源主要应用于供暖、洗浴、理疗、旅游、养殖等。其中,供暖是最主要的利用方式,占年总开采量的81.5%。建有地热供暖小区及公建项目496个,全市地热供暖总面积达3500×104 m2,占全市集中供暖面积的8%,是中国利用水热型地热资源供暖规模最大的城市。
东丽湖地区现有地热井34眼。其中,新近系明化镇组4眼,新近系馆陶组2眼,奥陶系3眼,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段25眼。年开采地热流体约395.44×104 m3,采用梯级、综合利用和群井联动回灌的开发模式,达到资源的优化配置和实时调控,地热利用率和回灌率达到95%以上,实现了资源的统一规划、统一开发和统一管理。地热资源广泛应用于供暖、温泉洗浴、养生理疗、康乐旅游、矿泉水开发等领域,建有东丽湖温泉旅游度假区,在发展温泉旅游产业,促进地区经济发展,保护生态环境方面取得了显著的成效。2008年12月25日和2011年12月30日,分别被中国矿业联合会和国土资源部命名为“中国温泉之乡”。
3. 深部热储探测方法
本次研究主要基于地质综合分析,采用地球物理探测、地热钻探、地球物理测井和热储试验相结合的方法开展探测研究。
3.1 地球物理探测
为满足深部储层探测需要,本次地球物理探测的主要目标确定为5 km以浅地层的结构探测,为地热钻探提供依据。由于探测深度大,且存在高压线、铁路等城市干扰源,本次地球物理探测采用了二维地震和时频电磁相结合的勘查方法,其中,时频电磁方法首次应用到地热勘查领域。时频电磁方法是通过大功率人工场源激发信号,测量研究区测线的电磁场分量,分析频率域信号的振幅和相位特征,来获得介质的地电参数(电阻率和极化率),把信号转换到时间域,建立高分辨的电法勘探的时间断面。较传统电磁方法,在应对强电磁干扰方面具有一定的优势(Dong et al., 2008; 周印明等, 2013, 2015)。
本次工作部署时频电磁法完成测线4条,剖面24.4 km,点距200 m,物理点128个;二维地震完成剖面3条,8.25 km,测点254个(图 4)。
地球物理探测结果初步揭示了天津东丽湖地区雾迷山组二段的分布。从TFEM-1测线地质剖面解译图(图 5)可以看出,F1沧东断裂西侧,电阻率异常特征从上至下依次为“低—高—低—高—次高—高”,表层低阻和浅层高、低阻分别是第四系、新近系明化镇组与馆陶组地层响应特征,电阻率过渡连续,无明显的错断。第二套高阻层为寒武系(Є) 与青白口系(Qb)的反映,深部的次高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组4段(Jxw4)的反映,深部的高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组2、3段(Jxw2-3)的反映。蓟县系雾迷山组四段埋深2300~3000 m,下部发育雾迷山组二段和三段地层,埋深在3000 m以下。因缺乏雾迷山组二、三段电性参数,不易进一步细分。从二维地震DZ01剖面解释图(图 6)可以看出,区内4000 m以浅揭示的地层分别为第四系、新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、寒武系、青白口系和蓟县系雾迷山组。新近系馆陶组底界以上主要标准反射界面清晰可辨,以下反射界面呈断续分布。推测第四系底界埋深341~363 m;新近系明化镇组底界埋深1123~1160 m,馆陶组底界埋深1347~1500 m;寒武系张夏组底界埋深1758~2033 m,馒头组底界埋深1786~2113 m,昌平组底界埋深1856~2164 m;青白口系底界埋深2196~2444 m;蓟县系雾迷山组四段底界埋深2802~3004 m,三段底界二段顶界埋深3552~3726 m。4000 m探测深度范围内未揭示蓟县系雾迷山组底界。
3.2 地热科学钻探
在天津东丽湖部署地热科学钻探CGSD-01井,目标层位为蓟县系雾迷山组二段。2017年11月20日开钻,2018年11月19日完钻。成井深度4051.68 m,3715 m进入雾迷山组二段储层,是当时天津最深的地热井。
该井井身结构为三开直井。其中,护壁段(0~76 m)采用Ф660.4 mm冲击钻钻头施工,下入Ф508 mm×8.0 mm无缝套管,总长度为74.42 m。一开井段(76~1469.53 m)采用Ф444.5 mm牙轮钻头钻进,入Ф339.7 mm×J55钢级套管,长度1469.84 m。二开井段(1469.53~2262.75 m)采用Ф311.2 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф244.5 mm×10.03 mm N80钢级套管,长度866.60 m,与一开套管重叠68.12 m。三开井段(2262.75~4051.68 m)采用Ф215.9 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф177.8 mm×9.19 mm N80钢级套管,长度1939.96 m,其中实管长度为1747.23 m,花管长度为192.73 m,与二开套管重叠151.03 m。钻进过程中,开展了岩屑和岩心采集工作。1500 m以浅每5 m捞取岩屑一次,1500 m以深每2 m捞取岩屑一次,全井共计捞取岩屑样1873个。500~4051.68 m井段采取定深分段采取岩心,累计取心37回次,进尺161.25 m,长度140.78 m,采取率85%。
3.3 地球物理测井
钻井过程中,对地热井开展了综合地球物理测井工作,主要包括温度测井、压力测井、井径测井、井斜测井、视电阻率测井、双感应测井、自然电位测井、自然伽马测井、声波测井、伽马-伽马测井和流体流量测井11项。
3.4 热储试验
钻探完成后,为获取蓟县系雾迷山组二段新储层热储参数,对地热井开展了3个落程的稳定流降压抽水试验。其中,大落程试验历时62 h,涌水量130.2 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间39.5 h;中落程试验历时24 h,涌水量94.5 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间16.5 h;小落程试验历时16 h,涌水量43.9 m3/h,水温度稳定在98℃,稳定时间8 h(图 7)。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1 热储结构特征
综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇地层包括:第四系、新近系、寒武系、青白口系及蓟县系。钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储(表 2)。
表 2 天津东丽湖CGSD-01井钻遇地层表Table 2. Geological stratum of well CGSD-01 in the Tianjin
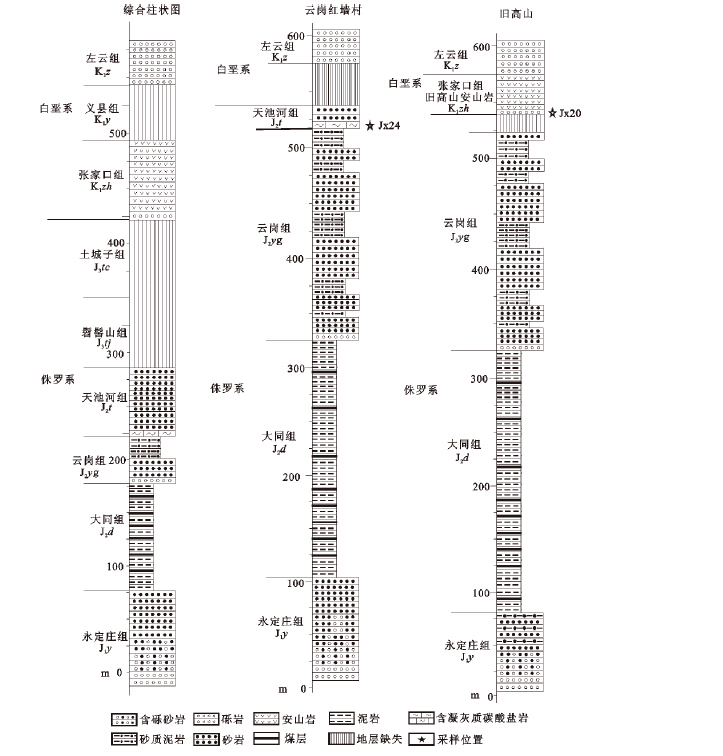
本次研究在地热井中实现雾迷山组四、三、二段精细划分,自上而下叙述如下。
雾迷山组四段(Jxw4):深度段为2258~2896 m,地层厚度638 m。上部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶白云岩,偶见少量深灰色厚层角砾状白云岩、灰白色硅质白云岩等;下部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩交互;底部主要发育灰黑色白云质泥岩夹细晶白云岩、泥晶白云岩、硅质白云岩。受原始沉积及沉积后多期次构造与岩溶作用等影响,雾迷山组四段白云岩层系整体较破碎,钻井岩心中裂隙和溶蚀孔洞极其发育,为地热水提供了良好的储集空间。
雾迷山组三段(Jxw3):深度段为2896~3715 m,地层厚度819 m。上部岩性主要为深灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩、白云质泥岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组三段上部的GR值较雾迷山组四段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也表现出类似特征;雾迷山组三段测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率值,下部整体较上部好(图 8);下部岩性主要发育浅灰—灰黑色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶—泥质白云岩、灰质泥晶白云岩及白云质泥岩;底部以发育一套紫红色泥质白云岩夹浅灰色细晶白云岩为典型特征,厚度约73 m,裂隙不发育,具有隔水—弱透水性质,作为与下伏雾迷山组二段的分界。
雾迷山组二段(Jxw2)深度段为3715~4051 m,地层厚度336 m,未钻穿。与上覆雾迷山组三段相比,雾迷山组二段的岩性及电测特征存在明显的差别(图 8)。岩性特征上,雾迷山组二段上部主要发育浅灰色细晶白云岩夹浅灰色粉晶白云岩、灰黑色泥质白云岩,之上为雾迷山组三段底部紫红色泥质白云岩作为两者明显分界;雾迷山组二段下部主要为浅灰色粉晶白云岩与灰黑色泥质白云岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组二段上部的GR值、自然电位值(SP)较雾迷山组三段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也体现出类似特征;雾迷山组二段上部的深侧向、浅侧向电阻率较雾迷山组三段底部高为特征。雾迷山组二段内部,自下而上,GR值、自然电位值(SP)、深侧向电阻率、浅侧向电阻率及测井解释的泥质含量呈逐渐变小趋势;声波时差呈逐渐变大趋势,测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率呈逐渐变大趋势,指示雾迷山组二段上部的热储层较下部更为发育。
4.2 温度特征
2018年11月19日对CGSD-01井开展了稳态测温。从测温曲线(图 9)可以看出,CGSD-01井底温度105℃。井温总体呈凸型曲线特征,体现了储盖层热传导机制为总体传导型、层间对流型。总体地温梯度2.4℃/100 m。其中,0~400 m第四纪地层地温梯度最高,可达8℃/100 m;400~2300 m新近系与寒武系盖层地温梯度次之,为2.4℃/100 m;2300~3500 m雾迷山组三、四段主力储层受对流作用影响,地温梯度最小,为0.83℃/100 m;3500 m以下雾迷山组二段储层地温梯度为1.7℃/100 m,对流作用较主力储层稍弱。
岩石热物性分析表明,雾迷山组二段岩石热导率在4.33~7.96 W/(m · K)(10个样品,表 3),平均值5.66 W/(m·K),略高于雾迷山组三四段平均值4.37 W/(m·K)。
表 3 CGSD-01井雾迷山组二段热储热导率测试值Table 3. Thermal conductivity test results of Wumishan Formation section 2 in well CGSD-01
4.3 热储参数
热储参数计算主要依据降压抽水试验计算。由于地热水密度与温度具有相关性,造成观测水位不能真实地反映地热井实际水位的变化,这种现象称之为“井筒效应”。资料整理过程中,以储层中部温度102.6℃作为储层温度对试验观测数据进行校准。校正后,做出的动水位埋深曲线如图 10。
采用Dupuit公式与W.Sihart公式对试验数据进行分析计算CGSD-01井的热储参数。本次抽水试验目标热储层为蓟县系雾迷山组二段,厚度336.68 m(未穿透),根据测井数据显示,裂隙厚度为123.1 m。根据降压抽水试验数据及相关校正,地热井基本参数见表 4。计算结果见表 5。依据降压抽水试验计算结果,取三个落程试验平均值可以得出,CGSD-01井单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d。
表 4 CGSD-01井热储参数计算基本参数Table 4. Reservoir parameters of well CGSD-01 表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
4.4 水化学特征
抽水试验过程中,采集样品对雾迷山组二段地热水进行了水化学、同位素和气体成分分析。
水化学分析表明,雾迷山组二段地热水水化学类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1770.0 mg/L,总硬度124.6 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值7.63。
结垢性和腐蚀性表明,地热水不生成碳酸钙垢,不生成硫酸钙垢,不生成硅酸盐垢,对管道及利用设施具有中等腐蚀性。
气体组分测试表明,溶解气体中以氮气和甲烷为主,分别占气体组分含量的66%和27%,还有少量乙烷、丙烷、异丁烷和异戊烷,指示储层处于还原环境。
同位素分析表明,地热水δD为-72‰~-72.7‰,δ18O为9.3‰~-9.5‰,δ13C为-3‰~-3.6‰,87Sr/86Sr为0.7113~0.7114。综合水化学和同位素特征,初步推断雾迷山组二段地热水来源于大气降水,主要发生混合、阳离子交替吸附、碳酸盐岩溶解、硫酸盐还原等作用,且未达到平衡。
4.5 开发利用潜力分析与建议
从区域地质背景和地层沉积序列看,雾迷山二段热储在潘庄凸起区全区均有分布,分布面积约604 km2,依据CGSD-01地热参数井信息,对潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量进行保守估算。年可开采热资源量按照100 a富水段可回收热量的0.01% 进行保守估算,其热量每年折合标煤250万t,初步估计可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
为了提高地热资源利用率,本文建议推广地热利用集约节约新技术,采用地热梯级利用联合水源热泵、地板辐射采暖、群井联动、地热与燃气或太阳能等多能源结合技术,降低尾水排放温度,实现地热资源利用最大化。
5. 结论
(1) 综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储。
(2) 雾迷山组二段上部单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d,岩石热导率5.66 W/(m · K),地热水类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1.7 g/L,热储参数与潘庄凸起三、四段热储相近。
(3) CGSD-01井降压抽水试验结果表明,蓟县系雾迷山组二段单井最大涌水量可达130 m3/h,出水温度100 ℃,单井可满足约30万m2建筑物供暖需求;初步估计潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
(4) 从区域地层沉积规律看,天津地区深部雾迷山组一段、杨庄组、高于庄组,厚度大、岩溶发育,与雾迷山组四、三、二段性质相似,均具有成为高产能新储层的可能性,加强深部地热探测研究意义重大。
-
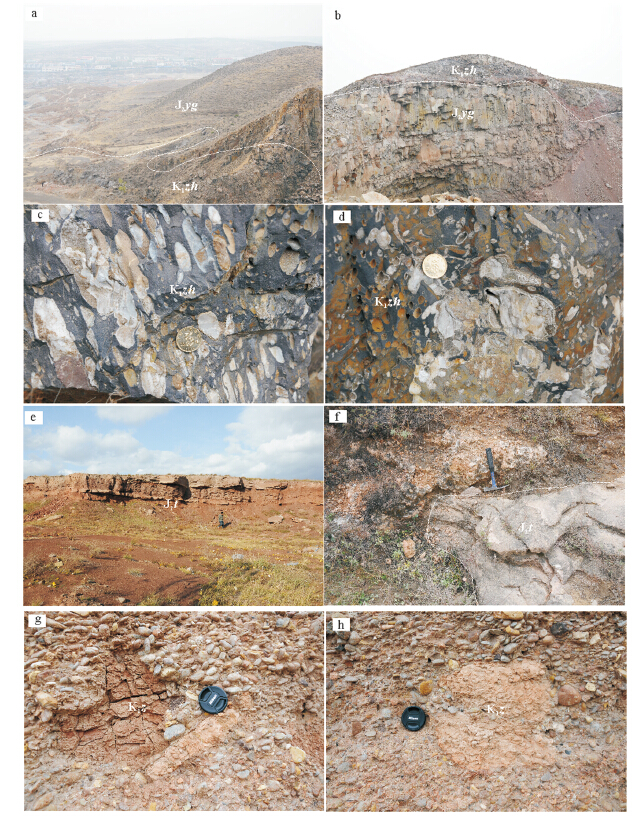
图 3 云岗盆地晚中生代地层野外露头典型照片
a,b—旧高山安山岩与云岗组地层接触关系(大同旧高山);c,d—旧高山安山岩气孔构造(大同旧高山);e—上侏罗统天池河组紫红色砂岩(大 同红墙村);f—上侏罗统天池河组凝灰质碳酸盐岩(大同红墙村);g,h—下白垩统左云组砾岩(左云县盐疙瘩);J2yg—中侏罗统云岗组; K1zh—下白垩统张家口组;J2t—中侏罗统天池河组;K1z—下白垩统左云组
Figure 3. Typical field outcrop photos of late Mesozoic strata in the Yungang basin
a,b-Contact relationship between andesite of Jiugaoshan and Yungang Formation(Jiugaoshan,Datong); c,d-Vesicular structure of andesite (Jiugaoshan,Datong); e-Purplish red sandstone of upper Jurassic Tianchihe Formation (Hongqiangcun,Datong); f-Tuffaceous carbonate of upper Jurassic Tianchihe Formation (Hongqiangcun,Datong); g,h-Conglomerate of the lower Cretaceous Zuoyun Formation (Yangeda,Zuoyun); J2yg-Middle Jurassic Yungang Formation; K1zh-Lower Cretaceous Zhangjiakou Formation; J2t-Middle Jurassic Tianchihe Formation; K1z-Lower Cretaceous Zuoyun Formation
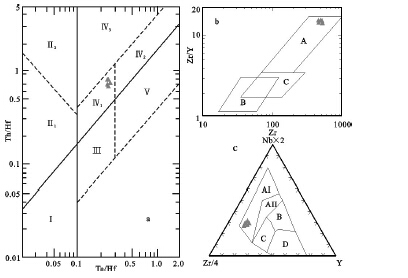
图 8 火山岩大地构造背景判别图
a—Ta/Hf-Th/Hf判别图[48]:Ⅰ—板块发散边缘N-MORB区;Ⅱ—板 块汇聚边缘(Ⅱ1—大洋岛弧玄武岩区;Ⅱ2—陆缘岛弧及陆缘火山弧 玄武岩区);Ⅲ—大洋板内洋岛、海山玄武岩区及T-MORB、EMORB;Ⅳ— 大陆板内(Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷及陆缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩区; Ⅳ2—陆内裂谷碱性玄武岩区;Ⅳ3—大陆拉张带或初始裂谷玄武岩 区);Ⅴ—地幔热柱玄武岩区;b—Zr-Zr/Y判别图[49]:A—板内玄武 岩;B-火山岛弧玄武岩;C—大洋中脊玄武岩; c—Y-Zr/4-Nb×2 判别图:AⅠ—AⅡ-大陆板内碱性玄武岩; AⅡ—C-大陆板内拉斑玄武岩;B—P MORB 洋中脊玄武岩;D— N MORB洋中脊玄武岩;C-D—山岛弧玄武岩
Figure 8. Tectonic setting identification of volcanic rocks
a-Ta/Hf-Th/Hf;b-Zr-Zr/Y; c-Y-Zr/4-Nb×2; a:Ⅰ-Margin of divergent oceanic plate; Ⅱ-Margin of convergent plate(Ⅱ1-Island arc of continental margin; Ⅱ2-Volcanic arc of continental margin); Ⅲ-Oceanic intraplate(Oceanic island and seamount,T-MORB, E-MORB); Ⅳ-Continental intraplate(Ⅳ1-Continental rift, Ⅳ2-tensional zone,Ⅳ3-Collision zone of two continental plates); Ⅴ-Mantle plume; b: A-Intraplate basalts; B-Island arc basalts; C-Mid ocean ridge basalts; c: AⅠ-AⅡ-Intraplate ALKaline basalts; AⅡ-C-Intraplate tholeiites; B-P MORB (Mid-ocean ridge basalts); D-N MORB (Mid-ocean ridge basalts); C-D-Volcanic arc basalts
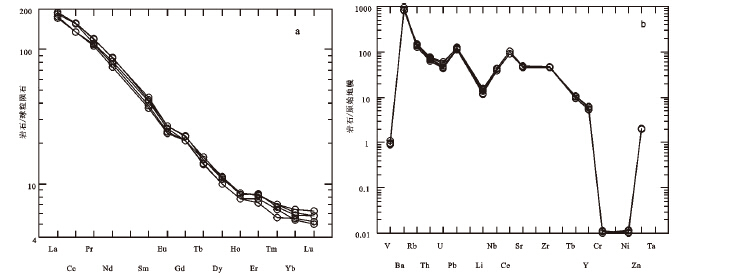
表 1 云岗盆地旧高山安山岩主量元素(%)、微量和稀土元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 1 Analyses of major elements(%),trace elements and REE(10-6) from the andesite of the Jiugaoshan in the Yungang basin

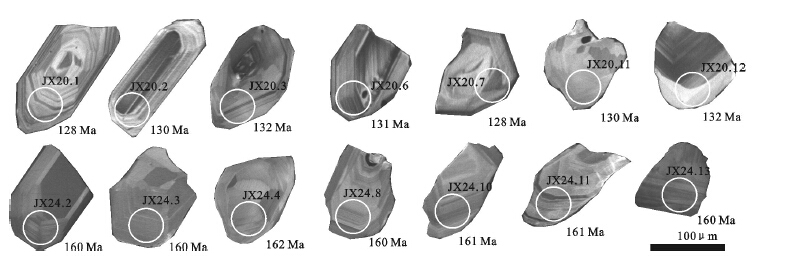
表 2 云岗盆地中侏罗统云岗组含凝灰质碳酸盐岩锆石U-Pb年龄数据(JX24)
Table 2 U-Pb isotope dating results for the tuffaceous carbonate zircons from the Middle Jurassic Yungang Formation in the Yungang basin

表 3 云岗盆地旧高山安山岩锆石U-Pb年龄数据(JX20)
Table 3 U-Pb isotope dating results for the Andesite zircons from the Jiugaoshan in the Yungang basin

-
[1] 赵祯祥,杜晋锋.晋东北地区燕山运动的基本特征——来自1:25万应县幅区域地质调查的总结[J].地质力学学报,2007,13(2):150-161. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200702008.htm Zhao Zhenxiang,Du Jinfeng.Basic Characteristics of the Yanshan movement in northeastern Shanxi——A summary of regional survey of the 1:250000 Yingxian county sheet[J].Journal of Geomechanics,2007,13(2):150-161(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200702008.htm
[2] 山西省地层表编写组.华北地区区域地层表山西省分册[M].北京:地质出版社,1979. Writing Group of Regional Stratigraphic Table of Shanxi Province.Regional Stratigraphic Table of North China-Volume of Shanxi Province[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1979(in Chinese).
[3] 山西省地质矿产局.山西省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社,1989. Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shanxi Province.Regional Geology of Shanxi Province[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House.1989(in Chinese).
[4] 赵越,徐刚,张栓宏,等.燕山运动与东亚构造体制的转变[J].地学前缘,2004,11(3):319-328. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403042.htm Zhao Yue,Xu Gang,Zhang Shuanhong,et al.Yanshanian movement and conversion of tectonic regimes in East Asia[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2004,11(3):319-328(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403042.htm
[5] 翟明国,孟庆任,刘建民,等.华北东部中生代构造体制转折峰期的主要地质效应和形成动力学探讨[J].地学前缘,2004,11:285-298. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403036.htm Zhai Mingguo,Meng Qingren,Liu Jianming,et al.Geological features of Mesozoic tectonic regime inversion in Eastern North China and implication for geodynamics[J].Earth Science Forntiers,2004,11:285-298(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403036.htm
[6] 陈根文,夏换,陈绍清.华北地区晚中生代重大构造转折的地质证据[J].中国地质,2008,35(6):1162-1177. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080612&flag=1 Chen Genwen,Xia huan,Chen Shaoqing.The geological evidences for the tectonic transition in late Mesozoic in North China[J].Geology in China,2008,35(6):1162-1177(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080612&flag=1
[7] 彭楠,柳永清,旷红伟,等.胶莱盆地早白垩世莱阳群沉积物源及地质意义[J].中国地质,2015,42(6):1793-1810. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150610&flag=1 Peng Nan,Liu Yongqing,Kuang Hongwei,et al.Provenance of Early Cretaceous Laiyang Group in Jiaolai Basin and its significance[J].Geology in China,2015,42(6):1793-1810(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150610&flag=1
[8] 杨莉,马伯永,李尚林,等.西藏羌塘盆地东部中侏罗统混合沉积层序地层学研究[J].中国地质,2015,42(4):1037-1045. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150418&flag=1 Yang Li,Ma Boyong,Li Shanglin,et al.An analysis of mixed silicic clastic and carbonate sedimentary sequence in the Middle Jurassic strata in the eastern part of the Qiangtang basin,Tibet[J].Geology in China,2015,42(4):1037-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150418&flag=1
[9] 李猛,王超,李荣社,等北祁连肃南地区阴沟群形成时代及沉积源区讨论——碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J].中国地质,2015,42(3):601-615. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150315&flag=1 Li Meng,Wang Chao,Li Rongshe,et al.Age and provenance of the Yingou Group in Sunan area of North Qilian Mountain:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb Dating[J].Geology in China,2015,42(3):601-615(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150315&flag=1
[10] Davis G A,Wang C,Zheng Y D,et al.The enigmatic Yinshan fold-and-thrust belt of northern China:new views on its intraplate contractional styles[J].Geology,1998,26:43-46. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0043:TEYFAT>2.3.CO;2
[11] Davis G A,Zheng Y D,Wang C,et al.Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt:with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces,northern China[J]//Hendrix,Davis (eds.).Paleozoic and Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia:From Continental Assembly to intracontinental Deformation.Boulder,Colorado.Geological Society of America Memoir,2001,194:1-10.
[12] 郑亚东,Davis G A,王琮,等.燕山带中生代主要构造事件与板块构造背景问题[J].地质学报,2000,74(4):289-302. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200004000.htm Zheng Yadong,Davis G A,Wang Cong,et al.Major Mesozoic tectonic events in the Yanshan Belt and the plate tectonic setting[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2000,74(4):289-302.(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200004000.htm
[13] 董树文,张岳桥,龙长兴,等.中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J].地质学报,2007,81(11):1449-1461. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200004000.htm Dong Shuwen,Zhang Yueqiao,Long Changxiang,et al.Jurassic Tectonic Revolution in China and New Interpretation of the Yanshan Movement[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(11):1449-1461(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200004000.htm
[14] 李三忠,刘建忠,赵国春,等.华北克拉通东部地块中生代变形的关键时限及其对构造的制约——以胶辽地区为例[J].岩石学报,2004,20(3):633-646. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200403027.htm Li Sanzhong,Liu Jianzhong,Zhao Guochun,et al.Key geochronology of Mesozoic deformation in the eastern block of the North China Craton and its constraints on regional tectonics:A case of Jiaodong and Liaodong Peninsula[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2004,20(3):633-646(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200403027.htm
[15] 邓晋福,苏尚国,刘翠,等.华北太行山-燕山-辽西地区燕山期(J-K)造山过程与成矿作用[J].现代地质,2007,21(2):232-240. Deng Jinfu,Su Shangguo,Liu Cui,et al.Yanshanian (Jura-Cretaceous) Orogenic Processes and Metallogenesis of the Taihangshan-Yanshan-West Liaoning Orogenic Belt,North Chin[J].Geoscience,2007,21(2):232-240.
[16] 张长厚,李程明,邓洪菱,等.燕山-太行山北段中生代收缩变形与华北克拉通破坏[J].中国科学(D辑),2011,41(5):593-617. Zhang Chagnhou,Li Chengming,Deng Huangling,et al.Mesozoic contraction deformation in the Yanshan and northern Taihang mountains and its implications to the destruction of the North China Craton[J].Science in China (Series D),2011,41(5):593-617(in Chinese).
[17] Wong W H.Crustal movement and ignous activities in eastern China since Mesozoic time[J].Bulletin of Geological Society of China,1927,6(1):9-36.
[18] Wong W H.The Mesozoic orogenic movement in eastern China[J].Bulletin of Geological Society of China,1929,8:33-44. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1552999594&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[19] 董树文,张岳桥,陈宣华,等.晚侏罗世东亚多向汇聚构造体系的形成与变形特征[J].地球学报,2008,29(3):306-317. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200803006.htm Dong Shuwen,Zhang Yueqiao,Chen Xuanhua,et al.The Formation and Deformational Characteristics of East Asia Multi-Direction Convergent Tectonic System in Late Jurassic[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2008,29(3):306-317(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200803006.htm
[20] 张岳桥,董树文,赵越,等.华北侏罗纪大地构造:综述与新认识[J].地质学报,2007,81(11):1462-1480. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200711003.htm Zhang Yueqiao,Dong Shuwen,Zhao Yue,et al.Jurassic tectonics of North China:a synthetic view[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(11):1462-1480(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200711003.htm
[21] Zheng Y D,Zhang Q,Wang Y,et a1. Great Jurassic Thrust Sheets in Beishan (North Mountain):Gobi Areas of China and Southern Mongolia.Journal of Structural Geology[J],1996,18:1111-1126. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(96)00038-7
[22] 钟福平,钟建华,艾合买提江·阿不都热合曼,等.华北克拉通破坏时间与破坏范围分布特征——来自银根-额济纳旗盆地苏红图坳陷早白垩世火山岩的启示[J].中国地质,2015,42(2):435-456. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150206&flag=1 Zhong Fuping,Zhong Jianhua,Ahmatjan Abdurahman,et al.Timing and scale of the destruction of the North China craton:Revelation from theEarly Cretaceous volcanic rocks in Suhongtu Depression of Inggen-Ejin Banner Basin[J].Geology in China,2015,42(2):435-456(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150206&flag=1
[23] 朱日祥,徐义刚,朱光,等.华北克拉通破坏[J].中国科学(D辑),2012,42(8):1135-1159. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201208002.htm Zhu Rixiang,Xu Yigang,Zhu Guang,et al.Destruction of the North China Craton[J].Science in China (Series D),2012,42(8):1135-1159(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201208002.htm
[24] 徐义刚,李洪颜,庞崇进,等.论华北克拉通破坏的时限[J].科学通报,2009,54:1974-1989. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200914005.htm Xu Yigang,Li Hongyan,Pang Chongjin,et al.On the timing and duration of destruction of the North China Craton[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2009,54:1974-1989(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200914005.htm
[25] Yang J H,Wu F Y,Wilde S A,et al.Mesozoic decratonization of the North China block[J].Geology,2008,36:467-470. doi: 10.1130/G24518A.1
[26] Nasdala L,Hofmeister W,Norberg N,et al.ZirconM257:A homogeneous natural reference material for the ion microprobe U-Pb analysis of zircon[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2008,32:247-265. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2008.32.issue-3
[27] Sláma J,Kosler J,Condon DJ,et al.Plesovice zircon:A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J].Chemical Geology,2008,249:1-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
[28] Sircombe K N.Tracing provenance through the isotope ages of littoral and sedimentary detrital zircon,eastern Australia[J].Sedimentary Geology,1999,124:47-367. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00120-1
[29] 李振宏,董树文,渠洪杰.晋东北侏罗纪盆地早中侏罗世沉积充填记录及其构造意义[J].地球学报,2014,35(3):285-294. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201403003.htm Li Zhenhong,Dong Shuwen,Qu Hongjie.Early-Middle Jurassic basin-fill record of the basin groups in Northeastern Shanxi and Its tectonic implications[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2014,35(3):285-294(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201403003.htm
[30] 李振宏,董树文,冯胜斌,等.鄂尔多斯盆地中-晚侏罗世构造事件的沉积响应[J].地球学报,2015,36(1):22-30. Li Zhenhong,Dong Shuwen,Feng Shengbin,et al.Sedimentary response to Middle-Late Jurassic tectonic events in the Ordos basin s[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2015,36(1):22-30(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] 尹能辉,周安朝.大同旧高山火山岩岩石学特征及构造意义[J].太原理工大学学报,2013,44(5):627-636. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201305018.htm Yin Nenghui,Zhou Anchao.Petrological characteristics and tectonic significance of the Jiugaoshan volcanic rock in Datong,Shanxi Province[J].Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology,2013,44(5):627-636(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201305018.htm
[32] Li Zhenhong,Dong Shuwen,Qu Hongjie.Timing of the initiation of the Jurassic Yanshan movement on the North China Craton:evidence from sedimentary cycles,heavy minerals,geochemistry,and zircon U-Pb geochronology[J].International Geology Review,2014,56(3):288-312. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.855013
[33] 张抗.鄂尔多斯断块构造与资源[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社,1989,1-394. Zhang Kang.Faulted block of Ordos and resource[M].Xi'an:Shaanxi Science and Technology Publishing House,1989,1-394(inChinese).
[34] 刘池洋,赵红格,桂小军,等.鄂尔多斯盆地演化-改造的时空坐标及其成藏(矿)效应[J].地质学报,2006,80(5):617-638. Liu Chiyang,Zhao Hongge,Gui Xiaojun,et al.Space-time coordinate of the evolution and reformation and mineralization response in Ordos basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2006,80(5):617-638(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 彭向东,徐仲元,刘正宏.大青山地区侏罗纪陆相沉积盆地形成、迁移及演化规律[J].世界地质,2001,20(3):231-236. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200103003.htm Peng Xiangdong,Xu Zhongyuan,Liu Zhenghong.The formation,moving and evolution pattern of Jurassic terrestrial deposit basin in Daqingshan region[J].Global Geology,2001,20(3):231-236(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200103003.htm
[36] 彭向东,徐仲元,刘正宏.内蒙古大青山地区中、上侏罗统大青山组的修订[J].地层学杂志,2003,27(1):67-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200301012.htm Peng Xiangdong,Xu Zhongyuan,Liu Zhenghong.Revision of the Middle and Upper Jurassic Daqingshan Formation in Daqingshan area,Inner Mongolia[J].Journal of Stratigraphy,2003,27(1):67-70(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200301012.htm
[37] Swisher C C,Wang X L,Zhou Z H.New evidence of the Yixian Formation isotopic age and the 40Ar-39Ar dating of the Tuchengzi Formation[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2001,46(23):2009-2013. doi: 10.1007/BF02901918
[38] Cope T C.Sedimentary Evolution of the Yanshan fold-thrustbelt,Northeast China[M].California:Stanford University,2003:1-230.
[39] Gao S,Rudnick R L,Yuan H L,et al.Recycling lower continental crust in the North China Craton[J].Nature,2004,432:892-897. doi: 10.1038/nature03162
[40] 和政军,李锦轶,牛宝贵,等.燕山-阴山地区晚侏罗世强烈推覆-隆升事件及沉积响应[J].地质论评,1998,44(4):407-418. He Zhengjun,Li Jinyi,Niu Baogui,et al.A Late Jurassic intensive thrusting-uplifting event in the Yanshan-Yinshan area,northern China,and its sedimentary response[J].Geological Review,1998,44(4):407-418(in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] 和政军,王宗起,任纪舜.华北北部侏罗纪大型推覆构造带前缘盆地沉积特征和成因机制初探[J].地质科学,1999,34(2):186-195. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX902.005.htm He Zhengjun,Wang Zongqi,Ren Jishun.A preliminary research on sedimentary features and genetic mechanism of frontal basins before Jurassic large-scale nappe in the northern region of North China[J].Scientia Geologica Sinica,1999,34(2):186-195(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX902.005.htm
[42] 徐洪林,张德全,孙桂英.胶东昆嵛山花岗岩的特征、成因及其与金矿的关系[J].岩石矿物学杂志,1997,16(2):131-143. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW702.003.htm Xu Honglin,Zhang Dequan,Sun Guiying.Chracteristics and genesis of Kunyushan granite and relation with gold deposits in Jiaodong[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,1997,16(2):131-143(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW702.003.htm
[43] 肖庆辉,刘勇,冯艳芳,等.中国东部中生代岩石圈演化与太平洋板块俯冲消减关系的讨论[J].中国地质,2010,37(4):1092-1101. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100422&flag=1 Xiao Qinghui,Liu Yong,Feng Yanfang,et al.A preliminary study of the relationship between Mesozoic lithosphere evolution in eastern China and the subduction of the Pacific plate[J].Geology in China,2010,37(4):1092-1101(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100422&flag=1
[44] 李三忠,张国伟,周立宏,等.中、新生代超级汇聚背景下的陆内差异变形:华北伸展裂解和华南挤压逆冲[J].地学前缘,2011,18(3):79-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201103012.htm Li Sanzhong,Zhang Guowei,Zhou Lihong,et al.The opposite Meso-Cenozoic Intracontinental deformations under the superconvergence:Rifting and extension in the North China Craton and shortening and thrusting in the South China Craton[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2011,18(3):79-107(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201103012.htm
[45] 葛肖虹,马文璞,刘俊来,等.中国区域大地构造学的研究展望[J].中国地质,2013,40(1):61-73. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130104&flag=1 Ge Xiaohong,Ma Wenpu,Liu Junlai,et al.Prospect of researches on regional tectonics of China[J].Geology in China,2013,40(1):61-73(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130104&flag=1
[46] 崔建军,张岳桥,董树文,等.华南陆缘晚中生代造山及其地质意义[J].中国地质,2013,40(1):86-105. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130106&flag=1 Cui Jianjun,Zhang Yueqiao,Dong Shuwen,et al.Late Mesozoic ore genesis along the coast of Southeast China and its geological significance[J].Geology in China,2013,40(1):86-105(in Chinese with English abstract). http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130106&flag=1
[47] Langmuir A D.William Farr:founder of modern concept of sofsurveillance[J].International Journal of Epidemiology,1976,5(1):13-18. doi: 10.1093/ije/5.1.13
[48] 汪云亮,张成江,修淑芝.玄武岩形成的大地构造环境的Th/Hf-Ta/Hf图解判别[J].岩石学报,2001,17(3):413-421. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm Wang Yunliang,Zhang Chengjiang,Xiu Shuzhi.Th/Hf-Ta/Hf indentification of tectonic setting of basalts[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2001,17(3):413-421(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm
[49] Meschede,M.A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites using the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J].Chemical Geology,1986,56:206-218. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222365828_A_method_of_discriminating_between_different_types_of_Mid-Ocean_Ridge_Basalts_and_continental_tholeiites_with_the_Nb-Zr-Y_diagram
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 何沛欣. 广东省粤中断裂型碳酸盐岩地热水的水文地球化学研究——以马星-隔陂地热系统为例. 广东化工. 2024(05): 67-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王君照,李胜涛,岳冬冬,张秋霞,李菊红,崔俊艳,杨骊. 基于GIS与GOCAD的天津双窑凸起构造区热储三维地质建模. 科学技术与工程. 2023(14): 5887-5902 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程正璞,雷鸣,李戍,连晟,魏强. 天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储时频电磁法探测及有利区预测. 华北地质. 2023(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 岳冬冬,贾小丰,张秋霞,冯昭龙,李胜涛. 天津山岭子地热田蓟县系雾迷山组热储流体同位素特征及其指示意义. 华北地质. 2023(02): 45-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘杰,宋美钰,胥博文,阮传侠,石峰. 天津市馆陶组地热流体可采量计算方法及适宜性分区研究. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1655-1666 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 杨吉龙,汪大明,牛文超,相振群,刘洋,赵泽霖,程先钰. 天津地热资源开发利用前景及存在问题. 华北地质. 2022(03): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王婷灏,汪新伟,毛翔,罗璐,高楠安,刘慧盈,吴陈冰洁. 沧县隆起北部地区地热资源特征及开发潜力. 中国地质. 2022(06): 1747-1764 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: