Geological background and accumulation models of gas hydrate reservoir in northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
中国南海北部陆坡区是天然气水合物成藏的理想场所,资源潜力巨大。文章基于天然气水合物勘探成果,结合南海北部天然气水合物成藏地质背景,从天然气水合物成藏的温压稳定条件、气源形成条件、构造输导条件和沉积储集条件4方面,系统分析了南海北部天然气水合物成藏的基本地质条件,探讨了南海北部陆坡中部神狐海域、南海北部陆坡西部海域和南海北部陆坡东北部海域天然气水合物的成藏类型与成因模式。结果认为,南海北部陆坡中部神狐海域主要发育扩散型水合物,而南海北部陆坡西部海域主要发育渗漏型水合物,南海北部陆坡东北部海域则发育兼具扩散型与渗漏型特征的复合型水合物。
Abstract:Exploration results reveal that the northern slope of South China Sea (SCS) is a favorable area for gas hydrate accumulation and hence has huge energy resources potential. Based on the results of gas hydrate exploration conducted in northern SCS and geological background of gas hydrate reservoir in the study area, the authors analyzed the conditions of temperaturepressure stability, gas source supply, migration conduction system and reservoir for gas hydrate accumulation in northern SCS. Moreover, the accumulation models of gas hydrate reservoir in Shenhu, the western slope of South China Sea areas and the northeastern slope of South China Sea areas were discussed as well. The results show that the diffusion gas hydrate reservoir is mainly accumulated in Shenhu area, while the western slope of South China Sea area is dominated by the leakage type of reservoir. On the northeastern slope of South China Sea area, gas hydrate accumulation is complex and is characterized by both diffusion and leakage types.
-
1. 引言
下扬子地区包括长江中下游和江南造山带两个构造单元(图 1a),以广泛发育燕山期岩浆作用为特点。对其中长江中下游地区的研究表明,岩浆事件主要可分为4期:第一期为145~135 Ma,包括发育在断隆区的高钾钙碱性闪长岩类,一般具有埃达克岩特征;第二期为135~128 Ma,以发育在断凹区的橄榄安粗岩系火山岩和双峰式火山岩为主;第三期为127~123 Ma,主要为A型花岗岩;第四期为109~101 Ma,以宁镇地区的中酸性侵入岩为主(毛景文等,2004;周涛发等,2008;闫峻等,2012;薛怀民等,2013;关俊朋等,2015;薛怀民等,2016;王继强等,2017;王存智等,2018;陈俊等,2018)。
![]() 图 1 大地构造位置图(a)、区域构造略图(b,据陈芳等,2014修改)及岩体地质简图(c)Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Lower Yangtze region showing the location of the studied area(a); tectonic sketch map of the studied area(b, after Chen Fang et al., 2014); and geological sketch map of the Yaocun pluton(c)
图 1 大地构造位置图(a)、区域构造略图(b,据陈芳等,2014修改)及岩体地质简图(c)Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Lower Yangtze region showing the location of the studied area(a); tectonic sketch map of the studied area(b, after Chen Fang et al., 2014); and geological sketch map of the Yaocun pluton(c)江南造山带的燕山期岩浆岩分布更加广泛,近年来大量的高精度年代学资料显示,皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆活动可分为两期:分别为152~137 Ma和136~122 Ma(Wu et al., 2012; 闫峻等,2017)。早期以花岗闪长岩为主,属于高钾钙碱性系列I型花岗岩(薛怀民等,2009;周翔等,2012;Wu et al., 2012;周洁等,2013);晚期以正长花岗岩为主,少量二长花岗岩,多数具有A型花岗岩的特征(薛怀民等,2009;Wu et al., 2012;Zhou et al., 2013;陈芳等,2014; 高冉等,2017)。
但是,目前对于皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆岩的研究多集中在皖南山区,对于北东段的工作明显偏弱,特别是关于姚村岩体的研究,仅有一个较为可靠的年代学资料(Wu et al., 2012)。本次工作对姚村岩体开展了详细的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、全岩主量和微量稀土元素、Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素组成的研究工作,以深入探讨姚村岩体的岩石成因类型、物质来源及构造环境。
2. 地质背景及岩体地质特征
下扬子地区位于扬子板块东部,其北和西北部以襄樊—广济断裂、郯庐断裂为界与大别造山带相邻,南以江绍断裂为界与华夏地块相接。通常以江南断裂为界,下扬子地区又可分为北西的长江中下游地区(沿江带)和南东的皖南江南造山带(江南带)两个构造单元(闫峻等,2017)(图 1a)。
姚村岩体位于皖南江南造山带北东段,地理位置处于安徽省郎溪县西南部的姚村乡。研究区内NE向断裂发育,并被少量NW向断裂所切。燕山期岩浆侵入活动强烈,多以中大型岩基或者复式岩体出露,如太平—黄山岩体、九华山岩体、刘村岩体及姚村岩体等(图 1b)。
姚村岩体呈北东向椭圆状侵入于志留系砂泥岩中(图 1c),出露面积约107 km2。岩体与围岩界线清晰,接触面呈波状或锯齿状,均外倾。接触带热变质作用强烈,形成宽500~1000 m角岩带。岩体边部局部发育宽窄不等的冷凝边,并偶见角岩化的砂岩捕虏体。姚村岩体主要由中心相的中粗粒正长花岗岩和边缘相的细粒似斑状正长花岗岩组成,两者呈渐变过渡关系,晚期还有细粒花岗岩侵入。
中粗粒正长花岗岩呈浅灰-肉红色,块状构造,中粗粒花岗结构(图 2a),局部呈似斑状。主要矿物成分为石英(30%~35%),斜长石(10%~15%,可见聚片双晶),条纹长石(45%~55%),黑云母(2%~5%)(图 2b)。副矿物有锆石、磷灰石、褐帘石等。
细粒似斑状正长花岗岩呈肉红—浅肉红色,块状构造,似斑状结构(图 2c)。斑晶以石英为主,次为钾长石。基质呈细粒结构,由条纹长石(45%~50%)、石英(25%~35%)、斜长石(10%~20%)及少量黑云母(2%~5%)组成(图 2d)。副矿物有锆石、磷灰石等。
3. 分析测试方法
全岩粉末样处理及锆石挑选工作在河北省廊坊辰昌岩矿检测技术服务有限公司进行,锆石制靶及阴极发光(CL)照相在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。
全岩主量和微量元素分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成,其中主量元素采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测定(仪器型号:PE300D),并采用等离子光谱和化学法测定进行互检。微量元素和稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)测定(型号:PW4400),同时分析2个国家标样(GSR3和GSR5)和3个平行样以保证分析结果的准确度,分析精度相对误差符合行业标准。
全岩Sr-Nd同位素在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。根据微量元素中Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd含量称取适量样品于Teflon闷罐中,加入87Rb-84Sr和149Sm-150Nd混合稀释剂并用HF、HNO3和HClO4充分溶解后用离子交换树脂分离出Rb、Sr、Sm和Nd,在ISOPROBE-T热电离质谱仪(TIMS)上测试。整个分析流程实验本底为:Rb、Sr < 100×10-12;Sm、Nd < 50×10-12。
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,锆石定年分析所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀所用斑束直径为25 μm,频率为10 Hz,能量密度约为2.5 J/cm2,以He为载气。LA-MC-ICP-MS激光剥蚀采用单点剥蚀的方法,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M127为外标进行校正。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal程序(Liu et al., 2008, 2010),锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot3.0程序获得(Ludwig, 2003)。详细参数及实验测试过程参见侯可军等(2009)。
锆石Hf同位素分析测试工作在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室完成。该项分析是在锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年的基础上,参照锆石CL图像,选择在原年龄测点位置或附近进行,所用仪器为New-wave UP193激光剥蚀系统及其相连接的Thermo Neptune Plus多接收等离子体质谱仪,以He作为载气,分析中使用的激光束斑直径为44 μm,频率为8 Hz,剥蚀时间为26 s,采用MT作为外部标样,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282530±0.000030。εHf(t) 计算采用的176Lu的衰变常数为1.865×10-11(Scherer et al., 2001),球粒陨石176Hf/177Hf=0.282772,176Lu/177Hf=0.0332(Blichert,1997)。亏损地幔Hf模式年龄(TDM1)采用176Hf/177Hf= 0.283251,176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Vervoot & Blichert-Toft,1999),二阶段Hf模式年龄(TDM2)采用平均大陆壳176Lu/177Hf=0.015计算(Griffin et al., 2002)。
4. 分析结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
对姚村岩体中的中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)进行了锆石U-Pb年代学研究。样品中锆石呈无色和淡黄色,形态为柱状,长100~120 μm,宽50~60 μm,长宽比一般在2∶1左右。在锆石阴极发光图像(CL)上(图 3a),所有锆石均发育清晰的震荡环带,显示岩浆锆石的特点。对样品进行了24个点的锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析,定年数据列于表 1。
![]() 图 3 姚村岩体代表性锆石CL图像(a)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)(实线小圈为锆石U-Pb同位素分析点,虚线大圈为Hf同位素分析点)Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons(a) and U-Pb Concordia diagrams of samples(b) from the YaocunA-type granitic pluton. Small solid circles are spots for U-Pb isotope analyses, and big dashed circles are spots for Hf isotope analyses表 1 姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb geochronology results in the Yaocun coarse-grained syenogranite
图 3 姚村岩体代表性锆石CL图像(a)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)(实线小圈为锆石U-Pb同位素分析点,虚线大圈为Hf同位素分析点)Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons(a) and U-Pb Concordia diagrams of samples(b) from the YaocunA-type granitic pluton. Small solid circles are spots for U-Pb isotope analyses, and big dashed circles are spots for Hf isotope analyses表 1 姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb geochronology results in the Yaocun coarse-grained syenogranite
这些锆石中Pb含量较低,变化于2×10-6~10× 10-6,Th含量介于58×10-6~306×10-6,U含量介于89×10-6~372×10-6。Th/U比值为0.60~1.06,均大于0.40,属典型的岩浆成因锆石(Wu and Zheng, 2004)。从测试结果看,样品206Pb/238U表面年龄都较为集中,24个点全部集中在125~135 Ma。但部分点(如1、2、3、4、5、12、13、19、22)207Pb/206Pb年龄与206Pb/238U相差太大,谐和度小于90%,除掉这9个不谐和的数据点外,其他15个点的分析数据在谐和曲线上成群分布(图 3b),206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(127.6 ±1.4)Ma(n=15,MSWD=0.31),代表了姚村岩体的形成时代,属早白垩世岩浆活动的产物。
4.2 全岩地球化学特征
对姚村岩体细粒似斑状正长花岗岩和中粗粒正长花岗岩进行了全岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析,结果列于表 2。姚村岩体均具有较高的SiO2(75.46%~77.55%)和全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量(8.11%~8.75%),较低的TiO2(0.08%~0.22%)、CaO(0.23%~ 0.65%)、MgO(0.07% ~0.29%)和P2O5(0.01% ~ 0.04%)含量。在TAS分类图解中(图 4a),所有样品全部投入花岗岩区域内,属于亚碱性系列。在SiO2-K2O图解中(图 4b),全部落入高钾钙碱性系列。Al2O3含量为11.85%~12.83%(平均12.42%),铝碱比(A/NK)介于1.08~1.18,铝过饱和度(A/CNK)为1.0~1.1,属弱过铝质岩石。
表 2 姚村岩体全岩主量元素(%)、稀土元素和微量元素含量(10-6)Table 2. The content of main elements (%), rare earth elements and trace elements(10-6) of the Yaocun pluton
![]() 图 4 姚村岩体TAS分类图解(a)(据Middlemost, 1994)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Peccerillo et al., 1976)(圆形为中粗粒正长花岗岩,正方形为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 4. Alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and SiO2-K2O diagram(b, after Peccerillo et al., 1976) of the Yaocun pluton(The circle represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the square represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
图 4 姚村岩体TAS分类图解(a)(据Middlemost, 1994)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Peccerillo et al., 1976)(圆形为中粗粒正长花岗岩,正方形为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 4. Alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and SiO2-K2O diagram(b, after Peccerillo et al., 1976) of the Yaocun pluton(The circle represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the square represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)姚村岩体REE总量为125×10-6~241×10-6,在球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素分布图上(图 5a),姚村岩体轻重稀土分馏明显,表现为LREE富集的右倾分布型式,轻重稀土明显分馏,(La/Yb)N=6.40~10.74(平均值为9.46),并且显示强烈的Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.22~0.46)。在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上(图 5b),所有样品具有明显的Rb、U、Th、K、Pb、Nd、Zr、Hf正异常,显著的Ba、Nb、Ta、Sr、P、Ti负异常。
![]() 图 5 姚村岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔的标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(红线为中粗粒正长花岗岩,蓝线为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution diagram of Yaocun pluton (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider (b) Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element date(b) for samples of the Yaocun pluton.(Normalizing values are from Sun & McDonough 1989). (The red line represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the blue line represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
图 5 姚村岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔的标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(红线为中粗粒正长花岗岩,蓝线为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution diagram of Yaocun pluton (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider (b) Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element date(b) for samples of the Yaocun pluton.(Normalizing values are from Sun & McDonough 1989). (The red line represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the blue line represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)4.3 全岩Sr-Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素特征
姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩全岩Sr、Nd同位素测试结果列于表 3。结果显示,姚村岩体具有均一的Sr、Nd同位素组成,87Sr/86Sr初始比值介于0.7098~0.7101,143Nd/144Nd值介于0.512207~0.512253,εNd(t)值变化于-6.2~-5.7,二阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2介于1493~1532 Ma。
表 3 姚村岩体全岩Sr-Nd同位素测试结果Table 3. Sr-Nd isotope compositions of representative samples from the Yaocun pluton
姚村岩体中的中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)锆石Hf同位素分析结果列于表 4。这些岩浆锆石具有相对均一的Hf同位素组成,176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf比值范围较大,分别变化于0.000949~0.001992和0.282303~0.282552,176Hf/177Hf初始比值介于0.282299~0.282548,εHf(t)值介于-13.9 ~ -5,TDM1介于1004~1364 Ma.,TDM2介于1508~2062 Ma。
表 4 姚村岩体(8849-1-1)锆石Hf同位素组成Table 4. Hf isotopic compositions of zircon grains from the Yaocun pluton determined by LA-MC-ICP-MS
5. 讨论
5.1 姚村岩体的成岩年龄
对于姚村岩体的成岩年龄,前人Rb-Sr法曾测得127 Ma的年龄结果(章邦栋,1989),Wu et al.(2012)也获得正长花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb年龄为(127.2±1.9)Ma。本次获得的姚村岩体似斑状正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)锆石U-Pb年龄为(127.6±1.4)Ma,与前人结果在误差范围内一致,代表了姚村岩体的成岩时代。因此,姚村岩体属于皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆活动的晚阶段,和带内其他A型花岗岩的侵入时代一致。
5.2 岩石类型
根据不同的源岩性质一般将花岗岩被分为I型、S型、M型(Whalen et al., 1987; Bonin, 2007)。而A型花岗岩最先由Loiselle和Wones(1979)提出,用来定义一类碱性(Alkaline)、无水(Anhydrous)、非造山(Anorogenic)的花岗岩,具有特殊的地球化学特征(Loiselle & Wones, 1979)。
姚村岩体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量(8.11%~8.75%)、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)比值(0.84~0.92)、高场强元素和稀土元素含量,同时具有较低的Ba、Sr、Ti和Eu含量,这些地球化学特征与典型的A型花岗岩类似(Loiselle & Wones, 1979; Whalen et al., 1987; Bonin, 2007; Frost & Frost, 2008)。在前人提出的花岗岩类型判别图解中(图 6),包括Na2O-K2O图解(图 6a,据Collins et al., 1982)、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)-SiO2图解(图 6b,据Frost & Frost, 2011)、(Na2O + K2O)/CaO-1000×Ga/Al和Nb-1000×Ga/Al图解(图 6c和图 6d,据Whalen et al., 1987),除个别样品点外,姚村岩体基本落入A型花岗岩范围内。
![]() 图 6 姚村A型花岗岩判别图解(底图a据Collins et al., 1982;底图b据Frost and Frost, 2011; 底图c和d据Whalen et al., 1987)(图例同图 4)Figure 6. Chemical discrimination diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton: (a) Na2O vs. K2O; (b) FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) vs.SiO2; (c) (K2O+Na2O) /CaO vs. 10, 000 Ga; (d) Nb vs. 10, 000 Ga (a after Collins et al., 1982; b after Frost and Frost, 2011; c and d after Whalen et al., 1987). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 6 姚村A型花岗岩判别图解(底图a据Collins et al., 1982;底图b据Frost and Frost, 2011; 底图c和d据Whalen et al., 1987)(图例同图 4)Figure 6. Chemical discrimination diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton: (a) Na2O vs. K2O; (b) FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) vs.SiO2; (c) (K2O+Na2O) /CaO vs. 10, 000 Ga; (d) Nb vs. 10, 000 Ga (a after Collins et al., 1982; b after Frost and Frost, 2011; c and d after Whalen et al., 1987). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4另外,根据Watson and Harrison(2005)提出的锆饱和温度计,计算得到的姚村岩体成岩温度为785 ~ 899℃(平均827℃),指示姚村岩体形成温度较高,与典型A型花岗岩类似,而明显高于一般的I型和S型花岗岩的锆石饱和温度(< 800℃)。因此,姚村岩体为A型花岗岩。
5.3 岩石成因及源区性质
尽管A型花岗岩一般认为形成于伸展的构造环境,但是对其成因过程还存在不同认识,主要有两种模式:(1)幔源玄武质岩浆的结晶分异,并伴随或不伴随地壳混染(Loiselle & Wones, 1979; Turner et al., 1992;Mushkin et al., 2003; Bonin, 2007);(2)特殊地壳原岩的部分熔融(Collins et al., 1982; Whalen et al., 1987; Creaser et al., 1991)。
通常由幔源玄武质岩浆结晶分异而成的A型花岗岩一般会和大规模基性岩共生(Turner et al., 1992),并具有亏损的同位素组成(Kemp and Hawkesworth, 2005)。宣城地区暂未发现与第三阶段岩浆作用同时期的基性岩浆岩。同时,姚村岩体εNd(t)值变化于-6.2~ -5.7,εHf(t)值介于-13.9 ~ -5,具有较为富集的同位素组成,据此推断,姚村岩体不是由幔源玄武质岩浆结晶分异而来,其主体上应为壳源岩浆岩。
(La/Sm)N对La以及Zr/Nb对Zr的正相关表明部分熔融可能是控制姚村岩体成因的主要岩浆过程(图 7)。在花岗岩源岩判别图解中,姚村岩体投影于变泥质和变杂砂岩的部分熔融产生的熔体区域内(图 8a),并且排除镁铁质组分的混入(图 8b),表明姚村岩体地球化学特征继承其原岩。
![]() 图 8 姚村岩体源岩判别图解:(a)摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT)-摩尔CaO/(MgO+FeOT)图解(据Altherr et al., 2000); (b)Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O图解(据Sylvester., 1998)(图例同图 4)Figure 8. (a) Molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT) vs. CaO/(MgO + FeOT) and (b) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton (a after Altherr et al., 2000 and b after Sylvester., 1998). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 8 姚村岩体源岩判别图解:(a)摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT)-摩尔CaO/(MgO+FeOT)图解(据Altherr et al., 2000); (b)Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O图解(据Sylvester., 1998)(图例同图 4)Figure 8. (a) Molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT) vs. CaO/(MgO + FeOT) and (b) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton (a after Altherr et al., 2000 and b after Sylvester., 1998). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4下扬子陆块具有“一盖两底”的格局,新太古代—新元古代崆岭群—董岭岩群为“江北型”基底,中新元古代双桥山群—溪口岩群(上溪群)为“江南型”基底(常印佛和董树文等,1996)。姚村正长花岗岩相比于崆岭群灰色片麻岩(Xing et al., 1994;凌文黎等,1998;Ma et al., 2000)及董岭岩群角闪岩(Xing et al., 1994)具有相对较高的Nd同位素。同时锆石Hf同位素显示,崆岭群TTG片麻岩和董岭岩群中锆石Hf同位素组成远比姚村正长花岗岩的锆石Hf同位素要富集(Zhang et al., 2006;Guo et al., 2014;Zhang et al., 2015;Chen et al., 2016),表明以崆岭群和董岭岩群所代表的古老地壳不是岩浆源区。
姚村岩体样品的Nd模式年龄(TDM2=1493~1532 Ma)及锆石Hf模式年龄(TDM2=1508~2062 Ma)表明原岩为中元古代时期物质。在t-εHf(t)图解中,姚村正长花岗岩的εNd(t)值落于双桥山群和溪口岩群的Nd同位素演化线范围内(图 9a),同样在t-εHf(t)图解中,由中元古代地壳部分熔融而成的新元古代花岗岩的Hf同位素演化线范围全部覆盖姚村岩体的εNd(t)值(图 9b)。以上同位素特征表明姚村岩体为这些中元古代地壳物质在约127 Ma时期重熔的产物。
![]() 图 9 姚村岩体全岩εNd(t)-t图解(a, 双桥山群和溪口岩群全岩Nd同位素据Chen & Jahn, 1998)和锆石εHf(t)-t图解(b,新元古代花岗岩锆石Hf同位素据Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013)Figure 9. εNd(t) vs. t diagram (a, after Chen & Jahn, 1998) and εHf(t) vs. t diagram (b, after Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013) of the Yaocun pluton
图 9 姚村岩体全岩εNd(t)-t图解(a, 双桥山群和溪口岩群全岩Nd同位素据Chen & Jahn, 1998)和锆石εHf(t)-t图解(b,新元古代花岗岩锆石Hf同位素据Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013)Figure 9. εNd(t) vs. t diagram (a, after Chen & Jahn, 1998) and εHf(t) vs. t diagram (b, after Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013) of the Yaocun pluton5.4 构造环境
对于华南东部燕山期构造背景,曾存在逆冲推覆成因(Hsü et al., 1988)、岩石圈伸展与软流圈地幔上涌(Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2003)、中生代开始的整个中国东海岸裂谷(Gilder et al., 1991)以及华南中生代地幔柱上升(Deng et al., 2004)等多种不同认识,但目前绝大多数学者已认可古太平洋板块对欧亚板块的俯冲消减作用才是形成华南东南部燕山期花岗质岩石-火山岩的根本动力学机制(Zhou & Li, 2000;Zhou et al., 2006;Li & Li, 2007;Sun et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2011; He & Xu, 2012; Li et al., 2012; 吕庆田等,2019)。
虽然俯冲作用的精细过程还存在多种观点,但对于华南东部(140~125 Ma)的岩浆活动,一般认为形成于伸展的构造环境(Li, 2000; Wang et al, 2003; Zhou et al., 2013; 邢光福等, 2017),皖南江南造山带晚期阶段136~122 Ma的岩浆活动也受控于此构造背景之下(闫峻等,2017)。
姚村A型花岗岩的侵位时代在127 Ma左右,邻区其他A型花岗岩,如刘村岩体(132 Ma,陈芳等,2014)、九华山岩体(130~131 Ma,Wu et al., 2012)、黄山岩体(125~127 Ma,薛怀民等,2009)、伏岭岩体(124 Ma,Zhou et al., 2013)、牯牛降岩体(130 Ma,谢建成等,2012)、铜山岩体(129 Ma, Jiang et al., 2011)、杨梅湾岩体(135 Ma, Yang et al., 2012)、白菊花尖岩体(126 Ma, Wong et al., 2009)、大茅山(126~ 122 Ma, Jiang et al., 2011)、三清山(132~130 Ma, Sun et al., 2015)、灵山岩体(134~132 Ma,Wang et al., 2018)等,年龄均集中在135~124 Ma。
广泛出露的A型花岗岩充分说明此时本区处于弧后的伸展环境(薛怀民等,2009;张舒等,2009;Wu et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2013; 陈芳等,2014;高冉等,2017)。从侏罗纪到白垩纪,随着板片俯冲角度增加,弧后延伸作用逐渐增强(Zhou et al., 2006)。后续的软流圈上涌导致了陆下岩石圈地慢的熔融,产生了大量的玄武质岩浆底侵至下地壳(Zhou & Li, 2000)。玄武质岩浆的底侵为中元古代基底沉积岩的大范围部分熔融提供了热源,从而产生了A型花岗质岩浆。
6. 结论
(1)姚村岩体形成年龄为(127.6 ±1.4)Ma,属早白垩世岩浆作用的产物,对应于皖南江南造山带第二阶段岩浆活动。
(2)姚村岩体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)比值、高场强元素和稀土元素含量,同时具有较低的Ba、Sr、Ti和Eu含量以及较高的锆石饱和温度,表明姚村岩体为A型花岗岩。
(3)全岩Sr-Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素特征指示姚村岩体为下扬子中元古代地壳物质部分熔融的产物,形成于早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲作用之后弧后拉伸环境下。
-
-
Borowski W S, Paull C K, Ussler Ⅲ W. 1999. Global and local variations of interstitial sulfate gradients in deep-water, continental margin sediments:Sensitivity to underlying methane and gas hydrates[J]. Marine Geology, 159(1-4):131-154. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00004-3
Collett T S. 1993.Natural gas hydrates of the Prudhoe Bay and Kuparuk River area, north slope, Alaska[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 77(5):793-812. http://www.mendeley.com/research/naturalgas-hydrates-prudhoe-bay-kuparuk-river-area-north-slope-alaska/
Collett T S, Lee M W, Agena W F, Miller J J, Lewis K A, Zyrianova M V, Boswell R, Inks T L. Permafrost-associated natural gas hydrate occurrences on the Alaska North Slope[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2):279-294. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.12.001
Collett T S, Dallimore S R. 2002. Detailed analysisof gas hydrate induced drilling and production hazards[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conferenceon Gas Hydrates, 47-52.
Collett T S, Ginsburg G D. 1998. Gas hydrates in the Messoyakha gas field of the west Siberian basin-A reexamination of the geologic evidence[J].International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering, 8(1):22-29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-02508-7_6/fulltext.html
Cook, A. E, D. Goldberg. 2008. Extent of gas hydrate filled fracture planes:Implications for in situ methanogenesis and resource potential.Geophysical Research Letters, (35):5.
Dickens G R, Castillo M M, Walker J C G. 1997.Ablast of gas in the latest Paleocene:Simulating firstorder effects of massive dissociation of oceanic methanehydrate[J]. Geology, 25:259-262. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0259:ABOGIT>2.3.CO;2
Holder G D, Malone R D, Lawson W F. 1987. Effects of gas composition and geothermal properties on the thickness and depth of natural-gas-hydrate zone[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1147-1152. doi: 10.2118/13595-PA
He Lijuan, Xiong Liangping, Wang Jiyang. 1998. The Geothermal Characteristics in South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 12(2):87-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199802002.htm
He Jiaxiong, Yao Yongjian, Liu Hailing, Wan Zhifeng. 2008. Genetic types of natural gas and characteristic of the gas source composition in marginal basins of the northern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 35(5):1007-1016(in Chinese with English abstract). http://xueshu.baidu.com/s?wd=paperuri%3A%28fbd58086938a4dd9143150998e1cc7ab%29&filter=sc_long_sign&tn=SE_xueshusource_2kduw22v&sc_vurl=http%3A%2F%2Fen.cnki.com.cn%2FArticle_en%2FCJFDTOTAL-DIZI200805021.htm&ie=utf-8&sc_us=15336929056568001837
He Jiaxiong, Ma Wenhong, Zhu Youhai, Gong Xiaofeng. 2011. Integrated identification and determination of genetic types and accumulation time in the marginal basin of northern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 38(1):145-160(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201101017.htm
He Jiaxiong, Chen Shenghong, Ma Wenhong. Gong Xiaofeng. 2012.The evolution, migration and accumulation regularity of oil and gas in Zhujiangkou basin, northeastern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 39(1):106-118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201201012.htm
Huang Yongyang, Zhang Guangxue. 2009. The Geologic Geophysical Characteristic and Foreground of Gas Hydrate in China Sea[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 95-105(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenhao, Zhang Zhihuan, Li Youchuan, Zhang Gongcheng, Fu Ning. 2014. The development characteristics of source rocks in the main deepwater petroliferous basins of the world and their enlightenment to the study of source rocks in deep-water area of northern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 41(5):1673-1681(in Chinese with English abstract).
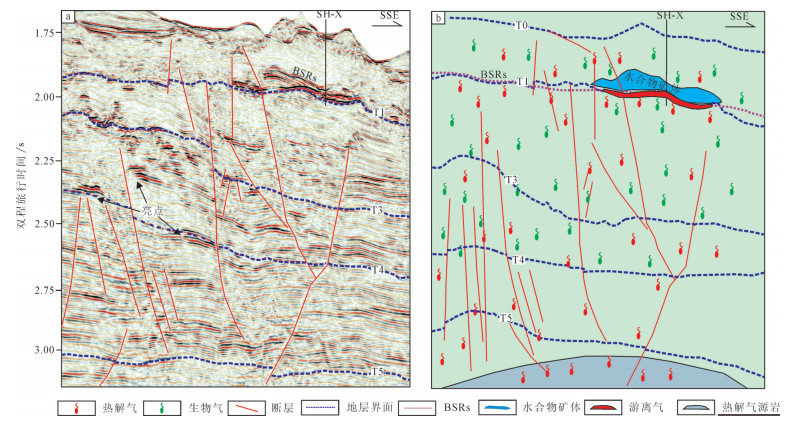
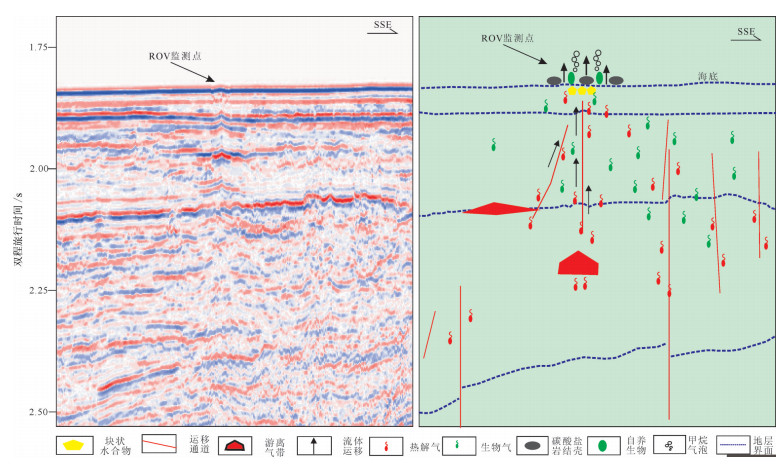
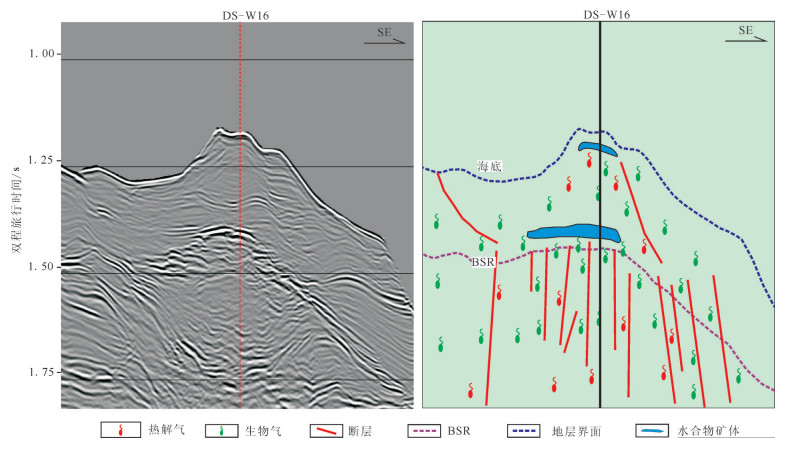
Liang Jianqiang, Zhang Guangxue, Lu Jianan, Su Pibo, Sha Zhibin, Gong Yuehua, Su Xin. 2016. Characteristics and Accumulating Behaviors of Gas Hydrate Reservoirs in the Northeastern Slope of South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 36(10):157-162(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1021/ef970164%2B?src=recsys
Milkov A V, Sassen R. 2001. Estimate of gas hydrate resource, northwestern Gulf of Mexico continental slope[J]. Marine Geology, 179(1):71-83. doi: 10.1007/s00343-010-0097-9
Milkov A V, Sassen R. 2002. Economic geology of offshore gas hydrate accumulations and provinces[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00047-2
Milkov A V. 2004.Global estimate of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments:how much is really out there?[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 66 (3-4):183-197. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2003.11.002
Su Pibo, Lei Huaiyan, Liang Jinqiang, Sha Zhibin, Fu Shaoying, Gong Yuehua. 2010.The Characteristics of Gas Sourse from Shenhu Area and Their Significance for Gas Hydrate formation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 30(10):103-108(in Chinese with English abstract).
Su Pibo, Liang Jinqiang, Sha Zhibin, Fu Shaoying, Lei Huaiyan, Gong Yuehua. 2011. Gas Hydrate Reservoir Simulation of Shenhu Area in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 32(2):226-232(in Chinese with English abstract).
Su Pibo, Liang Jinqiang, Sha Zhibin, Fu Shaoying. 2014.Gas Sources Condition of Gas Hydrate Formation in Shenhu Deepwater Zone[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 36 (2):1-8(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sloan E D, Koh C A. 2008. Clathrate Hydrate of Natural gases, 3d ed[M]. New York, CRC Press, Taylor and Frankcis Group, 721
Sloan E D. 1998. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gas[M]. New York:Marced Dekker, 726.
Torres, M.E. 2008.Methane hydrate formation in turbidite sediments of northern Cascadia, IODP Expedition 311:Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 170-180.
Tréhu A, RUPPEL C, HOLLAND M. 2006.Gas hydrates in marine sediments:lessons from scientific drilling[J]. Oceanography, 19(4):124-142. doi: 10.5670/oceanog
Wu Nengyou, Yang Shengxiong, Wang hongbin. 2009.Gas——bearing fluid influx sub-system for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(6):1641-1650. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract1078.shtml
Xu W, Ruppel C. 1999.Predicting the occurrence, distribution, and evolution of methane gas hydrate in porous marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104:5081-5095. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900092
Yu Xinghe, Zhang Zhijie. 2005. Characteristics of Neogene depositional systems on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea and their relationships with gas hydrate[J]. Geology in China, 32 (3):470-476(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11001-013-9191-7
Yao Bochu. 2001.The Gas Hydrate in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(2):20-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai Guangming, Wang shanshu. 1990. Petroleum Geology of China Vol.16[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press, 101-121(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Guangxue, Zhu Youhai, Liang, jinqiang. 2006.Tectonic Controls on Gas Hydrate Deposits and Their Characteristics[J].Geosciences, 20(4):605-612(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.nsfc.gov.cn/Portals/0/fj/english/fj/pdf/2009/021.doc
Zhang Gongcheng, Mi Lijun, Wu Shiguo. 2007.Deepwater area:The new prospecting targets of nort hern continental margin of South China Sea[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28 (2):15-21(in Chinese with English abstract).
何丽娟, 熊亮萍, 汪集旸. 1998.南海盆地地热特征[J].中国海上油气(地质); 12(2):87-90 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199802002.htm 何家雄, 姚永坚, 刘海龄, 万志峰. 2008.南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及气源构成特点[J].中国地质, 35(5):1007-1016. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080520&flag=1 何家雄, 马文宏, 祝有海, 龚晓峰. 2011.南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及成藏时间综合判识与确定[J].中国地质, 38(1):145-160. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110116&flag=1 何家雄, 陈胜红, 马文宏, 龚晓峰. 2012.南海东北部珠江口盆地成生演化与油气运聚成藏规律[J].中国地质, 39(1):106-118. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120111&flag=1 黄永样, 张光学. 2009.我国海域天然气水合物地质-地球物理特征及前景[M].北京:地质出版社, 95-105. 梁金强, 张光学, 陆敬安, 苏丕波, 沙志彬, 龚跃华, 苏新. 2016.南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物富集特征及成因模式[J].天然气工业, 36(10):157-162. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201610029.htm 李文浩, 张枝焕, 李友川, 张功成, 傅宁. 2014.世界深水含油气盆地烃源岩的发育特征及对中国南海北部深水区烃源岩的启示[J].中国地质, 41(5):1673-1681. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140521&flag=1 苏丕波, 雷怀彦, 梁金强, 沙志彬, 付少英, 龚跃华. 2010.神狐海域气源特征及其对天然气水合物成藏的指示意义[J].天然气工业, 30(10):103-108. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.10.025 苏丕波, 梁金强, 沙志彬, 付少英, 雷怀彦, 龚跃华. 2011.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏动力学模拟[J].石油学报, 32(2):226-232. doi: 10.7623/syxb201102006 苏丕波, 梁金强, 沙志彬, 付少英. 2014.神狐深水海域天然气水合物成藏的气源条件[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 36(2):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201402001.htm 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌. 2009.南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J].地球物理学报, 52(6):1641-1650. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200906028.htm 于兴河, 张志杰. 2005.南海北部陆坡区新近系沉积体系特征与天然气水合物的分布的关系[J].中国地质, 32(3):470-476. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050317&flag=1 姚伯初. 2001.南海的天然气水合物矿藏[J].热带海洋学报. 20(2):20-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY200102003.htm 翟光明, 王善书. 1990. 中国石油地质志(卷十六): 沿海大陆架及毗邻海域油气田[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 101-121. 张光学, 祝有海, 梁金强. 2006.构造控制型天然气水合物矿藏及其特征[J].现代地质, 20(4):605-612. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200604011.htm 张功成, 米立军, 吴时国. 2007.深水区南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J].石油学报, 28(2). doi: 10.7623/syxb200702001 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 张银国,陈建文,龚建明,梁杰,廖晶,王建强,杨长清,赵青芳,孙晶,杨传胜,雷宝华,袁勇. 青岛海洋地质研究所45年来海域油气资源调查进展. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(03): 1-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱清波,王存智,靳国栋,赵希林,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿构造混杂岩露头解剖及其对华南新元古代洋盆演化的启示. 地质通报. 2022(Z1): 388-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 谭满堂,龙文国,魏运许,邓新,田洋,王晶,金巍,徐大良,徐扬,黄皓. 湘东北仓溪岩群锆石U-Pb年龄及新元古代弧盆系演化. 华南地质. 2022(01): 120-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾庆友,林忠良,谢芳军,吴忠如,潘世语. 江西石坞金矿玄武岩地球化学特征及构造意义. 有色金属(矿山部分). 2021(04): 92-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱清波,靳国栋,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿混杂岩带1:50000专题地质图数据库. 中国地质. 2021(S2): 66-77 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 任雪斌,李学森. 赣东北樟树墩-西湾蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩和玄武岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 四川地质学报. 2020(03): 364-370 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘婷,郑有业,王朋冲,杨伟光,郭统军. 豆荚状铬铁矿床成矿地球化学指标对比和成矿作用讨论. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2019(01): 176-183+194 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘婷,郑有业,郭统军. 大中型豆荚状铬铁矿床地球化学特征研究. 地质科技情报. 2019(02): 217-225 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郑涛,黄德志,崔建军,徐益龙,周炜鉴. 皖南伏川SSZ型蛇绿岩的地球化学特征与构造意义. 矿物学报. 2019(03): 281-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 兰锐,徐梦婧. 中国造山带地幔橄榄岩的研究现状. 内蒙古石油化工. 2018(10): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: