-
摘要:
特提斯域是全球最重要的密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床富集区,矿床广泛地分布在陆-陆碰撞造山带两侧的陆块上,就位于碰撞形成的褶皱-逆冲带和前陆带内,成矿通常发生在碰撞挤压作用晚期或之后、区域处于走滑或伸展的阶段。矿床、矿体的就位与张性断裂密切相关,主要控矿因素有蒸发盐底辟构造、碳酸盐岩溶蚀垮塌构造、蒸发盐溶蚀垮塌构造、高孔隙度白云岩、含重晶石地层等。油气流体在许多矿床和矿集区出现,其主要通过与硫酸盐发生反应为铅锌成矿提供还原硫。陆-陆碰撞的大地构造环境、大量的蒸发盐、丰富的油气流体是特提斯域富集MVT矿床的重要原因,域内寻找MVT矿床的潜力巨大。
Abstract:The Tethyan domain hosts the world's most abundant Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) Pb-Zn deposits, which occur in fold-thrust belts and forelands on both sides of the continent-continent collisional zone through the whole Tethyan domain. Mineralization commonly took place when the ore districts were experiencing strike-slip or extensional deformation, which occurred after regional compression or during the late stage of a compressional deformation event. The main ore-controlling factors include extensional faults, evaporite diapir, carbonate dissolution and collapse, evaporite dissolution and collapse, porous dolostone, and barite-bearing strata. Records of hydrocarbon fluids are present in many Pb-Zn deposits and ore districts of the Tethyan domain. They reacted with (dissolved) sulfate to provide reduced sulfur for the ore formation. The generation of such abundant MVT Pb-Zn deposits in the Tethyan domain can be attributed to the continent-continent collisional tectonic setting, large amounts of evaporites, and plentiful hydrocarbon fluids. This study raises the exploration potential for MV TPb-Zn deposits in the Tethyan domain.
-
1. 引言
岩石包体是岩浆在形成、演化和迁移过程中从地下深处携带上来的岩石碎块,是壳幔相互作用和岩浆混合作用的产物(杜杨松等,2004)。包体研究,尤其是中酸性岩体中暗色包体成因研究,目前主要有3种成因类型:①同源岩浆分离(Noyes et al., 1983);②下地壳源区的残留体(Chappell et al., 1987;1992);③基性岩浆和酸性岩浆混合(Perugini et al., 2003;Barbarin,2005;王晓霞等,2005)。但是,在每一种认识中,对岩浆混合机理的认识问题依然有争论。随着研究的逐步深入,越来越多的研究成果显示,大部分暗色包体是岩浆混合的结果(Wiebe et al., 1997;王晓霞等,2005;Yang et al., 2007;Chen et al., 2009;张成立等,2009;Jiang et al., 2010)。目前,在中天山地区尚未见有关岩浆混合作用的报道,尤其是针对环状岩体这种特殊地质体中包体形成机制及其与寄主岩石之间的成因关系研究就少之又少。本次研究发现,在新疆哈密东天山的阿拉塔格铁矿北部,阿拉塔格环状岩体中的酸性岩中发育有大量暗色包体,作者旨在通过对这些暗色包体进行详细的岩石学、岩石地球化学以及U-Pb同位素分析,结合寄主岩石的研究成果(余吉远等, 2013), 探讨这些暗色包体的原始岩浆特征、岩浆混合的方式及成因,为深入研究该环状岩体的岩浆起源、演化及形成动力学背景提供重要依据。
2. 地质背景及环状岩体的基本特征
阿拉塔格环状岩体所处的大地构造位置为中天山构造带卡瓦布拉克地块,北邻康古尔塔格碰撞带和吐哈盆地南缘古生代岛弧,南邻南天山碰撞带和塔里木地块(图 1a)(李锦轶等, 2006), 是研究区出露规模最大、环状形态保存最好的岩体,因附近发现并开采的阿拉塔格铁矿而著名(图 1b)。
![]() 图 1 阿拉塔格岩体地质略图❶(李锦轶等,2006)Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the concentrically zoned Alatage igneous complex ❶ (Li et al., 2006) C2γδο
图 1 阿拉塔格岩体地质略图❶(李锦轶等,2006)Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the concentrically zoned Alatage igneous complex ❶ (Li et al., 2006) C2γδο阿拉塔格环状岩体为一个多期次侵入的杂岩体。经调查,该杂岩体主要包括基性岩体、中性岩体和酸性岩体3个部分。产出形态呈热气球状,岩性分带明显,总体上有从外到内,岩性从酸性岩到中性岩到基性岩的变化趋势。岩体与围岩为明显的侵入接触关系,基性岩与中性岩、酸性岩之间为侵入接触关系。围岩为蓟县系卡瓦布拉克岩群,主要岩性为大理岩、黑云石英片岩、火山碎屑岩等,为低绿片岩相变质,其原岩为碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩夹火山岩。而在酸性岩中发育大量基性岩脉,在中性岩和基性岩中几乎没有脉岩产出。
寄主岩石岩较简单,以二长花岗岩和似斑状花岗岩为主体,少量花岗闪长岩,经过岩石类型投图,寄主岩样品全部落入花岗岩区,与岩性定名基本吻合。在酸性岩体中采集的包体样品全部投入中性岩区域,为闪长质包体。其各岩石样品的镜下特征描述如下:
二长花岗岩(图 2a):肉红色,块状构造,花岗结构,主要组成矿物为钾长石(30%~40%)、斜长石(30%~40%)、石英(15%~30%)、黑云母(5%~15%)。钾长石内部发现有残留体斜长石,粒径从粗到细。斜长石常呈半自形变晶结构,局部有斜长石与钾长石形成的蠕虫结构,粒度粗-细,粒径在10~15 mm,可见环边交代,能见到细粒变晶集合体;石英呈不等粒集合体存在,看不见塑性变形;有少量团块状黑云母残留,细鳞片状集合体,绿泥石化。在粗晶长石之间,粗晶长石与石英集合体之间,都分布蠕虫状的长石,粒径一般为1~2 mm,还有微粒集合体的矿物粒径小于0.2 mm。
似斑状花岗岩(图 2b):浅褐色,似斑状结构,块状构造。钾长石斑晶最大达18 mm,可见环边结构(环边是钾长石的一部分)。主要组成矿物为石英(15% ~20%)、钾长石(30% ~40%)、斜长石(20% ~ 30%)、黑云母(10%~15%)。岩石可分为3个粒级:> 3 mm,1~2 mm和0.1~0.3 mm。大于3 mm粗粒级由条纹长石组成,可见明显环带,内有斜长石残留和石英包体。在斑晶之间充填中、细粒石英和黑云母;1~2 mm中粒级由斜长石和石英组成,石英呈粒状集合体,斜长石呈半自形单体或集合体出现;0.1~0.3 mm细粒级由石英、斜长石和微斜长石细粒集合体组成。
花岗闪长岩(图 2c):浅肉红色-肉红色,块状构造,花岗结构,主要矿物组成为石英(20%~35%)、斜长石(20%~35%)、钾长石(15%~20%)和暗色矿物黑云母(10%~15%)。后期碳酸盐化发育。斜长石为半自形-板柱状,石英、钾长石为他形粒状。局部有团块状石英集合体,少量钾长石与石英组成文象结构。
包体的宏观特征:花岗岩体中发育大量暗色包体,可分为捕虏体和岩浆暗色包体两类。捕虏体仅局部出现在岩体的边部,一般为棱角状或不规则状。岩浆暗色包体分布广泛,但分布极不均匀,在似斑状花岗岩体的东南角最为发育,以闪长质包体为主,是本文研究的对象。它们的形态一般为椭球状、浑圆状,大小不一(图 2e),小者粒径不足1 cm,大者可达50 cm,一般为5~15 cm,粒度明显比寄主岩石细小。包体与寄主岩石的界线清晰,有时可见细粒冷凝边,有时可见包体与寄主岩石成过渡关系,也可见二者构成似条带状构造。一般以细粒结构为主,少量半自形中粒结构,块状构造。部分包体中包含有寄主岩石中的长石斑晶(图 2f),表明包体和寄主岩石代表两种共存但成分截然不同的岩浆。
3. 测试方法
主量元素、微量元素、Sr-Nd同位素均由中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室分析测试。主量元素采用VF320单道荧光光谱仪(XRF)测定,分析精度优于5%。用碱熔法测Fe2O3,用酸溶法测FeO;微量、稀土元素采用Agilent 7500a等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,分析精度优于5%~10%,样品处理流程如下: (1)称取粉碎至大约200目的岩石粉末50 mg于Teflon溶样弹中,并用1.5 mL HNO3+1.5 mL HF在195℃条件下消解48h; (2)将其在115℃条件下蒸干后,用3mL HNO3在195℃条件下再次消解12h; (3)用2% HNO3稀释至约100g,定容于干净的聚酯瓶。详细方法及流程参见文献(Gao et al., 2002)。全岩Sr-Nd同位素分析利用Triton TI型热电离同位素质谱仪(TIMS)完成。样品处理流程如下:(1)称取粉碎至大约200目的岩石粉末50~100 mg Teflon溶样弹中,并用1.5 mL HNO3+ 1.5 mL HF在195℃条件下消解48 h; (2)将其在115℃条件下蒸干后,加入约1 mL HCl; (3)用AG50X8阳离子交换树脂分离Rb、Sr和REE,再用HDEHP萃淋树脂分离Sm和Nd。测得的87Sr /86Sr和143Nd /144Nd比值分别用86Sr/88Sr=0.1194和146Nd/144Nd=0.7219标准化。详细的实验流程和分析方法见文献(Ling et al., 2009)。
锆石样品(包体年龄样编号201311)通过人工重砂、电磁选和双目镜下挑选,锆石的CL图像和LA-ICP-MS法单颗粒锆石微区U-Pb年龄测定是在西北大学大陆动力学教育部重点实验室完成,其中CL发光仪为加载于扫描电镜上的英国Gatan公司的Mono CL3+型阴极荧光探头。LA-ICP-MS分析采用Agilent 7500型ICP- MS和德国LambdaPhysik公司的ComPex102 ArF准分子激光器(工作物质ArF,波长193 nm)以及MicroLas公司的GeoLas 200 M光学系统联机进行。激光束斑直径为30 μm,激光剥蚀样品的深度为20 ~ 40 μm。实验中采用He作为剥蚀物质的载气,用美国国家标准技术研究院研制的人工合成硅酸盐玻璃标准参考物质NIST SRM 610进行仪器最佳化,采样方式为单点剥蚀,数据采集选用一个质量峰一点的跳峰方式,每完成4~5个测点的样品测定,加测标样一次。在所测锆石样品分析15~20个点前后各测2次NIST SRM610。锆石年龄采用国际标准锆石91500作为外标标准物质,元素含量采用NIST SRM610作为外标,29Si作为内标。测试结果通过GLITTER (ver4.0, Mac-quaie University)软件计算得出。详细分析步骤和数据处理方法参见参考文献(Yuan et al.,2004)。
4. 包体地球化学、同位素组成
4.1 主量元素
暗色包体地球化学分析结果见表 1,为了便于对比,引用了寄主岩石(二长花岗岩、似斑状花岗岩和花岗闪长岩)的主量、微量及Sr-Nd同位素结果(余吉远等,2013)。在主量元素上,岩体中暗色岩浆包体的SiO2=56.72% ~61.80%,CaO=3.42% ~ 4.68%,明显比寄主岩石SiO2=66.29% ~77.47%,CaO=0.55%~2.26%更加偏基性。包体的全碱含量(K2O+Na2O=8.12%~10.55%)比寄主岩石的(K2O+ Na2O=6.75% ~9.93%)要高,里特曼指数σ =4.59~ 4.85,较寄主岩石σ =1.32~4.02偏碱性。包体A/NKC=1.16~1.24,寄主岩石A/NKC=1.19~1.50,总体上较为接近,均为过铝质岩石。同时,包体的K2O/ Na2O=0.42~0.66;而寄主岩石的K2O/Na2O=0.21~ 1.36,除一个样品较低外,总体上接近或大于1。包体在SiO2-K2O图上显示为高钾钙碱性系列(图 3),而寄主岩石主体显示为高钾钙碱性-钾玄岩系列。同时他们的SiO2与TiO2、FeO、MgO、CaO、MnO、Na2O、K2O具有良好的线性关系。除了K2O随SiO2的增加而增加外,其他TiO2、FeO、MgO、CaO、MnO、Na2O随SiO2的增加而减少(图 4)。在Al2O3/CaoNa2O/CaO,SiO2/CaO-Na2O/CaO,Al2O3/MgO- SiO2/ MgO,MgO/K2O-CaO/K2O的同分母双比值协变图(图 5)显示,包体和寄主岩之间具有良好的线性关系。莫宣学等(2006)认为岩浆混合作用可以通过岩浆作用的元素和同位素地球化学特征表现出来。这两种协变图中线性变化反映了包体及寄主岩石成分的变化与岩浆的混合作用有关,包体是岩浆混合作用的产物(周珣若,1994)。
表 1 阿拉塔格环状杂岩体中包体和寄主岩的主量元素(%)、微量元素(10-6)组成及有关参数Table 1. Major elements (10-2) and trace elements(10-6)of enclaves and host rocks of Alatage
![]() 图 3 包体及寄主岩石SiO2-K2O图(郭晓冬等,2011)Figure 3. SiO2-K2O diagram of enclaves and host rocks(after Guo et al., 2011)
图 3 包体及寄主岩石SiO2-K2O图(郭晓冬等,2011)Figure 3. SiO2-K2O diagram of enclaves and host rocks(after Guo et al., 2011)4.2 稀土元素特征
从包体及寄主岩稀土元素组成及相关特征参数(表 1)和稀土元素配分模式(图 6a、b)可以看出:包体稀土元素总量较高,∑ REE为294.73 × 10-6~ 426.38×10-6,平均为379.82×10-6; 轻稀土元素富集,LREE为245.27×10-6~347.50×10-6,平均为305.96× 10-6; LREE/HREE为3.73~4.96,(La/Yb)N为2.28~ 3.24,δEu=0.3~0.54、δCe=0.99~1.05,表现为明显的负铕异常,几乎没有铈异常; 相对于暗色包体,寄主岩石的稀土特征值略微偏低,∑REE为315.45×10-6~ 396.45 × 10-6,平均为347.28 × 10-6,LREE/HREE为5.92~7.59,(La/Yb)N为5.26~7.57(均大于4.3),反映具有LREE丰度相对较高的壳源物质参与岩浆作用的特点(董国臣等,2011)。δEu = 0.28~ 0.41、δCe = 0.82~0.86,亦表现出较明显的负铕异常和微弱的铈异常。由图 6可见,包体和寄主岩石的标准化曲线十分相似,它们均表现了轻稀土富集、重稀土平缓的曲线,弱的铕异常。稀土分配曲线型式的整体形态一致,说明它们在成因上有一定的亲缘关系。
4.3 微量元素特征
由包体及寄主岩微量元素分析结果(表 1)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 6c、d)可以看出:相对于原始地幔,包体及寄主岩石微量元素含量均相对富集,Nb、Sr、Ti元素亏损,其中Rb、Th、U、K、La、Ce强烈富集,wB(岩石) /wB(原始地幔)>100; Nd、Hf、Zr、Sm、Tb、Y、Yb、Lu显著富集,10<wB(岩石)/ wB(原始地幔)<100;而Eu则轻微富集,1<wB(岩石)/ wB (原始地幔)<10,表明微量元素在演化过程中发生了明显的分异。相对于寄主岩的似斑状花岗岩,Cr、Ni的含量总体较高,而Ta的含量变化要大,介于1.55~3.01,并表现为从包体向寄主岩有降低的趋势。从微量元素蛛网图(图 6c、d)可以看出,相对于原始地幔,它们明显富集大离子亲石元素(LILE) Rb、U、Sr和Ba及高场强元素(HFSE) Nb、Zr和Hf。包体曲线中出现明显的Ba、Sr、Ti槽和微弱的Nb-Ta槽(图 6d),而寄主岩中出现明显的Ba、Sr、Ti槽、Nb-Ta槽(图 6c)。总体上,二者在蛛网图中的曲线整体形态相似,反映包体微量元素含量与寄主岩石相当。已有的研究表明,同源岩浆的Nb/Ta值相同,在没有外来物质加入的前提下,岩浆演化的Nb/ Ta值可以保持一个定值(王晓霞等,2005)。而本次测得包体的Nb/Ta值为18.78~23.43,比富集地幔的Nb/Ta值(17.7)要高(Sun et al., 1989), 寄主岩的Nb/ Ta值为13.21~16.67,比下地壳的Nb/Ta值(8.3)明显偏高Rudnick,2003;同时微量元素相关图和同分母比值图上呈直线(图 7),这也说明包体岩浆与花岗质岩浆是有联系的,它们之间存在相互混合的关系。这与Nb、Sr、Ti元素亏损代表反映岩浆不同程度地受壳源物质的混染相吻合(董国臣等,2011)。
以上数据表明,包体岩浆可能起源于相对亏损地幔的镁铁质岩浆,微量元素显示的特征主要受下地壳酸性岩浆混染导致的;而寄主岩的岩浆上升侵位过程中,可能受到下地壳酸性岩浆混染。
4.4 同位素特征
4.4.1 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测试及结果
本文测定了闪长质包体中21个单颗粒锆石,共21个点,其测点位置见图 8。分析数据见表 3。暗色包体样品中锆石晶型较完整,为长柱状或短柱状,颗粒较小,一般长100~200 μm,宽50~100 μm。锆石透明度相对较差,透明至半透明,多数为浅黄色,少数为无色。从阴极发光照片(图 8)上可看出闪长质包体中锆石均具清晰的韵律环带结构,表明为岩浆成因(吴元保等,2004);从表 3中可看出包体中锆石的Th/U比值介于0.32~0.55,与前人认为的暗色包体中岩浆成因锆石的Th/U比值大于0.1相符(Hoskin et al., 2000;刘敏等, 2011), 也说明该样品的锆石为岩浆成因。
表 3 阿拉塔格岩体中暗色包体锆石U-Pb分析结果Table 3. U-Pb isotope analyses of zircons from MME OF the Alatage granitic rocks
表6中206Pb/238U年龄数据集中分布于300.1~ 308.4 Ma,所有数据点基本投影在谐和曲线上或其附近(图 9a),用Isoplot 2程序计算得到包体中锆石21个点的206Pb /238U加权平均年龄为(303.7±1.9) Ma (n=21,MSWD =0.33) (图 9b),可能代表了该暗色包体的成岩年龄。
4.4.2 Rb-Sr和Sm-Nd同位素特征
对7件包体作了Sr、Nd同位素测试(表 2)。εNd(t)和(87Sr/86Sr)t计算时采用的年龄值为303.7 Ma。包体和寄主岩石的Sr、Nd同位素组成有一定差异,包体87Sr/86Sr比值为0.711102~0.717918,明显小于寄主岩石的87Sr/86Sr比值0.71691~0.72397(余吉远等,2013);包体143Nd/144Nd比值为0.512629~0.512673,稍高于寄主岩石143Nd/144Nd比值0.512584~ 0.512593;包体和寄主岩石的εNd(t)=1.65~ 2.57,全部为正值,显示岩浆来源于亏损型地幔。而包体和寄主岩石的(87Sr/86Sr)t十分相似,分别为0.705204~ 0.705914和0.705615~0.705630,明显高于0.705,显示地幔物源或下地壳物质部分熔融的源区特征。在εNd(t)-(87Sr/86Sr)t图上图 10,可见全部样品落在大洋玄武岩形成的地幔阵列(mantle array)的右侧,Sr素变化明显,而Nd变化不大,Sr-Nd形成近水平的变化趋势。
表 2 阿拉塔格花岗岩及暗色包体Sr-Nd同位素组成Table 2. Sr-Nd isotopic analyses of Alatage granitic rocks and MME
![]() 图 10 阿拉塔格花岗岩体及包体(87Sr/86Sr)t-εNd(t)图(曹锐等,2012)Figure 10. (87Sr/86Sr)t-εNd(t) diagram of Alatage granites and MME(after Cao et al., 2012)
图 10 阿拉塔格花岗岩体及包体(87Sr/86Sr)t-εNd(t)图(曹锐等,2012)Figure 10. (87Sr/86Sr)t-εNd(t) diagram of Alatage granites and MME(after Cao et al., 2012)5. 讨论
5.1 包体的成因讨论
区域上,该环状杂岩体围岩为蓟县纪卡瓦布拉克岩群,主要岩性有黑云石英片岩、大理岩、火山碎屑岩等,为低绿片岩相变质,其原岩为碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩夹火山岩,与暗色包体在矿物成分和结构构造上差异明显,而且包体中不发育接触变质或接触交代现象;一般情况下,围岩捕虏体多为棱角状,而暗色包体形态多为浑圆状、椭球状,两者在形态上有较大的差别,而且镜下可以观察到典型的岩浆岩矿物组合和结构特点,未见富铝矿物石榴子石、堇青石、红柱石等,亦不具有变晶结构和面理构造等变质岩常见的特征(Rudnick et al., 2003), 因此可以排除暗色包体是围岩捕虏体和地壳深部变质岩残留体的可能性。
暗色包体的分布并非等体积地分布在整个花岗岩体中。在酸性单元的东南角集中分布,这可能与基性岩浆上升部位和基底断裂的扰动有关。这种分布说明包体不同于常见的均匀分布于岩体中的析离体。暗色包体主要呈浑圆状、椭圆状,包体与寄主岩接触界面为明显的圆弧形或港湾状,部分包体被拉长,这些均显示出明显的塑性流变特点,表明包体与寄主岩曾一度同为熔融态。部分暗色微粒包体与寄主岩的界线整体比较清晰,说明是基性岩浆混入酸性岩浆快速冷凝的结果;但有的界线较模糊呈渐变过渡关系,可能说明两种岩浆的温度差别不大,即花岗质岩浆处于过热的状态发生了岩浆混合作用。这说明岩浆混合作用不是简单的单一过程,可能是复杂的多期次作用过程(朱金初等,2006;陈国超,2013)。
因此,包体应是混入花岗质酸性岩浆的镁铁质岩浆固结所形成,是岩浆混合作用的产物,包体和寄主岩是同时或近同时所形成的,这得到了二者相近的锆石U-Pb年龄数据证实。另外,在寄主岩石和包体中都能观察到(图 2b)有钾长石斑晶岀露。从成分上来说,暗色包体的化学成分不适合较大的钾长石斑晶的结晶条件,因此钾长石应该来源于包体之外,是早先结晶的寄主花岗岩浆的斑晶,在镁铁质岩浆和花岗质岩浆混合时被带到镁铁质岩浆中(肖庆辉等,2002)。包体和寄主岩的界线有的截然,也有过渡接触关系,反映了两种岩浆在达到温度平衡后发生了不同程度的物质交换。根据物质交换程度高低,暗色包体的基性程度也不同。
除了宏观特征方面外,在岩浆混合过程中两种岩浆的物质交换可以通过包体与寄主岩的主量及稀土微量元素特征的相似性来判断。主量及微量元素的元素-元素协变图以及同分母双比值协变图良好的线性关系,即为岩浆混合过程中物质交换所致; 而包体与寄主岩石在稀土元素配分模式图、蛛网图上较为一致的变化特征,也正是物质进行充分交换的直观体现(Rudnick et al., 2003)。
在MgO-TFeO演化图(图 11)上,包体和寄主岩不是沿着玄武岩的结晶分异趋势Ⅰ演化,而是位于幔源岩浆和壳源岩浆混合线附近,且还表现出一定的线性关系,反映了形成包体和寄主岩的岩浆不是同源的,显示出包体与寄主岩的混合关系。另外,包体沿着靠近右侧的基性岩浆和壳源岩浆的混合线分布,表明形成包体的岩浆本身没有发生过明显的分离结晶作用。同时,在岩石硅酸盐成分的哈克图上(图 4)投影点呈连续一致的线性关系,在分离结晶作用中多为曲线,而不会是直线,这些图解中直线分布特征反映它们是岩浆混合作用的产物(邹涛等,2011)。
![]() 图 11 包体和寄主岩MgO-TFeO演化图解(Rudnick et al., 2003)Figure 11. Diagram of MgO-TFeO evolution of enclaves and host rocks(after Rudnick et al., 2003)
图 11 包体和寄主岩MgO-TFeO演化图解(Rudnick et al., 2003)Figure 11. Diagram of MgO-TFeO evolution of enclaves and host rocks(after Rudnick et al., 2003)在微量元素方面,包体和寄主岩石的蛛网图、稀土配分图都很相似(图 6),表明岩浆演化过程中微量元素也发生过交换,大离子亲石元素和轻稀土在混合过程中扩散较明显,它们在包体和寄主岩石中含量趋于相似(王晓霞等,2005)。在同位素方面,包体的(87Sr/86Sr)t值、εNd(t)值与寄主岩石的相近(图 10)。这也反映了两种岩浆混合成分交换后均一化现象,这种同位素均一化在很多地区的岩浆混合中普遍存在。同时,包体及寄主岩石的87Sr/86sr和143Nd/144Nd比值均高于原始地幔现代值0.70450(肖庆辉等,2002)和0.512638(邹涛等, 2011), εNd(t)值全是正值,这种高Sr、高Nd的特征不属于典型原始地幔或者典型大陆地壳的Sr-Nd同位素特征,指示岩浆源区为幔源岩浆,在成岩过程中可能有壳源组分的参与。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果表明,包体锆石U-Pb形成年龄为303.7 Ma,与寄主岩石年龄301.5 Ma ❶在误差范围内是一致的,排除了暗色包体为熔融残留体或浅部围岩捕虏体的可能性,同时也排除了基性岩浆在花岗质岩浆固结后才侵入的可能,为岩浆混合作用的存在提供了有力证据。说明阿拉塔格花岗岩体形成于晚石炭世。结合Sr-Nd同位素特征,表明是在后碰撞拉张的构造背景下酸性幔源岩浆在上升过程中发生壳幔混合的结果(余吉远等,2013)。而其中闪长质包体是基性的源岩浆与酸性岩浆不同程度混合的证据。
5.2 地质意义
阿拉塔格环状岩体位于哈萨克斯坦板块南部的晚古生代火山弧,其北侧的康古尔断裂带和沿此带分布的蛇绿岩带代表着晚石炭世碰撞带。阿拉塔格花岗岩体未变形的特征, 表明这类花岗岩是主碰撞和区域构造变形之后的产物,结合其石炭纪年龄数据,认为其形成于大陆碰撞后挤压-伸展转折阶段(Gu et al., 2006)。上述讨论表明, 阿拉塔格花岗岩岩浆在形成时至少出现过两种不同来源的岩浆, 即基性岩浆和酸性岩浆。基性岩浆可能起源于地慢, 底侵于下地壳。在此过程中产生的热和挥发分可能导致中天山造山带基底岩石部分熔融, 形成壳源酸性岩。这些岩体中发育的岩浆暗色包体具有壳幔混源岩浆的特征, 表明在酸性岩浆活动的同时该地区也有基性岩浆的活动。基性岩浆可能是以底侵的方式侵人到地壳的,这种作用本身就造成了地壳的垂向生长。同时, 寄主岩石的εNd(t)值比一般壳源花岗岩高, 表明在花岗岩浆形成过程中有较多的幔源物质参与。包体岩浆与壳源酸性岩浆的混合反映中天山在晚古生代后碰撞阶段有幔源物质通过花岗岩浆作用增添到了地壳中。根据Forst et al.(2001)的估算, 具这种εNd(t)值特征的花岗岩, 提供幔源物源的未出露的基性岩体积至少大于地表出露的花岗岩体积的10个数量级。由此可见, 包体和寄主岩石的特征均反映在晚古生代中天山造山带发生过一定程度的后碰撞地壳垂向生长。
6. 结论
(1) 阿拉塔格环状岩体中暗色岩浆包体SiO2、全碱含量、主要氧化物间线性关系显示,包体具有岩浆混合的岩石学和地球化学特征。
(2) 通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年获得阿拉塔格环状岩体中包体的年龄为(303.7±1.9) Ma,MSWD=0.33;在误差范围内与寄主岩石的301.5 Ma基本一致。
(3) 包体及寄主岩石的同位素所表现出的壳幔混合特征也证实了壳幔岩浆混合作用的存在,而闪长质包体是基性幔源岩浆和酸性幔源岩浆不同程度混合的物质记录。
注释
❶李建星, 余吉远, 孟勇. 1:5万双庆铜矿东幅区域地质调查报告.西安:西安地质调查中心, 2008.
-
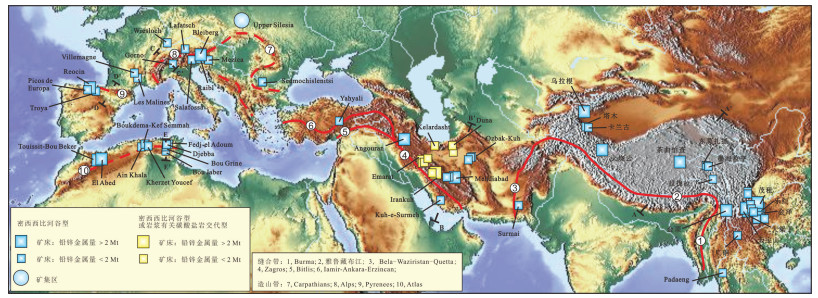
图 1 特提斯域的密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床分布(底图来自http://www.maps-for-free.com/)
Figure 1. Distribution of Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead–zinc deposits in the Tethyan domain (background map after http://www.maps-for-free.com/)
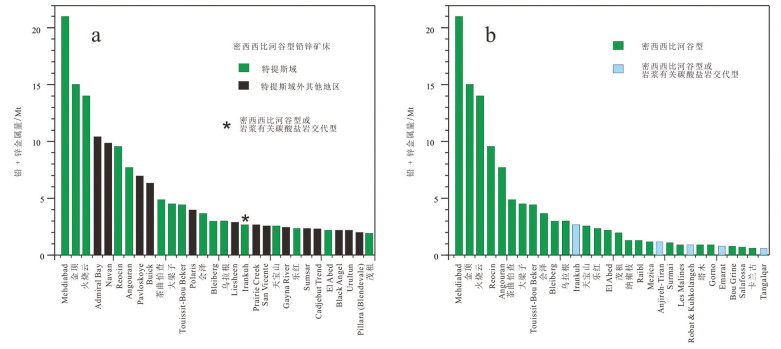
图 2 a-全球金属量排名前30位的密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床(根据表 1数据和Taylor et al., 2009统计,排名未区分储量和资源量的差别);b-特提斯域内金属量排名前30位的密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床(根据表 1数据统计,排名未区分储量和资源量的差别)
Figure 2. a-Top 30 Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead-zinc deposits in the world (based on data from Table 1 and Taylor et al., 2009; this ranking is regardless of category of resources); b-Top 30 Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead-zinc deposits in the Tethyan domain (based on data from Table 1; this ranking is regardless of category of resources)
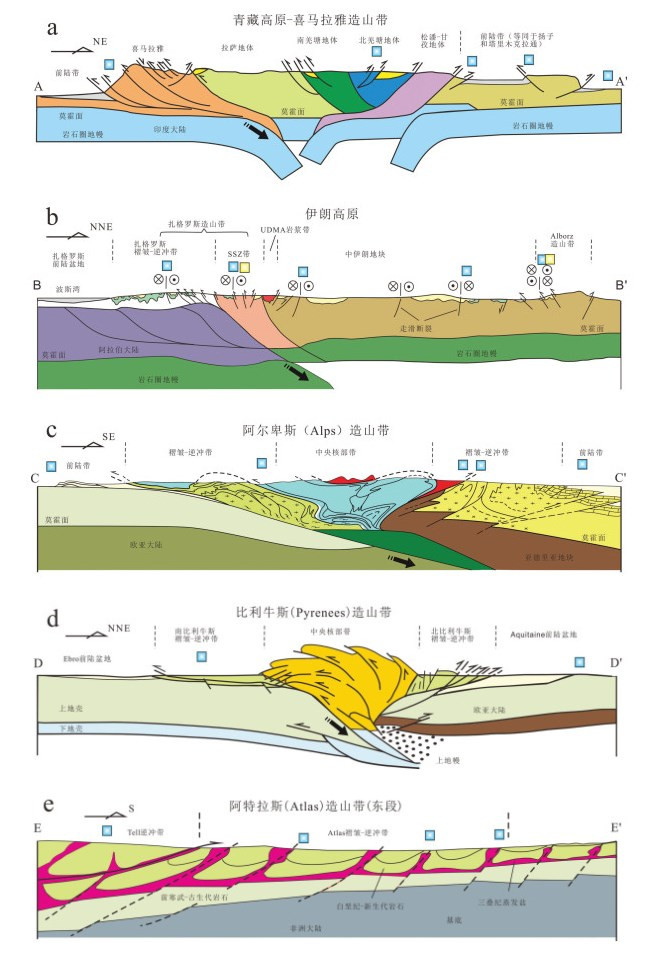
图 3 特提斯域重要陆−陆碰撞造山带剖面及密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床位置(a,据Li et al., 2015修改;b, 据Mouthereau et al., 2012修改;c, 据张洪瑞和侯增谦(2015)修改自Dal Piaz et al., 2003; d, 据Verges et al., 2002修改; e, 据Bouhlel et al., 2016.剖面位置见图 1,矿床图例同图 1)
Figure 3. Simplified geological cross-sections through some important collisional orogens in the Tethyan domain and distribution of Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead–zinc deposits (a, modified after Li et al., 2015; b, modified after Mouthereau et al., 2012; c, based on Zhang and Hou, 2015 modified after Dal Piaz et al., 2003; d, modified after Verges et al., 2002; e, modified after Bouhlel et al., 2016. See locations of the geological cross-sections legends for deposits in Fig. 1)
表 1 特提斯域密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床、矿集区的基本信息
Table 1 General features of Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead-zinc deposits in the Tethyan domain





-
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Whitechurch H, Vrielynck B, Spakman W, Monié P, Meyer B, Wortel R. 2011. Zagros orogeny:A subduction-dominated process[J]. Geological Magazine, 148 (5/6):692-725. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/geological-magazine/...
Ahsan S, Qureshi I. 1997. Mineral/rock resources of Lasbela and Khuzdar Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan[J]. Geol. Bull. Univ. Peshawar, 30:41-51. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0375674202002017
Alavi M. 2004. Regional stratigraphy of the Zagros fold-thrust belt of Iran and its proforeland evolution[J]. American Journal of Science, 304 (1):1-20. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.1.1
Alavi M. 2007. Structures of the Zagros fold-thrust belt in Iran[J]. American Journal of Science, 307(9):1064-1095. doi: 10.2475/09.2007.02
Allen M B, Kheirkhah M, Emami M H, Jones S J. 2011. Right-lateral shear across Iran and kinematic change in the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 184(2):555-574. doi: 10.1111/gji.2011.184.issue-2
Anhui Geological Survey. 2005. Report of 1:250, 000 Wenquan and Songxi Geological Maps[R]. Unpublished, Hefei (in Chinese).
Arlegui L. 2001. Paleostress reconstruction from Striated Fault Data Sets in the Kirthar Fold Belt, Southern Pakistan[J]. Int. Geol. Rev., 43(6):539-547. doi: 10.1080/00206810109465031
Ballato P, Nowaczyk N R, Landgraf A, Strecker M R, Friedrich A, Tabatabaei S H. 2008. Tectonic control on sedimentary facies pattern and sediment accumulation rates in the Miocene foreland basin of the southern Alborz mountains, northern Iran[J]. Tectonics, 27(6), doi:10.1029/2008TC002278, 2008.
Banerjee D M, Mazumdar A. 1999. On the Late Neoproterozoic-Early Cambrian Transition Events in Parts of East Gondwanaland[J]. Gondwana Research, 2(2):199-211. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70145-3
Beales F W, Hardy J L. 1980. Criteria for the recognition of diverse dolomite types with an emphasis on studies on host rocks for Mississippi Valley Type ore deposits[J]. SEPM Special Publication, 28:197-213. http://archives.datapages.com/data/sepm_sp/SP28/Criteria_for_the_Recognition_of_Diverse.htm?q=%2BtitleStrip%3Amississippi+titleStrip%3Aembayment
Bechstadt T. 1978. The lead-zinc deposit of Bleiberg-Kreuth(Carinthia, Austria):Palinspastic situation, paleogeography and ore mineralization[J]. Verhandlungen Geol. Bun'desanstal, 3:221-235. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-03054-7_16
Bechtel A, Pervaz M, Püttmann W. 1998. Role of organic matter and sulphate-reducing bacteria for metal sulphide precipitation in the Bahloul Formation at the Bou Grine Zn/Pb deposit (Tunisia)[J]. Chemical Geology, 144(1/2):1-21. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=10383595
Bechtel A, Shieh Y N, Pervaz M, Püttmann W. 1996. Biodegradation of hydrocarbons and biogeochemical sulfur cycling in the salt dome environment:inferences from sulfur isotope and organic geochemical investigations of the bahloul formation at the Bou Grine Zn/Pb ore deposit, Tunisia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(60):2833-2855. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001670379600138X
Blisniuk P M, Hacker B R, Glodny J, Ratschbacher L, Bi S, Wu Z, McWilliams M O, Calvert A. 2001. Normal faulting in central Tibet since at least 13.5 Myr ago[J]. Nature, 412(6847):628-632. doi: 10.1038/35088045
Boni M, Gilg H A, Balassone G, Schneider J, Allen C R, Moore F. 2007. Hypogene Zn carbonate ores in the Angouran deposit, NW Iran[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 42(8):799-820. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0144-4
Bouabdellah M. 2012. Genesis of the Touissit-Bou Beker Mississippi Valley-type district (Morocco-Algeria) and its relationship to the Africa-Europe collision[J]. Economic Geology, 107(1):117-146. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.1.117
Bouabdellah M, Brown A C, Sangster D F. 1995. Mechansims of formation of internal sediments at the Beddiane lead-zinc deposit, Touissit Mining district, northeastern Morocco[C]//International Field Conference on Carbonate-Hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits, Extended Abstract, St. Louis, Missouri USA.
Bouabdellah M, Niedermann S, Velasco F. 2015. The Touissit-Bou Beker Mississippi Valley-type district of northeastern Morocco:relationships to the Messinian salinity crisis, Late NeogeneQuaternary alkaline magmatism, and buoyancy-driven fluid convection[J]. Economic Geology, 110(6):1455-1484. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.6.1455
Bouhlel S, Johnson C A, Leach D L. 2007. The peridiapiric-type PbZn deposit at Fedj El Adoum, Tunisia:Geology, petrography, and stable isotopes[C]//Proceedings of the Ninth Biennial SGA Meeting, Dublin, Ireland, 1:323-326.
Bouhlel S, Leach D L, Johnson C A, Lehmann B. 2009. Ore Textures and isotope signatures of the peridiapiric carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit of Bougrine, Tunisia[C]//Proceedings of the Tenth Biennial Meeting of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits, Townsville, Queensland, 1:409-411.
Bouhlel S, Leach D L, Johnson C A, Marsh E, Salmi-Laouar S, Banks D A. 2016. A salt diapir-related Mississippi Valley-type deposit:the Bou Jaber Pb-Zn-Ba-F deposit, Tunisia:fluid inclusion and isotope study[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 51 (6):749-780. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0634-8
Bradley D C, Leach D L. 2003. Tectonic controls of Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc mineralization in orogenic forelands[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 38:652-667. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0355-2
Bradley D C, Leach D L, Symons D, Emsbo P, Premo W, Breit G, Sangster, D F. 2004. Reply to discussion on "Tectonic controls of Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc mineralization in orogenic forelands" by Kesler S E, Christensen J T, Hagni R D, Heijlen W, Kyle J R, Misra K C, Muchez P, Van der Voo R[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 39(4):515-519. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0360-9
Brevart O, Dupré B, Allegre C J. 1982. Metallogenic provinces and the remobilization process studied by lead isotopes; lead-zinc ore deposits from the southern Massif Central, France[J]. Economic Geology, 77(3):564-575. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.77.3.564
Brigo L, Omenetto P. 1979. The lead and zinc ores of the Raibl (Cave del Predil-northern Italy) Zone:new metallogenic data[J].Verh. Geol. Bundesaust (Austria), 3:241-247. http://mrdata.usgs.gov/sedexmvt/show.php?labno=177&place=fIT
Brugger J, McPhail D C, Wallace M, Waters J. 2003. Formation of Willemite in Hydrothermal Environments[J]. Economic Geology, 98(4):819-835. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.4.819
Burchfiel B C. 1980. Eastern European Alpine system and the Carpathian orocline as an example of collision tectonics[J]. Tectonophysics, 63(1/4):31-61. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0040195180901067
Cai J X, Zhang K J. 2009. A new model for the Indochina and South China collision during the Late Permian to the Middle Triassic[J]. Tectonophysics, 467(1/4):35-43. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195108006100
Charef A, Sheppard S M F. 1987. Pb-Zn mineralization associated with diapirism:fluid inclusion and stable isotope (H, C, O) evidence for the origin and evolution of the fluids at Fedj-elAdoum, Tunisia[J]. Chemical Geology, 61(1):113-134. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0009254187900325
Chen Wei, Kong Zhigang, Liu Fengxiang, Wang Xuewu, Deng Mingguo, Zhao Jianxing. 2017. Geology, geochemistry, and ore genesis of the Nayongzhi Pb-Zn deposit, Guizhou Province, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(6):1269-1284(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201706009.htm
Chi G, Xue C, Sun X, Lai J, Luo P, Song H, Li S, Zeng R. 2017. Formation of a giant Zn-Pb deposit from hot brines injecting into a shallow oil-gas reservoir in sandstones, Jinding, southwestern China[J]. Terra Nova, 29:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ter.2017.29.issue-5
Clayton C J, Baird A W. 1997. Fluid flow, Pb-Zn mineralization, hydrocarbon maturation and migration in the Tunisian Atlas[C]. Geofluids Ⅱ'97."International Conference on Fluid Evolution, Migration, and Interaction in Sedimentary Basins and Orogenic Belts, 2nd, Extended Abstracts.
Coppola V, Boni M, Gilg H A, Strzelska-Smakowska B. 2009. Nonsulfide zinc deposits in the silesia-cracow district, southern Poland[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 44(5):559-580. doi: 10.1007/s00126-008-0220-4
Cox S F, Knackstedt M A, Braun J. 2001. Principles of structural controls on permeability and fluid flow in hydrothermal systems[M]//Richards J P, Tosdal R M (ed.). Structural Controls on Ore genesis, Reviews in Economic Geology, 14:1-24.
Dal Piaz G V, Bistacchi A, Massironi M. 2003. Geological outline of the Alps[J]. Episodes, 26(3):175-180. https://boa.unimib.it/handle/10281/3676
Daliran F, Pride K, Walther J, Berner Z A. Bakker R J. 2013. The Angouran Zn (Pb) deposit, NW Iran:evidence for a two stage, hypogene zinc sulfide-zinc carbonate mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 53:373-402. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.02.002
DeCelles P G, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, Ding L. 2014. Paleocene-Eocene foreland basin evolution in the Himalaya of southern Tibet and Nepal:Implications for the age of initial India-Asia collision[J]. Tectonics, 33(5):824-849. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003522
Disnar J R. 1996. A comparison of mineralization histories for two MVT deposits, Trèves and Les Malines (Causses basin, France), based on the geochemistry of associated organic matter[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 11(1/3):133-156. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0169136895000194
Dong Lianhui, Xu Xingwang, Fan Tingbin, Qu Xun, Li Hao, Wan Jianling, An Haitao, Zhou Gang, Li Jihong, Chen Gang, Liu Chuan. 2015. Discovery of the Huoshaoyun super-Large exhalative-sedimentary carbonate Pb-Zn deposit in the Western Kunlun area and its great significance for regional metallogeny[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 33(1):41-50 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201501008.htm
Dzulynski S, Sass-Gustkiewicz M. 1977. Comments on the genesis of the eastern Alpine zinc-lead deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 12:219-288. doi: 10.1007/BF00206028
Ehya F. 2014. The Paleozoic Ozbak-Kuh carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit of East Central Iran:Isotope (C, O, S, Pb) geochemistry and ore genesis[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 108 (1):123-136. doi: 10.1007/s00710-013-0279-1
Ehya F, Lotfi M, Rasa I. 2010. Emarat carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit, Markazi Province, Iran:A geological, mineralogical and isotopic (S, Pb) study[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 37(2):186-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.007
Emsbo P. 2000. Gold in sedex deposits[J]. SEG Reviews, 13:427-437. http://www.mendeley.com/research/gold-sedex-deposits/
Fernandez F G, Both R A, Mangas J, Arribas A. 2000. Metallogenesis of Zn-Pb carbonate-hosted mineralization in the southeastern region of the Picos de Europa (central northern Spain) province:geologic, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope studies[J]. Economic Geology, 95(1):19-40. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.1.19
Fernandez-Martinez J, Velasco F. 1996. The Troya Zn-Pb carbonatehosted sedex deposit, northern Spain[J]. Carbonate-hosted leadzinc deposits.Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 4:364-377. http://www.oalib.com/references/17362257
Frizon de Lamotte D, Leturmy P, Missenard Y, Khomsi S, Ruiz G, Saddiqi O, Guillocheau F, Michard A. 2009. Mesozoic and Cenozoic vertical movements in the Atlas system (Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia):an overview[J]. Tectonophysics, 475(1):9-28. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.10.024
Gao Bingyu, Xue Chunji, Chi Guoxiang, Li Chao, Qu Wenjun, Du Andao. 2012. Re-Os dating of bitumen in the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan and its geological significance[J]. Acta petrologica Sinica, 28(5):1561-1567 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205020.htm
Gao Guangli. 1989. Tehtyan evaporite zone and corresponding mineral deposits in China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 14(5):545-551 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198905012.htm
Gilg H A, Boni M, Hochleitner R, Struck U. 2008. Stable isotope geochemistry of carbonate minerals in supergene oxidation zones of Zn-Pb deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 33(2):117-133. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.02.005
Golonka J. 2004. Plate tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Eurasia in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic[J]. Tectonophysics, 381(1-4):235-273. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2002.06.004
Gorecka E. 2013. Geological setting of the Silesian-Cracow Zn-Pb deposits[J]. Geological Quarterly, 37(2):127-146. https://gq.pgi.gov.pl/article/view/8458/0
Gu Xuexiang, Zhang Yongmei, Li Baohua, Xue Chunji, Dong Shuyi, Fu Shaohong. 2010. The coupling relationship between metallization and hydrocarbon accumulation in sedimentary basins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(2):83-105 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY201002013.htm
Guest B, Axen G J, Lam P S, Hassanzadeh J. 2006. Late cenozoic shortening in the west-central alborz mountains, northern Iran, by combined conjugate strike-slip and thin-skinned deformation[J]. Geosphere, 2(1):35-52. doi: 10.1130/GES00019.1
Han R S, Liu C Q, Huang Z L, Chen J, Ma D Y, Lei L, Ma G S. 2007, Geological features and origin of the Huize carbonate-hosted ZnPb-(Ag) district, Yunnan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1):360-383. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/544036?mode=full
Handy M R, Schmid S M, Bousquet R, Kissling E, Bernoulli D. 2010. Reconciling plate-tectonic reconstructions of Alpine Tethys with the geological-geophysical record of spreading and subduction in the Alps[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 102(3):121-158. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825210000668
He Guoxing, Sun Qiwu, Xia Chuanjian, Deng Binwu. 2006. Probe to genesis of Paoma Pb-Zn deposit, Ningnan county, Sichuan province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 21(b10):81-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2006S1020.htm
He L Q, Song Y C, Chen K X, Hou Z Q, Yu F M, Yang Z S, Wei J Q, Li Z, Liu Y C. 2009. Thrust-controlled, sediment-hosted, Himalayan Zn-Pb-Cu-Ag deposits in the Lanping foreland fold belt, eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1):106-132. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136808000991
He Shenghui, Rong Huifeng, Chen Xiansheng. 2014. Metallogenic geologic setting and mineralization process of the Maliping Pb-Zn deposit in Huize county, Yunnan[J]. Mineral Exploration, 5(5):712-719 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201405004.htm
Hitzman M W, Reynolds N A, Sangster D, Allen C R, Carman C E. 2003. Classification, genesis, and exploration guides for nonsulfide zinc deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 98(4):685-714. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.4.685
Hou Zengqian., Song Yucai, Li, Zheng, Wang Zhaolin, Yang Zhusen, Yang Zhiming, Liu Yingchao, Tian Shihong, He Longqing, Chen Kaixu, Wang Fuchun, Zhao Chengxiang, Xue Wanwen, Lu Haifeng. 2008. Thrust-controlled, sediments-hosted Pb-Zn-AgCu deposits in eastern and northern margins of Tibetan orogenic belt:Geological features and tectonic model[J]. Mineral Deposits, 27(2):123-144 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-kcdz200802002.htm
Hou Z, Cook N J. 2009. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan collisional orogen:A review and introduction to the special issue[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1):2-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136809000596
Hou Z, Zhang H. 2015. Geodynamics and metallogeny of the eastern Tethyan metallogenic domain[J]. Ore Geology. Reviews, 70:346-384. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.026
Hu X, Garzanti E, Moore T, Raffi I. 2015. Direct stratigraphic dating of India-Asia collision onset at the Selandian (middle Paleocene, 59±1 Ma)[J]. Geology, 43(10):859-862 doi: 10.1130/G36872.1
Hu, X, Garzanti E, Wang J, Huang W, An W, Webb A. 2016a. The timing of India-Asia collision onset-Facts, theories, controversies[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 160:264-299. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.07.014
Hu X, Wang J, Boudagher-Fadel M, Garzanti E, An W. 2016b. New insights into the timing of the India-Asia collision from the Paleogene Quxia and Jialazi formations of the Xigaze forearc basin, South Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 32:76-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.02.007
Jankovic S. 1984. Strata-bound low temperature Pb-Zn-Ba ±F deposits in carbonate rocks of western Asia:Geotectonic setting and main metallogenic features[C]. Berlin:Syngenesis and Epigenesis in the Formation of Mineral Deposits, Springer, 373-390.
Khan A, Kelling G, Umar M, Kassi A. 2002. Depositional environments and reservoir assessment of Late Cretaceous sandstones in the south central Kirthar foldbelt, Pakistan[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 25(4):373-406. doi: 10.1111/jpg.2002.25.issue-4
Kibitlewski S. 2013. Tectonic control of the origin of Zn-Pb deposits in the Chrzanów region[J]. Geological Quarterly, 37(2):229-240. https://gq.pgi.gov.pl/article/download/8464/pdf_539
Koptagel O, Ulusoy U, Fallick A E. 2007. Sulfur and Lead Isotope Investigations of the Carbonate-Hosted Pb-Zn Deposits in the Yahyalı Region, Kayseri, Southern Turkey[J]. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 16(1):57-76. https://gq.pgi.gov.pl/article/view/8464/pdf_539
Le Guen M, Orgeval J J, Lancelot J. 1991. Lead isotope behaviour in a polyphased Pb-Zn ore deposit:Les Malines (Cévennes, France)[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 26(3):180-188. doi: 10.1007/BF00209256
Leach D L, Apodaca L E, Kozłowski A, Landis G P, Hofstra A H. 1996. Fluid-inclusion gases in sphalerite, galena, and dolomite from the Silesian-Cracow Zn-Pb district, Poland[J]. PracePanstwowego Instytutu Geologicznego, 154:104-111. http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/70018127
Leach D L, Bradley D, Lewchuk M T, Symons D T, de Marsily G, Brannon J. 2001. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits through geological time:implications from recent age-dating research[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 36(8):711-740. doi: 10.1007/s001260100208
Leach D L, Bradley D C, Huston D, Pisarevsky S A, Taylor R D, Gardoll S J. 2010. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits in Earth history[J]. Economic Geology, 105(3):593-625. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.3.593
Leach D L, Sangster D F, Kelley K D, Large R R, Garven G, Allen C R, Gutzmer J, Walters S. 2005. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits:A global prospective[J]. Economic Geology, 100th Anniversary Volume, 561-607. https://eprints.utas.edu.au/6268/
Leach D L, Song Y C, Hou Z Q. 2017. The world-class Jinding ZnPb deposit:ore formation in an evaporite dome, Lanping Basin, Yunnan, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 52(3):281-296. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0668-6
Li Fayuan, Gu Xuexiang, Fu Shaohong, Zhang Ming. 2002. The role of organic matter in the formation of MVT Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemisty, 21(4):272-276 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200204014.htm
Li Lianting. 2014. The geological feature of Fulechang Pb-Zn deposit and inference of deep prospecting in Luoping, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 33(2):240-244 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.mindat.org/locentry-816432.html
Li Xiaoming, Tan Kaixuan, Gong Wenjun, Gong Gelian. 2000. Study on the metallogenic epoch of the Jinding lead-zinc deposit with apatite fission track analysis[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 24(3):282-286 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dgyk200003013.htm
Li Y L, Wang C S, Dai J, Xu G, Hou Y, Li X. 2015. Propagation of the deformation and growth of the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen:A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 143:36-61. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.01.001
Li Z, Ding L, Song P, Fu J, Yue Y. 2015. Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleolatitude of the Lhasa block during the early Cretaceous:implications for the onset of India-Asia collision and latitudinal shortening estimates across Tibet and stable Asia[J]. Gondwana Research, 41:352-372. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X15001343
Liaghat S, Moore F, Jami M. 2000. The Kuh-e-Surmeh mineralization, a carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit in the simply folded belt of the Zagros Mountains, SW Iran[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 35(1):72-78. doi: 10.1007/s001260050007
Lin Fangcheng. 2005. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of supper-large-scale Sedex-type stratiform lead-zinc deposits in the Dadu river valley on the western margin of the Yangtze craton[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(4):541-556 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200504017.htm
Liu Chenglin, Zhao Yanjun, Fang Xiaomin, Lu Fenglin, Wang Licheng, Yan Maodu, Zhang Hua, Ding Ting. Plate tectonics control on the distribution and formation of the marine potash deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(11):1893-1907 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jishun. 1996. Some problems in studies of the exhalative sedimentary mineralization[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 10(1):6-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD601.001.htm
Liu Yingchao, Hou Zengqian, Yang Zhusen, Tian Shihong, Song Yucai, Yang Zhiming, Wang Zhaolin, Li Zheng. 2008. Some insights and advances in study of Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) lead-zinc deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 27(2):253-264(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200802011.htm
Liu Y C, Hou Z Q, Yang Z S, Tian S H, Yang T N, Song Y C, Zhang H R, Carranza E J M. 2011. Formation of the Dongmozhazhua PbZn Deposit in the Thrust Fold Setting of the Tibetan Plateau, China:Evidence from Fluid Inclusion and Stable Isotope Data[J]. Resource Geology, 61(4):384-406. doi: 10.1111/rge.2011.61.issue-4
Liu Yingchao, Hou Zengqian, Yu Yushuai, Tian Shihong, Li Yulong, Yang Zhusen. 2013. Characteristics and genesis of Lalongla MVTlike deposit in Changdu region, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4):1407-1426 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Y C, Yang Z S, Tian S H, Song Y C, Zhang H R. 2015. Fluid origin of fluorite-rich carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn mineralization of the Himalayan-Zagros collisional orogenic system:A case study of the Mohailaheng deposit, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews. 70:546-561. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.004
Liu Yingying, Qi Liang, Huang Zhilong, Zhou Jiaxi, Zhu chuanwei, Huang Xiaowen. 2013. Re-Os dating of sulfides and geological implications in the Fule zinc-lead deposit, northeastern Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, S2:599-600 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s12583-015-0539-6
Liu Y Y, Qi L, Gao J F, Ye L, Huang Z L, Zhou J X. 2015. Re-Os dating of galena and sphalerite from lead-zinc sulfide deposits in Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 26(3):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s12583-015-0539-6
Makhoukhi S, Marignac C, Pironon J, Schmitt J M, Marrakchi C, Bouabdelli M, Bastoul A. 2003. Aqueous and hydrocarbon inclusions in dolomite fromTouissit-Bou Beker district, Eastern Morocco:a Jurassic carbonate hosted Pb-Zn (Cu) deposit[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 78:545-551. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0375674203000980
Metcalfe I. 1996. Gondwanaland dispersion, Asian accretion and evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 43(6):605-623. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728282
Metcalfe I. 2006. Palaeozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution and palaeogeography of East Asian crustal fragments:the Korean Peninsula in context[J]. Gondwana Research, 9(1):24-46. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X05000043
Mirnejad H, Simonetti A, Molasalehi F. 2015. Origin and formational history of some Pb-Zn deposits from Alborz and Central Iran:Pb isotope constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 57(4):463-471. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1013510
Mitsuishi M, Wallis S R, Aoya M, Lee J, Wang Y. 2012. E-W extension at 19Ma in the Kung Co area, S. Tibet:Evidence for contemporaneous E-W and N-S extension in the Himalayan orogen[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 325:10-20. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X11006704
Mladenova V, Valchev S. 1998. Ga/Ge ratio in sphalerite from the carbonate-hosted Sedmochislenitsi Deposit as a temperature indication of initial fluids[J]. Spis.Bulgar. Geol. Druzh, 59(2/3):49-54. http://mrdata.usgs.gov/sedznpb/show.php?labno=67
Jazi M A, Karimpour M H, Shafaroudi A M. 2017. Nakhlak carbonatehosted Pb (Ag) deposit, Isfahan province, Iran:a geological, mineralogical, geochemical, fluid inclusion, and sulfur isotope study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 80:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.010
Montacer M, Disnar J R, Orgeval J J, Trichet J. 1988. Relationship between Zn-Pb ore and oil accumulation processes:Example of the Bou Grine deposit (Tunisia)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 13(1):423-431. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=7180269
Mouthereau F, Lacombe O, Vergés J. 2012. Building the Zagros collisional orogen:timing, strain distribution and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence[J]. Tectonophysics 532:27-60. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195112000509
Omar H, Abdelhak B, Madjid C, Saadia Y, Hanafi H, Djamel B. 2016. Pb-Zn (Ba) deposits of the oriental Saharan Atlas (north-east of Algeria):distribution, control and implications for mining exploration[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(5):1-10. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1464343X16301923
Oszczypko N. 2010. Late Jurassic-Miocene evolution of the Outer Carpathian fold-and-thrust belt and its foredeep basin (Western Carpathians, Poland)[J]. Geological Quarterly, 50(1):169-194. http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-article-BUS2-0009-0017
Peng Song, Jin Zhongguo, Lin Guisheng, Zhu Youqing, Wang Bing. 2016. Analysis of pore-controlling factors and metallogenic model of Wuzhishan lead-zinc deposit, Guizhou:a case study of Nayongzhi deposit[J]. Mineral Exploration, 7(3):463-470 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pfaff K, Hildebrandt L H, Leach D L, Jacob D E, Markl G. 2010. Formation of the Wiesloch Mississippi Valley-type Zn-Pb-Ag deposit in the extensional setting of the Upper Rhinegraben, SW Germany[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 45(7):647-666. doi: 10.1007/s00126-010-0296-5
Plumlee G S, Leach D L, Hofstra A H, Landis G P, Rowan E L, Viets J G. 1994. Chemical reaction path modeling of ore deposition in Mississippi Valley-type Pb-Zn deposits of the Ozark region, U.S. Midcontinent[J]. Economic Geology, 89(6):1361-1383. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.89.6.1361
Puigdefabregas C, Muñoz J, Vergés J. 1992. Thrusting and foreland basin evolution in the southern Pyrenees[M]. Netherlands:Thrust tectonics, Springer, 247-254.
Qiu Dongzhou, Xie Yuan, Li Xiaoqing, Huang Fuxi. 2009. Geological Characteristics of Lithofacies Paleogeography and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Asian Tethyan Tectonic Domain[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 14(2):41-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HXYQ200902008.htm
Rajabi A, Rastad E, Canet C. 2012. Metallogeny of Cretaceous carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposits of Iran:geotectonic setting and data integration for future mineral exploration[J]. International Geology Review, 54(14):1649-1672. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2012.659110
Rajabi A, Rastad E, Canet C. 2013. Metallogeny of Permian-Triassic carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb and F deposits of Iran:A review for future mineral exploration[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 60(2):197-216. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2012.754792
Rddad L, Bouhlel S. 2016. The Bou Dahar Jurassic carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn-Ba deposits (Oriental High Atlas, Morocco):Fluid-inclusion and C-O-S-Pb isotope studies[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72:1072-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.011
Reichert J. 2007. A Metallogenetic Model for Carbonate-hosted Nonsulphide Zinc Deposits Based on Observations of Mehdi Abad and Irankuh, Central and Southwestern Iran[D]. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Martin-Luther-Universität, Halle-Wittenberg, 152P. http://hdl.handle.net/11858/00-1735-0000-0001-3146-2
Reichert J, Borg G. 2008. Numerical simulation and a geochemical model of supergene carbonate-hosted non-sulphide zinc deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 33(2):134-151. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.02.006
Reynolds N A, Chisnall T W, Kaewsang K, Keesaneyabutr C, Taksavasu T. 2003. The padaeng supergene nonsulfide zinc deposit, Mae Sod, Thailand[J]. Economic Geology, 98(4):773-785. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.4.773
Rouvier H, Perthuisot V, Mansouri A. 1985. Pb-Zn deposits and saltbearing diapirs in Southern Europe and North Africa[J]. Economic Geology, 80(3):666-687. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.80.3.666
Sarkarinejad K, Azizi A. 2008. Slip partitioning and inclined dextral transpression along the Zagros Thrust System, Iran[J].. Journal of Structural Geology, 30(1):116-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2007.10.001
Sass-Gustkiewicz M, Dzulynski S, Ridge J D. 1982. The emplacement of zinc-lead sulfide ores in the Upper Silesian District; a contribution to the understanding of mississippi valleytype deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 77(2):392-412. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.77.2.392
Schroll E, Rantitsch G. 2005. Sulphur isotope patterns from the Bleiberg deposit (Eastern Alps) and their implications for genetically affiliated lead-zinc deposits[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 84(1/2):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s00710-004-0071-3
Selby D, Creaser R A. 2005. Direct radiometric dating of the Devonian-Mississippian time-scale boundary using the Re-Os black shale geochronometer[J]. Geology, 33(7):545-548. doi: 10.1130/G21324.1
Sengor A M C. 1987. Tectonics of the Tethysides:orogenic collage development in a collisional setting[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 15(1):213-244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.15.050187.001241
Singer D A. 1995, World class base and precious metal deposits:A quantitative analysis[J]. Economic Geology, 90(1):88-104. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.1.88
Song Yucai, Hou Zengqian, Yang Tiannan, Tian Shihong, Liu Yingchao, Wang Xiaohu, Liu Yanxue, Xue Chuandong, Wang Guanghui, Li Zheng. 2011. Sediment-hosted Himalayan base metal deposits in Sanjiang area, S.W. China:characteristics and genetic types[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30 (3):355-380(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201103003.htm
Song Yucai, Hou Zengqian, Yang Tiannan, Li Shijing, Wang Fuchun, Gao Yongwang, Gong Xiugang, Yang Zhusen, Zhang Hongrui, Li Liansong, Wang Guiren, Wang Yuanquan, Liu Qun, Hao Hongda. 2013. Mineral prospecting and its related approaches in Duocaima Pb-Zn deposit, Tuotuohe, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 32(4):744-756 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/references/17340979
Song Yucai, Hou Zengqian, Wang Guiren, Li Liansong, Yang Tiannan, Zhang Hongrui, Liu Yanxue, Yang Zhusen, Tian Shihong, Liu Yingchao, Jia Zongyong, Wang Yuankui, Liu Qun, Yan Ming, He Li. 2015. Metallogenic features and guidelines for ore exploration in Tuotuohe area, northern Sanjiang orogenic belt, China[J]:Mineral Deposits, 34(1):1-20 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283172271_Mineralization...
Song Y C, Yang T N, Zhang H R, Liu Y C, Hao H D, Li Z. 2015. The Chaqupacha Mississippi Valley-type Pb-Zn deposit, central Tibet:Ore formation in a fold and thrust belt of the India-Asia continental collision zone[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70:533-545. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.021
Spangenberg J E, Herlec U. 2006. Hydrocarbon biomarkers in the Topla-Mežica zinc-lead deposits, northern Karavanke/Drau Range, Slovenia:Paleoenvironment at the site of ore formation[J]. Economic Geology, 101(5):997-1021. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.101.5.997
Spurlin M S, Yin A, Horton B K, Zhou J, Wang, J. 2005. Structural evolution of the Yushu-Nangqian region and its relationship to syncollisional igneous activity, east-central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 117(9/10):1293-1317. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=17084077
Stampfli G M. 2000. Tethyan oceans[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 173(1):1-23. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.173
Stampfli G M, Borel G D. 2002. A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrones[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 196 (1/2):17-33. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X0100588X
Suess E. 1893. Are great ocean depths permanent[J]. Nat. Sci., 2:180-187.
Symons D, Sangster D, Leach D. 1995. A Tertiary age from paleomagnetism for Mississippi Valley-type zinc-lead mineralization in Upper Silesia, Poland[J]. Econ. Geol., 90(4):782-794. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.4.782
Symons D T, Lewchuk M T, Kawasaki K, Velasco F, Leach D L. 2009. The Reocín zinc-lead deposit, Spain:paleomagnetic dating of a late Tertiary ore body[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 44(8):867-880. doi: 10.1007/s00126-009-0253-3
Talbot C, Aftabi P. 2004. Geology and models of salt extrusion at Qum Kuh, central Iran[J]. J. Geol. Soc., 161(2):321-334. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-102
Tang Yongyong, Bi Xianwu, Wu Liyan, Wang Lei, Zou Zhichao, He Liping. 2013. Re-Os isotopic dating of pyrite from Jinding Zn-Pb ore deposit and its geological significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(3):287-294 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201303004.htm
Taylor R D, Leach D L, Bradley D C, Pisarevsky S A. 2009. Compilation of mineral resource data for Mississippi Valley-type and clastic-dominated sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits[R]. Open-File Reprot 2009-1297, U.S. Geological Survey, 1-42.
Thom J, Anderson G M. 2008. The role of thermochemical sulfate reduction in the origin of Mississippi Valley-type deposits. I. Experimental results[J]. Geofluids, 8(1), 16-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2007.00201.x/full
Van Hinsbergen D J, Lippert P C, Dupont-Nivet G, McQuarrie N, Doubrovine P V, Spakman W, Torsvik T H. 2012. Greater India Basin hypothesis and a two-stage Cenozoic collision between India and Asia[J]. PNAS, 109(20):7659-7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117262109
Vandeginste V, Swennen R, Gleeson S A, Ellam R M, Osadetz K, Roure F. 2010. Zebra dolomitization as a result of focused fluid flow in the rocky mountains fold and thrust belt, Canada[J]. Sedimentology, 52(5):1067-1095. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2005.00724.x/references
Velasco F, Herrero J M, Yusta I, Alonso J A, Seebold I, Leach D. 2003. Geology and geochemistry of the Reocin zinc-lead deposit, Basque-Cantabrian Basin, Northern Spain[J]. Econ. Geol., 98(7):1371-1396. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.7.1371
Verges J, Fernàndez M, Martínez A. 2002. The Pyrenean orogen:Pre-, syn-, and postcollisional evolution[J]. J. Virtual Explor., 8:55-74. http://www.academia.edu/11943874/The_Pyrenean_orogen_pre-_syn-_and_post...
Wan Zhifeng, Xia Bin, Cai Zhourong, Liu Ping, Zhang Yi. 2008. Controls of the Tethyan tectonic evolution on the hydrocarbon accumulation in Northwest Africa[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 28(4): 24-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200804006.htm
Wang Licheng, Liu Chenglin, Zhang Hua. 2013. Tectonic and Sedimentary Settings of Evaporites in the Dengying Formation, South China Block: Implications for the Potential of Potash Formation[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(5): 585-593. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201305010.htm
Wang C S, Zhao X, Liu Z, Lippert P C, Graham S A, Coe R S, Yi H, Zhu L, Liu S, Li Y. 2008. Constraints on the early uplift history of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. PNAS, 105: 4987-4992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703595105
Wang J H, Yin A, Harrison T M, Grove M, Zhang Y Q, Xie G H. 2001. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 188(1):123-133. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X01003156
Wang Z, Wang A. 1985. Study of genesis of paleocave in the Tianbaoshan and Daliangzi deposits, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 10: 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Warren J K. 2006. Evaporites: sediments, resources and hydrocarbons[M]. Würzburg: Springer Science & Business Media, 1-1035.
Warren J K. 2016. Evaporites: A Geological Compendium[M]. Bangkok: Springer, 1-1813.
Wei A Y, Xue C D, Xiang K, Li J, Liao C, Akhter Q J. 2015. The oreforming process of the Maoping Pb-Zn deposit, northeastern Yunnan, China: Constraints from cathodoluminescence (CL)petrography of hydrothermal dolomite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 562-577. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.007
Wilkinson J J. 2014. Sediment-hosted zinc-lead mineralization:Processes and Perspectives[C]//Turekian HDHK (ed.). Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), Oxford. Elsevier, 219-249.
Williams H, Turner S, Kelley S, Harris N. 2001. Age and composition of dikes in Southern Tibet: New constraints on the timing of eastwest extension and its relationship to postcollisional volcanism[J]. Geology, 29(4): 339-342. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0339:AACODI>2.0.CO;2
Wu F Y, Ji W Q, Wang J G, Liu C Z, Chung S L, Clift P D. 2014. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic constraints on the onset time of India-Asia collision[J]. Am. J. Sci., 314: 548-579. doi: 10.2475/02.2014.04
Wu Yue. 2013. The Age and Ore-forming Process of MVT Deposits in the Boundary Zrea of Sichuan-Yunnano-Guizhou Provinces, Southwest China[D]. Beijing: Ph.D. thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-167(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue C, Chi G, Li Z, Dong X. 2014. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Cretaceous and Paleocene sandstone-and conglomerate-hosted Uragen Zn-Pb deposit, Xinjiang, China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 63: 328-342. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.005
Xue C, Zeng R, Liu S, Chi G, Qing H, Chen Y, Wang D. 2007. Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1): 337-359. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136806000540
Xue C J, Gao Y B, Chi G X, Leach D L. 2009. Possible former oil-gas reservoir in the giant Jinding Pb-Zn deposit, Lanping, NW Yunnan: the role in the ore accumulation[J]. Journal Earth Science Environoment, 31: 221-229 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200903001.htm
Yalikun Y, Xue C, Symons D T A. 2017. Paleomagnetic age and tectonic constraints on the genesis of the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0733-9.
Yan Zhigui, Xia Chuanjian, He Guangxing, Deng Binwu. 2006. Geological characteristics and ore potential analysis of Paoma PbZn deposit, Ningnan county, Sichuan province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 21: 77-80 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZZK2006S1019.htm
Ye Hefei, Luo Jianning, Li Yongtie, Tong Zhenyan, Yu Qian, Wang Xiaolong, Zhu Tongxing, Feng Xintao. 1999. Tethyan tectonic domain and petroleum exploration[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 20(1):1-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200001000.htm
Yigit O. 2009. Mineral deposits of Turkey in relation to Tethyan metallogeny: Implications for future mineral exploration[J]. Geology, 104(1): 19-51. http://economicgeology.org/content/104/1/19.short
Yin A, 2010. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: A preliminary synthesis[J]. Tectonophysics, 488(1): 293-325. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195109003217
Yuan B, Mao J W, Yan X H, Wu Y, Zhang F, Zhao L L. 2014. Sources of metallogenic materials and metallogenic mechanism of Daliangzi ore field in Sichuan Province: Constraints from geochemistry of S, C, H, O, Sr isotope and trace element in sphalerite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30: 209-220 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201401016.htm
Zeng Daoguo, Zhang Yingwen, Liu Kaikun. 2007. Geological characteristics and ore prospecting orientation of the Maomaochang-Zhazichang lead-zinc ore field in Northwestern Guizhou[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 21(4): 410-414 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200704003.htm
Zhang H, Hou Z. 2015. Pattern and Process of Continent-Continent Collision Orogeny:A Case Study of the Tethys Collisional Orogen[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(9):1539-1559 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXE201509002.htm
Zhang Changqing, Yu Jinjie, Mao Jingwen, Rui Zongyao. 2009. Advances in the study of Mississippi Valley-type deposits[J]. Mineral Deposis, 28(2): 195-210(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200902009.htm
Zhang C Q, Wu Y, Hou L, Mao J W. 2015. Geodynamic setting of mineralization of Mississippi Valley-type deposits in world-class Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Zn-Pb triangle, southwest China:Implications from age-dating studies in the past decade and the Sm-Nd age of Jinshachang deposit[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.013
Zhang Zhiyang. 2003. An analysis of geology and genesis of Lehong Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Yunnan Geology, 22: 97-106 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng M H, Wang X C. 1991. Genesis of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Sichuan, China[J].Economic Geology, 86: 831-846. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.86.4.831
Zheng Mianping, Qi Wen, Zhang Yongsheng. 2006. Present situation of potash resources and direction of potash search in China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(11): 1239-1246 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200611000.htm
Zhou Chaoxian, Wei Chunsheng. 1997. The Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 1: 65-75(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDQ199701011.htm
Zhou J X, Bai J H, Huang Z L, Zhu D, Yan Z F, Lv ZC. 2015. Geology, isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Jinshachang carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.024
Zhou J X, Gao J G, Chen D, LiuX K. 2013a. Ore genesis of the Tianbaoshan carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Southwest China:geologic and isotopic (C-H-O-S-Pb) evidence[J]. International Geology Review, 55: 1300-1310. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.782973
Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Bao G P. 2013b. Geological and sulfur-leadstrontium isotopic studies of the Shaojiwan Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China: Implications for the origin of hydrothermal fluids[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 128: 51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.01.007
Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Gao J G, Yan Z F. 2013c. Geological and C-OS-Pb-Sr isotopic constraints on the origin of the Qingshan carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Southwest China[J]. International Geology Review, 55: 904-916. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.767496
Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Zhou M F, Li X B, Jin Z G. 2013d. Constraints of C-O-S-Pb isotope compositions and Rb-Sr isotopic age on the origin of the Tianqiao carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 53: 77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.01.001
Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Yan Z F. 2013e. The origin of the Maozu carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China: constrained by C-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions and Sm-Nd isotopic age[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.031
Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Lv Z C, Zhu X K, Gao JG, Mirnejad H. 2014. Geology, isotope geochemistry and ore genesis of the Shanshulin carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 63: 209-225. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.05.012
Zhou J Y, Wang J H, Horton B K, Yin A, Spurlin M S. 2011. The closure of Paleogene basins of east-central Tibet in response to tectonic, sedimentation, magmatism and paleoclimate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(2): 172-178 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Xinyou, Wang Dongbo, Wang Shulai. 1998. Geology and sulfur isotope geochemistry of the Tamu-Kalangu lead-zinc deposits, Akto county, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 17(3): 204-214 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KCDZ199803001.htm
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, Dilek Y, Hou Z Q, Mo X X. 2013. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Res., 23 (4): 1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
Zhu Xinyou, Wang Jjingbin, Liu Zengren, Fang Tonghui. 2010. Geological characteristics and the genesis of the Wulagen leadzinc deposit, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84: 694-702 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201005009.htm
安徽省地质调查局. 2005. 1: 25万温泉幅-松西幅地质图[R]. 合肥. 陈伟, 孔志岗, 刘凤祥, 王学武, 邓明国, 赵剑星. 2017.贵州纳雍枝铅锌矿床地质、地球化学及矿床成因[J].地质学报, 91(6):1269-1284. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZXE201706009.htm 董连慧, 徐兴旺, 范廷宾, 屈迅, 李昊, 万建领, 安海涛, 周刚, 李基宏, 陈刚, 刘川. 2015.喀喇昆仑火烧云超大型喷流-沉积成因碳酸盐型Pb-Zn矿的发现及区域成矿学意义[J].新疆地质, 33: 42-50. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz2015010008 高炳宇, 薛春纪, 池国祥, 李超, 屈文俊, 杜安道. 2012.云南金顶超大型铅锌矿床沥青Re-Os法测年及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 28(5):1561-1567. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/9c0e3dff5901020206409caf.html 高广立. 1989.我国的特提斯聚盐带及有关矿产[J].地球科学, (5):545-551. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/198905/15371.html 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 李葆华, 薛春纪, 董树义, 付绍洪. 2010.沉积盆地中金属成矿与油气成藏的耦合关系[J].地学前缘, 17(2):83-105. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dxqy201002013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 贺光兴, 孙启武, 夏传见, 邓斌武. 2006.四川省宁南县跑马铅锌矿成因浅析[J].地质找矿论丛, 21(S1): 81-84. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90755X/2006B10/23083583.html 贺胜辉, 荣惠锋, 陈贤胜. 2014.云南麻栗坪铅锌矿床成矿地质背景及成矿作用[J].矿产勘查, 5(5): 712-719. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201405003 侯增谦, 宋玉财, 李政, 王召林, 杨志明, 杨竹森, 刘英超, 田世红, 何龙清, 陈开旭, 王富春, 赵呈祥, 薛万文, 鲁海峰. 2008.青藏高原碰撞造山带Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床新类型:成矿基本特征与构造控矿模型[J].矿床地质, 27(2): 123-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.02.001 李发源, 顾雪祥, 付绍洪, 章明. 2002.有机质在MVT铅锌矿床形成中的作用[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 21(4): 272-276. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/178721 李连廷. 2014.云南罗平富乐厂铅锌矿床地质特征及深部找矿推测[J].云南地质, 33(2): 240-244. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/4b709b90a76e58fafbb00313.html 李小明, 谭凯旋, 龚文君, 龚革联. 2000.利用磷灰石裂变径迹法研究金顶铅锌矿成矿时代[J].大地构造与成矿学, 24(3):283-286. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90781x/200003/4711393.html 林方成. 2005.扬子地台西缘大渡河谷超大型层状铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征及成因[J].地质学报, 79(4): 540-556. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/7a4443b108a1284ac950430c.html 刘成林, 赵艳军, 方小敏, 吕凤琳, 王立成, 颜茂都. 2015.板块构造对海相钾盐矿床分布与成矿模式的控制[J].地质学报, 89(11):1893-1907. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=... 刘继顺. 1996.喷流沉积成矿作用研究的若干问题[J].矿产与地质, 10(1): 6-10. http://www.docin.com/p-19801839.html 刘英超, 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 宋玉财, 杨志明. 2008.密西西比河谷型(MVT)铅锌矿床:认识与进展[J].矿床地质, 27(2): 253-264. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/cc812620ae45b307e87101f69e... 刘英超, 侯增谦, 于玉帅, 田世洪, 李玉龙, 杨竹森. 2013.西藏昌都地区拉拢拉类MVT铅锌矿床矿化特征与成因研究[J].岩石学报, 29(4): 1407-1426. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb201304024&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘莹莹, 漆亮, 黄智龙, 周家喜, 朱传威, 黄小文. 2013.滇东北富乐铅锌矿床硫化物Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].矿物学报, S2: 599-600. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95783X/2013S2/1005565737.html 彭松, 金中国, 林贵生, 朱尤青, 王兵. 2016.贵州五指山铅锌矿区控矿因素及成矿模式研究——以纳雍枝矿床为例[J].矿产勘查, 7(3): 463-470. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSJS201603013.htm 丘东洲, 谢渊, 李晓清, 黄福喜. 2009.亚洲特提斯域岩相古地理与油气聚集地质特征[J].海相油气地质, 14(2): 41-51. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4852297 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 王贵仁, 李连松, 杨天南, 张洪瑞, 刘燕学, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 刘英超, 贾宗涌, 汪元奎, 刘群, 闫明, 何利. 2015."三江"北段沱沱河地区的成矿规律与找矿方向[J].矿床地质, 34(1): 1-20. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2015.01.001.html 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 杨天南, 张洪瑞, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 刘英超, 王晓虎, 刘燕学, 薛传东, 王光辉, 李政. 2011."三江"喜马拉雅期沉积岩容矿贱金属矿床基本特征与成因类型[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 30(3): 355-380. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz201103002 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 杨天南, 李世金, 王富春, 高永旺, 巩秀钢, 杨竹森, 张洪瑞, 李连松, 王贵仁, 汪元奎, 刘群, 郝宏达. 2013.青海沱沱河多才玛特大型Pb-Zn矿床—定位预测方法与找矿突破过程[J].矿床地质, 32: 744-756. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=... 唐永永, 毕献武, 武丽艳, 邹志超, 和利平. 2013.云南金顶超大型铅锌矿床碳、氧、锶、铅同位素地球化学[J].地球化学, 42(5):467-480. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqhx201305007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 万志峰, 夏斌, 蔡周荣, 刘平, 张毅. 2008.特提斯构造演化对西北非地区油气成藏的控制作用[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 28(4): 24-27. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/57447a1ef12d2af90242e6ce.html 王立成, 刘成林, 张华. 2013.华南地块震旦纪晚期—早寒武世古大陆位置暨灯影组蒸发岩成钾条件分析[J].地球学报, 34(5):585-593. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/3d59564e10a6f524cdbf850c.html 王则江, 汪岸儒. 1985.四川天宝山、大梁子铅锌矿床古岩溶洞穴沉积成因研究[J].地质与勘探, 10: 10-17. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzkt198510002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 吴越. 2013. 川滇黔地区MVT铅锌矿床大规模成矿作用的时代与机制[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-167. 薛春纪, 高永宝, ChiG X, Leach D L. 2009.滇西北兰坪金顶可能的古油气藏及对铅锌大规模成矿的作用[J].地球科学与环境学报, 31(3):221-229. http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/handle/00001903-5/48659 晏子贵, 夏传见, 贺光兴, 邓斌武. 2006.四川省宁南县跑马铅锌矿地质特征及找矿前景分析[J].地质找矿论丛, 21(S1): 77-80. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90755X/2006B10/23083582.html 叶和飞, 罗建宁, 李永铁, 童箴言, 余谦, 王小龙, 朱同兴, 冯心涛. 1999.特提斯构造域与油气勘探[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 20(1):1-27. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98500A/200001/4155823.html 袁波, 毛景文, 闫兴虎, 吴越, 张锋, 赵亮亮. 2014.四川大梁子铅锌矿成矿物质来源与成矿机制:硫、碳、氢、氧、锶同位素及闪锌矿微量元素制约[J].岩石学报, 30(1):209-220. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb201401016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张洪瑞, 侯增谦. 2015.大陆碰撞造山样式与过程:来自特提斯碰撞造山带的实例[J].地质学报, 89(9):1539-1559. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4873665 张长青, 余金杰, 毛景文, 芮宗瑶. 2009.密西西比型(MVT)铅锌矿床研究进展[J].矿床地质, 28(2): 195-210. http://www.docin.com/p-1230112457.html 张自洋. 2003.乐红铅锌矿矿床地质与成因分析[J].云南地质, 22(1):97-106. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95791X/200301/7542474.html 曾道国, 张应文, 刘开坤. 2007.对黔西北猫猫厂—榨子厂铅锌矿区地质特征及找矿方向的几点不同认识[J].矿产与地质, 21(4):410-414. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96866X/200704/26087938.html 郑绵平, 齐文, 张永生. 2006.中国钾盐地质资源现状与找钾方向初步分析[J].地质通报, 25(11): 1239-1246. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/82590e8c2af90242a895e5fc.html 周朝宪, 魏春生, 叶造军. 1997.密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床[J].地质地球化学, 1: 65-75. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/13822f164431b90d6c85c7a5.html 祝新友, 汪东波, 王书来. 1998.新疆阿克陶县塔木—卡兰古铅锌矿带矿床地质和硫同位素特征[J].矿床地质, 17(3):204-214. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/34d2b9d626fff705cc170af2.html 祝新友, 王京彬, 刘增仁, 方同辉. 2010.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床地质特征与成因[J].地质学报, 84(5): 694-702. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/1323f636453610661ed9f41f.html -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 何碧,赵振琯,刘海生,张文斌,陈红旗. 东天山造山带黑尖山地区花岗闪长岩岩石成因及构造意义:来自岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学证据. 科学技术与工程. 2024(25): 10620-10634 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李生喜,何碧,杨博,魏志福,陶刚,甘保平,赵飞,孙平原,赵振琯,黄鹏飞. 南天山地块塔格拉克地区二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征:对壳源岩浆成因和构造背景的限定. 中国地质. 2023(02): 622-639 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 曹积飞,翁凯,Movlanov Jahongir Jurabekovich,Asrorovich Rustamov Akmal,马中平,刘明义. 乌兹别克斯坦中天山金铜成矿特征与找矿潜力评价. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1731-1744 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨波,孙栋华. 东天山某环状熔融岩体航空电磁场特征及深部找矿研究. 物探与化探. 2022(04): 816-823 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: