A study of an integrated anomaly model and an exploration model for uranium exploration in Yuhuashan area, Jiangxi Province
-
摘要:
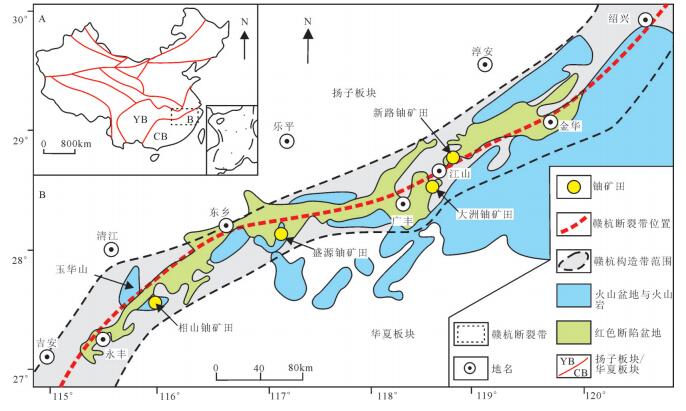
玉华山地区是赣杭构造带西南段重要的铀矿找矿远景区之一,毗邻中国最大的火山岩型铀矿田——相山铀矿田。玉华山地区基底变质岩、岩浆岩、断裂构造、热液活动和铀矿化特征指示区内具有较大的找矿潜力。与相山矿田对比,两者成矿条件基本相同,但在火山活动、晚期热液活动强度、剥蚀程度等方面存在较大差异。玉华山地区地球化学与地球物理异常特征表明,区内U-Th-Mo化探综合异常、正负磁异常交替和放射性正异常等异常叠加区是铀矿勘查的重点区域。同时,在成矿条件、地球化学条件与地球物理条件的基础上,构建了研究区综合信息找矿模型,为区内铀矿勘查工作提供了理论与实践依据。笔者认为为山—筒山断裂带是今后资源量突破所在,建议部署相关勘探工程,查明铀资源量。
Abstract:Located in the southwestern part of Gan-Hang tectonic zone and closed to the Xiangshan uranium orefield, the largest volcanic-type uranium orefield in China, the Yuhuashan area is a significant prospective prediction area for uranium ore deposit. In this paper, a systematic study of uranium metallogenic conditions such as metamorphic basement, magmation, fracture structure, and hydrothermal activity indicates that Yuhuashan area is an excellent potential area for uranium mineralizaiton. Compared with the Xiangshan uranium orefield, they have many great differences in such aspects as the degree of volcanic activity, the degree of late hydrothermal activity, and the denudation degree. The geochemical and geophysical anomalies of Yuhuashan area indicate that the area within the comprehensive anomaly of U -Th -Mo, the alternate magnetic positive and negative anomalies and positive radioactive anomalies are favorable areas for uranium exploration. Based on the ore-forming geological, geochemical and geophysical conditions, the authors established a comprehensive anomaly model and a uranium exploration model for Yuhuashan area, which will provide important theoretic and practical reference for uranium exploration in the future. Moreover, the authors hold that more exploration work should be preferentially carried out along the Weishan-Tongshan fault zone which is the key position of resource reserves.
-
Keywords:
- comprehensive information for exploration /
- exploratory model /
- uranium ore /
- Yuhuashan /
- Ziyunshan
-
1. 引言
遥感地质找矿是遥感信息获取、含矿信息提取以及含矿信息成矿分析与应用的过程, 近年来, 被广泛应用于地质、矿产资源及相关环境的调查中(刘燕君等, 1993; 朱振海, 1994; 郭德方, 1995; Sabins, 1999; Everett et al., 2002; 廖崇高等, 2002; 连长云等, 2005; 刘颖璠等, 2012; 钱建平等, 2012; 谭克龙等, 2012; 杜小弟等, 2015)。航空高光谱是当前遥感的前沿技术, 通过高光谱成像所获取的地球表面的图像包含光谱维信息融合为一体, 即“图谱合一” (束炯等, 2006), 具有波段数多, 波带窄, 对地物能定量分析等优点, 是20世纪末期以来遥感领域最大的技术进展(Campbell et al., 2011)。航空高光谱遥感技术相对于星载高光谱遥感技术, 可以获取高空间分辨率的高光谱遥感数据, 因而对微小地物具有更强的识别能力(刘德长等, 2015)。通过高光谱矿物填图, 可以大面积、快速提取蚀变矿物(Clack et al., 1990)。王润生等(2010)系统总结了高光谱矿物填图技术流程、工作方法和技术体系。中国国土资源航空物探遥感中心在新疆土屋东—三岔口地区, 应用HyMap航空成像光谱数据填绘出了白云母、绿泥石、绿帘石、绿泥石和绿帘石组合、高岭石、蒙脱石、透辉石、透闪石、蛇纹石、褐铁矿、方解石等矿物或矿物组合种类(王润生等, 2011)。
本文以新疆卡拉塔格地区获取的HyMap航空高光谱数据、地面准同步定标数据、地面高光谱数据为例, 提取并筛选了基于HyMap航空高光谱影像的成矿有利蚀变信息, 在此基础上对红山铜金矿床航空-地面高光谱提取的蚀变信息进行了综合剖析, 并结合矿区地质背景, 建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型, 圈定了2处找矿有利地段。
2. 研究区地质概况
研究区大地构造位于东天山吐哈盆地南缘、大南湖—头苏泉晚古生代岛弧带(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 新疆卡拉塔格地区地质矿产图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中—上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿Figure 1. Geological map of Kalatag area in Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit
图 1 新疆卡拉塔格地区地质矿产图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中—上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿Figure 1. Geological map of Kalatag area in Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit区内地层整体呈北西向产出, 由中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组(O2Hd)、中—上志留统红柳峡组(S2-3h)、下泥盆统大南湖组(D1d)、上石炭统脐山组(C2qs)、中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组(P2a)、上二叠统库莱组(P3k)、下侏罗统三工河组(J1s)、全新统(Qh)组成。
该区经历了多期次的构造变动, 区域构造形成类型多样、特征复杂, 褶皱、断裂和火山机构发育, 区域性的断裂构造控制着该区火山岩和侵入岩的展布, 次级断裂控制着矿化蚀变带的分布, 更次一级构造裂隙带控制着矿化体的产出。主要发育北西、北北西和北东东向三组断裂构造, 其中北西向断裂为该区主要控矿构造, 同火山断裂发育, 含矿火山热液沿断裂活动强烈。
区内火山活动强烈, 火山岩分布广泛。岩石类型以中基性火山岩为主, 中酸性火山岩次之, 从奥陶系至二叠系均有出露, 其中奥陶系最为发育, 其次为泥盆系、石炭系, 二叠系局部出现。侵入岩较为发育, 主要为一套古生代侵入体, 包括中酸性闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗岩等侵入岩, 中部为与铜金矿化直接相关的中生代中酸性火山机构, 主要由石英斑岩、钠长斑岩、英安岩、英安斑岩、安山玢岩、闪长玢岩和火山角砾集块岩等岩性构成。其中志留纪侵入岩由老到新依次为英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、二长花岗岩、花岗斑岩。该区经受了区域埋深变质作用, 变质程度较弱, 主要变质矿物为绿泥石、钠长石、葡萄石、石英、阳起石、方解石、绿帘石。
区内已知矿床自北西向南东依次产出有:红山铜金矿床→梅岭铜锌金矿床→红石铜金矿床→红海铜锌金矿床。
3. 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法用于寻找铜金矿床的原理
3.1 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法的依据
不同矿床类型由于岩石岩性和蚀变矿物不同, 它们的光谱特征有明显的差异(姚佛军, 2006)。铜金矿床属于内生金属矿床, 这类矿床与地表蚀变密切相关, 可以利用航空高光谱遥感影像进行蚀变矿物提取, 结合地表岩石光谱测试分析, 应用HyMap航空成像光谱仪和美国ASD公司的FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪对不同类型矿床的光谱特征进行测量, 分析其不同类型矿床的光谱特征, 进行蚀变矿物遥感信息提取, 开展高光谱遥感地空综合预测研究, 进而指导找矿。
3.2 蚀变矿物诊断性光谱特征分析
岩矿的光谱包含有一系列特征吸收谱带。每一个特征谱带或谱带组合与岩矿内部微粒的物质属性存在一定的对应关系(Povarennykh, 1978)。在短波红外光谱区域, 褐铁矿、黄钾铁矾、白云母、绿泥石等具有可以识别的诊断性光谱特征, 特征吸收波段的深度与岩石中这些矿物的含量密切相关(刘圣伟, 2006)。矿物诊断性光谱吸收包括金属阳离子在可见光区域的电子过程以及阴离子基团在近红外区域的振动过程。蚀变矿物的可见光−近红外范围内几种官能团主要包括Fe2+、Fe3+、Al−OH、Mg−OH、OH-、CO32-。
一般阴离子诊断谱带位于2000~2500 nm光谱区域。而Fe2+、Fe3+和Mn2+诊断谱带一般位于400~1200 nm光谱区域(甘甫平等, 2003)。所以根据400~1100 nm光谱区间的Fe吸收谱带和2000~2500 nm羟基和碳酸根谱带将矿物分为含铁矿物、含羟基矿物和含碳酸根矿物以及其他矿物(甘甫平, 2003)。褐铁矿的光谱吸收谷是矿物光谱分析、遥感铁染异常提取常用的波段。其中Fe3+离子的特征吸收谷位主要在600~800 nm, 中心位置在700 nm左右, Fe2+离子的特征吸收谷位主要在900~1500 nm, 中心位置在1200 nm左右; 白云母的诊断性光谱特征是Al−OH键在2180~2230 nm之间的尖锐而深的吸收特征, 以及在2340 nm和2440 nm附近的较弱Al−OH特征, Clark et al.(1990)在高光谱分辨率下, 检测到白云母矿物在2200 nm附近的吸收波段随Al含量的增加向长波方向的移动; 绿泥石的光谱具有Fe−OH和Mg−OH的诊断性吸收特征, 波长位置分别为2235~2255 nm和2320~2360 nm, 这些吸收特征的波长随着绿泥石中铁离子含量的增加而增大。
4. HyMap航空高光谱数据获取及处理
综合考虑仪器参数、成图精度的要求、研究区自然地理、地形起伏、野外工作条件等因素, 进行飞行方案的最优设计(表 1)。将HyMap成像光谱仪搭载在Y−12飞机上, 利用国外引进的HyMap航空高光谱遥感测量系统、地面ASD光谱测量系统。采集高光谱分辨率的HyMap航空高光谱遥感数据、地面准同步的地物光谱定标数据。具体获取过程分为3个步骤:首先对HyMap成像光谱仪进行实验室定标, 保证其性能指标达到项目要求, 以获取优质的高光谱影像数据; 其次进行HyMap仪器的安装和测试, 按照仪器安装规范方法, 将HyMap安装在Y−12飞机上, 保证机下的摄影窗口满足数据获取要求, 按照航空成像光谱数据获取规范进行地面测试; 最后为HyMap航空高光谱数据获取和初步质量检查。
表 1 HyMap航空成像光谱仪主要技术参数Table 1. Main technical parameters of HyMap aviation imaging spectroradiometer
在此基础上, 开展HyMap航空高光谱遥感数据辐射定标、大气校正光谱反演、几何校正和地理编码等数据处理工作。通过此项研究, 为高光谱遥感地空综合预测铜金矿床的技术方法研究和应用提供可靠的数据基础。
5. 地面高光谱数据获取及处理
地面光谱测量采用美国ASD公司生产的FieldSpec Pro FR地面光谱测量仪(表 2)。利用该仪器开展了地面光谱准同步定标。在HyMap高光谱数据获取过程中, 准同步布设黑白布定标场和明暗地物定标场, 利用FieldSpec Pro FR地面光谱测量仪进行光谱定标数据获取(图 2,图 3), 并基于经验线性模型法, 对高光谱影像进行大气校正和光谱比对分析。
表 2 FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪主要技术参数Table 2. Main technical parameters of FieldSpec Pro FR spectrometer
同时开展了典型铜金矿床地表蚀变围岩和其他相关的岩石地物的光谱测量, 完成了4条贯穿地层走向的成矿有利地质单元光谱测量和4条典型矿床光谱测量。共完成光谱测量点287个, 光谱测量曲线2870条。测量完成后, 开展了各岩石类型的岩矿光谱数据处理、光谱库建立、光谱特征分析等研究工作, 研究及分析结果为航空高光谱蚀变矿物信息提取、地面光谱验证、铜金矿床围岩蚀变信息筛选等提供重要的地面光谱信息支持。
地面高光谱数据处理采用ViewSpec Pro软件, 利用ViewSpec Pro软件挑选符合要求的地面岩矿光谱曲线, 并将这些曲线转换为txt格式的文件。由于受到太阳位置、角度条件、大气条件、地形影响及传感器本身性能的影响, 传感器所记录的数据与目标的光谱反射率或光谱辐射亮度值并不一致。需先将传感器记录的原始辐射值(DN值)转化为地物反射率(李志忠等, 2015)。
6. 蚀变矿物信息提取处理方法及分布特征
目前基于高光谱遥感影像数据提取矿物的处理方法可以分为2类: (1)通过像元光谱与矿物标准光谱曲线的匹配实现识别和量化目标矿物; (2)提取矿物光谱特征吸收波段参数作为识别和量化指标(卢燕, 2014)。前者在处理过程中光谱数据信息可能由于重定标而部分丢失。且基于单幅图像统计参数的处理方法难以做到无缝衔接, 该方法也涉及大量的运算。本次研究区蚀变矿物提取主要基于第2种方法。该方法利用ENVI软件, 基于可编程实现的特征提取处理通道, 该通道中脚本设计是基于提取光谱参数, 首先对影像光谱数据进行均值标准化、去连续统、卷积平滑等数据预处理, 在进行特征深度、特征面积、特征宽度、极小值波长、比值、算术和逻辑运算等特征参数提取。同时利用多个诊断性特征来标记或约束特定的矿物, 提取矿物的分布和相对含量, 并增强矿物识别的精度。
根据矿物光谱特征吸收波段参数的蚀变矿物提取方法, 在研究区提取了褐铁矿−黄钾铁矾、白云母−蒙脱石、绿泥石−绿帘石−碳酸盐、叶腊石等蚀变矿物或组合(图 4), 其中褐铁矿−黄钾铁矾、白云母−蒙脱石、绿泥石−绿帘石−碳酸盐等蚀变矿物组合在全区范围内分布, 且呈团块状、条带状及星散状。叶腊石则仅在研究区北东部呈星点状分布, 蚀变不明显, 对于指导找矿意义不大(黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置)。
![]() 图 4 新疆卡拉塔格地区HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物丰度图a—褐铁矿-黄钾铁矾; b—白云母-蒙脱石; c—绿泥石、绿帘石、碳酸盐; d—叶腊石, 黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置Figure 4. HyMap aviation hyperspectral alteration mineral abundance map of Kalatag area in Xinjianga-Limonite-jarosite; b-Muscovite-montmorillonite; c-Chlorite, epidote, carbonate; d-Pyrophyllite, yellow circle indicates pyrophyllite distribution position
图 4 新疆卡拉塔格地区HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物丰度图a—褐铁矿-黄钾铁矾; b—白云母-蒙脱石; c—绿泥石、绿帘石、碳酸盐; d—叶腊石, 黄色圈内为叶腊石分布位置Figure 4. HyMap aviation hyperspectral alteration mineral abundance map of Kalatag area in Xinjianga-Limonite-jarosite; b-Muscovite-montmorillonite; c-Chlorite, epidote, carbonate; d-Pyrophyllite, yellow circle indicates pyrophyllite distribution position7. 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的建立与找矿有利地段优选
7.1 矿区地质特征
红山铜金矿床是高硫型−浅成低温热液型矿床(董承维, 2013)。矿床产于陆相蚀变酸性火山穹窿及其通道中, 该次火山机构受近东西与北西向两组断裂控制, 且主要控岩控矿构造为北西向断裂。铜矿体受北西向断裂及其次级构造破碎带控制, 为浸染状辉铜矿化和黄铜矿化。金矿化主要与酸性次火山岩中的细粒黄铁矿有关(王瑞军等, 2014) (图 5)。
![]() 图 5 红山铜金矿区地质图(据王京彬, 2006)1—第四系残坡积物、风积物; 2—英安岩、英安斑岩、安山岩; 3—蚀变英安岩; 4—流纹斑岩、石英斑岩、霏细斑岩; 5—花岗岩; 6—花岗闪长岩脉; 7—闪长玢岩脉; 8—氧化带矿体; 9—推测断层; 10—片理化带; 11—金矿体; 12—铜矿体Figure 5. Geological map of the Hongshan Cu-Au deposit (after Wang, 2006)1-quaternary debris slope sediments, aeolian; 2-dacite, British Ann porphyry, andesite; 3-alteration dacite; 4-rhyolitic porphyry and quartz porphyry, faye fine porphyry; 5-granite; 6-granite diorite vein; 7-diorite Bin dike; 8-oxidation zone ore body; 9-speculation fault; 10-piece of physics and chemistry; 11-gold ore body; 12-copper ore body
图 5 红山铜金矿区地质图(据王京彬, 2006)1—第四系残坡积物、风积物; 2—英安岩、英安斑岩、安山岩; 3—蚀变英安岩; 4—流纹斑岩、石英斑岩、霏细斑岩; 5—花岗岩; 6—花岗闪长岩脉; 7—闪长玢岩脉; 8—氧化带矿体; 9—推测断层; 10—片理化带; 11—金矿体; 12—铜矿体Figure 5. Geological map of the Hongshan Cu-Au deposit (after Wang, 2006)1-quaternary debris slope sediments, aeolian; 2-dacite, British Ann porphyry, andesite; 3-alteration dacite; 4-rhyolitic porphyry and quartz porphyry, faye fine porphyry; 5-granite; 6-granite diorite vein; 7-diorite Bin dike; 8-oxidation zone ore body; 9-speculation fault; 10-piece of physics and chemistry; 11-gold ore body; 12-copper ore body矿区地表发育黄钾铁钒化、绢云母化、硅化、褐铁矿化、黄铁矿化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、青磐岩化。近矿蚀变以火山岩酸淋滤带蚀变体的黄钾铁矾化−明矾石化−高岭土化−石膏和中性斑岩体的绢云母化−硅化为显著特征, 远矿蚀变为青磐岩化(许英霞等, 2008)。矿区中心为泥化、硫酸盐带, 向北为硅化−伊利石化−绢云母化−褐铁矿化带。具有找矿标志的矿化蚀变为:硅化−绢云母化、伊利石化、褐铁矿化、硅化、高岭土化−明矾石化等。
红山铜金矿床矿化以铜、金矿为主, 赋矿岩性主要为流纹岩、英安岩、安山玢岩、闪长玢岩、火山角砾岩。矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿、蓝铜矿、闪锌矿、磁铁矿、赤铁矿、黄钾铁钒等。脉石矿物为石英、斜长石、绢云母、绿泥石等。矿石呈稠密浸染状、细脉状、角砾状构造(许英霞, 2010)。
7.2 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的建立
充分研究区域成矿有利的构造、地层、岩浆岩条件、变质条件的基础上, 结合区域控矿因素、矿床、矿化蚀变特征, 进行航空高光谱蚀变矿物分布特征分析及评价。本文截取了研究区内红山铜金矿床及外围基于HyMap航空高光谱遥感影像的蚀变矿物分布图(图 6), 图中显示红山铜金矿床中心位置处于开采状态, 呈黑白相间且颜色突变的色调, 影纹粗糙且不均匀, 矿床外围呈灰黑色、灰绿色色调, 影纹粗糙。与矿床有关的航空高光谱蚀变矿物组合主要为褐铁矿+黄钾铁钒、绢云母+蒙脱石等, 呈大面积的团块状分布。在矿床外围分布着呈星散状、星点状的绿泥石+绿帘石蚀变矿物组合, 该组蚀变为铜金矿床外围主要发育的蚀变组合, 对于寻找该类型矿床有一定的指示作用。
在红山铜金矿区收集了具体的剖线采样和光谱数据, 图 7为红山铜金矿区的地质光谱综合剖面, 出露的地层为中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组, 岩性主要为英安岩、片理化带、流纹斑岩、花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、构造蚀变岩以及铜金矿化体等。蚀变矿物主要有褐铁矿、黄钾铁钒、绢云母、石膏、高岭石、明矾石及方解石等。通过样品采集和光谱测试结果, 研究与该区铜金矿关系密切的几种赋矿岩性的光谱曲线, 分别为构造蚀变岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗岩、流纹斑岩、蚀变英安岩、及铜金矿化体。
![]() 图 7 红山铜金矿区剖线地面高光谱蚀变矿物分布图1—英安岩; 2—片理化带; 3—流纹斑岩; 4—花岗岩; 5—花岗闪长岩; 6—断裂构造; 7—地面光谱样采样点; 8—地面光谱测试点编号; 9—褐铁矿; 10—黄钾铁矾; 11—绢云母; 12—石膏; 13—高岭石; 14—明矾石; 15—方解石Figure 7. Surface hyperspectral alteration mineral distribution along geological section in the Hongshan copper gold orefield1-Dacite; 2-Schistosity zone; 3-Rhyolitic porphyry; 4-Granite; 5-Granite diorite; 6-Fracture structure; 7-Surface spectrum sampling site; 8-Serial number of spectrum test point; 9-Limonite; 10-Jarosite; 11-Sericite; 12-Gypsum; 13-Kaolinite; 14-Alunite; 15-Calcite
图 7 红山铜金矿区剖线地面高光谱蚀变矿物分布图1—英安岩; 2—片理化带; 3—流纹斑岩; 4—花岗岩; 5—花岗闪长岩; 6—断裂构造; 7—地面光谱样采样点; 8—地面光谱测试点编号; 9—褐铁矿; 10—黄钾铁矾; 11—绢云母; 12—石膏; 13—高岭石; 14—明矾石; 15—方解石Figure 7. Surface hyperspectral alteration mineral distribution along geological section in the Hongshan copper gold orefield1-Dacite; 2-Schistosity zone; 3-Rhyolitic porphyry; 4-Granite; 5-Granite diorite; 6-Fracture structure; 7-Surface spectrum sampling site; 8-Serial number of spectrum test point; 9-Limonite; 10-Jarosite; 11-Sericite; 12-Gypsum; 13-Kaolinite; 14-Alunite; 15-Calcite经研究分析发现:红山铜金矿床及外围不同岩性地面光谱特征各不相同, 各类岩性具体曲线(图 8)特征如下:
![]() 图 8 红山铜金矿床及外围各岩性光谱曲线对比图a—构造蚀变岩; b—花岗闪长岩; c—花岗岩; d—流纹斑岩; e—蚀变英安岩; f—铜金矿化体Figure 8. Comparison diagram of various lithology spectral curves from the Hongshan copper gold deposit and peripheral areasa-Tectonic altered rock; b-Granodiorite; c-Granite; d-Rhyolitic porphyry; e-Altered dacite; f-Copper gold mineralization body
图 8 红山铜金矿床及外围各岩性光谱曲线对比图a—构造蚀变岩; b—花岗闪长岩; c—花岗岩; d—流纹斑岩; e—蚀变英安岩; f—铜金矿化体Figure 8. Comparison diagram of various lithology spectral curves from the Hongshan copper gold deposit and peripheral areasa-Tectonic altered rock; b-Granodiorite; c-Granite; d-Rhyolitic porphyry; e-Altered dacite; f-Copper gold mineralization body构造蚀变岩(图 8-a)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的Fe3+特征吸收可能为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱吸收峰为发育弱绢云母化所致, 2260 nm处的较强吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化所致。故构造蚀变岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁矾+绢云母。
花岗闪长岩(图 8-b)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处较强的对称吸收峰为岩石发育褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处较强的吸收峰, 及右肩2250 nm处较弱次级吸收峰, 是Al−OH的特征吸收, 为明矾石化所致; 2350 nm处强的主吸收峰, 左肩2250 nm处较强的次级吸收峰, 是Mg−OH的特征吸收, 为绿泥石化所致。故其蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+明矾石+绿泥石。
花岗岩(图 8-c)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 910 nm处较弱的Fe3+特征吸收峰为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为绢云母化引起, 其右肩2250 nm处的较弱吸收峰可能为明矾石化所致; 2265 nm处的较弱吸收峰可能为黄钾铁矾化所致; 2330 nm处可见较强吸收峰, 是CO32-的特征吸收峰, 为岩石发育碳酸盐化所致, 故花岗岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁矾+绢云母+明矾石+方解石。
流纹斑岩(图 8-d)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的较强吸收峰为褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的强Al−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育绢云母化所致; 2265 nm处的弱Fe−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化所致, 故流纹斑岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+黄钾铁钒+绢云母。
蚀变英安岩(图 8-e)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的弱吸收峰为弱褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为绢云母化引起; 2350 nm处的较强主吸收峰及其左肩2250 nm处的较强次级吸收峰, 是Mg−OH的特征吸收峰, 为绿泥石化所致; 2330 nm处的较强主吸收峰以及1880 nm、2060 nm、2170 nm处较弱次级吸收峰, 是CO32-的特征吸收峰, 为岩石发育碳酸盐化所致; 1836 nm、1935 nm、2213 nm、2270 nm处可见多处较强吸收峰, 为岩石发育石膏所致。故蚀变英安岩蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+绢云母+绿泥石+方解石+石膏。
铜金矿化体(图 8-f)地面光谱曲线特征显示: 880 nm处的较强Fe3+特征吸收为岩石发育褐铁矿化所致; 2210 nm处的弱Al−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育绢云母化; 2265 nm处的弱Fe−OH特征吸收峰为岩石发育黄钾铁矾化; 1540 nm、1835 nm、1920 nm、2000 nm、2165 nm、2208 nm、2250 nm、2329 nm、2374 nm、2385 nm处可见多处较强吸收峰, 可能为岩石发育黝帘石化所致。故铜金矿化体蚀变矿物组合为:褐铁矿+绢云母+黄钾铁钒+黝帘石。
根据航空高光谱和地面高光谱蚀变矿物或组合的类型和分布特征, 结合红山铜金矿床的地质特征, 进行典型矿床航空−地面高光谱综合剖析, 最终建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型(表 3)。
表 3 红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型Table 3. Hyperspectral remote sensing air comprehensive prospecting model for the Hongshan copper gold deposit
7.3 铜金矿床找矿有利地段优选
在建立红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型的基础上, 结合地质、野外调查验证等多源地学信息, 运用高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法, 优选了2处与已知矿床航空−地面高光谱向类似的找矿有利地段, 分别为I−1和I−2(图 9)。
![]() 图 9 新疆卡拉塔格地区找矿有利地段优选图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中-上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿; 23—高光谱找矿有利地段Figure 9. Favorable ore-prospecting optimization segments in Kalatag area of Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit; 23-Hyperspectral favorable ore-prospecting segments
图 9 新疆卡拉塔格地区找矿有利地段优选图1—全新统:砂石及砾石沉积; 2—下侏罗统三工河组:粉砂质泥岩、泥质砂岩夹钙质砂岩; 3—上二叠统库莱组:砾岩、中粗粒岩屑砂岩; 4—中二叠统阿尔巴萨依组:凝灰岩、橄榄玄武岩; 5—上石炭统脐山组:玄武岩、安山岩; 6—下泥盆统大南湖组:安山岩、英安岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山角砾岩; 7—中-上志留统红柳峡组:凝灰质砾岩、晶屑岩屑凝灰岩; 8—中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组:玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩; 9—志留纪二长花岗岩; 10—志留纪花岗闪长岩; 11—志留纪英云闪长岩; 12—花岗岩体; 13—地质界线; 14—角度不整合界线; 15—岩相界线; 16—逆断层; 17—性质不明断层; 18—推测断层; 19—铜金矿; 20—铜锌矿; 21—铜锌金矿; 22—铜铁矿; 23—高光谱找矿有利地段Figure 9. Favorable ore-prospecting optimization segments in Kalatag area of Xinjiang1-Holocene, sand and gravel deposits; 2-Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation: river silty mudstone, argillaceous sandstone intercalated with calcareous sandstone; 3-Permian Kulai Formation: breccia, coarse grained lithic sandstone; 4-Middle Permian Aebasayi Formation: tuff, olivine basalt; 5-Carboniferous Qishan Formation: basalt, andesite; 6-Lower Devonian Dananhu Formation: andesite, dacite, welded tuff and volcanic breccia; 7-Middle-upper Silurian Hongliuxia Formation: tuffaceous conglomerate, wafer crumbs debris tuff; 8-Daliugou Formation of Ordovician Huangcaopo Group: basalt, andesite, dacite; 9-Silurian monzonitic granite; 10-Silurian granite diorite; 11-Silurian tonalite; 12-Granite rock mass; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Angular unconformity; 15-Petrofacies boundary; 16-Thrust; 17-Unknown fault; 18-Inferred fault; 19-Copper and gold deposit; 20-Copper and zinc deposit; 21-Copper zinc deposit; 22-copper deposit; 23-Hyperspectral favorable ore-prospecting segmentsI−1找矿有利地段分布在玉带铜金矿点北西侧一带, 呈北北西向展布, 面积约5.2 km2。区内分布的地层为中−上志留统红柳峡组(S2-3h)火山岩, 近东西向断裂构造发育, 区内多发育褐铁矿化、硅化、绿帘石化等蚀变。微量元素分析23个, 化学分析显示钛含量最高达0.23×10-2, 金红石含量最高达0.38×10-2。为铜、金、钛等元素多金属找矿有利地段(图 10)。
I−2找矿有利地段分布在东二区南东侧, 呈近东西向展布, 面积约6.8 km2。区内分布的地层为中奥陶统荒草坡群大柳沟组(O2Hd)火山岩, 北东东向断裂构造发育, 花岗闪长岩体呈近东西向展布, 区内多发育硅化、褐铁矿化、赤铁矿化、绿帘石化、孔雀石化等蚀变。微量元素分析15个, 化学分析显示钛元素含量最高达0.21×10-2, 金红石含量最高达0.35×10-2, 且区内已有红山铜金矿床分布, 为铜、金、钛等元素多金属找矿有利地段(图 11)。
8. 结论
(1) 新疆东天山卡拉塔格铜金多金属矿床集中, 地表具有指示意义的蚀变矿物分布较为典型, 适合利用高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法在该区寻找铜金及多金属矿床, 故该方法为寻找铜金矿床的有效技术方法。
(2) 在运用HyMap航空成像光谱仪和FieldSpec Pro FR光谱仪进行高光谱数据获取和处理的基础上, 结合HyMap航空高光谱蚀变矿物提取效果分析, 最终开展典型矿床航空−地面高光谱综合剖析研究, 建立了红山铜金矿床高光谱遥感地空综合找矿模型, 并综合地质、野外调查验证等多源地学信息, 圈定了I−1和I−2等两处找矿有利地段。
(3) 与常规的地质、区域化探等地质矿产勘查方法相比, 高光谱遥感地空综合预测方法具有低成本、快速高效的优势。但由于各类矿床的找矿标志和高光谱异常信息多种多样, 从而造成蚀变异常信息的多解性, 加上利用高光谱地空综合预测方法开展多金属矿产资源调查研究还比较少, 需要今后继续完善成熟。
致谢: 感谢匿名审稿专家及编辑部老师在本文修改过程中提出的宝贵意见。注释❶东华理工大学. 2015.江西玉华山火山盆地矿产远景调查成果报告[R].❷江西地质矿产调查研究大队. 1995. 1:5万七琴街幅、店下幅、洛市幅、白陂幅区域地质调查报告与附图[R].❸江西省核工业地质局261大队. 2009.江西省玉华山地区铀资源评价[R]. -
图 1 赣杭构造带铀矿地质简图(据余心起等, 2006修改)
Figure 1. Uranium geological sketch map of the Gan−Hang zone (after Yu Xinqi et al., 2006)
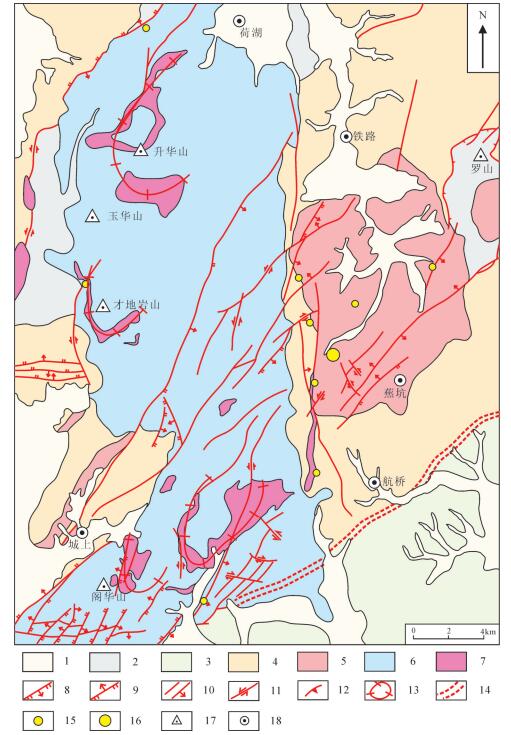
图 2 玉华山地区铀矿地质简图❷
1—第四纪砂砾岩; 2—晚三叠世砂砾岩夹煤层; 3—白垩纪砂砾岩; 4—中—新元古代浅变质岩; 5—晚侏罗世花岗岩; 6—早白垩世火山岩; 7—早白垩世次火山岩; 8—正断层; 9—逆断层; 10—性质不明断层及倾向; 11—平移断层; 12—推覆构造; 13—环形火山构造; 14—区域深大断裂; 15—铀矿点; 16—铀矿床; 17—山峰; 18—乡镇
Figure 2. Uranium geological sketch map of Yuhuashan area❷
1−Quaternary glutenite; 2−Late Triassic glutenite and coal bed; 3−Cretaceous glutenite; 4−Meso—Neoproterozoic epimetamorphic rock; 5−Late Jurassic granite; 6−Early Cretaceous volcanic rock; 7−Early Cretaceous sub-volcanic rock; 8−Normal fault; 9−Thrust fault; 10−Unknown fault and tendency; 11−Transcurrent fault; 12−Nappe structure; 13−Circular volcanic structure; 14−Regional fault; 15−Uranium ore occwrrence; 16−Uranium deposit; 17−Mountain peak; 18−Town
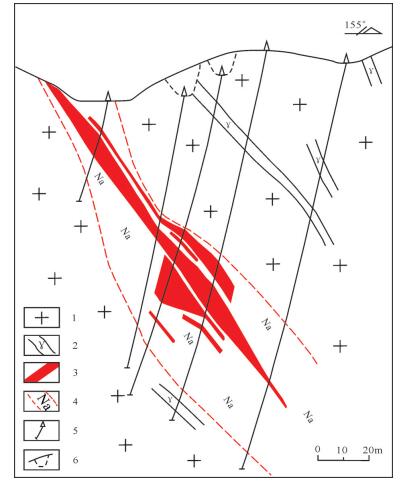
图 3 曲源铀矿床52号勘探线剖面图(周玉龙等, 2015)
1—黑云母花岗岩; 2—细粒花岗岩脉; 3—铀矿体; 4—钠交代岩; 5—钻孔; 6—低洼位置在剖面上的投影
Figure 3. Geological section along No. 52 exploration line of the Quyuan uranium deposit (after Zhou Yulong, et al., 2015)
1-Biotite granite; 2-Fine-grained granitic vein; 3-Uranium orebody; 4-Sodium metasomatic rock; 5-Drill hole; 6-Projection position of low-lying area at the section
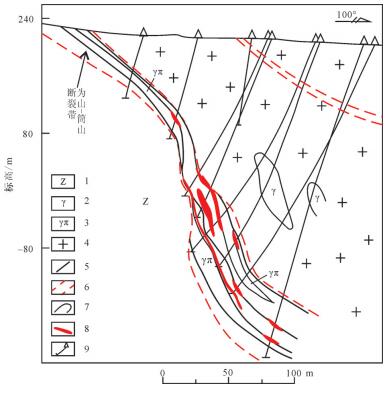
图 4 曲源铀矿床6号勘探线剖面图(周玉龙等, 2015)
—震旦系变质岩; 2—细粒花岗岩; 3—花岗斑岩; 4—中细粒黑云母花岗岩; 5—断裂构造; 6—构造破碎带范围; 7—地质界线; 8—铀矿体; 9—钻孔
Figure 4. Geological section along No. 6 exploration line of the Quyuan uranium deposit (after Zhou Yulong, et al., 2015)
1-Sinian metamorphic rock; 2-Fine-grained granite; 3-Granite porphyry; 4-Medium-fine grained biotite granite; 5-Fault structure; 6-Tectonic fracture zone; 7-Geological boundary; 8-Uranium orebody; 9-Drill hole
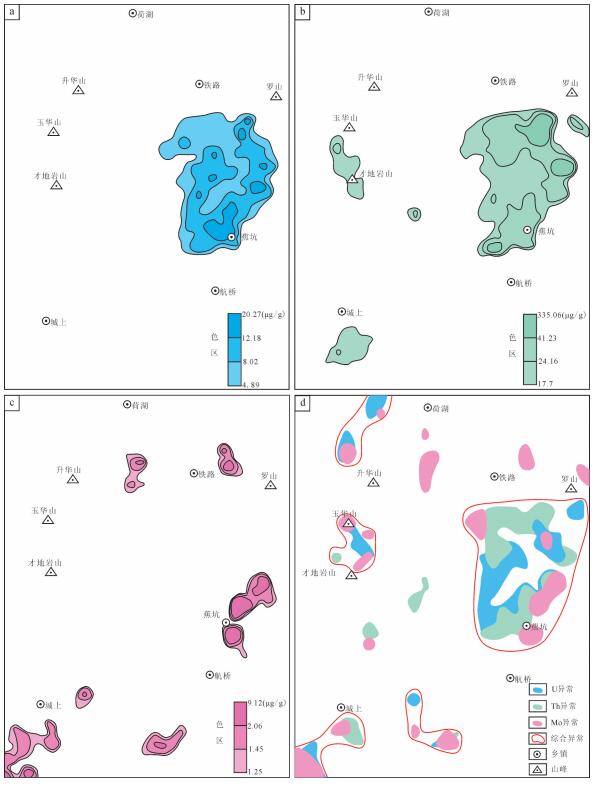
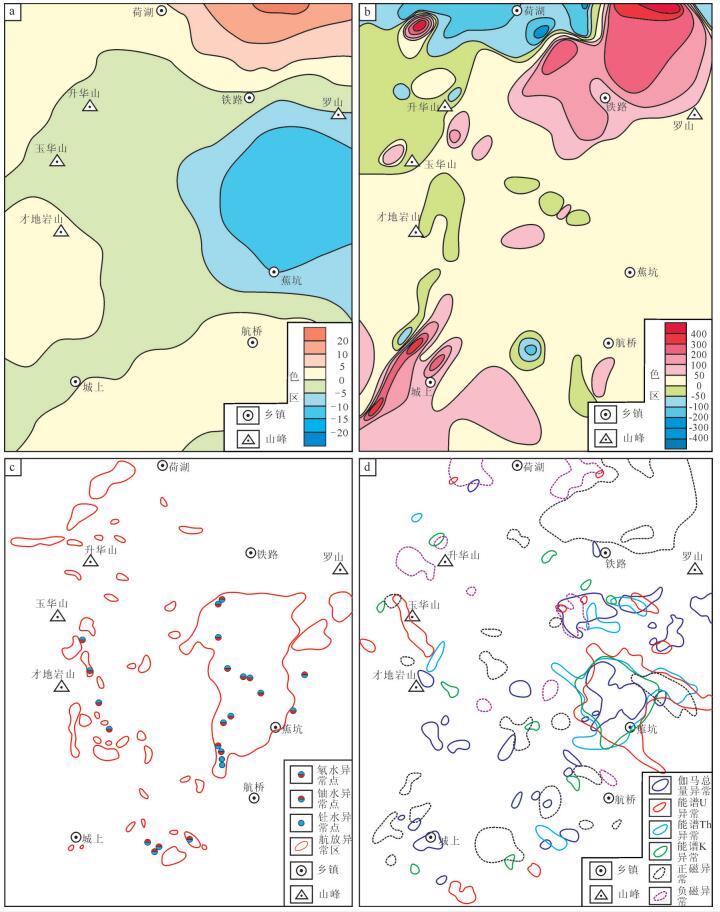
图 6 玉华山地区地球物理测量异常图
a—1:20万重力异常图❸; b—1:20万航磁异常图❸ c—1:20万航放异常图❸; d—1:5万放射性测量与高磁综合异常图
Figure 6. Geophysical survey anomaly map of Yuhuashan area
a-Gravity anomaly map (1: 200000); b-Aeromagnetic anomaly map (1: 200000); c-Airborne radioactivity anomaly map (1:200000); d-Integrated anomaly map of radioactivity and high precision magnetometry (1: 50000)
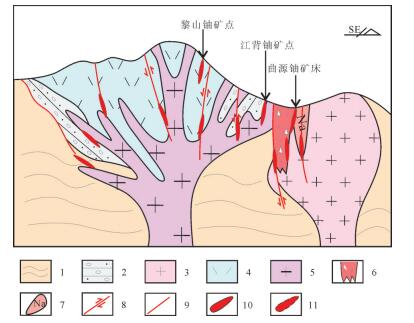
图 7 玉华山地区铀矿地质找矿模型
1—中—新元古代浅变质岩; 2—晚三叠世砂砾岩; 3—晚侏罗世花岗岩; 4—早白垩世火山岩; 5—早白垩世次火山岩; 6—隐爆角砾岩筒; 7—钠交代岩; 8—断层; 9—性质不明断层; 10—已探明铀矿体; 11—预测铀矿体
Figure 7. Uranium geological prospecting model of Yuhuashan area
1-Mesoproterozoic—Neoproterozoic metamorphic rock; 2-Late Triassic glutenite; 3-Late Jurassic granite; 4-Early Cretaceous volcanic rock; 5-Early Cretaceous sub-volcanic rocks; 6-Cryptoexplosive breccia pipe; 7-Sodium metasomatic rock; 8-Fault; 9-Unknown fault; 10-Identified uranium orebody; 11-Predicted uranium orebody
表 1 玉华山地区与相山铀矿田成矿地质条件对比(据刘小宇等, 1996; 邱爱金等, 2002修改)
Table 1 Comparison of metallogenic conditions between Yuhuashan area and the Xiangshan uranium orefield (after Liu Xiaoyu et al., 1996; Qiu Aijin et al., 2002)

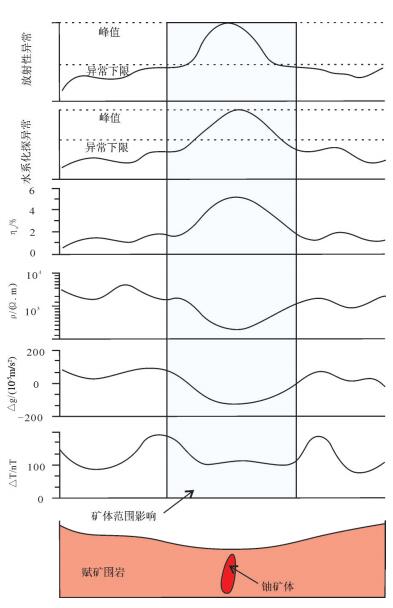
表 2 玉华山地区铀矿综合信息找矿参数特征
Table 2 Parameters of comprehensive information exploration for uranium ore deposit in Yuhuashan area

-
Asadi H, Kianpouryan S, Lu Y, Mccuaig T. 2014. Exploratory data analysis and C-a fractal model applied in mapping multi-element soil anomalies for drilling:a case study from the Sari Gunay epithermal gold deposit, NW Iran[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 145:233-241. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.07.005
Chen Diyun, Xu Weichang. 1993. Geochemical characteristics of uranium of Chencai group metamorphic rock[J]. Uranium Geology, 9(4):31-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199304004.htm
Chen Zhengle, Wang Yong, Zhou Yonggui, Han Fengbing, Wang Pingan, Gong Hongliang, Shao Fei, Tang Xiangsheng, Xu Jinshan. 2013. SHRIMP U-Pd dating of zircons from volcanic-intrusive complexes in the Xiangshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province, and its geological implications[J]. Geology in China, 354(1):217-231(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287843166_SHRIMP_U-Pb_dating_of_zircons_from_volcanic-intrusive_complexes_in_the_Xiangshan_uranium_orefield_Jiangxi_Province_and_its_geological_implications
Cuney M. 2009.The extreme diversity of uranium deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 44(1):3-9. doi: 10.1007/s00126-008-0223-1
Cuney M. 2014. Felsic magmatism and uranium deposits[J]. Bulletin De La Societe Geologique De France, 185(2):75-92. doi: 10.2113/gssgfbull.185.2.75
Dahlkamp F. 2013. Uranium Ore Deposits[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 1-460.
Deng Jiarui, Zhang Zhiping. 1989. Gan-Hang tectonic belt and its geologic significance[J]. Uranium Geology, 5(1):15-21(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198901003.htm
Deng Jiarui, Zhang Zhiping. 1999. Discussion on regional geotectonic setting of Ganhang tectonic belt[J]. Uranium Geology, 15(2):8-13(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1080/00206814.2011.588820?src=recsys
Du Letian. 1982. Corpus of Granite-type Deposits[M]. Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 1-404 (in Chinese).
Fan Honghai, Ling Hongfei, Wang Dezi, Shen Weizhou, Liu Changshi, Jiang Yaohui. 2001. Ore-forming material sources for Xiangshan uraium ore-field in Jiangxi Province:Evidence from Nd-Sr-Pb isotopes[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 7(2):139-145(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199801000.htm
Fang Xiheng, Fang Maolong, Luo Yi, Liu Rongrong, Liu Quan, Zhang Minglin, Wang Shuhong, Liu Hu, Fu Jing, Wang Yuanzhi, Zhan Junwei, Xie Yingchun. 2012. The potential evaluation of volcanic type uranium resources in China[J]. Uranium Geology, 28(6):342-348(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YKDZ201206007.htm
Feng Mingyue, He Debao. 2012. Uranium rich granite and uranium productive granite in South China[J]. Uranium Geology, 28(4):199-207(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YKDZ201204003.htm
Gilder S, Keller G, Luo M, Goodell P. 1991. Eastern Asia and the Western Pacific timing and spatial distribution of rifting in China[J]. Tectonophysics, 197(2):225-243. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519190043R
Goodell P, Gilder S, Fang X. 1991. A preliminary description of the Gan-Hang failed rift, southeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 197(2):245-255. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519190044S
Hu Gongren, Liu Congqiang, Zhang Bangtong, Yu Ruilian. 2000.Composition and structural metamorphism-deformation features of the central Jiangxi metamorphic zone[J]. Regional Geology of China, 19(4):375-381 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200004006.htm
Hu Gongren, Yu Ruilian. 2004. Redivision of the metamorphic facies zonation and definition of metamorphism P-T of metamorphic rocks belt in central Jiangxi province[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 26(2):65-75(in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC200402000.htm
Hu Gongren, Zhang Bangtong. 1997. Composition, evolution and basic structural framework of the central Jiangxi metamorphic basement[J]. Jiangxi Geology, 11(3):47-51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Gongren, Zhang Bangtong. 1998. Nerodymium isotope composition and source materials of the meta-basement in central Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 17(1):36-41(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hua Renmin, Chen Peirong, Zhang Wenlan, Lu Jianjun. 2005. Three major metallogenic events in Mesozoic in South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(2):99-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284690423_Three_major_metallogenic_events_in_Mesozoic_in_South_China
Huang Changsheng, Liao Xianzheng, Lei Liangcheng.2001.The fixed position mechanism of high intrusive mixtite in Yuhua mountain[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 24(2):104-108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ200102002.htm
Jiang Shaoqing, Sun Xingguo, Yang Tiezheng, Yin Xianbo, Wang Ce, Pan Yanbin. 2014. Integrated anomaly model and metallogenci prediction of the Duolong porphyry copper-gold ore concentration area in northern Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 361(2):497-509(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Y, Zhao P, Zhou Q, Liao S Y, Jin G D. 2011. Petrogenesis and tectonic Implications of early cretaceous S and A-type Granites in the Northwest of the Gan-Hang Rift, Se China[J]. Lithos, 121(1):55-73. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493710002847
Jin Jingfu, Hu Ruizhong. 1990. Physicochemical conditions of mineralization of XW uranium deposit[J]. Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 17(3):1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CDLG199003000.htm
Li Xiang. 2012. Petrogenesis and uranium-bearing capability evaluation of the Yuhuahsan volcanic-intrusive complex in the Jiangxi Province[D]. Nangjing:Nanjing University, 1-45(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Xiaoyu, Chen Zhaobo. 1996. Continental Volcanism and Uranium Mineralization[M]. Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 1-167(in Chinese).
Liu Ying. 2013. Geochronology and Geochemical of Ziyunshan Pluton at Yuhuashan Area in Jiangxi and it's Geological Significance[D]. Nanchang:East China University of Technology, 1-51(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mercadier J, Annesley I, Mckechnie C, Bogdan T, Creighton S. 2013.Magmatic and metamorphic uraninite mineralization in the western margin of the trans-hudson orogen (saskatchewan, Canada):A uranium source for unconformity-related uranium deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 108(5):1037-1065. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.5.1037
Pei Rongfu, Mei Yanxiong, Qu Hongying, Wang Haolin. 2013.Geological tectonic settings, depositional environments and orehosting rock assemblages for mineral deposits model with universality[J]. Geology in China, 354(1):31-41(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201301004.htm
Qiu Aijin, Guo Lingzhi, Zheng Dayu. 2002. The Constraint of Xiangshan Super Mineralization from Continental Tectonics[M]. Beijing:Geological Press, 1-103(in Chinese).
Seo J, Choi S, Dong W, Park J, Chang W. 2015. A new genetic model for the Triassic Yangyang iron-oxide-apatite deposit, South Korea:constraints from in situ U-Pb and trace element analyses of accessory minerals[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70:110-135. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.009
Shan Lin, Liu Xiaodong. 1985. A study on inclusions of main rocks in Xiangshan and some other volcanic basins[J]. Acta Pertrologica Mineralogica et Analytica, 4(4):289-294 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX198504000.htm
Shao Fei. 2011. Trisection distribution pattern of volcanic type uranium deposits and metallogenic prognosis in northeast section of Qinhang metallogenic belt[J]. Uranium Geology, 27(5):286-292(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201105005.htm
Shao Fei, Zhu Yonggang, Li Jia, He Xiaomei. 2010. Uranium metallogenic regularity and further exploration in Gan-Hang tectono-volcanic belt[J]. Shanghai Geology, 31(Supp.):133-136(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SHAD2010S1040.htm
Shen Weizhou, Zhang Zuhuan, Zhang Bangtong. 1988. Strontium, oxygen and lead isotopic geochemical studies of U-bearing granites in Southern China[J]. Uranium Geology, 4(1):23-30(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-ykdz198801005.htm
Sun Jian, Chen Yuelong, Li Dapeng. 2011. New advances in geochemical exploration of concealed deposits[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 200(8):822-836(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.adearth.ac.cn/EN/abstract/abstract8800.shtml
Tan Hua, Chen Guoyong, Zhao Zheng, Lu Guangyan, Zou Jianbo. 2015. Achievements an significance of lead-zinc exploration in Zhangwei-Wuzhishan area of Guizhou Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 7(4):1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDC201504001.htm
Tang Juxing. 2003.The study on Metallogeny and Localizing Forecast of Yulong Porphyry Copper-molybdenum Mineralization, Xizang(Tibet)[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 1-175(in Chinese with English abstract).
Thomas D, Matthews R, Sopuck V. 2002. Athabasca basin (Canada)unconformity-type uranium deposits:Exploration model, current mine developments and exploration directions[J]. Geology and Ore Deposits, 24:15-18.
Wang Dezi, Zhou Jincheng. 1983. Autoclases volcanic rock-intrusive rock and exploring significance[J]. Geology in China, 8(10):21-23(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.nsfc.gov.cn/Portals/0/fj/fj20160106_01.xls
Wang Jianfeng. 1986. Uranium Geochemical Tutorial[M]. Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 1-572(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Shicheng. 2010. The new development of theory and method of synthetic information mineral resources prognosis. Geological Bulletin of China[J], 29(10):1399-1403(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/298469139_The_new_development_of_theory_and_method_of_synthetic_information_mineral_resources_prognosis
Xia Lingqi, Xia Zuchun, Zhang Cheng, Clocchiatti R, Joron JL, Dardel J. 1992. Differentiation mechanism and evolution of high level magma reservoir from Xiangshan, China[J]. Acte Retrologica Science, 8(3):205-221, 303(in Chinese with English abstract). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqhb199201003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Xu Haijiang, Lai Shaocong. 1988. Approach to the lithologic features and the origin of the volcanic rocks in Xiangshan and its adjacent areas[J]. Geoscience, 2(4):440-450(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDDZ198804004.htm
Yang Shuiyuan. 2013. Petrogenesis and Geodynamic Setting of Magmatic Rocks from Uranium-bearing Volcanic Basins, GanHang belt, Southeast China[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University, 1-130(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Dagan. 1992a. The structure environment, rock-magma system mineral-forming series and pattern of volcanic mineral-forming of uranium deposit in southeast of China[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 15(1):11-22(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HDDZ199201001.htm
Yu Dagan. 1992b. Metallogenetic environment and genetic model of uranium in meso-cenozoic volcano-magmatic belt in Southeast China[J]. Uranium Geology, 8(2):75-82(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/4573488
Yu Dagan, Wu Rengui, Chen Peirong. 2005. Uranium Geology[M]. Harbin:Harbin Engineering University Press, 1-450(in Chinese).
Yu X, Wu G, Zhang D, Yan T, Di Y. 2006. Cretaceous extension of the Gan-Hang tectonic belt, Southeastern China:Constraints from geochemistry of volcanic rocks[J]. Cretaceous Research, 27(5):663-672. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2006.03.008
Yu Xinqi, Wu Ganguo, Shu Liangshu, Yan Tiezeng, Zhang Da, Di Yongjun. 2006. The cretaceous tectonism of the Gan-Hang tectonic belt, Southeastern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(3):31-43(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284915273_The_Cretaceous_tectonism_of_the_Gan-Hang_Tectonic_Belt_southeastern_China
Zhang Bangtong, Ni Qisheng, Dai Yongshan, Wang Xiangsheng. 1988.The relationships of the formation of genaite-type uranium deposits with the crustal evolution along the active continental margin of south China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 7(4):43-51(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080959757011220
Zhang Chengjiang. 1996. The genesis of uranium and non-uranium bearing granites from several complexes in South China and their relationship to uranium mineralization[J]. Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 23(4):33-40(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295564964_The_genesis_of_uranium-_and_non-uranium-bearing_granites_from_several_complexes_in_south_China_and_their_relationship_to_uranium_mineralization
Zhai Jianping. 1990. Three kinds of genetic models for granite type uranium deposits and their significance search of deposit[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Science Edition), 26(1):124-130(in Chinese with English abstract). https://pubs.usgs.gov/bul/b1693/html/bull1nzi.htm
Zhai Yusheng. 2007. Earth system, metallogenic system to exploration system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(1):172-178(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285716082_Earth_system_metallogenic_system_to_exploration_system
Zhang C, Yu J, O'reilly S, Griffin W L, Qian J. 2016. Granulite facies xenoliths from the Yuhuashan complex, central Jiangxi, South China:Constraints on Late Palaeozoic orogeny and middle-lower crust components[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 34(1):45-61. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2016.34.issue-1
Zhang Xingpu. 1999.Formation and evolution of Mesozoic volcanic basins in Gan-Hang tectonic belt[J]. Uranium Geology, 15(1):19-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXW200002015.htm
Zhang Wanliang, Liu Dechang, Li Ziying. 2005. Comparative research of lithogeochemistry for Jiulongzhang and Xiangshan volcanointrusive complexes[J]. Geoscience, 19(2):205-210(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200502006.htm
Zhang Wangliang, Li Ziying, Liu Dechang, Zhao Yingjun. 2015. The geotectonic activity trail of Fuzhou-Yongfeng fault and its significance to uranium ore exploration in central Jiangxi Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 30(1):23-29(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZZK201501003.htm
Zhong Fujun, Pan Jiayong, Liu Xiansen, Zhang Yong, Liu Guoqi, Liu Ying. 2014. A metallogenic model based on comprehensive information and genesis analysis for the Houerdaogou copper-gold deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 452(3):432-444(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136817300501
Zhou Xuegui, Chen Lugeng, Fan Bin.1994.Lithodemic division and emplacement mechanism of high compound plutonic complex in Yuhuashan, Jiangxi[J]. Jiangxi Geology, 8(4):296-308(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JXDZ404.005.htm
Zhou Yulong, Cheng Jixing, Fu Jianping. 2015. Ore-controlling characteristics of Weishan-Tongshan fault zone in the uranium deposit of volcanic basin of Yuhua mountain[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 126(1):13-18(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GWYD201501003.htm
陈迪云, 徐伟昌. 1993.陈蔡群变质岩铀的地球化学特征[J].铀矿地质, 9(4):31-37. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91728X/199304/4001492929.html 陈正乐, 王永, 周永贵, 韩凤彬, 王平安, 宫红良, 邵飞, 唐湘生, 徐金山. 2013.江西相山火山-侵入杂岩体锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 354(1):217-231. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130115&flag=1 邓家瑞, 张志平. 1989.赣杭构造带及其地质意义[J].铀矿地质, 5(1):15-21. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB201503009.htm 邓家瑞, 张志平. 1999.赣杭构造带区域大地构造背景的探讨[J].铀矿地质, 15(2):8-13. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91728X/199902/3486271.html 杜乐天. 1982.花岗岩型铀矿床文集[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1-404. 范洪海, 凌洪飞, 王德滋, 沈渭洲, 刘昌实, 姜耀辉. 2001.江西相山铀矿田成矿物质来源的Nd、Sr、Pb同位素证据[J].高校地质学报, 7(2):139-145. http://www.docin.com/p-512629490.html 方锡珩, 方茂龙, 罗毅, 刘蓉蓉, 刘权, 张明林, 王树红, 刘祜, 付锦, 汪远志, 张俊伟, 谢迎春. 2012.全国火山岩型铀矿资源潜力评价[J].铀矿地质, 28(6):342-348. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ykdz201206007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 冯明月, 何德宝. 2012.华南富铀花岗岩和产铀花岗岩特征[J].铀矿地质, 28(4):199-207. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykdz201204002 胡恭任, 刘丛强, 章邦桐, 于瑞莲. 2000.赣中变质岩带的组成及构造变质变形特征[J].地质通报, 19(4):375-381. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95894X/200004/4720283.html 胡恭任, 于瑞莲. 2004.赣中变质岩带变质带的重新划分及变质作用P-T条件的确定[J].化工矿产地质, 26(2):65-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX602.001.htm 胡恭任, 章邦桐. 1997.赣中变质基底的组成演化及其基本结构格局[J].江西地质, 11(3):47-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXDZ703.007.htm 胡恭任, 章邦桐. 1998.赣中变质基底的Nd同位素组成和物质来源[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 17(1):36-41. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4339620 华仁民, 陈培荣, 张文兰, 陆建军. 2005.论华南地区中生代3次大规模成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 24(2):99-107. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200502002 黄长生, 廖显珍, 雷良诚. 2001.玉华山高位侵入杂岩定位机制[J].华东地质学院学报, 24(2):104-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ200102002.htm 江少卿, 孙兴国, 杨铁铮, 李丽, 印贤波, 王策, 潘燕兵. 2014.藏北多龙斑岩铜金矿集区综合信息找矿模型研究[J].中国地质, 361(2):497-509. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140214&flag=1 金景福, 胡瑞忠. 1990. XW铀矿床成矿物理化学条件[J].成都地质学院学报, 17(3):1-9. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91405X/199003/222395.html 李响. 2012. 江西玉华山火山-侵入杂岩成因机制及产铀能力评价[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 1-45. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10284-1014451367.htm 刘小宇, 陈肇博. 1996.大陆火山作用与铀成矿[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1-167. 刘颖. 2013. 江西省玉华山地区紫云山岩体年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[D]. 南昌: 东华理工大学, 1-51. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10405-1013045629.htm 裴荣富, 梅燕雄, 瞿泓滢, 王浩琳. 2013.矿床类型模型的地质构造背景、成矿环境和容矿岩石组合[J].中国地质, 354(1):31-42. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130102&flag=1 邱爱金, 郭令智, 郑大瑜. 2002.大陆构造作用对相山富大铀矿形成的制约[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-103. 单林, 刘晓东. 1985.相山等火山盆地主体岩石包裹体研究[J].岩石矿物及测试, 4(4):289-294. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ykcs198504000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 邵飞, 朱永刚, 李嘉, 何晓梅. 2010.赣杭构造火山岩带铀成矿规律及深入找矿[J].上海地质, 31(增刊):133-136. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=shad2010s1040&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 邵飞. 2011.钦杭成矿带北东段火山岩型铀矿定向三等距分布规律及成矿预测[J].铀矿地质, 27(5):286-292. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykdz201105005 沈渭洲, 张祖还, 章邦桐. 1988.华南产铀花岗岩锶、氧和铅同位素地球化学研究[J].铀矿地质, 4(1):23-30. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4884968 孙剑, 陈岳龙, 李大鹏. 2011.隐伏矿床勘查地球化学新进展[J].地球科学进展, 200(8):822-836. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4171058 谭华, 陈国勇, 赵征, 陆光艳, 邹建波. 2015.贵州张维-五指山地区铅锌矿评价成果及意义[J].中国地质调查, 7(4):1-7. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/72008X/201504/665610144.html 唐菊兴. 2003. 西藏玉龙斑岩铜(钼)矿成矿作用与矿床定位预测研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 1-175. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-2004085841.htm 王德滋, 周金城. 1983.自碎火山-侵入岩及其找矿意义[J].中国地质, 8(10):21-23. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dizi198310004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 王剑峰. 1986.铀地球化学教程[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1-572. 王世称. 2010.综合信息矿产预测理论与方法体系新进展[J].地质通报, 185(10):1399-1403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.10.002 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 张诚, Clocchiatti R, Joron J. L, Dardel J. 1992.相山高位岩浆房分异机制和演化[J].岩石学报, 8(3):205-221, 303. http://www.oalib.com/paper/1471635 徐海江, 赖绍聪. 1988.相山及邻区七个火山盆地火山岩岩性特征及成因探讨[J].现代地质, 2(4):440-450. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HSDZ199204003.htm 杨水源. 2013. 华南赣杭构造带含铀火山盆地岩浆岩的成因机制及动力学背景[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 1-130. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10284-1013190823.htm 余达淦, 吴仁贵, 陈培荣. 2005.铀资源地质学[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 1-450. 余达淦. 1992a.中国东南部火山岩型铀矿成矿构造环境、岩浆岩体系、成矿系列及成矿模式[J].华东地质学院学报, 15(1):11-22. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hddz199201001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 余达淦. 1992b.中国东南部中新生代火山-岩浆带中铀的成矿环境及成矿模式[J].铀矿地质, 8(2):75-82. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ykdz199202002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 余心起, 吴淦国, 舒良树, 颜铁增, 张达, 狄永军. 2006.白垩纪时期赣杭构造带的伸展作用[J].地学前缘, 13(3):31-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNGD201502027.htm 翟建平. 1990.花岗岩型铀矿床的三种成矿模式及其找矿意义[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 26(1):124-130. http://www.adearth.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9003.shtml 翟裕生. 2007.地球系统、成矿系统到勘查系统[J].地学前缘, 14(1):172-181. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/9abfcffa0912a2161579299a-2.html 张成江. 1996.华南几个杂岩体中产铀与非产铀花岗岩的成因及其与铀成矿关系[J].成都理工学院学报, 23(4):33-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199301004.htm 张万良, 李子颖, 刘德长, 赵英俊. 2015.赣中抚州-永丰断裂新构造活动踪迹及其找矿意义[J].地质找矿论丛, 30(1):23-29. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.01.003 张万良, 刘德长, 李子颖. 2005.江西九龙嶂和相山火山-侵入杂岩岩石地球化学的对比研究[J]现代地质, 19(2):205-210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200403010.htm 张星蒲. 1999.赣杭构造带中生代火山盆地的形成和演化[J].铀矿地质, 15(1):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.1999.01.003 章邦桐, 倪琦生, 戴永善, 王湘生. 1988.华南花岗岩型铀矿床的形成与活动大陆边缘陆壳演化的关系[J].矿床地质, 7(4):43-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201312001.htm 钟福军, 潘家永, 刘贤森, 张勇, 刘国奇, 刘颖. 2014.内蒙后二道沟铜金矿床综合信息找矿模型及矿床成因探讨[J].地质与勘探, 452(3):432-444. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/dd0f232ace2f0066f53322fa.html 周雪桂, 陈鲁根, 范斌. 1994.江西玉华山高位复式深成杂岩体岩石谱系单位划分及定位机制[J].江西地质, 8(4):296-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ200102002.htm 周玉龙, 程纪星, 付建平. 2015.玉华山火山盆地铀矿床为山-筒山断裂带控矿特征[J].世界核地质科学, 126(1):13-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201501003.htm -
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 戴鹏飞,苟学明,何大鹏,韩栋昱,娄汉生. 北山南部炭窑井地区花岗岩型铀矿地质特征及找矿模型. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 10-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 许谱林,唐湘生,郭福生,吕川,熊建,黎广荣,聂涛,钟鹏飞. 赣杭带中段天台山火山盆地铀矿控矿因素及找矿方向. 金属矿山. 2022(02): 146-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘伟,黄理善,丁汝福,徐文杰,胡乔帆,周守余,赵毅. 广西五圩矿田箭猪坡锑多金属矿综合信息找矿模型. 中国地质. 2022(04): 1250-1261 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 金中国,刘开坤,郑明泓,罗开,杨胜发,淳果,王琼,范云飞. 贵州三穗铀矿床矿石矿物学特征及其对找矿的指示. 中国地质. 2022(04): 1236-1249 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 庞薇,杜景勇,张雷,艾成辉,钟福军,潘家永,许健俊,王海洋. 赣杭铀成矿带北禾山地区绿泥石矿物学特征及找矿启示. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(05): 419-430 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 白德胜,李水平,纵瑞,程华,齐勇攀,张爱玲,孙进,赵华奇. 豫西董家埝构造蚀变岩型银矿物化探异常特征及找矿模型. 地质与勘探. 2021(02): 241-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 朱青,郭熙,韩逸,江叶枫,余慧敏,傅聪颖. 南方丘陵区土壤硒空间分异特征及其影响因素——以丰城市为例. 土壤学报. 2020(04): 834-843 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张雷,涂传辉,揭伟成. 玉华山盆地濂坑地区成矿地质特征及远景分析. 世界有色金属. 2020(22): 93-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. Yang-sen Yuan,Shui-ping Li,Jun Peng,Jian-tao Si,Hua Cheng,Jin Sun,Jian-zheng Wei,Jiang-bo Shao. An integrated ore prospecting model for the Nyasirori gold deposit in Tanzania. China Geology. 2019(04): 407-421 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: