-
摘要:
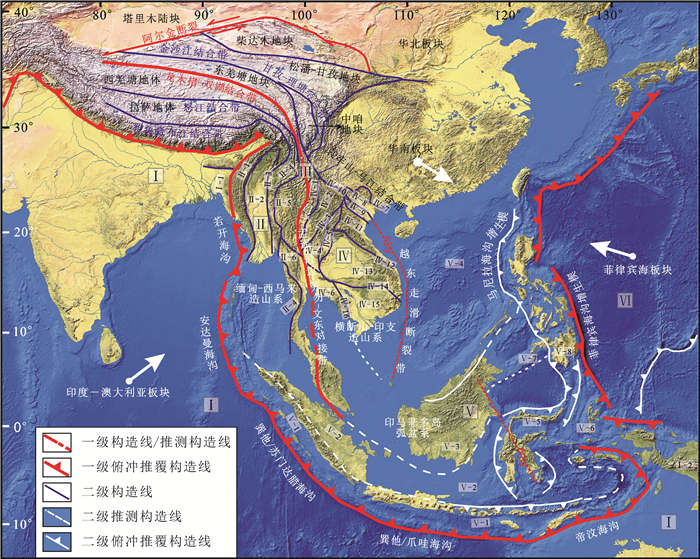
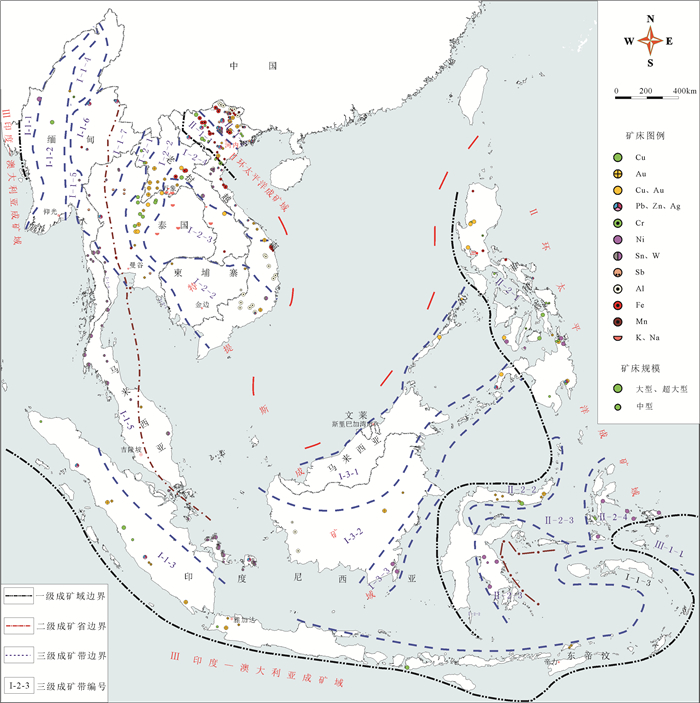
东南亚地区位于全球特提斯成矿域、环太平洋成矿域与印度-澳大利亚成矿域的交汇地带。构造演化独特,先后经历了原-古-中-新特提斯增生造山、印度-欧亚陆陆碰撞造山、太平洋俯冲等多期次构造-岩浆事件,形成了多条火山弧带、蛇绿混杂带以及同碰撞和后碰撞岩浆岩带。本文在总结前人大地构造研究成果基础上,将东南亚地区划分为6个一级构造单元、32个二级构造单元和57个三级构造单元。伴随着原-古-中-新特提斯构造演化、印度-欧亚大陆碰撞、太平洋俯冲等多期次构造域事件,以构造单元划分为基础,将东南亚地区划分为3个一级成矿域,6个二级成矿省,21个三级成矿带,并结合构造演化初步探讨了主要成矿事件。
Abstract:Southeast Asia is located at the intersection of the Tethys, the circum-Pacific and the India-Australia metallogenic domain. The tectonic evolution is unique in that it has experienced multi-stage tectonic-magmatic events including the Proto-, Paleo-, Meso-, and Neo-Tethys accreting orogenesis, collisional orogenesis between the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate, and the Pacific plate subduction. These activities have developed many volcanic arcs, ophiolite belts, and post-collision magmatic belts in Southeast Asia. Based on the previous tectonic researches, this paper divides Southeast Asia into 6 first-order, 32 second-order and 57 third-order tectonic units. Along with the multi-stage tectonic events including evolution of the Proto-, Paleo-, Meso-, and Neo-Tethys, the Indian-Eurasian collision, and the Pacific subduction and on the basis of the tectonic-unit division, this paper divides the Southeast Asian region into 3 first-level metallogenic domains, 6 second-level metallogenic provinces, and 21 thirdlevel metallogenic belts. The main metallogenic events are discussed in combination with tectonic evolution.
-
走滑断裂是沉积盆地中特殊而且力学机制复杂的断裂系统,走滑断裂及其破碎带本身是重要的储油气空间,同时,高角度的走滑断裂常常沟通地层深部流体,是油气运聚的输导体系,对储层的形成与油气的分布具有重要的控制作用。近期针对大型走滑断裂及其破碎带的直接钻探在塔里木盆地奥陶系层间岩溶区的塔中I号气田、哈拉哈塘油田和轮古东气田均取得了预期效果[1-4],极大地拓展了油气勘探开发领域,也使得对塔里木盆地走滑断裂的研究与认识更进一步深化。一方面加强走滑断裂的识别、构造样式的刻画及力学机制的研究[1-7];另一方面对走滑断裂破碎带结构的研究引起关注,张庆莲等[8],潘文庆等[9]对塔里木盆地西北缘的柯坪—巴楚露头区野外裂缝地质建模明确走滑断裂控制的裂缝发育带具有明显的分带性,距断层由近及远可细分为“破碎带、劈理带、菱形裂缝带、稀疏裂缝带”;邬光辉等[10]通过野外与井下地质建模,指出塔里木盆地奥陶系沿走滑断裂带走向上断裂相具有分段性和差异性,可定性分为高渗透相和致密相区;孙东等[11]通过地震储层正演明确断层面及断裂破碎带能产生串珠状反射。这些研究成果对认识走滑断裂破碎带在三维空间复杂结构及解译其与油气富集规律提供了新的思路和方法。
前期针对轮古东气田断裂系统的研究,由于受地震资料品质和勘探开发程度的限制,对走滑断裂的解释有待深入,对断裂破碎带及伴生裂缝发育特征研究较少[4],本文以最新处理完成的轮古东300 km2叠前深度偏移地震资料为基础,结合区域已有钻井资料综合分析轮古东气田走滑断裂的识别、发育特征、断裂破碎带的组合方式以及控储控藏特征,以期为该区进一步勘探开发提供指导。
1. 地质背景
轮古东气田地处新疆轮台县境内,构造上隶属于塔里木盆地塔北隆起轮南低凸起中部。奥陶纪地层发育齐全,可细分为上奥陶统桑塔木组、良里塔格组和吐木休克组(又称恰尔巴克组)、中奥陶统一间房组及中下奥陶统鹰山组和蓬莱坝组。
主要勘探目的层为一间房组和鹰山组,其次为良里塔格组,一间房组埋藏深度5050~6700 m,厚度10.5~42 m,发育台缘和台内丘滩复合体沉积,岩性以浅褐灰-灰褐色亮晶砂屑灰岩、亮晶鲕粒灰岩和亮晶藻屑砂屑灰岩为主,在AG35、AG621等井都发现托盘类生物礁。鹰山组自上而下可细分为4段:鹰一段(O1-2y1)、鹰二段(O1-2y2)、鹰三段(O1-2y3)和鹰四段(O1-2y4),本区绝大多数钻井仅钻揭鹰一段,主要发育亮晶砂屑灰岩、泥晶灰岩,为开阔台地相的台内滩和滩间海沉积。
研究区东邻草湖生油凹陷,南接满加尔生油坳陷,位于油气运移主要方向的前沿部位,构造位置十分有利。以近南北向轮东I号走滑断裂带为界,构造西缓东陡,总体为一东南倾大型斜坡(图 1),一间房组顶面构造高差1650 m,奥陶系油气主力产层一间房组在西北部受剥蚀而尖灭。储层以裂缝孔洞型储层为主,发育少量洞穴型储层,整体表现为受断裂和沉积相带分割,局部断块含少量边、底水的大型准层状凝析气藏[12-13]。
2. 断裂与裂缝特征
2.1 地震资料断裂识别
平剖结合,多方法开展工区断裂解释,小断层产状较陡,主要根据上下地层即寒武系和良里塔格顶面存在断距和挠曲,以及地震同相轴存在变化进行识别[3]。在此基础上,通过沿层切片、相干属性等技术实现断裂与裂缝的平面识别,以垂直剖面为主精细解释断层。
2.1.1 断裂平面识别
相干体技术是一种不连续的检测手段,当地下有断层、裂缝或地质异常体(如洞穴、河道、串珠等)时,地层产生横向不均匀现象,相邻地震道之间的反射波在振幅、频率及相位等方面都将发生不同程度的变化,进而达到检测断层、反映岩性异常体的目的,相干体切片比常规切片能更好地表现断层和沉积特征。从沿层相干切片结果分析,中深层断裂平面上主要分4组:走滑断层主要呈近南北、北东和北西向3组断裂,且北东向断层错断北西向断层;逆冲断裂为近东西走向,主要位于工区西部(图 2~图 3)。石炭系以上以雁列式走滑断层和逆冲断裂为主,走滑断层主要发育近南北向以及两条近北东向断裂(图 4)。
2.1.2 断裂剖面识别
根据区域构造运动背景以及断层平剖面特征,研究区断裂可划分为3期4组。中晚加里东期走滑断裂、晚海西期逆冲断裂以及喜山期走滑断裂(图 1、图 5)。
早加里东期寒武系—中下奥陶统,塔北隆起稳定沉积,无大的构造活动,断裂不发育,沉积大套灰岩地层。中晚加里东期断裂开始活动,沉积地层由碳酸盐岩向碎屑岩过渡,发育近北西和北东向走滑断层,延伸距离约10~25 km,剖面上,断裂近乎陡直,向下断入震旦系,向上消失于奥陶系桑塔木组,断距一般小于100 m(图 5-c)。该期断层是晚加里东期寒武系—下奥陶统烃源岩的原油充注的主要通道,沿断层分布形成古油藏。
晚海西期受区域性南北向挤压应力作用,工区西部发育两条近东西走向的逆冲断裂(桑塔木南断裂和桑塔木北断裂),剖面上呈“y”字形特征,其中桑塔木北断裂是一条主断裂,东西延伸约18 km,断距大,垂向断距最大达200 m,断开层位多,上至三叠系底,下至寒武系、震旦系;桑塔木南断裂是桑塔木北断裂的一条大的伴生断裂,断开层位少,上部仅断开石炭系,下部消失在奥陶纪地层中,垂向断距最大达150 m(图 5-a)。桑塔木断裂控制了局部构造形态,构造脊部裂缝发育,井间连通性好。根据挤压应力的剪切分量分析,推测该时期南北向轮东1号走滑断裂已开始发育,整体表现为压扭性特征。
喜山期受张剪应力作用,贯穿工区的南北向轮东1号走滑断裂进一步活动,表现为右旋走滑特征,并伴生一些列北东-南西向次级走滑断裂,控制工区构造格局,轮东1号断裂区内延伸21.8 km,断开层位从基底至侏罗系,断距20~100 m。石炭系以下表现为压扭性质,在工区AG35和AG35-1井附近表现最为明显,奥陶系断面倾向多变,工区南部东倾,中部西倾,北部东倾,具有典型丝带状效应;同时平面上断层两盘高低关系一直在变化,具有明显海豚效应(图 5-b)。石炭系及以上地层剖面上表现为负花状构造,断层性质由压扭转化为张扭性质,呈明显负反转构造,平面上表现为雁列式右旋走滑特征。轮东I号断裂是喜山期寒武系原油裂解气的主要充注通道,沿断裂走向裂缝发育,天然气富集。
2.2 岩心薄片裂缝特征
由于碳酸盐岩储层强非均质性,储层发育井段往往发生漏失,取心困难,岩心分析仅代表基质物性[1]。研究区岩心常规物性分析孔隙度样品1259块,渗透率样品963块,平均孔隙度1.615%,平均渗透率2.82×10-3μm2。基质孔隙度差,次生的溶蚀孔、洞和裂缝是主要的储集空间,裂缝既是储集空间,又是渗滤通道。研究区9口井428.89 m岩心统计,共发育裂缝965条,其中未充填和半充填缝649条,占裂缝总数的67.3%,以倾角 > 75°的高角度缝为主,缝密度1.22条/m(图 6~图 7)。
![]() 图 6 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩心照片a—AF127井,5569.8 m,O1-2y,泥晶灰岩,高角度构造缝,缝宽2~4 mm,沿缝部分充填方解石;b—AN631井,5791.5 m,O3t,亮晶生屑灰岩,二组构造缝斜交,沿裂缝溶蚀和充填,缝面见氧化边;c—AN62井,5782.3 m,O1-2y,颗粒灰岩,晚期水平裂缝切割早期缝合线,沿晚期裂缝部分溶蚀;d—AG392井,6264.5 m,O2y,藻粘结砂砾屑灰岩,高角度构造缝,半充填方解石,岩心上见构造缝不连续延伸;e—AN621井,5766.2 m,O3t,颗粒灰岩,早期缝合线被晚期高角度构造缝切割,半充填泥质;f—AG35井,6158.4 m,O3t,砂屑生屑灰岩,早期溶洞充填角砾与巨晶方解石,晚期裂缝切割早期裂缝,沿晚期裂缝扩溶;g—AN631井,5973.1 m,O1-2y,早期网状裂缝呈龟背状充填方解石,晚期沿部分宽缝充填泥质,岩心部分大理岩化;h—AG391井,5817.2 m,O3l,生物砾屑灰岩,生物为珊瑚和藻类,为洞穴充填角砾,砾间充填泥质;i-AG392井,6345.7 m,O1-2y,亮晶颗粒灰岩,缝合线发育Figure 6. Core photos of Ordovician carbonate rock in Lungudong gas fielda-Well AF127, 5569.8 m, O1-2y, cryptite, high angle structural fracture, width of fracture 2-4 m, partly filled with calcite along fractures; b-Well AN631, 5791.5 m, O3t, calcsparite bioclastic limestone, two groups of structural fractures obliquely crossing, corroded and filled along fractures, oxidation edge distributed in fracture panel; c-Well AN62, 5782.3 m, O1-2y, grained limestone, late period horizontal fractures cutting early stage furrow lines, partly corroded along late period fractures; d-Well AG392, 6264.5 m, O2y, algal bound gritty limestone, high angle structural fracture, half filled with calcite, structural fractures discontinuously extending in core; e-Well AN621, 5766.2 m, O3t, grained limestone, late period high angle structural fractures cuting early stage furrow lines, half filled with shale; f-Well AG35, 6158.4 m, O3t, gritty bioclastic limestone, early period limestone cave filled with rubble giant crystal calcite, late period fractures cutting early period fractures. corroded along late period fractures; g-Well AN631, 5973.1 m, O1-2y, early period calcite filling fractures like turtleback, late period part of broad fractures filled with shale, core partly marbleized; h-Well AG391, 5817.2 m, O3l, bioclastic calcirudite, bioclasts consisting of coral and algae, cave filled with rubble stone, shale filling inter gravel; i-Well AG392, 6345.7 m, O1-2y, calcsparite grained limestone, developing furrow lines
图 6 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩心照片a—AF127井,5569.8 m,O1-2y,泥晶灰岩,高角度构造缝,缝宽2~4 mm,沿缝部分充填方解石;b—AN631井,5791.5 m,O3t,亮晶生屑灰岩,二组构造缝斜交,沿裂缝溶蚀和充填,缝面见氧化边;c—AN62井,5782.3 m,O1-2y,颗粒灰岩,晚期水平裂缝切割早期缝合线,沿晚期裂缝部分溶蚀;d—AG392井,6264.5 m,O2y,藻粘结砂砾屑灰岩,高角度构造缝,半充填方解石,岩心上见构造缝不连续延伸;e—AN621井,5766.2 m,O3t,颗粒灰岩,早期缝合线被晚期高角度构造缝切割,半充填泥质;f—AG35井,6158.4 m,O3t,砂屑生屑灰岩,早期溶洞充填角砾与巨晶方解石,晚期裂缝切割早期裂缝,沿晚期裂缝扩溶;g—AN631井,5973.1 m,O1-2y,早期网状裂缝呈龟背状充填方解石,晚期沿部分宽缝充填泥质,岩心部分大理岩化;h—AG391井,5817.2 m,O3l,生物砾屑灰岩,生物为珊瑚和藻类,为洞穴充填角砾,砾间充填泥质;i-AG392井,6345.7 m,O1-2y,亮晶颗粒灰岩,缝合线发育Figure 6. Core photos of Ordovician carbonate rock in Lungudong gas fielda-Well AF127, 5569.8 m, O1-2y, cryptite, high angle structural fracture, width of fracture 2-4 m, partly filled with calcite along fractures; b-Well AN631, 5791.5 m, O3t, calcsparite bioclastic limestone, two groups of structural fractures obliquely crossing, corroded and filled along fractures, oxidation edge distributed in fracture panel; c-Well AN62, 5782.3 m, O1-2y, grained limestone, late period horizontal fractures cutting early stage furrow lines, partly corroded along late period fractures; d-Well AG392, 6264.5 m, O2y, algal bound gritty limestone, high angle structural fracture, half filled with calcite, structural fractures discontinuously extending in core; e-Well AN621, 5766.2 m, O3t, grained limestone, late period high angle structural fractures cuting early stage furrow lines, half filled with shale; f-Well AG35, 6158.4 m, O3t, gritty bioclastic limestone, early period limestone cave filled with rubble giant crystal calcite, late period fractures cutting early period fractures. corroded along late period fractures; g-Well AN631, 5973.1 m, O1-2y, early period calcite filling fractures like turtleback, late period part of broad fractures filled with shale, core partly marbleized; h-Well AG391, 5817.2 m, O3l, bioclastic calcirudite, bioclasts consisting of coral and algae, cave filled with rubble stone, shale filling inter gravel; i-Well AG392, 6345.7 m, O1-2y, calcsparite grained limestone, developing furrow lines![]() 图 7 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层铸体薄片a—AN48井,5548.5 m,O2y,泥粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,沿缝见扩溶现象,红色铸体;b—AN621井,5778.3 m,O1—2y,亮晶颗粒灰岩,压溶和溶蚀缝,红色铸体;c—AN14井,5335.6 m,O3l,泥粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,红色铸体;d—AG18井,5540.2 m,O2y,粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,红色铸体;e—AG39井,5832.5 m,O2y,泥—亮晶颗粒灰岩,沿构造缝扩溶后,部分方解石充填,红色铸体;f—AG391井,5810.1 m,O3l,泥—亮晶颗粒灰岩,压溶缝,红色铸体Figure 7. Cast slice of Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Lungudong gas fielda-Well AN48, 5548.5 m, O2y, powder micrite limestone, structural fractures interleave, expanded corrosion along fractures, red cast; b-Well AN621, 5778.3 m, O1–2y, calcsparite grained limestone, pre-solution and corroded fractures, red cast; c-Well AN14, 5335.6 m, O3l, powder micrite limestone, structural fractures interleave, red cast; d-Well AG18, 5540.2 m, O2y, crystal powder limestone, structural fractures interleave, red cast; e-Well AG39, 5832.5 m, O2y, micrite-calcsparite grained limestone, after expanding corrosion along fractures, partly filled with calcite, red cast; f-Well AG391, 5810.1 m, O3l, micrite-calcsparite grained limestone, pre-solved fractures, red cast
图 7 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层铸体薄片a—AN48井,5548.5 m,O2y,泥粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,沿缝见扩溶现象,红色铸体;b—AN621井,5778.3 m,O1—2y,亮晶颗粒灰岩,压溶和溶蚀缝,红色铸体;c—AN14井,5335.6 m,O3l,泥粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,红色铸体;d—AG18井,5540.2 m,O2y,粉晶灰岩,构造缝交织分布,红色铸体;e—AG39井,5832.5 m,O2y,泥—亮晶颗粒灰岩,沿构造缝扩溶后,部分方解石充填,红色铸体;f—AG391井,5810.1 m,O3l,泥—亮晶颗粒灰岩,压溶缝,红色铸体Figure 7. Cast slice of Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Lungudong gas fielda-Well AN48, 5548.5 m, O2y, powder micrite limestone, structural fractures interleave, expanded corrosion along fractures, red cast; b-Well AN621, 5778.3 m, O1–2y, calcsparite grained limestone, pre-solution and corroded fractures, red cast; c-Well AN14, 5335.6 m, O3l, powder micrite limestone, structural fractures interleave, red cast; d-Well AG18, 5540.2 m, O2y, crystal powder limestone, structural fractures interleave, red cast; e-Well AG39, 5832.5 m, O2y, micrite-calcsparite grained limestone, after expanding corrosion along fractures, partly filled with calcite, red cast; f-Well AG391, 5810.1 m, O3l, micrite-calcsparite grained limestone, pre-solved fractures, red cast根据形成机理,裂缝分为构造缝、压溶缝和溶蚀缝。构造缝约占区内裂缝总数的60%,缝宽一般小于5 mm,主要为剪切缝,其次为张性缝。构造缝以垂直缝最为发育,早期构造缝平行排列,局部呈枝叉状和雁行状,多数已被方解石、泥质和沥青质全充填或半充填,局部区域多期不同产状的裂缝相互交切形成网状裂缝。压溶缝是由沉积负荷引起的压实作用和压溶作用形成,主要表现为缝合线,产状多与层面平行,呈锯齿状和肠状弯曲延伸,常被泥、铁质半充填或全充填,约占裂缝总数的20%。溶蚀缝主要由地表水和地下水沿早期的裂缝系统溶蚀扩大产生,呈弯曲分布,延伸短,缝宽一般 > 1 mm,沿断裂面上生长晶形完好的方解石晶体或晶簇,约占裂缝总数的15%(图 6~图 7)。
2.3 成像测井裂缝特征
成像测井是识别井周裂缝发育条数、产状和有效性等的直接手段。构造缝形成后,在后期应力和溶蚀改造下,会不断改变赋存状态,其中多期应力的改造作用目前测井技术不能有效识别,后期溶蚀作用造成的裂缝形态变化则能较好地从井壁图像上识别并确定[14-15]。
利用工区完钻32口井的成像测井资料,成像测井可识别的裂缝主要为构造缝、溶蚀缝和钻井诱导缝。构造缝主要为构造应力成因,裂缝形态完整,轨迹闭合;溶蚀缝由后期扩溶作用形成,缝面基本闭合,多不完整,呈不规则扩溶特征;钻井诱导缝为人工裂缝,由钻具机械诱导和地层应力释放造成,多为无效裂缝(图 8)。
![]() 图 8 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩测井裂缝发育特征a、b、c、d—高角度构造窄裂缝,缝面形态基本完整,轨迹闭合;e、f、g、h—高角度构造窄裂缝,沿缝不规则扩溶;i、j、k、l—斜交羽状诱导微裂缝Figure 8. Ordovician carbonate logging fracture development characteristics in Lungudong gas fielda, b, c, d-High angle structural narrow fracture, fracture plane form is mostly intact, track closed; e, f, g, h-High angle structural narrow fracture, irregular broaden corrosion; i, j, k, l-Obliquely crossing pinnate lead tiny fracture
图 8 轮古东气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩测井裂缝发育特征a、b、c、d—高角度构造窄裂缝,缝面形态基本完整,轨迹闭合;e、f、g、h—高角度构造窄裂缝,沿缝不规则扩溶;i、j、k、l—斜交羽状诱导微裂缝Figure 8. Ordovician carbonate logging fracture development characteristics in Lungudong gas fielda, b, c, d-High angle structural narrow fracture, fracture plane form is mostly intact, track closed; e, f, g, h-High angle structural narrow fracture, irregular broaden corrosion; i, j, k, l-Obliquely crossing pinnate lead tiny fracture平面上,工区裂缝以高角度(45°~75°)裂缝为主,走向以NE-SW为主。有效裂缝具有更强的岩石切割破坏能力,裂缝宽度和密度越大,取心收获率越低,裂缝有效性越好。纵向上,良里塔格组裂缝发育受岩性控制,裂缝发育密度与自然伽马值(泥质-泥灰质含量)成反比,自然伽马值增大,泥质-泥灰质含量增高,裂缝发育密度降低,良里塔格组内部自然伽马值从约11 API变化到60 API以上,泥质-泥灰质含量从5%上升至40%以上,当自然伽马值达到45 API,泥质-泥灰质含量超过30%时,裂缝不发育。良里塔格组裂缝平均4条/100 m,以不规则网状交切微细裂缝为主要特征,裂缝开度较小,少见大开度(窄缝以上)的构造缝,平均缝宽26.9μm,中缝及宽缝(石油行业标准SY/T 6286-1997)发育率6.9%。一间房和鹰山组岩性较纯,自然伽马值普遍低于25 API,平均约16.8 API,层组内泥质-泥灰质含量没有明显变化,泥质含量平均约2.3%。裂缝发育主要受断裂(应力强度)及构造控制,岩性控制不明显,裂缝发育程度高,开度相对较大,缝面溶蚀特征明显,一间房组14条/100 m,平均缝宽44.5μm,中缝及宽缝发育率9.1%;鹰山组6条/ 100 m,平均宽度37.5μm,中缝及宽缝发育率9.8%。
2.4 地震预测裂缝特征
裂缝的存在会造成地震波频率随方位角变化,在裂缝的法线方向,频率随方位角的衰减不同于裂缝的走向方向,地震波的衰减强度与裂缝的密度成正比,裂缝越发育,频率随方位角变化就越明显,频率椭圆扁率的大小代表了频率的各向异性强度,并且用这种强度来指示裂缝发育的强度。为得到准确的裂缝密度信息,多井结合约束裂缝密度发育门槛,利用研究区取心和成像测井对裂缝发育井和不发育井共同约束,得到最终的裂缝预测数据体并进行裂缝平面预测(图 9)。
研究区一间房组裂缝最发育,利用成像测井资料约束,FRS叠前裂缝预测表明,现今最大水平主应力方向、裂缝走向、裂缝分布范围及发育密度主要受断裂控制。
现今最大水平主应力方向指示地层岩石所承受的最大应力方向,在同样的地层岩性、相似岩石机械强度条件下,走向平行于最大水平主应力方向的裂缝系统在力学上最容易保存,与之相交或垂直的裂缝则趋于闭合。轮古东气田成像测井解释仅AN171、AG38C井周边由于应力的复杂,裂缝走向与主应力走向存在较大夹角,其余区域裂缝走向与主应力走向基本一致,裂缝走向以NE-SW向为主,指示轮古东斜坡断裂系统更容易保持开启,也更容易获得高产。不同期次、走向的断裂控制的裂缝走向略有差异,南北向轮古东I号走滑断裂周边井裂缝走向主要为NE 30°~50°;北东向走滑断裂周边井裂缝走向主要为NE 30°~80°。
平面上,裂缝主要分布在断裂周围1 km范围内,成像测井及FRS叠前裂缝预测表明,随着井点距断裂距离增大,裂缝发育强度(裂缝线密度)呈指数降低,当井点距断裂距离 < 0.25 km,裂缝发育密度快速增加,当井点距断裂距离 > 1 km,裂缝发育差或不发育(图 9,图 10),与塔里木盆地西北缘柯坪—巴楚露头区多条走滑断裂的调查结论类似,即随着距断裂距离的增大,断裂控制的裂缝密度与距断裂距离呈指数递减关系[8-9]。
3. 断裂破碎带结构及与油气关系
3.1 断裂破碎带结构
走滑断裂构造样式,一般由一系列产状陡倾的大型-巨型平移断层及其间的断夹块体组成,平面上表现为雁列式、斜列式或帚状构造样式,在剖面上表现为陡立的断层带或断夹块的相间排列[16-19]。由于力学机制复杂,走滑断裂构造样式的差异造成走滑断裂破碎带在三维空间具有复杂的结构,对断裂破碎带组合方式的刻画对储层与油气运聚关系密切[8-11, 16-19]。针对研究区气藏特征,以主干走滑断裂为主线,以次级和微断裂为骨架,以裂缝为脉络,将研究区断裂破碎带平面上划分为“羽状破碎带、转换破碎带、斜列破碎带、复合破碎带”4种组合模式(图 11)。
“羽状破碎带”指次级和微断裂发育,储层沿破碎带呈散开状发育,剖面上为正花状断裂,平面上次级裂缝沿主干断裂呈羽状分布。羽状破碎带为有利的储层发育区,轮古东目前AG341、AG353、AG391C等高产井钻探区域为羽状破碎带。AG391井钻探断裂下盘的羽状破碎带,取心和成像测井证实,鹰山组发育II类裂缝孔洞型储层51.5 m/8层,平均孔隙度2.83%;III类孔洞型储层13 m/1层,孔隙度1.8%。鹰山组裂缝发育,为高角度的窄缝,以构造剪切缝为主,底部存在少量的构造张性缝,且沿裂缝有扩溶作用,该井累产油0.16×104 t,累产气0.25×108 m3;AG391C井钻探临近的断裂上盘的羽状破碎带,效果要好于AG391井,目前已累产油0.55×104 t,累产气0.61×108 m3,一方面表明羽状破碎带局部构造高点油气更为富集;另一方也证实,羽状破碎带内部结构复杂,断裂上盘和下盘之间存在油气的侧向封堵。目前塔里木盆地塔中I号气田Z15井区已通过水平井穿主干断裂钻探羽状破碎带的多个串珠集合体,完钻13井取得预期效果,已建成黑油年产能25×104 t[2]。
“转换破碎带”指走滑断裂转换部位,应力从一条断层逐渐转至另一条断层,特定部位同时发育两条走滑断裂,裂缝主要发育于两断层叠置的转换破碎带内。研究区仅AG39井发育,剖面上为正花状断裂,平面上轮东1号断裂AG39构造分段转换形成局部构造,主要的构造变形层系位于中上奥陶统,石炭系地层无明显的构造变形,上奥陶统良里塔格组地层厚度没有明显变化。AG39井钻探构造高点,实钻证实储层发育,上奥陶统良里塔格组与下奥陶鹰山组均发育储层且测试均获得高产,成相测井解释储层以裂缝孔洞型储层为主,II类储层2.5 m/1层,孔隙度3%,III类储层66.5 m/7层,平均孔隙度1.63%,裂缝主要集中发育于良里塔格组表层,以构造张性缝为主,扩溶现象明显,裂缝走向为东西向,应力走向为北东向,与裂缝走向存在40°夹角。该井良里塔格试采,已累产油0.94×104 t,累产气1.32×108 m3。
“斜列破碎带”指裂缝在主干和次级断裂集中发育,储层沿走滑断裂呈线性分布,剖面上次级断裂与主干断裂近平行排列,呈近直立状,平面上次级断裂和裂缝分布于主干断裂的二侧,呈大角度斜交。目前轮古东区块仅轮古35-1钻遇该破碎带,测井解释II类储层4.5 m/1层,孔隙度2.7%;III类储层36 m/5层,平均孔隙度1.72%。由于该井井下落鱼未能投产,产能情况有待后续评价。
“复合破碎带”指走滑断裂和逆冲断裂相互作用,裂缝在断裂交汇部位集中发育。研究区仅发育在桑塔木断垒带东部,由于东西向的逆断裂形成于海西期,控制了桑南断垒带的构造形态,构造高部位裂缝发育且断裂的多期活动,油气多期充注与调整,该区为复式油气聚集区,已经在奥陶系、石炭系和三叠系多个层段获得工业产能,建成黑油年产能规模30万t[13]。奥陶系碳酸盐岩以裂缝孔洞型储层为主,除个别井分析困难外,近20多年的开发已基本证实,构造高部位整体连通。
3.2 断裂破碎带与油气关系
轮古东奥陶系碳酸盐岩凝析气藏优质储层的发育主要受控于岩溶作用与断裂活动,羽状破碎带以高角度断裂及伴生微裂缝发育为主,多期多组断裂裂缝叠加,是岩溶储层发育最有利部位,分布面积最广,是油气最富集的区域。
在加里东晚期,轮古东东倾斜坡形成,顺层岩溶开始发育;晚加里东末期—早海西期的地层抬升过程中,构造运动产生了大量裂缝,部分裂缝沟通地表水,顺层溶蚀形成大量次生溶蚀孔、洞和缝;在海西末期—印支初期的第二次抬升中,断裂活动形成的众多断裂及伴生裂缝,可能会使早期充填的裂缝重新开启,对储集体的改造起重要作用;燕山—喜山期,轮古东内幕储层被迅速埋藏,从中生代晚期开始的有机质热演化所产生的酸性水沿裂隙渗入,内幕原有的孔、洞、缝发生扩溶。可见,加里东期地层短期暴露,加里东期走滑断裂及其破碎带是岩溶作用的先期通道,增加了地表水及地下水与碳酸盐岩的接触面积和溶蚀范围,甚至在碳酸盐岩内部形成一个连续的淡水溶蚀系统,再加之海西期构造运动使部分裂缝开启,极大的改善了碳酸盐岩的渗滤能力[20-21]。
轮古东气田天然气主要来源于寒武系,原油主要来源于中-上奥陶统[13]。“十五”以来,中石油塔里木油田分公司针对奥陶系碳酸盐岩的科技攻关及勘探开发实践已经证实,油气的远距离和超远距离及水平运聚难度较大,主要以“原地垂向立体网状运移”为主要特征。轮古东走滑断裂及其破碎带以高角度断裂为主,沟通下部烃源岩,是油气运移的主要输导体系。由于断裂的多期活动和断层性质的相互转化,轮古东走滑断裂附近集中了未饱和凝析气藏并控制了垂向上含气饱和度的变化,天然气晚期充注时,沿断裂向上运移的大量天然气的气侵作用造成油气相态分异,从而造成轮古东现今油气分布状况,即以轻质油和天然气为主,局部缝洞体中含有早期充注的中质和重质原油。中质和重质原油主要分布于北西向次级走滑断裂及伴生裂缝不发育且晚期气侵作用较弱区域。此外,盖层控制了轮古东气田相态的保存,轮古东地区上奥陶统桑塔木组泥岩横向分布稳定,纵向上分布较集中,厚度490~660 m,且岩性致密,垂向断层对气藏的破坏作用较弱,封隔条件较好,是中下奥陶统储层的良好盖层。
4. 结论
(1)轮古东气田主干断裂分3期4组。第一期为中晚加里东期近北东、北西向走滑断裂;第二期为晚海西期近东西向逆冲断裂;第三期为喜山期近南北、北东向走滑断裂。
(2)裂缝主要为高角度(45°~75°)构造窄裂缝,沿缝存在溶蚀,走向主要为NE-SW。纵向上,裂缝发育密度与自然伽马值(泥质-泥灰质含量)成反比,一间房组裂缝发育密度最大(14条/100 m),其次为鹰山组(6条/100 m)和良里塔格组(4条/100 m);平面上,裂缝主要分布在主干断裂周边1 km范围内,随着距断裂距离增大,裂缝发育强度(裂缝线密度)呈指数降低。
(3)断裂破碎带平面上划分为“羽状破碎带、转换破碎带、斜列破碎带、复合破碎带”4种结构。走滑断裂及其破碎带是油气的主要输导体系,控制了油气的富集与油气相态的分异,羽状破碎带分布面积广,是油气最富集的区域。
-
图 3 东南亚特提斯构造演化与成矿图(据Zaw et al., 2014修改)
Figure 3. Tectonic evolution and metallogeny of Southeast Asia (after Zaw et al., 2014)
表 1 东南亚地区大地构造分区表
Table 1 Tectonic units of Southeast Asia

表 2 东南亚地区典型矿床
Table 2 Typical deposits in Southeast Asia

-
Advokaat E L, Hall R, White L T, Watkinson Ian M, Rudyawan A, BouDagher-Fadel, Marcelle K. 2017. Miocene to recent extension in NW Sulawesi, Indonesia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 147. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017JAESc.147..378A
Aldiss D T, Ghazali S A. 1984. The regional geology and evolution of the Toba volcano-tectonic depression, Indonesia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 141(3):487-500. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.141.3.0487
Barley M E, Pickard A L, Zaw K, Rak P, Doyle M G. 2003. Jurassic to Miocene magmatism and metamorphism in the Mogok metamorphic belt and the India-Eurasia collision in Myanmar[J]. Tectonics, 22(3):4. doi: 10.1029-2002TC001398/
Blanchard S, Rossignol C, Bourquin S, Dabard M P, Hallot E, Nalpas T. 2013. Late Triassic volcanic activity in South-East Asia:New stratigraphical, geochronological and paleontological evidence from the Luang Prabang Basin (Laos)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 71(1):8-26. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bcef199e0dd18aa7fc42dd35c705eb5d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Breitfeld H T, Hall R, Galin T, Forster M A, Boudagher-Fadel M K. 2016. A Triassic to Cretaceous Sundaland-Pacific subduction margin in West Sarawak, Borneo[J]. Tectonophysics, 694:35-56. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195116305881
Cai Wenjie, Zhu Guanghui, Jiang Ye, Yang Songling, Li Aishan. 2012. Petroleum geologic characteristics and exploration potential of accretionary wedge in Myanmar[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 23(4):742-747 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201204017
Chambers J L C, Daley T. 1995. A tectonic model for the onshore Kutai Basin, East Kalimantan, based on an integrated geological and geophysical interpretation[J]. Search and Discovery. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=38487cd6d85b4830c6e40b369a522949&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Charlton T R, Hall R, Partoyo E. 1991. The geology and tectonic evolution of Waigeo Island, NE Indonesia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 6(3/4):289-297. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0743954791900748
Charusiri P, Pongsapich W, Sutthirat C. 1996. Petrochemistry of probable gem-bearing basalts in Sop Prap-Ko Kha Area, Changwat Lampang[R]. Research report.
Charusiri P. 2002. Geotectonic evolution of Thailand:A new synthesis[J]. J. Geol. Soc. Thai, 1.
Chen Yongqing, Huang Jingning, Zhai Xiaoming, Lu Yingxiang, Cheng Zhizhong, Li Jianrong. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of granitoids within Jinla Pb-Zn-Ag polymetallic ore field across China and Myanmar[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(1):344-362 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60070-6
Chen Yongqing, Liu Junlai, Feng Qinglai. 2010. Geology and Ore Deposits Associated with Granites in Indo-China Peninsula of Southeastern Asia[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-213 (in Chinese).
Cottam M A, Hall R, Ghani A A. 2013. Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic tectonics of the Malay Peninsula constrained by thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 76(20):241-257. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0231764746
Cromie P W, Zaw K. Smith S., 2006. The Sepon sedimentary-rock hosted gold deposit. Laos: Gold-ore paragenesis and geochemical investigation[C]. SEG Conference, 14-16. May, 2006, Denver.
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Hou Z Q, Jiang C Z, Danyushevsky L. 2015a. Geology and genesis of the giant Beiya porphyry-skarn gold deposit, northwestern Yangtze Block[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70:457-485. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.015
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Li C S, Wang C M. 2014a. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(2):419-437. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectonomagmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 138:268-299. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Zhao Y. 2015b. Structural control and genesis of the Oligocene Zhenyuan orogenic gold deposit, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 65:42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.002
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J. 2017. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China[J]. Gondwana Research, 50:216-266. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005
Deng J, Wang Q F. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 36:219-274. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
Deng Jun, Ge liangsheng, Yang Liqiang. 2013. Tectonic dynamic system and compound orogeny:Additionally discussing the temporalspatial evolution of Sanjiang orogeny, Southwest China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4):1099-1114(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201304001.htm
Deng Jun, Li Wenchang, Mo Xuanxue, et al. 2016. Multiple orogenic and metallogenesis of the Sanjiang Tethys[M]. Science Press: 1-622(in Chinese).
Deng Jun, Wang Changming, Li Gongjian. 2012. Style and process of the superimposed mineralization in the Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5):1349-1361(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201205001
Deng Jun, Yang Liqiang, Wang Changming. 2011. Research advances of superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9):2501-2509(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201109001
Feng Qinglai, Shen Shangyue, Liu Benpei, Helmcke D, Qian Xianggui, Zhang Weiming. 2002. Study on radiolaria, siliceous rocks and basalts in the Daxinshan Formation in the Lancangjiang structural belt, southwestern Yunnan[J]. Science in China (Series D), 32(3):220-226 (in Chinese).
Feng Qinglai, Yang Wenqiang, Shen Shangyue, Chongpan Chonglakmani, Kitsana Malila. 2008. Seamount stratigraphic sequence and its tectonic and paleo-geographical significance, Chiang Mai, northern Thailand[J]. Science in China (Series D), 38(11):1354-1360 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG200812011.htm
Gabo J A S, Dimalanta C B, Asio M G S, Queaño K L, Jr G P Y, Imai A. 2009. Geology and geochemistry of the clastic sequences from Northwestern Panay (Philippines):Implications for provenance and geotectonic setting[J]. Tectonophysics, 479(1):111-119. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195109000754/pdf?md5=b14a2546b9b25c8396fa2da8d53225ea&pid=1-s2.0-S0040195109000754-main.pdf&_valck=1
Guo Yuansheng, Luo Yufu, Cui Yingliang et al. 2013. Geology and exploration of laterite-type nickel deposits in China and Southeast Asia[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 64-76 (in Chinese).
Hall R, Ali J R, Anderson C D, Baker S J. 1995. Origin and motion history of the Philippine Sea Plate[J]. Tectonophysics, 251(1-4):229-250. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00038-0
Hall R, Hattum M W A V, Spakman W. 2008. Impact of India-Asia collision on SE Asia:The record in Borneo[J]. Tectonophysics, 451(1):366-389. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195107004295
Hall R, Morley C K. 2004. Sundaland Basins[J]. Washington Dc American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph, 149:55-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0230452688/
Hall R, Spakman W. 2015. Mantle structure and tectonic history of SE Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 658:14-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.003
Hall R, Wilson M E J. 2000. Neogene sutures in eastern Indonesia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(6):781-808. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00040-7
Hall R. 1997. Cenozoic plate tectonic reconstructions of SE Asia[J]. Petroleum Geology of Southeast Asia, 126(1):11-23. doi: 10.1144-GSL.SP.1997.126.01.03/
Hall R. 1998. The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea[J]. Biogeography & Geological Evolution of Se Asia, 99-132. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=14697ca32fede98ff81c768066ce6d66&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Hall R. 2002. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific:computer-based reconstructions, model and animations[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4):353-431. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00069-4
Hall R. 2011. Australia-SE Asia collision:plate tectonics and crustal flow[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 355(1):75-109. doi: 10.1144/SP355.5
Hall R. 2011. Cenozoic reconstructions of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Changing patterns of land and sea[M]. Marx, method, and the division of labor, University of Illinois Press: 1492-1495.
Hall R. 2012. Late Jurassic-Cenozoic reconstructions of the Indonesian region and the Indian Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics, 570-571(11):1-41. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195112002533
Hall R. 2016. Southeast Asia:New Views of the Geology of the Malay Archipelago[J].Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 45(1). doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-063016-020633
Harbury N A, Jones M E, Audley-Charles M G, Metcalfe I, Mohamed K R. 1990. Structural evolution of Mesozoic Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 147(1):11-26. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.147.1.0011
Hennig J, Breitfeld H T, Hall R, Nugraha A M S. 2017. The Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution at the Paleo-Pacific subduction zone in West Borneo[J]. Gondwana Research, 48:292-310. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.05.001
Hennig J, Hall R, Armstrong R A. 2016. U-Pb zircon geochronology of rocks from west Central Sulawesi, Indonesia:Extension-related metamorphism and magmatism during the early stages of mountain building[J]. Gondwana Research, 32:41-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.12.012
Hollings P, Cooke D R, Waters P J, Cousens B. 2011. Igneous geochemistry of mineralized rocks of the baguio district, philippines:implications for tectonic evolution and the genesis of porphyry-style mineralization[J]. Economic Geology, 106(8):1317-1333. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.106.8.1317
Hou Zengqian, Wang Erchie, Mo Xuanxue, et al. 2007. Collisional orogeny and metallogenesis of the Tibetan plateau[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 789-963(in Chinese).
Idrus A, Kolb J, Meyer F M. 2007. Chemical Composition of RockForming Minerals in Copper-Gold-Bearing Tonalite Porphyries at the Batu Hijau Deposit, Sumbawa Island, Indonesia:Implications for Crystallization Conditions and Fluorine -Chlorine Fugacity[J]. Resource Geology, 57(2), 102-113. doi: 10.1111/rge.2007.57.issue-2
Kamvong T, Zaw K, Meffre S, Maas R., Stein H, Lai CK. 2014. Adakites in the Truong Son and Loei fold belts, Thailand and Laos:genesis and implications for geodynamics and metallogeny[J]. Gondwana Research, 26, 165-184. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.011
Kamvong T, Zaw K. 2009. The origin and evolution of skarn-forming fluids from the Phu Lon deposit, northern Loei Fold Belt, Thailand. Evidence from fluid inclusion and sulfur isotope studies[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34:624-633. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.09.004
Kamvong T. 2006. Geology and genesis of porphyry-skarn Cu-Au deposits at the northern Loei Fold Belt, northeast Thailand and Laos-a progress report, Progress Report 5, Geochronology, metallogenesis and deposit styles of Loei Foldbelt in Thailand and Laos PDR, ARC Linkage Project.
Kamvong T., 2007, Geology and genesis of porphyry-skarn Cu-Au deposits at the northern Loei Fold Belt, northeast Thailand and Laos Final Report, Geochronology, metallogenesis and deposit styles of Loei Foldbelt in Thailand and Laos PDR, ARC Linkage Project.
Katili J A. 1989. Review of past and present geotectonic concepts of eastern Indonesia[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 24(2):103-129. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0077757989901439
Le Van De, 1997. Outline of plate-tectionic evolution of continental crust of Vietnam[C]//Dheeradilok P(eds.). Proceedings of the International Conferences on Stratigraphy and Tectoinc Evolution of Southeast Asia and the South Pacific.
Li Wenguang, Fu Caoyi, Yao Zhongyou, Xin Di, Ge Zhiliang, Song Xuexin, Wang Tiangang. 2014a. Tectonic settings, genetic types and main metallogenic fea-tures of copper-gold deposits in Papua New Guinea[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(2/3):270-282(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenguang, Wang Tiangang, Yao Zhongjun, Li Hongjun, Zhu Yiping. 2014b. Ore-controlling factors and exploration indicators of alkaline magmatism re-lated epithermal gold deposits:A case study of the Porgera gold deposit in Papua New Guinea[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(2/3):308-317(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286392014_Ore-controlling_factors_and_exploration_indicators_of_alkaline_magmatism_related_epithermal_gold_deposits_A_case_study_of_the_Porgera_gold_deposit_in_Papua_New_Guinea
Li Wenchang, Pan Guitang, Hou Zengqian, et al. 2010. Archipelagic Arc-basin System, Metallogenic Model for Collision Orogeny and Geotechnical exploration in the Sanjiang Region, SW China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-491(in Chinese).
Li Xingzhen, Jiang Xinsheng, Sun Zhiming, Shen Ganfu, Du Dexun. 2002. Collision orogenic process in Sanjiang area, Southwest China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-213 (in Chinese).
Li Xingzhen, Liu Chaoji, Ding Jun. 2004. Correlation and connection of the main suture zones in the Greater Mekong Subregion[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 24(4):1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200404001
Li Xinren, Zhou Xilin, Yan Chengmin, Wang Changbing, Li Yubing. 2017. Division and characteristics of the geotectonic units of Myanmar[J]. Geology and Resources, 26(1):99-104 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201701018
Lin Fangcheng; Shi Meifeng, Li Xingzhen, et al. 2010. Geological Background and Metallogenic Regularities of the Sanjiang -Mekong Metallogenic Belt[R]. Internal Materials of Chengdu Center, China Geological Survey, 1-437 (in Chinese).
Lingmu Weiyuan, Shen Yaolong. 1989. History of geological tectonic development in the Philippine Islands[J]. Offshore Oil, 9(5):28-37 (in Chinese).
Liu C Z, Chung S L, Wu F Y, Zhang C, Xu Y, Wang J G, Chen Y, Guo S. 2016. Tethyan suturing in Southeast Asia:zircon U-Pb and HfO isotopic constraints from Myanmar ophiolites[J]. Geology, 44(4):311-314. doi: 10.1130/G37342.1
Liu Guichun, Sun Zaibo, Zeng Wentao, Feng Qinglai, Huang Liang, Zhang Hu. 2017. The age of Wanhe ophiolitic mélange from Mengku area, Shuangjiang County, Western Yunnan Province, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 36(2):163-174 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201702003
Liu Junlai, Song Zhijie, Cao Shuyun, Zhai Yunfeng, Wang Anjian, Gao Lan, Xiu Qunye, Cao Dianhua. 2006. The dynamic setting and processes of tectonic and magmatic evolution of the oblique collision zone between Indian and Eurasian plates:Exemplified by the tectonic evolution of the Three River region, eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4):775-786 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e686ed6b6b00c74deb5ccc2b1ed81f35&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Junlai, Tang Yuan, Song Zhijie, Tran My Dung, Zhai Yunfeng, Wu Wenbin, Chen Wen. 2011. The Ailaoshan Belt in Western Yunnan:Tectonic Framework and Tectonic Evolution[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition). 41(5):1285-1303 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=27416a31f85afccb27af3e6940820b00&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Shusheng, Fan Wenyu, Luo Maojin, Tang Fawei, Zhu Huaping, Chen Wenfeng. 2014. Ziron U-Pb dating and geochemistry characteristics of the bimodal volcanic rocks in Phlaythong area, Southern Laos[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 44(2):540-553(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201402014.htm
Lu Yingxiang, Liu Hongguang, Huang Jingning, Zhang Hongyuan, Chen Yongqing. 2009. Preliminary division of the metallogenetic belts in the Central South Peninsula of Southeast Asia and their regional ore-forming characteristics[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28 (2-3):314-325 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200902027
Makoundi C, Zaw K, Large R R, Meffre, S, Lai C K, Hoe T G. 2014. Geology, geochemistry and metallogenesis of the Selinsing gold deposit, central Malaysia[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(1):241-261. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.023
Metcalfe I. 2013. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 66:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
Mitchell, A.H.G., Win Myint, Kyi Lynn, Myint Thein Htay, Maw Oo, Thein Zaw, 2011. Geology of the high-sulfidation copper deposits, MonywaMine, Myanmar[J]. Resource Geology 61, 1-29. doi: 10.1111/rge.2011.61.issue-1
Mo Xuanxue, Lu Fengxiang, Shen Shangyue, Zhu Qinwen, Hou Zengqian, Yang Kaihui. 1993. The Volcanism and Mineralization of Tethys in Sanjiang[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-269 (in Chinese).
Morley C K. 2012. Late Cretaceous-Early Palaeogene tectonic development of SE Asia[J]. Earthence Reviews, 115(1-2):37-75. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.08.002
Moss S J, Chambers J, Cloke I, Satria D, Ali J R, Baker S, Milsom J, Carter A. 1997. New observations on the sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Tertiary Kutai Basin, East Kalimantan[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 126(1):395-416. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1997.126.01.24
Nakano N, Osanai Y, Owada M, Nam T N, Toyoshima T, Binh P, Tsunogae T, Kagami H. 2007. Geologic and metamorphic evolution of the basement complexes in the Kontum Massif, central Vietnam[J]. Gondwana Research, 12(4):438-453. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.01.003
Pan Guitang, Lu Songnian, Xiao Qinghui, Zhang Kexin, Yin Fuguang, Hao Guojie, Luo Mansheng, Ren Fei, Yuan Sihua. 2016. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6):1-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201606001
Pan Guitang, Xiao Qinghui, Lu Songnian, Deng Jinfu, Feng Yimin, Zhang Kexin, Zhang Zhiyong, Wang Fangguo, Xing Guangfu, Hao Guojie, Feng Yanfang. 2009. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1):1-4 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201804003
Pan Guitang. 2013. Tectonic Map and Instructions for the Tibet Plateau and Adjacent Areas[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Peng Zhimin, Geng Quanru, Wang Liquan, Zhang Zhang, Guan Junlei, Cong Feng, Liu Shusheng. 2014. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic characteristics of Granitic gneiss from Bunsumco, Central Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(26):2621-2629 (inChinese). doi: 10.1360/N972014-00014
Peng Zhimin, Zhang Ji, Guan Junlei, Zhang Zhang, Han Wenwen, Fu Yuzhen. 2018. The discovery of Early-Middle Ordovician granitic gneiss from the giant Lincang Batholith in Sanjiang area of Western Yunnan and its geological implications[J]. Earth Science, 43(8):2571-2585 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201808003
Phan C T. 2000. The Permian of Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia and its interregional correlation[J]. Developments in Palaeontology and Stratigraphy, 18(00):99-109. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920544600800072
Pigram C J. 1987. Terranes and the accretion history of the papua new guinea orogeny[J]. Bmrj.aust.geol. and Geophys, 10(3).
Qian Kun, Yan Yi, Huang Qiyu, Chen Wenhuang, Yu Mengming, Tian Zhixian. 2016. Sea floor spreading of South China Sea and its depositional records of sea and land changes[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 32(8):10-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201608002
Robert Jak McCarroll, Ian T. Graham, Russell Fountain, Karen Privat, Jon Woodhead. 2014. The Ojolali region, Sumatra, Indonesia:Epithermal gold-silver mineralisation within the Sunda Arc[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(1):218-240. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.013
Rossignol C, Bourquin S, Poujol M, Hallot E, Dabard MP, Nalpas T. 2016. The volcaniclastic series from the Luang Prabang Basin, Laos:A witness of a triassic magmatic arc?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 120:159-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.02.001
Salam A, Zaw K, Meffre S, Mcphie J, Lai C K. 2014. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Chatree epithermal gold-silver deposit:Implications for the tectonic setting of the Loei Fold Belt, Central Thailand[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(1):198-217. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.10.008
Schwartz MO, Rajah SS, Askury AK and Putthapiban P. 1995. The Southeast-Asian Tin belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 38(2-4):95-286. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(95)00004-T
Sevastjanova I, Hall R, Rittner M, Paw S M T L, Naing T T, Aldertona D H, Comfort G. 2016. Myanmar and Asia united, Australia left behind long ago[J]. Gondwana Research, 32:24-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.02.001
Shao Lei, You Hongqing, Hao Hujun, Wu Guoxuan, Qiao Peijun, Lei Yongchang. 2007. Petrology and depositional environments of Mesozoic strata in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Geological Review, 53(2):164-169 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200702003
Shi M F, Lin F C, Fan W Y, Deng Q, Cong F, Tran M D, Zhu H P, Wang, H. 2015. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of granitoids in the Truong Son terrane, Vietnam:Tectonic and metallogenic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 101:101-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.02.001
Shi Meifeng, Lin Fangcheng, Fan Wenyu, Wang Hong, Cong Feng, Zhu Huaping. 2015. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the monzogranites in the Pilok tintungsten mining area, western Thailand, and its geological implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(4):769-779(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201504016.htm
Shi Meifeng, Lin Fangcheng, Li Xingzhen, Ling Xiaoming, Shi Hongzhao. 2011. Stratigraphic zoning and tectonic events in Indochina and adjacent areas of southwest China[J]. Geology in China, 38(5):1244-1256. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201105011
Shi Meifeng, Lin Fangcheng, Liiu Chaoji, Li Xingzhen, Wang Hong. 2013. Classification and metallogenesis of metallogenic belts in Southeast Asia and the neighbouring southwestern part of China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 33(2):103-110(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl201302015
Smyth H R, Hamilton P J, Hall R, Kinny P D. 2007. The deep crust beneath island arcs:Inherited zircons reveal a Gondwana continental fragment beneath East Java, Indonesia[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 258(1):269-282. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X07002087
Sone M, Metcalfe I. 2008. Parallel Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia:New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 340(2/3):166-179. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S163107130700260X
Spakman W, Hall R. 2010. Surface deformation and slab-mantle interaction during Banda arc subduction rollback[J]. Nature Geoscience, 3(8):562-566. doi: 10.1038/ngeo917
Suggate S M, Cottam M A, Hall R, Sevastjanova I, Forster M A, Whitea L T, Armstrongc R A, Carterd A, Mojares E. 2014. South China continental margin signature for sandstones and granites from Palawan, Philippines[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(2):699-718. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.006
Sun Zhen, Zhao Zhongxian, Zhou Di, Yang Shaokun, Lin Heming, Chen Guanghao. 2011. The stratigraphy and the sequence achitecture of the basins in Nansha region[J]. Earth Science, 36(5):798-806 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201105003
Waipan N S, Whitehouse M J, Searle M P, Robb L J, Ghani A A, Chung S L, et al. 2015. Petrogenesis of Malaysian granitoids in the Southeast Asian tin belt:Part 2. U-Pb zircon geochronology and tectonic model[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 127. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-data_query?bibcode=2015GSAB..127.1209W&db_key=PHY&link_type=ABSTRACT
Wang Anjian, Cao Dianhua, Guan Ye, Liu Junlai, Li Wenchang. 2009. Metallogenic Belts of Southern Three Rivers Region, Southwest China:Distribution, Characteristics and Discussion[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(10):1365-1375. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=84718b5c63ad7ca2b28ece0dc756721b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Hong, Lin Fangcheng, Li Xingzhen, Shi Meifeng, Liu Chaoji, Shi, Hongzhao. 2012. Tectonic unit division and Neo-Tethys tectonic evolution in north-central Myanmar and its adjacent areas[J]. Geology in China, 39(4):912-922 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201204007.htm
Wang Hong, Lin Fangcheng, Li Xingzhen, Shi Meifeng. 2015. The division of tectonic units and tectonic evolution in Laos and its adjacent regions[J]. Geology in China, 42(1):71-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi2015010006
Wang Zhiyao, Qian Maolu, Su Junqing, Hu Jungang, Wang Yu, Liu Zhiying. 2017. Genesis analysis of gas source of biogenic gas reservoir in rakhine basin, Myanmar[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 24(2):46-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201702007.htm
Watkinson I M, Hall R, Ferdian F. 2011. Tectonic re-interpretation of the Banggai-Sula-Molucca Sea margin, Indonesia[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 355(1):203-224. doi: 10.1144/SP355.10
White L T, Hall R, Armstrong R A. 2014. The age of undeformed dacite intrusions within the Kolaka Fault zone, SE Sulawesi, Indonesia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 94(3):105-112. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912014003575
Xin Di, Liu Jing, Li Lei, Ran Li, Song Xuexin. 2014. Metallogenic characteristics and controlling factors of the Ok Tedi Cu-Au deposit, Pap-ua New Guinea[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(2/3):299-307(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZQYD2014Z1018.htm
Yang Wenqiang. 2010. Tectonic evolution of Nan-Uttaradit and Loei suture zones, Thailand and Lao P.D.R.[D]. China University of Geosciences: Doctoral dissertation (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao Y J, Liu H L, Yang C P, Han B, Tian J J, Yin Z X, Gong J L, Xu Q Y. 2012. Characteristics and evolution of cenozoic sediments in the liyue basin, se south china sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 60(Complete):114-129. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912012003422
Yao Zhongyou, Wang Tiangang, Fu Caoyi, Ma Chun, Qi Liping, Kong Hongjie, Wang Zhuansheng, Li Wanggang, Chen Gang. 2014. Geological framework and dominant mineral resources of Oceania[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(2/3):143-158(in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201402003
Zaw K, Meffre S, Lai CK, Burrett C, Santosh M, Graham I, Manaka T, Salam B, Kamvong T, Cromie P. 2014. Tectonics and metallogeny of mainland Southeast Asia-A reviewand contribution[J]. Gondwana Research, 5-30. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X13003572
Zhang Kexin, Pan Guitang, He Weihong, Xiao Qinghui, Xu Yadong, Zhang Zhiyong, et al. 2015. New division of tectonic-strata superregion in China[J]. Earth Science, 40(2):206-233 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502004
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, Dilek Y, Wang Q, Li W H, Dong G C, Sui Q L, Liu Y S, Yuan H L, Mo X X. 2012. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane, southern Tibet:Record of an early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian protoTethyan margin[J]. Chemical Geology, 328(11):290-308. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254112000034
Zhu Huaping, Fan Wenyu, Mao Hongjiang, Wu Zhenbo, Gao Jianhua, Liu Shusheng. 2014. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of the PHaLek iron deposit in Vientiane Province, Laos[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 44(5):1492-1501(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201405010.htm
Zhu Huaping, Lin Fangchen, Shi Meifeng, Wang Hong. 2016. Analysis of Geotectonic Environment, Metallogenic Potential and Prospecting direction of Important Mining Areas in Eastern Tethys[R]. 213-216 (in Chinese).
Zimmermann S, Hall R. Provenance of Triassic and Jurassic sandstones in the Banda Arc:Petrography, heavy minerals and zircon geochronology[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 37:1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.06.001
Zin-Maung-Maung-Thein, Takai M, Tsubamoto T, Egi N, ThaungHtike, Nishimura T, Maung-Maung, Zaw-Win. 2010. A review of fossil rhinoceroses from the Neogene of Myanmar with description of new specimens from the Irrawaddy sediments[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 37(2):154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.009
蔡文杰, 朱光辉, 姜烨, 杨松岭, 李爱山. 2012.增生楔油气地质特征及勘探潜力——以缅甸某区块为例[J].天然气地球科学, 23(4):742-747. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201204017 陈永清, 黄静宁, Zhai Xiaoming, 卢映祥, 程志中, 李建荣. 2009.中缅毗邻区金腊Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿田花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年与地球化学特征[J].地学前缘, 16(1):344-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.01.036 陈永清, 刘俊来, 冯庆来. 2010.东南亚中南半岛地质及与花岗岩有关的矿床[M].北京:地质出版社, 76-89. 邓军, 葛良胜, 杨立强. 2013.构造动力体制与复合造山作用-兼论三江复合造山带时空演化[J].岩石学报, 29(4):1099-1114. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YSXB201304001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 邓军, 李文昌, 莫宣学, 等. 2016.三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用[M].科学出版社: 1-622. 邓军, 王长明, 李龚健. 2012.三江特提斯叠加成矿作用样式及过程.岩石学报, 28 (5):1349-1361. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201205001 邓军, 杨立强, 王长明. 2011.三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究进展[J].岩石学报, 27(9):2501-2509. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201109001 冯庆来, 沈上越, 刘本培, Helmcke D, 钱祥贵, 张伟明. 2002.滇西南澜沧江构造带大新山组放射虫、硅质岩和玄武岩研究[J].中国科学:地球科学, 32(3):220-226. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200203006 冯庆来, 杨文强, 沈上越, Chongpan Chonglakmani, Kitsana Malila. 2008.泰国北部清迈地区海山地层序列及其构造古地理意义[J].中国科学:地球科学, 38(11):1354-1360. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802144796 郭远生, 罗玉福, 崔银亮. 2013.中国和东南亚红土型镍矿地质与勘查[M].北京:地质出版社, 64-76. 侯增谦, 王二七, 莫宣学. 2007.青藏高原碰撞造山与成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 798-963. 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦. 2010.西南"三江"多岛弧盆-碰造山成矿理论与勘查技术[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-491. 李文光, 傅朝义, 姚仲友, 信迪, 葛之亮, 宋学信, 王天刚. 2014a.巴布亚新几内亚铜金矿床大地构造背景、成因类型与成矿特征[J].地质通报, 33 (2/3):270-282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201402015 李文光, 王天刚, 姚仲友, 李红军, 朱意萍. 2014b.与碱性岩有关的浅成低温热液型金矿特征与控矿因素——以巴布亚新几内亚波尔盖拉金矿为例[J].地质通报, 33 (2/3):308-317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201402018 李新仁, 周喜林, 严城民, 王长兵, 李于冰. 2017.缅甸大地构造单元的划分与特征[J].地质与资源, 26(1):99-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2017.01.018 李兴振, 江新胜, 孙志明, 沈敢富, 杜德勋. 2002.西南三江地区碰撞造山过程[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-213. 李兴振, 刘朝基, 丁俊. 2004.大湄公河次地区主要结合带的对比与连接[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 24(4):1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2004.04.001 林方成, 施美凤, 李兴振. 2010.三江-湄公河成矿带地质背景和成矿规律对比研究专题成果报告[R].中国地质调查局成都地质调查中心内部资料, 1-437. 铃木尉元, 沈耀龙. 1989.菲律宾群岛地质构造发育史[J].海洋石油, 9(5):28-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001538857 刘桂春, 孙载波, 曾文涛, 冯庆来, 黄亮, 张虎. 2017.滇西双江县勐库地区湾河蛇绿混杂岩的形成时代、岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 36(2):163-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.02.003 刘俊来, 宋志杰, 曹淑云, 翟云峰, 王安建, 高兰, 修群业, 曹殿华. 2006.印度-欧亚侧向碰撞带构造-岩浆演化的动力学背景与过程——以藏东三江地区构造演化为例[J].岩石学报, 22(4):775-786. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604002 刘俊来, 唐渊, 宋志杰, Tran My Dung, 翟云峰, 吴文彬, 陈文. 2011.滇西哀牢山构造带:结构与演化[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(5):1285-1303. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201105003 刘书生, 范文玉, 罗茂金, 唐发伟, 朱华平, 陈文峰. 2014.老挝南部帕莱通双峰式火山岩锆石U-Pb定年及岩石地球化学特征[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 44(2):540-553. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=CCDZ201402014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 卢映祥, 刘洪光, 黄静宁, 张宏远, 陈永清. 2009.东南亚中南半岛成矿带初步划分与区域成矿特征[J].地质通报, 28(2/3):314-325. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200902027 莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 侯增谦, 杨开辉. 1993.三江特提斯火山作用与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-269. 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 张克信, 尹福光, 郝国杰, 骆满生, 任飞, 袁四化. 2016.中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J].地学前缘, 23(6):1-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201606001 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 邓晋福, 冯益民, 张克信, 张智勇, 王方国, 邢光福, 郝国杰, 冯艳芳. 2009.中国大地构造单元划分[J].中国地质, 36(1):1-4. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090101&flag=1 潘桂棠等. 2013.青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书[M].北京:地质出版社. 彭智敏, 耿全如, 王立全, 张璋, 关俊雷, 丛峰, 刘书生. 2014.青藏高原羌塘中部本松错花岗质片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J].科学通报, 59(26):2621-2629. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201426014.htm 彭智敏, 张辑, 关俊雷, 张璋, 韩文文, 付于真. 2018.滇西"三江"地区临沧花岗岩基早-中奥陶世花岗质片麻岩的发现及其意义[J].地球科学, 43(8):2571-2585. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201808003 钱坤, 闫义, 黄奇瑜, 陈文煌, 余梦明, 田陟贤. 2016.南海扩张过程及海陆变迁沉积记录[J].海洋地质前沿, 32(8):10-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201608002 邵磊, 尤洪庆, 郝沪军, 吴国瑄, 乔培军, 雷永昌. 2007.南海东北部中生界岩石学特征及沉积环境[J].地质论评, 53(2):164-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.02.003 施美凤, 林方成, 李兴振, 凌小明, 石洪召. 2011.东南亚中南半岛与中国西南邻区地层分区及沉积演化历史[J].中国地质, 38(5):1244-1256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.011 施美凤, 林方成, 刘朝基, 李兴振, 王宏. 2013.东南亚缅泰老越柬五国与中国邻区成矿带划分及成矿特征[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 33(2):103-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2013.02.015 施美凤, 林方成, 范文玉, 王宏, 丛峰, 朱华平. 2015.泰国西部比洛克(Pilok)锡钨矿区二长花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 34(4):769-779. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.04.016 孙珍, 赵中贤, 周蒂, 杨少坤, 林鹤鸣, 陈广浩. 2011.南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J].地球科学, 36(5):798-806. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201105003 王安建, 曹殿华, 管烨, 刘俊来, 李文昌. 2009.西南三江成矿带中南段金属矿床成矿规律与若干问题探讨[J].地质学报, 83(10):1365-1375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.10.001 王宏, 林方成, 李兴振, 施美凤, 刘朝基, 石洪召. 2012.缅甸中北部及邻区构造单元划分及新特提斯构造演化[J].中国地质, 39(4):912-922. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.04.006 王宏, 林方成, 李兴振, 施美凤. 2015.老挝及邻区构造单元划分与构造演化[J].中国地质, 42(1):71-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.006 王芝尧, 钱茂路, 苏俊清, 胡俊刚, 王瑀, 刘志英. 2017.缅甸若开海域生物气藏气源成因分析[J].油气地质与采收率, 24(2):46-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqdzycsl201702007 信迪, 刘京, 李雷, 冉丽, 宋学信. 2014.巴布亚新几内亚奥克泰迪铜金矿床成矿特征和控制因素[J].地质通报, 33 (2-3):299-307. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201402017 杨文强. 2010.泰国和老挝难河-程逸及黎府缝合带构造演化[D].中国地质大学: 博士学位论文. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-2010250456.htm 姚仲友, 王天刚, 傅朝义, 马春, 齐立平, 孔红杰, 汪传胜, 李文光, 陈刚. 2014.大洋洲地区大地构造格架与优势矿产资源[J].地质通报, 33 (2/3):143-158. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201402003 张克信, 潘桂棠, 何卫红, 肖庆辉, 徐亚东, 张智勇, 等. 2015.中国构造-地层大区划分新方案[J].地球科学, 40(2):206-233. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502004 朱华平, 范文玉, 毛洪江, 吴振波, 高建华, 刘书生. 2014.老挝万象省爬立山(PhaLek)铁矿床地质特征及成矿作用分析[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44 (5):1492-1501. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201405011 朱华平, 林方成, 施美凤, 王宏. 2016.东特提斯地区重要矿区产出环境、成矿潜力和找矿方向分析[R]. 213-216. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 魏信祥,李江. 煤炭资源开发利用过程中铀迁移产生的环境影响研究进展. 科学技术与工程. 2023(10): 4033-4043 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邸齐梦,董一慧,李佳乐,徐卫东,高柏,陈功新. 何魁核电站拟选厂址水体天然放射性核素分布特征及健康风险评价. 有色金属工程. 2023(07): 134-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 魏信祥,李江. 石煤中铀在水-岩作用下浸出释放的环境影响及控制因素. 有色金属(冶炼部分). 2023(11): 63-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 汪媛媛,郑刘根,吴盾,陈永春. 小尺度矸石堆场及其周边土壤中放射性元素特征分析及风险评价. 环境化学. 2022(11): 3640-3649 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王珍珍,李进孝,张珂,马家亮,张绍韡,Maksim G Blokhin,张飘飘,蔺敬妍,孙明晓,申伟刚,赵存良. 山西沁水煤田首阳山矿15~#煤的稀土元素分布规律、赋存状态及其对成煤环境的指示. 中国地质. 2021(03): 777-784 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: