A study of genetic type characteristics and important distribution zones of global iron deposits
-
摘要:
中国是全球铁矿石第一消费大国,每年进口铁矿石量已超过9亿t,进口量超过全球铁矿石贸易量的60%,对全球铁矿主要类型特征及重要分布区带总结和潜力分析研究具有重要的理论和现实意义。本文总结了全球铁矿资源的禀赋特征,将全球铁矿床分为BIF相关型、沉积型、火山成因型、岩浆型、接触交代-热液型(矽卡岩型)5种成因类型,重点总结分析了BIF相关型和火山成因型铁矿地质特征、成因和找矿标志等。根据铁矿床产出的大地构造单元、地层层序、含矿建造特征及矿床类型、成矿时代等综合因素,在全球主要大地构造单元中共圈出33个铁矿分布区,47个铁矿重要分布区带,并对各重要分布区带的资源潜力进行了探讨。
Abstract:China is the world's largest consumer of iron ore. The annual import of iron ore has exceeded 900 million tons, and its imports exceed 60% of the global iron ore trade volume. The summarization and potential analysis of global iron ore type characteristics and important distribution zones are of important theoretical and practical significance. This paper sums up the endowment characteristics of global iron ore resources. The authors divide global iron deposits into five genetic types:BIF-related, sedimentary, volcanic, magmatic, and contact-hydrothermal (skarn) deposits, with the emphasis placed on the analysis of geological characteristics of BIF-related and volcanic iron ore deposits as well as genesis and prospecting indicators. According to the comprehensive factors such as tectonic units, stratigraphic sequence, ore-bearing structure characteristics, deposit types and metallogenic ages of iron ore deposits, a total of 33 iron ore distribution areas and 47 important distribution belts of iron ore deposits are delineated in the major geotectonic units of the world. In addition, the resource potential of each important distribution belt is discussed.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
锗(Ge)是一种典型的稀散元素,其地壳丰度为1.5×10-6,主要富集在煤和铅锌矿床中。统计结果显示,闪锌矿是铅锌矿床中Ge的主要载体矿物,但不同类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量存在差异。除热液脉型和浅成热液型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量较高(可达2500×10-6)外,其他主要类型(如喷流沉积型,SEDEX;火山块状硫化物型,VMS;密西西比河谷型,MVT,等)铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的平均含量通常 < 300×10-6。本次发现贵州贵定竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的显著超常富集现象,现报道如下。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
在细致深入的矿床学和矿物学研究基础上,利用激光剥蚀等离子质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)对竹林沟锌矿床主要金属矿物闪锌矿进行原位微量元素组成分析。统计闪锌矿中Ge等元素的富集特征,结合相关分析和以往研究成果,揭示竹林沟锌矿床中Ge的超常富集机制。
3. 研究结果(Results)
竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量为592×10-6~1100×10-6(平均764×10-6,表 1),锌矿石中Ge的平均品位97.9×10-6。闪锌矿LA-ICP-MS微区原位Ge含量分析资料显示,扬子板块及其周缘地区MVT铅锌矿床,如牛角塘、会泽、毛坪、富乐等,其闪锌矿中Ge的含量均 < 652×10-6,即便富乐矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量最高,但其平均含量也仅为191×10-6,明显比竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)低。
表 1 竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿部分元素含量(10-6)Table 1. The part elemental contents of sphalerite from the Zhulingou Zn deposit(10-6)
与世界上主要类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿LA-ICP-MS微区原位Ge含量分析资料相比,竹林沟矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量比SEDEX(Ge含量通常 < 50×10-6)、VMS(Ge含量多数 < 100×10-6)和MVT(Ge含量n×10-6~n×102×10-6,Ge平均含量 < 300×10-6)等闪锌矿中Ge的含量高出一个数量级。竹林沟矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量与法国Noailhac-Saint Salvy热液脉型Zn-Ge-Ag-Pb-Cd矿床(Ge平均含量750×10-6)和玻利维亚Porco浅成热液型Ag-Zn-Pb-Sn-Ge矿床(n×102×10-6~2500×10-6)等少数类型铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)相当。
可见,竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量比目前已知扬子板块及其周缘地区MVT矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)都高,且明显高出全球主要类型(除岩浆热液型和热液脉型外)铅锌矿床闪锌矿中Ge的含量(特别是Ge的平均含量)一个数量级,具有显著超常富集特征(接近Ge地壳丰度的1000倍)。
初步分析显示,竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中Zn与Ga和Cd之间具有正相关关系;相反,Fe与Ga和Cd之间均具有负相关关系,这表明该矿床闪锌矿中Ga和Cd很可能不是直接替代Zn而是替代Fe,与笔者前期认识基本一致。然而,不难发现该矿床闪锌矿中Zn与Ge之间呈一定的负相关关系,但Fe和Ge之间则呈一定的正相关关系,进一步地Zn与Fe之间具有显著的负相关关系,且Zn与Fe+Ge之间负相关性更显著(图 1)。目前,闪锌矿中主要有六种Ge替代Zn的方式:(1)2Cu++Cu2++Ge4+↔4Zn2+;(2)Ge2+↔Zn2+;(3)2Ag++Ge4+↔3Zn2+;(4)2Cu++Ge4+↔3Zn2+;(5)□(晶体空位)+Ge4+↔2Zn2+;(6)nCu+Ge↔(n+1)Zn。可见,这六种替代方式均不能解释竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿Zn和Fe+Ge之间的强烈负相关关系。因此,笔者推测该矿床中Ge很可能是与Fe一起共同替代Zn进入闪锌矿晶格(Fe+Ge↔2Zn),是一种新的Ge替代方式。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
竹林沟锌矿床闪锌矿中显著超常富集锗,锗的富集程度接近1000倍,且锗与铁一起共同替代锌进入闪锌矿晶格,是一种新的锗替代方式。初步估算竹林沟锌矿床锗金属储量超过400 t,而竹林沟锌矿床外围还有半边街等锌矿床,初步预测研究区锗资源量可能达到超大型规模(>1000 t),一个新的国家级乃至世界级锗资源基地曙光已现。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgments)
感谢科技部、国家自然科学基金委、云南省科技厅和云南大学对本项目的支持。
致谢: 本文得到了国土资源部科技成果奖评审委员的肖庆辉研究员、国土资源部咨询研究中心李裕伟研究员、国土资源部信息中心马建民研究员、首钢地质勘查院施性明教授、中国地质调查局发展研究中心邱瑞照、叶锦华研究员精心指导和帮助, 编辑部的专家和老师在成文中给予了精心指导, 谨此一并表示诚挚的感谢! -
图 2 全球主要铁矿石生产国家铁矿石平均品位情况(USGS, 2015; 李莎, 2017)
Figure 2. Average grade of iron ore in the world's major iron ore production countries (modified after USGS, 2015; Lisha, 2017)
图 4 铁建造的时间与发育程度(丰度)关系示意图, 包括一些重要的铁建造及其产地(据Trendall, 2002和Klein, 2005修改)
Figure 4. Schematic diagram showing the relationship between the formation time of IF and its development degree (abundance), including some significant IF and major IF regions (modified after Trendall 2002 and Klein, 2005)
图 5 BIF沉积环境示意图(据Wang et al., 2009和Bekker et al., 2010修改)
地幔柱成因的科马提岩与海底热液相互作用析出Si和Fe交替沉淀形成了铁建造
Figure 5. Sketch map of sedimentary environment of BIF and GIF (modified after Wang et al., 2009 and Bekker et al., 2010)
The interaction between the seafloor hydrothermal fluids and komatiites generated by mantle plumes released silica and iron, which precipitated alternately to form iron formation
图 6 澳大利亚哈默斯利盆地铁矿区地质略图(Taylor et al., 2001)及哈默斯利群地层柱状图及SHRIMP年龄(Barley et al., 1997)
Bo-布尔吉达组(Boolgeeda); WR-温佳拉组(Woongarra Rhyolite); WW-威利-沃利组(Weeli Wolli); Ya-彦地克吉纳段(Yandicoogina); Jo-乔费尔段(Joffre); Wb-维尔贝克段(Whaleback); DG-谷峡谷段(Dales Gorge); Mmc-姆克雷斯组(Mount Mcrae); MS-希尔维亚山组(Mount Sylvia); WT-威特努姆组(Wittennoom); MM-马拉曼巴组(Marra Mamba); J-纪日纳赫组(Jeerinah)
Figure 6. Sketch geological map of the major iron orebodies in the Hamersley iron province (after Taylor et al., 2001) and stratigraphic columnar section of the Hamersley iron province and available SHRIMP ages (after Barley et al., 1997)
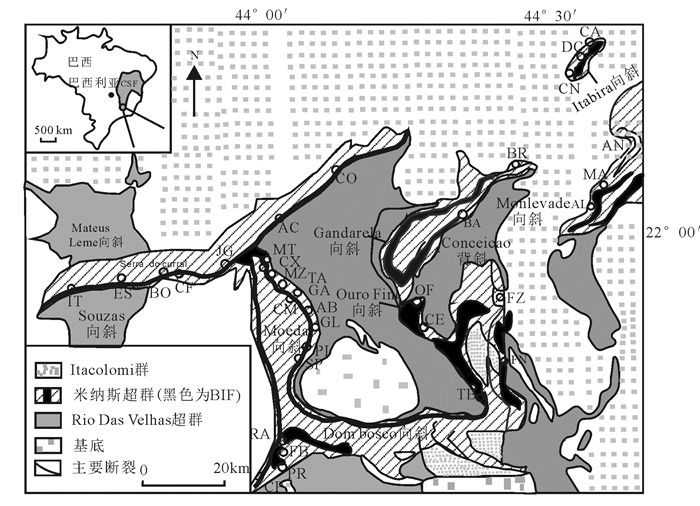
图 7 巴西铁四角地区地质简图(据赵宏军等, 2017)
Figure 7. Simplified geological map of the Quadrilatero Ferrifero (after Zhao Hongjun et al, 2017)
AB-Aboboras; AC-AguasClaras; AG-Alegria; AL-AguaLimpa; AN-Andrade; BA-Bau; BO-Bocaina; CA-Cau; CF-CorregodoFeijao; BR-Brucutu; CM-CapitaodoMato; CE-Capanema; CN-Conceicao; CO-Corregodo Meio; CP-CasadePedra; CX-CapaoXavier; DC-DoisCorregos; ES-Esperanca; B-Fabrica; GL-Galinheiro; FN-FabricaNova; FZ-Fazendao; IT-Itatiaiucu; JG-Jangada; MA-MorroAgudo; MT-Mutuca; MZ-MarAzul; OF-OuroFino; PI-Pico; PR-Pires; RA-RetiroDasAlmas; SP-Sapecado; TA-Tamandua; TB-Timbopeba
图 8 库尔斯克磁异常区的磁异常和含铁石英岩系的岩相分带示意图(冶金部情报标准研究所, 1975)
1-含铁岩系的外尖灭亚带, 由含铁石英岩和千枚岩互层组成(西部亚带在西南异常带内, 东部亚带在东北异常带内), 含铁石英岩主要由硅酸盐和磁铁矿组成, 主要发育宽条带状构造, 局部发育有薄条带状的铁云母-磁铁石英岩; 2-中央亚带, 其内产有两个很厚的含铁石英岩段, 两者间为千枚状的片岩所隔开。含铁石英岩主要为赤铁矿和磁铁矿, 具薄条带状构造; 3-含铁岩系的内尖灭亚带, 位于库尔斯克-科罗查复背斜的两翼附近。尖灭带内的含铁石英岩常呈微条带状和块状; 4-泥盆纪地层分布的南界; 5-维宪期地层分布的北界; 6-多内昔期地层分布的界线; 7-磁异常; 8-富铁矿床。西南异常带:①-新雅尔廷矿床; ②-米哈伊洛夫矿床; ③-季齐年矿床; ④-奥里霍瓦特矿床; ⑤-马利诺夫矿床; ⑥-雅克普列夫矿床; ⑦-捷捷列温矿床; ⑧-戈斯提舍夫矿床; ⑨-别尔哥罗德矿床; ⑩-霍赫洛沃-伊古缅矿床; ⑪ -梅里霍沃-舍别金矿床; ⑫ -博利舍特罗伊茨矿床; 东北异常带:⑬ -科罗布科夫矿床; ⑭ -列别丁矿床; ⑮ -斯托伊连矿床; ⑯ -萨尔提科夫矿床; ⑰ -波格罗梅茨矿床; ⑱ -切尔年矿床
Figure 8. Schematic map of magnetic anomalies in the Kursk magnetic anomaly zone and lithofacies zoning of the iron-bearing quartzite series (after Institute of Information Standards, Ministry of Metallurgy, 1975)
1-Outer tipping out of sub-belt of the iron-bearing rock series, composed of interbedded layers of iron-bearing quartzite and phyllite; 2-Central sub-band, which contains two very thick iron-bearing quartzite segments separated by thousands of schists; 3-Inner tipping of sub-belt of ironbearing rock series, located near the two wings of the Kursk-Krocha complex anticline; 4-The southern boundary of the Devonian stratigraphic distribution; 5-The northern boundary of the stratigraphic distribution of the Victorian period; 6-The boundary of the stratigraphic distribution of the Done period; 7-Magnetic anomaly; 8-Rich iron deposit.Southwest Anomaly Belt:①-New Yaltin deposit; ②-Mikhailov deposit; ③-Jiqinian deposit; ④-Orihowate deposit; ⑤-Malinov deposit; ⑥-Jacqueslev deposit; ⑦-Jiejie Liewen deposit; ⑧-Gostisev deposit; ⑨-Belgorod deposit; ⑩-Hochlovo-Igoumen deposit; ⑪ -Merihuwo-Shebe gold deposit; ⑫ -Bolischerotitz deposit; Northeast Anomaly Belt:⑬ -Korobkov deposit; ⑭ -Lebidin deposit; ⑮ -Stojlian deposit; ⑯ -Saltikov deposit; ⑰ -Pogremetz deposit; ⑱ -Chelian deposit
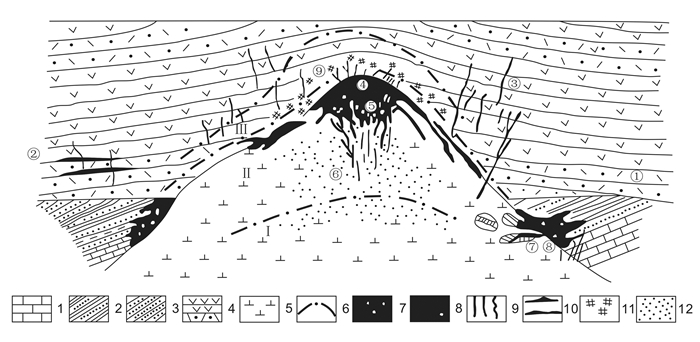
图 10 玢岩铁矿的理想模式图(转引宁芜研究项目编写小组, 1978)
1-青龙群石灰岩(T1-2Q); 2-黄马青组砂页岩(T3h); 3-象山群砂岩(J1-2X); 4-龙王山、大王山两旋回火山岩(J3/K1); 5-辉长闪长玢岩-辉长闪长岩; 6-蚀变分带界线; 7-角砾岩化带及角砾状矿石; 8-块状矿石; 9-镜铁矿或磁铁矿脉; 10-层状铁矿; 11-黄铁矿化; 12-浸染状磁铁矿化; ①-龙旗山式; ②-竹园山式; ③-龙虎山式; ④-梅山式; ⑤-凹山式; ⑥-陶村式; ⑦-向山式(黄铁矿); ⑧-姑山式; ⑨-凤凰山式; 蚀变带:Ⅰ-下部浅色蚀变带; Ⅱ-中部深色蚀变带; Ⅲ-上部浅色蚀变带
Figure 10. Ideal modal map for the porphyritic iron deposits (after Research Group of the Ning-Wu Project, 1978)
1-Qingling Group (T1-2Q) limestone; 2-Huangmaqing Formation (T3h) siltstones; 3-Xiangshan Group (J1-2X) sandstone; 4-Longwangshan and Dawangshan Cycles (J3/K1) volcanic rocks; 5-Gabbro diorite and gabbro diorite porphylite; 6-Boundary of alteration belt; 7-Breccia belt and breccia ore; 8-Massive ore; 9-Specularote or magnetite veins; 10-Bedded iron ore; 11-Pyritization; 12-Disseminated magnetite; Deposit types:①-Longqishan type; ②-Zhuyuanshan type; ③-Longhushan type; ④-Meishan type; ⑤-Aoshan type; ⑥-Taocun type; ⑦-Xiangshan type(pyrite); ⑧-Gushan type; ⑨-Fenghuangshan type; Alteration belts:Ⅰ-Ieucoctatic alteration in lower part; Ⅱ-deep color alteration in middle part; Ⅲ-Ieucoctatic alteration in the upper part
表 1 全球铁矿资源量统计
Table 1 Global iron ore resource statistics

表 2 全球及重要铁矿资源国家大型、超大型铁矿床统计
Table 2 Statistics of large and giant iron deposits in the world and important iron ore resources countries

表 3 两种BIF矿床地质特征对比(王长乐等, 2012)
Table 3 Comparison of geological features between two types of BIF abroad (after Wang et al., 2012)

表 4 全球重要铁矿床(区)地质特征
Table 4 Geological characteristics of important iron deposits (regions) in the world

表 5 全球主要铁矿分布区带
Table 5 Distribution of major iron ore deposits in the world

-
Alexander B W, Bau M, Andersson P, Dulski P. 2008. Continentally-derived solutes in shallow Archean seawater:Rare earth element and Nd isotope evidence in iron formation from the 2.9 Ga Pongola Supergroup, South Africa[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72:378-394. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.10.028
Barley M E, Pickard A L, Sylvester P J. 1997. Emplacement of a large igneous province as a possible cause of banded iron formation 2.45 billion years ago[J]. Nature, 385:55-58. doi: 10.1038/385055a0
Basta F F, Maurice A E, Fontbotéc L, Favargerd P Y. 2011. Petrology and geochemistry of the banded iron formation (BIF) of Wadi Karim and Um Anab, Eastern Desert, Egypt:Implications for the origin of Neoproterozoic BIF[J]. Precambrian Research, 187:277-292. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.03.011
Bekker A, S lack J F, Planavsky N, Krape B, Hofmann A, Konhauser K O, Rouxel O J. 2010.Iron formation:The sedimentary product of acomplex interplay amongmantle, tectonic, oceanic, and biospheric processes[J].Econ.Geol., 105(3):467-508. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.3.467
Cordani U G, Milani E J, Thomaz Filho A. 2000. Tectonic Evolution of South America[D]. Rio de Janerio: 31#International Geological Congress: 1-856.
Dai Yanpei, Zhu Yudi, Zhang Lianchang, Waang Changle, Chen Chao, Xiu Di.2016. An Overview of Studies on Precambrian Banded Iron Formations (BIFs) in China and Abroad[J]. Geological Review, 62(3):735-757 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201603016
Dai Yanpei, Zhang Lianchang, Zhu Mingtian, Wang Changle, Liu Li, Xiang Peng. 2014. The composition and genesis of Mesoarchean Dagushan banded iron formation in the Anshan area, the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Review, 63:353-373 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.013
Deb M. 2014. Precambrian geodynamics and metallogeny of the Indian shield[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 57:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.08.022
Dorr J V N. 1969. Physiographic, stratigraphic and structural development of the Quadrilatero Ferrifero, Minas Gerais, Brazil. United States Geological Survey Professional Paper, 641-A.
Editorial Committee of A DICTIONARY OF EARTH SCIENCES. 2005. A Dictionary of Earth Sciences, Applied Science Volume[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 641-645 (in Chinese).
Fei Xuejin, Qiu Dianyun. 1994. Present conditions and future of the development of mineral resources in deep sea[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 12(6):6-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400581937
Gross G A. 1980. A classification of iron formations based on deposit ional environments[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 18(2):215-222. http://rruff.info/doclib/cm/vol18/CM18_215.pdf
Gross G A. 1983. Tectonic systems and the deposition of ironformation[J]. Precambrian Research, 20(2/4):171-187. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0301926883900724
Gross G A.1965.Geology of iron deposits in Canada, Vol.1.General Geology and Evaluation of Iron Deposits[R]. Geological Survey of Canada, Economic Report 22.
Guo Weimin, Dong Yongguan, Xing Guangfu, Zeng Yong. 2013. New Research Progress on Iron Deposits in Quadrilatero Ferrifero District, Brazil[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information. 32 (5):79-85 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201305014.htm
Niu Hecai, Luo Yong, Li Ningbo, Jiang Yuhang, Yang Wubin, Shan Qiang, Yu Xueyuan. 2012. Study on the Cu-mineralization of the Chagangnuoer Fe-deposit in the Awulale area, Xinjiang[J].Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 48(3):256-265 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201203003
Huston D L, Logan G A. 2004. Barite, BIFs and bugs:Evidence for the evolution of the Earth's early hydrosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 220:41-55.http://www.SNLMetalsEconomics.com; SNLinfo@snl.com. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00034-2
Isley A E. 1995. Hydrothermal plumes and the delivery of iron to banded iron format ion[J]. The Journal of Geology, 103(2):169-185. doi: 10.1086/629734
James H L.1954.Sedimentary facies of iron-formation[J]. Econ.Geol., 49(3):235-293. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.49.3.235
James H L, Trendall A F. 1982. Banded iron-formation: Distribution in time and paleoenvironmental significance[C]//Holland H D, Schidlowski M(eds.). Mineral Deposits and the Evolution of the Biosphere. New York: Springer Verlag Press, 199-218. doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-642-68463-0_11
Jiang Sihong, Liang Qingliang, Nie Fengjun, Liu Yifei, Bai Daming, Liu Yan, Chen Chunliang.2013. Geological characteristics and metallogeny of the Mount Whaleback iron deposit in Pilbara Region, Western Australia[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information. 32(5):95-105 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201305016.htm
Klein C. 2005. Some Precambrian banded iron-formations (BIFs) from around the world:Their age, geologic setting, mineralogy, metamorphism, geochemistry, and origin[J]. American Mineralogist, 90 (10):1473-1499. doi: 10.2138/am.2005.1871
Kneeshaw M. Mt.1975. Whaleback iron orebody, Hamersley Iron Province[M]: Australasian Inst. Mining Metallurgy, Mon. 5: 910-916.
Lan Tingguang, Fan Hongrui, Santosh M, Hu Fangfang, Yang Kuifeng, Liu Yongsheng. 2014. U-Pb zircon chronology, geochemistry and isotopes of the Changyi banded iron formation in the eastern Shandong Province:Constraints on BIF genesis and implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 56:472-486 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.008
Liao Hang. 2015. Genesis of Lomoteng Fe-Mn deposit in South Africa and technical performance evaluation of ore processing[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 29(4):509-513 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcydz201504019
Li Houmin, Liu Mingjun, Li Lixing, Yang Xiuqing, Chen Jing, Yao Liangde, Hong Xuekuan, Yao Tong. 2012. Geology and geochemistry of the marble in the Gongchangling iron deposit in Liaoning Province and their metallogenic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(11):3497-3512 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201211005
Li Houmin, Liu Mingjun, Li Lixing, Yang Xiuqing, Yao Liangde, Chen Jing, Yao Tong. 2014. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of zircons from the garnet-rich altered rocks in the mining area Ⅱ of the Gongchangling iron deposit:Constraints on the ages of the high grade iron deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(5):1205-1217.
Li Houmin, Wang Denghong, Li Lixing, Chen Jing, Yang Xiuqing, Liu Mingjun. 2012. Metallogeny of iron deposits and resource potential of major iron minerogenetic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 39(3):559-580 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201203001
Li Shuguang. 1982. Geochemical Model for the Genesis of Gongchangling rich Magnetite deposit in China[J].Geochimica, 34(2):113-121 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/BF03180110
Li Yanhe, Zhang Zengjie, Hou Kejun, Duan Chao, Wang Defang, Hu Guyue. 2014. The genesis of Gongchangling high-grade-iron oes, Anshan-Benxi area, Liaoning Province, NE China:Evidence from Fe-Si-O-S isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12):2351-2372 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136814001358
Liu Huashan, Li Qiulin, Yu Pusheng, Wu Jieren. 1998. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Jingtieshan type iron-copper deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1:25-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ801.003.htm
Liu Mingjun. 2013. Hydrothermal Metasomatism and Its Metallogenic Significance of the Gongchangling iron Deposit, Liaoning, China[D]. Dissertation Master Degree, China University of Geosciences (Beijing).
Lu Lina, Wu Cen. 2013. Iron Ore Deposit Distribution and Genetic Analysis in Western Australia State[J]. Coal Geology of China, 25(12):106-111 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGMT201312025.htm
Lv Linsu, Wang Yunfeng, Li Hongbo, Zhou Zhenhua, Zhang Zuoheng, Xie Guiqing. 2011. Disscussion on the metallogenesis of Bushveld magmatic Cu-Ni-PGEsulphide deposit in South Africa[J]. Mineral Deposits, 30(6):1129-1153 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201106014.htm
Morris R C.1985. Genesis of iron ore in banded iron-formation by supergene and supergene-metamorphic processes: A conceptual model[C]//Wolff K H. Handbook of Strata-bound and Stratiform Ore Deposits. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 13: 73-235.
Powell C McA, Oliver N H, Li Z X, et al. 1999. Synorogenic hydrothermal origin for giant Hamersley iron oxide ore bodies[J]. Geology, 27:175-178. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0175:SHOFGH>2.3.CO;2
Qiu Ruizhao, Tan Yongjie, Zhu Qun, Li Baoqiang, Lin Fangcheng, Lu Minjie. 2012. Comparative Study on Metallogenic Regularity of Important Metallogenic Belts in China and Its Neighboring Areas[M]. Beijing:Geoligical Publishing House.
Research Group of the Ning-Wu Project. 1978. Porphyrite Iron Deposits of Ningwu Area[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:1-130 (in Chinese).
Rosiere C A, Spier C A, Rios F J. 2004. The itabirites of the QuadrilateroFerrifero and related high-grade iron ore deposits:Anoveriew[J]. Reviews in Economic Geology, 15:223-254. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235995275_The_itabirite_from_the_Quadrilatero_Ferrifero_and_related_high-grade_ores_an_overview
Rosiere C A, Spier C A, Rios F J. 2008. The itabirites of the Quadrilatero Ferrifero and related high-grade iron ore deposits:An overview[J]. Reviews in Economic Geology, 15:223-254. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8ae07430ca3b44ce1664f7a53b482b2e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Shen Chengheng, Wang Shoulun, Chen Senhuang. 1995. Black Metallic Mineral Resources in the World[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:1-130 (in Chinese).
Shi Junfa, Tang Jinrong, Zhou Ping, Jin Qinghua. 2010. World Prospecting Models and Mineral Prospectin[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 491 (in Chinese).
Spier C A, Oliveira S M B, Sial A N. 2007. Geochemistry and genesis of the banded iron formations of the Caue Formation, QuadrilateroFerrifero, Minas Gerais, Brazil[J]. Precambrian Reserch, 152:170-260. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.10.003
Taylor D, Dalstra H J, Harding A E, Broadbend G C, Barler M E. 2001. Genesis of high grade hematite orebodies of the Hamersley province, Western Australia[J].Economic Geology, 96:837-873. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=577e6a07d4913a46250dda9deb4c8767&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Trendall A F.1983. Introduction[C]//Trendall A F, Morris R C(eds.). Iron-formation: Facts and Problems. Amsterdam: Elsevier Press.1-11.
Trendall A F. 2002. The significance of iron-formation in the Precambrian stratigraphic record[J]. Special Publication International Association of Sedimentologists, 33(1):33-66. doi: 10.1002/9781444304312.ch3/summary
Tyler I M, Thorne A M.1990. The northern margin of the Capricorn Orogen, Western Australia:An example of an Early Proterozoic collisional zone[J]. J. Struct. Geol. 12:685-701. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(90)90082-A
U. S. Geological Survey. 2017. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2017[M].
U. S. Geological Survey. 2015. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2015[M].
Van Hise C R, Leith C K. 1911. The Geology of the Lake Superior Region[M]. Monogr. US Geol. Surv., 52.641.
Wang Changle, Zhang Lianchang, Liu li, Dai Yanpei. 2012. Research progress of Precambrian iron formations abroad and some problems deserving further discussion[J]. Mineral Deposits, 31(6):1311-1325 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201206015
Wang Ende, Xia Jianming, Zhao Chunfu, Fu Jianfei, Hou Genqun. 2012. Forming mechanism of high-grade magnetite bodies in Gongchangling, Liaoning Province[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(11):1761-1772 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d17d7326c4c1ee096cac390e17be3a6f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Fengxiang, Nie Fengjun, Zhang Weibo, Cao Yi, Xie Xiaoying. 2013. Research progress on the world largest underground mining Iron deposit-Kiruna deposit in northern Sweden[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information. 32 (5):79-85 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201305023.htm
Wang Yongchun, Li Mengmeng, Tan Liang, Liang Shuai, Liu Xing. 2015. Metallogenic model and potentiai analysis of the Canadian Labrador Lake Superior-type iron formation[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 30(1):36-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZZK201501005.htm
Wang Yifei, Xu Huifang, Merino E, Konishi H. 2009. Generation of banded iron formations by internal dynamics and leaching of oceanic crust[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2(11):781-784. doi: 10.1038/ngeo652
Warren T, Steffen H. 2009. Oxygen isotope compositions of Iron Oxides from high-grade BIF-Hosted Iron ore deposits of the Central Hamersley Province, Western Australia:Constraints on the evolution of hydro-thermal fluids[J]. Economic Geology, 104:1019-1035. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.104.7.1019
Webb A, Clout J. 2008. Banded iron formation-related iron ore deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia[J]. Econ.Geol., 15(3):197-221. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b7d5e9cd4891438faabdc0bb49491761&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xu ZhiGang. 2014. A Review:"The research of Ning-Wu porphylite Iron Deposit" and some further research problems[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12):2394-2412 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_e972cb8721790ac56d29796ae5bae480
Yan Shuang, Jiang Yuhang, Zeng Lingjun. 2013. Discussion on metallogenic types and metallogenic mechanism of iron ore deposits in the Awulale metallogenic belt, West Tianshan[J]. Mineral Science(Supp.), 139-140 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao Chunyan, Dong Yongguan, Zeng Yong, Guo Weimin. 2014. Hydrothermal Genesis of High-grade Iron Deposits in North Ore Belt of Caracas Mines, Brazil[C]. China Earth Science Federation Annual Conference: 1137-1138 (in Chinese).
Yao Chunyan, Dong Yongguan, Zeng Yong, Guo Weimin. 2014. Study on metallogenic characteristics and prospecting area of the Imataka iron ore belt in Venezuela[J]. Mineral Deposits, 33(Supp.):1137-1138 (in Chinese).
Yao Chunyan, Dong Yongguan, Zhang Xiaoyong, Zeng Yong, Guo Weimin. 2012.Briefly Discussion on the Metallogenesis of the Carajas Precambrian BIF, Brazil[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 27:281-285 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXJZ2012S1095.htm
Yao Chunyan, Yao Zhongyong, Xu Ming, Gao Weihua, Li Hongjun. 2014. Metallogenic characteristics and ore-control factors of the high-grade BIF of the Hamersley iron province in western Australia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(2/3):215-227 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=472eb68313fe639b0347a00d5542d275&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zappettini E O, Kilibarda C R, Schobbenhaus C. 2005. Metallogenicmap of South America at the scale of 1: 5000000[M]. Buenos Aires: The Commission for the Geological Map of the World, 1-274.
Zeng Yong, Guo Weimin, Xiang Hongli, Yao Chunyan, Dong Yongguan. 2015. Massive Fe-Cu-Au polymetallic deposits metallogenesis in Carajás mineral province of Brazil[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(4):828-841 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zhaochong, Li Jianwei, John Encarnacion. 2014. Iron metallogeny in China-An introduction to the special issue[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 57:243-246. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.010
Zhang Zhaochong, Santosh M, Li Jianwei. 2015. Iron deposits in relation to magmatism in China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113:951-956. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.09.026
Zhang Zuoheng, Hong Wei, Jiang Zongsheng, Duan Shigang, Li Fengming, Shi Fupin. 2014. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of iron deposits in western Tianshan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 57:425-440. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.012
Zhang Zuoheng, Hong Wei, Jiang Zongsheng, Duan Shigang, Wang Zhihua, Li Fengming, Shi Fupin, Zhao Jun, Zheng Renqiao. 2012. Geological features, mineralization types and metallogenic setting of Late Paleozoic iron deposits in western Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 31(5):941-964(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201205002.htm
Zhao Hongjun, Lu Minjie, Zhou Shangguo, Ye Jinhua, Chen Xiufa, Zhang Chao, Guo Weimin, Huang Feixin, Yao Chunyan. 2017. A study on key metallogenetic zones and principal metallogenetic Regularities of Iron ore resources in south American Countries[J]. Geology in China, 44(4):690-716 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201704005.htm
代堰锫, 朱玉娣, 张连昌, 王长乐, 陈超, 修迪. 2016.国内外前寒武纪条带状铁建造研究现状[J].地质论评, 62(3):735-757. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201603016 地质科学大辞典编委会. 2005.地质科学大辞典(应用科学卷)[M].北京:地质出版社. 费雪锦, 邱电云. 1994.深海底矿物资源开发现状及前景[J].中国锰业, 12(6):6-10. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10276-2005070419.htm 郭维民, 董永观, 邢光福, 曾勇. 2013.巴西铁四角地区铁矿床研究进展[J].地质科技情报, 32 (5):79-85. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1017055370.htm 江思宏, 梁清玲, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 白大明, 刘妍, 陈春良. 2013.西澳皮尔巴拉地区鲸背山铁矿床地质特征与形成规律[J].地质科技情报, 32(5):95-105. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZKQ201305016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 廖航. 2015.南非Lomoteng铁锰矿矿床成因及矿石加工技术性能评价[J].矿产与地质, 29(4):509-513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.04.019 李厚民, 刘明军, 李立兴, 杨秀清, 陈靖, 姚良德, 洪学宽, 姚通. 2012.辽宁弓长岭铁矿区大理岩地质地球化学特征及其成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 28(11):3497-3512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201211005 李厚民, 刘明军, 李立兴, 杨秀清, 姚良德, 陈靖, 姚通. 2014.弓长岭铁矿二矿区蚀变岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 30(5):1205-1217. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201405002 李厚民, 王登红, 李立兴, 陈靖, 杨秀清, 刘明军.2012.中国铁矿成矿规律及重点矿集区资源潜力分析[J].中国地质, 39(3):559-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.03.001 李莎.2017.铁矿石专题报告二:海外矿VS国内矿.广发证券钢铁专题研究[R]. 李曙光. 1982.弓长岭富磁铁矿床成因的地球化学模型[J].地球化学, 34(2):113-121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1982.02.001 刘华山, 李秋林, 于浦生, 邬介人. 1998. "镜铁山式"铁铜矿床地质特征及其成因探讨[J].矿床地质, 1:25-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.1998.01.003 刘明军, 辽宁弓长岭沉积变质型铁矿热液改造作用及其成矿意义[D].中国地质大学(北京). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1013266077.htm 吕立娜, 吴岑.2013.西澳大利亚州铁矿分布规律及矿床成因分析[J].中国煤炭地质, 25(12):106-111. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgmtdz201312024 吕林素, 汪云峰, 李宏博, 周振华, 张作衡, 谢桂青. 2011.南非布什维尔德岩浆型Cu-Ni-PGE硫化物矿床成因探讨[J].矿床地质, 30(6):1129-1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.06.013 李延河, 张增杰, 侯可军, 段超, 万德芳, 胡古月. 2014.辽宁鞍本地区沉积变质型富铁矿的成因:Fe、Si、O、S同位素证据[J].地质学报, 88(12):2351-2372. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201412015 宁芜研究项目编写小组. 1978.宁芜玢岩铁矿[M].北京:地质出版社. 1-196 牛贺才, 罗勇, 李宁波, 姜玉航, 杨武斌, 单强, 于学元. 2012.新疆阿吾拉勒地区查岗诺尔铁矿床铜矿化的成因探讨[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 48(3):256-265. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201203003 邱瑞照, 谭永杰, 朱群, 李宝强, 林方成, 卢民杰. 2012.中国及邻区重要成矿带成矿规律对比研究[M].北京:地质出版社. 沈承珩, 王守伦, 陈森煌. 1995.世界黑色金属矿产资源[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-130. 施俊法, 唐金荣, 周平, 金庆花. 2010.世界找矿模型与矿产勘查[M].北京:地质出版社. 491. 王长乐, 张连昌, 刘利, 代堰锫. 2012.国外前寒武纪铁建造的研究进展与有待深入探讨的问题[J].矿床地质, 31(6):1311-1325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.06.015 王恩德, 夏建明, 赵纯福, 付建飞, 侯根群. 2012.弓长岭铁矿床磁铁富矿形成机制探讨[J].地质学报, 86(11):1761-1772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.005 王丰翔, 聂凤军, 张伟波, 曹毅, 谢小颖. 2013.世界最大井采铁矿床——基鲁纳铁矿床研究现状与新进展[J].地质科技情报, 32(5):146-152. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZKQ201305023&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 王永春, 李猛猛, 谭亮, 梁帅, 刘行. 2015.加拿大拉布拉多地区Superior湖型铁建造成矿模式及资源潜力分析[J].地质找矿论丛, 30(1):36-42. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzzklc201501005 徐志刚. 2014. "宁芜玢岩铁矿研究"回顾及某些问题的深化研究——贺陈毓川先生80华诞[J].地质学报, 88(12):2394-2412. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95080X/201412/663537816.html 严爽, 姜玉航, 曾令君.2013.西天山阿吾拉勒成矿带铁矿铁矿床成矿类型及成矿机制探讨[J].矿物学报(增刊), 139-140. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301100 姚春彦, 董永观, 张晓勇, 曾勇, 郭维民. 2012.浅谈巴西地区前寒武纪条带状含铁建造的成矿作用[J].地球科学进展, 27:281-285. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7956070 姚春彦, 董永观, 曾勇, 郭维民. 2014.巴西帕拉州卡拉加斯成矿带北矿带高品位铁矿床的热液成因[C]//中国地球科学联合会学术年会: 1137-1138. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201410068023.htm 姚春彦, 董永观, 曾勇, 郭维民. 2014.委内瑞拉伊玛塔卡铁矿带成矿特征及找矿选区研究[J].矿床地质, 33:1137-1138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8450732 姚春彦, 姚仲友, 徐鸣, 高卫华, 李红军. 2014.澳大利亚西部哈默斯利铁成矿省BIF富铁矿的成矿特征与控矿因素[J].地质通报, 33(2/3):215-227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201402010 冶金部情报标准研究所. 1976.国外前寒武纪铁硅建造风化淋滤型富铁矿[M].冶金工业出版社. 曾勇, 郭维民, 项红莉, 姚春彦, 董永观. 2015.巴西卡拉加斯地区大规模铁-铜-金多金属矿床的成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 34(4):828-841. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201504012 张作衡, 洪为, 蒋宗胜, 段士刚, 王志华, 李凤鸣, 石福品, 赵军, 郑仁乔. 2012.新疆西天山晚古生代铁矿床的地质特征、矿化类型及形成环境[J].矿床地质, 31(5):941-964. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.05.001 赵宏军, 卢民杰, 周尚国, 叶锦华, 陈秀法, 张潮, 郭维民, 黄费新, 姚春彦. 2017.南美洲铁矿重要成矿区带与成矿规律研究[J].中国地质, 44(4):690-716. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170404&flag=1 中国产业信息.2015. 2015-2020年中国铁矿石行业前景预测及投资战略研究报告[R].http://www.chyxx.com 中国海关统计数据. http://www.customs.gov.cn/ 中华人民共和国地质矿产行业标准DZ/T 0200-2002.铁、锰、铬矿地质勘查规范[S]. -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 程涌,周家喜,孙国涛,黄智龙. 贵州半边街锗锌矿床锗的富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2024(01): 43-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何叶,周高明,钟华,程涌,岳正鹏,刘和松,周家喜. 云南毛坪铅锌矿床新发现Ⅵ号矿带硫化物稀散元素富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2023(10): 2985-3001 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄亮,周家喜,孙载波,熊波,龙天祥,王晓林,吴嘉林. 滇西漕涧地区发现流纹岩型铌矿化. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2022(01): 185-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨昌华,周家喜,罗开,姜永果,李晓红,杨丰铭,陶永林. 云南省兰坪-思茅盆地发现钴超常富集矿化点. 大地构造与成矿学. 2022(06): 1167-1169 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨德智,周家喜,孔志岗,吴越,黄智龙,金中国. 闪锌矿矿物结构对Ge超常富集的制约:以贵州竹林沟Ge-Zn矿床为例. 大地构造与成矿学. 2022(06): 1120-1136 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 罗开,周家喜,徐畅,贺康建,王永彬,孙国涛. 四川乌斯河大型锗铅锌矿床锗超常富集特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报. 2021(09): 2761-2777 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周家喜,杨德智,余杰,周祖虎,罗开,徐阳东. 贵州黄丝背斜地区实现大型共(伴)生锗矿床找矿突破. 矿物学报. 2020(06): 772 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: