Chronology and geochemical characteristics of granite in Weilianhe of Inner Mongolia and its geological significance
-
摘要:
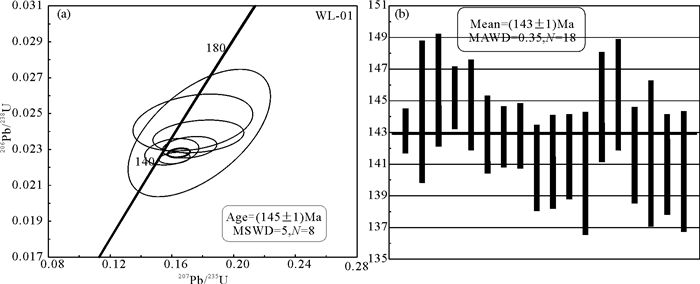
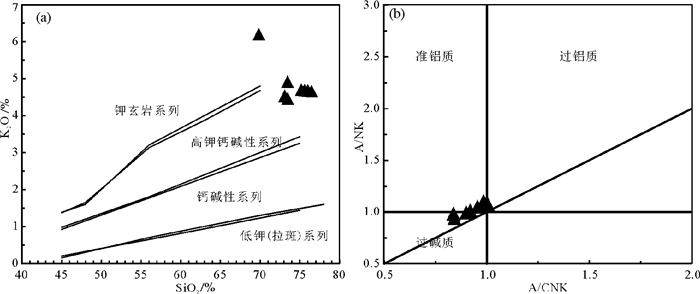
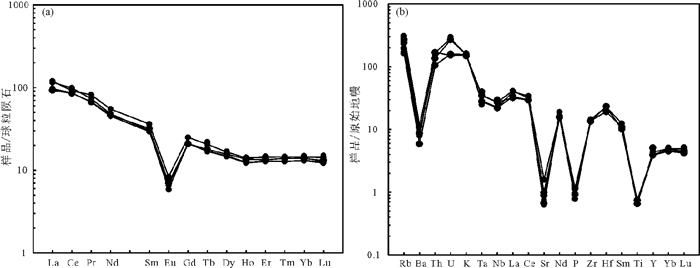
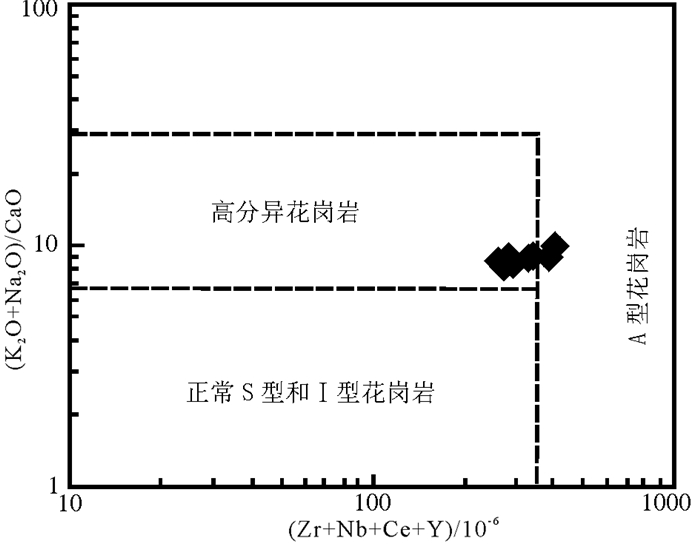
内蒙古苇莲河地区是近年来进行黑钨矿找矿勘查的区域,位于兴蒙造山带中东部,大兴安岭主脊中部。矿床类型可能为典型的石英脉型黑钨矿。黑钨矿石英脉以近于直立(75°)的平直脉体产于花岗岩内或岩体与地层的外接触带,脉体向下尖灭于岩体内部,主要的矿化蚀变类型有钾长石化、绿帘石化、绢云母化、硅化等。本文在初步研究矿床地质特征的基础上,对成矿岩体——花岗岩进行高精度LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及地球化学分析。UPb测年结果显示,206Pb/238U谐和年龄为(145±1)Ma,加权平均年龄为(143±1)Ma。地球化学特征显示,岩体具有典型的富硅、富碱特征,SiO2平均74.13%,(Na2O+K2O)平均9.44%,Na2O/K2O平均0.95,属高钾钙碱性系列岩石;Al2O3平均为12.91%,铝饱和指数A/CNK全部靠近1.0,为准铝质到弱过铝质花岗岩类,相对贫Mg;稀土总量较低,∑REE变化于122.02×10-6~235.79×10-6,表现为右倾稀土元素配分模式,弱富集轻稀土,并具有强烈的负铕异常,高场强元素Th、U、Nd、Hf明显富集,而Ba、Sr、P、Ti、Nb显著亏损;低Sr,高Yb,Nb/Ta比值变化于12.12~13.78,强不相容元素Rb高度富集,Rb/Sr比值1.25~14.58,Ti/Y比值42.49~114.48,Ti/Zr比值5.20~8.45;总体为壳源岩浆的特征。苇莲河花岗岩侵位时代为早白垩世,属燕山期构造岩浆活动的产物,其可能的形成构造背景为古太平洋板块斜向俯冲后,后退过程中的伸展滑塌背景。
Abstract:The Weilianhe W deposit in eastern Ujumchin of Inner Mongolia is a quartz-vein type deposit in the mid-eastern part of the Central Asian Orogen. Based on spatial relationships, the authors revealed that granite is closely associated with mineralization. The authors conducted precise laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (LA-ICP-MS) U-Pb zircon dating and geochemical analysis of the granite. The U-Pb dating shows that the granite is (145 ±1)Ma, and the weighted average age is (143±1)Ma. Major and trace element geochemistry shows that the granite is characterized by high SiO2 and K2O content, a "rightinclined" shape of the chondrite normalized REE patterns, enrichment of large ion lithophile elements (LILEs), and depletion of high field strength elements (HFSEs) such as Nb, P, Ba. The granite is high-K calc-alkaline, has a strong negative Eu anomaly (Eu/Eu*=0.22-0.42), low P2O5 content, A/CNK near the value of 1, enriched in large-ion lithophile elements (LILEs such as Th, U, Nd, and Hf), and notably depleted in Ba, Sr, P, Ti, and Nb. These characteristics define the Weilianhe granite as a highly fractionated peraluminous granite. According to the granite age and the characteristics of granite, the authors hold that the Weilianhe deposit is related to a major Early Cretaceous mineralizing event in China known as the Yanshanian movement. The tectonic setting for the ore deposit was the post-tectonic stretching setting after the oblique subduction of the Pacific plate.
-
Keywords:
- Inner Mongolia /
- wolframite /
- geochronology /
- quartz vein /
- granite /
- LA-ICP-MS /
- geochemistry /
- Weilianhe
-
1. 引言
锶作为岩石圈上部含量最大的微量元素(胡进武等,2004;黄奇波等,2011),广泛存在于自然界中但分布非常不均,锶的分布状态及其存在形态受到自然条件、人类活动等多种因素的影响,导致锶在分布上富集或贫乏(Comar et al., 1957; 范伟等2010)。在不同的时期、不同岩性的基岩地层中锶元素的丰度存在明显的差异性,一般在海相沉积的碳酸盐岩中锶的丰度最高,在含锶矿物的闪长岩、花岗岩、黏土岩以及碳酸盐岩中,锶含量相对比较富集,黏土、砂中锶的丰度最低(刘庆宣等,2004)。作为微量元素,锶主要存在于各种造岩矿物和副矿物中,也能形成一些独立的矿物,主要为存在于碳酸盐岩中的菱锶矿(SrCO3)和天青石(SrSO4),同时文石、方解石、钙长石及石膏等矿物中亦常见锶置换钙的类质同像现象(Clow et al., 1997;文冬光等,1998)。岩石中的锶是地下水中锶的主要物质来源,锶在赋存母岩中主要经风化、淋滤后在地下水流作用下进行迁移转化(文冬光等,1998;康志强等,2011;苏春田等, 2017a, b),进而进入人类及其他动植物的物质循环。前人研究表明,地下水中锶的分布与富集受渗流地层岩性、溶滤强度、水化学条件(王增银等,2003;祁晓凡等,2009;范伟等, 2010)等因素的影响。目前,各国根据锶的含量及其生理医学作用制定了锶矿泉水的标准,参照饮用天然矿泉水国家标准(GB8537- 2016),地下水的质量浓度达到0.2mg/L,可命名为富锶矿泉水,规定的限值为5mg/L。岩溶水作为山区居民主要饮用的水源,关乎百姓的生活与饮食健康,因而查明地下水中锶的分布状态,揭示锶的动态变化,分析锶的富集规律,具有较大的研究意义与实际价值。
前人对富锶地下水的研究多集中在赋存条件、水质评价等方面,多集中在非岩溶地区(孙岐发等,2019),针对西南岩溶区富锶地下水的研究还较少(祁晓凡等,2009;康志强等,2011;苏春田等, 2017a, b),针对三峡岩溶区的研究则更少。本文选取湖北秭归地区两个岩溶流域为研究区,以岩溶水系统为单元,从锶的物质来源条件入手,分析岩溶水系统中锶的水岩作用过程,研究不同含水岩组、不同水流条件下地下水中锶的分布与富集特征,探讨宜昌三峡岩溶去地下水中锶富集的条件与规律。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 自然地理概况
本文主要针对秭归地区的茅坪河和九畹溪两个岩溶流域开展研究。研究区地处长江之滨、西陵峡畔、清江以北,属于中国地形第二、三阶梯的过渡地带,为川东褶皱与鄂西山地交汇地,境内山脉为大巴山、巫山余脉,地形起伏较大。该地区属于亚热带季风气候,气候温暖、降雨充沛,年降雨量在900~1200 mm,其中汛期降雨量占绝大部分,受季风气候和山峦起伏的影响,降雨量的季节变化和空间差异明显,小气候特征比较显著。秭归县位于鄂西褶皱山地,西南高东北低,平均海拔高程千米以上,山峰耸立,河谷深切,相对高差一般在500~1300 m。其中中低山区多分布于秭归盆地周边,斜坡倾角介于15~25°,面积960 km2;大于25°以上的斜坡主要分布在长江峡谷区、中高山向中低山过渡地带,陡缓变化较大,多形成陡崖。
2.2 地质概况
研究区地处黄陵穹隆西南缘,自北东向西南从侵入岩体、前震旦纪到三叠纪地层连续出露且较齐全,区内南沱组角度不整合于侵入岩与变质岩基底之上,第四系与下伏地层为角度不整合,其余地层之间均为整合与平行不整合接触关系(南沱组与陡山沱组呈平行不整合,纱帽组与云台观组呈平行不整合)。区域内地层主要是以沉积岩为主,累计沉积岩岩层最大厚度约7567 m,其中碳酸盐岩总厚度达到3443 m,占沉积岩总厚度的45.5%,碳酸盐岩地层主要有震旦系,寒武系、奥陶系、志留系、二叠系及三叠系,岩性以灰岩、白云岩为主,非碳酸盐岩地层有志留系、泥盆系、白垩系,岩性以碎屑岩为主,尤以仙女山一带的白垩系的碎屑砾岩、砂岩为特殊,常常发育有可溶性砾岩裂隙孔洞水。
2.3 岩溶含水系统划分
前人在进行岩溶含水系统划分过程中,主要考虑了含水岩组、空间介质结构、组合特征、岩溶水径流方式、埋藏条件等因素(裴建国等,2008; 梁永平等,2015)。秭归地区属于南方岩溶的范畴,多种地层组合特征、构造条件下发育多样的岩溶水系统,既发育有管道裂隙集中排泄型系统、也有裂隙分散排泄型岩溶水系统。根据区域地层的含水性分析,大致可划分为3个岩溶含水系统(图 1):上震旦岩溶含水系统(Z2d、Z2∈1d)、下寒武—奥陶岩溶含水系统(∈1t、∈1sl、∈2q、∈2O1l、O1n、O1g、O2-3b)、石炭—三叠岩溶含水系统(P1q、P1m、P2w、T1d、T2j),进一步可细分为7个岩溶含水子系统(表 1)。本文依据空间结构、含水介质、排泄方式、代表水流、标高、流量等特征数据,并结合野外调查资料,对岩溶子含水单元排泄特征进行整理划分(表 1)。
表 1 岩溶含水子系统的介质结构及排泄特征Table 1. Structure and drainage characteristics of karst water-bearing units
3. 样品采集与测试
3.1 样品采集与处理
2016—2018年期间,本文依托中国地质调查局二级项目“宜昌长江南岸岩溶流域水文地质环境地质调查”,系统地采集了研究区泉水、典型断面地表水样品,对重点岩溶泉点进行月度监测,并选送测区内主要含水岩组的岩样进行岩石矿物组成分析。针对不同岩溶水系统,选取了31组岩溶泉点作为长期监测点(长观站)(图 1),用于分析地下水的动态变化规律。本文的研究数据来源于区域水文地质调查,及31个岩溶泉长期监测点(长观站)月度样采集,共整理了415组水样数据,93组岩矿分析数据,基于此对锶的分布特征进行分析。
水样采集采用600 mLPVC瓶,现场用水样涮洗3次,同时对水样水温、pH、电导率、流量等指标进行现场测定。此后样品在12 h内送回室内,采用《中华人民共和国地质矿产行业标准DZ/T 0064.49- 93地下水水质检验方法》酸碱滴定法测试并计算碱度。同时将水样用孔径0.45 μm的醋酸纤维膜过滤后,分装于2个50 mLPET瓶中分别用于阴阳离子测试,其中阳离子测试样会使用分析纯HNO3酸化至pH<2,阴离子样则不加处理。
3.2 样品测试
水化学样品的测试在中国地质大学(武汉)地质调查研究院实验中心完成,阴离子由戴安离子色谱仪ICS2100测试,阳离子由赛默飞公司生产的ICP-OES(ICAP6300)测试;岩石样品矿物组成测试在澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司测试完成,锶等矿物组分均采用封闭酸溶-电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测试。
4. 分析与讨论
4.1 锶的物源条件分析
通过对93组岩矿分析数据分析可知,不同地质年代的沉积地层中锶的含量大不相同(表 2),在震旦系地层中,灯影组地层锶含量比陡山沱组高,灯影组锶含量可达到2900 μg/g,均值为1121 μg/g,且组内不同段含量差异明显,如灯影组二段的白云质灰岩中锶含量介于800~2600 μg/g,其含量较一段和三段的白云岩大,灯影组地层整体变异系数为88.2%(n=10);寒武系上统娄山关组白云岩中锶含量介于77~2500 μg/g,变异系数为62.5%(n=11),锶含量均值大但分布上存在差异性;奥陶系地层锶含量均不高,介于100~400 μg/g,变异系数相对较低;嘉陵江组地层锶的含量较高,均值为2861 μg/g,变异系数也较高,为137.3%(n=17)。
表 2 秭归岩溶地层中锶含量概况统计Table 2. Statistics of Sr contents in karst strata in the Zigui area
可知,秭归地区富锶地层主要为灯影组、娄山关组、嘉陵江组。从沉积相来看,上述沉积地层均为干旱气候条件下碳酸盐台地浅滩、潮坪-潟湖沉积(徐长昊,2016),为封闭性较好的沉积环境,是蒸发沉积富锶地层发育的良好条件。
同时对区内浅层包气带内岩样分析发现,表层岩石中天青石矿物较少,锶含量偏低且与CaO的相关性较好,而与MgO、SO3、Al2O3的相关性一般。主要是由于表层岩石受到较强的淋滤作用而导致锶的流失,此外浅循环系统中的锶会以类质同像形式存在于方解石矿物中。
对由钻孔揭露深层封闭地层岩样分析发现,锶主要以天青石形式存在,常常与石膏矿物共存。如钻孔ZK05揭露的娄山关组地层中,锶含量普遍较高且与SO3有较好的相关性(R2=0.737,n=10)。另在对钻孔ZK03揭露的奥陶系岩心分析发现,随着MgO含量的增大,岩性逐渐白云岩化,同时锶含量逐渐减小(图 2);此外,锶的含量会随着碳酸盐中泥质含量的增大(SiO2含量增大)而减小(图 2)。
4.2 锶的水岩作用过程分析
通过对茅坪河与九畹溪两个流域岩溶地下水样分析,从富锶水化学类型、水岩作用程度、物理化学条件等方面,对该区地下水锶分布与富集展开讨论。
针对研究区所采集的415组水样,从Piper三线图(图 3)来看,地下水中锶含量大于2 mg/L时,水中阳离子以Ca2+、Mg2+为优势离子,阴离子以SO42-为主;地下水中锶含量在0.70~10 mg/L时,水中阳离子以Na+为主,阴离子以Cl-为主;地下水中锶含量小于0.70 mg/L时,水中阴离子以HCO3-为主。因此,锶浓度相对较高的地下水化学类型主要包括SO4型和Cl型,其中尤以SO4型地下水的锶浓度最高。
岩溶地下水中离子组分主要来源于对母岩的溶滤作用,其决定着地下水中主要水化学过程(康志强等,2011; 苏春田等,2017a)。母岩中锶含量影响着水流系统地下水中锶的分布(文冬光等,1998;苏春田等,2017b)。地下水中锶离子主要来源于富锶矿物(天青石、菱锶矿),赋存在方解石、文石及白云石类质同像形态的锶,以及铝硅酸盐中的锶等的溶解(徐兴国,1984),具体的化学反应方程式如下:

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 表层岩溶泉可反映局部水流系统的水化学特征。基于所采集的334处表层岩溶泉,绘制出研究区锶在表层岩溶水中的分布规律,发现全区存在5处富锶地下水分布区(图 4),且这些富锶地下水分布与富锶地层的分布表现出一致性,二叠系阳新组岩溶水,三叠系嘉陵江组岩溶水,寒武系娄山关组岩溶水,寒武系水井沱组岩溶水及震旦系灯影组岩溶水。其中杨新组表层岩溶水中Sr含量介于0.26~ 0.76 mg/L;嘉陵江组介于0.23~0.60 mg/L;娄山关组介于0.13~0.43 mg/L;水井沱组与灯影组介于0.22~0.72 mg/L。
对于排泄区,选取研究区内4处锶含量较高的地层中出露的地下水点为例,即白龙潭、龙洞、迷宫泉和龙王洞(表 1)。从锶离子与硫酸根离子、重碳酸根离子的浓度关系(图 5)发现,嘉陵江组白龙潭岩溶泉水锶含量较高,与硫酸根离子有较好的一致性(R2=0.707,n=5),另知嘉陵江组岩矿分析中SO3含量较高,反映出在该泉域的径流途径上有天青石的存在;娄山关组迷宫泉与重碳酸根离子和硫酸根离子均呈现较好的相关性(R2=0.668,n=10;R2= 0.768,n=13),反映出径流途径中存在两种富锶矿物溶解。此外,针对地下水中丰、枯两季表现出差异性(图 5),主要是由于研究区具有典型南方岩溶管道-裂隙水系统,地下水径流路径和径流时间短、水岩作用不充分(罗明明等,2015),表现出枯季地下水中锶含量普遍比丰水期的要高。由上可知,岩溶水中锶离子含量与各岩溶水系统中富锶矿物含量密切相关,流经的地层岩性差异导致各岩溶水流系统表现出不同的水岩作用过程,或受石膏、天青石矿物溶解的影响,或受菱锶矿溶解的影响,或受多种锶源的混合补给。
4.3 地下水流系统中锶的分布规律
对于锶在多级水系系统中的分布规律,本文以泗溪流域庙坪—鱼泉洞多级水流系统为例(图 1b),不同级次的地下水中锶含量及饱和程度易表现出差异性(表 3,图 6)。庙坪洼地表层岩溶泉为局部水流系统,锶含量均值为0.08 mg/L,si_Str与si_Cel均比较低(表 3),多为方解石中类质同像锶的溶解释放;鱼泉洞泉水为中间水流系统,地下水锶含量均值为0.22 mg/L,si_Stron与SI_Cel相比于局部水流系统稍高但未达到饱和(表 3),但冬季其锶的饱和指数相对夏季要高,主要由于冬季水流滞缓,水岩作用相对充分(表 3);以钻孔ZK04揭露的区域水流系统,其锶均值在2.33 mg/L,si_Str、si_Cel、si_Cal、si_Dol均趋于饱和(图 6)。可知地下水与母岩水岩相互作用的时间与水流路径长短决定了地下水中富锶矿物的饱和程度及地下水中锶含量(张群利等,2011;苏春田等,2017a)。
表 3 不同级次水流水化学信息统计表Table 3. Hydrochemistry of different water flow levels
此外,通过对钻孔ZK04及钻孔ZK05中锶含量分析(表 3,图 6),发现两者锶离子浓度均很大。在两孔钻进施工中,均有H2S与CH4等还原性气体溢出,且岩心中有机炭的含量相对较高,尤其是ZK05岩矿组分中发现有单质S存在。推知两孔均混有碳酸盐岩和硫酸盐岩(富含大量的石膏),且均为相对封闭的还原环境。
在这种封闭缺氧还原环境中,地下水中的SO42-在有机炭和脱硫细菌作用下,容易发生脱硫酸作用(刘硕等,2016),其化学反应式为:

(4) 
(5) 当地层中含有大量铁的时候S2-便会与铁结合,逐渐生成黄铁矿,而硫化氢气体极易溶于水(溶解比例约为1∶3),在氧气充足的时候,H2S会被氧化成硫酸与碳酸盐结合形成石膏矿物沉淀,但当氧气不足的时候,少部分的H2S会被氧化成单质S,更大一部分仍以气体的形式存在于封闭的还原条件中,这也就是ZK05孔岩心组分中单质S存在的原因。硫酸根离子的转化,促进了石膏、天青石的溶解过程,致使地下水中锶离子富集,甚至使天青石溶解达到饱和,同时菱锶矿的溶解也增大了地下水中锶的含量(罗璐等,2015)。
5. 结论
本文通过对秭归岩溶流域锶的分布与迁移进行分析,得到以下结论:
(1)研究区内嘉陵江组、娄山关组、灯影组地层中的锶含量最高,代表着潮坪-潟湖沉积相;区内浅层岩石中天青石矿物较少,锶含量偏低;深层封闭地层岩样中锶主要以天青石形式存在,常常与石膏矿物共存。
(2)富锶岩溶水的水化学类型主要包括SO4型和Cl型,尤以SO4型地下水的锶浓度最高;母岩中锶的含量决定了地下水中锶的浓度,且锶主要通过溶滤作用进入地下水中。
(3)地下水水流系统中水岩作用程度及地下水的滞留时间均影响地下水中锶的浓度,浅循环岩溶地下水流系统中锶均未达到饱和,少数深循环区域地下水流系统中锶浓度趋近饱和状态。对于富含石膏、天青石的封闭还原环境有利于地下水中锶的富集。
致谢: 本论文的野外工作受到内蒙古自治区第六地质矿产勘查开发院全体员工的大力支持;在样品的测试分析中得到中国冶金地质总局第一地质勘查院测试中心、中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国家重点实验室等相关单位和个人的大力支持与帮助,在此一并表示诚挚的感谢。 -
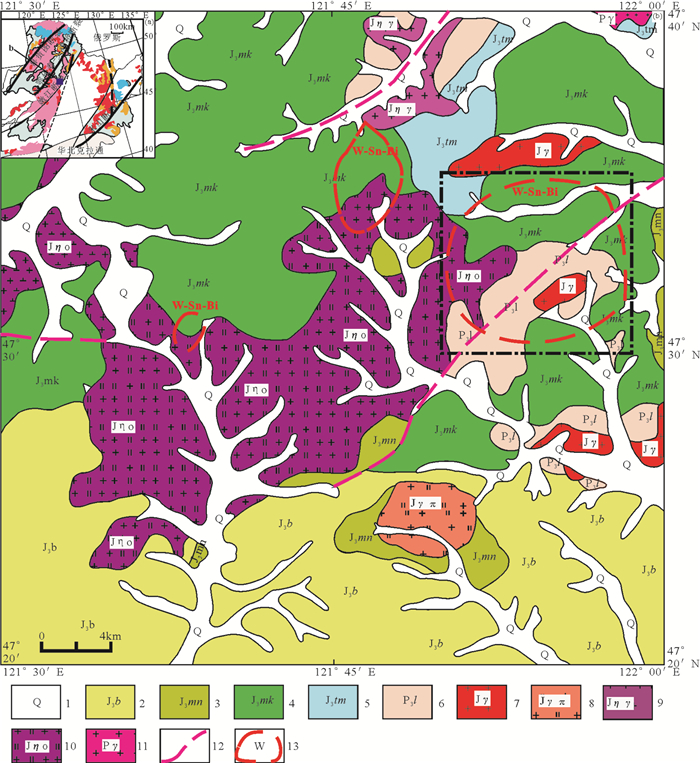
图 1 苇莲河矿区区域地质图(据1:20万区域地质图修改)
1—第四系;2—侏罗系白音高老组;3—侏罗系玛尼吐组;4—侏罗系满克头鄂博组;5—侏罗系塔木兰沟组;6—二叠系林西组;7—侏罗纪花岗岩;8—侏罗纪花岗斑岩;9—侏罗纪二长花岗岩;10—侏罗纪石英二长岩;11—二叠纪花岗岩;12—断层;13—区域化探异常
Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Weilianhe W ore district (modified after 1:200000 regional geological map)
1-Quaternary; 2-Jurassic Baiyingaolao Formation; 3-Jurassic Ma'nitu Formation; 4-Jurassic Manketou'ebo Formation; 5-Jurassic Tamulangou Formation; 6-Permian Linxi Formation; 7-Jurassic granite; 8-Jurassic granite porphyry; 9-Jurassic Monzonite granite; 10-Jurassic quartz monzonite; 11-Permian granite; 12-Fault; 13-Geochemical anomaly
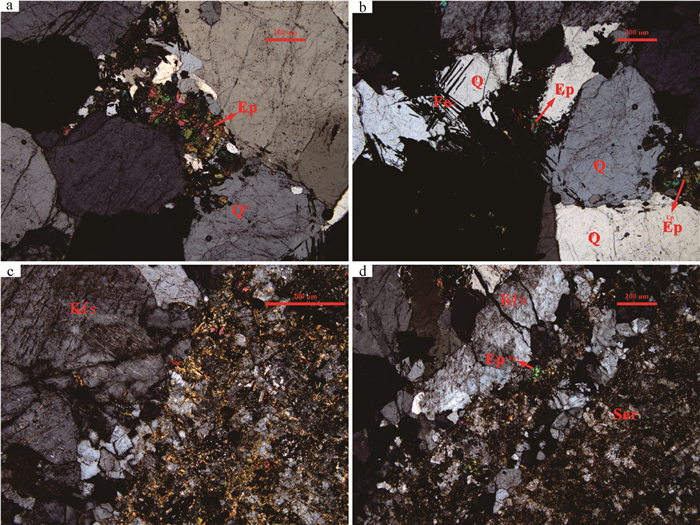
图 3 苇莲河矿区围岩蚀变特征
a—绿帘石化花岗岩;b—磁铁矿化、绿帘石化花岗岩;c—云母化;d—绿帘石化、绢云母化花岗岩;Ep—绿帘石,Ser—绢云母,Q—石英,Kfs—钾长石
Figure 3. Alteration characteristics of wall rock in the Weilianhe W ore district
a-Epidotization of granite; b-Magnetite and Epidotization of granite; c-Sericitization; d-Epidotization and Sericitization of granite; Ep-epidote; Ser-Sericite; Q-quartz; Kfs-potash feldspar
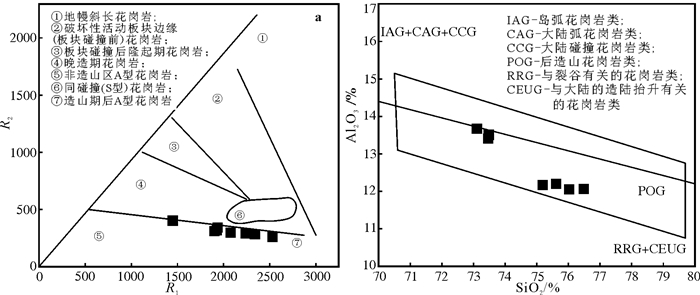
图 10 苇莲河花岗岩主量元素构造判别图
a—R1-R2构造判别图(据Civetta et al., 1998; R1=4Si-11(Na+K)-2(Fe+Ti); R2=6Ca+2Mg+Al);b—SiO2-Al2O3构造判别图;
Figure 10. The major elements tectonic discrimination diagrams for the granite from Weilianhe ore district
a-R1 versus R2 diagram; b-SiO2 versus Al2O3 diagram
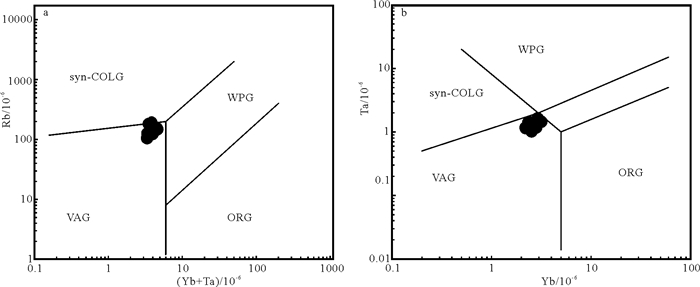
图 11 苇莲河花岗岩微量元素构造判别图解
VAG—弧火山花岗岩;COCG—同碰撞花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩(Pearce et al, 1984)
Figure 11. Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the granite from from the Weilianhe ore district
VAG-Volcanic arc granite; syn-COCG-syn-Collisional granite; WPG-Within plate granite; ORG-Oceanic ridge granite(after Pearce et al, 1984)
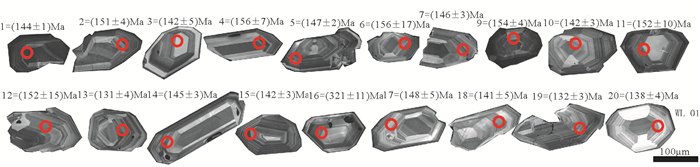
表 1 苇莲河钨矿区花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素分析数据
Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb isotopic data for the granite from the Weilianhe W ore district

表 2 苇莲河钨矿区花岗岩主微量(%)及微量(10-6)元素分析结果
Table 2 Major elements (%), trace elements (10-6) composition of the granite in the Weilianhe W ore district

-
Chen Yuchuan, Wang Denghong. 2012. Four Main Topics Concerning the Metallogeny Related to Mesozoic Magmatism in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 36(3):315-321 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201203004.htm
Chen Yuchuan, Wang Denghong, Xu Zhigang, Huang Fang. 2014. Outline of Regional Metallogeny of Ore Deposits Associated with the Mesozoic Magmatism in South China[J]. Geotectonicaet Metallogenia, 38(2):219-229 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DGYK201402002.htm
Chen Zh G, Zhang L Ch, Wan B, Wu H Y, Cleven N. 2011. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Wunugetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in NE china, and their geological significance[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 43:92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.08.007
Claesson S, Vetrin V, Bayanova T, Downes H. 2000. U-Pb zircon age from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola peninsula, Russia:A record of geological evolution from the Archaean to the Palaeozoic[J]. Lithos, 51 (1/2):95-108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&md5=6cdb70f9b4446472f6199bd71ad85567&_udi=B6V6J-3YSY1JK-6&_user=6894003&_coverDate=03%2F01%2F2000&_rdoc=6&_fmt=high&_orig=browse&_origin=browse&_zone=rslt_list_item&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%235816%232000%23
Ge Wenchun, Sui Zhenmin, Wu Fuyuan, Zhang Jiheng, Xu Xuechun, Cheng Ruiyu. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic characteristics and their implications of the Early Paleozoic granites in the northeastern Da Hinggan Mountains., northeastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):423-440 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702022.htm
Guo C L, Chen Y Ch, Zeng Z L, Lou F Sh. 2012. Petrogenesis of the Xihuashan granites in southeastern China:Constraints from geochemistry and in-situ analyses of zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopes[J]. Lithos, 148:209-227. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.014
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Tian Yourong. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(4):481-492 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200904010
Hofmann A W. 1988. Chemical differentiation of the earth:The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters, 90(3):297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X
Jiang S H, Bagas L, Hu P, Han N, Chen C L, Liu Y, Kang H. 2016. Muscovite Ar-Ar, molybdenite Re-Os and zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the highly fractionated granite-related Shamai tungsten deposit in East Inner Mongolia, China:implications for the timing of mineralization and ore genesis[J]. Lithos, 261:322-339. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.12.021
Liu J, Mao J W, Wu G, Wang F, Luo D F, Hu Y Q. 2014. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating of the Chalukou porphyry Mo deposit in the northern Great Xing'an Range, China and its geological significance[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 79:696-709. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.06.020
Liu Jun, Mao Jingwen, Wu Guang, Luo Dafeng, Wang Feng, Zhou Zhenhua, Hu Yanqing. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating for the magmatic rock in the Chalukou porphyry Mo deposit in the northern Great Xing'An Range, China, and its Geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(2):208-226 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.jstor.org/stable/463687
Li Jingyi, Qu Junfeng, Zhang Jin, Liu Jianfeng, Xu Wenliang, Zhang Shuangquan, Guo Ruiqing, Zhu Zhixin, Li Yaping, Li Yongfei, Wang Tao, Xu Xueyi, Li Zhipei, Liu Yongqing, Sun Lixin, Jian Ping, Zhang Yu, Wang Jiali, Peng Shuhua, Feng Qianwen, Wang Yu, Wang Hongbo, Zhao Xixi. 2013. New Developments on the Reconstruction of Phanerozoic Geological History and Research of Metallogenic Geological Settings of the Northern China Orogenic Region[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(2/3):207-219 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZQYD2013Z1000.htm
Mao Jingwen, Xie Guiqing, Cheng Yanbo, Chen Yuchuang. 2009. Mineral Deposit Models of Mesozoic Ore Deposits in South China[J]. Geological Review, 55(03):347-354 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000004258
Mao J W, Zhang Z C, Zhang Z H, Du A D. 1999. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenites in the Xiaoliugou W(Mo) deposit in the Northern Qilian Mountains and its geological significance[J].Geochimca et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(11/12):1815-1818. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703799001659
Mao J W, Wang Y T, Zhang Z H, Yu J J, Niu B G. 2003a. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in North China and adjacent areas[J]. Science in China 46(8):839-851 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yu_Jinjie/publication/225908317_Geodynamic_settings_of_Mesozoic_large-scale_mineralization_in_North_China_and_adjacent_areas/links/00b4952ca22f5e901c000000.pdf?origin=publication_list
Mao J W, Franco P, Nigel C. 2011. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings-An introduction to the special issue[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 43:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.003
Martin H, Smithies R H, Rapp R, Moyen J F, Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid:Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 79(1/2):1-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449370400266X
Nie Fengjun, Hu Peng, Jiang Sihong, Liu Yifei. 2010. Geological Features, Geochronology and Origin of the tungsten and tungsten(-molybdenum) deposits in the Shamai-Yuguzer Mineralization Concentrated Camp along the Sino-Mongolian Border[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 31(3):383-394 (in Chinese with English abstract).000 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201003015.htm
Ouyang H G, Mao J W, Santosh M, Zhou J, Zhou Zh H, Wu Y, Hou L. 2013. Geodynamic setting of Mesozoic magmatism in NE China and surrounding regions:Perspectives from spatio-temporal distribution patterns of ore deposits[J]. Asian Earth Sciences, 78:222-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.011
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Rayner N, Stern R A, Carr S D. 2005. Grain-scale variations in trace element composition of fluid-altered zircon, Acasta Gneiss Complex, northwestern Canada[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol, 148(6):721-734. doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0633-8
Rubatto D. 2002. Zircon trace element geochemistry:partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism[J]. Chem. Geol., 184:123-138. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00355-2
Sláma J, Kosler J, Condon D J, Crowley J L, Gerdes A, Hanchar J M, Horstwood M S A, Morris G A, Nasdala L, Norberg N, Schaltegger U, Schoene B, Tubrett M N, Whitehouse M J. 2008. Plesovice zircon-A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 249:1-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
Song X Y, Zhou M F, Gao Z M, Robinson P T. 2004. Late Permian rifting of the South China Craton caused by the Emeishan mantle plume?[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 161, 773-781. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-135
She Hongquan, Li Jinwen, Xiang Anping, Guan Jidong, Zhang Dequan, Yang Yuncheng, Tan Gang, Zhang Bin. 2012. U-Pb ages of the zircons from primary rocks in middle-northern Daxinganling and its implications to geotectonic evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2):571-594(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202018
Wang Denghong, Tang Juxing, Ying Lijuan, Chen Zhenhui, Xu Jianxiang, Zhang Jiajing, Li Shuiru, Zen Zailin. 2010. Application of "Five levels + Basement" model for prospecting deposits into depth[J]. Journal of Jilin University, (Earth Science Edition), 40(4):733-738 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201004003.htm
Wang T, Guo L, Zhang L, Yang Q, Zhang J, Tong Y, Ye K. 2015a. Timing and evolution of Jurassic-Cretaceous granitoid magmatisms in the Mongol-Okhotsk belt and adjacent areas, NE Asia:implications for transition from contractional crustal thickening to extensional thinning and geodynamic settings[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 97:365-392. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.005
Wang F, Xu W L, Xu Y G, Gao F H, Ge W C. 2015b. Late Triassic bimodal igneous rocks in eastern Heilongjiang Province, NE China:implications for the initiation of subduction of the PaleoPacific Plate beneath Eurasia[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 97:406-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.025
Wang Z Z, Han B F, Feng L X, Liu B. 2015c. Geochronology, geochemistry and origins of the Paleozoic-Triassic plutons in the Langshan area, western Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 97:337-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.005
Wang Z W, Pei F P, Xu W L, Cao H H, Wang Z J. 2015d. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Devonian and early Carboniferous igneous rocks of central Jilin Province, NE China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 97:260-278. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.06.028
Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis A Global Tectonic Approach[J]. London, Unwin Hyman, 466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.1989.tb00357.x/pdf
Xiang A P, Chen Y C, Bagas L, She H Q, Kang Y J, Yang W S, Li C J. 2016. Molybdenite Re-Os and U-Pb zircon dating and genesis of the Dayana W-Mo deposit in eastern Ujumchin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews 78:268-280. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.03.012
Xu B, Charvet J, Chen Y, Zhao P, Shi G Z. 2013. Middle Paleozoic convergent orogenic belts in western Inner Mongolia (China):Framework, kinematics, geochronology and implications for tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Res., 23:1342-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.05.015
Xu B. 2015a. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt in northern China:Preface[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 97, 179-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.019
Xu B, Song S, Nie F. 2015b. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt in northern China:Preface[J]. Asian Earth Sci., 97:179-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.019
Xu B, Zhao P, Wang Y Y, Liao W, Luo Z W, Bao Z W, Zhou Y H. 2015c. The pre-Devonian tectonic framework of Xing'anMongolia orogenic belt (XMOB) in north China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97:183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.020
Xu Jianxiang, Zen Zailin, Wang Denghong, Chen Zhenhui, Liu Shanbao, Wang Chenghui, Ying Lijuan. 2008. A new type of tungsten deposit in southern Jiangxi and the new model of "Five Floors + Basement" for prospecting[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(7):880-887(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiang Anping, Yang Yuncheng, Li Guitao, She Hongquan, Guan Jidong, Li Jinwen, Guo Zhijun. 2012. Diagenetic and metallogenic ages of Duobaoshan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 31(6):1237-1248 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201206010.htm
Xiang Anping, Wang Yajun, Qin Dajun, She Hongquan, Han Zenggaung, Guan Jidong, Kang Yongjian. 2014. Study on the metallogenic and diagenetic age of Hong-Hua-Er-Ji tungsten polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 02:428-439 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KCDZ201402015.htm
陈毓川, 王登红. 2012.华南地区中生代岩浆成矿作用的四大问题[J].大地构造与成矿, 36(3):315-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.002 陈毓川, 王登红, 徐志刚, 黄凡. 2014.华南区域成矿和中生代岩浆成矿规律概要[J].大地构造与成矿, 38(2):219-229. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201402002 葛文春, 隋振民, 吴福元, 张吉衡, 徐学纯, 程瑞玉. 2007.大兴安岭东北部早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 23(02):423-440. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702021 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位UPb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 28(4):481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 刘军, 毛景文, 武广, 罗大锋, 王峰, 周振华, 胡妍青. 2013.大兴安岭北部岔路口斑岩钼矿床岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 87 (2):208-226. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201302006 李锦轶, 曲军峰, 张进, 刘建峰, 许文良, 张拴宏, 郭瑞清, 朱志新, 李亚萍, 李永飞, 王涛, 徐学义, 李智佩, 柳永清, 孙立新, 简平, 张昱, 王励嘉, 彭树华, 冯乾文, 王煜, 王洪波, 赵西西. 2013.中国北方造山区显生宙地质历史重建与成矿地质背景研究进展[J].地质通报, 32 (2/3):207-219. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201302001 毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 王义天, 牛宝贵. 2003.华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学背景:从金属矿床年龄精测得到的启示[J].中国科学, 33(4):289-299. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200304001 毛景文, 谢桂青, 程彦博, 陈毓川. 2009.华南地区中生代主要金属矿床模型[J].地质论评, 55(03):347-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.03.005 聂凤军, 胡朋, 江思宏, 刘翼飞. 2010.中蒙边境沙麦-玉古兹尔地区钨和钨(钼)矿床地质特征, 形成时代和成因机理[J].地球学报, 31(3):383-394. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201003012 佘宏全, 李进文, 向安平, 关继东, 杨郧城, 张德全, 谭刚, 张斌. 2012.大兴安岭中北段原岩锆石U-Pb测年及其与区域构造演化关系[J].岩石学报, 28(2):571-594. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202018 王登红, 唐菊兴, 应立娟, 陈郑辉, 许建祥, 张家菁, 李水如, 曾载淋. 2010. "五层楼+地下室"找矿模型的适用性及其对深部找矿的意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40 (4):733-738. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201004001 许建祥, 曾载淋, 王登红, 陈郑辉, 刘善宝, 王成辉, 应立娟. 2008.赣南钨矿新类型及"五层楼+地下室"找矿模型[J].地质学报, 82(7):880-887. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.003 向安平, 杨郧城, 李贵涛, 佘宏全, 关继东, 李进文, 郭志军.黑龙江多宝山斑岩Cu-Mo矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J].矿床地质, 2012, 06:1237-1248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.06.009 向安平, 王亚君, 秦大军, 佘宏全, 韩增光, 关继东, 康永建. 2014.内蒙古红花尔基钨多金属矿床成岩成矿年代学研究[J].矿床地质, 02:428-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.02.015 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王鹤源,王泽堃,谷思莹,杨烁暄,赵梓垚,陈旭. 宜昌—武汉长江沿岸典型砾石层对比分析. 高校地质学报. 2024(01): 47-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林旭,李玲玲,刘静,吴中海,李长安,刘维明,向宇,刘海金,陈济鑫. 长江早更新世向江汉盆地输送碎屑物质:来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄的约束. 地球科学. 2023(11): 4214-4228 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙杨,谢远云,迟云平,康春国,吴鹏. 大兴安岭东麓龙江县白土山组地层特征:化学风化、沉积循环、源-汇体系和沉积环境. 山地学报. 2022(01): 14-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏松林,孙全,陈平,杜林诚. 基于航测无人机的卵石三轴粒径计算及精度评估. 工程勘察. 2022(11): 68-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王令占,杨博,涂兵. 鄂东南咸宁北部冲洪积物的ESR年代及意义. 华南地质. 2021(02): 127-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: