Zircon U-Pb ages of the Neoproterozoic Jiuling complex granitoid in the eastern segment of the Jiangnan orogen and its tectonic significance
-
摘要:
江南造山带东段的九岭岩体为华南分布面积最大的新元古代花岗质侵入体。据其岩石组合、结构构造及野外侵入关系,可将其解体为由早到晚3个侵入序次的复式岩体,依次为黑云母花岗闪长岩、英云闪长岩及黑云母二长花岗岩。其中,黑云母花岗闪长岩分布面积最广,黑云母二长花岗岩次之,英云闪长岩分布面积最小,围岩为新元古代双桥山群浅变质岩系。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果表明,黑云母花岗闪长岩、英云闪长岩、黑云母二长花岗岩分别形成于821.6~824.0 Ma、819.5~823.6 Ma、820.4~824.5 Ma,指示它们基本同时侵位,但三者均具有自SE向NW时代变新的趋势。九岭岩体与围岩(双桥山群)的侵入接触面具有南陡北缓、角岩化带南窄北宽且围岩捕掳体及捕获锆石也呈南少北多的特征,表明九岭岩体SE侧岩体剥蚀深度强于NW侧,可能暗示了新元古代华夏板块向扬子板块碰撞拼贴过程中,研究区SE侧岩浆起源深度较深,剥蚀程度较高,且形成时代较早,并逐渐向NW侧迁移(岩浆起源深度变浅、时代变新)。
Abstract:Located in eastern Jiangnan orogen, the Jiuling pluton is the largest Neoproterozoic granitoid intrusion in South China. According to mineral assemblage, structure and intrusive contact relationships, Jiuling pluton can be divided into complex massif with 3 intrusion orders, followed by biotite-granodiorite, tonalite and biotite-monzogranite from early to late respectively. Among them, granodiorite are distributed most widely, followed by biotite-monzogranite, while tonalite is only distributed in a minimum area. They intruded into the surrounding epimetamorphic rocks of Neoproterozoic period. The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that the biotite-granodiorite, tonalite and biotite-monzogranite were formed in 821.6-821.6 Ma, 819.5-823.6 Ma and 820.4-824.5 Ma, respectively, which indicates that they belong to the product of contemporary magmatic activity. On the whole, however, the ganitoids tend to be younger from the southeast side to the northwest side. Besides, the dip angle of contact interface between Jiuling pluton and surrounding rocks (Shuangqiaoshan Group) is steep in the south and smooth in the north, hornfelsic belt is narrow in the south and wide in the north, and the xenoliths from the surrounding rock (Shuangqiaoshan Group) and the captured zircons also tend to decrease in size from south to north. These characteristics show that the rocks on the southeast side was eroded deeper than those on the northwest side, probably implying that, during the collision between Cathaysia plate and Yangtze plate in Neoproterozoic, the original depth of the granitic magma on the southeast side was deeper, the denudation was more intense, and the magma was formed earlier than the magma on the northwest side and gradually migrated northwestward, i.e., the origin depth of magma became shallow and the formation time became younger.
-
Keywords:
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- S-type granite /
- Neoproterozoic /
- Jiuling Pluton /
- Jiangnan orogen
-
1. 引言
江西金属矿产素有南钨北铜的分布格局, 近年赣北地区新发现了大湖塘与朱溪两个世界级钨矿床, 彻底改变江西乃至世界钨资源的分布格局。朱溪原为热液脉型小铜矿, 断断续续采探十余年, 一直没有取得突破性进展。2009年, 江西省地勘基金以系列成矿理论为指导、按照“就矿找矿、以脉找体”思路, 揭示朱溪“上铜下钨”矿化分带模式, 在铜矿体的深部探获了延伸稳定(超2000 m)、厚度大(平均150 m余)、品位高(平均0.571%)的钨矿体, 矿床资源储量世界第一(Wang et al., 2014; 王先广等, 2015, 2018; 胡正华等, 2018a, 2018b), 目前矿床仍在勘查, 钨资源规模有望达到500万t。九瑞矿集区位于长江中下游Cu-Au-Mo(Fe)成矿带的转折端, 是中国铜矿大型资源基地, 查明铜资源储量313万t, 约占长江中下游铜总量的1/3。矿集区内勘查工作始于20世纪50年代, 开始以寻找铁矿为目的, 历经60余年的勘查总结出九瑞地区“上铁下铜(钼)”的矿化分带规律, 并发现了武山、城门、洋鸡山等一批大型铜金矿床。赣北地区钨矿存在3期成岩成矿作用, 自早至晚分别为: 160 Ma→150~145 Ma→135~125 Ma, 并且以150~145 Ma、135~125 Ma这两期为主(胡正华, 2018c)。大湖塘和朱溪、阳储岭钨矿床的成岩时代基本一致, 均为150~145 Ma(胡正华等, 2018a, 2018b, 2018c)。长江中下游成矿带鄂东南、宁镇、庐枞等矿集区亦发现了钨矿床(朱增青, 1987; 徐跃通等, 1992; 聂利青等, 2016)。通江岭铜钨矿床位于九瑞矿集区北侧, 是江西省地质勘查基金重点勘查项目, 近年通过系统勘查在矿区深部新发现了厚大的铜钨矿体, 成为九瑞矿集区新发现钨铜矿体的首个矿床。通江岭矿区深部钨铜矿体的发现, 极大丰富了九瑞矿集区找矿空间、找矿思路和找矿方向。通江岭铜钨矿床的研究程度较低, 仅进行了少量矿床地质特征的研究(胡正华等, 2018b), 本文拟通过对通江岭成矿岩浆岩年代学研究, 揭示矿床成矿岩浆岩形成时代, 为九瑞矿集区仍至长江中下游成矿带研究及下一步找矿方向提供建议。
2. 成矿背景
九瑞矿集区位于扬子板块南东缘襄广断裂与阳常断裂交汇处(图 1), 区内地层具有双层结构, 基底为新元古代双桥山群, 盖层从震旦纪至第四纪地层均有, 其中与成矿密切相关的地层主要为奥陶系与石炭系碳酸盐岩, 为区内主要赋矿地层。矿集区内褶皱与断裂构造发育, 褶皱为一系列轴向NE的褶皱带(王先广等, 2014); 断裂构造主要为NW—NNW和NE—NNE向两组, 这两组断裂构造的交汇部位是主要控岩控矿构造(翟裕生等, 1999; 包家宝等, 2002; 胡正华, 2015a)。矿集区内共出露31个岩体, 呈岩株、岩墙、岩脉状产出, 单个岩体出露面积为0.04~1.6 km2(翟裕生等, 1999)。岩株受NW—NNW向隐伏基底断裂控制, 呈等距状产出。岩脉受NE—NEE向断裂、NE向褶皱带、层间不整合面及层内薄弱面贯入式侵位产出, 自北至南发育6个岩浆岩带:即, 东雷湾—通江岭花岗闪长斑岩亚带、宝山—大桥花岗闪长斑岩亚带、宋家湾—武山花岗闪长斑岩亚带、大冲—丁家山石英闪长玢岩—花岗闪长斑岩亚带、城门山—十六公里花岗闪长斑岩—石英闪长玢岩亚带、沙河—狮子山花岗闪长斑岩—石英闪长玢岩亚带。区内矿产以铜、钼、金为主, 成矿岩浆岩均为高钾钙碱性Ⅰ型岩浆岩系列, 成岩时代集中于145 Ma左右(吴良士等, 1997; 李进文等, 2007; 蒋少涌等, 2008; 陈志洪等, 2011; 胡正华等, 2015a, 2018b, 2018c)。
![]() 图 1 长江中下游九瑞矿集区地质简图(据Pan et al., 1999修改)(A—长江中下游构造简图;B—九瑞矿集区地质简图)
图 1 长江中下游九瑞矿集区地质简图(据Pan et al., 1999修改)(A—长江中下游构造简图;B—九瑞矿集区地质简图)
1—奥陶系;2—志留系;3—泥盆—石炭系;4—二叠系;5—三叠系;6—第四系;7—岩体;8—地质界线/河流;9—矿床(点)位置及名称;10—城市位置及名称;11—矿集区;12—通江岭矿区位置Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Jiurui ore concentration area in the middle-lower Yangtze River Valley (modified from Pan et al., 1999)(A-Structure diagram of the middle-lower Yangtze River Valley; B-Geological map of the Jiurui ore concentration area)
1-Ordovician; 2-Silurian; 3-Devonian, Carboniferous; 4-Permian; 5-Triassic; 6-Quaternary; 7-Lithesome; 8-Geological boundary/river; 9-Locations and names of deposits; 10-Locations and names of cities; 11-Ore concentration areas; 12-Location of Baoshan ore deposit3. 矿床地质
通江岭矿区位于九瑞地区龙泉古寺—牛头山背斜核部。区内出露的地层自老至新有中二叠统茅口组(P2m)、上二叠统龙潭组(P3l)、上二叠统长兴组(P3c)、下三叠统殷坑组(T1y)、下三叠统青龙组(T1q)、下三叠统周冲村组(T1z)(图 2), 地层总体走向北东, 以龙泉古寺—牛头山背斜核部为界。区内断裂构造发育, 根据走向可分为3组:北东向(F1、F2、F3)、北西向(F4)、近南北向(F5)断裂, 其中北东向F2断裂为区内主要控岩控矿构造。花岗闪长斑岩沿龙泉古寺—牛头山背斜核部与F2断裂呈NE向岩墙展布。
![]() 图 2 九瑞矿集区通江岭矿区地质简图1—第四系;2—下三叠统周冲村组;3—下三叠统青龙组;4—中二叠统茅口组;5—花岗闪长斑岩;6—断层及编号/地质界线;7—勘探线及其编号;8—钻孔及其编号Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Tongjiangling ore deposit in the Jiurui ore concentration area1-Quaternary; 2-Lower Triassic Zhouchongcun Formation; 3-Lower Triassic Qinglong Formation; 4-Middle Permian Maokou Formation; 5-Granodiorite porphyry; 6-Fault and its number/ geological boundary; 7-Exploration line and its number; 8-Drill hole and its number
图 2 九瑞矿集区通江岭矿区地质简图1—第四系;2—下三叠统周冲村组;3—下三叠统青龙组;4—中二叠统茅口组;5—花岗闪长斑岩;6—断层及编号/地质界线;7—勘探线及其编号;8—钻孔及其编号Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Tongjiangling ore deposit in the Jiurui ore concentration area1-Quaternary; 2-Lower Triassic Zhouchongcun Formation; 3-Lower Triassic Qinglong Formation; 4-Middle Permian Maokou Formation; 5-Granodiorite porphyry; 6-Fault and its number/ geological boundary; 7-Exploration line and its number; 8-Drill hole and its number通江岭铜钨矿由14条矿体(M1~M14)组成, 总体走向NEE, 倾向东, 呈似层状、透镜状产出于花岗闪长斑岩与茅口组(P2m)碳酸盐的内、外接触带(图 3)。矿石类型以铜矿石和铜钨矿石为主; 矿石矿物以白钨矿、黄铜矿为主, 脉石矿物长石、石英、绿泥石、高岭石、石榴子石、透辉石、透闪石、长石、石英、绿泥石、方解石等为主; 矿石构造以脉状、浸染状、块状为主; 矿石结构以结晶结构、交代结构和固溶体分离结构为主。区内矿化垂向上具有“上铜下钨铜”的分带模式, 上部矿化以铜矿化为主, 矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿, 脉石矿物主要为长石、石英、高岭土、绿泥石和石榴子石等矽卡岩矿物; 黄铜矿主要以脉状、浸染状、块状赋存于矽卡岩、矽卡岩化大理岩和蚀变花岗闪长斑岩中。下部以钨铜矿化为主, 矿石矿物以黄铜矿、白钨矿为主, 脉石矿物主要为石榴子石、透辉石、透闪石等矽卡岩矿物。
![]() 图 3 通江岭矿区9号勘探线剖面图1—下三叠统青龙组;2—中二叠统茅口组;3—花岗闪长斑岩;4—铜矿体;5—铜钨矿体;6—矿体及编号;7—地质界线;8—断层及编号;9—锆石U-Pb样采集位置及编号Figure 3. Geological section along No. 9 exploration line in the Tongjiangling minging area1-Lower Triassic Qinglong Formation; 2-Middle Permian Maokou Formation; 3-Granodiorite porphyry; 4-Copper orebody; 5-Coppertungsten orebody; 6-Orebody and its number; 7-Geological boundary; 8-Fault and its number
图 3 通江岭矿区9号勘探线剖面图1—下三叠统青龙组;2—中二叠统茅口组;3—花岗闪长斑岩;4—铜矿体;5—铜钨矿体;6—矿体及编号;7—地质界线;8—断层及编号;9—锆石U-Pb样采集位置及编号Figure 3. Geological section along No. 9 exploration line in the Tongjiangling minging area1-Lower Triassic Qinglong Formation; 2-Middle Permian Maokou Formation; 3-Granodiorite porphyry; 4-Copper orebody; 5-Coppertungsten orebody; 6-Orebody and its number; 7-Geological boundary; 8-Fault and its numberM9矿体为区内规模最大的铜钨矿体, 走向延伸超1200 m, 倾向延深超500 m, 真厚度10.43~27.66 m; Cu品位多介于0.45%~0.68%, 最高可达9.73%; WO3品位多介于0.05%~0.17%, 局部伴生Mo、Zn、Ag等, M9矿体矿石矿物以黄铜矿、白钨矿为主, 矿石构造以浸染状、细脉—网脉状为主。矿体具有“上铜下钨铜”的矿化分带特征。
4. 样品分析与测试结果
4.1 样品采集与测试
锆石U-Pb样品采自9线ZK0903孔885 m处M9矽卡岩矿体底板的花岗闪长斑岩(图 3)。花岗闪长斑岩(图 4)呈灰白-浅灰色, 斑状结构、块状构造, 斑晶(约64%)包括斜长石(约30%)、石英(约20%)、钾长石(约10%)、黑云母(约4%)。斜长石斑晶, 半自形板状, 粒径2~5 mm, 聚片双晶和卡钠复合双晶发育, 局部发育环带构造, 部分绢云母化; 石英斑晶, 他形粒状, 粒径2~3.5 mm。钾长石斑晶, 半自形粒状为主, 粒径2 mm左右, 常见高岭石化; 黑云母斑晶, 片状, 片径2~2.5 mm, 褐色, 多色性浅黄褐—黄褐色, 常见绿泥石化。基质(约36%)呈显微粒状结构, 由长英质及少量黑云母构成, 粒径一般为0.05~2 mm, 长石类可见绢云母化、高岭石化。
锆石U-Pb测年样品, 先破碎至60目, 采用浮选、磁选方法初步分离筛选出锆石, 然后在双目镜下将挑选色泽、晶形较好, 透明度较高的锆石颗粒, 用于锆石制靶, 拍摄阴极发光(CL)图像, 观察锆石内部结构, 选择环带清晰的岩浆岩锆石作为待测点。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的测试工作在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所LA-ICP-MS实验室完成, 测试仪器为Agilent 7500a型ICP-MS与激光剥蚀系统ComPex 102 Excimer。为确保LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄测试的精确度, 每测试5个点加测标样91500和NIST610一次, 并测量一个锆石Plesovice来确定仪器运行状态是否正常。锆石年龄测试结果用Isoplot 3.0程序处理, 具体分析步骤和数据处理过程参见文献(柳小明等, 2002)。
4.2 测试结果
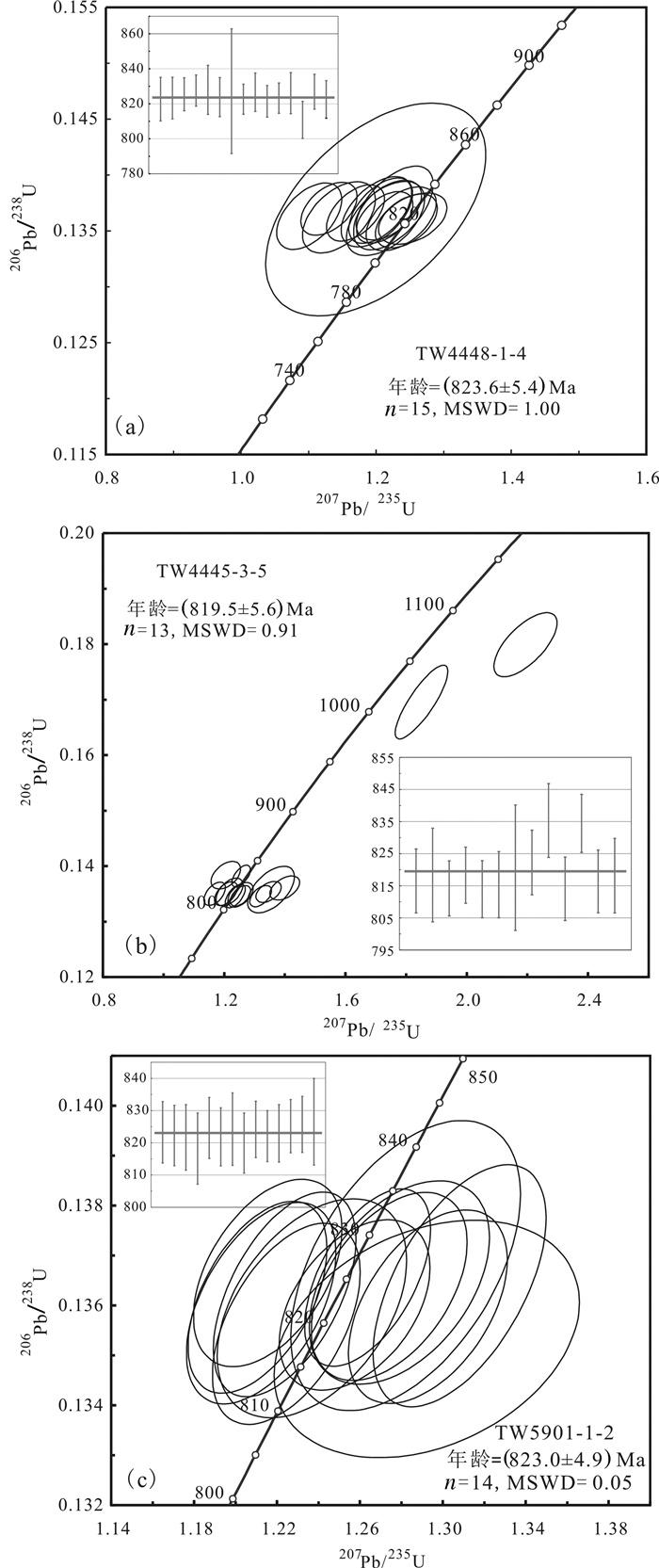
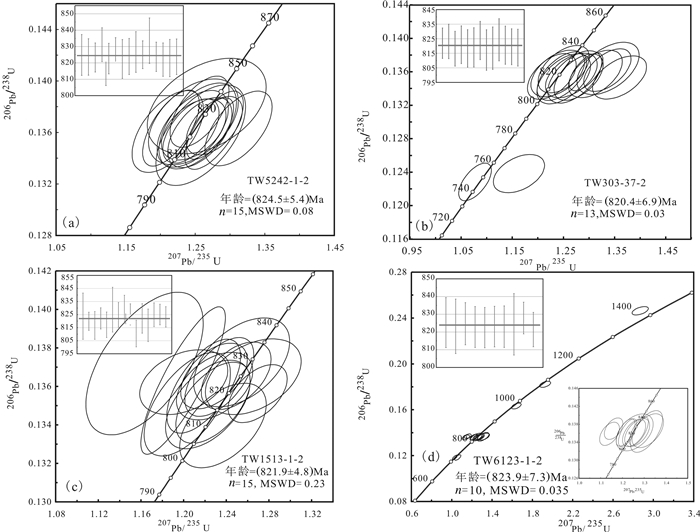
花岗闪长斑岩内锆石无色, 透明, 主要呈长柱状, 部分锆石内见细小的包裹体及裂纹(图 5), 锆石粒径在50 μm×110 μm~90 μm×180 μm。阴极发光图像显示锆石成分含量比较均匀, 主要以振荡环带为主, 少量锆石发育扇状环带和无环带现象。为确保定年结果的准确性, 实验中选择具有明显振荡环带锆石的边缘进行测试。本样品中挑取的锆石长轴和短轴之比在2:1~4:3 (图 5), 测点Th、U含量分别为107~266 μg/g, 269~653 μg/g(表 1)。Th/U比值大多介于0.34~0.71 (表 1), 与岩浆锆石的特征相似(吴元保等, 2004)。经测定15个有效锆石测点的207Pb/235U、206Pb/238U分析结果在误差范围内基本一致, 206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均值为(143.31±2.70)Ma (MSWD=0.62, n=15)(表 1, 图 6)。
表 1 通江岭矿区花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age data of granodiorite porphyry in The Tongjiangling mining area
5. 讨论
5.1 成矿岩体及其成岩时代
通江岭矿区自花岗闪长斑岩体至茅口组碳酸盐岩具有绿泥石化-硅化-高岭土化(花岗闪长斑岩) →石榴子石-透辉石-透闪石矽卡岩→矽卡岩化化大理岩→大理岩蚀变分带, 区内黄铜矿、白钨矿物等矿石矿物主要呈细脉状、浸染状产出于花岗闪长岩与茅口组碳酸盐岩接触带的矽卡岩中, 部分以浸染状产出于蚀变花岗闪长斑岩中, 矿体垂向上自围岩至岩体(自浅至深)显示出“中温→中高温”的元素分带性, 即具有“上铜下钨铜”的矿化分带特征, 与典型的斑岩-矽卡岩型矿床的蚀变分带特征基本一致(王先广等, 2015; 唐菊兴等, 2017; 胡正华等, 2018c), 指示出花岗闪长斑岩为通江岭矿床的成矿岩浆岩, 矿床类型为斑岩-矽卡岩型。通江岭铜钨矿成矿花岗闪长斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(143.31±2.70) Ma(MSWD=0.62, n=15), 代表了成矿花岗闪长斑岩的成岩年龄。
5.2 找矿潜力剖析
长江中下游成矿带鄂东南、宁镇、庐枞等矿集区已发现钨矿体或钨矿化体的报道, 如鄂东南矿集区阳新阮家湾和傅家山(朱增青, 1987; 徐跃通等, 1992)、大冶龙角山等矽卡岩型钨铜钼矿床(朱增青, 1987); 宁镇矿集区谏壁发现过中型斑岩型钨、钼矿床(杨松生等, 1985; 马春等, 2003); 庐枞矿集区东顾山矽卡岩型钨多金属矿床(聂利青等, 2016)。聂利青等(2016)提出长江中下游成矿带除铁、铜外, 亦具有良好找钨前景。九瑞矿集区受长江断裂西段北西西向的鄂州—九江深断裂带上盘控制, 两端为北北东向的麻城—湘东、赣江断裂带截接制约, 并与瑞昌弧形构造东部的北东东向反S形褶皱与走向断裂以及北北西向张裂隙带复合, 形成一个以北西西向为主轴的菱形构造网络结点控制着内岩浆岩侵位以及矿床的分布(包家定等, 2002)。矿集区内存在“多层结构”赋矿模式, 即层状矽卡岩矿体赋存于奥陶系、石炭系、二叠系、三叠系碳酸盐岩地层, 以石炭系地层为主(王先广等, 2014; 胡正华等, 2015a)。近年, 赣北地区新发现的朱溪世界最大钨矿床、武宁县东坪超大型石脉型黑钨矿床均具有上铜下钨的分带特征。朱溪钨矿的成岩成矿时代为145 Ma左右(王先广等, 2015; 胡正华, 2018c), 主矿体赋存于花岗岩与黄龙组碳酸盐岩接触带的矽卡岩中。近年, 江西省地质勘查基金管理中心在九瑞矿集区武山、南港矿区边深部均已发现了似层状斑岩-矽卡岩型铜钨矿体, 主要赋存于黄龙组碳酸盐岩与成矿岩浆岩的接触带附近, 成矿岩体均为花岗闪长斑岩或石英斑岩, 成矿岩年龄均为145 Ma左右(胡正华等, 2015a); 并且垂向上均具有“上铜下钨铜”的矿化分带特征, 中武山矿区深部的矽卡岩型钨铜矿体中钨资源规模达到大型。上石炭统黄龙组碳酸盐岩是赣北地区矽卡岩型矿床的主要赋矿围岩, 通江岭铜钨矿区目前仅在二叠系碳酸盐岩与花岗闪长斑岩接触带发现了斑岩-矽卡岩型铜钨矿体。通江岭矿区ZK0903孔790.15 m处花岗斑岩与碳酸盐岩接触带的矽卡岩中, 发现真厚度十余米的铜(钨)矿体, Cu品位多介于0.45%~0.68%, 最高可达9.73%; WO3平均品位0.067%, 最高达0.17%。区内其他钻孔在矽卡岩中亦揭示了钨矿化现象, 进一步表明通江岭矿区深部具有发现厚大钨矿体的潜能, 尤其是在矿区深部石炭系、奥陶系碳酸盐岩与花岗闪长斑岩的接触带或五通面、奥陶—志留系所形成的硅钙界面, 找矿潜能大。
6. 结论
(1) 通江岭铜钨矿成矿岩浆岩为花岗闪长斑岩, 其锆石U-Pb年龄为(143.31±2.70) Ma (MSWD=0.62, n=15), 代表了成矿花岗闪长斑岩成岩年龄。
(2) 九瑞矿集区具有“上铜下钨铜”的矿化分带趋势, 通江岭矿区石炭系、奥陶系碳酸盐岩与花岗闪长斑岩接触带或五通面、奥陶—志留系所形成的硅钙界面, 找钨潜能大。
-
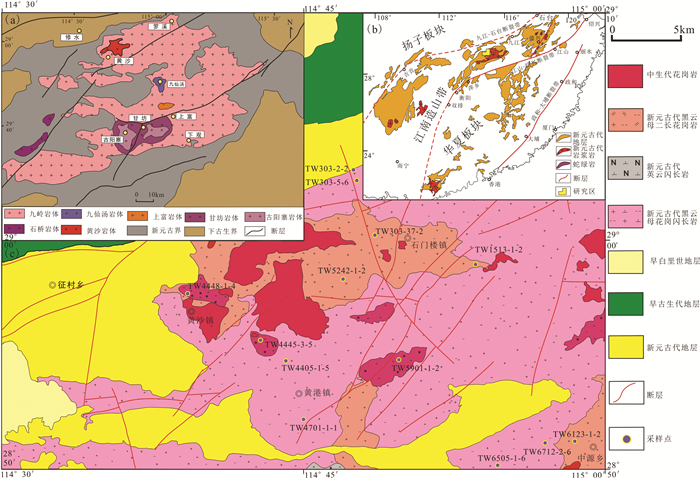
图 1 九岭岩体地质简图(a)、华南前寒武纪岩石分布地质简图(b,修改自Yao et al., 2014)及赣西北修水—武宁地区地质简图(c,据1: 5万罗溪幅、黄沙桥幅、石门楼幅地质图改绘)
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Jiuling pluton (a), simplified geological map of South China (b, modified from Yao et al., 2014), simplified geological map of Xiushui-Wuning area in northwest Jiangxi Province (c, modified from 1: 50, 000 Luoxi Sheet, Huangshaqiao Sheet, Shimenlou Sheet geological map)
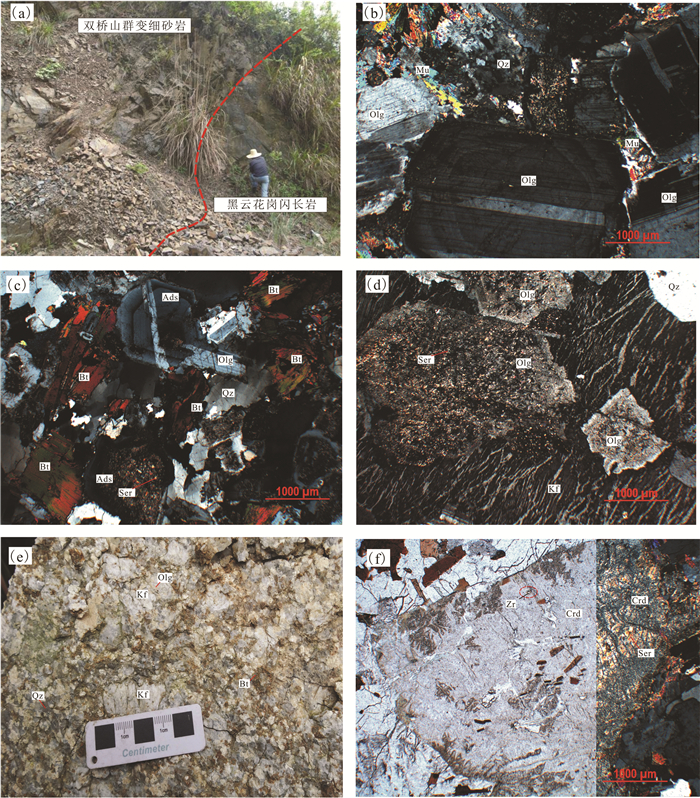
图 2 研究区新元古代花岗岩类野外露头及岩石学特征
a—研究区新元古代黑云母花岗闪长岩侵入于双桥山群变细砂岩之中;b—黑云母花岗闪长岩镜下特征,正交偏光;c—英云闪长岩镜下特征;d, e—钾长石巨斑晶黑云母二长花岗岩镜下特征(d,正交偏光)及野外特征(e);f—黑云母花岗闪长岩中堇青石显微特征,沿裂理绢云母化,且锆石包裹体周围发育柠檬黄多色晕,左为单偏光,右为正交偏光; Olg—更长石;Kf—钾长石;Ads—中长石;Qz—石英;Bt—黑云母;Crd—堇青石;Ser—绢云母;Mu—白云母;Zr—锆石
Figure 2. Petrological and field outcrops characteristics of Neoproterozoic granitoids in the study area
a-Neoproterozoic biotite granodiorite intruding into meta-sandstone of Shuangqiaoshan Group in the study area; b-Microscopic characteristics of biotite-granodiorite, perpendicular polarized light; c-Microscopic characteristics of tonalite; d, e-Microscopic characteristics of biotitemonzogranite with giant potassium feldspar phenocryst (d) and its outcrops characteristics in the field (e); f-Microscopic characteristics of the cordierite with sericitization along its rifts and showing the lemon yellow multi-color halo developed around the zircon inclusions from biotite granodiorite, the right side is perpendicular polarized light, the left side is plane polarized light. Olg-Oligoclase; Kf-K-feldspar; Ads-Adesine; Qz-Quartz; Bt-Biotite; Crd-Cordierite; Ser-Sericite; Mu-Muscovite; Zr-Zircon
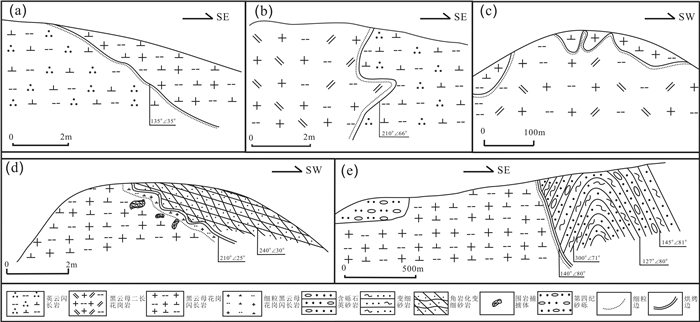
图 3 研究区新元古代花岗岩接触关系地质简图
a—英云闪长岩侵入于黑云母花岗闪长岩之中;b—黑云母二长花岗岩侵入于英云闪长岩之中;c—黑云母二长花岗岩侵入于黑云母花岗闪长岩之中;d—研究区北部黑云母花岗闪长岩与双桥山群侵入接触关系;e—研究区南部黑云母花岗闪长岩与双桥山群侵入接触关系
Figure 3. Geological sketch map of contacting relationships of the Neoproteozoic granitoids in the study area
a-Tonalite intruding the biotite-granodirite; b-Biotite-monzogranite intruding the tonalite; c- Biotite-monzogranite intruding biotite-granodirite; d-The contacting relationship between the biotite-granodiorite and the Shuangqiaoshan Group in northern study area; e-The contacting relationship between the biotite-granodiorite and the Shuangqiaoshan Group in northern study area
表 1 江南造山带新元古代花岗岩年代学资料
Table 1 Geochronological data for Neoproterozoic granites in Jiangnan orogen

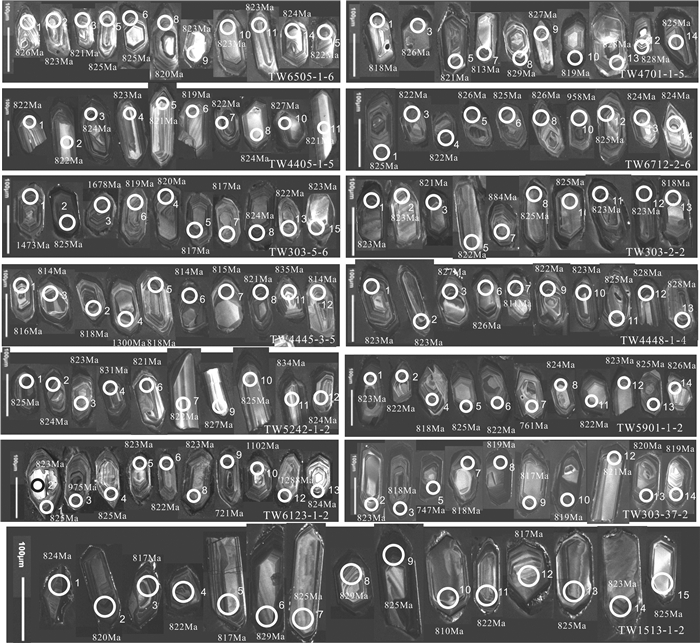
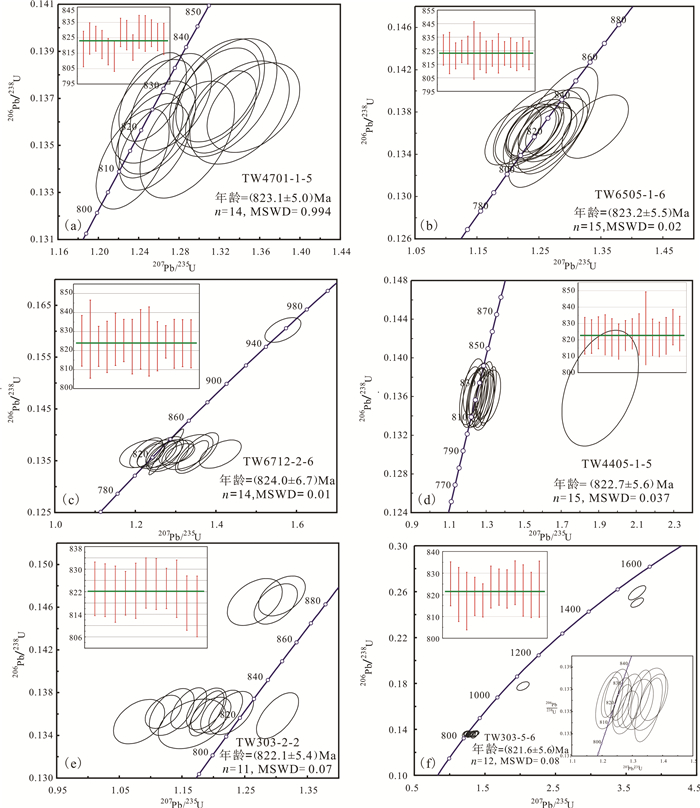
表 2 九岭岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析数据
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating data of Jiuling Pluton

-
Anderson D L. 1989. Composition of the Earth[J]. Science, 243(4889):367-370. doi: 10.1126/science.243.4889.367
Barbarin B, 1999. A review of the relationships between granitoid types:their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 46:605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
Charvet J. 2013. The Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Block:An overview[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 74:198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.015
Cox J, Searle M, Pedersen R. 1999. The petrogenesis of leucogranitic dykes intruding the northern Semail ophiolite, United Arab Emirates:field relationships, geochemistry and Sr/Nd isotope systematics[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 137:267-287. doi: 10.1007/s004100050550
Charvet J, Shu Liangshu, Shi Yangshen, Guo Lingzhi, Faure M. 1996.The building of south China:collision of Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks, problems and tentative answers[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 13(3/5):223-235. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0743954796000293
Chen Zhihong, Guo Kunyi, Dong Yongguan, Chen Rong, Li Longming, Liang Yihong, Li Chunhai, Yu Ximing, Zhao Ling, Xing Guangfu. 2009a. Possible early Neoproterozoic magmatism associated with slab window in the Pingshui segment of the Jiangshan-Shaoxing suture zone:evidence from zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Science China, Series D Earth Science, 52:925-939. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0071-6
Chen Zhihong, Xing Guangfu, Guo Kunyi, Dong Yongguan, Chen Rong, Zeng Yong, Li Longming, He Zhenyu, Zhao Ling. 2009b.Petrogenesis keratophyres in the Pingshui Group, Zhejiang:constraints from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54:1570-1578. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXTW200909017.htm
Chen Xin, Wang Di, Wang Xiaolei, Gao Jianfeng, Shu Xujie, Zhou Jincheng, Qi Liang. 2014. Neoproterozoic chromite-bearing highMg diorites in the western part of the Jiangnan orogen, southern China:geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 200-201:35-48. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.04.007
Ding Binghua, Shi Rendeng, Zhi Chenxia, Zheng Lei, Chen Lei. 2008.Neoproterozoic (850Ma) subduction in the Jiangnan orogen:Evidence from the SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the SSZ-type ophiolite in southern Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 27(5):375-388 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong Yunpeng, Liu Xiaoming, Santosh M, Chen Qing, Zhang Xiaoning, Li Wei, He Dengfeng, Zhang Guowei. 2012.Neoproterozoic accretionary tectonics along the northwestern margin of the Yangtze Block, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Precambrian Research, 196-197:247-274. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.12.007
Dong Shuwen, Xue Huaimin, Xiang Xinkui, Ma L C. 2010. The discovery of Neoproterozoic pillow lava in spilite-ceratophyre of Lushan area, northern Jiangxi Province, and its geological significance[J]. Geology in China, 37 (4):1021-1033 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201004017
Duan Zheng, Xing Guangfu, Liao Shengbing, Chu Pingli, Huang Wencheng, Zhu Yanhui, Shu Xujie, Li Changbo. 2017.Compositional difference from the sources of Jiuling Neoproterozoic granite complex in Eastern Segment of the Jiangnan Orogen:Constraints from geochemistry and Hf isotope of zircons[J]. Acta Petrologica sinica. 33(11):3610-3634. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201711019.htm
Duan Zheng, Xing Guangfu, Liao Shengbing, Chu Pingli, Huang Wencheng, Zhu Yanhui, Shu Xujie, Li Changbo. 2018.Petrogenesis of the microcrystalline-dioritic enclaves from Jiuling granitoids in the eastern segment of Jiangnan Orogen and constraints on magma source materials[J]. China Geology, 3:374-391. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c88ee1c20839e41d008bd494659af193&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Gao Linzhi, Dai Chuangu, Ding Xiaozhong, Wang Min, Liu Yanxue, Wang Xuehua, Chen Jianshu. 2011. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of intrusive alaskite in the Fanjigshan Group and alaskite basal conglomerates:Constraints on the deposition of the Xiajiang Group[J]. Geology in China. 38(6):1413-1420 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=37e5620cedcbf77e1ed62447e2ffe8ea&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Gao Linzhi, Dai Chuangu, Liu Yanxue, Wang Min, Wang Xuehua, Chen Jianshu, Ding Xiaozhong, Zhang Chuanheng, Cao Qian, Liu Jianhui. 2010. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of tuff bed of the Sibao Group in southeastern Guizhounorthern Guangxi area, China and its stratigraphic implication[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29 (9):1259-1268 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201009001
Ge Wenchun, Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Zhou Hanwen, Lee Chiyu. 2001. Geochemical studies on two types of Neoproterozoic peraluminous granitoids in northern Guangxi[J]. Geochimica, 30(1):24-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200101004
Greentree M R, Li Zhengxiang, Li Xianhua, Wu, Huaichun. 2006. Late Mesoproterozoic to earliest Neoproterozoic basin record of the Sibao orogenesis in western South China and relationship to the assembly of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 151:79-100. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.08.002
Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, Pearson N J and O'Reilly S Y. 2004. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:UPb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 131:231-282. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.011
Hu Shiling, Wang Songshan, Sang Haiqing, Qiu Ji, Liu Jiayuan. 1985.An application of the fast-neutron activation dating technique to approach the age of early emplacement of Jiuling granodiorite of Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrology of Sinica, 1(3):29-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-ysxb198503002.htm
Huang Lanchun, Jiang Shaoyong. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the porphyric-like muscovite granite in the Dahutang tungsten deposit, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28 (12):3887-3900 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201212008
Jayananda M, Moyen J F, Martin H, Peucat J J, Auvray B, Mahabaleswar B. 2000. Late Archaean (2550-2520 Ma) juvenile magmatism in the Eastern Dharwar craton, southern India:constraints from geochronology, Nd-Sr isotopes and whole rock geochemistry[J]. Precambrian Research, 99:225-254. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(99)00063-7
Li Fengchun, Hou Minglan, Luan Rijian, Lin Peijun, Li Zengsheng, Zhao Long, Wang Jilin, XU Shuang. 2016. Optimization of analytical conditions for LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Journal of Rock and Mineral Analysis, 35(1):17-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201601005
Li Wuxian, Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Lou Fasheng. 2008d.Obduction-type granites within the NE Jiangxi Ophiolite:Implications for the final amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 13:288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.12.010
Li Wuxian, Li Xianhua. 2003. Adakitic granites within the NE Jiangxi ophiolites, South China:geochemical and Nd isotopic evidence[J]. Precambrian Research, 122:29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00206-1
Li Xianhua, Li Wuxian, Li Zhengxiang, Liu Yin. 2008b. 850-790 Ma bimodal volcanic and intrusive rocks in northern Zhejiang, South China:A major episode of continental rift magmatism during the breakup of Rodinia[J]. Lithos, 102:341-357. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.007
Li Xianhua, Li Wuxian, Li Zhengxiang, Lo Chinghua, Wang Jian, Ye Meifang, Yang Yueheng. 2009. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks in South China:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 174:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004
Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Ge Wenchun, Zhou Hanwen, Li Wuxian and Wingate M T D. 2003a. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Crystal melting above a mantle plume at ca. 825Ma?[J]Precambrian Research, 122:45-83. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3
Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Ge Wenchun, Zhou Hanwen, Li Wuxian, Liu Yin. 2001. U-Pb ziron ages of the Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China and their tectonic implications[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 20(4):271-273 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200104019
Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Sinclair J A, Li Wuxian and Garreth C. 2006. Revisiting the "Yanbian Terrane":Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic Evolution of the western Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 151 (1/2):14-30. doi: 10.1016-j.precamres.2006.07.009/
Li Xianhua, Zhu Weiguang, Zhong Hong, Wang Xuance, He Defeng, Bai Zhongjie, Liu Feng. 2010. The Tongde picritic dikes in the western Yangtze Block:Evidence for ca. 800Ma mantle plume magmatism in South China During the breakup of Rodinia[J]. Journal of Geology, 118(5):509-522. doi: 10.1086/655113
Li Zhengxiang, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, Davidson A, De Waele B, Ernst R E, Fitzsimons I C W, Fuck R A, Gladkochub D P, Jacobs J, Karlstrom K E, Lu S, Natapov L M, Pease V, Pisarevsky S A, Thrane K, Vernikovsky V. 2008c. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia:a synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 160:179-210. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021
Li Zhengxiang, Li Xianghua, Zhou Hanwen, Kinny, P D. 2002.Grenvillian continental collision in South China:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon results and implications for the configuration of Rodinia[J]. Geology, 30:163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0163:GCCISC>2.0.CO;2
Li Zhengxiang, Li Xianhua, Kinny P D, Wang Jian, Zhang S, Zhou H. 2003b. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents:Evidence For a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 122 (1/4):85-109. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f37b2e324eb8eddd96446f3e3d501681&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Zhengxiang, Li Xianhua, Kinny P D, Wang Jian. 1999. The breakup of Rodinia:Did it start with a mantle plume beneath South China?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 173 (3):171-181. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00240-X
Li Zhengxiang, Li Xianhua, Li Wuxian, Ding Shijiang. 2008a. Was Cathaysia part of Proterozoic Laurentia? New data from Hainan Island, south China[J]. Terra Nova. 20:154-164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2008.00802.x
Li Zhengxiang, Wartho J A, Occhipinti S, Zhang Chuanlin, Li Xianhua, Wang Jian, Bao Chaomin, 2007. Early history of the eastern Sibao Orogen (South China) during the assembly of Rodinia:new mica 40Ar/39Ar dating and SHRIMP U-Pb detrital zircon provenance constraints[J]. Precambrian Research, 159:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.05.003
Li Zhengxiang, Zhang Linghua, Powell C M. 1995. South China in rodinia:Part of The missing link between Australia-East Antarctica and Laurentia?[J]. Geology, 23 (5):407-410. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0407:SCIRPO>2.3.CO;2
Liu Yongsheng, Gao Shan, Hu Zhaochu, Gao Changgui, Zong Keqing, Wang Dongbing. 2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recyclinginduced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2):537-571. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Keqing_Zong2/publication/268411794_Continental_and_Oceanic_Crust_Recycling-Induced_Melt_Peridotite_Interactions_in_the_Trans-North_China_Orogen_UPb_Dating_Hf_Isotopes_and_Trace_Elements_in_Zircons_from_Mantle_Xenoliths/links/551434ad0cf2eda0df306881/Continental-and-Oceanic-Crust-Recycling-Induced-Melt-Peridotite-Interactions-in-the-Trans-North-China-Orogen-UPb-Dating-Hf-Isotopes-and-Trace-Elements-in-Zircons-from-Mantle-Xenoliths.pdf
Liu Yongsheng, Hu Zhaochu, Gao Shan, Günther D, Xu Juan, Gao Changgui, Chen Haihong. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257(1/2):34-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=babd721ac13e2675d9485b52683be64c
Liu Yongsheng, Hu Zhaochu, Zong Keqing, Gao Changgui, Gao Shan, Xu Juan, Chen Haihong. 2010b. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICPMS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Ludwig K R, 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, California, Berkeley, 39 pp.
Ma Tieqiu, Chen Lixin, Bai Daoyuan, Zhou Kejun, Li Gang, Wang Xianhui. 2009. Zircon SHRIMP dating and geochemical characteristics of Neoproterozoic granites in southeastern Hunan[J]. Geology in China 36 (1):65-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200901004
Shu Liangshu, Zhou Guoqing, Shi Yangshen., Yin Jun. 1994. Study of high pressure metamorphic blueschist and its late Proterozoic age in the eastern Jiangnan belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 39:1200-1204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXTW199414012.htm
Shu Liangshu. 2012. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31 (7):1035-1053 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201207003
Wang Xuance, Li Xianhua, Li Wuxian, Li Zhengxiang. 2007a. Ca. 825Ma komatiitic basalts in south China:First evidence for> 1500℃ mantle melts by a Rodinian mantle plume[J]. Geology, 35(12):1103-1106. doi: 10.1130/G23878A.1
Wang Xuance, Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Li Qiuli, Tang Guoqiang, Gao Yuya, Zhang Qirui, Liu Yin. 2012a. Episodic Precambrian crust growth:evidence from U-Pb ages and Hf-O isotopes of zircon in the Nanhua Basin, central South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 222-223:386-403. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.06.001
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Qiu Jiansheng. Gao Jianfeng. 2004.Petrogenesis of Neoproterozoic peraluminous granites from northeastern Hunan province:chronological and geochemical constraints[J]. Geological Review, 50(1):65-76 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005348
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Qiu Jiansheng, Zhang Wenlan, Liu Xiaoming, Zhang Guilin. 2006. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China:implications for petrogenesis and tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 145:111-130. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.014
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Qiu, Jiansheng, Zhang Wenlan, Liu Xiaoming, Zhang Guilin. 2006. Petrogenesis of the Neoproterozoic strongly peraluminous granitoids from Northern Guangxi:Constraints from zircon geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrology Sinica, 22(2):326-342 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200602007.htm
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Griffin W L, Wang Rucheng, Qiu Jiansheng, O'Reilly S Y, Xu Xisheng, Liu Xiaoming, Zhang Guilin. 2007. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen:Dating the assembly of the Yangtze Cathaysia blocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 159:117-131. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.005
Wang Xiaolei, Zhao Guochun, Zhou Juncheng, Liu Yongsheng, Hu Jian. 2008. Geochronology and Hf iso-topes of zircon from volcanic rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, South China:Implications for the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Jiangnanorogen[J]. Gondwana Research. 18:355-367. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X08000701
Wang Xiaolei, Shu Liangshu, Xing Guangfu, Zhou Jincheng, Tang Ming, Shu Xujie, Qi Liang. Hu Yanhua. 2012b. Post-orogenic extension in the eastern part of the Jiangnan orogen:Evidence from ca 800-760 Ma volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 222-223:404-423. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.07.003
Wang Wei, Zhou Meifu, Yan Danping, Li Jianwei. 2012c. Depositional age, provenance, and tectonic setting of the Neoproterozoic Sibao Group, southeastern Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 192-195, 107-124. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.10.010
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Wan Yusheng, Kitajima K, Wang Di, Bonamici C, Qiu Jiansheng, Sun Tao. 2013. Magmatic evolution and crustal recycling for Neoproterozoic strongly peraluminous granitoids from southern China:Hf and O isotopes in zircon[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 366:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.02.011
Wang Xiaolei, Zhou Jincheng, Griffin W L, Zhao Guochun, Yu Jinhai, Qiu Jiansheng, Zhang Yanjie, Xing Guangfu. 2014. Geochemical zonation across a Neoproterozoic orogenic belt:Isotopic evidence from granitoids and metasedimentary rocks of the Jiangnan orogen, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 242:154-171. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.023
Wang Yuejun, Zhang Feifei, Fan Weiming, Zhang Guowei, Chen Shiyue, Cawood P A, Zhang Aimei. 2010. Tectonic setting of the South China Block in the early Paleozoic:Resolving intracontinental and ocean closure models from detrital zircon UPb geochronology[J]. Tectonics, 29(6):1-70. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=65c5ce42f543ca6546e1a80e4a7c9491&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Yuejun, Zhang Aimei, Fan Weiming., Zhao Guochun, Zhang Guowei, Zhang Feifei, Zhang Yuzhi, Li Sanzhong. 2011.Kwangsian crustal anatexis within the eastern South China Block:geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic fingerprints from the gneissoid granites of Wugong and WuyiYunkai Domains[J]. Lithos, 127:239-260. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.027
Wu Rongxin, Zheng Yongfei, Wu Yuanbao, Zhao Zifu, Zhang Shaobing, Liu Xiaoming, Wu Fuyuan. 2006. Reworking of juvenile crust:element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 146:179-212. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.012
Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15):1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
Xue Huaimin, Ma Fang, Song Yongqin, Xie Yaping. 2010.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic granitoid association from eastern segment of the Jiangnan orogen, China:Constraints on the timing and process of amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica. 26(11):3215-3244 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201011006.htm
Xu Xianbing, Tang Shuai, Li Yuan, Zhang Zejun. 2015. Characteristics of Neoproterozoic-Early Mesozoic multiphase orogenic activities of eastern Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Geology in China, (1):33-50(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi2015010004
Xia Yan, Xu Xisheng, Niu Yaolin, Liu Lei. 2018. Neoproterozoic amalgamation between Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks:The magmatism in various tectonic settings and continent-arccontinent collision[J]. Precambrian Research, 309:56-87. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.02.020
Yan Shengwu, Bai Xianzhou, Wu Wenxiang, Zhu Bing, Zhan Qiongyao, Wen Long, Yang Hui, Wang Yuting. 2017. Genesis and geological implications of the Neoproterozoic A-type granite from the Lugu area, western Yangtze block[J]. Geology in China, 44(1):136-150(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201701010
Yang Zhenyu, Sun Zhiming, Yang Tienshui, Pei Junling. 2004. A long connection (750-380 Ma) between South China and Australia:paleomagnetic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 220:423-434. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00053-6
Ye Meifang, Li Xianhua, Li Wuxian, Liu Ying, Li Zhengxiang. 2007.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronological and whole-rock geochemical evidence for an early Neoproterozoic Sibaoan magmatic arc along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Gondwana Research, 12:144-156. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.09.001
Yu Jinhai, O' Reilly S Y, Wang Lijuan, Griffin W L, Zhang, Ming, Wang Rucheng, Jiang Shaoyong, Shu Liangshu. 2008. Where was South China in the Rodinia supercontinent? Evidence from U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 164, 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.03.002
Yao Jinlong, Shu Liangshu, Santosh M, Li Jinyi. 2013. Geochronology and Hf isotope of detrital zircons from Precambrian sequences in the eastern Jiangnan Orogen:Constraining the assembly of Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science. 74, 225-243. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.010
Yao Jinlong, Shu Liangshu, Santosh M, Zhao Guochun. 2014.Neoproterozoic arc-related mafic-ultramafic rocks and syncollision granite from the western segment of the Jiangnan Orogen, South China:constraints on the Neoproterozoic assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 243:39-62. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.027
Zeng Wen, Zhou Hanwen, Zhong Zengqiu, Zeng Zhaoguang, Li Huimin. 2005. Single zircon U-Pb ages and their tectonic implications of Neoproterozoic magmatic rocks in southeastern Guizhou, China[J]. Geochemica, 34(6):548-556 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200506002
Zhang Shaobing, Wu Rongxin, Zheng Yongfei. 2012a. Neoproterozoic continental accretion in South China:geochemical evidence from the Fuchuan ophiolite in the Jiangnan orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 220-221:45-64. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.07.010
Zhang Yuzhi, Wang Yuejun, Fan Wweimin, Zhang Aimei, Ma Liyan. 2012b. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the metasomatised source for the Neoproterozoic (~825 Ma) high-mg volcanic rocks from the Cangshuipu area (Hunan Province) along the Jiangnan domain and their tectonic implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 220-221:139-157. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.07.003
Zhang Chuanlin, Santosh M, Zou Haibo, Li Haikun, Huang Wencheng. 2013. The Fuchuan ophiolite in Jiangnan Orogen:geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and implications for the Neoproterozoic assembly of South China[J]. Lithos 179:263-274. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.08.015
Zhang Feifei, Wang Yuejun, Fan Weiming, Zhang Aimei, Zhang Yuzhi. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of the Neoproterozoic granites in the central of Jiangnan uplift[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35 (1):73-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201101008
Zhao Guochun, Cawood P A. 1999. Tectonothermal evolution of the Mayuan assemblage in the Cathaysia Block:implications for Neoproterozoic collisionrelated assembly of the South China craton[J]. American Journal of Science, 299:309-339. doi: 10.2475/ajs.299.4.309
Zhao Guochun, Cawood P A. 2012. Precambrian geology of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 222-223:13-54. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017
Zhao Junhong, Zhou Meifu, Yan Danping, Zheng Jianping, Li Jianwei. 2011. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:no connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J]. Geology, 39:299-302. doi: 10.1130/G31701.1
Zhao Junhong, Zhou Meifu. 2009. Neoproterozoic high-Mg basalts formed by melting of ambient mantlein South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 233:193-205. https://core.ac.uk/display/38034939
Zheng Yongfei, Zhang Shaobing, Zhao Zifu, Wu Yuanbao, Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Wu Fuyuan. 2007. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 96:127-150. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.003
Zheng Yongfei, Wu Rongxin, Wu Yuanbao, Zhang Shaobing, Yuan Honglin, Wu Fuyuan. 2008. Rift melting of juvenile arc-derived crust:Geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 163:351-383. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.01.004
Zhong Yufang, Ma Changqian, Lin Guangchun, Xu Haijin, Wang Rrenjing. 2005. The SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of zircons from the composite batholith of Jiulingshan granitoids, Jiangxi Province[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences. 30(6):685-691 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Meifu, Kennedy A K, Sun Min, Malpas J, Lesher C M. 2002a.Neoproterozoicarc related mafic intrusions along the northern margin of South China:Implications for the accretion of Rodinia[J]. The Journal of Geology, 110 (5):611-618. doi: 10.1086/341762
Zhou Meifu, Yan Danping, Kennedy A K, Li Yunqian, Ding Jun. 2002b. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196 (1/2):51-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fa451c838d83ba45f2729cf180d2373c
Zhou Jincheng, Wang Xiaolei, Qiu Jiansheng, Gao Jiangfeng. 2004.Geochemistry of Meso and Neoproterozoic mafic ultramafic rocks from northern Guangxi, China:Arc or plume magmatism?[J]Geochemical Journal, 38 (2):139-152. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.38.139
Zhou Jincheng, Wang Xiaolei, Qiu Jiansheng. 2009. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic mafic rocks and sandstones from northeastern Guizhou, South China:Coeval arc magmatism and sedimentation[J]. Precambrian Research, 170:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.11.002
丁炳华, 史仁灯, 支霞臣, 郑磊, 陈雷. 2008.江南造山带存在新元古代(850Ma)俯冲作用来自皖南SSZ型蛇绿岩锆石SHRIMP UPb年龄证据[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 27(5):375-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.05.001 董树文, 薛怀民, 项新葵, 马立成. 2010.赣北庐山地区新元古代细碧-角斑岩系枕状熔岩的发现及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 37(4):1021-1033. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.017 段政, 邢光福, 廖圣兵, 褚平利, 黄文成, 朱延辉. 2017.江南造山带东段九岭新元古代复式花岗岩源区性质的差异:来自地球化学及锆石Hf同位素的制约[J].岩石学报, 33(11):3610-3634. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201711019 高林志, 戴传固, 丁孝忠, 王敏, 刘燕学, 王雪华, 陈建书. 2011.侵入梵净山群白岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及白岗岩底砾岩对下江群沉积的制约[J].中国地质, 38(6):1413-1420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.001 高林志, 戴传固, 刘燕学, 王敏, 王雪华, 陈建书, 丁孝忠, 张传恒, 曹茜, 刘建辉. 2010.黔东南-桂北地区四堡群凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J].地质通报, 29(9):1259-1267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.09.001 葛文春, 李献华, 李正祥, 周汉文, 李寄嵎. 2001.桂北新元古代两类强过铝质花岗岩的地球化学研究[J].地球化学, 30:24-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX200101003.htm 黄兰椿, 蒋少涌. 2012.江西大湖塘钨矿床似斑状白云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及成因研究[J].岩石学报, 28 (12):3887-3900 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201212008 胡世玲, 王松山, 桑海清, 裘冀, 刘家远.应用40Ar/39Ar快中子活化定年技术探讨江西九岭花岗闪长岩体的早期侵位时代[J].岩石学报, 1(3):29-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB198503002.htm 李凤春, 侯明兰, 栾日坚, 林培军, 李增胜, 赵龙, 王继林, 徐爽. 2016.电感耦合等离子体质谱仪与激光器联用测量条件优化及其在锆石U-Pb定年中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 35(1):17-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykcs201601005 李献华, 李正祥, 葛文春, 周汉文, 李武显, 刘颖. 2001.华南新元古代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义.矿物岩石地球化学通报[J], 20(4):271-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.019 马铁球, 陈立新, 柏道远, 周柯军, 李纲, 王先辉. 2009.湘东北新元古代花岗岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 36(1):65-73. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090104&flag=1 舒良树. 2012.华南构造演化基本特征[J].地质通报, 31(7):1035-1053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003 王孝磊, 周金城, 邱检生, 高剑峰. 2004.湘东北新元古代强过铝花岗岩的成因:年代学和地球化学证据[J].地质论评, 50(1):65-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.01.009 王孝磊, 周金城, 邱检生, 张文兰, 柳小明, 张桂林. 2006.桂北新元古代强过铝花岗岩的成因:锆石年代学和Hf同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 22(2):326-342. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200602007 薛怀民, 马芳, 宋永勤, 谢亚平. 2010.江南造山带东段新元古代花岗岩组合的年代学和地球化学:对扬子与华夏地块拼合时间与过程的约束[J].岩石学报, 26(11):3215-3244. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201011006 徐先兵, 汤帅, 李源, 章泽军. 2015.江南造山带东段新元古代至早中生代多期造山作用特征[J].中国地质, 2015, (1):33-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.004 鄢圣武, 白宪洲, 伍文湘, 朱兵, 詹琼窑, 文龙, 杨辉, 王玉婷. 2017.扬子地块西缘新元古代泸沽A型花岗岩成因与变泥质岩熔融[J].中国地质, 44(1):136-150. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170110&flag=1 张菲菲, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 张爱梅, 张玉芝. 2011.江南隆起带中段新元古代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素组成研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 35(1):73-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.01.008 曾雯, 周汉文, 钟增球, 曾昭光, 李惠民. 2005.黔东南新元古代岩浆岩单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].地球化学, 34(6):548-556. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.06.002 钟玉芳, 马昌前, 佘振兵, 林广春, 续海金, 王人镜, 杨坤光, 刘强. 2005.江西九岭岩类复式岩基锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 30(6):685-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200506005 -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王海,付海平,李永胜,钟福军,王颖,吉鸿杰,徐林,胡朗明,杨世彪. 江西通江岭铜(钨)矿床石榴子石和锆石LA-ICP-MS原位U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地质学报. 2023(07): 2281-2292 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王先广,曹圣华,龚良信,胡正华,曹明轩,张德富,陈麒如. 江西钨锡多金属矿床成矿系列与找矿. 地球学报. 2023(05): 916-932 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 高任,谢桂青,冯道水,纪云昊,钟浩,张磊. 江西武山铜矿区新发现钨矿(化)体特征和其成因——来自矿相学、白钨矿原位U-Pb年代学和元素地球化学的约束. 矿床地质. 2023(06): 1139-1158 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高任,谢桂青,查志强,童继中,樊涛,章平,罗建安. 江西城门山铜矿床伴生稀散金属矿化特征及其地质意义. 地质与勘探. 2022(03): 514-531 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 毛景文,周涛发,谢桂青,袁峰,段超. 长江中下游地区成矿作用研究新进展和存在问题的思考. 矿床地质. 2020(04): 547-558 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 毛景文,吴胜华,宋世伟,戴盼,谢桂青,苏蔷薇,刘鹏,王先广,余忠珍,陈祥云,唐维新. 江南世界级钨矿带:地质特征、成矿规律和矿床模型. 科学通报. 2020(33): 3746-3762 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 胡正华,王先广,陈毓川,周卫,王彦媛,龚良信,杨舒钧. 江南钨矿带(江西段)成矿规律. 中国钨业. 2020(05): 10-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨世文,楼法生,丁沛勋,张芳荣. 赣北中生代岩浆作用与钨成矿特征. 中国钨业. 2020(05): 53-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: