Discussion on the initial timing of the Indosinian movement in the Ordos basin and the Sichuan basin: Constraints from growth strata evidence
-
摘要:
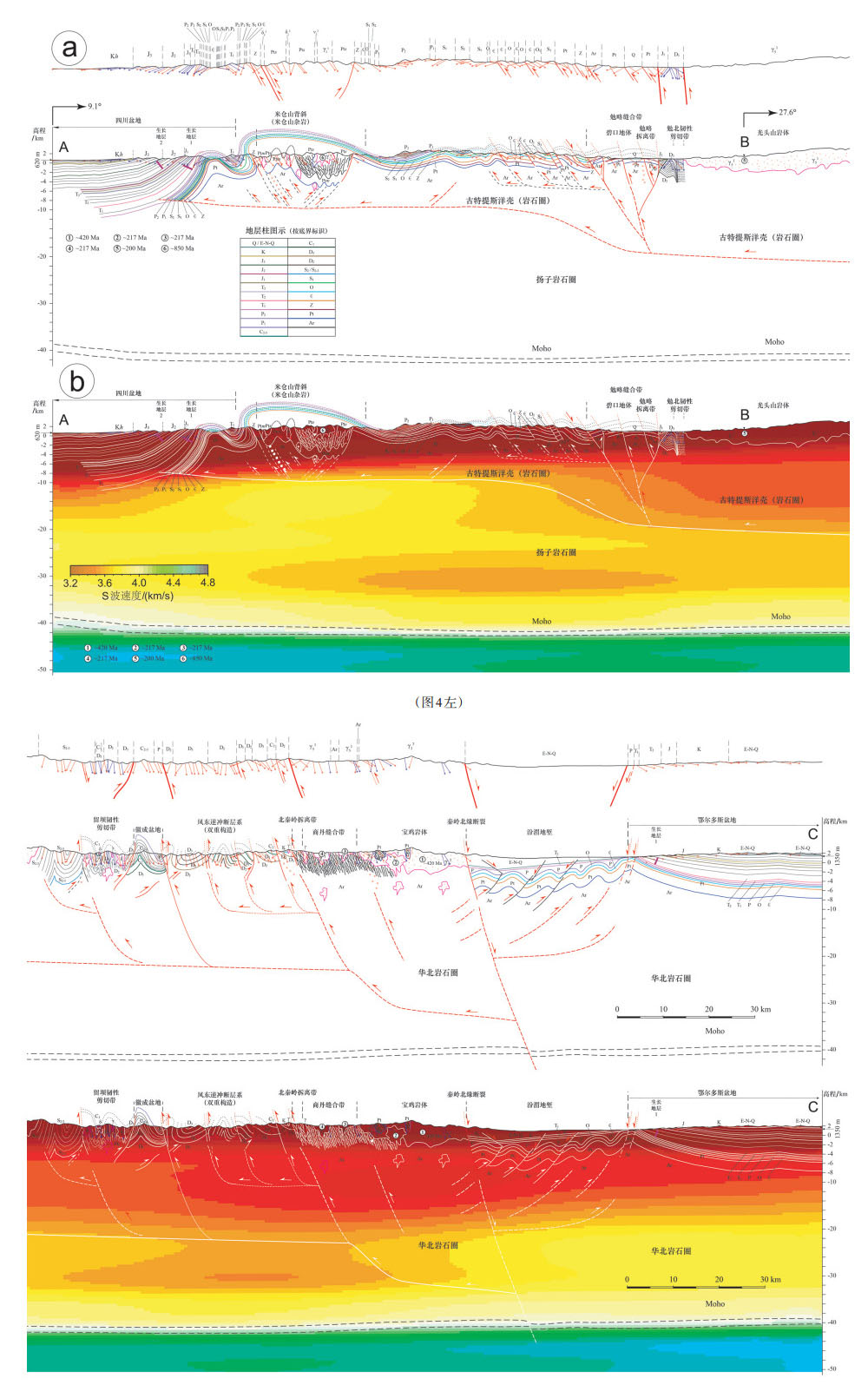
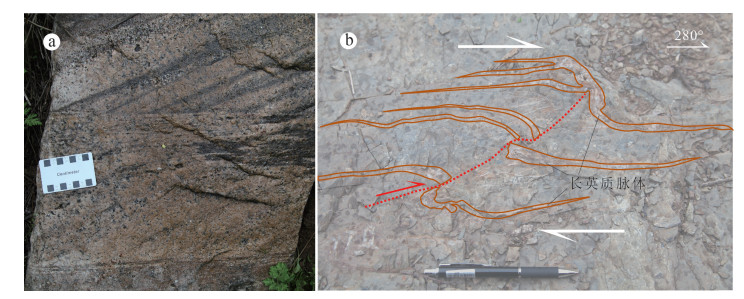
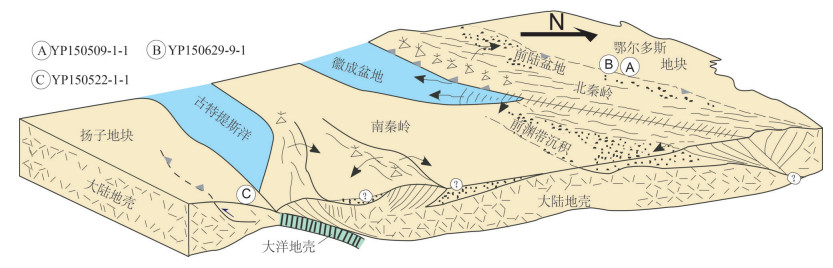
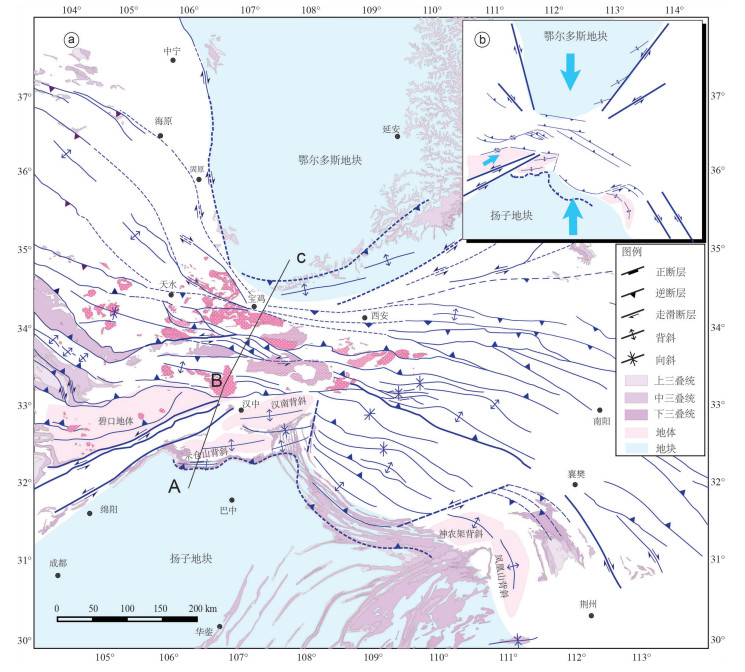
造山带的形成、演化与周缘盆地受统一构造事件影响,"盆"与"山"在构造和沉积方面相互耦合,沉积盆地存在造山事件的响应,如生长地层、包卷层理等。生长地层为同构造或同变形阶段沉积,其沉积时代可以有效约束构造事件时代。中央造山带近东西向展布,北侧为鄂尔多斯地块,南侧为扬子地块。中央造山带的形成主要源于原-古特提斯洋的闭合,原特提斯洋在早古生代闭合,古特提斯洋在中生代闭合,后者改造前者并响应全球印支运动。印支运动的启动,一方面促使现今中国大陆雏形的形成,另一方面响应Pangea超大陆的最终汇聚,具有重要的大地构造意义。古特提斯洋闭合,华南地块和华北地块汇聚拼贴,并在鄂尔多斯盆地和四川盆地沉积地层中保留了很好的记录。笔者在鄂尔多斯盆地南缘上三叠统识别出一套生长地层,通过最年轻碎屑锆石与区内相同地层凝灰岩锆石对比,限定印支运动启动时间为233 Ma左右;在四川盆地北缘上三叠统须家河组识别出一套生长地层,通过对比分析,推测印支运动启动时间为216 Ma左右。
Abstract:The formation and evolution of the orogenic belt and the peripheral basin were controlled by some genetic tectonic events. The "basin" and "range" are coupled to some extent both in structure and sedimentation. Sedimentary structures can always respond to related orogenic events, such as growth strata and convolute bedding. Growth strata are sedimentary records of the tectonic events, and the analysis of their deposit age can effectively constrain the timing of the tectonic events. The Central China Orogen is distributed in the east-west direction. The north side of the central segment is the Ordos block, and the south side is the Yangtze block. The Central China Orogen mainly resulted from the closure of the Pro-Paleo Tethys Ocean, the extinction of ProTethys Ocean happened in the Paleozoic and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean was closed in the Mesozoic. Notably, the latter modified the orogen resulting from the former and responded to the global Indosinian movement. The Indosinian movement not only facilitated the final assembly of supercontinent Pangea, but also was of great significance in the formation of the rudimentary sketch of China's mainland today. In the process of the Indosinian movement, the South China block and the North China block were collaged, and the Indosinian movement was initiated. The Ordos Basin and the Sichuan Basin recorded the orogenic events well in sedimentary strata. In this paper, the authors identified growth strata in the Upper Triassic on the south margin of the Ordos Basin. The starting time of the Indosinian movement in the Ordos Basin is about 233 Ma. A sets of growth strata were identified in the Upper Triassic on the north margin of the Sichuan Basin and the start time was about 216 Ma.
-
1. 引言
黄河自桃花峪的出山口至垦利县的入海口称为黄河下游段。黄河下游河道为强烈堆积型河道,河水泥沙含量高且落淤强烈,致使黄河的河床高出背河地面数米,形成世界上著名的地上悬河(魏常兴等,2002)。黄河水位高于两岸的地下水位,河水源源不断地渗漏进含水层补给地下水,黄河侧渗补给地下水的宽度被称为黄河影响带(赵云章等,2003)。黄河影响带反映的是黄河水对两岸地下水的直接作用能力,黄河影响带的确定是地表水-地下水转换关系方面研究的重点与难点(刘昌明等,2020)。黄河水的渗漏是引起黄河径流量损失的原因之一,影响带内的地下水水质水量对黄河水有积极的响应。黄河影响带的确定不仅是黄河下游区地下水系统划分和水循环研究的基础,同时也关系着沿黄区水资源的利用、水循环强度和区域发展等问题(曹剑峰等,2005;张金良等,2018;董战峰等,2020)。
关于黄河下游侧渗影响带的研究主要集中在21世纪初,在小浪底水库建成前和刚建成的几年内,赵云章(2003, 2004)、平建华(2004)、崔亚莉(2005)等学者基于地下水流场、氢氧稳定同位素和氚同位素的分析等进行了大量的研究,刻画出小浪底水库运行初期黄河侧渗影响带,为沿黄区水资源评价提供基础依据。当前,小浪底水库已运行20年,黄河下游平原下垫面发生了显著变化,黄河不再断流,河道下切明显(王英珍等,2020;余阳等,2020)。在小浪底水库建立运行20年后,黄河水和两岸地下水联系程度是否发生变化?决定黄河影响带变化的因素是什么?掌握此类问题不仅可以提高对黄河下游区域水循环的认识,同时,有利于黄河下游区水资源的合理开发利用和生态环境的保护。
地下水动力场是地下水流动的直接表现,反映出地下水流动的驱动力。地下水中的稳定同位素2H、18O和放射性同位素3H的含量随着水体的运移和转化呈现出不同的特征,能够反映出不同水体的联系和转化过程。国内外大量的研究成果表明上述方法在水体运移和转化中的适用性(孙从建,2018;Joshi et al., 2018;陈松等,2019;苏晨等,2019;Birks et al., 2019;Jiang et al., 2019;Su et al., 2020)。以往的黄河影响带研究也正是在地下水动力条件的基础上,结合此类同位素示踪而展开的,取得了丰硕的成果(赵云章等,2004;王福刚,2006;史超,2009)。
本次基于2020年黄河下游平原区地下水位统测(5个点/100 km2的监测密度)和地下水-地表水样品的数据,以黄河下游平原区地下水的动力特征为基础,结合稳定同位素2H、18O和放射性同位素3H,确定小浪底水库运行后20年后黄河侧渗的影响范围及其变化,并分析黄河影响带演变的控制因素,以及黄河对沿岸水环境的影响。本次研究可为黄河下游沿黄区地下水和地表水资源的科学管理提供依据,是黄河下游区生态环境可持续发展和高质量发展的基础内容。
2. 研究区概况
黄河自河南桃花峪出山至山东垦利入海之间被称为黄河下游段(图 1),此时的黄河主要在黄淮海平原内流动,黄河下游干流区北部为海河平原,南部为淮河平原。黄河下游段处于暖温带半湿润、半干旱季风气候区,多年平均气温11~14.5℃,多年平均降水量为571.0~762.9 mm(平建华等,2004)。黄河水、大气降水和农业灌溉水为黄河下游两岸的地下水系统提供了丰富的水资源(崔亚莉等,2005)。
小浪底水库是黄河进入下游段之前的最后一道蓄水工程,自1999年运行以来,下游黄河来水来沙得到改善,最为突出的是黄河不再断流,河床得到普遍侵蚀下切,同流量下河水水位普遍降低,河床行洪能力较以前有所提高,黄河年内水位流量基本稳定(尚红霞等,2008;刘慰等,2020)。但是,黄河的地上悬河状态没有改变,河水仍然是沿岸地下水的主要来源。
黄河下游段两岸地区可分为剥蚀溶蚀丘陵、冲洪积平原、冲积扇平原、黄河冲积平原、冲积海积平原、海积平原、三角洲平原七种地貌单元(图 1)。黄河侧渗主要发生在冲积平原和冲积扇平原浅部的松散岩类孔隙含水层内。浅部含水层主要由全新统、上更新统的砂层组成,含水层厚度30~80 m(图 2)。浅部地下水主要接受大气降水的入渗、灌溉水的入渗和黄河水的渗漏等补给,地下水开采、潜水蒸发和侧向径流是浅层水的主要排泄方式。地下水总体流动方向呈现出以黄河为中心,向东北和西南方向流动的趋势。
3. 研究方法及样品分析
3.1 地下水动力场分析
本次基于2019年5月对黄河下游区浅层地下水位的统测,刻画出黄河下游区地下水的流动方向和流动特征,进而判断地下水受到黄河影响的范围。本次统测在15 d内完成,对黄河下游两岸约70000 km2内3500多眼井的水位进行测量,地下水位点的测量基本基于浅层井完成。本次水位统测的时长符合要求,统测密度约为5个/100 km2,符合统测要求,能够较为准确地刻画出地下水的流动特征。
3.2 同位素样品的采集和分析
选取垂直黄河的剖面进行黄河影响带的研究。样品采集主要考虑:(1)在黄河从下游出山至黄河入海之间,在上段和下段均有样品的采集;(2)地下水样品主要沿着黄河南北两岸地下水的流动方向采集,以便能更加真实地反映黄河的影响特征;(3)样品的选取基本在浅层水,排除深层水对分析的影响。
在查明研究区内水文地质条件和地下水动力特征的基础上,于2019年5月在黄河下游平原内垂直黄河的2个剖面(剖面位置见图 3)——A-A'剖面(花园口剖面)和B-B’剖面(济阳剖面)上,分别采取黄河水和沿岸地下水样品。本次共采集水体样品26组,其中包括浅层水样品24组, 黄河水样品2组。水样主要进行稳定同位素2H、18O和放射性同位素3H的测试。样品测试在中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所完成,样品的采集、处理、分析测试均符合国家质量认证标准,误差在允许范围内。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1 黄河影响带的分布
4.1.1 地下水流动特征反映的黄河影响带分布
黄河下游平原浅层地下水的流动特征为:以黄河为中心轴,地下水呈放射状向东南和东北方向流动(图 3)。但在黄河近岸地区,受黄河水向两岸含水层侧渗的影响,地下水的流向表现出垂直黄河河道的特征。因此,基于黄河近岸区地下水的流动方向可判断黄河的侧渗影响范围(赵云章等,2003)。对于没有形成明显的局部地下水位降落漏斗的区域,黄河影响带主要为地下水流向近似垂直河道的区域。在黄河沿岸地下水开采程度强烈区,即已形成明显的局部地下水位降落漏斗的区域内,黄河影响带边界为地下水位降落漏斗外侧的地下水分水岭。
基于浅层地下水的流场特征(图 3),北岸的影响带基本与天然文岩渠、金堤河、徒骇河等河流平行,且黄河侧渗影响已至此类河流的北侧。黄河南岸河南境内目前受地下水开采强度大的影响,已经形成了郑州漏斗和开封漏斗,在漏斗外侧存在分水岭。受到漏斗的影响,分水岭以北区域黄河渗透的水体向漏斗中心汇集。在济南以东的滨海地区,黄河水和地下水的联系程度减弱,黄河的侧渗影响范围相对于其上游明显较小,集中在河道南北两岸5 km以内的范围。
当前,黄河以北的影响带范围大于黄河以南的区域,北部的影响带最大可至25 km,南部的影响带最大可至15 km;黄河河南段的影响带大于山东段的影响带,河南境内的影响带多位于15~25 km范围内,而山东境内的黄河影响带多位于5~15 km范围内;黄河在新乡—开封等区域的影响带最大,可至25 km,而在黄河临海的区域最小,仅在5 km范围内。
4.1.2 同位素18O和3H反映的影响带分布
地下水中的同位素含量随着水体运移而发生规律性变化,是寻求不同水体联系和转化的重要手段(Su et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2019)。黄河水和大气降水是黄河下游段两岸地下水的主要补给源,两者在稳定同位素δ18O值和放射性同位素3H的含量上存在明显的差别,为研究黄河影响带的范围提供了依据(史超,2009)。影响带范围内,浅层水的δ18O值随着距离变化的图形上,呈现出以黄河水为最低的“∨”型变化;在3H含量随着距离变化的图形上,呈现出以黄河水为最高的“∧”型变化。在影响带的边界,地下水基本呈现出大气降水的同位素特征。
从花园口剖面A-A'(图 4)可见,浅层水的δ18O值曲线和3H含量曲线均体现出“∨”型变化和“∧”型变化,虽然在变化过程中存在起伏,但总体趋势能反映出黄河的影响范围。在黄河北岸的A1#点和A2#点处,无论是同位素含量还是水化学类型均与北岸靠近黄河的地下水有明显的差别。A1#点和A2#点处地下水的3H含量迅速增大至高于黄河水的氚值,而地下水的δ18O值接近大气降水的δ18O值。由此可见,A2#点附近为黄河影响范围的北边界,花园口剖面处黄河影响带北部范围为20~25 km。影响带范围外的地下水受降水入渗的影响,同位素特征明显向着大气降水靠近。
花园口剖面黄河南岸地下水的δ18O值低于黄河北岸地下水的δ18O值,而3H含量却高于黄河北岸地下水值。南岸近岸地下水的δ18O值和3H含量更接近黄河水,表明黄河水对南岸近岸区地下水的影响程度较大。南岸地下水自A11#点起向南(远离黄河的方向),δ18O值和3H含量基本呈现出稳定的状态,接近大气降水的同位素含量,反映出黄河南岸的影响带范围在A11#点附近,距离黄河约15 km。黄河南岸已形成地下水降落漏斗,降落漏斗的形成加速了黄河水渗漏补给的速率,强烈地袭夺黄河水,因此,南岸影响带内地下水同位素特征更加接近黄河水。南岸影响带边界主要受控于漏斗,地下水自南向北流动的天然特征和以漏斗为中心的流场达到平衡,因此,南岸影响带范围内的同位素含量均维持在较为稳定的水平。基于上述分析可知,花园口剖面内黄河影响带南部范围在15 km以内。
济阳剖面B-B'内,浅层水的δ18O值曲线和3H含量曲线也体现出“∨”型变化和“∧”型变化(图 5)。该剖面处于冲积平原和海积平原的过渡区,地下水的径流条件远不及其西部平原,相对于花园口剖面,地下水的3H含量较小,δ18O值较低。
从图 5可见,在北岸B2#点和南岸B11#点之间,地下水的同位素含量比较稳定,同黄河水较为接近。在北岸B2#点北侧(远离黄河方向)和南岸B11#点南侧(远离黄河方向),地下水的3H含量显著增大,δ18O值向着大气降水的方向移动。由此可知,在济阳剖面,黄河的影响带范围在北岸B2#点和南岸B11#点之间,北岸影响带宽度约13 km,南岸宽度约10 km。
4.1.3 现状黄河影响带范围的界定
区域地下水流动特征反映的是黄河影响带的整体分布情况,典型剖面仅是对影响带局部特征的进一步刻画和验证。从地下水流动特征反映的影响带可见,在花园口附近,黄河北岸的影响带为25 km左右,黄河南岸的影响带在15 km左右;在济阳附近,黄河北岸的影响带为15 km左右,黄河南岸的影响带在10 km左右。在花园口剖面和济阳剖面处,同位素信息反映的黄河影响带范围和水动力场表现出的影响带范围接近。由此可见,水动力场刻画的黄河影响带是合理和可靠的。
本次研究认为黄河影响带范围最大处在新乡—郑州方向,北岸的影响大最大达到25 km,最小的影响带范围在黄河入海前的海积平原,影响带范围在5 km以内。随着黄河出山至入海口,随着黄河悬河特征的减缓,影响带范围有减小的趋势。
4.2 黄河影响带范围的变化和影响因素
4.2.1 黄河影响带范围的变化程度
小浪底水库运行初期,黄河影响带的范围主要为(史超,2009;赵云章等,2014):河南境内10~20 km,山东境内10~15 km,黄河北岸的影响带在天然文岩渠、金堤河和徒骇河南侧,黄河南岸区受地下水开采的影响,黄河影响带在地下水降落漏斗南侧。相比于小浪底水库运行初期,当前的黄河影响带范围已经发生了一定的变化。在黄河下游段河南境内,黄河影响带有增大的趋势,尤其在黄河北岸的新乡县、开封县附近,影响带增大了5 km,当前的黄河影响带范围已达25 km左右。在黄河下游的济南以东区域,黄河影响带的范围变化不明显,而在鲁东沿海地区,黄河影响带范围甚至有减小的趋势(图 6)。
4.2.2 黄河影响带变化的因素
(1)黄河河床介质的变化
黄河河床是黄河向含水层渗漏的直接通道。受小浪底水库调水冲砂的控制,黄河河道淤积情况得到较为明显的改善,河道内沉积的渗透性较差的淤泥物质逐步被冲刷,河床逐渐粗化(彭红等,2009)。
据黄河下游水文站监测数据(彭红等,2009),在小浪底水库运行后,同一测站相同流量下的黄河的水位下降了1~2 m,反映出河道下切深度至少和此量相当(图 7)。当前河床沉积物的中值粒径比值为1.5~2.1,全下游主槽床沙化明显。在小浪底水库运行后,黄河河道下切是明显的特征,由此带来的直接影响就是河床沙化,渗透性增强,黄河测渗断面增大。
(2)黄河侧渗的能量变化
黄河水位和沿岸地下水的水头差,是黄河侧向流动的动力。基于黄河下游水文站实测资料的统计,小浪底水库运行以来,黄河水位呈现出逐年降低的趋势(图 8)。2008—2018年,黄河水位累计下降2 m左右,不同水文站处有一定的差别,花园口水文站处黄河水位下降较大,利津水文站处下黄河水位下降较小。
黄河沿岸是人类活动的重要区域,地下水开采强烈,地下水位呈现出逐渐下降的趋势,尤其是黄河北岸的华北平原区,地下水位下降程度较大。在黄河入海前的海积平原内,由于两岸主要为矿化度大于2 g/L的咸水,地下水开发利用程度较低有关,地下水并没有表现出明显的下降趋势。从花园口站和利津站处不同年份的水位变化可看出黄河水和沿岸地下水的水位变化特征(图 9)。
在黄河南北两岸的广大平原内,地下水的下降程度大于黄河水位的下降程度,使得黄河和地下水的水位差增大,黄河水的侧向流动动力增强。此外,黄河南北两岸冲积平原内,含水层主要以砂层为主,渗透系数相对较大,地下水流动能力较强,因此,黄河水的测向流动范围扩大。在黄河入海前的海积平原内,虽然黄河水位下降约1 m,但沿岸地下水的水位没有明显的变化。黄河水和沿岸地下水的水头差变小,地下水的侧向径流动的动力减弱,因此,在黄河入海前的区域内,黄河的影响带范围呈现出逐渐变小的趋势。
(3)黄河侧渗的补给源变化
黄河水在径流途中,逐步下渗补给地下水,然后随着地下水向远离河岸的方向流动。黄河水是黄河影响带范围内地下水的重要补给源。
在小浪底水库运行前,黄河下游经常性出现断流现象(陈霁巍,2000)。枯水期河道干枯,黄河水对地下水基本不产生直接影响,不能提供黄河侧向流动的物质来源。
在小浪底水库运行后,黄河下游现断流的现象不复存在。小浪底水库的调蓄作用,控制黄河径流量平缓而稳定(图 10),黄河水源源不断地向含水层渗漏,为地下水侧向径流提供了持续的物质来源。
(4)黄河影响带变化的决定因素
黄河影响带主要由介质条件,补给源条件和能量条件影响。在小浪底水库运行后,黄河下游河床沙化明显,河床渗透性增强,提高了黄河水的渗漏能力。此外,黄河不再断流,黄河水可源源不断地渗漏补给沿岸的地下水,提高了黄河水的物质来源持续时间。介质条件和补给条件为黄河侧渗提供了物质和流通基础。但是,在黄河下游入海前的海积平原内,黄河的影响带范围并没有发生明显的扩大现象,甚至出现影响带范围缩小的趋势。在海积平原内,黄河水位和沿岸地下水的水头差减小,黄河侧渗的能量条件变弱。由此可见,黄河水和沿岸地下水的水头差,是黄河影响带的决定因素,即能量条件是决定黄河影响带的决定因素。
4.3 黄河对地下水环境的影响
小浪底水库运行后,黄河下游段最为明显的特征为黄河河道下切、黄河河床沙化、黄河水位降低和黄河流量持续。在此类河道和水文条件变化的基础上,除东部海积平原,黄河下游平原普遍发生黄河侧渗影响带扩大的现象。黄河水渗漏能力的增强,也增强了黄河对沿岸含水层水质水量的影响。
黄河水是黄河影响带内地下水的主要补给源,黄河水渗漏到含水层中,其本身的水化学组分也进入到含水层中。当前,黄河下游的水质类型主要为HCO3·SO4型和HCO3·SO4·Cl型。沿着黄河流动的方向,黄河水的矿化度、总硬度、HCO3-、Cl-、SO42-等离子含量都呈增加之势。在小浪底水库运行后,黄河河道下切和河床沉积物的沙化,意味着河床对黄河水的“过滤和净化”能力减弱,区域地下水质对黄河水的积极响应将更加明显。
虽然黄河水的水质只是影响沿黄区地下水质量的一方面,水质背景含量和沿黄区的人类生产和生活带来的废水也是直接影响地下水质的重要因素(高宗军等,2010;Sun et al., 2017;Yang et al., 2017)。但是,源头的水质控制和改善是提高沿黄区水质的起点。黄河侧渗影响带的扩大意味着黄河水质的影响范围增大。此外,黄河两岸引黄灌区分布众多,此类地区主要靠黄河水直接灌溉,若黄河水质没有得到有效的控制和改善,则相当于将“差水”直接远源补给进入含水层中,进一步影响地下水质。因此,黄河水质的改善和控制,是当前亟需解决和重点关注的问题(石建省等,2000;吕振豫等,2017)。
当前,黄河流域高质量发展是目标,黄河下游区发展是重点,而保质保量的水资源是发展的基础(刘昌明等,2020;贾绍凤等,2020)。黄河水渗漏补给及引黄灌溉渗漏补给是黄河影响带内特有的地下水补给方式。在控制和改善黄河水质的基础上,适当地增加浅层地下水的开采量,可促进地下水的循环,缩短地下水的更新周期,从而降低蒸发浓缩作用以及人类活动产生的污水和废水对浅层地下水质量的影响,可为黄河下游区发展提供可靠的水源保障。
5. 结论
基于地下水动力场的刻画,地下水-地表水的18O和3H同位素含量分布特征的分析,本次研究认为:
(1)在小浪底水库运行20年后,黄河影响带在济南以西地区有明显增大,在济南以东地区有略微减小的趋势。当前黄河下游侧渗影响范围主要为5~25 km,最大的影响带位于郑州—新乡方向,可至25 km,最小的影响带在东部沿岸区域,影响带范围仅5 km。
(2)黄河河道的介质条件和黄河的补给条件为黄河侧渗提供了物质和流通基础。黄河水和沿岸地下水的水头差,是黄河影响带的决定因素。
(3)小浪底水库运行后,河道下切,河床渗透性增强,降低了河床物质对黄河水的“吸附和净化”能力。保护和控制黄河的水质,是黄河下游区地下水资源保护的基础,是黄河流域高质量发展的基础。
致谢: 本文在完成的过程中,参与过野外工作的有李江瑜、史建杰、张艳国、罗英杰等;室内工作得到王亚莹和苗慧心等人的帮助,在此一并致谢。 -
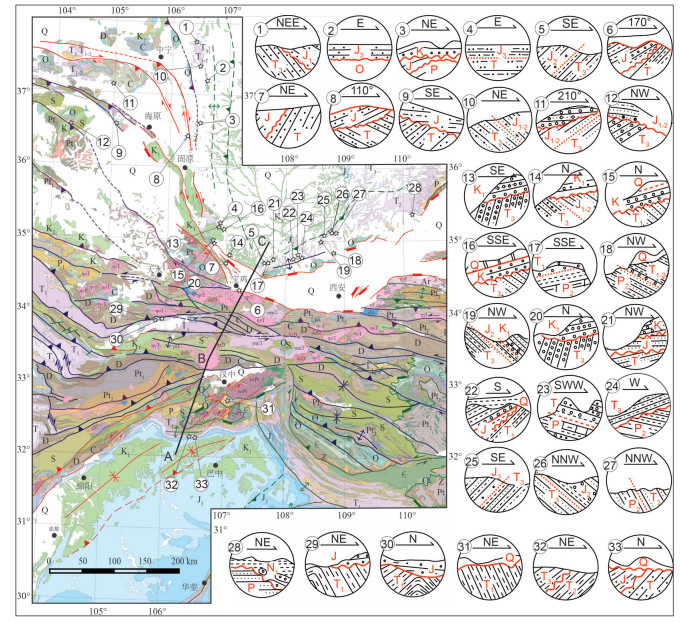
图 3 研究区区域角度不整合接触
(1~9据Guo et al., 2017;10~15据Chen et al., 2007;16~19据时建超,2010; 20~28据高飞,2009;29~33为本文资料)
Figure 3. Regional unconformity contacts in the study area
(1~9 after Guo et al., 2017; 10~15 after Chen et al., 2007; 16~19 after Shi, 2010; 20~28 after Gao, 2009; 29~33 in this study)
表 1 华北地块和华南地块汇聚代表性模型
Table 1 Classic convergence models between North and South China blocks

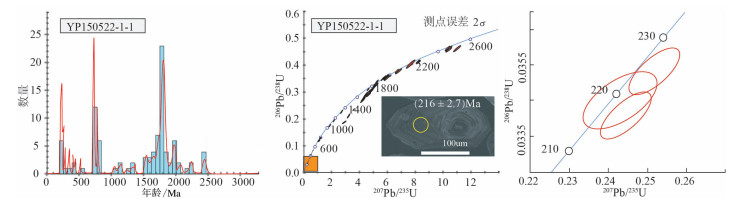
表 附表2 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘和四川盆地北缘生长地层最年轻碎屑锆石U-Pb同位素测试数据
Table 附表2 Zircon U-Pb isotope data of the youngest zircon U-Pb ages of the growth strata from the southern margin of Ordos basin and the northern margin of Sichuan basin

-
Andersen T. 2005. Detrital zircons as tracers of sedimentary provenance:Limiting conditions from statistics and numerical simulation[J]. Chemical Geology, 216(3/4):249-270. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009254104004796
Bian Qiantao, Luo Xiaoquan, Li Dihui, Zhao Dasheng, Chen Haihong, Xu Guizhong, Chang Chengfa, and Gao Yanlin. 2001.Geochemistry and formation environment of the Buqingshan ophiolite comples, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(1):45-55(in Chinese with English abstract).
Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, Aleinikoff J N, Davis D W, Korsch R J. 2003. TEMORA 1:A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic UPb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 200(1/2):155-170. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009254103001657
Chang E Z. 1996. Collision orogen between north and south china and its eastern extension in the korean peninsula[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 13(3/5):267-277.
Chang Yuan, Xu Changhai, Peter W.Reiners, and Zhou Zuyi. 2010.The exhumation evolutioin of the Micangshan Hanan uplift since Cretaceous:Evidence from apatite (U-Th)/He dating[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(4):912-919(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Gang, Wang Zhiwei, Bai Guojuan, Sun Jianbo, Zhang Huiruo, Li Xiangdong. 2007. Meso-Cenozoic peak-age events and their tectono-sedimentary response in the Ordos basin[J]. Geology in China, 34(3):375-383. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200703002
Chen J L, Xu X Y, Wang Z Q, Yan Q R, Wang H L, Zeng Z X, and Li P. 2008. Geological featuresand SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the Yanwan-Yinggezui ophiolitic melange in the Taibai area, West Qinling, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27:500-509. http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-zqyd200804008.htm
Chen Xuanhua, Li Jiangyu, Dong Shuwen, Shi Wei, Bai Yanfei, Zhang Yiping, and Ding Weicui. 2019. Tectonic Deformation of Jurassic Ningwu-Jingle Basin and its implication for the beginning of Yanshanian Orogeny in Central North China Craton[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(3):389-408(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201903002
Diwu C R, Sun Y, Liu L, Zhang C L, and Wang H L. 2010. The disintegration of Kuanping Group in North Qinling orogenic belts and Neoproterozoic N-MORB[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26:2025-2038.
Dong Yunpeng, Zhou Dingwu, and Liu Liang. 1995. Deformation and evolution of Songshugou ophiote in Eastern Qinling[J], Northwest Geoscience, 2:37-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK502.005.htm
Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Neubarer F, Liu X, Genser, J, and Hauzenberger C. 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen, China:Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41:213-237 doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002
Dong Y P, Liu, X M, Neubauer F, Zhang G W, Tao N, Zhang, Y G, Zhang X N, Li W. 2013. Timing of Paleozoic amalgamation between the North China and South China Blocks:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Tectonophysics, 586:173-191. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.11.018
Dong Y P, and Santosh M. 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China[J]. Gondwana Research, 29(1):1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009
Du Siqing, Wei Xiangui. 1998. The NE-SW Nappe tectonic of superposed E-W structure in Hannan-Micangshan Area[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 3:367-374(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-cdlg803.002.htm
Feng Q L, Du Y S, Yin H F, Sheng J H, Xu J F. 1996. Carboniferous radiolaria fauna firstly discovered in Mian-Lue ophiolitic melange belt of south Qinling Mountains[J]. Science in China (Series D), 39:87-91. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG1996S1010.htm
Gao Fei. 2009. Meso-Cenozoic Structural Characteristics and Its Evolution and Reformation in Weibei Area[D]. Xi'an: Northwest Universiy(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gilder S A, Leloup P H, Courtillot V. 1999. Tectonic evolution of tancheng-lujiang (tan-lu) fault via middle triassic to early cenozoic paleomagnetic data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 104(15):365-375. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3fed0f8748710f26eda61c91cd0554fb
Guan Shuwei, Li Benliang, He Dengfa, Wang Xin, and Supp J. 2007.Geometrical Methods of complicated structural analysis and their application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 42(4):722-739(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo P, Liu C, Wang J, Deng Y, Mao G, and Wang W. 2017. Detritalzircon geochronology of the Jurassic coal-bearing strata in the western Ordos Basin, North China:Evidences for multi-cycle sedimentation[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 9(6):136-154.
Huang Jiqing. 1960. The Main Characteristics of the Structure of China:Preliminary Conclusions[J]. Scientia Sinica, 9(4):492-544(in Chinese with English edition). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_b964a982a6ad9bc5b6636b9c9ce3e734
He Dengfa, Jia Chengzao, Li Desheng, Zhang Chaojun, Meng Qinren, and Shi Xin. 2005. Formation and evolution of polycyclic superimposed Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 26(1):64-77(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200501010
Jahn B M, Fan Q, Yang J J, and Henin O. 2003. Petrogenesis of the maowu pyroxenite-eclogite body from the uhp metamorphic terrane of Dabieshan:Chemical and isotopic constraints[J]. Lithos, 70(3):243-267.
Jahn B M, Chen B. 2007. Dabieshan uhp metamorphic terrane:sr-ndpb isotopic constraint to pre-metamorphic subduction polarity[J]. International Geology Review, 49(1):14-29. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.1.14
Jiang Chunfa. 1994. Main geologic-tectonic characteristics of the Central China Orogen[C]//Corpus of Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences(in Chinese).
Lan H Y, Li S Z, Li X Y, Wang P C, Somerville I D, Guo L L, Wang Q, Guo R H, Zhang J, Tao J L. 2017. Early mesozoic intracontinental deformation in the eastern North China block:Implication for an indentation model of North China to south China blocks[J]. Geological Journal, 52(S1):8-21. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321108952_Early_Mesozoic_intracontinental_deformation_in_the_eastern_North_China_Block_Implication_for_an_indentation_model_of_North_China_to_South_China_blocks
Li S G, Hou Z H, Yang Y C, Sun W D, Zhang G W, Li Q L. 2004.Timing and geochemistry characters of the Sanchazi magmatic arc in Mianlue tectonic zone, South Qinling[J]. Science in China(Series D), 47:317-328. doi: 10.1360/02YD0490
Li Fengjie, Zheng Rongcai, and Jiang Bin. 2008. Main basin and mountain coupling systems and their characteristics in China continent[J]. Lithologic Reservoris, 20(4):26-32(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxyqc200804005
Li Huaikun, Geng Jianzhen, Hao Shuang, Zhang Yongqing, Li Huimin. 2009. Research on the zircon U-Pb isotopic age by Iaser Ablation Multi-Receiver Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-MCICPMS)[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 29(1):600-601(in Chinese).
Li J H, Zhang Y, Dong S, Shi W. 2013. Structural and geochronological constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the North Dabashan zone, South Qinling, central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 64(64):99-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=31a4716cfd01eca95a9c230662d98d54
Li S Z, Jahn B M, Zhao S, Dai L, Li X, Suo Y. 2017. Triassic southeastward subduction of north China block to south China block:insights from new geological, geophysical and geochemical data[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 166:270-285. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.009
Liu S F, Li W, Wang K, Qian T, Jiang C. 2015. Late Mesozoic development of the southern Qinling-Dabieshan foreland foldthrust belt, Central China, and its role in continent-continent collision[J]. Tectonophysics, 644:220-234. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195115000591
Liu Shaofeng, Zhang Guowei. 2008. Evolution and Geodynamics of basin/mountain systems in East Qinling-Dabieshan and its adjacent regions, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(12):1943-1960(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu G, Dong S W, Chen X H, Cui J J. 2017. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of Suining Formation sandstone from the Daba Mountains, northeastern Sichuan and its stratigraphic implications[J]. Palaeoworld, 26(2):380-395. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2017.03.002
Ludwig K R. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication No. 4a, Berkeley, CA.
Leiss Otto.1990. New interpretations of geodynamics and orogeny as a result of synorogenic Cretaceous deposits within the Northern Calcareous Alps[J].Geologische Rundschau, 79(1):47-84. doi: 10.1007/BF01830447
Pei X Z, Ding S P, Li Z C, Liu Z Q, Li GY, Li R B, Wang F, Li F J. 2007. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Gabbro from the Guanzizhen Ophiolite in the North Margin of the Western Qinling and its geologic siginificance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81:1550-1561.
Qin J F, Lai S C, Li Y J. 2008. Slab breakoff model for the Triassic post-collisional adakitic granitoids in the Qinling Orogen, Central China:Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints[J]. International Geology Review 50:1080-1104. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.50.12.1080
Qiu Xinwei. 2008. Characteristics and Sedimentary Environment of Tuff in Yanchang Formation of Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Jishun. 2004. Some problems on the Kunlun-Qinling orogenic system[J]. Northwest Geolgoy, 37(1):1-5(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200401001
Shi Jianchao. 2010. The Mesozoic-Cenozoic Structural Characteristics and Its Evolution in Southern Ordos Region[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi W, Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Hu J M, Wiesinger M, Ratschbacher L, Jonckheere R, Li J H, Tian M, Chen H, Wu G L, Qu H J, Ma L C, Li H L. 2012. Intra-continental Dabashan orocline southwestern Qinling central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 46:20-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.10.005
Shi W, Dong S W, Ratschbacher L, Tian M, Li J H, Wu G L. 2013.Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Dangyang Basin northcentral Yangtze craton central China[J]. International Geology Review, 55 (3):382-396. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2012.715732
Suppe J, Chou G T, Hook S C. 1992. Rates of folding and faulting determined from growth strata[C]//McClay K R(ed.). Thrust Tectonics. Chapman & Hall, New York. 105-121.
Tian Yuntao, Zhu Chuanqing, Xu Ming, Rao Song, Barry P. Kohn, and Hu Shengbiao. 2010. Exhumation history of the Micangshan Hannan Dome since Cretaceous and its tectonic significance:evidence from Apatite fission Track analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(4):920-930(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Duoyun, Xin Bushe, Yang Hua, Fu Jinhua, Yao Jingli, and Zhang Yu. 2004. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and geological implications of tuff at the bottom of Chang-7 Member of Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Science China:Earth Science, 10:2160-2171(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4979-0
Wang X, Wang T, Haapala I. 2008. P-T conditions of crystallization and origin of plagioclase-mantled alkali feldspar megacrysts in the Mesozoic granitoids in the Qinling orogen (China)[J]. Lithos, 103:289-308. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.09.020
Wang X, Wang T, Zhang C. 2013. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China:Constraints on orogenic process[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72(4):129-151. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912012005238
Wang T, Wang X X, Tian W, Zhang C L, Li W P, Li S. 2009. North Qinling Paleozoic granite associations and their variation in space and time:Implications for orogenic processes in the orogens of central China[J]. Science in China (Series D) 52:1359-1384. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0129-5
Xue F, Kröner A, Reischmann T, Lerch M F. 1996. Palaeozoic preand post-collision calc-alkaline magmatism in the Qinling orogenic belt, central China, as documented by zircon ages on granitoid rocks[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 153:409-417. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.153.3.0409
Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Li Huaqi, Wang Ruirui, and Cai Zhihui. 2012. Indosinian collision-orogenic system of Chinese continent and its orogenic mechanism[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6):1697-1709(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206001
Yamamoto H, Terabayashi M, Okura H, Matsui T, Kaneko Y, and Ishikawa M. 2013. Northward extrusion of the ultrahigh-pressure units in the southern dabie metamorphic belt, east-central china[J]. Island Arc, 22(1):51-62. doi: 10.1111/iar.12004
Yin A, Nie S Y. 1993. An indentation model for the north and south china collision and the development of the tan-lu and honam fault systems, eastern asia[J]. Tectonics, 12(4):801-813. doi: 10.1029/93TC00313
Zhao T, Zhu G, Lin S, Wang H. 2016. Indentation-induced tearing of a subducting continent:evidence from the tan-lu fault zone, east china[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 152:14-36. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.11.003
Zhang Yuanqing, Qian Xianglin. 2001. Concepts and Mechanism of Basin-Range Coupling[J]. Geolgoy in China, 28(3):47(in Chinese).
Zhang Guowei, Zhang Benren, Yuan Xuecheng, Xiao Qinghui. 2001.Qingling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1-855(in Chinese).
Zhang Jin, Ma Zongjin, Ren Wenjun. 2004. Thingking on the present research of Basin-Mountain coupling[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 26(2):169-175(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200402008.htm
Zhang Yiping, Xiao Wenxia, Zhang Jin, Chen Xuanhua, Zhang Beihang, Zhao Heng, Wang Yannan, Li Jiangyu, Shi Jianjie. 2015.A discussion on the provenance and age of Xiangshan Group in Eastern Hexi Corridor[J]. Geology in China, 42(6):1774-1792(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201506009
Zhang Yiping, Zhang Jin, Chen Bihe, Wang Zongxiu, Zhang Beihang, Zhao Heng. 2015b. Geochronology of Baimashan granitic composite batholith of Hunan Province and its constraints on the timing of regional deformation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(1):1-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12390
Zhang Y P, Chen X H, Zhang J. 2016. Geochronology and tectonic implications of diabase intruded into Xiangshan Group in the Southeastern Alxa Block, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 90(s1):88-91. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12904
Zhang Y P, Zhang J, Chen X H, Wang Y N, Zhao H, Nie F J, Zhang B H. 2017. Late Palaeozoic tectonic setting of the southern Alxa Block, NW China:Constrained by age and composition of diabase[J]. International Geology Review, 59(8):1028-1046. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1253036
Zhang Yiping, 2018, Mesozoic Range-basin Coupling and Tectonic Evolution of the Mid-segment of the Central China Orogen[D]. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences(in Chinese with English abstract).
边千韬, 罗小全, 李涤徽, 赵大升, 陈海泓, 徐贵忠, 常承法, 高延林. 2001.青海省阿尼玛卿带布青山蛇绿混杂岩的地球化学性质及形成环境[J].地质学报, 75(1):45-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.01.005 常远, 许长海, Peter W.Reiners, 周祖翼. 2010.米仓山-汉南隆起白垩纪以来的剥露作用:磷灰石(U-Th)/He年龄记录[J].地球物理学报, 53(4):912-919. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.016 陈刚王志维白国绢孙建博章辉若李向东.鄂尔多斯盆地中新生代峰值年龄事件及其沉积-构造响应[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(3):375-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.03.002 陈宣华, 李江瑜, 董树文, 施炜, 白彦飞, 张义平, 丁伟翠. 2019.华北克拉通中部宁武-静乐盆地侏罗纪构造变形与燕山期造山事件的启动[J].大地构造与成矿学, 43(3):389-408. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201903002 杜思清, 魏显贵. 1998.汉南-米仓山区叠加东西向隆坳的北东向推覆构造[J].成都理工学院学报, 3:367-374. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CDLG803.002.htm 董云鹏, 周鼎武, 刘良. 1995.东秦岭松树沟蛇绿岩构造变形及其演化[J].西北地质科学, 2:37-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBFK502.005.htm 高飞. 2009.渭北地区中新生代构造特征及其演化和改造[D].西安: 西北大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2009088525.htm 管树巍, 李本亮, 何登发, 汪新, Suppe J. 2007.复杂构造解析中的几何学方法与应用[J].地质科学, 42(4):722-739. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.04.008 黄汲清. 1960.中国地质构造基本特征的初步总结[J].地质学报, 1:3-137. 何登发, 贾承造, 李德生, 张朝军, 孟庆任, 石昕. 2005.塔里木多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J].石油与天然气地质, 26(1):64-77. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.01.010 姜春发. 1994.中央造山带主要地质构造特征[C]//中国地质科学院地质研究所文集. 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 张永清, 李惠民. 2009.用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J].矿物学报, 29(1):600-601. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7298171 李凤杰, 郑荣才, 蒋斌. 2008.中国大陆主要盆山耦合系统及其特征[J].岩性油气藏, 20(4):26-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.04.005 刘少峰, 张国伟. 2008.东秦岭-大别山及邻区盆-山系统演化与动力学[J].地质通报, 27(12):1943-1960. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.12.001 邱欣卫. 2008.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组凝灰岩夹层特征和形成环境[D].西北大学. 1-112. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2008077096.htm 任纪舜. 2004.昆仑-秦岭造山系的几个问题[J].西北地质, 37(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2004.01.001 时建超. 2010.鄂尔多斯南缘中新生代构造特征及演化[D].西安: 西北大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2010118921.htm 田云涛, 朱传庆, 徐明, 饶松, Barry, Kohn P.. 2010.白垩纪以来米仓山-汉南穹隆剥蚀过程及其构造意义:磷灰石裂变径迹的证据[J].地球物理学报, 53(4):920-930. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.017 王多云, 辛补社, 杨华, 付金华, 姚泾利, 张瑜. 2014.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7底部凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].中国科学:地球科学, 10:2160-2171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK201410005.htm 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李化启, 王瑞瑞, 蔡志慧. 2012.中国大陆印支碰撞造山系及其造山机制[J].岩石学报, 28(6):1697-1709. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206001 张原庆, 钱祥麟. 2001.盆山耦合概念及机制[J].中国地质, 28(3):47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200103009 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 肖庆辉. 2001.秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1-855. 张进, 马宗晋, 任文军. 2004.对盆山耦合研究的新看法[J].石油实验地质, 26(2):169-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.02.008 张义平, 肖文霞, 张进, 陈宣华, 张北航, 赵衡, 王艳楠, 李江瑜, 史建杰. 2015.河西走廊东部香山群时代和物源讨论[J].中国地质, 2015a, 42(6): 1774-1792. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DIZI201506009.htm 张义平, 张进, 陈必河, 王宗秀, 张北航, 赵衡, 2015b.湖南白马山复式花岗岩基年代学及对区域构造变形时间的约束[J].地质学报, 89(1):1-17. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201501001 张义平, 2018.中央造山带中部中生代盆山耦合与构造演化[D].北京: 中国地质科学院. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1018203936.htm -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. LI He,PING Jianhua,LENG Wei,MEI Xuemei,ZHANG Min,LIU Jiaqi. Attribution analysis of groundwater level fluctuation in the Xinxiang section of the Lower Yellow River's suspended river after the construction of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir. Journal of Geographical Sciences. 2024(07): 1348-1375 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 崔向向,张学庆,田夏,苏晨,郭春艳,孟素花. 黄河下游典型悬河段地表水-地下水对湿地形成条件影响. 水文. 2024(03): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄惠衡. 水利水电工程对下游水质的影响及防控策略研究. 水上安全. 2024(19): 110-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周申蓓,黄媛媛,吕玲玲. 小浪底工程建设后黄河河岸带生态系统服务价值变化. 人民黄河. 2022(09): 122-125+154 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王虎,黄博,孙永福. 基于化学示踪的海床细颗粒渗流测量方法研究. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2022(06): 200-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: