-
摘要:
新生代以来,欧亚与印度两大板块间的碰撞拼合及后续的汇聚挤压塑造了现今青藏高原的高海拔地形地貌和巨厚地壳。位于青藏高原最北缘的榆木山构造带,其内部构造变形的几何学和运动学特征记录了地球最新演化历史过程中,构造、剥蚀和气候变化之间的复杂关系。长期以来,其构造成因和属性一直存在争议。本文通过对最近完成的深地震反射剖面的初步处理,其反射剖面初步揭示了榆木山构造带的深部地壳结构:榆木山构造带之下莫霍面深度为45~48 km,整体由北向南加深;同时,深部反射和地表层析速度成像结果显示榆木山下方存在明显的反射透明区、高速异常体,结合地表地质调查,推测其可能为花岗岩体,同早古生代祁连洋的闭合有关;在榆木山构造带之下存在明显的壳内滑脱面,推测其隆升受控于两条背向逆冲断裂带的控制。本文同时结合其他地质地球物理资料,初步提出了青藏高原北缘的演化模型,为青藏高原北缘的向北扩展、盆山耦合及块体间关系提供了新的思路。
Abstract:Since early Cenozoic, the collision and ongoing continuous convergence of the Indian and Eurasian plates have resulted in the high elevation and thick crust of the Tibetan Plateau. Yumushan thrust belt is located at the north front of the Qilian Mountain, and is the newest joined part of the Tibetan Plateau. Its geometry and kinematics of the crustal deformation recorded the complex relationship between the tectonics, erosion and climate change of the newest evolution of the earth. The deep structure and uplift mechanism have been controversial for a long time. In this paper, the authors unraveled the crustal structure of the Yumushan thrust belt by the newest acquired deep seismic reflection profile. The Moho depth beneath the Yumushan belt is 45-48 km with a shallower trend to the north; the deep reflection structure and subsurface tomography velocity structure show the apparent transparent zone and high velocity zone beneath the Yumushan, which may represent the intrusion of a large amount of granitoids beneath the Yumushan related to the closure of the Qilian Ocean in early Paleozoic, and the uplift was driven by two back-back thrust faults. Combined with other geological and geophysical data, the authors propose a new growth pattern in the northmost Tibetan Plateau, which may shed some light on the northward growth as well as the basin-range coupling relation.
-
1. 引言
水系沉积物是岩石风化的产物,是上游汇水盆地物质的天然组合,在化学成分上与所流经汇水盆地内受剥蚀的地质体有明显的继承性和代表性(蒋敬业等,2006;郝立波等,2007;陆顺富等,2014)。利用这一特点,水系沉积物地球化学测量可以有效获取隐伏、半隐伏矿和难识别矿的成矿信息,为进一步开展地质勘查工作提供依据(夏祥标等,2009;李玉芹等,2011;宋贺民等2014;刘邦定等,2015),因而在金属矿产资源勘查中发挥着愈来愈重要的作用(杨伟寿等,2007;朱建华,2007;师淑娟等,2011;张江华等,2013;赵武强等,2014)。
完达山地区主要由一套近南北走向的玄武岩、堆晶岩、(超)基性熔岩、硅质岩和泥质岩组成(张兴洲,2010),是中国东部唯一的中生代海相地层发育区域(周建波等,2005;田东江,2007),出露有太平洋板块俯冲形成的增生杂岩组合(Kojima et al., 1987, 1989;Zheng, 1990;张世红等,1991;唐克东等,1995;张庆龙等,1997;田东江等,2006;张雪锋等,2014;王庆双等,2015;韦延兰等,2015),且中生代蛇绿岩发育,为中国典型的蛇绿岩发育地区之一(田东江,2007;Zhang et al., 2013)。研究区内矿产资源丰富,但受年均7~8个月的结冰期及森林植被覆盖影响,地质找矿勘查工作并不理想,在一定程度上制约了区域成矿规律的研究和资源评价工作的安排。有鉴于此,笔者从完达山1:20万水系沉积物测量数据入手,分析水系沉积物地球化学异常与地层、构造、岩浆岩及矿床之间的关系,阐明地球化学异常的控制因素,圈定有利的找矿靶区,为完达山地区整体找矿工作部署和区域成矿规律研究提供科学依据。
2. 成矿地质背景
完达山地区位于中国东北地区东部, 是完达山—锡霍特—阿林超地体在中国境内的出露部分, 西与南以宝清大和镇断裂和敦密断裂为界,东与北至乌苏里江边和小佳河镇胜利农场,东西宽约80 km,南北长约240 km,总体上呈近南北向略向西突出的弧形分布,并向宝清过渡带逆掩推覆。该区缺失太古宇、古生界的古老地层,而发育中生代和新生代地层(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 完达山地区区域地质图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Wanddashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)
图 1 完达山地区区域地质图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Wanddashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)区内构造较为发育,以北东向和北西向构造为主,主要包括敦化—密山断裂、大和镇断裂、富锦—小佳河断裂、饶河北西向断层束和饶河北北东向断层束。
区内岩浆岩十分发育,主要发育有晚古生代(超)基性岩、早中生代(超)基性岩和晚中生代酸性岩浆岩。晚古生代(超)基性岩分布于研究区西南部跃进山—曙光村—东方红一带,为跃进山蛇绿岩的重要组成部分,岩性为玄武岩、角闪辉长岩、辉长岩、蛇纹石化橄榄辉石岩等。早中生代(超)基性岩分布于研究区东部八里桥—仙人台一带,为饶河蛇绿岩的重要组成部分,岩性为玄武岩、枕状玄武岩、角闪辉长岩、单辉橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩等。晚中生代酸性岩浆岩由酸性侵入岩和酸性火山岩组成,酸性侵入岩出露于蛤蚂河、蛤蟆通水库和东方红镇西北部,岩性为花岗闪长岩、正长花岗岩、斜长花岗岩和二长花岗岩等。酸性火山岩位于研究区南部大塔山林场组和皮克山组地层中,岩性为流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩、流纹质凝灰熔岩、热液角砾岩等。
区内金属矿产主要与晚中生代晚期酸性岩浆岩和早中生代(超)基性岩有关,矿种为金、银、铜、镍、钴等,到目前为止,已发现中型矿床1座(四平山金矿床),小型矿床4座(先锋北金矿床、258高地金矿床、358高地金矿床、跃进山铜金属矿床),矿点10余处(蛤蟆河金矿点、宝丰村金矿、永幸铜镍矿点等)。
3. 地球化学特征
3.1 样品采集加工与分析质量
样品采集严格遵守1:20万水系沉积物测量规范,平均采样密度为1.18个/4 km2,采集样品2114件(不包括重复密码分析样)。采样点主要分布在二、三级水系内,长度为1~2 km的一级水系口,长度大于2 km的一级水系内适当增加采样点,采样介质为活性水系沉积物(如:淤泥、粉砂),每个样品在采样点附近30~50 m范围内进行多点(不少于3点)采集,合并为一个样品,样品重量过筛后不少于300 g,取10~60目粒度作为分析样品(杨小峰等,2007;李林山等,2009;朴寿成等,2009)。分析测试单位为国土资源部哈尔滨矿产资源监督检测中心,分析测试方法采用原子吸收分光光度法(AAS)、原子荧光分光光度法(AFS)、X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)和电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)等方法,样品分析项目为As、Au、Hg、Sb、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、Bi、Mo、Sn、W、Co、Cr、Ni、V。
根据森林沼泽区技术方法研究要求,在分析元素、测试分析配套方案、测试分析质量监控方法等方面制定了统一的技术方法。其中,测试分析质量监控采用外部质量监控和内部质量监控相结合的方法,实验室内部按样品总数随机抽取5%的重份样品进行分析,合格率为100%,同时随机抽取8%的样品进行随机重复密码分析,合格率为97%。综上所述,分析报告中的化探数据可靠,分析质量达到或优于规范质量等级。
3.2 元素含量特征
采用元素含量最高值(CMax)、最低值(CMin)、平均值(X)、标准离差(S)、变异系数(CV)、富集系数(K)等地球化学参数来阐明和讨论1:20万水系沉积物地球化学特征及规律。浓集系数(K)为研究区元素平均值与全省元素平均值之比,变异系数(CV)为元素标准偏差与均值之比。
研究区内Au、Cu、Pb、Zn、Sn、W、Co、Ni、V、Cr元素的浓集系数均大于1.00,表明这些元素在完达山地区具有一定的次生富集倾向,有利于成矿;Ag、Hg、Bi、Sn、Mo元素的浓集系数小于1.00(表 1),表明这些元素在完达山地区趋于贫化,成矿作用相对较弱。结合研究区各元素变异系数由Bi−Cr−Au−Ni−Hg−Ag−As−Sn−Sb−Cu−Co−Mo−W−Zn−V−Pb逐渐下降,意味着从Bi到Pb成矿作用依次减弱。
表 1 完达山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征参数Table 1. Geochemical parameters of the stream sediment samples from Wandashan area
3.3 元素变化特征
水系沉积物样品中各元素原始数据的变异系数(CV1)(薛水根,1979;刘劲松等,2016)和背景数据(采用>X+3S及<X−3S迭代剔除,直至无离群点数值可剔除为止,即所有数据全部分布>X-3S与<X+3S间)的变异系数(CV2)反映了数据处理前后的离散程度(张运强等,2015),CV1/CV2反映背景拟合处理时离散值的削平程度。因而可以利用CV1和CV1/CV2制作变异系数图解,从变异系数图解(图 2)中可以看出,区内Bi含量变化幅度最大,高强度数据最多,分布极不均匀,成矿特别有利;Au、Ni、Cr、Hg高强度数据较多,变异系数较大,有利于成矿,且大多数异常内已发现矿床(点)(如四平山金矿、先锋北山金矿、跃进山金矿、永幸铜镍矿点等);Ag、As、Sn、Sb、Cu、Co、Mo、W、Zn、V、Pb在测区中的CV1和CV1/CV2值都比较低,成矿可能性较低。
3.4 元素分布特征
通对完达山地区2114件水系沉积物样品的地球化学数据统计,得到各元素丰度直方图。由该元素丰度直方图(图 3)可知,Au、Bi、Ni、Cr元素的标准偏差分别为1.22、0.49、32.88、106.75,变异系数分别为1.05、1.42、0.99、1.21,呈非正态分布,具有较强的成矿潜力;Hg、Ag、Cu、Co元素的标准偏差分别为42.25、52.88、11.21、6.22,变异系数分别为0.99、0.58、0.44、0.40,呈近似正态分布,具有一定的成矿潜力;As、Sb、Pb、Zn、W、Mo、Sn、V元素的标准偏差分别为5.00、0.22、3.50、21.89、0.67、0.49、1.75、18.07,变异系数分别为0.53、0.47、0.15、0.25、0.35、0.40、0.53、0.23,服从正态分布,成矿潜力较弱。
3.5 元素相关性特征
3.5.1 聚类分析
由表 2可知,Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、V元素呈显著正相关,Au、As、Sb、Bi、Sn元素之间呈正强相关。在R聚类分析图中(图 4),以R= 0. 3为界成矿元素可分5类。
表 2 完达山地区水系沉积物成矿元素相关系数矩阵Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix of metallogenic elements from Wandashan area
第一类Bi、Sn:主要分布于完达山西南部蛤蟆通岩体内,其次分布于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带中,反映与高温热源作用相关的矿化信息。
第二类Au、Ag、Hg:异常分布与岩浆岩体相关,Au与Ag、Hg相关性较强,代表低温热液矿化作用,组合异常是测区寻找Au、Ag矿床的重要地球化学找矿标志。
第三类Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn:位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带和跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,Co、Cr、Ni密切相关,反映Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn元素富集与蛇绿岩中(超)基性岩形成相关。
第四类W、Mo:与Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn和As、Sb、Pb、V均具有一定的相关性,其成因复杂,既受岩浆热液控制又受地层控制。
第五类As、Sb、Pb、V:元素具有一定相关性,其富集作用主要与三叠纪地层相关,为层控元素。
3.5.2 因子分析
样品原始数据因子分析的相关矩阵特征根和累积百分比见表 3,前6个特征根代表的方差占总方差的68.6%,因此视这前6个因子为主要因子。
表 3 完达山水系沉积物成矿元素主因子分析Table 3. Principal factor analysis of metallogenic elements from Wandashan area
F1因子贡献率最大,变量元素有Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、V,以亲铁元素为主,与区内蛇绿岩中的(超)基性岩体相关。F2因子的元素组合为Au、Bi、Sn,反映岩浆岩矿化作用,低温的Au元素可能与高温的Bi、Sn元素具有同源关系。F3因子的元素为Au、As、Sb,是本区最为重要的一种元素组合,与酸性岩浆岩相关,反映中低温热液矿化作用。
F4、F5因子的元素组合为W、Mo、Cu和Ag、Cu、Zn、Pb,分别代表研究区高温与中温矿化阶段。F6因子的变量元素仅有熔点较低Hg元素,Hg迁移能力非常强,暗示本区内多金属成矿作用与中酸性含矿热液沿构造充填作用有关。
4. 地球化学异常分析
4.1 单元素异常特征
文中异常外带边界、中带边界和内带边界分别由异常下限、2倍异常下限和4倍异常下限确定。异常下限计算公式为:Ct=X+2δ (X为背景平均值,δ为标准离差,Ct为异常下限)。
由图 5可知,完达山地区共圈出Au元素异常9处,Au−2、Au−3、Au−7、Au−8为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,具有较强的找矿意义,是重要的Au找矿靶区;Au−1、Au−4、Au−5、Au−6、Au−9为多点中带异常,为找矿远景区。Au−2异常位于哈蚂河岩体内,面积约为49.01 km2,呈闭合的不规则椭圆状,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为16.83×10-9,258金矿床就位于该Au异常带内;Au−3异常位于四平山附近,面积约为49.13 km2,为闭合的不规则状,呈北东向展布,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为19.60×10-9,四平山金矿床处于该Au异常带内;Au−8异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,面积约为59.15 km2,为闭合的不规则状,呈北东向展布,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为20.80×10-9。
As元素异常总体规模较小,无多点内带异常,5处多点中带异常。其中,As−3、As−5异常分别与Au −3、Au−9和Ag−5、Ag−7等元素异常完全套,表明As可作为寻找Au、Ag矿床(体)的指示元素。
Sb元素异常规模较小,无多点内带异常,4处多点中带异常。其中,Sb−2异常与Au−3和Ag−5套和较好,Sb−4异常与Au−9和Ag−7套和较好。
Hg元素异常3处,Hg−1为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,呈闭合的不规则状,面积约为50.01 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1600.00×10-9;Hg−2位于四平山金矿区附近,为多点中带异常,与Au−3和Ag−5套和较好,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为60.46 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为160.00×10-9。Hg−3为多点中带异常,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为12.57 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为206.00×10-9。
Ag元素异7处,Ag−2、Ag−6为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,具有重要找矿意义,可以作为Ag找矿靶区;Ag−1、Ag−3、Ag−4、Ag−5、Ag−7为多点中带异常,可以作为找矿远景区。Ag−2异常位于研究区北部,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为17.85 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1220.00×10-9,目前尚未发现Ag矿床(点),找矿潜力较大;Ag−6异常位于跃进山附近,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为20.00 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1610.00×10-9,跃进山铜金矿床位于该异常内;Ag−5异常位于四平山附近,面积约为35.43 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为285.00×10-9,四平山金矿床位于该异常内;Ag−7异常位于先锋北山附近,面积约为61.27 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为455.00×10-9,先锋北山金矿床位于该异常内。虽然,Ag−3、Ag−4异常内尚未发现相应的Ag矿床(点),但这两处异常带规模较大,异常衬度较高,找矿潜力较好。
Cu元素异常8处,Cu−7为多点内带异常,其他7处均为多点中带异常。Cu−1、Cu−2、Cu−3、Cu−4异常分布与八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩带分布基本一致;Cu−5、Cu−6、Cu−7、Cu−8异常与跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带套合较好。
Pb、Zn异常主要分布于研究区东部和西南部,规模较小,无异常内带,形成铅、锌矿床的可能性较小,找矿潜力不大。
W元素异常3处,W−1位于矿区东部,为多点内带异常,面积约为204.35 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为13.60×10-6,异常面积大、衬度高,异常内已发现小别拉坑钨锡矿点,具有一定的找矿前景,可以作为W的找矿靶区。
Mo元素异常3处,Mo−3位于研究区东部,为多点内带异常,衬度高,面积约为41.66 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为13.75×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,可作为钼矿找矿靶区。
Sn元素异常3处,Sn−1位于蛤蟆岩体南部边缘,为多点中带异常,面积约为57.41 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为9.00×10-6,主要受蛤蟆河岩体控制;Sn−2异常位于研究区东部(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,面积约为32.79 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为26.00×10-6;Sn−3异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,为多点内带异常,面积约为94.01 km2,有5个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为45.00×10-6。
Bi元素异常共5处,Bi−1、Bi−2位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,面积和浓集中心最大值分别为23.98 km2、26.31 km2和1.62×10−6、1.25×10-6;Bi−3、Bi−4位于研究区中部,为多点中带异常,面积和浓集中心最大值分别为20.13 km2、11.55 km2和1.60×10-6、6.20×10-6;Bi−5异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,为多点内带异常,面积约为126.91 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为12.59×10-6。
Co元素异常3处,Co−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,异常衬度高,面积约为396.13 km2,有6个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为97.80×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,为钴矿找矿靶区。Co−2异常位于龙间山附近,面积约为9.13 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为48.70×10-6;Co−3异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,衬度高,面积约为99.98 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为78.20×10-6。
Ni元素异常5处,Ni−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,异常衬度高,面积约为335.86 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为714.80×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,异常内已发现永幸铜镍矿点;Ni−4异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,面积约为102.19 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为132.30×10-6;Ni−2、Ni−3、Ni−5异常为中异常,异常面积小,衬度低,找矿潜力不大。
Cr元素异常3处,Cr−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,呈近南北向分布,面积约为511.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1771.30×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Cr−3异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,多点中带异常,面积约为218.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为892.60×10-6。
V异常总体规模较小,较为分散,且无中带或内带异常,形成矿床的可能性较小,找矿潜力不大。
4.2 组合元素异常特征
在单元素异常的基础上,根据异常性质、组合特征以及异常所处的地质背景、成矿地质条件等因素共圈出6个组合异常(图 6)。其特征如下:
4.2.1 HS−1号组合异常
HS−1号组合异常仅有一个Au−2异常,考虑Au−2异常的重要性,特将它圈定为一个组合异常,强调其重要性。Au−2异常位于哈蚂河岩体内,出露岩性主要为花岗闪长岩,局部见有北东向闪长玢岩脉。Au−2为多点内带异常,呈闭合的不规则状,北东向展布,分布面积约为49.01 km2,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为16.83×10-9,区内已发现258金矿床。
4.2.2 HS−2号组合异常
HS−2号组合异常规模大,强度高,为Cu−Cr−Ni −Co−Bi−Sn−Mo−W元素组合异常,与区内八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩体带的分布位置基本一致,呈北北东向展布,面积为693.75 km2,长约为46 km,宽为7~26 km,主要以Cu、Ni、Cr、Co异常为主。Cu、Ni、Cr元素异常分布面积大,含量高,Cu异常具中带、外带,面积约为289.53 km2,浓集中心最大值为130.10×10-6;Ni异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为359.88 km2,浓集中心最大值为714.80×10-6;Cr异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为511.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1771.30×10-6。Cu、Cr、Ni、Co、Bi、Sn、Mo、W单元素异常套合性较好,浓集中心一致,结合区域地质特征可知,该组合异常与(超)基性岩带相关性较强,且组合异常内发现多处矿(化)点(如:永幸铜镍点、向阳铜矿点、小别拉坑钨锡矿点等),因此,该区域应该重点寻找与(超)基性岩相关的Cu、Ni、Cr等矿产资源。
4.2.3 HS−3号组合异常
HS−3号组合异常位于八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩体带西侧的大岭桥组杂砂岩、泥粉质砂岩、砂质板岩和泥岩中,呈北北东向展布,面积为200.36 km2,长约为25 km,宽为3~12 km,主要以Ag异常为主。Ag异常具有中等、外带,面积约为85.20 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为400.00×10-9。Ag、Bi、Sn、As等元素异常套合较好,浓集中心基本一致。受工作环境的影响,该组合异常区内尚未发现Ag、Bi、Sn矿床(点)。
4.2.4 HS−4号组合异常
HS−4号组合异常位于四平山—358高地一带,呈北东向展布,面积为141.26 km2,以Au异常为主,出露岩性为流纹岩、花岗岩、硅质岩、砂岩、杂砂岩和泥岩等。Au、Ag、Hg、Sn元素异常套合较好,浓集中心基本一致。Au异常由Au−3和Au−4异常组成,四平山金矿床和358金矿床分别位于Au−3和Au−4异常内。
4.2.5 HS−5号组合异常
HS−5号组合异常为Au−Hg−Sn−Bi−Ni−Cr−W元素组合异常,位于红旗屯—炮手营—东旺屯附近,出露岩性为中生代的硅质岩、砂岩、杂砂岩及泥岩,呈北西向展布,分布面积为181.03 km2,主要以Au异常为主。Au异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为32.83 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为9.50×10-9。由于工作程度较低,该异常区尚未发现Au矿床(点),找矿潜力较大。
4.2.6 HS−6号组合异常
HS−6号组合异常规模大,强度高,为Au−Ag−Sb−As−Cu−Ni−Cr−Co−Bi−Pb−Zn元素组合异常,位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红一带,出露岩性为(超)基性岩和酸性侵入岩,呈北北东向展布,面积372.60 km2,主要以Au、Cu、Ni、Cr、Co异常为主。Au异常由Au−8和Au−9组成(Au−8和Au−9异常特征在单元素异常中已详细描述),受酸性侵入岩控制,具有较好的找矿潜力。Cu、Ni、Cr、Co元素主要受跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带控制,Cu异常为多点内带异常,面积约为370.63 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为174.70×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Cr异常为多点内带异常,面积约为218.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为892.60×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Ni异常面积约为102.19 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为132.30×10-6,具有一定的找矿潜力。
5. 成矿远景区圈定与评价
根据成矿地质背景、控矿条件、区域地球化学异常、区域航磁异常、区域重力异常以及区内矿床(点)分布规律等特征,研究区内共圈定4处成矿远景区:258高地金、银成矿远景区(YJQ−1);八里桥—仙人台铜、镍、钨、锡成矿远景区(YJQ−2);四平山— 358高地金、银成矿远景区(YJQ−3);跃进山—先锋北山金、银、铜、铁成矿远景区(YJQ−4) (图 7)。
![]() 图 7 完达山地区成矿远景区划分图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 7. Metallogenic prospective areas in Wandashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)
图 7 完达山地区成矿远景区划分图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 7. Metallogenic prospective areas in Wandashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)5.1 258高地金成矿远景区
258高地成矿远景区位于完达山地区北部蛤蟆河岩体内,呈北东—南东向L形展布,长16~17 km,宽8~10 km,面积约220 km2。区内断裂构造发育,对成矿有利的侵入岩为早白垩世晚期酸性侵入岩体。1:20万水系沉积物化学异常以Au−2异常为主,Au−2异常面积较大,约为32.83 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带和2个浓集中心。已知矿床(点)有258金矿床和蛤蟆河金矿化点。围岩蚀变强烈,主要有硅化、绢云母化、高岭土化、绿泥石化,主攻矿种为金,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金矿床。
5.2 八里桥—仙人台铜镍钨锡成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区东北部,呈北北东向长条状展布,长约41 km,宽约13 km,面积近500 km2。区内断裂构造以北北东向为主,北西向、北东向次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,与成矿关系密切的岩体为八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩带。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Cu−2、Cu−4、Co−1、Ni−1、Cr−1、Sn−2、W−1异常为主,Cu、Co、Ni、Cr、W、Sn元素异常套和较好,面积较大,除Cu元素只有异常中等和外带外,其他元素均具有异常内带、中等、外带和多个浓集中心。区内已发现矿(化)点有向阳铜矿点、永幸铜镍矿点、小别拉坑钨锡矿点等。围岩蚀变较为发育,主要有硅化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化,主攻矿种为铜、钴、镍、铬、钨、锡等中高温元素和亲铁元素,主攻矿床类型为岩浆熔离型铜镍铬矿床和细脉侵染型铜钨锡矿床。
5.3 四平山—358高地金银成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区东部,呈北西向长条状展布,长约20 km,宽约10 km,面积约200 km2。区内以北北东向和北东向构造为主,北西向构造次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,上三叠统—下侏罗统大岭桥组粉砂岩、砂岩夹薄层硅质岩,下白垩统穆棱组砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,四平山组泉胶砾岩夹泉胶砂岩、硅质岩。与成矿相关的岩体主要为白垩系流纹岩、花岗斑岩和花岗闪长玢岩。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Au−3、Au−4、Ag−5异常为主,Au−3和Ag−5异常位于四平山矿区附近,套和较好。Au−3异常面积约为49.13 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为19.60×10-9;Ag−5具有异常中等、外带。Au−4异常位于358金矿区附近,具有异常中等、外带,2个浓集中心。区内发现的矿床(点)有四平山金矿床、358高地金矿床。围岩蚀变强烈,主要有硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、叶腊石化、碳酸盐化等,主攻矿种为金、银,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金、银矿床。
5.4 跃进山—先锋北山金银铜铁成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区西南部,呈南北向长条状展布,长约30 km,宽约12 km,面积近63 km2。区内以北西向和北东向构造为主,近东西向和近南北向构造次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,下白垩统穆棱组砂岩、泥质粉砂岩。金、银矿化主要与酸性侵入岩体(蛤蟆通岩体、尖山子岩体以及后期侵入的酸性岩株、岩脉)相关,铜、铁、镍矿化主要与跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带相关。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Au−8、Ag−6、Ag−7、Cr −3、Cu−6、Cu−7、Cu−8、Ni−4、Sn−3异常为主。其中,Au、Ag异常分布于酸性侵入岩中及其附近,与酸性侵入岩体套和较好。Au−8异常面积约为59.15 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为20.80×10-9;Ag−7异常面积约为61.27 km2,具有异常中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为455.00×10-9。Cu、Ni、Sn等单元素异常位于(超)基性岩带内及其附近。Cu−7异常面积约为17.75 km2,具有异常中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为174.70×10-6;Cu−8异常面积约为103.66 km2,具有异常中等、外带和3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为109.90×10-6。Ni−4异常和Sn−3异常主要位于(超)基性岩带内,异常面积大,Ni−4、Sn−3异常与(超)基性岩体套和较好,具有异常中等、外带和多个浓集中心。区内已发现的矿床(点)有先锋北山金矿床、跃进山铁矿床、跃进山铜金矿床、曙光村铜矿点等。围岩蚀变较为发育,且分带性明显,主要有硅化、绿泥石化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、叶腊石化,主攻矿种为金、银、铜、镍、铬、锡等,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金银矿床、火山热液型金银矿床和熔离型铜镍铬矿床。
6. 结论
(1) 研究区内Au、Ni、Cr、Bi、Hg异常高值点多、变异系数值高、离散性强,地质及地球化学条件优越,成矿潜力强。
(2) Au、Ag、Hg、As、Sb异常规模较大、套合好,多富集于中酸性岩浆岩体内及其附近,与低温热液型成矿作用相关;Cr、Ni、Co、V、Cu、Zn异常套合较好,主要分布于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带和跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,与高温岩浆熔离型成矿作用相关。
(3) 完达山地区共优选出4处成矿远景区,分别为258高地金成矿远景区、八里桥—仙人台铜镍钨锡成矿远景区、四平山—358高地金银成矿远景区和跃进山—先锋北山金银铜铁成矿远景区。
致谢: 中石化石油工程地球物理有限公司华北分公司承担了本次野外地震数据采集任务,谨向他们在野外工作中付出的辛苦表示感谢。 -
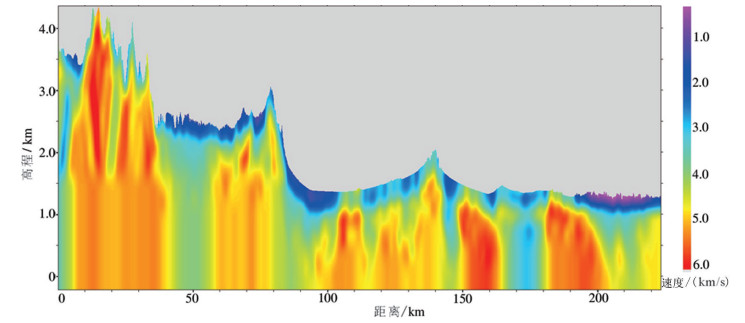
图 1 青藏高原东北缘及周缘构造位置图(修改自Duvall et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2013; Gao et al., 2013; Zuza and Yin, 2016;红线为2016年采集的深地震反射剖面位置)
Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of the northeastern Tibet and adjacent regions (modified from Duvall et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2013; Gao et al., 2013; Zuza and Yin, 2016; Red line represents the deep seismic reflection profile acquired in 2016)
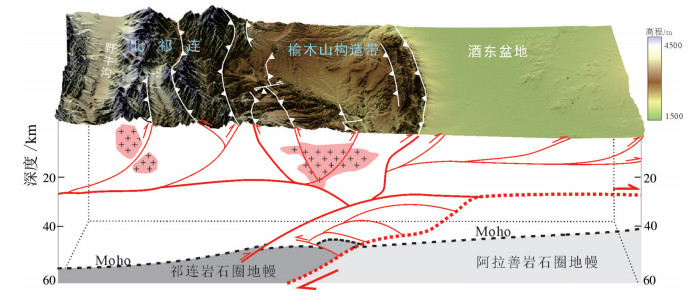
图 3 榆木山构造带地质简图(修改自陈宣华等,2019)
Q4—全新统; Q3—上更新统; Q2—中更新统; Q1—下更新统; N2—上新统; N1—中新统; E—古近系; K1—下白垩统; J—侏罗系; T—三叠系; P—二叠系; C2—上石炭统; C1—下石炭统; D—泥盆系; S3—上志留统; S2—中志留统; S1—下志留统; O3—上奥陶统; O2—中奥陶统; O1—下奥陶统; Є—寒武系; Pt1—古元古界; NQLF—祁连山北缘断裂; NYMF—榆木山北缘断裂; SYMF—榆山南缘断裂; LSF—龙首山断裂; LYF—梨园堡断裂; SNF—肃南断裂; DGF—大更子断裂; XGF—小更子断裂
Figure 3. Geological sketch map of the Yumushan thrust belt (modified from Chen et al., 2019)
Q4-Holocene; Q3-Upper Pleistocene; Q2-Middle Pleistocene; Q1-Lower Pleistocene; N2-Pliocene; N1-Miocene; E-Paleogene; K1-Lower Cretaceous; J-Jurassic; T-Triassic; P-Permian; C2-Upper Carboniferous; C1-Lower Carboniferous; D-Devonian; S3-Upper Silurian; S2-Middle Silurian; S1-Lower Silurian; O3-Upper Ordovician; O2-Middle Ordovician; O1-Lower Ordovician; Є-Cambrian; Pt1-Paleoproterozoic; NQLF-North Qilian Mountain fault; NYMF-North Yumushan Mountain fault; SYMF-SouthYumushan Mountain Fault; LSF-Longshoushan Mountain fault; LYF-Liyuanpu Fault; SNF-Sunan Fault; DGF-Dagengzi Fault; XGF-Xiaogengzi Fault
图 6 榆木山构造带及邻区地表露头(详细位置见图 3)
a—酒东盆地内发育的逆冲断层;b—白垩纪逆冲于Q1之上;c—Q3不整合覆盖于K之上;d—Q1与Q3角度不整合;e—泥盆系逆冲于白垩系之上;f—榆木山反冲断裂
Figure 6. The outcropped thrust deformation in the Yumushan tectonic belt (the locations shown in Fig. 3)
a-Thrust faults in Jiudong basin; b- Cretaceous strata overthrusted on the Q1 strata; c-Q3 unconformably covering Cretaceous strata; d- Angular unconformity between the Q1 and Q3; e- Devonian strata overthrusted on the Cretaceous strata; f- The Yumushan back thrust faults
表 1 采集参数表
Table 1 Acquisition parameters

-
Bian Qingkai, Zhang Peizhen, Su Xiangzhou. 2001. The tectonic topography feature of the faults in north Yumushan Mountain and its faulting activity[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 19(3):41-49 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdzkx200103005
Burchfiel B C, Zhang Peizhen, Wang Yipeng, Zhang Weiqi, Song Fangmin, Deng Qidong, Molnar Peter, Royden Leigh. 1991.Geology of the Haiyuan fault zone, Ningxia-Hui Autonomous Region, China, and its relation to the evolution of the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 10(6):1091-1110. doi: 10.1029/90TC02685
Chen Bailin, Wang Chunyu, Gong Hongliang, Liu Jianming, Zhang Shuangshuang, Liu Jiansheng. 2007. A new understanding of the characteristics of Late Quaternary activity of the northern Yumushan marginal fault in the Hexi corridor, northwestern China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(8):976-983 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200708009
Chen Gan, Zheng Wenjun, Wang Xulong, Zhang Peizhen, Xiong Jianguo, Yu Jingxing, Liu Xingwang, Bi Haiyun, Liu Jinrui, Ai Ming. 2017. Present kinematics characteristics of the northern Yu Mushan active fault and its response to the northeastward growth of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(5):871-888(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Xuanhua, Shao Zhaogang, Xiong Xiaosong, Gao Rui, Xu Shenglin, Zhang Yiping, Li Bing, Wang Ye. 2019. Early Cretaceous overthrusting of Yumu Mountain and Hydrocarbon Prospect on the northern margin of the Qilian Orgenic Belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 40(3):377-392 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201903001.htm
Clark Marin K, Farley Kenneth A, Zheng Dewen, Wang Zhicai, Duvall Alison R. 2010. Early Cenozoic faulting of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin from apatite (U-Th)/He ages[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 296(1/2):78-88. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X10003031
Clark Marin Kristen. 2012. Continental collision slowing due to viscous mantle lithosphere rather than topography[J]. Nature, 483(7387):74-77. doi: 10.1038/nature10848
Dai Shuang, Fang Xiaomin, Zhang Xiang, Fangcheng Wang. 2003.The origin and tectonic settings of diorite granitoid in the centre of Beishan Region of Gansu[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 39(1):86-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lzdxxb200301019
Du Yuan sheng, Zhu Jie, Han Xing, Gu Songzhu. 2004. From the back-arc basin to foreland basin-Ordovician-Devonian sedimentary basin and tectonic evolution in the North Qilian orogenic belt[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9/10):911-917(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200409013
Duvall Alison R, Clark Marin K, Kirby Eric, Farley Kenneth A, Craddock William H, Li Chuanyou, Yuan Daoyang. 2013. Lowtemperature thermochronometry along the Kunlun and Haiyuan Faults, NE Tibetan Plateau:Evidence for kinematic change during late-stage orogenesis[J]. Tectonics, 32(5):1190-1211. doi: 10.1002/tect.20072
Fang Xiaomin, Liu Dongliang, Song Chunhui, Dai Shuang, Meng Qingquan. 2013. Oligocene slow and Miocene-Quaternary rapid deformation and uplift of the Yumu Shan and North Qilian Shan:evidence from high-resolution magnetostratigraphy and tectonosedimentology[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 373(1):149. doi: 10.1144/SP373.5
Gao Li'e, Zeng Lingsen, Gao Jiahao, Shang Zhen, Hou Kejun, Wang Qian. 2016. Oligocene crustal anatexis in the Tethyan Himalaya, southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 264:201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.038
Ge Xiaohong, Zhang Meisheng, Liu Yongjiang, Ye Huiwen, Shi Caidong. 1998. Scientific problems and research ideas of Altun Fault research[J]. Geoscience, 12(3):295-301 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gehrels G, Kapp P, DeCelles P, Pullen A, Blakey R, Weislogel A, Ding Lin, Guynn J, Martin A, McQuarrie N. 2011. Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen[J]. Tectonics, 30(5):TC5016. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ff67eabc1332d9c10c9875cd3f2e8732
Gehrels George E, Yin An, Wang Xiaofeng. 2003. Detrital-zircon geochronology of the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 115(7):881-896. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2003)115<0881:DGOTNT>2.0.CO;2
Gehrels George E, Yin An, Wang Xiaofeng. 2003. Magmatic history of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 108(B9), 2423. doi: 10.1029-2002JB001876/
Harrison T Mark, Copeland Peter, Kidd W S F, Yin An. 1992. Raising Tibet[J]. Science, 255(5052):1663-1670. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5052.1663
He Guangyu, Yang Shufeng, Chen Hanlin, Xian Ancheng, Chen Xiaogan. 2004. New ideas about the Early Cretaceous basins in western Gansu Corridor and nearby regions[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 25(6):18-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb200406004
Horton B K, Dupont-Nivet Guillaume, Zhou J, Waanders G L, Butler Robert F, Wang J. 2004. Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of the Xining-Minhe and Dangchang basins, northeastern Tibetan Plateau:Magnetostratigraphic and biostratigraphic results[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 109(B4):B04402. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280086752_Mesozoic-Cenozoic_evolution_of_the_Xining-Minhe_and_Dangchang_basins_northeastern_Tibetan_Plateau_Magnetostratigraphic_and_biostratigraphic_results
Institute of Geology China Earthquake Adiministration, Province Earthquake Adiministration of Gansu.1993. Active Fault System in Qilian Mountain-Hexi Corridor[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jing Qing. 2011. Late Quaternary Tectonic Activities and Risk Assessment of Large Earthquakes in the Yumushan Fault Zone[D]. China Earthquake Administration Earthquake Administration of Gansu Province (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lai Xingrong, Jiang Sihong, Qiu Xiaoping, Liu Yan, Hu Peng, Zhang Wanyi. 2007.40Ar-39Ar age and geochemical features of Hercynian intermediate a cidity rock in Beidashan rock belt, Alxa[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(3):370-380(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200703008.htm
Li Yonghua, Xu Xiaoming, Zhang Enhui, Gao Jiayi. 2014. ThreeDimensional crust structure beneath SE Tibetan Plateau and its seismotectonic implications for the Ludian and Jinggu earthquakes[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(4):1204-1216. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDZ201404021.htm
Li Youli, Yang Jingchun, Li Baojun, Tan Lihua. 1997. On the tectonic land form of the Yumu Mountain, Hexi Corridor, Gansu province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 3(4):20-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX704.002.htm
Li Yulong, Xing Chengqi. 1988. Researc on the Fundamental Characteristics of the geological structures of the Hexi Corridor and the active faults of the northern and eastern fkank of the Yumushan Mountin[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 10(2):35-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lui Dongliang, Song Chunhui, Fang Xiaomin, Dai Shuang, Li Haibing. 2012. Magneteostratigraphy of Yumen conglomerate in the Yumushan Region and its implication for deformation and uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(6):898-905 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201206005
Métivier Francois, Gaudemer Yves, Tapponnier Paul, Meyer Bertrand. 1998. Northeastward growth of the Tibet plateau deduced from balanced reconstruction of two depositional areas:The Qaidam and Hexi Corridor basins, China[J]. Tectonics, 17(6):823-842. doi: 10.1029/98TC02764
Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:Effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 189(4201):419-426.Molnar Peter, England Philip, Martinod Joseph. 1993. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian monsoon[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 31(4):357-396. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419
Molnar Peter, Stock Joann M. 2009. Slowing of India's convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics[J]. Tectonics, 28(3):TC002271. doi: 10.1029-2008TC002271/
Molnar Peter. 2005. Mio-Pliocene growth of the Tibetan Plateau and evolution of East Asian climate[J]. Palaeontologia Electronica, 8(1):1-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Open J-Gate000001515315
Palumbo L, Hetzel R, Minxing T, Li X, Guo J. 2009. Uplift and denudation rates of an actively growing mountain range inferred from in-situ produced cosmogenic 10Be: the Yumu Shan (NE Tibetan Plateau)[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 2789.
Palumbo Luigi, Hetzel Ralf, Tao M, Li X. 2010. Topographic and lithologic control on catchment-wide denudation rates derived from cosmogenic 10Be in two mountain ranges at the margin of NE Tibet[J]. Geomorphology, 117(1/2):130-142. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d52f1f1ad0a66172d1c5bcc2ae8f450b
Palumbo Luigi, Hetzel Ralf, Tao Mingxin, Li Xiaobin, Guo Jianming. 2009. Deciphering the rate of mountain growth during topographic presteady state:An example from the NE margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 28(4).doi: 10.1029/2009TC002455.2009.
Pan Hongxun, Ge Xiaohong, Liu Junlai.Query To The Yumushan uplift on The north margin of Qilian Mountain[J]. Journal of Changchun Univers ty of Science and Technology, 30(1): 9-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200001002.htm
Ren Jishun, Jiang Chunfa.1981. Deep fault in China[C]//A Collection of Theses on Geotectonics in China and Its Neighbouring Areas.Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 32 (in Chinese).
Gansu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources.1989b.Gansu Province Regional Geology[J]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 224 (in Chinese).
Seong Yeong Bae, Kang Hee-Cheol, Ree Jin-Han, Choi JeongHeon, Lai Zhonping, Long Hao, Yoon Hye On. 2011. Geomorphic constraints on active mountain growth by the lateral propagation of fault-related folding:A case study on Yumu Shan, NE Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(2):184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.01.015
Song Shuguang, Niu Yaoling, Su Li, Xia Xiaohong. 2013. Tectonics of the north Qilian orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(4):1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004
Song Shuguang, Zhang Lifei, Niu Yaoling, Su Li, Song Biao, Liu Dunyi. 2006. Evolution from oceanic subduction to continental collision:a case study from the Northern Tibetan Plateau based on geochemical and geochronological data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 47(3):435-455. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi080
Song Shuguang. 1997. Tectonic evolution of subductive complex belts in the north Qilain mountains[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 12(4):351-365 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tapponnier P, Meyer B, Avouac J Ph, Peltzer G, Gaudemer Y, Shunmin Guo, Hongfa Xiang, Kelun Yin, Zhitai Chen, Shuahua Cai. 1990. Active thrusting and folding in the Qilian Shan, and decoupling between upper crust and mantle in northeastern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 97(3/4):382-403. doi: 10.1016-0012-821X(90)90053-Z/
Tapponnier P, Meyer B, Avouac J P, Peltzer G, Gaudemer Y, Guo Shunmin, Xiang Hongfa, Yin Kelun, Chen Zhitai, Cai Shuahua, Dai Huagang. 1990. Active thrusting and folding in the Qilian Shan, and decoupling between upper crust and mantle in northeastern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 97(3):382-403. doi: 10.1016-0012-821X(90)90053-Z/
Tapponnier Paul, Peltzer GLDAY, Le Dain A Y, Armijo Roland, Cobbold P. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 10(12):611-616. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<611:PETIAN>2.0.CO;2
Tapponnier Paul, Zhiqin Xu, Roger Francoise, Meyer Bertrand, Arnaud Nicolas, Wittlinger Gérard, Jingsui Yang. 2001. Oblique Stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547):1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
Team China Earthquake Administration "Altyn active fault zone" studying.1992. Altyn Active Fault Zone[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press (in Chinese).
Wang Chengshan, Gao Rui, Yin An, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yuxiu, Guo Tonglou, Li Qusheng, Li Yalin. 2011. A mid-crustal straintransfer model for continental deformation:A new perspective from high-resolution deep seismic-reflection profiling across NE Tibet[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 306(3):279-288. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X11002160
Wang Duojie. 1989. Geomorphology features of the Minle Basin Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Geology, 10:88-99.
Wang Quan, Liu Xueya. 1981. Ophiolite belt and platetectonics in China[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 72-81(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xingchen, Ding Zhifeng, Wu Yan, Zhu Lupei. 2017. Crustal thicknesses and Poisson's ratios beneath the northern section of the northsouth seismic belt and surrounding areas in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(6):2080-2090 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWX201706006.htm
Wang Xingchen, Ding Zhifeng, Wu Yan, Zhu Lupei. 2017. Crustal thicknesses and Poisson's ratios beneath the northern section of the northsouth seismic belt and surrounding areas in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(6):2080-2090 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWX201706006.htm
Wang Yizhou, Zheng Dewen, Pang Jianzhang, Zhang Huiping, Wang Weitao, Yu Jingxing, Zhang Zhuqi, Zheng Wenjun, Zhang Peizhen, Li Youjuan. 2018b. Using slope-area and apatite fission track analysis to decipher the rock uplift pattern of the Yumu Shan:New insights into the growth of the NE Tibetan Plateau[J].Geomorphology, 308:118-128. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.02.006
Wu Cailai, Xu Xueyi, Gao Qianming, Li Xiangmin, Lei Min, Gao Yuanhong, B Frost R, JL Wooden. 2010. Early Palaezoic grranitoid magmation and tectonic evolution in North Qilian, NW China.[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(4):1027-1044 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Cailai, Yang Jingsui, Yang Hungyi, Wooden Joseph L, Shi Rendeng, Chen Songyoung, Zheng Qiuguang. 2004. Dating of two types of granite from north Qilian, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3):425-432 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxb-e200502005
Wu Cailai, Yao Shangzhi, Yang Jingsui, Zeng Lingseng, Chen Songyong, Li Haibing, Wei Xuexiang, Wooden Joseph L, Mazdab Frank K. 2006. Granite evidence of two-year subduction of the Early Paleozoic in the North Qilian Ocean[J]. Geology in China, 33(6):1197-1208.
Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi. 1998. Early Palaeozoic mid-ocean ridge-ocean islan and back-arc basin volcanism in the North Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 72(4):301-312 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzxe199804001.htm
Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Ren Youxiang, Xu Xueyi, Yang Hequn, Li Zhipei, Yang Jianguo, Li Wenyuan, Zhao Donghun, Song Zhongbao. 2001. The Structure-Volcanic Magma Metallogenic Dynamics in the North Qilian Mountain[M]. Beijing:China Land Press (in Chinese).
Xiao Wenjiao, Windley Brian F, Yong Yong, Yan Zhen, Yuan Chao, Liu Chuanzhou, Li Jiliang. 2009. Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the Qilian Shan, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3/4):323-333. doi: 10.1016-j.jseaes.2008.10.001/
Xiao Xuchang, Li Yandong, Li Guangcen, Chang Chengfa, Yuan Xuecheng. 1988. Himalayan Lithospheric Tectonic Evolution[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Xu Xiangke, Yi Chaolu. 2014. Little ice age on the Tibetan Plateau and its bordering mountains:Evidence from moraine chronologies[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 116:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.02.003
Xu Zhiqin, Xu Huifeng, Zhang Jianxin, Li Haibing, Zhu Zhizhi, Qu Jiangchuan, Chen Daizhang, Chen Jinlu, Yang Kaichun. 1994. The Zhoulangnanshan Caledonian subductive complex in the Northern Qilian Mountains and its dynamics[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 68(1):1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400804917
Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Jiang Mei, Li Haibing. 1999. Continental subduction and uplifting of the orogenic belts at the margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(3):139-151(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY199903018.htm
Yin An, Harrison T. Mark. 2000. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1):211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
Yin An, Manning Craig E, Lovera Oscar, Menold Carrie A, Chen Xuanhua, Gehrels George E. 2007. Early Paleozoic tectonic and thermomechanical evolution of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks in the northern Tibetan Plateau, northwest China[J]. International Geology Review, 49(8):681-716. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.8.681
Yuan Daoyang, Ge Weipeng, Chen Zhenwei, Li Chuanyou, Wang Zhicai, Zhang Huiping, Zhang Peizhen, Zheng Dewen, Zheng Wenjun, Craddock William H. 2013. The growth of northeastern Tibet and Its relevance to large-scale continental geodynamics:A review of recent studies[J]. Tectonics, 32(5):1358-1370. doi: 10.1002/tect.20081
Zhang Huiping, Zhang Peizhen, Zheng Dewen, Zheng Wenjun, Chen Zhengwei, Wang Weitao. 2012. Structural features of the Qilian Mountains:implications for Late Cenozoic tectonic deformation and geomorphic evolution in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geology, 32(5):907-920(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Peizhen, Zheng Dewen, Yin Gongming, Yuan Daoyang, Zhang Guangliang, Li Chuanyou, Wang Zhicai. 2006. Discussion on Late Cenozoic growth and rise of northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(1):5-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200601002
Zhang Z, Liang Y, Mei Y, Sun W, Wang W, Gong X, Li Z, Tang J. 2018. Prevalence of osteoarthritis in high altitude area of Tibet[J]. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 26:S222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f75d064fe50c0af66b9b58c23742c8e7
Zheng Dewen, Clark Marin K, Zhang Peizhen, Zheng Wenjun, Farley Kenneth A. 2010. Erosion, fault initiation and topographic growth of the North Qilian Shan (northern Tibetan Plateau)[J]. Geosphere, 6(6):937-941. doi: 10.1130/GES00523.1
Zheng Wenjun, Yuan Daoyang, Zhang Peizhen, Yu Jingxing, Lei Qiyun, Wang Weitao, Zheng Dewen, Zhang Huiping, Li Xinnan, Li Chuanyou, Liu Xingwang. 2016. Techtonic geometry and kinematic dissipation of active faults in the northeastern Tibetan plateau and their implications for understanding northeastward geowth of the plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 36(4):775-788 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Wenjun, Zhang Peizhen, Ai Daoyang, Zheng Dewen. 2009. Deformation on the nothern of the Tibetan plateau from GPS measurement and geologic rates of Late Quaternary along the major fault[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(10):2491-2508(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Wenjun, Zhang Zhuqi, Zhang Peizhen, Liu Xingwang, Guo Xiao, Pang Jianzhang, Ge Weipeng, Yu Jingxing. 2013. Seismogenic structure and mechanism of the 1954 M 71 (1/4) Shandan Earthquake, Gansu Province, Western China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(3): 916-928. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201303021.htm
Zhong Dalai, Ding Lin. 1996. Discussion on the uplift process and its mechanism of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science in China(Series D), 26(4):289-295 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zuo Guochao, Liu Jichen. 1987. The evolution of tectonic of Early Paleozoic in North Qilian range, China[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinca, (1):14-24. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198701001.htm
Zuza Andrew V, Cheng Xiaogan, Yin An. 2016. Testing models of Tibetan Plateau formation with Cenozoic shortening estimates across the Qilian Shan-Nan Shan thrust belt[J]. Geosphere, 12(2):501-532. doi: 10.1130/GES01254.1
Zuza Andrew, Wu Chen, Reith Robin, Yin An, Li Jianhua, Zhang Jinyu, Zhang Yuxiu, Wu Long, Liu Wencan. 2018. Tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan:An early Paleozoic orogen reactivated in the Cenozoic[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 130(5/6):881-925. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321553679_Tectonic_evolution_of_the_Qilian_Shan_An_early_Paleozoic_orogen_reactivated_in_the_Cenozoic
边庆凯, 张培震, 苏向洲. 2001.榆木山北缘断裂的构造地貌特征与断层活动性[J].华北地震科学, 19(3):41-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2001.03.005 陈柏林, 王春宇, 宫红良, 刘建民, 张永双, 刘建生.2007.关于河西走廊盆地榆木山北缘断裂晚第四纪活动特征的新认识[J].地质通报, 8:976-983. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.009 陈干, 郑文俊, 王旭龙, 张培震, 熊建国, 俞晶星, 刘兴旺, 毕海芸, 刘金瑞, 艾明. 2017.榆木山北缘断裂现今构造活动特征及其对青藏高原北东扩展的构造地貌响应[J].地震地质, 39(5):871-888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.05.001 陈宣华, 邵兆刚, 熊小松, 高锐, 徐盛林, 张义平, 李冰, 王叶. 2019.祁连山北缘早白垩世榆木山逆冲推覆构造与油气远景[J].地球学报, 40(3):377-392. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201903001 戴霜, 方小敏, 张翔, 王方成. 2003.北山中部地区闪长岩花岗岩类成因及构造背景[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 39(1):86-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0455-2059.2003.01.019 杜远生, 朱杰, 韩欣, 顾松竹. 2004.从弧后盆地到前陆盆地——北祁连造山带奥陶纪-泥盆纪的沉积盆地与构造演化[J].地质通报, 23(9/10):911-917. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200409013 甘肃省地质矿产局.1989.甘肃省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 224. 葛肖虹, 张梅生, 刘永江, 叶慧文, 石采东. 1998.阿尔金断裂研究的科学问题与研究思路[J].现代地质, 12(3):295-301. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDDZ803.000.htm 国家地震地质研究所, 国家地震局兰州地质研究所.1993.祁连山-河西走廊活动断裂系[M].北京:地震出版社. 国家地震局《阿尔金活动断裂带》课题组.1992.阿尔金活动断裂带[M].北京:地震出版社. 何光玉, 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 肖安成, 程晓敢. 2004.河西走廊西段及邻区早白垩世盆地的重新厘定[J].石油学报, 25(6):18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2004.06.004 金卿.2011.榆木山断裂带晚第四纪构造活动与大震危险性评价[D], 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85403-1014240178.htm 赖新荣, 江思宏, 邱小平, 刘妍, 胡朋, 张万益. 2007.阿拉善北大山岩带海西期中酸性岩40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地球化学特征[J].地质学报, 81(3):370-380. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200703009 李有利, 杨景春. 1997.河西走廊榆木山边缘断层构造地貌研究[J].地质力学学报, 3(4):20-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700066522 李玉龙, 邢成起. 1988.河西走廊地质构造基本特征以及榆木山北麓与黑河口上龙王活断层研究[J].地震工程学报, (2):37-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZBDZ198802004.htm 刘栋梁, 宋春晖, 方小敏, 戴霜, 李海兵. 2012.榆木山地区玉门砾岩磁性地层及其对青藏高原东北部变形隆升意义[J].地质学报, 86(6):898-905. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.06.005 潘宏勋, 葛肖虹, 刘俊来. 2000.对祁连山北缘榆木山隆起的质疑[J].长春科技大学学报, 30(1):9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2000.01.002 任纪舜, 姜春发. 1981.中国的深断裂[C]//中国及其邻区大地构造论文集.北京: 地质出版社. 宋述光.1997.北祁连山俯冲杂岩带的构造演化[J].地球物理学进展, 12(3):351-365. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/93494 王成善, 朱利东, 刘志飞. 2004.青藏高原北部盆地构造沉积演化与高原向北生长过程[J].地球科学进展, 19(3):373-381. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.005 王多杰. 1989.民乐盆地及邻区构造地貌特征[J].甘肃地质, (10):88-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSDZ199000006.htm 王荃, 刘雪亚. 1981.中国的蛇绿岩带与板块构造[J].长春地质学院学报, (1):72-81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1981-CCDZ198101007.htm 王兴臣, 丁志峰, 武岩, 朱露培. 2017.中国南北地震带北段及其周缘地壳厚度与泊松比研究[J].地球物理学报, 60(6):2080-2090. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201706006.htm 吴才来, 徐学义, 高前明, 李向民, 雷敏, 郜源红, Frost R B, Wooden Joseph L. 2010.北祁连早古生代花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J].岩石学报, 26(4):1027-1044. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201004003 吴才来, 杨经绥, 杨宏仪, Wooden Joseph L, 史仁灯, 陈松永, 郑秋光. 2004.北祁连东部两类Ⅰ型花岗岩定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 20(3):425-432. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200403006 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 任有祥, 徐学义, 杨合群, 李智佩, 杨建国, 李文渊, 赵东宏, 宋忠宝.2001.北祁连山构造-火山岩浆-成矿动力学[M].北京:中国大地出版社. 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.1998.北祁连山早古生代洋脊-洋岛和弧后盆地火山作用[J].地质学报. 72(4):301-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1998.04.002 肖序常, 李廷栋, 李光岑.1988.喜马拉雅岩石圈演化总论[M].北京:地质出版社. 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 张建新, 李海兵, 朱志直, 曲景川, 陈代璋, 陈金禄, 杨开春. 1994.北祁连走廊南山加里东俯冲杂岩增生地体及其动力学[J].地质学报, 68(1):1-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400804917 许志琴, 杨经绥, 姜枚, 李海兵. 1999.大陆俯冲作用及青藏高原周缘造山带的崛起[J].地学前缘, 6(3):139-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.03.014 张会平, 张培震, 郑德文, 郑文俊, 陈正位, 王伟涛. 2012.祁连山构造地貌特征:青藏高原东北缘晚新生代构造变形和地貌演化过程的启示[J].第四纪研究, 32(5):907-920. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.05.08 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 袁道阳, 张广良, 李传友, 王志才.2006.有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J].第四纪研究, 26(1):5-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.01.002 郑文俊, 袁道阳, 张培震, 俞晶星, 雷启云, 王伟涛, 郑德文, 张会平, 李新男, 李传友. 2016.青藏高原东北缘活动构造几何图像, 运动转换与高原扩展[J].第四纪研究, 36(4):775-788. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201604001 郑文俊, 张培震, 袁道阳, 郑德文. 2009. GPS观测及断裂晚第四纪滑动速率所反映的青藏高原北部变形[J].地球物理学报, 52(10):2491-2508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.10.008 钟大赉, 丁林. 1996.青藏高原的隆起过程及其机制探讨[J].中国科学(D辑), 26(4):289-295. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.04.001




 下载:
下载: