The discovery of the Paleoproterozoic syenite in Helishan, Gansu Province, and its implications for the tectonic attribution of the Alxa Block
-
摘要:
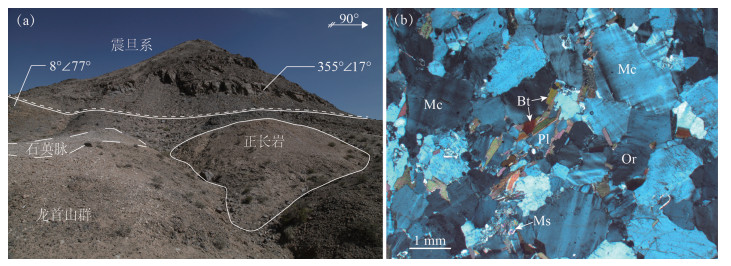
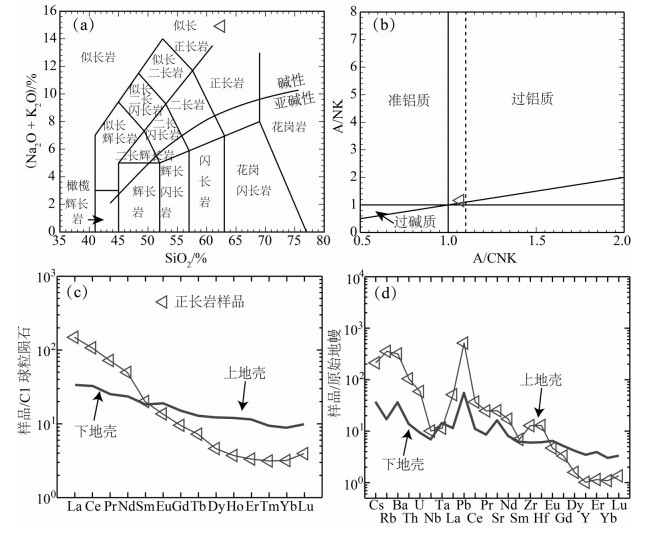
阿拉善地块的大地构造属性是近年来地质界激烈争论的科学问题:是华北克拉通的一部分,还是在前寒武纪尚未与华北克拉通拼合?研究阿拉善地块的基底并与华北克拉通主体进行对比,对探讨这一问题具有重要启示。阿拉善地块的基底仅在其东部和西南缘零星出露,且前人的研究主要集中在地块东部。在阿拉善地块西部的合黎山地区,有正长岩侵入龙首山群,并被震旦系不整合覆盖。该正长岩强烈富钾(K2O=13.77%),轻、重稀土明显分异((La/Yb)N=46.62),显示Nb-Ta负异常和Pb-Zr-Hf正异常,并具有高Sr低Nd的同位素特征(εNd(t)=-5.05),表明该岩体源于玄武质下地壳的部分熔融。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年表明,该正长岩形成于(1872 ±12)Ma,即古元古代,并记录了~2.7 Ga的地壳生长以及~2.5 Ga和~1.95 Ga的岩浆活动。合黎山古元古代正长岩的发现补充了阿拉善地块前寒武纪基底的组成,进一步完善了阿拉善地块新太古代-古元古代基底和构造热事件的时代格架,且与华北克拉通主体十分相似,指示二者具有明显的亲缘性。
Abstract:The tectonic affinity of the Alxa block has long been in debate. It may be part of the North China Craton (NCC), or independent from the NCC during the Precambrian. The comparison of basements between the Alxa block and the NCC would be helpful to solving this dispute, but the Alxa basement is relatively poorly studied due to limited outcrops, with most of available data reported in eastern Alxa. Recently, a syenite that intruded into the Longshoushan Group has been sampled in Helishan area, western Alxa, and both of them are unconformably covered by Sinian strata. The Helishan syenite is characterized by extremely enriched K2O (13.77%) and LREE[(La/Yb)N=46.62], and shows distinct negative and positive anomalies of Nb-Ta and Pb-Zr-Hf, respectively, with EM-I type Sr-Nd isotope features (εNd(t)=-5.05), implying partial melting of basaltic lower crust. Moreover, LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data indicate that this syenite was formed during Paleoproterozoic (1872 ±12) Ma and display records of~2.7 Ga crustal growth and~2.5, 2.1 and 1.95 Ga magmatic activities. According to data from this study and previously published data, the Neoarchean-Pelaoproterozoic basements and tectono-thermal events of the Alxa block and the NCC are geochronologically consistent, indicating very close affinity between them.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
莱阳是我国著名的恐龙之乡,晚白垩世鸭嘴龙类的骨骼化石十分丰富,但早白垩世恐龙则发现不多,仅有少量鹦鹉嘴龙类。2000年,曾在莱阳早白垩世龙旺庄组发现过兽脚类足迹化石。最近,我们在海阳凤城镇凤翔路附近(36°43'17"N,121°14'40"E)发现了一个新的小型兽脚类恐龙足迹化石点。本项研究的目的,是确定造迹恐龙的类型,并探讨其足迹分类意义,为早白垩世胶莱盆地恐龙群面貌恢复提供重要化石依据。
2. 研究方法(Methords)
采用传统的地层学、古生态学研究方法。首先,野外测制含化石层位的地层剖面,分层并进行岩性描述,标注足迹化石的产出层位,测量足迹大小等参数、绘制足迹产出状态图、采集有关的足迹标本等;其次,根据区域地质资料确定足迹的产出层位,室内绘制地层剖面图和足迹平面分布图等;最后,开展恐龙足迹的古生态学研究,查明造迹恐龙的种类,探讨其行为习性及生活环境等。
3. 研究结果(Results)
恐龙足迹产于中层灰绿色、灰紫色粉砂岩、细砂岩中。根据岩性组合、沉积特征及与区域地层对比,确认其产出层位为早白垩世莱阳群杨家庄组,为一套河湖湘沉积。该组与以往报道的莱阳地区产兽脚类足迹拟跷脚龙足迹Paragrallator的龙旺庄组及下伏的水南组时代相当。
此次共发现较清晰的恐龙足迹化石26个。其中,15个产于层面上,为正常凹型足迹,未能采集(图 1);7个位于岩层底面,为凸型足迹,分布于2块标本上,已被采集(图 2)。足迹均为小的三趾型,最大的长10.0 cm,宽5.3 cm;最小的长5.0 cm,宽4.0 cm。因为足长大于宽,足迹较窄且爪迹明显,应为小型兽脚类恐龙的足迹。根据足迹大小、长宽比值以及Ⅱ、Ⅳ趾间角的大小,可将这些足迹分为a、b、c 3个形态类群(表 1)。类型a:长略大于宽,足长和宽均值分别为6.0 cm和4.7 cm;类型b:长远大于宽,长和宽均值为7.3 cm和3.6 cm(图 2b);类型c:只有一个足迹,长10.0 cm,宽5.3 cm。研究认为,类型a类似于山东诸城黄龙沟同时期的兽脚类足迹强壮足迹Corpulentapus,但后者个体要大得多,几乎是其2倍;类型b与山东莒南后左山早白垩世田家楼组的甄朔南小龙足迹Minisauripus zhenshuonani大小相似,但后者的长宽比值较小,特别是类型b的Ⅲ趾更长直、粗壮,这点又与后左山的跷脚龙足迹Grallator isp.相似,因此,其应为二者之间的过渡类型;类型c根据形态、大小等则可归入Grallator isp.。Grallator是最早被命名的恐龙足迹属之一,足迹长一般不超过15 cm,三趾型,两侧趾间夹角较小,中趾较两侧趾前伸明显(大于Eubrontes或Anchisauripus),足迹狭窄,长宽比值大于或等于2。以往足长小于15 cm的三趾型兽脚类足迹往往归于该足迹属。需要指出的是,恐龙足迹的分类主要是根据形态,受底质等环境因素影响很大,往往同一个恐龙个体可以形成不同的足迹属。因此,研究者对于对于足迹的分类比较谨慎,本文也对类型a和b进行进一步的分类归并。需要指出,这些小型足迹的层面分布相对密集、方向性较为杂乱,可能意味着它们的造迹恐龙具有群居特征,起码足迹的产地是一个小型恐龙经常聚会的地区。此外,根据有关的经验公式,可以推测造迹恐龙的大小,一般身高是足长的4倍,而身长是身高的3倍。据此推测这批足迹的造迹恐龙体长约为80~90 cm,高近30 cm。但由于这些足迹杂乱,加之出露局限,难以识别出完整的行迹(trackway),因此,步长及运动速度等参数暂时无法获取。
表 1 海阳恐龙足迹主要特征Table 1. Main characteristics of dinosaur footprints in Haiyang
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1) 凤城镇的足迹三趾型,由小型兽脚类恐龙形成,它们是海阳地区恐龙足迹的首次发现,时代为早白垩世中晚期,产出地层层位是下白垩统莱阳群杨家庄组。
(2) 可以识别出26个恐龙足迹,采集的两块标本含8个足迹,另外18个足迹仍然保持在野外。这些足迹可分为3个形态类型。类型a类似于Corpulentapus,但个体偏小;类型b应为足迹属Minisauripus与Grallator之间的过渡类型,将在小型兽脚类恐龙足迹的分类中占据重要位置;类型c则可归入Grallator isp。
(3) 尽管该地没有发现兽脚类骨骼化石,但此次恐龙足迹的发现表明,在早白垩世,胶莱盆地东南部的海阳为河湖相环境,生活着体长80~90 cm群居的小型肉食性兽脚类恐龙群。因此,恐龙足迹是恐龙研究的重要内容,特别在缺乏恐龙骨骼化石的情况下,足迹化石是研究恐龙的绝佳材料。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
本文为国家自然科学基金项目(41741008)和中国地质调查局项目“1:100万天津幅海洋区域地质调查”(1212011220113)资助的成果。
致谢: 感谢审稿人对本文的宝贵意见!感谢邵浩浩、苗慧心和史建杰在野外及实验过程中的帮助,锆石U-Pb定年和全岩Sr-Nd同位素测试过程中中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所王倩和中国地质科学院地质研究所唐索寒研究员的帮助! -
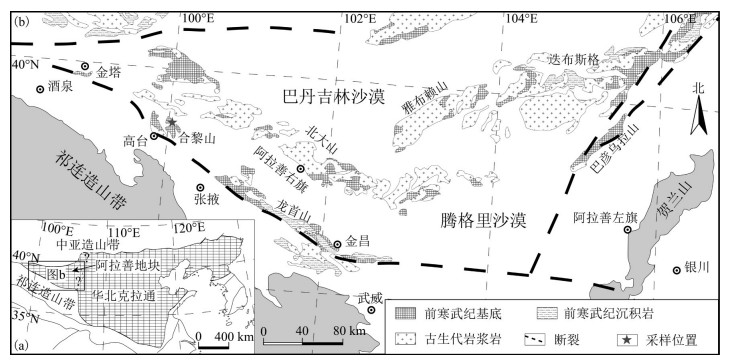
图 1 阿拉善地块大地构造位置(a据Zhao et al., 2005修改)和地质简图(b据Gong et al., 2012修改)
Figure 1. Tectonic map of the Alxa Block (a, modified from Zhao et al., 2005) and Geological sketch map of the Alxa Block (b, modified from Gong et al., 2012)
图 4 合黎山正长岩主量及微量元素特征
(下地壳平均组分参考Rudnick and Gao, 2003)
Figure 4. Diagrams showing major and trace element features of the Helishan syenite
(the composition of lower crust after Rudnick and Gao, 2003)
表 1 合黎山古元古代正长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb data for the Paleoproterozoic syenite in Helishan

表 2 合黎山正长岩主量(%)及微量元素(10-6)含量
Table 2 Major (%) and trace element (10-6) concentrations of the Paleoproterozoic syenite in Helishan

表 3 合黎山正长岩Sr-Nd同位素数据
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the Helishan syenite

-
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Nei Mongol Autonomous Region. 1991. Regional Geology of Nei Mongol(Inner Mongolia) Autonomous Region[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cai J, Liu F, Liu P, Liu C, Wang F, Shi J, 2014. Metamorphic P-T path and tectonic implications of pelitic granulites from the Daqingshan Complex of the Khondalite Belt, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 241:161-184. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.11.012
Chen Xuanhua, Shao Zhaogang, Xiong Xiaosong, Gao Rui, Xu Shenglin, Zhang Yiping, Li Bing, Wang Ye. 2019. Early Cretaceous overthrusting of Yumu Mountain and hydrocarbon prospect on the northern margin of the Qilian Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40:377-392 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201903001
Dan W, Li X H, Guo J, Liu Y, Wang X C. 2012. Paleoproterozoic evolution of the eastern Alxa Block, westernmost North China:Evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb dating and Hf-O isotopes[J]. Gondwana Research, 21:838-864. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.004
Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, Wang X C, Liu Y. 2014. Neoproterozoic Stype granites in the Alxa Block, westernmost North China and tectonic implications:In situ zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopic and geochemical constraints[J]. American Journal of Science, 314:110-153. doi: 10.2475/01.2014.04
Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, Wang X C, Wyman D A, Liu Y. 2016.Phanerozoic amalgamation of the Alxa Block and North China Craton:Evidence from Paleozoic granitoids, U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotope geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 32:105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.02.011
Depaolo D J, Linn A M, Schubert G, 1991. The continental crustal age distribution:Methods of determining mantle separation ages from Sm-Nd isotopic data and application to the Southwestern United States[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 96(B2):2071-2088. doi: 10.1029/90JB02219
Dong C, Wan Y, Xu Z, Liu D, Yang Z, Ma M, Xie H. 2013. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of Late Paleoproterozoic kondalites in the Daqing Mountains area on the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(1):115-125. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ed201301012
Geng Yuansheng and Zhou Xiwen, 2010. Early Neoproterozoic granite events in Alxa area of Inner Mongolia and their geological significance:Evidence from geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 29(6):779-795 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Geng Yuansheng, Wang Xinshe, Shen Qihan, Wu Chunming. 2006.Redefinition of the Alxa Group-Complex (Precambrian metamorphic basement) in the Alxa area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 33(1):138-145 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200601015
Geng Yuansheng, Wang Xinshe, Wu Chunming, Zhou Xiwen. 2010.Late Paleoproterozoic tectonothermal events of the metamorphic basement in Alxa area:Evidence from geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(4):1159-1170 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201004014.htm
Gong Jianghua, Zhang Jianxin, Yu Shengyao. 2011. The origin of Longshoushan Group and associated rocks in the southern part of the Alxa Block:Constraint from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon dating[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(5):795-818 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201105006.htm
Gong J, Zhang J, Wang Z, Yu S, Li H, Li Y. 2016. Origin of the Alxa Block, western China:New evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of the Longshoushan Complex[J]. Gondwana Research, 36:359-375. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.014
Gong J, Zhang J, Yu S, Li H, Hou K. 2012. Ca. 2.5 Ga TTG rocks in the western Alxa Block and their implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57:4064-4076. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5315-8
Han B F, Xu Z, Ren R, Li L L, Yang J H, Yang Y H. 2012. Crustal growth and intracrustal recycling in the middle segment of the Trans-North China Orogen, North China Craton:A case study of the Fuping Complex[J]. Geological Magazine, 149:729-742. doi: 10.1017/S0016756811001014
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Tian Yourong. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(4):481-492 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200904010
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Zou Tianren, Qu Xiaoming, Shi Yuruo, Xie Guiqing, 2007. Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10):2595-2604 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu J, Gong W, Wu S, Liu Y, Liu S. 2014. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Langshan Group in the northeast margin of the Alxa block, with tectonic implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 255(2):756-770. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d3b6d224e161ba2340eff59b6fde5125
Jacobsen S B. 1988. Isotopic constraints on crustal growth and recycling[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90:315-329. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90133-1
Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B, 2000. Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia:Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Episodes, 23:82-92. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2000/v23i2/001
Jian P, Kröner A, Windley B F, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Zhang L. 2012.Episodic mantle melting-crustal reworking in the late Neoarchean of the northwestern North China Craton:Zircon ages of magmatic and metamorphic rocks from the Yinshan Block[J]. Precambrian Research, 222-223:230-254. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.03.002
Jiang N, Guo J, Zhai M, Zhang S. 2010. -2.7 Ga crust growth in the North China craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 179:37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.010
Li Jinyi, Zhang Jin, Qu Junfeng. 2012. Amalgamation of the North China Craton with Alxa Block in the late of Early Paleozoic:Evidence from sedmentary sequences in the Niushou Mountain, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, NW China[J]. Geological Review, 58(2):208-214 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu B, Feng S, Ji J, Wang S, Zhang J, Yuan H, Yang G. 2017.Lithospheric structure and faulting characteristics of the Helan Mountains and Yinchuan Basin:Results of deep seismic reflection profiling[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60:589-601. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5069-4
Ludwig K R. 2009. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.70. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, 1-76.
Ma M, Wan Y, Santosh M, Xu Z, Xie H, Dong C, Liu D, Guo C. 2012.Decoding multiple tectonothermal events in zircons from single rock samples:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb data from the late Neoarchean rocks of Daqingshan, North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research 22:810-827. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.020
Peng P. 2015. Precambrian mafic dyke swarms in the North China Craton and their geological implications[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58:649-675.
Peng P, Zhai M G, Li Q, Wu F, Hou Q, Li Z, Li T, Zhang Y. 2011.Neoproterozoic (~900 Ma) Sariwon sills in North Korea:Geochronology, geochemistry and implications for the evolution of the south-eastern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 20:243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.011
Rudnick R L and Gao S. 2003. Composition of the Continental Crust[C]//Turekian, H D H K(Ed.). Treatise on geochemistry[M]. Pergamon, Oxford, 1-64.
Song Biao, Zhang Yuhai, Wan Yusheng, Jian Ping. 2002. Mount making and procedure of the SHRIMP dating[J]. Geological Review, 48:26-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005931
Song D, Xiao W, Collins A S, Glorie S, Han C, Li Y. 2017. New chronological constrains on the tectonic affinity of the Alxa Block, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 299:230-243. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.07.015
Tang Suohan, Li Jin, Liang Xirong, Zhang Liguo, Li Guozhan, Pu Wei, Li Chaofeng, Yang Yueheng, Chu Zhuyin, Zhang Jun, Hou Kejun, Wang Xiaoming. 2017. Reference material preparation of 143Nd/144Nd isotope ratio[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 36(2):163-170 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201702009
Tang Zhongli, Bai Yunlai. 1995. Geotectonic framework and metallogenic system in the southwest margin of north China paleocontinent[J]. Earth science Frontiers (China University of Geosciences, Beijing), 6(2):271-283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tung K, Yang H, Liu D, Zhang J, Tseng C, Wan Y. 2007. SHRIMP UPb geochronology of the detrital zircons from the Longshoushan Group and its tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(10):1414-1425. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0189-x
Wan Y, Song B, Liu D, Wilde S A, Wu J, Shi Y, Yin X, Zhou H. 2006.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton:Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event[J]. Precambrian Research, 149:249-271. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.06.006
Wan Y, Xie S, Yang C, Kröner A, Ma M, Dong C, Du L, Xie H, Liu D.2014. Early Neoarchean (-2.7 Ga) tectono-thermal events in the North China Craton:A synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 247:45-63. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.03.019
Wang X C, Wilde S A, Xu B, Pang C J. 2016a. Origin of arc-like continental basalts: Implications for deep-Earth fluid cycling and tectonic discrimination. Lithos, 261: 5-45.
Wang A, Liu Y. 2012. Neoarchean (2.5-2.8 Ga) crustal growth of the North China Craton revealed by zircon Hf isotope:A synthesis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 3:147-173. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.006
Wang Z Z, Han B F, Feng L X, Liu B, Zheng B, Kong L J. 2016.Tectonic attribution of the Langshan area in western Inner Mongolia and implications for the Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic evolution of the Western North China Craton:Evidence from LAICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Langshan basement[J]. Lithos, 261:278-295. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.03.005
Wu F, Zhao G, Wilde S A, Sun D. 2005. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5):523-545. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011
Wu S, Hu J, Ren M, Gong W, Liu Y, Yan J. 2014. Petrography and zircon U-Pb isotopic study of the Bayanwulashan Complex:Constrains on the Paleoproterozoic evolution of the Alxa Block, westernmost North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 94:226-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.011
Xia X, Sun M, Zhao G, Luo Y. 2006. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons from the Jining Complex, North China Craton and its tectonic significance[J]. Precambrian Research, 144:199-212. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.004
Xiu Qunye, Lu Songnian, Yu Haifeng, Yang Chunliang. 2002. The isotopic age evidence for main Longshoushan Group contributing to Paleoproterozoic[J]. Progress in Precambrian Research, 25(2):93-96 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin C, Zhao G, Guo J, Sun M, Xia X, Zhou X, Liu C. 2011. U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of zircons of the Helanshan Complex:Constrains on the evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the Western Block of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 122(1/2):25-38. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493710003233
Yin C, Zhao G, Sun M, Xia X, Wei C, Zhou X, Leung W. 2009. LAICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of the Qianlishan Complex:Constrains on the evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the Western Block of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 174(1/2):78-94.
Yin C, Zhao G, Wei C, Sun M, Guo J, Zhou X. 2014. Metamorphism and partial melting of high-pressure pelitic granulites from the Qianlishan Complex:Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 242(0):172-186. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926814000072#!
Yuan W, Yang Z. 2015. The Alashan Terrane was not part of North China by the Late Devonian:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Gondwana Research, 27:1270-1282. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1342937X13004139
Zhai Mingguo, Hu Bo, Peng Peng, Zhao Taiping. 2014. MesoNeoproterozoic magmatic events and multi-stage rifting in the NCC[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1):100-119 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai M G, Santosh M. 2011. The early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton:A synoptic overview[J]. Gondwana Research, 20(1):6-25. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1342937X11000402
Zhang B H, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Nie F. 2016a.Tectonic affinity of the Alxa Block, Northwest China:Constrained by detrital zircon U-Pb ages from the early Paleozoic strata on its southern and eastern margins[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 339:289-303. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.02.017
Zhang Jianxin, Gong Jianghua. 2018. Revisiting the nature and affinity of the Alxa Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(4):940-962 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201804006
Zhang J, Gong J, Yu S, Li H, Hou K. 2013a. Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic multiple tectonothermal events in the western Alxa block, North China Craton and their geological implication:Evidence from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic composition[J]. Precambrian Research, 235:36-57. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.05.002
Zhang J, Li J, Liu J, Feng Q. 2011. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages of Middle Ordovician flysch sandstones in the western ordos margin:New constraints on their provenances, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42:1030-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.009
Zhang Jin, Li Jinyi, Liu Jianfeng, Li Yanfeng, Qu Junfeng, Feng Qianwen. 2012. The relationship between the Alxa Block and the North China Plate during the Early Paleozoic:New information from the Middle Ordovician detrital zircon ages in the eastern Alxa Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(9):2912-2934 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1475273
Zhang J, Li J, Xiao W, Wang Y, Qi W. 2013b. Kinematics and geochronology of multistage ductile deformation along the eastern Alxa block, NW China:New constraints on the relationship between the North China Plate and the Alxa block[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 57:38-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2013.10.002
Zhang J, Wang T, Zhang L, Tong Y, Zhang Z, Shi X, Guo L, Huang H, Yang Q, Huang W, Zhao J, Ye K, Hou J. 2015a. Tracking deep crust by zircon xenocrysts within igneous rocks from the northern Alxa, China:Constraints on the southern boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 108:150-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.019
Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhao H. 2016b. Timing of amalgamation of the Alxa Block and the North China Block:Constraints based on detrital zircon U-Pb ages and sedimentologic and structural evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 668-669:65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.006
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Xiao W, Wang Y, Zhang B. 2015b. Linking the Alxa Terrane to the eastern Gondwana during the Early Paleozoic:Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Cambrian sedimentary records[J]. Gondwana Research, 28:1168-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.012
Zhao G, Cawood P A, Li S, Wilde S A, Sun M, Zhang J, He Y, Yin C. 2012. Amalgamation of the North China Craton:Key issues and discussion[J]. Precambrian Research 222-223:55-76. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.016
Zhao G, Sun M, Wilde S A, Li S Z. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 136:177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
Zhao G, Wilde S A, Guo J, Cawood P A, Sun M, Li X. 2010. Single zircon grains record two Paleoproterozoic collisional events in the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 177:266-276. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.12.007
Zhao Zhenhua. 2005. Advances in trace element geochemistry[C]//Zhang Benren, Fu Jiamo (eds.). Advances in Geochemistry.Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 199-248 (in Chinese).
陈宣华, 邵兆刚, 熊小松, 高锐, 徐盛林, 张义平, 李冰, 王叶. 2019.祁连山北缘早白垩世榆木山逆冲推覆构造与油气远景[J].地球学报, 40(3):377-392. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201903001 董国安, 杨洪仪, 刘敦一, 张建新, 曾建元, 万渝生. 2007.龙首山岩群碎屑锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 52(6):688-697. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.06.014 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 吴春明. 2006.内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质基底阿拉善群的再厘定[J].中国地质, 33(1):138-145. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060115&flag=1 耿元生, 王新社, 吴春明, 周喜文, 2010.阿拉善变质基底古元古代晚期的构造热事件[J].岩石学报, 26(4):1159-1170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201004013 耿元生, 周喜文. 2010.阿拉善地区新元古代岩浆事件及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 29(6):779-795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.014 宫江华, 张建新, 于胜尧. 2011.阿拉善地块南缘龙首山岩群及相关岩石的起源和归属——来自LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的制约[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 30(5):795-818. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.05.005 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位UPb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 28(4):481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 曲晓明, 石玉若, 谢桂青, 2007. LA-MCICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 23(10):2595-2604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025 李锦轶, 张进, 曲军峰. 2012.华北与阿拉善两个古陆在早古生代晚期拼合[J].地质论评, 58(2):208-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.02.002 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局, 1991.内蒙古自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社. 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 简平. 2002.锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J].地质论评, 48:26-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005931 汤中立和白云来, 1999.华北古大陆西南边缘构造格架与成矿系统[J].地学前缘, 6(2):271-283. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.02.006 唐索寒, 李津, 梁细荣, 张利国, 李国占, 濮巍, 李潮峰, 杨岳衡, 储著银, 张俊, 侯可军, 王晓明. 2017.钕同位素比值~(143)Nd/~(144)Nd标准溶液研制[J].岩矿测试, 36(2):163-170. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YKCS201702010.htm 修群业, 陆松年, 于海峰, 杨春亮. 2002.龙首山岩群主体划归古元古代的同位素年龄证据[J].前寒武纪研究进展, 25(2):93-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2002.02.005 翟明国, 胡波, 彭澎, 赵太平. 2014.华北中-新元古代的岩浆作用与多期裂谷事件[J].地学前缘, 21(1):100-119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201401013.htm 张建新, 宫江华, 2018.阿拉善地块性质和归属的再认识[J].岩石学报, 34(4):940-962. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201804006 张进, 李锦轶, 刘建峰, 李岩峰, 曲军峰, 冯乾文. 2012.早古生代阿拉善地块与华北地块之间的关系:来自阿拉善东缘中奥陶统碎屑锆石的信息[J].岩石学报, 28(9):2912-2934. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201209020 赵振华. 2005.微量元素地球化学研究进展[M].北京:化学工业出版社. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李炎桂,姚华舟,William J.Foster,邢立达,王传尚,Asma Tahir,Junaid Khan,安志辉,赵赫,王建雄. 藏东昌都地区首次发现中侏罗世兽脚类恐龙行迹. 地球科学. 2022(11): 4222-4244 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: