The Early Cretaceous granodiorites in the Aweng Co area, Tibet: Evidence for the subduction of the Bangong Co-Nujiang River oceanic crust to the south
-
摘要:
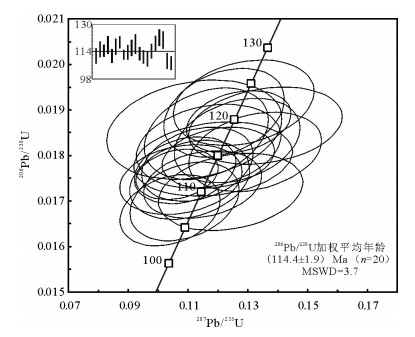
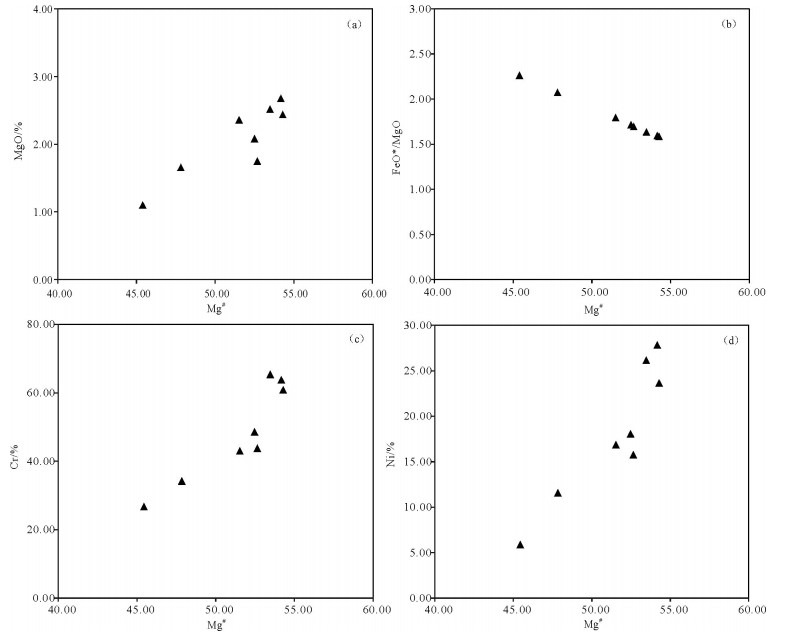
对拉萨地块北部阿翁错地区花岗闪长岩进行了年龄分析、岩石地球化学研究。锆石LA-ICP-MS定年测得花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄为(114.4±1.9)Ma,属于早白垩世晚期岩浆活动的产物。花岗闪长岩地球化学特征表明,其具有典型镁安山岩/闪长岩(MA)的地球化学特征,所有样品均具有较高Mg#值(45.42~54.29),低的TFeO*/MgO值(1.58~2.26);所有样品都显示轻稀土元素富集,富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素的特征。研究表明,阿翁错花岗闪长岩是班公湖-怒江洋壳在俯冲消减背景下,由俯冲洋壳脱水熔融产生的溶体与地幔橄榄岩发生交代作用的产物,为晚中生代班公湖-怒江洋盆的南向俯冲消减提供了直接的岩石学、地球化学、年代学证据。
Abstract:This paper reports zircon U-Pb data of major and trace elements for the granodiorites from the Aweng Co area in northern Lhasa block. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of granodiorite yielded an age of 163.3 ±1.7 Ma, suggesting that the intruded rocks were formed in late Early Cretaceous period. Geochemical studies show that Aweng Co granodiorites have typical geochemical characteristics similar to the magnesian andesite/diorite (MA). They are characterized by high Mg# values (45.42~54.29) and low TFeO*/MgO ratios (1.58~2.26). They are enriched in LREE in the chondrite-normalized REE patterns, and are enriched in large ion lithophile elements (LILEs) and depleted in high field strength elements (HFSEs). Geochemical features of the Aweng Co magnesian granodiorites are considered to have been generated by the southward subduction of Bangong Co-Nujiang River oceanic lithosphere, and can be genetically regarded as resulting from partial melting of dewatered and subducted oceanic crust melts, which had been metasomatized by mantle peridotite under the condition of oceanic crust subduction. These results provide direct petrologic evidence of the intruded rocks for the southward subduction of the Bangong Co-Nujiang River Ocean.
-
1. 引言
华南广泛发育的中生代岩浆岩(图 1a)长期受到地质学家的关注(Jahn, 1974; Zhou et al., 2000; 王强等, 2005; 孙涛, 2006; 周新民, 2007; Li and Li, 2007; 杨明桂等, 2009; 徐先兵等, 2009; 舒良树, 2012; Wang et al., 2013; 郑永飞等, 2013; 崔建军等, 2013; 李三忠等, 2018;苑新晨等,2021)。尤其对华南晚中生代花岗岩类进行了较深入的研究,对其时空分布格局、岩石成因、形成构造背景及与成矿关系等方面取得了一系列的进展(Zhou and Li, 2000; 王强等, 2005; 孙涛, 2006; 周新民, 2007; 付建明等, 2007; 柏道远等, 2008; 肖庆辉等, 2010; 舒良树, 2012; 阳杰华等, 2017; 贾丽辉, 2018; Chen et al., 2019; 袁永盛等,2020;李宏卫等,2021)。其中,发现100 Ma左右的岩浆岩在东南沿海地区大量发育(王德滋和沈渭洲, 2003; 肖娥等, 2007; 李良林等, 2013; Chen et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2016; Yan et al., 2016; 贾丽辉, 2018),而华南腹地(特别是南岭地区)该时期的岩浆活动较少(王强等, 2005; 蔡明海等, 2006; 贾小辉等, 2014; Wang et al., 2018)。对其成因及形成的构造环境仍存在争议,提出了如活动大陆边缘构造-岩浆作用(Jahn, 1974; Zhou et al., 2006)、大陆伸展-裂解(Gilder et al., 1991)、阿尔卑斯型碰撞造山(Hsu et al., 1990)等不同的认识。
![]() 图 1 华南主要构造单元和中生代岩浆岩分布图(a, 据Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013修改)、连阳岩体地质简图(b, 据高剑峰等, 2005修改;同位素年龄数据马星华等, 2014)及研究区地质简图与采样位置图(c, 据袁永盛等, 2020修改)1—燕山期火山岩;2—燕山期侵入岩;3—印支期侵入岩;4—大地构造单元界线;5—深大断裂;6—晚白垩世花岗斑岩;7—晚白垩世第五侵入次花岗岩;8—晚白垩世第四侵入次二长花岗岩;9—晚白垩世第三侵入次二长花岗岩;10—晚白垩世第二侵入次二长花岗岩;11—晚白垩世第一侵入次二长花岗岩;12—早白垩世正长花岗岩;13—地质界线;14—断层;15—采样位置;Q—第四系;K—白垩系;J—侏罗系;T—三叠系;C—石炭系;Є—寒武系;Є-K—寒武系—白垩系Figure 1. Geological sketch map of main tectonic units and Mesozoic igneous rocks in South China (a, modified from Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013), geological sketch of the Lianyang pluton (b, modified from Gao Jianfeng et al., 2005; isotopic age from Ma Xinhua et al., 2014), geological sketch and sampling location of the investigated area (c, modified from Yuan Yongsheng et al., 2020)1-Yanshanian volcanics; 2-Yanshanian intrusives; 3-Indosinian intrusives; 4-Boundary between tectonic block; 5-Deep fault; 6-Late Cretaceous granite porphyry; 7-The fifth intrusive episodes granite in Late Cretaceous; 8-The fourth intrusive episodes monzogranite of Late Cretaceous; 9-The third intrusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 10-The second intrusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 11-The first in-trusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 12-Early Cretaceous syenogranite; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Fault; 15-Sampling location; Q-Quaternary; K-Cretaceous; J-Jurassic; T-Triassic; C-Carboniferous; Є-Cambrian; Є-K-Cambrian-Cretaceous
图 1 华南主要构造单元和中生代岩浆岩分布图(a, 据Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013修改)、连阳岩体地质简图(b, 据高剑峰等, 2005修改;同位素年龄数据马星华等, 2014)及研究区地质简图与采样位置图(c, 据袁永盛等, 2020修改)1—燕山期火山岩;2—燕山期侵入岩;3—印支期侵入岩;4—大地构造单元界线;5—深大断裂;6—晚白垩世花岗斑岩;7—晚白垩世第五侵入次花岗岩;8—晚白垩世第四侵入次二长花岗岩;9—晚白垩世第三侵入次二长花岗岩;10—晚白垩世第二侵入次二长花岗岩;11—晚白垩世第一侵入次二长花岗岩;12—早白垩世正长花岗岩;13—地质界线;14—断层;15—采样位置;Q—第四系;K—白垩系;J—侏罗系;T—三叠系;C—石炭系;Є—寒武系;Є-K—寒武系—白垩系Figure 1. Geological sketch map of main tectonic units and Mesozoic igneous rocks in South China (a, modified from Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013), geological sketch of the Lianyang pluton (b, modified from Gao Jianfeng et al., 2005; isotopic age from Ma Xinhua et al., 2014), geological sketch and sampling location of the investigated area (c, modified from Yuan Yongsheng et al., 2020)1-Yanshanian volcanics; 2-Yanshanian intrusives; 3-Indosinian intrusives; 4-Boundary between tectonic block; 5-Deep fault; 6-Late Cretaceous granite porphyry; 7-The fifth intrusive episodes granite in Late Cretaceous; 8-The fourth intrusive episodes monzogranite of Late Cretaceous; 9-The third intrusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 10-The second intrusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 11-The first in-trusive episodes monzogranite in Late Cretaceous; 12-Early Cretaceous syenogranite; 13-Geological boundary; 14-Fault; 15-Sampling location; Q-Quaternary; K-Cretaceous; J-Jurassic; T-Triassic; C-Carboniferous; Є-Cambrian; Є-K-Cambrian-Cretaceous位于南岭西段的连阳花岗岩体曾被认为是复式侵入体,主要由晚侏罗世产出的粗—中粒花岗岩主体和早白垩世晚期侵位的中—细粒花岗岩补体构成(高剑峰等, 2005; 马星华等, 2014; 袁永盛等, 2020)。连阳岩体虽然位于南岭成矿带南部,但此前因为与其相关的矿产发现较少,所以对其研究在过去未得到足够重视。随着近年的矿产勘查与1∶5万地质调查工作的开展,在岩体与围岩接触带附近新发现了多处矽卡岩型磁铁矿、铁多金属矿以及矽卡岩型-热液脉型多金属矿床等。李晶等(2010)曾对连阳岩体北侧姓坪矽卡岩型钼多金属矿进行辉钼矿Re-Os法定年,获得其模式年龄范围为99.7~ 92.1 Ma,等时线年龄为97.9 Ma,与连阳花岗岩体侵位年龄相一致,表明成矿与岩体的形成密切相关。
由于此前位于洽水地区的连阳岩体南部及南侧的白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头等花岗岩体缺乏精确的年代学资料,曾被认为均是晚侏罗世岩浆活动的产物(高剑峰等, 2005; 广西壮族自治区地质调查院,2005❶)。笔者近年来在粤西北洽水地区开展了1∶5万区域地质调查,在详细的野外地质调查及岩相学工作的基础上,对岩体进行侵入期次划分,并通过系统的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb法精确测年,厘定上述岩体为100 Ma左右岩浆活动的产物。结合前人对华南同期(110~90 Ma)岩浆岩类的研究成果,进一步探讨连阳及其南侧一些花岗岩体的成因和华南晚中生代岩石圈伸展过程的地球动力学机制。
2. 区域地质背景及岩体地质概况
华南陆块紧邻太平洋板块西缘,由华夏地块和扬子地块于新元古代沿NE向的江—绍断裂带(大致与十—杭带重合)发生碰撞-拼贴形成(图 1a),并在显生宙主要经历了早古生代、早中生代和晚中生代3期强烈的构造-岩浆活动的改造(Wang et al., 2012)。自中侏罗世开始,华南陆块逐渐转变成以伸展为主的构造环境,岩浆事件频繁。晚侏罗世—早白垩世形成了大规模呈NE—NNE向展布的穹隆构造和断陷火山-沉积盆地,并发育大量流纹质岩石、I型、A型花岗岩和少量玄武质岩石等火山-侵入岩类,岩浆岩以广泛分布的钙碱性岩石为主,并呈现出向洋年轻化的分布规律(王德滋和沈渭洲, 2003; Zhou et al., 2006; 周新民, 2007; Chen et al., 2008)。晚白垩世岩浆活动主要分布在浙闽粤沿海区域,受余姚—丽水—政和—大埔断裂、温州—镇海断裂及长乐—南澳断裂所控制,以I型、A型花岗岩、流纹质-玄武质岩石等双峰式火山岩为主,呈NE向分布(Chen et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 2015)。
连阳岩体地处粤西北,位于郴州—临武大断裂东侧、华夏地块西部的南岭纬向构造-岩浆岩带南带(花山—连阳—佛冈—新丰江岩带)的西段,出露面积约1600 km2,为一大型花岗质岩基(高剑峰等, 2005; 马星华等, 2014; 袁永盛等, 2020),与加里东期大宁岩体和广宁岩体在空间上密切共生(图 1b)。本文报道的洽水地区花岗岩体,包括连阳岩基南部及其南侧的白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头等岩株,以100 Ma左右的岩浆活动为主,可划分为5个侵入次(图 1c,详见后述)。另见很少量114 Ma的细粒少斑黑云母正长花岗岩(ζγK1)(另文发表)。区内地层主要为寒武系、石炭系、三叠系、侏罗系及白垩系,除寒武系岩性以变质砂岩、板岩等变质岩为主外,其他地层岩性主要为灰岩、白云质灰岩、砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩等。岩体主要受近SN向及NE—NNE向断裂控制。围岩与岩体接触带附近发生一定程度的角岩化、矽卡岩化、大理岩化等接触变质或接触交代变质作用,并新发现了多处矽卡岩型磁铁矿、铁多金属矿以及矽卡岩型-热液脉型多金属矿床等。
3. 岩石学特征
依据岩性\特征的不同及野外穿切关系,洽水地区(连阳岩体南部及南侧的白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头小岩体)约100 Ma花岗岩体从早到晚可分为5个侵入次(图 1c),分别为第一侵入次粗—中粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK21)、第二侵入次中—细粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK22)、第三侵入次中—细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK23)、第四侵入次中—细粒含斑黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK24)和第五侵入次细粒含斑黑云母正长花岗岩(γK25)。各侵入次之间均具有较为明显的接触界线,并呈侵入接触关系(图 2a、b)。
![]() 图 2 洽水地区第一和第四侵入次、第四和第五侵入次花岗岩的接触特征a—第四侵入次花岗岩(左)侵入到第一侵入次花岗岩中;b—第五侵入次花岗岩侵入到第四侵入次花岗岩中Figure 2. Contacts between the first and fourth, and the fourth and fifth intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regiona-The fourth episode(left) intruded into the first intrusive episode granite; b-The fifth episode intruded into the fourth intrusive episode granite
图 2 洽水地区第一和第四侵入次、第四和第五侵入次花岗岩的接触特征a—第四侵入次花岗岩(左)侵入到第一侵入次花岗岩中;b—第五侵入次花岗岩侵入到第四侵入次花岗岩中Figure 2. Contacts between the first and fourth, and the fourth and fifth intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regiona-The fourth episode(left) intruded into the first intrusive episode granite; b-The fifth episode intruded into the fourth intrusive episode granite第一侵入次粗—中粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK21):块状构造,似斑状结构(图 3a、b)。主要由钾长石斑晶(7% ~25%)和基质钾长石(20% ~ 26%)、斜长石(26%~35%)、石英(25%~28%)、黑云母(4%~8%)及角闪石(0.5%~2%)等组成。副矿物主要有磁铁矿、褐帘石、钛铁矿、榍石、锆石、磷灰石和绿帘石,含少量黄铁矿和萤石。钾长石斑晶粒径8~40 mm,以半自形—他形为主,具条纹结构,常见有斜长石、黑云母、石英等包裹体,部分边缘可见有浅色斜长石围绕形成的“环斑”结构。基质主要为粗—中粒花岗结构,粒径2~6 mm为主,斜长石半自形板柱状,少量见环带结构,据电子探针分析结果(附表略,下同),其斜长石牌号An值为19.6~32.7;黑云母,鳞片状为主,局部丛状,据电子探针分析结果(附表略,下同),MF值0.30~0.39,属铁质黑云母(图 4a);角闪石,半自形长柱状,据电子探针分析结果(附表略,下同),按Leake et al.(1997)的分类方案,属铁角闪石(图 4b)。该次侵入岩中常见有浑圆状、椭圆状、不规则状暗色微粒包体(MME),大小一般为1 cm×2 cm~ 12 cm×15 cm,与主岩界线多较截然,个别为渐变,部分可见暗色矿物团粒(双包体)及长石、石英混染“斑晶”,其中有的石英“斑”具有眼斑结构(图 3a),即石英“斑”遭受熔蚀并与岩浆反应生成角闪石、黑云母等暗色矿物环边。MME的基质为微细粒结构,粒径一般为0.01~0.5 mm,矿物组成:角闪石约25%,黑云母约20%,斜长石约52%,副矿物主要有磁铁矿、榍石、磷灰石。斜长石常为自形长板条状,磷灰石常为针状。
![]() 图 3 洽水地区第一、第二和第三侵入次花岗岩野外与显微照片第一侵入次花岗岩(含MME)露头(a)及镜下特征(b);第二侵入次花岗岩露头(c)及镜下特征(d);第三侵入次花岗岩露头(e)及镜下特征(f);Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Pl—斜长石;Bt—黑云母;MME—暗色微粒包体Figure 3. Field and microscope photos of the first, second and third intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regionOutcrop (a) and microscopic characteristics (b) of the first intrusive episode (MME-bearing); Outcrop (c) and microscopic characteristics (d) of the second intrusive episode; Outcrop (e) and microscopic characteristics (f) of the third intrusive episode; Q-Quartz; Kfs-K-feldspar; Pl-Plagioclase; Bt-Biotite; MME-Mafic magmatic enclave
图 3 洽水地区第一、第二和第三侵入次花岗岩野外与显微照片第一侵入次花岗岩(含MME)露头(a)及镜下特征(b);第二侵入次花岗岩露头(c)及镜下特征(d);第三侵入次花岗岩露头(e)及镜下特征(f);Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Pl—斜长石;Bt—黑云母;MME—暗色微粒包体Figure 3. Field and microscope photos of the first, second and third intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regionOutcrop (a) and microscopic characteristics (b) of the first intrusive episode (MME-bearing); Outcrop (c) and microscopic characteristics (d) of the second intrusive episode; Outcrop (e) and microscopic characteristics (f) of the third intrusive episode; Q-Quartz; Kfs-K-feldspar; Pl-Plagioclase; Bt-Biotite; MME-Mafic magmatic enclave![]() Figure 4. Composition classification diagrams for biotite (a, after Foster, 1960) and amphibole (b, after Leake et al., 1997) from the granites in Qiashui area
Figure 4. Composition classification diagrams for biotite (a, after Foster, 1960) and amphibole (b, after Leake et al., 1997) from the granites in Qiashui area第二侵入次中—细粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK22):块状构造,似斑状结构(图 3c、d)。斑晶粒径多在6~40 mm,以钾长石(10%~20%)为主,常见斜长石、黑云母、石英等包裹体,部分边缘可见有浅色斜长石围绕形成的“环斑”结构,偶见角闪石斑晶,局部见少量石英、斜长石斑晶。基质为中—细粒花岗结构,主要由粒径0.3~4 mm的钾长石(20% ~25%)、斜长石(25% ~33%)、石英(25% ~ 29%)、黑云母(5%~6%)和角闪石(1%~2%)等组成,副矿物主要有磁铁矿、褐帘石、钛铁矿、榍石和锆石,含少量黄铁矿、磷灰石及绿帘石。斜长石,半自形板柱状,少量见环带结构,An值绝大多数为15~ 27.9,个别35.5;黑云母,鳞片状—丛状,MF值0.24~0.38, 属铁质黑云母;角闪石,半自形长柱状,属铁角闪石。该次侵入岩中也常见浑圆状、椭圆状、不规则状暗色微粒包体(MME),与第一侵入次中的MME特点类似。
第三侵入次中—细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγK23):块状构造,似斑状结构(图 3e、f)。主要由粒径8~30 mm的钾长石斑晶(7%~15%)和粒径0.3~4 mm的钾长石(20%~25%)、斜长石(23%~33%)、石英(28%~32%)和黑云母(4%~6%)等基质组成。钾长石斑晶部分边缘可见有浅色斜长石围绕形成的“环斑”结构,常见有斜长石、黑云母、石英等包裹体。钾长石,具条纹结构,半自形板柱状—他形粒状;斜长石,半自形板柱状,少量见环带结构,An值为15.1~29.9;黑云母,鳞片状—丛状,MF值0.24~ 0.37, 属铁质黑云母。副矿物主要有磁铁矿、褐帘石、榍石、锆石、钛铁矿和磷灰石,含少量萤石和绿帘石。该次侵入岩见少量MME,特点与第一侵入次中的类似。
第四侵入次中—细粒含斑黑云母二长花岗岩((ηγK24):块状构造,似斑状结构(图 5a、b)。主要由粒径6~18 mm的钾长石斑晶(1% ~5%)和粒径0.3~3.5 mm的钾长石(35%~42%)、斜长石(21% ~ 29%)、石英(29%~33%)和黑云母(4%~5%)等基质组成。副矿物主要有磁铁矿、钛铁矿、独居石、褐帘石、锆石和绿帘石,含少量黄铁矿、榍石及磷灰石。钾长石斑晶中见有斜长石、黑云母、石英等包裹体。基质为中—细粒花岗结构,钾长石,具条纹结构,半自形板柱状—他形粒状,常高岭土化;斜长石,半自形板柱状,少量见环带结构,An值多为10.2~24.7,个别28~36.2,常绢云母化、黝帘石化;黑云母,鳞片状—丛状,MF值一般0.20~0.35,多属铁质黑云母,少部分属铁黑云母。靠近MME的主岩中个别黑云母MF值达0.53~0.74,可能是从MME中混染的黑云母。该次侵入岩局部可见少量MME。
![]() 图 5 洽水地区第四、第五侵入次花岗岩野外与显微照片第四侵入次花岗岩露头(a)及镜下特征(b);第五侵入次花岗岩露头(c)及镜下特征(d);Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Pl—斜长石;Bt—黑云母Figure 5. Field and microscope photos of the fourth and fifth intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regionOutcrop (a) and microscopic characteristics (b) of the fourth intrusive episode; Outcrop (c) and microscopic characteristics (d) of the fifth intrusive episode; Q-Quartz; Kfs-K-Feldspar; Pl-Plagioclase; Bt-Biotite
图 5 洽水地区第四、第五侵入次花岗岩野外与显微照片第四侵入次花岗岩露头(a)及镜下特征(b);第五侵入次花岗岩露头(c)及镜下特征(d);Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Pl—斜长石;Bt—黑云母Figure 5. Field and microscope photos of the fourth and fifth intrusive episodes granites in Qiashui regionOutcrop (a) and microscopic characteristics (b) of the fourth intrusive episode; Outcrop (c) and microscopic characteristics (d) of the fifth intrusive episode; Q-Quartz; Kfs-K-Feldspar; Pl-Plagioclase; Bt-Biotite第五侵入次细粒含斑黑云母正长花岗岩(γK23):块状构造,似斑状结构(图 5c、d)。斑晶粒径多在2~ 13 mm,以钾长石(1%~3%)为主,少量石英、斜长石斑晶,偶见黑云母斑晶,斑晶钾长石中可见细小斜长石、黑云母、石英等包裹体。基质主要为细粒花岗结构,常见显微文像结构,主要由粒径0.2~1.5 mm的钾长石(39%~45%)、斜长石(14%~21%)、石英(30%~34%)和黑云母(2%~5%)等组成。副矿物主要有磁铁矿、钛铁矿、黄铁矿、独居石和锆石,含少量萤石、磷灰石。钾长石,具条纹结构,半自形板柱状—他形粒状,常泥化;斜长石,半自形板柱状,少量见环带结构,An值1.0~27.8,且多低于17,常绢云母化;黑云母,鳞片状—丛状,MF值绝大多数0.13~0.21,个别0.28,绝大多数属铁黑云母。
5个侵入次岩石的岩性特征表明,洽水地区(连阳岩体南部和南侧小岩体)花岗岩从早期侵入次到晚期侵入次,矿物颗粒粒度、暗色矿物含量总体逐渐降低,表现为黑云母含量逐渐下降,其MF值逐渐降低,从铁质黑云母变为铁黑云母。角闪石从有到无,斜长石牌号(An值)逐渐降低。岩石副矿物含量变化较大,其中早期侵入体的副矿物含量较高,晚期副矿物含量逐渐减少,主要表现为磁铁矿、榍石含量随岩浆演化不断降低,但钛铁矿和独居石有所增加,晚期还常出现萤石,总体副矿物组合为典型的磁铁矿-钛铁矿-榍石-锆石组合系列。第一和第二侵入次岩石中常见有MME,第三和第四侵入次岩石中含少量MME。MME多呈椭圆状或浑圆状,具有石英“眼斑”结构及斜长石自形长板条结构、磷灰石针状结构等岩相学特征,表明其为幔源岩浆与壳源岩浆(主岩)发生混合的产物(Xie et al., 2020)。第一至第三侵入次的主岩中常见钾长石斑晶的“环斑”结构(幔状长石结构),也反映了壳-幔岩浆混合作用(Narayana et al., 2000; 王超等, 2008)。综合分析表明,洽水地区壳源花岗质岩浆经历了较明显的分离结晶作用和一定程度的壳幔岩浆混合作用(袁永盛等, 2020)。
4. 采样位置与测试方法
本次工作在洽水地区的连阳岩体南部及其南侧的白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头花岗岩体共采集了12件新鲜的锆石U-Pb年代学样品。其中DP222-1、PM06-3采自第一侵入次粗—中粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩,PM06-54采自第二侵入次中—细粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩,PM06-53、DP225-1和DP245-1采自第三侵入次中—细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩,PM06-1、DP204-1、D2029-1、D3178-1和D3020-1采自第四侵入次中—细粒含斑黑云母二长花岗岩,DP202-1采自第五侵入次细粒含斑黑云母正长花岗岩(图 1c)。
野外在岩体新鲜未蚀变位置采集样品5 kg,采用人工重砂法分选出锆石。锆石颗粒用环氧树脂固定并抛光露出核部(宋彪等, 2002),然后进行透射光和反射光照相,并使用JXA 8100型电子探针进行阴极发光(CL)照相(图 6)。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年工作在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室完成,使用Agilent 7500a ICP-MS连接起来的New Wave 213 nm激光剥蚀系统完成。分析过程中,激光束斑直径32 μm,频率5 Hz。U-Pb分馏采用澳大利亚锆石标样GEMOC GJ-1 (207Pb/206Pb年龄为(608.5 ± 1.5)Ma, Jackson et al., 2004) 进行校正,以Mud Tank((732 ± 5)Ma, Black and Gulson, 1978)作为内标控制分析精度。U-Pb年龄计算由GLITTER软件(4.4) 在线获得。使用ComPbCorr#3-15G程序(Andersen, 2002)进行普通铅校正。年龄数据处理采用ICPMS Data Cal(8.9)(Liu et al., 2008)和Isoplot(3.0)(Ludwig, 2003)软件进行。详细测试方法和流程见Griffin et al.(2004)。
5. 分析结果
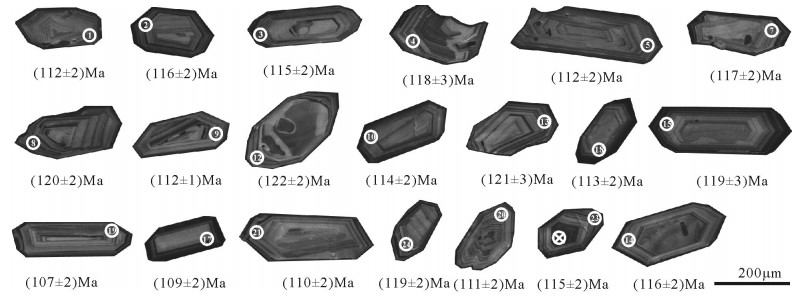
12件样品中锆石以无色或浅黄色、黄粉色、褐粉色为主,透明—半透明,金刚光泽,多呈自形—半自形双锥柱状、柱状,晶内裂纹较发育,部分可见黑色包体,柱面以(110)占绝对优势,表明锆石形成温度较高。在阴极发光(CL)图像上(图 6),大部分锆石具有典型酸性岩浆锆石的振荡环带,且Th/U比值较高(为0.1~3.9,平均值为0.9,表 1),均显著>0.1,表明锆石为岩浆成因(周剑雄和陈振宇, 2007)。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果分别如下所述:
表 1 洽水地区第一至第五次花岗岩锆石 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 测年结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of the first to fifth episodes granites in Qiashui region
第一侵入次:样品DP222-1共分析了21个测点,结果见表 1和图 7a。其中19个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在106~95 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(100.2±1.8)Ma(n=19,MSWD=4.0)。16号点明显偏离谐和线,15号点给出了112 Ma的谐和206Pb/238U表面年龄,且该点的CL图像具有典型岩浆锆石振荡环带,为捕获锆石,因此上述测点在计算年龄时未统计在内。样品PM06-3共分析了22个测点,结果见表 1和图 7b。其中21个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在105~95 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(98.9 ± 1.1)Ma(n=21,MSWD= 4.3)。10号点给出了126 Ma的谐和206Pb/238U表面年龄,且该点的CL图像具有典型岩浆锆石振荡环带,为捕获锆石,计算年龄时未统计在内。
第二侵入次:样品PM06-54共分析了24个测点,结果见表 1和图 7c。其中22个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在105~96 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(99.9±0.9)Ma(n= 22,MSWD=2.6)。8号点明显偏离谐和线,14号点为捕获锆石(135 Ma),计算年龄时未统计在内。
第三侵入次:样品PM06-53共分析了12个测点,结果见表 1和图 7d。所有测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在102~93 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(97.1 ± 1.7)Ma(n=12,MSWD=4.1)。样品DP225-1共分析了20个测点,结果见表 1和图 7e。所有测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在105~97 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(101.4±0.9)Ma(n=20,MSWD= 0.9)。样品DP245-1共分析了20个测点,结果见表 1和图 7f。所有测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在103~97 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(100.9±0.9)Ma(n=20,MSWD=1.4)。
第四侵入次:样品PM06-1共分析了25个测点,结果见表 1和图 8a。其中13个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在103~98 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(100.1±0.8)Ma(n=13,MSWD=1.4)。9、13、16和18号点明显均偏离谐和线;11号点给出了87 Ma的谐和206Pb/238U表面年龄,且该点的CL图像具有典型岩浆锆石振荡环带,表明可能为另一期岩浆活动产物;1、2、7、10、12、22和23号点均位于锆石核部,为捕获锆石(132~109 Ma),因此上述测点在计算年龄时未统计在内。样品DP204-1共分析了20个测点,结果见表 1和图 8b。其中17个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在105~94 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(98.0 ± 1.4)Ma(n=17,MSWD=2.6)。20号点给出了113 Ma的谐和206Pb/238U表面年龄,可能为捕获锆石;12、15号点给出了87 Ma的表面年龄,且该点的CL图像具有典型岩浆锆石振荡环带,表明可能为另一期岩浆活动产物,因此上述测点在计算年龄时未统计在内。样品D2029-1共分析了24个测点,结果见表 1和图 8c。其中16个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在106~98 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(101.1 ± 1.1)Ma(n=16,MSWD= 2.0)。14号点明显偏离谐和线,5、7、20、22和23号点为捕获锆石(144~109 Ma),13、17号点给出了63.8 Ma、53.9 Ma的谐和表面年龄,可能为另一期岩浆细脉混入。因此上述测点在计算年龄时未统计在内。样品D3178-1共分析了27个测点,结果见表 1和图 8d。其中19个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在104~97 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(99.9 ± 1.0)Ma(n=19,MSWD=3.6)。7、15和24号点明显偏离谐和线,4、5、14、21和22号点可能为捕获锆石(112~108 Ma),因此上述测点在计算年龄时未统计在内。样品D3020-1共分析了14个测点,结果见表 1和图 8e。所有测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在103~94 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(99.5±1.1)Ma(n=14,MSWD=1.1)。
第五侵入次:样品DP202-1共分析了22个测点,结果见表 1和图 8f。其中21个测点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在107~96 Ma,且全落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,计算其加权平均年龄为(101.8±1.5)Ma(n=21,MSWD=2.4)。22号点获得明显偏年轻的206Pb/238U表面年龄(63±1)Ma,可能为另一期岩浆细脉混入。
总体而言,12件样品的有效测点数据均落在U-Pb年龄谐和线上或附近,具有非常一致的206Pb/238U年龄,总体集中在107~93 Ma,其加权平均年龄变化于(101.8±1.5)~(97.1±1.7)Ma,在误差范围内基本一致。上述年龄可代表洽水地区(连阳岩体南部和南侧小岩体)第一到第五侵入次花岗岩体的结晶(侵位)时代。
6. 讨论
6.1 洽水地区花岗岩体的形成时代
对于洽水地区(连阳岩体南部及南侧白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头小岩体)花岗岩体的形成时代,由于缺乏精确的同位素年龄,前人曾认为其均是晚侏罗世岩浆活动的产物(高剑峰等, 2005; 广西壮族自治区地质调查院, 2005❶)。前人曾获得连阳岩体黑云母K-Ar年龄为99~98 Ma和130~125 Ma(全国同位素地质年龄数据汇编第四集, 1986; 广东省地质矿产局, 1988),全岩Rb-Sr年龄为104~100 Ma(广西壮族自治区地质调查院, 2005❶)。由于上述方法获得的年龄有可能是受热事件改造的年龄,无法确凿地解释为连阳岩体的形成时代。近年来,利用更高精度及地质解释更明确的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb法获得连阳岩体中北部中—细粒花岗岩同位素年龄为104~81 Ma(马星华等, 2014; 中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心, 2015❷),连阳岩体南部粗—中粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩的同位素年龄为(99.4±0.7)Ma(袁永盛等, 2020)。本次采用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb法获得洽水地区第一侵入次粗—中粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩、第二侵入次中—细粒斑状含角闪石黑云母二长花岗岩、第三侵入次中—细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩、第四侵入次中—细粒含斑黑云母二长花岗岩和第五侵入次细粒含斑黑云母正长花岗岩的成岩年龄分别为(100.2±1.8)~(98.9±1.1)Ma、(99.9±0.9)Ma、(101.4±0.9)~(97.1±1.7)Ma、(101.1±1.1)~(98.0±1.4)Ma和(101.8±1.5)Ma,年龄在误差范围内基本一致,代表连阳岩体南部及其南侧的白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头花岗岩体的形成时代属早—晚白垩世之交(100 Ma±)。
值得一提的是,此次在洽水地区12件样品中获得了21颗捕获锆石,其年龄主要集中于114~108 Ma(n=13),剩余在144~123 Ma(n=8)(表 1,图 7,图 8),显示研究区曾存在过这些时代范围的岩浆活动。另外,作者还获得连阳岩体南部的寨坳细粒少斑黑云正长花岗质岩株的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(114.4±1.0)Ma(另文发表)。据此,结合本次获得的连阳岩体南部及南侧小岩体的同位素年龄综合分析,认为高剑峰等(2005)所报道的144 Ma的粗—中粒花岗岩可能仅为整个连阳岩基的局部产物,表明144 Ma左右的岩浆活动在洽水地区不是主要期次,连阳岩体应该主要于~100 Ma形成。
6.2 华南燕山晚期岩浆活动时空分布
综合已有资料,华南燕山期岩浆活动的时间可大致归纳为“两期3阶段”,分别是燕山早期(190~140 Ma)、燕山晚期第1阶段(140~120 Ma)和燕山晚期第2阶段(120~80 Ma)(图 9)。空间上,燕山早期花岗质岩浆活动主要分布于华南内陆地区,如闽西南、赣南、粤北及湘南等地,主体呈NE向分布,而在南岭地区为近EW向分布;燕山晚期的岩浆活动则广泛发育在长江中下游、浙闽沿海、琼南等一带,以NNE向展布(孙涛, 2006)。
![]() Figure 9. Histograms of isotopic ages for Yanshanian igneous rocks in South China (modified from Li et al., 2010; Jia Lihui, 2018)
Figure 9. Histograms of isotopic ages for Yanshanian igneous rocks in South China (modified from Li et al., 2010; Jia Lihui, 2018)近年来发表的一系列年代学成果(表 2)显示早—晚白垩世之交(110~90 Ma)是华南重要的构造-岩浆活动时期之一(图 9),该时期岩浆岩的空间分布与燕山晚期岩浆活动范围基本一致,集中分布于政和—大埔断裂以东的东南沿海地区,内陆则产出局限,且大部分岩体以岩株形式产出(图 10)。该时期东南沿海地区形成了大量中酸性岩浆岩(I型、A型花岗岩)及少量玄武质岩石(王德滋和沈渭洲,2003),如浙闽沿海地区的普陀山—大洞岙碱长花岗岩(98~96 Ma)(Zhao et al., 2016)、蜡江—东埔黑云母花岗岩(110.1~105.3 Ma)与石湖黑云母二长花岗岩((105.1±0.5)Ma)(丁聪, 2013),粤东三饶花岗闪长岩((102±1.9)Ma)、新圩花岗闪长岩(106~105 Ma)和石英闪长岩((103.5 ± 1.2)Ma)(贾丽辉, 2018),云开地区的天堂二长花岗斑岩((104.5±0.4)Ma)、石菉花岗闪长岩((103.7±0.5)Ma)和石英闪长岩(104.1~103.2 Ma)(郑伟, 2016)等I型花岗岩,大青山—桃花岛—虾峙岛过碱性花岗岩(89~86 Ma)(Zhao et al., 2016)、瑶坑碱性花岗岩((91.3 ± 2.5)Ma)(肖娥等, 2007)、太姥山—鼓山黑云母花岗岩(99.4~96.6 Ma)(李良林等, 2013)、石牛山正长花岗斑岩((93.8±1.3)Ma)(邢光福等, 2009)、洪山花岗岩(99 Ma)(黄泉祯, 1998)等A型花岗岩,以及少量主要受长乐—南澳断裂所控制的中基性脉岩、玄武质岩石,如福建永泰玄武岩(~85 Ma)(Meng et al., 2012)等。
表 2 华南 110~90 Ma 花岗岩类年代学资料Table 2. Geochronological data of the 110-90 Ma granitoids in South China
![]() 1—燕山期火山岩;2—燕山期侵入岩;3—燕山期玄武质岩石;4—代表性花岗岩体;5—代表性玄武岩体;6—地质块体边界;7—深大断裂;8—岩体名称及年龄/Ma(资料来源见表 2)Figure 10. Distribution of the 110-90 Ma granitoids and basaltic rocks in South China (modified from Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013)1-Yanshanian volcanics; 2-Yanshanian intrusives; 3-Yanshanian basaltic rocks; 4-Representative granitoid pluton; 5-Representative basaltic pluton; 6-Geological block boundary; 7-Deep fault; 8-Name and isotopic age /Ma of pluton (See Table 2 for data source)
1—燕山期火山岩;2—燕山期侵入岩;3—燕山期玄武质岩石;4—代表性花岗岩体;5—代表性玄武岩体;6—地质块体边界;7—深大断裂;8—岩体名称及年龄/Ma(资料来源见表 2)Figure 10. Distribution of the 110-90 Ma granitoids and basaltic rocks in South China (modified from Zhou and Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2013)1-Yanshanian volcanics; 2-Yanshanian intrusives; 3-Yanshanian basaltic rocks; 4-Representative granitoid pluton; 5-Representative basaltic pluton; 6-Geological block boundary; 7-Deep fault; 8-Name and isotopic age /Ma of pluton (See Table 2 for data source)而华南腹地该期岩浆活动范围较窄,主要以零星状态分布,除本文及前人报道的连阳花岗岩体((106.4±0.7)~(97.6±1.5)Ma)(高剑峰等, 2005; 马星华等, 2014; 袁永盛等,2020)外,尚有广西大厂黑云母花岗岩((93±1)Ma)和斑状花岗岩((91±1)Ma)(蔡明海等, 2006)、米场角闪黑云母花岗闪长岩(110~109 Ma)、三叉冲黑云母花岗岩((103 ± 1)Ma)、油麻坡花岗闪长岩((105±1)Ma)(Wang et al., 2018),湘南界牌岭花岗斑岩((92.0±1.6)Ma)(卢友月等, 2013),粤北新坪花岗闪长岩((104.6±1.8)Ma)(李宏卫等, 2021)、雪山嶂花岗斑岩((103.4±1.2)Ma)(贾小辉等, 2014)等。
综上所述,早—晚白垩世之交(110~90 Ma)发生了华南燕山晚期一次重要的构造-岩浆事件,广泛发育了碱性花岗岩、A型花岗岩、I型花岗岩、中基性脉岩、玄武质岩石等双峰式岩浆岩及一系列断陷拉张盆地等(Li, 2000; 杨振等, 2014)。
6.3 构造环境
关于华南燕山期花岗岩形成的大地构造背景及深部动力学机制已先后提出了如活动大陆边缘(Zhou and Li, 2000)、岩石圈伸展减薄与拆沉(张旗等, 2001)、板内伸展-裂谷环境(陈志刚等, 2003)、弧后环境(孙涛等, 2003)、平板俯冲(Li and Li, 2007)等不同模式。目前普遍认为,自燕山期以来华南腹地已经逐渐转变成以伸展拉张为主的构造环境,并经历了多期重要的伸展事件,古太平洋板块俯冲/后撤背景下幔源玄武质岩浆的底侵作用可能是导致华南晚中生代花岗质岩浆活动的重要原因(Zhou and Li, 2000; Zhou et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2012; Duan et al., 2017; 李三忠等, 2018)。
大地构造位置上,研究区位于郴州—临武深大断裂附近(图 10)(高剑峰等, 2005; 马星华等, 2014),该断裂被认为是华夏地块与扬子地块的岩石圈尺度缝合线(即十—杭带)(Gilder et al., 1996),是一个反复活化、深达软流圈的古构造薄弱带(Xie et al., 2020), 沿该断裂带分布有大量的燕山期幔源玄武质岩石(178~63 Ma),如湖南宁远—道县玄武岩(Li et al., 2004)、回龙圩煌斑岩(Wang et al., 2003)、长城岭斜斑玄武岩(Zhao et al., 1998; 杨帆等, 2018)、衡阳玄武岩和赣西北禾埠玄武岩(Meng et al., 2012)等,与同期花岗岩近于同时产出。华南内陆同期基性岩浆整体上具有更加亏损的Sr-Nd同位素组成,表现出从岛弧玄武岩向板内玄武岩逐步转变的趋势(杨帆等, 2018),暗示华南内陆在燕山期(特别是燕山晚期)可能经历了持续的伸展拉张作用,致使深部的软流圈幔源物质向上迁移。前人曾在华南识别出多条具低TDM-高εNd(t)值的燕山期花岗岩带,其中华夏地块TDM<1.7 Ga,εNd(t)>-7.0被认为是幔源物质参与岩浆演化过程的重要体现(Chen et al., 1998; 陈江峰等, 1999)。连阳花岗岩体具相对较高的εNd(t)值(-10.6~-4.2)、较年轻的二阶段Nd模式年龄(TDM2)(1.79~1.24 Ga)和较大变化范围的εHf(t)值(-10.5~+1.2)(高剑峰等, 2005; 马星华等, 2014; 袁永盛等, 2020; 作者未发表数据),在空间上正处于华南内陆的杭州—诸广山—花山低TDM-高εNd(t)值带附近(Chen and Jahn, 1998),这进一步明确了幔源岩浆不仅提供了源区岩石熔融所需的热,也一定程度为区内花岗岩提供了成岩物质。该结论与前述根据岩相学特征认为MME发生了幔源与壳源岩浆的混合作用的推论相一致。
相对于燕山晚期东南沿海发育大面积与俯冲相关的陆缘弧岩浆活动,同时期岩浆作用在华南内陆地区表现较为微弱(周新民, 2007)。燕山期华南内陆地区的构造-岩浆活动同东南沿海地区并不一致。笔者认为连阳岩体的形成并非直接起源于大洋板块或其上覆地幔楔,而可能与古太平洋板块不规则反复俯冲/后撤所导致的陆内或弧后剪切拉张环境相关,伴随该后撤作用发育大量的伸展构造活动(Li and Li, 2007; 郑永飞等, 2013),伸展活动影响华南内陆原先存在的郴州—临武等深大断裂,使其重新活化,软流圈地幔流沿这些薄弱带向上侵蚀上涌,导致岩石圈减薄,引起软流圈及上覆的富集岩石圈地幔发生部分熔融,形成幔源玄武质岩浆,并底侵华南中元古代陆壳基底岩石使其部分熔融形成花岗质岩浆,随后,花岗质岩浆可与玄武质岩浆发生岩浆混合。
7. 结论
(1)洽水地区(连阳岩体南部及南侧白水寨、鸡笼岭、将军头小岩体)花岗岩体的岩性主要为粒度不等的(角闪)黑云母二长花岗岩,少量黑云正长花岗岩,依据岩性特征及穿切关系的不同可划分为5个侵入次。
(2)通过锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年,新获得洽水地区第一到第五侵入次的年龄分别为102~ 97 Ma,均属燕山晚期早—晚白垩世之交(100 Ma±)的岩浆产物。认为连阳岩体主要于~100 Ma形成,144~123 Ma和~114 Ma的岩浆活动在洽水地区仅局部产出。
(3)综合分析表明,早—晚白垩世之交是华南一次重要的构造-岩浆活动时期。同期古太平洋板块向欧亚板块的俯冲/后撤所诱发的伸展作用,导致华南内陆的郴州—临武等古深大断裂重新活化,并引起软流圈上涌和岩石圈减薄,进而导致较强烈的幔源和壳源岩浆活动。连阳岩体的形成与此密切相关。
注释
❶广西壮族自治区地质调查院. 2005. 1∶250 000贺州市幅区域地质调查报告.
❷中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心. 2015. 1∶50 000南乡、上程、福堂圩、小三江等4幅区域地质矿产调查报告.
❸中国人民武装警察部队黄金第九支队. 2016. 1∶50 000博白县幅、六万山幅区域地质矿产调查报告.
致谢: 两位匿名审稿专家对本文提出了建设性的意见和建议,在此表示衷心的感谢! -
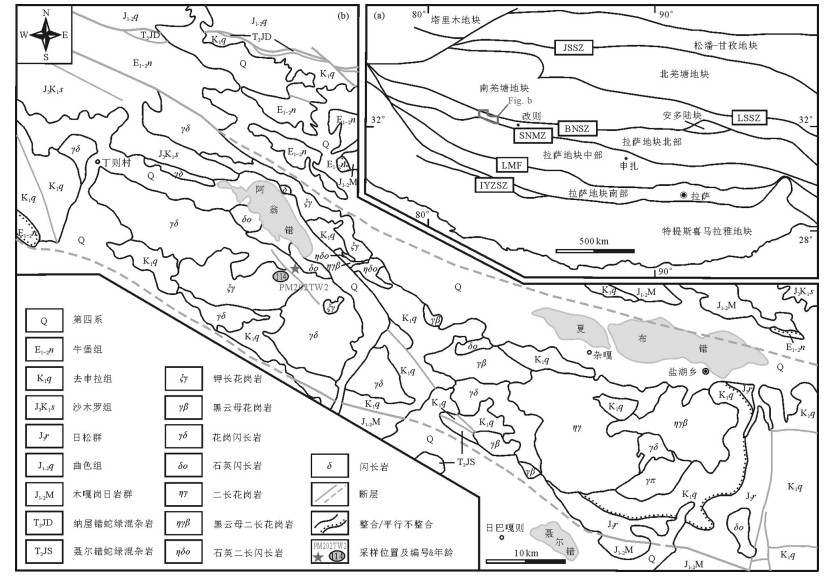
图 1 阿翁错—盐湖地区地质图及采样位置
a—青藏高原构造单元划分(JSSZ,金沙江缝合带;LSSZ,龙木错—双湖缝合带;BNSZ,班公湖—怒江缝合带;SNMZ,狮泉河—纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF,洛巴堆—米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ,印度河—雅鲁藏布缝合带.据Zhu et al., 2013修改);b—研究区地质图
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Aweng Co-Yanhu region, Tibet and sampling locations
a- Geological sketch map of tectonic outline of the Tibetan Plateau(JSSZ = Jinsha jiang suture zone; LSSZ = Longmu Co-Shuanghu suture zone; BNSZ = Bangong Co -Nujiang River Suture Zone; SNMZ =Shiquan River-Nam Co mélange zone; LMF = Luobadui-Milashan fault; IYZSZ = Indus-Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, after Zhu et al., 2013); b-Geological map of the study area
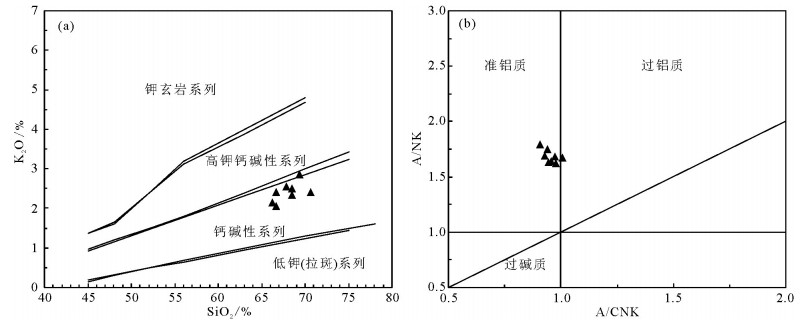
图 4 阿翁错花岗闪长岩K2O-SiO2(a,据Rickwood,1989)及A/CNK-A/NK(b,据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989)图解
Figure 4. Diagrams of K2O-SiO2(a, after Rickwood, 1989) and A/CNK-A/NK(b, after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) of the Aweng Co granodiorites
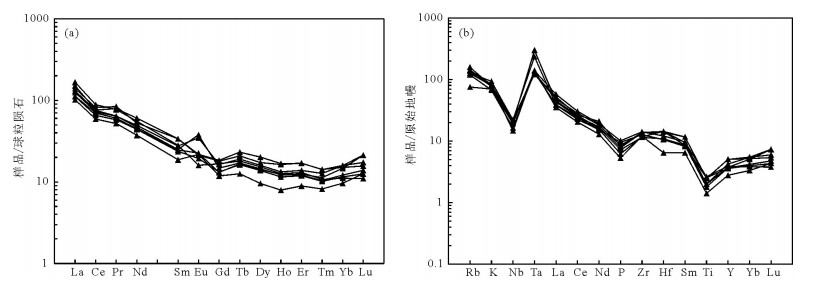
图 5 阿翁错花岗闪长岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线图(a,标准化值据Boynton,1984)及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b,标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams(b, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)for the Aweng Co granodiorites
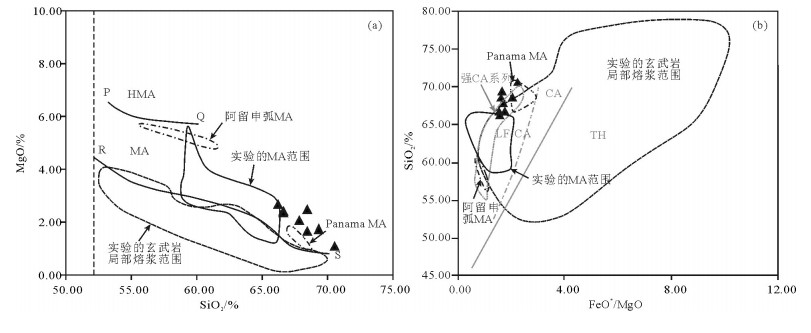
图 6 MA的SiO2-MgO图(a)和SiO2-FeO*/MgO图(b)(据Deng et al., 2009修改)
(a)实线范围为实验的MA;虚线为实验的玄武岩局部熔浆(即非MA);点划线范围为阿留申弧MA;双点划线为Panamn MA;上、下两条实线PQ和RS分别为HMA/MA与MA/非MA的边界,竖虚线表示SiO2=52%(b)黑线范围所代表的与6-a中一样(见图中标注);灰色直线为Miyashiro的CA与TH分界线,灰色点划线范围为Yogodzinski等的强CA系列,灰色双点线为Arculus的低Fe(LF-CA)与中Fe系列的边界
Figure 6. SiO2-MgO diagram (a) and SiO2- FeO/MgO diagram (b) of MA (simplified from Deng et al., 2009)
(a)The area of solid line represents MA from experiment; the area of dashed line represents partial melt of basalt from experiment (non-MA); the area of dot-dash line represents the MA of Aleutian; the area of double-dot dash line represents the MA of Panamn; the lines PQ and RS mean the boundary of HMA/MA and MA/non-MA respectively. The dashed line means SiO2=52%. (b)The areas defined by different dark lines are the same as those in Fig. 3-a; the gray straight line is the CA/TH boundary by Miyashiro. The gray dot line is strong CA series by Yogodzinski. The gray double-dot line is the boundary between low Fe and medium Fe, which is named low Fe CA (LF-CA) in this paper
表 1 阿翁错花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Aweng Co granodiorites

表 2 阿翁错花岗闪长岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major elements(%) and trace elements(10-6)compositions of the Aweng Co granodiorites

-
Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Atherton M P, Petford N. 1993. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 362:144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
Barth M G, McDonough W F, Rudnick R L.2000. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 165(3-4):197-213. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00173-4
Boynton W V.1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P(ed.) Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[J]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 63-114.
Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C, Wang S.1986. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic-rocks from Central and Southern Tibet 39Ar-40Ar dating, petrological Characteristics and geodynamical significance[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 79:281-302. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90186-X
Defaut M J, Richerson P M, Deboer J Z, Stewart R H, Maury R C, Bellon H, Drummond M S, Feigenson M D and Jackson T E.1991.Dacite genesis via both Slab melting and differentiation:Petrogenesis of La Yeguada volcanic complex, Panama[J].Journal of Petrology, 32:1101-1142. doi: 10.1093/petrology/32.6.1101
Deng J F, Flower M F J, Liu C, Mo Xuanxue. 2009. Nomeuclature, diagnosis and oringin of high-magnesian andesites (HMA) and magnesian andesites (MA): A review from petrographic and experimental data[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(13): Issue 13 Supplement 1, A279.
Deng Jinfu, Liu Cui, Feng Yanfang, Xiao Qinghui, Su Shangguo, Zhao Guochun, Kong Weiqiong, Cao Wenyan. 2010. High-magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks (HMA) and magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks (MA):Two igneous rock types related to oceanic subduction[J]. Geology in China, 37:1112-1118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201004027.htm
Ding X, Hu Y H, Zhang H, Li CY, Ling M X, Sun W D.2013.Major Nb/Ta fractionation recorded in garnet amphibolite facies metagabbro[J]. Journal of Geology 121, 255-274. doi: 10.1086/669978
Du Daode, Qu Xiaoming, Wang Genghou, Xin Hongbo, Liu Zhibo. 2011. Bidirectional subduction of the Middle Tethys oceanic basin in the west segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang suture, Tibet:Evidence from zircon U-Pb LA-ICP-MS dating and petrogeochemistry of arc granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7):1993-2002(in Chinese with English abstract).
Foley S, Tiepolo M, Vannucci R.2002. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones[J]. Nature, 417:837-840. doi: 10.1038/nature00799
Hu Jun, Wan YongWen, Tao Zhuan, Zhang Dan, Chen GuoDong.2014 Newgeochemisty and geochronology evidences related to southward subduction of Tethys Ocean basin in west segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang suture belt[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 41(4):505-515(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kang Zhiqiang, Xu Jifeng, Wang Baodi, Dong Yanhui, Wang Shuqing, Chen Jianlin. 2009. Geochemistry of Cretaceous volcanic rocks of Duoni Formation in Northern Lhasa Block:Discussion of tectonic Setting[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences, 34(1):89-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.009
Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, Heizier M, Ding L. 2007.Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geol. Soc. Am.Bull., 119:917-932. doi: 10.1130/B26033.1
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison TM, Ding L.2005.Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 117:865-878. doi: 10.1130/B25595.1
Kay RW. 1978. Aleutian magnesian andesites:Melts from subductcd Pacific Ocean crust[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 4(1/2):117-132.
Kelemen P B. Genesisof high Mg-number andesites and the continental-crust[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 120(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/BF00311004
Leier A L, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, DeCelles P G. 2007. Detrital zircon geochronology of Carboniferous? Cretaceous strata in the Lhasa terrane, Southern Tibet[J]. Basin Research, 19:361-378. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2007.00330.x
Liang J L, Ding X, Sun X M, Zhang Z M, Zhang H, Sun W D. 2009.Nb/Ta fractionation observed in eclogites from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project[J]. Chemical Geology, 268:27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.006
Liu Yongsheng, Hu Zhaochu, Zong Keqing, Gao Changgui, Gao Shan, Xu Juan, Chen Haihong. 2010b. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICPMS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55:1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, Gao C G, Zong K Q, Wang D B. 2010a.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2):537-571. doi: 10.1093-petrology-egp082/
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, Gunther D, Xu J, Gao C G, Chen H H. 2008.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257: 34-43.
Ludwig K R. 2003.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Exce[M]. Berkeley Geochronological Center, Special Publication, Berkeley, 4: 1-71.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Qian Bing, Zhang ZhaoWei, Lu PengRui, Wang YaLei.2018.Petrogenesis and Geodynamics Processes of Early Paleozoic Niubiziliang High-Mg Diorites in West Segment of North Qaidam, Qinghai[J].Earth Science, 43(12):4375-4389 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201812008
Rickwood P C.1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Sui Qinglin. 2014. Chronology, Petrogenesis, and Tectonic Implication of Magmatic Rocks from Yanhu in Northern Lhasa Terrane, Tibet[M].Beijing:China University of Geosciences(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes.[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J (eds.). Magmatism in the Oceanic Basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345.
Tang Gongjian, Wang Qiang.2010. High-Mg andesites and their geodynamic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(8):2495-2512(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201008021
Tatsumi Y, Ishizaka K. 1982. Origin of high-magnesium andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, Southwest Japan, I.petrographical and chemical characteristics[J].EPSL, 60:293-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90008-5
Tiepolo M, Vannucci R, Obert R, Foley S, Bottazzi P, Zanetti A.2000.Nb and Ta incorporation and fractionation in titanian pargasite and kaersutite:crystal-chemical constraints and implications for natural systems[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 176:185-201. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00004-2
Wu Hao, Li Cai, Xu Mengjing, Li Xingkui. 2015. Early Cretaceous adakitic magmatism in the Dachagou area, northern Lhasa terrane, Tibet:Implications for slab roll-back and subsequent slab breakoff of the lithosphere of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97:51-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.014
Xiao Yilin, Sun Weidong, Hoefs Jochen, Simon Klaus, Zhang Zeming, Li Shugang, Hofmann Albrecht W. et al. 2006. Making continental crust through slab melting:Constraints from niobium-tantalum fractionation in UHP metamorphic rutile[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70:4770-4782. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.07.010
Yogodzinski G M, Kay R W, Volynets O N, Koloskov A V, Kay S M. 1995. Magnesian andestites in the western Aleutions Komandorsky region:Implications for slab melting and processes in the mantle wedge[J]. GSA Bull., 107(5):505-519. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1995)107<0505:MAITWA>2.3.CO;2
Zhang K J, Xia B D, Wang G M, Li Y T, Ye H F. 2004. Early Cretaceous stratigraphy, depositional environments, sandstone provenance, and tectonic setting of central Tibet, western China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 116(9/10):1202-1222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2dde0cdfe5346a052582ae71bfa7b881
Zhao Zhenghua, Wang Qiang, Xiong Xiaolin, Niu Hecai, Zhang Haixiang, Qiao Yulou.2007. Magnesian igneous rocks in northern Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7):1696-1707(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200707015
Zhu Dicheng, Zhao Zhidan, Niu Yaolin, Dilek Yildirim, Mo Xuanxue. 2011b. Lhasa Terrane in southern Tibet came from Australia[J]. Geology, 39:727-730. doi: 10.1130/G31895.1
Zhu Dicheng, Zhao Zhidan, Niu Yaolin, Mo Xuanxue, Chung Sunlin, Hou Zengqian, Wang Liquan, Wu Fuyuan. 2011a. The Lhasa Terrane:Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 301:241-255. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
Zhu Dicheng, Mo Xuanxue, Zhao Zhidan, Xu Jifeng, Zhou Changyong, Sun Chenguang, Wang Liquan, Chen Haihong, Dong Guochen, Zhou Su. 2008. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of Zenong Group volcanic rocks in Coqen area of the Gangdese, Tibet and tectonic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3):401-412(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200803001
Zhu Dicheng, Pan Guitang, Mo Xuanxue, Wang Liquan, Liao Zhongli, Zhao Zhidan, Dong Guochen, Zhou Changyong. 2006. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting in middle-northern Gangdese:New insights from volcanic rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3):534-546(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB200603002.htm
Zhu Dicheng, Zhao Zhidan, Niu Yaolin, Dilek Y, Hou Zengqian, Mo Xuanxue.2013. The Origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research 23:1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
Zhu Dicheng, Mo Xuanxue, Niu Yaolin, Zhao Zhidan, Wang Liquan, Liu Yongsheng, Wu Fuyuan.2009. Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 268:298-312. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.008
Zhu Dicheng, Zhao Zhidan, NiuYaoling, Wang Qing, Yildirim DILEK, Dong Guochen, Mo Xuanxue. 2012. Origin and Paleozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Lhasa Terrane[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 18(1):1-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201201003.htm
杜道德, 曲晓明, 王根厚, 辛洪波, 刘治博.2011.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带西段中特提斯洋盆的双向俯冲:来自岛弧型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和元素地球化学的证据[J].岩石学报, 27(7):1993-2002. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107008 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 赵国春, 孔维琼, 曹文燕.2010.高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩闪长岩类(MA):与洋壳俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩类[J].中国地质, 37:1112-1118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.025 胡隽, 万永文, 陶专, 张旦, 陈国东.2014.班公湖-怒江缝合带西段特提斯洋盆南向俯冲的地球化学和年代学证据[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4):505-515. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2014.04.14 康志强, 许继峰, 王保弟, 董彦辉, 王树庆, 陈建林.2009.拉萨地块北部白垩纪多尼组火山岩的地球化学:形成的构造环境[J].地球科学, 34(1):89-104 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200901009 隋清霖.2014.西藏拉萨地块盐湖地区早白垩世岩浆岩年代学、岩石成因及构造意义[D].北京: 中国地质大学. 钱兵, 张照伟, 吕鹏瑞, 王亚磊.2018.柴北缘西段晚古生代牛鼻子梁高镁闪长岩成因机制及地球动力学过程[J].地球科学, 43(12):4375-4389. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201812008 唐功建, 王强.2010.高镁安山岩及其地球动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 26(8):2495-2512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201008021 赵振华, 王强, 熊小林, 牛贺才, 张海祥, 乔玉楼, 2007.新疆北部的富镁火成岩[J].岩石学报, 23(7):1696-1707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.07.015 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 许继峰, 周长勇, 孙晨光, 王立全, 陈海红, 董国臣, 周肃.2008.西藏冈底斯带措勤地区则弄群火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学格架及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 24(3):401-412. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200803001 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 王立全, 廖忠礼, 赵志丹, 董国臣, 周长勇.2006.冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境:火山岩约束[J].岩石学报, 22(3):534-546. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603002 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 王青, Yildirim DILEK, 董国臣, 莫宣学.2012.拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化[J].高校地质学报, 18(1):1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.001 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 马兴涛. 土壤水入渗参数非线性预测模型改进及应用研究. 水利技术监督. 2024(04): 238-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘泳佚,史婷婷,王清,刘添文,刘亚磊,李梦茹. 江汉平原过渡带黏性层状土弥散试验与模拟研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2023(01): 41-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘广景. 煤层气高产水井原因分析及水源识别——以沁水盆地柿庄南区块3号煤井为例. 天然气勘探与开发. 2023(03): 123-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏玉涛,刘明欢,刘可,普薇如. 多尺度土壤水监测研究进展. 中国农学通报. 2021(26): 140-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: