Linear structure extraction and quantitative analysis of multi-source remote sensing information in West Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
夹持在近东西向额尔齐斯断裂和天山走滑断裂系统之间的西准噶尔地区,经历了自晚古生代晚期以来长期复杂的陆内构造变形历史。线性构造的长度、方向以及空间分布能够反映构造变形的强度和样式,指示应力作用的方式。本文选取新疆西准噶尔地区为研究区,利用ASTER、Landsat等多源遥感数据通过彩色合成、主成分分析、波段比值和Sobel滤波等增强显示断裂构造在遥感影像上的空间分布和光谱信息,并利用Canny边缘检测与人工解译相结合的方法提取研究区内线性构造;运用地质统计学的原理和方法对提取出的线性构造进行定量分析。结果表明,研究区内依长度优选方位确定的主断裂走向为N50°~60°E,代表了区域一级构造即达拉布特断裂展布的方位;依线性构造数量优选方位确定的次级断裂走向为80°~90°(近东西向),代表了区域三级构造的方位;介于以上两者之间的线性构造,即数量与长度均适中的线性构造,代表了区域二级构造的方位。线性构造的区域分布,揭示了在南北向主压应力作用下,西准噶尔地区构造体系的组成与构造变形特征。由此说明,多源遥感信息提取的线性构造定量分析,对于区域断裂构造体系的厘定具有重要意义。
Abstract:The western Junggar region, which is sandwiched between the nearly EW-trending Irtys fault and the Tianshan strikeslip fault system, has experienced long and complicated history of intracontinental tectonic deformation since the Late Paleozoic. The length, direction and spatial distribution of tectonic lineaments can not only reflect the strength and style of structural deformation but also indicate the mode of stress action. In this paper, the western Junggar region in northwest Xinjiang was selected as the research area. The spatial distribution and spectral information of fault structures in multi-source data such as ASTER and Landsat were displayed by color composite, principal component analysis(PCA), band ratio and Sobel filtering. The linear structures in the study area were extracted by combining Canny edge detection and visual interpretation. The principle and method of geostatistics were used to quantitatively analyze the extracted linear structures. The results show that the strike of the main faults determined by the optimum orientation of length in the study area is N50°-60°E, which represents the orientation of the distribution of the regional first-order structure, namely the Dalabut fault. The strike of the secondary faults determined by the optimum orientation of the number of linear structures is 80°-90° (in nearly EW direction), which represents the orientation of the regional third-order structures. The linear structures between the above two structures, namely moderate structures in number and length, represent the orientation of the regional secondary structure. The regional distribution of linear structures reveals the structural system composition and deformation characteristics of the western Junggar region under the action of the principal compressive stress in the NS direction. Therefore, the quantitative analysis of linear structures extracted from multi-source remote sensing image is of great significance for the determination of regional fault tectonic system.
-
1. 引言
传统的野外地质工作,由于观测视域的限制,对断裂分布构架的认识具有一定的局限性。而遥感影像由于其观测区域广阔,能够客观、真实、全面记录总体和个体线性构造的几何形态及其物理特征,信息量大且连续性好,为研究线性构造的空间分布提供了全面的信息(Zhang et al., 2013; Jakob et al., 2015; 李晨伟等,2018; Binam Mandeng et al., 2018)。西准噶尔地区的各级构造体系发育,处于内陆干旱半干旱地区, 地表植被稀疏,地质构造(断裂构造等)在遥感影像上显示清晰,可为研究该地区发育的构造体系提供准确的信息(J Ramón Arrowsmith et al., 2009; Klinger et al., 2011; He et al., 2011; 何宏林等,2011;齐信等,2012;罗国文等,2012;姚生海等,2014;魏永明等,2015;Ding et al., 2019)。由于遥感影像的分辨率不同,采取单一分辨率的影像数据会导致对不同尺度的构造信息提取不全面(颜蕊等,2008;刘新星等,2015;李雪等,2017),需要利用不同分辨率的多元数据进行综合解译。
本文选择西准噶尔地区为研究区,利用ASTER、ETM+等多源遥感影像数据解译研究区域内的线性、环形以及半环形构造(吴传庆等,2015;王阳明等,2018;姜文亮等,2018;张景发等,2018;王德华等,2018),并引入地统计学理论对线性构造进行定量分析(隋志龙等,2002;邓启东等,2004;余勇等,2005;陈建强等,2005;李宗仁等,2016)。从数学观点看,遥感线性构造具有不规则性和空间复杂性,而其构造长度、方位的大小则是表现其发育数量、规模、空间展布规律、构造演化的重要统计量(Masoud et al., 2011; 徐俊龙,2014;余敏等,2014)。通过对线性构造的定量分析,能够反映出线性构造的空间几何展布情况、构造活动的强弱(孔凡臣等,1991)、构造应力的相对大小和方向来源(王楠等,2013;宿渊源等,2015),进而揭示西准噶尔地区断裂构造的演化特征。
2. 区域地质概况
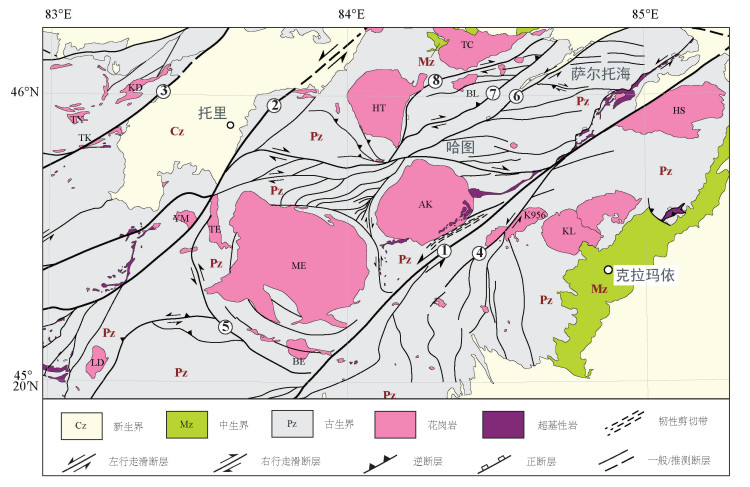
西准噶尔地区位于新疆西北部,是天山断裂系与额尔齐斯断裂之间的一个NE-SW向地块,与区内分布的NE向左行走滑断裂方向一致;处于准噶尔盆地西北缘,巴尔喀什地区东部,多发育石炭纪地层、花岗岩类岩体和岩脉、蛇绿岩套、超基性岩和双向走滑断裂体系(陈宣华等,2009;林伟等,2017;史建杰等,2017)。西准噶尔断裂构造体系是巴尔喀什马蹄形构造成矿带的向东延伸部分(陈宣华等,2011),区域上表现为夹持在右行走滑成吉斯—准噶尔断裂、近EW向额尔齐斯走滑断裂和天山断裂系之间的一个NE向地块,是中亚造山带(成矿域)西部的核心地区之一(陈宣华等,2017;Xu et al., 2019),发育了一系列NE走向、平行展布的左行走滑断裂,构成了具有斜向挤压特征的多米诺式走滑断裂构造体系(陈宣华等, 2010, 2012, 2014;王志宏等,2012)。
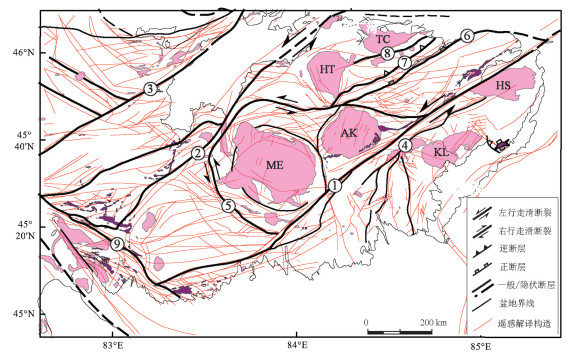
区域一级断裂是长达200余千米、呈北东走向平行展布的达拉布特断裂、玛依勒断裂和巴尔鲁克断裂,它们对区内的次级构造发育起着分隔作用,造成了断裂南北两侧次级构造显著不同。与达拉布特断裂等相平行,规模稍小的安齐断裂、哈图断裂和别鲁阿尕西断裂等,构成了区域二级断裂,具有与区域一级断裂类似的走滑性质(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 西准噶尔地区构造地质简图(据陈宣华等,2011修改)①—达拉布特断裂;②—玛依勒断裂;③—巴尔鲁克断裂;④一家人断裂;⑤—塔尔根断裂;⑥—安齐断裂;⑦—哈图断裂;⑧—别鲁阿尕西断裂;AK—阿克巴斯套岩体;BE—布尔克斯台岩体;BL—别鲁阿尕西岩体;HT—哈图岩体;HS—红山岩体;KL—克拉玛依岩体;K956—K956岩体(夏尔莆岩体);KD—康德萨依岩体;LD—拉巴河东岩体;TC—铁厂沟岩体;TK—塔尔根岩体;ME—庙尔沟岩体;YM—雅玛图西南岩体Figure 1. Structural geological map of West Junggar region (modified from Chen et al., 2011)①-Darabut fault; ②-Mayile fault; ③-Baerluke fault; ④-Yijiaren fault; ⑤-targen fault; ⑥-Anqi fault; ⑦-Hatu fault; ⑧-Bieluagaxi fault.AK-Aketiereke pluton; BE- Buerkesitai pluton; BL-Bieluagaxi pluton; HT: Hatu pluton; HS-Hongshan pluton; KL-Karemay pluton; K956- K956 pluton; KD- Kangde pluton; LD-Labahedong pluton; TC-Tiechanggou pluton; TK- Targen pluton; ME-Miaoergou batholith; YM- Yamatu pluton
图 1 西准噶尔地区构造地质简图(据陈宣华等,2011修改)①—达拉布特断裂;②—玛依勒断裂;③—巴尔鲁克断裂;④一家人断裂;⑤—塔尔根断裂;⑥—安齐断裂;⑦—哈图断裂;⑧—别鲁阿尕西断裂;AK—阿克巴斯套岩体;BE—布尔克斯台岩体;BL—别鲁阿尕西岩体;HT—哈图岩体;HS—红山岩体;KL—克拉玛依岩体;K956—K956岩体(夏尔莆岩体);KD—康德萨依岩体;LD—拉巴河东岩体;TC—铁厂沟岩体;TK—塔尔根岩体;ME—庙尔沟岩体;YM—雅玛图西南岩体Figure 1. Structural geological map of West Junggar region (modified from Chen et al., 2011)①-Darabut fault; ②-Mayile fault; ③-Baerluke fault; ④-Yijiaren fault; ⑤-targen fault; ⑥-Anqi fault; ⑦-Hatu fault; ⑧-Bieluagaxi fault.AK-Aketiereke pluton; BE- Buerkesitai pluton; BL-Bieluagaxi pluton; HT: Hatu pluton; HS-Hongshan pluton; KL-Karemay pluton; K956- K956 pluton; KD- Kangde pluton; LD-Labahedong pluton; TC-Tiechanggou pluton; TK- Targen pluton; ME-Miaoergou batholith; YM- Yamatu pluton3. 多源遥感数据的断裂提取
3.1 数据来源
研究区域范围N45°~46°10’、E82°30’~85°20’,遥感影像以ASTER和LandSat7 ETM+数据为主,配合使用Google影像数据(空间分辨率为约2 m),作为局域尺度地质构造分析的辅助资料。ASTER是搭载在美国NASA Terra卫星上的一种高级光学传感器,该影像共有14个波段,分别处于可见光/近红外、短波红外和热红外波段。可见光/近红外(1~3)波段空间分辨率为15 m,短波红外(4~9)波段空间分辨率为30 m,热红外波段(10~14)波段空间分辨率为90 m(李海涛等,2004)。获取ASTER影像地质概况和构造特征需要用到可见光、近红外和短波红外波段,因此采用影像对应的9个波段,用于该研究区的中等尺度及以下断裂构造、褶皱构造及环形构造的遥感解译等(魏永明等,2015)。ETM+是搭载在美国NASA的陆地卫星(Landsat)上的光学传感器,影像共8个波段,其中波段1~5及波段7空间分辨率均为30 m,波段8为全色波段空间分辨率为15 m,波段6为热红外波段空间分辨率为60 m(陈小瑜等,2014)。波段7为中红外波段,对岩石、矿物有较好的分辨作用。本文采用的数据有2001—2003年的ETM+数据共6景,2017年的ASTER-1B数据共23景,另外还借助不同分辨率的Google影像来辅助研究区线性构造解译工作。
3.2 影像增强
在对遥感影像进行构造解译提取之前,需要对其进行假彩色合成,波段比值运算等来突出影像中不同等级、不同形态的构造线性体信息(隋志龙等,2002),为地质构造目视解译提供可解译性强的基础遥感图像(刘新星等,2015),从而辅助计算机提取遥感断层信息。
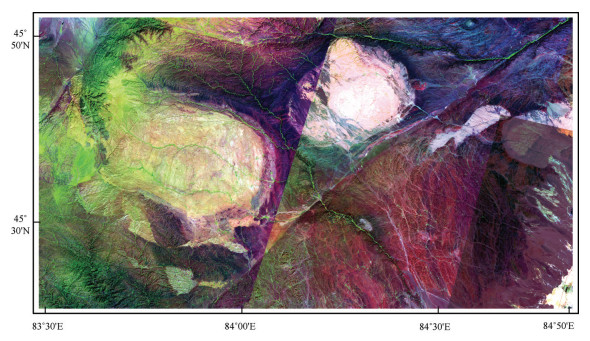
(1)假彩色合成:为突出研究区域的地形地貌、水系格局、地质线性体等特征,采用假彩色合成以便于对影像的直接目视解译和构造弱信息的提取(袁小样,2011)。经验证,ASTER影像采用波段6、3、1组合(图 2),ETM+影像采用波段7、4、1组合(图 3;穆媛芮等,2017),能清楚显示各种构造形迹(褶皱及断裂)以及岩石区边界,影像可解译程度高。
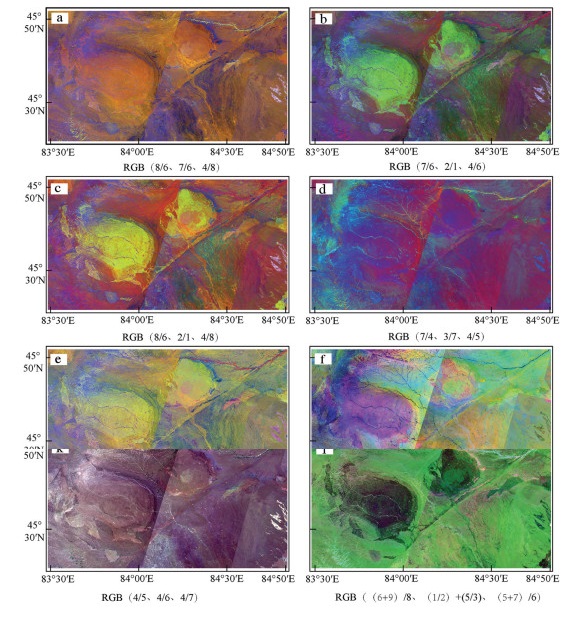
(2)波段比值运算:一些学者(罗国文等,2012;Sandra Jakob et al., 2015)结合ETM+与TM影像多次波段比值来提取断裂信息。波段比值运算后的图像能扩大断裂两侧不同地物之间的微小亮度差异,有利于突出线性断裂。利用波段之间的相关性,对研究区域的ASTER影像进行了波段比值的假彩色合成。由实验可知:发现组合e(8/6、8/7、4/7)、组合g(7/6、6/5、6/4)、组合((j 2+4)/5、(5+7)/6、(7+ 9)/8)对于断裂的突出效果较好,表现为达拉布特断裂特征清晰,断裂本身和两侧地物色调差异明显。组合b(7/6、2/1、4/6)、组合c(8/6、2/1、4/8)对庙尔沟—阿克巴斯套岩体的识别有较好的效果(图 4)。
3.3 主成分分析与滤波处理
利用主成分分析可以去除影像波段之间的冗余信息,将多波段的图像信息压缩到比原波段更有效的少数且互不相关的几个波段(Carr, 1998)。对研究区域的ETM+影像进行主成分分析,其第一主成分主要反映了原始影像的总反照率差异(Zumsprekl,2000;方洪宾等,2002),能突出亮度和地形信息,有利于断裂信息的提取。
Sobel滤波主要是对图像中的线性信息以及边缘信息进行检测,可突出遥感影像中的线性构造以及环形构造形迹。对主成分分析得到的第一变量进行Sobel滤波,如图 5所示。安齐断裂以及庙尔沟—阿克巴斯套岩体的环形构造特征明显,达拉布特断裂的色调与岩体的色调一致,反映了该断裂走向以及几何展布特征。达拉布特河在图 5中也清晰的显示出来,这说明Sobel滤波可突出该地区的地形、水系、断裂等信息,有利于遥感线性构造信息的提取。
3.4 边缘检测
遥感图像上断裂构造的识别多采用Canny边缘检测方法,断裂构造在图像上呈现出一定规模的连续边界特征。
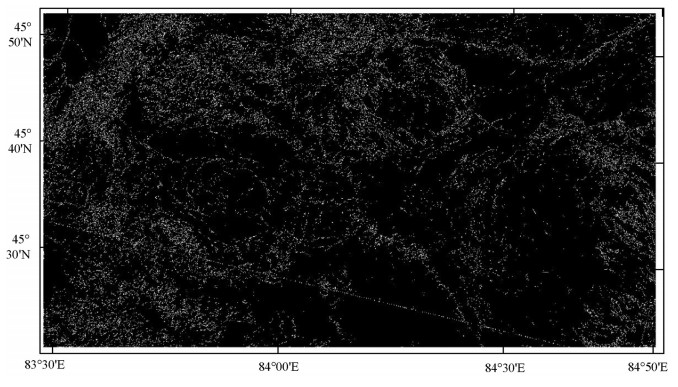
对Sobel滤波图像进行Canny边缘检测,图中边缘信息丰富,以白色像素显示,部分断裂构造信息可识别。由图 6可知,Canny边缘检测对研究区内的环形构造提取效果较好,对研究区内的达拉布特断裂只提取了部分线性特征,研究区左上方的安齐断裂在Canny检测图中线性特征也比较清晰。一些小的线性构造和河流的特征也被提取出来。
4. 线性构造目视解译及统计分析
4.1 遥感线性构造目视解译
对ETM+数据进行主成分分析、Sobel滤波和Canny边缘检测等计算机解译处理,得到研究区内的线性构造栅格数据。ETM+和ASTER影像经过图像增强(彩色合成、波段比值)与目视解译处理,作为计算机构造解译的辅助手段,从而提取出研究区内断裂构造几何分布的矢量数据。
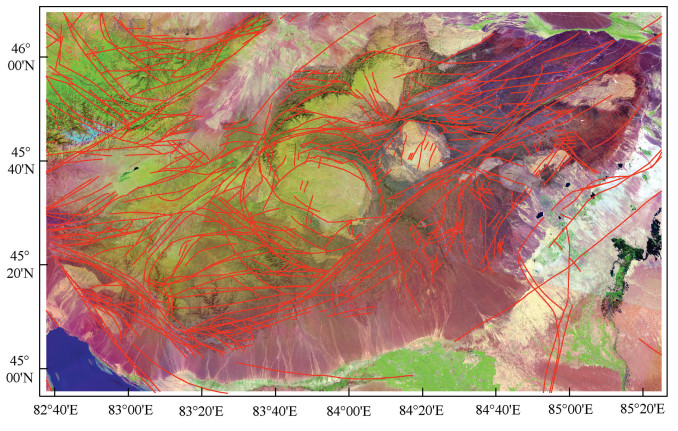
在区域地质资料的约束下,经Canny边缘检测得到的影像和目视解译等操作,以ArcGIS为平台,得到研究区的线性构造图(图 7)。通过和已有的地质资料进行对比分析,边缘检测结果能满足该区域内大部分线性构造提取的精度。对于细小的断层信息,根据现有地质资料补充,得到区域内完整的断层构造解译图,用于研究区内线性构造的定量分析。
此次目视解译出构造693条,其中包括线性、环状、半环状的断裂构造。由图 7可看出,断裂构造的主体走向为NNW向、NW向、NE向、NEE向,在研究区中西部,主要发育为NNW向和NW向断裂,东部及南部发育NE向和NEE向断裂,环状或半环状显示扭性特征。
4.2 线性构造统计分析
结合地质资料的遥感影像解译得到的线性构造可认为是不同构造应力下得到的产物。为客观和准确分析线性构造的内在数学统计特征和空间分布规律,可利用统计地质学的理论和方法对提取的线性构造进行统计分析。
4.2.1 线性构造长度
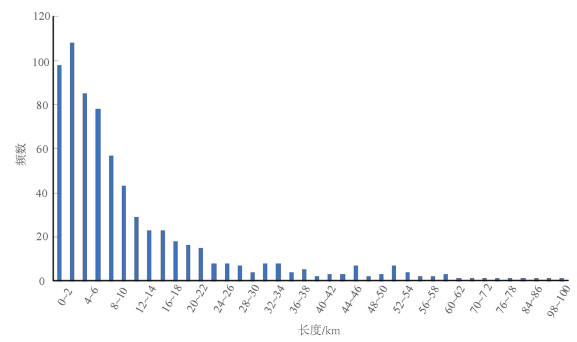
对线性构造的长度以2 km为间隔进行统计分析(图 8),横坐标为线性构造体的长度,纵坐标为长度区间内线性构造的频数,作出研究区线性构造的长度-频数图。由图 8可知,数量最多的线性构造长度大多集中在2~10 km,而100 km以上的线性构造数量较少。随着长度的增加,线性构造的数量呈对数分布。
4.2.2 线性构造方位
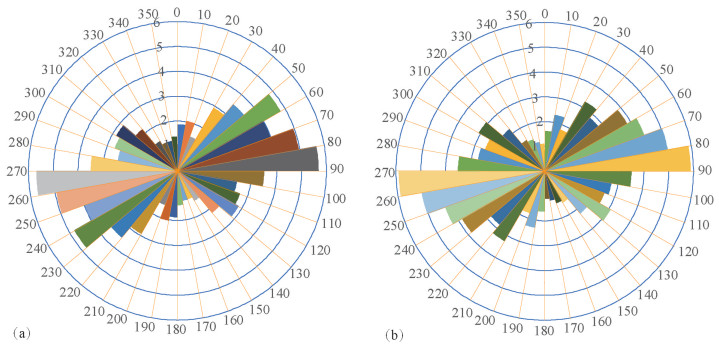
为统计研究区内主断裂走向,根据线性体方位角10°为间隔统计出每个区间内的构造线长度均值,作出方位-长度(均值)玫瑰花图(图 9a),其中半径为每个区间内的构造线均值占总和的百分比。图 9a可直观反映该地区主要断裂的走向,50°~60°的线性构造长度最长,这说明该方向的断裂规模最大,可以作为研究区域内主断裂的方向。根据线性体方位角10°为间隔统计出每个区间内的构造线数量,作出方位-频数玫瑰花图(图 9b),其中半径为每个区间内的构造线数量占总和的百分比。由图 9b可知,研究区内线性构造最多的是80°~90°方向,其次是70°~80°方向,说明该地区这两个方向的断层数量多。图 9a统计结果与该地区的断裂包括达拉布特断裂、玛依勒断裂和巴尔布鲁克断裂等3条区域Ⅰ级断裂以及规模较小的安齐断裂、哈图断裂和别鲁阿尕西断裂等Ⅱ级断裂的走向完全一致。结合图 9a、b可知,研究区域内主断裂走向是50°~60°,由于该方向的构造应力使得80°~90°方向之间的断裂数量最多。这表明线性构造的方位-频数与方位-长度统计可以表明研究区域内断裂的规模以及走向,从而进一步指示了该地区构造应力的大小及方向。
4.2.3 线性构造密度和强度
为进一步证明西准区域中的断裂构造受地区应力以及构造活动的持续时间和大小,本节分析了西准地区线性构造的密度和强度。线性构造密度(P)是指单位网格内构造线数量的多少,线性构造强度(Q)是指单位网格中线的长度总和(徐俊龙,2014)。利用密度公式(1)和强度公式(2)计算出每个格网内的密度和强度。其中A表示单元格网的面积,n表示单元格网内构造线的数量,l表示单元格网内构造线的总长度。但是为了使统计量为整数以便分析,统一将A的值取1。因此,密度(P)和强度(Q)公式可以用公式(3)和(4)表示。

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
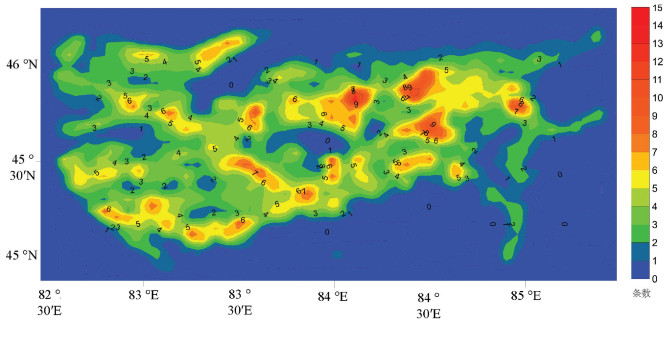
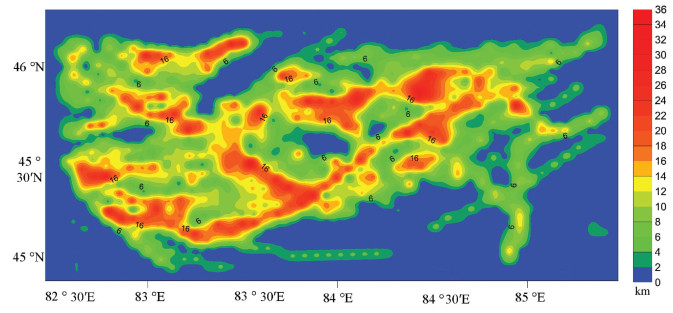
(4) 将研究区域划分为边长为5000 m的1457个正方形,统计出每个正方形内线性构造的数量(n)以及构造线长度和(l),作出密度和强度等值线图(图 10,图 11)。线性构造密度的发育指示着断裂构造活动的强弱,通过其密度值的高低可以推测出区域构造活动的规模以及隐伏断裂的发育情况。由图 10和图 11可以看出,线性构造密度大的区域也有着较高的强度,空间展布特征基本一致。线性构造密度和强度值同时较高的区域,说明该地区的构造运动持续时间长和构造应力规模较大。图 10中,红色区域代表线性构造密度高,红色区域均位于西准噶尔地区内的几条主断裂附近,这说明在主断裂形成的过程中,由于构造应力的影响,主断裂附近形成细小断裂且数量较多。图 11中,沿NE-SW、NWSE两个方向延长的带状中高值区,这与该地区的达拉布特断裂、玛依勒断裂及安齐断裂等主断裂方向一致,在主断裂周围区域由中心向外呈递减分布,这也充分说明该方向的线性构造十分发育。从而指示了该区域在来自南北向西伯利亚板块和塔里木板块的挤压下,断裂的左行走滑导致了该区域内的主断裂方向为NE向。
5. 讨论
5.1 线性构造反映断裂构造体系特征
本文在区域地质调查成果资料的约束下,通过对遥感影像进行解译得到的线性构造可认为是断裂等地质构造的表现。因此,对解译得到的线性构造进行定量统计分析,从而能进一步反映西准噶尔地区的断裂构造体系特征。
对线性构造的长度-频数进行统计分析,可依据长度指标将线性构造进行分级,从而进一步揭示研究区的基本构造格局。该研究区内的Ⅰ级断裂包括达拉布特断裂、玛依勒断裂、巴尔鲁克断裂及安齐断裂规模较大,走向延长最高超过200 km(陈宣华等,2012)。因此,将长度超过30 km的认为是区域Ⅰ级断裂,而长度低于30 km的认为是次级断裂。利用长度指标可确定该地区断裂体系的次级关系,线性构造的长度与断裂规模的大小呈负相关关系,即长度越长(即规模越大)、构造数量越少,长度越短(规模越小),构造数量越多。通过对线性构造的方位-频数、方位-长度进行分析,发现50°~60°方向的线性构造长度最长,这说明该方向的断裂规模最大,可作为该地区断裂构造体系的主方向。而80°~90°方向的构造数量最多,是该区域断裂构造的优选方位,所以线性构造的数量指标不能用来指示断裂的主方向。
通过长度和方位统计,可进一步反映出西准噶尔地区发育了具有一系列平行展布的NE走向的断裂构造(图 11),区域Ⅰ级断裂对区内的次级构造发育起到分隔作用,造成断裂两侧次级构造方向不同。在NE向近乎平行的3条主断裂区域内,次级断裂走向大多为NE、NW向,而在主断裂区域外,断裂构造走向多为NW向(图 12)。对线性构造的定量统计分析可以反映出该区域斜向挤压特征的多米诺式走滑断裂构造体系。
5.2 优选构造方位与构造变形特征
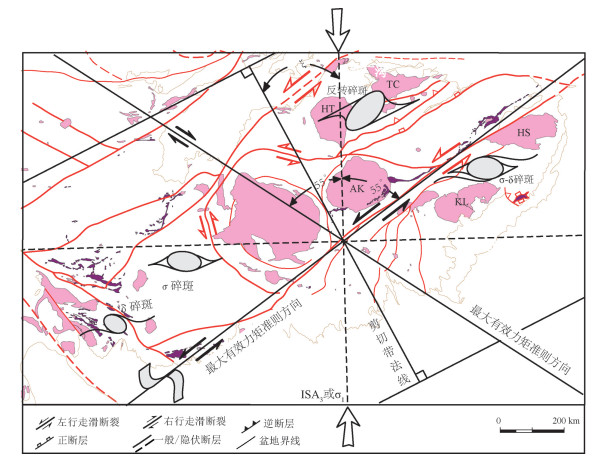
将西准地区走滑断裂体系的运动学涡度图(郑亚东等,2008;刘江等,2011)与遥感解译的线性构造进行分析如图 13所示。两条最大有效力矩的准则方向之间的夹角是110°。图 13中可以看出,NE向的最大有效力矩与西准地区的主断裂方向一致,具有左行走滑性质。该断裂下盘的岩体旋转方式与剪切带的剪切方式一致,即随剪切作用向前旋转,形成具有σ型、δ型、σ-δ型拖尾的碎斑,如图中的红山岩体和克拉玛依岩体;而断裂上盘的岩体旋转方式与剪切带的剪切方式相反,即发生逆向旋转形成反转碎斑,如图中的哈图岩体和铁厂沟岩体。由于南北向的挤压以及左行走滑断裂的运动学特征使得该地区的岩体发生不同形式的旋转。
![]() 图 13 西准噶尔部分构造类型及取向(据郑亚东等,2008修改)Figure 13. Types and orientation of partial structures in Western Junggar (modified from Zheng et al., 2008)
图 13 西准噶尔部分构造类型及取向(据郑亚东等,2008修改)Figure 13. Types and orientation of partial structures in Western Junggar (modified from Zheng et al., 2008)NE向最大有效力矩与解译得到的部分线性构造方向一致,该方向的线性构造长度最长,规模最大,代表西准地区的主断裂方向。而数量最多的线性构造的方向几乎近东西向,这说明在主断裂走滑的过程中形成大量的细小断裂,从而在一定程度上揭示了该地区的主断裂方向。在南北向的挤压下,该方向的断裂数量最少,在遥感解译图上也有所体现,反映了西准地区挤压方向特征。
将西准地区的部分构造类型和遥感解译得到的线性构造进行叠加,从断裂的应力场方向、性质以及数量等方面对该地区的断裂构造体系进行综合分析,从而使得遥感解译得到的线性构造具有可信性。
6. 结论
本文基于多源遥感影像数据,提取研究区域(西准噶尔地区)的线性构造,并利用统计地质学方法对其进行定量分析。综合分析研究区的线性区域构造特征,对该区域展开影像增强目视解译、断裂提取计算机解译和线性构造定量分析等操作,得出以下结论:
(1)通过对遥感影像信息增强以及线性构造提取处理,得到该地区遥感解译线性构造分布图,有利于西准地区遥感线性构造的目视解译,从而为宏观分析构造的空间分布提供有效方法。
(2)对研究区内的线性构造的长度-频数进行统计分析,其长度与数量呈负相关关系。从而反映研究区域内构造发育的次序关系。结合线性构造的长度、方位、密度以及强度进行分析,区域内优选构造方位为数量最多的线性构造的方位,为80°~ 90°;主导性构造方位为长度最长的线性构造长度的方位,为50°~60°;数量最少的线性构造的方位反映西准地区的挤压方向(南北)特征。
(3)遥感影像解译得到的线性构造揭示了西准地区地区的断裂构造规模、方位特征,很好的反映了该地区在晚古生代闭合洋陆转换过程中形成的左行走滑断裂构造体系。
致谢: 本文的研究工作得到了中国地质科学院深部探测中心深部地质与地壳演化研究室各位老师的大力支持与帮助,作者谨表忠心感谢。 -
图 1 西准噶尔地区构造地质简图(据陈宣华等,2011修改)
①—达拉布特断裂;②—玛依勒断裂;③—巴尔鲁克断裂;④一家人断裂;⑤—塔尔根断裂;⑥—安齐断裂;⑦—哈图断裂;⑧—别鲁阿尕西断裂;AK—阿克巴斯套岩体;BE—布尔克斯台岩体;BL—别鲁阿尕西岩体;HT—哈图岩体;HS—红山岩体;KL—克拉玛依岩体;K956—K956岩体(夏尔莆岩体);KD—康德萨依岩体;LD—拉巴河东岩体;TC—铁厂沟岩体;TK—塔尔根岩体;ME—庙尔沟岩体;YM—雅玛图西南岩体
Figure 1. Structural geological map of West Junggar region (modified from Chen et al., 2011)
①-Darabut fault; ②-Mayile fault; ③-Baerluke fault; ④-Yijiaren fault; ⑤-targen fault; ⑥-Anqi fault; ⑦-Hatu fault; ⑧-Bieluagaxi fault.AK-Aketiereke pluton; BE- Buerkesitai pluton; BL-Bieluagaxi pluton; HT: Hatu pluton; HS-Hongshan pluton; KL-Karemay pluton; K956- K956 pluton; KD- Kangde pluton; LD-Labahedong pluton; TC-Tiechanggou pluton; TK- Targen pluton; ME-Miaoergou batholith; YM- Yamatu pluton
图 13 西准噶尔部分构造类型及取向(据郑亚东等,2008修改)
Figure 13. Types and orientation of partial structures in Western Junggar (modified from Zheng et al., 2008)
-
Binam Mandeng E P, Bondjè Bidjeck L M, Takodjou Wambo J D, Taku A Jr; Bineli Betsi T, Solange Ipan A, Tchami Nfada L, Bitom Dieudonné L. 2018. Lithologic and structural mapping of the Abiete-Toko gold district in southern Cameroon, using Landsat 7 ETM+/SRTM[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 350(3):130-140. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=18bb42a7a2c2ad7bd6f5abb41e2f7972&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Carr J R. 1998. Visual basic program for principal components transformation of digital images[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 24(3):209-218. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ce75b7c790e793614f9c48cb5096e564
Cheng Lyu, Cheng Qiuming, Zuo Renguang, Wang Xueping. 2017. Mapping spatial distribution characteristics of lineaments extracted from remote sensing image using fractal and multifractal models[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 28(3):507-515. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx-e201703010
Chen Jianqiang, Wu hong.2005. Extraction and quantitative analysis of remote sensing geotectonic information in Dachang area[C]//Fifth China Academic Conference on Mine Geology and High-level Forum on Revitalizing Production Mine Resources in Northeast China(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Xiaoyu, Liu Zhiping, Zheng Weimin. 2014. Fusion of ETM + image optimal bands composite and its quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2:218-222(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xysfxyxb-zrkx201402014
Chen Xuanhua, Chen Zhengle, Han Shuqin, Wang Zhihong, Yang Qi, Ye Baoying. 2012. Geothermochronology Of Mo-W Deposits in Balkhash Metallogenic Belt, Kazakhstan, Central Asia[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 37(5):878-892(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201205002
Chen Xuanhua, Chen Zhengle, Han Shuqin. 2017. TectonicMagmatic-Metallogenesis Evolution in Barkash-Western Junggar and its Adjacent Areas[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Xuanhua, Chen Zhengle, Yang Nong. 2009. Study on regional mineralizations and ore-field structures:Building of mineralizing tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(1):1-19 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzlx200901002.htm
Chen Xuanhua, Nie Lanshi, Ding Weicui, Wang Xueqiu, Wang Zhihong, Ye Baoying. 2015.The relationship between strike-slip tectonic system and geochemical anomalies in the West Junggar, northwestern China and its implication for mineral exploration[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(2):371-387(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201502006
Chen Xuanhua, Wang Zhihong, Ye Nong, Chen Zhengle, Han Shuqin. 2010. Geological characteristics of and metallogenic model for large-scale sayak copper ore field in Balkhash metallogenic belt, Centralasia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 16(2):189-202(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201002009.htm
Chen Xuanhua, Yang Nong, Ye Baoying, Wang Zhihong, Chen Zhengle. 2010. Tectonic system and its control on metallogenesis in Western Junggar as part of the central Asia multi-core metallogenic system[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(3):325-338(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201103001
Ding Weicui, Li Tingdong, Chen Xuanhua, Chen Jianping, Xu Shenglin, Zhang Yiping, Li Bing, Yang Qiang. 2019. IntraContinental deformation and tectonic evolution of the West Junggar Orogenic Belt, Central Asia:Evidence from remote sensing and structural geological analyses[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, DOI: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.08.001.
Fan Chun, Su Zhe, Zhou Li. 2014. Kinematic features of Darlbute fault in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 49(4):1045-1058(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx201404002
He HongLin. 2011. Some problems of aerial photo interpretation in active fault mapping[J]. Seismology & Geology, 33(4):938-950(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz201104017
J Ramón Arrowsmith, Zielke O. 2009. Tectonic geomorphology of the San Andreas fault zone from high resolution topography:An example from the Cholame segment[J]. Geomorphology, 113(1/2):0-81. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222832427_Tectonic_geomorphology_of_the_San_Andreas_Fault_zone_from_high_resolution_topography_An_example_from_the_Cholame_segment?ev=auth_pub
Jakob S, Bühler B, Gloaguen R, Breitkreuz C, Eliwa H A, El Gameel K. 2015. Remote sensing based improvement of the geological map of the Neoproterozoic Ras Gharib segment in the Eastern Desert (NE-Egypt) using texture features[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 111:138-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fb262937dbfd56a9c9aef893f2973e38
Jiang Wenliang, Zhang Jingfa, Shen Xuhui, Jiao Qisong, Tian Tian, Wang Xin. 2018. Application of high resolution remote sensing technology in the study of active faults[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(S1):192-211(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhen201703013
Klinger Y, Etchebes M, Tapponnier P. 2011. Characteristic slip for five great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China[J]. Nat. Geosci., 4(6):389-392. doi: 10.1038-ngeo1158/
Kong Fanchen, Ding Guoyu. 1991. The implications of the fractal dimension values of lineaments[J]. Earthquake, 5:33-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000214087
Li Chenwei, Zhang Ruisi, Zhang Zhutong, Ceng Min. 2018. Tectonic interpretation and analysis based on multi-source remote sensing sata:A case study of Jitai River in Chayi, Tibet[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33(4):657-665(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li haitao, Tian Qingjiu. 2004. Introduction of ASTER data products'characteristics and plans[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 3:53-55, 47(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Xue, Li Xiaoli, Wang Qiuliang, Li Jinggang, Zhang Lifen, Liao Wulin. 2017. Research on faults extraction method based on multisource remote sensing data:A case of central water source area of the middle route of south-to-north water diversion project[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 37(2):132-136(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Zongren, Zhang Kun, Li Xiaomin, Li Delin, Ma Shibin. 2016. Analysis of linear structural characteristics of remote sensing and prediction of ore finding[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 31(3):115-121(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ygxx201603018
Lin Wei, Sun Ping, Xue Zhenhua, Zhang Zhongpei. 2017. Structural analysis of Late Paleozoic deformation of central Dalabutefault zone, West Junggar, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(10):2987-3001(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201710001
Liu Jiang, Zhang Jinjiang, Guo Lei, Qi Guowei. 2011. Kinematic Vorticity of the Daqingshan Detachment Fault and its Structural Implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(1):1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201101001
Liu Xinxing, Chen Jianping, Zeng Min, Dai Jingjing, Pei Yingru, Ren Mengyi, Wang Na. 2015. Geological structural interpretation of Qiangduo area in Tibet based on multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 27(3):154-160(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gtzyyg201503024
Luo Guowen, Yin Zhihong, Yang Shuwen, 2015. Present condition and prospect of ertracton and identification methods by using remote sensing technology in faults[J]. Land and Resources in Shangdong Province, 28(2):29-33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sddz201202010
Masoud A A, Koike K. 2011. Auto-detection and integration of tectonically significant lineaments from SRTM DEM and remotely-sensed geophysical data[J]. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 66(6):818-832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=803cba4d7f1488a16b4f3b52af209161
Mu YuanRui, Kong Jie, Zhu YuFang, Zhang Jianshou. 2017. Lithology extraction from ASTER images in the east of setura town, Pishan county, west KunLun, Xinjiang[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 29(6):143-145, 148(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qi Xin, Shao Changsheng, Chen Zhoufeng, Li Xue. 2012. Application of multi-source remote sensing data in fault structure interpretation[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 32(4):90-93(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201204021
Sharifi A, Malian A, Soltani A. 2018. Efficiency evaluating of automatic lineament extraction by means of remote sensing (Case Study:Venarch, Iran)[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 13:1-12. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326286228_Efficiency_Evaluating_of_Automatic_Lineament_Extraction_by_Means_of_Remote_Sensing_Case_Study_Venarch_Iran
Shi Jianjie, Chen Xuanhua, Ding Weicui, Li Bing. 2017. Late Paleozoic ocean-continent transition in West Junggar, central Asian orogenic belt:Evidence from Late Carboniferous rhyolites[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1):150-160(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzxb-e201902002
Su Yuanyuan, Zhang Jingfa, He Zhongtai, Jiang Wenliang, Jiang Hongbo, Li Qiang. 2015. Assessment of applying ZY-3 DEM data to quantitative study of active structures[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 27(4):122-130(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gtzyyg201504019
Sui Zhilong, Li Dewei, Huang Chunxia, 2002. Remote sensing methods for research of fault structures[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 18(3):34-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wthtjsjs201802019
Wang Dehua, Zhang Jingfa, Yang Jiajia, Jiang Wenliang, Jiao Qisong. 2018. Application of remote sensing data in active fault surveying of Damxung area[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 38(5):51-56, 79(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz201805010
Wang Yangming, Zhang Jingfa, Liu Zhirong, Shen Xuhui. 2018.Active faults interpretation of Shannan area in Tibet based on multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 30(3):230-237(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201803031
Wei Yongming, Lin Qizhong, Xiao Sang, Chen Yu, Wang Qinjun, Liu Qingjie, Wei Xianhu. 2015. Remote sensing identification of geological structures at different scales in western Junggar, Xinjiang and its prospecting significance[J] Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(1):76-92(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201501008
Xu Junlong, Wen Xingping, Yu Min, Li Chao, Wang Jun, Zhang Lijuan, Zhou Yang, Qiao Xu. 2014. An analysis of linear structures in the huize lead-zinc mine based on remote sensing images using the principle of geostatistics[J]. Geology and Exploration, 50(4):763-771(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201404016
Xu Junlong. 2014. Statistical Characteristics Analysis of Remote Sensing Linear Structures and Extraction of Alteration Information in Huize Lead-Zinc Mine, Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming University of Science and Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Shenglin, Chen Xuanhua, Li Tingdong, Shi Jianjie, Ding Weicui, Li Bing, Huang Penghui, Zhang Yiping, Zhang Yaoyao, Ma Feizhou. 2019.The Late Carboniferous-Early Permian OceanContinent Transition in the West Junggar, Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Constraints from Columnar Jointed Rhyolite[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 93(2):265-282. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXW201902002.htm
Yan Rui, Zhang Jingfa, Jiang Wenliang, Jiao Mengmei. 2008. The interpretation of faults in Hangjinqi area of Ordos Basin using Multi-Source Rs Images[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2:88-91, 122(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gtzyyg200802020
Yao Shenghai, Huang Wei, Jiang Wenliang, Wang Xin. 2014. Late Quaternary activity characteristics of faults (Xitieshan section) in the northern margin of Qaidam basin[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 37(S1):50-54(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Min, Wen Xingping, Xu Junlong, Chao Jiangqin, Yang Yang, Wang Jun, Yi Bangjin. 2014. Application of extraction of remote sensing alteration anomalies based on fractal theory in Maoping lead-zinc deposit[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 29(5):853-860(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygjsyyy201405020
Yu Yong, Yuan Aiping. 2005. Quantitative analysis with high resolution remote sensing lineament in Gaolong gold deposit[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 12(3):200-202 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxkx200503013
Yuan Xiaoxiang. 2011. Multi-source Remote Sensing Data Application in Information Extraction of Active Tectonics[D]. Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, CEA(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jingfa, Jiang Wenliang, Tian Tian, Wang Xin. 2016. High resolution remote sensing application research in active fault surveying[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 38(3):386-398(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhen201603006
Zhang Wei, Yao Qi, Chen Hanlin, Yang Jinzhong. 2013. Remote sensing interpretation and extraction of structural information about active faults at Hangzhou, China, and their surroundings[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 24(6):1056-1067. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx-e201306017
Zheng Yadong, Wang Tao, Zhang Jinjiang. 2008. Theory and practice of kinematic vorticity[J].Geoscience Frontiers, 3:209-220(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200803017
Zumsprekel H, Prinz T. 2000. Computer-enhanced multispectral remote sensing data:A useful tool for the geological mapping of Archean terrains in (semi)arid environments[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 26(1):87-100. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=13f72b295e7d470280c4f51645842e89&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
陈建强, 吴虹. 2005.大厂地区遥感地质构造信息提取及定量分析[C]//中国矿山地质学术会议暨振兴东北生产矿山资源高层论坛. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYN200508001024.htm 陈小瑜, 刘志平, 郑伟民, 陈文成. 2014. ETM+遥感影像最佳波段融合质量评价[J].信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版)2:218-222. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xysfxyxb-zrkx201402014 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 韩淑琴. 2017.巴尔喀什-西准噶尔及邻区构造-岩浆-成矿作用演化[M].北京:地质出版社. 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 韩淑琴, 王志宏, 杨屹, 叶宝莹. 2012.中亚巴尔喀什成矿带钼-钨矿床的地质热年代学[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 37(5):878-892. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201205002 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 杨农. 2009.区域成矿与矿田构造研究——构建成矿构造体系[J].地质力学学报, 15(1):1-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200901001 陈宣华, 聂兰仕, 丁伟翠, 王学求, 王志宏, 叶宝莹. 2015.西准噶尔走滑断裂系元素分布特征及其成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 31(2):371-387. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201502006 陈宣华, 王志宏, 杨农, 陈正乐, 韩淑琴. 2010.中亚巴尔喀什成矿带萨亚克大型铜矿田矿床地质特征与成矿模式[J].地质力学学报, 16(2):189-202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201002008 陈宣华, 杨农, 叶宝莹, 王志宏, 陈正乐. 2010.中亚成矿域多核成矿系统西准噶尔成矿带构造体系特征及其对成矿作用的控制[J].大地构造与成矿学, 35(3):325-338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201103001 何宏林. 2011.活动断层填图中的航片解译问题[J].地震地质, 33(4):938-950. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz201104017 姜文亮, 张景发, 申旭辉, 焦其松, 田甜, 王鑫. 2018.高分辨率遥感技术在活动断层研究中的应用[J].遥感学报, 22(S1):192-211. http://www.jors.cn/jrs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=ygxb-22-zk-jiangwenliang&flag=1 孔凡臣, 丁国瑜, 1991.线性构造分数维值的含义[J].地震, 5:33-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000214087 李晨伟, 张瑞丝, 张竹桐, 曾敏. 2018.基于多源遥感数据的构造解译与分析——以西藏察隅吉太曲流域为例[J].遥感技术与应用, 33(4):657-665. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YGJS201804010.htm 李海涛, 田庆久. 2004. ASTER数据产品的特性及其计划介绍[J].遥感信息, 3:53-55, 47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygxx200403014 李雪, 刘小利, 王秋良, 李井冈, 张丽芬, 廖武林. 2017.基于多源遥感数据的断裂构造提取方法研究——以南水北调中线工程核心水源区为例[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 37(2):132-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201702005 李宗仁, 张焜, 李晓民, 李得林, 马世斌. 2016.遥感线性构造特征分析与找矿预测[J].遥感信息, 31(3):115-121. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygxx201603018 林伟, 孙萍, 薛振华, 张仲培.2017.西准噶尔达拉布特断裂带中段晚古生代构造分析[J].岩石学报, 33(10):2987-3001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201710001 刘江, 张进江, 郭磊, 戚国伟. 2011.大青山伸展拆离断层运动学涡度研究及构造指示意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 35(1):1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201101001 吴传庆, 殷守敬, 朱利, 马万栋, 吴迪. 2015.基于多源遥感数据的西藏羌多地区地质构造解译[J].国土资源遥感, 27(3):154-160. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201503024 罗国文, 阴志宏, 杨树文.2012.断裂构造遥感识别和提取方法的现状与展望[J].山东国土资源, 28(2):29-33. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sddz201202010 穆媛芮, 孔婕, 朱玉芳, 张建收. 2017.新疆西昆仑皮山县赛图拉镇东ASTER影像岩性提取研究[J].西部探矿工程, 29(6):143-145+148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbtkgc201706045 齐信, 邵长生, 陈州丰, 李雪. 2012.多源遥感数据在断裂构造解译中的应用[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 32(4):90-93. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz201204021 史建杰, 陈宣华, 丁伟翠, 李冰. 2017.中亚造山带西准噶尔晚古生代洋陆转换与构造演化——来自晚石炭世流纹岩的证据[J].地质力学学报, 23(1):150-160. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201701011 隋志龙, 李德威, 黄春霞, .2002.断裂构造的遥感研究方法综述[J].地理与地理信息科学, 18(3):34-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxygtyj200203008 王德华, 张景发, 杨佳佳, 姜文亮, 焦其松. 2018.遥感技术在西藏当雄地区活动断裂调查中的应用[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 38(5):51-56, 79. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz201805010 王阳明, 张景发, 刘智荣, 申旭辉. 2018.基于多源遥感数据西藏山南地区活动断层解译[J].国土资源遥感, 30(3):230-237. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201803031 魏永明, 蔺启忠, 肖磉, 陈玉, 王钦军, 刘庆杰, 2015.新疆西准噶尔地区不同尺度地质构造的遥感标识特征及找矿意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 39(1):76-92 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201501008 宿渊源, 张景发, 何仲太, 姜文亮, 蒋洪波, 李强. 2015.资源卫星三号DEM数据在活动构造定量研究中的应用评价[J].国土资源遥感, 27(4):122-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201504019 徐俊龙, 温兴平, 余敏, 李超, 王军, 张丽娟, 2014.基于地质统计学原理的会泽铅锌矿遥感线性构造解析[J].地质与勘探, 50(4):763-771. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201404016 徐俊龙, 2014.云南会泽铅锌矿遥感线性构造统计特征分析及蚀变信息提取研究[D].昆明理工大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1014356287.htm 王飞跃, 吴军虎, 王俊峰, 赵小峰. 2008.多源遥感数据综合解译鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区地质构造[J].国土资源遥感, 2:88-91, 122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg200802020 姚生海, 黄伟, 姜文亮, 王鑫. 2014.柴达木盆地北缘断裂(锡铁山段)晚第四纪活动性特征[J].地震研究, 37(S1):50-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZYJ2014S1009.htm 余敏, 温兴平, 徐俊龙, 晁江琴, 杨炀, 王军.2014.基于分形的遥感蚀变异常提取在毛坪铅锌矿中的应用[J].遥感技术与应用, 29(5):853-860. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygjsyyy201405020 余勇, 袁爱平.2014.高龙金矿区高分辨率遥感线性构造定量分析[J].广西科学, 12(3):200-202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxkx200503013 袁小祥, 2011.多源遥感数据在活动构造信息提取中的应用研究[D].中国地震局地震预测研究所. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85405-1011159292.htm 张景发, 姜文亮, 田甜, 王鑫. 2016.活动断裂调查中的高分辨率遥感技术应用方法研究[J].地震学报, 38(3):386-398. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhen201603006 郑亚东, 王涛, 张进江.2008.运动学涡度的理论与实践[J].地学前缘, 3:209-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200803017 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 刘诚,唐卫东,杨凯,李含,贺景龙,姚川,李新斌. 荒漠浅覆盖区萤石矿定位预测技术研究. 西北地质. 2024(04): 144-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张昆,刘磊,马兴知,杨雨凡. 长江中下游成矿带物性结构揭示的成矿深部背景和过程. 地质通报. 2024(11): 2044-2061 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨剑,王桥,王绪本,宁括步,郭镜,周清,高慧. 四川攀枝花晶质石墨矿电性特征及找矿评价. 中国地质. 2022(01): 284-297 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 何胜,苏世杰,侯利朋. 综合物探在柴达木盆地盐湖深层卤水钾矿勘查中的应用. 地质与资源. 2021(05): 628-636 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吕庆田,孟贵祥,严加永,张昆,龚雪婧,高凤霞. 长江中下游成矿带铁-铜成矿系统结构的地球物理探测:综合分析. 地学前缘. 2020(02): 232-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: