Characteristics and tectonic setting of volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula of Xi Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
大兴安岭中生代火山岩的成因和构造背景一直存在争议。内蒙古西乌旗地区发育大面积的晚中生代火山岩,是中国东部巨型火山岩带的重要组成部分。本文对西乌旗罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩开展了野外地质、岩石学、锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学研究,以便对其岩石成因和构造背景给予制约。白音高老组火山岩主要由流纹岩及流纹质火山碎屑岩等一套中酸性火山岩组成。采集其中的球粒流纹岩和英安斑岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb测年,测年锆石的CL图和Th/U值(0.34~1.25)指示其为岩浆成因锆石,测年结果分别为(140±0.8)Ma和(133±0.7)Ma,表明这套火山岩的形成时代为早白垩世早期。岩石地球化学研究表明,白音高老组火山岩属高钾钙碱性系列,具高硅、富碱、贫镁、钙,高FeOT/MgO比值,低Mg#值、Nb/Ta比值的特征;相对富集轻稀土元素,亏损重稀土元素;大部分样品富集LILE,而亏损Ba、Sr和HFSE,具A型花岗岩地球化学特征,形成于伸展构造背景,为地壳部分熔融的结果。结合区域中生代火山岩的空间展布特征,认为该火山岩形成应与蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合碰撞后伸展和古太平洋板块的俯冲作用有关。
Abstract:There exist different opinions concerning the petrogenesis and tectonic background of Mesozoic volcanic rocks developed in the Da Hinggan Mountains. The Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Xi Ujimqin Banner of Inner Mongoliais a very important part of the huge volcanic rock belt in eastern China.The authors studied the volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula of Xi Ujimqin Banner in such aspects as field occurrence,petrology,zircon U-Pb isotopic geochronology and geochemisty in order to constrain their petrogenesis and tectonic background. The volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation are composed of rhyolite and volcanic clastic,which are a set of felsic volcanic rocks. The cathodoluminescence (CL) images of analyzed zircons of the pyromeride and dacite porphyry from Baiyingaolao Formation and their Th/U ratios(0.34-1.25) imply the igneous origin. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating shows that their ages are about(140±0.8) Ma and(133±0.7) Ma respectively,suggesting the early period of Early Cretaceous. Petrological and geochemical data reveal that the rocks belong to the high potassium calc-alkaline rock series characterized by rich Si and alkali,poor magnesium and calcium,high FeOT/MgO ratio and low Mg#,Nb/Ta ratio. LREE are richer than HREE.The trace element geochemistry is characterized evidently by enrichment of LILE,depletion of Ba,Sr and HFSE. All these geochemical characteristics of rocks show an affinity with the A-type granites,which were most probably formed in an extensional setting and originated from the partial melting of the crust. Combined with spacial distribution of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks,the authors hold that they were probably related to the post-orogenic extension following the closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk orogen,and were also affected by the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate.
-
-
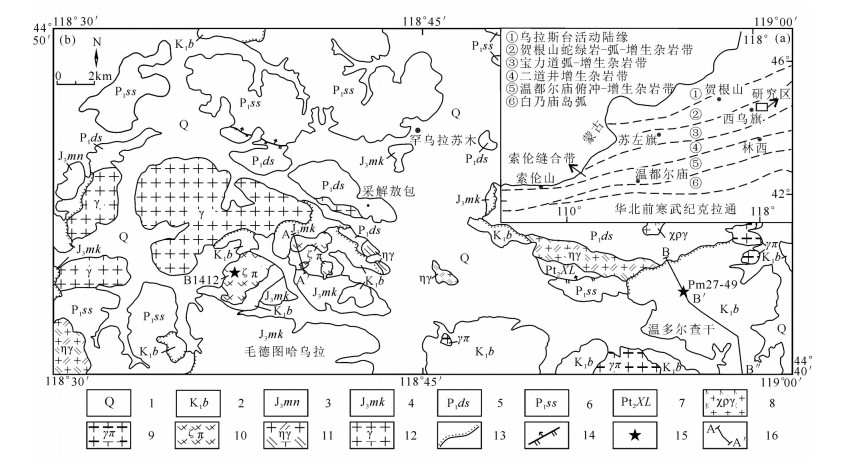
图 1 研究区大地构造位置图(a,据Xiao et al., 2003)及区域地质简图(b)
1—第四系;2—下白垩统白音高老组;3—上侏罗统玛尼吐组;4—上侏罗统满克头鄂博组;5—下二叠统大石寨组;6—下二叠统寿山沟组;7—中元古界锡林浩特岩群;8—早白垩世碱长花岗岩;9—早白垩世花岗斑岩;10—早白垩世英安斑岩;11—早中三叠世侵入岩;12—早二叠世侵入岩;13—不整合接触界线;14—实测断层;15—同位素年龄采样点及编号;16—剖面位置
Figure 1. Regional geological location of the study area (a, after Xiao et al., 2003) and geological sketch map of the study area (b)
1-Quaternary; 2−Lower Cretaceous Baiyingaolao Formation; 3−Upper Jurassic Manitu Formation; 4−Upper Jurassic Manketouebo Formation; 5−Lower Permian Dashizhai Formation; 6−Lower Permian Shoushangou Formation; 7−Middle Proterozoic Xilinhot Group; 8−Early Cretaceous alkali–feldspar granite; 9−Early Cretaceous granite porphyry; 10−Early Cretaceous dacite porphyry; 11−Early–Middle Triassic intrusive rock; 12− Early Permian intrusive rock; 13−Unconformity; 14−Measured fault; 15−Isotopic age sampling position and serial number; 16−Location of section
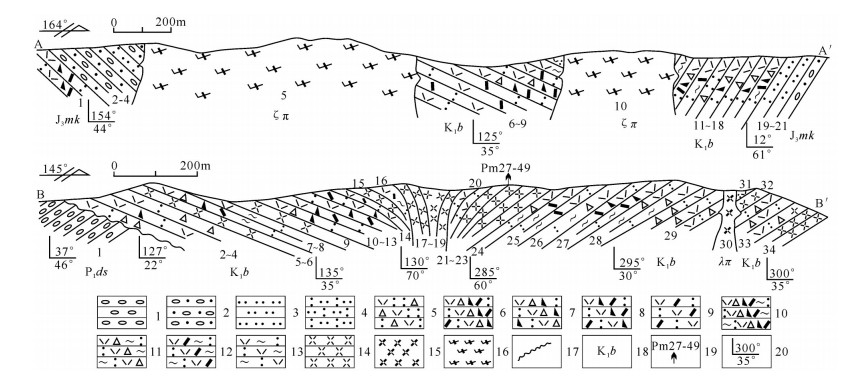
图 2 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩实测剖面
1—砾岩;2—砂砾岩;3—粉砂岩;4—凝灰质粉砂岩;5—流纹质凝灰角砾岩;6—流纹质含角砾岩屑晶屑凝灰岩;7—流纹质含角砾岩屑凝灰岩;8—流纹质岩屑晶屑凝灰岩;9—流纹质晶屑凝灰岩;10—流纹质含角砾岩屑晶屑熔结凝灰岩;11—流纹质含角砾熔结凝灰岩;12—流纹质晶屑熔结凝灰岩;13—流纹质熔结凝灰岩;14—流纹岩;15—流纹斑岩;16—英安斑岩;17—不整合界线;18—地质代号;19—同位素年龄采样点及编号;20—产状
Figure 2. Measured geological section of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula
1−Conglomerates; 2−Glutenites; 3−Siltstones; 4−Tuffaceous siltstones; 5−Rhyolitic tuff breccias; 6−Rhyolitic tuffs with breccia lithic and crystal clasts; 7−Rhyolitic tuffs with breccia and lithic clasts; 8−Rhyolitic tuffs with lithic and crystal clasts; 9−Rhyolitic tuffs with crystal clasts; 10−Rhyolitic welded tuffs with breccia lithic and crystal clasts; 11−Rhyolitic welded tuffs with breccia clasts; 12−Rhyolitic welded tuffs with crystal clasts; 13−Rhyolitic welded tuffs; 14−Rhyolite; 15−Rhyolite porphyry; 16−Dacite porphyry; 17−Unconformity; 18−Geological code; 19− Isotopic age sampling position and serial number; 20−Attitude
图 3 白音高老组火山岩野外及显微照片
a, b—流纹岩; c, d—球粒流纹岩; e, f—流纹质晶屑熔结凝灰岩; g, h—英安斑岩; Q—石英; Pl—斜长石; Kf—钾长石; Bi—黑云母
Figure 3. Field outcrop and microscopic characteristics of Baiyingaolao Formation
a, b-Rhyolite; c, d-Pyromeride; e, f-Rhyolitic welded tuffs with crystal clasts; g, h-Dacite porphyry; Q−Quartz; Pl−Plagioclase; Kf−K-feldspar; Bi−Biotite
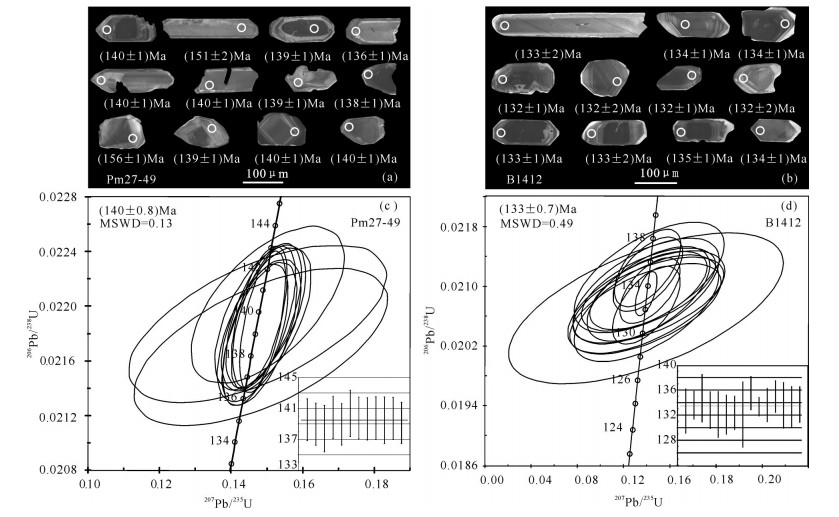
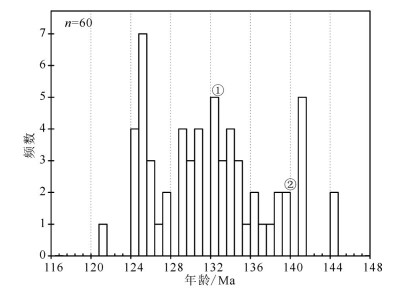
图 4 罕乌拉地区白音高老组球粒流纹岩(Pm27−49)和英安斑岩(B1412)代表性单颗粒锆石阴极发光(CL)图像及其表面年龄(Ma)(a、b);罕乌拉地区白音高老组球粒流纹岩(Pm27−49)和英安斑岩(B1412)LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄谐和图(c、d)
Figure 4. Cathodoluminescence images of typical single−crystal zircons and their apparent ages (Ma) for the pyromeride(Pm27−49) and dacite porphyry (B1412)of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula (a, b); LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb concordant age diagram for the pyromeride (Pm27−49) and dacite porphyry (B1412) of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula (c, d)
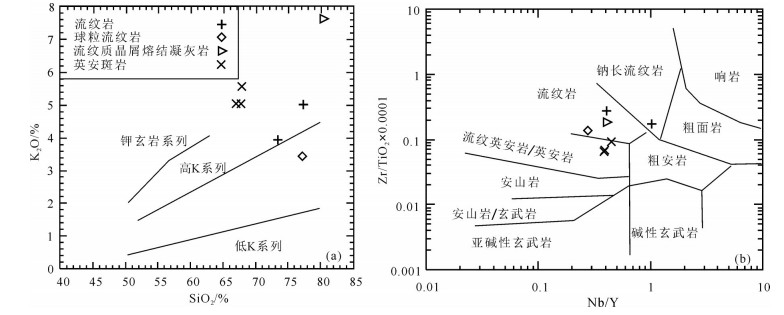
图 5 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩SiO2−K2O图解(a)(转引自Rollinson,1993)和Nb/Y−Zr/TiO2分类命名图解(b)(转引自Wilson,1989)
Figure 5. SiO2−K2O diagrams (a, after Rollinson, 1993) and Nb/Y−Zr/TiO2 classifying−naming diagrams (b, after Wilson, 1989) for volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula
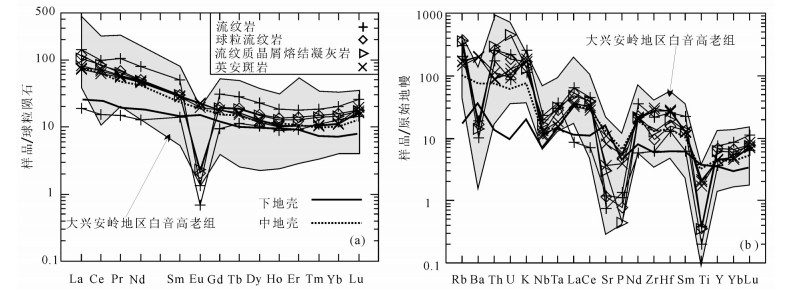
图 6 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)(球粒陨石标准化数据引自Boynton, 1984)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(原始地幔标准化数据引自Sun and MC Donough., 1989)
下地壳、中地壳据Rudnick et al., 2003;大兴安岭地区白音高老组火山岩数据据苟军等, 2010;Dong et al., 2014;Kong et al., 2014;秦涛等, 2014;聂立军等, 2015;王雄等, 2015;Yang et al., 2015;张乐彤等, 2015;张学斌等, 2015
Figure 6. Chondrite−normalized REE patterns(a)(normalization values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle−normalized trace element spider diagrams (b)(normalization values after Sun and Mc Donough., 1989) for volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula lower crust, middle Crust(after Rudnick et al., 2003); data of Baiyingaolao Formation in the Da Hinggan Mountains
(after Gou Jun et al., 2010; Dong Yu et al., 2014; Kong Yuanming et al., 2014;Qin Tao et al., 2014; Nie Lijun et al., 2015;Wang Xiong et al., 2015; Yang Wubin et al., 2015;Zhang Letong et al., 2015;Zhang Xuebin et al., 2015)
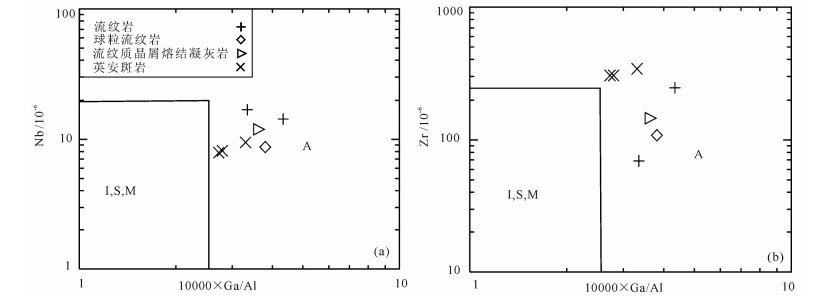
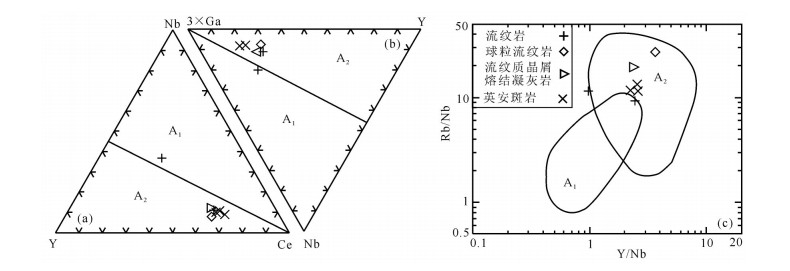
图 8 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩10000×Ga/Al−Nb图解(a)和10000×Ga/Al−Zr图解(b)(a、b,据Whalen et al., 1987)
Figure 8. Diagrams of 10000×Ga/Al−Nb (a) and 10000×Ga/Al−Zr (b)(a, b, after Whalen et al., 1987) for volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula
表 1 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩球粒流纹岩(Pm27-49)和英安斑岩(B1412)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotope analysis results for the pyromeride(Pm27-49) and dacite porphyry(B1412) of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula

表 2 罕乌拉地区白音高老组火山岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10–6)分析结果
Table 2 Major(%) and trace element (10–6) analysis results of volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Hanwula

表 3 大兴安岭地区白音高老组火山岩年龄测定结果
Table 3 The ages of volcanic rocks of Baiyingaolao Formation in Da Hinggan Mountains

-
Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 192(1/2):59-79.
Belousova E, Griffin W, O'Reilly S Y. 2002. Igneous zircon:Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock Type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
Bonin B. 2007. A-type granites and related rocks:Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 97:1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P(ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elservier, 63-114.
Chen Liang. 2010. Mesozoic Magma Evolution and Metallogenesis of Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit in Aershan Area, Da Hinggan Mountains[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-125(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yanjing, Zhang Cheng, Wang Pin, Pirajno F, Li Nuo. 2016. The Mo deposits of Northeast China:A powerful indicator of tectonic settings and associated evolutionary trends[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 205:168-184.
Chen Yingfu, Wang Genhou, Duan Bingxin. 2012. Zircon SHRIMP geochronology and geochemistry of Late Jurassic volcanic rocks in Huiyin Obo area of Dong Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 39(6):1690-1699(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201206017
Dash B, Yin An, Jiang Neng, Tseveendorj B, Han Baofu. 2016.Petrology, structural setting, timing, and geochemistry of Cretaceous volcanic rocks in eastern Mongolia:Constraints on their tectonic origin[J]. Gondwana Research, 27:281-299.
Davis G A, Zheng Yadong, Wang Cong, Darby B J, Zhang Changhou, Gehrels G. 2001. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces, northern China[J].Memoirs-Geological Society of America, 194:171-197. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bjdz200204001
Defant M J, Drummond M S.1994. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 347(6294):662-665.
Dong Yu, Ge Wenchun, Yang Hao, Zhao Guochun, Wang Qinghai, Zhang Yanlong, Su Li. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks from the Baiyingaolao Formation in hte central Great Xing'an Range, NE China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 205:168-184. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.07.004
Du Yuchun. 2015. Early Cretaceous Volcanic Rock and Cause Analysis in Zhalantun Area[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 1-73(in Chinese with English abstract).
Eby. 1990. The A-type granitoids:a review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 20:115-134.
Eby. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 20:641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Fan Weiming, Guo Feng, Wang Yuejun, Lin Ge. 2003. Late Mesozoic calcalkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 121(1/2):115-135.
Fang Hongwei. 2010. Characteristics and Tectonic Setting of the Volcanic Rocks from Mesozoic Baiyin'gaolao Formation in Wuchagou area, Middle of Daxing'anling[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-69(in Chinese with English abstract).
Frost B R, Arculus R J, Barnes C G, Collins W J, Ellis D J, Frost C D. 2001. A geochemical classification of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 42:2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
Gao Xiaofeng, Guo Feng, Fan Weiming, Li Chaowen, Li Xiaoyong. 2005. Origin of late Mesozoic intermediate-felsic volcanic rocks from the northern Da Hinggan Mountain, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3):737-748(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503014
Ge Wenchun, Lin Qiang, Sun Deyou, Wu Fuyuan, Yuan Zhongkuan, Li Wenyuan, Chen Mingzhi, Yin Chengxiao. 1999. Geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic basalts in Da Hinggan Ling:Evidence of the mantle-crust interaction[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(3):397-407 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ge Wenchun, Li Xianhua, Lin Qiang, Sun Deyou, Wu Fuyuan, Yun Sunghyo. 2001. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous alkaline rhyolites from Hulun Lake, Daxing'anling and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(2):176-183(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200102005
Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Zhou Changyong, Zhang Jiheng. 2005.Zircon U-Pb ages and its significance of the Mesozoic granites in the Wulanhaote region, central Da Hinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3):749-762(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503015
Ge Wenchun, Sui Zhenmin, Wu Fuyuan, Zhang Jiheng, Xu Xuechun, Cheng Ruiyu. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic characteristics and their implications of the Early Paleozoic granites in the northwestern Da Hinggan Mts, northeastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):423-440(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gou Jun, Sun Deyou, Zhao Zhonghua, Ren Yunsheng, Zhang Xueyuan, Fu Changliang, Wang Xi, Wei Hongyan. 2010. Zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of rhyolites in Baiyingaolao Formation from the southern Manzhouli, Inner-Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(1):333-344(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201001036
Guan Huimei, Liu Junlai, Ji Mo, Zhao Sheng jin, Hu Ling, Davis G A. 2008. Discovery of the Wanfu metamorphic core complex in southern Liaoning and its regional tectonic implication[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(3):199-208(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200803016
Guo Feng, Fan Weiming, Wang Yuejun, Lin Ge. 2001. Petrogenesis of the Late Mesozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the southern Da Hinggan Mts, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(1):161-168(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao Bin, Song Jiang, Li Chaozhu, Yang Xinde. 2016. Zircon U-Pb Age and Geochemical Characteristics of the Late Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in Chifeng area[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(6):1261-1274(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201606013
He Fubing, Xu Jixiang, Gu Xiaodan, Cheng Xinbin, Wei Bo, Li Zhao, Liang Yanan, Wang Zelong, Huang Qi. 2013. Ages, Origin and Geological Implications of the Amuguleng Composite Granite in East Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Review, 59(6):1150-1164(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201306016
Huang Fan, Wang Denghong, Wang Ping'an, Wang Chenghui, Liu Shanbao, Liu Cuihui, Xie Youwei, Zheng Binghua, Li Songbai. 2014. Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Chronology of the Yili Mo Deposit in the Northern Great Khing'an Ranges[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(3):361-379(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201403006
Huang Meng. 2014. The Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Setting of Volcanic Rock in Baiyinggaolao Formation from Xiwuzhumuqin area Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-53(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Mingda, Cui Xiaozhuang, Pei Shengliang, Zhang Hengli, Zhang Jianqiang. 2016. Rhyolite zircon U-Pb dating and its tectonic significance in Bayan Gol Formation, Hinggan Massif[J]. Coal Geology of China, 28(11):30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgmtdz201611007
Jahn BM, Wu Fuyuan, Chen Bin. 2000. Massive granitoid generation in central Asia:Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Episodes, 23:82-92. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2000/v23i2/001
Jahn B M, Wu Fuyuan, Capdevila R, Martineay F, Zhao Zhenhua, Wang Yixian. 2001. Highly evolved juvenile granites with tetrad REE patterns:the Woduhe and Baerzhe granites from the Great Xing'an Mountains in NE China[J]. Lithos, 59:171-198. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00066-4
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, Allen C M. 1997.Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
Kong Yuanming. 2014. Characteristics and Tectonic Setting of Acid Volcanic Rocks in Early Cretaceous Baiyingaolao Formation from Keyouzhongqi Area, Inner Mongolia[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kong Yuanming, Ma Rui, He Zhonghua, Yang Deming, Wu Qing, Wang Yang. 2014. Characteristics and tectonic setting of volcanic rocks in Early Cretaceous Baiyingaolao Formation of Keyouzhouqi area, Inner Mongolica[J]. Global Geology, 17(2):78-85.
Kravchinsky V A, CognèJ P, Harbert W P, Kuzmin M I. 2002.Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeomagnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suture zone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 148:34-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01557.x
Li Huaikun, Zhu Shixing, Xiang Zhenqun, Su Wenbo, Lu Songnian, Zhou Hongying, Geng Jianzhen, Li Sheng, Yang Fengjie. 2010.Zircon U-Pb dating on tuffbed from Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Yanqing, Beijing:Further constraints on the new subdivision of the Mesoproterozoic stratigraphy in the northern North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7):2131-2140(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jie, Lü Xinbiao, Chen Chao, Gun Minshan, Yang Yongsheng, Xu Yiqun, Wang Lin, Zhang Shuai. 2016. Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the rhyolites in Taerqi of middle Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(6):906-918(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201606008
Li Jinyi, Mo Shenguo, He Zhengjun, Sun Guihua, Chen Wen. 2004.The timing of crustal sinistral strike-slip movement in the northern Great Khing'an ranges and its constraint on reconstruction of the crustal tectonic evolution of NE China and adjacent areas since the Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3):157-168(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200403017
Li Jingyan, Guo Feng, Li Chaowen, Li Hongxia, Zhao Liang. 2014.Neodymium isotopic variations of Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic Iand A-type granitoids in NE China:Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7):1995-2008(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Ke, Zhang Zhicheng, Li Jianfeng, Tang Wenhao, Feng Zhishuo, Li Qiugen. 2012. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Xi Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(5):671-685(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201205004
Li Pengchuan, Li Shichao, Liu Zhenghong, Li Gang, Bai Xinhui, Wan Le. 2016. Formation age and tectonic environment of volcanic rocks from Manketouebo Formation in Linxi area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Global Geology, 35(1):77-88(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz201601008
Li Tiegang, Wu Guang, Liu Jun, Wang Guorui, Hu Yanqing, Zhang Yunfu, Luo Dafeng, Mao Zhihao, Xu Bei. 2016. Geochronology, fluid inclusions and isotopic characteristics of the Chaganbulagen Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Lithos, 17(2):78-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=74b4b6d88fdc1109e86d0c12a978573e
Li Wenguo, Li Qingfu, Jiang Wande. 1996. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Lithostratigraphic[M]. Wuhan:Chinese Geology University Press:1-344(in Chinese).
Li Yan, Wang Jian, Han Zhibin, Hou Xiaoguang, Wang Shiyan. 2017.Zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of the Early Jurassic rhyolite in Badaguan area, northern Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geology in China, 44(2):346-357(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201702010
Li Yu, Ding Leilei, Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Tang Jie, Zhao Shuo, Wang Zijin. 2015. Geochronology and geochemistry of muscovite granite in Sunwu area, NE China:Implications for the timing of closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):56-66(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Qiang, Ge Wenchun, Sun Deyou, Wu Fuyuan, Chong Kwan Won, Kyung Duck Min, Myung Shik Jin, Moon Wonlee, Chi Soon Kwon, Sung Hyo Yun. 1998. Tectonic significance of mesozoic volcanic rocks in northeastern China[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 33(2):129-139(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069875
Lin Qiang, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Zao Lin. 2004.Geochemistry of Mesozoic granites in Da Hinggan Ling ranges[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3):403-412(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200403004
Lin Wei, Wang Jun, Liu Fei, Ji Wenbin, Wang Qingchen. 2013. Late Mesozoic extension structures on the North China Craton and adjacent regions and its geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5):1791-1810(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201305023
Liu Ge, Lü Xinbiao, Chen Chao, Yang Yongsheng, Wang Qingjun, Sun Yaofeng. 2014. Zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic bimodal volcanic rocks from Nenjiang area in Da Hinggan Mountains and their tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 33(3):458-470(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201403004
Liu Junlai, Guan Huimei, Ji Mo, Hu Ling. 2006. Late Mesozoic metamorphic core complexes:New constraints on lithosphere thinning in North China[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 16:633-638. doi: 10.1080/10020070612330045
Liu Junlai, Davis GA, Ji Mo, Guan Huimei, Bai Xiangdong. 2008.Crustal detachment and destruction of the North China craton:constraints from Late Mesozoic extensional structures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(3):72-81(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60063-9
Liu Junlai, Ji Mo, Shen Liang, Guan Huimei, Davis G A. 2011. Early Cretaceous extensional structures in the Liaodong Peninsula:Structural associations, geochronological constraints and regional tectonic implications[J]. Sci. China Earth Sci., 54:823-842(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4189-y
Liu Kai, Wu Taotao, Liu Jinlong, Bao Qingzhong, Du Shouying. 2018.Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks in Manketou'ebo Formation of Tulihe area, northern Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geology in China, 45(2):367-376(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zhe, Xue Huaimin, Cao Guangyue. 2017. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, intraplate extensional environment and genesis of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Zhenglan Banner area, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geology in China, 44(1):151-176(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201701011
Ludwig K R. 2003. Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 1-70.
Lü Zhicheng, Duan Guozheng, Hao Libo, Li Dianchao, Pan Jun, Wu Fengchang. 2004. Petrological and Geochemical Studies on the Intermediate-Basic Volcanic Rocks from the Middle-South Part of the Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 10(2):186-198(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200402005
Ma Yubo, Xing Shuwen, Xiao Keyan, Zhang Tong, Tian Fang, Ding Jianhua, Zhang Yong, Ma Lukuo. 2016. Geological characteristics and mineral resource potential of the Cu-Mo-Ag metallogenic belt in Daxinganling Mountains[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(7):1316-1333(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201607005
Meng En, Xu Wenliang, Yang Debin, Qiu Kunfeng, Li Changhua, Zhu Hongtao. 2011. Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry of Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Lingquan basin in Manzhouli area, and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4):1209-1226(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201104025
Meng Fanchao, Liu Jiaqi, Cui Yan, Gao Jinliang, Liu Xiang, Tong Ying. 2014. Mesozoic tectonic regimes transition in the Northeast China:Constriants from temporal-spatial distribution and associations of volcanic rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(12):3569-3586(in Chinese with English abstract).
Nie Lijun, Jia Haiming, Wang Cong, Lu Xingbo. 2015. Chronology, geochemistry of rhyolites from Baiyingaolao Formation in the middle part of Da Hinggan Mountains and its tectonic implications[J]. Global Geology, 34(2):296-304(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz201502004
Ouyang Hegen, Mao Jingwen, Santosh M, Zhou Jie, Zhou Zhenhua, Wu Yue, Hou Lin. 2013. Geodynamic setting of Mesozoic magmatism in NE China and surrounding regions:Perspectives from spatio-temporal distribution patterns of ore deposits[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 78:222-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.011
Ouyang Hegen, Mao Jingwen, Zhou Zhenhua, Su Huiming. 2015. Late Mesozoic metallogeny and intracontinental magmatism, southern Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China[J]. Gondwana Research, 27:1153-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.08.010
Pearce J A. 1983. The Role of Sub-continental Lithosphere in Magma Genesis at Destructive Plate Margins[M]. Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths. Chester: Nantwich Shiva Academic Press, 1153-1172.
Pei Fuping, Xu Wenliang, Yang Debin, Ji Weiqiang, Yu Yang, Zhang Xingzhou. 2008. Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the southern Songliao basin:Zircon U-Pb ages and their constraints on the nature of basin basement[J]. Earth Science, 33(5):603-617(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qin Tao, Zheng Changqing, Cui Tianri, Li linchuan, Qian Cheng, Chen Huijun. 2014. Volcanic rocks of the Baiyingaolao Formation in the Southwest of Zhalantun, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 23(2):146-153 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201402011
Qin Xuliang. 2014. The Petrology Characteristics of the Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in Sonid Zuoqi Area of Inner Mongolia[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 1-49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rollinson H R. 1993. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Presentation, Interpreation[M]. New York:Longman, 1-352.
Rudnick R L, Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 4:1-51.
Sen C, Dunn T. 1994. Dehydration melting of a basaltic composition amphibolite at 1.5 and 2.0 GPa:Implication for the origin of adakites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 117(4):394-409. doi: 10.1007/BF00307273
Shao Ji'an, Mu Baolei, Zhu Huizhong, Zhang Lüqiao. 2010. Material source and tectonic settings of the Mesozoic mineralization of the DaHing gan Mts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(3):649-656(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shao Ji'an, Tang Kedong. 2015. Research on the Mesozoic oceancontinent transitional zone in the Northeast Asia and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10):3147-3154(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shao Jidong, Tan Qiang, Wang Hui, Zhang Ming, He Hongyun. 2011.The Mesozoic Strata and the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary in the Daxinganling region[J]. Geology and Resources, 20(1):4-11(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201101002
She Hongquan, Li Jinwen, Xiang Anping, Guan Jidong, Yang Yuncheng, Zhang Dequan, Tan Gang, Zhang Bin. 2012. U-Pb ages of the zircons from primary rocks in middle-northern Daxinganling and its implications to geotectonic evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2):571-594(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201202018
Shen Liang, Liu Junlai, Hu Ling, Ji Mo, Guan Huimei, Davis G A. 2011. The Dayingzi detachment fault system in Liaodong Peninsula and its regional tectonic significance[J]. Sci. China Earth Sci., 54(10):1469-1483(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4202-5
Shi Lu, Zheng Changqing, Yao Wengui, Li Juan, Xu Jiulei, Gao Yuan, Cui Fanghua. 2013. Geochronology, petro-geochemistry and Tectonic setting of the Hamagou Forest Farm A-Type granites in the Wuchagou Region, central great Xinggan range[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(9):1264-1276(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201309006
Si Qiuliang, Cui Tianri, Wang Ende, Ding Shu. 2016. Zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of the Baiyingaolao Formation rhyolites in Chaihe area, Great Xing'an Range[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 37(3):412-415(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sorokin A A, Yarmolyuk V V, Kotov A B, Sorokin A P, Kudryashov N M, Li Jinyi. 2004. Geochronology of Triassic-Jurassic granitoids in the southern framing of the Mongol-Okhotsk fold belt and the problem of Early Mesozoic granite formation in central and eastern Asia[J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 399(8):1091-1094.
Sui Zhenmin, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Zhang Jiheng, Xu Xuechun, Cheng Ruiyu. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry and its petrogenesis of Jurassic granites in northeastern part of the Da Hinggan Mts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):461-480(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200702023
Sun Deyou, Wu Fuyuan, Zhang Yanbin, Gao Shan. 2004. The final closing time of the west Lamulun River-Changchun-Yanji plate suture zone:Evidence from the Dayushan granitic pluton, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 34(2):174-181(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Deyou, Wu Fuyuan, Gao Shan, Lu Xiaoping. 2005. Confirmation of two episodes of A-type granite emplacement during Late Triassic and Early Jurassic in the central Jilin Province, and their constraints on the structural pattern of eastern Jilin-Heilongjiang area, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(2):263-275(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200502028
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Sunders A D, Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 42: 313-345.
Wang Fei, Zhou Xinhua, Zhang Liancheng, Ying Jifeng, Zhang Yutao, Wu Fuyuan, Zhu Rixiang. 2006. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range(NE China):Timing and implications for the dymamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 251:179-198. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.09.007
Wang Jianguo, He Zhonghua, Xu Wenliang. 2013. Petrogenesis of riebeckite rhyolites in the southern Da Hinggan Mts.:Geohronological and geochemical evidence[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3):853-863(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xing'an, Xu Zhongyuan, Liu Zhenghong, Zhu Kai. 2012.Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the K-feldspar granites in Chaihe area, central Great Xing'an Range:constraints from petrogeochemistry and zircon U-Pb isotope chronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(8):2647-2655(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiong, Chen Yuejun, Li Yong, Li Senlin, Wang Changbing, Liu Yongjun, Zhu Huailiang, Wu Guoxue. 2015. Geochemical characteristics and geological implication of volcanic rocks in Early Cretaceous Baiyingaolao Formation from Taerqi area, middle-north part of Da Hinggan mountains[J]. Global Geology, 34(1):25-33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz201501005
Watson E B, Harrison T M. 1983. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. 1987. A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics discrimination and petrogeneisis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Springer, 295-323.
Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Lin Qiang. 1999. Petrogenesis of the Phanerozoic granites and crustal growth in Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2):181-189(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Li Huimin, Jahn B M, Wilde S A. 2002. Atype granites in northeastern China:Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 187(1/2):143-173.
Wu Fuyuan, Jahn B M, Wilde S A, Lo Chunhua, Yui Tzenfu, Lin Qiang, Ge Wenchun, Sun Deyou. 2003. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China(I):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 66:241-273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0
Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Ge Wenchun, Zhang Yanbin, Grant M L, Wilde S A, Jahn B M. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Wu Guang, Chen Yanjing, Sun Fengyue, Li Jingchun, Li Zhitong, Wang Xijin. 2008. Geochemistry of the Late Jurassic granitoids in the northern end area of Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological and prospecting implication[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4):899-910(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu TaoTao, Chen Cong, Liu Kai, Bao Qingzhong, Zhou Yongheng, Song Wanbing. 2016. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Monzonite Granite in Yitulihe area, Northern Great Xing'an Range[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(10):2637-2647(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201610007
Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15):1554-1569(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
Xiao Wenjiao, Windley B F, Hao Jie, Zhai Mingguo. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonics, 22(6):1069-1089.
Xu Meijun, XU Wenliang, Meng En, Wang Feng. 2011. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Shanghulin-Xiangyang basins in Ergun area, northeastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(9):1321-1338(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Wenliang, Pei Fuping, Wang Feng, Meng En, Ji Weiqiang, Yang Debin, Wang Wei. 2013a. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China:Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 74:167-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.003
Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Pei Fuping, Meng En, Tang Jie, Xu Meijun, Wang Wei. 2013b. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional oreforming background in NE China:Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2):339-353(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jianguo, Wu Heyong, Liu Junlai. 2006. Stratigraphic correlation of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic in the outer basins of the Daqing exploration area, Heilongjiang, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(9/10):1088-1093(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200609017
Yang Wubin, Niu Hecai, Cheng Liren, Shan Qiang, Li Ningbo. 2015.Geochronology, geochemistry and geodynamic implications of the Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the southern Great Xing'an Mountains, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113:454-470. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.12.002
Yang Yang, Gao Fuhong, Chen Jingsheng, Zhou Yi, Zhang Jian, Jin Xin, Zhang Yanlong. 2012. Zircon U-Pb ages of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Chifeng area[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 42(Suppl. 2):257-268(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxb-e201902021
Yin Zhigang, Wang Wencai, Zhang Yuelong, Wang Yang, Han Yu, Cao Zhongqiang, Zheng Bei. 2016. Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Yilehuli area:Zircon U-Pb ages and their constraints on the magmatic events[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 46(3):766-780(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ying Jifeng, Zhou Xinhua, Zhang Lianchang, Wang Fei. 2010.Geochronological framework of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China and their geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39:786-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.035
Zhang Changhou, Wang Genhou, Wang Guosheng, Wu Zhengwen, Sun Lusuo, Sun Weihua. 2002. Thrust tectonics in the eastern segment of the intraplate Yanshan orogenic belt, western Liaoning Province, North China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 76(1):64-76(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200201009
Zhang Hong, Wei Zhongliang, Liu Xiaoming, Li Dong. 2008.Tuchengzi Formation LA-ICP-MS dating in northern Hebei-western Liaoning[J]. Science in China(Series D), 38(8):960-970(in Chinese).
Zhang Jiheng, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Wilde S A, Yang Jinhui, Liu Xiaoming. 2008. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range, Northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 102:138-157. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.011
Zhang Jiheng. 2009. Geochronology and geochemistry of the mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jiheng, Gao Shan, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Yang Jinhui, Wilde S A, Li Ming. 2010. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 276(3/4):144-165.
Zhang Letong, Li Shichao, Zhao Qingying, Li Xuefei, Wang Lu, Li Zihao. 2015. Formation age and geochemical characteristics of volcanic rocks from Baiyingaolao Formation of middle Da Hinggan mountains[J]. Global Geology, 34(1):44-54(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz201501007
Zhang Lianchang, Zhou Xinhua, Ying Jifeng, Wang Fei, Guo Feng, Wan Bo, Chen Zhiguang. 2008. Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of Early Cretaceous basalts from the Great Xing'an Range, NE China:Implications for their origin and mangle source characteristics[J]. Chemical Geology, 256:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.004
Zhang Lüqiao, Shao Ji'an, Zheng Guangrui. 1998. Metamorphic core complex in ganzhuermiao, Inner Mongolia[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 33(2):140-146(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069873
Zhang Qi. 2013. Is the Mesozoic magmatismin eastern China related to the westward subduction of the Pacific plate?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(1):113-128(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xuebin, Zhou Changhong, Lai Lin, Xu Cui, Tian Ying, Chen Lizhen, Wei Min. 2015. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating of volcanic rocks in eastern Xilin Hot, Inner Mongolia and their geological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 51(2):290-302(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt201502010
Zhang Yaming, Du Yuchun, Cui Tianri, Li Linchuan, Qin Tao. 2014.Baiyingaolao Group volcanic rock characteristics and genesis in Zhalantun region[J]. Metal Mine, (6):101-104(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsks201406020
Zhang Yutao, Zhang Lianchang, Ying Jifeng, Zhou Xinhua, Wang Fei, Hou Quanlin, Liu qing. 2007. Geochemistry and source characteristics of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks in Tahe, North Da Hinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11):2811-2822(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200711012
Zhao Guolong, Yang Guiling, Wang Zhong, Fu Jiayou, Yang Yuzhuo. 1989. Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in the Central-Southern Da Hinggan Ling Range[M]. Beijing:Beijing Press of Science and Technology, 1-260 (in Chinese).
Zhao Pizhong, Xie Xuejing, Cheng Zhizhong. 2014. Regional geochemical background and metallogenic belt division of North Da Hinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(1):99-108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201401009
Zhao Yue, Yang Zhenyu, Ma Xinghua. 1994. Geotectonic transition from PaleoAsian system and Paleo-Tethyan system to PaleoPacific active continental margin in eastern Asia[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 29(2):105-119(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yue, Xu Gang, Zhang Shuanhong, Yang Zhenyu, Zhang Yueqiao, Hu Jianmin. 2004. Yanshanian movement and conversion of tectonic regimes in East Asia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3):319-328(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200403030
Zorin Y A. 1999. Geodynamics of the western part of the Mongolia Okhotsk collisional belt, Trans-Baikal region(Russia)and Mongolia[J]. Tectonophysics, 306(1):33-56. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00042-6
陈良. 2010.大兴安岭阿尔山地区中生代岩浆演化与斑岩钼矿成矿作用[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 1-125. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2010085692.htm 陈英富, 王根厚, 段炳鑫. 2012.内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗辉音敖包一带晚侏罗世火山岩特征及时代[J].中国地质, 39(6):1690-1699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.017 杜玉春. 2015.扎兰屯地区早白垩世火山岩特征及成因分析[D].阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学硕士论文, 1-73. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10147-1016057251.htm 方红薇. 2010.大兴安岭中段五岔沟一带中生代白音高老组火山岩特征及其构造背景[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 1-69. 高晓峰, 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 李超文, 李晓勇. 2005.南兴安岭晚中生代中酸性火山岩的岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 21(3):737-748. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503014 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 吴福元, 元钟宽, 李文远, 陈明植, 尹成孝. 1999.大兴安岭中生代玄武岩的地球化学特征:壳幔相互作用的证据[J].岩石学报, 15(3):396-407. 葛文春, 李献华, 林强, 孙德有, 吴福元, 尹成孝. 2001.呼伦湖早白垩世碱性流纹岩的地球化学特征及其意义[J].地质科学, 36(2):176-183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.02.005 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 张吉衡. 2005.大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 21(3):749-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503015 葛文春, 隋振民, 吴福元, 张吉衡, 徐学纯, 程瑞玉. 2007.大兴安岭东北部早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 23(2):423-440. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200702021 苟军, 孙德有, 赵忠华, 任云生, 张学元, 付长亮, 王晰, 魏红艳. 2010.满洲里南部白音高老组流纹岩锆石U-Pb定年及岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 26(1):333-344. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201001036 关会梅, 刘俊来, 纪沫, 赵胜金, 胡玲, Davis G A. 2008.辽宁南部万福变质核杂岩的发现及其区域构造意义[J].地学前缘, 15(3):199-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.016 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 林舸. 2001.大兴安岭南段晚中生代双峰式火山作用[J].岩石学报, 17(1):161-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200101017 郝彬, 宋江, 李朝柱, 杨欣德. 2016.赤峰地区晚中生代火山岩锆石UPb年代学及地球化学特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 40(6):1261-1274. 何付兵, 徐吉祥, 谷晓丹, 程新彬, 魏波, 李昭, 梁亚南, 王泽龙, 黄淇. 2013.内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗阿木古楞复式花岗岩体时代、成因及地质意义[J].地质论评, 59(6):1150-1164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201306016 黄凡, 王登红, 王平安, 王成辉, 刘善宝, 刘翠辉, 谢有炜, 郑兵华, 李松柏. 2014.大兴安岭北段宜里钼矿岩石成因及成岩成矿年代学[J].地质学报, 88(3):361-379. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201403006 黄猛. 2014.内蒙古西乌旗地区白音高老组火山岩地球化学特征及其构造环境[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 1-53. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1015517960.htm 黄明达, 崔晓庄, 裴圣良, 张恒利, 张建强. 2016.兴安地块白音高老组流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].中国煤炭地质, 28(11):30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2016.11.07 孔元明. 2014.内蒙古科右中旗地区早白垩世白音高老组酸性火山岩特征及形成的构造背景[D].长春: 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 1-52. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10183-1014281768.htm 李怀坤, 朱士兴, 相振群, 苏文博, 陆松年, 周红英, 耿建珍, 李生, 杨锋杰. 2010.北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束[J].岩石学报, 26(7):2131-2140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201007015 李杰, 吕新彪, 陈超, 衮民汕, 杨永胜, 徐益群, 王琳, 张帅. 2016.大兴安岭中段塔尔气地区流纹岩年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 35(6):906-918. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.06.008 李锦轶,莫申国,和政军,孙桂华,陈文. 2004. 大兴安岭北段地壳左行走滑运动的时代及其对中国东北及邻区中生代以来地壳构造演化重建的制约[J]. 地学前缘,11(3):157-168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.017 李竞妍,郭峰,李超文,李红霞,赵亮. 2014. 东北地区晚古生代-中生代 I型和 A型花岗岩 Nd同位素变化趋势及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报,30(7):1995-2008. 李可,张志诚,李建锋,汤文豪,冯志硕,李秋根. 2012. 内蒙古乌珠穆沁地区中生代中酸性火山岩 SHRIMP锆石 U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报,31(5):671-685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.004 李鹏川,李世超,刘正宏,李刚,白新会,万乐. 2016. 内蒙古林西地区满克头鄂博组火山岩形成时代及构造环境[J]. 世界地质,35(1):77-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2016.01.008 李文国,李庆富,姜万德. 1996. 内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社:1-344. 李研,王建,韩志滨,侯晓光,王石岩. 2017. 大兴安岭北段八大关地区早侏罗世流纹岩锆石 U-Pb定年与岩石成因[J]. 中国地质,44(2):346-357. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170210&flag=1 李宇,丁磊磊,许文良,王枫,唐杰,赵硕,王子进. 2015. 孙吴地区中侏罗世白云母花岗岩的年代学与地球化学:对蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合时间的限定[J]. 岩石学报,31(1):56-66. 林强,葛文春,孙德有,吴福元,元钟宽,闵庚德,陈明植,李文远,权致纯, 尹成孝. 1998. 中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J]. 地质科学,33(2):129-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069875 林强,葛文春,吴福元,孙德有,曹林. 2004. 大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J]. 岩石学报,20(3):403-412. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200403004 林伟,王军,刘飞,冀文斌,王清晨. 2013. 华北克拉通及邻区晚中生代伸展构造及其动力学背景的讨论[J]. 岩石学报,29(5):1791-1810. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201305023 刘阁,吕新彪,陈超,杨永胜,王庆军,孙耀锋. 2014. 大兴安岭嫩江地区中生代双峰式火山岩锆石 U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,33(3):458-470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.03.004 刘俊来,Davis G A,纪沫,关会梅,白相东. 2008. 地壳的拆离作用与华北克拉通破坏:晚中生代伸展构造约束[J]. 地学前缘,15(3):72-81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.005 刘俊来,纪沫,申亮,关会梅,Davis G A. 2011. 辽东半岛早白垩世伸展构造组合、形成时代及区域构造内涵[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,41(5):618-637. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201105003 刘凯,吴涛涛,刘金龙,鲍庆中,杜守营. 2018. 大兴安岭北段图里河地区满克头鄂博组火山岩年代学及地球化学[J]. 中国地质,45(2):367-376. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180211&flag=1 刘哲,薛怀民,曹光跃. 2017. 内蒙古正蓝旗地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb 年龄与板内伸展环境成因讨论[J]. 中国地质,44(1):151-176. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170111&flag=1 吕志成,段国正,郝立波,李殿超,潘军,吴丰昌. 2004. 大兴安岭中南段中生代中基性火山岩岩石学地球化学研究[J]. 高校地质学报,10(2):186-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2004.02.005 马玉波,邢树文,肖克炎,张彤,田放,丁建华,张勇,马路阔. 2016. 大兴安岭 Cu-Mo-Ag 多金属成矿带主要地质成矿特征及潜力分析[J]. 地质学报,90(7):1316-1333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.07.005 孟恩,许文良,杨德彬,邱昆峰,李长华,祝洪涛. 2011. 满洲里地区灵泉盆地中生代火山岩的锆石 U-Pb 年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,27(4):1209-1226. 孟凡超,刘嘉麒,崔岩,高金亮,刘祥,童英. 2014. 中国东部地区中生代构造体制的转变:来自火山岩时空分布与岩石组合的制约[J]. 岩石学报,30(12):3569-3586. 聂立军,贾海明,王聪,卢兴波. 2015. 大兴安岭中段白音高老组流纹岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质,34(2):296-304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.02.004 裴福萍,许文良,杨德彬,纪伟强,于洋,张兴洲. 2008. 松辽盆地南部中生代火山岩:锆石 U-Pb年代学及其对基底性质的制约[J]. 地球科学,33(5):603-617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.05.003 秦涛,郑常青,崔天日,李林川,钱程,陈会军. 2014. 内蒙古扎兰屯地区白音高老组火山岩地球化学、年代学及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源,23(2):146-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2014.02.011 秦旭亮. 2014. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗地区中生代火山岩岩石学特征[D]. 石家庄:石家庄经济学院硕士学位论文,1-49. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10077-1015900041.htm 邵济安,牟保磊,朱慧忠,张履桥. 2010. 大兴安岭中南段中生代成矿物质的深部来源与背景[J]. 岩石学报,26(3):649-656. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201003001 邵济安,唐克东. 2015. 东北亚中生代洋陆过渡带的研究及启示[J]. 岩石学报,31(10):3147-3154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201510015 邵积东,谭强,王慧,张明,贺宏云. 2011. 大兴安岭地区中生代地层特征及侏罗-白垩纪界限的讨论[J]. 地质与资源,20(1):4-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2011.01.002 佘宏全,李进文,向安平,关继东,杨郧城,张德全,谭刚,张斌. 2012. 大兴安岭中北段原岩锆石 U-Pb测年及其与区域构造演化关系[J]. 岩石学报,28(2):571-594. 申亮,刘俊来,胡玲,纪沫,关会梅,Davis G A. 2011. 辽东半岛大营子拆离断层系及其区域构造意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,41(4):437-451. 施璐,郑常青,姚文贵,李娟,徐久磊,高源,崔芳华. 2013. 大兴安岭中段五岔沟地区蛤蟆沟林场 A型花岗岩年代学、岩石地球化学及构造背景研究[J]. 地质学报,87(9):1264-1276. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201309006 司秋亮,崔天日,王恩德,丁姝. 2016. 大兴安岭柴河白音高老组流纹岩锆石 U-Pb定年及成因探讨[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),37(3):412-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.03.023 隋振民,葛文春,吴福元,张吉衡,徐学纯,程瑞玉. 2007. 大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石 U-Pb 年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报,23(2):461-468. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200702023 孙德有,吴福元,张艳斌,高山. 2004. 西拉木伦河-长春-延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),34(2):174-181. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200402003 孙德有,吴福元,高山,路孝平. 2005. 吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质 A 型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约[J]. 地学前缘,12(2):264-275. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200502028 王建国,和钟铧,许文良. 2013. 大兴安岭南部纳闪石流纹岩的岩石成因:年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报,29(3):853-863. 王兴安,徐仲元,刘正宏,朱凯. 2012. 大兴安岭中部柴河地区钾长花岗岩的成因及构造背景:岩石地球化学、锆石 U-Pb同位素年代学的制约[J]. 岩石学报,28(8):2647-2655. 王雄,陈跃军,李勇,李森林,王长兵,刘永俊,朱怀亮,吴国学. 2015. 大兴安岭中北段塔尔气地区早白垩世白音高老组火山岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 世界地质,34(1):25-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.01.004 吴福元,孙德有,林强. 1999. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报,15(2):181-189. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98199902003 吴涛涛,陈聪,刘凯,鲍庆中,周永恒,宋万兵. 2016. 大兴安岭北部伊图里河地区二长花岗岩的成因及构造背景[J]. 地质学报,90(10):2637-2647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.10.007 吴元保,郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对 U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报,49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 武广,陈衍景,孙丰月,李景春,李之彤,王希今. 2008. 大兴安岭北端晚侏罗世花岗岩类地球化学及其地质和找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报,24(4):899-910. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200804028 徐美君,许文良,孟恩,王枫. 2011. 内蒙古东北部额尔古纳地区上护林-向阳盆地中生代火山岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石 U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报,30(9):1321-1338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.001 许文良,王枫,裴福萍,孟恩,唐杰,徐美君,王伟. 2013b. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报,29(2):339-353. 杨建国,吴河勇,刘俊来. 2006. 大庆探区外围盆地中、新生代地层对比及四大勘探层系[J]. 地质通报,25(9/10):1088-1093. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200609017 杨杨,高福红,陈井胜,周漪,张健,金鑫,张彦龙. 2012. 赤峰地区中生代火山岩锆石 U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),42(增刊 2):257-268. 尹志刚,王文材,张跃龙,王阳,韩宇,曹忠强,郑贝. 2016. 伊勒呼里山中生代火山岩:锆石 U-Pb年代学及其对岩浆事件的制约[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),46(3):766-780. 张长厚,王根厚,王果胜,吴正文,张路锁,孙卫华. 2002. 辽西地区燕山板内造山带东段中生代逆冲推覆构造[J]. 地质学报,76 (1):64-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.01.009 张宏,韦忠良,柳小明,李栋. 2008. 冀北-辽西地区土城子组的 LAICP-MS测年[J]. 中国科学(D辑),38(8):960-970. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2008.08.004 张吉衡. 2009. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,1-105. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-2009153771.htm 张乐彤,李世超,赵庆英,李雪菲,王璐,李子昊. 2015. 大兴安岭中段白音高老组火山岩的形成时代及地球化学特征[J]. 世界地质,34(1):44-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.01.006 张履桥,邵济安,郑广瑞. 1998. 内蒙古甘珠尔庙变质核杂岩[J]. 地质科学,33(2):140-146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069873 张学斌,周长红,来林,徐翠,田颖,陈丽贞,魏民. 2015. 锡林浩特东部早白垩世白音高老组岩石地球化学特征、LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探,51(2):290-302. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt201502010 张亚明,杜玉春,崔天日,李林川,秦涛. 2014. 扎兰屯地区白音高老组火山岩特征及成因[J]. 金属矿山,(6):101-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsks201406020 张玉涛,张连昌,英基丰,周新华,王非,侯泉林,刘庆. 2007. 大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J]. 岩石学报, 23(11):2823-2835. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.013 赵国龙,杨桂林,王忠,傅嘉友,杨玉琢. 1989. 大兴安岭中南部中生代火山岩[M]. 北京:北京科学技术出版社:1-260. 赵丕忠,谢学锦,程志中. 2014. 大兴安岭成矿带北段区域地球化学背景与成矿带划分[J]. 地质学报,88(1):99-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201401009 赵越,杨振宇,马醒华. 1994. 东亚大地构造发展的重要转折[J]. 地质科学,29(2):105-119. 赵越,徐刚,张拴宏,杨振宇,张岳桥,胡健民. 2004. 燕山运动与东亚构造体制的转变[J]. 地学前缘,11(3):319-328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.030 -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. Jian-yu Liu,Hong-feng Nie,Liang Xu,Chun-lei Xiao,Wei Li,Guo-li Yuan,Yan-peng Huang,Xin-yang Ji,Tian-qi Li. Assessment of ecological geological vulnerability in Mu Us Sandy Land based on GIS and suggestions of ecological protection and restoration. China Geology. 2025(01): 117-143 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 祝晓松,裴小龙,王伟,张中跃,孙伟涛,倪舒博,公为鑫. 山丘区地表基质空间异质性特征及其对植被生态影响. 地质通报. 2024(09): 1544-1554 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘洪,李文昌,欧阳渊,张景华,张腾蛟,李佑国,黄瀚霄,黄勇,李富,陈敏华,李樋,吴君毅. 基于地质建造的西南山区生态地质编图探索与实践——以邛海—泸山地区为例. 地质学报. 2023(02): 623-638 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 息朝庄,吴林锋,张鹏飞,杨茗钛,范云飞,夏浩东,邓会娟. 贵州省惠水土壤-灌溉水-雨水-大气降尘中Cd、As等微量元素特征及来源讨论. 中国地质. 2023(01): 192-205 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王东晓,袁德志. 锶在土壤-作物中迁移富集机制及作物富锶标准探讨:以河南固始史河一带为例. 现代地质. 2023(03): 767-777 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 唐智明. 水肥一体化技术及其在柑橘种植上的应用. 现代农业科技. 2022(01): 73-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 习文勇,傅佩红. 基于模糊数学的柑橘种植土地适宜性评价. 浙江农业学报. 2022(01): 141-152 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张哲寰,杨佳佳,宋运红,贺鹏飞. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤质量与绿色产地适宜性评价. 地质与资源. 2022(02): 183-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 贾磊,刘洪,欧阳渊,张伟,窦磊,刘子宁,莫滨,陈恩,张腾蛟. 基于地质建造的南方山地-丘陵区地表基质填图单元划分方案——以珠三角新会—台山地区为例. 西北地质. 2022(04): 140-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李海山. 柑橘种植与机械化节水灌溉技术探讨. 农业开发与装备. 2021(10): 225-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 欧阳渊,张景华,刘洪,黄瀚霄,张腾蛟,黄勇. 基于地质建造的西南山区成土母质分类方案——以大凉山区为例. 中国地质调查. 2021(06): 50-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: