The discrimination of Jinningian MORB-like basalt and intra-oceanic subduction in the Dahongshan area, Northern Hubei
-
摘要:
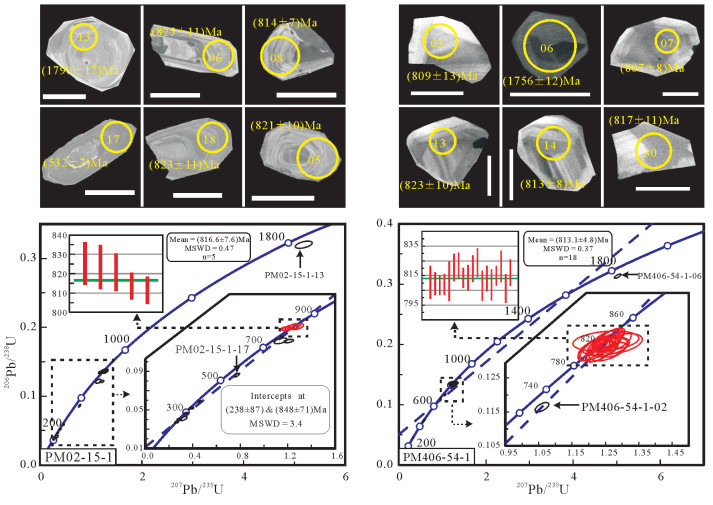
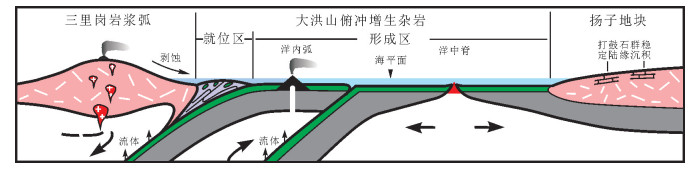
鄂北随州大洪山地区出露大量镁铁质岩(如:辉长岩、辉绿岩、(枕状)玄武岩),它们主要以岩块的形式构造混杂在一套碎屑岩中,表现为典型造山带基质-岩块混杂的特征。大洪山镁铁质岩为拉斑玄武岩系列岩石组合,地球化学方面,不相容元素Rb、Ba、K、Th、U富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta亏损,表现为岛弧玄武岩的特点,而平坦的稀土配分模式(ΣLREE/ΣHREE=1.41~4.48,LaN/YbN=0.76~4.79),Zr/Y=2.65~5.38,Ti/V=29.19~54.97,又可与洋中脊玄武岩对比。因此,我们推测大洪山镁铁质岩属于MORB-like玄武岩(或前弧玄武岩)类岩石组合,其形成于洋内初始俯冲环境,成岩岩浆由俯冲洋板片脱水交代亏损洋中脊地幔减压熔融产生。通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,分别获得南风垭、绿林寨玄武岩(816.6±7.6)Ma(MSWD=0.47)、(813.1±4.8)Ma(MSWD=0.37)的成岩年龄,结合已经取得的杨家棚辉长岩947 Ma、厂河枕状玄武岩824 Ma、绿林辉绿岩820 Ma的年龄结果,说明大洪山地区的这套前弧镁铁质岩组合大致形成于817~947 Ma,它们可能是多阶段洋内俯冲的产物。大洪山地区这套前弧镁铁质岩的厘定说明扬子地块与桐柏-大别地块之间晋宁期发生过一定规模的洋内-洋陆俯冲和造山运动,二者可能曾在青白口纪晚期拼合到一起。
Abstract:There are numerous mafic rocks e.g., gabbro, diabase, basalt, pillow basalt, fumarolic-amygdaloidal basalt, in the Dahongshan area, Suizhou City, northern Hubei Province. They are mainly in the form of block structurally mixed in a set of clastic rock, characterized by mélange of exotic blocks and matrix strata, suggesting a typical orogenic belt. The mafic rocks from Dahongshan area show the features of tholeiite series, and are geochemically enriched in incompatible elements such as Rb, Ba, K, Th and U and depleted in high field strength elements such as Nb and Ta, similar to features of island arc basalts. Nevertheless, the features of flat REE patterns (ΣLREE/ΣHREE=1.41-4.48, LaN/YbN=0.76-4.79, Zr/Y=2.65-5.38 and Ti/V=29.19-54.97) are the same as features of mid-ocean ridge basalt. Therefore, the geochemical signatures and regional geological characteristics show that these mafic rocks should be part of MORB-like/fore-arc basalts, formed along intra-ocean arc where the subduction-initiation happened. Their parent magma was produced by the nascent depleted MORB mantle and interacted with the contribution of fluids from the slab sinking plate with decompression melting. The basalts from Nanfengya and Lulinzhai yielded LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of (816.6±7.6) Ma (MSWD=0.47) and (813.1±4.8) Ma (MSWD=0.37) respectively, interpreted as their crystallization age. Combined with the previous research results of gabbro in Yangjiapeng (947 Ma), pillow basalt in Changhe (824 Ma), and diabase in Luling (820 Ma), it is held that mass mafic rocks were formed in Jinningian period (817-947 Ma) in the Dahongshan area. They may be the products of multi-stage intra-ocean subduction. The discrimination of Jinningian ore-arc/MORB-like basalt in the Dahongshan suggests that it experienced a certain scale of ocean-ocean to ocean-continent subduction and orogeny between Yangtze block and Tongbai-Dabie block in Jinningian period, and the two blocks might have been aggregated together in late Qingbaikou period.
-
1. 引言
通常情况下,土壤水是指吸附于土壤颗粒表面和存在于土壤孔隙中的水(土壤孔隙水),包括吸湿水、薄膜水、毛管水、重力水,土壤孔隙水仅包括毛管水与重力水(雷志栋等,1988)。土壤水是地面以下至地下水位以上土壤层中的水分,是区域水循环的重要一环(张小娟等,2015)。土壤水是联系地表水-地下水、大气降雨-地下水相互转换的纽带,起着物质、能量传递的关键性作用(武倩倩等,2008;张小娟等,2015;刘君等,2016;孙芳强等,2017;徐英德等,2018;马迎宾等,2018;姬王佳等,2019)。
大气降雨是地下水十分重要的补给来源,氢氧稳定同位素作为水分子的组成部分,对水分运动具有良好的指示作用,相比其他传统方法而言具有较高的灵敏度和准确性,可以用来揭示土壤水的来源、入渗、蒸发等各种水运移过程(刘君等,2012;张小娟等,2015;戴军杰等,2019)。应用稳定同位素D、18O示踪包气带中地下水的运移规律和计算入渗补给量,前人已经做过许多研究,但大多限于干旱地区(Zimmermann et al., 1967;Liu et al., 1995;Prudhomme et al., 2003; 马斌等,2014;孙芳强等,2017)。一般在干旱、半干旱地区土壤水中的稳定同位素组成主要受蒸发控制,而在湿润地区,由于不同降水事件的干扰,土壤水中稳定同位素组成变得复杂(Hsieh et al., 1998;Song et al., 2009)。张翔等(2015)研究鄱阳湖湿地土壤水中稳定同位素的组成发现土壤水在旱、雨季的补给来源各异;王福刚等(2007)应用D、18O同位素峰值位移法计算了湿润、半湿润地区河南新乡市原阳县大宾乡降水入渗补给量,并表示稳定同位素峰值位移法最适合于温带湿润地区的降水入渗研究。
本文展示孝感试验场区两个不同垂向间隔及深度进行取样的钻孔(ZK1、ZK2,间距为9 m),应用稳定氢氧同位素D、18O指示土壤水入渗补给来源及时间-剖面深度位置的年际对应关系。利用孝感站(站号57482)年均气温、年降雨量数据和18O同位素垂向剖面明显特征值的位置,确定特定年份的入渗深度,进一步结合土壤含水率,利用18O峰值位移法分析入渗补给量的变化特征。
2. 研究区概况
研究区位于江汉平原北部孝感市肖港镇(图 1),地理坐标为东经113°55′58″,北纬31°03′58″,属中纬度亚热带温湿季风气候区,四季分明,雨量充沛,温暖湿润,光照充足。年均气温在15.6~16.5℃,冬季气温(1月)平均2~4℃,夏季气温(7月)平均28~29℃,累年年均降水量为1152 mm,降水年际变化大。受季风气候影响,研究区降水量年内分布不均,雨季(5-8月)降水量约占全年降水量的70%,在年际尺度下全年降雨量大小变化可用于表征夏季(6-8月)与秋季(9-11月)孝感试验场土壤水补给来源量的大小变化。研究区暴雨、干旱等灾害频发,自1957-2018年,大水年份有1968、1983、1995、1996、1998、2008、2010、2016(夏萍应等,2014;余宏阳,2016)。
张涛等(2010)研究发现孝感市(孝感站,站号57482)近50年(1957-2006年)年降水存在3年、6年、11年、20年四个尺度的周期性干湿变化,对此期间年降水、四季降水变化进行小波方差分析,发现年降水量呈微弱增加趋势(图 2),变化量约为5.9 mm/(10 a),年降雨量变化具有年际尺度(3~7 a)与年代际尺度(9~13 a,20 a左右)变化特征,年际尺度变化周期以准6 a、准3 a为主,年代际尺度变化周期以准11 a、准20 a为主;夏季降水波动主要表现为准6 a、准11 a、准3 a三个尺度,与年降雨量变化周期较为匹配。在此基础上,笔者收集了孝感市(中国气象科学数据共享服务网,气象站点为孝感站,站号57482)2006-2018年的降雨量数据,并绘制了2006-2018年降雨量变化图(图 3)。
![]() 图 2 1957-2006年孝感市年降水量变化图(张涛等,2010)Figure 2. Xiaogan's mean precipitation from 1957 to 2006 (Zhang et al., 2010)表 1 试验场区地质结构信息表Table 1. Geological structure information of test site
图 2 1957-2006年孝感市年降水量变化图(张涛等,2010)Figure 2. Xiaogan's mean precipitation from 1957 to 2006 (Zhang et al., 2010)表 1 试验场区地质结构信息表Table 1. Geological structure information of test site
江汉平原普遍存在第四系黏性土覆盖层,黏性土的渗透系数极低,极大阻碍了大气降雨对地下水的补给,黏性土土壤水水分及溶质运移研究耗时较长,研究难度大,其水分与溶质运移机理尚不清晰。厚层黏性土覆盖层下大气降雨补给地下水规律及补给量对江汉平原区水资源评价与开发、地下水环境保护和干旱洪涝灾害防治等方面具有重要的理论与实践意义。
3. 样品采集与测试
ZK1与ZK2两个钻孔皆位于试验场区附近(图 1),土壤质地相同,两钻孔间距为9m。ZK1取样间隔不一,遵循浅层密,中层疏,深层密的取样原则,取样深度达15 m,同时在试验场地下水监测井取地下水样1个,共采集13个样品;ZK2取样间隔为0.1 m,取样深度为6.2 m,在试验场地下水监测井取地下水样1个,共采集58个样品。
试验场土壤质地样品(表 2)在中国地质大学(武汉)构造与油气资源教育部重点实验室测样,测试仪器为美国贝克曼库尔特公司生产的全自动激光粒度分析仪(LS230),根据粒径大小分黏粒(< 0.005 mm)、粉粒(0.005~0.05 mm)和砂粒(0.05~2 mm)统计其所占百分比(100%)利用三元命名法进行水文地质岩性命名(中国地质调查局,2012)。试验场土壤渗透系数送往武汉九方安达工程技术集团有限责任公司进行测试,岩土透水性按照《水利水电工程地质勘察规范》(GB 50487-2008)进行分级。
表 2 试验场区土壤岩性命名及垂向渗透系数Table 2. Soil texture and vertical hydraulic conductivity of the test site
对第二次(2019/7/25)所取土壤部分层位样品采用烘干法进行土壤体积含水率测定,测得土壤体积含水率区间为36.8%~44.1%(表 3),试验场区土壤容重为1.44~1.66 g/cm3,故正常情况下1.0 kg土壤样品可提取220~306 g供分析用土壤水。
表 3 试验场区土壤体积含水率Table 3. Soil volumetric moisture content (VWC) of test site
ZK1、ZK2钻孔土壤样品中土壤水提取采取低温真空蒸馏的方法,利用LI-2100全自动真空冷凝抽提系统进行提取,提取的水样送往中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心进行测试分析,测试仪器为美国LGR公司的激光水稳定同位素分析仪(LWA-45EP),该仪器D、18O的测试精度分别为±0.50‰、± 0.10‰。同位素浓度采用维也纳标准平均海洋水标准(Vienna Standard Mean Oceanic Water, VSMOW)计算(表 4、表 5),测得样品中的δD和δ18O用同位素千分偏差(张小娟等,2015;邓志民等,2016;董小芳等,2017;姬王佳等,2019)来表示。
表 4 ZK1土壤水及地下水的δD、δ18O值表(2019/4/12)Table 4. δD、δ18O of soil water in ZK1 and groundwater 表 5 ZK2土壤水及地下水的δD、δ18O值(2019/7/25)Table 5. δD、δ18O of soil water in ZK2 and groundwater
表 5 ZK2土壤水及地下水的δD、δ18O值(2019/7/25)Table 5. δD、δ18O of soil water in ZK2 and groundwater
表达式为:

式中,Rsample为样品的D和18O同位素比率,Rstandard为维也纳标准平均海水D和18O的同位素比率。
4. D、18O同位素分布与运移规律
4.1 大气降雨、地下水氢氧稳定同位素特征
试验场区自2018年9月19日至2019年9月19日共收集大气降雨的同位素样品43件,根据测试结果回归拟合出试验场区的大气降雨线(Local Meteoric Water Line, LMWL)为:

研究区大气降雨线(LMWL)与全球降水线δD= 8δ18O + 10(Global Meteoric Water Line, GWML)(Craig, 1967;何军等,2015;邓志民等,2016;董小芳等,2017)相比(图 4),斜率与截距明显低于全球大气降雨线,研究区地下水与大气降雨的δD值和δ18O值接近。
根据气象学定义春季为3-5月,夏季为6-8月,秋季为9-11月,冬季为12月至次年1月。从图 5可知,大气降雨同位素的季节变化很大,春季降雨δD与δ18O最为富集,夏季、秋季较为贫化,这是由于温度会直接影响降水过程中氢氧同位素分馏程度,春季干暖的环境有利于雨滴的同位素蒸发富集作用,夏季孝感市主要受印度洋(西南季风)与太平洋(东南季风)的双重影响(邓志民等,2016;董小芳等,2017),水汽向大陆迁移的过程中,重同位素先凝结产生降水,剩余水汽越深入产生的降水氢氧同位素越偏负,故春季大气降雨δD与δ18O最富集,夏秋季贫乏。
4.2 土壤水氢氧稳定同位素特征
4.2.1 土壤水、地下水δD、δ18O的组成及来源
根据ZK1、ZK2剖面不同深度土壤水测试结果(表 4,表 5),ZK1土壤水垂向剖面上δD值的变化范围为-55.7‰~-40.7‰,平均值为-46.46‰,δ18O值的变化范围为-8.52‰~-5.50‰,平均值为-6.581‰;ZK2土壤水垂向剖面上δD值的变化范围为-53.8‰~-42.0‰,平均值为-47.89‰,δ18O值的变化范围为-7.26‰~-5.67‰,平均值为-6.36‰;地下水中的δD的平均值为-35.3‰,δ18O的平均值为-5.19‰(表 6)。土壤水中的δD、δ18O平均值低于试验场含水层地下水的平均值。
表 6 大气降雨、土壤水及地下水的氢氧稳定同位素组成特征表Table 6. Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of soil moisture, precipitation and groundwater
根据试验场土壤垂向剖面ZK1与ZK2中不同深度土壤水稳定氢氧同位素δD、δ18O的分布特征,确定了ZK1与ZK2的蒸发线:

根据大气降雨、土壤水、地下水稳定同位素δD、δ18O关系图(图 6),可知土壤水、地下水的δD、δ18O值分布在研究区大气降雨线(LMWL)右下方,显示土壤包气带与地下水接受大气降雨的补给,大气降雨在入渗过程经历了一定强度的蒸发作用。大气降雨夏、秋季δD和δ18O降雨量加权平均值与土壤水δD、δ18O值相近,可知夏季与秋季的大气降雨为土壤水的主要补给来源(曹建文等,2019)。地下水的δD、δ18O值比土壤水δD、δ18O值大,更接近大气降雨线,地下水D、18O更富集,说明地下水除接受土壤水垂向补给外,更大程度上接受比土壤水δD、δ18O值更偏正的水分补给。
4.2.2 土壤水D、18O同位素剖面分布特征
ZK2剖面不同深度土壤水的δD、δ18O值变化明显(图 7),两者波动基本一致,整条曲线可划分为三个大区段(0~0.6 m,0.8~2.0 m,2.1~6.2 m)与多个小区段,第一区段深度土壤受蒸发作用影响大,表层蒸发最强烈,其中蒸发前锋深度小于0.4 m,蒸发锋面D、18O最富集(胡海英等,2008);第二区段深度内,随着深度的增大,δD、δ18O值总体上呈振荡指数型增大的趋势,显示了入渗过程中降水量对δD、δ18O的影响特征;第三区段深度内,随着深度的增大,δD、δ18O值总体上呈振荡指数型减小的趋势。0.4~6.2 m深度范围由上至下大致可分为9个小区段,具体如下:
(1)0.4~0.6 m:δD值的变化范围为-53.3‰~-42.0‰,平均值为-48.33‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-7.08‰~-5.67‰,平均值为-6.49‰。δD与δ18O值均呈持续减小趋势。
(2)0.8~1.5 m:δD值的变化范围为-53.8‰~-49.4‰,平均值为-51.34‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-7.26‰~-6.17‰,平均值为-6.72‰。δD值先增大后减小再增大,出现两个波峰与一个波谷;δ18O值先振荡减小后振荡增大,出现一个明显波谷,振幅较大。
(3)1.6~2.0m:δD值的变化范围为-49.9‰~-47.9‰,平均值为-48.48‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.82‰~-6.50‰,平均值为-6.60‰。δD值与δ18O值均呈振荡减小趋势,δ18O值振幅较大,局部存在波谷。
(4)2.1~3.0 m:δD值的变化范围为-48.0‰~-43.2‰,平均值为-46.26‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.11‰~-5.91‰,平均值为-6.05‰。δD值与δ18O值均先减小后增大,存在一个波谷与一个波峰,其中后部分δ18O值急剧增大。
(5)3.1~3.7 m:δD值的变化范围为-46.5‰~-44.9‰,平均值为-45.96‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.34‰~-6.02‰,平均值为-6.20‰。δD值稳定在-48.5‰附近振荡变化,振幅较小;δ18O值呈振荡减小趋势。
(6)3.8~4.4 m:δD值的变化范围为-48.5‰~-45.7‰,平均值为-47.03‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.41‰~-6.00‰,平均值为-6.23‰。δD值呈振荡增大趋势,存在两个波峰与两个波谷;δ18O值呈振荡减小趋势,振幅较大。
(7)4.5~4.8 m:δD值的变化范围为-49.3‰~-45.9‰,平均值为-47.35‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.56‰~-6.12‰,平均值为-6.41‰。δD值与δ18O值均呈先减小后增大趋势,存在一个波峰与一个波谷,振幅较大。
(8)4.9~5.4 m:δD值的变化范围为-48.9‰~-47.0‰,平均值为-48.03‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.58‰~-6.02‰,平均值为-6.32‰。δD值先减小后增大,存在一个波峰与一个波谷;δ18O值呈振荡减小趋势,存在两个波峰与两个波谷,振幅较大。
(9)5.5~6.2 m:δD值的变化范围为-50.0‰~-47.1‰,平均值为-48.46‰;δ18O值的变化范围为-6.66‰~-6.16‰,平均值为-6.48‰。δD值在-48.5‰附近振荡减小变化,先急剧增加稳定在-48.5‰附近,后部分振幅较大,存在三个波峰与三个波谷;δ18O值呈振荡减小趋势,先急剧减小至-6.53‰后逐渐减小,存在两个波峰与两个波谷,振幅较小。
ZK1剖面不同深度土壤水的δD、δ18O值变化虽然明显(图 8),两者波动基本一致,总体呈增大-减小-增大-减小的趋势变化,但其取样间隔较大,由于黏性土渗透系数较小,土壤水分运移速率较慢,稳定D、18O同位素剖面缺失了许多具有明显指示意义的特征值。故选用ZK2剖面进行补给时间-剖面深度位置分析。
4.2.3 入渗补给时间-剖面深度位置分析
ZK2剖面的δD、δ18O值的振幅随着埋深的增大并未趋于平缓(图 7),入渗补给的水分在土壤剖面上具有明显分层。试验场区土壤水以活塞流的方式向下推移入渗,剖面土壤水稳定D、18O同位素具有明显的指示意义。孝感市1960-2010年年平均气温呈缓慢上升趋势,夏秋季温度变化较为平缓,变化较小,气候倾向率约为0.18℃/10a(孝感站,站号57482),孝感市雨季(5-8月)降水量约占全年降水量的70%,在年际尺度下全年降雨量大小变化可用于表征夏季与秋季孝感试验场土壤水补给来源量的大小变化。当降雨量大时(丰水年),降雨入渗补给进入土壤水的δD、δ18O值偏小;当降雨量小时(枯水年),土壤表层蒸发作用大,降雨入渗补给进入土壤水的δD、δ18O值偏大。剖面土壤水δD、δ18O值变化可与年降雨量变化形成较好的对应关系,由此可对大气降雨补给时间-剖面深度位置进行分析。
自1957年以来,研究区年降雨量出现了多个降雨量较少(降雨变化周期内低值,枯水年)的年份与降雨量较多(降雨变化周期内高值,丰水年)的年份(表 7),降雨最少年份为1966年,降雨最多年份为1983年,最多降雨量为最少降雨量的1.8倍。
表 7 孝感市1957-2018年丰水年、枯水年一览Table 7. Low flow year and high flow year in Xiaogan from 1957 to 2018
根据1957-2018年的年降雨量变化特征(图 2,图 3)、ZK2剖面的土壤水δD、δ18O分布特征(图 7),对入渗补给时间-剖面深度位置等作如下分析:
(1)0.4~0.6 m:取样时间为2019年7月25日,当年5、6月份降雨量累计为283.3 mm,7月份降雨量仅4.7 mm,7月份温度较高,土壤受蒸发作用影响大,表层蒸发最强烈,随深度增加逐渐减小,土壤表层δD、δ18O值偏正,0.6 m深度处δD、δ18O值分别为-53.3‰、-7.08‰,为该深度范围极小值,与当年6月份降雨δD、δ18O值相近,为2019年6月降雨入渗补给。
(2)0.8~1.5 m:2011-2018年,年降雨量呈先增大后减小的趋势,其中2016年为显著丰水年,1.1 m深度处土壤水δD、δ18O值出现谷值,分别为-53.8‰、-7.26‰,为2016年雨季时期具有较轻同位素组成的强降雨的入渗补给(马斌等,2014),受蒸发作用较小,降雨量效应明显。2011年与2018年为枯水年,0.8 m与1.5 m深度处土壤水δD、δ18O值出现峰值,皆是由于降雨量相对较小,蒸发作用影响较大,导致降雨入渗过程中产生同位素分馏,使得补给土壤的水分中δD、δ18O值偏正,0.8 m与1.5 m分别对应2018年夏季与2011年夏季降雨入渗补给。
(3)1.6~2.0 m:2007-2011年,年降雨量先增大后减小再增大,其中2008年为显著的丰水年,2010年较2009、2011年降雨量多,1.6 m与2.0 m深度土壤水δD、δ18O值出现谷值,分别为2010、2008年夏季较轻同位素组成的降雨入渗补给。
(4)2.1~3.0 m:2000-2007年,降雨量呈现减小-增大-减小-增大的变化趋势,其中两个显著枯水年为2001年、2006年,显著丰水年为2003年,由图 7发现2.1-3.0m深度范围δ18O值出现两个峰值2.4 m(-5.91‰)与3.0m(-5.91‰),分别对应2006年夏季与2001年夏季的降雨入渗补给,降水在入渗过程中由于雨量小,蒸发作用影响较大,使得补给土壤的水分中δD、δ18O值偏正。2.7 m深度处δD、δ18O值出现谷值-47.2‰、-6.17‰,对应2003年夏季较轻同位素的降雨入渗补给。
(5)3.1~3.7 m:1994-2000年,年降雨量变化较小,基本稳定在1000 mm左右,振幅小于100 mm,1993年为显著的丰水年,与1992年降雨量差值在500 mm左右。由图 7发现3.1~3.7 m深度范围δ18O值出现三个谷值3.2 m(-6.28‰)、3.4 m(-6.26‰)与3.6 m(-6.34‰),分别对应1998年夏季、1996年夏季与1993年夏季的降雨入渗补给,3.7 m深度处δ18O值出现峰值-6.01‰,对应1992年夏季降雨入渗补给。
(6)3.8~4.4 m:1984-1992年,年降雨量总体呈振荡增加的趋势,其中1984年为显著的枯水年,1991年为显著的丰水年,1987年、1989年、1991年降雨量为振荡增加期的降雨量周期内峰值。由图 7发现3.8~4.4 m深度范围δ18O值出现三个谷值3.8 m(-6.32‰)、4.0 m(-6.39‰)与4.2 m(-6.41‰),分别对应1991年夏季、1989年夏季与1987年夏季的降雨入渗补给,4.4 m处δ18O值出现峰值-6.00‰,对应1984年夏季降雨入渗补给。
(7)4.5~4.8 m:1981-1984年,年降雨量先增加,后减少,其中1983年为近60年降雨量最大的显著丰水年,降雨量近1900 mm,与显著枯水年1981年、1984年年降雨量差值近1100 mm。由图 6发现4.5~4.8 m深度范围δ18O值出现一个极小谷值4.5 m(-6.56‰),对应1983年夏季具有较轻同位素组成的强降雨的入渗补给,4.8 m处δ18O值出现峰值-6.12‰,对应1981年夏季降雨入渗补给。
(8)4.9~5.4 m:1977-1981年,年降雨量呈振荡增加的趋势,振荡幅度较大,最大振幅近1000 mm,其中1978年为显著的枯水年,1980年为显著的丰水年。由图 6发现4.9~5.4 m深度范围δ18O值出现一个明显谷值5.2 m(-6.57‰),对应1980年夏季的降雨入渗补给,5.4 m处δ18O值出现偏正峰值-6.02‰,对应1978年夏季降雨入渗补给。
(9)5.5~6.2 m:1971-1977年,年降雨量呈振荡增加的趋势,振荡幅度小于200 mm,其中1977年为较显著的丰水年,1973年、1975年、1977为降雨量小周期峰值,1971年、1974年、1976年为降雨量小周期谷值,由图 6发现5.5~6.2 m深度范围δ18O值出现三个谷值5.6 m(-6.53‰)、5.9 m(-6.66‰)和6.1 m(-6.57‰),分别对应1977年夏季、1975年夏季与1973年夏季的降雨入渗补给,δ18O值出现三个峰值5.8 m(-6.47‰)、6.0 m(-6.52‰)和6.2 m(-6.44‰),分别对应1976年夏季、1974年夏季、1971年夏季降雨入渗补给。
以上分析结果发现孝感大气降雨的年际尺度变化周期与稳定氢氧同位素δD、δ18O值的变化趋势相一致,具有较好的匹配度,ZK2以0.1 m为取样间隔,δD、δ18O值可较明显指示大气降雨入渗补给时间-剖面深度位置的年际对应关系。
5. 入渗补给量的计算
孝感试验场处于江汉平原区,地形平缓,高程变化小,厚层黏性土土壤水分运移以垂向为主,试验场地原土地利用类型为旱田,作物根系活动层主要分布在0~50 cm范围内,历史耕种的作物会在土壤中残留大孔隙,产生优先流,本次研究土壤取样深度大部分位于植物根部以下。由于试验场区土壤质地为黏性土,土壤密实,故本次计算以40 cm深度定为土壤水“活塞流”的起始点,排除了土壤根部大孔隙导致优先流出现对土壤水运移的影响,土壤水分以“活塞流”进行垂向运移。大气降雨入渗补给具有不同的氢氧同位素组成,且土壤垂向剖面不同深度层位土壤水的δD、δ18O值具有明显分层,满足D、18O同位素峰值位移法的适用条件。
利用土壤水分稳定同位素补给时间-剖面深度的对应关系,计算不同深度土壤水分运移的流速,再结合不同深度土壤体积含水量,便可计算出间隔时间内的入渗补给量(王福刚等,2007;马斌等,2014)。
假定在Z1、Z2深度处δD、δ18O的峰值分别对应的是t1、t2时间的入渗补给,包气带稳定同位素剖面上,存在如下关系式:

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 式中:v为在t1~t2(Δt)时段内土壤水垂向入渗的平均流速;R为入渗补给量;θ为Z1、Z2深度之间土壤平均体积含水量;ΔD=Z1-Z2;R为t1~t2(Δt)时段内的入渗补给强度。
根据ZK2剖面深度位置与入渗时间的对应关系,以40 cm深度土壤层为“活塞流”起点,利用公式(1)~(3)计算入渗补给量,结果如表 8所示。
表 8 年均入渗补给量Table 8. Yearly average annual recharge
从多年尺度(50 a)来看,降雨入渗补给土壤水的垂向运移速度为10.8~15.0 cm/a,年均入渗补给量为43.1~58.1 mm,由于土壤密实,土壤孔隙小,渗透系数小(10-6 cm/s),虽然处于湿润多雨的亚热带季风区,土壤体积含水率高,但是多年年均入渗补给量依旧小于马斌等(2014)在华北平原石家庄地区利用稳定氢氧同位素峰值运移法计算(粉砂)壤土、壤质砂土计算的入渗补给量。大气降雨在黏性土地层的入渗补给速率极小,大气降雨年均入渗补给量约占多年年均降雨量(1152 mm)的4.01%,对地下水补给贡献较小。
6. 结论
(1)研究区大气降雨同位素的季节变化很大,春季δD与δ18O最为富集,夏季、秋季较为贫化,大气降雨夏、秋季δD和δ18O降雨量加权平均值与土壤水δD、δ18O值相近,可知夏、秋季的大气降雨为土壤水的主要补给来源。
(2)ZK2剖面土壤水的δD、δ18O值变化明显,具有明显分层,总体可划分为三个区段:0~0.6 m土壤受蒸发作用影响大;0.8~2.0 m δD、δ18O值随深度的增大,呈振荡指数型增大的趋势;2.1~6.2 m δD、δ18O值随深度的增大,呈振荡指数型减小的趋势。试验场土壤水以活塞流的方式向下推移入渗,以0.1 m为取样间隔,土壤水δD、δ18O值可较明显指示降雨在包气带剖面上的运移。
(3)确定了近50年包气带入渗补给时间-剖面深度位置的年际对应关系,发现近50年大气降雨入渗补给的运移深度为6.2 m,运移速度为10.8~15.0 cm/a,据此推算降水入渗补给需要近130年才能穿透15 m厚层黏性土补给至含水层,且年均入渗补给量为43.1~58.1 mm,占多年年均降水量的4.01%,大气降雨对地下水补给量的贡献较小,江汉平原试验场区厚层黏性土的防污性能良好。上述所揭示的黏性土中土壤水入渗迁移历史演化特征及补给年际对应关系,对江汉平原极其类似地区水资源评价、地下水等生态环境保护、旱涝灾害防治等具有重要意义。
致谢: 感谢肖庆辉研究员、陆松年研究员、潘桂棠研究员等的技术指导,感谢彭练红教授、邓兴博士等的有益讨论,感谢审稿专家提出的建设性意见。 -
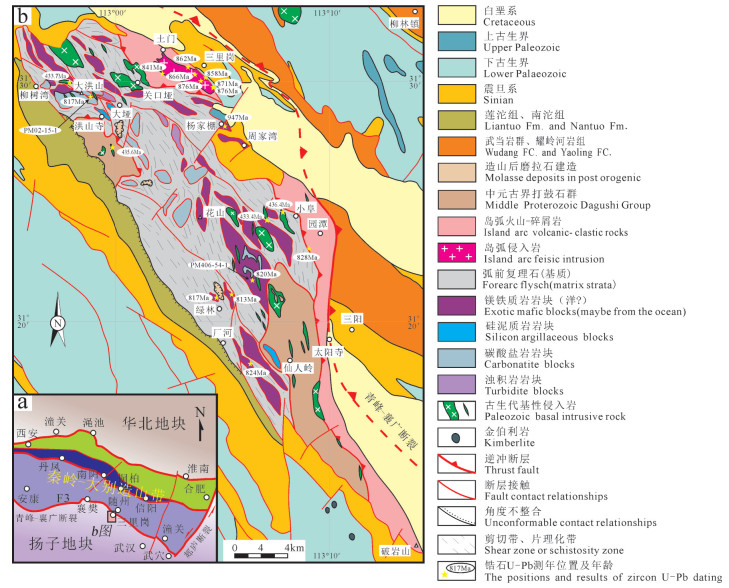
图 1 大洪山地区地质简图
(图中相关测年位置及数据参考Shi et al., 2007; 胡正祥等, 2015a, 2017; 廖明芳等, 2016; Xu et al., 2016; 陈超等, 2017a, b, 2018)
Figure 1. The geological sketch map of Dahongshan area
(Locations and results of zircons U-Pb dating in the map after Shi et al., 2007; Hu Zhengxiang et al., 2015a, 2017; Liao Mingfang et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2016; Chen Chao et al., 2017a, b, 2018)
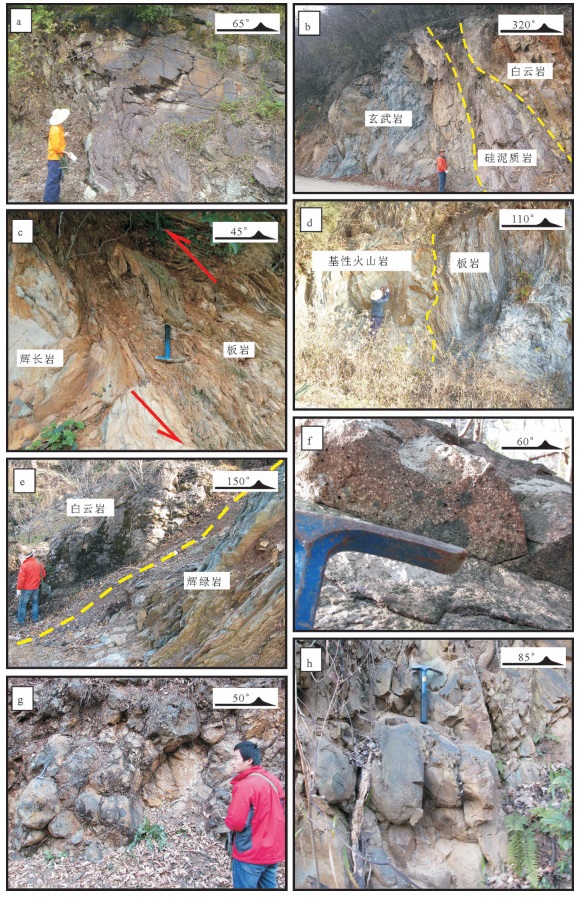
图 2 大洪山俯冲增生杂岩及镁铁质岩野外特征
a—厂河砂岩中发育同斜倒转褶皱;b—南风垭玄武岩、紫红色硅泥质岩、白云岩混杂;c—关口垭粉砂质板岩逆冲到辉长岩之上,二者接触面上发育构造透镜体;d—关口垭绢云母板岩中夹基性火山岩岩块;e—罗家咀硅质条带白云岩中的辉绿岩脉,辉绿岩发生强片理化;f—罗家咀北气孔-杏仁状玄武岩;g—厂河枕状玄武岩;h—姚家冲西枕状玄武岩
Figure 2. Field photos of the subduction accretionary complex and mafic rocks in Dahongshan
a-Synclinal overturned fold developed in the sandstone in Changhe; b-Mélange in Nanfengya composed of basalt, fuchsia siliceous argillaceous rock and dolomite; c-Silty argillaceous thrust up to the gabbro, and tectonic lenses developed between them in the Guankouya; d-Basic volcanic rock mass mixed in the sericite slate in Guankouya; e-Strong foliated doleritic vein developed in the siliceous band dolomite in Luojiaju; f-Amygdaloidal basalts outcropped in the north of Luojiaju; g-Pillow basalts outcrop in Changhe; h-Pillow basalts outcrop in the west of Yaojiachong
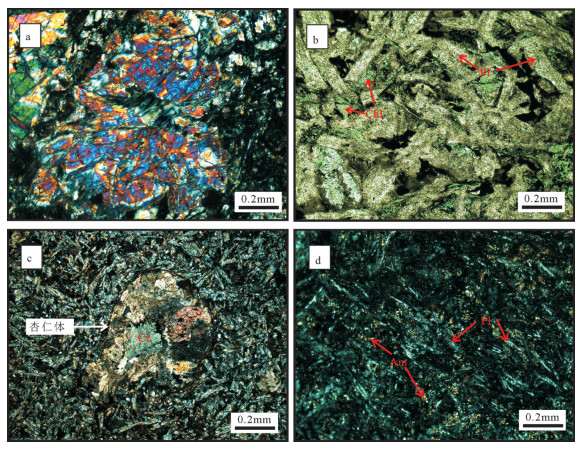
图 3 大洪山镁铁质岩镜下特征
a—关口垭辉长岩中辉石局部蚀变成透闪石、绿泥石,斜长石基本被粘土矿物交代(+);b—罗家咀辉绿岩中的辉绿结构,辉石基本被绿泥石取代(-);c—厂河东气孔-杏仁状玄武岩中的杏仁构造,充填物主要为方解石(+);d—厂河枕状玄武岩间粒结构(+);Am—角闪石,Aug—普通辉石,Cc—方解石,Chl—绿泥石,Pl—斜长石
Figure 3. Photomicrographs of the mafic rocks in Dahongshan
a-Pyroxenes altered into amphibole and chlorite locally, and plagioclases basically replaced by clay minerals in the gabbro in Guankouya (+); b-The diabasic structure in the diabase in Luojiaju, where pyroxene is basically replaced by chlorite (-); c-Almond texture of Changhe basalt, with the filling materials being mainly calcite (+); d-Pillow basalt of Changhe with intergranular texture (+); Am-Amphibole, Aug-Augite, Cc-Calcite, Chl-Chlorite, Pl-Plagioclase
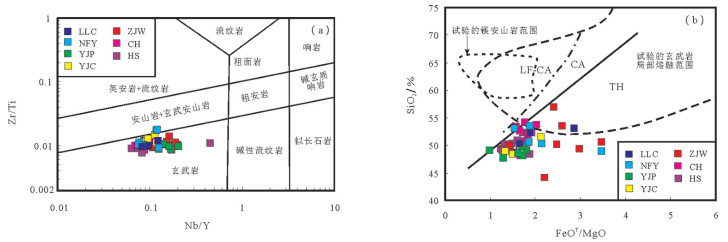
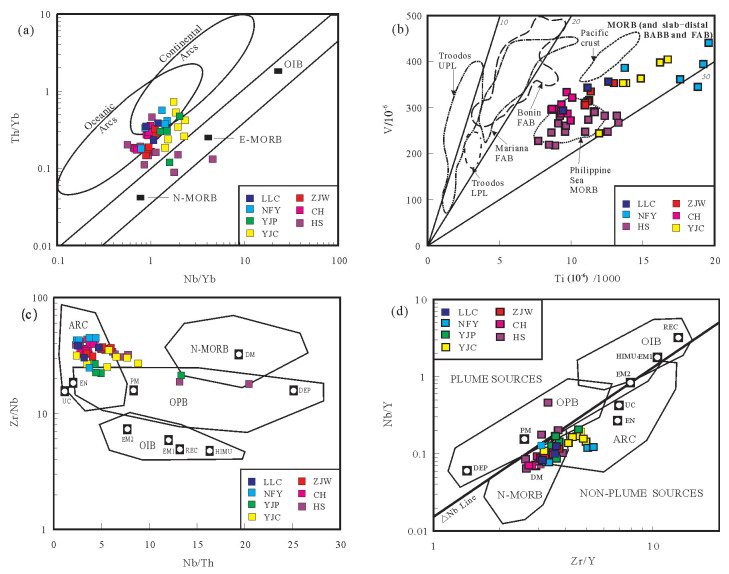
图 4 大洪山镁铁质岩Nb/Y-Zr/Ti图(a)(底图据Pearce, 2014)和FeOT/MgO-SiO2图(b)(底图据Miyashiro, 1974; 邓晋福等, 2010)
LLC—六里冲辉长岩,数据来源于胡正祥等, 2015a;NFY—南风垭玄武岩;YJP—杨家棚玄武岩和辉长岩,数据来源于石玉若等, 2003, 2005b;YJC-姚家冲玄武岩和辉绿岩,ZJW—周家湾玄武岩,数据来源于董云鹏等, 2003;CH—厂河枕状玄武岩,数据来源于Deng et al., 2013;HS—花山玄武岩,数据来源于董云鹏等, 1999, 后文图片中代号与此图一致
Figure 4. Nb/Y -Zr/Ti (a) (after Pearce, 2014) and FeOT/MgO-SiO2diagram (b)(after Miyashiro, 1974; Deng Jinfu et al., 2010)of the mafic rocks in Dahongshan
LLC-Gabbros of Liulichong, data from Hu Zhengxiang et al., 2015a; NFY-Basalts of Nanfengya, YJP-Basalts and gabbros of Yangjiapeng, data from Shi Yuruo et al., 2003, 2005b; YJC-Basalts and diabases of Yangjiapeng, ZJW-Basalts of Zhoujiawan, data from Dong Yunpeng et al., 2003; CH-Pillow basalts of Changhe, data after Deng et al., 2013; HS-Basalts of Huashan, data from Dong et al., 1999. The Abbreviations in the figures below are coincident.
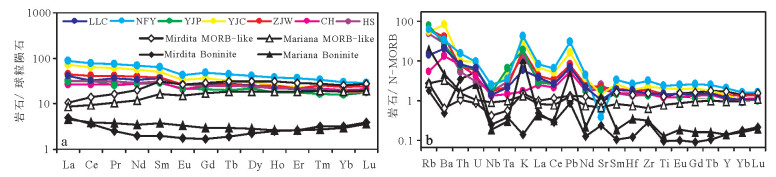
图 5 大洪山地区镁铁质岩球粒陨石标准化REE配分图(a,Sun et al., 1989)和N-MORB标准化蛛网图(b,Ishizuka et al., 2009)
(图中均为平均值. Mirdita MORB-like和Mirdita Boninite分别代表阿尔卑斯-喜马拉雅造山带西段Mirdita地区的前弧玄武岩和高镁安山岩,数据来源于Dilek and Furnes, 2009a;Mariana MORB-like和Mariana Boninite分别代表西太平岩俯冲带马里亚纳前弧玄武岩和高镁安山岩,数据来源于Reagan et al., 2010)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, after Sun et al., 1989) and N-MORB-normalized spidergrams (b, after Ishizuka et al., 2009) of the mafic rocks in Dahongshan
(Data in the picture stand for average data. Data of Mirdita MORB-like basalt and Mirdita Boninite after Dilek and Furnes, 2009a; Mariana MORBlike basalt and Mariana Boninite after Reagan et al., 2010)
图 7 大洪山地区镁铁质岩环境判别图解
a—Th/Yb-Nb/Yb图(Pearce, 2014);b—V-Ti/1000图(Shervais, 1982; Ishizuka et al., 2014a);c—Zr/Nb-Nb/Th图(Condie, 2003; Velásquez et al., 2011);d-Nb/Y-Zr/Y图(Fitton et al., 1997; Condie, 2003);Troodos UPL-塞浦路斯上部枕状熔岩;Troodos LPL-塞浦路斯下部枕状熔岩;Bonin FAB、Mariana FAB—小笠原、马里亚纳前弧玄武岩,Philippine Sea MORB-菲律宾海盆洋中脊玄武岩;Pacific crust-太平洋洋壳;ARC—与岛弧相关的玄武岩;N—MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;OPB—洋底高原玄武岩,DM—亏损地幔;EN—富集组分;PM—原始地幔;REC—循环组分;UC—大陆上地壳;DEP—亏损地幔组分;HIMU—高U/Pb比值的地幔;EM1、EM2—富集地幔
Figure 7. Tectonic discrimination diagram of the mafic rocks in the Dahongshan area
a-Th/Yb-Nb/Yb diagram (after Pearce, 2014), b-V-Ti/1000 diagram (after Shervais, 1982; Ishizuka et al., 2014a, ) c-Zr/Nb-Nb/Th diagram (after Condie, 2003; Velásquez et al., 2011), d-Nb/Y - Zr/Y diagram (after Fitton et al., 1997; Condie, 2003). Troodos UPL-Upper pillow basalt of Troodos; Troodos LPL-Lower pillow basalt of Troodos; Bonin FAB-Fore-arc basalt of Bonin, Mariana FAB-Fore-arc basalt of Mariana; Philippine Sea MORB- Mid- oceanic ridge basalt of Philippine Sea; ARC- Basalt associated with the island arc, N- MORB- Normal mid- ocean ridge basalt; OIB- Ocean island basalt, OPB- Ocean floor plateau basalt; DM- Depleted mantle; EN- Enriched components; PM- Primitive mantle; REC- Recirculated components; UC- Upper crust; DEP- Depleted mantle components; HIMU- High U/Pb ratio mantle; EM1, EM2-Enriched mantle 1, enriched mantle 2
表 1 大洪山地区镁铁质岩主量元素(%)、微量元素和稀土元素(10-6)地球化学分析数据
Table 1 Mayor elements (%) and trace elements (10-6) compositions of the mafic rocks in Dahongshan area

表 2 南风垭、绿林寨玄武岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年数据
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic data of the basalt from Nanfengya and Lulinzhai

-
Chen Chao, Mao Xinwu, Hu Zhengxiang, Yang Jinxiang, Yang Cheng, Kong Lingyao, Zheng Meng. 2017a. Discovery of ~817 Ma oceanic island basalts in the Dahongshan region, northern Hubei province and its significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 36(6):22-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX198606013.htm
Chen Chao, Xiong Baocheng, Hu Zhengxiang, Zhou Feng, Yang Cheng, Kong Lingyao. 2017b. A rustic opinion of Neoproterozoic Ocean-continent coversion events on the northern margin of Yangtze Block[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 31(6):1-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdk201706001
Chen Chao, Yuan Jinling, Kong Lingyao, Ye Zhujun, Yang Qingxiong, Yang Cheng, Zhou Feng. 2018. Documentation of early Paleozoic Mafic Dykes in the Dahongshan region, northern Yangze block and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science, 43(7):2370-2388(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201807012
Condie Kent C. 2003. Incompatible element ratios in oceanic basalts and komatiites:Tracking deep mantle sources and continental growth rates with time[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4(1):1-28. doi: 10.1029-2002GC000333/
Deng Jinfu, Feng Yanfang, Di Yongjun, Liu Cui, Xiao Qinghui, Su Shangguo, Zhao Guochun, Meng Fei, Ma Shuai, Yao Tu. 2015.Magmatic arc and ocean-continent transition:Discussion[J]. Geological Review, 61(3):473-484(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201503001
Deng Jinfu, Liu Cui, Feng Yanfang. 2010. High magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks (HMA) and magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks(MA):Two igneous rock types related to oceanic subduction[J]. Geology in China, 37(4):1112-1118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004027.htm
Deng Qi, Wang Jian, Wang Zhengjiang, Wang Xuance, Qiu Yansheng, Yang Qingxiong, Du Qiuding, Cui Xiaozhuang, Zhou Xiaolin. 2013. Continental flood basalts of the Huashan Group, northern margin of the Yangtze block——Implications for the breakup of Rodinia[J]. International Geology Review, 55(15):1865-1884. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.799257
Dilek Yildirim, Furnes Harald. 2009a. Structure and geochemistry of Tethyan ophiolites and their petrogenesis in subduction rollback systems[J]. Lithos, 113:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.022
Dilek Yildirim, Thy Peter. 2009b. Island arc tholeiite to boninitic melt evolution of the Cretaceous Kizildag (Turkey) ophiolite:Model for multi-stage early arc-forearc magmatism in Tethyan subduction factories[J]. Lithos, 113:68-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.05.044
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, Liu Xiaoming, Lai Shaocong. 1998. Disintegration of the Huashan Group in the Dahongshan Mountain Area, northern Hubei[J]. Regional Geology of China, 17(4):371-376(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, Lai Shaocong, Zhou Dingwu, Zhu Bingquan. 1999. An ophiolitic tectonic melange first discovered in Huashan area, south margin of Qinling Orogenic Belt, and its tectonic implications[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 43(3):292-302. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=34a8b6231e2e5df6c6b6afb8a0d6d76a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, Lai Shaocong, Zhou Dingwu, Zhu Bingquan. 1999. An ophiolitic teconic melange first discovered in Huashan area, south margin of Qinling Orogenic Belt, and its tectonic implication[J]. Science in China (Series D), 29(3):222-231(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG199903007.htm
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, Zhao Xia, Yao Anping, Liu Xiaoming. 2006. Geochemistry of the subduction-related magmatic rocks in the Dahong Mountains, northern Hubei Province[J]. Science in China Ser. D Earth Sciences, 47(4):366-377. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e1223c7319df7d5bd03e6b7775ad45a9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, Zhao Xia, Yao Anping, Liu Xiaoming. 2003. Geochemistry and tectonic implication of igneous rocks in the northern Hubei Province:New evidence of subduction and eastward extension of the Mianlue ocean in the south Qinling[J]. Science of China (Series D), 33(12):1143-1153(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Xiaoning, Liu Xiaoming, Li Wei, Chen Qing, Zhang Guowei, Zhang Hongfu, Yang Zhao, Sun Shengsi, Zhang Feifei. 2015. Propagation tectonics and multiple accretionary processes of the Qinling Orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 104:84-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.007
Fitton J G, Saunders A D, Norry M J, Hardarson B S, Taylor R N. 1997. Thermal and chemical structure of the Iceland plume[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 153:197-208. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00170-2
Goodenough Kathryn M, Thomas Robert J, Styles Michael T, Schofield David I, MacLeod Christopher J. 2014. Records of ocean growth and destruction in the Oman-UAE Ophiolite[J]. Elements, 10:105-110. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=713feada2d9804d2b0914b7c6557054c
Hastie A R, Kerr A C, Pearce J A, Mitchell S F. 2007. Classification of altered volcanic island arc rocks using immobile trace elements:Development of the Th-Co Discrimination Diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 48(12):2341-2357. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egm062
Hu Zhengxiang, Chen Chao, Mao Xinwu, Deng Qianzhong, Yang Jinxiang, Li Linjing, Kong Lingyao. 2015a. Documentation of Jingningian Island-arc Volcanic Rocks and Accretionary complexes in the Dahongshan Region, Northern Hubei and Its tectonic Significance[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 29(6):757-766(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HBDK201506003.htm
Hu Zhengxiang, Mao Xinwu, Tian Wangxue, Li Xiongwei. 2015b.Discovery of the Jinningian Orogenic Belt on the Northern Margin of Yangtze Craton in Mountain Dahong[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2(2):33-39(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdzdc201502004
Hu Zhengxiang, Chen Chao, Mao Xinwu, Yang Qingxiong, Deng Qianzhong, Kong Lingyao, Yang Cheng. 2017. The Qingbaikouan tumen formation-complex island arc volcanic-clastic rocks on the northern margin of yangtze block and its significance. Journal of Stratigraphy[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 41(3):304-317(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ishizuka Osamu, Tani Kenichiro, Reagan Mark K. 2014a. Izu-BoninMariana Forearc Crust as a Modern Ophiolite Analogue[J]. Elements, 10:115-120. doi: 10.2113/gselements.10.2.115
Ishizuka Osamu, Geshi Nobuo, Kawanabe Yoshihisa, Ogitsu Itaru, Taylor Rex N, Tuzino Taqumi, Sakamoto Izumi, Arai Kohsaku, Nakano Shun. 2014b. Long-distance magma transport from arc volcanoes inferred from the submarine eruptive fissures offshore Izu-Oshima volcano, Izu-Bonin arc[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 285:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.08.006
Ishizuka Osamu, Umino Susumu, Taylor Rex N, Kanayama Kyoko. 2014c. Evidence for hydrothermal activity in the earliest stages of intraoceanic arc formation:Implications for ophiolite-hosted hydrothermal activity[J]. Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.Economic Geology, 109(8):2159-2177. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.109.8.2159
Ishizuka Osamu, Yuasa Makoto, Taylor Rex N, Sakamoto Izumi. 2009.Two contrasting magmatic types coexist after the cessation of back-arc spreading[J]. Chemical Geology, 266:274-296. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.06.014
Lai Shaocong, Zhong Jianhua. 1999. Geochemical features and its tectonic significance of the meta-basalt in Zhoujiawan area, Mianlue suture zone, Qinling-Dabie mountains, Hubei province[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2(8):127-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800851500
Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B. 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkalisilica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27:745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
Li Huaikun, Tian Hui, Zhou Hongying, Zhang Jian, Liu Huan, Geng Jianzhen, Ye Lijuan, Xiang Zhenqun, Ju Lesheng. 2016.Correlation between the Dagushi Group in the Dahongshan Area and the Shennongjia Group in the Shennongjia Area on the northern margin of the Yangtze Craton:Constraints from zircon UPb ages and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6):186-201(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liao Mingfang, Xie Yingbo, Li Linjing, Yang Jinxiang, Mao Xinwu, Deng Qianzhong, Kong Lingyao, Li Qiwen, Chen Chao. 2016.Discussion about genesis and formation age of Sanligang Pluton in the Dahongshan Region, Hubei[J]. Resources Enviroment & Engineering, 30(2):143-150(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdk201602004
Liu Xiaochun, Li Sanzhong, Jahn Bor-ming. 2015. Tectonic evolution of the Tongbai-Hong'an orogen in central China:From oceanic subduction/accretion to continent-continent collision[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(9):1477-1496. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5145-z
Liu Yongsheng, Hu Zhaochu, Gao Shan, Günther Detlef, Xu Juan, Gao Changgui, Chen Haihong. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Lu Yuanfa. 2004. GeoKit-A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Geochimica, 33(5):459-464(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200405004
Ludwig Kennethr. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center.
Ma Tianfang, Li Xiaoli, Chen Yongyun, Deng Zhenp, Li Guohui. 2011.Interchangeable Analysis of Method on the X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 30(4):486-490(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201104020
Mattash M A, Pinarelli L, Vaselli O, Minissale A, Al-Kadasi M, Shawki M N, Tassi F. 2013. Continental Flood Basalts and Rifting:Geochemistry of Cenozoic Yemen Volcanic Province[J]. International Journal of Geosciences, 4:1459-1466. doi: 10.4236/ijg.2013.410143
Miyashiro Akiho. 1974. Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins[J]. American Journal of Science, 274:321-355. doi: 10.2475/ajs.274.4.321
Pearce J A, Robinson P T. 2010. The Troodos ophiolite complex probably formed in a subduction initiation, slab edge setting[J]. Gondwana Research, 18:60-81. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.12.003
Pearce J. A. 2014. Immobile Element fingerprinting of ophiolites[J]. Elements, 10:101-108. doi: 10.2113/gselements.10.2.101
Polat A, Hofmann A. W. 2003. Alteration and geochemical patterns in the 3.7-3.8 Ga Isua greenstone belt, West Greenland[J]. Precambrian Research, 126:197-218. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00095-0
Reagan Mark K, Ishizuka Osamu, Stern Robert J, Kelley Katherine A, Ohara Yasuhiko, Blichert-Toft Janne, Bloomer Sherman H, Cash Jennifer, Fryer Patricia, Hanan Barryb, Hickey-Vargas Rosemary, Ishii Teruaki, Kimura Jun-Ichi, Peate David W, Rowe Michael C, Woods Melinda. 2010. Fore-arc basalts and subduction initiation in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana system[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 11(3):10-1029. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b5af3257e3988f69b82da5ef31f082ff&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Ren Jishun, Zhao Lei, Li Chong, Zhu Junbin, Xiao Liwei. 2017.Thinking on Chinese tectonics——Duty and responsibility of Chinese geologists[J]. Geology in China, 44(1):33-43(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201701004.htm
Savov Ivanp, Ryan J G, D'Antonio M. 2015. Petrology and geochemistry of West Philippine basin Basalts and Early Palau-Kyushu arc volcanic clasts from ODP Leg 195, Site 1201D:Implications for the Early History of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc[J]. Journal of Petrology, 47:277-299. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2e2e24cb3e46a5253e7a012d772d6380&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Shervais John W. 1982. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 59:101-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90120-0
Shi Yuruo, Zhang Zongqing, Liu Dunyi, Tang Suohan, Wang Jinhui. 2003. A study on Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic chronology of the Huashan ophiolitic Melange in the Suizhou Area, Hubei Province[J]. Geological Review, 49(4):367-373(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLP200304004.htm
Shi Yuruo, Zhang Zongqing, Liu Dunyi, Tang Suohan, Wang Jinhui, Chen Wen, Zhang Sihong, Liu Xinyu. 2005a. Rb-Sr and 40Ar/39Ar ages of the adamellite in Sanligang Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 26(1):17-20(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200501003
Shi Yuruo, Zhang Zongqing, Liu Dunyi, Tang Suohan, Wang Jinhui, Liu Tao. 2005b. Rb-Sr isotope dating of gabbro from Yangjiapeng Area in Suizhou, Hubei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 26(6):521-524(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200506006
Shi Yuruo, Liu Dunyi, Zhang Zongqing, Miao Laicheng, Zhang Fuqin, Xue Hongmei. 2007. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of gabbro and granite from the Huashan ophiolite, oinling orogenic belt, China:Neoproterozoic suture on the northern margin of the Yangtze Craton[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(2):239-243. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2007.tb00947.x
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Velásquez Germán, Béziat Didier, Salvi Stefano, Tosiani Tommaso, Debat Pierre. 2011. First occurrence of Paleoproterozoic oceanic plateau in the Guiana Shield:The gold-bearing El Callao Formation, Venezuela[J]. Precambrian Research, 186:181-192. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.01.016
Wang Qingchen, Lin Wei. 2002. Geodynamics of the Dabieshan collisional orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 9(4):257-265(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200204005
Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16):1589-1604(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589
Xiao Qinghui, Li Tingdong, Pan Guitang, Lu Songnian, Ding Xiaozhong, Deng Jinfu, Feng Yimin, Liu Yong, Kou Caihua, Yang Linlin. 2016. Petrologic ideas for identification of ocean-continent transition:Recognition of intra-oceanic arc and initial subduction[J]. Geology in China, 43(3):721-737(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201603003.htm
Xu Yang, Yang Kunguang, Polat Ali, Yang Zhenning. 2016. The-860Ma mafic dikes and granitoids from the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China:A record of oceanic subduction in the early Neoproterozoic[J]. Precambrian Research, 275:310-331. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.01.021
Yan Zaifei, Huang Zhilong, Chen Mi, Zhou Jiaxi, Zhao Zheng, Ding Wei. 2010. Two distinct mantle sources for high-Ti basalts in the Emeishan overfall basalt province[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 40(6):1311-1322(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201006012
Yang Shao, Li Dewei, Chen Guifan, Li Hualiang, Zhang Shuo, Zhou Tao. 2018. The discovery of the Wuluqiong magnetite deposit in Tibet and its geological characteristics[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1214-1227(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201806012
Zhang Guowei, Dong Yunpeng, Lai Shaocong, Guo Anlin, Meng Qingren, Liu Shaofeng, Cheng Shunyou, Yao Aanping, Zhang Zongqing, Pei Xianzhi, Li Sanzhong. 2003. Mianlue tectonic zone and Mianlue suture zone on southern margin of Qinling Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Science in China (Series D), 33(12):1121-1135(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Guowei, Cheng Shunyou, Guo Anlin, Dong Yunpeng, Lai Shaocong, Yao Anping. 2004. Mianlue paleo-suture on the southern margin of the Central Orogenic System in QinlingDabie——with a discussion of the assembly of the main part of the continent of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9/10):846-853(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zongqing, Zhang Guowei, Liu Dunyi, Wang Zongqi, Tang Suohan, Wang Jinhui. 2006. Isotopic Geochrology and Geochemistry of Ophiolites, Granites and Clastic Sedimentary Rocks in the Qinling Orogenic Belt[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-348(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Liangliang, Wei Junqi, Wang Fang, Chou Xiumei. 2017.Optimizationof the working parameters of LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 36(04):350-359(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201704003
陈超, 毛新武, 胡正祥, 杨金香, 杨成, 孔令耀, 峥孟. 2017a.鄂北大洪山地区~817Ma洋岛玄武岩的发现及意义[J].地质科技情报, 36(6):22-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201706004.htm 陈超, 熊保成, 胡正祥, 周峰, 杨成, 孔令耀. 2017b.扬子北缘新元古代洋陆转换事件刍议[J].资源环境与工程, 31(6):1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201706001 陈超, 苑金玲, 孔令耀, 叶竹君, 杨青雄, 杨成, 周峰. 2018.扬子北缘大洪山地区早古生代基性岩脉的厘定及其地质意义[J].地球科学, 43(7):2370-2388. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201807012 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 刘翠, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 赵国春, 孟斐, 马帅, 姚图. 2015.岩浆弧火成岩构造组合与洋陆转换[J].地质论评, 61(3):473-484. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201503001 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 赵国春, 孔维琼, 曹文燕. 2010.高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩/闪长岩类(MA):与洋俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩类[J].中国地质, 37(4):1112-1118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.025 董云鹏, 张国伟, 赖绍聪, 周鼎武, 朱炳泉. 1999.随州花山蛇绿构造混杂岩的厘定及其大地构造意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 29(3):222-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199903004 董云鹏, 张国伟, 柳小明, 赖绍聪. 1998.鄂北大洪山地区"花山群"的解体[J].中国区域地质, 17(4):371-376. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD804.005.htm 董云鹏, 张国伟, 赵霞, 姚安平, 柳小明. 2003.鄂北大洪山岩浆带地球化学及其构造意义——南秦岭勉略洋盆东延及其俯冲的新证据[J].中国科学(D辑), 33(12):1143-1153. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200312003 胡正祥, 陈超, 毛新武, 邓乾忠, 杨金香, 李琳静, 孔令耀. 2015a.鄂北大洪山晋宁期岛弧火山岩和增生杂岩的厘定及地质意义[J].资源环境与工程, 29(6):757-766. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201506002 胡正祥, 毛新武, 田望学, 李雄伟. 2015b.扬子陆块北缘大洪山地区发现晋宁期造山带[J].中国地质调查, 2(2):33-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdzdc201502004 胡正祥, 陈超, 毛新武, 杨青雄, 邓乾忠, 孔令耀, 杨成. 2017.扬子北缘青白口系土门岩组岛弧火山-碎屑岩的定义及意义[J].地层学杂志, 41(3):304-317. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DCXZ201703009.htm 李怀坤, 田辉, 周红英, 张健, 刘欢, 耿建珍, 叶丽娟, 相振群, 瞿乐生. 2016.扬子克拉通北缘大洪山地区打鼓石群与神农架地区神农架群的对比:锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素证据[J].地学前缘, 23(6):186-201. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201606013 廖明芳, 谢应波, 李琳静, 杨金香, 毛新武, 邓乾忠, 孔令耀, 李启文, 陈超. 2016.湖北省大洪山地区三里岗岩体成因及时代探讨[J].资源环境与工程, 30(2):143-150. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdk201602004 路远发. 2004. GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J].地球化学, 33(5):459-464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004 马天芳, 李小莉, 陈永君, 邓震平, 李国会. 2011. X射线荧光光谱分析方法的共享[J].岩矿测试, 30(4):486-490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.020 任纪舜, 赵磊, 李崇, 朱俊宾, 肖黎微. 2017.中国大地构造研究之思考——中国地质学家的责任与担当[J].中国地质, 44(1):33-43. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170103&flag=1 石玉若, 张宗清, 刘敦一, 唐索寒, 王进辉. 2003.湖北省随州花山蛇绿混杂岩Sm-Nd、Rb-Sr同位素年代研究[J].地质论评, 49(4):367-373. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.04.005 石玉若, 张宗清, 刘敦一, 唐索寒, 王进辉, 陈文, 张思红, 刘新宇. 2005a.湖北省随州三里岗地区二长花岗岩Rb-Sr、40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄[J].地球学报, 26(1):17-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200501003 石玉若, 张宗清, 刘敦一, 唐索寒, 王进辉, 刘涛. 2005b.湖北省随州杨家棚地区辉长岩Rb-Sr同位素年龄[J].地球学报, 26(06):521-524. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200506006 王清晨, 林伟. 2002.大别山碰撞造山带的地球动力学[J].地学前缘, 9(4):257-265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.04.005 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 肖庆辉, 李廷栋, 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 丁孝忠, 邓晋福, 冯益民, 刘勇, 寇彩化, 杨琳琳. 2016.识别洋陆转换的岩石学思路——洋内弧与初始俯冲的识别[J].中国地质, 43(3):721-737. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160303&flag=1 严再飞, 黄智龙, 陈觅, 周家喜, 赵正, 丁伟. 2010.峨眉山溢流玄武岩省高钛玄武岩的两种不同地幔源特征[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40(6):1311-1322. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201006012 杨绍, 李德威, 陈桂凡, 李华亮, 张硕, 周涛. 2018.西藏乌鲁穷含铜磁铁矿床的发现及地质特征[J].中国地质, 45(6):1214-1227. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180611&flag=1 张国伟, 程顺有, 郭安林, 董云鹏, 赖绍聪, 姚安平. 2004.秦岭-大别中央造山系南缘勉略古缝合带的再认识——兼论中国大陆主体的拼合[J].地质通报, 23(9/10):846-853. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200409005 张国伟, 董云鹏, 赖绍聪, 郭安林, 孟庆任, 刘少峰, 程顺有, 姚安平, 张宗清, 裴先治, 李三忠. 2003.秦岭-大别造山带南缘勉略构造带与勉略缝合带[J].中国科学(D辑), 33(12):1121-1135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200312001 张宗清, 张国伟, 刘敦一, 王宗起, 唐索寒, 王进辉. 2006.秦岭造山带蛇绿岩、花岗岩和碎屑沉积岩同位素年代学和地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-348. 周亮亮, 魏均启, 王芳, 仇秀梅. 2017. LA-ICP-MS工作参数优化及在锆石U-Pb定年分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 36(4):350-359. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201704003 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 马兴涛. 土壤水入渗参数非线性预测模型改进及应用研究. 水利技术监督. 2024(04): 238-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘泳佚,史婷婷,王清,刘添文,刘亚磊,李梦茹. 江汉平原过渡带黏性层状土弥散试验与模拟研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2023(01): 41-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘广景. 煤层气高产水井原因分析及水源识别——以沁水盆地柿庄南区块3号煤井为例. 天然气勘探与开发. 2023(03): 123-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏玉涛,刘明欢,刘可,普薇如. 多尺度土壤水监测研究进展. 中国农学通报. 2021(26): 140-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: