Characteristics of Jurassic sequence boundary surfaces on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin and their constraints on the spatial-temporal properties of sandstone uranium mineralization
-
摘要:
依据野外露头、钻井岩芯、地震、测井及地球化学等资料,对鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘侏罗系延安组(J1-2y)和含铀岩系——直罗组(J2z)关键层序界面进行了系统研究。延安组—直罗组层序界面在露头剖面和钻井岩芯上表现为铁质风化壳、削截侵蚀面或岩性岩相转化面等特征;地震剖面上表现为上超、下超、削截等反射特征;测井曲线岩电关系和微量元素地球化学均表现为不同类型的突变特征。由此识别出10个不同级次层序界面,其中包括3个Ⅰ型层序界面(TSB1~TSB3)和7个Ⅱ型层序界面(SB1~SB7)。Ⅰ型层序界面主要包括:侏罗系延安组(J1-2y)与上三叠统延长组(T3y)之间的界面TSB1—对应地震剖面上的Ty;延安组(J1-2y)与直罗组(J2z)界面TSB2—对应地震剖面上的Tz-1;侏罗系与白垩系层序界面TSB3—对应地震剖面上的Tk。TSB1、TSB2和TSB3Ⅰ型层序界面主要为区域性质的不整合面,反映了中生代构造活动在盆地中的响应;Ⅱ型层序界面主要为气候转化面,反映了层序地层单元形成过程中古气候因素引起的旋回变化。微量元素Sr、Cu、Sr/Cu、FeO/MnO、Al2O3/MgO等比值垂向变化总体上反映延安期至直罗期古气候环境经历了温暖潮湿—干湿交替—干旱—半干旱的转变过程,直罗组底部不整合界面TSB2及上段红层广泛发育的起始界面SB6为古气候环境突变的关键界面。此外,本区三维地层结构显示,侏罗系延安组至直罗组具有明显的“垂相分带”特征,铀矿层在三维空间中主要呈板状赋存于TSB2界面之上的“泛连通厚”辫状河道砂体中,其产出明显受侏罗系垂相分带结构和古气候环境变迁因素的共同制约。本文建立的综合识别层序界面方法减少了层序地层研究中依靠人为经验识别的随意性,为本区侏罗系层序划分和等时地层格架建立提供重要依据。关键层序界面的时空属性及其所指示的地质意义对揭示燕山幕式构造活动发生、发展过程对古气候条件变迁和砂岩型铀大规模成矿作用的影响具有重要意义。
Abstract:On the basis of outcrop, drilling cores seismic, logging and geochemical data, the main sequence boundary surfaces of the Yan'an and Zhiluo Formation of Jurassic on the northeast margin of Ordos basin were systematically studied. On outcrop profiles and drilling cores, the sequence boundary surfaces show characteristics of iron weathering crust, truncation and lithologiclithofacies transformation. On seismic profiles, the boundaries are featured by onlap, downlap and truncation. The rock-electricity relation indicates different types of mutations. The trace elements also show mutation characteristics. Ten different orders of sequence boundaries were identified, including three I-type(TSB1-TSB3)and seven Ⅱ-type(SB1-SB7)sequence boundary surfaces. Ⅰ-type boundaries include TSB1 sequence boundary surface between Yan'an(J1-2y)and Yanchang Formation(T3y), corresponding to Ty in seismic profiles; TSB2 sequence boundary surface between Yan'an(1-2y)and Zhiluo Formation(J2z), corresponding to Tz-1 in seismic profiles; TSB3 sequence boundary surface between Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous, corresponding to Tk in seismic profiles. As regional unconformities, Ⅰ-type sequence boundaries including TSB1, TSB2, TSB3 reflected tectonic activity during Mesozoic period. The Ⅱ-type sequence boundaries were main climate transformation surfaces and showed the cyclic changes in climate factors. The vertical variations of values of Sr, Cu, Sr/Cu, FeO/MnO and Al2O3/MgO indicate that the paleoclimate and paleoenvironment experienced a changing process from warm-humid climate to dry-wet alternation, arid and semi-arid climate; TSB2 and SB6 were main climate transformation surfaces. Vertical zonation of stratigraphic structure is obvious between Yan'an and Zhiluo Formation on the 3D models of the study area. The uranium bodies mainly lie in the large sandstone overlying TSB2 sequence boundary surface, in the form of plate on the 3D models of sandstone and uranium mineralization bed. The uranium bed was obviously influenced by the vertical zonation of stratigraphic structure and paleoclimate transformation. The integrated identification of sequence boundaries will not only reduce the casualty of artificial empirical recognition but also provide a basis for the division of Jurassic sequences and the establishment of isochronous sequence stratigraphic framework. The research on space-time attributes and the indicated geological meanings of the main sequence boundary surfaces will be helpful to revealing the process of "Yanshan movement" and its influence on the paleoclimate transformation and sandstone-type uranium mineralization.
-
1. 引言
莱州湾位于渤海盆地南部,湾口朝北,呈半圆形,系渤海南部最大海湾,东部与胶东半岛相连,西部与现代黄河三角洲接壤。自晚更新世以来,随着冰期、间冰期气候变化以及海面多次升降,渤海发生了沧州海侵、献县海侵和黄骅海侵以及它们之间的海退事件(秦蕴珊,1985)。期间,相应沉积了海相、陆相及陆海交互相沉积层,在莱州湾南岸由弥河、白浪河、虞河、潍河、胶莱河等共同形成了多源、短源河流三角洲沉积体系,潍河—弥河三角洲向海进积20~55 km,现今海岸局部加积厚度超过20 m(薛春汀,2008)。
莱州湾潮流属于非正规半日潮,以往复流为主。在黄河口附近流速达最大,从湾口向湾顶递减。莱州湾南岸系中国典型的淤泥质海岸,地处济阳坳陷中的潍北凹陷构造单元,并长期处于沉降活动中。进入晚更新世以来,受全球气候环境变化的影响,海侵—海退活动与海岸线变迁频繁,交替发育了海相和陆相地层,蕴涵丰富的沉积环境演化信息,吸引众多学者对本区沉积环境的研究兴趣(李守军等,2017;彭子成等,1992;庄振业等,1999)。如利用钻孔沉积记录,重建渤海西岸沉积演化历史,定量讨论全新世相对海面变化(陈永胜等,2016)。进行中国近海沿岸沉积地球化学变异特征与物源及气候效应分析(赵一阳等,2002),探讨渤海西部沉积物稀土元素分布特征及其物源约束,开展海底沉积物来源、形成条件和控制因素研究(刘建国等, 2010;蓝先洪等, 2016)。彭子成等(1992)等运用热释光测年和地球化学数据揭示了晚更新世以来莱州湾沉积特征。庄振业等(1999)以S3钻孔为主,阐明渤海南部莱州湾晚第四纪以来海陆变迁及古环境演变。韩德亮(2001)发现元素特征值周期性旋回及突变,作为第四纪地层划分指标。刘恩峰等(2004)基于莱州湾南岸A1钻孔孢粉,分析植被及古气候交替变化,重建120 ka B.P.以来莱州湾古气候环境特征,探讨沉积物元素与陆源输入联系(杨守业和李从先,1999)。王志才等(2006)认为构造活动、海面变化以及陆源河流输入控制着莱州湾晚更新世以来沉积地层变化。总体上,黄河所提供的沉积物对渤海沉积控制作用明显,但不应忽视入海的中小短源河流(如弥河、白浪河、潍河等)对莱州湾沉积贡献。本文选择莱州湾剖面进行沉积地层划分和对比,结合调查资料和测试数据,初步建立浅地层沉积格架,深入了解沉积环境差异性,为陆海统筹、围填海工程及海洋环境提供沉积环境依据。
2. 材料和方法
沉积物样品均取自于研究区钻孔,样品间隔取样深度为2~10 cm,样品编号按井号加上取样顺序编录,对该孔岩心进行了岩性描述、14C测年、光释光测年以及粒度等测试,以获得研究区110 ka B.P.以来的沉积地层和沉积环境的演化特征以及沉积物源变迁过程。采用X荧光光谱法(XRF)、等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)以及原子荧光光谱法(AF)进行沉积物样品元素化学测试,样品测试由国土资源部青岛海洋地质实验检测中心完成。AMS14C样品测试由美国BETA实验室完成,测年的半衰期为4850 a。测试完成后,依据样品的δ13C测试数据,并结合分馏效应对数据进行校正,得到惯用年龄。
物源指数(PI)反映的是沉积物间化学成分接近程度,PI值介于0和1之间。选择差别较大的元素区分端元物源,当PI值小于0.5,表明待判沉积物与端元沉积物1化学组成相近;而PI值大于0.5,表明待判沉积物与端元沉积物2化学组成相近。用物源指数(PI)分析物源变化和计算沉积贡献(蓝先洪等,2010;庞守吉等,2008),PI计算公式如下:

式中:i为元素或两元素之比;Cix为待判沉积物中元素i的含量;Ci1、Ci2为端元沉积物1和端元沉积物2中元素i含量,本文指黄河与白浪河沉积物。
3. 沉积特征
WFZK07孔位于山东潍坊北部的围填海区,距莱州湾南岸白浪河入海口东约1 km处(图 1)。该孔于2013年6月完成施工,孔深80.0 m,人工回填深度5.80 m。沿南北方向将该孔与渤海其他钻孔进行沉积对比,综合莱州湾地质浅钻的岩心记录、测试数据以及前人研究成果(彭子成等,1992;庄振业等,1999;Yao et al., 2014),依据钻孔沉积物沉积特征,进行不同沉积单元沉积相划分,共划分为5个沉积单元(DU1~DU5),初步建立莱州湾浅部沉积结构框架(图 2)。其中,BH-1301、WFZK06、WFZK04、WFZK09、WFZK03、WFZK04"孔的数据来源于中国地质调查项目“山东半岛海岸带综合地质调查与监测”(项目编号:GZH201200505),BH08孔的数据来源于Yao et al., 2014;WFZK06、WFZK09、WFZK03孔未作测年)。
沉积单元DU1:以黏土质粉砂、粉砂为主,在BH-1301和WFZK07孔中DU1单元的底部有约2 cm厚泥炭层,该泥炭层在莱州湾分布广泛,据AMS14C测年为9649 cal a B.P.,可作为全新世底界标志层,如图 2所示,沉积厚度相对稳定(< 30 m),由海向陆沉积减薄。主要为河流—三角洲/潮坪—滨浅海相沉积。
沉积单元DU2:细砂—中砂,沉积厚度4~10 m,多以河流相沉积为主,由海向陆沉积减薄。系晚更新世晚期玉木晚冰期的河流—三角洲—滨浅海相沉积。
沉积单元DU3:以黏土质粉砂、粉砂为主。陆相层为细砂夹粉砂。系晚更新世玉木冰期亚间冰期的河流—三角洲/潮坪—浅海相沉积,由于海面频繁波动,形成数个海陆交互相沉积地层。此间沉积厚度10~20 m,尤其在三角洲前缘沉积厚度较大。
沉积单元DU4:BH1301孔中以黏土质粉砂和粉砂为主,WFZK07孔以砂为主,夹粉细砂和泥砾透镜体。该单元形成于晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期,沉积厚度十余米,在三角洲前缘沉积厚度较大。通过与邻近海域和陆上钻孔对比,三角洲和河流相沉积发育,前三角洲黏土质粉砂是多条短源河流共同贡献的结果,各河流形成的三角洲前缘主要由极细砂组成,河口间湾主要为黏土质粉砂沉积,由于分流河道的频繁迁移,三角洲前缘极细砂和河口间湾黏土质粉砂在纵向上叠置出现。
沉积单元DU5:以黏土质粉砂为主,夹粉细砂层,有粉砂质透镜体和黏土质条带,系晚更新世里斯—玉木间冰期的河流—三角洲/潮坪—浅海相沉积,沉积厚度较稳定,十几米不等,海相沉积厚度薄。
4. 沉积物源
本文以WFZK07孔的δEuN-ΣREEs关系和物源判别指数(PI)进行沉积物源分析,研究渤海南部短源河流(白浪河)和黄河的陆源输入对沉积体系的贡献。
据本文实测和文献数据(古森昌等,1989;吴明清等,1991;石学法等,1996),δEuN与ΣREEs关系曲线如图 3(y=-170.61nx + 63.38,R2=0.729)。在WFZK07孔的5个沉积单元选取15个样品,进行数据成图。图中可见,数据点分布相对均匀,深度5.80~18.58 m、23.27~49.15 m和18.58~23.70 m的样品多数分布于白浪河沉积区,而深度49.15~63.70 m和63.70~80.00 m的样品大都集中落在黄河沉积区。白浪河数据大都落于曲线下方(白浪河沉积区),黄河数据多落在曲线上方(黄河沉积区)。
相关性分析可知,白浪河中La/Sm及ΣLREE/ ΣHREE与粒度的相关性弱;与黄河沉积物稀土元素含量对比(蓝先洪等,2009;Lim,2006),白浪河沉积物中的La、Sm、LREE、HREE含量相对偏差均大于10%。因此,本文采用对粒度影响较小的La/Sm及LREE/HREE比值计算物源指数。
WFZK07孔沉积物中的La/Sm及LREE/HREE比值及所计算的PI值表明(表 1),以49.15 m为界,上部以白浪河沉积贡献为主,下部黄河沉积贡献加大。5.80~18.58 m底界面AMS14C测年为11.6 ka B. P.,为全新世以来的海陆交互层,包括早全新世陆相层、中全新世黄骅海侵层和晚全新世陆相层。此阶段全新世的黄骅海侵范围较大,持续时间短,加之黄河频繁改道,物源以白浪河为主。18.58~23.70 m底界面OSL测年为24.0 ka B.P.,为晚更新世晚期玉木主冰期河流相沉积。此阶段海面下降,以近源河流为主,远源的陆源输入较少。23.27~49.15 m底界面OSL测年为61.0 ka B.P.,为晚更新世晚期形成的献县海侵层及其陆相层。以上海侵事件,以晚更新世晚期的献县海侵范围最小。此外,晚更新世晚期海退期的古黄河三角洲沉积物重矿物组合受现代黄河沉积物的物源控制(蓝先洪等,2010),因黄河已流入黄海陆架区,是东海陆架和黄海区的主要物源(韩有松和吴洪发,1982),黄河对莱州湾的沉积贡献相对减小,以白浪河等短源河流为主要物源。
表 1 莱州湾WFZK07孔沉积物物源指数(PI)比较Table 1. Comparison of provenance indexes (PI) of sediments in Core 07
49.15~63.70 m底界面OSL测年为74.0 ka B.P.,为晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期的陆相层,以浅灰、浅黄色黏土质粉砂夹细粉砂及薄互层为主。受区域新构造活动影响,早更新世发生由相对隆起向绝对沉降转换,黄河贯通成为可能(杨守业等,2001)。因此,早更新世黄河全河贯通而形成一条完整河流,影响华北平原地区(Wang,2007),现代黄河改道几乎都经历漫流、汊流、归股、改道等阶段(庄振业,1991)。在地质历史时期,黄河改道频繁且河道行踪不定,晚更新世晚期黄河由东入海的格局转到向北入渤海的过渡阶段,发生漫流和汊流,使其可能成为主要物源。63.70~80.00 m底界面OSL测年为128 ka B.P.,为晚更新世早期的沧州海侵层。在地史时期,黄河主要流路位于华北平原。短源河流输入量小,易受气候变化影响。在海面上升期,以黄河为主要物源,表现退积的叠加样式。
总体上,海侵期温暖湿润,沉积物粒度细,以化学风化为主,矿物元素富集。海退期寒冷干燥,化学风化作用弱,以物理风化为主,矿物含量较低(操应长等,2007)。如Si/Al和Ti/Al在垂向上的变化反映了莱州湾在全新世和晚更新世的冰期搬运动力及化学风化作用相对较弱;与之对应,从晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期到晚更新世早期,化学风化较强(Nesbitt et al., 1997;Zabel et al., 2001),Rb/Sr值与风化强度成正比。Mg/Ca从晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期到晚更新世早期发生较大波动,表明莱州湾沉积环境及物源在晚更新世晚期发生了重要的转变。全新世、晚更新世早期及晚期的海相层中常微量元素及特征值元素呈明显的旋回变化,对应多个峰值。在晚更新世晚期的陆相地层中,矿物元素变化弱;晚更新世早期陆相地层中,元素变化幅度较小,对应多个峰值。矿物元素的变化所反映的沉积特征与晚更新世以来的气候和海面的变化有对应关系,指示海侵海退过程中的沉积环境及海面可能发生过多次改变。此外,在海退成陆时期,长期蒸发作用和季节性河流物质运输形成卤水存储,在蒸发泵和回流渗滤的共同作用下,发生盐份的向下运移、累积、分馏、矿物蚀变,陆相沉积物掩埋了前期高盐水成为地下卤水(高茂生等,2015;彭子成等,1992)。其中,第Ⅰ海相层中卤水TDS值50~130 g/ L,第Ⅱ海相层中卤水TDS值50~165 g/L,第Ⅲ海相层中卤水TDS值50~140 g/L,以第Ⅱ海相层的卤水TDS值高,储量大。
5. 讨论
晚更新世早期的沧州海侵期海相层(Qp31,距今约124.6~72.0 ka B.P.):海面上升,PI平衡线向陆源移动(图 4a)。古岸线大致在花官—卧铺南部—寿光北部—潍北总场—龙池北部一带(郑懿珉等,2014),此阶段海面处于上升期,陆源碎屑物质供应少,为退积叠加。黄河与白浪向海沉积贡献量降低,但在波浪、潮汐及沿岸流影响下,远源河流平均径流量大,携带大量泥沙的黄河沉积贡献仍大于白浪河,为晚更新世以来全球最高海面期。据渤海南岸羊口盐场附近E钻孔(韩德亮等,2001),现代黄河三角洲的9个钻孔(王绍鸿等,1979)以及本文研究,此阶段气候温暖湿润,化学风化较强,北部河流相发育,三角洲发育不全,向南过渡为以细粒为主的潮坪或沼泽沉积。
![]() 图 4 莱州湾主要海侵线、地下卤水分布及PI平衡线图(据高茂生等,2015修改)Figure 4. Three transgressions, underground brine and PI in Laizhou Bay
图 4 莱州湾主要海侵线、地下卤水分布及PI平衡线图(据高茂生等,2015修改)Figure 4. Three transgressions, underground brine and PI in Laizhou Bay晚更新世晚期的玉木早冰期陆相层(Qp33,距今72.0~60.0 ka B.P.):海面下降,以黄河为主的陆源输入量增加,PI平衡线向河流漂移(图 4b)。由于黄河径流量大,携带泥沙多,影响范围广,南部河流发育,向北发展为三角洲—浅海相沉积。进积时间短,陆源输入量充足,与沧州海侵期的沉积相差不大。
晚更新世晚期献县海侵层(Qp33,距今60.0~ 24.4 ka B.P.):海面上升幅度大,PI平衡线向北离陆移动。海侵范围远,古岸线大致在莱州湾南岸的广饶南—寿光—固堤北—昌邑北—新河—土山—沙河口一带。碎屑物质供应少,黄河、白浪河的沉积贡献降低,但沉积空间增大,属沉积退积。晚更新世晚期黄河已流入黄海陆架区,短源河流为主要物源。南部河流沉积发育,向北过渡到三角洲或潮坪、沼泽沉积,再到浅海相沉积。
此期有多个波峰和波谷,对应多次海面波动发生,形成海陆交互层。与沧州海侵相比,此阶段气候暖湿,化学风化作用弱。与刘恩峰等(2004)用孢粉反演古气候的变化一致,气候属于由干冷向暖湿转变的过渡期,受波浪和潮汐的共同作用,海相层发育。经历了“陆—海—陆”的演变,属于大理亚间冰期的滨岸湖沼相沉积环境。
晚更新世晚期玉木主冰期陆相层(Qp33,距今24.4~10.2 ka B.P.):PI平衡线向黄河(西北方向)偏移。此阶段天气寒冷干燥,海面处于下降阶段,莱州湾大部分地区有陆相河流沉积,厚度小。黄河沉积贡献增加,表现为进积的叠加样式。
全新世黄骅海侵(Qh,距今10.2~4.0 ka B.P.):PI平衡线向北移动加剧(图 4c)。海侵范围最远达到花官北—寿光北—固堤南—昌邑北—新河—土山—虎头崖一带。海面处于上升期,沉积退积。白浪河和黄河沉积贡献逐渐降低,黄河频繁改道,不同地区的物源存在差异性。北部滨浅海相沉积发育,南向三角洲、潮坪、沼泽过渡。在此时期,多数矿物元素对应1个峰和1个谷,表明海面发生过一次升降和气候冷暖变化。依据刘恩峰等(2004)研究,在10.0~4.0 ka B. P.期间莱州湾沿岸属于暖湿的滨海沉积,渤海西岸海侵事件比本区晚约2000a(徐家声,1994),在全新世中期(6.0 ka B.P.)海侵范围达到最远,此后海水消退。在全新世晚期,海面开始下降,现代河流沉积发育。
总体上,海侵期,由陆向海黄河泥沙贡献增加,白浪河等短源河流沉积贡献降低;浅海相沉积发育,以三角洲、潮坪为沉积过渡,表现为退积叠加。海退期,陆源输入增加,河流或湖泊沉积发育,表现为进积叠加。晚更新世以来莱州湾大致经历了浅海—三角洲—潮坪—浅海—三角洲—陆相或湖泊的沉积演化。
全球海面变化研究表明(Waelbroeck,2002),晚更新世以来至少存在3次高海面时期和2次低海面时期。莱州湾晚更新世的海面变化也出现“三高两低”的趋势。但由于区域差异和构造背景的不同,莱州湾海面升降时间与升降幅度与相邻海区存在差异性。
莱州湾从128.0 ka B.P.开始进入晚更新世,其中124.6~72.0 ka B.P.为温暖的末次间冰期,对应发育有沧州海侵层;晚更新世的后半段,72.0~10.2 ka B. P.为寒冷的末次冰期;全新世(10.2~0.0 ka B.P.)为温暖的冰后期。末次间冰期气候相对温暖湿润,沉积物粒度小,化学风化作用较强,常微量元素在此阶段地层中富集。末次冰期气候寒冷干燥,以物理风化为主,多数元素在此阶段的沉积含量较低。Si/Al和Ti/Al在剖面上的变化反映了莱州湾在全新世和晚更新世的冰期搬运动力及化学风化作用相对较弱;与此对应,CIA相对不高,从晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期到晚更新世早期,化学风化作用较强,晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期之后,化学风化作用减弱;Rb/ Sr值与风化强度成正比。Mg/Ca从晚更新世晚期玉木早冰期到晚更新世早期才发生较大的波动,表明莱州湾的沉积环境及物源在晚更新世晚期发生了重要转变。在全新世、晚更新世早期及晚期的海相层中,常量、微量元素及元素特征值呈明显的旋回变化,对应多个峰值。在晚更新世晚期的陆相地层变化小;晚更新世早期陆相地层中变化较缓,对应多个峰值。这种元素地球化学变化指示了海侵—海退过程中的沉积环境以及海面发生过多次改变,所反映的沉积特征与晚更新世以来的气候和海面变化有较好的对应关系。
莱州湾在124.6~72.0 ka B.P.,60.0~24.4 ka B.P.,10.2~0.0 ka B.P.出现3次暖湿期,分别对应于沧州海侵、献县海侵、黄骅海侵,在3次暖湿期中发育海陆交互相滨浅海、三角洲相或潮坪及河流相沉积环境,分别对应里斯—玉木间冰期、玉木亚间冰期以及玉木冰后期。3次海侵的范围分别在花官—卧铺南部—寿光北部—潍北总场—龙池北部、广饶南—寿光—固堤北—昌邑北—新河—土山—沙河口和花官北—寿光北—固堤南—昌邑北—新河—土山—虎头崖一带,献县海侵的范围最远,其次为全新世的黄骅海侵,晚更新世早期的沧州海侵范围最近。这与吕厚远(1989)利用渤海南部的4个钻孔和2个剖面的孢粉样分析的结果相吻合,即渤海南部晚更新世以来有3次较湿润期和2次高降水量较大期。在72.0~60.0 ka B.P.和24.4~10.2 ka B.P.期间,为2次干冷的陆相沉积环境,分别对应玉木早冰期和玉木晚冰期。而地球化学元素所反映的晚更新世以来莱州湾古气候演化与全球性的气候事件及渤海沿岸古环境变化有较好的可比性。
6. 结论
(1)受控于黄河陆源碎屑输入和南部中小河流的共同影响,二者在各自阶段对莱州湾沉积演化起主导作用,莱州湾沉积物源存在阶段性和分期性。
(2)莱州湾地球化学变化所反映的沉积特征与晚更新世以来的气候和海面变化有明显的对应关系,晚更新世以来经历的3次高海面和2次低海面期,对应发生了3次海侵及海退事件。晚更新世早期PI线向陆南移,晚更新世晚期海面上升,PI线向海北移,全新世PI线北移加剧。
(3)晚更新世以来莱州湾经历了浅海—三角洲—潮坪—滨浅海—三角洲—陆相或湖泊的演化过程。海侵期主要发育滨浅海相沉积,向南退积为三角洲/潮坪—河流沉积;由陆向海,短源河流沉积贡献降低,黄河沉积贡献增加。海退期陆源输入增加,河流相及三角洲进积发育。
-
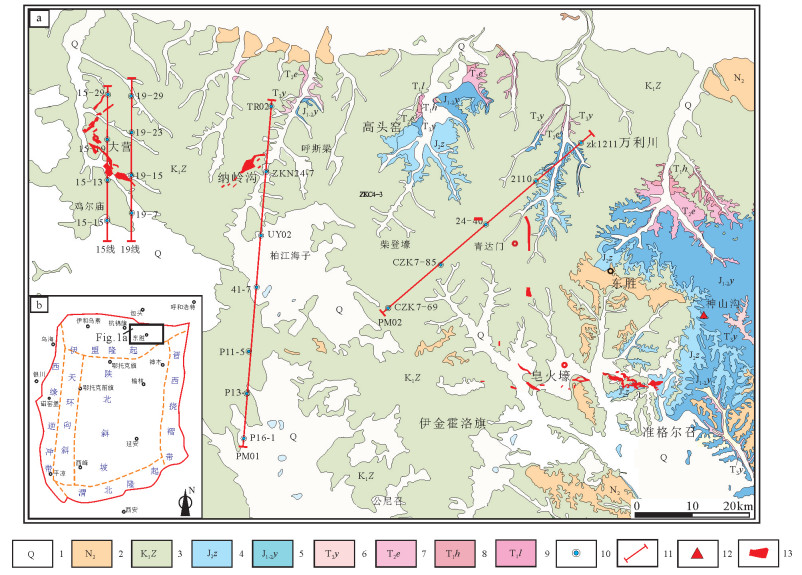
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘东胜地区地质简图(a)及构造位置图(b,据杨俊杰和裴锡古,1996修改)
1—第四系;2—新近系上新统;3—下白垩统志丹群;4—中侏罗统直罗组;5—中—下侏罗统延安组;6—上三叠统延长组;7—中三叠统二马营组;8—下三叠统和尚沟组;9—下三叠统刘家沟组;10—主要钻孔位置;11—文中剖面位置;12—地球化学和孢粉样品取样位置;13—砂岩铀矿床
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Dongsheng area on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin (a) and tectonic division of the study area(b, modified from Yang Junjie and Pei Xigu, 1996)
1-Quaternary; 2-Pliocene; 3-Lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 4-Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 5-Lower-Middle Jurassic Yan, an Formation; 6-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 7-Middle Triassic Ermaying Formation; 8-Lower Triassic Heshanggou Formation; 9-Lower Triassic Liujiagou Formation; 10-Location of drill hole; 11-Location of stratigraphic correlation profiles; 12-Sampling location; 13-Sandstone-type uranium deposits
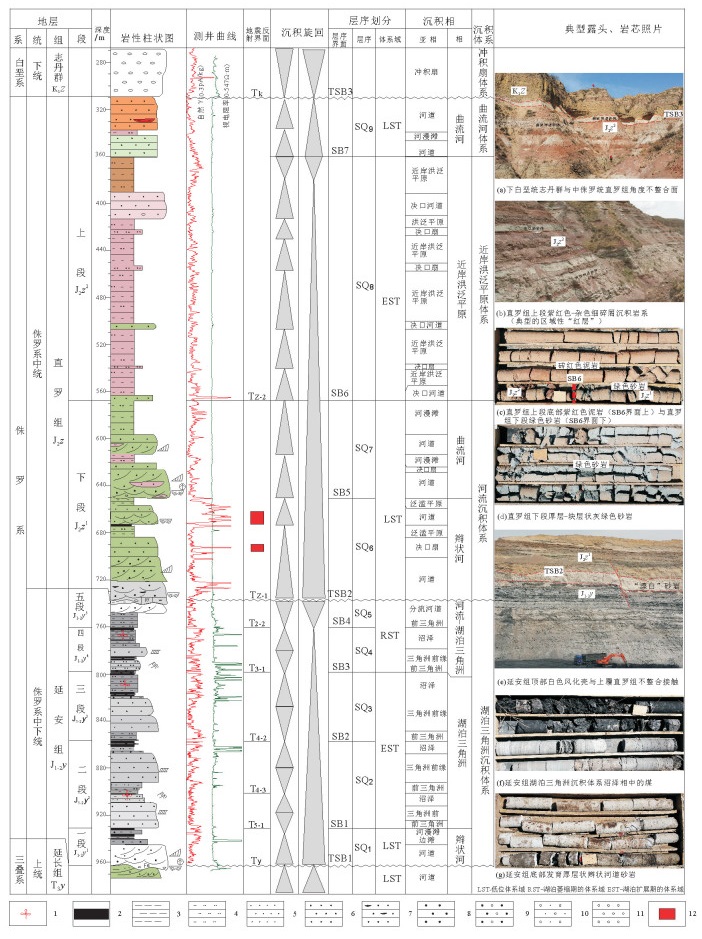
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地大营地区侏罗系典型剖面层序地层划分及关键层序界面
1—植物化石;2—煤层;3—泥岩;4—粉砂岩;5—细砂岩;6—中砂岩;7—含炭屑砂岩;8—粗砂岩;9—含砾粗砂岩;10—砂质砾岩;11—砾岩;12—铀矿层
Figure 2. Sequence classification and main sequence boundary surfaces of the Jurassic in the Daying area on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin
1-Fossil; 2-Coal bed; 3-Mudstone; 4-Siltstone; 5-Fine sandstone; 6-Sandstone; 7-Carbon-bearing sandstone; 8-Gritstone; 9-Conglomerate-bearing gritstone; 10-Sandy conglomerate; 11-Conglomerate; 12-Uranium bed
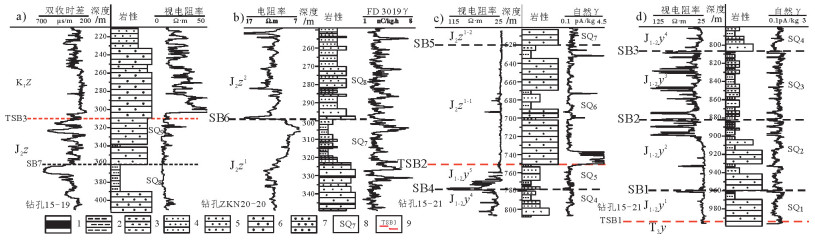
图 3 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘高头窑—神山沟地区侏罗系延安组—直罗组层序界面露头特征
a、b—神山沟和高头窑地区下白垩统志丹群不整合超覆于侏罗系、三叠系不同地层单元之上, 不整合界面TSB3之上砂砾充填削切了下伏的部分地层;c—神山沟地区直罗组上段与下段整合接触面(层序界面SB6),直罗组下段内部发育1~2条薄煤层(区域上连续性差);d—神山沟地区直罗组与延安组微角度不整合面(层序界面TSB2);延安组顶部发育厚层高岭土化“漂白”砂岩;e—神山沟地区延安组内部四段与五段整合面(层序界面SB4),延安组五段顶部由于煤自燃形成的烧变岩;f—延安组区域性水进界面的露头识别标志—植物根土层;g、h—高头窑地区延安组与延长组角度不整合面(层序界面TSB1),发育区域性的铁质风化壳
Figure 3. Outcrop profiles characteristics of sequence boundary surfaces from Yan'an Formation to Zhiluo Formation in the Gaotouyao and Shenshangou area on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin
a, b-Unconformable contact between Lower Cretaceous Zhidan Formation and Jurassic/Triassic in the Gaotouyao and Shenshangou area; c-SB6 sequence boundary between upper and lower member of Zhiluo Formation.1-2 coal line inside lower member of Zhiluo Formation; d-Microunconformable contact between Yan, an and Zhiluo Formation in the Shenshangou area; kaolinization sandstone on the top of Yan'an Formation; eSB4 sequence boundary conformable contact inside Yan'an Formation; burned sandstone on the top of Yan'an Formation; f-Plant root soil being the identification symbol of the sequence boundary inside Yan'an Formation; g, h-Regional iron weathering crust (TSB1) : Unconformable contact between Yan'an and Yanchang Formation
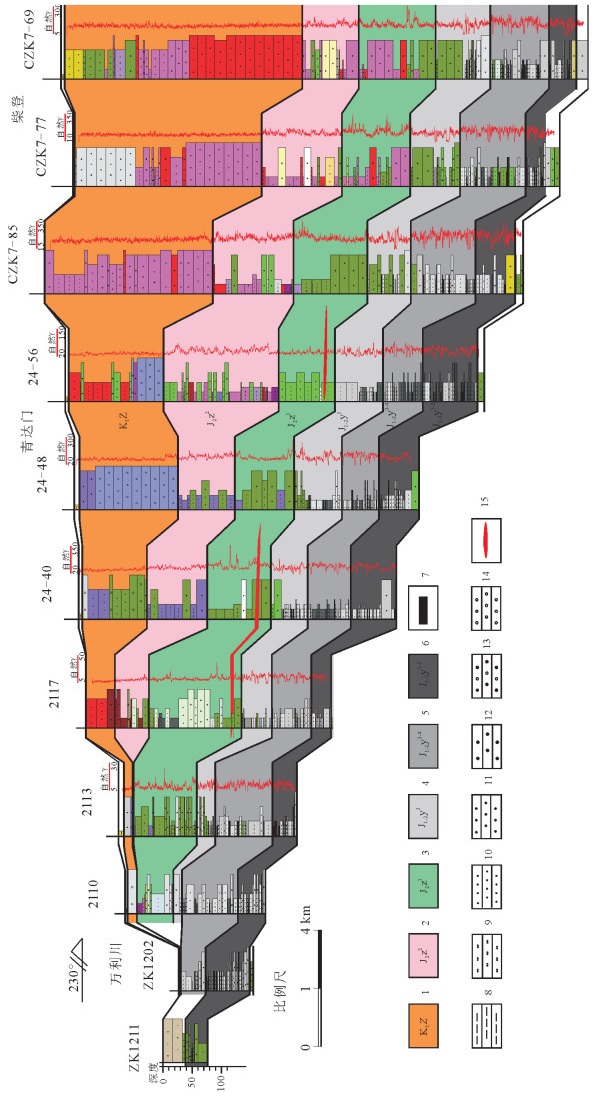
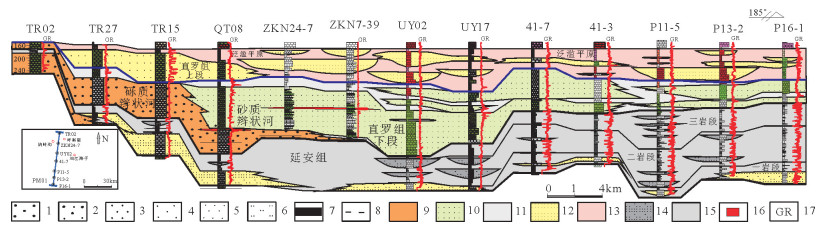
图 10 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘万利川—柴登地区侏罗系—下白垩统地层对比剖面(PM2,北东-南西向)
1—下白垩统志丹群;2—中侏罗统直罗组上段;3—中侏罗统直罗组下段;4—中—下侏罗统延安组五段;5—中—下侏罗统延安组三至四段;6—中—下侏罗统延安组一至二段;7—煤层;8—泥岩;9—粉砂岩;10—细砂岩;11—中砂岩;12—粗砂岩;13—含砾粗砂岩;14—砾岩;15—铀矿层
Figure 10. Stratigraphic correlation profile of Jurassic and lower Cretaceous in the Wanlichuang-Chaideng area, the northeastern margin of Ordos basin (PM2, Direction NE-SW
1-The lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 2-The upper member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 3-The lower member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 4-The fifth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 5-The third-fourth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 6-The first-second part of Yan, an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 7-Coal bed; 8-Mudstone; 9-Siltstone; 10-Fine sandstone; 11-Sandstone; 12-Gritstone; 13-Conglomerate-bearing gritstone; 14-Conglomerate; 15-Uranium bed
图 4 鄂尔多斯盆地大营地区侏罗系延安组—直罗组在地震剖面上的反射终止类型与层序界面的识别
1—下白垩统志丹群;2—中侏罗统直罗组上段;3—中侏罗统直罗组下段;4—中—下侏罗统延安组;5—上三叠统延长组;6—煤层;7—泥岩;8—粉砂岩;9—细砂岩;10—中砂岩;11—粗砂岩;12—含砾粗砂岩;13—砂质砾岩;14—砾岩;15—自然γ曲线;16—视电阻率曲线;17—层序界面;18—地震反射界面
Figure 4. Types of reflection termination and sequence boundaries identification of the Jurassic Yan'an—Zhiluo Formation on seismic profiles in the Daying area, Ordos basin
1-Lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 2-The upper member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 3-The lower member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 4-Lower-Middle Jurassic Yan, an Formation; 5-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 6-Coal bed; 7-Mudstone; 8-Siltstone; 9-Fine sandstone; 10-Sandstone; 11-Gritstone; 12-Conglomerate-bearing gritstone; 13-Sandy conglomerate; 14-Conglomerate; 15-Natural gamma ray curve; 16-Apparent resistivity curve; 17-sequence boundary; 18-Reflection termination of seismic profile
图 5 鄂尔多斯盆地大营地区侏罗系延安组—直罗组层序界面岩—电响应特征
1—煤层;2—泥岩;3—粉砂岩;4—细砂岩;5—中砂岩;6—粗砂岩;7—砾岩;8—层序;9—层序界面
Figure 5. Electrical properties of sequence boundary surfaces from the Jurassic Yan'an Formation to Zhiluo Formation in the Daying area, Ordos basin
1-Coal bed; 2-Mudstone; 3-Siltstone; 4-Fine sandstone; 5-Sandstone; 6-Gritstone; 7-Conglomerate; 8-Sequence; 9-Sequence boundary
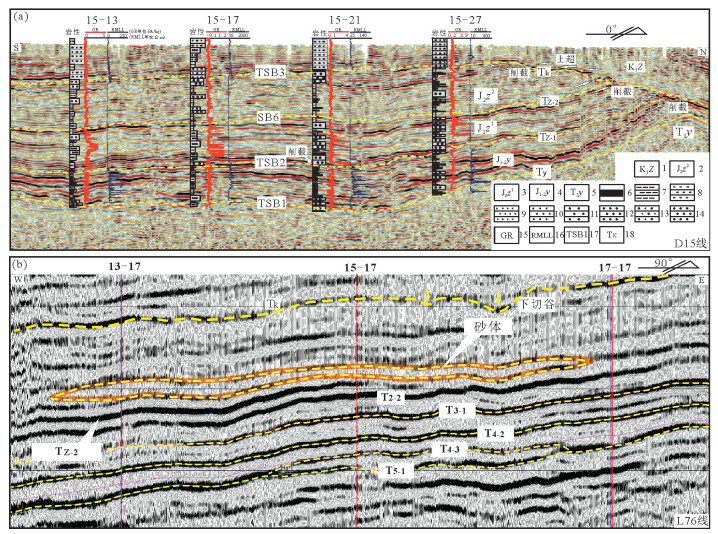
图 7 鄂尔多斯盆地大营地区侏罗系延安组—直罗组关键层序界面及地层结构特征(15勘探线)
1—下白垩统志丹群;2—中侏罗统直罗组上段;3—中侏罗统直罗组下段;4—中—下侏罗统延安组五段;5—中—下侏罗统延安组三至四段;6—中—下侏罗统延安组一至二段;7—上三叠统延长组;8—自然γ曲线;9—层序界面
Figure 7. Characteristics of the main sequence boundary surfaces and stratigraphic structure of the Jurassic Yan'an and Zhiluo Formation in the Daying area, Ordos basin (No. 15 exploration line)
1-The lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 2-The upper member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 3-The lower member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 4-The fifth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 5-The third-fourth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 6-The first-second part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 7-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 8-Natural gamma ray curve; 9-Sequence boundary
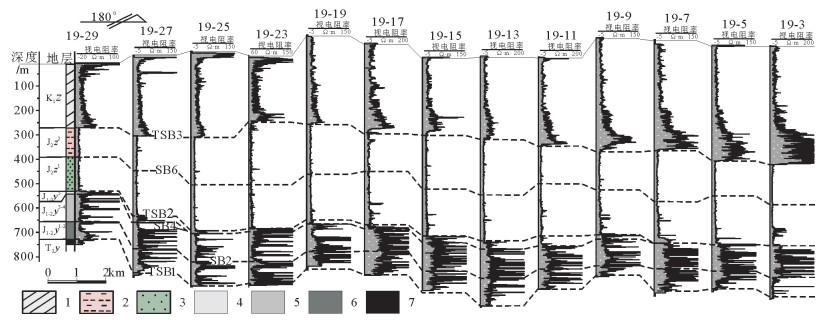
图 6 鄂尔多斯盆地大营地区侏罗系延安组—直罗组视电阻率连井剖面图(19号勘探线)
1—下白垩统志丹群;2—中侏罗统直罗组上段;3—中侏罗统直罗组下段;4—中—下侏罗统延安组五段;5—中—下侏罗统延安组三至四段;6—中—下侏罗统延安组一至二段;7—上三叠统延长组
Figure 6. Apparent resistivity profile of the Jurassic Yan'an and Zhiluo Formation in the Daying area, Ordos basin (No. 19 exploration line)
1-The lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 2-The upper member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 3-The lower member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 4-The fifth part of Yan, an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 5-The third-fourth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 6-The first-second part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 7-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation
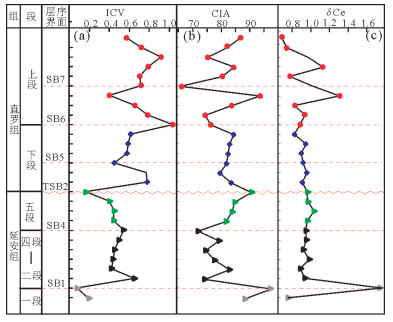
图 8 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘侏罗系关键层序界面在微量元素比值上的响应特征(据张天福等,2016修改)
Figure 8. Trace elements ratios characteristics of main Jurassic sequence boundary surfaces on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin (modified from Zhang Tianfu et al., 2016)
图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗系延安组、直罗组ICV、CIA指数值及δCe值随剖面垂向上变化趋势图(样品均采自鄂尔多斯市神山沟地区,岩性为泥岩、粉砂质泥岩,图据张天福等,2016修改)
Figure 9. Variable trend map of ICV, CIA & Ce for Yan'an Formation and Zhiluo Formation on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin(All of 28 mudstone and siltstone samples from Shen Shangou area, the northeastern margin of Ordos basin; modified from Zhang Tianfu et al., 2016)
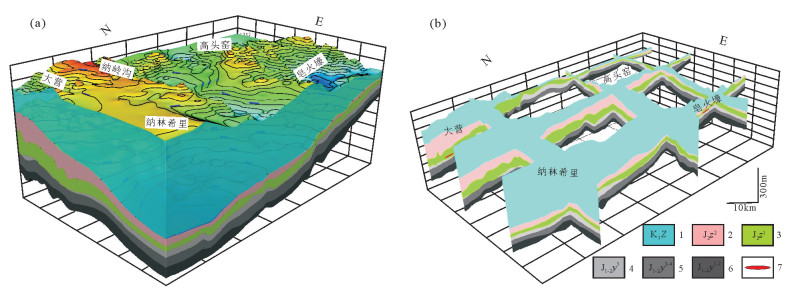
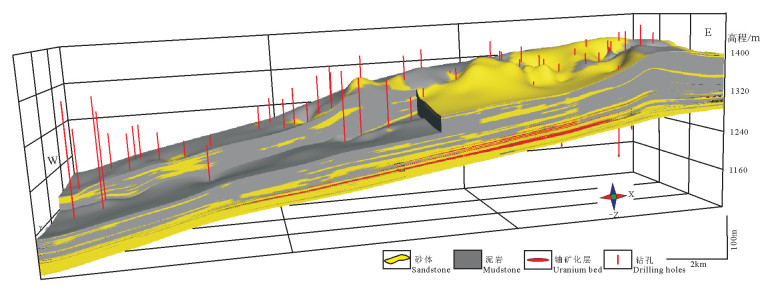
图 11 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘三维地层结构模型及栅格图(基于3200口钻孔数据,平均钻孔网度2km×2km)
1—下白垩统志丹群;2—中侏罗统直罗组上段;3—中侏罗统直罗组下段;4—中—下侏罗统延安组五段;5—中—下侏罗统延安组三至四段;6—中—下侏罗统延安组一至二段;7—铀矿层
Figure 11. Models of 3D stratigraphic structure and grid map on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin(based on 3200 drill holes, average drilling grid 2km×2km)
1-The lower Cretaceous Zhidan Group; 2-The upper member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 3-The lower member of Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 4-The fifth part of Yan, an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 5-The third-fourth part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 6-The first-second part of Yan'an Formation, Lower-Middle Jurassic; 7-Uranium bed
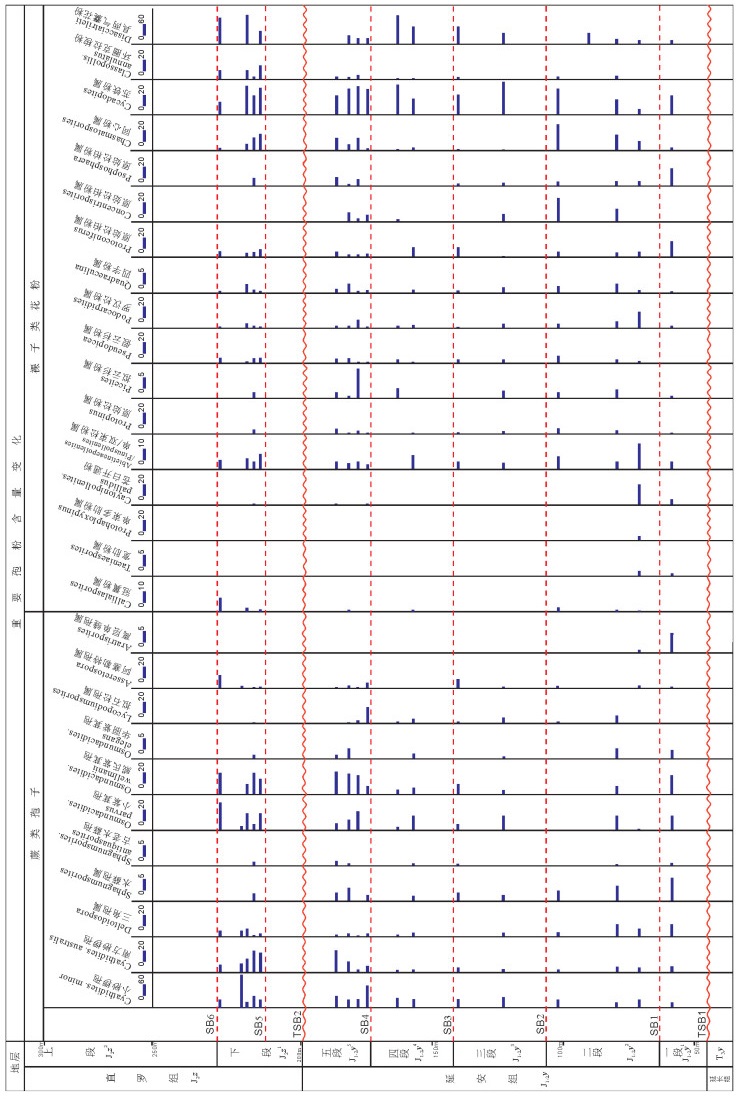
图 13 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘神山沟延安组—直罗组孢粉含量变化图(据孙立新等,2017修改)
Figure 13. The variation of sporopollen content of the Yan'an Formation and Zhiluo Formation in Shenshangou area, the northeastern margin of Ordos basin (modified from Sun Lixin et al., 2017)
图 14 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘呼斯梁—纳林希里地区延安组和直罗组沉积相剖面(PM01)
1—砾岩;2—砂砾岩;3—粗砂岩;4—中砂岩;5—细砂岩;6—粉砂岩;7—煤层;8—泥岩;9—冲积沉积;10—辫状河道;11—河道间;12—曲流河道;13—泛滥平原;14—湖泊三角洲前缘砂体;15—湖相细碎屑岩;16—铀矿体;17—伽马曲线
Figure 14. Sedimentary facies profile of the Yan'an and Zhiluo Formation in the Husiliang—Nalinxili area, the northeastern margin of Ordos basin (PM01)
1-Conglomerate; 2-Gritstone-bearing conglomerate; 3-Gritstone; 4-Sandstone; 5-Fine sandstone; 6-Siltstone; 7-Coal bed; 8-Mudstone; 9-Alluvial; 10-The channel of braided river; 11-Inter-channel; 12-The channel of meandering river; 13-Floodplain; 14-Lake delta front sandstone; 15-Lacustrine fine clastic rock; 16-Uranium orebody; 17-γ curve
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘侏罗系延安组—直罗组泥岩微量元素比值判别指标统计表(数据引用张天福等,2016)
Table 1 Geochemical statistics of trace elements ratios of mudstone from Yan'an Formation and Zhiluo Formation on the northeastern margin of Ordos basin(data from Zhang Tianfu et al., 2016)

-
Cao Ke, Li Xianghui, Wang Chenshan, Wang Licheng, Wang Pingkang. 2010. Clay minerals of the Middle Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous in the Guangyuan area, Northern Sichuan:Implications to paleoclimate[J]. Journal of Mineral and Petrol, 30(1):41-46(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9e2173228de54c2ef15e2f1b728f8f34&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Cox R, Lowe D R, Cullers R L. 1995. The infuence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the south-westen United States[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59:2919-2940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
Chen Yin, Feng Xiaoxi, Chen Lulu, Jin Ruoshi, Miao Peisen, Sima Xianzhang, Miao Aisheng, Tang Chao, Wang Gui, Liu Zhongren. 2017. An analysis of U-Pb dating of detrital zircons and modes of occurrence of uranium minerals in the Zhiluo Formation of northeastern Ordos Basin and their indication to uranium sources[J]. Geology in China, 44(6):1190-1206(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706013
Deng Hongwen, Qian Kai. 1993. Sedimentary Geochemistry and Environmental Analysis[M]. Lanzhou:Gansu Science and Technology Press, 1-154(in Chinese).
Dong Shuwen, Zhang Yueqiao, Long Changxing, Yang Zhenyu, Ji Qiang, Wang Tao, Hu Jianmin, Chen Xuanhua. 2007. Jurassic tectonic revolution in China and new interpretation of the Yanshan Movement[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(11):1449-1461(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=71e687e29af5f4b95d3f3278c4be24f6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Feng Xiaoxi, Teng Xueming, He Youyu. 2019. Study on land subsidence assessment in evaluation of carrying capacity of geological environment[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 42(2):96-103 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201902004
Huang Gang, Zhou Xiqiang, Wang Zhengquan. 2009. Provenance analysis of the Yanan Formation in Mid-Jurassic at the Southeast area of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 28(3):252-258. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200903007.htm
Jones B, Manning D A C.1994. Comparion of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 111(1/4):111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-x
Ji Qiang, Chen Wen, Wang Wuli, Jin Xiaochi, Zhang Jianpimg, Liu Yongqing, Zhang Hong, Yao Peiyi, Ji Shu'an, Yuan Chongxi, Zhang Yan, You Hailu. 2004. Mesozoic Jehol Biota of Western Liaoxi, China[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-357 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiao Yangquan, Chen Anping, Wang Minfang, Wu Liqun, Yuan Haitao, Yang Qin, Zhang Chengze, Xu Zhicheng. 2005.Genetic Analysis of the Bottom Sandstone of Zhiluo Formation, Northeastern Ordos Basin-Predictive base of spatial orientation of sandstone-type uranium deposit[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 23(3):371-379(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200503001
Jiao Yangquan, Wu Liqun, Peng Yunbiao, Rong Hui, Ji Dongmin, Miao Aisheng, Li Hongliagn. 2015. Sedimentary-tectonic setting of the deposition-type uranium deposits forming in the PaleoAsian tectonic domain, North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1):189-205 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.016
Jin Ruoshi, Cheng Yinhang, Yang Jun, Ao Cong, Li Jianguo, Li Yanfeng, Zhou Xiaoxi. 2016. Classification and correlation of Jurassic uranium bearing series in the Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(12):3293-3309 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201612001
Jin Ruoshi, Cheng Yinhang, Li Jianguo, Sima Xianzhang, Miao Peisen, Wang Shaoyi, Ao Cong, Li Hongliang, Li Yangfeng, Zhang Tianfu. 2017. Late Mesozoic continental basin "Red and Black beds" coupling formation constraints on the sandstone uranium mineralization in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 44(2):205-223(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201702001
Lermanm, A. 1978. Lakes:Chemistry, Geology, Physics[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 79-83.
Liang Bin, Wang Quanwei, Kan Zezhong. 2006. Geochemistry of early Jurassic mudrocks from Ziliujing Formation and implications for source-area and weathering in dinosaur fossils site in GongXian, Sichuang Province[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 26(3):94-99(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1109/TPSD.2006.5507455
Li Sitian, Cheng Shoutian, Yang Shigong, Huang Qisheng, Xie Xinong, Jiao Yangquan, Lu Zongsheng, Zhao Genrong. 1990.Sequence Stratigraphy and Depositional System Analysis of the Northeastern Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:1-194 (in Chinese).
Li S T, Yang S G, Tomasz J.1995. Upper Triassic-Jurassic foreland sequences of the Ordos Basin in China stratigraphic, evolution of foreland basins[J]. SEPM Special Publication, 52:233-241. doi: 10.2110/pec.95.52.0233
Li Zhenghong, Dong Shuwen, Feng Shengbin, Qu Hongjie. 2015.Sedimentary response to Middle-Late Jurassic tectonic events in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 36(1):22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201501003
Liu Chiyang, Zhao Hongge, Gui Xiaojun, Yue Leping, Zhao Junfeng, Wang Jianqiang. 2006. Space-time coordinate of the evolution and reformation and mineralization response in Ordos Basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(5):617-638(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200605001
Liu Gang, Zhou Dongsheng.2007. Application of micro elements analysis in identifying sedimentary environment[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 29(3):307-314(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zhengbang, Jiao Yangquan, Xue Chunji, Miao Aisheng, Gu hao, Wu Yaping, Rong Hui, Ding Ye. 2013.The correlation between sandstone uranium ore-body and coal bed in Jurassic System, Dongsheng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(1):146-153(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201301013
Mitchum R M. 1977.Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level.Part1:Glossary of terms used sersmic stratigraphy[C]//Payton C E(eds.). Seismic Stratigraphy-Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. AAPG Memoir, 26:205-212. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8be34e83af9105f5f14ff6fe20a8cb4c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Nameroff T J, Calvert S E, Murray J W. 2004. Glacial-interglacial variability in the eastern tropical North Pacific oxygen minimum zone recorded by redox-sensitive trace metals[J]. Paleoceanography 19, PA1010.doi:10. 1029/2003PA000912.
Nesbitt H W, Young G M. 1982.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 299:715-717. doi: 10.1038-299715a0/
Ratschbacher L, Hacker B R, Webb L E, McWilliam M, Ireland T, Dong S W, Calvert A, Chateigner D, Wenk H R. 2000. Exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China:Cretaceous and Cenozoic unroofing and the Tanlu fault[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105:13303-13338. doi: 10.1029/2000jb900040
Shao Hongshun, Huang Difan. 1965. Some preliminary data of the salt content of the Paleo-lakes in the Dzungar and Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 45(3):337-347(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE196503009.htm
Sun Lixin, Zhang Yun, Zhang Tianfu, Cheng Yinhang, Li Yanfeng, Ma Hailin, Lu Chao, Yang Cai, Guo Jiacheng, Guo Genwan, Zhou Xiaoguang. 2017. Jurassic sporopollen of Yanan Formation and Zhiluo Formation and its paleoclimatic significance in the northeast Ordos basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(1):32-51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tan Xianfeng, Jiang Yanxia, Tian Jingchun, Zou Guoliang, Li Hang, Wang Weiqing. 2014. Sequence interface characteristics and spatial and temporal properties of Kongdian Formation of Paleogene in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 36(2):136-143(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201402003
Tribovillard N, Averbuch O, Devleeschouwer X, Racki G, Riboulleau A. 2004. Deep-water anoxia over the Frasnian-Famennian boundary (La Serre, France):A tectonically-induced oceanic anoxic event?[J]. Terra Nova, 16:288-295. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=55c57d2d449e84a1e4525c03e15cbd39&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, Riboulleau A. 2006. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies:An update[J]. Chem.Geol., 232:12-32. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6fc9d263314bdb8c0318cbc2ab305e94&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Vail P R, Audemard F, Bowman S A. 1991. The sratigraphic signature of tectonics, eustasy and sedimentation-An overview[C]//Einsele G, et al. (eds.). Cycles and Events in Stratigraphy[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 617-659.
van Wagoner J C, Posamentier H W, Mitchum R M. 1988. An overview of the fundamentals of sequence stratigraphy and Key definitions. In C K Wilgus, B S Hastings, G G St C Kendall, H W Posamentier, C A Ross, J C Van Wagoner, eds. Sea level changes: an integrated approach[J]. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication, 42: 39-45.
van Wagoner J C, Mitchum R M, Campion K M. 1990. Siliciclastic sequences stratigraphy in well logs, cores and outcrops:concepts for high-resolution correlation of time and facies[J].AAPG Methods in Exploration Series, 7:1-57. doi: 10.1306/Mth7510
Wang Qingchen. 2009. Topographic evolution and lithosphere dynamics in Central Asia since Mesozoic[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 44(3):791-810(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200903002
Wang Longjun, Lei Huawei, Zhou Shenglun. 2019. Analysis on the main controlling factors of Y-9 reservior in Jingbian oilfield[J]. Geology and resources, 28(4):372-377 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xia Yuliang, Liu Hanbin, Lin Jinrong, Fan Guang, Hou Yanxian. 2003.Research on geochronology and uranium source of sandstonehosted uranium ore-formation in major uranium productive basins, Northern China[J]. Uranium Geology, 19(3):129-136.(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHBG200402009.htm
Yang Junjie, Pei Xigu. 1996. Naturalgas Geology in China[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press:3-20 (in Chinese).
Yu Jian, Zhang Yan, Zhao Huitao, Hou Xiao, Hou Yingdong, Luo Shunshe. 2019. Characteristics and evaluation of C-10 reservoir in Zhijiang-Ansai area, Ordos basin[J]. Geology and resources, 28(4):364-371 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Reng'an, Sima Xianzhang, Jin Ruoshi, Miao Peisen, Peng Shenglong. 2019. The new discovery of the Large-scale uranium deposit in the Northeast Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20191226.1700.014.html(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Kang. 1989. Tectonics and Resources of Ordos Fault Block[M]. Xian:Shanxi Science and Technology Press, 1-94(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Qi, Wang Yuanlong, Jin Weijun, Li Chengdong. 2008. Eastern China Plateau during the Late Mesozoic:evidence, problems and implication[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 27(9):1404-1430(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0beac664aa35c0b32f7a45d88d7458f4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang Tianfu, Sun Lixin, Zhang Yun, Cheng Yinhang, Li Yanfeng, Ma Haili, Lu Chao, Yang Cai, Guo Genwan. 2016. Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironmental implications of Jurassic Yan, an & Zhiluo Formation, northern margin of Ordos basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(12):3454-3472 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2df4b19343ebb1a1da02abe39646f970&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang Tianfu, Zhang Yun, Cheng Yinhang, Miao Peisen, Ao Cong, Jin Ruoshi, Duan Lianfeng, Duan Xiaolong. 2019. Integrated identification of sequence boundary through outcrop, seismic, logging and geochemistry:A case of Jurassic, the northeastern margin of Ordos basin[J]. COAL Geology & Exploration, 47(1):40-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtdzykt201901006
Zhang Tianfu, Zhang Yun, Miao Peisen, Yu Reng an, Li Jianguo, Jin Ruoshi. 2018. Study on the chemical index of alteration of the Middle and Late Jurassic Strata in the western margin of Ordos basin and its implications[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 41(4):258-279 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201804002
Zhang Yueqiao, Liao Changzhen. 2006. Transition of the Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic regimes and modification of the Ordos basin[J]. Geology in China, 33(1):28-40(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200601003
Zhang Yueqiao, Liao Changzhen, Shi Wei, Zhang Tian, Guo Fangfang. 2007. On the Jurassic tectonics in and around the Ordos basin, north China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(2):186-196(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1872579107600165
Zhang Yun, Sun Lixin, Zhang Tianfu, Ma Haili, Lu Chao, Li Yanfeng, Cheng Yinhang, Yang Cai, Guo Jiacheng, Zhou Xiaoguang. 2016.The study on sequence stratigraphy of coal-uranium bearing measures and occurrence regularity of coal-uranium in northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(12):3424-3440(in Chinese with English abstract).
曹珂, 李祥辉, 王成善, 王立成, 王平康. 2010.四川广元地区中侏罗世-早白垩世黏土矿物与古气候[J].矿物岩石, 30(1):41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2010.01.008 陈印, 冯晓曦, 陈路路, 金若时, 苗培森, 司马献章, 苗爱生, 汤超, 王贵, 刘忠仁.2017.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组内碎屑锆石和铀矿物赋存形式简析及其对铀源的指示[J].中国地质, 44(6):1190-1206. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170613&flag=1 邓宏文, 钱凯.1993.沉积地球化学与环境分析[M].甘肃:甘肃科学技术出版社, 1-154. 董树文, 张岳桥, 龙长兴, 杨振宇, 季强, 王涛, 胡建民, 陈宣华.2007.中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J].地质学报, 81(11):1449-1461. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200711001 冯晓曦, 滕雪明, 何友宇.2019.初步探讨鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿田成矿作用研究若干问题[J].地质调查与研究, 42(2):96-103. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201902003 黄岗, 周锡强, 王正权.2009.鄂尔多斯盆地东南部中侏罗统延安组物源分析[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 28(3):252-258. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb200903008 季强, 陈文, 王五力, 金小赤, 张建平, 柳永清, 张宏, 姚培毅, 姬书安, 袁崇喜, 张彦, 尤海鲁.2004.中国辽西中生代热河生物群[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-357. 焦养泉, 陈安平, 王敏芳, 吴立群, 原海涛, 扬琴, 张承泽, 徐志成. 2005.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组底部砂体成因分析——砂岩型铀矿床预测的空间定位基础[J].沉积学报, 23(3):371-379. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb200503001 焦养泉, 吴立群, 彭云彪, 荣辉, 季东民, 苗爱生, 里宏亮.2015.中国北方古亚洲构造域中沉积型铀矿形成发育的沉积-构造背景综合分析[J].地学前缘, 22(1):189-205. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201501018.htm 金若时, 程银行, 杨君, 奥琮, 李建国, 李艳锋, 周小希.2016.准噶尔盆地侏罗纪含铀岩系的层序划分与对比[J].地质学报, 90(12):3293-3309. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201612001 金若时, 程银行, 李建国, 司马献章, 苗培森, 王少轶, 奥琮, 里宏亮, 李艳锋, 张天福.2017.中国北方晚中生代陆相盆地红-黑岩系耦合产出对砂岩型铀矿成矿环境的制约[J].中国地质, 44(2):205-223. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170201&flag=1 梁斌, 王全伟, 阚泽忠.2006.珙县恐龙化石埋藏地自流井组泥质岩地球化学特征及其对物源区和古风化作用的指示[J].矿物岩石, 26(3):94-99. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys200603015 李思田, 程守田, 杨士恭, 黄其胜, 解习农, 焦养泉, 卢宗盛, 赵根榕. 1990.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部层序地层及沉积体系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-194. 李振宏, 董树文, 冯胜斌, 渠洪杰.2015.鄂尔多斯盆地中-晚侏罗世构造事件的沉积响应[J].地球学报, 36(1):22-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201501003 刘池洋, 赵红格, 桂小军, 岳乐平, 赵俊峰, 王建强.2006.鄂尔多斯盆地演化——改造的时空坐标及其成藏(矿)响应[J].地质学报, 80(5):617-638. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200605001 刘刚, 周东升.2007.微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用[J].石油实验地质, 29(3):307-314. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz200703016 刘正邦, 焦养泉, 薛春纪, 苗爱生, 顾浩, 吴亚平, 荣辉, 丁叶.2013.内蒙古东胜地区侏罗系砂岩型铀矿体与煤层某些关联性[J].地学前缘, 20(1):146-153. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201301015.htm 邵宏舜, 黄第藩.1965.对准噶尔与鄂尔多斯盆地古湖含盐量的初步认识[J].地质学报, 45(3):337-347. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE196503009.htm 孙立新, 张云, 张天福, 程银行, 李艳峰, 马海林, 杨才, 郭佳成, 鲁超, 周晓光.2017.鄂尔多斯北部侏罗纪延安组、直罗组孢粉化石及其古气候地质意义[J].地学前缘, 24(1):32-51. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2017.01.003 谭先锋, 蒋艳霞, 田景春, 邹国亮, 李航, 王伟庆.2015.济阳坳陷古近系孔店组层序界面特征及时空属性[J].石油实验地质, 36(2):136-143. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz201402003 王清晨.2009.中亚地区中生代以来的地貌巨变与岩石圈动力学[J].地质科学, 44(3):791-810. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx200903002 王龙军, 雷华伟, 周升沦.2019.鄂尔多斯盆地靖边油田东坑大阳湾区延9油藏主控因素分析[J].地质与资源, 28(4):372-377. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201904010 夏毓亮, 刘汉彬, 林锦荣, 范光, 侯艳先.2003.中国北方主要产铀盆地砂岩铀矿成矿年代学及成矿铀源研究[J].铀矿地质, 19(3):129-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001899134 俞礽安, 司马献章, 金若时, 苗培森, 彭胜龙.2019.鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘发现大型砂岩型铀矿床[J].中国地质, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20191226.1700.014.html. 喻建, 张严, 赵会涛, 杨孝, 侯英东, 罗顺社.2019.鄂尔多斯盆地志靖-安塞地区延长组长10储层特征及评价[J].地质与资源, 28(4):364-371. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201904009 杨俊杰, 裴锡古.中国天然气地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1996:3-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqgy200602003 张抗.1989.鄂尔多斯断块构造和资源[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1-94. 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 李承东.2008.晚中生代的中国东部高原:证据、问题和启示[J].地质通报, 27(9):1404-1428. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200809004 张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 程银行, 李艳峰, 马海林, 鲁超, 杨才, 郭根万. 2016.鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量元素、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J].地质学报, 90(12):3454-3472. 张天福, 张云, 程银行, 苗培森, 奥琮, 金若时, 段连峰, 段宵龙.2019.利用露头、井震及地球化学综合厘定层序界面——以鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘侏罗系为例[J].煤田地质与勘探, 47(1):40-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtdzykt201901006 张天福, 张云, 苗培森, 俞礽安, 李建国, 金若时, 孙立新.2018.鄂尔多斯盆地西缘中晚侏罗世地层化学蚀变指数(CIA)研究及其意义[J].地质调查与研究, 41(04):258-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201804002 张岳桥, 廖昌珍.2006.晚中生代-新生代构造体制转换与鄂尔多斯盆地改造[J].中国地质, 33(1):28-40. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060103&flag=1 张岳桥, 廖昌珍, 施炜, 张田, 郭芳芳.2007.论鄂尔多斯盆地及其周缘侏罗纪变形[J].地学前缘, 14(2):186-96. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200702015 张云, 孙立新, 张天福, 马海林, 鲁超, 李艳峰, 程银行, 杨才, 郭佳城, 周晓光.2016.鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘煤铀岩系层序地层与煤铀赋存规律研究[J].地质学报, 90(12):3424-3440. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201612011 -
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 钟林,张文超,王国荣,张林锋,王党飞,余兴勇. 固态流化双射流开采天然气水合物颗粒回收. 科学技术与工程. 2025(05): 1878-1886 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 崔少云,陈杨明. 地震诱发浅层海底滑坡易发性概率评价方法. 科技创新与应用. 2024(11): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 袁胜,张伟,吴庐山,刘鹏奇,王阔,季春生,王力峰,王飞飞. 琼东南盆地天然气水合物发育区地质灾害发育特征与成因探讨. 地质学报. 2024(09): 2753-2765 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李彦杰,朱友生,陈冠军,王姝,王微微. 基于AUV观测数据的南海东沙北部浅表层精细地质特征及其灾害因素分析. 热带海洋学报. 2023(01): 114-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 年廷凯,王国栋,郑德凤,王大伟. 南海北部陆坡区典型峡谷陡坡群地震稳定性. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2023(06): 1785-1798 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 余兴勇,钟林,王国荣,李绪深,方小宇,张计春. 固态流化单喷嘴破碎水合物深度预测新模型及验证. 天然气工业. 2022(03): 150-158 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘乐军,修宗祥,周庆杰,高珊. 能源安全的海洋地质灾害研究发展与展望. 海岸工程. 2022(04): 451-466 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 万庭辉,张可倪,李占钊,王静丽,于彦江. 天然气水合物非成岩出砂储层砂流数值模拟. 科学技术与工程. 2021(17): 7027-7033 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 姚哲,张金锋,朱继田,方小宇,罗钧升. 琼东南盆地深水区天然气水合物运聚成藏模式. 海洋地质前沿. 2021(07): 22-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张乐,贺甲元,王海波,岑学齐,陈旭东. 天然气水合物藏开采数值模拟技术研究进展. 科学技术与工程. 2021(28): 11891-11899 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 谭琳,刘芳. 水合物开采中深海古滑坡体的再启滑机制初探. 工程地质学报. 2021(06): 1907-1915 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 何梅兴,方慧,祝有海,孙忠军,胡祥云,张鹏辉,王小江,裴发根,仇根根,杜炳锐,吕琴音. 祁连山哈拉湖坳陷地质构造特征及天然气水合物成藏地质条件研究. 中国地质. 2020(01): 173-187 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 马明,漆家福,张远泽,苗全芸,陈玮常,张帅. 珠江口盆地新生代沉降特征及其影响因素分析. 中国地质. 2019(02): 269-289 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 杨浦,王国荣. 固态流化法射流下的破碎颗粒运移规律的数值模拟. 中国造船. 2019(04): 108-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. Yao-hong Shi,Qian-yong Liang,Jiang-pin Yang,Qing-meng Yuan,Xue-min Wu,Liang Kong. Stability analysis of submarine slopes in the area of the test production of gas hydrate in the South China Sea. China Geology. 2019(03): 276-286 .  必应学术
必应学术
16. 孔媛,雷怀彦,许江,王斌,潘富龙,张劼,陈勇,程伟东. 南海北部天然气水合物的形成分解与微生物的偶联关系. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版). 2018(06): 768-777 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. Jian-liang Ye,Xu-wen Qin,Hai-jun Qiu,Qian-yong Liang,Yi-fei Dong,Jian-gong Wei,Hai-long Lu,Jing-an Lu,Yao-hong Shi,Chao Zhong,Zhen Xia. Preliminary results of environmental monitoring of the natural gas hydrate production test in the South China Sea. China Geology. 2018(02): 202-209 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: