Mineral chemistry of clinopyroxene from the Hongshan syenite complex in Wu'an, Hebei Province: Implications for magma evolution
-
摘要:
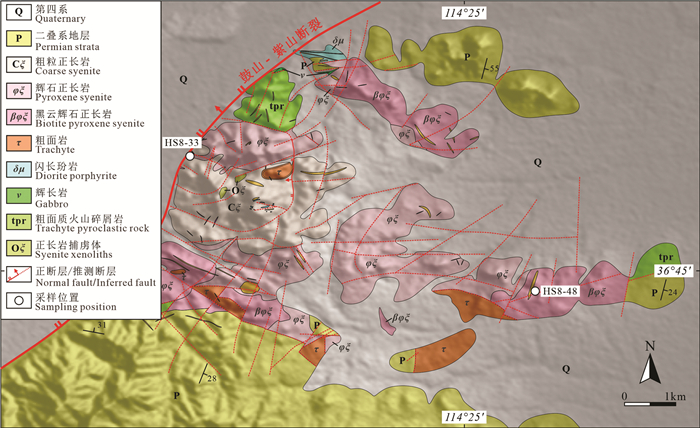
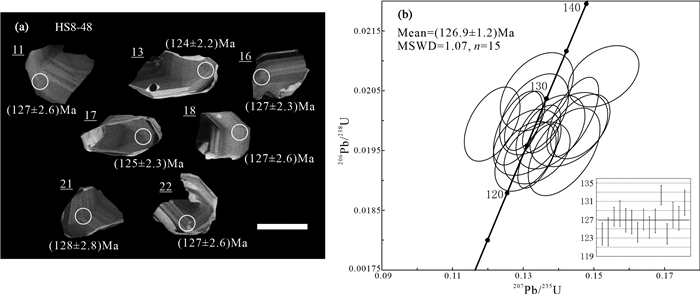
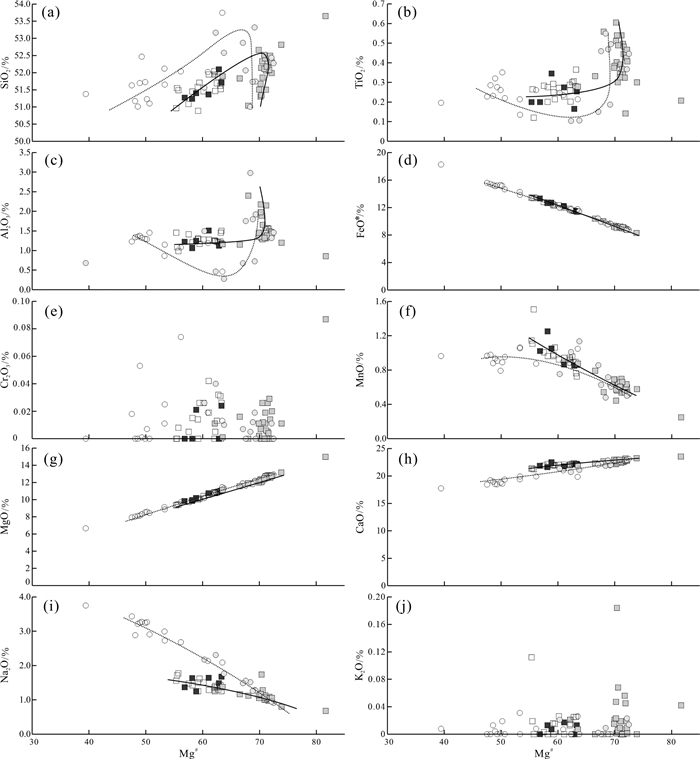
洪山正长岩杂岩体发育较多的具有核-边(核-幔-边)结构的单斜辉石,通过研究单斜辉石成分的变化,可以获得岩石成因及演化信息。本文在详细野外地质调查的基础上,采用锆石U-Pb年代学、矿物学研究,获得洪山正长岩杂岩体内黑云辉石正长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(126.9±1.2)Ma,是华北克拉通岩石圈减薄峰期的产物;洪山正长岩杂岩体内辉石正长岩与黑云辉石正长岩中单斜辉石Mg#值分别在39.4~72.5、55.4~81.7,具有较高FeO、Na2O、CaO含量,较低Al2O3、MgO、TiO2含量的特征;单斜辉石总体具有透辉石→霓石的演化趋势,并与熔体达到平衡状态,单斜辉石在初始演化时具有Fe2+对Mg2+的取代关系,随着演化的进行,岩浆更加富钠、富铁,反映了岩浆体系具有高温、中等氧逸度和富碱的特点。结合单斜辉石核-边(核-幔-边)具有截然的接触关系和不连续的化学组成,表明洪山正长岩杂岩体在形成后还经历了富钠、富铁流体的改造,致使单斜辉石形成了具有富钠、富铁的边部,流体可能是由西向东(或者由洪山正长岩杂岩体中部向外部)对杂岩体进行改造的。
Abstract:Hongshan syenite complex has fairly abundant clinopyroxene with core-rim (core-mantle-rim) structure. By studying the changes in the composition of clinopyroxene,information on the genesis and evolution of rocks can be obtained. Based on detailed field geological survey,the authors used zircon U-Pb chronology and mineralogical studies to obtain the biotite pyroxene syenite zircon U-Pb dating data of Hongshan syentite complex,with the age being(126.9±1.2)Ma,suggesting a product of the thinning peak period of the North China Craton lithosphere. The Mg# values of clinopyroxene from pyroxene syenite and biotite pyroxene syenite in the Hongshan syenite complex are 39.4-72.5 and 55.4-81.7,with characteristics of high FeO,Na2O and CaO content and low Al2O3,MgO and TiO2 content. The clinopyroxene generally had the evolutionary trend of diopside and aegirine,and reached an equilibrium state with the melt. The clinopyroxene had a Fe2+ to Mg2+ substitution relationship during the initial evolution. With the evolution,the magma became richer in sodium and iron,which suggests that the magma system had the characteristics of high temperature,medium oxygen fugacity and richness in alkali. Combined with the clinopyroxene core-rim (core-mantle-rim),the authors hold that there existed a clear contact relationship and discontinuous chemical composition. It is shown that,after the formation of the Hongshan syenite complex,it also underwent the transformation of sodium-rich and iron-rich fluids,causing the clinopyroxene to form a sodium-rich and iron-rich rim. The fluid may have modified the complex from west to east or from the inside of the Hongshan syenite complex to the outside.
-
Keywords:
- syenite complex /
- clinopyroxene /
- mineralogy /
- zircon U-Pb chronology /
- Mesozoic /
- magma evolution /
- sodium-rich fluid /
- geological survey engineering /
- Wu'an /
- Hebei Province
-
1. 引言
锶作为岩石圈上部含量最大的微量元素(胡进武等,2004;黄奇波等,2011),广泛存在于自然界中但分布非常不均,锶的分布状态及其存在形态受到自然条件、人类活动等多种因素的影响,导致锶在分布上富集或贫乏(Comar et al., 1957; 范伟等2010)。在不同的时期、不同岩性的基岩地层中锶元素的丰度存在明显的差异性,一般在海相沉积的碳酸盐岩中锶的丰度最高,在含锶矿物的闪长岩、花岗岩、黏土岩以及碳酸盐岩中,锶含量相对比较富集,黏土、砂中锶的丰度最低(刘庆宣等,2004)。作为微量元素,锶主要存在于各种造岩矿物和副矿物中,也能形成一些独立的矿物,主要为存在于碳酸盐岩中的菱锶矿(SrCO3)和天青石(SrSO4),同时文石、方解石、钙长石及石膏等矿物中亦常见锶置换钙的类质同像现象(Clow et al., 1997;文冬光等,1998)。岩石中的锶是地下水中锶的主要物质来源,锶在赋存母岩中主要经风化、淋滤后在地下水流作用下进行迁移转化(文冬光等,1998;康志强等,2011;苏春田等, 2017a, b),进而进入人类及其他动植物的物质循环。前人研究表明,地下水中锶的分布与富集受渗流地层岩性、溶滤强度、水化学条件(王增银等,2003;祁晓凡等,2009;范伟等, 2010)等因素的影响。目前,各国根据锶的含量及其生理医学作用制定了锶矿泉水的标准,参照饮用天然矿泉水国家标准(GB8537- 2016),地下水的质量浓度达到0.2mg/L,可命名为富锶矿泉水,规定的限值为5mg/L。岩溶水作为山区居民主要饮用的水源,关乎百姓的生活与饮食健康,因而查明地下水中锶的分布状态,揭示锶的动态变化,分析锶的富集规律,具有较大的研究意义与实际价值。
前人对富锶地下水的研究多集中在赋存条件、水质评价等方面,多集中在非岩溶地区(孙岐发等,2019),针对西南岩溶区富锶地下水的研究还较少(祁晓凡等,2009;康志强等,2011;苏春田等, 2017a, b),针对三峡岩溶区的研究则更少。本文选取湖北秭归地区两个岩溶流域为研究区,以岩溶水系统为单元,从锶的物质来源条件入手,分析岩溶水系统中锶的水岩作用过程,研究不同含水岩组、不同水流条件下地下水中锶的分布与富集特征,探讨宜昌三峡岩溶去地下水中锶富集的条件与规律。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 自然地理概况
本文主要针对秭归地区的茅坪河和九畹溪两个岩溶流域开展研究。研究区地处长江之滨、西陵峡畔、清江以北,属于中国地形第二、三阶梯的过渡地带,为川东褶皱与鄂西山地交汇地,境内山脉为大巴山、巫山余脉,地形起伏较大。该地区属于亚热带季风气候,气候温暖、降雨充沛,年降雨量在900~1200 mm,其中汛期降雨量占绝大部分,受季风气候和山峦起伏的影响,降雨量的季节变化和空间差异明显,小气候特征比较显著。秭归县位于鄂西褶皱山地,西南高东北低,平均海拔高程千米以上,山峰耸立,河谷深切,相对高差一般在500~1300 m。其中中低山区多分布于秭归盆地周边,斜坡倾角介于15~25°,面积960 km2;大于25°以上的斜坡主要分布在长江峡谷区、中高山向中低山过渡地带,陡缓变化较大,多形成陡崖。
2.2 地质概况
研究区地处黄陵穹隆西南缘,自北东向西南从侵入岩体、前震旦纪到三叠纪地层连续出露且较齐全,区内南沱组角度不整合于侵入岩与变质岩基底之上,第四系与下伏地层为角度不整合,其余地层之间均为整合与平行不整合接触关系(南沱组与陡山沱组呈平行不整合,纱帽组与云台观组呈平行不整合)。区域内地层主要是以沉积岩为主,累计沉积岩岩层最大厚度约7567 m,其中碳酸盐岩总厚度达到3443 m,占沉积岩总厚度的45.5%,碳酸盐岩地层主要有震旦系,寒武系、奥陶系、志留系、二叠系及三叠系,岩性以灰岩、白云岩为主,非碳酸盐岩地层有志留系、泥盆系、白垩系,岩性以碎屑岩为主,尤以仙女山一带的白垩系的碎屑砾岩、砂岩为特殊,常常发育有可溶性砾岩裂隙孔洞水。
2.3 岩溶含水系统划分
前人在进行岩溶含水系统划分过程中,主要考虑了含水岩组、空间介质结构、组合特征、岩溶水径流方式、埋藏条件等因素(裴建国等,2008; 梁永平等,2015)。秭归地区属于南方岩溶的范畴,多种地层组合特征、构造条件下发育多样的岩溶水系统,既发育有管道裂隙集中排泄型系统、也有裂隙分散排泄型岩溶水系统。根据区域地层的含水性分析,大致可划分为3个岩溶含水系统(图 1):上震旦岩溶含水系统(Z2d、Z2∈1d)、下寒武—奥陶岩溶含水系统(∈1t、∈1sl、∈2q、∈2O1l、O1n、O1g、O2-3b)、石炭—三叠岩溶含水系统(P1q、P1m、P2w、T1d、T2j),进一步可细分为7个岩溶含水子系统(表 1)。本文依据空间结构、含水介质、排泄方式、代表水流、标高、流量等特征数据,并结合野外调查资料,对岩溶子含水单元排泄特征进行整理划分(表 1)。
表 1 岩溶含水子系统的介质结构及排泄特征Table 1. Structure and drainage characteristics of karst water-bearing units
3. 样品采集与测试
3.1 样品采集与处理
2016—2018年期间,本文依托中国地质调查局二级项目“宜昌长江南岸岩溶流域水文地质环境地质调查”,系统地采集了研究区泉水、典型断面地表水样品,对重点岩溶泉点进行月度监测,并选送测区内主要含水岩组的岩样进行岩石矿物组成分析。针对不同岩溶水系统,选取了31组岩溶泉点作为长期监测点(长观站)(图 1),用于分析地下水的动态变化规律。本文的研究数据来源于区域水文地质调查,及31个岩溶泉长期监测点(长观站)月度样采集,共整理了415组水样数据,93组岩矿分析数据,基于此对锶的分布特征进行分析。
水样采集采用600 mLPVC瓶,现场用水样涮洗3次,同时对水样水温、pH、电导率、流量等指标进行现场测定。此后样品在12 h内送回室内,采用《中华人民共和国地质矿产行业标准DZ/T 0064.49- 93地下水水质检验方法》酸碱滴定法测试并计算碱度。同时将水样用孔径0.45 μm的醋酸纤维膜过滤后,分装于2个50 mLPET瓶中分别用于阴阳离子测试,其中阳离子测试样会使用分析纯HNO3酸化至pH<2,阴离子样则不加处理。
3.2 样品测试
水化学样品的测试在中国地质大学(武汉)地质调查研究院实验中心完成,阴离子由戴安离子色谱仪ICS2100测试,阳离子由赛默飞公司生产的ICP-OES(ICAP6300)测试;岩石样品矿物组成测试在澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司测试完成,锶等矿物组分均采用封闭酸溶-电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测试。
4. 分析与讨论
4.1 锶的物源条件分析
通过对93组岩矿分析数据分析可知,不同地质年代的沉积地层中锶的含量大不相同(表 2),在震旦系地层中,灯影组地层锶含量比陡山沱组高,灯影组锶含量可达到2900 μg/g,均值为1121 μg/g,且组内不同段含量差异明显,如灯影组二段的白云质灰岩中锶含量介于800~2600 μg/g,其含量较一段和三段的白云岩大,灯影组地层整体变异系数为88.2%(n=10);寒武系上统娄山关组白云岩中锶含量介于77~2500 μg/g,变异系数为62.5%(n=11),锶含量均值大但分布上存在差异性;奥陶系地层锶含量均不高,介于100~400 μg/g,变异系数相对较低;嘉陵江组地层锶的含量较高,均值为2861 μg/g,变异系数也较高,为137.3%(n=17)。
表 2 秭归岩溶地层中锶含量概况统计Table 2. Statistics of Sr contents in karst strata in the Zigui area
可知,秭归地区富锶地层主要为灯影组、娄山关组、嘉陵江组。从沉积相来看,上述沉积地层均为干旱气候条件下碳酸盐台地浅滩、潮坪-潟湖沉积(徐长昊,2016),为封闭性较好的沉积环境,是蒸发沉积富锶地层发育的良好条件。
同时对区内浅层包气带内岩样分析发现,表层岩石中天青石矿物较少,锶含量偏低且与CaO的相关性较好,而与MgO、SO3、Al2O3的相关性一般。主要是由于表层岩石受到较强的淋滤作用而导致锶的流失,此外浅循环系统中的锶会以类质同像形式存在于方解石矿物中。
对由钻孔揭露深层封闭地层岩样分析发现,锶主要以天青石形式存在,常常与石膏矿物共存。如钻孔ZK05揭露的娄山关组地层中,锶含量普遍较高且与SO3有较好的相关性(R2=0.737,n=10)。另在对钻孔ZK03揭露的奥陶系岩心分析发现,随着MgO含量的增大,岩性逐渐白云岩化,同时锶含量逐渐减小(图 2);此外,锶的含量会随着碳酸盐中泥质含量的增大(SiO2含量增大)而减小(图 2)。
4.2 锶的水岩作用过程分析
通过对茅坪河与九畹溪两个流域岩溶地下水样分析,从富锶水化学类型、水岩作用程度、物理化学条件等方面,对该区地下水锶分布与富集展开讨论。
针对研究区所采集的415组水样,从Piper三线图(图 3)来看,地下水中锶含量大于2 mg/L时,水中阳离子以Ca2+、Mg2+为优势离子,阴离子以SO42-为主;地下水中锶含量在0.70~10 mg/L时,水中阳离子以Na+为主,阴离子以Cl-为主;地下水中锶含量小于0.70 mg/L时,水中阴离子以HCO3-为主。因此,锶浓度相对较高的地下水化学类型主要包括SO4型和Cl型,其中尤以SO4型地下水的锶浓度最高。
岩溶地下水中离子组分主要来源于对母岩的溶滤作用,其决定着地下水中主要水化学过程(康志强等,2011; 苏春田等,2017a)。母岩中锶含量影响着水流系统地下水中锶的分布(文冬光等,1998;苏春田等,2017b)。地下水中锶离子主要来源于富锶矿物(天青石、菱锶矿),赋存在方解石、文石及白云石类质同像形态的锶,以及铝硅酸盐中的锶等的溶解(徐兴国,1984),具体的化学反应方程式如下:

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 表层岩溶泉可反映局部水流系统的水化学特征。基于所采集的334处表层岩溶泉,绘制出研究区锶在表层岩溶水中的分布规律,发现全区存在5处富锶地下水分布区(图 4),且这些富锶地下水分布与富锶地层的分布表现出一致性,二叠系阳新组岩溶水,三叠系嘉陵江组岩溶水,寒武系娄山关组岩溶水,寒武系水井沱组岩溶水及震旦系灯影组岩溶水。其中杨新组表层岩溶水中Sr含量介于0.26~ 0.76 mg/L;嘉陵江组介于0.23~0.60 mg/L;娄山关组介于0.13~0.43 mg/L;水井沱组与灯影组介于0.22~0.72 mg/L。
对于排泄区,选取研究区内4处锶含量较高的地层中出露的地下水点为例,即白龙潭、龙洞、迷宫泉和龙王洞(表 1)。从锶离子与硫酸根离子、重碳酸根离子的浓度关系(图 5)发现,嘉陵江组白龙潭岩溶泉水锶含量较高,与硫酸根离子有较好的一致性(R2=0.707,n=5),另知嘉陵江组岩矿分析中SO3含量较高,反映出在该泉域的径流途径上有天青石的存在;娄山关组迷宫泉与重碳酸根离子和硫酸根离子均呈现较好的相关性(R2=0.668,n=10;R2= 0.768,n=13),反映出径流途径中存在两种富锶矿物溶解。此外,针对地下水中丰、枯两季表现出差异性(图 5),主要是由于研究区具有典型南方岩溶管道-裂隙水系统,地下水径流路径和径流时间短、水岩作用不充分(罗明明等,2015),表现出枯季地下水中锶含量普遍比丰水期的要高。由上可知,岩溶水中锶离子含量与各岩溶水系统中富锶矿物含量密切相关,流经的地层岩性差异导致各岩溶水流系统表现出不同的水岩作用过程,或受石膏、天青石矿物溶解的影响,或受菱锶矿溶解的影响,或受多种锶源的混合补给。
4.3 地下水流系统中锶的分布规律
对于锶在多级水系系统中的分布规律,本文以泗溪流域庙坪—鱼泉洞多级水流系统为例(图 1b),不同级次的地下水中锶含量及饱和程度易表现出差异性(表 3,图 6)。庙坪洼地表层岩溶泉为局部水流系统,锶含量均值为0.08 mg/L,si_Str与si_Cel均比较低(表 3),多为方解石中类质同像锶的溶解释放;鱼泉洞泉水为中间水流系统,地下水锶含量均值为0.22 mg/L,si_Stron与SI_Cel相比于局部水流系统稍高但未达到饱和(表 3),但冬季其锶的饱和指数相对夏季要高,主要由于冬季水流滞缓,水岩作用相对充分(表 3);以钻孔ZK04揭露的区域水流系统,其锶均值在2.33 mg/L,si_Str、si_Cel、si_Cal、si_Dol均趋于饱和(图 6)。可知地下水与母岩水岩相互作用的时间与水流路径长短决定了地下水中富锶矿物的饱和程度及地下水中锶含量(张群利等,2011;苏春田等,2017a)。
表 3 不同级次水流水化学信息统计表Table 3. Hydrochemistry of different water flow levels
此外,通过对钻孔ZK04及钻孔ZK05中锶含量分析(表 3,图 6),发现两者锶离子浓度均很大。在两孔钻进施工中,均有H2S与CH4等还原性气体溢出,且岩心中有机炭的含量相对较高,尤其是ZK05岩矿组分中发现有单质S存在。推知两孔均混有碳酸盐岩和硫酸盐岩(富含大量的石膏),且均为相对封闭的还原环境。
在这种封闭缺氧还原环境中,地下水中的SO42-在有机炭和脱硫细菌作用下,容易发生脱硫酸作用(刘硕等,2016),其化学反应式为:

(4) 
(5) 当地层中含有大量铁的时候S2-便会与铁结合,逐渐生成黄铁矿,而硫化氢气体极易溶于水(溶解比例约为1∶3),在氧气充足的时候,H2S会被氧化成硫酸与碳酸盐结合形成石膏矿物沉淀,但当氧气不足的时候,少部分的H2S会被氧化成单质S,更大一部分仍以气体的形式存在于封闭的还原条件中,这也就是ZK05孔岩心组分中单质S存在的原因。硫酸根离子的转化,促进了石膏、天青石的溶解过程,致使地下水中锶离子富集,甚至使天青石溶解达到饱和,同时菱锶矿的溶解也增大了地下水中锶的含量(罗璐等,2015)。
5. 结论
本文通过对秭归岩溶流域锶的分布与迁移进行分析,得到以下结论:
(1)研究区内嘉陵江组、娄山关组、灯影组地层中的锶含量最高,代表着潮坪-潟湖沉积相;区内浅层岩石中天青石矿物较少,锶含量偏低;深层封闭地层岩样中锶主要以天青石形式存在,常常与石膏矿物共存。
(2)富锶岩溶水的水化学类型主要包括SO4型和Cl型,尤以SO4型地下水的锶浓度最高;母岩中锶的含量决定了地下水中锶的浓度,且锶主要通过溶滤作用进入地下水中。
(3)地下水水流系统中水岩作用程度及地下水的滞留时间均影响地下水中锶的浓度,浅循环岩溶地下水流系统中锶均未达到饱和,少数深循环区域地下水流系统中锶浓度趋近饱和状态。对于富含石膏、天青石的封闭还原环境有利于地下水中锶的富集。
-
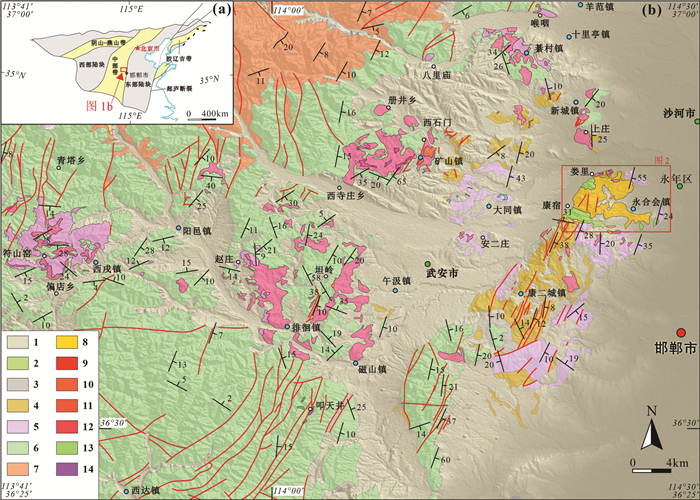
图 1 华北克拉通基底构造单元划分图(a, 据Zhao et al., 2005)和邯邢地区区域地质图(b, 据资料❶, ❷修编)
1—第四系;2—白垩纪火山岩地层;3—三叠纪沉积地层;4—二叠纪沉积地层;5—石炭纪沉积地层;6—奥陶纪沉积地层;7—前寒武变质地层;8—正长岩;9—二长岩;10—二长闪长岩;11—闪长岩;12—角闪闪长岩;13—橄榄辉长岩;14—辉橄岩
Figure 1. Tectonic subdivision of the North China Craton (a, after Zhao et al., 2005) and geological map of the Handan-Xintai area (b, modified from Zhao et al., 2008❶; Zhang et al., 2014❷)
1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous volcanic strata; 3- Triassic sedimentary strata; 4-Permian sedimentary strata; 5-Carboniferous sedimentary strata; 6-Ordovician sedimentary strata; 7-Precambrian metamorphic strata; 8-Syenite; 9-Monzonite; 10-Monzodiorite; 11-Diorite; 12-Hornblende diorite; 13-Olivine gabbro; 14-Pyroxene peridotite
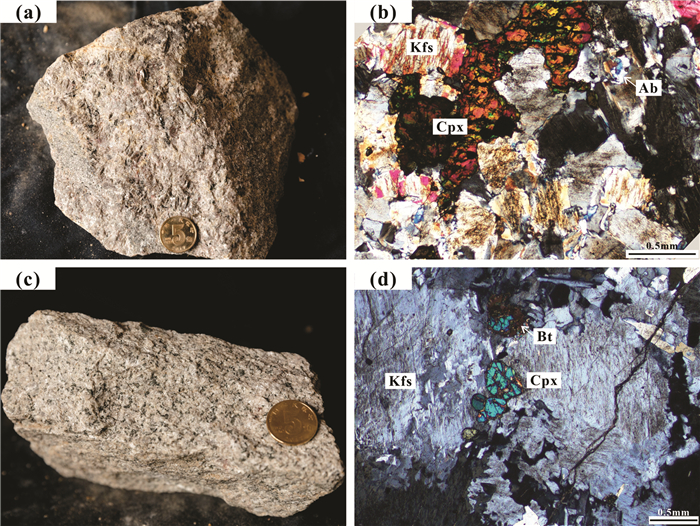
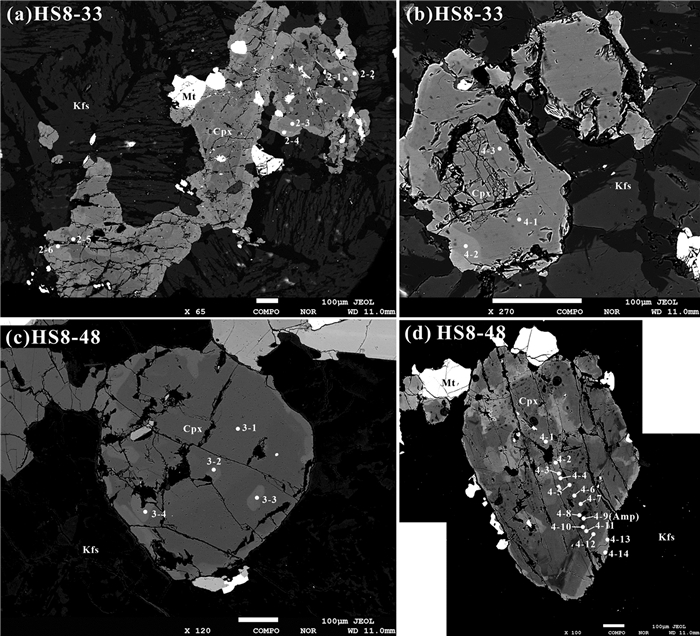
图 5 洪山正长岩杂岩体中代表性单斜辉石的BSE图像
a, b—辉石正长岩(HS8-33);c, d—黑云辉石正长岩(HS8-48);Cpx—单斜辉石;Kfs—钾长石;Amp—角闪石;Mt—磁铁矿
Figure 5. Representative BSE images of the of clinopyroxene from the Hongshan syenite complex
a, b-Pyroxene syenite (HS8-33); c, d-Biotite pyroxene syenite (HS8-48); Cpx-clinopyroxene; Kfs-K-feldspar; Amp-Amphibole; Mt-Magnetite
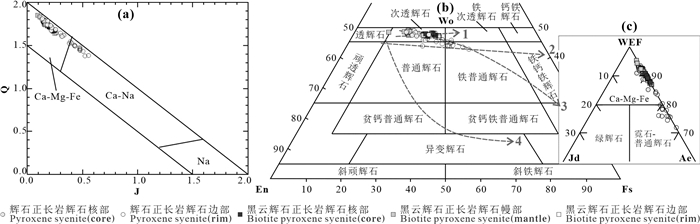
图 6 洪山正长岩杂岩体单斜辉石系列划分图解(a)和单斜辉石分类图解(b、c)(据Morimoto, 1988;邱家骧和廖群安, 1996修改)
Wo—硅灰石; En—斜顽辉石; Fs—斜铁辉石; WEF—Wo-En-Fs端元; Jd—硬玉; Ae—霓石; 图b中演化趋势分别为: 1—钙铁辉石→透辉石(Baie-des-Moutons正长岩质杂岩体早期正长岩中,Lalonde and Marin, 1983); 2—透辉石→钙铁辉石(日本碱性玄武岩系列, Aoki, 1964; Shiant Isles岩体,Gibb, 1972); 3—透辉石→霓石(Shonkin Sag岩体, Nash and Wilkinson, 1970); 4—透辉石→易变辉石(日本拉斑质玄武岩,Kuno, 1955)
Figure 6. Discrimination diagram of the series for pyroxene (a) and discrimination diagram of clinopyroxene (b, c) from the Hongshan syenite complex (modified from Morimoto, 1988; Qiu Jiaxiang and Liao Qun'an, 1996)
Wo-Wollastonite; En-Clinoenstatite; Fs-Clinoferro; WEF-Wo-En-Fs end member; Jd-Jadeite; Ae-Aegirine; Fig. b shown for comparison exhibiting crystallization trends of other different types of magmas; 1- Hedenbergite → diopside (Baie -des- Moutons syenitic complex, early- group syenites. After Lalonde and Marin, 1983); 2- Diopside → hedenbergite (Japanese alkaline basalt series, after Aoki, 1964; Shiant lsles sill, Gibb, 1972); 3- Diopside → aegirine (Shonkin Sag laccolith, after Nash and Wilkinson, 1970); 4- Diopside → ferropigeonite (Japanese tholeiite series, after Kuno, 1955)
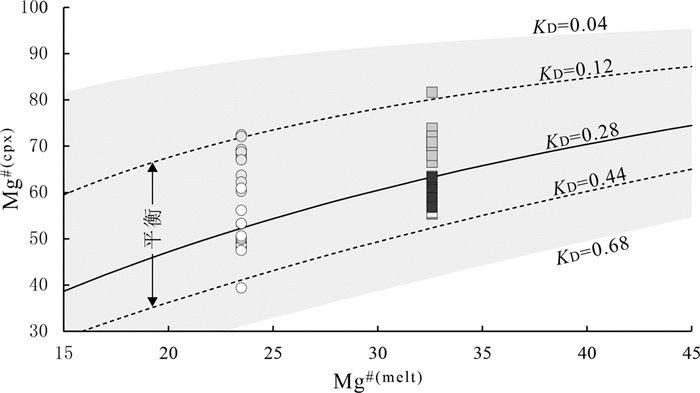
图 8 洪山正长岩杂岩体单斜辉石罗德图(据Rhodes et al., 1979; Di et al., 2020修改, 图例同图 6)
Figure 8. Rhodes diagram for clinopyroxenes form the Hongshan syenite complex (modified from Rhodes et al., 1979; Di et al., 2020, symbols as for Fig. 6)
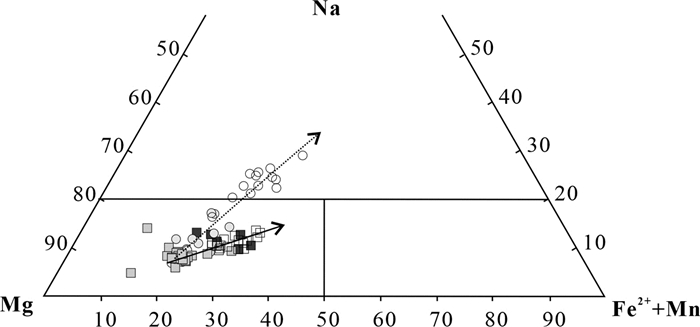
图 9 洪山正长岩杂岩体单斜辉石Mg-Na-(Fe2++Mn)图解(据Eby et al., 1998修改, 图例同图 6)
Figure 9. Mg-Na-(Fe2++Mn) diagram for clinopyroxenes from the Hongshan syenite complex (modified from Eby et al., 1998, symbols as for Fig. 6)
表 1 洪山正长岩杂岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of Hongshan syenite complex

表 2 洪山正长岩杂岩体中单斜辉石电子探针数据(%)
Table 2 Electron microprobe analyses of clinopyroxene from Hongshan syenite complex (%)

-
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 192(1/2):59-79. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S000925410200195X
Aoki K I. 1964. Clinopyroxenes from alkaline rocks of Japan[J]. American Mineralogist:Journal of Earth and Planetary Materials, 49(9/10):1199-1223. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a6ae5588155525e3e1c066ffd2334324&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Bai Zhimin. 2000. Mineral chemistry and genetic significance of clinopyroxenes from the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Western Hills of Beijing[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 19(2):174-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200002010
Chen B, Tian W, Jahn B M, Chen Z C. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages and in-situ Hf isotopic analysis for the Mesozoic intrusions in South Taihang, North China craton:Evidence for hybridization between mantle-derived magmas and crustal components[J]. Lithos, 102(1/2):118-137. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6b68908e5e5b30564cdc9fc3603d55d4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen Chunliang, Jiang Sihong, Liang Qingling, Liu Yuan, Han Ning. 2014. The Hf Iisotopic characteristics of the zircons from Wulingshan complex in Hebei and regional comparative study[J]. Geoscience, 28(4):663-673(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDDZ201404001.htm
Chen L, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F. 2018. Geochemical insights from clinopyroxene phenocrysts into the effect of magmatic processes on petrogenesis of intermediate volcanics[J]. Lithos, 316:137-153. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9c4c1c3cd520cebe6d0ef6ab0586a685
Deng X D, Li J W, Wen G. 2015. U-Pb geochronology of hydrothermal zircons from the early Cretaceous iron skarn deposits in the Handan-Xingtai district, North China craton[J]. Economic Geology, 110(8):2159-2180 doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.8.2159
Di Y K, Tian W, Chen M M, Li Z F, Chu Z Y, Liang J. 2020. A method to estimate the pre-eruptive water content of basalts:Application to the Wudalianchi-Erkeshan-Keluo volcanic field, Northeastern China[J]. American Mineralogist:Journal of Earth and Planetary Materials, 105(2):149-161.
Dobosi G, Fodor R V. 1992. Magma fractionation, replenishment, and mixing as inferred from green-core clinopyroxenes in Pliocene basanite, southern Slovakia[J]. Lithos, 28(2):133-150. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=80724b36defb568e92216eae1d285a4f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Duan Youqiang, Zhang Zhengwei, Yang Xiaoyong. 2015. The continental dynamics of Zhangshiying pluton at the southern margin of the North China Craton:Evidence from geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(7):1995-2008(in Chinese with English abstract).
Eby G N, Woolley A R, Din V, Platt G. 1998. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of nepheline syenites:Kasungu-Chipala, Ilomba, and Ulindi nepheline syenite intrusions, North Nyasa alkaline province, Malawi[J]. Journal of Petrology, 39(8):1405-1424. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.8.1405
Huang Xiaolong, Xu Yigang, Yang Qijun, Chen Linli. 2007. Genesis of compositional zoning of clinopyroxene phenocrysts in the Wozhong Late Eocene high-Mg ultrapotassic lavas, western Yunnan, China:Magma replenishment-mixing process[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(2):250-260 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huo Tengfei, Yang Debin, Shi Jiangpeng, Xu Wenliang, Yang Haotian. 2016. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous alkali-rich intrusive rocks in the central North China Block:Constraints from zircon UPb chronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(3):697-712(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Xu W L, Yuan H L, Liu Y S, Walker R J, Puchtel I S, Liu X M, Huang H, Wang X R, Yang J. 2008. Recycling deep cratonic lithosphere and generation of intraplate magmatism in the North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 270(1/2):41-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=069b1caaa140b2d4abd620f71a2cb0bf
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Yuan H L, Liu X M, Liu Y S, Xu W L, Ling W L, Ayers J, Wang X C, Wang Q H. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton[J]. Nature, 432(7019):892-897. doi: 10.1038/nature03162
Gibb F G F. 1973. The zoned clinopyroxenes of the Shiant Isles sill, Scotland[J]. Journal of Petrology, 14(2):203-230. doi: 10.1093/petrology/14.2.203
Goleń M, Puziewicz J, Matusiak-Małek M, Ntaflos T. 2015.Clinopyroxene phenocrysts from the Księginki nephelinite (SW Poland)[J]. Geoscience Records, 1(1/2):1-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=georec-2015-0001
Jiang Shaoyong, Zhao Kuidong, Jiang Yaohui, Ling Hongfei, Ni Pei. 2006. New type of tin mineralization related to granite in South China:Evidence from mineral chemistry, element and isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10):2509-2516 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Shaoyong, Li Liang, Zhu Bi, Ding Xin, Jiang Yaohui, Gu Lianxing, Ni Pei. 2008.Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of granodiorite from the Wushan copper deposit, Jiangxi Province and their implications for petrogenesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1679-1690 (inChinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200808002
Le Bas M J. 1962. The role of aluminum in igneous clinopyroxenes with relation to their parentage[J]. American Journal of Science, 260(4):267-288. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=67035106cc1af6c6c76a5a1ecb1175c4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Suimin, Li Yucheng, Zhao Shumei, Zhang Liangliang, Wang Junge, Han Tengfei, Sun Zhiwei, Han Yuchou, Li Tong. 2020. Ar-Ar and U-Pb ages of Hongshan copper deposit, Handan and their limitation on mineralization time[J/OL]. Geology in China, [2020-02-04]: 1-17(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Xin, Tang Yanjie. 2018. The characteristics and implication of the zonation in clinopyroxene phenocrysts from the Yaojiazhuang ultramafic-syenitic complex, northwestern Hebei Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(11):3315-3326 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201811015
Luo Zhaohua, Deng Jinfu, Han Xiuqing. 1999. Characteristics of Magmatic Activities and Orogenic Process of Taihangshan Intraplate Orogen[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-132 (in Chinese).
Ludwig K R. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.0: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publications, 4.
Marks M, Halama R, Wenzel T, Markl G. 2004. Trace element variations in clinopyroxene and amphibole from alkaline to peralkaline syenites and granites:Implications for mineral-melt trace-element partitioning[J]. Chemical Geology, 211(3/4):185-215. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=24b8ec91737a42bbbf2b790c1c2896be&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Morimoto N. 1988. Nomenclature of pyroxenes[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 39(1):55-76. doi: 10.1007/BF01226262
Nash W P, Wilkinson J F G. 1970. Shonkin Sag Laccolith, Montana[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 25(4):241-269. doi: 10.1007/BF00399286
Niu Xiaolu, Chen Bin, Ma Xu. 2009. Clinopyroxenes from the Fanshan pluton, Hebei[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2):359-373(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200902010
Putirka K D. 2008. Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems[J]. Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, 69(1):61-120. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.3
Qiu Jiaxiang, Liao Qunan. 1987. The main characteristics and petrological significance of low pressure clinopyroxenes in the Cenozoic basalts from eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 3(4):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rhodes J M, Dungan M A, Blanchard D P, Long P E. 1979. Magma mixing at mid-ocean ridges:evidence from basalts drilled near 22°N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Tectonophysics, 55(1/2):35-61.
Su Shangguo, Jian Dongchuan, Xie Yuchun, Luo Zhaohua, Jiang Junyi, Liu Lulu, Huo Yanan, Cui Xiaoliang, Zhang Bo, Gu Dapeng, Wang Yu. 2017. The practice of thematic geological mapping in medium-large scale for intermediate-basic intrusive rocks:A case study of the Wu'an iron ore concentration area, Hebei Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 36(11):1987-1998(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun J F, Zhang J H, Yang J H, Yang Y H, Chen S. 2019. Tracing magma mixing and crystal-melt segregation in the genesis of syenite with mafic enclaves:Evidence from in situ zircon Hf-O and apatite Sr-Nd isotopes[J]. Lithos, 334:42-57. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c9e3223a1142b334d5432389a3c6d79e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Y, Sun L X, Zhou L Y, Xie Y T. 2018. Discussion on the relationship between the Yanshanian Movement and cratonic destruction in North China[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 61:499-514. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9177-2
Wang Yaying, Cai Jianhui, Yan Guohan, Yan Zhijiao, Song Jianqiang. 2015. Geochemistry and mineral characteristics of Zijinshan alkaline complex from Linxian, Shanxi Province and its Petrogenesis[J]. Geoscience, 29(4):896-911 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201504020
Wu Fuyuan, Xu Yigang, Gao Shan, Zheng Jianping. 2008.Lithospheric thinning and destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6):1145-1174(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8529d40ce3ff5806bc85560db8f6b765&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wu Fuyuan, Yang Jinhui, Liu Xiaoming. 2005. Geochronological framework of the Mesozoic granitic magmatism in the Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(3):305-317(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200503003
Xu Wenliang, Yang Chenghai, Yang Debin, Pei Fuping, Wang Qinghai, Ji Weiqiang. 2006. Mesozoic high-Mg diorites in eastern North China craton:Constraints on the mechanism of lithospheric thinning[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(2):120-129(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=18e1c5e30efd9a7dc5488913e0c5b52f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xu Wenliang, Yang Debin, Pei Fuping, Yu Yang. 2009. Petrogenesis of Fushan high-Mg# diorites from the southern Taihang Mts. in the central North China Craton:Resulting from interaction of peridotite-melt derived from partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8):1947-1961(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200908019
Xu Y G, Li H Y, Pang C J, He B. 2009. On the timing and duration of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19):3379-3396. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb-e200919004
Yan Guohan, Cai Jianhui, Ren Kangxu, He Guoqi, Mou Baolei, Xu Baoliang, Li Fengtang, Yang Bin. 2007. Intraplate extensional magmatism of North China Craton and break-up of three supercontinents and their deep dynamics[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(02):161-174(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200702003
Yan G H, Xu B L, Mu B L, Wang G Y, Chang Z S, Chen T L, Zhao Y C, Wang X F, Zhang R H, Qiao G S, Chu Z Y. 2000. Alkaline intrusives at the east foot of the Taihang-Da Hinggan Mountains:Chronology, Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic characteristics and their implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 74(4):774-780.
Yang H J, Frey F A, Clague D A, Garcia M O. 1999. Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii:implications for magmatic processes within Hawaiian rift zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 135(4):355-372. doi: 10.1007/s004100050517
Yang X K, Chao H X, Volkova N I, Zheng M L, Yao W H. 2009.Geochemistry and SHRIMP geochronology of alkaline rocks of the Zijinshan massif in the eastern Ordos basin, China[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 50(9):751-762. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2009.08.002
Yang Zhaoyao, Xu Yaoming, Zhu Zhiyong, Zhou Wei, Bai Cheng. 2015. Mineral chemistry of pyroxene in lamprophyre from the Nangang prospecting area in the Jiurui ore district of Jiangxi Province:Implication for magma evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(3):675-685(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, Li H M, Günther D, Wu F Y. 2004.Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
Zhang Bo, Su Shangguo, Mo Xuanxue, Feng Shaochong, Wu Yue, Jiang Xiao, Feng Yanfang, Liu Jiangtao. 2020. Magmatic response to lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton: Evidence from porphyritic aegirite-bearing syenite in Wuan, Hebei, China[J/OL]. Earth Science Frontiers, [2020-01-22]: 1-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang H F, Sun M, Zhou X H, Ying J F. 2005. Geochemical constraints on the origin of Mesozoic alkaline intrusive complexes from the North China Craton and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 81(1/4):297-317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=655aa3a0f89c1cc9822036ceec6c947e
Zhai M G, Zhu R X, Liu J M, Meng Q R, Hou Q L, Hu S B, Liu W, Li Z, Zhang H F, Zhang H F. 2004. Time range of Mesozoic tectonic regime inversion in eastern North China Block[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 47(2):57-65. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bfed048a533eb31b4148954304047eb9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, Li S Z. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 136(2):177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
Zheng Y F, Xu Z, Zhao Z F, Dai L Q. 2018. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in North China:Implications for thinning and destruction of cratonic lithosphere[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(4):353-385. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9160-3
Zou Jinxi, Liu Xianfan, Deng Jianghong, Deng Jianghong, Li Chunhui, Huang Yupeng, Dong Yi, Yi Liwen. 2012. Mineralogical composition characteristics and geological significance of the clinopyroxene from ultrabasic-basic rocks at Luoji village, Shangri-La County, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(5):701-711 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201205008
Zhu R X, Chen L, Wu F Y, Liu J L. 2011. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6):789-797. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4
Zhu R X, Xu Y G. 2019. The subduction of the west Pacific plate and the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences), 62(9):1340-1350. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9356-y
Zhu R X, Xu Y G, Zhu G, Zhang H F, Xia Q K, Zheng T Y. 2012a.Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 55(10):1565-1587. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4516-y
Zhu R X, Yang J H, Wu F Y. 2012b. Timing of destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 149:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.013
白志民. 2000.北京西山中生代火山岩中单斜辉石矿物化学及成因意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, (2):174-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2000.02.010 陈春良, 江思宏, 梁清玲, 刘源, 韩宁. 2014.河北雾灵山杂岩体锆石Hf同位素特征及其区域对比研究[J].现代地质, 28(4):663-673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.04.001 段友强, 张正伟, 杨晓勇. 2015.华北克拉通南缘张士英岩体大陆动力学背景:来自地球化学, 锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素的证据[J].岩石学报, 31(7):1995-2008. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201507015.htm 黄小龙, 徐义刚, 杨启军, 陈林丽. 2007.滇西莴中晚始新世高镁富钾火山岩中单斜辉石斑晶环带结构的成因:岩浆补给-混合过程[J].高校地质学报, (2):250-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.009 霍腾飞, 杨德彬, 师江朋, 许文良, 杨浩田. 2016.华北地块中部早白垩世富碱侵入岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 32(3):697-712. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201603005 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 凌洪飞, 倪培. 2006.华南与花岗岩有关的一种新类型的锡成矿作用:矿物化学, 元素和同位素地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 22(10):2509-2516. 蒋少涌, 李亮, 朱碧, 丁昕, 姜耀辉, 顾连兴, 倪培. 2008.江西武山铜矿区花岗闪长斑岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成及成因探讨[J].岩石学报, 24(8):1679-1690. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200808002 李随民, 李玉成, 赵淑梅, 张良良, 王俊革, 韩腾飞, 孙志伟, 韩玉丑, 李樋. 2020.邯郸洪山铜矿Ar-Ar和U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时代的限定[J/OL].中国地质, [2020-02-04]: 1-17. 刘鑫, 汤艳杰. 2018.冀西北姚家庄超镁铁岩-正长岩杂岩体中辉石的环带特征及意义[J].岩石学报, 34(11):3315-3326. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201811015 罗照华, 邓晋福, 韩秀卿. 1999.太行山造山带岩浆活动及其造山过程反演[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-132. 牛晓露, 陈斌, 马旭. 2009.河北矾山杂岩体中单斜辉石的研究[J].岩石学报, 25(2):359-373. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200902010 邱家骧, 廖群安. 1996.浙闽新生代玄武岩的岩石成因学与Cpx矿物化学[J].火山地质与矿产, 17(1):16-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600241803 苏尚国, 简东川, 谢玉淳, 罗照华, 蒋俊毅, 刘璐璐, 霍延安, 崔晓亮, 张波, 顾大鹏, 王玉. 2017.中基性侵入岩中-大比例尺专题地质填图实践——以河北武安铁矿集区填图试点为例[J].地质通报, 36(11):1987-1998. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.009 王亚莹, 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 闫志娇, 宋建强. 2015.山西临县紫金山岩体地球化学、矿物学特征及岩体成因[J].现代地质, 29(4):896-911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.04.020 吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明. 2005.辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J].高校地质学报, 11(3):305-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.003 吴福元, 徐义刚, 高山, 郑建平. 2008.华北岩石圈减薄与克拉通破坏研究的主要学术争论[J].岩石学报, 24(6):1145-1174. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200806001 许文良, 杨承海, 杨德彬, 裴福萍, 王清海, 纪伟强. 2006.华北克拉通东部中生代高Mg闪长岩——对岩石圈减薄机制的制约[J].地学前缘, 13(2):120-129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.010 许文良, 杨德彬, 裴福萍, 于洋. 2009.太行山南段符山高镁闪长岩的成因——拆沉陆壳物质熔融的熔体与地幔橄榄岩反应的结果[J].岩石学报, 25(8):1947-1961. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200908019 阎国翰, 蔡剑辉, 任康绪, 何国琦, 牟保磊, 许保良, 李凤棠, 杨斌. 2007.华北克拉通板内拉张性岩浆作用与三个超大陆裂解及深部地球动力学[J].高校地质学报, 13(2):161-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.003 杨照耀, 徐耀明, 朱志勇, 周巍, 柏成. 2015.江西九瑞矿集区南港成矿远景区煌斑岩中辉石矿物成分特征与岩浆演化过程[J].岩石学报, 31(3):675-685. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201503003 张波, 苏尚国, 莫宣学, 冯少憧, 伍月, 蒋校, 冯艳芳, 刘江涛. 2020.华北克拉通减薄的岩浆岩响应: 来自河北武安洪山含霓石斑状正长岩的证据[J/OL].地学前缘, [2020-01-22]: 1-14. 邹金汐, 刘显凡, 邓江红, 邓江红, 李春辉, 黄玉蓬, 董毅, 易立文. 2012.云南香格里拉洛吉乡基性-超基性岩中单斜辉石矿物成分特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 31(5):701-711. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.05.008 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王鹤源,王泽堃,谷思莹,杨烁暄,赵梓垚,陈旭. 宜昌—武汉长江沿岸典型砾石层对比分析. 高校地质学报. 2024(01): 47-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林旭,李玲玲,刘静,吴中海,李长安,刘维明,向宇,刘海金,陈济鑫. 长江早更新世向江汉盆地输送碎屑物质:来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄的约束. 地球科学. 2023(11): 4214-4228 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙杨,谢远云,迟云平,康春国,吴鹏. 大兴安岭东麓龙江县白土山组地层特征:化学风化、沉积循环、源-汇体系和沉积环境. 山地学报. 2022(01): 14-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏松林,孙全,陈平,杜林诚. 基于航测无人机的卵石三轴粒径计算及精度评估. 工程勘察. 2022(11): 68-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王令占,杨博,涂兵. 鄂东南咸宁北部冲洪积物的ESR年代及意义. 华南地质. 2021(02): 127-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: