Discovery of Late Permian pollen and spores in TD-2 borehole in Tuquan Basin of Hinggan League of Inner Mongolia and their oil and gas geological implications
-
摘要:
松辽盆地西缘的突泉盆地是在古生界之上形成的中生代盆地,近年因在侏罗系发现轻质原油而备受关注。然而,对于该盆地古生代下伏地层及其油气资源前景的研究,过去并未系统开展过。本次运用岩石地层、微体化石和烃源岩样品测试分析等方法对突泉盆地南部牤牛海凹陷TD-2井的岩心开展系统分析,TD-2井在中侏罗世万宝组砂砾岩之下发育一套以暗色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩为主的沉积,产孢粉化石19属26种,包括:Leiotriletes adnatus,Punctatisporites debilis,Cyclogranisporites sp.,Alisporites auritus,Al.communis,Al.stenoholcus,Al.sp.?,Klausipollenites schaubergeri,Pityosporites evolutus,Sulcatisporites dalongkouensis,S.ovatus,S.sp.?,Hamiapollenites indistinctus,Lunatisporites tersus,Piceaepollenites opimus,P.sp.,Voltziaceaesporites xinjiangensis,Crucisaccites variosulcatus,Divarisaccus cinctus,Plicatipollenites cf.densus,Parcisporites scabratus,Platysaccus sp.,P.papilionis,Cycadopites caperatus,Samoilovitchisaccites chordens,孢粉指示的地质时代为晚二叠世;烃源岩分析结果显示,这套暗色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩的烃源岩指标较好,具良好的油气资源前景。岩石地层和生物地层综合对比研究表明,TD-2井下部发育的这套以暗色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩为主的细碎屑沉积为晚二叠世林西组,且其具有良好的生烃基础。该发现为研究松辽盆地西缘晚古生代地层序列奠定了基础,对探讨松辽及周边盆地上古生界油气资源具有重要意义。
Abstract:Tuquan Basin near the west boundary of the Songliao Basin is a Mesozoic sedimentary basin formed above the Paleozoic strata,which has aroused much attention from geologists due to the discovery of light crude oil from the Jurassic strata in recent years. In the past,systematic research on the oil and gas resources from the Paleozoic was very insufficient. In this paper,the methods such as stratigraphic (lithostratic) and sporopollen analysis and source rock test were conducted so as to analyze synthetically the core samples collected from TD-2 well in the Mangniuhai depression of Tuquan Basin. A stratigraphic unit composed of grayish black mudstone and siltstone beneath the Middle Jurassic conglomerate was discovered in TD-2 well,and some spores and pollen were extracted from the unit,which consist of 26 species and 19 genera,including Leiotriletes adnatus,Punctatisporites debilis,Alisporites auritus,A. communis,A. stenoholcus,Klausipollenites schaubergeri,Pityosporites evolutus,Sulcatisporites dalongkouensis,Hamiapollenites indistinctus,Piceaepollenites opimus etc. indicating Late Permian. Combined with the research results such as the stratigraphy (lithostratic) and source rock test,it is reasonably assigned to Late Permian Linxi Formation,and some high-quality source rocks are discovered in this unit. This discovery is significant for confirming the existence of Permian strata in the Tuquan Basin and also for exploring the late Paleozoic oil and gas resources in the Songliao Basin and adjacent regions.
-
1. 引言
淮河流域是中国中东部地区重要的商品粮主产区及能源资源供应区,流域内交错叠加了淮河生态经济区、山东半岛蓝色经济区、长江三角洲一体化发展区等重要国家战略规划,地理位置极其重要。1970年代以前淮河流域地下水长期处于自然因素主导的补排平衡状态,70年代中后期人工开采量增大,世纪之交达到巅峰并持续了十多年(葛伟亚,2007)。长期过量开采造成了诸多环境地质问题:地下水位持续下降、地面沉降、水质劣化(文冬光等,2012;陆徐荣等,2014),据2020年统计资料,流域浅层地下水位强下降区面积超过30000 km2。过量开采地下水造成的环境地质问题制约着区域社会经济发展,需要深入、持续开展地下水资源评价与开发利用潜力研究,为流域经济可持续发展提供地质数据支撑及解决方案。
流域地下水资源评价及研究工作在欧美起步较早,1930年代美国已经陆续开展了流域尺度地下水资源研究工作,德国中南部开展了持续的地下水要素评价、监测、示踪研究工作。20世纪中叶,以海河流域及淮河流域北部地区为首的流域地下水资源相关研究逐步开展。淮河流域已开展3次地下水资源评价工作,基本查明了不同时序、动态要素制约下的阶段性地下水资源禀赋。基于供水安全目的的流域尺度地下水化学特征调查开展多次,基本查明了流域地下水分布特征及水质现状❶(张炎斋和吴培任,2005;水艳和张炎斋,2009)。针对地下水开采引发的环境地质问题专项调查开展多次,如地面沉降调查、劣质水区地方病环境地质问题调查、苏北沿海环境地质问题综合调查等,阶段性查明流域环境地质问题,并建立了部分水文要素监测设施(陶月赞和岳文君,2003)。总之,淮河流域地下水相关调查及研究积累了大量的数据及成果,为区域水资源可持续开发利用提供了相当丰硕的参考依据,但也存在一定的讨论空间:一是更高生态约束条件下的地下水资源评价和开发潜力研究尚需深入开展工作;二是地下水资源动态平衡特征需要进一步研究。本文数据基于“沙颍河-涡河流域水文地质调查”项目,在第二次全国地下水资源评价数据基础上,利用区内20年来开展的1∶5万水文地质调查成果、蚌埠和郑州水文试验站试验成果、2019年以来的流域专项水文试验成果,校核更新了流域水文地质参数,重点参考2019、2020年水均衡要素数据,在流域新的生态约束条件下开了淮河流域地下水资源特征和开发潜力研究。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 范围
淮河流域(包括山东半岛)位于111°55′~122°45′E、30°55′~38°05′N,面积约33万km2,流域主要覆盖河南、安徽、江苏、山东四省(图 1)。
2.2 降水特征
淮河流域处于中国南北气候过渡带,流域内多年平均降水量600~1400 mm,空间上降水量由南向北递减。降雨量的年际、年内分布极不均匀,差异较大,汛期(6—9月)降水占全年降水的50%~70%(图 2)。
2.3 含水系统
淮河流域地下水主要分为松散岩类孔隙水、碳酸盐岩类裂隙岩溶水和基岩裂隙水3种类型。其中分布最广的为松散岩类孔隙水,其次为岩溶水和基岩裂隙水,但有供水意义的主要为孔隙水和岩溶水。
平原区松散岩类孔隙水在区内分布最为广泛,按其埋藏深度可分为浅层地下水和深层地下水。在流域内平原区地表下30~55 m,区域上广泛分布有一层14~20 m厚的黏性土层,因此,传统上大致以地表下50 m为界限,将埋深小于和大于50 m的松散岩类孔隙含水层组分别划分为浅层含水岩组和深层含水岩组(葛伟亚,2006)。
淮河流域上游地区地下水基本是由西北流向东南,南部西部则由西向东流。北部岗状平原区浅层孔隙地下水水位埋深一般大于6 m;北部低缓平原区地下水水位埋深大部分为2~4 m;南部地下水水位埋深大部分小于2 m。浅层孔隙地下水水位主要受降水和蒸发及地表水影响,水位变幅一般为1.5~2.5 m。淮河流域深层地下水整体流向为从山前向平原径流,整体水位稳定,受季节影响较小,在阜阳—太和、亳州等地形成地下水位降落漏斗,江苏省盐城市附近深层地下水位呈逐年上升趋势。
3. 研究方法及数据来源
3.1 评价方法
山区采用径流模数法进行地下水资源评价,平原区采用均衡法进行评价。平原区地下水以孔隙水为主要评价本体。流域内承压孔隙水补给条件艰苛,深层承压孔隙地下水年龄均在25 ka以上(龚建师,2005),目前生态约束条件下,认为该层地下水为不可更新地下水,未做资源评价。
地下水质量评价依据《地下水质量标准》(GB/T14848-2017), 采用单因子综合评价法,对35项常规无机化学指标进行评价。
地下水开采潜力评价参照《地下水潜力评价技术要求》(GWI-D4)开展相关评价,潜力表征参数为开采潜力系数,该系数为可采量与现状开采量的比值,系数≥1.4,表示潜力大,1.2~1.4表示潜力较大,1.0~1.2,表示潜力较小,系数<1.0表示无潜力。
3.2 数据来源
以第二次地下水资源评价数据为基础,汇总域内2000年以来开展的120余幅1∶5万水文地质调查工作成果、城市地质调查成果,参考域内两个水文试验站相关试验成果,结合“沙颍河—涡河流域水文地质调查”项目野外实验,校核更新了流域的降雨入渗系数、含水层导水系数、山丘区地下水径流模数、山前侧向补给系数、弹性释水系数、渠系入渗系数等水文地质参数。
通过收集气象部门数据,汇总更新了流域降水、蒸发数据。
通过收集水利公报数据,结合野外典型断面校核实测数据,融合汇总了流域水文参数及地下水资源开发利用数据。
4. 结果与分析
4.1 水循环要素演变
4.1.1 降水补给要素变化
降雨量按照多年平均降雨量统计,统计结果如图 3所示。结果显示,不同阶段淮河流域多年平均降雨量差异不大,1980年以前为2390亿m3/a,1980—1999年为2317亿m3/a,2000—2018年为2339.8亿m3/a。
4.1.2 蒸散发排泄要素变化
2000年以前的蒸散发量按《淮河流域水污染治理与水资源可持续利用》中给出的蒸散发量进行统计,2000—2018年蒸散发量按照降雨量、产流、入渗、其他排泄量等进行计算(吴祖成,2016;薛阳等,2017)。淮河流域多年平均蒸散发量变化如图 4所示。1980年以前,流域多年平均蒸散发量1560.67亿m3/a,1980—1999年多年平均蒸散发量1538.49亿m3/a,2000—2018年多年平均蒸散发量为1529.6亿m3/a。数值差异不大,但呈持续微弱下降趋势。
4.1.3 人工开采要素变化
淮河流域开发利用地下水历史较早,以开采平原区浅层地下水用于农业灌溉为主。建国初期,只有少量的土井开采地下水用作农灌和居民生活,工业用水开采地下水很少。
从淮河流域开采量历史变化(图 5)可以看出,30多年来地下水开采量增长迅速。20世纪70年代地下水开采量约79.81亿m3/a,80年代地下水开采量约87.28亿m3/a,90年代地下水开采量约为131.28亿m3/a,到了2000—2004年年均地下水开采量增加到138.03亿m3/a。70年代、80年代开采量变化不大,到了90年代跨越式增长,2000—2018年开采量呈波动稳定状态。通过上述数据,结合流域社会经济发展阶段,以及2000年加大治淮力度等时间节点,可以把淮河流域人工开采地下水历史划为3个典型阶段,即1980年以前,1980—1999年,2000—2018年3个阶段(图 6)。
4.1.4 地下水位变化
淮河流域地下水循环条件演化的主导因素为人工开采,在流域内人工开采最严重的为豫东平原、鲁西南地区、皖北平原、苏北平原。据2005年及2020年流域地下水位统测数据,淮河流域浅层地下水水位大部分呈下降趋势,15年来浅层地下水明显下降区面积达3.2万km2。
4.2 地下水资源状况
4.2.1 地下水资源评价分区
根据统一性、系统性、层次性、继承性原则,结合淮河流域特殊的地理、气象、地质地貌背景,有针对性的对淮河流域进行地下水资源分区。淮河流域可划分为1个一级分区、3个二级分区、6个三级分区、15个四级分区(表 1、图 8)。
表 1 淮河流域水文地质单元划分表Table 1. Hydrogeological unit division of Huaihe River Basin
4.2.2 地下水资源及空间分布
流域浅层天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,其中平原区天然资源量为234.8502亿m3/a,山丘区天然资源量为94.6929亿m3/a,山丘和平原区重复计算量为2.5775亿m3/a。按地下水四级区统计,南四湖水系平原天然资源量为17.91亿m3/a;淮河水系近代黄泛平原区天然资源量为31.68亿m3/a;南四湖水系山区天然资源量为4.11亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系平原区天然资源量为5.69亿m3/a;沂沭河水系平原区天然资源量为40.31亿m3/a;沂沭河水系山区天然资源量为23.61亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵南坡诸河水系区天然资源量为10.20亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵北坡诸河水系区天然资源量为5.56亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系山区天然资源量为14.00亿m3/a;淮河水系波状平原天然资源量为13.86亿m3/a;淮河水系与长江水系过渡区天然资源量为13.73亿m3/a;黄淮冲积、海积平原天然资源量为84.10亿m3/a;淮河流域大别山区天然资源量为21.89亿m3/a;淮河水系山前平原天然资源量为22.89亿m3/a;淮河流域伏牛山区天然资源量为17.41亿m3/a。按省统计,山东天然资源量为82.515亿m3/a;河南天然资源量为83.203亿m3/a;安徽天然资源量为71.134亿m3/a;江苏天然资源量为87.755亿m3/a,湖北浅层水天然资源量为2.359亿m3/a(图 9、图 10)。
4.3 地下水质量现状
利用2019年国家地下水监测工程780个测孔测试数据及2019年区域460组水化学测试数据,基于35个常规无机化学指标,开展流域主要平原地区地下水质量评价。结果显示,淮河流域地下水质量总体一般,浅层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比6.7%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比93.3%,深层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比8.5%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比91.5%。浅层地下水和深层地下水主要影响因子均为铁、锰、硬度等指标,淮北平原、苏北局部地区、豫东鲁西南局部地区深层地下水砷、氟超标严重。
与2005、2010年淮河流域地下水质量评价结果对比,现状浅层地下水质量在经历了2005—2010年显著恶化后,近年在地表水质量总体好转的情况下,仍在趋于恶化,总体超标水比例增加了4.3%,但Ⅴ类水降低了6.2%(图 11)。
深层水超标率从2005年的51.6%到2010年65.9%,近年呈现出显著恶化趋势,2019年超标水比例已上升25.6%,达2005—2010年恶化趋势的1.8倍,且Ⅳ、Ⅴ均呈大幅上升趋势。
4.4 地下水开采潜力
采用开采潜力系数法进行区域地下水开采潜力评价。由于区域深层地下水在新的生态约束条件下无可利用资源量,故现状深层地下水开采区均为无潜力区。
浅层地下水(含基岩裂隙水)开采潜力总体上南部大于北部,山区-平原复合行政区大于纯平原行政区。其中江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区、河南南部地区浅层地下水开采潜力较大,豫东地区、山东大部分地区开采潜力小,郑州、开封、许昌、漯河、商丘、周口、济宁、淄博、菏泽超采严重,已无潜力(表 2)。
表 2 浅层地下水开采潜力状况(108m3/a)Table 2. Exploitation potential of shallow groundwater (108 m3/a)
5. 讨论与建议
淮河流域人均水资源量为475 m3,不足全国人均水资源量(2012年,2100 m3)的1/4,加上水质劣化,使得水资源供需矛盾更加突出。南水北调中线工程对豫东供水、东线工程对苏皖鲁供水一定程度缓解了域内缺水问题,但在新时期高质量发展导向的生态约束条件下,水资源供需形势仍然严峻。且一定程度的人工干预水资源配置造成了水文要素异化反馈,亟待开展相关科学研究。为进一步缓解淮河流域水资源供需矛盾,优化水资源配置问题,提出以下建议:
(1)深入开展流域尺度地下水地表水一体化调查研究,逐步寻求科学途径,解决流域水资源配置现状。目前,流域内重地表水配置、轻地下水参与,如2001—2019年,地表水利用率达65.2%,地下水利用率为53.1%,应合理配置不同时空条件下的地表水、地下水利用占比。
(2)开展劣质水区地下水资源系统调查,提出基于水质安全的可持续供水建议。淮河流域地下水质量问题是困扰流域浅层地下水开发的主要问题,部分地区高氟、高砷、高碘地下水造成的地方病在区内仍有发生,2019年测试数据显示豫东皖北苏北等地浅层地下水样本氟化物含量超标占比26.22%,碘化物超标占比20.64%,豫东皖北苏北等地深层水样本氟化物含量超标率27.92%,碘化物超标47.17%。安全供水需求导向的水资源调查工作需要深入开展。
(3)南水北调东线工程、引江济淮工程在改善北方缺水地区水资源利用问题的同时,也造成了沿线部分受水区水位不稳定变化,由此引起一定生态响应,如土壤盐渍化、水质变化等,需要加强沿线受水影响区水文要素监测工作,为水资源配置精细化管理、生态响应科学问题研究提供支撑。
6. 结论
(1)受人工开采持续增大影响,流域地下水循环特征发生变化,浅层地下水位持续下降,豫东、鲁西南地区2005年以来浅层地下水位下降5 m以上面积超过30000 km2。浅层地下水位下降导致有效蒸发强度变弱,蒸发量持续下降,多年平均有效蒸发强度从2000年前的1538.49 mm降至近期的1529.6 mm。
(2)淮河流域浅层地下水天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,人均171.19亿m3/a,地下水资源相对一般。
(3)淮河流域平原地区地下水总体一般,浅层、深层孔隙水Ⅴ类水占比分别达47.7%、44.9%;与2005年、2010年历史数据相比,水质呈劣化趋势,2019年测试数据显示区域地下水中高氟水、高碘水占比仍在20%以上,深层地下水碘化物超标近半。
(4)浅层地下水开发盈余量总体南多北少、山区多平原少;江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区总体开采潜力大,可采系数均在1.0以上,最大达103.92×108 m3/a,豫东、鲁西南地区开采潜力小,部分地市如漯河、周口、菏泽等地超采严重,已无潜力。
注释
❶叶念军,葛伟亚,龚建师,杨则东,左正金,陆徐荣,徐建国,王献坤,杨小双,彭玉怀,王付军,赵华荣,刘红樱,朱恒华,陆华,杨佩明,徐华,陈秀其,杨磊,程生平,周锴锷,邢怀学,穆倩,朱春芳,陈鸿汉,李炳华. 2012. 淮河流域环境地质调查报告[R]. 南京:中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心.
致谢: 本文写作过程中,吉林大学古生物学与地层学研究中心的孙跃武教授和张淑芹研究员给予了悉心指导和大力帮助;野外及样品采集过程中得到长江大学邓超伟的协助;文献收集方面得到了长江大学的董曼老师、沈阳师范大学梁飞老师、吉林大学郎嘉彬老师、李宁老师、那玉玲博士、李云峰博士、黄薇博士和李想等的帮助,在此一并致谢。 -
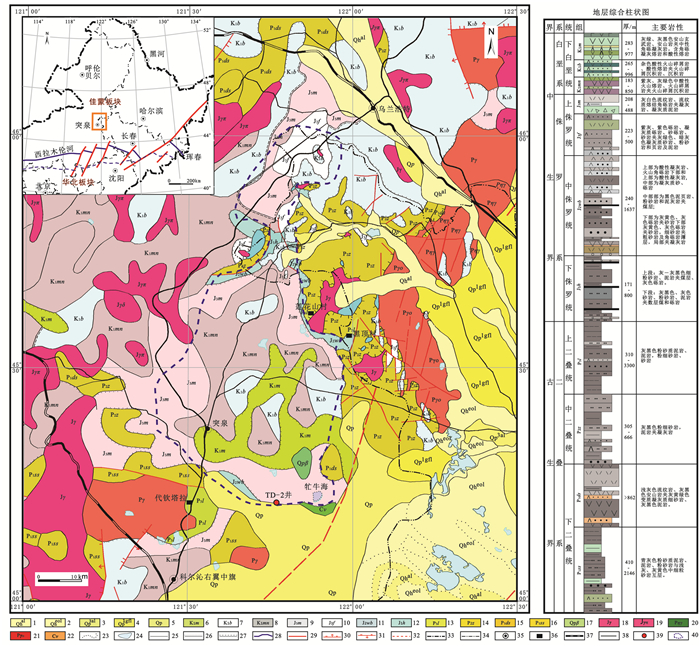
图 1 内蒙古突泉县突地2(TD2)井位置图
1—全新统湖冲积物;2—全新统风积物;3—上更新统冲洪积物;4—下更新统冰水堆积物;5—更新统;6—梅勒图组;7—白音高老组;8—玛尼吐组;9—满克头鄂博组;10—付家洼子组;11—万宝组;12—红旗组;13—林西组;14—哲斯组;15—寿山沟组;16—大石寨组;17—更新统玄武岩;18—侏罗纪花岗岩;19—侏罗纪花岗斑岩;20—二叠纪二长斑岩;21—二叠纪斜长花岗岩;22—石炭纪辉长岩;23—风沙沉积;24—湖泊;25—整合;26—平行不整合;27—角度不整合;28—缝合线;29—断裂;30—正断层;31—逆断层;32—推测断层;33—中国东北大陆边界;34—省界;35—城镇;36—乡村;37—铁路;38—公路;39—TD-2井;40—推测突泉盆地边界
Figure 1. Location of TD2 borehole in Tuquan County, Inner Mongolia
1-Qhal; 2-Qheol; 3-Qp3al; 4-Qp1gfl; 5-Qp; 6-K1m; 7-K1b; 8-K1mn; 9-J3m; 10-J3f; 11-J2wb; 12-J1h; 13-P3l; 14-P2z; 15-P1ss; 16-P1ds; 17-Qpβ; 18-Jγ; 19-Jγπ; 20-Pηπ; 21-Pγo; 22-Cν; 23-Aeolian landform; 24-Lake; 25-Conformity; 26-Parallel unconformity; 27-Angular unconformity; 28-Suture; 29-Fault structure; 30-Normal fault; 31-Reverse fault; 32-Speculated fault; 33-Land boundary of the northeast China; 34-Provincial boundary; 35-Town; 36-Village; 37-Railway; 38-Highway; 39-TD-2 well; 40-Inferred boundary of the Tuquan Basin
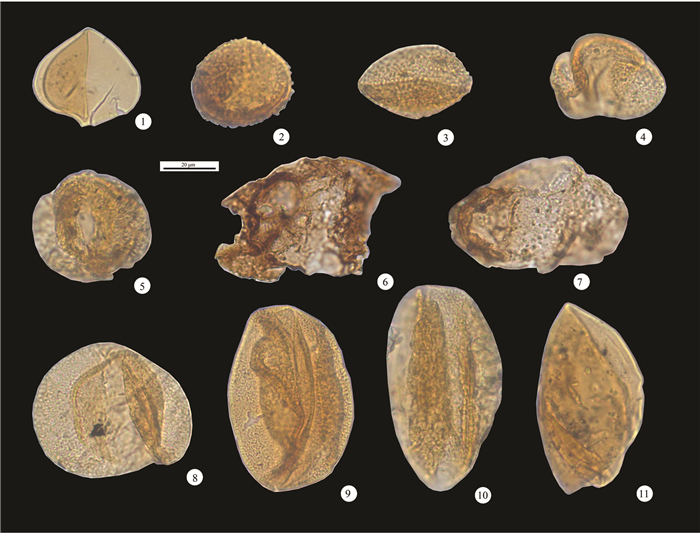
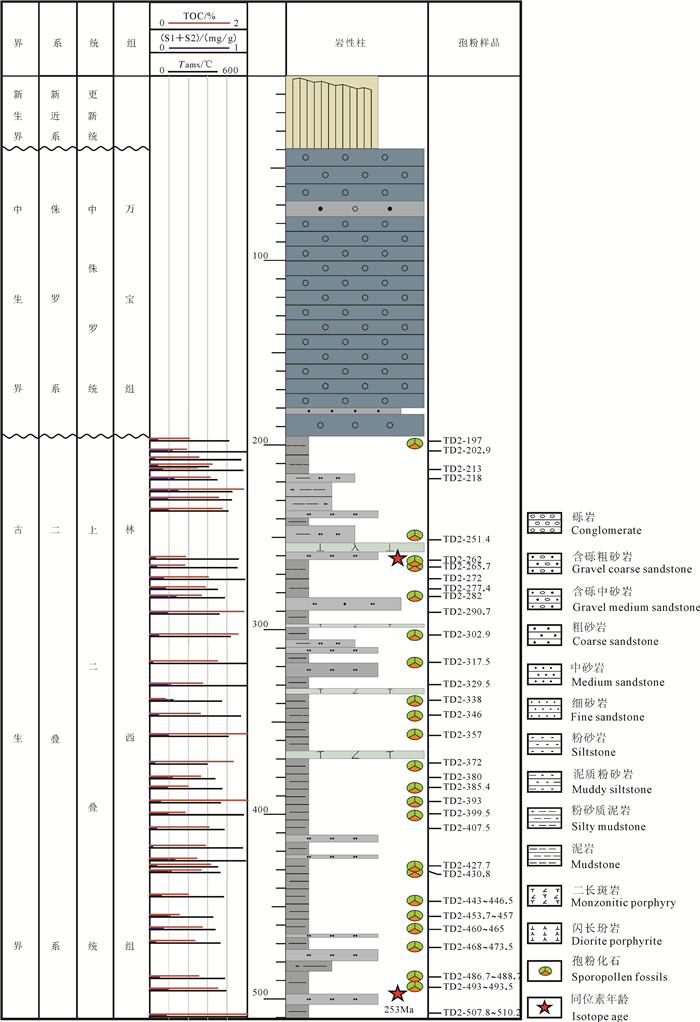
图 3 内蒙古突泉县牤牛海地区突地2井(TD2)上二叠统林西组孢粉化石
1—弓形堤光面三缝孢;2, 3—圆形粒面孢(未定种);4—展开松型粉;5—粗糙雏囊粉;6—整洁四肋粉;7—复网残缝粉;8—拟云杉粉(未定种);9, 10—大龙口具沟双囊粉;11—皱粒苏铁粉
Figure 3. Spores and pollen from the Upper Permian Linxi Formation in TD2 borehole of Mangniuhai, Tuquan County, Inner Mongolia
1-Leiotriletes adnatus (Kosanke) Potonie et Kremp; 2, 3- Cyclogranisporites sp.; 4-Pityosporites evolutus Ouyang; 5-Parcisporites scabratus Ouyang; 6-Lunatisporites tersus Ouyang; 7-Vestigisporites complexus Ouyang; 8-Piceaepollenites sp.; 9, 10-Sulcatisporites dalongkouensis Ouyang; 11- Cycadopites caperatus (Luber) Hart
-
Chen Shuwang, Ding Qiuhong, Zheng Yuejuan, Li Yongfei, Wang Jie, Zhang Jian, Su Fei, Gao Xiaoyong, Li Xiaohai, Zhang Yongsheng, Fang Hui, Zhang Minghua, Zhong Qing. 2010. Earl Jurassic-Late Paleizoic hydrocarbon potential analysis in the periphery of Songliao Basin[J]. Mineral Deposits, 29(Supp.):1037-1038 (in Chinese).
Chen Shuwang, Zhang Haihua, Zheng Yuejuan, Bian Xiongfei, Zhang Jian, Su Fei, Gong Fanhao, Huang Xin, Zhen Zhen. 2015. Detrital zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age of the Late Permian Linxi Formation in Horqin Right Wing Middle Banner-Tuquan area of Inner Mongolia and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(10):1869-1877(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201510011
Crippa G, Angiolini L, Van W I, Crow M J, Hasibuan F, Stephenson M H, Ueno K. 2014. Brachiopods, fusulines and palynomorphs of the Mengkarang Formation (Early Permian, Sumatra) and their palaeobiogeographical significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79:206-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.030
Du Fengjun, Lu Shuwei, Gao Lianda, Zhang Yanqi, Jia Gong-xiang. 2006. Characteristics and significance of the Late Permian sporopollen assemblage in the Gongjiubu area, Ngamring, southern Tibet, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25 (1/2):168-172(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200601026
Diéguez Carmen, Barrón Eduardo. 2005. Late Permian flora and vegetation changes near the Permian-Triassic boundary in the Landete section of the Alcotas Formation (SE Iberian Ranges, Spain)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 229(1/2):54-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=216bd29dcf9541d09a923d6c2b093b56
Dimitrova Tatiana K H, Cleal Christopher J, Thomas Barry A. 2005.Palynology of late Westphalian-early Stephanian coal-bearing deposits in the eastern South Wales Coalfield[J]. Geological Magazine, 142(6):809-821. doi: 10.1017/S001675680500107X
Falcon Rosemary S. 1975. Palyno-stratigraphy of the lower Karroo sequence in the central Sebungwe District, Mid-Zambezi Basin, Rhodesia[J]. Palaeont. Afr., 18:1-29.
Foster C B, Afonin S A. 2005. Abnormal pollen grains:an outcome of deteriorating atmospheric conditions around the Permian-Triassic boundary[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 162(4):653-659. doi: 10.1144/0016-764904-047
Gao Lianda, Shen Zhida, Qin Dianxi. 1989. Discovery of early Permian sporopopollen assemdlages from Kaili County, Guizhou and staligrephic significance[J]. Guizhou Geology, 6(2):97-109(in Chinese with English absteact).
Huang Benhong. 1983. On Late Paleozoic Palaeophytogeographic Regions of Eastern Tianshan-Hingan Foldbelt and Its Geological Significance[C]//Tang Kedong(ed.). Contributions for the Project of Plate Tectonics in Northern China, No. 1. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 135-155 (in Chinese).
Huang Benhong. 1983. Plant fossils of the Taohaiyingzi Formation in the eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Plant Journal, 26(6):580-583(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Benhong. 1993. Carboniferous and Permian Systems and Floras in the Da Hinggan Range[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-141 (in Chinese).
Huang Pin, Zhu Huaicheng, Wang Ayun. 2002. Palynofloras of the Shanxi Formation from the Wangzhuang Coal Mine of Xuzhou, Jiangsu and their stratigraphical significance[J]. Acta Micropala eontologica Sinica, 19(3):33-52 (in Chinese with English Absteact). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtgswxb200201003
Huang Xin, Zheng Yuejuan, Bao Qingzhong. 2015. New discovery of sporopollen fossils from Linxi Formation in Arun Qi, Inner Mongolia[C]//Chinese Society of Paleontology. Abstracts of Papers of the 28th Annual Meeting of Chinese Paleontology Society.Shenyang: Chinese Paleontology Society, 87 (in Chinese).
Jan I U, Stephenson M H, Khan F R. 2009. Palynostratigraphic correlation of the Sardhai Formation (Permian) of Pakistan[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 158(1):72-82. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b8a2500737fccde083e50d8cd726b8eb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Jha Neerja, Aggarwal Neha. 2012. Permian-Triassic palynostratigraphy in Mailaram area, Godavari Graben, Andhra Pradesh, India[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 121(5):1257-1285. doi: 10.1007/s12040-012-0224-4
Kang Xiaoqian, Feng Xuan, Hou Hesheng, Sun Chengcheng, Liu Qian, Yu Hailong. 2019. Carboniferous-Permian stratigraphic thickness innorthern Songliao Basin:Evidence from deep reflection seismic data[J]. Geology in China, 46(5):1116-1125 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380408600191
Kang Yuzhu. 2009. The Oil and Gas prospect of Paleozoic in several areas of the Northeast, North and the West China[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 31(3):1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnsyxyxb200903001
Kyle Rosemary A. 1977. Palynostratigraphy of the Victoria Group of South Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 20(6):1081-1102. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1977.10420697
Li Fulai, Qu Xiyu, Liu Li, Yang Deming, Wang Dehai, Zhao Guoxiang. 2009. Sedimentary environment of the Upper Permian Linxi Formation in Northeastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27(2):265-272 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Shizhen, Zhou Xingui, Wang Dandan, Lin Yanhua, Zhang Wenhao. 2015. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil and oil-source correlation of well Tucan 1, Tuquan Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(10):1946-1951 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201510019
Li Shoujun, Zhao Xiuli, Yin Tiantao, Yuan Liyuan, He Miao, Xu Fenglin, Chen Ru, Huang Pengpeng. 2013. The characteristics of Early to Middle Permian sporopollen assemblages in Pengzhuang, Shangong Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(2):1819-1825(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Tianyi, Liu Jingdang, Zhang Yanfei, Wang Gang, Wang Yan, Ding Wei, Zhang Hailong. 2019. Marine facies oncolite found in Permian Linxi Formation in middle Da Higgnan Mountains in Northeast China[J]. Geology in China, 46(1):213-214 (in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201901019
Li Wenguo, Li Qingfu, Jiang Wande. 1996. Stratigraphy (Lithostratic)of Nei Mongol Autonomous Region[M]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press, 1-344 (in Chinese).
Lindstrom Sofie. 2003. Carboniferous palynology of the Loppa High, Barents Sea, Norway[J]. Norsk Geologisk Tidsskrift, 83(4):333-350. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=35ba653b8b28ab17c8030fdf9780d702&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Feng, Zhu Huaicheng, Ouyang Shu. 2015. Late Pennsylvanian to Wuchiapingian palynostratigraphy of the Baode section in the Ordos Basin, North China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111:528-552. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.06.013
Liu Ling, Zhang Minghua, Tian Qianning, Shang Longping. 2013. The method of using gravity and magnetic data for Gravity field separating in Tuquan Basin and 3D inversion of rock[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 37(2):242-245 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201302011
Liu Zhaosheng. 2000. The Permian-Triassic boundary on the Northern Margin of the Turpan-Hami basin of Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 24(4):310-314 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Loinaze VS Perez, Césari Silvia Nelida, Gamundí O López, Buatois L. 2010. Palynology of the Permian San Miguel Formation (Western Paraná Basin, Paraguay):Gondwanan biostratigraphic correlations[J]. Geologica Acta, 8(4):483-493.
Lu Yanban Yuan Xiurun. 1988. Sporopollen assemblage in Late Paleozoic Coal series of Dangshan, Anhui Province[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 10(1):44-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-sysd198801004.htm
Meyen S V. 1991. Paleozoic Floras and Phytogeography of Eurasia[M]//Yao Zhaoqi(ed.). Nanjing:Nanjing University Press, 1-177 (in Chinese).
Murthy S, Kavali P S. 2015. Bernardes-de-Oliveira M. E. C. Latest Permian palynomorphs from Jharia Coalfield, Damodar Basin, India and their potential for biostratigraphic correlation[J]. Revue de Micropaléontologie, 58(3):167-184. doi: 10.1016/j.revmic.2015.06.001
Ouyang Shu. 1962. The microspore assemblage from the Lungtan Series of Changhsing, Chekiang[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 10(1):76-141 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX196201008.htm
Ouyang Shu, John Utting. 1990. Palynology of Upper Permian and Lower Triassic rocks, Meishan, Changxing County, Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 66(1):65-103. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003466679090029I
Ouyang Shu, Wang Zhi, Zhan Jiazhen. 2003. Palynology of the Carboniferous and Permian Strata of Northern Xinjiang, Northwestern China[M]. Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China Press, 1-700 (in Chinese).
Ouyang Shu, Zhu Huaicheng, Zhan Jiazhen, Wang Zhi. 2004.Comparison of Permian Palynofloras from the Junggar and Tarim Basins and its bearing on phytoprovincialism and stratigraphy[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 28(3):194-207 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200403001
Qiu Shilong, Zhao Qingying, Li Shichao, Li Zihao, Tian Zilong, Li Shixian, Zheng Zeyu. 2018. The Late Jurassic I-type granite from Baohetun of Tuquan region in Eastern Inner Mongolia:Geochemistry, petrogenesis and geologic implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 27(2):107-116(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201802001
Qu Yonggui. 1986. A new cognition on the Permian System in the Yiema Area, Western Jilin[J]. Jilin Geology, 1:58-65 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JLDZ198601009.htm
Ren Shoumai, Qiao Dewu, Zhang Xingzhou, Liu Yongjiang, Wang Nan, Sun Yuewu, Tang Zhenxing, Cui Yongqian. 2011. The present situation of oil & gas resources exploration and strategic selection of potential area in the Upper Paleozoic of Songliao Basin and surrounding area, NE China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(2/3):197-204 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2011Z1004.htm
Schneebeli Hermann Elke, Bucher Hugo. 2015. Palynostratigraphy at the Permian-Triassic boundary of the Amb section, Salt Range, Pakistan[J]. Palynology, 39(1):1-18. doi: 10.1080/01916122.2014.921648
Shi Xiao, Yu Jianxin, Chen Bin, Huang Cheng, Gu Songzhu, Li Hui, Chi Hongfei. 2004. Palynology of the Lower Permian Dazhuyuan and Liangshan Formations in Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen area, northern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 16(2):217-226 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201402007
Spina Amalia, Cirilli Simonetta, Utting John, Jansonius Jan. 2015. Palynology of the Permian and Triassic of the Tesero and Bulla sections (Western Dolomites, Italy) and consideration about the enigmatic species Reduviasporonites chalastus[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 218:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2014.10.003
Spina A, Aria-Nasab M R, Cirilli S, Stephenson M H. 2015.Palynostratigraphy of the Permian Faraghan Formation in the Zagros Basin, Southern Iran:preliminary studies[J]. Executive Notes, (61):1-22. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0034666703001222
Steiner M B, Eshet Y, Rampino M R, Schwindt D M. 2003. Fungal abundance spike and the Permian-Triassic boundary in the Karoo Supergroup (South Africa)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 194(4):405-414. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00230-X
Su Fei, Li Zhen, Zhang Jian, Tang Youjun, Zhang Haihua. 2017.Discovery of the soure rock from Upper Permian Linxi Formation in Tuquan Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 26(3):268-274 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201703009
Sun Chunlin, Li Tao, Wu Wenhao, Wang Lixia, Zhang Lijun. 2012. An aquatic fern leaf from the Late Triassic of Western Liaoning, China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan, 58:227-228. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5a67b1176db02a2877ca79242425f726&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Sun Yuewu, Zhang Shuqin, Wan Chuanbiao, Zhang Dejun, Li Mingsong. 2012. Lopingian palynomorphs in the Linxi Formation, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan, 58:228. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f0fe6ecc4870c40d8573f76d5fdcfd28&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Upshaw Charles F, Creath Wilgus B. 1965. Pennsylvanian miospores from a cave deposit in Devonian limestone, Callaway County, Missouri[J]. Micropaleontology, 11(4):431-448. doi: 10.2307/1484779
Van der Voo R, Spakman W, Bijw aard H. 1999. Mesozoic subducted slabs under Siberia[J]. Nature, 397(6716):246-249. doi: 10.1038/16686
Wang Chengwen, Jin Wei, Zhang Xingzhou, Ma Zhihong, Chi Xiaoguo, Liu Yongjiang, Li Ning. 2008. New understanding of the Late Paleozoic tectonics in Northeastern China and adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 32(2):119-136(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200802001
Wang Chenwen, Sun Yuewu, Li Ning, Liu Huan, Zhao Guowei. 2009.On the distribution of Late Palaeozoic strata in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 33(1):56-61(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200901006
Wang Shixin, Hu Chang' an, Luo Guichang, Li Hui, Wang Ping, Gan Jijun, Yang Yan. 2011. Recognition of the Late Permian Strata in Shaerhu coalfield in Turpan-Hami Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 29(3):275-283 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjdz201103006
Wang Wuli, Li Yongfei, Guo Shengzhe. 2014. The northeast China Block Group and Its tectonic evolution[J]. Geology and Resources, 23(1):4-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8cf9f3086209f1f427059fd992ec3d2a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wilson Graeme J. 1976. Notes from the New Zealand geological survey-9:Permian palynomorphs from the Mangarewa Formation, Productus Creek, southland, New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 19(1):136-140. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1976.10423555
Yanev Slavcho. 2009. Stratigraphy ànd sedimentology of the Stephanian and Permian in the Lozen Mts. and Vakarel Hills[J]. Geological Institute, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, 70(1/3):73-89 (in Russian with English summary).
Yang Bing, Zhang Xionghua, Ge Mengchun, Zhao Shengmin, Wei Yi, Huang Xing, Luan Tengfei, Wei Xinxiang, Yang Zhiyong. 2014.Late Permian-Early triassic palynological assemblages in Linxi, Inner Mongolia and discovery of Triassic strata[J].Earth Sciene(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 39(7):784-794(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.074
Yang Xuelin, Sun LiWen. 1985. Jurassic fossil plants from the Southearn part of Dahingganling, China[J]. Bull. Shenyang Inst.Geol. Min. Res., Chinese Acad. Geol. Sci., 12:98-114(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Xuelin, Sun LiWen. 1985. Strata of the Early and Middle Jurassic in the Southearn part of Dahingganling, China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 9(1):56-61 (in Chinese).
Yao Jianxin, Xiao Xuchang, Gao Lianda, Wang Naiwen, Ji Wenhua, Wang Shiyan, WangYong, Chi Zhenqing. 2007. Discovery of Permian sporopollen from Daftar, Taxkorgan, Xinjiang and their geological implications[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 252(1):66-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0e7ea977b7e1df355475812b0708f706
Yin Hongfu, Yang Fengqing, Yu Jianxin, Peng Yuanqiao, Wang Shangyan, Zhang Suxin. 2007. An accurately delineated PermianTriassic Boundary in continental successions[J]. Science in China(Series D:Earth Sciences), 50(9):1281-1292. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0048-2
Zélia Pereiraa, Paulo Fernandesb, Gilda Lopesc, João Marquesd, Lopo Vasconcelose. 2016. The Permian-Triassic transition in the Moatize-Minjova Basin, Karoo Supergroup, Mozambique:A palynological perspective[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 226:1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2015.12.001
Zhang Dejun, Sun Yuewu, Ding Haisheng, Yang Zhenyuan, Tang Lijing. 2014. Lopingian mixed floras from Linxi Formation in Soron area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Global Geology, 17(2):67-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dbydxyj-e201402001
Zhang Dejun, Zhang Jian, Zheng Yuejuan, Chen Shuwang, Su Fei, Huang Xin, Zhang Haihua. 2019. Study on the Middle Jurassic flora in Southern Tuquan Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 28(1):7-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201901002
Zhang Haihua, Zheng Yuejuan, Chen Shuwang, Zhan Jian, Gong Fanhao, Su Fei, Huang Xin. 2015. Age of Xingfuzhilu Formation and contact relationship between Permian and Triassic strata in southern Da Hinggan Mountains:Constraints from the tuff zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Geology in China, 42(6):1754-1764 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7d03b6afe9073e4aa9db6577dca47811&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang Meisheng, Peng Xiangdong, Sun Xiaomeng. 1998. The Paleozoic Tectonic Geographical Pattern of Northeast China[J]. Liaoning Geology, 1 (2):91-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800391956
Zhang Yongsheng, Tian Shugang, Li Zishun, Gong Yuexuan, Xing Enyuan, Wang Zhuozhuo, Zhai Daxing, Cao Jie, Sui Kui, Wang Meng. 2013. Discovery of marine fossils in the upper part of the Permaian Linxi Formation in Lopingian, Xingmeng area, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58:3429-3439 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-33-3429
Zhao Yue, Yang Zhenyu, Ma Xinghua. 1994. Geotectonic transition from PaleoAsian system and Paleo-Tethyan system to PaleoPacific active continental margin in eastern Asia[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 29(2):105-119 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKX402.000.htm
Zhen Zhen, Chen Shuwang, Zheng Yuejuan, Zhang Jian, Li Yongfei, Su Fei, Huang Xin, Gong Fanhao. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of Linxi Formation along Taohaiyingzi section in Ar Horqin Banner, Inner Mongolia, and the constraint on the provenances and the tectonic settings[J].Geology in China, 45(5):1011-1022(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201805010
Zheng Yuejuan, Zhang Jian, Chen Shuwang, Huang Xin, Zhang Lijun, Wang Wuli. 2013. New fossil discovery along the section of Linxi Formation at Taohaiyingzi in Ar Horqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(8):1269-1276(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201308013
Zhu Huaicheng, Ouyang Shu, Zhan Jiazhen, Wang Zhi. 2005.Comparison of Permian palynological assemblages from the Junggar and Tarim Basins and their phytoprovincial significance[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 136(3):181-207. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2ec10de7b87faba8d518ebb584b26544&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
陈树旺, 丁秋红, 郑月娟, 李永飞, 王杰, 张健, 苏飞, 郜晓勇, 李晓海, 张永生, 方慧, 张明华, 钟清. 2010.松辽外围早侏罗世-晚古生代油气远景分析[J].矿床地质, 29(Z1):1037-1038. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7413014 陈树旺, 张海华, 郑月娟, 卞雄飞, 张健, 苏飞, 公繁浩, 黄欣, 甄甄. 2015.内蒙古科右中旗-突泉地区晚二叠世林西组碎屑岩LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 34(10):1869-1877. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201510011 杜凤军, 卢书炜, 高联达, 张彦启, 贾共祥. 2006.藏南昂仁县贡久布地区晚二叠世孢粉组合的特征及其意义[J].地质通报, 25(1):168-172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200601026 高联达, 沈志达, 秦典燮. 1989.贵州凯里地区早二叠世早期孢子花粉的发现及其地层意义[J].贵州地质, 6(2):97-109. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1989-GZDZ198902000.htm 黄本宏. 1983.天山-兴安褶皱区东部古生代末植物地理区系及其地质意义[C]//唐克东编.中国北方板块构造文集(第一集).沈阳: 中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所: 138-155. 黄本宏. 1983.内蒙古东部陶海营子组植物化石[J].植物学报, 25(6):580-583. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZWXB198306013.htm 黄本宏. 1993.大兴安岭地区石炭、二叠系及植物群[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-141. 黄嫔, 朱怀诚, 王阿云. 2002.徐州王庄煤矿山西组孢粉植物群及其地层意义[J].微体古生物学报, 19(3):33-52. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtgswxb200201003 黄欣, 郑月娟, 张健.鲍庆中. 2015.内蒙古阿荣旗林西组孢粉化石新发现[C]//中国古生物学会.中国古生物学会第28届学术年会论文摘要集.沈阳: 中国古生物学会, 87. 康晓倩, 冯晅, 侯贺晟, 孙成城, 刘乾, 俞海龙. 2019.松辽盆地北部石炭-二叠纪地层厚度:来自深反射地震的证据[J].中国地质, 46(5):1116-1125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201905013 康玉柱. 2009.中国东北、华北、西部等地区古生界油气前景探讨[J].西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 31(3):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnsyxyxb200903001 梁天意, 刘敬党, 张艳飞, 王刚, 汪岩, 丁伟, 张海龙. 2019.中国大兴安岭中段二叠系林西组发现海相核形石[J].中国地质, 46(01):213-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201901019 李福来, 曲希玉, 刘立, 杨德明, 王德海, 赵国祥. 2009.内蒙古东北部上二叠统林西组沉积环境[J].沉积学报, 27(2):265-272. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7587939 李世臻, 周新桂, 王丹丹, 林燕华, 张文浩. 2015.内蒙古突泉盆地突参1井原油地球化学特征与油源分析[J].地质通报, 34(10):1946-1951. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201510019 李守军, 赵秀丽, 殷天涛, 原丽媛, 贺淼, 徐凤琳, 陈茹, 黄彭彭. 2013.山东彭庄早、中二叠世孢粉组合特征[J].地质学报, 87(2):1819-1825. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201312005 李文国, 姜万德, 王慧. 1996.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1-344. 刘玲, 张明华, 田黔宁, 尚龙平. 2013.突泉盆地磁性体重力场剥离的方法技术及岩体三维显示[J].物探与化探, 37(2):242-245. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201302011 刘兆生. 2000.吐哈盆地北缘二叠系与三叠系界线[J].地层学杂志, 24(4):310-314. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dcxzz200004011 陆彦邦, 袁修润. 1988.安徽砀山晚古生代煤系的孢粉组合[J].石油实验地质, 10(1):44-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYSD198801004.htm 梅因C B, 姚兆奇编译. 1991.欧亚大陆古生代植物群和植物地理学[M].南京: 南京大学出版社. 1-177. 欧阳舒. 1962.浙江长兴龙潭组孢子花粉组合[J].古生物学报, 10(1):76-141. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSWX196201008.htm 欧阳舒, 王智, 詹家祯. 2003.新疆北部石炭纪-二叠纪孢子花粉研究[M].合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社:1-700. 欧阳舒, 朱怀诚, 詹家桢, 王智. 2004.新疆准噶尔盆地和塔里木盆地二叠纪孢粉组合的比较及其植物区系和地层意义[J].地层学杂志, 28(3):193-207. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dcxzz200403001 邱士龙, 赵庆英, 李世超, 李子昊, 田子龙, 李湜先, 郑泽宇.2018.内蒙古东部突泉地区宝合屯晚侏罗世Ⅰ型花岗岩——地球化学特征、岩石成因及地质意义[J].地质与资源, 27(2):107-116, 136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201802001 曲永贵. 1986.吉林省西部野马地区二迭系的新认识[J].吉林地质, 1:58-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JLDZ198601009.htm 任收麦, 乔德武, 张兴洲, 刘永江, 王楠, 孙跃武, 唐振兴. 2011.松辽盆地及外围上古生界油气资源战略选区研究进展[J].地质通报, 30(2/3):197-204. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201102003 史骁, 喻建新, 陈斌, 黄程, 顾松竹, 李慧. 2014.黔北务川-正安-道真地区下二叠统大竹园组和梁山组孢粉学研究[J].古地理学报, 16(2):217-226. 苏飞, 李臻, 张健, 唐友军, 张海华. 2017.内蒙古突泉盆地突D2井上二叠统林西组烃源岩新发现[J].地质与资源, 26(03):268-274. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201703009 王成文, 金巍, 张兴洲, 马志红, 迟效国, 刘永江, 李宁. 2008.东北及邻区晚古生代大地构造属性新认识[J].地层学杂志, 32(2):119-136. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dcxzz200802001 王成文, 孙跃武, 李宁, 刘欢, 赵国伟. 2009.东北地区晚古生代地层分布规律[J].地层学杂志, 33(1):56-61. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dcxzz200901006 王世新, 胡长安, 罗桂昌, 李慧, 王平, 甘继军, 杨艳. 2011.吐哈盆地沙尔湖煤田晚二叠世地层再认识[J].新疆地质, 29(3):275-283. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz201103006 王五力, 李永飞, 郭胜哲. 2014.中国东北地块群及其构造演化[J].地质与资源, 23(1):4-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201401002 杨兵, 张雄华, 葛梦春, 赵省民, 韦一, 黄兴, 栾腾飞, 魏信祥, 杨志勇. 2014.内蒙古林西地区晚二叠世-早三叠世孢粉组合及三叠系的发现[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 39(7):784-794. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201407002 杨学林, 孙礼文. 1985.大兴安岭南部侏罗纪植物化石[J].中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所刊, 12:98-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001811678 杨学林, 孙礼文. 1985.大兴安岭南部早、中侏罗世地层[J].地层学杂志, 9(1):10-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DCXZ198501001.htm 张德军, 张健, 郑月娟, 陈树旺, 苏飞, 黄欣, 张海华. 2019.内蒙古突泉盆地南部中侏罗世植物群初探[J].地质与资源, 28(1):7-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201901002 张海华, 郑月娟, 陈树旺, 张健, 公繁浩, 苏飞, 黄欣. 2015.大兴安岭南部幸福之路组的时代及二叠-三叠系界线研究——来自凝灰岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J].中国地质, 42(6):1754-1764. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201506007 张梅生, 彭向东, 孙晓猛. 1998.中国东北区古生代构造古地理格局[J].辽宁地质, 1(2):91-96. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800391956 张永生, 田树刚, 李子舜, 宫月萱, 邢恩袁, 王卓卓, 翟大兴, 曹洁, 苏奎, 王猛. 2013.兴蒙地区二叠系乐平统林西组上部发现海相化石[J].科学通报, 58(33):3429-3439. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201333009 赵越, 杨振宇, 马醒华. 1994.东亚大地构造发展的重要转折[J].地质科学, 29(2):105-119. doi: 10.1016-j.archoralbio.2010.05.016/ 甄甄, 陈树旺, 郑月娟, 张健, 李永飞, 苏飞, 黄欣, 公繁浩. 2018.内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁旗陶海营子剖面林西组地球化学特征及其对物源-构造背景的制约[J].中国地质, 45(5):1011-1022. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201805010 郑月娟, 张健, 陈树旺, 黄欣, 张立君, 王五力. 2013.内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁旗陶海营子剖面林西组化石新发现[J].地质通报, 32(8):1269-1276. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201308013




 下载:
下载: