The characteristics and formation mechanism of Ordovician dolomite in Member 6 of Majiagou Formation in South Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
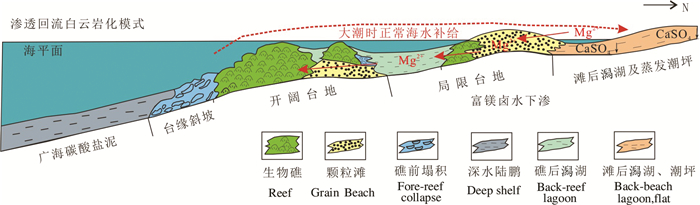
鄂尔多斯盆地马六段在盆地大部分地区被剥蚀,仅在盆地周缘地区分布,因此,有关该盆地马六段白云岩成因研究较少。本文通过对马六段白云岩岩石学特征、阴极发光特征、微量元素特征以及碳氧同位素地球化学特征进行分析,对鄂尔多斯盆地南部马六段白云岩特征及形成机制进行了研究。研究结果表明,盆地南部马六段白云岩主要由细—中晶白云岩组成,白云石具“雾心亮边”结构,阴极发光呈暗红色光。微量元素总体上具有较低的Fe、Mn值,平均值分别为447×10-6和62×10-6,较高的K、Na值,平均值分别为517×10-6和252×10-6,以及中等含量的Sr元素值,平均值为155×10-6。δ13C值平均为-0.617‰,δ18O值平均为-7.6‰,以上特征均反映出海源流体特征。白云石的“雾心”和“亮边”结构中微量元素含量相差不大,认为是在相同成岩环境的不同成岩阶段形成,其中“雾心”形成于浅埋藏环境的渗透回流白云石化作用,而“亮边”是在深埋藏环境下对早期白云石的调整和加强。
Abstract:Member 6 of Majiagou Formation in south Ordos basin has been eroded in most part of the south Ordos basin,and is hence only distributed in the periphery of the basin. Therefore,less studies have been done on the origin of dolomite in member 6 of Majiagou Formation of the basin. Based on petrologic analysis,cathodoluminescence images,trace elements and carbon and oxygen isotope characteristics,the authors studied the characteristics and formation mechanism of dolomite in member 6 of Majiagou Formation in south Ordos basin. The results reveal that the dolomite of member 6 in south Ordos basin is mainly composed of finemedium crystal dolomite with cloudy cores and clear rims as well as dark red luminescence. The dolomite has relatively low Fe and Mn content (average of 447×10-6 and 62×10-6),relatively high K and Na content (average of 517×10-6 and 252×10-6) and moderate content of Sr (average of 155×10-6). Average value of δ13C and δ18O is -0.617‰ and -7.6‰ respectively,moderate indicating its marine origin. The trace element content of cloudy cores is close to that of clear rims,which indicates that they were formed in similar diagenesis environments. The cloudy cores were formed in a shallow buried environment by seepage reflux dolomitization model,while the clear rims were recrystallized and adjusted in a deep buried environment.
-
1. 引言
水系沉积物是岩石风化的产物,是上游汇水盆地物质的天然组合,在化学成分上与所流经汇水盆地内受剥蚀的地质体有明显的继承性和代表性(蒋敬业等,2006;郝立波等,2007;陆顺富等,2014)。利用这一特点,水系沉积物地球化学测量可以有效获取隐伏、半隐伏矿和难识别矿的成矿信息,为进一步开展地质勘查工作提供依据(夏祥标等,2009;李玉芹等,2011;宋贺民等2014;刘邦定等,2015),因而在金属矿产资源勘查中发挥着愈来愈重要的作用(杨伟寿等,2007;朱建华,2007;师淑娟等,2011;张江华等,2013;赵武强等,2014)。
完达山地区主要由一套近南北走向的玄武岩、堆晶岩、(超)基性熔岩、硅质岩和泥质岩组成(张兴洲,2010),是中国东部唯一的中生代海相地层发育区域(周建波等,2005;田东江,2007),出露有太平洋板块俯冲形成的增生杂岩组合(Kojima et al., 1987, 1989;Zheng, 1990;张世红等,1991;唐克东等,1995;张庆龙等,1997;田东江等,2006;张雪锋等,2014;王庆双等,2015;韦延兰等,2015),且中生代蛇绿岩发育,为中国典型的蛇绿岩发育地区之一(田东江,2007;Zhang et al., 2013)。研究区内矿产资源丰富,但受年均7~8个月的结冰期及森林植被覆盖影响,地质找矿勘查工作并不理想,在一定程度上制约了区域成矿规律的研究和资源评价工作的安排。有鉴于此,笔者从完达山1:20万水系沉积物测量数据入手,分析水系沉积物地球化学异常与地层、构造、岩浆岩及矿床之间的关系,阐明地球化学异常的控制因素,圈定有利的找矿靶区,为完达山地区整体找矿工作部署和区域成矿规律研究提供科学依据。
2. 成矿地质背景
完达山地区位于中国东北地区东部, 是完达山—锡霍特—阿林超地体在中国境内的出露部分, 西与南以宝清大和镇断裂和敦密断裂为界,东与北至乌苏里江边和小佳河镇胜利农场,东西宽约80 km,南北长约240 km,总体上呈近南北向略向西突出的弧形分布,并向宝清过渡带逆掩推覆。该区缺失太古宇、古生界的古老地层,而发育中生代和新生代地层(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 完达山地区区域地质图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Wanddashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)
图 1 完达山地区区域地质图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Wanddashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)区内构造较为发育,以北东向和北西向构造为主,主要包括敦化—密山断裂、大和镇断裂、富锦—小佳河断裂、饶河北西向断层束和饶河北北东向断层束。
区内岩浆岩十分发育,主要发育有晚古生代(超)基性岩、早中生代(超)基性岩和晚中生代酸性岩浆岩。晚古生代(超)基性岩分布于研究区西南部跃进山—曙光村—东方红一带,为跃进山蛇绿岩的重要组成部分,岩性为玄武岩、角闪辉长岩、辉长岩、蛇纹石化橄榄辉石岩等。早中生代(超)基性岩分布于研究区东部八里桥—仙人台一带,为饶河蛇绿岩的重要组成部分,岩性为玄武岩、枕状玄武岩、角闪辉长岩、单辉橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩等。晚中生代酸性岩浆岩由酸性侵入岩和酸性火山岩组成,酸性侵入岩出露于蛤蚂河、蛤蟆通水库和东方红镇西北部,岩性为花岗闪长岩、正长花岗岩、斜长花岗岩和二长花岗岩等。酸性火山岩位于研究区南部大塔山林场组和皮克山组地层中,岩性为流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩、流纹质凝灰熔岩、热液角砾岩等。
区内金属矿产主要与晚中生代晚期酸性岩浆岩和早中生代(超)基性岩有关,矿种为金、银、铜、镍、钴等,到目前为止,已发现中型矿床1座(四平山金矿床),小型矿床4座(先锋北金矿床、258高地金矿床、358高地金矿床、跃进山铜金属矿床),矿点10余处(蛤蟆河金矿点、宝丰村金矿、永幸铜镍矿点等)。
3. 地球化学特征
3.1 样品采集加工与分析质量
样品采集严格遵守1:20万水系沉积物测量规范,平均采样密度为1.18个/4 km2,采集样品2114件(不包括重复密码分析样)。采样点主要分布在二、三级水系内,长度为1~2 km的一级水系口,长度大于2 km的一级水系内适当增加采样点,采样介质为活性水系沉积物(如:淤泥、粉砂),每个样品在采样点附近30~50 m范围内进行多点(不少于3点)采集,合并为一个样品,样品重量过筛后不少于300 g,取10~60目粒度作为分析样品(杨小峰等,2007;李林山等,2009;朴寿成等,2009)。分析测试单位为国土资源部哈尔滨矿产资源监督检测中心,分析测试方法采用原子吸收分光光度法(AAS)、原子荧光分光光度法(AFS)、X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)和电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)等方法,样品分析项目为As、Au、Hg、Sb、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、Bi、Mo、Sn、W、Co、Cr、Ni、V。
根据森林沼泽区技术方法研究要求,在分析元素、测试分析配套方案、测试分析质量监控方法等方面制定了统一的技术方法。其中,测试分析质量监控采用外部质量监控和内部质量监控相结合的方法,实验室内部按样品总数随机抽取5%的重份样品进行分析,合格率为100%,同时随机抽取8%的样品进行随机重复密码分析,合格率为97%。综上所述,分析报告中的化探数据可靠,分析质量达到或优于规范质量等级。
3.2 元素含量特征
采用元素含量最高值(CMax)、最低值(CMin)、平均值(X)、标准离差(S)、变异系数(CV)、富集系数(K)等地球化学参数来阐明和讨论1:20万水系沉积物地球化学特征及规律。浓集系数(K)为研究区元素平均值与全省元素平均值之比,变异系数(CV)为元素标准偏差与均值之比。
研究区内Au、Cu、Pb、Zn、Sn、W、Co、Ni、V、Cr元素的浓集系数均大于1.00,表明这些元素在完达山地区具有一定的次生富集倾向,有利于成矿;Ag、Hg、Bi、Sn、Mo元素的浓集系数小于1.00(表 1),表明这些元素在完达山地区趋于贫化,成矿作用相对较弱。结合研究区各元素变异系数由Bi−Cr−Au−Ni−Hg−Ag−As−Sn−Sb−Cu−Co−Mo−W−Zn−V−Pb逐渐下降,意味着从Bi到Pb成矿作用依次减弱。
表 1 完达山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征参数Table 1. Geochemical parameters of the stream sediment samples from Wandashan area
3.3 元素变化特征
水系沉积物样品中各元素原始数据的变异系数(CV1)(薛水根,1979;刘劲松等,2016)和背景数据(采用>X+3S及<X−3S迭代剔除,直至无离群点数值可剔除为止,即所有数据全部分布>X-3S与<X+3S间)的变异系数(CV2)反映了数据处理前后的离散程度(张运强等,2015),CV1/CV2反映背景拟合处理时离散值的削平程度。因而可以利用CV1和CV1/CV2制作变异系数图解,从变异系数图解(图 2)中可以看出,区内Bi含量变化幅度最大,高强度数据最多,分布极不均匀,成矿特别有利;Au、Ni、Cr、Hg高强度数据较多,变异系数较大,有利于成矿,且大多数异常内已发现矿床(点)(如四平山金矿、先锋北山金矿、跃进山金矿、永幸铜镍矿点等);Ag、As、Sn、Sb、Cu、Co、Mo、W、Zn、V、Pb在测区中的CV1和CV1/CV2值都比较低,成矿可能性较低。
3.4 元素分布特征
通对完达山地区2114件水系沉积物样品的地球化学数据统计,得到各元素丰度直方图。由该元素丰度直方图(图 3)可知,Au、Bi、Ni、Cr元素的标准偏差分别为1.22、0.49、32.88、106.75,变异系数分别为1.05、1.42、0.99、1.21,呈非正态分布,具有较强的成矿潜力;Hg、Ag、Cu、Co元素的标准偏差分别为42.25、52.88、11.21、6.22,变异系数分别为0.99、0.58、0.44、0.40,呈近似正态分布,具有一定的成矿潜力;As、Sb、Pb、Zn、W、Mo、Sn、V元素的标准偏差分别为5.00、0.22、3.50、21.89、0.67、0.49、1.75、18.07,变异系数分别为0.53、0.47、0.15、0.25、0.35、0.40、0.53、0.23,服从正态分布,成矿潜力较弱。
3.5 元素相关性特征
3.5.1 聚类分析
由表 2可知,Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、V元素呈显著正相关,Au、As、Sb、Bi、Sn元素之间呈正强相关。在R聚类分析图中(图 4),以R= 0. 3为界成矿元素可分5类。
表 2 完达山地区水系沉积物成矿元素相关系数矩阵Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix of metallogenic elements from Wandashan area
第一类Bi、Sn:主要分布于完达山西南部蛤蟆通岩体内,其次分布于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带中,反映与高温热源作用相关的矿化信息。
第二类Au、Ag、Hg:异常分布与岩浆岩体相关,Au与Ag、Hg相关性较强,代表低温热液矿化作用,组合异常是测区寻找Au、Ag矿床的重要地球化学找矿标志。
第三类Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn:位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带和跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,Co、Cr、Ni密切相关,反映Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn元素富集与蛇绿岩中(超)基性岩形成相关。
第四类W、Mo:与Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn和As、Sb、Pb、V均具有一定的相关性,其成因复杂,既受岩浆热液控制又受地层控制。
第五类As、Sb、Pb、V:元素具有一定相关性,其富集作用主要与三叠纪地层相关,为层控元素。
3.5.2 因子分析
样品原始数据因子分析的相关矩阵特征根和累积百分比见表 3,前6个特征根代表的方差占总方差的68.6%,因此视这前6个因子为主要因子。
表 3 完达山水系沉积物成矿元素主因子分析Table 3. Principal factor analysis of metallogenic elements from Wandashan area
F1因子贡献率最大,变量元素有Co、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、V,以亲铁元素为主,与区内蛇绿岩中的(超)基性岩体相关。F2因子的元素组合为Au、Bi、Sn,反映岩浆岩矿化作用,低温的Au元素可能与高温的Bi、Sn元素具有同源关系。F3因子的元素为Au、As、Sb,是本区最为重要的一种元素组合,与酸性岩浆岩相关,反映中低温热液矿化作用。
F4、F5因子的元素组合为W、Mo、Cu和Ag、Cu、Zn、Pb,分别代表研究区高温与中温矿化阶段。F6因子的变量元素仅有熔点较低Hg元素,Hg迁移能力非常强,暗示本区内多金属成矿作用与中酸性含矿热液沿构造充填作用有关。
4. 地球化学异常分析
4.1 单元素异常特征
文中异常外带边界、中带边界和内带边界分别由异常下限、2倍异常下限和4倍异常下限确定。异常下限计算公式为:Ct=X+2δ (X为背景平均值,δ为标准离差,Ct为异常下限)。
由图 5可知,完达山地区共圈出Au元素异常9处,Au−2、Au−3、Au−7、Au−8为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,具有较强的找矿意义,是重要的Au找矿靶区;Au−1、Au−4、Au−5、Au−6、Au−9为多点中带异常,为找矿远景区。Au−2异常位于哈蚂河岩体内,面积约为49.01 km2,呈闭合的不规则椭圆状,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为16.83×10-9,258金矿床就位于该Au异常带内;Au−3异常位于四平山附近,面积约为49.13 km2,为闭合的不规则状,呈北东向展布,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为19.60×10-9,四平山金矿床处于该Au异常带内;Au−8异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,面积约为59.15 km2,为闭合的不规则状,呈北东向展布,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为20.80×10-9。
As元素异常总体规模较小,无多点内带异常,5处多点中带异常。其中,As−3、As−5异常分别与Au −3、Au−9和Ag−5、Ag−7等元素异常完全套,表明As可作为寻找Au、Ag矿床(体)的指示元素。
Sb元素异常规模较小,无多点内带异常,4处多点中带异常。其中,Sb−2异常与Au−3和Ag−5套和较好,Sb−4异常与Au−9和Ag−7套和较好。
Hg元素异常3处,Hg−1为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,呈闭合的不规则状,面积约为50.01 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1600.00×10-9;Hg−2位于四平山金矿区附近,为多点中带异常,与Au−3和Ag−5套和较好,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为60.46 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为160.00×10-9。Hg−3为多点中带异常,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为12.57 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为206.00×10-9。
Ag元素异7处,Ag−2、Ag−6为多点内带异常,异常面积大、衬度高,具有重要找矿意义,可以作为Ag找矿靶区;Ag−1、Ag−3、Ag−4、Ag−5、Ag−7为多点中带异常,可以作为找矿远景区。Ag−2异常位于研究区北部,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为17.85 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1220.00×10-9,目前尚未发现Ag矿床(点),找矿潜力较大;Ag−6异常位于跃进山附近,呈闭合的圆形,面积约为20.00 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1610.00×10-9,跃进山铜金矿床位于该异常内;Ag−5异常位于四平山附近,面积约为35.43 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为285.00×10-9,四平山金矿床位于该异常内;Ag−7异常位于先锋北山附近,面积约为61.27 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为455.00×10-9,先锋北山金矿床位于该异常内。虽然,Ag−3、Ag−4异常内尚未发现相应的Ag矿床(点),但这两处异常带规模较大,异常衬度较高,找矿潜力较好。
Cu元素异常8处,Cu−7为多点内带异常,其他7处均为多点中带异常。Cu−1、Cu−2、Cu−3、Cu−4异常分布与八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩带分布基本一致;Cu−5、Cu−6、Cu−7、Cu−8异常与跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带套合较好。
Pb、Zn异常主要分布于研究区东部和西南部,规模较小,无异常内带,形成铅、锌矿床的可能性较小,找矿潜力不大。
W元素异常3处,W−1位于矿区东部,为多点内带异常,面积约为204.35 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为13.60×10-6,异常面积大、衬度高,异常内已发现小别拉坑钨锡矿点,具有一定的找矿前景,可以作为W的找矿靶区。
Mo元素异常3处,Mo−3位于研究区东部,为多点内带异常,衬度高,面积约为41.66 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为13.75×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,可作为钼矿找矿靶区。
Sn元素异常3处,Sn−1位于蛤蟆岩体南部边缘,为多点中带异常,面积约为57.41 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为9.00×10-6,主要受蛤蟆河岩体控制;Sn−2异常位于研究区东部(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,面积约为32.79 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为26.00×10-6;Sn−3异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,为多点内带异常,面积约为94.01 km2,有5个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为45.00×10-6。
Bi元素异常共5处,Bi−1、Bi−2位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,面积和浓集中心最大值分别为23.98 km2、26.31 km2和1.62×10−6、1.25×10-6;Bi−3、Bi−4位于研究区中部,为多点中带异常,面积和浓集中心最大值分别为20.13 km2、11.55 km2和1.60×10-6、6.20×10-6;Bi−5异常位于蛤蟆通岩体内,为多点内带异常,面积约为126.91 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为12.59×10-6。
Co元素异常3处,Co−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,异常衬度高,面积约为396.13 km2,有6个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为97.80×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,为钴矿找矿靶区。Co−2异常位于龙间山附近,面积约为9.13 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为48.70×10-6;Co−3异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,衬度高,面积约为99.98 km2,有1个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为78.20×10-6。
Ni元素异常5处,Ni−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,为多点内带异常,异常衬度高,面积约为335.86 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为714.80×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力,异常内已发现永幸铜镍矿点;Ni−4异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,为多点中带异常,面积约为102.19 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为132.30×10-6;Ni−2、Ni−3、Ni−5异常为中异常,异常面积小,衬度低,找矿潜力不大。
Cr元素异常3处,Cr−1异常位于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带内,呈近南北向分布,面积约为511.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1771.30×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Cr−3异常位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,多点中带异常,面积约为218.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为892.60×10-6。
V异常总体规模较小,较为分散,且无中带或内带异常,形成矿床的可能性较小,找矿潜力不大。
4.2 组合元素异常特征
在单元素异常的基础上,根据异常性质、组合特征以及异常所处的地质背景、成矿地质条件等因素共圈出6个组合异常(图 6)。其特征如下:
4.2.1 HS−1号组合异常
HS−1号组合异常仅有一个Au−2异常,考虑Au−2异常的重要性,特将它圈定为一个组合异常,强调其重要性。Au−2异常位于哈蚂河岩体内,出露岩性主要为花岗闪长岩,局部见有北东向闪长玢岩脉。Au−2为多点内带异常,呈闭合的不规则状,北东向展布,分布面积约为49.01 km2,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为16.83×10-9,区内已发现258金矿床。
4.2.2 HS−2号组合异常
HS−2号组合异常规模大,强度高,为Cu−Cr−Ni −Co−Bi−Sn−Mo−W元素组合异常,与区内八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩体带的分布位置基本一致,呈北北东向展布,面积为693.75 km2,长约为46 km,宽为7~26 km,主要以Cu、Ni、Cr、Co异常为主。Cu、Ni、Cr元素异常分布面积大,含量高,Cu异常具中带、外带,面积约为289.53 km2,浓集中心最大值为130.10×10-6;Ni异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为359.88 km2,浓集中心最大值为714.80×10-6;Cr异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为511.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为1771.30×10-6。Cu、Cr、Ni、Co、Bi、Sn、Mo、W单元素异常套合性较好,浓集中心一致,结合区域地质特征可知,该组合异常与(超)基性岩带相关性较强,且组合异常内发现多处矿(化)点(如:永幸铜镍点、向阳铜矿点、小别拉坑钨锡矿点等),因此,该区域应该重点寻找与(超)基性岩相关的Cu、Ni、Cr等矿产资源。
4.2.3 HS−3号组合异常
HS−3号组合异常位于八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩体带西侧的大岭桥组杂砂岩、泥粉质砂岩、砂质板岩和泥岩中,呈北北东向展布,面积为200.36 km2,长约为25 km,宽为3~12 km,主要以Ag异常为主。Ag异常具有中等、外带,面积约为85.20 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为400.00×10-9。Ag、Bi、Sn、As等元素异常套合较好,浓集中心基本一致。受工作环境的影响,该组合异常区内尚未发现Ag、Bi、Sn矿床(点)。
4.2.4 HS−4号组合异常
HS−4号组合异常位于四平山—358高地一带,呈北东向展布,面积为141.26 km2,以Au异常为主,出露岩性为流纹岩、花岗岩、硅质岩、砂岩、杂砂岩和泥岩等。Au、Ag、Hg、Sn元素异常套合较好,浓集中心基本一致。Au异常由Au−3和Au−4异常组成,四平山金矿床和358金矿床分别位于Au−3和Au−4异常内。
4.2.5 HS−5号组合异常
HS−5号组合异常为Au−Hg−Sn−Bi−Ni−Cr−W元素组合异常,位于红旗屯—炮手营—东旺屯附近,出露岩性为中生代的硅质岩、砂岩、杂砂岩及泥岩,呈北西向展布,分布面积为181.03 km2,主要以Au异常为主。Au异常具有内带、中等、外带,面积约为32.83 km2,有2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为9.50×10-9。由于工作程度较低,该异常区尚未发现Au矿床(点),找矿潜力较大。
4.2.6 HS−6号组合异常
HS−6号组合异常规模大,强度高,为Au−Ag−Sb−As−Cu−Ni−Cr−Co−Bi−Pb−Zn元素组合异常,位于跃进山—曙光村—东方红一带,出露岩性为(超)基性岩和酸性侵入岩,呈北北东向展布,面积372.60 km2,主要以Au、Cu、Ni、Cr、Co异常为主。Au异常由Au−8和Au−9组成(Au−8和Au−9异常特征在单元素异常中已详细描述),受酸性侵入岩控制,具有较好的找矿潜力。Cu、Ni、Cr、Co元素主要受跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带控制,Cu异常为多点内带异常,面积约为370.63 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为174.70×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Cr异常为多点内带异常,面积约为218.55 km2,有4个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为892.60×10-6,具有较好的找矿潜力;Ni异常面积约为102.19 km2,有3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为132.30×10-6,具有一定的找矿潜力。
5. 成矿远景区圈定与评价
根据成矿地质背景、控矿条件、区域地球化学异常、区域航磁异常、区域重力异常以及区内矿床(点)分布规律等特征,研究区内共圈定4处成矿远景区:258高地金、银成矿远景区(YJQ−1);八里桥—仙人台铜、镍、钨、锡成矿远景区(YJQ−2);四平山— 358高地金、银成矿远景区(YJQ−3);跃进山—先锋北山金、银、铜、铁成矿远景区(YJQ−4) (图 7)。
![]() 图 7 完达山地区成矿远景区划分图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 7. Metallogenic prospective areas in Wandashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)
图 7 完达山地区成矿远景区划分图(据张国宾, 2014修改)Figure 7. Metallogenic prospective areas in Wandashan area (modified after Zhang, 2014)5.1 258高地金成矿远景区
258高地成矿远景区位于完达山地区北部蛤蟆河岩体内,呈北东—南东向L形展布,长16~17 km,宽8~10 km,面积约220 km2。区内断裂构造发育,对成矿有利的侵入岩为早白垩世晚期酸性侵入岩体。1:20万水系沉积物化学异常以Au−2异常为主,Au−2异常面积较大,约为32.83 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带和2个浓集中心。已知矿床(点)有258金矿床和蛤蟆河金矿化点。围岩蚀变强烈,主要有硅化、绢云母化、高岭土化、绿泥石化,主攻矿种为金,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金矿床。
5.2 八里桥—仙人台铜镍钨锡成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区东北部,呈北北东向长条状展布,长约41 km,宽约13 km,面积近500 km2。区内断裂构造以北北东向为主,北西向、北东向次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,与成矿关系密切的岩体为八里桥—仙人台(超)基性岩带。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Cu−2、Cu−4、Co−1、Ni−1、Cr−1、Sn−2、W−1异常为主,Cu、Co、Ni、Cr、W、Sn元素异常套和较好,面积较大,除Cu元素只有异常中等和外带外,其他元素均具有异常内带、中等、外带和多个浓集中心。区内已发现矿(化)点有向阳铜矿点、永幸铜镍矿点、小别拉坑钨锡矿点等。围岩蚀变较为发育,主要有硅化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化,主攻矿种为铜、钴、镍、铬、钨、锡等中高温元素和亲铁元素,主攻矿床类型为岩浆熔离型铜镍铬矿床和细脉侵染型铜钨锡矿床。
5.3 四平山—358高地金银成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区东部,呈北西向长条状展布,长约20 km,宽约10 km,面积约200 km2。区内以北北东向和北东向构造为主,北西向构造次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,上三叠统—下侏罗统大岭桥组粉砂岩、砂岩夹薄层硅质岩,下白垩统穆棱组砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,四平山组泉胶砾岩夹泉胶砂岩、硅质岩。与成矿相关的岩体主要为白垩系流纹岩、花岗斑岩和花岗闪长玢岩。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Au−3、Au−4、Ag−5异常为主,Au−3和Ag−5异常位于四平山矿区附近,套和较好。Au−3异常面积约为49.13 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为19.60×10-9;Ag−5具有异常中等、外带。Au−4异常位于358金矿区附近,具有异常中等、外带,2个浓集中心。区内发现的矿床(点)有四平山金矿床、358高地金矿床。围岩蚀变强烈,主要有硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、叶腊石化、碳酸盐化等,主攻矿种为金、银,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金、银矿床。
5.4 跃进山—先锋北山金银铜铁成矿远景区
该成矿远景区位于完达山地区西南部,呈南北向长条状展布,长约30 km,宽约12 km,面积近63 km2。区内以北西向和北东向构造为主,近东西向和近南北向构造次之。出露地层为上三叠统—中三叠统大佳河组硅质岩夹泥岩、粉砂岩,下白垩统穆棱组砂岩、泥质粉砂岩。金、银矿化主要与酸性侵入岩体(蛤蟆通岩体、尖山子岩体以及后期侵入的酸性岩株、岩脉)相关,铜、铁、镍矿化主要与跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带相关。1:20万水系沉积物地球化学异常主要以Au−8、Ag−6、Ag−7、Cr −3、Cu−6、Cu−7、Cu−8、Ni−4、Sn−3异常为主。其中,Au、Ag异常分布于酸性侵入岩中及其附近,与酸性侵入岩体套和较好。Au−8异常面积约为59.15 km2,具有异常内带、中等、外带,2个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为20.80×10-9;Ag−7异常面积约为61.27 km2,具有异常中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为455.00×10-9。Cu、Ni、Sn等单元素异常位于(超)基性岩带内及其附近。Cu−7异常面积约为17.75 km2,具有异常中等、外带,浓集中心最大值为174.70×10-6;Cu−8异常面积约为103.66 km2,具有异常中等、外带和3个浓集中心,浓集中心最大值为109.90×10-6。Ni−4异常和Sn−3异常主要位于(超)基性岩带内,异常面积大,Ni−4、Sn−3异常与(超)基性岩体套和较好,具有异常中等、外带和多个浓集中心。区内已发现的矿床(点)有先锋北山金矿床、跃进山铁矿床、跃进山铜金矿床、曙光村铜矿点等。围岩蚀变较为发育,且分带性明显,主要有硅化、绿泥石化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、叶腊石化,主攻矿种为金、银、铜、镍、铬、锡等,主攻矿床类型为浅成低温热液型金银矿床、火山热液型金银矿床和熔离型铜镍铬矿床。
6. 结论
(1) 研究区内Au、Ni、Cr、Bi、Hg异常高值点多、变异系数值高、离散性强,地质及地球化学条件优越,成矿潜力强。
(2) Au、Ag、Hg、As、Sb异常规模较大、套合好,多富集于中酸性岩浆岩体内及其附近,与低温热液型成矿作用相关;Cr、Ni、Co、V、Cu、Zn异常套合较好,主要分布于大顶子—仙人台(超)基性岩带和跃进山—曙光村—东方红(超)基性岩带内,与高温岩浆熔离型成矿作用相关。
(3) 完达山地区共优选出4处成矿远景区,分别为258高地金成矿远景区、八里桥—仙人台铜镍钨锡成矿远景区、四平山—358高地金银成矿远景区和跃进山—先锋北山金银铜铁成矿远景区。
致谢: 感谢中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心天山—兴蒙工程首席周新桂研究员,西部大型盆地碳酸盐岩项目负责人赵省民研究员对本文的指导;感谢两位审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵意见! -
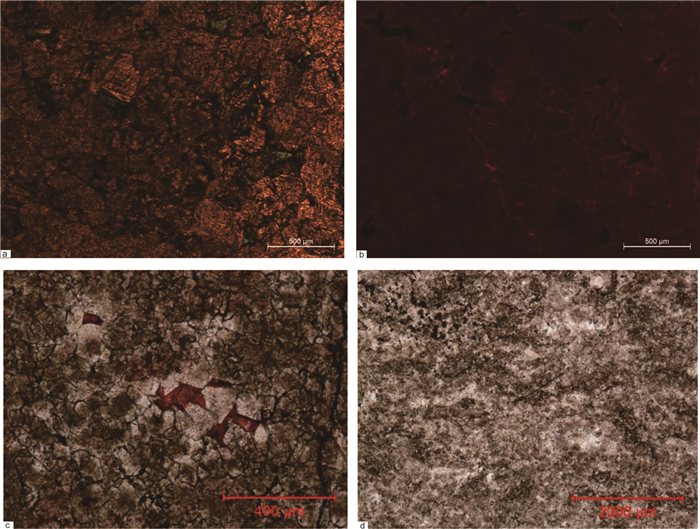
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马六段白云岩储层岩石学特征
a—中—细晶白云岩,3301.62 m,马六,旬探1井,单偏光;b—图a的阴极发光CL;c—细晶残余砂屑云岩,粒间晶间孔被方解石充填,面孔率1%,2710 m,马六,淳探1,单偏光;d—细晶残余砂屑云岩,残余藻纹层构造,4274.28 m,马六,淳2,单偏光
Figure 2. Petrologic characteristics of dolomite reservoir of member 6 in the south Ordos basin
a-Medium-fine crystal dolomite, 3301.62 m, member 6, Xuntan1 well (-); b-Cathodoluminescence image of Fig. 1; c-Fine residual arene dolomite, pores in grains and crystals filled by cement with porosity of 1% (-), 2710 m, member 6, Chuntan1 well; d-Fine residual arene dolomite, residual algae laminae texture (-), 4274.28 m, member 6, Chuntan2 well
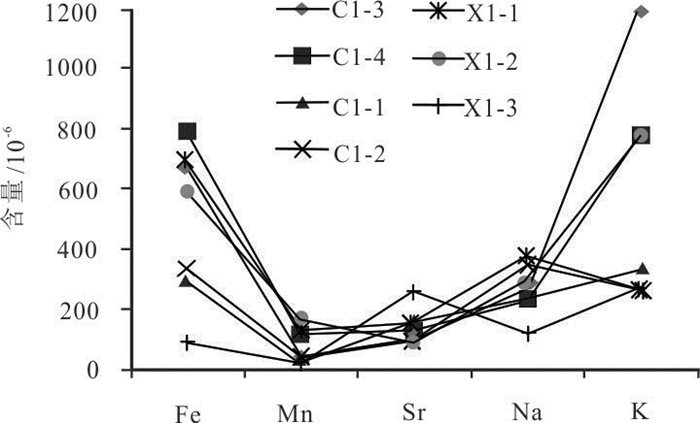
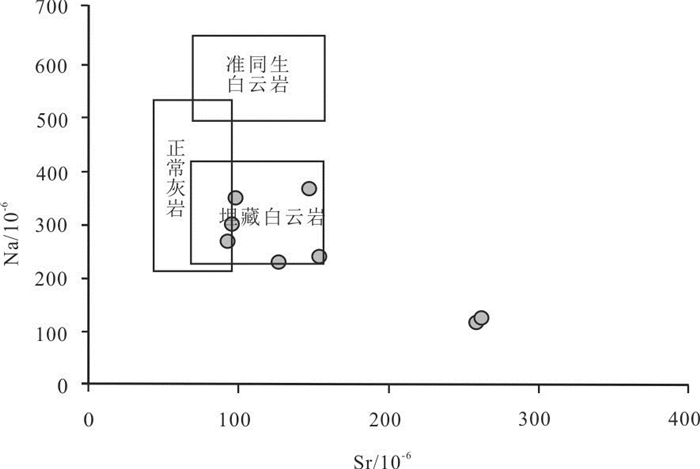
图 4 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马六段白云岩微量元素含量分布图(图中代号见表 2)
Figure 4. Trace element diagram of dolomite in member 6 of Majiagou Formation in the south Ordos basin
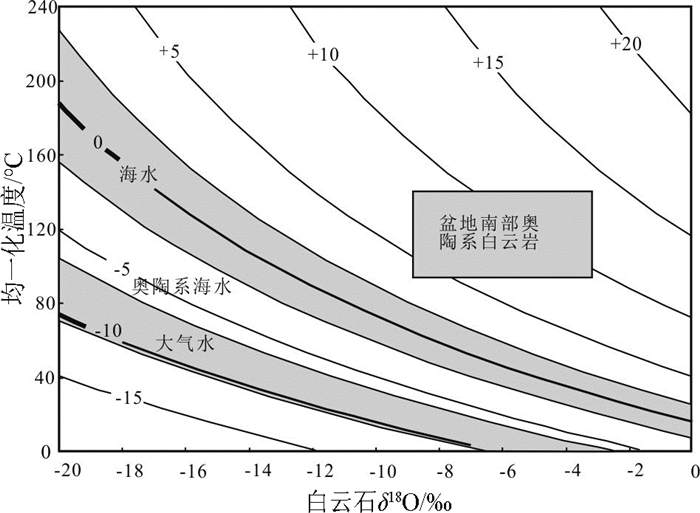
图 7 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部奥陶系白云岩环边流体包裹体均一化温度和氧同位素组成投点图
等值线是与方解石平衡的水的氧同位素组成,根据张理刚(1985)的公式计算,海水的δ18O值范围按现代海水值,大气水的δ18O值范围的中间值按任建国(2000)西太平洋15个现代雨水的δ18O平均值,奥陶系海水的δ18O值据Veizer等(1999)
Figure 7. Fluid inclusion homogenization temperature with carbon and oxygen isotope composition plot for Ordovician carbonates in the southeast Ordos basin
Isoline is the oxygen isotope of fluids (after Zhang et al., 1985). The δ18O value of meteoric water is that of modern seawater (after Ren et al., 2000). The δ18O value of Ordovician seawater is after Veizer et al. (1999)
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地南部旬探1井白云石电子探针分析数据(%)
Table 1 Electron microprobe analyses (%) of dolomite in Xuntan1 well in the south Ordos basin

表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地南部白云石微量元素含量/10-6
Table 2 Trace element data (10-6) of dolomite in the south Ordos basin

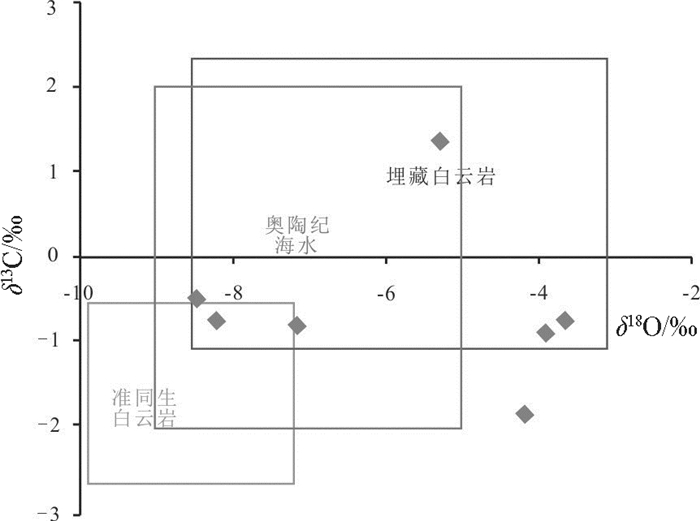
表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地南部白云岩C、O同位素含量
Table 3 Carbon and oxygen isotope content of dolomite in the south Ordos basin

-
Badiozamani K. 1973. The dorag dolomitization model application to the middle Ordovician of Wisconsin[J]. Sedimentary Petrology, 43(4):965-984. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=10e845575eceac229b426cb246fb970e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Bai Haifeng, Ma Zhanrong, Liu Baoxian. 2010. Reservoir-forming potential of Majiagou formation Ma-6 section in lower Ordovician in southern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 43(1):107-114 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201001011
Bao Hongping, Yang Fan, Cai Zhenghong, Wang Qianping, Wu Chunying. 2017. Origin and reservoir characteristics of Ordovician dolostones in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 37(1):32-45 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=dd30c1aea6c5fd942ad27b8aba7f710f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen Xiaowei, Mou Chuanlong, Zhou Kenken, Kang Jiangwei, Wang Qiyu, Ge Xiangying, Liang Wei. 2014. Lithofacies-paleogeography of Middle-Late Ordovician Daping stage-Aijiashan stage on the western margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 41(6):2028-2038 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201406017
Feng Zengzhao, Bao Zhidong, Zhang Yongsheng. 1998. Stratigraphy Petrology Lithofacies[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
He Yu, Ren Li, Deng Nan. 2020. The characteristics of the small faults in Mesozoic strata of ywb area in the south of Ordos Basin and its significance for oil and gas exploration[J]. Northwestern Geology, 53(1):189-194(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz202001017
Hird K. 1987. The composition of carbonate and oxygen isotope in the ancient dolomite[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 34(4):156-232. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X18300578
Hou Xinsheng, Ma Yingjie, Fang Fang, Qiao Yuande, Zhou Rongsheng. 2001. An application of NAA in analyzing the quality of coal[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 24(4):264-268 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjs200104005
Huang Qingyu, Zhang Shaonan, Ding Xiaoqi, Duan Jie, Xiang Lei. 2010. Origin of dolomite of Ordovician Majiagou Formation, western and southern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 32(2):147-153 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201002009
Huang Sijing, Qing Hairuo, Hu Zuowei, Zou Mingliang, Feng Wenli, Wang Chunmei, Gao Xiaoyong, Wang Qingdong. 2007. Closedsystem dolomitization and the significance for petroleum and economic geology:An example from Feixianguan carbonates, Triassic, NE Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11):2955-2962 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Sijing, Qing Hairuo, Hu Zuowei, Pei Changrong, Wang Qingdong, Wang Chunmei, Gao Xiaoyong. 2008.Cathodoluminescence and diagenesis of the carbonate rocks in Feixianguan Formation of Triassic, Eastern Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosiences, 33(1):26-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200801004
Huang Sijing, Tong Hongpeng, Liu Lihong, Hu Zuowei, Zhang Xuehua, Huan Jinlai, Huang Keke. 2009. Petrography, geochemistry and dolomitization mechanisms of Feixianguan dolomites in Triassic, NE Sichuan, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(10):2363-2372 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200910006
Hu Mingyi, Hu Zhonggui, Li Sitian, Wang Yanqi. 2011. Geochmical characteristics and genetic mechanism of the Ordovician dolostone in the Tazhong area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(12):2060-2069 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Fengjie, Du Lingchun, Zhao Junxing, Li Yuegang, Xian Fang, Li Fuping. 2016. Dolomite genesis in Member Ma55 of Majiagou Formation, Sudong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(3):328-338 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201603005
Lippman F. 1973. Sedimantary carbonate minerals[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 150.
Liu Lihong, Huang Sijing, Wang Chunlian, Huang Keke, Tong Hongpeng, Zhong Qianqian. 2010. Cathodoluminescence zonal texture of calcite cement in carbonate rock and its relationship with trace element composition:A case of Ordovician carbonate rock of Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 15(1):55-60 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Lihong, Du Xiaodi, Xu Shouli, Wen Huaguo. 2017a.Characteristics and formation of the Cambrian dolomite in MiddleSouth Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(3):775-784 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2096249517300157
Liu Lihong, Wang Chunlian, Wang Daming, Wang Haida. 2017b. A new example of retrograde solubility model for carbonate rocks[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 91(3):1145-1146. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=99bb845532364b8bfae5fdc17a0ff064&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lohmann K C. 1988. Geochemical patterns of meteoric diagenetic systems and their application to studies of paleokast[J]. Paleokarst.New York:Springer-Verlag, 58-80.
Ren Jianguo, HuangYipu, Fang Zhishan, Wang Xianbin. 2000. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope composition of meteoric water in the tropical West Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 22(5):60-64 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb200005007
Ren Junfeng, Yang Wenjing, Ding Xuefeng, Zhao Weibo, Huang Zhengliang, Wei Liubin. 2016. Discussion on characteristics and origin of Majiagou Formation dolomite reservoir in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 43(3):274-281(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201603003
Shao Longyi, He Hong, Peng Suping, Li Ruijun. 2002. Types and origin dolostones of the Cambrian and Ordovician of Bachu uplift area in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 4(2):19-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb200202003
Shields G A, Garden G A F, Veizer J, Meidla T, Rong J Y, Rong Y L. 2005. Sr, C and O isotope geochemistry of Ordovician brachiopods:A major isotope event around the Middle-Late Ordovician transition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(11):2005-2025, 2003. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5e2ceeb30578f96ad59b735a20cea8c1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Su Zhongtang, Chen Hongde, Ouyang Zhengjian, Jin Xueqiang. 2012.Sequence-based lithofacies and paleogeography of Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 39(3):623-633(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201203006
Su Zhongtang, Chen Hongde, Xu Fenyan, Jin Xueqiang. 2013. Genesis and reservoir property of lower Ordovician Majiagou dolostones in Ordos Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 18(2):15-22(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201302003
Veizer J, Ala D, Azmy K, Bruckschen P, Buhl D. 1999. 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater[J]. Chem. Geol., 161:59-88.
Warren J. 2000. Dolomite:occurrence, evolution and economically important associations[J]. Earth-Science Review, 52:1-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201712020
Wu Shiqiang, Zhu Jingquan, Wang Guoxue, Hu Wenxuan, Zhang Juntao, Wang Xiaolin. 2008. Types and origin of CambrianOrdovician dolomites in Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6):1390-1400 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285992803_Types_and_origin_of_Cambrian-Ordovician_dolomites_in_Tarim_basin
Yan Ronghui, Bai Haifeng, Liu Baoxian, Zhang Shuncun. 2009.Genesis and reservoir property of Lower Ordovician Majiagou dolostones in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 20(5):738-743. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201302003
Yang Junjie, Li Keqin, Zhang Dongsheng. 1992. Petroleum Geology of China: Vol. 20 Changqing Oil Field[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 64-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Hui'an. 1988. Phase Equilibrium in Petrology[M]. Beijing:Geologic Publishing House, 264-275 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yi Haisheng, Chen Zhiyong, Ji Changjun, Yang Xiaoping, Xia Guoqing, Wu Chihua. 2014. New evidence for deep burial origin of sucrosic dolomites from Middle Jurassic Buqu Formation in southern Qiangtang basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(3):737-746 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201403013
Yuan Lupeng, Zhou Hongrui, Jing Xiuchun, Wang Zhentao, Chuan Tingting, Fang Qiang. 2014. Microfacies and facies analysis of the Ordovician carbonates in the south margin of the Ordos Basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(3):421-432 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201403010
Zhang Chuanlu, Zhang Yongsheng, Kang Qifa, Luo Jian, Qi Lianshuang. 2001. Origin of Ordovician dolomite in Member Six of Majiagou Formation in South Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 22(3):22-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Ligang. 1985. The Application of the Stable Isotope to Geology[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science & Technology Press, 267 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xuefeng, Hu Wenxuan, Zhang Juntao, Wang Xiaolin, Xie Xiaomin. 2008. Geochemical analyses on dolomitizing fluids of Lower Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Tarim basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(2):80-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200802010
Zhang Yongsheng. 2000. Mechanism of deep burial dolomitization of massive dolostones in the middle Majiagou group of the Ordovician, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 18(3):424-430 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200003017
Zhao Junxing, Chen Hongde, Zhang Jinquan, Liu Xiaoli, Fu Suotang. 2005. Genesis of dolomite in the fifth member of Majiagou Formationin the middle Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 26(5):42-45, 51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Dingwu, Li Wenhou, Zhang Yunxiang. 2002. The Practice and Method of Regional Geology Comprehensive Study[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 305-309 (in Chinese with English abstract).
白海峰, 马占荣, 刘宝宪. 2010.鄂尔多斯盆地南缘下奥陶统马家沟组马六段成藏潜力分析[J].西北地质, 43(1):107-114. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz201001011 包洪平, 杨帆, 蔡郑红, 王前平, 武春英. 2017.鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系白云岩成因及白云岩储层发育特征[J].天然气工业, 37(1):32-45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201701004 陈小炜, 牟传龙, 周恳恳, 康建威, 王启宇, 葛祥英, 梁薇. 2014.鄂尔多斯西缘中晚奥陶世大坪阶-艾家山阶岩相古地理[J].中国地质, 41(6):2028-2038. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140617&flag=1 冯增昭, 鲍志东, 张永生. 1998.鄂尔多斯奥陶纪地层岩石岩相古地理[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-9. 何羽, 任丽, 邓楠.2020.鄂尔多斯盆地南部ywb地区中生界小断层特征及其油气勘探意义[J].西北地质, 53(1):189-194. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz202001017 侯新生, 马英杰, 方方, 邱元德, 周蓉生. 2001.中子活化分析在煤质分析中的应用[J].核技术, 24(4):264-268. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjs200104005 黄擎宇, 张哨楠, 丁晓琪, 段杰, 向雷. 2010.鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘奥陶系马家沟组白云岩成因研究[J].石油实验地质, 32(2):147-153. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201002009 黄思静, QING HaiRuo, 胡作维, 邹明亮, 冯文立, 王春梅, 郜晓勇, 王庆东. 2007.封闭系统中的白云石化作用及其石油地质学和矿床学意义——以四川盆地东北部三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩为例[J].岩石学报, 23(11):2955-2962. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200711026 黄思静, 卿海若, 胡作维, 裴昌蓉, 王庆东, 王春梅, 郜晓勇. 2008.川东三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩的阴极发光特征与成岩作用[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 33(1):26-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200801004 黄思静, 佟宏鹏, 刘丽红, 胡作维, 张雪花, 郇金来, 黄可可. 2009.川东北飞仙关组白云岩的主要类型、地球化学特征和白云化机制[J].岩石学报, 25(10):2363-2372. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200910006 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 李思田, 王延奇. 2011.塔中地区奥陶系白云岩岩石地球化学特征及成因机理分析[J].地质学报, 85(12):2060-2069. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201112008 李凤杰, 杜凌春, 赵俊兴, 李跃刚, 向芳, 李浮萍. 2016.鄂尔多斯盆地苏东地区马家沟组五段5亚段白云岩成因[J].石油学报, 37(3):328-338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201603005 刘丽红, 黄思静, 王春连, 黄可可, 佟宏鹏, 钟倩倩. 2010.碳酸盐岩中方解石胶结物的阴极发光环带与微量元素构成的关系——以塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩为例[J].海相油气地质, 15(1):55-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201001009 刘丽红, 杜小弟, 徐守礼, 文华国. 2017.四川盆地中南部寒武系白云岩特征及形成机制[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(3):775-784. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201703011 任建国, 黄奕普, 方志山, 王先彬. 2000.热带西太平洋雨水的氢氧同位素组成[J].海洋学报, 22(5):60-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb200005007 任军峰, 杨文敬, 丁雪峰, 赵伟波, 黄正良, 魏柳斌. 2016.鄂尔多斯盆地马家沟组白云岩储层特征及成因机理[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 43(3):274-281. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdlgxyxb201603003 邵龙义, 何宏, 彭苏萍, 李瑞军. 2002.塔里木盆地巴楚隆起寒武系及奥陶系白云岩类型及形成机理[J].古地理学报, 4(2):19-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200202003 苏中堂, 陈洪德, 欧阳征健, 金学强. 2012.鄂尔多斯地区马家沟组层序岩相古地理特征[J].中国地质, 39(3):623-633. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120306&flag=1 苏中堂, 陈洪德, 徐粉燕, 金学强. 2013.鄂尔多斯盆地马家沟组白云岩成因及其储集性能[J].海相油气地质, 18(2):15-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201302003 吴仕强, 朱井泉, 王国学, 胡文喧, 张军涛, 王小林. 2008.塔里木盆地寒武-奥陶系白云岩结构构造类型及其形成机理[J].岩石学报, 24(6):1390-1400. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200806022 阎荣辉, 白海峰, 刘宝宪, 张顺存. 2009.鄂尔多斯盆地南缘下奥陶统马家沟组马六段成藏条件分析[J].天然气地球科学, 20(5):738-743. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx200905015 杨俊杰, 李克勤, 张东生. 1992.中国石油地质志:卷十二长庆油田[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 64-71. 殷辉安. 1988.岩石学相平衡[M].北京:地质出版社, 264-275. 伊海生, 陈志勇, 季长军, 杨晓萍, 夏国清, 吴池华. 2014.羌塘盆地南部地区布曲组砂糖状白云岩埋藏成因的新证据[J].岩石学报, 30(3):737-746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201403013 袁路朋, 周洪瑞, 景秀春, 王振涛, 传婷婷, 房强. 2014.鄂尔多斯盆地南缘奥陶系碳酸盐微相及其沉积环境分析[J].地质学报, 88(3):421-432. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201403010 张传禄, 张永生, 康祺发, 罗健, 祁连爽. 2001.鄂尔多斯南部奥陶系马家沟群马六组白云岩成因[J].石油学报, 22(3):22-26. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=5371011 张理刚. 1985.稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 267. 张学丰, 胡文瑄, 张军涛, 王小林, 谢小敏. 2008.塔里木盆地奥陶统白云岩化流体来源的地球化学分析[J].地学前缘, 15(2):80-89. 张永生. 2000.鄂尔多斯地区奥陶系马家沟群中部块状白云岩的深埋藏白云石化机制[J].沉积学报, 18(3):424-430. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb200003017 赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 张锦泉, 刘小丽, 付锁堂. 2005.鄂尔多斯盆地中部马五段白云岩成因机理研究[J].石油学报, 26(5):42-45, 51. 周鼎武, 李文厚, 张云翔. 2002.区域地质综合研究的方法与实践[M].北京:科学出版社, 305-309.




 下载:
下载: