Grain size distribution of sediment of core YRD-1101 in the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since the latest Pleistocene and its environmental change
-
摘要:
对现代黄河三角洲地区YRD-1101孔上部岩心开展粒度分析,并结合AMS14C和光释光(OSL)年代学测试结果、沉积特征、微体古生物鉴定及周边钻孔对比,建立了MIS5期以来的地层框架,揭示出该地区主要经历了3个阶段的沉积环境演化过程:(1)晚更新世—早全新世河流与海相交替沉积,其中MIS5c阶段海侵水动力环境中等,MIS3期海侵水动力环境较弱,MIS2期河流沉积水动力较强;(2)全新世滨、浅海沉积环境,动力环境整体较强,相对比较稳定;(3)1855年至今形成的黄河三角洲沉积,水动力强度较弱到中等。海平面变化和构造沉降是影响研究区晚更新世以来沉积演化的主要因素,此外,黄河带来的大量泥沙对海侵强度也有显著影响。
Abstract:Three stages of sedimentary environment evolution since MIS 5 were recognized based on the data of grain size analysis, AMS14C dating, OSL dating, sedimentary characteristics, benthic foraminifera and ostracoda identification in the upper part of core YRD-1101 drilled in the modern Yellow River Delta, and comparison with surrounding boreholes. Three stages of sedimentary evolution are identified. (1)Interactive deposition of rivers and marine facies were formed during the Late Pleistocene-Early Holocene. Among them, the transgressive sediments in the MIS5c phase were formed in a medium hydrodynamic conditions, the transgressive sediments in the MIS3 phase were formed in a weak hydrodynamic environment, and the river sediments in the MIS2 phase were formed in a strong hydrodynamic environment. (2) The nearshore and shallow sea deposits during the Holocene formed in a strong and stable environment. (3) Modern Yellow River Delta sediments deposited since 1855 A.D. were formed in weak to medium sedimentary dynamic environments. Sea-level changes and neotectonic subsidence have been the major factors controlling the sedimentary evolution on the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since MIS 5. In addition, the sediments were transported to the study area from Yellow River, which had a significant influence on transgression intensity.
-
1. 前言
太行山存在重力梯度带是华北克拉通最显著的地质特征之一,该梯度带两侧的地貌、大地热流值、地壳厚度和岩石圈厚度存在明显的差异,造成这种差异的原因是华北岩石圈减薄存在时空不均一性[1]。沿该重力梯度带北东向发育大量的晚中生代侵入-火山岩带,特别是在太行山北段。前人对这些侵入岩开展了大量的年代学和地球化学研究[2-3],取得了重要进展。同时在太行山中北段探明存在多个中小型矽卡岩铜多金属矿[4-5]和石湖大型金矿床[6]。近几年在该地区新探明了木吉村大型斑岩型铜(钼)矿[7]和安妥岭大型斑岩型钼矿[8],暗示太行山北段具有很大的找矿潜力。区域地质工作显示,赤瓦屋岩体是太行山北段南部典型的杂岩体[9],前人虽然对该岩体开展过一些锆石测年工作,但多限于岩体边缘相石英闪长岩的研究[10-13],最近的找矿工作新类型铜钨矿体主要集中于岩体中心相斑状花岗闪长岩。因此,本文对赤瓦屋岩体不同岩相开展详细的锆石U-Pb 测年工作,结合区域含矿岩体的年代学资料,以期对太行山北段中生代金属矿床的成矿规律有更明确的认识。
2. 区域地质
研究表明,太行山北段的构造演化大致经历了3 个主要阶段,分别为太古宙变质基底形成阶段、元古宙至古生代稳定发展阶段和中生代活化阶段[14]。阜平杂岩是华北克拉通太古宙变质结晶基底的一部分,现今表现为NE向展布的穹隆状构造,主要岩性为黑云斜长片麻岩、角闪斜长片麻岩、浅粒岩夹斜长角闪岩,该套岩石地层单元普遍遭受强烈区域变质及混合岩化作用[15]。除了阜平杂岩以外,还发育一系列元古宙—侏罗纪沉积地层。岩浆岩是太行山北段中生代活化阶段的产物,沿太行山重力梯度带呈NNE向展布(图 1-a),其分布受东、西两侧分布的NNE 向紫荆关断裂和乌龙沟断裂带控制[5],由NNE向分布的多个岩基(体)和髫髻山组火山岩组成,由北向南依次发育大河南、王安镇岩基和麻棚、赤瓦屋岩体(图 1-b),这些岩体为中酸性高钾钙碱性花岗质岩石[2]。其中王安镇岩基周缘探明了多个斑岩-矽卡岩型多金属矿床,新发现的木吉村大型斑岩铜钼矿和安妥岭大型斑岩型钼矿分别位于该岩基的南缘和北缘;在麻棚岩体西侧1~4 km探明了太行山地区最大的金矿——石湖金矿(图 1-b)。
赤瓦屋岩体位于太行山北段北东向岩浆带的南端,该岩体平面上呈近圆状,直径约5 km,面积约63 km2。根据前人资料和本次野外地质考察,该岩体由不同岩相组成(图 2),自岩体中部向外呈同心圆状展布: 中心相为斑状花岗闪长岩,中粗粒斑状结构,向外过渡为细中粒花岗闪长岩; 边缘相为细粒石英闪长岩(图 3)。不同岩相的黑云母和角闪石含量不同[9],边缘相的黑云母和角闪石含量分别为15%和10%,过渡相分别为10%和5%~10%,中心相角闪石少见,黑云母含量为5%,由边部向内部暗色矿物逐渐减少,暗示岩浆9 演化程度越来越高。除此以外,还发育大量的南北向花岗闪长斑岩脉。
此次野外观察可见,大小为2~10 m的黑色闪长质包体呈椭圆体和透镜状普遍发育于花岗闪长岩中,与寄主岩体边缘清楚。前人对太行山北段岩体开展过成矿潜力评价,赤瓦屋岩体的岩浆分异指数(DI)为75.04,轻重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)均较高,为20.2,黑云母MgO为12.80%~14.28%,石英Ti 含量为17×10-6,全岩的氧同位素为8.89%,暗示赤瓦屋岩体具有较大的成矿潜力[9]。早期资料显示该岩体有铜矿化,最近地勘队发现中心相斑状花岗闪长岩中发育铜钨多金属矿化,可见早阶段NE 向石英黄铁矿白钨矿脉和晚阶段SN 向黄铜矿脉,辉钼矿呈细脉浸染状产于岩体中,多与黄铜矿、黄铁矿共生。
3. 样品采集与测试方法
本次测年工作采集4 个不同岩性的样品,分别为石英闪长岩(CWW14)、花岗闪长岩(CWW2)、斑状花岗闪长岩(CWW12) 和花岗闪长斑岩脉(CWW1),具体采样位置见图 2。将测年样品破碎后,经常规重力和磁选方法分选出锆石,在双目镜下挑纯。将待测锆石颗粒置于环氧树脂中制靶,然后磨至一半用于后期测试。锆石阴极发光在中国地质科学院地质研究所离子探针室HITACHIS3000-N型扫描电子显微镜上完成。在透射光、反射光显微镜观察及阴极发光研究的基础上,选择合适的锆石颗粒进行锆石U-Pb定年测试。
LA-MC-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 定年测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,定年分析所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICPMS及与之配套的Newwave UP 213 激光剥蚀系统。所用激光剥蚀斑束直径为25 μm,频率为10 Hz,能量密度约为2.5 J/cm2,以He 为载气。信号较小的207Pb、206P、204Pb(+204Hg)、202Hg 用离子计数器(multi-ion-counters)接收,208Pb、232Th、238U信号用法拉第杯接收,实现了所有目标同位素信号的同时接收,并且不同质量数的峰基本上都是平坦的,可以获得高精度的数据。均匀锆石颗粒207Pb/206Pb、206Pb/238U、207Pb/235U的测试精度(2σ )均为2%左右,对锆石标准样品的定年精度和准确度在1%(2σ )左右。LA-MC-ICPMS 激光剥蚀采样采用单点剥蚀的方式,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1 调试仪器,使之达到最优状态,锆石U-Pb 定年以锆石GJ-1 为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M257(U: 923×10-6; Th: 439×10-6; Th/U:0.475)[16]为外标进行校正。测试过程中每测定5~7个样品前后重复测定2 个锆石标准样品,对样品进行校正,并测量一个锆石标准Plesovice,观察仪器的状态以保证测试精确度。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal 程序,测量过程中绝大多数分析点206Pb/204Pb>1000,未进行普通铅校正,204Pb 由离子计数器检测,204Pb 含量异常高的分析点可能受包体等普通Pb 的影响,在计算时予以剔除,锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot 3.0 程序获得。样品分析过程中,Plesovice 标样作为未知样品的分析结果为(337.3±1.1)Ma(n=5,2σ),对应的年龄推荐值为(337.13±0.37)Ma(2σ)[17],两者在误差范围内完全一致,测试数据精度较好。
4. 分析结果
赤瓦屋不同岩相花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb 分析测试结果见表 1,锆石U-Pb 谐和图见图 4。由图 4可知,石英闪长岩样品CWW14 锆石多呈长柱状,长为80~250 μm,宽为40~120 μm。本文对石英闪长岩中15 颗锆石进行年代学测试,Th 和U含量分别为100×10-6~306×10-6和150×10-6~347×10-6,其Th/U为0.4~1.5(表 1),谐和年龄为(134±1)Ma,MSWD=3.4; 加权平均年龄为(134±2)Ma,MSWD=0.62(图 4-a)。
表 1 太行山北段赤瓦屋铜钨矿区不同岩相的花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄测年结果Table 1. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb data of different petrofacies of granitoids in Chiwawu area,Northern Taihang Mountain
花岗闪长岩样品CWW2 锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长20~320 μm,宽40~120 μm。本文分析了花岗闪长岩中23 颗锆石,Th 和U 含量分别为59.2×10-6~197×10-6 和105×10-6~289×10-6,其Th/U 为0.4~1.0(表 1),谐和年龄为(133±1)Ma,MSWD=2.3; 加权平均年龄为(133±2)Ma,MSWD=0.37(图 4-b)。
斑状花岗闪长岩样品CWW12锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长120~500 μm,宽80~100 μm。本文分析了斑状花岗长岩中12 粒锆石,Th 和U含量分别为88.6×10-6~492×10-6和227×10-6~596×10-6,其Th/U为0.3~0.8(表 1),谐和年龄为(131±2)Ma,MSWD=2.6; 加权平均年龄为(132±4)Ma,MSWD=0.68(图 4-c)。
花岗闪长斑岩脉样品CWW1锆石多呈长柱状,锆石长200~360 μm,宽10~100 μm。本文分析了斑状花岗长岩中28 粒锆石,Th和U含量分别为45.6×10-6~1303×10-6和83.1×10-6~775×10-6,其Th/U比值为0.4~1.7(表 1),谐和年龄为(128 ±1)Ma,MSWD=6.2; 加权平均年龄为(128±1)Ma,MSWD=2.4(图 4-d)。
5. 讨论
5.1 赤瓦屋岩体时代
赤瓦屋岩体位于太行山北段中生代岩浆带的南部(图 1-b),其形成时代受到高度关注。喻学惠等[5]提出该岩体由同心环状的不同岩相带(石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和斑状花岗闪长岩)组成,全岩Rb-Sr 等时线年龄为135.2 Ma;刘阳等[10] 利用SHRIMP测年获得该岩体北部和西部边缘相石英闪长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄分别为(134.0±5.3)Ma 和(139.8±3.1)Ma;李林林等[12]获得该岩体西部边缘相石英闪长岩的LA-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 年龄为(126.4±2.4) Ma。该岩体北部边缘相花岗闪长岩和闪长岩包体的LA-ICPMS 锆石U-Pb 年龄分别为(130±1.0) Ma和(128.2±1.5) Ma[13]。
如前文所述,赤瓦屋岩体除边缘相石英闪长岩外,还存在过渡相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期酸性岩脉,已有的锆石U-Pb 测年工作主要集中于边缘相[10, 12-13]。本文获得赤瓦屋岩体边缘相石英闪长岩、边缘相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期花岗闪长岩岩脉的锆石LAICPMS谐和年龄分别为(134 ±1)Ma、(133±1)Ma、(131±2)Ma和(128±1)Ma,其中本次边缘相的锆石U-Pb 年龄与前人获得的锆石U-Pb 年龄在误差范围内基本一致,表明本次测年数据是可靠的。本文测年数据表明,赤瓦屋岩体不同岩相体形成时代(134~131 Ma)在识差范围内基本一致,暗示岩浆经历了快速侵位、快速冷却结晶的地质过程,类似于邻区的麻棚岩体[12]。据野外实地观察,赤瓦屋岩体形成时代(134~131 Ma)略早于花岗闪长斑岩脉(128Ma),这些与地质穿插关系观察一致。因此,赤瓦屋杂岩体形成于早白垩世,与太行山北段岩基和岩体的时代基本一致(见下文讨论)。
5.2 两期岩浆-成矿事件
由图 1-a 可知,NE向太行山北段岩浆带位于重力梯度带附近,其侵入岩的年龄一直受到高度关注,该带已有的晚中生代岩浆岩锆石U-Pb 年龄数据见表 2。由表 2 可知,太行山北段大河南岩基的石英二长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为127 Ma[18];王安镇岩基中酸性岩浆和包体形成于132~126 Ma,东南部辉石闪长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为138 Ma[3, 18-19];赤瓦屋岩体中酸性岩和包体形成于132~126 Ma[10, 12-13];麻棚中酸性岩体和包体形成于131~124 Ma[6, 10, 12, 20]。除此之外,木吉村斑岩铜矿含矿岩体-闪长玢岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄为144.7 Ma[7]和144.1 Ma[21],石湖金矿区石英闪长岩脉的锆石U-Pb 年龄为130 Ma[6]。由此可见,太行山北段晚中生代侵入岩存在2 期岩浆事件,分别为144~138 Ma和132~124 Ma,其中以第二期岩浆事件形成大面积的中酸性岩基和岩体为显著特征,而第一期岩浆事件形成的侵入岩规模相对较小,主要有集中分布于王安镇岩基东南部的辉石闪长岩和木吉村与斑岩铜矿成矿密切相关的闪长玢岩。最近研究表明:木吉村斑岩铜矿区的闪长玢岩是髫髻山火山旋回晚阶段次火山岩相的产物[7],最新测年资料显示,太行山北段和燕山东部北东向发育的髫髻山组火山岩形成于晚侏罗世—早白垩世(151~131 Ma)[22],这些火山岩可能是太行山北段第一期岩浆事件的产物。
表 2 太行山北段晚中生代侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年龄Table 2. Compilation of isotopic ages for important Late Mesozoic intrusions in Northern Taihang Mountain
太行山北段与晚中生代岩浆事件密切相关的成矿作用存在2 期矿化事件,第一期主要为与髫髻山组火山作用相关的斑岩铜钼多金属矿床,如木吉村大型斑岩铜钼矿(图 1-b),其辉钼矿Re-Os 模式年龄为(138.5±1.9) ~(142.7±2.0) Ma[21],5 个辉钼矿Re-Os 样品等时线年龄为(142.5±1.4) Ma[7];在其南侧10 km处的中型大湾斑岩型锌钼矿(图 1-b)的辉钼矿Re-Os模式年龄为(144.4 ± 7.4) Ma[23]。位于大河南与王安镇岩基之间大型安妥岭斑岩钼矿(图 1-b)的5 个辉钼矿Re-Os 样品等时线年龄为(147.3±3.7) Ma[8]或(147.8 ± 0.95) Ma[24]。
在第二期王安镇岩基周围发现了多个铜金矿床,如在木吉村矿区北侧的浮图峪矿田发现60 余处铜矿床(或矿点)(图 1-b),金矿床和矿点更是星罗棋布,遍及全区[5],这些铜矿多为矽卡岩铜铁矿[4]。目前还缺少对这些中小型矽卡岩铜矿成矿时代的精确测年数据,根据含矿岩体的年龄推测,它们可能为第二期的产物。本次野外实地观察发现,赤瓦屋地区早阶段钨矿和晚阶段铜矿呈脉状产于岩体内部相的斑状花岗闪长岩中((131 ±2)Ma),暗示钨铜矿化形成时代不早于131 Ma,赤瓦屋铜钨矿化是第二期成矿事件的产物。另外,在麻棚岩体南缘探明了与岩体密切相关的石英脉状金矿(石湖大型金矿)、隐爆角砾岩型银矿和斑岩钼矿[20],石湖金矿区石英闪长岩脉的锆石U-Pb 年龄为130 Ma,石湖金矿热液钾长石K-Ar 年龄为132~120 Ma[6],麻棚岩体周缘金银钼矿是第二期成矿事件的产物。由此可见,太行山北段晚中生代至少存在两期岩浆-成矿事件,具有较大的找矿潜力。与第一期斑岩型铜钼矿床相比,第二期成矿事件具有成矿类型多样性,晚中生代两期成矿事件特征类似于华南地区[25]。
6. 结论
(1)赤瓦屋岩体边缘相石英闪长岩、过渡相花岗闪长岩、中心相斑状花岗闪长岩和后期花岗闪长岩岩脉形成时代分别为(134 ± 1) Ma、(133 ±1) Ma、(131 ±2) Ma和(128 ±1) Ma,这些数据表明该岩体形成于早白垩世。
(2)太行山北段晚中生代存在两期岩浆-成矿事件,具有较大的找矿潜力。
-
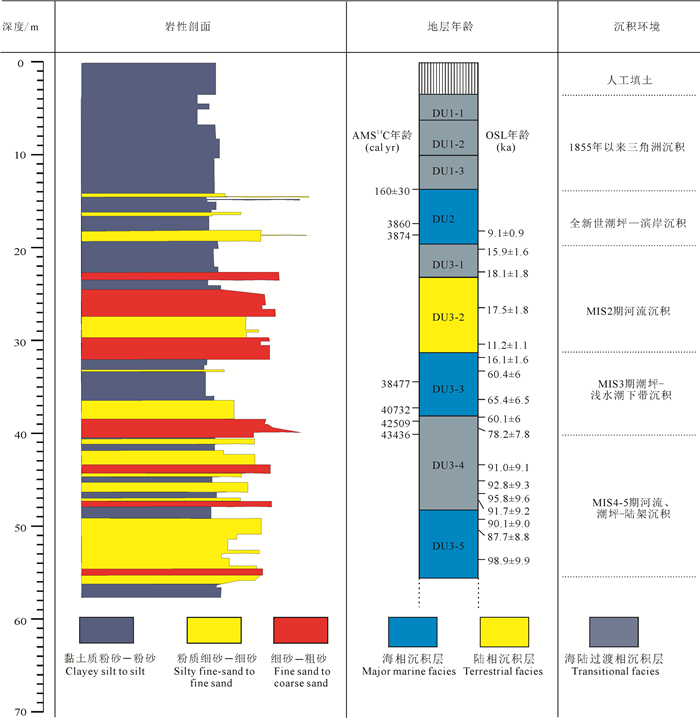
图 2 YRD-1101孔岩性特征及地层划分(据Liu et al., 2016修改)
Figure 2. Lithology and depositional sequences of core YRD-1101 (modified from Liu et al., 2016)
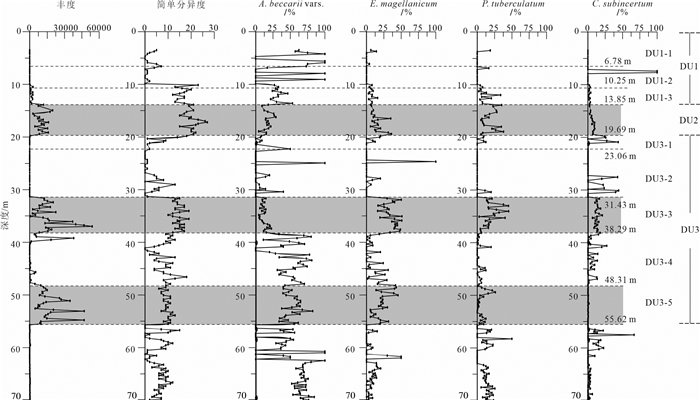
图 3 YRD-1101孔上部70 m有孔虫丰度、简单分异度和主要属种变化(据Liu et al., 2016修改)
灰色阴影代表晚更新世和全新世三个主要海相沉积层
Figure 3. Downcore changes in foraminiferal abundance and simple diversity, and the relative abundance of the main foraminiferal species in the uppermost 70 m of core YRD-1101(modified from Liu et al., 2016)
The grey shading indicates the three major marine sedimentary beds during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene
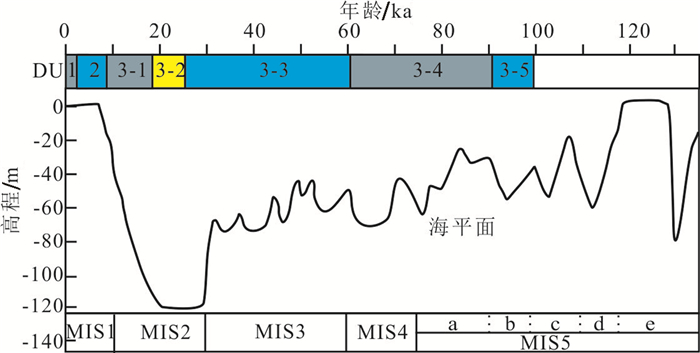
图 8 MIS5期以来黄海及其邻近海区海平面变化曲线(根据文献Chappell et al., 1996; Lambeck et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2010修改)与YRD-1101孔沉积序列对应关系
Figure 8. Curve of sea-level changes of Yellow Sea and adjacent areas since 120 ka (modified from Chappell et al., 1996; Lambeck et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2010) and its relationship with the depositional sequences of core YRD-1101
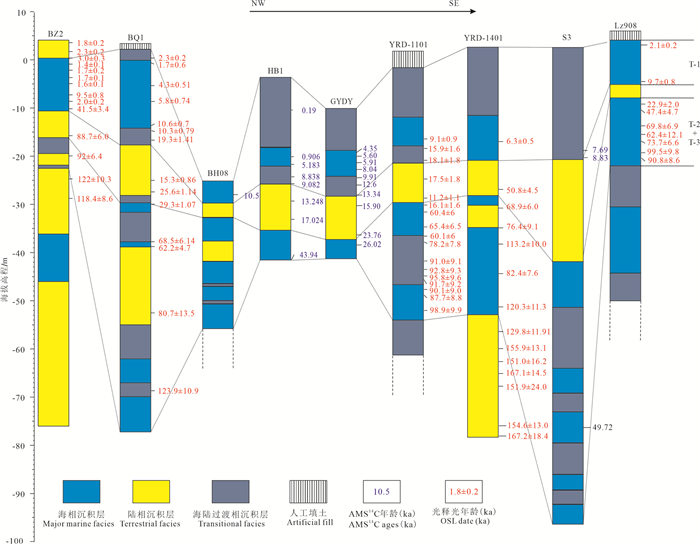
图 9 渤海西岸晚更新世和全新世以来沉积序列对比(据庄振业等, 1999; 阎玉忠等, 2006; 陈宇坤等, 2008; Liu et al., 2009; 赵广明等, 2014; 刘世昊等, 2015; Yi et al., 2015;Liu et al., 2016; 张欣等, 2016; Shi et al., 2016)
Figure 9. Regional correlation of sedimentary sequence during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene near the west coast of the Bohai Sea (after Zhuang et al., 1999; Yan et al., 2006; Chen et al., , 2008; Liu et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2015; Yi et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2016; Shi et al., 2016)
表 1 本文涉及钻孔的位置、高程及长度等基本信息
Table 1 Locations, core site elevations, and lengths of all cores in this paper

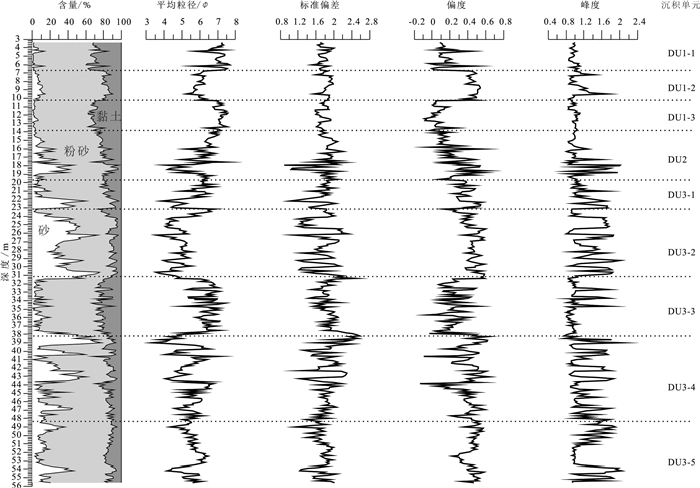
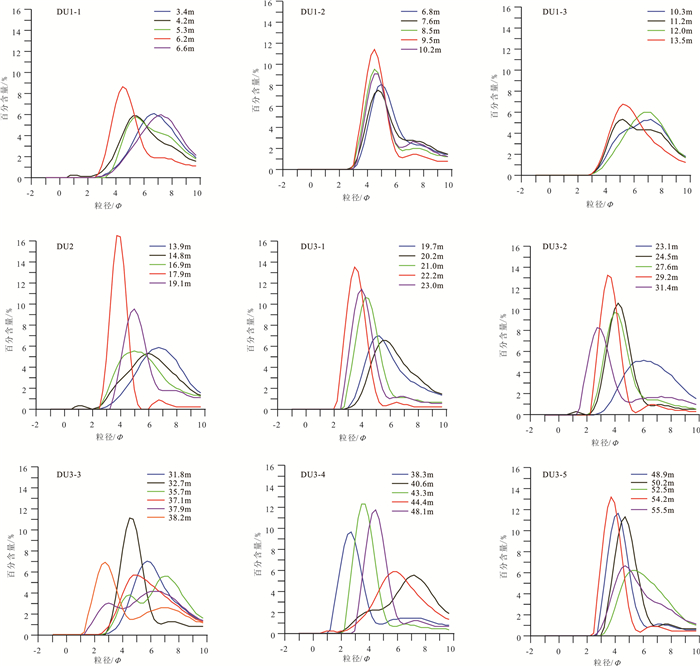
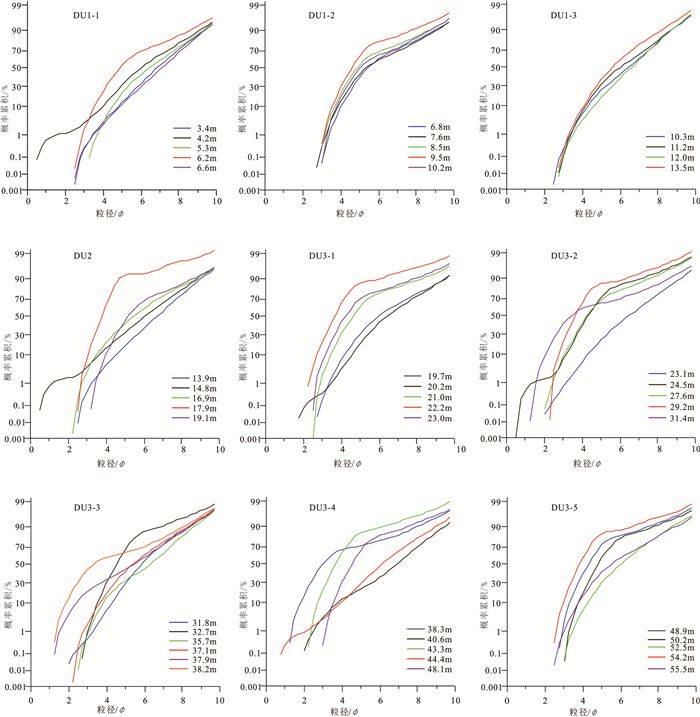
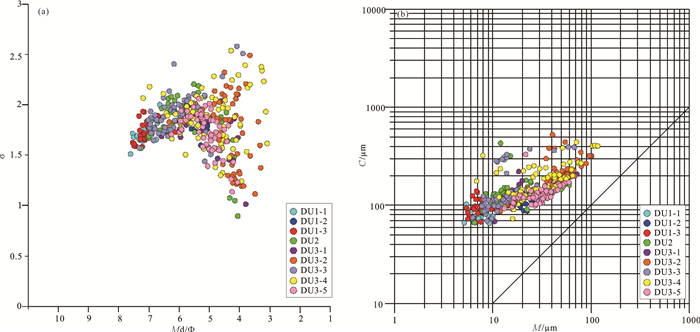
表 2 YRD-1101孔DU1-3岩心段沉积物粒度参数统计
Table 2 Statistics of grain size parameters of the DU1-3 in core YRD-1101

-
Chappell J, Omura A, Esat T, McCulloch M, Pandolfi J, Ota Y, Pillans B. 1996.Reconciliation of late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep-sea oxygen isotope records[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 141:227-236. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=625f81fed1ebfaa3e4a51f6203c9e4c2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen L, Cheng C, Wei Z. 2009.Seismic evidence for significant lateral variations in lithospheric thickness beneath the central and western North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 286(1):171-183. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=340097a71a8f610b8e339abb110a44f8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen Xiaoying, Liu Dahai, Yin Ping, Liu Jinqing, Cao Ke, Gao Fei, 2019. Temporal and spatial evolution of surface sediments characteristics in the Dagu River estuary and their dynamic response mechanism[J]. China Geology, 2, 325-332. doi: 10.31035/cg2018092.
Chen Yukun, Li Zhenhai, Shao Yongxin, Wang Zhisheng, Gao Wuping, Yang Xulian. 2008. Study on the Quaternary chronostratigraphic section in Tianjin Area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30 (2):483-493 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz200802005
Chen Yongsheng, Wang Hong, Pei Yandong, Tian Lizhu, Li Jianfen, Shang Zhiwen. 2012. Division and its geological significance of the late Quaternary marine sedimentary beds in the west coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(3):747-759(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201203018
Ding Dalin, Zhang Xunhua, Yu Junjie, Wang Liyan, Wang Feng, Shang Shouwei, 2019. Sediment grain size distribution patterns of the late Quaternary on the back side of northern Yangtze River Delta and their environmental implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(4):34-45 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904004
Dou Yanguang, Chen Xiaohui, Li Jun, Cai Feng, Wen Zhenhe, Xu Gang, Zou Liang, 2018. Origin and provenance of the surficial sediments in the subenvironments of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(4):21-31(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201804002
Duan Yonghou.1998. New tectonic movement and the formation and evolution of the Bohai Sea and their effects on the current geological environment[J].The Chinese Journal of Geological hazard and control, 9(S1):106-113.
Fang Jingtao. 2020. Comprehensive evaluation on the geoenvironment of coastal zones in Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 29(1):85-90, 100(in Chinese with English abstract).
Fang Wenli, Yao Zhengquan, Shi Xuefa, Ge Chendong, Qiao Shuqing, Li Xiaoyan, Dong Zhi, Wang Ying, 2019. Millennial-scale paleoenvironment and paleoclimate changes recorded in the Bohai Seas. Marine Geology& Quaternary Geology, 39(3):61-71. (in Chinese, with English Abstract).
Folk R L, Ward W C. 1957. Brazos River bar:A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 27(1):3-26.
Gao Maosheng, Guo Fei, Hou Guohua, Qiu Jiandong, Kong Xianghuai, Liu Sen, Huang Xueyong, Zhuang Haihai. 2018. The evolution of sedimentary environment since late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Geology in China, 45(1):59-68(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Haipeng, Bai Jinbin, Zhang Youquan, Wang Liya, Shi Jusong, Li Wenpeng, Zhang Zuozhen, Wang Yunlong, Zhu Juyan, Wang Haigang. 2017. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China, 44(6):1115-1127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706008
Huang Xiaoxuan, Wang Rujian, Xiao Wenshen, Zhang Taoliang, 2018.Transportation mechanism of terrigenous sediment and its paleoenvironmental implications on the Chukchi Plateau, western Arctic Ocean during the late Quaternary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(2):52-62(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802005
Lambeck Kurt, ESAT, Tezer M, Potter Emma-Kate. 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years[J]. Nature, 419.6903:199-206. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=852b67da3853a15162382315250c245f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Fenglin, Wang Hong, Yan Yuzhong, Wang Yunsheng, Zhang Jinqi, Zhao Changrong, Zhang Yufa, Li Jianfen, Lin Fang. 2004. The significance of the depositional hiatuses on the coastal plain of West Bohai Bay since the Late Quaternary period[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 27(3):177-183 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz200403008
Liu J, Satio Y, Wang H, Zhou L Y, Yang Z G. 2009. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 36(4-5):318-331. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1a063be96b0bd980e206c9a5e3a9e699&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Jie, Li Rihui, Yang Shixiong, Chen Xiaohui, Chen Shanshan, 2018.Pollen spore assemblages and induced palaeoenvironmental changes in the western Bohai Sea since Late Pleistocene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(2):115-128 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802012
Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X H, Wang H, Wen C, Yang Z G, Nakashima R. 2010. Delta development and channel incision during marine isotope stages 3 and 2 in the western South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 278:54-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9c7322595f1f6ce2db864df80595cc52
Liu J, Wang H, Wang F F, Qiu J D, Saito Y, Lu J F, Zhou L Y, Xu G, Du X L, Chen Q. 2016.Sedimentary evolution during the last~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 451:84-96. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9fc04f1a91f971360b822b7445ebc75b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Li Peiying, Du Jun, Li Ping, Gao Wei. 2014.Evolution of the buried channel systems under the modern Yellow River delta since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary International, 349(3):327-338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=63076a55758d02d922916f575d9dc2d5
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Li Peiying, Du Jun, Li Ping, Gao Wei. 2015.High-resolution grain size distribution and evolution of the sediment-dynamic environment in the modern yellow river delta since the latest Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary, 35(2):291-306 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201502005
Liu S H, Li P Y, Feng A P, Du J, Gao W, Xu Y Q, Yu X X, Li P, Nan X L. 2016.Seismic and core investigation on the modern Yellow River Delta reveals the development of the uppermost fluvial deposits and the subsequent transgression system since the postglacial period[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 128:158-180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b0c1cb74cf671d744a150db32b89cc79
Mei Xi, Li Rihui, Zhang Xunhua, Wang Zhongbo, Zhang Yong, 2019.Reconstruction of phytoplankton productivity and community structure in the South Yellow Sea[J]. China Geology, 2, 315-324.doi: 10.31035/cg2018091.
Mi Beibei, Wang Zhongbo, Qiu Xiaohua, Zhang Yong, Lan Xianhong, 2019. Reconstruction of the redox environment in Okinawa Trough and its climatic implications since mid-Holocence[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(04):107-115 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Qin Yunshan, Zhao Yiyang, Zhao Songling(eds.). 1985.Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 212-223 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Saito Y, Yang Z, Hori K. 2001. The Huanghe(Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas:a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 41(2):219-231.
Shang Zhiwen, Wang Fu, Li Jianfen, Jiang Xingyu, Chen Yongsheng, Wang Hong. 2016. The age of the second marine layer in coastal lowland of Bohai Bay revealed by AMS14C dating method(II)[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 35(10):1591-1595(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, Larrasoaña J C, Bai Y Z, Liu Y G, Liu J H, Cao P, Li X Y, Qiao S Q, Wang K S, Fang X S, Xu T Y. 2016. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1Ma and implications for sea-level changes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 451:10-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f9716556de4445d320e63ea8d71ae2f1
Sun L S, Liu J, Qiu J D, Li G T, Xiang L H. 2014. Studies on magnetostratigraphy of core YRD-1101 sediments on the north shore of modern Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology& Quaternary Geology, 34(4):31-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404005
Vandenberghe J. 2013. Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:A powerful proxy for process identification[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 121(3):18-30. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5698ebd0d007408c1e9c9d0b8a1b0cc6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J, Thompson C E L, Gao J H, Yang Y. 2012.Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Marine Geology, 291-294:147-161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=91ddd20b8b820492bfc4866afb24df00
Wang Zhongbo, Li Rihui, Yang Shouye, Bai Fenglong, Mei Xi, Zhang Jian, Lu Kai, 2019. Comparison of detrital mineral compositions between stream sediments of the Yangtze River (Changjiang) and the Yellow River (Huanghe) and their provenance implication[J]. China Geology, 2, 169-178. doi: 10.31035/cg2018065.
Wu Tong, Yang Zhenjing, Wang Yiming, Wang Pan, Peng Peihao, Zhang Peixin, 2019. Marine stratigraphy since Late Pleistocene on Wenzhou coastal plain[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(04):148-162 (in Chinese, with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904015
Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang, Zhang Jinqi, Qin Yafei. 2011.Stratigraphic division of the late Quaternary strata along the coast of Bohai Bay and its geology significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(8):1352-1367(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201108009
Xu Q, Yang J, Yuan G, Chu Z X, Zhang Z K. 2015. Stratigraphic sequence and episodes of the ancient Huanghe Delta along the southwestern Bohai Bay since the LGM[J]. Marine Geology, 367:69-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=511420d1ffa16cd00a89c98f269e6128
Xue C T. 1993. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 113(3/4):321-329. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8e3fd2676c359579b2920305231196e4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Yao Z Q, Guo Z T, Xiao G Q, Wang Q, Shi X F, Wang X Y. 2012.Sedimentary history of the western Bohai coastal plain since the late Pliocene:Implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 54-55(4):192-202. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba30303741852157889ced1ac6369de7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Yan Yuzhong, Wang Hong, Li Fenglin, Li Jianfen, Zhao Changrong, Lin Fang. 2006. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by Borehole BQ1 on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China. 25(3):357-382(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200603006
Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, Xu X Y, Chen S L, Ge J Y, Hao Q Z, Yao J, Shi X F, Peng S Z. 2012. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 329-330(3):101-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e49fa43a9d0ffd03f5f16a195b120c3e
Yi L, Deng C L, Xu X Y, Yu H J, Qiang X K, Jiang X Y, Chen Y P, Su Q, Chen G Q, Li P, Ge J Y, Li Y. 2015. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary:Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology. 319:1-12.
Yin Ping, Lin Liangjun, Chen Bin, Xiao Guoqiang, Cao Ke, Yang Jilong, Li Meina, Duan Xiaoyong, Qiu Jiandong, Hu Yunzhuang, Wang Lei, Sun Xiaoming. 2017. Coastal zone geo-resources and geo-environment in China[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):842-856(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xin, Liu Jian, Qiu Jiandong, Wang Shuang. 2016. Study of optically stimulated luminescence(OSL) chronology and sedimentary environments of the Yellow River Delta area with core YRD-1402[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, (3):11-22.(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603003
Zhao G M, Ye Q, Ye S Y, Ding X G, Yuan H M, Wang J. 2014.Holocene stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental evolution of the northern Yellow river delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(5):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405003
Zhuang Zhenye, Xu Weidong, Liu Dongsheng, Zhuang Lihua, Liu Baozhu, Cao Youyi, Wang Qiang. 1999. Division and environmental evolution of late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 19(2):27-35(in Chinese, with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz199902004
陈宇坤, 李振海, 邵永新, 王志胜, 高武平, 杨绪连. 2008.天津地区第四纪年代地层剖面研究[J].地震地质, 30 (2):483-493. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz200802005 陈永胜, 王宏, 裴艳东, 田立柱, 李建芬, 商志文. 2012.渤海湾西岸晚第四纪海相地层划分及地质意义[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 42(3):747-759. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201203018 丁大林, 张训华, 于俊杰, 王丽艳, 王丰, 商守卫, 2019.长江三角洲北翼后缘晚第四纪以来的沉积粒度特征及环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(04):34-45. 窦衍光, 陈晓辉, 李军, 蔡峰, 温珍河, 徐刚, 邹亮, 2018.东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽不同沉积单元底质沉积物成因及物源分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(04):21-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201804002 段永侯.1998.环渤海新构造活动与渤海形成演化对现今地质环境之影响[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 9(S1):106-113. 方静涛. 2020.辽宁省海岸带地质环境综合评价研究[J].地质与资源, 29(1):85-90, 100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz202001011 方文丽, 姚政权, 石学法, 葛晨东, 乔淑卿, 李小艳, 董智, 王颖, 2019.渤海沉积记录的末次冰期千年尺度古环境与古气候变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(3):61-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201903006 高茂生, 郭飞, 侯国华, 仇建东, 孔祥淮, 刘森, 黄学勇, 庄海海. 2018.渤海南部莱州湾晚更新世以来沉积演化特征[J].中国地质, 45(1):59-68. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180106&flag=1 郭海朋, 白晋斌, 张有全, 王丽亚, 石菊松, 李文鹏, 张作辰, 王云龙, 朱菊艳, 王海刚. 2017.华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J].中国地质, 44(6):1115-1127. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170607&flag=1 黄晓璇, 王汝建, 肖文申, 章陶亮, 2018.西北冰洋楚科奇海台晚第四纪以来陆源沉积物搬运机制及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(2):52-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802005 李凤林, 王宏, 阎玉忠, 王云生, 张金起, 赵长荣, 张玉发, 李建芬, 林防.2004.渤海湾西岸滨海平原晚第四纪以来的沉积间断[J].地质调查与研究, 27(3):177-183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz200403008 李杰, 李日辉, 杨士雄, 陈晓辉, 陈珊珊, 2018.渤海西部海域晚更新世以来的孢粉组合及古环境变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(2):115-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802012 刘世昊, 丰爱平, 李培英, 杜军, 李平, 高伟. 2015.现代黄河三角洲地区晚更新世以来高分辨率沉积粒度特征及动力沉积环境演化[J].第四纪研究, 35(2):291-306. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201502005 密蓓蓓, 王中波, 仇晓华, 张勇, 蓝先洪, 2019.中全新世以来冲绳海槽氧化还原环境重建及其气候效应[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(4):107-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904011 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 赵松龄主编. 1985.渤海地质[M].科学出版社, 212-223. 商志文, 王福, 李建芬, 姜兴钰, 陈永胜, 王宏. 2016.AMS14C测年揭示的渤海湾沿海低地第Ⅱ海相层年龄(II)[J].地质通报, 35(10):1607-1613. 孙丽莎, 刘健, 仇建东, 李国涛, 项立辉. 2014.现代黄河三角洲北岸YRD-1101孔岩心磁性地层学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(4):31-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404005 吴同, 杨振京, 王一鸣, 王攀, 彭培好, 张培新, 仓飞, 2019.温州沿海平原晚更新世以来的海相地层特征及沉积环境[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(4):148-162. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904015 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 秦亚飞. 2011.渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J].地质学报, 85(8):1352-1367. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201108009 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 李建芬, 赵长荣, 林防. 2006.渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J].地质通报, 25(3):357-382. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200603006 印萍, 林良俊, 陈斌, 肖国强, 曹珂, 杨吉龙, 李梅娜, 段晓勇, 仇建东, 胡云壮, 王磊, 孙晓明. 2017.中国海岸带地质资源与环境评价研究[J].中国地质, 44(5):842-856. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170502&flag=1 张欣, 刘健, 王飞飞, 仇建东, 王双. 2016.黄河三角洲地区yrd-1402孔沉积物光释光年代学与沉积环境.海洋地质与第四纪地质, (3):11-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603003 赵广明, 叶青, 叶思源, 丁喜桂, 袁红明, 王锦. 2014黄河三角洲北部全新世地层及古环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(5):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405003 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 庄丽华, 刘宝柱, 曹有益, 王强. 1999.渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 19(2):27-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz199902004 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 孙杨,谢远云,迟云平,康春国,吴鹏. 大兴安岭东麓龙江县白土山组地层特征:化学风化、沉积循环、源-汇体系和沉积环境. 山地学报. 2022(01): 14-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 仲米山,吕东霖,王岐,张化南,敖光,吴子杰,杨运来,王艺龙,谭超. 大兴安岭中段索伦地区林西组岩石地球化学特征与沉积构造环境. 中国地质调查. 2022(05): 89-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张海华,李晓海,张健,郑月娟,陈树旺,张德军,苏飞,卞雄飞,孙雷. 松辽盆地北部上二叠统林西组古生物年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 现代地质. 2021(02): 568-578 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张健,张海华,陈树旺,郑月娟,张德军,苏飞,黄欣. 松辽盆地北部上二叠统林西组地球化学特征及地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2020(02): 518-530 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张德军,张健,郑月娟,陈树旺,苏飞,黄欣,张海华,甄甄. 内蒙古自治区兴安盟突泉盆地TD-2井晚二叠世孢粉的发现及其油气地质意义. 中国地质. 2020(03): 798-809 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 邢作昌,张忠涛,林畅松,张博,洪方浩,张正涛. 珠江口盆地荔湾凹陷上渐新统—早中新统物源特征及其对沉积充填的影响. 中国地质. 2020(05): 1577-1588 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 陈兴,彭成龙,陈建书,吴开彬,张德明,王文明,龚桂源,邓贵标,骆珊. 右江盆地中三叠世碎屑岩地球化学特征及其物源分析∶以贵州册亨地区为例. 高校地质学报. 2020(06): 639-655 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: