Grain size distribution of sediment of core YRD-1101 in the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since the latest Pleistocene and its environmental change
-
摘要:
对现代黄河三角洲地区YRD-1101孔上部岩心开展粒度分析,并结合AMS14C和光释光(OSL)年代学测试结果、沉积特征、微体古生物鉴定及周边钻孔对比,建立了MIS5期以来的地层框架,揭示出该地区主要经历了3个阶段的沉积环境演化过程:(1)晚更新世—早全新世河流与海相交替沉积,其中MIS5c阶段海侵水动力环境中等,MIS3期海侵水动力环境较弱,MIS2期河流沉积水动力较强;(2)全新世滨、浅海沉积环境,动力环境整体较强,相对比较稳定;(3)1855年至今形成的黄河三角洲沉积,水动力强度较弱到中等。海平面变化和构造沉降是影响研究区晚更新世以来沉积演化的主要因素,此外,黄河带来的大量泥沙对海侵强度也有显著影响。
Abstract:Three stages of sedimentary environment evolution since MIS 5 were recognized based on the data of grain size analysis, AMS14C dating, OSL dating, sedimentary characteristics, benthic foraminifera and ostracoda identification in the upper part of core YRD-1101 drilled in the modern Yellow River Delta, and comparison with surrounding boreholes. Three stages of sedimentary evolution are identified. (1)Interactive deposition of rivers and marine facies were formed during the Late Pleistocene-Early Holocene. Among them, the transgressive sediments in the MIS5c phase were formed in a medium hydrodynamic conditions, the transgressive sediments in the MIS3 phase were formed in a weak hydrodynamic environment, and the river sediments in the MIS2 phase were formed in a strong hydrodynamic environment. (2) The nearshore and shallow sea deposits during the Holocene formed in a strong and stable environment. (3) Modern Yellow River Delta sediments deposited since 1855 A.D. were formed in weak to medium sedimentary dynamic environments. Sea-level changes and neotectonic subsidence have been the major factors controlling the sedimentary evolution on the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since MIS 5. In addition, the sediments were transported to the study area from Yellow River, which had a significant influence on transgression intensity.
-
1. 引言
在资源枯竭、经济发展和环境保护的三重压力下,寻找并开发利用新型清洁能源是关系国计民生和社会可持续发展的紧迫任务。推动绿色发展,构建清洁、安全、高效的能源体系已成为时代的要求。地热资源作为清洁能源的重要组成部分被寄予厚望。
天津市地热资源条件优越,地热开发利用水平一直处于全国前列。天津地热勘查研究工作开始于20世纪70年代,李四光同志主导的天津地热会战掀起了全国地热勘查研究的第一个春天,并发现了新近系和奥陶系两个热储。80年代以来,在市政府和原地矿部的支持以及联合国开发计划署的援助下,地热勘查开始向深部基岩热储发展,先后完成王兰庄、山岭子、塘沽地区三个地热田的勘查工作。自此之后,天津的地热研究与开发工作一直处于中国前列。先后发现地热田8个,已发现两大类6个热储,即孔隙型热储(新近系明化镇组、馆陶组热储和古近系东营组)和裂隙溶隙型热储(奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储),3000 m以浅年可开采地热流体为7606×104 m3。其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储是天津地热开发的主力储层。随着开发强度不断增大,部分地区开采潜力已达极限(天津地热勘查开发设计院, 2000;Wang, 2008;王继革等,2013)。
随着钻探技术的不断进步和清洁能源需求的持续增长,向地球深部进军,探测深部地热资源、开辟深部热储第二空间、增加可开采资源量,成为保障天津地区地热可持续开发的有效途径之一。为此,2017年以来,中国地质调查局在天津东丽湖地区部署了深部地热探测工作,并在主力储层下部探获雾迷山组二段高产能新储层。本文主要介绍天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储探测和高产能地热井参数研究取得的新成果、新进展。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 地热地质背景
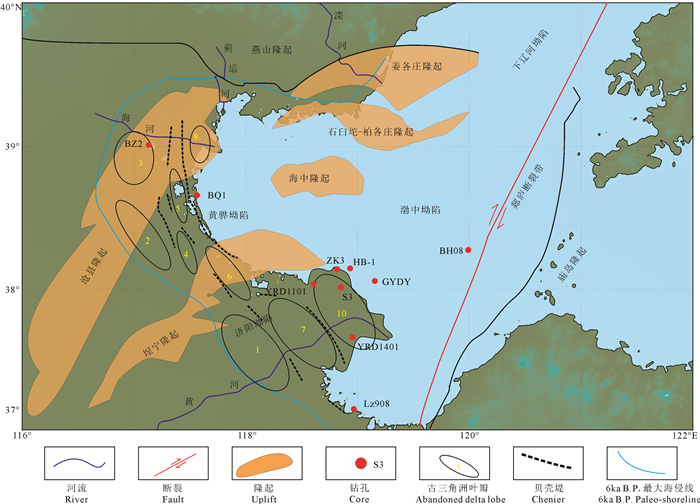
天津市地处Ⅰ级构造单元华北地台北缘,以宁河—宝坻断裂为界分为北部山区和南部平原区。其中,南部平原区属Ⅱ级构造单元华北断坳区,是中、新生代断陷、坳陷盆地。区内Ⅲ级构造单元包括一隆两坳即沧县隆起、冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷。隆起和坳陷及其间分布的诸多Ⅳ级构造单元凸起、凹陷的延伸方向和较大断裂的走向均呈北北东(NNE)向,形成雁行式相间排列的构造格局(陈墨香, 1988)(图 1)。
宝坻—宁河断裂以南为天津南部平原区,总面积8700 km2,地热资源条件优越。发育有王兰庄、山岭子、滨海、武清、潘庄—芦台、宁河—汉沽、万家码头和周良庄等8个地热田,年可开采地热流体7606×104 m3(图 2)。各地热田均位于华北断坳范围内,地面均为第四系松散沉积物覆盖,厚度可达数百米。其下是巨厚的新生界陆相碎屑岩沉积,是一套半胶结的砂岩和泥岩地层,沉积厚度在沧县隆起相对较薄,在冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷沉积较厚,最大厚度可达近万米。在新生界的巨大不整合覆盖之下,主要是古生界和中上元古界的基底地层,在坳陷中还有局部中生界分布。区内地热资源主要赋存于两大类6个储层中:一类为孔隙型热储,包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组和古近系东营组热储;一类为裂隙溶隙型热储,包括奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组热储(张百鸣等, 2006; Wang, 2008)(图 3)。
东丽湖地区位于天津市东部,隶属于天津市东丽区,位于Ⅳ级构造单元潘庄凸起上,发育有著名的山岭子地热田。依据研究区内地热井的钻探资料,揭露的地层从新到老为:新生界(第四系和新近系)、古生界(奥陶系和寒武系)、中新元古界(青白口系和蓟县系)(表 1)。区内已发现新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、奥陶系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段4个热储。其中,雾迷山组三、四段为当前主力储层,沧县隆起上钻孔揭露顶板埋深为1752~2016 m,揭露厚度为480~1032 m,单井出水量为70~120 m3/h,最大可达204 m3/h,出水温度为88~102℃,孔隙度1%~5.8%,渗透率5.52×10-14 m2,水化学类型为Cl · HCO3·SO4-Na或Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na型,总矿化度为1670~2200 mg/L,总硬度为120~240 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值为7.3~8.4(林黎等, 2007; 王继革等, 2013)。从区域地质资料看(高昌,2003;赵苏民等, 2006),区内雾迷山组厚度约3500 m,岩石组合为一套富镁碳酸盐岩,岩性主要为白云岩。燧石条带白云岩、硅质白云岩夹2~5层棕红、紫红色泥岩和页岩,可作为雾迷山组三、四段和一、二段的分界线。从岩性组合的相似性可以推测,雾迷山组一、二段可作为未来深部热储探测的重要方向,也是本次研究的重点。
表 1 天津东丽湖地区综合地层简表Table 1. The simplified table of geological strata in Donglihu area, Tianjin
2.2 开发利用现状
天津地热资源开发利用水平在全国居于较高地位,也是全国中低温地热直接利用规模最大的城市,是全国第一批“中国温泉之都”。自20世纪30年代以来,经过80多年的发展,天津地热资源开发利用从浅到深、从无序到有序、从粗放到精细,逐渐形成了规模化、产业化,在中国地热勘查开发利用史上具有举足轻重的作用。截至2017年,天津市共有地热开采井466眼,年开采总量为5181.08×104 m3,其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段约占开采总量的54%。地热资源主要应用于供暖、洗浴、理疗、旅游、养殖等。其中,供暖是最主要的利用方式,占年总开采量的81.5%。建有地热供暖小区及公建项目496个,全市地热供暖总面积达3500×104 m2,占全市集中供暖面积的8%,是中国利用水热型地热资源供暖规模最大的城市。
东丽湖地区现有地热井34眼。其中,新近系明化镇组4眼,新近系馆陶组2眼,奥陶系3眼,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段25眼。年开采地热流体约395.44×104 m3,采用梯级、综合利用和群井联动回灌的开发模式,达到资源的优化配置和实时调控,地热利用率和回灌率达到95%以上,实现了资源的统一规划、统一开发和统一管理。地热资源广泛应用于供暖、温泉洗浴、养生理疗、康乐旅游、矿泉水开发等领域,建有东丽湖温泉旅游度假区,在发展温泉旅游产业,促进地区经济发展,保护生态环境方面取得了显著的成效。2008年12月25日和2011年12月30日,分别被中国矿业联合会和国土资源部命名为“中国温泉之乡”。
3. 深部热储探测方法
本次研究主要基于地质综合分析,采用地球物理探测、地热钻探、地球物理测井和热储试验相结合的方法开展探测研究。
3.1 地球物理探测
为满足深部储层探测需要,本次地球物理探测的主要目标确定为5 km以浅地层的结构探测,为地热钻探提供依据。由于探测深度大,且存在高压线、铁路等城市干扰源,本次地球物理探测采用了二维地震和时频电磁相结合的勘查方法,其中,时频电磁方法首次应用到地热勘查领域。时频电磁方法是通过大功率人工场源激发信号,测量研究区测线的电磁场分量,分析频率域信号的振幅和相位特征,来获得介质的地电参数(电阻率和极化率),把信号转换到时间域,建立高分辨的电法勘探的时间断面。较传统电磁方法,在应对强电磁干扰方面具有一定的优势(Dong et al., 2008; 周印明等, 2013, 2015)。
本次工作部署时频电磁法完成测线4条,剖面24.4 km,点距200 m,物理点128个;二维地震完成剖面3条,8.25 km,测点254个(图 4)。
地球物理探测结果初步揭示了天津东丽湖地区雾迷山组二段的分布。从TFEM-1测线地质剖面解译图(图 5)可以看出,F1沧东断裂西侧,电阻率异常特征从上至下依次为“低—高—低—高—次高—高”,表层低阻和浅层高、低阻分别是第四系、新近系明化镇组与馆陶组地层响应特征,电阻率过渡连续,无明显的错断。第二套高阻层为寒武系(Є) 与青白口系(Qb)的反映,深部的次高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组4段(Jxw4)的反映,深部的高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组2、3段(Jxw2-3)的反映。蓟县系雾迷山组四段埋深2300~3000 m,下部发育雾迷山组二段和三段地层,埋深在3000 m以下。因缺乏雾迷山组二、三段电性参数,不易进一步细分。从二维地震DZ01剖面解释图(图 6)可以看出,区内4000 m以浅揭示的地层分别为第四系、新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、寒武系、青白口系和蓟县系雾迷山组。新近系馆陶组底界以上主要标准反射界面清晰可辨,以下反射界面呈断续分布。推测第四系底界埋深341~363 m;新近系明化镇组底界埋深1123~1160 m,馆陶组底界埋深1347~1500 m;寒武系张夏组底界埋深1758~2033 m,馒头组底界埋深1786~2113 m,昌平组底界埋深1856~2164 m;青白口系底界埋深2196~2444 m;蓟县系雾迷山组四段底界埋深2802~3004 m,三段底界二段顶界埋深3552~3726 m。4000 m探测深度范围内未揭示蓟县系雾迷山组底界。
3.2 地热科学钻探
在天津东丽湖部署地热科学钻探CGSD-01井,目标层位为蓟县系雾迷山组二段。2017年11月20日开钻,2018年11月19日完钻。成井深度4051.68 m,3715 m进入雾迷山组二段储层,是当时天津最深的地热井。
该井井身结构为三开直井。其中,护壁段(0~76 m)采用Ф660.4 mm冲击钻钻头施工,下入Ф508 mm×8.0 mm无缝套管,总长度为74.42 m。一开井段(76~1469.53 m)采用Ф444.5 mm牙轮钻头钻进,入Ф339.7 mm×J55钢级套管,长度1469.84 m。二开井段(1469.53~2262.75 m)采用Ф311.2 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф244.5 mm×10.03 mm N80钢级套管,长度866.60 m,与一开套管重叠68.12 m。三开井段(2262.75~4051.68 m)采用Ф215.9 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф177.8 mm×9.19 mm N80钢级套管,长度1939.96 m,其中实管长度为1747.23 m,花管长度为192.73 m,与二开套管重叠151.03 m。钻进过程中,开展了岩屑和岩心采集工作。1500 m以浅每5 m捞取岩屑一次,1500 m以深每2 m捞取岩屑一次,全井共计捞取岩屑样1873个。500~4051.68 m井段采取定深分段采取岩心,累计取心37回次,进尺161.25 m,长度140.78 m,采取率85%。
3.3 地球物理测井
钻井过程中,对地热井开展了综合地球物理测井工作,主要包括温度测井、压力测井、井径测井、井斜测井、视电阻率测井、双感应测井、自然电位测井、自然伽马测井、声波测井、伽马-伽马测井和流体流量测井11项。
3.4 热储试验
钻探完成后,为获取蓟县系雾迷山组二段新储层热储参数,对地热井开展了3个落程的稳定流降压抽水试验。其中,大落程试验历时62 h,涌水量130.2 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间39.5 h;中落程试验历时24 h,涌水量94.5 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间16.5 h;小落程试验历时16 h,涌水量43.9 m3/h,水温度稳定在98℃,稳定时间8 h(图 7)。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1 热储结构特征
综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇地层包括:第四系、新近系、寒武系、青白口系及蓟县系。钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储(表 2)。
表 2 天津东丽湖CGSD-01井钻遇地层表Table 2. Geological stratum of well CGSD-01 in the Tianjin
本次研究在地热井中实现雾迷山组四、三、二段精细划分,自上而下叙述如下。
雾迷山组四段(Jxw4):深度段为2258~2896 m,地层厚度638 m。上部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶白云岩,偶见少量深灰色厚层角砾状白云岩、灰白色硅质白云岩等;下部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩交互;底部主要发育灰黑色白云质泥岩夹细晶白云岩、泥晶白云岩、硅质白云岩。受原始沉积及沉积后多期次构造与岩溶作用等影响,雾迷山组四段白云岩层系整体较破碎,钻井岩心中裂隙和溶蚀孔洞极其发育,为地热水提供了良好的储集空间。
雾迷山组三段(Jxw3):深度段为2896~3715 m,地层厚度819 m。上部岩性主要为深灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩、白云质泥岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组三段上部的GR值较雾迷山组四段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也表现出类似特征;雾迷山组三段测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率值,下部整体较上部好(图 8);下部岩性主要发育浅灰—灰黑色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶—泥质白云岩、灰质泥晶白云岩及白云质泥岩;底部以发育一套紫红色泥质白云岩夹浅灰色细晶白云岩为典型特征,厚度约73 m,裂隙不发育,具有隔水—弱透水性质,作为与下伏雾迷山组二段的分界。
雾迷山组二段(Jxw2)深度段为3715~4051 m,地层厚度336 m,未钻穿。与上覆雾迷山组三段相比,雾迷山组二段的岩性及电测特征存在明显的差别(图 8)。岩性特征上,雾迷山组二段上部主要发育浅灰色细晶白云岩夹浅灰色粉晶白云岩、灰黑色泥质白云岩,之上为雾迷山组三段底部紫红色泥质白云岩作为两者明显分界;雾迷山组二段下部主要为浅灰色粉晶白云岩与灰黑色泥质白云岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组二段上部的GR值、自然电位值(SP)较雾迷山组三段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也体现出类似特征;雾迷山组二段上部的深侧向、浅侧向电阻率较雾迷山组三段底部高为特征。雾迷山组二段内部,自下而上,GR值、自然电位值(SP)、深侧向电阻率、浅侧向电阻率及测井解释的泥质含量呈逐渐变小趋势;声波时差呈逐渐变大趋势,测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率呈逐渐变大趋势,指示雾迷山组二段上部的热储层较下部更为发育。
4.2 温度特征
2018年11月19日对CGSD-01井开展了稳态测温。从测温曲线(图 9)可以看出,CGSD-01井底温度105℃。井温总体呈凸型曲线特征,体现了储盖层热传导机制为总体传导型、层间对流型。总体地温梯度2.4℃/100 m。其中,0~400 m第四纪地层地温梯度最高,可达8℃/100 m;400~2300 m新近系与寒武系盖层地温梯度次之,为2.4℃/100 m;2300~3500 m雾迷山组三、四段主力储层受对流作用影响,地温梯度最小,为0.83℃/100 m;3500 m以下雾迷山组二段储层地温梯度为1.7℃/100 m,对流作用较主力储层稍弱。
岩石热物性分析表明,雾迷山组二段岩石热导率在4.33~7.96 W/(m · K)(10个样品,表 3),平均值5.66 W/(m·K),略高于雾迷山组三四段平均值4.37 W/(m·K)。
表 3 CGSD-01井雾迷山组二段热储热导率测试值Table 3. Thermal conductivity test results of Wumishan Formation section 2 in well CGSD-01
4.3 热储参数
热储参数计算主要依据降压抽水试验计算。由于地热水密度与温度具有相关性,造成观测水位不能真实地反映地热井实际水位的变化,这种现象称之为“井筒效应”。资料整理过程中,以储层中部温度102.6℃作为储层温度对试验观测数据进行校准。校正后,做出的动水位埋深曲线如图 10。
采用Dupuit公式与W.Sihart公式对试验数据进行分析计算CGSD-01井的热储参数。本次抽水试验目标热储层为蓟县系雾迷山组二段,厚度336.68 m(未穿透),根据测井数据显示,裂隙厚度为123.1 m。根据降压抽水试验数据及相关校正,地热井基本参数见表 4。计算结果见表 5。依据降压抽水试验计算结果,取三个落程试验平均值可以得出,CGSD-01井单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d。
表 4 CGSD-01井热储参数计算基本参数Table 4. Reservoir parameters of well CGSD-01 表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
4.4 水化学特征
抽水试验过程中,采集样品对雾迷山组二段地热水进行了水化学、同位素和气体成分分析。
水化学分析表明,雾迷山组二段地热水水化学类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1770.0 mg/L,总硬度124.6 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值7.63。
结垢性和腐蚀性表明,地热水不生成碳酸钙垢,不生成硫酸钙垢,不生成硅酸盐垢,对管道及利用设施具有中等腐蚀性。
气体组分测试表明,溶解气体中以氮气和甲烷为主,分别占气体组分含量的66%和27%,还有少量乙烷、丙烷、异丁烷和异戊烷,指示储层处于还原环境。
同位素分析表明,地热水δD为-72‰~-72.7‰,δ18O为9.3‰~-9.5‰,δ13C为-3‰~-3.6‰,87Sr/86Sr为0.7113~0.7114。综合水化学和同位素特征,初步推断雾迷山组二段地热水来源于大气降水,主要发生混合、阳离子交替吸附、碳酸盐岩溶解、硫酸盐还原等作用,且未达到平衡。
4.5 开发利用潜力分析与建议
从区域地质背景和地层沉积序列看,雾迷山二段热储在潘庄凸起区全区均有分布,分布面积约604 km2,依据CGSD-01地热参数井信息,对潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量进行保守估算。年可开采热资源量按照100 a富水段可回收热量的0.01% 进行保守估算,其热量每年折合标煤250万t,初步估计可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
为了提高地热资源利用率,本文建议推广地热利用集约节约新技术,采用地热梯级利用联合水源热泵、地板辐射采暖、群井联动、地热与燃气或太阳能等多能源结合技术,降低尾水排放温度,实现地热资源利用最大化。
5. 结论
(1) 综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储。
(2) 雾迷山组二段上部单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d,岩石热导率5.66 W/(m · K),地热水类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1.7 g/L,热储参数与潘庄凸起三、四段热储相近。
(3) CGSD-01井降压抽水试验结果表明,蓟县系雾迷山组二段单井最大涌水量可达130 m3/h,出水温度100 ℃,单井可满足约30万m2建筑物供暖需求;初步估计潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
(4) 从区域地层沉积规律看,天津地区深部雾迷山组一段、杨庄组、高于庄组,厚度大、岩溶发育,与雾迷山组四、三、二段性质相似,均具有成为高产能新储层的可能性,加强深部地热探测研究意义重大。
-
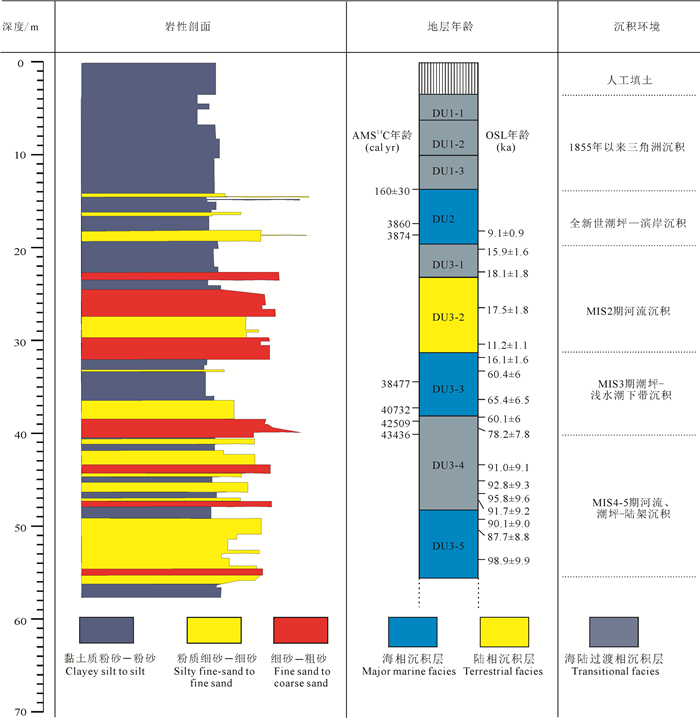
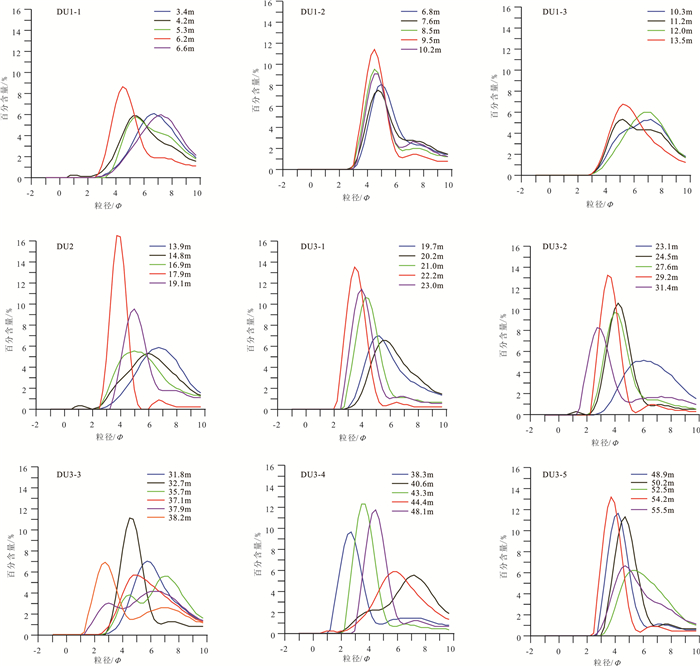
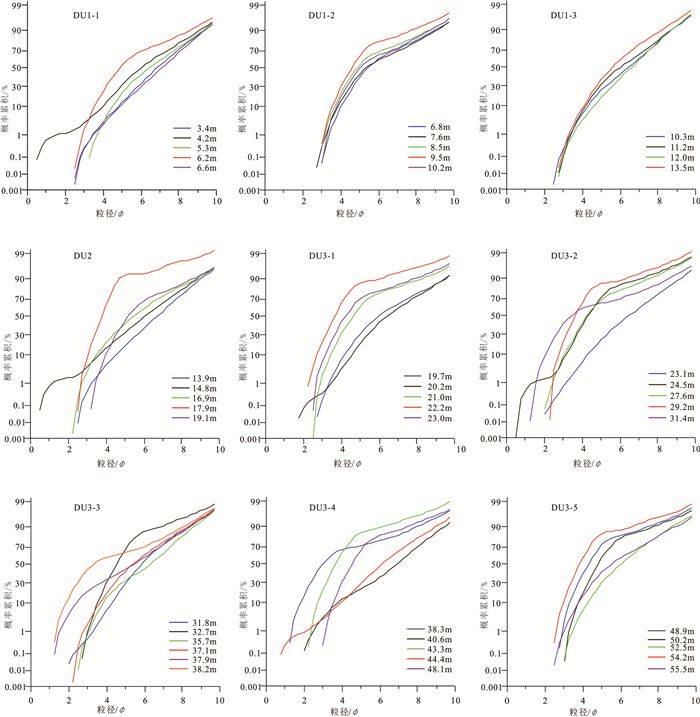
图 2 YRD-1101孔岩性特征及地层划分(据Liu et al., 2016修改)
Figure 2. Lithology and depositional sequences of core YRD-1101 (modified from Liu et al., 2016)
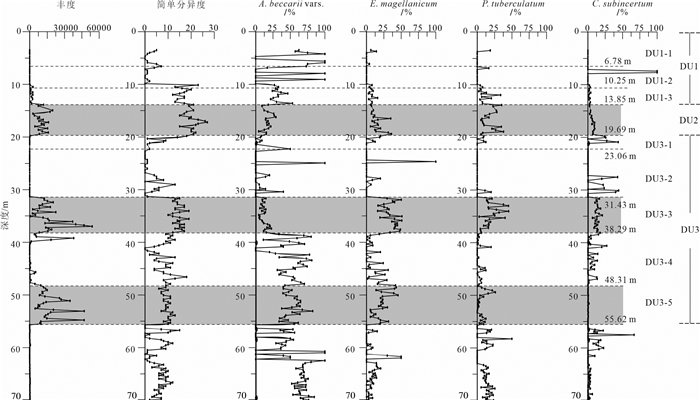
图 3 YRD-1101孔上部70 m有孔虫丰度、简单分异度和主要属种变化(据Liu et al., 2016修改)
灰色阴影代表晚更新世和全新世三个主要海相沉积层
Figure 3. Downcore changes in foraminiferal abundance and simple diversity, and the relative abundance of the main foraminiferal species in the uppermost 70 m of core YRD-1101(modified from Liu et al., 2016)
The grey shading indicates the three major marine sedimentary beds during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene
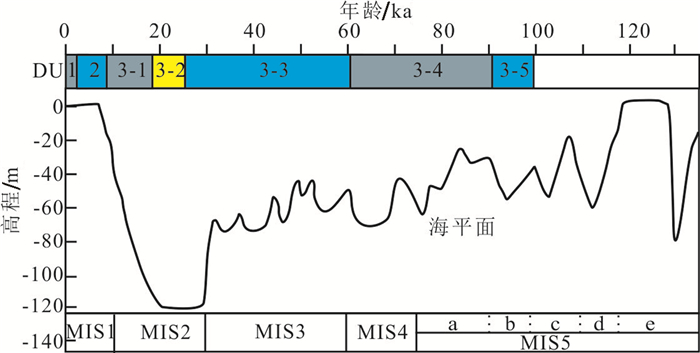
图 8 MIS5期以来黄海及其邻近海区海平面变化曲线(根据文献Chappell et al., 1996; Lambeck et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2010修改)与YRD-1101孔沉积序列对应关系
Figure 8. Curve of sea-level changes of Yellow Sea and adjacent areas since 120 ka (modified from Chappell et al., 1996; Lambeck et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2010) and its relationship with the depositional sequences of core YRD-1101
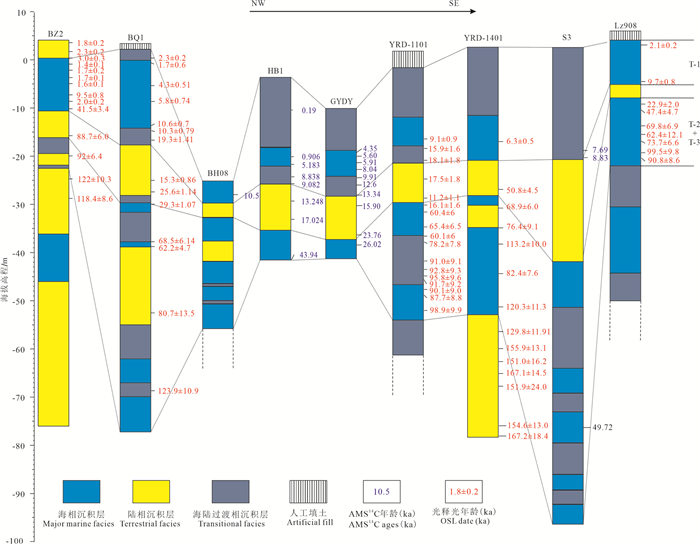
图 9 渤海西岸晚更新世和全新世以来沉积序列对比(据庄振业等, 1999; 阎玉忠等, 2006; 陈宇坤等, 2008; Liu et al., 2009; 赵广明等, 2014; 刘世昊等, 2015; Yi et al., 2015;Liu et al., 2016; 张欣等, 2016; Shi et al., 2016)
Figure 9. Regional correlation of sedimentary sequence during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene near the west coast of the Bohai Sea (after Zhuang et al., 1999; Yan et al., 2006; Chen et al., , 2008; Liu et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2015; Yi et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2016; Shi et al., 2016)
表 1 本文涉及钻孔的位置、高程及长度等基本信息
Table 1 Locations, core site elevations, and lengths of all cores in this paper

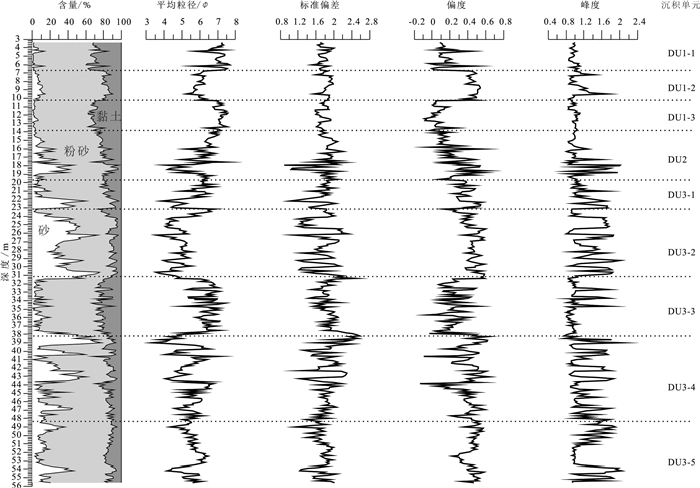
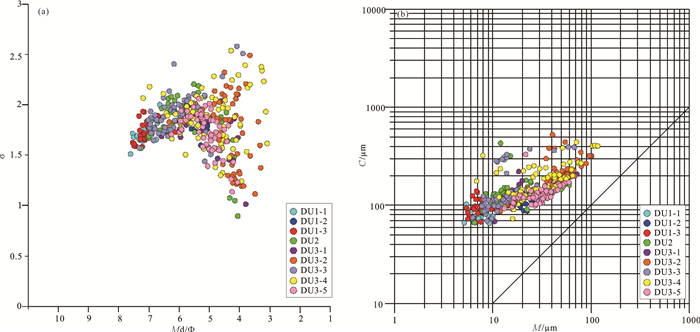
表 2 YRD-1101孔DU1-3岩心段沉积物粒度参数统计
Table 2 Statistics of grain size parameters of the DU1-3 in core YRD-1101

-
Chappell J, Omura A, Esat T, McCulloch M, Pandolfi J, Ota Y, Pillans B. 1996.Reconciliation of late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep-sea oxygen isotope records[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 141:227-236. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=625f81fed1ebfaa3e4a51f6203c9e4c2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen L, Cheng C, Wei Z. 2009.Seismic evidence for significant lateral variations in lithospheric thickness beneath the central and western North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 286(1):171-183. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=340097a71a8f610b8e339abb110a44f8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen Xiaoying, Liu Dahai, Yin Ping, Liu Jinqing, Cao Ke, Gao Fei, 2019. Temporal and spatial evolution of surface sediments characteristics in the Dagu River estuary and their dynamic response mechanism[J]. China Geology, 2, 325-332. doi: 10.31035/cg2018092.
Chen Yukun, Li Zhenhai, Shao Yongxin, Wang Zhisheng, Gao Wuping, Yang Xulian. 2008. Study on the Quaternary chronostratigraphic section in Tianjin Area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30 (2):483-493 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz200802005
Chen Yongsheng, Wang Hong, Pei Yandong, Tian Lizhu, Li Jianfen, Shang Zhiwen. 2012. Division and its geological significance of the late Quaternary marine sedimentary beds in the west coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(3):747-759(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201203018
Ding Dalin, Zhang Xunhua, Yu Junjie, Wang Liyan, Wang Feng, Shang Shouwei, 2019. Sediment grain size distribution patterns of the late Quaternary on the back side of northern Yangtze River Delta and their environmental implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(4):34-45 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904004
Dou Yanguang, Chen Xiaohui, Li Jun, Cai Feng, Wen Zhenhe, Xu Gang, Zou Liang, 2018. Origin and provenance of the surficial sediments in the subenvironments of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(4):21-31(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201804002
Duan Yonghou.1998. New tectonic movement and the formation and evolution of the Bohai Sea and their effects on the current geological environment[J].The Chinese Journal of Geological hazard and control, 9(S1):106-113.
Fang Jingtao. 2020. Comprehensive evaluation on the geoenvironment of coastal zones in Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 29(1):85-90, 100(in Chinese with English abstract).
Fang Wenli, Yao Zhengquan, Shi Xuefa, Ge Chendong, Qiao Shuqing, Li Xiaoyan, Dong Zhi, Wang Ying, 2019. Millennial-scale paleoenvironment and paleoclimate changes recorded in the Bohai Seas. Marine Geology& Quaternary Geology, 39(3):61-71. (in Chinese, with English Abstract).
Folk R L, Ward W C. 1957. Brazos River bar:A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 27(1):3-26.
Gao Maosheng, Guo Fei, Hou Guohua, Qiu Jiandong, Kong Xianghuai, Liu Sen, Huang Xueyong, Zhuang Haihai. 2018. The evolution of sedimentary environment since late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Geology in China, 45(1):59-68(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Haipeng, Bai Jinbin, Zhang Youquan, Wang Liya, Shi Jusong, Li Wenpeng, Zhang Zuozhen, Wang Yunlong, Zhu Juyan, Wang Haigang. 2017. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China, 44(6):1115-1127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706008
Huang Xiaoxuan, Wang Rujian, Xiao Wenshen, Zhang Taoliang, 2018.Transportation mechanism of terrigenous sediment and its paleoenvironmental implications on the Chukchi Plateau, western Arctic Ocean during the late Quaternary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(2):52-62(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802005
Lambeck Kurt, ESAT, Tezer M, Potter Emma-Kate. 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years[J]. Nature, 419.6903:199-206. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=852b67da3853a15162382315250c245f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Fenglin, Wang Hong, Yan Yuzhong, Wang Yunsheng, Zhang Jinqi, Zhao Changrong, Zhang Yufa, Li Jianfen, Lin Fang. 2004. The significance of the depositional hiatuses on the coastal plain of West Bohai Bay since the Late Quaternary period[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 27(3):177-183 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz200403008
Liu J, Satio Y, Wang H, Zhou L Y, Yang Z G. 2009. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 36(4-5):318-331. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1a063be96b0bd980e206c9a5e3a9e699&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li Jie, Li Rihui, Yang Shixiong, Chen Xiaohui, Chen Shanshan, 2018.Pollen spore assemblages and induced palaeoenvironmental changes in the western Bohai Sea since Late Pleistocene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(2):115-128 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802012
Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X H, Wang H, Wen C, Yang Z G, Nakashima R. 2010. Delta development and channel incision during marine isotope stages 3 and 2 in the western South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 278:54-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9c7322595f1f6ce2db864df80595cc52
Liu J, Wang H, Wang F F, Qiu J D, Saito Y, Lu J F, Zhou L Y, Xu G, Du X L, Chen Q. 2016.Sedimentary evolution during the last~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 451:84-96. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9fc04f1a91f971360b822b7445ebc75b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Li Peiying, Du Jun, Li Ping, Gao Wei. 2014.Evolution of the buried channel systems under the modern Yellow River delta since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary International, 349(3):327-338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=63076a55758d02d922916f575d9dc2d5
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Li Peiying, Du Jun, Li Ping, Gao Wei. 2015.High-resolution grain size distribution and evolution of the sediment-dynamic environment in the modern yellow river delta since the latest Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary, 35(2):291-306 (in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201502005
Liu S H, Li P Y, Feng A P, Du J, Gao W, Xu Y Q, Yu X X, Li P, Nan X L. 2016.Seismic and core investigation on the modern Yellow River Delta reveals the development of the uppermost fluvial deposits and the subsequent transgression system since the postglacial period[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 128:158-180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b0c1cb74cf671d744a150db32b89cc79
Mei Xi, Li Rihui, Zhang Xunhua, Wang Zhongbo, Zhang Yong, 2019.Reconstruction of phytoplankton productivity and community structure in the South Yellow Sea[J]. China Geology, 2, 315-324.doi: 10.31035/cg2018091.
Mi Beibei, Wang Zhongbo, Qiu Xiaohua, Zhang Yong, Lan Xianhong, 2019. Reconstruction of the redox environment in Okinawa Trough and its climatic implications since mid-Holocence[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(04):107-115 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Qin Yunshan, Zhao Yiyang, Zhao Songling(eds.). 1985.Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 212-223 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Saito Y, Yang Z, Hori K. 2001. The Huanghe(Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas:a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 41(2):219-231.
Shang Zhiwen, Wang Fu, Li Jianfen, Jiang Xingyu, Chen Yongsheng, Wang Hong. 2016. The age of the second marine layer in coastal lowland of Bohai Bay revealed by AMS14C dating method(II)[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 35(10):1591-1595(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, Larrasoaña J C, Bai Y Z, Liu Y G, Liu J H, Cao P, Li X Y, Qiao S Q, Wang K S, Fang X S, Xu T Y. 2016. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1Ma and implications for sea-level changes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 451:10-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f9716556de4445d320e63ea8d71ae2f1
Sun L S, Liu J, Qiu J D, Li G T, Xiang L H. 2014. Studies on magnetostratigraphy of core YRD-1101 sediments on the north shore of modern Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology& Quaternary Geology, 34(4):31-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404005
Vandenberghe J. 2013. Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:A powerful proxy for process identification[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 121(3):18-30. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5698ebd0d007408c1e9c9d0b8a1b0cc6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J, Thompson C E L, Gao J H, Yang Y. 2012.Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Marine Geology, 291-294:147-161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=91ddd20b8b820492bfc4866afb24df00
Wang Zhongbo, Li Rihui, Yang Shouye, Bai Fenglong, Mei Xi, Zhang Jian, Lu Kai, 2019. Comparison of detrital mineral compositions between stream sediments of the Yangtze River (Changjiang) and the Yellow River (Huanghe) and their provenance implication[J]. China Geology, 2, 169-178. doi: 10.31035/cg2018065.
Wu Tong, Yang Zhenjing, Wang Yiming, Wang Pan, Peng Peihao, Zhang Peixin, 2019. Marine stratigraphy since Late Pleistocene on Wenzhou coastal plain[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 39(04):148-162 (in Chinese, with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904015
Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang, Zhang Jinqi, Qin Yafei. 2011.Stratigraphic division of the late Quaternary strata along the coast of Bohai Bay and its geology significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(8):1352-1367(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201108009
Xu Q, Yang J, Yuan G, Chu Z X, Zhang Z K. 2015. Stratigraphic sequence and episodes of the ancient Huanghe Delta along the southwestern Bohai Bay since the LGM[J]. Marine Geology, 367:69-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=511420d1ffa16cd00a89c98f269e6128
Xue C T. 1993. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 113(3/4):321-329. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8e3fd2676c359579b2920305231196e4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Yao Z Q, Guo Z T, Xiao G Q, Wang Q, Shi X F, Wang X Y. 2012.Sedimentary history of the western Bohai coastal plain since the late Pliocene:Implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 54-55(4):192-202. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba30303741852157889ced1ac6369de7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Yan Yuzhong, Wang Hong, Li Fenglin, Li Jianfen, Zhao Changrong, Lin Fang. 2006. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by Borehole BQ1 on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China. 25(3):357-382(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200603006
Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, Xu X Y, Chen S L, Ge J Y, Hao Q Z, Yao J, Shi X F, Peng S Z. 2012. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 329-330(3):101-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e49fa43a9d0ffd03f5f16a195b120c3e
Yi L, Deng C L, Xu X Y, Yu H J, Qiang X K, Jiang X Y, Chen Y P, Su Q, Chen G Q, Li P, Ge J Y, Li Y. 2015. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary:Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology. 319:1-12.
Yin Ping, Lin Liangjun, Chen Bin, Xiao Guoqiang, Cao Ke, Yang Jilong, Li Meina, Duan Xiaoyong, Qiu Jiandong, Hu Yunzhuang, Wang Lei, Sun Xiaoming. 2017. Coastal zone geo-resources and geo-environment in China[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):842-856(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xin, Liu Jian, Qiu Jiandong, Wang Shuang. 2016. Study of optically stimulated luminescence(OSL) chronology and sedimentary environments of the Yellow River Delta area with core YRD-1402[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, (3):11-22.(in Chinese with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603003
Zhao G M, Ye Q, Ye S Y, Ding X G, Yuan H M, Wang J. 2014.Holocene stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental evolution of the northern Yellow river delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(5):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405003
Zhuang Zhenye, Xu Weidong, Liu Dongsheng, Zhuang Lihua, Liu Baozhu, Cao Youyi, Wang Qiang. 1999. Division and environmental evolution of late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 19(2):27-35(in Chinese, with English Abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz199902004
陈宇坤, 李振海, 邵永新, 王志胜, 高武平, 杨绪连. 2008.天津地区第四纪年代地层剖面研究[J].地震地质, 30 (2):483-493. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz200802005 陈永胜, 王宏, 裴艳东, 田立柱, 李建芬, 商志文. 2012.渤海湾西岸晚第四纪海相地层划分及地质意义[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 42(3):747-759. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201203018 丁大林, 张训华, 于俊杰, 王丽艳, 王丰, 商守卫, 2019.长江三角洲北翼后缘晚第四纪以来的沉积粒度特征及环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(04):34-45. 窦衍光, 陈晓辉, 李军, 蔡峰, 温珍河, 徐刚, 邹亮, 2018.东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽不同沉积单元底质沉积物成因及物源分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(04):21-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201804002 段永侯.1998.环渤海新构造活动与渤海形成演化对现今地质环境之影响[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 9(S1):106-113. 方静涛. 2020.辽宁省海岸带地质环境综合评价研究[J].地质与资源, 29(1):85-90, 100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz202001011 方文丽, 姚政权, 石学法, 葛晨东, 乔淑卿, 李小艳, 董智, 王颖, 2019.渤海沉积记录的末次冰期千年尺度古环境与古气候变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(3):61-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201903006 高茂生, 郭飞, 侯国华, 仇建东, 孔祥淮, 刘森, 黄学勇, 庄海海. 2018.渤海南部莱州湾晚更新世以来沉积演化特征[J].中国地质, 45(1):59-68. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180106&flag=1 郭海朋, 白晋斌, 张有全, 王丽亚, 石菊松, 李文鹏, 张作辰, 王云龙, 朱菊艳, 王海刚. 2017.华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J].中国地质, 44(6):1115-1127. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170607&flag=1 黄晓璇, 王汝建, 肖文申, 章陶亮, 2018.西北冰洋楚科奇海台晚第四纪以来陆源沉积物搬运机制及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(2):52-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802005 李凤林, 王宏, 阎玉忠, 王云生, 张金起, 赵长荣, 张玉发, 李建芬, 林防.2004.渤海湾西岸滨海平原晚第四纪以来的沉积间断[J].地质调查与研究, 27(3):177-183. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz200403008 李杰, 李日辉, 杨士雄, 陈晓辉, 陈珊珊, 2018.渤海西部海域晚更新世以来的孢粉组合及古环境变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(2):115-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802012 刘世昊, 丰爱平, 李培英, 杜军, 李平, 高伟. 2015.现代黄河三角洲地区晚更新世以来高分辨率沉积粒度特征及动力沉积环境演化[J].第四纪研究, 35(2):291-306. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201502005 密蓓蓓, 王中波, 仇晓华, 张勇, 蓝先洪, 2019.中全新世以来冲绳海槽氧化还原环境重建及其气候效应[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(4):107-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904011 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 赵松龄主编. 1985.渤海地质[M].科学出版社, 212-223. 商志文, 王福, 李建芬, 姜兴钰, 陈永胜, 王宏. 2016.AMS14C测年揭示的渤海湾沿海低地第Ⅱ海相层年龄(II)[J].地质通报, 35(10):1607-1613. 孙丽莎, 刘健, 仇建东, 李国涛, 项立辉. 2014.现代黄河三角洲北岸YRD-1101孔岩心磁性地层学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(4):31-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404005 吴同, 杨振京, 王一鸣, 王攀, 彭培好, 张培新, 仓飞, 2019.温州沿海平原晚更新世以来的海相地层特征及沉积环境[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(4):148-162. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904015 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 秦亚飞. 2011.渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J].地质学报, 85(8):1352-1367. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201108009 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 李建芬, 赵长荣, 林防. 2006.渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J].地质通报, 25(3):357-382. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200603006 印萍, 林良俊, 陈斌, 肖国强, 曹珂, 杨吉龙, 李梅娜, 段晓勇, 仇建东, 胡云壮, 王磊, 孙晓明. 2017.中国海岸带地质资源与环境评价研究[J].中国地质, 44(5):842-856. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170502&flag=1 张欣, 刘健, 王飞飞, 仇建东, 王双. 2016.黄河三角洲地区yrd-1402孔沉积物光释光年代学与沉积环境.海洋地质与第四纪地质, (3):11-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603003 赵广明, 叶青, 叶思源, 丁喜桂, 袁红明, 王锦. 2014黄河三角洲北部全新世地层及古环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(5):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405003 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 庄丽华, 刘宝柱, 曹有益, 王强. 1999.渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 19(2):27-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz199902004 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 何沛欣. 广东省粤中断裂型碳酸盐岩地热水的水文地球化学研究——以马星-隔陂地热系统为例. 广东化工. 2024(05): 67-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王君照,李胜涛,岳冬冬,张秋霞,李菊红,崔俊艳,杨骊. 基于GIS与GOCAD的天津双窑凸起构造区热储三维地质建模. 科学技术与工程. 2023(14): 5887-5902 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程正璞,雷鸣,李戍,连晟,魏强. 天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储时频电磁法探测及有利区预测. 华北地质. 2023(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 岳冬冬,贾小丰,张秋霞,冯昭龙,李胜涛. 天津山岭子地热田蓟县系雾迷山组热储流体同位素特征及其指示意义. 华北地质. 2023(02): 45-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘杰,宋美钰,胥博文,阮传侠,石峰. 天津市馆陶组地热流体可采量计算方法及适宜性分区研究. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1655-1666 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 杨吉龙,汪大明,牛文超,相振群,刘洋,赵泽霖,程先钰. 天津地热资源开发利用前景及存在问题. 华北地质. 2022(03): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王婷灏,汪新伟,毛翔,罗璐,高楠安,刘慧盈,吴陈冰洁. 沧县隆起北部地区地热资源特征及开发潜力. 中国地质. 2022(06): 1747-1764 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: