-
摘要:
本文以地球科学基础学科的基本知识和矿床实例首次论述了雪峰隆起带内板岩、变质砂岩等浅变质的区域变质作用不能使岩石中的金活化迁移富集成矿;断裂构造在动力变质过程中本身并不成矿,断裂破碎带的地层中金只是带内金矿体金金属量的0.123%;流体包裹体测定的金矿成矿温度主要区间在200~300℃,说明雪峰隆起带岩金矿床不是地下水热液成因;金矿床的一些矿石矿物、伴共生组分、微量元素、同位素地球化学等特征与花岗岩类岩浆岩的相似性也说明了两者间的成因关系;重磁资料推断地表无岩浆岩出露的岩金矿床下部有大面积的隐伏岩体。以上论述和排除法均说明雪峰隆起带上岩金矿床成因类型是岩浆热液矿床。
Abstract:Based on basic knowledge in geosciences and instances of ore deposits, the authors firstly put forward the argument that gold within rocks in the Xuefeng uplift zone can't be mobilized, migrated and enriched for mineralization by low-grade regional metamorphism of such rocks as slate and meta-sandstone. The fault structure itself cannot be mineralized in the process of dynamic metamorphism. The content of gold in strata in the fracture zone is only 0.123% of that in the orebody. The metallogenic temperature of the gold deposit determined by fluid inclusions mainly ranges from 200 ℃ to 300 ℃, which indicates that the rock gold deposit in the Xuefeng uplift zone was not sourced from underground hydrothermal solutions. The similarity between some ore minerals, associated components, trace elements, and isotopic geochemistry of gold deposits and the similarity of granitic magmatic rocks show their genetic relationships. The gravitational and magnetic data suggest that there might exist a large concealed intrusion under the gold deposit where there are no magmatic rocks exposed on the surface. The above discussion and exclusion suggest that the genetic type of rock gold deposits in Xuefeng uplift belt is magmatic hydrothermal deposit.
-
1. 引言
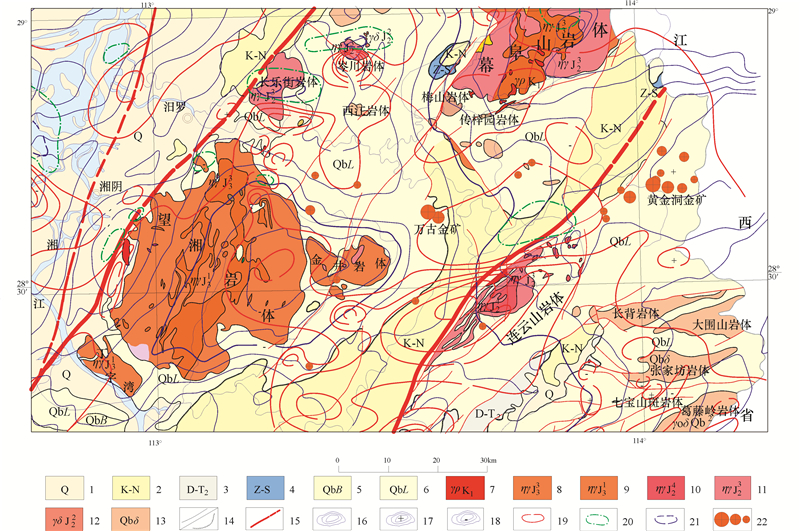
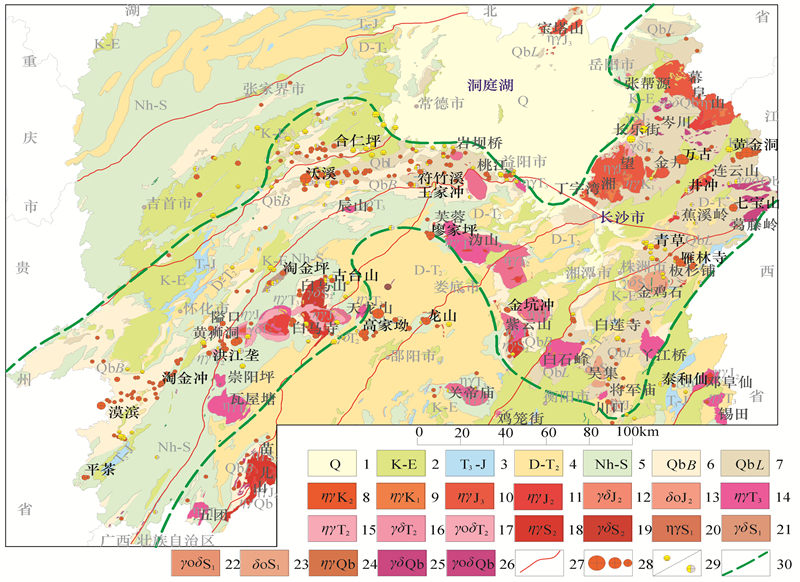
雪峰隆起带(含湘东北隆起带),又称为雪峰弧形构造带或雪峰造山带,是江南地块与华南地块的碰撞带,雪峰山湘西隆起带—湘东北隆起带—江西金山隆起带构成了巨大的金成矿带。雪峰隆起带是湖南的金腰带,是湖南金的主要生产基地和重要金矿资源基地,湖南主要的大型、超大型金矿床均产于雪峰隆起带。金矿床(点)占全省金矿床(点)的80%以上,有名的沃溪金矿、黄金洞金矿、铲子坪金矿、万古金矿等大型—超大型矿床均产于该带内。近年来新增加的金资源储量,以及新发现的金矿产地、金矿找矿靶区,主要来自雪峰隆起带(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 湖南雪峰隆起带地质图1—第四系;2—白垩系至古近系;3—上三叠统至侏罗系;4—泥盆系至中三叠统;5—南华系至志留系;6—青白口系板溪群;7—青白口系冷家溪群;8—晚白垩世黑云母二长花岗岩;9—早白垩世二长花岗岩;10—晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗世黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—中侏罗世黑云母石英闪长岩;14—晚三叠世二长花岗岩;15—中三叠世二长花岗岩;16—中三叠世黑云母花岗闪长岩;17—中三叠世黑云母石英闪长岩;18—中志留世黑云母二长花岗岩;19—中志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;20—早志留世二长花岗岩;21—早志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;22—早志留世黑云母英云闪长岩;23—早志留世石英闪长岩;24—青白口系二长花岗岩;25—青白口系黑云母花岗闪长岩;26—青白口系黑云母英云闪长岩;27—主要断裂带;28—大中小型金矿床;29—砂金矿床/伴生金矿床;30—雪峰隆起边界线Figure 1. Geological map of Xuefeng uplift zone in Hunan1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous to Paleogene; 3-Upper Triassic to Jurassic; 4-Devonian to middle Triassic; 5- Nanhua Period to Silurian; 6-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou system; 7-Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 8-Late Cretaceous biotite monzogranite; 9-Early Cretaceous monzogranite; 10-Late Jurassic monzogranite; 11-Middle Jurassic monzogranite; 12-Middle Jurassic biotite granodiorite; 13-Middle Jurassic biotite quartz diorite; 14-Late Triassic monzogranite; 15-Middle Triassic monzogranite; 16-Middle Triassic biotite granodiorite; 17-Middle Triassic biotite quartz diorite; 18-Middle Silurian biotite monzogranite; 19-Middle Silurian biotite granodiorite; 20-Early Silurian monzogranite; 21-Early Silurian biotite granodiorite; 22-Early Silurian biotite tonalite; 23-Early Silurian quartz diorite; 24-Qingbaikou Period monzogranite; 25-Qingbaikou Period biotite granodiorite; 26-Qingbaikou Period biotite tonalite; 27-Major fault zones; 28-Large and medium sized gold deposits; 29-Placer gold deposit/associated gold deposit; 30-Xuefeng uplift boundary
图 1 湖南雪峰隆起带地质图1—第四系;2—白垩系至古近系;3—上三叠统至侏罗系;4—泥盆系至中三叠统;5—南华系至志留系;6—青白口系板溪群;7—青白口系冷家溪群;8—晚白垩世黑云母二长花岗岩;9—早白垩世二长花岗岩;10—晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗世黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—中侏罗世黑云母石英闪长岩;14—晚三叠世二长花岗岩;15—中三叠世二长花岗岩;16—中三叠世黑云母花岗闪长岩;17—中三叠世黑云母石英闪长岩;18—中志留世黑云母二长花岗岩;19—中志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;20—早志留世二长花岗岩;21—早志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;22—早志留世黑云母英云闪长岩;23—早志留世石英闪长岩;24—青白口系二长花岗岩;25—青白口系黑云母花岗闪长岩;26—青白口系黑云母英云闪长岩;27—主要断裂带;28—大中小型金矿床;29—砂金矿床/伴生金矿床;30—雪峰隆起边界线Figure 1. Geological map of Xuefeng uplift zone in Hunan1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous to Paleogene; 3-Upper Triassic to Jurassic; 4-Devonian to middle Triassic; 5- Nanhua Period to Silurian; 6-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou system; 7-Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 8-Late Cretaceous biotite monzogranite; 9-Early Cretaceous monzogranite; 10-Late Jurassic monzogranite; 11-Middle Jurassic monzogranite; 12-Middle Jurassic biotite granodiorite; 13-Middle Jurassic biotite quartz diorite; 14-Late Triassic monzogranite; 15-Middle Triassic monzogranite; 16-Middle Triassic biotite granodiorite; 17-Middle Triassic biotite quartz diorite; 18-Middle Silurian biotite monzogranite; 19-Middle Silurian biotite granodiorite; 20-Early Silurian monzogranite; 21-Early Silurian biotite granodiorite; 22-Early Silurian biotite tonalite; 23-Early Silurian quartz diorite; 24-Qingbaikou Period monzogranite; 25-Qingbaikou Period biotite granodiorite; 26-Qingbaikou Period biotite tonalite; 27-Major fault zones; 28-Large and medium sized gold deposits; 29-Placer gold deposit/associated gold deposit; 30-Xuefeng uplift boundary雪峰隆起带的金矿主要产于新元古界青白口系,南华系、震旦系中有少量产出,湖南最老的青白口系板溪群和冷家溪群中金矿床(点)最多,规模最大。新元古代岩性主要为浅变质板岩,次为浅变质砂岩等粉砂质、黏土质、凝灰质碎屑岩,局部夹有基性、酸性火山岩。金矿体受断裂构造控制,围岩主要为粉砂质板岩等浅变质细碎屑岩。对雪峰隆起带产于老地层中金矿床的成因,多数人的传统观念认为是变质热液矿床,认为成矿物质来源于前寒武纪老地层,老地层是矿源层,由于区域变质作用和动力变质作用,使老地层中的金活化转移到断裂破碎带中沉淀成矿。笔者研究认为雪峰隆起带上的金矿床,成矿物质直接来源不是前寒武纪老地层,主要的成矿热液不是来源于区域变质作用和动力变质作用,而是来源于岩浆期后热液,新元古代老地层只是初始矿源层,壳熔花岗岩化作用和同熔花岗岩化作用使老地层中金元素熔融到花岗岩类岩浆中,在岩浆期后热液中富集,然后进入断裂构造中沉淀成矿。矿床成因类型应为岩浆期后热液金矿床,矿床工业类型主要为破碎带蚀变岩型和含金石英脉型金矿床。下面分析提出这一认识的主要依据和矿床实例。
2. 主要依据
2.1 岩石学依据
雪峰隆起带出露主要地层是湖南境内最老的板溪群和冷家溪群,是境内区域变质作用最强和最广泛的地层,然而也只是轻微的浅变质作用,变质岩石以板岩为主,次为浅变质砂岩等碎屑岩,金矿体主要产于粉砂质板岩中。《变质岩石学》明确指出:板岩具有明显的板理构造,板理(或劈理)构造一般为低级区域变质或区域动力变质时,在应力强温度低的条件下形成。板岩是指原岩矿物成分基本没有重结晶的泥质、粉砂质低级变质岩,也包括一部分中酸性凝灰质岩石。原岩的矿物成分没有明显的重结晶现象,新生矿物很少,仍以隐晶质为主。显微镜下除偶见一些细小不均匀分布的石英、绢云母、绿泥石等矿物外,大部分仍为隐晶质黏土矿物,以及炭质、铁质粉末,可能存在残留的泥质、粉砂质岩石结构,或者变余层理结构(贺同兴等,1979)。既然在形成板岩的变质过程中矿物成分没有重结晶,大部分仍为隐晶质黏土矿物,那就不可能形成使原岩中的金元素活化迁移的变质热液,否则就会出现大量的蚀变矿物和普遍的重结晶现象,那就不是浅变质的板岩,而是深变质岩了。雪峰隆起带形成板岩的区域变质作用不可能形成变质热液矿床。前寒武纪青白口系板溪群、冷家溪群等老地层也不是直接的矿源层,区域浅变质作用并不能形成金矿床。
2.2 构造地质学依据
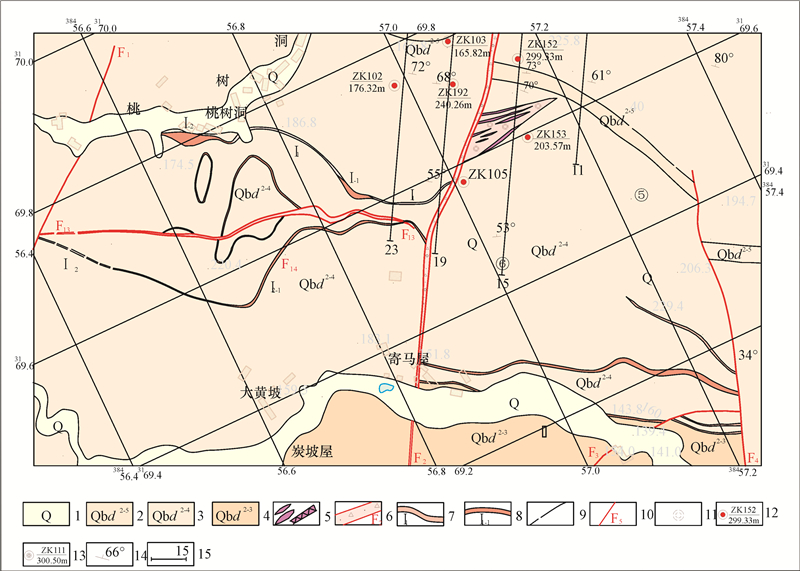
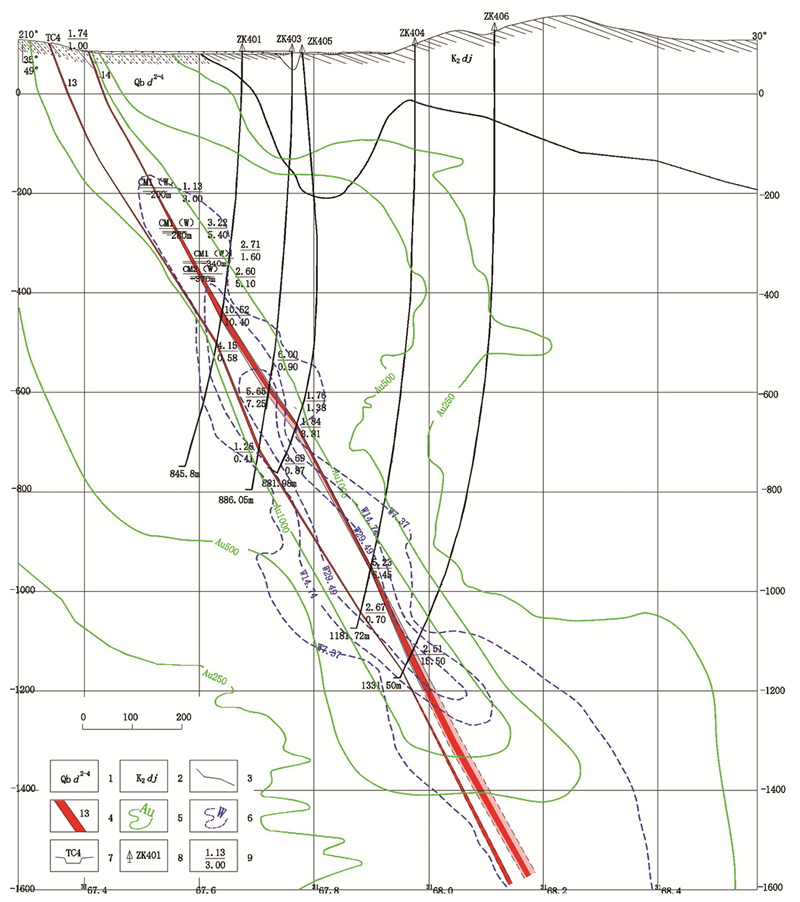
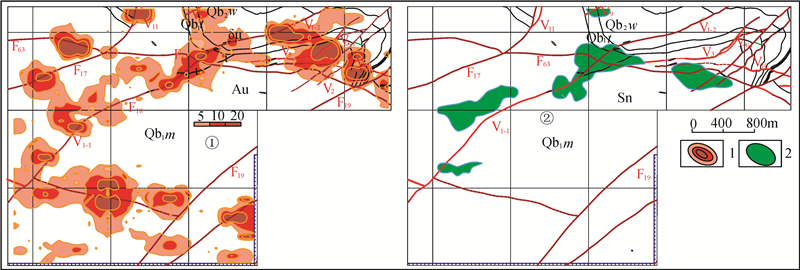
雪峰隆起带的金矿体受断裂构造控制。区域性大断裂一般为导矿构造,次级断裂为容矿构造,断裂带本身只提供含矿热液运移的通道和矿质沉淀的空间。如果没有外部成矿物质来源,断裂本身的动力变质作用并不能成矿。动力变质作用并不是一种成矿作用,其最终结果是产生断裂构造和褶皱构造而释放应力和能量。断裂构造的主体和主要表现形式是各种构造岩和断裂面,地球应力作用于地质体,通过地质体的压缩或拉伸变形、破裂、碎裂、角砾岩化、糜棱岩化等动力变质作用释放应力,其中一部分应力转变为热能,能够使动力变质岩石中的部分孔隙水、结晶水变成热水溶液进入构造面和断裂带中,并成为断裂的润滑剂,加速地体的破裂和运移,最终应力因为地体的变形和断裂而完全释放。断裂面是受力最强的结构面,断裂面上的矿物有压溶和重结晶现象,也会出现绢云母、绿泥石、石英、方解石等变质矿物。但是断裂不会形成较大的成矿热流体。《构造地质学》中明确指出,即便是动力变质作用最强、粒度最细(小于0.02 mm)的超糜棱岩规模也不大,且分布局限,常呈数厘米厚的不连续的透镜体夹于糜棱岩中,由于断层强烈挤压、错动和摩擦而产生的高温,可使超糜棱岩局部熔融而后又迅速冷却,形成黑色玻璃质岩石,称“玻化岩” (武汉地质学院等,1979)。有人认为玻化岩是假熔岩,也有经过X光研究和光学研究证明是隐晶质的,是岩石高度压碎的产物,并没有经过真正的融化(贺同兴等,1979)。还有一种观点认为,糜棱岩的细化并不是脆性破碎和研磨的结果,而是矿物晶体塑性变形的结果(宋鸿林等,2015)。所以不管哪种说法,都认为断裂构造不会形成成矿热流体。湘东北万古金矿区F12、F13、F14均产于冷家溪群大药姑组这个所谓的“矿源层”中的同一脉带中(图 9),且F13为夹在F12、F14中间的同方向同性质断裂,早期形成的F12、F14为含矿断裂,而后期形成的F13断裂带,经5个工程的系统采样分析,金含量只有0.02×10-6~0.26×10-6,为无矿断裂❶。如果断裂构造本身的动力变质作用能够成矿,那么同在“矿源层”中的F13断裂带也应该成矿。
![]() 图 9 湖南省平江县万古矿区Ⅰ1、Ⅰ2号金矿脉地质图1—第四系;2—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第五岩性段;3—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第四岩性段;4—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第三岩性段;5—石英脉;6—断层破碎带;7—实(推)测含金蚀变破碎带及矿脉编号;8—矿体及编号;9—实(推)测地层界线;10—实测断层及编号;11—硅化;12—见矿钻孔位置、编号,孔深;13—见矿化钻孔位置、编号及孔深;14—岩层产状;15—勘探线位置及编号Figure 9. Geological map of gold vein Ⅰ1 and Ⅰ2 in Wangu mining area, Pingjiang County, Hunan Province1-Quaternary; 2-Second section fifth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 3-Second section fourth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 4-Second section third lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 5-Quartz vein; 6-Fault fracture zone; 7-Gold-bearing alteration fracture zone and vein number; 8-Orebody and its serial number; 9-Actual (inferred) stratigraphic boundary; 10-Fault and its serial number; 11-Silicification; 12- Ore-intersecting drilling position, serial number, hole depth; 13-Mineralization-intersecting drilling location, serial number and depth; 14-Stratigraphic attitude; 15- Exploration line location and serial number
图 9 湖南省平江县万古矿区Ⅰ1、Ⅰ2号金矿脉地质图1—第四系;2—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第五岩性段;3—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第四岩性段;4—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第三岩性段;5—石英脉;6—断层破碎带;7—实(推)测含金蚀变破碎带及矿脉编号;8—矿体及编号;9—实(推)测地层界线;10—实测断层及编号;11—硅化;12—见矿钻孔位置、编号,孔深;13—见矿化钻孔位置、编号及孔深;14—岩层产状;15—勘探线位置及编号Figure 9. Geological map of gold vein Ⅰ1 and Ⅰ2 in Wangu mining area, Pingjiang County, Hunan Province1-Quaternary; 2-Second section fifth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 3-Second section fourth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 4-Second section third lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 5-Quartz vein; 6-Fault fracture zone; 7-Gold-bearing alteration fracture zone and vein number; 8-Orebody and its serial number; 9-Actual (inferred) stratigraphic boundary; 10-Fault and its serial number; 11-Silicification; 12- Ore-intersecting drilling position, serial number, hole depth; 13-Mineralization-intersecting drilling location, serial number and depth; 14-Stratigraphic attitude; 15- Exploration line location and serial number在雪峰隆起带的金矿床没有见到垂直矿脉的阿尔卑斯型侧分泌矿脉,没有见到金矿脉(体)的围岩向金矿脉(体)输送成矿物质的地质痕迹和地质现象,只见到金矿脉(体)的围岩蚀变和金矿化,以及从金矿体中伸到围岩裂隙中的金矿(化)脉,含金石英脉型金矿床的“热液活动仅见一系列石英脉大致平行蚀变破碎带产出”❶。说明成矿热液是从下向上沿断裂破碎带充填交代而成矿,成矿物质并非来自断裂两侧的围岩。
河南省三门峡市崤山金矿,矿体产于变质核杂岩穹隆构造的环形拆离滑脱断裂带糜棱岩中的后期浅层脆性断裂中,后期浅层脆性断裂产状与糜棱岩一致,含金石英脉和含金破碎带蚀变岩仅发育在浅层脆性断裂中,虽然糜棱岩是由金丰度值较高的太古宙太华群和古元古代熊耳群老地层形成,但糜棱岩没有金矿化,成矿物质来源于后期的岩浆热液❷。
山东焦家金矿是典型的破碎带蚀变岩型金矿,即焦家式金矿,焦家式金矿受到再生花岗岩体与胶东群接触带控制,矿化发育在主断裂带下盘角砾岩、碎裂岩、破碎状花岗岩当中(国土资源部,2002;宋明春等,2010)。而上盘却没有金矿体,如果金矿化是由于断裂构造压碎老地层而形成,那么断裂构造上下两盘都应该有金矿体的产出,这说明成矿热液是从下向上沿断裂下盘运移的,这也说明断裂构造本身并不成矿。
以上事实说明形成断裂构造的动力变质作用不是直接的成矿作用,断裂构造本身并不能单独成矿,所以雪峰隆起带金矿不是动力变质矿床。
2.3 矿物学依据
《结晶学与矿物学》明确指出,白钨矿、黑钨矿、锡石是与花岗岩类岩浆岩有成因关系的特征矿物,白钨矿主要产于接触交代矿床,或产于气化,高温热液脉中及其围岩蚀变中,与黑钨矿、锡石共生;黑钨矿主要是由气化-高温热液作用形成的矿物,以产于高温热液石英脉以及脉旁云英岩化花岗岩中者为常见,在成因上与花岗岩有关;锡石主要产于蚀变花岗岩顶部、高温热液石英脉、云英岩脉,以及接触交代变质岩中(南京大学地质学系,1978);雪峰隆起带上的许多金矿床发育了花岗岩类岩浆岩的特征矿物白钨矿、黑钨矿、锡石、电气石、辉钼矿、磁铁矿等矿物,这些矿物在浅变质的老地层中则没有出现或极少发现,而在金矿脉体中以及蚀变围岩中出现频率较高,并具有一定的量,常与金矿共、伴生,说明这些矿物是在金的矿化过程中形成的。
雪峰隆起带上的湘西沃溪金矿,是W、Sb、Au共生的矿床,WO3含量高达0.43%(钨矿床的最低工业品位是0.12%),WO3的资源储量达到了5000多吨。对沃溪金矿W、Sb、Au矿床矿石矿物的研究表明,该类型矿床具有复杂多样的矿石矿物组成。这种复杂的矿石矿物组成特征预示成矿并非沉积或热卤水喷流沉积所致,考虑矿床成矿与区域花岗岩浆作用的成因联系,可以认为沃溪金矿床深部可能有寻找大型多金属矿床的前景(彭渤等,2018);雪峰隆起带上的新化县古台山金矿,是Au-Cu-W-Sb共生的矿床,WO3含量达0.187%。河南省三门峡市崤山金矿伴生钨矿,9号金矿脉伴生的WO3达到了0.042%,估算了98 t WO3资源量;湖南黄金洞金矿的矿石矿物组成十分复杂,据不完全统计共有38种之多,其中白钨矿、磁铁矿、电气石等矿物是岩浆岩的特征矿物,矿石矿物的多样性和复杂性,也是岩浆热液矿床的一个特征。湘西铲子坪金矿矿石中与岩浆岩有关的特征矿物有辉铋矿、黑钨矿、电气石、钾长石、钠长石等。常见金矿石与W、Sn、Mo、Bi等矿物的一种或多种伴(共)生。花岗岩类岩浆岩对钨矿、锡矿、铋矿、钼矿、稀有、稀土金属矿物等具有成矿专属性;但是,也有一些金矿床没有发现这些矿物和元素异常,它是由多种因素决定的,其中一个原因是在金矿的早期找矿勘查过程中可能就没有认识到金矿与钨、锡、钼、铋等元素的相关性,在岩矿样品测试项目中,没有做这些元素和矿物的分析研究,所以就未能发现这些元素或矿物与金矿的成因上的关系。
雪峰隆起带上金矿的一些矿石矿物、脉石矿物与岩浆岩的特征矿物的相似性、显示出金矿的成矿与岩浆岩的成因关系。
2.4 地球物理依据
在一些金矿床内或者附近较大范围内并没有发现岩浆岩,或者仅见少量小的岩脉出现,地球物理和地球化学资料说明这些金矿床下部往往存在有隐伏岩体。
理论和实践证明隐伏的花岗岩类岩体的地球物理特征显示为正磁异常和负的重力异常,雪峰隆起带一些金矿床和附近较大范围内地表没有发现岩浆岩,或只发现一些小的岩脉,但其上部明显存在一定范围的正磁异常和重力负异常,如湘东北隆起区黄金洞金矿区和万古金矿区分别距出露的连云山花岗岩体、望湘—金井花岗岩体达13 km和10~15 km(图 1);在黄金洞—万古地区的广大区域,分布有多处面积较大的正磁异常和负的重力异常, 在花岗岩出露区,重磁异常中心尤为明显,望湘花岗岩体正磁异常和负的重力异常中心明显向岩体东偏移较大的距离,说明望湘花岗岩体的实际中心在出露岩体中心东部较大距离的隐伏区内。湖南省重磁成果研究明确指出,凡是出露的花岗岩体上,均出现负值的重力低异常,但是有些异常中心与岩体的出露中心不一致,这说明岩体的整体中心并不是出露范围的中心,而是在重力异常中心的下方。望湘岩体异常中心向东偏移距离17.5 km❸。那么岩体的东边界也要东移17.5 km,这样隐伏岩体就已经超过了万古金矿区的范围,万古金矿就在隐伏岩体上方。含矿的岩浆热液通过北东向的导矿断裂进入近东西向的断裂构造中成矿。望湘岩体、金井岩体及其周边的小岩体, 实际上其下部是相连的一个整体(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 湘东北黄金洞—万古地区综合地质图1—第四系;2—白垩系—新近系;3—泥盆系至中三叠统;4—震旦系至志留系;5—青白口系板溪群;6—青白口系冷家溪群;7—早白垩世花岗伟晶岩;8—晚侏罗世第一次中细粒二云母二长花岗岩;9—晚侏罗世第一次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;10—中侏罗世第四次中细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世第三次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗纪世第二次细斑状黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—青白口系闪长岩;14—地质界线/不整合地质界线;15—实测、推测区域大断裂;16—重力等值线;17—重力高;18—重力低;19—航磁异常正等值线;20—航磁异常零值线;21—航磁异常负等值线;22—大中小型金矿床Figure 2. Comprehensive geological map of Huangjingdong- Wangu area in northeast Hunan Province1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous - Neogene; 3-Devonian to middle Triassic; 4-Sinian to Silurian; 5-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 6- Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 7-Granite pegmatite in early Cretaceous; 8-First medium-fine two-mica monzogranite in Late Jurassic; 9-First medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in late Jurassic; 10-Fourth medium-fine porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 11-Third medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 12-Second fine porphyritic biotite granodiorite in Middle Jurassic; 13- Diorite of Qingbaikou System; 14-Geological boundary / unconformity geological boundary; 15-Measured and inferred regional faults; 16-Gravity contour; 17-High gravity; 18-Low gravity; 19-Aeromagnetic anomaly positive contour; 20-Zero value line of aeromagnetic anomaly; 21- Aeromagnetic anomaly negative contour; 22-Large, medium and small gold deposits
图 2 湘东北黄金洞—万古地区综合地质图1—第四系;2—白垩系—新近系;3—泥盆系至中三叠统;4—震旦系至志留系;5—青白口系板溪群;6—青白口系冷家溪群;7—早白垩世花岗伟晶岩;8—晚侏罗世第一次中细粒二云母二长花岗岩;9—晚侏罗世第一次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;10—中侏罗世第四次中细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世第三次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗纪世第二次细斑状黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—青白口系闪长岩;14—地质界线/不整合地质界线;15—实测、推测区域大断裂;16—重力等值线;17—重力高;18—重力低;19—航磁异常正等值线;20—航磁异常零值线;21—航磁异常负等值线;22—大中小型金矿床Figure 2. Comprehensive geological map of Huangjingdong- Wangu area in northeast Hunan Province1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous - Neogene; 3-Devonian to middle Triassic; 4-Sinian to Silurian; 5-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 6- Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 7-Granite pegmatite in early Cretaceous; 8-First medium-fine two-mica monzogranite in Late Jurassic; 9-First medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in late Jurassic; 10-Fourth medium-fine porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 11-Third medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 12-Second fine porphyritic biotite granodiorite in Middle Jurassic; 13- Diorite of Qingbaikou System; 14-Geological boundary / unconformity geological boundary; 15-Measured and inferred regional faults; 16-Gravity contour; 17-High gravity; 18-Low gravity; 19-Aeromagnetic anomaly positive contour; 20-Zero value line of aeromagnetic anomaly; 21- Aeromagnetic anomaly negative contour; 22-Large, medium and small gold deposits雪峰隆起带上的黄金洞金矿,属于含金石英脉-破碎带蚀变岩型金矿,产于长平大断裂东侧复式背斜的冷家溪群地层中,离连云山花岗岩体热变质角岩区约6 km,矿区的北边是幕阜山花岗岩基,西部是大大小小的花岗岩体群,西南部是连云山等数个较大的花岗岩体,黄金洞金矿处在一近南北向负重力低异常带内的负重力异常中,重力异常的负值比出露的望湘花岗岩体上的部分重力负异常值还要低(图 2),这说明在黄金洞金矿赋矿地层冷家溪群这个高密度体下部存在着厚大的低密度的花岗岩体。黄金洞金矿及外围的地质勘查工作已发现大量大小不等的石英脉和少量的花岗岩脉、煌斑岩脉❹。黄金洞金矿外围北东方向的一小区域内,遥感影像已发现清晰的环形构造,其间还有近东西向的线形构造发育,推断环形影像深部存在有隐伏岩体❺。这些资料均说明黄金洞地区有隐伏的岩浆岩存在。
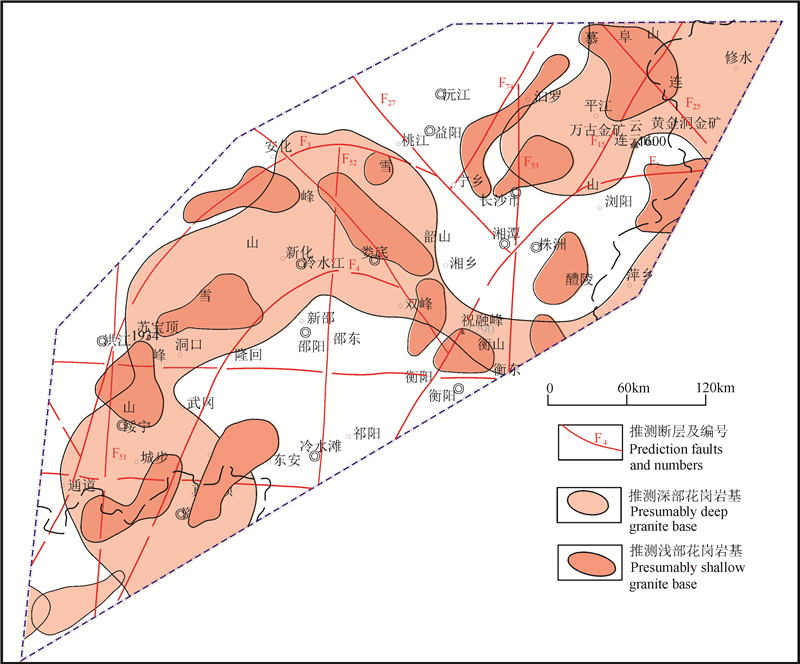
根据地质矿产部《重点成矿区物探、化探、遥感综合成果研究报告》提出的断裂-岩浆岩推断图,从湖南长沙往东到南昌260 km,往北东200 km到湖北嘉鱼的三角形广大区域内(含湘东北地区),几乎全为出露的花岗岩和隐伏的花岗岩岩基,湘东北地区的黄金洞、万古大型金矿床等一批金矿床分布在这一片隐伏花岗岩基之上。雪峰隆起带上湘西隆起区,也有约70%的区域为出露的花岗岩和推断的隐伏花岗岩基❻(图 3)。岩浆成矿作用是最广泛、最强的成矿作用。以岩浆喷出-火山活动为主要成矿作用之一形成的金矿床,其金总储量仅次于兰德型古砂矿,占第2位(姜福芝等,2003),那么整个岩浆成矿作用所形成的金矿床的储量就更大了;王成辉等(2012)指出,中国金矿类型以岩浆热液型、微细浸染型、火山岩型金矿最重要;美国的卡林型(微细浸染型)金矿在其下部已发现多处岩浆岩,研究认为微细浸染型金矿与岩浆岩有成因关系;南美洲由于大规模的构造岩浆活动而产生了大规模的金矿成矿作用,形成了不同类型的许多个大型、超大型金矿床,如安第斯成矿带,大规模的构造岩浆活动,在该带形成大量的金属矿床,其中有巨量的金银钼相伴生的大型、超大型斑岩型金铜矿床(崔敏利等,2017)。这都说明了岩浆成矿作用是最重要最广泛的金成矿作用,实际上也是内生矿床的最重要最广泛的成矿作用。雪峰隆起带上岩浆岩大范围的存在,是雪峰隆起带上金矿床多、规模大而成为湖南金腰带的一个重要因素。
2.5 地球化学依据
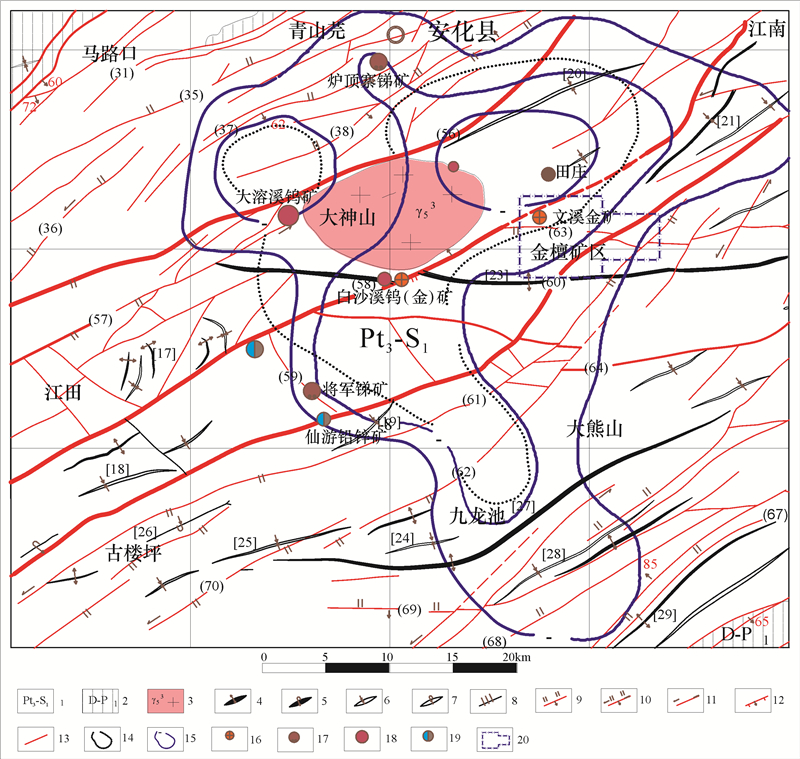
金的地球化学测量除了出现Au、Sb、Hg、As等异常外,常见在这些异常中出现与岩浆热液有关的W、Sn、Mo、Bi等元素的异常,湖南省安化县金檀金矿区土壤化学测量成果图表明,在椭圆形金异常内出现了大致成环状分布的Sn异常(图 10)。矿区地表和钻孔中见到了花岗细晶岩脉和闪长玢岩脉,金檀金矿区位于大神山岩体东南部(图 10),金矿床的形成与岩浆岩密切相关❼。
![]() 图 10 湖南省安化县金檀矿区区域构造图1—板溪群—志留系;2—泥盆系—二叠系;3—加里东期花岗岩;4—背斜;5—倒转背斜;6—向斜;7—倒转向斜;8—挤压带;9—逆冲断层;10—斜冲断层;11—平移断层;12—张性断层;13—性质不明断层;14—重力负异常;15—推测隐伏岩体范围;16—金矿点;17—锑矿点;18—钨矿点;19—铅锌矿点;20—矿区范围Figure 10. Regional structural map of the Jintan mining area in Anhua County, Hunan Province1-Banxi Group to Silurian; 2-Devonian to Permian; 3-Caledonian granite; 4-Anticline; 5-Reverse Anticline; 6-Syncline; 7-Reverse Syncline; 8-Extrusion belt; 9-Thrust fault; 10-Oblique thrust fault; 11-Translational fault; 12- Extensional fault; 13-Unknown fault; 14-Negative gravity anomaly; 15-Inferred hidden rock mass range; 16-Gold depositsite; 17-Antimony deposit spot; 18-Tungsten ore deposit; 19-Lead-zinc deposit spot; 20-Mining area
图 10 湖南省安化县金檀矿区区域构造图1—板溪群—志留系;2—泥盆系—二叠系;3—加里东期花岗岩;4—背斜;5—倒转背斜;6—向斜;7—倒转向斜;8—挤压带;9—逆冲断层;10—斜冲断层;11—平移断层;12—张性断层;13—性质不明断层;14—重力负异常;15—推测隐伏岩体范围;16—金矿点;17—锑矿点;18—钨矿点;19—铅锌矿点;20—矿区范围Figure 10. Regional structural map of the Jintan mining area in Anhua County, Hunan Province1-Banxi Group to Silurian; 2-Devonian to Permian; 3-Caledonian granite; 4-Anticline; 5-Reverse Anticline; 6-Syncline; 7-Reverse Syncline; 8-Extrusion belt; 9-Thrust fault; 10-Oblique thrust fault; 11-Translational fault; 12- Extensional fault; 13-Unknown fault; 14-Negative gravity anomaly; 15-Inferred hidden rock mass range; 16-Gold depositsite; 17-Antimony deposit spot; 18-Tungsten ore deposit; 19-Lead-zinc deposit spot; 20-Mining area有的金矿床在钻孔的金矿体围岩中,从下到上出现了W、Sn等元素异常带,湘东北隆起区大万金矿区4号勘探线钻孔Au、W原生晕异常,在矿体的上下围岩中圈出了含量14.74×10-6~29.46×10-6厚10~40 m的W异常带(图 4),并且在岩矿心和坑道中多处见到了白钨矿❽。
![]() 图 4 大万金矿区4线Au、W原生晕异常图1—青白口系大药菇组第二段第4亚段;2—白垩系戴家坪组;3—角度不整合接触界线;4—矿脉及编号;5—Au异常线;6—W异常线;7—施工探槽及编号;8—施工钻孔及编号;9—平均厚度/平均品位Figure 4. Diagram of of Au and W primary halo anomaly of exploration line 4 in Dawan gold mining area1-Section 2, sub-section 4 of Qingbaikou System Dayaogu Formation; 2-Cretaceous Daijiaping Formation; 3-Angular unconformity contact boundary; 4-Vein and its number; 5-Au anomaly line; 6-W anomaly line; 7-Construction trench and number; 8-Construction drilling and its serial number; 9-Average thickness / average grade
图 4 大万金矿区4线Au、W原生晕异常图1—青白口系大药菇组第二段第4亚段;2—白垩系戴家坪组;3—角度不整合接触界线;4—矿脉及编号;5—Au异常线;6—W异常线;7—施工探槽及编号;8—施工钻孔及编号;9—平均厚度/平均品位Figure 4. Diagram of of Au and W primary halo anomaly of exploration line 4 in Dawan gold mining area1-Section 2, sub-section 4 of Qingbaikou System Dayaogu Formation; 2-Cretaceous Daijiaping Formation; 3-Angular unconformity contact boundary; 4-Vein and its number; 5-Au anomaly line; 6-W anomaly line; 7-Construction trench and number; 8-Construction drilling and its serial number; 9-Average thickness / average grade湖南金的平均背景值为1.84×10-9,金异常带的元素组合主要有Hg、Ag、As、Sb、Pb、Zn、Cu、W、Sn、Mo、Bi、稀有、稀土元素等,说明湖南金矿与花岗岩类岩浆岩的特征元素W、Sn、Mo、Bi、稀有、稀土元素有普遍的相关性,也显现出金与花岗岩类岩浆岩的成因关系❾。
雪峰隆起带上的湘西沃溪W、Sb、Au矿床,矿石矿物中含有复杂的微量元素组成,这些微量元素组成特征可与雪峰隆起南缘白马山岩体等一些印支—燕山期花岗岩的微量元素组成相类比(彭渤,2002)。
沃溪、龙山、锡矿山等一些典型矿床的最新成矿年龄的同位素定年结果反应了成矿与岩浆作用的同步关系,这种同步关系绝非偶然,而暗示了重要的矿床成因信息;因此,认为W、Sb、Au矿床成矿与印支—燕山期岩浆作用不但具有直接的时空关系,而且具有成矿物质方面的成因联系(曹亮等,2015)。
中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院邵拥军等,在雪峰隆起带安化县金檀矿区金矿(化)体上的西部、中部和东部分别采取了含金硫化物的石英或方解石流体包裹体样品,流体包裹体测试结果和研究显示,包裹体以气体、液体两相包裹体为主,含少量的二氧化碳包裹体和含矿流体、含子晶包裹体,流体温度183.2~344.0℃,主要集中在220~320℃,最高流体温度为331.5~340℃❿。流体包裹体盐度具有中—高盐度的特点,为(18~23.0)% NaCl,岩浆热液往往会形成中高盐度的成矿热液(陈衍景等,2007),因此推断成矿热液可能为岩浆热液。电子探针结果显示该区含金黄铁矿和毒砂为热液产物,其中部分黄铁矿为沉积型黄铁矿后经岩浆改造而成,部分黄铁矿生存环境为中—深部环境,应为岩浆热液生成,金檀矿区内地表和钻孔多处见到中酸性岩脉,西部为大神山岩体,附近有多个金、钨、锑、铅锌矿床(点);因此,推断矿床成因与岩浆热液相关联⓫。
湘东北大万金矿含金石英脉的流体包裹体测定的成矿温度是220~260℃,属于中温矿床(安江华等,2011),盐度为(0.04~11.58)%NaCl,电子探针测定的大万金矿区矿石中毒砂的As原子含量平均值为28.6,其对应的成矿温度为(245±20)℃。大万矿区金矿的稀土元素特征及其他微量元素特征与其附近的金井岩体具有相似性, 这种关系说明大万金矿与金井岩体具有成因联系⓬。
雪峰山铲子坪金矿流体包裹体确定的成矿温度范围为157~402℃,温度集中区为160~220℃和280~360℃(崔敏利等,2017)。
湘西(沃溪)金矿及外围石英脉包裹体温度;层间含金石英脉温度范围170~234℃,集中温度区间为177~226℃, 节理石英脉温度范围148~202℃,集中温度范围160~193℃(陈辉雄,2003)。
湘东北万古金矿石英包裹体成矿温度为205~322℃,最为集中的温度区间为220~235℃ (毛景文等,1997)。平江黄金洞金矿成矿温度为250~400℃(罗献林,1988;马东升等,1991);雁林寺金矿第一阶段的成矿温度是250~350℃,第二阶段的成矿温度是300~400℃ (柳德荣等,1994;董国军等, 2008)。
《矿床学》明确指出,地下水热液矿床的成因有沉积说、卤水成矿说、新侧分泌说、沉积再造说等多种说法,相应的矿床就有热卤水矿床、沉积再造矿床、沉积改造矿床等类型,对地下水热液矿床矿物包裹体的研究表明,矿物形成的温度为50~100℃,很少超过200℃(袁见齐等,1979)。雪峰隆起带上已知的金矿流体包裹体测温数据均大于136℃,集中的温度在200~300℃,峰值温度多在300℃以上,且许多金矿床具有两个成矿温度区间,这是地下水热液矿床所不具备的特征,所以雪峰隆起带上的金矿床不可能是地下水热液矿床。
2.6 同位素地球化学
2.6.1 硫同位素分析
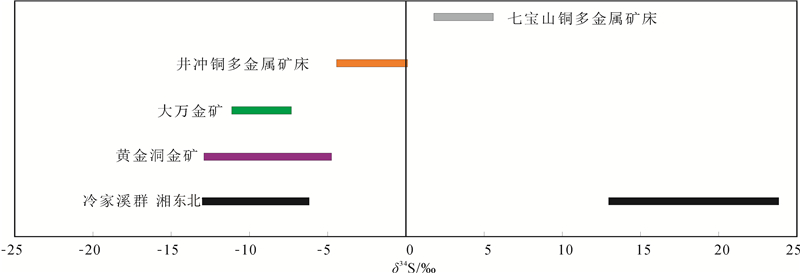
毛景文等(1997)对大万金矿床主要矿体中的硫化物进行了硫同位素测试分析,除1件辉锑矿的硫同位素值为-17.27‰,其余硫化物的硫同位素δ34S为-7.57‰~-9.42‰ (表 1,图 5)。通过与区域上广泛分布的冷家溪群的硫同位素对比,发现大万金矿床的硫同位素值基本上落在了湘东北地区冷家溪群的δ34S值范围内,说明在成矿过程中硫主要来自于冷家溪群,这与围岩地层具有的高的Au成矿元素背景值结果一致。
表 1 大万金矿床硫同位素分析结果Table 1. Sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfides from the Dawan gold deposit
2.6.2 氢、氧同位素分析
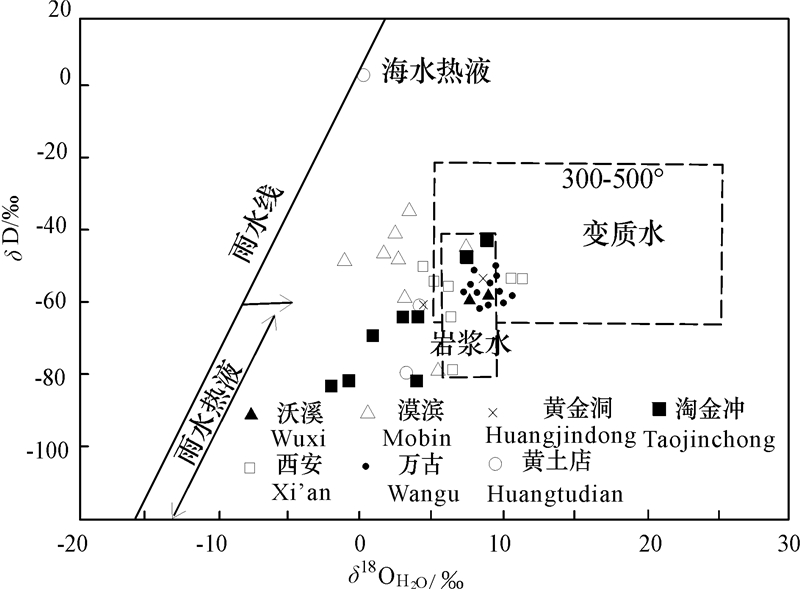
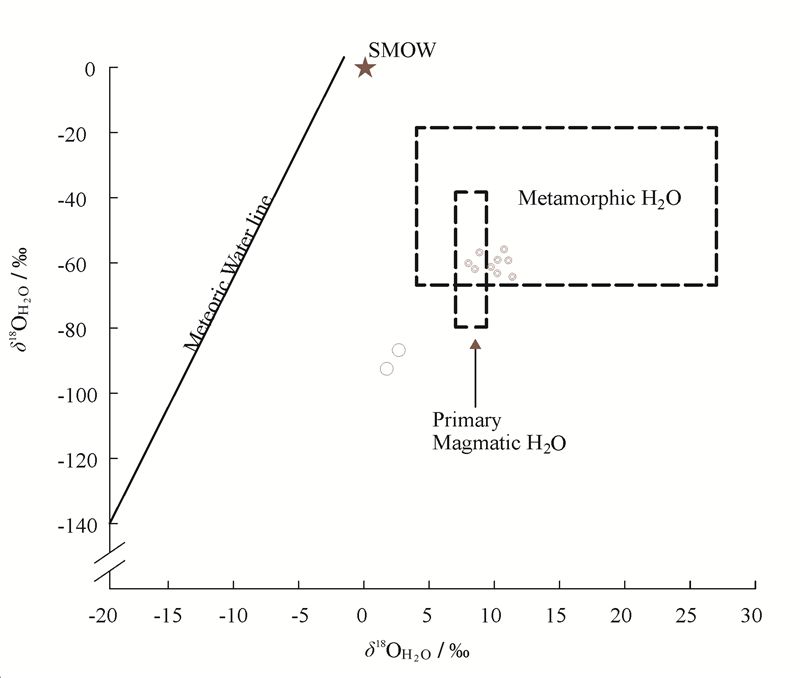
毛景文等(1997)对大万金矿床12件和黄金洞金矿床2件石英样品进行了氢、氧同位素测试分析(表 2),并收集了沃溪、淘金坑、黄土店、西安和漠滨5个矿床的有关资料。测试结果为本区石英矿物的δ18O分布于15‰~21‰,以富δ18O为特征。按石英-水氧同位素分馏公式1000lnα=3.38×10-6T -2-3.40(200~500℃)计算出平衡条件下流体的δ18OH2O值,大万金矿床的δ18OH2O变化范围为7.4‰~10.9‰, 氢同位素值δD=-56‰~-64‰。在氢-氧同位素图解中(图 6),主要落在岩浆水范围内,少量落在变质水值范围内,反映成矿流体以岩浆水和变质建造水为特征。
表 2 大万、黄金洞金矿床成矿流体氢、氧同位素组成Table 2. The δ18O and δD values (‰) of ore-forming fluids of the Dawan and Huangjindong gold deposits
2.6.3 氦-氩同位素分析
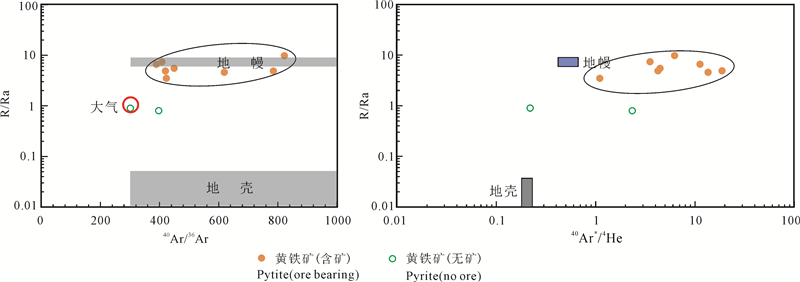
对采自万古矿区的8件含矿石英脉和2件不含矿石英脉中的黄铁矿进行了压碎法流体包裹体的氦-氩同位素分析(Mao et al., 2002)。由于样品均是在地下坑道中采集,故可排除宇宙放射性3He的来源。测试结果(表 3)表明黄铁矿中流体包裹体的He-Ar结果可明显分为两组:含矿石英脉中黄铁矿的流体包裹样品中的3He/4He(R)值较高,为4.9×10-6~13.7×10-6,R/Ra=3.5~9.8(Ra为空气的3He/4He值=1.4×10-6),40Ar/36Ar值变化较大,为389~822;不含矿石英脉中的黄铁矿的流体包裹样品中的3He/4He(R)值较低,为1.1×10-6~1.2×10-6,R/Ra=0.8~0.9,40Ar/36Ar值为301~397。由结果可知万古金矿床中明显富集3He,其中含矿石英脉的3He/4He值大大高于地壳的相应值(0.01~0.05 R/Ra)、接近地幔惰性气体的成分(6~9 R/Ra),40Ar/36Ar值明显高于大气的相应值(295.5);不含矿石英脉的3He/4He值略小于大气的相应值(1 R/Ra),40Ar/36Ar值略高于大气的相应值。由图 7可知,两种类型的黄铁矿中流体包裹体的He组成差异是由幔源和壳源流体的不同比例混合造成的。根据公式4Hemantle=(R-Rc)/(Rm-Rc)×100可计算出地幔来源He的比例,结果见表 3,含矿石英脉中黄铁矿的地幔He组分(>45.2%)远远大于不含矿石英脉中的黄铁矿(10.2%~11.5%)。由于He在大气中的丰度极低(Kendrick et al., 2001),很难影响成矿流体的He同位素组成,因此本区黄铁矿的He主要是地幔来源,并混有不同程度的地壳流体成分,而接近大气的Ar同位素组成则暗示了有大气氩的加入。同时还对相应的两种类型石英脉中的石英开展了流体包裹体研究(Mao et al., 2002),结果表明含矿石英脉中的石英包裹体有高的均一温度(207~310℃)、盐度为(3.0~4.5)% NaCl equiv,并以碳水溶液包裹体为特征,δD(-56‰~-64‰)和δ18O值(17.8‰~19.6‰)与岩浆流体特征一致(图 8);而不含矿石英脉中的石英均一温度较低,为138~145℃,盐度高于含矿石英脉,为(5.5~6.0)% NaCl equiv,主要为水溶液包裹体,其δD(-86‰~-92‰)和δ18O(17.7‰~22.0‰)值接近演化的大气降水(Mao et al., 2002)。
表 3 万古矿区黄铁矿的流体包裹体He-Ar同位素分析结果Table 3. He-Ar isotopic compositions of pyrites from the Wangu mining area
综合上述分析可知,成矿阶段流体包括挥发份主要是岩浆来源(包括幔源),演化到成矿晚阶段则混有大量的大气降水。
综前所述,本区冷家溪群是金的初始矿源层,深部热流体促进了金的活化、迁移与富集,在地层、热液、构造活动等多因素耦合作用过程中,形成大万金矿床。
3. 典型矿床实例分析
3.1 湖南省平江县万古矿区Ⅰ1和Ⅰ2矿脉金矿详查❶
万古金矿是湘东北隆起区的一个大型金矿床,自20世纪90年代初至今一直在进行外围和深部的金矿勘查工作,不断取得新的找矿突破和较大的勘查成果。本文采用的是20世纪90年代针对Ⅰ号矿脉带Ⅰ1和Ⅰ2两条矿脉浅部详查地质报告的有关资料。
万古金矿位于雪峰隆起带湘东北隆起区安化—黄金洞东西向成矿带与华夏系北东向幕阜山(岩体)—望湘(岩体)隆起带的相交部位,区域构造为北东向大断裂。万古金矿的周边区域分布有大大小小的岩体或岩体群,距最近的望湘—金井花岗岩体约10 km,其东部约40 km为黄金洞大型金矿床。区域内大面积出露的是新元古代青白口纪冷家溪群,其次为白垩系、古近—新近系,除此之外的其他时代地层出露均很少,且主要分布在隆起带边部。金矿床产于青白口系冷家溪群地层中(图 1,图 9)。
3.1.1 矿区地层
矿区内出露新元古代青白口纪冷家溪群大药姑组第2段Qbd2,第2段共分为6个亚段,矿区内主要分布第3、4、5三个亚段。
Qbd2-5:主要岩性为变质杂砂岩,向西相变为砂岩夹板岩、粉砂质板岩,厚15~75 m。
Qbd2-4:岩性为粉砂质板岩、绢云母板岩,偶夹浅变质细砂岩透镜体,板岩矿物成分主要为绢云母黏土类矿物,含量为75%~85%,其次为石英粉砂及少量绿泥石、电气石、金红石、锆石、榍石等,已知Ⅰ1、Ⅰ2等多条矿脉分布在该亚段,该亚段总厚度575 m。
Qbd2-3:为变质杂砂岩夹砂质板岩,厚度20~150 m。
3.1.2 矿区构造
矿区以断裂构造为主,褶皱不发育,主要断裂构造有两组。
F12、F13、F14为北西向断裂,经历了3期构造活动,该组断裂形成时间相差较大,早期形成的F12(Ⅰ1号矿脉)、F14(Ⅰ2号矿脉)为控容矿断裂;后期形成的F13断裂为无矿的断裂,虽然发育了团块状、透镜状、细脉状石英,经5个工程的系统采样分析,金含量只有0.02×10-6~0.26×10-6。该组断裂走向与区域地层走向一致,顺层产出,断裂破碎带中角砾岩发育,角砾多呈棱角状、次棱角状,构造透镜体、片理化带少见,局部可见断层泥,具有扭张性质。
矿区内F2和F4断裂为北北东向—南北向断裂,均为成矿后断裂。断裂破碎带主要由构造角砾岩和断层泥组成,见少量脉石英团块,以及少量石英脉穿插,金矿化微弱。
3.1.3 矿脉地质特征
Ⅰ1矿脉产于F12断裂中,矿脉长430 m,走向280~320°,倾向北东,倾角32~74°,控制斜深124 m,破碎带平均厚3.04 m,上缓下陡,矿脉由构造角砾岩、破碎粉砂质板岩组成,局部见石英细脉穿插。蚀变主要有硅化、褐铁矿化、方铅矿化、闪锌矿化、黄铁矿化、毒砂化等。本矿脉一共圈出Ⅰ1-1、Ⅰ1-2两个金矿体。
Ⅰ2矿脉产于F14断裂中,与Ⅰ1矿脉大致平行,矿脉长450 m,控制斜深93 m,厚0.28~13.33m,平均厚度3.70 m,矿脉由破碎板岩、粉砂质板岩和大透镜体石英脉组成。Ⅰ2矿脉一共圈出Ⅰ2-1、Ⅰ2-2两个金矿体。
3.1.4 矿体地质特征
Ⅰ1-1金矿体长150 m,控制斜深25.77 m,矿体由含金构造角砾岩、石英脉以及破碎粉砂质板岩组成,矿体为透镜状,矿体厚1.08~5.8 m,平均厚度2.30 m,矿体平均金品位6.74×10-6。
Ⅰ1-2金矿体地表出露长41 m,控制矿体斜深45 m,矿体为透镜状,矿体厚度3.72~8.47 m,平均厚6.43 m,矿体由含金构造角砾岩以及含金石英脉组成,含金石英脉厚度大、破碎强烈地段金品位最高,破碎粉砂质板岩一般位于矿脉底部,含金较低,矿体平均金品位10.28×10-6。
Ⅰ2-1金矿体长283 m,控制矿体斜深89.92 m,矿体呈似层状、透镜状,矿体厚0.16~9. 11 m,平均厚度2.87 m,矿体由含金石英脉,含金构造角砾岩和矿化破碎粉砂质板岩组成,含金石英脉厚度大,破碎强烈的地段金品位特高,单个样品最高品位138×10-6,矿体平均品位8.48×10-6。
Ⅰ2-2金矿体地表长80 m,无深部工程控制,矿体呈似层状、透镜状,矿体厚0.75~2.13 m,平均厚1.44 m,平均品位12.10×10-6,矿体由含金构造角砾岩,破碎粉砂质板岩,破碎含金石英脉组成。
矿体受断裂破碎带控制,呈似层状、透镜状,并非顺层产出,矿体走向与地层走向相近,矿体局限于大药姑组中。
热液活动主要为一系列石英脉大致平行蚀变破碎带产出。
矿石的矿物组成:脉石矿物有石英、长石、云母、绿泥石、黏土矿物、硫化物等,其中石英约占40%,长石、云母、绿泥石约占30%,黏土矿物约占25%,硫化物以及次生硫化物约占2%;矿石中黏土矿物的含量较地层中有较大幅度的减少,石英含量有较大幅度的增加。矿石矿物有磁铁矿、硬锰矿、白钨矿、锡石、锆石、金红石、锐钛矿等,磁铁矿、白钨矿、锡石等花岗岩类岩浆岩的特征矿物是在地层中没有出现的矿物。
本次浅部详查一共圈出了Ⅰ1-1、Ⅰ1-2、Ⅰ2-1、Ⅰ2-2 4个金矿体,提交详查金储量2678 kg,平均品位8.77×10-6。2005年深部详查,Ⅰ1矿脉新增金储量861 kg,Ⅰ2矿脉新增储量1748 kg❾,两次勘查共探明Ⅰ1矿脉金储量1541 kg、Ⅰ2矿脉探明金储量3746 kg。
3.1.5 矿床提供的成因方面的证据
1 断裂构造在形成过程中本身并不能成矿
被认为是矿源层的冷家溪群老地层中的断裂构造并不都含矿,如果金矿是冷家溪群老地层受断裂破碎带的动力变质作用而形成,那么这些产于所谓矿源层的断裂都应该成矿,但事实并非如此,就连与Ⅰ1、Ⅰ2两条矿脉大致平行、性质相似但不同时期形成的F13断裂也不含矿,这说明断裂构造形成过程中的动力变质作用并不成矿。含矿断裂的破碎带中角砾岩发育,角砾多呈棱角状、次棱角状,构造透镜体、片理化带少见,说明含矿断裂剪切作用不强,因为板岩等浅变质岩抗压能力弱,压碎作用就强。在前面的构造地质学依据中指出了最强的动力变质作用所产生的超糜棱岩也没有产生熔融作用或者仅局部形成细小的不连续的玻化岩,所以断裂在形成过程中并不能使地层岩石形成热流体而成矿。断裂本身在形成过程中并不成矿。
假如金矿体成矿物质来源于控矿断裂的老地层破碎带,可以计算一下断裂破碎带能否提供所探明的金的资源储量;以F14(Ⅰ2)矿脉为例进行计算,Ⅰ2矿脉在垂直深度373.09 m的范围内探明金储量3746 kg,矿脉长450 m, 矿脉平均厚度(即断裂破碎帯厚度)3.70 m,控制最大斜深548 m,赋矿地层冷家溪群大药姑组在冷家溪群各组地层中金的背景值(几何均值)最高,为1.99×10-9⓬,矿石体重为2.52 t/m3,那么在F14断裂内的Ⅰ2矿脉全部地层金也只有4.6 kg金金属量,只是Ⅰ2矿脉内金矿体金金属量3746 kg的0.123%,金矿体体积内的老地层原始金含量所占比例则更小,即使把F14(Ⅰ2矿脉)断裂破碎带厚度、长度、深厚、地层中金的背景值等因素综合扩大100倍,也只是金矿体金金属量的12.3%,远达不到脉内金矿体的金金属量。
以上事实说明了前寒武纪老地层不是矿源层,形成断裂构造的动力变质作用本身并不成矿。
2 成矿热液不是来源于围岩老地层
“矿床的热液活动仅见一系列石英脉大致平行蚀变破碎带产出”❶,说明没有垂直或者斜交断裂带的侧分泌作用形成的金矿(化)脉体,也没有金矿脉(体)的围岩向金矿脉(体)输送成矿物质的地质痕迹和地质现象,只见到金矿脉(体)的围岩蚀变和金矿化, 说明成矿物质和成矿热液不是来源于围岩老地层,而是来自于下部的成矿热液沿断裂带充填交代而成。
3 区域浅变质作用不能成矿
矿区“赋矿地层粉砂质板岩的矿物成分主要为黏土矿物,含量75%~85%,其次为石英粉砂和少量的绢云母、绿泥石等矿物❶。”这与前面“岩石学”定义的“板岩是指原岩矿物成分基本没有重结晶的泥质,粉砂质低级别的变质岩”是一致的,进一步说明了区域浅变质作用不可能形成变质热液或熔融体成矿。
4 金矿石具有花岗岩类岩浆岩的一些特征矿物
地层中没有出现磁铁矿、白钨矿、锡石等花岗岩类岩浆岩的特征矿物,而在金矿石的矿石矿物中出现了较多的磁铁矿、白钨矿、锡石等矿物,说明矿区金矿的形成与花岗岩类岩浆岩有成因关系。
矿床地质特征说明了万古金矿的形成与花岗岩类岩浆岩密切相关。
3.2 湖南省安化县金檀金矿
湖南省安化县金檀金矿位于雪峰隆起带向东转折段的南侧、冷家溪隆起的南部,是赋存在新元古代青白口系冷家溪群老地层中受断裂构造控制的破碎带蚀变岩型金矿,金矿处于大神山花岗岩体东2 km处,大神山岩体的内外接触带及附近分布有W(Sn)Pb、Zn、Sb、Au等矿床(点)(图 10)。
重磁资料显示大神山岩体的南部和北东部存在大面积的隐伏花岗岩体,NW角也有较大面积的隐伏岩体存在。
矿区土壤化探金异常整体呈东西向的椭圆型,Sn异常呈环状分布在金异常内环,AS、Sb、W等元素异常也大致呈环状分布在金异常周围,异常分布在NE和NWW两组断裂相交组成的平行四边形的边线附近,呈椭圆状分布, 但异常仅局限于椭圆型环内,并没有沿着断裂延伸(图 11),说明矿区内的环状异常带是一个环状地质体所引起的,这个地质体可能就是一个隐伏岩浆岩体,矿区地表出露多处细晶岩脉和蚀变闪长岩脉,深部有几个钻孔也见到了蚀变闪长岩脉❼。流体包裹体测试结果和研究成果显示该矿床成因与岩浆热液相关联,所以认为金檀金矿的成矿物质应该主要来源于岩浆岩。
4. 结论
《变质岩石学》明确指出板岩为低级区域变质,原岩矿物成分为基本没有重结晶的泥质、粉砂质低级变质岩,新生矿物很少,仍以隐晶质为主的黏土矿物。所以雪峰隆起带上的区域变质作用不能形成热液流体使老地层中金析出成矿。雪峰隆起带金矿不是区域变质矿床。
动力变质作用最强、粒度最细的超糜棱岩在断裂带中,常呈数厘米厚的不连续的透镜体夹于糜棱岩中,局部可见细小的,不连续的黑色玻化岩,但是,不会形成成矿的热流体。计算了万古金矿区F14(Ⅰ2矿脉)含矿断裂破碎带的地层金金属量只是金矿体金金属量的0.123%,断裂构造在形成过程中的动力变质作用本身不会成矿。所以雪峰隆起带金矿不是动力变质矿床。
雪峰隆起带上主要金矿床的大量流体包裹体的测温数据显示;金矿成矿温度集中区间在200~300℃,地下水热液矿床的成矿温度一般在50~100℃。说明雪峰隆起带上金矿床不是地下水热液矿床。
据《中国区域地质志·湖南志》:“湖南的火山岩不发育,地表出露面积仅76 km2,与火山岩相关的金矿化,仅见益阳市邓石桥地区,地表及钻孔所见玄武质岩石的金平均含量分别为27×10-9、53×10-9”(湖南省地质调查院,2017)。金石桥金矿勘查结果认为金矿与后期石英脉密切相关,金矿类型则有石英脉型和剪切带型之说。雪峰隆起带上现有金矿床不具有火山热液矿床的特征不是火山热液矿床。
大量的同位素样品分析数据说明雪峰隆起带金矿床的成矿物质主要来源于前寒武纪老地层重熔花岗岩类岩浆或同熔的花岗岩类岩浆,前寒武纪老地层只是初始矿源层。
雪峰隆起带一些金矿床与钨矿、锡矿、钼矿、铋矿等矿产伴、共生,矿石矿物中常出现白钨矿、黑钨矿、锡矿、辉钼矿、辉铋矿、电气石、钾长石、钠长石等酸性岩浆岩的特征矿物和专属性矿物,金矿石的某些微量元素特征与酸性岩浆岩的微量元素特征相似,金矿床的土壤地球化学和岩石地球化学测量出现了W、Sn、Mo、Bi等一些与酸性岩浆岩相同的元素异常,这些现象说明雪峰隆起带上的金矿与酸性岩浆岩有成因上的关联。
物探、化探、遥感综合成果研究推断雪峰隆起带上的大部分区域分布有隐伏半隐伏的花岗岩体,雪峰隆起带上的大多数金矿床产于隐伏的花岗岩体之上或花岗岩体周边,有的金矿体就产在花岗岩脉中,说明了雪峰隆起带上的金矿床与岩浆岩的成因关系。
《湖南省金矿第二轮成矿远景区划报告》总结的湖南各类岩金矿床均为热液成因矿床⓬,雪峰隆起带金矿既然不是区域变质(热液)矿床,不是动力变质(热液)矿床,不是地下水热液矿床,也不是火山热液矿床,更不是沉积型岩金矿床。根据雪峰隆起带金矿床的岩石学、矿物学、构造地质学及地球物理、地球化学特征与岩浆岩成因上的密切关联性,雪峰隆起带金矿成因类型应该是岩浆热液矿床。按照排除法,雪峰隆起带金矿成因类型也只能是岩浆热液矿床,其主要成矿物质来源于岩浆岩。
同样道理,雪峰隆起带及相似地质背景和成矿条件的某些沉积变质、层控变质等热液矿床的成因亦值得进一步探讨,其成因很可能还是与岩浆热液有关。
因此,雪峰隆起带金矿的找矿与勘查,应重视和深入研究岩浆活动对成矿的重要作用,拓宽找矿思路和找矿类型,以更好地提高找矿勘查成效。
注释
❶湖南省地质矿产勘查开发局402队.1993.湖南省平江县万古矿区Ⅰ号矿脉带金矿详查报告[R].
❷河南省地质矿产勘查开发局第一地质矿产调查院,新华联集团矿业有限公司崤山金矿. 2011.河南省三门峡市崤山金矿勘查总结报告[R].
❸湖南省地质学校.1989.湖南省区域重磁成果研究报告[R].
❹湖南省地质建设集团总公司.2008.湖南省平江县桥上矿区金矿预查报告[R].
❺湖南省核工业地质局311大队.2014.湖南省平江县黄金洞矿区金矿勘查报告[R].
❻地质矿产部重点成矿区物探、化探、遥感编图成果综合研究项目组.1999.重点成矿区物探化探遥感编图成果综合研究报告[R].
❼湖南省核工业地质局304地质大队. 2016.湖南省安化县金檀矿区金矿勘查阶段性成果报告[R].
❽中国地质调查局发展研究中心,湖南省地质矿产勘查开发局402队. 2019.湖南省平江地区金矿矿产调查与找矿预测子项目成果报告[R].
❾湖南省地质研究所. 1998.在湖南寻找大型特大型Au(Ag Sb)矿床综合方法研究[R].
❿中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院. 2018.湖南省安化—桃江地区金属矿产成矿地质条件研究与靶区优选科研报告[R].
⓫湖南省地质矿产勘查开发局402队.2005.湖南省平江县万古矿区金矿详查报告[R].
⓬湖南省地质研究所.1993.湖南省金矿第二轮成矿远景区划报告[R].
⓭中国科学院广州地球化学研究所,湖南省地质调查院.2016.湖南省金井—九岭地区成矿规律与三维地质建模研究报告[R].
致谢: 感谢王学明责任编辑提出的宝贵修改意见及正确指导; 感谢新华联三门峡市崤山金矿熊卫桃总经理、曹振帅总工程师为本文的现场考察和资料收集所提供的大力支持。 -
图 1 湖南雪峰隆起带地质图
1—第四系;2—白垩系至古近系;3—上三叠统至侏罗系;4—泥盆系至中三叠统;5—南华系至志留系;6—青白口系板溪群;7—青白口系冷家溪群;8—晚白垩世黑云母二长花岗岩;9—早白垩世二长花岗岩;10—晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗世黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—中侏罗世黑云母石英闪长岩;14—晚三叠世二长花岗岩;15—中三叠世二长花岗岩;16—中三叠世黑云母花岗闪长岩;17—中三叠世黑云母石英闪长岩;18—中志留世黑云母二长花岗岩;19—中志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;20—早志留世二长花岗岩;21—早志留世黑云母花岗闪长岩;22—早志留世黑云母英云闪长岩;23—早志留世石英闪长岩;24—青白口系二长花岗岩;25—青白口系黑云母花岗闪长岩;26—青白口系黑云母英云闪长岩;27—主要断裂带;28—大中小型金矿床;29—砂金矿床/伴生金矿床;30—雪峰隆起边界线
Figure 1. Geological map of Xuefeng uplift zone in Hunan
1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous to Paleogene; 3-Upper Triassic to Jurassic; 4-Devonian to middle Triassic; 5- Nanhua Period to Silurian; 6-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou system; 7-Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 8-Late Cretaceous biotite monzogranite; 9-Early Cretaceous monzogranite; 10-Late Jurassic monzogranite; 11-Middle Jurassic monzogranite; 12-Middle Jurassic biotite granodiorite; 13-Middle Jurassic biotite quartz diorite; 14-Late Triassic monzogranite; 15-Middle Triassic monzogranite; 16-Middle Triassic biotite granodiorite; 17-Middle Triassic biotite quartz diorite; 18-Middle Silurian biotite monzogranite; 19-Middle Silurian biotite granodiorite; 20-Early Silurian monzogranite; 21-Early Silurian biotite granodiorite; 22-Early Silurian biotite tonalite; 23-Early Silurian quartz diorite; 24-Qingbaikou Period monzogranite; 25-Qingbaikou Period biotite granodiorite; 26-Qingbaikou Period biotite tonalite; 27-Major fault zones; 28-Large and medium sized gold deposits; 29-Placer gold deposit/associated gold deposit; 30-Xuefeng uplift boundary
图 9 湖南省平江县万古矿区Ⅰ1、Ⅰ2号金矿脉地质图
1—第四系;2—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第五岩性段;3—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第四岩性段;4—冷家溪群大药姑组第二段第三岩性段;5—石英脉;6—断层破碎带;7—实(推)测含金蚀变破碎带及矿脉编号;8—矿体及编号;9—实(推)测地层界线;10—实测断层及编号;11—硅化;12—见矿钻孔位置、编号,孔深;13—见矿化钻孔位置、编号及孔深;14—岩层产状;15—勘探线位置及编号
Figure 9. Geological map of gold vein Ⅰ1 and Ⅰ2 in Wangu mining area, Pingjiang County, Hunan Province
1-Quaternary; 2-Second section fifth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 3-Second section fourth lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 4-Second section third lithologic section of Dayaogu Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 5-Quartz vein; 6-Fault fracture zone; 7-Gold-bearing alteration fracture zone and vein number; 8-Orebody and its serial number; 9-Actual (inferred) stratigraphic boundary; 10-Fault and its serial number; 11-Silicification; 12- Ore-intersecting drilling position, serial number, hole depth; 13-Mineralization-intersecting drilling location, serial number and depth; 14-Stratigraphic attitude; 15- Exploration line location and serial number
图 2 湘东北黄金洞—万古地区综合地质图
1—第四系;2—白垩系—新近系;3—泥盆系至中三叠统;4—震旦系至志留系;5—青白口系板溪群;6—青白口系冷家溪群;7—早白垩世花岗伟晶岩;8—晚侏罗世第一次中细粒二云母二长花岗岩;9—晚侏罗世第一次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;10—中侏罗世第四次中细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;11—中侏罗世第三次中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;12—中侏罗纪世第二次细斑状黑云母花岗闪长岩;13—青白口系闪长岩;14—地质界线/不整合地质界线;15—实测、推测区域大断裂;16—重力等值线;17—重力高;18—重力低;19—航磁异常正等值线;20—航磁异常零值线;21—航磁异常负等值线;22—大中小型金矿床
Figure 2. Comprehensive geological map of Huangjingdong- Wangu area in northeast Hunan Province
1-Quaternary; 2-Cretaceous - Neogene; 3-Devonian to middle Triassic; 4-Sinian to Silurian; 5-Banxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 6- Lengjiaxi Group of Qingbaikou System; 7-Granite pegmatite in early Cretaceous; 8-First medium-fine two-mica monzogranite in Late Jurassic; 9-First medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in late Jurassic; 10-Fourth medium-fine porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 11-Third medium porphyritic biotite monzogranite in Middle Jurassic; 12-Second fine porphyritic biotite granodiorite in Middle Jurassic; 13- Diorite of Qingbaikou System; 14-Geological boundary / unconformity geological boundary; 15-Measured and inferred regional faults; 16-Gravity contour; 17-High gravity; 18-Low gravity; 19-Aeromagnetic anomaly positive contour; 20-Zero value line of aeromagnetic anomaly; 21- Aeromagnetic anomaly negative contour; 22-Large, medium and small gold deposits
图 10 湖南省安化县金檀矿区区域构造图
1—板溪群—志留系;2—泥盆系—二叠系;3—加里东期花岗岩;4—背斜;5—倒转背斜;6—向斜;7—倒转向斜;8—挤压带;9—逆冲断层;10—斜冲断层;11—平移断层;12—张性断层;13—性质不明断层;14—重力负异常;15—推测隐伏岩体范围;16—金矿点;17—锑矿点;18—钨矿点;19—铅锌矿点;20—矿区范围
Figure 10. Regional structural map of the Jintan mining area in Anhua County, Hunan Province
1-Banxi Group to Silurian; 2-Devonian to Permian; 3-Caledonian granite; 4-Anticline; 5-Reverse Anticline; 6-Syncline; 7-Reverse Syncline; 8-Extrusion belt; 9-Thrust fault; 10-Oblique thrust fault; 11-Translational fault; 12- Extensional fault; 13-Unknown fault; 14-Negative gravity anomaly; 15-Inferred hidden rock mass range; 16-Gold depositsite; 17-Antimony deposit spot; 18-Tungsten ore deposit; 19-Lead-zinc deposit spot; 20-Mining area
图 4 大万金矿区4线Au、W原生晕异常图
1—青白口系大药菇组第二段第4亚段;2—白垩系戴家坪组;3—角度不整合接触界线;4—矿脉及编号;5—Au异常线;6—W异常线;7—施工探槽及编号;8—施工钻孔及编号;9—平均厚度/平均品位
Figure 4. Diagram of of Au and W primary halo anomaly of exploration line 4 in Dawan gold mining area
1-Section 2, sub-section 4 of Qingbaikou System Dayaogu Formation; 2-Cretaceous Daijiaping Formation; 3-Angular unconformity contact boundary; 4-Vein and its number; 5-Au anomaly line; 6-W anomaly line; 7-Construction trench and number; 8-Construction drilling and its serial number; 9-Average thickness / average grade
图 6 成矿流体的氢、氧同位素图
(据马东升等, 1997, 1999, 2002;毛景文等,1997;王秀璋等,1999;Mao et al., 2002)
Figure 6. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of ore-forming fluids
(after Ma Dongsheng et al., 1997, 1999, 2002; Mao Jingwen et al., 1997; Wang Xiuzhang et al., 1999; Mao et al., 2002)
表 1 大万金矿床硫同位素分析结果
Table 1 Sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfides from the Dawan gold deposit

表 2 大万、黄金洞金矿床成矿流体氢、氧同位素组成
Table 2 The δ18O and δD values (‰) of ore-forming fluids of the Dawan and Huangjindong gold deposits

表 3 万古矿区黄铁矿的流体包裹体He-Ar同位素分析结果
Table 3 He-Ar isotopic compositions of pyrites from the Wangu mining area

-
An Jianghua, Li Jie, Chen Bihe, Tang Fenpei, Tan Shimin, He Chunping.2011.Fluid inclusion study of Wangu gold deposit, Northeastern Hunan Province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 27:169-173(in Chinenese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hndzykc201102014
Cao Liang, Duan Qifa, Peng Sanguo. 2015. Fluid Inclusion features and geological significance of the Chanziping gold deposit, Xuefeng Mountain[J].Geology and Prospecting, 31 (2):212-222(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Mengxiong. 2003. Study on the characteristics of quartz vein inclusions and the gold-bearing properties of quartz veins in the Xiangxi gold deposit and its periphery, Hunan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, (4):519-522.
Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Fan Hongrui, Pirajno F, Lai Yong, Su Wenchao, Zhang Hui. 2007. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9):2085-2108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB200709009.htm
Cui Minli, Zhang Zuolun, Chen Yuming, Chen Fangge. 2017. South America large and super large gold deposits, geological characteristics and mineralization[J]. Geology in China, 44(4) 642-663(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201704003
Department of Geology, Nanjing University 1978. Crystallography and Mineralogy[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 247-389(in Chinese).
Dong Guojun, Xu Deru, Wang Li, Chen Guanghao, He Zhuanli, Fu Gonggu, Wujun, Wang Zhilin. 2008. Determination of mineralization ages on gold deposits in the eastern Hunan province, South China and isotopic tracking on ore forming fluids-redisscussion gold ore deposit type[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 32:482-491(in Chinese with English abstract).
He Tongxing, Lu Liangzhao, Li Shuxun.1979. Metamorphic Petrology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 97-117(in Chinese).
Hunan Geological Survey Institute. 2017. China Regional Geology. Hunan Geology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 78(in Chinese).
Jiang Fuzhi, Wang Yuwang, Volcanic activity and gold mineralization[J]. 2003. Geology in China, 30 (1):90-92(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kendrick M A, Burgess R, Pattrick R A D, Turner G. 2001. Fluid inclusion noble gas and Halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-porphyry mineralizing fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(16):2651-2668. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00618-4
Liu Derong, Wu Yanzhi, Liu Shinian.1994.Geochemistry of Wangu gold deposit[J]. Hunan Geology, 13(2):83-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HNDZ402.005.htm
Luo Xianlin, 1988. On the genesis and metallogenic model of the Huangjindong gold deposit from Hunan[J]. Guilin Colloge of Geology, 8:225-239(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GLGX198803002.htm
Ma Dongsheng, Liu Yingjun. 1991.Study on the geochemical characteristics of stratum controlled gold mines in Jiangnan gold metallogenic belt and its genesis[J]. Science in China(B), 4:424-433(in Chinese).
Ma Dongsheng. 1997. Metallogenic phenomenon and geochemical tracing associated with large-scale fluid movement in crust[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 33(Special edition for geofluids):1-10(in Chinenese with English abstract).
Ma Dongsheng. 1999. Regional pattern of element composition and fluid character in medium-low temperature metallogenic province of South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 18 (4):347 -358(in Chinenese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz199904008
Ma Dongsheng, Pan Jiayong, Lu Xinwei. 2002. Geochemical singals for ore-forming process by mid-low temperature fluid in Au-Sb deposits in NW-Central Hunan, China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 38(3):435-445(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mao Jingwen, Li Hongyan, Xu Jue, Luo Futing. 1997. Geology and Genesis of Gold Deposits in Wangu Area, Hunan Province[M].Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 78-101(in Chinese).
Mao J, Kerrich R, Li H, Li Y. 2002. High 3He/4He ratios in the Wangu gold deposit, Hunan province, China:Implications for mantle fluids along the Tanlu deep fault zone[J]. Geochemical journal Japan, 36(3):197-208. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.36.197
Ministry of land And Resources, 2002. Standard For Geological Exploration of Rock Gold Deposits[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1224-1225(in Chinese).
Peng Bo. 2002. New Progress of Hunan Geosciences (2)[M].Changsha:Hunan Science and Technology Press, 106-112(in Chinese).
Peng Bo, Liu Shengwen, Tang Xiaoyan, Yu Changxun, Xie Shurong. 2018. Ore mineralogical characteristics and deep prospecting significance of Woxi gold deposit, Western Hunan[J]. Geology in China, 35 (6):1286-1289(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI200806026.htm
Song Honglin, Zhang Changhou, Wang Genhou.2015. Structural Geology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 227-244(in Chinese).
Song Mingchun, Cui Shuxue, Yin Pihou. 2010. Prospecting and Metallogenic Model of Large and Super Large Deep Gold Deposits in the Gold Concentration Area of Northwest Jiaozhou[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House(in Chinese).
Wang Chenghui, Wang Denghong, Huang Fan, Xu Yu, Chen Zheng Hui, Ying Li, Liu Shanbao. 2012. Exploration on China's gold deposit concentration area and its resource potential[J]. Geology in China, 39 (5) 1125-1140(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiuzhang, Liang Huaying, Shan Qiang, Cheng Jingping, Xia Ping. 1999. Metallogenic age of the Jinshan gold deposit and Caledonian gold mineralization in South China[J]. Geological Review, 45(1):19-25(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wuhan Institute of Geology Chengdu Institute of Geology Hebei Institute of Geology Nanjing University Department of Geology. 1979. Structural Geology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House. 123-138.
Yuan Jianqi, Zhu Shangqing, Zhai Yusheng. 1979. Depositology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 201-209(in Chinese).
安江华, 李杰, 陈必河, 唐分配, 谭仕敏, 贺春平. 2011.湘东北万古金矿的流体包裹体特征[J].华南地质与矿产27:169-173 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2011.02.014 曹亮, 段其法, 彭三国. 2015.雪峰山铲子坪金矿流体包裹体特征及地质意义[J].地质与勘探, 31(2):212-222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt201502002 陈梦雄. 2003.湖南湘西金矿及外围石英脉包裹体特征与石英脉含金性质研究[J].矿产与地质, (4):519-522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2003.04.005 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, Pirajno F, 赖勇, 苏文超, 张辉. 2007.不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J].岩石学报, 23(9):2085-2108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.009 董国军, 许德如, 王力, 陈广浩, 贺转利, 符巩固, 吴俊, 王智琳. 2008.湘东地区金矿床矿化年龄的测定及含矿流体来源的示踪——兼论矿床成因类型[J].大地构造与成矿学32:482-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.04.012 崔敏利, 张作伦, 陈玉明, 陈方戈.2017.南美洲大型超大型金矿地质特征与成矿作用研究[J].中国地质, 44(4):642-663. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170402&flag=1 国土资源部. 2002.岩金矿地质勘查规范[M].北京:地质出版社, 1224-1225. 贺同兴, 卢良兆, 李树勋.1979.变质岩石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 97-117. 湖南省地质调查院. 2017.中国区域地质志.湖南志[M].北京:地质出版社, 78. 姜福芝, 王玉往. 2003.火山活动与金成矿[J].中国地质, 30 (1):90-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.01.019 柳德荣, 吴延之, 刘石年. 1994.平江万古金矿床地球化学研究[J].湖南地质, 13(2):83-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400206490 罗献林. 1988.论湖南黄金洞金矿床的成因及成矿模式[J].桂林冶金地质学院学报8:225-239. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GLGX198803002.htm 马东升, 刘英俊.1991江南金成矿带层控金矿的地质地球化学特征和成因研究[J].中国科学(B), 4:424-433 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBXK199104011.htm 马东升. 1997.地壳中大规模流体运移的成矿现象和地球化学示踪[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 33:1-10. 马东升. 1999.华南中、低温成矿带元素组合和流体性质的区域分布规律——兼论华南燕山期热液矿床的巨型分带现象和大规模成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 18 (4):347 -358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.1999.04.008 马东升, 潘家永, 卢新卫. 2002.湘西北-湘中地区金-锑矿床中-低温流体成矿作用的地球化学成因指示[J].南京大学学报(自然科学), 38(3):435-445. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njdxxb200203017 毛景文, 李红艳, 徐珏, 罗福亭. 1997.湖南万古地区金矿地质与成因[M].北京:原子能出版社, 78-101. 南京大学地质学系.1978.结晶学与矿物学[M].北京:地质出版社, 247-389. 彭渤. 2002.湖南地学新进展(2)[M].长沙:湖南科学技术出版社, 106-112. 彭渤, 刘升文, 唐晓燕, 余昌训, 谢淑容.2018.湘西沃溪西金矿床矿石矿物学特征及深部找矿意义[J].中国地质, 35(6):1286-1289. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200806024 宋鸿林, 张长厚, 王根厚.2015.构造地质学[M].北京:地质出版社, 227-244. 宋明春, 崔书学, 尹丕厚等.2010.胶西北金矿集中区深部大型超大型金矿找矿与成矿模式[M].北京:地质出版社. 王成辉, 王登红, 黄凡, 徐玉, 陈郑辉, 应立绢, 刘善宝. 2012.中国金矿集区及其资源潜力探讨[J].中国地质, 39(5):1125-1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.002 王秀璋, 梁华英, 单强, 程景平, 夏萍. 1999.金山金矿成矿年龄测定及华南加里东成金期的讨论[J].地质论评, 45(1):19-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1999.01.004 武汉地质学院, 成都地质学院, 河北地质学院, 南京大学地质系.1979.构造地质学[M].北京:地质出版社, 123-138 袁见齐, 朱上庆, 翟裕生.1979.矿床学[M].北京:地质出版社, 201-209. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 曾钦旺,石少华,钱滔,吴承东,潘军华,魏元泵,陈雨林. 几种重要热液矿床成矿的岩浆作用贡献探讨. 地球学报. 2024(03): 337-348 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁梓焜,邵拥军,刘清泉,张毓策,王智琳. 湘东北万古金矿田江东金矿床成因——流体包裹体和H-O同位素制约. 黄金科学技术. 2024(04): 559-578 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙立吉,廖珊,郝立波,赵新运. 湘西雪峰构造带金控矿因素与成矿机理. 黄金. 2023(06): 64-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 申燕元,高磊. 湘西北沧山金矿床地质特征及找矿标志. 黄金. 2023(08): 92-97+112 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 金妮,金小燕,刘湘勤,李雄. 雪峰弧形成矿带西南段金矿成矿规律及成矿模式研究. 矿产与地质. 2022(03): 547-556 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: