Coupling relationship of sedimentation-reservoir and comprehensive quantitative evaluation of braided river delta facies in Upper Karamay Formation, Hongshanzui area, northwestern margin of Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
综合岩心、薄片、分析测试资料厘定辫状河三角洲不同相带储层特征及控制因素,选取孔隙度、含砂率、优势砂厚、优势砂岩分层系数及杂基含量作为评价参数,基于灰色关联法确定权重、拐点法确定分类阈值对储层进行综合定量评价。结果表明辫状河三角洲下平原地区由于储层物性好且优势砂岩(粗砂岩)占比高而Ⅰ类储层发育;三角洲上平原地区砂体发育但以砾岩沉积为主,杂基含量高而储层质量差,多为Ⅱ类储层;三角洲前缘地区正韵律特征显著,中、粗砂岩储层质量要优于细砂岩,但优势砂岩发育规模有限,因此多以Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类储层为主。该成果可为复杂砂砾岩储层的定量评价提供借鉴。
Abstract:Core observation, thin section identification and data test were applied to analyzing the characteristics and quality-controlling factors of reservoirs in braided river delta. 5 parameters of porosity, ratio of sandbody, effective sandbody thickness, stratification coefficient of effective sandbody and matix content were chosen to evaluate the reservoir quantitatively, and gray correlation method was used to determine the weight coefficient and make critical point analysis to confirm the threshold value of various reservoirs. The results show that the lower delta plain is mainly classified as TypeⅠreservoir due to its good reservoir physical property and well-development of effective sandbody, while, in the upper delta plain, conglomerates of high matix content and poor physical property are assigned to typeⅡreservoir. The reservoir quality in delta front varies as its remarkable grain rhythm, with good quality in medium and coarse sandstone and poor quality in fine sandstone. And a limited development scale of the effective sandbody causes the delta front to be more likely recognized as TypeⅡand type Ⅲ reservoir. The results can provide reference for the quantitative evaluation of complex conglomerate reservoirs.
-
Keywords:
- braided river delta /
- sedimentation /
- reservoir evaluation /
- Upper Karamay Formation /
- Hongshanzui area /
- Junggar
-
1. 引言
准噶尔西北缘地区是盆地油气资源最为富集、勘探程度最高的区域(鲜本忠等, 2008), 以发育大量岩性-地层油气藏为特点, 主要储集体为二叠—三叠纪的冲积扇、粗粒三角洲等砂砾岩沉积体(蔚远江等, 2007;贺正军等, 2013)。砂砾岩沉积的典型特点是其纵向厚度变化大、相变快、岩性复杂而非均质性强烈, 因而有利储集相带的存在与分布也成为制约油气藏勘探与开发效果的关键问题(Colella et al., 1990;邹才能等, 2007)。虽然目前对于砂砾岩沉积储层的成岩作用已多有研究, 但学者仍认为沉积作用是控制储层物性的关键因素(Longhitano et al., 2015;Liang et al., 2015;于兴河等, 2015)。如张顺存等(2015)在对玛北地区扇三角洲的研究中即指出了不同岩性相对于储层的控制作用, 并以水下河道砂砾岩相、河口坝—远砂坝砂岩相为优。殷建国等(2015)在对阜东斜坡区辫状河三角洲的研究中指出在前缘地区水下分流河道与席状砂由于分选好、杂基含量低而往往形成优质储层。
事实上, 沉积作用不仅在成因机理上控制着储层质量的好坏, 同时也在宏观展布上决定着优质储层发育的潜在丰度(强昆生等, 2018;宋光永等, 2020)。如粗粒三角洲平原地区由于丰富的物源供给与快速的堆积作用, 其砂体规模与频率均大于前缘地区(谭程鹏等, 2014;高阳等, 2016), 因此可在砂体发育程度上弥补其物性较差的不足。然而在以往对于砂砾岩储层的研究中, 学者们或是以沉积参数(砂岩厚度、含砂率)为基准进行沉积体系刻画(于兴河等, 2013), 或是通过沉积、成岩研究单纯对储层质量差异进行定性、半定量的成因机理分析与评价(Solano et al., 2016;Mohammadmoradi et al., 2016;周军良等, 2017), 而综合考虑储层规模与物性参数的定量评价则少见报道(宋子齐等, 2007;陈欢庆等, 2017)。因此, 本文在梳理不同沉积作用产物的储层特征基础上, 明确储层质量差异, 优选能够反映储层性质的评价参数进行综合定量评价, 以期深化对于辫状河三角洲沉积储层非均质特征的认识, 并为油田开发决策提供依据。
2. 地质概况
红山嘴地区在区域构造上处于准噶尔盆地西北缘红车断裂带北段, 北为克乌断裂带, 南为沙湾凹陷, 东西两侧分别被车排子凸起与中拐凸起所限(图 1), 是西北缘地区的有利油气聚集带(程亮等, 2008)。钻井揭示该区地层自下而上发育石炭系、三叠系、侏罗系以及白垩系, 石炭系与中三叠统呈角度不整合接触, 缺失二叠系与下三叠统百口泉组。石炭—二叠纪, 准噶尔地块俯冲于其西北方向的哈萨克斯坦板块之下, 西北缘残余洋消亡而隆起成陆, 冲断系统发育而造山运动强烈(雷振宇等, 2005;蔚远江等, 2005)。至三叠纪盆地进入陆内坳陷阶段, 该时期气候湿润、湖平面上升趋势显著, 沉积体系表现为由早期克下组的冲积扇、河流向晚期克上组三角洲、白碱滩组湖泊沉积过渡的特点(丘东洲, 1994;王龙樟, 1994;杨烨等, 2016)。
3. 不同相带沉积作用及其储层响应
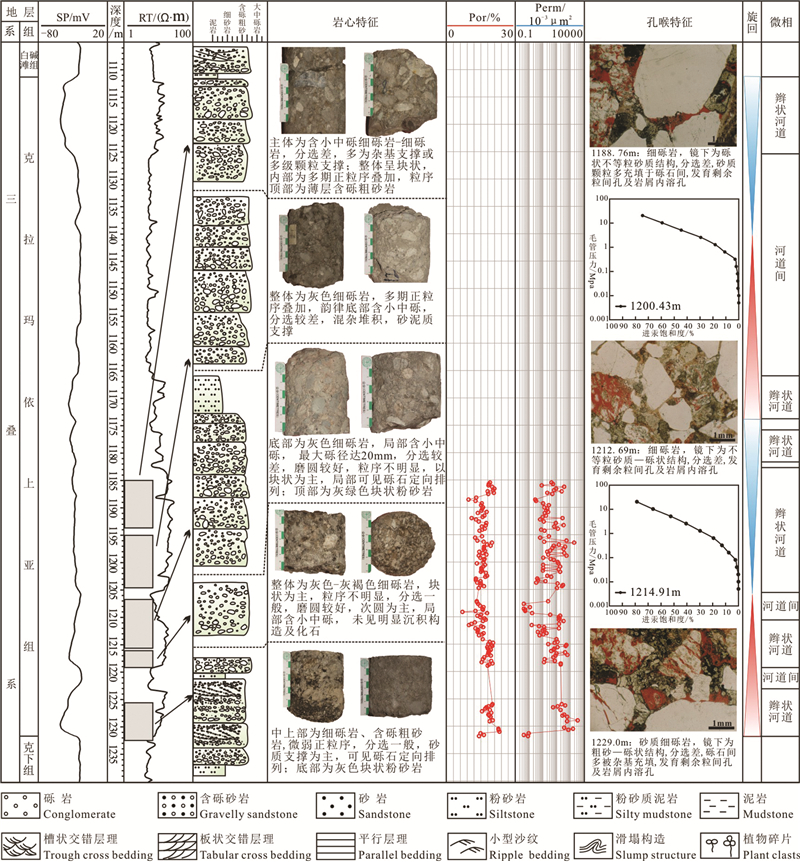
研究区克上组岩性以灰色、灰绿色的砾岩、不等粒砂岩以及红褐色、灰黑色泥岩为主, 岩石颗粒分选差, 磨圆度为次棱—次圆状, 砾岩多为块状, 部分砾岩中可见砾石的定向排列, 同时岩心中可见交错层理以及植物碎屑的发育(图 2), 整体为一套气候湿润背景下的辫状河三角洲沉积体系, 并可进一步分为上平原、下平原、前缘以及前三角洲4个亚相。其中上平原以砾质沉积为主, 含砂率多在60%以上, 而下平原与前缘以砂质沉积为主, 含砂率小于60%(王雅宁等, 2009;高阳等, 2016)。不同相带由于其各自的水动力与物源供给条件差异, 也造就了特征迥异的沉积-储层发育特点。
![]() 图 2 克上组辫状河三角体系沉积岩石学特征a—灰绿色块状中砾岩, 分选差, 次棱—次圆, 为碎屑流快速堆积结果;b—灰色砂质细砾岩, 可见砾石定向排列, 反映牵引流底负载沉积;c—灰色细砾岩, 正粒序, 槽状交错层理发育, 为河道下切充填产物;d—深灰色粗砂岩, 槽状交错层理;e—灰褐色含砾粗砂岩, 块状, 反映物源供给充足且快速沉积;f—深灰色粗砂岩, 板状交错层理, 反映河道顺流加积或侧积;g—灰色中砂岩, 平行层理, 河道序列顶部高流态层流产物;h—灰色粗砂岩, 见泥岩滑塌, 多为前缘快速堆积背景下滑塌结果;i—灰黑色粉砂岩, 浪成沙纹, 反映波浪淘洗作用;j—深灰色粉砂质泥岩, 水平层理, 反映静水沉积环境;k—灰绿色细砾岩, 基质支撑;l—红褐色块状泥岩;m—红褐色粉砂质泥岩, 与l主要响应陆上暴露环境;n—灰黑色泥岩, 块状, 代表静水还原环境;o—深灰色泥岩, 见碳化植物茎干, 说明沉积时期地层坡度大, 沉积物快速堆积埋存Figure 2. Sedimentary petrological characteristics of braided river delta system in Upper Karamay Formationa- Grayish green massive medium conglomerate, poorly sorted, sub-edge to sub-circle, which is the result of rapid accumulation of clastic flow; b- Gray sandy fine conglomerate with directional arrangement of gravels, reflecting the bottom load deposition of traction flow; c-Gray fine conglomerate, fining-upward sequence, trough cross bedding, mostly the product of channel cutting and filling; d-Dark gray coarse sandstone with trough cross bedding; e- Grayish brown gravelly coarse sandstone, massive bedding, showing that the source supply is sufficient and deposition rate is fast; f- Dark gray coarse sandstone, tabular cross bedding, reflecting the downstream accretion or lateral deposition of the channel; g-Gray medium sandstone, parallel bedding, developed at the top of the channel sequence in a high flowing laminar flow; h-Gray coarse sandstone, mudstone slump seen, which is mostly the result of rapid accumulation of delta front; i- Grayish black siltstone, with small-scale wave-ripple cross bedding, reflecting the wave washing; j- Dark gray silty mudstone with horizontal bedding, deposited in the still water sedimentary environment; k- Grayish green fine conglomerate, supported by matrix; l-Reddish brown block mudstone; m- Reddish brown silty mudstone, like l, mainly responding to a exposure environment; n- Grayish black block mudstone, representing a still water, restore environment; o-Dark gray mudstone, with carbonized plant stems, indicating that the terrain slope was large during the sedimentation period, and the sediments were rapidly accumulated and buried
图 2 克上组辫状河三角体系沉积岩石学特征a—灰绿色块状中砾岩, 分选差, 次棱—次圆, 为碎屑流快速堆积结果;b—灰色砂质细砾岩, 可见砾石定向排列, 反映牵引流底负载沉积;c—灰色细砾岩, 正粒序, 槽状交错层理发育, 为河道下切充填产物;d—深灰色粗砂岩, 槽状交错层理;e—灰褐色含砾粗砂岩, 块状, 反映物源供给充足且快速沉积;f—深灰色粗砂岩, 板状交错层理, 反映河道顺流加积或侧积;g—灰色中砂岩, 平行层理, 河道序列顶部高流态层流产物;h—灰色粗砂岩, 见泥岩滑塌, 多为前缘快速堆积背景下滑塌结果;i—灰黑色粉砂岩, 浪成沙纹, 反映波浪淘洗作用;j—深灰色粉砂质泥岩, 水平层理, 反映静水沉积环境;k—灰绿色细砾岩, 基质支撑;l—红褐色块状泥岩;m—红褐色粉砂质泥岩, 与l主要响应陆上暴露环境;n—灰黑色泥岩, 块状, 代表静水还原环境;o—深灰色泥岩, 见碳化植物茎干, 说明沉积时期地层坡度大, 沉积物快速堆积埋存Figure 2. Sedimentary petrological characteristics of braided river delta system in Upper Karamay Formationa- Grayish green massive medium conglomerate, poorly sorted, sub-edge to sub-circle, which is the result of rapid accumulation of clastic flow; b- Gray sandy fine conglomerate with directional arrangement of gravels, reflecting the bottom load deposition of traction flow; c-Gray fine conglomerate, fining-upward sequence, trough cross bedding, mostly the product of channel cutting and filling; d-Dark gray coarse sandstone with trough cross bedding; e- Grayish brown gravelly coarse sandstone, massive bedding, showing that the source supply is sufficient and deposition rate is fast; f- Dark gray coarse sandstone, tabular cross bedding, reflecting the downstream accretion or lateral deposition of the channel; g-Gray medium sandstone, parallel bedding, developed at the top of the channel sequence in a high flowing laminar flow; h-Gray coarse sandstone, mudstone slump seen, which is mostly the result of rapid accumulation of delta front; i- Grayish black siltstone, with small-scale wave-ripple cross bedding, reflecting the wave washing; j- Dark gray silty mudstone with horizontal bedding, deposited in the still water sedimentary environment; k- Grayish green fine conglomerate, supported by matrix; l-Reddish brown block mudstone; m- Reddish brown silty mudstone, like l, mainly responding to a exposure environment; n- Grayish black block mudstone, representing a still water, restore environment; o-Dark gray mudstone, with carbonized plant stems, indicating that the terrain slope was large during the sedimentation period, and the sediments were rapidly accumulated and buried3.1 辫状河三角洲上平原
辫状河三角洲上平原地区距离物源近而地形坡度大、是辫状河三角洲水体能量最强、物源供给最为充足的地带, 以辫状河道沉积作用为主, 其沉积物的粒度最粗、砂体也最为发育。岩性上辫状河道以灰绿色的块状中砾岩、细砾岩为主, 杂基含量高, 可见砾石呈漂浮状存在于基质中, 是洪峰期流水所携带的大量泥、砂、砾混合物在河道中快速充填堆积结果。后期随着洪水消退, 在辫状河道序列顶部可发育少量颗粒支撑的细砾岩或含砾粗砂岩, 其砾石可具有一定的定向排列特征, 河道表现为微弱正粒序特点(图 3)。随着河道的不断冲刷充填以及迁移摆动, 辫状河道往往表现出多期叠置的特点, 并在空间上相互拼接而形成广泛分布的厚层砂砾岩体, 其含砂率可以达到60%以上。
虽然三角洲上平原砂体在整个辫状河三角洲体系最为发育, 但辫状河道的储层质量并不理想。其储层孔隙度多在6.9%~23.1%, 平均16.3%, 而渗透率分布在0.04×10-3~336.89×10-3 μm2, 平均17.14×10-3 μm2, 属于中孔低渗储层。储层储集空间主要为砾石颗粒之间的剩余粒间孔以及部分岩屑内的溶蚀孔隙, 而高杂基与岩屑含量使其受成岩压实、溶解作用影响较大, 孔喉的分布极不均匀, 在压汞曲线上表现为“单段”未分选的特点, 体现了不同粒级颗粒逐级充填的特点, 且排驱压力往往较大, 通常大于0.1 MPa(图 3)。相对来说河道序列顶部的含砾粗砂岩储层物性较好, 孔隙度可达20%以上, 储集空间也以剩余粒间孔与原生粒间孔为主, 但在辫状河道中, 该类储层往往呈薄层出现, 并不占据主导。
3.2 辫状河三角洲下平原
进入三角洲下平原地区后, 水体能量及物源供给均有所减弱, 辫状河道分叉增多, 砾质沉积减少, 主要形成辫状分流河道与辫流坝两种成因砂体, 含砂率通常在45%~60%。辫状分流河道岩性以细砾岩、砂质细砾岩以及粗砂岩为主, 砂质成分所占比重增大, 并常构成向上变细的正粒序, 底部可见砾石的叠瓦排列, 而上部牵引流为主体的交错层理则更为发育。辫状分流河道序列下部储层特征与辫状河道相似, 孔喉小而分选差, 而顶部由于杂基的减少孔喉半径有所增大, 压汞上排驱压力有减小趋势, 但仍表现为未分选的特点。整体上辫状分流河道储层孔隙度可在7.5%~25.6%, 平均18.4%, 渗透率跨度比较大, 最高可达1000×10-3 μm2以上, 平均454.2×10-3 μm2(图 4)。
辫流坝为辫状分流河道内部的顺流加积砂坝, 岩性以含砾粗砂岩与中、粗砂岩为主, 分选、磨圆均较好, 以板状交错层理与平行层理砂岩的交互发育为特点。辫流坝储层孔隙度可到28%, 平均23.5%, 而渗透率最大也可达2000×10-3 μm2以上, 平均1400.5×10-3 μm2, 压汞曲线表现为分选好、中粗歪度的特点, 是辫状河三角洲环境中的最有利储集相带(图 4)。
3.3 辫状河三角洲前缘
辫状河平原河道入湖后, 其物源供给与水动力条件均有所减弱, 砂体粒度与发育规模相应较小, 其含砂率常介于15%~45%, 粒度上也多以中、细砂以及少量粗砂为主。对于水下分流河道来说其正粒序特征更为显著, 河道底部发育交错层理中、粗砂岩, 而顶部则发育小型沙纹粉、细砂岩以及深灰色炭质泥岩。其储层孔喉特征仍表现为未分选的特点、且为细歪度, 孔隙度多在10.8%~22.4%, 平均16.8%, 渗透率最大可达400×10-3 μm2以上, 平均51.9×10-3 μm2, 且物性较好部位主要位于河道底部和河口坝顶部中砂岩中, 细砂岩物性较差(图 5)。
4. 储层质量控制因素及其评价参数
在影响储层质量的诸多沉积因素中, 沉积相、粒度、杂基含量以及含砂率等各变量之间均或多或少存在交集(王成等, 2006;孟祥超等, 2015), 如从三角洲上平原的辫状河道微相到三角洲下平原的辫状分流河道与辫流坝微相, 岩石杂基含量逐渐降低, 颗粒分选变好, 粒度变细而砂质成分增加, 储层物性逐渐变好(图 6)。因此需要在这诸多因素中甄选出对储层质量反映最敏感的参数, 从而确保评价参数选取的有效性与可操作性。
4.1 储层质量主控因素
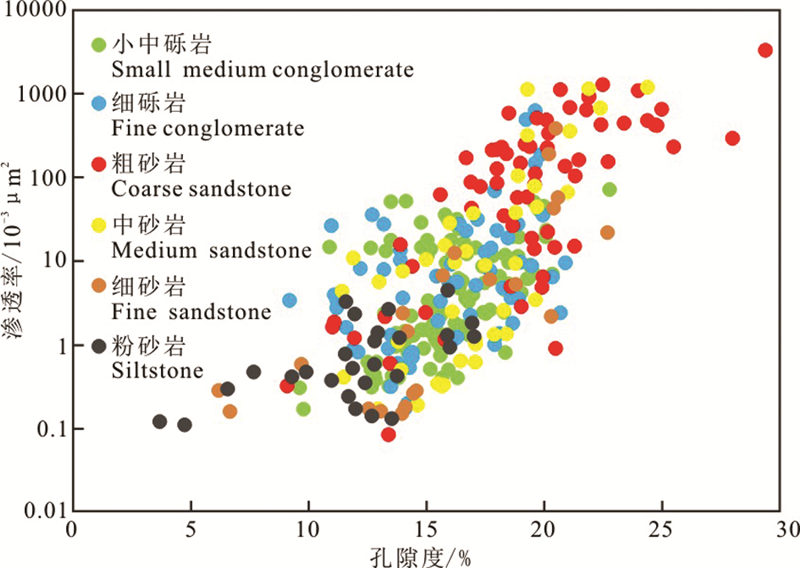
实际上, 粒度、分选以及砂质含量等因素均可以归结到岩性上, 而不同沉积微相的储层质量差异本质上也是其岩性的差异造成的(曹刚等, 2016)。通过岩心观察可将研究区岩石类型分为中砾岩、细砾岩、(含砾)粗砂岩、中砂岩以及细砂岩, 而粉砂岩未达到物性下限, 已不能作为储层。5类岩性中以粗砂岩与部分中砂岩储层物性最优, 细砾岩次之, 而细砂岩与中砾岩物性最差。显然在岩性上, 砂岩储层因其好的分选而整体物性要优于砾岩储层, 同时随着粒度变粗储层物性逐渐变好, 这主要是由于在牵引流搬运机制下, 粒度粗是强水流的指示, 其淘洗作用强而砂质纯度高, 因而粒度越粗储层物性越好。而在砾岩储层中, 随着粒度变大, 指示堆积方式更为迅速而分选更差, 储层物性相应变差(图 7)。
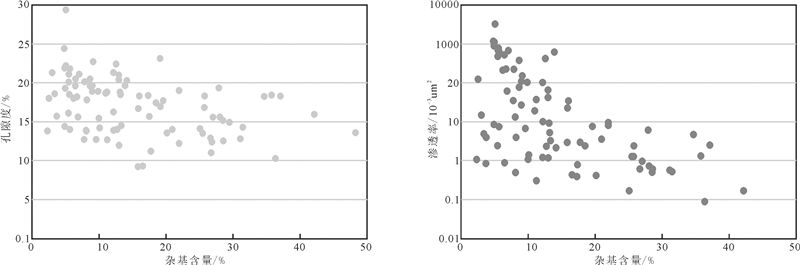
杂基含量是砂质纯度的侧面反映, 并在一定程度上可以反应岩性与物性。岩心分析数据表明中砾岩杂基含量最高, 平均26.6%, 细砾岩次之, 平均21.2%。而砂质沉积杂基含量常在10%左右。随着杂基含量的增加, 储层物性也是逐渐变差, 尤其是对于渗透率参数而言, 表现为指数下降的趋势。如果说储层岩性决定了提供孔隙的多少, 则杂基含量参数更多表征的是储层的渗流状况(图 8)。
4.2 评价参数的选择
不同相带不仅在储层质量上有所差异, 同时受沉积环境所限其发育规模也是不尽相同, 因此需要综合有关储层质量、砂体规模的多种参数来反映储层不同方面的特征, 以体现评价的综合性(程启贵等, 2010)。鉴于杂基含量对于岩性及物性的有效响应, 将其作为评价参数首选。而作为最有效储层的粗砂岩(姑且定义为优势砂岩), 其发育程度也尤为关键, 因此将优势砂岩的累计厚度纳入综合评价体系, 用以表征优质储层的丰度。又由于优势砂岩在砾岩沉积中多呈薄层状产出, 因此引入优势砂岩分层系数的概念(优势砂岩层数/优势砂岩总厚度)来反映其层内非均质程度(图 9)。最后辅以含砂率与孔隙度2个较为宏观的参数, 来反映砂体整体的发育频率与物性分布格局。
5. 储层综合定量评价
评价参数的选取与权重的确定构成了储层综合定量评价的核心, 其结果描述了对某个对象多种影响因素的单项评语的综合评判, 相较以往的定性、半定量评价其结果将更为客观和准确(彭仕宓等, 1994;刘吉余等, 2005;程启贵等, 2010)。
5.1 权系数的确定
本文采用灰色关联法确定各评价参数权系数。灰色关联分析明确了事物内部各影响因素之间的数值关系, 克服了以往储层评价权重计算时专家打分的人为因素, 也解决了单因素评价的矛盾问题, 近年来在储层评价方面有诸多应用(郭少斌等, 2014;涂乙等, 2016)。在实际应用中灰色关联分析主要涉及母、子序列的选定, 关联系数与关联度的计算, 权系数的确定(刘吉余等, 2005)。
选取孔隙度这一反映储层质量好坏的直观参数作为母序列, 其他参数为子序列。采用极大值方法对各参数进行无量纲化处理, 标准化后母、子序列可分别记为{Xt(0)}与{Xt(i)}, 而母、子序列之间的关联系数Lt(i, 0)与关联度ri, 0表示为:

式中, △t(i, 0)={Xt(i)-Xt(0)}

t(t=1, 2, 3, …, n)表示的每个序列中有n个参数值, i表示所选用的m个子序列(i=1, 2, …, m);△t(i, 0)为某一时刻相比较序列的绝对差值;△max, △min分别代表比较序列各个时刻绝对差中的最大值和最小值。ρ为介于0~1的分辨系数, 其目的是削弱因最大绝对差数值太大而失真的影响, 从而提高关联系数之间的差异显著性(程启贵等, 2010), 本文取值0.25。
关联度表征了各子序列与母序列之间的关系, 其值越接近1, 表明对母序列的影响作用越大, 反之亦然。通过对关联度的归一化处理即可得出各子序列的权系数(表 1):
表 1 不同储层质量评价参数权重系数Table 1. Weight coefficient of different reservoir quality evaluation parameters

5.2 分类标准建立
以各子序列无量纲化处理后的结果作为各单因素的得分, 则储层综合评价指标可定义为:

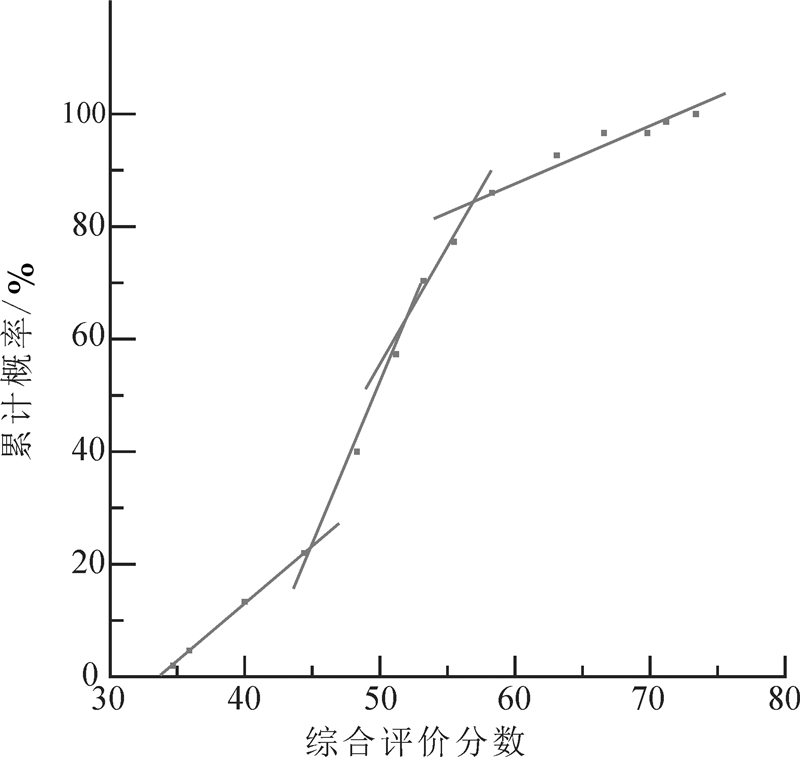
在储层评价指标值累计概率图上, 相同类型储层的综合评价指标值应落在同一条直线上(图 10), 以此拐点即可作为储层评价的分类阈值(程启贵等, 2010;郭少斌等, 2014), 从而界定出不同类型储层的综合评价指标标准与各项参数分布情况(表 2), 进而确定优质储层空间展布特点(图 11)。
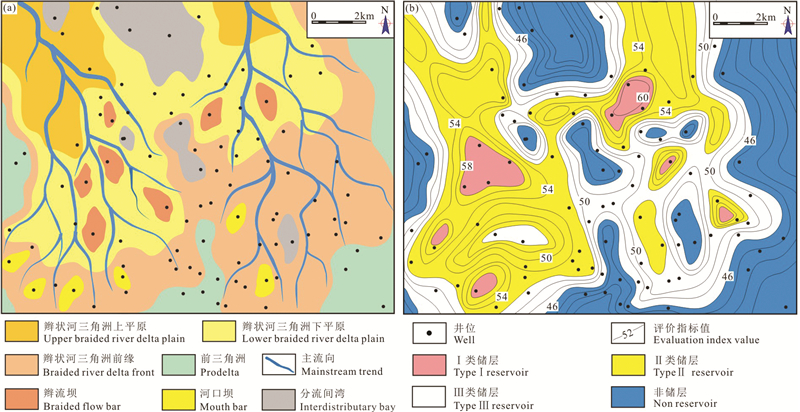
![]() 图 11 沉积微相与储层评价结果展布特征对比a—MSC1上升半旋回沉积微相平面展布图;b—MSC1上升半旋回储层综合评价结果平面图展布Figure 11. Comparison of sedimentary microfacies and reservoir evaluation resultsa-Plane distribution of MSC1 rising sub-cycle sedimentary microfacies; b-Plan view distribution of comprehensive evaluation results of MSC1 rising sub-cycle reservoir表 2 辫状河三角洲体系储层综合定量评价参数统计特征Table 2. Parameter characteristics of reservoir evaluation in braided river delta
图 11 沉积微相与储层评价结果展布特征对比a—MSC1上升半旋回沉积微相平面展布图;b—MSC1上升半旋回储层综合评价结果平面图展布Figure 11. Comparison of sedimentary microfacies and reservoir evaluation resultsa-Plane distribution of MSC1 rising sub-cycle sedimentary microfacies; b-Plan view distribution of comprehensive evaluation results of MSC1 rising sub-cycle reservoir表 2 辫状河三角洲体系储层综合定量评价参数统计特征Table 2. Parameter characteristics of reservoir evaluation in braided river delta
5.3 储层综合评价结果
依据分类阈值, 可将克上组储层分为3类。Ⅰ类储层综合评价指标大于57, 孔隙度平均22%, 含砂率平均48.82%, 而优势砂岩厚度可达到30 m。Ⅱ类储层评价指标在51~57, 孔隙度、含砂率及优势砂厚均较Ⅰ类储层略有所降低, 优势砂厚平均11.12 m。Ⅲ类储层为较差储层, 评价指标介于45~51, 杂基含量增加明显而物性变差, 杂基含量可达28%, 孔隙度平均16.52%, 且砂体与优势砂岩均不发育。当REI < 45时为非储层(表 2)。
在辫状河三角洲体系, Ⅰ类储层多呈土豆状零星分布, 主要分布于三角洲下平原与前缘地区, 尤其是下平原地区, 由于粗砂岩较为发育, 杂基含量低而物性好, 同时砂体规模较大, 因此往往成为Ⅰ类储层富集区。而三角洲上平原地区由于砾岩沉积发育而储层物性差、前缘地区虽然发育部分优势砂岩, 但砂体往往不如下平原地区富集, 因此两者综合评价结果均要差于下平原地区, 主要以Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类储层为主, 且其中Ⅱ类储层占据了三角洲体系的大部分区域, 而Ⅲ类储层主要对应于河道侧翼以及前缘较薄层砂质沉积中, 呈环带状分布于Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类储层四周。至于前三角洲与分流间湾已为非储层(图 11)。
6. 结论
(1) 红山嘴地区克上组发育辫状河三角洲沉积, 岩性包括细砾岩、中砾岩以及各粒级砂岩, 岩石成分、结构成熟度较低, 可进一步划分为上平原辫状河道、下平原辫状分流河道与辫流坝, 以及前缘水下分流河道等微相。
(2) 岩性与杂基含量为控制储层发育的主要因素。粗砂岩与中砂岩因其分选好、杂基含量低而成为最有利储层, 主要发育于辫流坝微相, 在辫状分流河道与河口坝序列顶部以及水下分流河道序列底部也有少量发育;细砾岩与中砾岩分选差而杂基含量高, 储层质量稍差, 其中细砾岩物性稍优于中砾岩, 两者分别为辫状分流河道与辫状河道的主要岩性组成;细砂岩主要发育于前缘地区, 虽分选较好但胶结致密, 储层物性差。
(3) 选取含砂率、孔隙度、杂基含量、优势砂厚以及优势砂岩分层系数作为评价参数进行储层综合评价。下平原地区由于较高的物性与优势砂岩占比而成为优质储层发育区, 上平原地区由于砾岩沉积发育而储层物性通常较差, 前缘地区虽然储层物性较好, 但其砂体发育程度较差, 因此经综合评判后多为Ⅱ、Ⅲ类储层。
-
图 2 克上组辫状河三角体系沉积岩石学特征
a—灰绿色块状中砾岩, 分选差, 次棱—次圆, 为碎屑流快速堆积结果;b—灰色砂质细砾岩, 可见砾石定向排列, 反映牵引流底负载沉积;c—灰色细砾岩, 正粒序, 槽状交错层理发育, 为河道下切充填产物;d—深灰色粗砂岩, 槽状交错层理;e—灰褐色含砾粗砂岩, 块状, 反映物源供给充足且快速沉积;f—深灰色粗砂岩, 板状交错层理, 反映河道顺流加积或侧积;g—灰色中砂岩, 平行层理, 河道序列顶部高流态层流产物;h—灰色粗砂岩, 见泥岩滑塌, 多为前缘快速堆积背景下滑塌结果;i—灰黑色粉砂岩, 浪成沙纹, 反映波浪淘洗作用;j—深灰色粉砂质泥岩, 水平层理, 反映静水沉积环境;k—灰绿色细砾岩, 基质支撑;l—红褐色块状泥岩;m—红褐色粉砂质泥岩, 与l主要响应陆上暴露环境;n—灰黑色泥岩, 块状, 代表静水还原环境;o—深灰色泥岩, 见碳化植物茎干, 说明沉积时期地层坡度大, 沉积物快速堆积埋存
Figure 2. Sedimentary petrological characteristics of braided river delta system in Upper Karamay Formation
a- Grayish green massive medium conglomerate, poorly sorted, sub-edge to sub-circle, which is the result of rapid accumulation of clastic flow; b- Gray sandy fine conglomerate with directional arrangement of gravels, reflecting the bottom load deposition of traction flow; c-Gray fine conglomerate, fining-upward sequence, trough cross bedding, mostly the product of channel cutting and filling; d-Dark gray coarse sandstone with trough cross bedding; e- Grayish brown gravelly coarse sandstone, massive bedding, showing that the source supply is sufficient and deposition rate is fast; f- Dark gray coarse sandstone, tabular cross bedding, reflecting the downstream accretion or lateral deposition of the channel; g-Gray medium sandstone, parallel bedding, developed at the top of the channel sequence in a high flowing laminar flow; h-Gray coarse sandstone, mudstone slump seen, which is mostly the result of rapid accumulation of delta front; i- Grayish black siltstone, with small-scale wave-ripple cross bedding, reflecting the wave washing; j- Dark gray silty mudstone with horizontal bedding, deposited in the still water sedimentary environment; k- Grayish green fine conglomerate, supported by matrix; l-Reddish brown block mudstone; m- Reddish brown silty mudstone, like l, mainly responding to a exposure environment; n- Grayish black block mudstone, representing a still water, restore environment; o-Dark gray mudstone, with carbonized plant stems, indicating that the terrain slope was large during the sedimentation period, and the sediments were rapidly accumulated and buried
图 11 沉积微相与储层评价结果展布特征对比
a—MSC1上升半旋回沉积微相平面展布图;b—MSC1上升半旋回储层综合评价结果平面图展布
Figure 11. Comparison of sedimentary microfacies and reservoir evaluation results
a-Plane distribution of MSC1 rising sub-cycle sedimentary microfacies; b-Plan view distribution of comprehensive evaluation results of MSC1 rising sub-cycle reservoir
表 1 不同储层质量评价参数权重系数
Table 1 Weight coefficient of different reservoir quality evaluation parameters

表 2 辫状河三角洲体系储层综合定量评价参数统计特征
Table 2 Parameter characteristics of reservoir evaluation in braided river delta

-
Cao Gang, Zou Jingyun, Qu Quangong, Hou Jiagen. 2016. Controlling factors of effective reservoirs in glutenite body of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yong 1 block, Dongying Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 28(1):30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxyqc201601004
Chen Huanqing, Mu Jiandong, Wang Yu, Deng Xili. 2017. Reservoir characteristics of fan delata deposits and its quantitative evaluation:Taking Yulou oil bearing sets in a certain experimental area of west depression in Liaohe Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(1):14-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201701002.htm
Cheng Liang, Guan Lijun, Wang Zhenqi, Peng Yazhong, Guan Jian. 2008. Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Triassic of Hongshanzui Area, Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-block Oil & Gas Field, 15(6):28-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkyqt200806008
Cheng Qigui, Guo Shaobin, Wang Haihong, Wang Chengyu, Liang Xiaowei. 2010. Comprehensive reservoir evaluation of Chang-6 oil-bearing layers in Midwest Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 32(5):415-419(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201005002
Colella A, Prior D B. 1990. Coarsed-Grained Deltas[M]. Oxford:The Alden Press, 3-27.
Gao Yang, Yu Xinghe, Liu Wenfeng, Zhao Yanwei, Huang Dingjie, Wang Jin. 2016. Analysis of characteristics and dominating factors of sandbody distribution of Karamay Formation in Hongshanzui Area, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 31(5):11-19(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xasyxyxb201605002
Guo Shaobin, Zhao Keying. 2014. Gas-bearing influential factors and estimation of shale reservoirs in Upper Paleozoic, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 36(6):678-691(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201406003
He Zhengjun, Wu Zhenzhen, Yang Xiaofa. Gong Changming. 2013. Sequences and conglomerate reserves distribution of the permian fan-delta in the northwest margin of Junggar basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 48(1):191-203(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx201301012
Lei Zhenyu, Lu Bing, Yu Yuanjiang, Zhang Liping, Shi Xin. 2005. Tectonic evolution and development and distribution of fans on northwestern edge of Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 26(1):86-91(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200501012
Liang R, Schruff T, Jia X D, Schüttrumpf H, Frings R M. 2015. Validation of a stochastic digital packing algorithm for porosity prediction in fluvial gravel deposits[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 329:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.09.002
Liu Jiyu, Peng Zhichun, Guo Xiaobo. 2005. Application of grey relation analysis to reservoir evaluation-taking Bei2 area, Saertu oilfield, Daqing, as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 12(2):13-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqdzycsl200502004
Longhitano S G, Sabato L, Tropeano M, Murru M, Carannante G, Simone S, Cilona A, Vigorito M. 2015. Outcrop reservoir analogous and porosity changes in continental deposits from an extensional basin:The case study of the upper Oligocene Sardinia Graben System, Italy[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 67:439-459. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.022
Meng Xiangchao, Chen Nenggui, Wang Haiming, Xu Yang, Xie Zongrui, Zou Zhiwen, Guo Huajun, Li Yazhe. 2015. Sedimentary characteristics of dlutenite and its favourable accumulati facies:A case study from T1b, Mabei Slope, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 33(6):1235-1246(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mohammadmoradi P, Kantzas A. 2016. Pore-scale permeability calculation using CFD and DSMC techniques[J] Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 146:515-525. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.07.010
Peng shimi, Xiong Qihua, Wang Caijing, Cai Yi. 1994. A method of principal component analysis in comprehensive reservoir evaluation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 15(Suppl):187-194(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYXB4S1.023.htm
Qiang Kunsheng, Zhang Guangxue, Zhang Li, Lü Baofeng, Zhong Guangjian, Feng Changmao, Yi Hai, Zhao Zhongquan, Yang Zhen, Yan Wei. 2018. A study of depositional characteristics of the Jurassic strata in Chaoshan Sub-basin, northern South China Sea, and its control on reservoir beds[J]. Geology in China, 45(1):48-585(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801005
Qiu Dongzhou. 1994. Exploration of the concealed oil-gas trap of Triassic-Jurassic in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xin Jiang Petroleum Geology, 15(1):1-9(in Chinese with English abstract).
Solano N A, Clarkson C R, Krause F F. 2016. Characterization of fine-scale rock structure and differences in mechanical properties in tight oil reservoirs:An evaluation at the scale of elementary lithological components combining photographic and X-ray computed tomographic imaging, profile-permeability and microhardness testing[J] Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, 15:22-42. doi: 10.1016/j.juogr.2016.04.003
Song Guangyong, Gong Qingshun, Pang Hao, Xia Zhiyuan, Li Senming, Wu Jin, Tian Mingzhi, Huang Xuebing. 2020. High-precision sequence stratigraphy and sandbody architecture of the Lower Xiaganchaigou Formation in the slope area of Western Qaidam Basin[J]. Geology in China, 47(1):188-200(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi202001015
Song Ziqi, Yang Lilei, Cheng Ying, Wang Nan, Ding Jian. 2007. Comprehensive evaluation of heterogeneity conglomerate reservoirs-taking conglomerate reservoirs in Qizhong and Qidong area of Karamay Oil Field as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 29(4):11-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYSD200704015.htm
Tan Chengpeng, Yu Xinghe, Li Shengli, Qu Jianhua, Wei Lingyun, Li Xiaolu, Du Yonghui. 2014. The response relationship between base-level cycle and reservoirs of fan delta in Badaowan Formation, Southern Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 41(1):197-205(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201401015
Tu Yi, Xie Chuanli, Liu Chao, Li Jiajia. 2012. Application of grey correlation analysis method in reservoir evaluation of Qingdong Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 23(2):381-386(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201202027
Veloso F M L, Navarrete R, Soria A R, Melendez N. 2016. Sedimentary heterogeneity and petrophysical characterization of Barremian tsunami and barrier island/inlet deposits:The Aliaga outcrop as a reservoir analogue (Galve sub-basin, eastern Spain)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 73:188-211. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.032
Wang cheng, Guan Yanhua, Xiao Limei, Shao Hongmei, Hong Shunxin, Yang Lianhua, Wang Ping, 2006. Characteristics of deep conglomerate reservoir in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 27(supp.):52-56(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb2006z1010
Wang Longzhang. 1994. Approaches to curves for the lake-level fluctuations in the Junggar Basin during Meso-Cenozoic time[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 14(6):1-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YXGD406.000.htm
Wang Yaning, Zhang Shangfeng, Zhao Weijun, Liang Zeliang. 2009. Sedimentary facies of Triassic in Hong-Che Area in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 30(1):68-72(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz200901018
Xian Benzhong, Xu Huaibao, Jin Zhenkui, Wang Chunsheng, Lu Yang, Huang Liliang. 2008. Sequence stratigraphy and subtle reservoir exploration of Triassic System in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 14(2):139-146(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200802002
Yang Ye, He Zhongbo. 2016. Characteristics of Mesozonic-Cenozoic paleoclimate evolution and its constraint on mineralization of sandstone type uranium deposit in Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 33(3):140-145(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Jianguo, Liu Xu, Bai Yu, Liu Jun, Kang Li, Zhang Shuncun. 2015. The characteristics of depositional facies and their influence on reservoir properties in Fudong slope, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(supp.2):23-31(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Xinghe, Li Shengli, Li Shunli. 2013. Texture-genetic classifications and mapping methods for deltaic deposits[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(5):782-797(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CJXB201305005.htm
Yu Xinghe, Qu Jianhua, Tan Chengpeng, Zhang Lei, Li Xiaolu, Gao Zhaopu. 2014. Conglomerate lithofacies and origin models of fan deltas of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 35(6):619-627(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz201406001
Yu Yuanjiang, Hu Suyun, Lei Zhenyu, He Dengfa, Zhang Liping, Xu Shijun. 2005, Sedimentary response to Triassic-Jurassic thrust faulting in the foreland thrust belt of the northwestern Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(4):423-437(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200504011
Yu Yuanjiang, Li Desheng, Hu Suyun, Lei Zhenyu, He Dengfa. 2007. Fans sedimentation and exploration direction of fan hydrocarbon reservoirs in foreland thrust belt of the northwestern Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 28(1):62-71(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200701010
Zhang Shuncun, Shi Ji-an, Chang Qiusheng, Lu Xinchuan, Zou niuniu. 2015. Controlling effect of lithofacies on reservoirs of Baikouquan formation in Mabei area[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 44(6):1017-1024(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkydxxb201506009
Zhou Junliang, Hu Yong, Li Chao, Fu Rong, Lai Youchun. 2017. Characteristics and controlling factors of fan delta facies low permeability reservoirs in Bohai A oilfield, the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 38(1):71-78(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201701009
Zou Caineng, Hou Lianhua, Kuang Lichun, Kuang Jun. 2007. Genetic mechanism of diagenesis-reservoir facies of the fan-controlled permo-Triassic in the western marginal area, Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 42(3):587-601(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200703014
曹刚, 邹婧芸, 曲全工, 侯加根. 2016.东营凹陷永1块沙四段砂砾岩体有效储层控制因素分析[J].岩性油气藏, 28(1):30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2016.01.004 陈欢庆, 穆剑东, 王珏, 邓西里. 2017.扇三角洲沉积储层特征与定量评价——以辽河西部凹陷某试验区于楼油层为例[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(1):14-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201701002 程亮, 关利军, 王振奇, 彭亚中, 关键. 2008.红山嘴地区三叠系油气成藏主控因素[J].断块油气田, 15(6):28-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkyqt200806008 程启贵, 郭少斌, 王海红, 王成玉, 梁晓伟. 2010.鄂尔多斯盆地中西部长6油层组储层综合评价[J].石油实验地质, 32(5):415-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.05.002 高阳, 于兴河, 刘文峰, 赵延伟, 黄丁杰, 王进. 2016.准噶尔盆地红山嘴地区克拉玛依组砂体展布特征及其主控因素分析[J].西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 31(5):11-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2016.05.002 郭少斌, 赵可英. 2014.鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界泥页岩储层含气性影响因素及储层评价[J].石油实验地质, 36(6):678-691. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201406003 贺正军, 吴珍珍, 阳孝法, 巩长明. 2013.准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系扇三角洲层序特征及砾岩油藏分布规律[J].地质科学, 48(1):191-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2013.01.012 雷振宇, 鲁兵, 蔚远江, 张立平, 石昕. 2005.准噶尔盆地西北缘构造演化与扇体形成和分布[J].石油与天然气地质, 26(1):86-91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.01.012 刘吉余, 彭志春, 郭晓博. 2005.灰色关联分析法在储层评价中的应用——以大庆萨尔图油田北二区为例[J].油气地质与采收率, 12(2):13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2005.02.004 孟祥超, 陈能贵, 王海明, 徐洋, 谢宗瑞, 邹志文, 郭华军, 李亚哲. 2015.砂砾岩沉积特征分析及有利储集相带确定——以玛北斜坡区百口泉组为例[J].沉积学报, 33(6):1235-1246. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201506016 彭仕宓, 熊琦华, 王才经, 蔡毅. 1994.储层综合评价的主成分分析方法[J].石油学报, 15(增刊):187-194. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400462652 强昆生, 张光学, 张莉, 吕宝凤, 钟广见, 冯常茂, 易海, 赵忠泉, 杨振, 鄢伟. 2018.南海北部潮汕坳陷侏罗系沉积特征及对储层的控制作用研究[J].中国地质, 45(1):48-58. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180105&flag=1 丘东洲. 1994.准噶尔盆地西北缘三叠-侏罗系隐蔽油气圈闭勘探[J].新疆石油地质, 15(1):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XJSD401.000.htm 宋光永, 宫清顺, 庞皓, 夏志远, 李森明, 伍劲, 田明智, 黄学兵. 2020.柴达木盆地西部斜坡区下干柴沟组下段高精度层序地层及砂体构型分析[J].中国地质, 47(1):188-200. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200115&flag=1 宋子齐, 杨立雷, 程英, 王楠, 丁健. 2007.非均质砾岩储层综合评价方法——以克拉玛依油田七中、东区砾岩储层为例[J].石油实验地质, 29(4):11-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200704016 谭程鹏, 于兴河, 李胜利, 瞿建华, 魏凌云, 李晓路, 杜永慧. 2014.准噶尔盆地南缘八道湾组扇三角洲露头基准面旋回与储层的响应关系[J].中国地质, 41(1):197-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.015 涂乙, 谢传礼, 刘超, 李佳佳. 2012.灰色关联分析法在青东凹陷储层评价中的应用[J].天然气地球科学, 23(2):381-386. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201202027 王成, 官艳华, 肖利梅, 邵红梅, 洪淑新, 杨连华, 王平. 2006.松辽盆地北部深层砾岩储层特征[J].石油学报, 27(增刊):52-56. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb2006z1010 王龙樟. 1994.准噶尔盆地中新生代湖水位升降曲线的建立与剖析[J].岩相古地理, 14(6):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YXGD406.000.htm 王雅宁, 张尚锋, 赵卫军, 梁则亮. 2009.准噶尔盆地红车地区三叠系沉积相分析[J].新疆石油地质, 30(1):68-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz200901018 蔚远江, 胡素云, 雷振宇, 何登发, 张立平, 许世军. 2005.准噶尔西北缘前陆冲断带三叠纪-侏罗纪逆冲断裂活动的沉积响应[J].地学前缘, 12(4):423-437. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.011 蔚远江, 李德生, 胡素云, 雷振宇, 何登发. 2007.准噶尔盆地西北缘扇体形成演化与扇体油气藏勘探[J].地球学报, 28(1):62-71. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2007.01.010 鲜本忠, 徐怀宝, 金振奎, 王春生, 鲁阳, 黄立良. 2008.准噶尔盆地西北缘三叠系层序地层与隐蔽油气藏勘探[J].高校地质学报[J], 14(2):139-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.02.002 杨烨, 何中波. 2016.准噶尔盆地中新生代古气候演化特征及对砂岩型铀成矿作用的制约[J].世界核地质科学, 33(3):140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2016.03.003 殷建国, 刘旭, 白雨, 刘军, 康莉, 张顺存. 2015.准噶尔盆地阜东斜坡区沉积相特征及其对储层物性的控制作用[J].天然气地球科学, 26(增刊2):23-31. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97226X/2015S2/84687588504849538350484851.html 于兴河, 李胜利, 李顺利. 2013.三角洲沉积的结构——成因分类与编图方法[J].沉积学报, 31(5):782-797. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201305005 于兴河, 瞿建华, 谭程鹏, 张磊, 李晓路, 高照普. 2014.玛湖凹陷百口泉组扇三角洲砾岩岩相及成因模式[J].新疆石油地质, 35(6):619-627. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz201406001 张顺存, 史基安, 常秋生, 鲁新川, 邹妞妞. 2015.岩性相对玛北地区百口泉组储层的控制作用[J].中国矿业大学学报, 44(6):1017-1024. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkydxxb201506009 周军良, 胡勇, 李超, 付蓉, 来又春. 2017.渤海A油田扇三角洲相低渗储层特征及物性控制因素[J].石油与天然气地质, 38(1):71-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201701009 邹才能, 侯连华, 匡立春, 况军. 2007.准噶尔盆地西缘二叠-三叠系扇控成岩储集相成因机理[J].地质科学, 42(3):587-601. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.03.014 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 孟庆龙,成亚斌,滕菲,李健,吴刚,赵林丰. 远岸水下扇储层构型及剩余油分布特征——以黄骅坳陷NS断块为例. 华北地质. 2024(01): 66-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗旭东,韩东威,张方贵,张斌,冯雪,陈清清. 玛湖446井区克拉玛依组储层特征及有利区预测. 西北地质. 2024(05): 166-180 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐睿,张飞,蔡珺君,毛正林,李文,周芳芳,胡怡,田野. 基于储层发育主控因素的碳酸盐岩储层定量分类评价——以四川盆地安岳气田台内带灯影组四段气藏为例. 天然气勘探与开发. 2024(06): 62-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾晓华,孟迪,彭文丰,陈之贺,骆逸婷,肖大志. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷W油田储层综合评价研究. 石油科学通报. 2023(01): 20-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 董雪梅,李静,潘拓,徐倩,陈亮,任军民,金科. 准噶尔盆地红车断裂带油气成藏条件及勘探潜力. 石油学报. 2023(05): 748-764 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 何艺玮,房元龙,冯文杰,刘远航,范洋,郭华粘,张佩,贾风娟. 辫状河三角洲沉积特征与生长演变规律——水槽沉积模拟实验研究. 地质论评. 2023(04): 1564-1580 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李积永,张平,胡光明,蒲勇,王军林,祁青山,吴涛. 一种单砂体多因素分类评价方法——以柴达木盆地扎11井区下油砂山组为例. 科学技术与工程. 2021(10): 4005-4010 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: