Zircon U-Pb dating, Hf isotopic characteristics and genesis of the intrusive rocks in the Jiaochong deposit, Tongling area, Anhui Province
-
摘要:
安徽铜陵矿集区出露的侵入岩可划分为高钾钙碱性和橄榄安粗岩系列,作为铜陵7大矿田之一的焦冲地区是否也存在两个系列侵入岩?它们的时代及成因与整个铜陵地区的侵入岩是否相同?这些问题目前仍不清楚。本文选择铜陵焦冲矿田的侵入岩开展了岩相学、岩石地球化学、LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年及原位Hf同位素地球化学研究。结果表明,焦冲矿田也存在高钾钙碱性系列和橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩,前者的主要岩石类型为石英二长闪长岩、花岗闪长岩,后者为辉石二长闪长岩。LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩年代与铜陵地区其他矿区同类岩石年代相同,约为142 Ma;而橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩年代比铜陵地区其他矿区同类岩石年轻,约为136 Ma。总体上看,铜陵地区两个系列侵入岩具有多期次侵位的特征。焦冲高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩含有较多的老的继承性锆石,说明本区古老地壳卷入了岩浆形成过程。结合铜陵地区侵入岩的特征和焦冲矿田侵入岩岩石地球化学研究结果,笔者认为,焦冲矿田两个系列侵入岩成因与铜陵地区侵入岩相似,即橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩是来自莫霍面附近深部位岩浆房富碱基性岩浆结晶分异后的产物,而高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩是深位岩浆房分异后的岩浆与浅位岩浆房长英质岩浆混合后的产物。
-
关键词:
- 锆石LA-CPMS U-Pb定年 /
- 岩石地球化学 /
- 侵入岩 /
- 铜陵焦冲
Abstract:The intrusive rocks in Tongling area can be separated into a high-K calc-alkaline series and a shoshonitic series. The Jiaochong orefield is one of the seven orefields in Tongling area. The problems as to whether there are two series of intrusive rocks in the Jiaochong orefield or not and whether they have the same age and genesis as compared with the other intrusions in Tongling area are not clear. Therefore, this research was focused on the study of petrography, geochemistry, LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating and in situ Hf isotopic analysis. It turns out that there are two series of intrusive rocks in the Jiaochong orefield. The high-K calc-alkaline series mainly contains quartz monzodiorite and granodiorite, and the shoshonitic series consists of pyroxene monzodiorite. The results of LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating show that the age of the high-K calc-alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield is about 142 Ma, identical with the age of the other orefields in Tongling area; the age of the shoshonitic series is around 136 Ma, which is younger than that of the other intrusive bodies in Tongling area. In general, the two series of intrusions indicate the features of the multiphase emplacement. Furthermore, lots of zircons having old inherited core in the high-K calc-alkaline series reveal the existence of the materials of old crust in the magma-forming process. Combined with the characteristics of the intrusive rocks in Tongling area and the geochemical features of Jiaochong intrusions, it is obvious that the genesis of the two series of intrusions in the Jiaochong orefield is similar to that of other intrusions in Tongling area. In other word, the intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series were formed by the fractional crystallization of the alkali-rich basic magma that originated from the deep magma chamber near the Moho. In the meanwhile, the high-K calc-alkaline series is the product of the magma mixing between the felsic magma derived from the shallow magma chamber and the magma that suffered from the fractional crystallization and originated from the deep magma chamber.
-
1. 引言
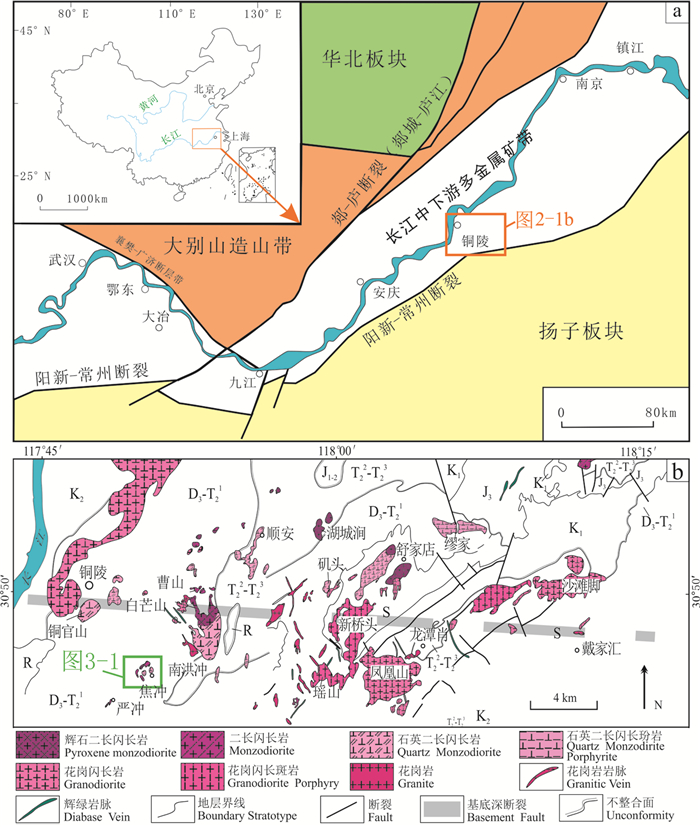
铜陵地区位于安徽省境内长江南岸,长江中下游铁铜等多金属成矿带的中部(图 1a)。长江中下游地区有7个矿化集中区(矿集区),从西到东分别是:鄂东、九瑞、安庆—贵池、铜陵、庐枞、宁芜、宁镇矿集区。铜陵矿集区是其中一个重要的矿集区,以盛产铜矿而著名,且已有几千年的开采历史,被誉为中国的古铜都。区内主要产出矽卡岩型、层控矽卡岩型、斑岩型铜矿,同时伴生有金、钼、铅锌等多金属矿床(常印佛等, 1983, 1991, 2017;Wu et al., 2000, 2001;张旗等,2001;王强等,2003;狄永军等,2003;杜杨松等, 2004, 2007;吴才来等,2008;吕庆田等,2009)。这些矿床主要集中分布在铜官山、狮子山、新桥、凤凰山、舒家店、沙滩脚、焦冲矿田内。大量的研究工作表明,这些矿田内的金属矿床与区内中酸性侵入岩关系十分密切(周泰禧等,1987;常印佛等,1991;徐夕生等,2004;杜杨松等, 2004, 2007;吴才来等, 2010, 2013;黄文明等,2019)。区内出露高钾钙碱性和橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩,其中橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩时代为145~138 Ma,而高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩年代为152~130 Ma(王彦斌等,2004;Di et al., 2005;张达等,2006;楼亚儿等,2006;吴淦国等,2008;吴才来等, 2008, 2010, 2013)。然而,区内同一系列同一类型的侵入岩具有不同的时代,不同矿田内侵入岩的年龄、系列及成因均有一定的变化,是什么机制导致这种变化?同时,不同矿田侵入岩及矿床的研究程度也存在较大的差异,特别是焦冲矿田侵入岩的研究程度相对较低。焦冲矿田内也存在两个系列侵入岩吗?他们形成的时代与铜陵地区其他岩体的时代一致吗?这些问题仍不清楚。因此,本文试图通过铜陵焦冲矿田侵入岩的锆石U-Pb定年、Hf同位素分析和岩石地球化学研究,对上述问题进行探讨。
2. 地质背景及岩体地质特征
铜陵地区位于扬子地块东北缘的中部,区内沉积了志留纪到三叠纪的海相、滨海相、浅海相及海陆交互相的碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩及硅质岩,以及中三叠世上部月山组到新近纪的陆相碎屑岩夹火山岩(图 1b)。印支运动使中三叠世以前的地层(盖层)发生了一系列褶皱和断裂。褶皱构造自西向东分别为金口岭向斜、铜官山背斜、大通—顺安复向斜(包括青山次级背斜、朱村向斜)、永村桥—舒家店背斜、新屋里复向斜和戴公山背斜(常印佛等,1991;吴才来等,2013;张志辉等,2013)。盖层之下的基底构造分别由东西向、南北向、北北东向3组深大断裂组成,特别是东西向基底构造制约着铜陵地区侵入岩及相关矿产的分布,构成了铜陵地区东西向宽约20 km的构造-岩浆-成矿带(常印佛等,1991)。区内侵入岩可划分为高钾钙碱性系列和橄榄安粗岩系列:前者包括花岗闪长岩、花岗闪长斑岩、石英二长闪长岩、石英二长闪长玢岩,后者包括辉石二长闪长岩、二长岩、石英二长岩等(王强等,2003;吴淦国等,2008;杨小男等,2008;阙朝阳等,2013;吴才来等,2013;Wu et al., 2014, 2017),这些侵入岩均分布在近东西向构造-岩浆-成矿带上(常印佛等,1991;吴才来等,2003;姚孝德等,2012)。研究表明,铜陵高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩中存在大量的暗色微粒闪长质包体和富云母包体,且与铜矿化关系密切;橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩中存在大量的深源堆积岩包体,且与金矿化关系密切(杨小男等,2007;徐晓春等,2008;吴才来等, 2010, 2013)。
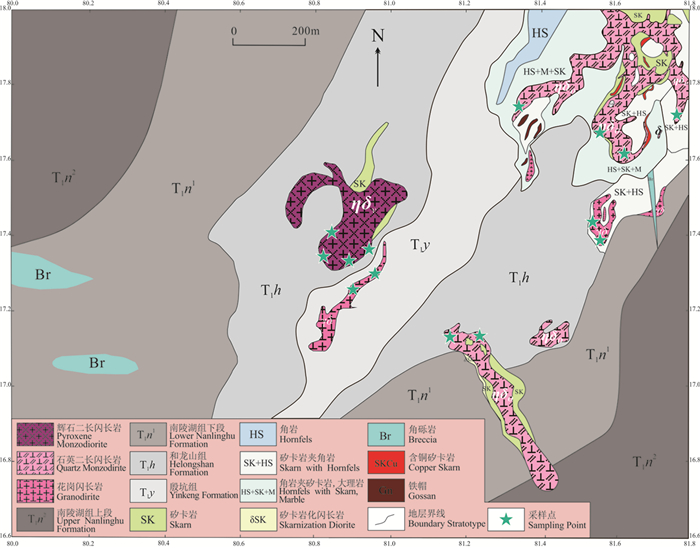
焦冲矿田位于大通—顺安复向斜中的青山次级背斜核部(图 2)。核部最老地层为下三叠统塔山组条带状灰岩(T1t),两边依次为中三叠统南陵湖组薄层灰岩(T2n),及中三叠统分水岭组灰岩夹硅质岩(T2f)。焦冲矿田主要出露辉石二长闪长岩、石英二长闪长岩和花岗闪长岩,岩体呈岩株、岩枝状产出,出露面积很小,约0.1 km2。岩体与围岩接触带发育矽卡岩化、大理岩化及角岩化。区内主要产出层控矽卡岩型金矿,金矿体主要赋存在不同岩性的岩体接触带附近硅质岩中。其中,辉石二长闪长岩位于矿田的中部,呈不规则的北东向,接触带局部地方发育矽卡岩;花岗闪长岩呈北东向岩枝状,分布在辉石二长闪长岩的东南外围;石英二长闪长岩呈不规则岩脉或岩枝状产出,延伸方向以北东向为主,其次为北西向,主要侵位于塔山组地层中,部分呈北西向的岩体侵入到塔山组和南陵湖组灰岩中(图 2)。
3. 定年样品岩石学特征
选择6个岩石样品(10CL506、10CL507、10CL521、17CL505、17CL511、17CL516)开展LAMC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,主要岩性为辉石二长闪长岩、石英二长闪长岩和花岗闪长岩。各定年样品岩石学特征分述如下:
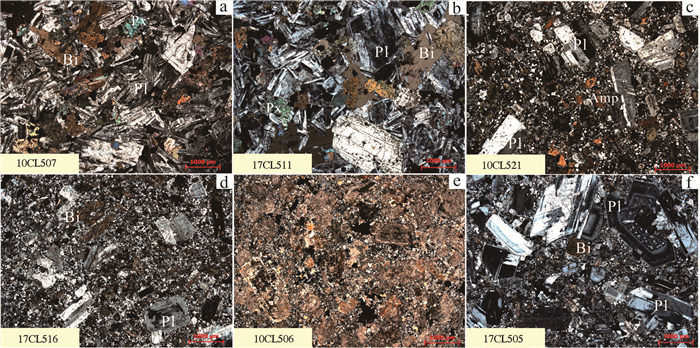
辉石二长闪长岩(样品10CL507、17CL511):岩石呈灰黑色,具有半自形板柱状粒状结构,块状构造。主要矿物有斜长石、辉石,其次为黑云母和碱性长石,副矿物为锆石、磷灰石。镜下观察,斜长石为自形—半自形长板状,含量60%~70%;辉石为半自形柱粒状,含量15%~20%;黑云母为片状,含量7%~8%;碱性长石为他形粒状,含量8%~12%。锆石呈柱粒状,磷灰石为自形长柱状。岩石局部具有碳酸盐化,部分黑云母被绿泥石交代(图 3a、b)。不透明矿物主要为他形粒状磁黄铁矿,其次为半自形粒状黄铁矿和他形不规则粒状黄铜矿。矿物生成顺序为辉石→斜长石→碱性长石→黑云母→绿泥石→方解石。
石英二长闪长岩(样品10CL506、17CL505、17CL516),呈深灰色,具有半自形粒状不等粒结构和似斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶主要为自形—半自形板柱状斜长石,粒径1~2.5 mm。部分样品的斜长石发生绢云母化和碳酸盐化(如样品10CL506),形成鳞片状绢云母和他形粒状方解石,局部绢云母结晶颗粒粗大,形成少量片状白云母,部分角闪石、黑云母发生绿泥石化。基质主要为他形粒状石英,其次为钾长石(图 3d、e、f)。各主要矿物含量为:斜长石55%~65%,石英10%~15%,钾长石15%,角闪石5%~8%,黑云母5%~7%。不透明矿物主要为半自形粒状磁黄铁矿,其次为自形—半自形粒状黄铁矿、半自形—他形闪锌矿和不规则状黄铜矿。其中,磁黄铁矿先生成,但晚于方解石,黄铁矿后生成,晚于绢云母。根据镜下观察可知透明矿物生成顺序为:角闪石→斜长石→黑云母→石英→钾长石→方解石→绢云母→白云母。
花岗闪长岩(样品10CL521):呈灰白色,具有似斑状不等粒结构,块状构造。斑晶为半自形短柱状斜长石,片状黑云母及半自形—他形角闪石。显微镜下观察,斜长石斑晶大小约为1 mm,具明显的环带结构和聚片双晶。少量斜长石斑晶绢云母化和绿泥石化,局部有黑云母交代角闪石,并残留一部分角闪石,少量斜长石被钾长石交代。薄片中见长英质岩脉的穿插,岩脉主要由半自形粒状石英组成,含少量碱性长石和不透明矿物。基质成分主要为他形粒状碱性长石及少量的他形粒状石英和少量他形不规则状方解石(图 3c)。各主要矿物含量分别为:斜长石50%~65%,石英15%~25%,钾长石10%,角闪石5%~10%,黑云母5%。不透明矿物主要为磁黄铁矿,其次为黄铁矿和黄铜矿。可推测矿物生成顺序为:斜长石→角闪石→黑云母→石英→碱性长石。
4. 分析方法
4.1 锆石U-Pb定年
采集样品各2 kg,破碎至80~120目,用水淘洗粉尘后,先用磁铁吸出磁铁矿等磁性矿物,再用重液选出锆石,最后在双目镜下人工挑出锆石。锆石的分选由河北廊坊区调院完成。锆石和标样一起黏在玻璃板上后,用环氧树胶浇铸,制成薄片再抛光,并拍照反射光和阴极发光照片,最后在激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS)上测定锆石的U、Th、Pb含量及定年。测年工作在中国地质科学院地质研究所大陆构造及动力学重点实验室完成,标样为91500,206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均值误差为± 2σ。U/Pb比值数据处理使用软件LaDating@Zrn,校正Pb同位素使用软件ComPb corr#3-18(Anderson, 2002),校正后的数据使用美国Berkeley地质年代学中心编制的ISOPLOT和SQUID(Ludwing, 2003)程序进行处理,得到年龄结果。详细分析方法如袁洪林等(2003)的描述。
4.2 锆石Hf同位素分析
锆石Hf同位素测试是在中国地质科学院地质研究所大陆构造及动力学重点实验室完成,所用仪器为Neptune多接收等离子质谱和Newwave UP213紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA-MC-ICP-MS),实验过程中采用He作为剥蚀物质载气。根据锆石大小,剥蚀直径采用44 μm,测定时使用国际上通用的锆石标样GJ1作为参考物质,分析过程中锆石标样GJ1的176Hf/177Hf测试加权平均值为0.282015±8(2σ,n= 10)。相关仪器运行条件及详细分析流程见侯可军等(2007)。
4.3 全岩化学分析
本文对岩石样品(含定年样品)进行了化学全分析(表 1),由中国地质科学院测试所(国家地质实验测试中心)完成。用X荧光光谱仪(3080E)对氧化物进行测试,并执行标准分别为:Al2O3、CaO、Fe2O3、K2O、MgO、MnO、Na2O、P2O5、SiO2和TiO2执行GB/ T14506.28- 1993标准,FeO执行GB/T14506.14- 1993标准;CO2执行GB9835-1988标准;H2O+执行GB/T14506.2-1993标准;LOI执行LY/T1253-1999标准;稀有元素和微量元素As、Ba、Be、Bi、Cd、Ce、Co、Cs、Cu、Dy、Er、Eu、Ga、Gd、Hf、Ho、La、Li、Lu、Mo、Nb、Nd、Ni、Pb、Pr、Rb、Sb、Sc、Sm、Sn、Sr、Ta、Tb、Th、Tm、U、W、Y、Yb、Zn和Zr用等离子质谱(Xseries)执行DZ/T0223-2001标准。用不同的分析方法交叉检查,参考国际标准GBW矫正。分析精度分别为:主要氧化物Na2O、MgO、Al2O3、SiO2、K2O、CaO和FeO为1%,Fe2O3、P2O5、TiO2、MnO、H2O+和CO2为10%,微量元素La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Y、Sr、V、Zn、Ga、Rb、Cs、Pb、Th、Nb、Zr和Ba为15%,Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Er、Yb、V、Co、Ni、U、Hf、Ta和Sc为20%,Tb、Ho、Tm和Lu为25%。
表 1 焦冲锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年数据Table 1. Data of zircon La-ICPMS U-Pb dating from granites in Jiaochong
5. 分析结果
5.1 锆石U-Pb定年
样品锆石特征及定年结果分述如下:
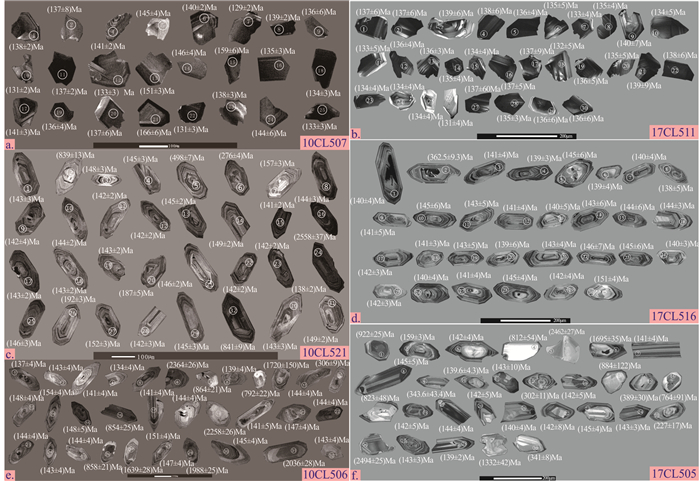
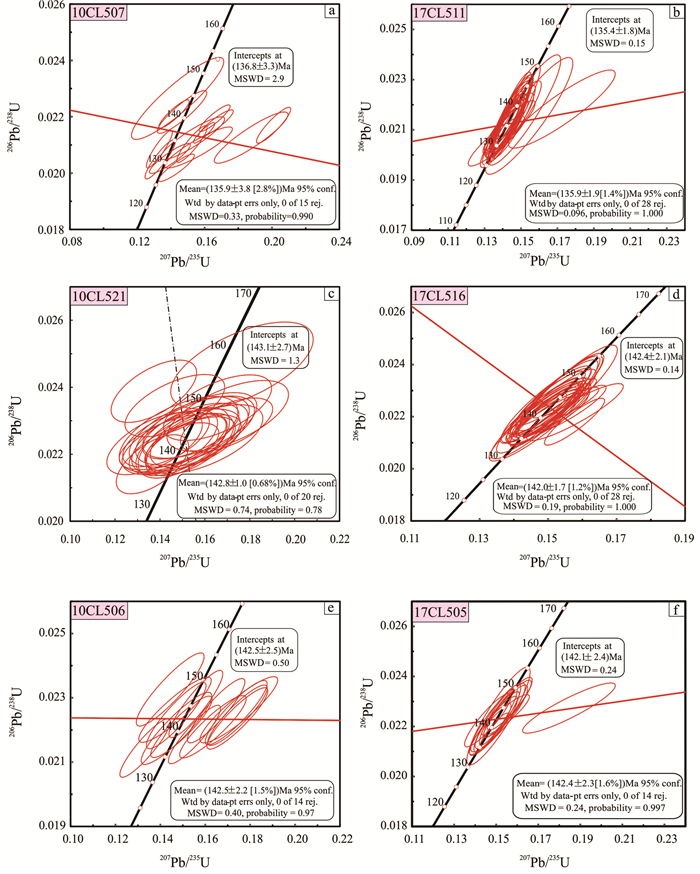
样品10CL507(辉石二长闪长岩):该样品中的锆石多为短柱状或粒状,长宽比值约为1:1。阴极发光(CL)图像能够揭示锆石内部结构(Vavran et al., 1999)。CL图像显示该样品中的一部分锆石为均匀的灰黑色,部分具有扇状结构,不含有矿物包裹体和继承性核(图 4a)。锆石中U和Th含量分别为84.1×10-6~1956×10-6和67.0×10-6~1115×10-6,Th/U比值变化较大,为0.26~1.95,平均值为0.66(表 1)。其中锆石的206Pb/238U年龄变化范围为(129±2)Ma~(166±6)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算平均年龄为(135.9±3.8)Ma。207Pb/235U- 206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(136.8±3.3)Ma(图 5a),与平均年龄在误差范围内基本一致。
![]() 图 4 锆石CL阴极发光图像a— 10CL507-辉石二长闪长岩; b—17CL511-辉石二长闪长岩; c—10CL521-花岗闪长岩; d—17CL516-石英二长闪长岩; e—10CL506-石英二长闪长岩; f—17CL505-石英二长闪长岩Figure 4. Cathodoluminescence images of zircona-10CL507-pyroxene monzodiorite; b-17CL511-pyroxene monzodiorite; c-10CL521-granodiorite; d-17CL516-granodiorite; e-10CL506-quartz monzodiorite; f-17CL505-quartz monzodiorite
图 4 锆石CL阴极发光图像a— 10CL507-辉石二长闪长岩; b—17CL511-辉石二长闪长岩; c—10CL521-花岗闪长岩; d—17CL516-石英二长闪长岩; e—10CL506-石英二长闪长岩; f—17CL505-石英二长闪长岩Figure 4. Cathodoluminescence images of zircona-10CL507-pyroxene monzodiorite; b-17CL511-pyroxene monzodiorite; c-10CL521-granodiorite; d-17CL516-granodiorite; e-10CL506-quartz monzodiorite; f-17CL505-quartz monzodiorite样品17CL511(辉石二长闪长岩):该样品中的锆石和样品10CL507中的相似,为短柱状或粒状,长宽比为1:1~1.5:1。从CL图像看,锆石内部不具有老的继承性核,部分锆石具有环带结构,显示出岩浆成因锆石的特点(图 4b)。锆石中的U和Th含量分别为85.1×10-6~1912×10-6和56.1×10-6~1173× 10-6,Th/U比值变化较大,为0.18~1.55,平均值为0.60(表 1)。同时锆石的206Pb/238U年龄变化范围为(131.1±4.1)Ma~(140.0±7.0)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算加权平均年龄是(135.9 ± 1.9)Ma。207Pb/235U- 206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(135.4±1.8)Ma(图 5b),与平均年龄在误差范围内基本一致。
样品10CL506(石英二长闪长岩):该样品中的锆石为柱状,具有较好的柱面和锥面,长宽比值为2׃1。该样品中的锆石内部结构清晰,具有较好的振荡环带结构,不含有矿物包裹体(图 4e),这是典型的岩浆结晶锆石(Pidgeon et al., 1998)。锆石的CL特征由内部元素分布规律决定,其发光强度主要与锆石中U和Th含量相关(Hanchar et al., 1993)。样品中U和Th含量相对较低,分别为50.3×10-6~389× 10-6和6.4×10-6~346×10-6,Th/U比值变化较大,为0.12~1.40,平均值为0.62(表 1)。其中锆石6、7、9、10、12、16、19、26、27、29和31含有老的继承性核,年龄分别为2364 Ma、864 Ma、792 Ma、1714 Ma、306 Ma、854 Ma、2258 Ma、858 Ma、1639 Ma、1988 Ma、2036 Ma,Th/U平均值为0.64。岩浆结晶锆石的206Pb/238U年龄变化范围是从(134±4)Ma~(154± 4)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算加权平均年龄为(142.5±2.2)Ma。207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(142.5±2.5)Ma(图 5e),与平均年龄基本一致。
样品17CL505(石英二长闪长岩):该样品中锆石多具有柱状或长柱状,长宽比值为1:1~2.5:1。锆石内部结构清晰,具有较好的振荡环带结构,不含有矿物包裹体(图 4f)。锆石中U和Th含量分别为17.2×10-6~1056×10-6和11.2×10-6~868×10-6,Th/ U比值为0.3~1.8,平均值为0.74(表 1)。其中锆石1、4、5、6、9、12、14、15、16、17、25、26、29和30含有老的继承性核,其年龄分别为923 Ma、812 Ma、2462 Ma、1695 Ma、344 Ma、302 Ma、885 Ma、389 Ma、764 Ma、823 Ma、227 Ma、2494 Ma、1332 Ma和341 Ma,Th/U平均值为0.71。岩浆结晶锆石的206Pb/238U年龄为(139.2±5)Ma~(159.7±5)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算平均年龄为(142.4 ± 2.3)Ma。207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(142.1±2.4)Ma(图 5f),与平均年龄在误差范围内基本一致。
样品17CL516(石英二长闪长岩):该样品中锆石多具有柱状或长柱状,长宽比值为1.5:1~3:1。锆石内部结构清晰,具有较好的振荡环带结构,不含有矿物包裹体(图 4d)。锆石中U和Th含量变化范围相对小,分别为178 × 10-6~521 × 10-6和94 × 10-6~514×10-6,Th/U比值范围是0.51~1.08,平均值为0.75(表 1)。其中锆石2含有老的继承性核,其年龄为363 Ma,Th/U比值为0.77。岩浆结晶锆石的206Pb/238U年龄为(138±5)Ma~(151±5)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算平均年龄为(142.8 ± 1.0)Ma。207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(142.0±1.0)Ma(图 5d),与平均年龄在误差范围内基本一致。
样品10CL521(花岗闪长岩):该样品中的锆石多为长柱状,长宽比值为2:1~3:1。CL图像显示,锆石具有较好的振荡环带结构,不含有矿物包裹体(图 4c)。岩浆结晶锆石的U和Th含量分别为203.4×10-6~1080.7×10-6和46.5×10-6~580.9×10-6,Th/U比值变化范围为0.18~0.98(表 1),平均值为0.61。其中锆石2、5、6、16、和30为老的继承性核,年龄分别为839 Ma、498 Ma、276 Ma、2558 Ma和841 Ma,Th/U平均值为0.96,其余岩浆结晶锆石的206Pb/238U年龄变化于(138 ± 2.5)Ma~(192 ± 2.5)Ma,除去不谐和年龄测点,计算平均年龄为(142.82±0.98)Ma。207Pb/235U- 206Pb/238U比值得出谐和线交点年龄为(142.99±0.98)Ma(图 5c),与平均年龄基本一致。
5.2 锆石Hf同位素特征
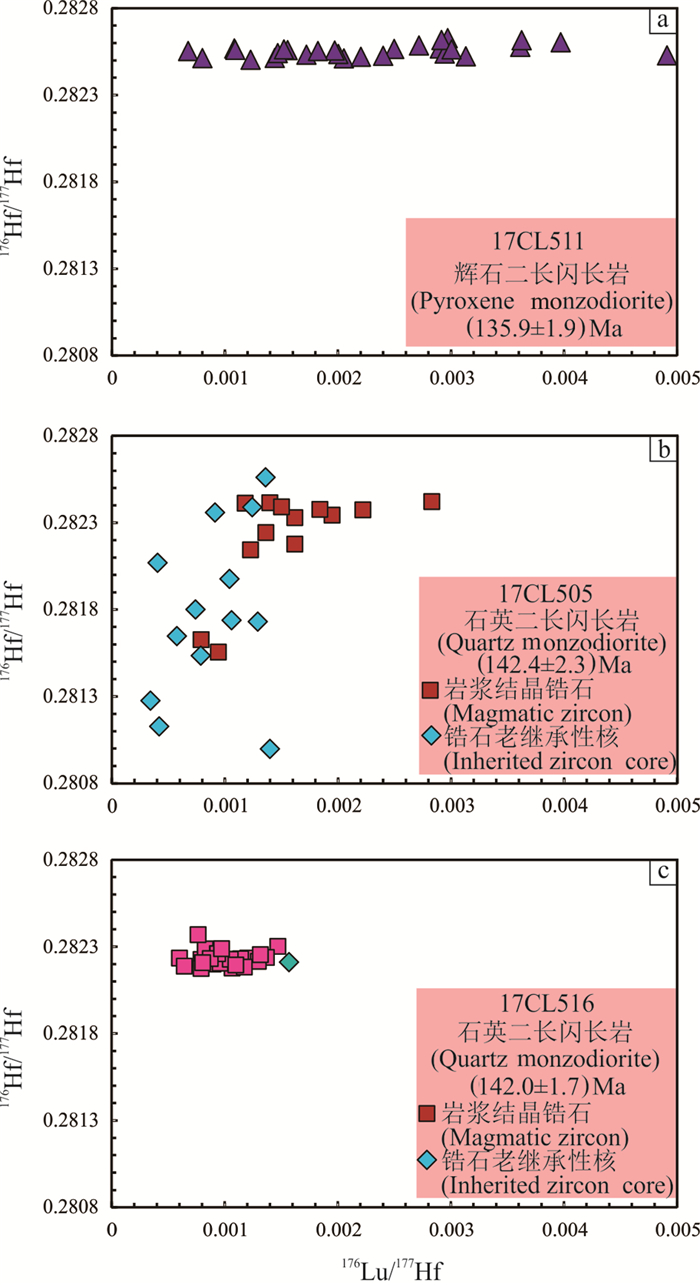
选择3个定年样品(17CL511、17CL505、17CL516)开展Hf同位素分析,结果列于表 2。
表 2 锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果Table 2. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic data of intrusive rocks from the Jiangchong deposit
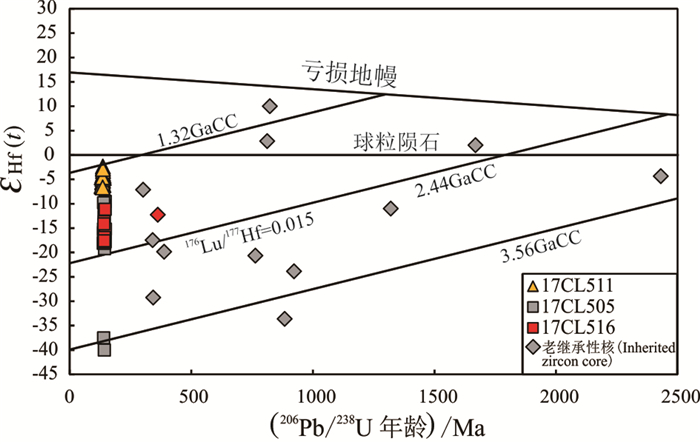
由表 2可见,样品17CL505取自焦冲石英二长闪长岩。26颗锆石中有12颗老的继承性核,剩下的14颗锆石为岩浆结晶锆石。岩浆结晶锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值变化范围是0.000404~0.002829,平均值为0.001489(表 2)。176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围是0.281556~0.282422,平均值为0.282206(表 2,图 6a);岩浆结晶锆石的εHf(t)值均为负值,变化范围是-40.0~-9.5,总平均值为-16.7(表 2),二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)变化范围在690~3558 Ma,平均值为2052 Ma(表 2)。老的继承性锆石核的176Lu/177Hf比值变化范围是0.000341~0.001397,平均值为0.000929(表 2);176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围是0.280998~0.282561,平均值为0.281762(表 2,图 6a);其中锆石4、6和17的εHf(t)值为正值,分别为2.9、2.0和10,平均值为4.9,二阶段模式年龄分别为1048 Ma、1526 Ma、2760 Ma,平均值1778 Ma;其余老的继承性锆石核εHf(t)值均为负值,变化范围是- 33.6~-4.3,总平均值为-18.6(表 2,图 7),二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)变化范围在1747~3853 Ma,平均值为2960 Ma(表 2)。
样品17CL516取自焦冲荷花形石英二长闪长岩。25颗锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值变化范围是0.0006~ 0.001569,176Lu/177Hf比值均小于0.002,总的176Lu/177Hf平均值为0.001014(表 2)。176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围是0.282175~0.282370,平均值为0.282233(表 2,图 6b)。样品中锆石的εHf(t)值均为负值,变化范围是-18.1~-11.1,总平均值为-15.9(表 2,图 7),二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)变化范围在1906~2339 Ma,平均值为2201 Ma(表 2)。
样品17CL511取自焦冲辉石二长闪长岩。28颗锆石中的17个锆石176Lu/177Hf比值小于0.002,平均值为0.001619;剩余11个锆石的176Lu/177Hf的比值大于0.002,平均值0.003337(表 2)。176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围是0.282503~0.282628,平均值为0.282555(表 2,图 6c)。样品中εHf(t)值均为负值,变化范围是-6.6~-2.4,总平均值为-4.9(表 2,图 7),二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)变化范围在1340~1613 Ma,平均值为1502 Ma(表 2)。
5.3 岩石地球化学
对不同的岩石样品进行了主量元素、稀土元素和微量元素的化学分析,结果如表 3。
表 3 铜陵焦冲矿区侵入岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)含量Table 3. Content of major (%) and trace elements (10-6) of whole rock for the intrusive rocks from Jiaochong, Tongling
5.3.1 主量元素
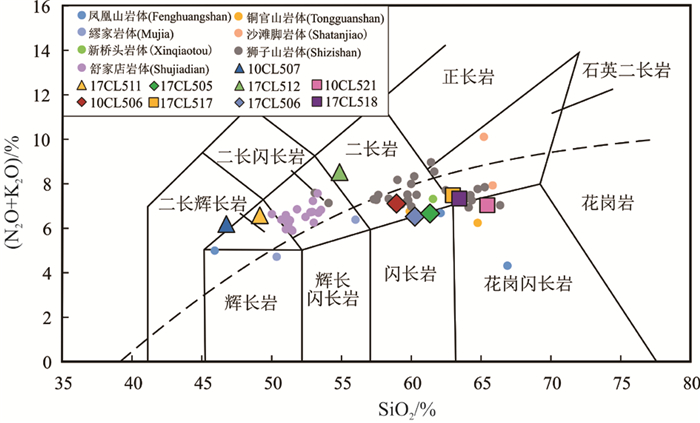
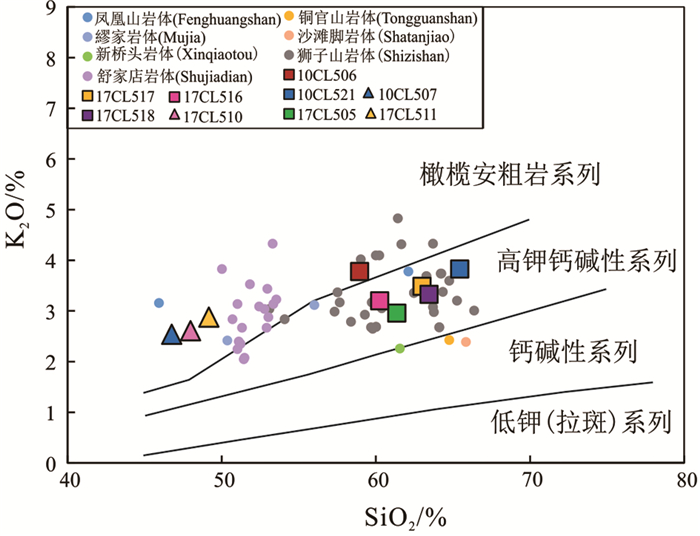
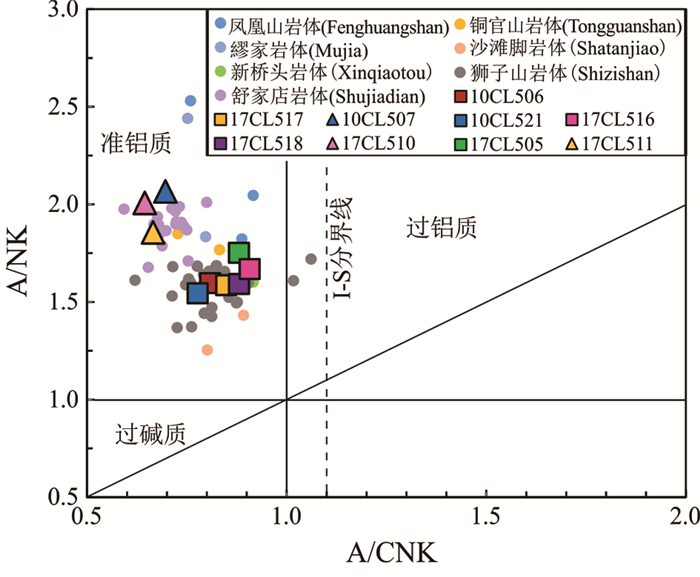
橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩(10CL507、10CL510和10CL511)中的SiO2含量比高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩(10CL506、10CL521、17CL505、17CL516、17CL517和17CL518)中的要低,为46.76%~49.16%(表 3)。里特曼指数(σ)大于4.0(5.82~8.12),在SiO2- (Na2O + K2O)图解(Irvine and Baragar, 1971;Middlemost, 1994)中,辉石二长闪长岩落于二长辉长岩和二长闪长岩中,为碱性系列。高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩的SiO2含量为58.94%~65.44%,里特曼指数小于3.3(2.16~2.87),在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解中,落于花岗闪长岩和二长岩区域,为亚碱性系列(图 8)。从SiO2- K2O图解(Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)可以看出,本区侵入岩样品可划分为高钾钙碱性系列和橄榄安粗岩系列(图 9),两个系列侵入岩的ASI均小于1,介于0.68~0.93,为准铝质(图 10),具有I型花岗岩的地球化学属性(Frost et al., 2001;Frost and Frost, 2008)。根据前人已发表的铜陵地区其他岩体主量元素地球化学数据,结合镜下特征,铜陵地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩为辉长闪长岩、石英二长闪长岩、花岗闪长岩,橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩主要为辉石二长闪长岩、二长岩、石英二长岩(吴才来等, 2010, 2013)。焦冲地区主要岩石类型与其相对应,为石英二长闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和辉石二长闪长岩,分别为高钾钙碱性系列(前两者)和橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩(后者)(图 8,图 9)。
![]() 图 8 岩体岩石地球化学分类TAS判别图解(据Middlemost, 1994; Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
图 8 岩体岩石地球化学分类TAS判别图解(据Middlemost, 1994; Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
(虚线为Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性)三角代表橄榄安粗系列侵入岩样品,方块代表高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩样品。区域上其他岩体的岩石化学数据来自吴才来等(2003,2010,2013a,b),黄顺生(2004),王云健等(2007),瞿泓滢等(2011),赖小东等(2012),陆顺富等(2014)。以下图中数据来源相同Figure 8. Diagram of SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) for the intrusive rocks(after Middlemost, 1994; Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
The dashed line represents boundary between alkaline and subalkaline series. Squares-Intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series in the Jiaochong orefield. Blocks- Intrusive rocks of the high- K, calc- alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield. Dots- Data of other deposits in Tonling area after Wu Cailai et al.(2003, 2010, 2013a, b), Huang Sunsheng (2004), Wang Yunjian et al. (2007), Qu Hongying et al. (2011), Lai Xiaodong et al. (2010), Lu Fushun et al. (2014). The data using in the following diagrams after the same sources![]() 图 9 侵入岩SiO2-K2O图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)(图例同图 8)Figure 9. Diagram of K2O versus SiO2 of the intrusive rocks (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Symbols as for Fig. 8
图 9 侵入岩SiO2-K2O图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)(图例同图 8)Figure 9. Diagram of K2O versus SiO2 of the intrusive rocks (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Symbols as for Fig. 8![]() Figure 10. Diagram of A/NK versus A/CNK (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989). A= Molar Al2O3, N= Molar Na2O, K= Molar K2O, and C= Molar CaO. Symbols as for Fig. 8
Figure 10. Diagram of A/NK versus A/CNK (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989). A= Molar Al2O3, N= Molar Na2O, K= Molar K2O, and C= Molar CaO. Symbols as for Fig. 85.3.2 微量元素
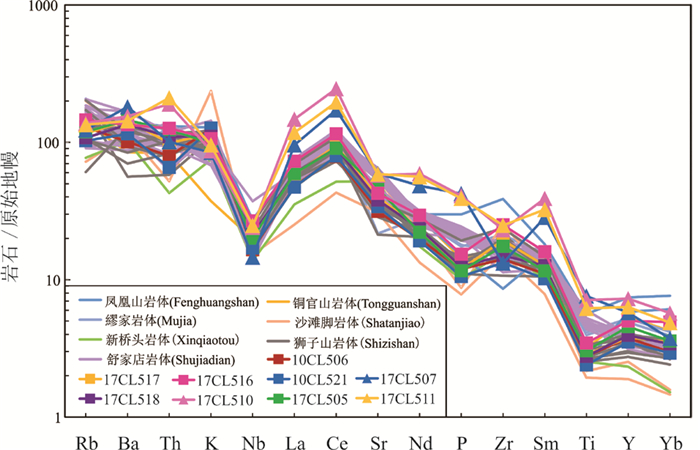
由表 3可见,橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩比高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩含有较高的过渡族元素(表 3)。随着SiO2含量的增加,两系列岩石的TiO2、FeOT、CaO、MgO、P2O5和大多数微量元素如V、Co、Sr、Y的含量减少(表 3);同时Al2O3和Nb、Ni也相对减少,而Na2O、Zr、U、Hf、Ta和Th的含量随SiO2的增加而增加(表 3)。在微量元素蛛网图中,两个系列侵入岩表现出Nb、Ti和P的负异常,及稍微的Sr正异常(图 11)。
![]() 图 11 微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)三角代表橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩样品,方块代表高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩样品,直线代表铜陵地区其他岩体Figure 11. N-MORB normalized trace element spider diagrams of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)Squares-Intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series in the Jiaochong orefield. Blocks- Intrusive rocks of the high- K, calc- alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield. Lines-Data of other deposits in Tongling area
图 11 微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)三角代表橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩样品,方块代表高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩样品,直线代表铜陵地区其他岩体Figure 11. N-MORB normalized trace element spider diagrams of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)Squares-Intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series in the Jiaochong orefield. Blocks- Intrusive rocks of the high- K, calc- alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield. Lines-Data of other deposits in Tongling area5.3.3 稀土元素
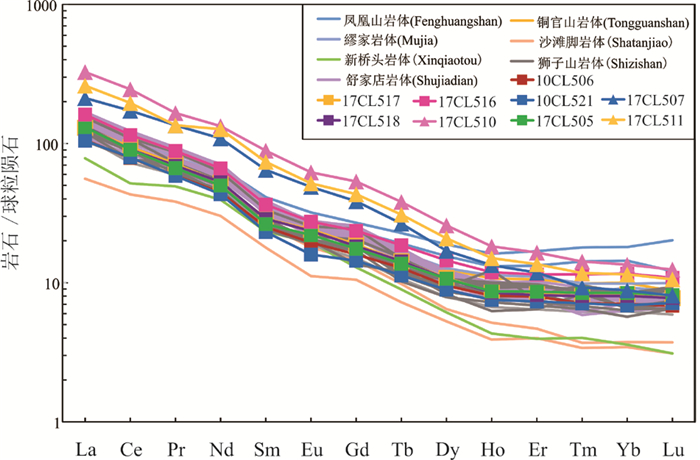
橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩的稀土元素总量为325×10-6~454×10-6,明显高于高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩(147×10-6~221×10-6)(表 3)。稀土元素总量的高低主要取决La、Ce和Sm的含量,因为这些元素是不相容元素,在岩浆结晶的早期阶段,不易进入结晶相而保留在残余岩浆中。橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩的LREE/HREE比值(13~13.4)略高于高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩(11.2~12.2),两者的轻重稀土元素比值远远大于1,显示稀土元素分异程度大,轻稀土富集。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图中,两个系列侵入岩均表现出轻稀土分异明显,重稀土相对分异弱,不具有Eu负异常的特点。从表 3中发现,随SiO2含量增加,两个系列侵入岩La、Ce、Yb和REE减少,LREE/HREE和La/Sm比值增加,说明岩浆演化过程中赋存稀土元素的矿物如磷灰石等发生了分离结晶作用。两个系列侵入岩的稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线相似,均无明显的正负Eu异常的右倾型,与铜陵地区其他岩体稀土元素配分曲线基本一致,但焦冲橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩的稀土配分曲线位置高于其他岩石(由于稀土含量较高)(图 12)。
![]() Figure 12. Chondrite- normalized REE patterns of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Taylor and McLennan, 1985). Symbols as for Fig. 11
Figure 12. Chondrite- normalized REE patterns of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Taylor and McLennan, 1985). Symbols as for Fig. 116. 讨论
6.1 岩浆活动期次
根据前人研究,铜陵矿集区中生代岩浆活动最早开始时间为152 Ma(狄永军等,2005),而高峰期为140 Ma左右,成矿作用与岩浆活动时间相近或略晚(常印佛等,1991;吴才来等, 2003, 2008, 2010a; 杨小男等, 2007, 2008;杜杨松等, 2007b, 2010b;徐晓春等,2008;谢建成等,2008)。表 4是收集的前人发表的区内侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年龄。由表 4可见,铜陵矿集区内橄榄安粗岩系列中的舒家店和曹山辉石二长闪长岩年龄分别为142 Ma、145 Ma(王彦斌等,2004;吴才来等,2010),而白芒山辉石二长闪长岩年龄为138 Ma(吴才来等,2008)。高钾钙碱性系列湖城涧辉长闪长岩年龄为142 Ma,然而,吴才来等(2010)根据铜陵狮子山矿田橄榄安粗岩系列白芒山岩体SHRIMP-RG锆石U-Pb定年结果认为,该区辉石二长闪长质岩浆最早侵位时间可能为142 Ma,138 Ma为后期一次较大规模的岩浆侵入活动,而133 Ma是区域上发生的又一次岩浆构造热事件,因此,本区岩浆活动存在多期次侵位的特点。本文研究的焦冲地区辉石二长闪长岩,锆石U-Pb年龄为136 Ma,比铜陵矿集区其他同类型岩石的年龄小,说明岩浆侵位晚于邻区狮子山矿田白芒山岩体(142 Ma、138 Ma)和曹山岩体的年龄(145 Ma)及舒家店岩体(142 Ma)。由此可见,整个铜陵地区相同类型的岩浆侵位期次不同,反映了岩浆活动具有多期次性的特点。焦冲地区辉石二长闪质岩浆活动可能是铜陵地区橄榄安粗岩系列岩浆活动的较晚一次。
表 4 铜陵地区侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄统计Table 4. Statistics of zircon U-Pb ages of intrusive rocks from Tonling
铜陵地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩年龄为152~ 130 Ma(Wu et al., 2000;杜杨松等,2004;徐夕生等,2004;王彦斌等,2004;狄永军等,2005;楼亚儿等,2006;张达等,2006;杨小男等,2007;谢建成等,2008;吴才来等, 2008, 2010)(表 4),其中的(130±3)Ma为长英岩脉的年龄(狄永军等,2005)。从这些定年数据可以得出,铜陵地区高钾钙碱性系列岩浆活动大约起始于152 Ma,并持续到130 Ma,岩浆活动持续22 Ma。橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩浆侵入起始于145 Ma,延续到136 Ma,岩浆活动持续9 Ma。可见,橄榄安粗岩系列岩浆活动起始的时间晚于高钾钙碱性系列岩浆,但岩浆活动结束的时间早于高钾钙碱性系列岩浆。其中,焦冲矿区高钾钙碱性系列中石英二长闪长岩和花岗闪长岩的年龄均为142 Ma、143 Ma,属铜陵地区早白垩世岩浆活动的产物,而焦冲矿区橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩年龄为136 Ma,是铜陵地区较晚一期的岩浆活动产物。
6.2 岩石成因与岩浆活动构造环境
研究表明,铜陵地区中生代构造运动经历了两次转变:(1)在中三叠世,构造由拉张转为强烈的挤压状态(Deng et al., 2011)。在此期间,岩石圈加厚,并且形成了一系列北东向褶皱;由于盖层中的层间顺层断裂十分发育,并且被纵向深大断层切割,为后期的岩浆侵位和成矿作用提供了构造空间。(2)在晚侏罗世—早白垩世,铜陵地区构造环境从挤压状态转变成拉伸状态,此转换期间加厚的岩石圈发生拆沉作用,导致软流圈物质上涌,引起了强烈的壳幔相互作用,并在莫霍面附近形成一个巨大的深位岩浆房,并发生分异结晶作用(Deng et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2014, 2017)。深位岩浆房的热及其结晶潜热引起上部地壳低熔点的组分发生部分熔融,形成长英质岩浆,在上地壳与中下地壳之间形成浅位岩浆房(Wu et al., 2014)。在构造作用下,岩浆房中的岩浆上升侵位,形成不同岩性的侵入体。
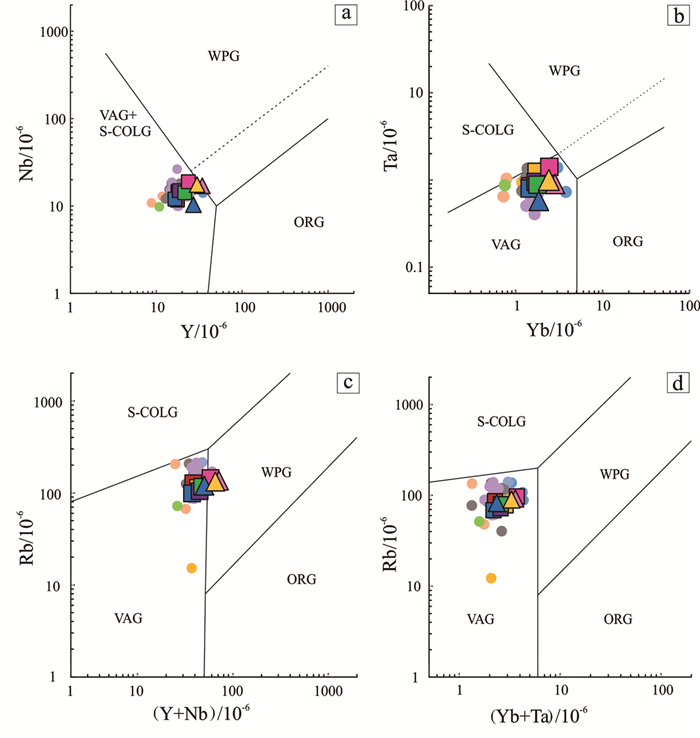
焦冲地区存在高钾钙碱性系列和橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩,前者主要岩石代表为石英二长闪长岩、花岗闪长岩,后者主要代表岩性为辉石二长闪长岩。其中,部分高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩的地球化学特征与埃达克岩相似,主要表现为SiO2>56%,Al2O3>15%,N2O>K2O,富碱、贫镁、高铝、富集大离子亲石元素(Sr、Ba)和LREE,相对亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti、Zr、Hf等),无正负Eu异常、轻稀土分异明显、重稀土分异相对较弱的特点,显示出I型火成岩的特征,而两个系列侵入岩的Sr/Y比值较高,为38.77~104.47,(La/Yb)N值12.95~15.25,又显示出埃达克质岩石的地球化学属性。另外,焦冲地区两个系列侵入岩的ASI<1,在A/CNK-A/NK图解中,均为准铝质岩石,类似于I型花岗岩类(图 8)。并且,岩石具有相似的稀土配分模式和微量元素配分模式,及La/Nb比值变化较大,为1.2~6.3,Zr/Ba比值为0.11~0.26(大多数小于0.2),反映其原始岩浆可能含有地幔成分(Ormerod et al., 1988; DePaolo et al., 2000)。焦冲高钾钙性系列岩石中发现大量的不同年龄的老的继承性锆石,表明古老地壳参与了岩浆的形成过程。从锆石Hf同位素特征来看,焦冲橄榄安粗岩系列辉石二长闪长岩的锆石εHf(t)值为-6.6~-2.4,二阶段模式年龄为1340~1613 Ma,而高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩的锆石εHf(t)值为-40.0~-9.5,二阶段模式年龄为690~3558 Ma,说明两个系列侵入岩均含有富集岩石圈地幔的成分,且橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩含有较多的幔源物质,而高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩含有更多的壳源物质,与前人的研究结果吻合(Müller and Groves, 1993; Wang et al., 2004b; Li et al., 2009b)。从高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩中老的继承性锆石Hf同位素成分来看,εHf(t)负值为主(-33.6~-4.3),tDM2=1747~3853 Ma,也有部分正值(+2~+10),tDM2=1048~2760 Ma,说明高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩源岩以地壳源为主,同时也混合有幔源物质。在Pearce et al. (1984)图解中(图 13),焦冲地区两个系列侵入岩均落于火山弧花岗岩范围内,表明它们具有火山弧岩浆岩的地球化学属性,但并不代表它们中生代就是形成于岛弧环境,而是反映了岩浆源区和岩浆演化过程的特征,这可能是与新元古代华南板块俯冲于扬子板块之下形成富集地幔有关(Wu et al., 2014, 2017)。因为,太平洋板块俯冲带离铜陵地区差不多1000 km,不可能在铜陵地区形成岛弧。有人提出洋脊俯冲模型来解释铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩的特征(Ling et al., 2009, 2011; Liu et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2010),但与岩石的Sr、Nd同位素(ISr= 0.7068 ~ 0.7100, εNd(t)= -8.2 ~ -16.2)和锆石Hf同位素(εHf(t)= -40.0 ~ -2.4)特征不吻合,洋脊俯冲熔融形成的岩石具有ISr<0.706, εNd(t)>0)和锆石Hf同位素(εHf(t)>0)的特征(Wu et al., 2014, 2017)。因此,笔者认为,铜陵地区受太平洋板块俯冲的远程效应影响,加上附近北东向郯庐断裂的走滑活动,导致铜陵地区深部岩石圈的拆沉作用,引发富集的岩石圈地幔部分熔融形成富碱的基性岩浆,这些岩浆在下地壳莫霍面附近聚集形成深位岩浆房,并发生分离结晶作用,形成堆积岩;同时,巨大的深位岩浆房本身产生的热和岩浆结晶潜热使得上部地壳低熔点的组分发生部分熔融形成长英质的浅位岩浆房。随着区域上深大断裂切割地壳由浅变深,深位岩浆房中分异的岩浆一部分上升到浅位岩浆房,发生岩浆混合,形成高钾钙碱性系列石英二长闪长岩和花岗闪长质岩浆,岩体中出现大量的暗色微粒闪长质包体;另一部分深位岩浆房分异的岩浆直接上升到地壳浅部盖层岩石中,形成橄榄安粗岩系列辉石二长闪长岩(Wu et al., 2014, 2017)。焦冲地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩浆活动时间与区域上同类岩浆活动时间相同,但橄榄安粗岩系列岩浆晚于区域上同类岩浆活动。
![]() 图 13 Y-Nb (a)、Yb-Ta (b)、Rb - (Y+Nb)(c)和Rb - (Yb+Ta) (d)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)(VAG+S-COLG—火山弧和同碰撞花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋中脊花岗岩;图例如图 8)Figure 13. Diagrams of Y versus Nb (a), Ta versus Yb (b), Rb versus (Y+Nb) (c), Rb versus (Yb+Ta) (d) (after Pearce et al., 1984)(VAG+S-COLG-Volcanic arc and syn-collision granites; WPG-Within plate granites; ORG-Oceanic ridge granites. Symbols as for Fig. 8)
图 13 Y-Nb (a)、Yb-Ta (b)、Rb - (Y+Nb)(c)和Rb - (Yb+Ta) (d)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)(VAG+S-COLG—火山弧和同碰撞花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋中脊花岗岩;图例如图 8)Figure 13. Diagrams of Y versus Nb (a), Ta versus Yb (b), Rb versus (Y+Nb) (c), Rb versus (Yb+Ta) (d) (after Pearce et al., 1984)(VAG+S-COLG-Volcanic arc and syn-collision granites; WPG-Within plate granites; ORG-Oceanic ridge granites. Symbols as for Fig. 8)7. 结论
(1)LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年结果表明,焦冲地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩年龄约为142 Ma;橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩年龄约为136 Ma。与区域上侵入岩相比,焦冲地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩的年龄与整个铜陵地区同类岩石的年龄相似,而橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩比铜陵地区同类岩石年龄年轻,可能是该系列岩浆活动最晚期的产物,由此也说明铜陵地区两个系列侵入岩具有多期次侵位的特点。
(2)根据锆石CL图像分析及定年结果,焦冲地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩体含有较多的老的继承性锆石核,说明其源岩含有古老的地壳物质。根据岩石地球化学特征,该系列侵入岩具有岛弧I型花岗岩类地球化学属性。同时,该系列岩石中含有大量的暗色闪长质微粒包体,反映了岩浆的混合成因;而橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩体并未发现继承性锆石,但含有大量的辉石堆积岩包体,说明其原始岩浆可能来自富集上地幔,并发生强烈的岩浆分离结晶作用。
-
图 4 锆石CL阴极发光图像
a— 10CL507-辉石二长闪长岩; b—17CL511-辉石二长闪长岩; c—10CL521-花岗闪长岩; d—17CL516-石英二长闪长岩; e—10CL506-石英二长闪长岩; f—17CL505-石英二长闪长岩
Figure 4. Cathodoluminescence images of zircon
a-10CL507-pyroxene monzodiorite; b-17CL511-pyroxene monzodiorite; c-10CL521-granodiorite; d-17CL516-granodiorite; e-10CL506-quartz monzodiorite; f-17CL505-quartz monzodiorite
图 8 岩体岩石地球化学分类TAS判别图解
(据Middlemost, 1994; Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
(虚线为Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性)三角代表橄榄安粗系列侵入岩样品,方块代表高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩样品。区域上其他岩体的岩石化学数据来自吴才来等(2003,2010,2013a,b),黄顺生(2004),王云健等(2007),瞿泓滢等(2011),赖小东等(2012),陆顺富等(2014)。以下图中数据来源相同Figure 8. Diagram of SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) for the intrusive rocks
(after Middlemost, 1994; Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
The dashed line represents boundary between alkaline and subalkaline series. Squares-Intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series in the Jiaochong orefield. Blocks- Intrusive rocks of the high- K, calc- alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield. Dots- Data of other deposits in Tonling area after Wu Cailai et al.(2003, 2010, 2013a, b), Huang Sunsheng (2004), Wang Yunjian et al. (2007), Qu Hongying et al. (2011), Lai Xiaodong et al. (2010), Lu Fushun et al. (2014). The data using in the following diagrams after the same sources图 9 侵入岩SiO2-K2O图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)
(图例同图 8)
Figure 9. Diagram of K2O versus SiO2 of the intrusive rocks (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Symbols as for Fig. 8
图 10 A/CNK-A/NK图解(据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989; 图例同图 8)
Figure 10. Diagram of A/NK versus A/CNK (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989). A= Molar Al2O3, N= Molar Na2O, K= Molar K2O, and C= Molar CaO. Symbols as for Fig. 8
图 11 微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
三角代表橄榄安粗岩系列侵入岩样品,方块代表高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩样品,直线代表铜陵地区其他岩体
Figure 11. N-MORB normalized trace element spider diagrams of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Squares-Intrusive rocks of the shoshonitic series in the Jiaochong orefield. Blocks- Intrusive rocks of the high- K, calc- alkaline series in the Jiaochong orefield. Lines-Data of other deposits in Tongling area
图 12 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图(标准化值据Taylor and McLennan, 1985)(图例同图 11)
Figure 12. Chondrite- normalized REE patterns of the intrusive rocks (normalizing values after Taylor and McLennan, 1985). Symbols as for Fig. 11
图 13 Y-Nb (a)、Yb-Ta (b)、Rb - (Y+Nb)(c)和Rb - (Yb+Ta) (d)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)
(VAG+S-COLG—火山弧和同碰撞花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋中脊花岗岩;图例如图 8)
Figure 13. Diagrams of Y versus Nb (a), Ta versus Yb (b), Rb versus (Y+Nb) (c), Rb versus (Yb+Ta) (d) (after Pearce et al., 1984)
(VAG+S-COLG-Volcanic arc and syn-collision granites; WPG-Within plate granites; ORG-Oceanic ridge granites. Symbols as for Fig. 8)
表 1 焦冲锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年数据
Table 1 Data of zircon La-ICPMS U-Pb dating from granites in Jiaochong

表 2 锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic data of intrusive rocks from the Jiangchong deposit

表 3 铜陵焦冲矿区侵入岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)含量
Table 3 Content of major (%) and trace elements (10-6) of whole rock for the intrusive rocks from Jiaochong, Tongling

表 4 铜陵地区侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄统计
Table 4 Statistics of zircon U-Pb ages of intrusive rocks from Tonling

-
Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 192(1/2):59-79. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/el/00092541/2002/00000192/00000001/art00005
Castillo P R. 2006. An overview of adakite petrogenesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51:257-268. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-0257-7
Castillo P R. 2012. Adakite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 134:304-316.
Chang Yinfu, Liu Xiangpei, Wu Yanchang. 1991. The Copper-Iron Belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Changjiang River[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-379 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chang Yinfu, Liu Xuegui.1983. Stratabound skarn type deposits-a case study of Lower Yangtzi depression within Anhui Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2(1):11-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chang Yinfo, Pei Rongfu, Hou Zengqian, Yang Zhusen. 2017. Geochemical dataset of the Shizishan magmatic fluid system in the Tongling ore concentration area, Anhui Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(S1):49-55(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng Jun, Wang Qingfei, Xiao Changhao, Yang Liqiang, Liu Huan, Gong Qing, Zhang Jing. 2011. Tectonic-magmatic-metallogenic system, Tongling ore cluster region, Anhui Province, China[J]. International Geology Review, 53(5/6):449-476. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/00206814.2010.501538
DePaolo D J, Daley E E. 2000. Neodymium isotopes in basalts of the southwest basin and range and lithospheric thinning during continental extension[J]. Chemical Geology, 169:157-185. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00261-8
Di Yongjun, Wu Ganguo, Zhang Da, Song Biao, Zang Wenshuan, Zhang Zhongyi, Li Jinwen. 2005. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Geochronology of Xiaotongguanshan and Shatanjiao intrusive rocks from Tongling and their petrological significance[J]. Acta Geologinica Sinica, 79(6):804-812 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Du Yangsong, Qin Xinlong, Lee Huanju. 2004. Mesozoic mantle-derived magma underplating in Tongling, Anhui Province:Evidence from megacrysts and xenoliths[J]. Acta Petrol. Mineral., 23(2):109-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200402001.htm
Du Yangsong, Li Shunting, Cao Yi, Qin Xinlong, Lou Yaer. 2007. UAFC-related origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Tongguanshan ore field, Tongling, Anhui Province, east China[J]. Geoscience, 21(1):71-77 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200701008
Frost B R, Frost C D. 2008. A geochemical classification for feldspathic igneous rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 49(11):1955-1969. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egn054
Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, Arculus R J, Ellis D J, Frost C D. 2001. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 42(11):2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
Hanchar J M, Miller C F. 1993. Zircon zonation patterns as revealed by cathodoluminescence and backscattered electron images:Implications for interpretation of complex crustal histories[J]. Chemical Geology, 110:1-13. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90244-D
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Zou Tianren. 2007. Laser ablation-MC-ICPMS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications[J]. Acta Petrol. Sinica, 23(10):2595-2604 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Wenming, Wu Cailai, Gao Dong, Wu Di, Liu Chuanyun, Zeng Quan. 2019. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the intermediate-acid plutons in Shatanjiao ore-field, Tongling, Anhui[J]. Geology in China, 46(4):861-877(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201904016
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8:523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
Lai Xiaodong, Yang Xiaoyong, Sun Weidong, Cao Xiaosheng. 2012. Chronological-geochemical characteristics of the Shujiadian intrusion, Tongling ore cluster field:Its significance to metallogenesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(3):470-485 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201203010.htm
Li Jianwei, Zhao Xinfu, Zhou Meifu, Ma Changqian, Souza Z S, Vasconcelos P. 2009. Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China:U-Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamic implications[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 157:383-409. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0341-x
Ling Mingxing, Wang Fangyue, Ding Xing, Zhou Jibin, Zartman R E, Yang Xiaoyong, Sun Weidong. 2009. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 104(2):303-321. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303
Ling Mingxing, Wang Fangyue, Ding Xing, Zhou Jibin, Sun Weidong. 2011. Different origins of adakites from the Dabie Mountains and the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China:Geochemical constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 53(5/6), 727-740. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2010.482349
Liu Yongsheng, Gao Shan, Hu Zhaochu, Gao Changgui, Zong keqing, Wang, Dongbing. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2):537-571. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010JPet...51..537L/abstract
Lou Yaer, Du Yangsong. 2006. Characteristics and zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in Fanchang, Anhui Province[J]. Geochimica, 35(4):359-366 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200604003
Lu Shunfu, Zeng Jiannian, Li Jinwei, Wu Yafei, Li Xiaofen, Huang Zhiwei. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hucun granodiorite in the Shizishan area, Tongling[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 33(3):355-365 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201403011
Ludwig K R. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4:1-70.
Lü Qingtian, Meng Guixiang, Yan Jiayong, Zhang Kun, Zhao Jinhua, Gong Xuejing. 2019. Multi-scale exploration of mineral system:Concept and progress-A case study in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt[J]. Geology in China, 46(4):673-689(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201904002.htm
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101:635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Middlemost E A K. 1994. Naming materials in magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Müller D, Groves D. 1993. Direct and indirect associations between potassic igneous rocks, shoshonites and gold-copper deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 8(5):383-406. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016913689390035W
Ormerod D S, Hawkesworth C J, Rogers N W, Leeman W P, Menzies M A. 1988. Tectonic and magmatic transitions in the Western Great Basin, USA. Nature, 333 (26):349-353.
Pearce J A, Harris N B M, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jonernal of Petrology, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Pidgeon R T, Nemchin A A, Hitchen G J. 1998. Internal structures of zircons from Archean granites from the Darling Range batholith:Implications for zircon stability and the interpretation of zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 132:288-299. doi: 10.1007/s004100050422
Que Chaoyang, Wu Ganguo, Zhang Da, Zhang Zhihui, Di Yongjun, Fang Hongwei, Yuan Qin. 2013. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of dioritic prophyrite in Jiaochong Au-S deposit, Tongling area, and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 32(6):1221-1235 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J(eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 42: 313-345. https://www.mendeley.com/catalogue/16ceaf7e-712c-3281-b537-f96b72c38763/
Sun Weidong, Ling Mingxing, Yang Xiaoyong, Fan Weiming, Ding Xing, Liang Huaying. 2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization:An overview[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 53(4):475-484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG201004001.htm
Taylor S R, McClennan S. 1985. The Continental Crust:Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 54:209-230.
Vavra G, Schmid R, Gebauer D. 1999. Internal morphology, habit and U-Th-Pb microanalysis of amphibolite-to-granulite facies zircons:geochronology of the Ivrea Zone (South Alps)[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 134:380-404. doi: 10.1007/s004100050492
Wang Qiang, Xu Jifeng, Zhao Zhenhua, Xiong Xiaolin, Bao Zhiwei. 2003. The genesis of the yanshan intrusive rocks in Tonling area, Anhui, and its restriction on the deep dynamic process[J]. Science in China (Series D), 33(4):323-334 (in Chinese).
Wang Yanbin, Liu Dunyi, Zeng Pusheng, Yang Zhusen, Tian Shihong. 2004a. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of gabbro-diorite in the Chaoshan gold deposit and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(4):423-427 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yanbin, Liu Dunyi, Zeng Pusheng, Yang Zhusen, Meng Yifeng, Tian Shihong. 2004b. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of Xiaotongguanshan quartz-dioritic intrusions in Tongling district and its petrogenetic implications[J]. Acta Petrol. Mineral., 23(4):298-304 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200404002
Wu Cailai, Chen Songyong, Shi Rendeng, Hao Meiying. 2003. Origin and features of the Mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusive in Tongling area, Anhui, China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 24 (1):41-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301007.htm
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Guo Heping, Guo Xiangyan, Gao Qianming, Liu Lianggen, Chen Qilong, Le Min, Wooden J L, Mazadab F K, Mattinson C. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of intrusive rocks and hypomagmatic process from Shizishan, Tongling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1801-1812 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200808012
Wu Cailai, Gao Qianming, Guo Heping, Guo Xiangyan, Liu Lianggen, Gao Yuahong, Lei Min, Qin Haipeng. 2010. Petrogenesis of the intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and zircon SHRIMP dating in Tongling, Anhui, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9):2630-2652 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201009011
Wu Cailai, Guo Xiangyan, Wang Cisong, Wu Xiuping, Gao Yuanhong, Lei Min, Qin Haipeng, Liu Chunhua, Li Mingze, Chen Qilong. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating of high-K calc-alkaline intrusive rocks from Tonling:Implication for the tectonic setting[J]. Geochimica, 42(1):11-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201301003.htm
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Paul T, Robinson B, Ronald Frost, Gao Yuanhong, Lei Min, Chen Qilong, Qin Haipeng. 2014. Petrogenesis of high-K, calc-alkaline and shoshonitic intrusive rocks in Tongling area, Anhui Province (eastern China), and their tectonic implications[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 126 (1-2):78-102. doi: 10.1130/B30613.1
Wu Cailai, Chen Songyong, Hao Meiying, Shi Rendeng. 2001. The origin and features of the two intermediate-acid intrusive series in Tongling area, Anhui, China[J]. Continental Dynamics, 6(1):1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dldlx-e200101001
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Wu Di, Zhang Xin, Ernst W G. 2017. Late Mesozoic high-K calc-alkaline magmatism in SE China: The Tongling Example[J]. International Geology Review. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2017.1313137.
Xu Xiaochun, Chen Sanming, Xie Qiaoqin, Bai Lin, Chu Guozheng. 2008. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb dating for the magmatic rocks in Shizishan ore-field of Tongling, Anhui Province, and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 62(4):500-509 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200804007
Xu Xisheng, Fan Qincheng, O'Reilly S Y, Jiang Shaoyong, Griffin W L, Wang Rucheng, Qiu Jiansheng. 2004. Zircon U-Pb dating of the quartz diorite and its enclaves in Tongguanshan, Anhui province:Discussion on the petrologic genesis[J]. Chinese Science Bullatin, 49(18):1883-1891 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-18-1883
Xie Jiancheng, Yang Xiaoyong, Du Jianguo, Sun Weidong. 2008. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Tongling region:Implications for copper-gold mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1782-1800 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200808011.htm
Yuan Honglin, Wu Fuyuan, Gao Shan, Liu Xiaoming, Xu Ping, Sun Deyou. 2003. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb age and REE of Cenozoic pluton in NE China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(14):1511-1520 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2003-48-14-1511
Yao Xiaode, Du Jianguo, Xu Wei, Chen Fang, Tan Dexing. 2012. Regional metallogenic model in Tongling ore cluster are, Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science), 35(7):965-976 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE201207025.htm
Yang Xiaonan, Xu Zhaowen, Xu Xisheng, Ling Hongfei, Liu Suming, Zhang Jun, Li Haiyong. 2008. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and its implication for the temperature of Yanshanian magma in Tongling, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 62(4):510-516 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200804008
Qu Hongying, Chang Guoxiong, Pei Rongfu, Wang Haolin, Mei Yanxiong, Wang Yonglei. 2011. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Shizishan orefield in Anhui Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 30(4):430-439 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Qian Qing. 2001. The characteristics and tectonic-metallogenic significances of the adakites in Yanshan period from eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(2):236-244 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200102008
Zhang Da, Wu Ganguo, Di Yongjun, Zang Wenshuan, Shao Yongjun, Yu Xinqi, Zhang Xiangxin, Wang Qunfeng. 2006. Emplacement dynamics of Fenghuangshan pluton (Tongling, Anhui Province):Constraints from U-Pb SHRIMP dating of zircons and structural deformation[J]. Earth Science, 31(6):823-829 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Taixi, Li XueMing, Zhao Junshen, Zhang Futao. 1987. Geochronology of igneous rocks from Tongguanshan ore area of Anhui Province[J]. Journal of China University of Science and Technology, 17:403-407 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJD198703014.htm
常印佛, 刘湘培, 吴言昌. 1991.长江中下游铁铜成矿带[J].北京:地质出版社, 1-379. 常印佛, 刘学圭. 1983.铜陵地区层控矽卡岩矿床研究[J].矿床地质, 2(1):11-20. 常印佛, 裴荣富, 侯增谦, 杨竹森. 2017.安徽省铜陵矿集区狮子山岩浆流体系统地球化学测试数据集[J].中国地质, 44(S1):49-55. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2017S106&flag=1 杜杨松, 秦新龙, 李铉具. 2004.安徽铜陵地区中生代幔源岩浆底侵作用——来自矿物巨晶和岩石包体的证据[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 23(2):109-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2004.02.002 杜杨松, 李顺庭, 曹毅, 秦新龙, 楼亚儿. 2007.安徽铜陵铜官山矿区中生代侵入岩的形成过程——岩浆底侵、同化混染和分离结晶[J].现代地质, 21(1):71-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.01.008 狄永军, 吴淦国, 张达, 宋彪, 藏文栓, 张忠义, 李进文. 2005.铜陵地区小铜官山和沙滩脚岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究及其岩石学意义[J].地质学报, 79(6):804-812. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.023 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人. 2007. LA-MS-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 23(10):2595-2604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025 黄文明, 吴才来, 高栋, 吴迪, 刘川云, 曾全. 2019.安徽铜陵沙滩脚矿田中酸性侵入岩成因及构造意义[J].中国地质, 46(4):861-877. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190416&flag=1 赖小东, 杨晓勇, 孙卫东, 曹晓生. 2012.铜陵舒家店岩体年代学、岩石地球化学特征及成矿意义[J].地质学报, 86(3):471-485. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201203009 楼亚儿, 杜杨松. 2006.安徽繁昌中生代侵入岩的特征和锆石SHRIMP测年[J].地球化学, 35(4):333-345. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2006.04.001 陆顺富, 曾建年, 李锦伟, 吴亚飞, 李小芬, 黄志伟. 2014.铜陵狮子山地区胡村岩体年代学及地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 33(3):355-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.03.010 吕庆田, 孟贵祥, 严加永, 张昆, 赵金花, 龚雪婧. 2019.成矿系统的多尺度探测:概念与进展——以长江中下游成矿带为例[J].中国地质, 46(4):673-689. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190401&flag=1 阙朝阳, 吴淦国, 张达, 张志辉, 狄永军, 方红薇, 袁琴. 2013.铜陵地区焦冲金硫矿床闪长玢岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].矿床地质, 32(6):1221-1235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.06.009 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华, 熊小林, 包志伟. 2003.安徽铜陵地区燕山期侵入岩的成因及其对深部动力学过程的制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 33(4):323-334. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200304005 王彦斌, 刘郭一, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 蒙义峰, 田世洪. 2004a.安徽铜陵地区幔源岩浆底侵作用的时代——朝山辉石闪长岩锆石SHRIMP定年[J].地球学报, 25(4):423-427. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQXB200404005.htm 王彦斌, 刘郭一, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 蒙义峰, 田世洪. 2004b.铜陵地区小铜官山石英闪长岩锆石SHRIMP的U-Pb年龄及其成因知识[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 23(4):298-304. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/yskwxzz200404002 吴才来, 陈松永, 史仁灯, 等. 2003.铜陵中生代中酸性侵入岩特征及成因[J].地球学报, 24(1):41-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.01.007 吴才来, 董树文, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 高前明, 刘良根, 陈其龙, 雷敏, Wooden J L, Mazadab F K, Mattinson C. 2008.铜陵狮子山地区中酸性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及岩浆作用的深部过程[J].岩石学报, 24(8):1801-1812. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200808012 吴才来, 高前明, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 刘良根, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏. 2010.铜陵中酸性侵入岩成因及锆石SHRIMP定年[J].岩石学报, 26(9):2630-2652. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201009011 吴才来, 郭祥焱, 王次松, 武秀平, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏, 刘春花, 李名则, 陈其龙. 2013.铜陵地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J].地球化学, 42(1):11-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.01.004 徐晓春, 陈三明, 谢巧勤, 柏林, 褚国正. 2008.安徽铜陵狮子山矿田岩浆岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其成因意义[J].地质学报, 8(4):500-509. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.04.007 徐夕生, 范钦成, O'Reilly S Y, 蒋少涌, Griffin W L, 王汝成, 邱检生. 2004.安徽铜官山石英闪长岩及其包体锆石U-Pb定年与成因探讨[J].科学通报, 49(18):1883-1891. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.18.012 谢建成, 杨晓勇, 杜建国, 孙卫东. 2008.安徽铜陵地区中生代侵入岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学及Cu-Au成矿指示意义[J].岩石学报, 24(8):1782-1800. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200808011.htm 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 柳小明, 徐平, 孙德友. 2003.中国东部新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J].科学通报, 48(14):1511-1520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008 姚孝德, 杜建国, 徐卫, 陈芳, 谭德兴. 2012.安徽省铜陵矿集区区域成矿模式[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 35(7):965-976. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hfgydxxb201207024 杨小男, 徐兆文, 徐夕生, 凌洪飞, 刘苏明, 张军, 李海勇. 2008.安徽铜陵狮子山矿田岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄意义[J].地质学报, 82(4):510-516. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200804008 瞿泓滢, 常国雄, 裴荣富, 王浩琳, 梅燕雄, 王永磊. 2011.安徽铜陵狮子山铜矿田岩石的地球化学特征[J].岩矿测试, 30(4):430-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.009 张旗, 王焰, 钱青. 2001.中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 17(2):236-244. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200102008 张达, 吴淦国, 狄永军, 藏文栓, 邵拥军, 余心起, 张祥信, 王群峰. 2006.铜陵凤凰山岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄与构造变形及其对岩体侵位动力学背景的制约[J].地球科学, 31(6):823-829. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2006.06.010 周泰禧, 李学明, 赵俊深, 张富陶. 1987.安徽铜陵铜官山矿田火成岩的同位素地质年龄[J].中国科学技术大学学报, 17(3):403-407. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1987-ZKJD198703014.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 何碧,赵振琯,刘海生,张文斌,陈红旗. 东天山造山带黑尖山地区花岗闪长岩岩石成因及构造意义:来自岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学证据. 科学技术与工程. 2024(25): 10620-10634 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李生喜,何碧,杨博,魏志福,陶刚,甘保平,赵飞,孙平原,赵振琯,黄鹏飞. 南天山地块塔格拉克地区二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征:对壳源岩浆成因和构造背景的限定. 中国地质. 2023(02): 622-639 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 曹积飞,翁凯,Movlanov Jahongir Jurabekovich,Asrorovich Rustamov Akmal,马中平,刘明义. 乌兹别克斯坦中天山金铜成矿特征与找矿潜力评价. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1731-1744 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨波,孙栋华. 东天山某环状熔融岩体航空电磁场特征及深部找矿研究. 物探与化探. 2022(04): 816-823 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: