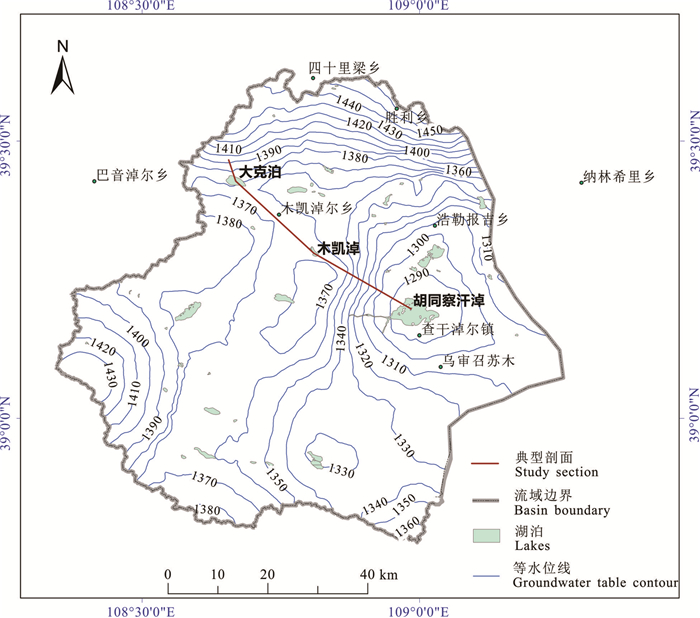
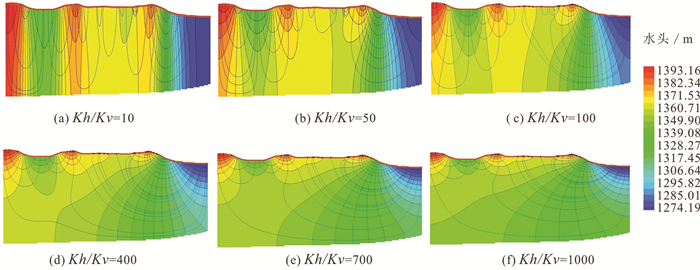
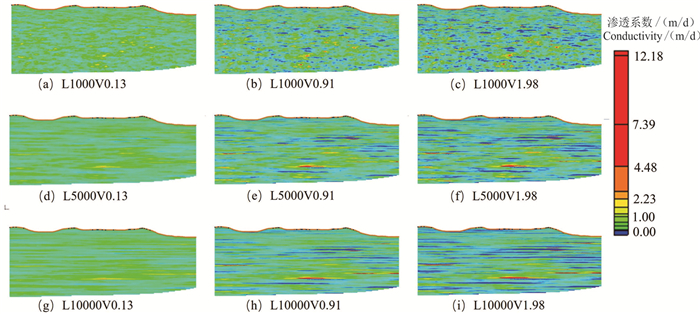
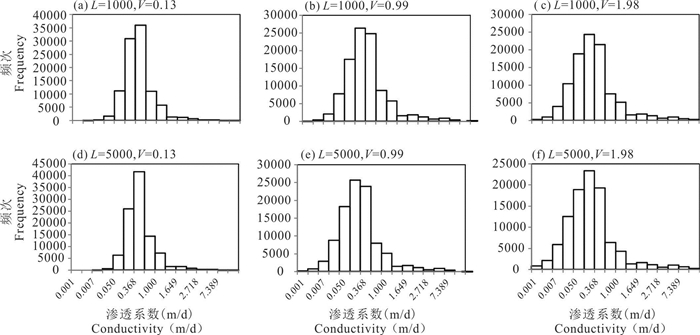
-
摘要:
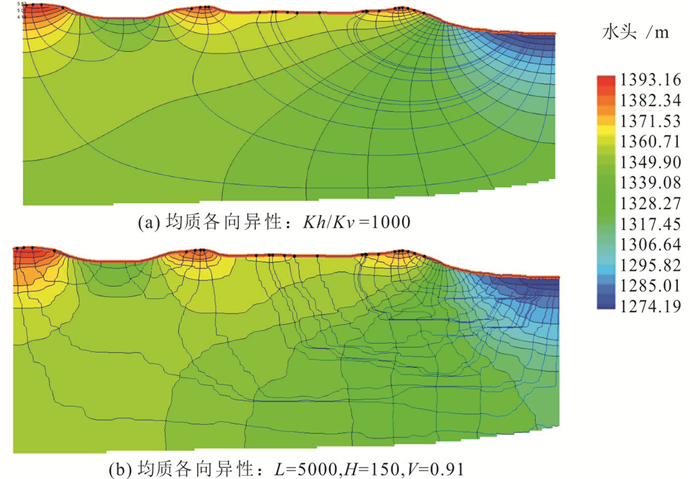
区域尺度上含水层非均质具有复杂的结构性和随机性,难以准确刻画,造成非均质对区域地下水流系统的影响机制研究不够深入。本文以鄂尔多斯盆地白垩系地下水流系统为研究实例,选择典型剖面,采用剖面二维随机数值模拟方法,通过对比不同非均质刻画方法下地下水流场的变化,探讨含水层层状非均质对地下水流系统的影响机制。结果显示,均质条件下模型各向异性(含水层水平和垂向渗透系数比值Kh/Kv)取值为1000时,地下水流场与实际条件较为接近;非均质条件下,渗透系数方差取值0.91,水平相关长度取值5000 m,Kh/Kv取值150时,接近实际条件。研究表明,在大尺度地下水流模拟研究中,采用水平相关长度、渗透系数方差和各向异性值三个变量生成的随机场能很好地刻画含水层的层状非均质特征及其对水流系统的影响控制作用。由于含水层不同尺度层状非均质的叠加效应,采用均质各向异性介质等效概化含水层层状非均质性会造成等效各向异性值偏大失真的效应。
Abstract:Aquifer heterogeneity is an important factor influencing regional groundwater flow patterns. The complex structural and stochastic characteristics of regional-scale aquifer heterogeneity are difficult to characterize,which leads to insufficient understanding of the effects of heterogeneity on groundwater flow systems in practice. In this paper,the Cretaceous groundwater flow system in the Ordos Basin is studied based on the selected typical geological section. Stochastic numerical simulation of the two-dimensional section is employed to analyze the influence mechanism of aquifer layered heterogeneity on groundwater flow systems by comparing the changes of the groundwater flow field under different heterogeneity conditions. The results show that the groundwater flow net is close to the actual conditions when the ratio of horizontal to vertical conductivity (Kh/Kv) is 1000 in model for homogeneous aquifer. It is close to the actual conditions when the variance of conductivity is 0.91,the horizontal correlation length is 5000 m and Kh/Kv is 150 for heterogeneous aquifers. The stochastic simulated aquifer generated by three parameters (i.e.,horizontal correlation length,variance of permeability coefficient,and anisotropy ratio) can well characterize the layered heterogeneity of aquifer and its influence on the groundwater flow systems. Due to the superposition of layered heterogeneity at different scales,equivalent homogeneous,anisotropic model for conceptualizing layered heterogeneous medium in large-scale groundwater flow simulation may lead to a much larger horizontal-to-vertical anisotropy ratio than the ratio between horizontal and vertical correlation scales.
-
1. 引言
四川盆地东部长兴组礁滩相储层为重要的天然气勘探目的层,且主要分布于开江-梁平海槽的东西两侧[1-5]。碳酸盐沉积后作用与储层储集性能的关系十分密切,碳酸盐岩孔隙的形成、增大、减少甚至消失的整个演化历史,除受沉积作用和沉积环境的控制外,更受碳酸盐沉积物的各种沉积后作用的控制[6-8]。环开江-梁平海槽礁滩相储层在埋藏成岩过程中,各种成岩作用对礁滩体孔隙结构影响较大,次生孔隙在长兴组碳酸盐岩中广泛发育,为研究区最主要的储集空间之一,其发育程度直接决定着礁滩体的储集能力。因此,成岩作用研究对于认识川东北环开江-梁平海槽长兴组礁滩相储层的形成演化、控制因素具有很强的借鉴作用。鉴于此,笔者通过前期钻井和最新钻井的岩石宏微观研究和常规物性分析结合前人研究成果,对环开江-梁平海槽长兴组礁滩相储层的特征进行阐述,并进一步探讨储层发育的主要成岩作用,最终为储层的形成机制及有利储层的分布预测提供理论依据。
2. 区域地质背景
开江-梁平海槽位于四川盆地东部,属于扬子板块北缘的一部分(图 1)。晚二叠世龙潭(吴家坪)期在华蓥山以西,由沼泽潮坪相过渡到河流相与康滇古陆相邻,以东为局限海台地相[9]。长兴期大规模海侵,使局限海台地相移至华蓥山以西,沼泽潮坪相和河流相依次向古陆退却,以东为开阔海台地相。受盆地多期构造运动(特别是峨眉地裂运动)影响,开江-梁平海槽发育于中二叠世晚期区域拉张应力背景,形成和发展于晚二叠世长兴期勉略洋扩张和NW向基底断裂活动的断陷期,消亡于早三叠世飞仙关期的勉略洋闭合阶段[10, 11]。基底正断活动通过对古地理的影响来实现对生物礁的控制,生物礁受张性正断层上升盘“断隆”控制,分布于基底断裂古上升盘断阶处,如环开江-梁平海槽台地边缘礁滩体[12]。
长兴末期世界范围内海平面均发生了一次一定幅度的下降事件[13-21],盆地内多个野外露头的长兴组顶部均发现了相关的沉积-成岩响应,如川东涪陵地区二龙口剖面长兴组顶部风化壳岩溶不整合的发现[21],蜀南地区长兴组顶部岩溶不整合的发现[17],形成的岩溶组构(溶沟、溶缝、溶洞及岩溶角砾)表明长兴组在长兴末期受到了表生岩溶水的明显改造。
3. 储层特征
3.1 岩性特征
环开江-梁平海槽长兴组岩性较多,而能成为储层的岩性主要为“花斑状”生屑云岩和生物礁云岩。
(1)“花斑状”生屑云岩为滩相沉积,主要由棘屑滩、藻屑滩和少量砂屑组成,以棘屑滩为主,多与生物礁复合构成礁滩复合体。受早成岩期岩溶[22, 23]影响强烈,表现出典型的“花斑状”特征(图 2-a),其灰白色部分为基岩,灰黑色部分为遭受烃类侵位的岩溶系统[24]。该类岩石由于沉积时具有较高的原始孔隙度,同时有利于后期流体改造,因而具有较好的储集性;宏观上形成大量针孔和溶蚀孔洞,且岩溶系统中溶蚀孔洞明显较基岩发育,为区内最主要的储集岩。
![]() 图 2 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组储集岩及储集空间照片a-龙岗82井4220.11~4220.32 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,深色岩溶系统内溶孔洞发育;b-龙岗84井4507.46~4507.61 m,岩溶改造的生物礁云岩,溶蚀孔洞发育;c-峰003-x3井4845.5~4845.63 m,岩溶改造的生物礁云岩,网状缝发育,见巨晶方解石近全充填溶洞;d-黄龙004-2井3511.9 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,粒间孔、粒间溶孔、晶间孔, 扫面电镜;e-龙岗82井4237.8 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,粒内溶孔,铸体薄片,单偏光;f-池24井-106块,“花斑状”生屑云岩,岩溶系统中的晶间(溶)孔,见渗流粉砂(示顶底构造),铸体薄片,单偏光Figure 2. The photos of reservoir rocks and reservoir spaces of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Longgang 82-4220.11-4220.32m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, dissolved pores developed in dark-colored karst system; b-Longgang84-4507.46-4507.61 m, reef dolomite modified by karstification, dissolved pores developed well; c-Feng003-x3-4845.5-4845.63 m, reef dolomite reformed by karstification, reticular fractures, megacryst calcite almost fully-filling caves; d-Huanglong004-2-3511.9 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, intergranular pores, dissolved intergranular pores and intercrystalline pores, SEM; e-Longgang82-4237.8 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, dissolved intergranular pores, casting thin section, plainlight; f-Chi24-the 106th block, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, (dissolved) intercrystalline pores developed in karst system, vadose silt (geopetal structure), casting thin section, plainlight
图 2 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组储集岩及储集空间照片a-龙岗82井4220.11~4220.32 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,深色岩溶系统内溶孔洞发育;b-龙岗84井4507.46~4507.61 m,岩溶改造的生物礁云岩,溶蚀孔洞发育;c-峰003-x3井4845.5~4845.63 m,岩溶改造的生物礁云岩,网状缝发育,见巨晶方解石近全充填溶洞;d-黄龙004-2井3511.9 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,粒间孔、粒间溶孔、晶间孔, 扫面电镜;e-龙岗82井4237.8 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,粒内溶孔,铸体薄片,单偏光;f-池24井-106块,“花斑状”生屑云岩,岩溶系统中的晶间(溶)孔,见渗流粉砂(示顶底构造),铸体薄片,单偏光Figure 2. The photos of reservoir rocks and reservoir spaces of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Longgang 82-4220.11-4220.32m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, dissolved pores developed in dark-colored karst system; b-Longgang84-4507.46-4507.61 m, reef dolomite modified by karstification, dissolved pores developed well; c-Feng003-x3-4845.5-4845.63 m, reef dolomite reformed by karstification, reticular fractures, megacryst calcite almost fully-filling caves; d-Huanglong004-2-3511.9 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, intergranular pores, dissolved intergranular pores and intercrystalline pores, SEM; e-Longgang82-4237.8 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, dissolved intergranular pores, casting thin section, plainlight; f-Chi24-the 106th block, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, (dissolved) intercrystalline pores developed in karst system, vadose silt (geopetal structure), casting thin section, plainlight(2)生物礁云岩为褐灰色、黑灰色溶孔洞粉-细晶云岩(图 2-b、c),是区内重要的储集岩类之一。通过岩心及镜下观察发现,区内无论是障积-黏结礁还是海绵骨架礁均在不同程度上受岩溶影响,且骨架礁云岩溶蚀孔洞发育程度优于障积-粘结礁云岩。
3.2 储渗空间特征
研究区长兴组储层的储渗空间成因复杂,类型多样,通过145张薄片(海槽东西两侧若干口长兴组储层段取心井,1 m内岩心近等间距选择3张薄片)的详细观察、统计,认为该区的储渗空间有粒间孔、粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔、铸模孔、晶间孔、晶间溶孔、裂缝和溶洞,且以前三者为主要储集空间(图 2,图 3):
(1)粒间孔和粒间溶孔主要发育于“花斑状”生屑云岩中,是区内长兴组储层最主要的储集空间,在统计的145张薄片中,粒间孔和粒间溶孔各占储集空间频率分别为20.7%和25.5%(图 3)。长兴组生屑滩形成后,生屑(主要为棘屑)或生物间保留大量的粒间孔,经压实、胶结作用以后,粒间依然保存一定量的孔隙;残余的粒间孔隙受酸性成岩流体的溶蚀,扩溶形成粒间溶孔。宏观上形成“针孔”(图 2-a、b),面孔率3%~5%,局部可达5%~7%,扫面电镜下,颗粒边界溶蚀现象明显(图 2-d)。
(2)粒内溶孔和铸模孔主要发育在“花斑状”生屑云岩中,在生物礁云岩中也常见,占储集空间频率分别为22.1%和7.6%(图 3)。粒内溶孔为选择性溶解生物体腔或外壳而形成的孔隙(图 2-b、e),当颗粒的外部轮廓保存较好时,则称为印模孔或铸模孔。生屑常为棘皮、有孔虫、蜓等,受生屑颗粒大小及外形的控制,孔径大小不一,本身连通性较差,需要有后期裂缝或(溶扩)残余粒间孔才能与外界连通。
(3)晶间孔和晶间溶孔在区内长兴组白云岩中均有发育,其中以生屑云岩的岩溶系统中最为发育,占储集空间频率分别为6.9%和9%(图 3)。镜下晶间孔呈不规则多边形,孔径0.05~0.15 mm不等,若后期遭受溶蚀则形成具港湾状溶蚀边的晶间溶孔,晶间(溶)孔常为沥青及渗流粉砂部分充填(图 2-f),原岩发生白云石化强改造,原始沉积结构难以识别。
(4)裂缝作为一种特殊的孔隙类型,同时起到了储集空间和渗滤通道两种作用,沿裂缝的溶蚀常常形成各式的溶洞,它和裂缝一起构成裂缝溶洞系统(图 2-c)。在本区长兴组中,压溶缝少见,而构造缝较为常见,多期裂缝相交常有大的孔洞发育,从岩心上看,溶洞大小不一,洞径几毫米至几十厘米不等,巨晶方解石半充填,是长兴组较为重要的储集空间。
3.3 物性特征
通过对研究区遍布海槽东西两侧台缘的数十口长兴组取心井(图 1中只标示了工区内部分取心井)的1156个岩心样品的小直径基质孔隙常规物性分析化验结果得出(图 4),本区长兴组的物性总体表现为中等。孔隙度平均值为2.74%,最小值为0.42%,最大值为16.68%。样品分布随孔隙度增大而递减,孔隙度小于6%的样品占样品总数的百分比超过90%,而孔隙度大于6%的样品仅占总样品数的8.6%左右。长兴组的渗透率相对较差,最小值小于0.001 mD,最大值为599 mD。渗透率小于0.01 mD占到18.4%,渗透率在0.01~0.1 mD样品占总样品总数的18.8%,位于0.1~1 mD范围内的样品占44.1%,只有18.8%的样品渗透率大于1 mD。
将区内长兴组795个孔渗配套岩心样品的孔隙度和渗透率数据绘制散点图(图 5),从孔渗散点图可以看出长兴组孔渗数据分散,无明显规律。既存在“低孔高渗”型储层(对应于A区),渗透率受孔隙度影响不大,具有裂缝渗流特征;也存在“中孔中渗”型储层(对应于C区),表现为渗透率随孔隙度的增加而增加的孔隙型储层特征;介于两个区域之间的B区,为两类的过渡性储层,裂缝和孔隙对储层的影响均较强;而D区为“高孔低渗”型储层,可能为长兴组相对孤立的溶洞或礁格架孔。长兴组复杂的孔渗关系表明,长兴组储层孔隙结构复杂,类型多样,礁滩储层的形成受多种因素影响。
4. 储层成岩作用
碳酸盐岩成岩作用受沉积环境和成岩环境的控制,而成岩环境是在沉积环境的基础上继承和发展起来的,它既受沉积环境的制约,更受埋藏深度、海平面升降变化、地下水介质条件等因素的影响和控制。开江-梁平地区长兴组礁滩储层埋藏较深,成岩作用复杂,经历了多期胶结、压实、白云岩化、溶蚀、构造破裂等成岩作用。这些成岩作用对礁滩储层储渗性能的影响具有双重性,既有充填和破坏孔隙降低储渗性的一面,如胶结充填作用、压实作用等;又有改善原有孔隙或形成新孔隙提高储渗性的一面,如溶蚀作用、白云石化作用等。现将各类成岩作用的机理、产物、期次及其对储层发育的影响简述如下:
4.1 胶结充填作用
胶结充填作用是破坏和降低孔隙度的最主要因素之一,本区碳酸盐岩储层主要胶结充填物为方解石和白云石,其次为少量石膏。根据胶结物的特征和生成环境,区内可识别出八期胶结充填作用。
第一期胶结充填作用发生在海底高能环境的原地生物岩中,礁体水浅光照充足,钻孔藻和真菌发育造成泥晶化作用普遍(图 6-a),生物化学作用促使泥晶方解石围绕着生物骨胳外壁沉淀,因含有比较多的有机质而呈现暗色,为同生期胶结[25, 26]。第二期和第三期胶结物分别为原生孔隙中的纤维状胶结和叶片状胶结,二者呈过渡特征(图 6-a)。它们的结晶习性表明,纤维状方解石的原始矿物成分可能是文石或高镁方解石,叶片状方解石可能是镁方解石[25],其碳、氧同位素值与沉积原始组分灰泥相似,说明它们具有共同的海水来源特征[26]。第四期胶结物为他形-半自形粒状胶结,与叶片状胶结物呈“结构不整合”接触(图 6-a),多在淡水潜流带形成。第五期胶结充填作用多发生在第四期之后,为自形程度较高的白云石胶结(图 6-b)和石英胶结(图 6-c),白云石晶粒发育尖顶,晶面弯曲,见波状消光,可见内生裂隙;石英晶体干净明亮,正低突起,无节理。第六期胶结充填作用发生在白云石胶结之后,在埋藏环境中形成的自生硬石膏胶结充填(图 6-b),硬石膏晶体呈板状和长柱状,3组节理完全,三级鲜艳干涉色。第七期胶结充填作用发生在液烃充注之后,晶体较粗大明亮,多为中-粗晶方解石或巨晶方解石胶结,多形成于深埋藏环境(图 6-d),黑色沥青常充填于白云石晶粒与连晶方解石之间,说明液烃充注发生在连晶方解石胶结充填之前。最后一期为喜山运动导致的构造破裂被方解石胶结充填,在深埋环境下部分构造裂缝被连晶方解石胶结,且连晶方解石切割先期被沥青充填的岩溶系统(图 6-e)。
![]() 图 6 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组储层主要成岩作用照片a-天东74井-4146.64 m,生物礁云质灰岩,同生期泥晶化胶结和随后的三期胶结物,铸体薄片,单偏光;b-天东021-4井-4460.11 m,生物礁云质灰岩,白云石胶结和石膏胶结,普通薄片,正交光;c-云安012-2井-4795.95 m,“花斑状”生屑含硅质云岩,自生石英充填胶结,普通薄片,正交光;d-龙岗82井-4226.99 m,“花斑状”生屑灰质云岩,岩溶系统中的自形白云石和沥青被方解石(红色部分)胶结致密化,普通染色薄片,单偏光;e-龙岗82井-4222.10 m,“花斑状”生屑灰质云岩,连晶方解石胶结切割充填沥青的岩溶系统(黄色箭头所指),普通薄片,单偏光;f-龙岗82井-4231.22 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,压溶缝被泥质、沥青等全充填,铸体薄片,单偏光;g-天东10井-3783.88 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,鞍状白云石,普通薄片,正交光;h-天东10井-3783.88 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,岩溶系统中孔隙(黑色部分)发育,阴极发光下基岩(它形白云石)发暗红光,岩溶系统中自形-半自形白云石具有多结构的阴极发光环带,铸体薄片,阴极发光;i-天东74井-4156.60 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,与早期溶洞相关的埋藏溶蚀,铸体薄片,单偏光Figure 6. Photos of the main diagenesis of reservoir of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Tiandong74-4146.64m, reef dolomitic limestone, syngenetic micritization and the three phases of cements in later period, casting thin section, plainlight; b-Tiandong021-4-4460.11m, reef dolomitic limestone, dolomite cementation and anhydrite cementation, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; c-Yunan012-2-4795.95 m, "piebald"bioclastic siliceous bearing dolomite, authigenic quartz cementation, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; d-Longgang82-4226.99 m, "piebald"bioclastic calcitic dolomite, tight contacts seen between calcite, euhedral dolomites and asphalt developed in karst system after calcite cementation, conventional stained thin section, plainlight; e-Longgang82-4222.10 m, "piebald"bioclastic calcitic dolomite, intergrowing calcite cementation after fracture cutting the karst system where asphalt exists, conventional thin section, plainlight; f-Longgang82-4231.22 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, silts and asphalt filling stylolite, casting thin section, plainlight; g-Tiandong10-3783.88 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, saddle dolomite, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; h-Tiandong10-3783.88 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, massive intercrystalline pores developed in karst system, dark red light of matrix (allotriomorphic dolomites) and clear oscillatory zoning of euhedral and subhedral dolomites in karst system observed in the cathodoluminescence images, casting thin section, cathodoluminescence; i-Tiandong74-4156.60 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, minorburial dissolution exists in the previous caves, casting thin section, plainlight
图 6 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组储层主要成岩作用照片a-天东74井-4146.64 m,生物礁云质灰岩,同生期泥晶化胶结和随后的三期胶结物,铸体薄片,单偏光;b-天东021-4井-4460.11 m,生物礁云质灰岩,白云石胶结和石膏胶结,普通薄片,正交光;c-云安012-2井-4795.95 m,“花斑状”生屑含硅质云岩,自生石英充填胶结,普通薄片,正交光;d-龙岗82井-4226.99 m,“花斑状”生屑灰质云岩,岩溶系统中的自形白云石和沥青被方解石(红色部分)胶结致密化,普通染色薄片,单偏光;e-龙岗82井-4222.10 m,“花斑状”生屑灰质云岩,连晶方解石胶结切割充填沥青的岩溶系统(黄色箭头所指),普通薄片,单偏光;f-龙岗82井-4231.22 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,压溶缝被泥质、沥青等全充填,铸体薄片,单偏光;g-天东10井-3783.88 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,鞍状白云石,普通薄片,正交光;h-天东10井-3783.88 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,岩溶系统中孔隙(黑色部分)发育,阴极发光下基岩(它形白云石)发暗红光,岩溶系统中自形-半自形白云石具有多结构的阴极发光环带,铸体薄片,阴极发光;i-天东74井-4156.60 m,“花斑状”生屑云岩,与早期溶洞相关的埋藏溶蚀,铸体薄片,单偏光Figure 6. Photos of the main diagenesis of reservoir of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Tiandong74-4146.64m, reef dolomitic limestone, syngenetic micritization and the three phases of cements in later period, casting thin section, plainlight; b-Tiandong021-4-4460.11m, reef dolomitic limestone, dolomite cementation and anhydrite cementation, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; c-Yunan012-2-4795.95 m, "piebald"bioclastic siliceous bearing dolomite, authigenic quartz cementation, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; d-Longgang82-4226.99 m, "piebald"bioclastic calcitic dolomite, tight contacts seen between calcite, euhedral dolomites and asphalt developed in karst system after calcite cementation, conventional stained thin section, plainlight; e-Longgang82-4222.10 m, "piebald"bioclastic calcitic dolomite, intergrowing calcite cementation after fracture cutting the karst system where asphalt exists, conventional thin section, plainlight; f-Longgang82-4231.22 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, silts and asphalt filling stylolite, casting thin section, plainlight; g-Tiandong10-3783.88 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, saddle dolomite, conventional thin section, crossed nicols; h-Tiandong10-3783.88 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, massive intercrystalline pores developed in karst system, dark red light of matrix (allotriomorphic dolomites) and clear oscillatory zoning of euhedral and subhedral dolomites in karst system observed in the cathodoluminescence images, casting thin section, cathodoluminescence; i-Tiandong74-4156.60 m, "piebald"bioclastic dolomite, minorburial dissolution exists in the previous caves, casting thin section, plainlight胶结作用是典型的破坏性成岩作用,是导致孔隙度显著减少的主要原因,但早期发育的胶结物堵塞喉道也可以起到使孔隙免遭后期充填的作用,其对孔隙的保存仍具有积极的一面。
4.2 压实、压溶作用
压实、压溶作用对储层具有双重影响。一方面随压实强度的增大,颗粒从漂浮状逐渐过渡为点接触、点线接触、线接触(图 6-f),使得原始储集空间减少,甚至消失;另一方面,早期压实作用使渗滤通道堵塞,有利于原生孔的保存。颗粒岩在沉积期及沉积后一段时间内,以塑性为主,由于上覆沉积物引起的初期压实和胶结作用,颗粒呈点-线接触,甚至是凹凸接触,从而使孔隙呈孤立状,阻碍了成岩作用的进一步进行,有利于原生孔的保存。
此外,压溶缝可以作为流体运移通道,有利于酸性成岩流体和烃类运移,甚至沿压溶缝扩溶形成新的储集空间。区内压溶缝常发育于灰岩及云质灰岩中,多形成于早期胶结物形成之后。缝合线常呈水平状或斜穿层面,缝中常充填黑色的泥质和沥青(图 6-f)。
4.3 白云岩化作用
四川盆地长兴组白云岩成因目前尚存争议。李文平在1989年就认识到长兴组礁岩的白云岩化有多种成因[9];雷卞军等提出礁体的白云岩主体是埋藏成岩环境中形成的[27];郑荣才等及党录瑞等通过岩石学及地球化学的相关分析,认为长兴组白云岩主要有准同生期白云岩与埋藏白云岩两种,后者才是白云岩储集层形成的主要原因,其白云石化流体来自于上覆地层飞仙关组的高盐度海源地层水[28, 29];李志明等也认为储集性能良好的结晶白云岩也形成于埋藏白云石化,但白云石化流体来自于二叠纪的海源地层水[30];成晓啭等通过对兴隆场长兴组白云岩精细的地球化学分析也得到了类似的结论,认为长兴组的白云石化流体来自于同层的泥晶灰岩及泥灰岩孔隙中封存的海源地层水[3];然而,陈琪等通过对盘龙洞剖面详细的野外调查及薄片、扫描电镜等资料的分析,却认为混合水白云石化才是长兴组生屑云岩及礁白云岩形成的主要原因[31];田永净等同样也认为具有储集意义的礁盖白云岩应该为混合水白云岩化形成,仅礁间的泥晶云岩等为准同生期白云岩化所致[32];最近,赵锐等通过川东北长兴组白云岩组构定向与统计特征和白云岩地球化学特征,认为白云化流体应为低温、高盐度的下渗卤水,渗透回流模式应适用于长兴组白云岩化[33, 34]。笔者通过对岩心、薄片资料的精细分析,认为区内长兴组白云岩主要由渗透回流白云岩化作用及构造热液白云岩化作用形成。
岩心及镜下薄片观察表明,区内长兴组白云岩中白云石类型大致有泥-粉晶白云石、细-中晶白云石及中-粗晶鞍状白云石3种。泥-粉晶白云石多发育于礁底或礁间潟湖等低能沉积中,晶粒细小他形,形成的岩石致密少孔,发育少量微裂缝,孔隙度、渗透率均较低,储渗性能差。细-中晶白云石有两种类型,一类为发育于礁底或礁间泻湖等低能沉积中的它形粒状致密白云石,发育少量微裂缝,孔隙度、渗透率均较低,储渗性能差;另一类为发育于礁基/盖生屑滩云岩中,晶粒为中-细晶,自形-半自形,形成的岩石疏松多孔,发育残余粒间孔及溶蚀孔洞,储集性能较好,表现为中孔中渗的特征。鞍状白云石常发育于礁基/盖生屑滩云岩及礁核海绵骨架礁云岩的溶蚀孔洞和较宽的裂缝中,为乳白色、灰白色的亮晶白云石晶体,发育独特的尖顶,可见其晶面弯曲,为弯月刀状,内部可见内生裂纹,正交光下见波状消光(图 6-b、g)。
现代生物礁生态学及沉积学研究表明,生物礁的礁顶、礁间及礁后都常形成局限-半局限的水体环境(如澳大利亚大堡礁)。随着海平面的下降或蒸发作用的增强,其水体盐度逐渐趋于异常,其高镁粒间盐水,在对表层沉积物白云化的同时,由于其密度较大,在重力作用下必然会向下回流渗透。这种向下回流渗透的高镁水,在其穿过下伏的碳酸钙沉积物或石灰岩时,必然会使它们发生白云岩化作用,从而形成白云岩或部分白云化的石灰岩。礁顶、礁间及礁后形成的局限-半局限环境中沉淀的大量灰泥逐渐在富镁水体中被交代为泥晶白云石。区内长兴组发育的礁底及礁间的泥粉晶云岩多为此成因。早期浅埋藏的泥晶灰岩和同生期已经白云岩化的泥粉晶白云岩,在受到上覆富镁的高盐度海水的影响下会进一步形成他形粒状粉-细晶白云石,甚至是他形中晶白云石(图 7)。在重力及盐度梯度的作用下,上覆富镁的高盐度海水向侧向及下伏的高孔隙度颗粒岩中渗透并发生白云石化作用,由于其有较充裕的生长空间,白云石晶粒为中-细晶,甚至是粗晶,自形-半自形,形成的岩石疏松多孔。区内砂糖状白云岩大部分是这一作用形成。
![]() 图 7 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组礁底或礁间潟湖相沉积a-天东021-4井-4540.28 m,粉-细晶白云岩,致密无孔,铸体片,单偏光;b-天东021-4井-4552.70 m,粉-细晶白云岩,裂缝扩溶,铸体片,单偏光Figure 7. Reef base or inter-reefs lagoonal sediments of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Tiandong021-4-4540.28 m, silty-fine dolomite, non-porous, casting thin section, plainlight; b-Tiandong021-4-4541.10 m, silty-fine dolomite, dissolved fissures, casting thin section, plainlight
图 7 环开江-梁平海槽长兴组礁底或礁间潟湖相沉积a-天东021-4井-4540.28 m,粉-细晶白云岩,致密无孔,铸体片,单偏光;b-天东021-4井-4552.70 m,粉-细晶白云岩,裂缝扩溶,铸体片,单偏光Figure 7. Reef base or inter-reefs lagoonal sediments of Changxing Formation around Kaijiang-Liangping Trougha-Tiandong021-4-4540.28 m, silty-fine dolomite, non-porous, casting thin section, plainlight; b-Tiandong021-4-4541.10 m, silty-fine dolomite, dissolved fissures, casting thin section, plainlight实际上,渗透回流白云石化作用对区内颗粒岩类的改造只是一个方面。从裂缝和孔洞中的鞍状白云石以及储层主要发育部位来看,岩溶系统中热液白云石化作用形成的白云岩可能才是最终长兴组的主要白云岩储层,即受早期岩溶作用明显的生屑云岩和生物礁云岩。
研究区地质背景是利于热液白云岩发育的。平面上,区内生物礁发育主要受到基底断裂控制[12],罗冰等在重庆北碚飞仙关组中曾发现大量震积岩的相关沉积构造及序列,并指出华蓥山断裂带强烈活动诱发地震是飞一段震积岩形成的动力机制[35],这说明早印支初期四川盆地基底的正断活动可能仍在继续。而这势必使得分布在基底断裂附近且已浅埋藏的长兴组生物礁滩受到来自基底的热液的影响,礁盖/基生屑滩云岩和礁核海绵骨架礁云岩中发育的鞍状白云石、自生石英和萤石即是基底活动热水上涌的产物,也是热液白云石化作用发生过的最有力证据。沿基底断裂上涌的热水进入生物礁体后,长兴组沉积末期暴露形成的岩溶系统成为高效的输导体系,使得白云石化作用在其中广泛发生,形成大量晶粒较大、自形程度高的白云石,并改造早期渗透回流白云石化形成的白云石晶粒(图 6-h)。然而,在热液供给不足的灰岩地区,随着热液白云岩化的进行,Mg2+浓度逐渐降低,白云岩化作用进行不彻底,将存在白云石向方解石过渡的区域(图 6-b)。
白云岩化作用对区内长兴组储层的影响主要体现在两个方面:白云岩化作用一方面形成一定量的晶间孔隙,虽然微细的晶间孔隙不能对孔隙度改善多少,但却极大地改善储层的渗透性能;另一方面,晶间孔隙的形成为后期溶蚀流体的运移提供通道条件,有利于溶蚀作用发育,为储层的进一步改造奠定了基础。
4.4 岩溶作用
区内长兴组礁滩储层受多期岩溶作用的影响,早成岩期(长兴末期)岩溶作用是其形成的关键。岩溶作用对碳酸盐储层来说,无疑是一种提高孔隙性和渗透性的重要的建设性成岩作用。通过岩心和镜下薄片观察,发现研究区长兴组礁滩储层主要发育各种溶蚀孔洞,储层的最终形成与岩溶作用的参与密不可分。根据沉积特征、孔隙类型及孔隙充填物特征分析,认为研究区长兴组生物礁储层发育多期岩溶作用,主要有同生期岩溶作用、早成岩期岩溶作用和埋藏期岩溶作用。
(1)同生期岩溶作用发生于同生期大气成岩环境中。受次级沉积旋回的控制,长兴组沉积期区内浅水环境发育的生物礁伴随海平面的暂时性相对下降而出露海面或处于淡水透镜体内形成“礁岛”。在淋滤作用下,“礁岛”内发生选择性溶蚀,形成大小不一、形态各异的各种孔隙和溶洞。它多以选择性溶蚀由文石和高镁方解石矿物组成的颗粒或第二、三期胶结物,形成粒内溶孔、铸模孔和粒间溶孔(图 2-d、e)。
(2)早成岩期(长兴末期)岩溶作用是储层形成的关键。长兴末期世界范围内海平面均发生了一次一定幅度的下降事件[13-21],区内礁基/盖生屑滩云岩、礁核障积-粘结或海绵骨架礁云岩、礁底及礁间细粒碳酸盐岩均受到了不同程度的岩溶改造,形成特征的岩溶组构。
礁基/盖生屑滩云岩发育由灰白色的基岩和灰黑色的岩溶系统两部分组成的花斑岩溶(图 2-a)。岩溶系统中充填渗流粉砂(图 2-f),是大气淡水渗流带成岩环境的标志。此外,岩溶系统内颗粒高度离散,发育大量残余粒间孔、晶间孔及大直径溶蚀孔洞(图 2-f,图 6-h),储集性能优异,正是早成岩期岩溶改造的结果。礁核障积-粘结或海绵骨架礁云岩的花斑岩溶发育程度不及礁基/盖生屑滩云岩。由于处于较强水动力条件下的礁核孔隙中,水体交换频繁,有利于海水中二氧化碳脱气作用的发生,加之藻类及微生物等的作用,其极易早成岩并形成坚硬的骨架,且骨架孔隙中的胶结充填作用也相当强烈,这些因素均不利于表生岩溶水的后期改造,因而其花斑组构的发育程度不及礁基/盖生屑滩云岩,储集性能也次于生屑云岩。礁底及礁间的细粒碳酸盐岩(泥晶灰岩、泥晶云岩、细粉晶云岩),因其致密的岩性不利于后期表生岩溶水的改造,所以花斑组构最不发育,其储集性能也是最差的。综上,区内长兴组礁滩储层的储集性能主要受到早成岩期岩溶改造程度的控制,因此早成岩期(长兴末期)岩溶作用才是储层形成的关键。
(3)埋藏期溶蚀作用主要与上二叠统烃源岩成油期产生的有机酸有关,时间大致在三叠纪末-中侏罗世末,埋深2000~4500 m[36, 37]。该期溶蚀作用对储层整体的储集面貌改变不大,以对孔隙或溶洞的少量溶蚀为主,且在溶蚀孔洞中形成沥青(图 6-i)。
4.5 构造破裂作用
区内长兴组生物礁中构造破裂发育,裂缝、微裂缝在岩心及薄片中常见(图 2-c)。构造破裂对储层具有两个方面的影响:直接影响是网状裂缝沟通相对孤立的孔隙,形成相对连通的储渗体系统,进而改造储层;间接影响是裂缝为埋藏溶蚀提供溶蚀通道,沿裂缝发育溶蚀,形成扩溶的裂缝孔洞系统,进而起到改善储层的作用。对于区内长兴组礁滩型储层,构造破裂对储层的最大影响是其与埋藏溶蚀作用的共生。表现为两种形式:一种是储集岩是低孔隙度的灰岩,先期孔隙层不发育,由于断裂-裂缝系统的发育,酸性流体仅能在直接的裂缝系统附近产生扩溶,形成孔洞-裂缝型储层,这类储层单个储渗体系规模较小,虽然可以短暂获得高产,但是产能衰减快,勘探效益低下;另一种是具有先期保存孔隙的礁、滩储层,由于断裂-裂缝系统的沟通,使生物礁储层得到优化,加上沿裂缝的溶蚀作用的进一步叠加改造,形成优质储层。
5. 成岩演化序列
至此,不难重建出区内长兴组礁滩储层成岩演化的大致过程(图 8):首先,同生期海底胶结之后,准同生期礁间、礁顶泻湖等局限-半局限环境由于相对海平面下降,蒸发作用加强,形成高盐度海水使得其底部灰泥发生云化,并侧向及向下将早期浅埋藏的泥晶灰岩和同生期已经白云岩化的泥粉晶白云岩,进一步云化形成他形粒状粉-细晶白云岩,甚至是他形中晶白云岩,并将高孔隙度颗粒岩云化,形成自形-半自形中-细晶,甚至是粗晶白云岩。之后,长兴末期海退导致长兴组生物礁发生表生暴露,此时二叠纪末扬子地区位于赤道附近的低纬度热带地区[38-42],往往为多雨的湿热气候,强烈的大气淡水淋滤作用形成特征的花斑岩溶,并将同生、准同生期形成的石膏溶蚀殆尽,形成的CaSO4流体沿同时期岩溶系统通道进入一些半封闭的溶蚀孔洞并保存下来。随后,浅埋藏期沿基底断裂上涌的热液进入生物礁体,并沿岩溶系统发生白云岩化作用,形成了现今长兴组白云岩面貌的雏形;在继续埋藏压实的过程中,之前保存于溶蚀孔洞中的CaSO4流体饱和并沉淀出自生石膏。在三叠纪末-中侏罗世末,上二叠统烃源岩成熟排烃,造成液态烃侵位,并发生与成油期产生的有机酸相关的埋藏溶蚀。在进一步深埋的过程中,发生深埋环境下的铁方解石胶结。最后,喜山运动导致岩层破裂,在深埋环境下部分裂缝被连晶方解石胶结。
6. 结论
(1)四川盆地东部长兴组礁滩相储层为重要的天然气勘探目的层,其储集性能较好。储集岩主要为溶蚀孔洞发育的“花斑状”屑云岩和生物礁云岩,储层孔隙结构复杂,类型多样。储层在成岩阶段经历了多期胶结、压实、白云岩化、溶蚀、构造破裂等成岩作用。
(2)成岩作用是储层形成的控制因素。海底早期胶结和浅埋藏压实作用使得原生孔隙大幅度减少,早成岩期(长兴末期)岩溶作用是储层形成的关键,随后的热液白云岩化作用极大地改善储层的渗透性能。原生粒间孔和早成岩期岩溶及热液白云岩化作用形成的早期孔隙不仅是现今储层储集空间的雏形,也基本决定了储层的最终面貌。
-
-
Ameli A A, McDonnell J J, Bishop K. 2016. The exponential decline in saturated hydraulic conductivity with depth:A novel method for exploring its effect on water flow paths and transit time distribution[J]. Hydrological Processes, 30(14):2438-2450. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10777
Begg S H, King P R. 1985.Modelling the effects of shales on reservoir performance: Calculation of effective vertical permeability[C]//SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers.
Bethke C M. 1989. Modeling subsurface flow in sedimentary basins[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 78(1):129-154. doi: 10.1007/BF01988357
Cai Yuemei, Wang Wenxiang, Zhang Mingjiang, Yin Xiulan, Cai Wutian, Wang Ruijiu, Li Wenpeng. 2016. An analysis of the groundwater flow system based on environmental isotopes in Turpan basin[J]. Geology in China, 43(4):1439-1445(in Chinese).
Cao G, Han D, Currell M J, Zhang C. 2016. Revised conceptualization of the North China Basin groundwater flow system:Groundwater age, heat and flow simulations[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 127:119-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.05.025
Cardenas M B, X W Jiang. 2010. Groundwater flow, transport, and residence times through topography-driven basins with exponentially decreasing permeability and porosity[J]. Water Resouras Research, 46, W11538.
Chen Mengxiong, Ma Fengshan. 2002. China Groundwater Resources and Environment[M].Beijing:Seismological Press (in Chinese).
Deutsch C. 1989. Calculating effective absolute permeability in sandstone/shale sequences[J]. SPE Formation Evaluation, 4(03):343-348. doi: 10.2118/17264-PA
Fogg G E. 1986. Groundwater flow and sand body interconnectedness in a thick, multiple-aquifer system[J]. Water Resources Research, 22(5):679-694. doi: 10.1029/WR022i005p00679
Fogg G E.1986. Groundwater flow and sand body interconnectedness in a thick, multiple-aquifer system[J]. Water Resources Research, 22(5):679-694. doi: 10.1029/WR022i005p00679
Freeze R A, Witherspoon P A. 1967. Theoretical analysis of regional groundwater flow:2. Effect of water-table configuration and subsurface permeability variation[J]. Water Resources Research, 3(2):623-634. doi: 10.1029/WR003i002p00623
Gleeson T, Manning A H. 2008. Regional groundwater flow in mountainous terrain:Three-dimensional simulations of topographic and hydrogeologic controls[J]. Water Resources Research, 44(10):. doi: 10.1029/2008WR006848
Haitjema H M, S Mitchell-Bruker. 2005. Are water tables a subdued replica of the topography?[J]. Ground Water, 43(6):781-786. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.00090.x.
Hao Z, Kang S. 2006. Current situation and development trend of numerical simulation of groundwater system[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 26(1):77-81. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292779887_Current_situation_and_development_trend_of_numerical_simulation_of_groundwater_system
Hou Guangcai, Zhang Maosheng. 2008.The Research of Groundwater Exploration in the Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
James R Craig. 2008. Analytical solutions for 2D topography-driven flow in stratified and syncline aquifers[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 31:1066-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.04.011
Jiang X W, Wan L, Ge S, Cao G L, Hou G C, Hu F S, Wang X S, Li H L, Liang S H. 2012. A quantitative study on accumulation of age mass around stagnation points in nested flow systems[J]. Water Resources Research, 48(12):1-14.
Jiang X W, X S. Wang L. Wan, S Ge. 2011. An analytical study on stagnation points in nested flow systems in basins with depthdecaying hydraulic conductivity[J]. Water Resources Research, 47:1-16. doi: 10.1029/2010WR009138
Koltermann C E, Gorelick S M. 1996. Heterogeneity in sedimentary deposits:A review of structure-imitating, process-imitating, and descriptive approaches[J]. Water Resources Research, 32(9):2617-2658. doi: 10.1029/96WR00025
Lee S Y, Carle S F, Fogg G E. 2007. Geologic heterogeneity and a comparison of two geostatistical models:Sequential gaussian and transition probability-based geostatistical simulation[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 30(9):1914-1932. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.03.005
Liang X, Quan D, Jin M, Liu Y, Zhang R Q. 2013. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow patterns using flux as upper boundary[J]. Hydrological Processes, 27:3475-3483. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9477
Liang Xin, Zhang Renquan, Niu Hong, Jin Menggui, Sun Ronglin. 2012. Development of the theory and research method of groundwater flow system[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 31(5):143-150 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo Jie, Wang Wenke, Duan Lei, Li Ying, Zhang Zaiyong. 2020.Dynamic analysis of groundwater level in Yinchuan Plain[J]. Northwestern Geology, (1):195-204(in Chinese with English abstract).
Marklund L, Wörman A. 2007. The impact of hydraulic conductivity on topography driven groundwater flow[J]. Publs Inst. Geophys Pol Acad Sc E-7:159-167.
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tóth J. 1963. A theoretical analysis of groundwater flow in small drainage basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 68(16):4795-4812. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i016p04795
Tóth J. 1999. Groundwater as a geologic agent:An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 7(1):1-14.
Winter T C. 1999. Relation of streams, lakes, and wetlands to groundwater flow systems[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 7(1):28-45.
Yeh T C J, Jin M, Hanna S. 1996. An iterative stochastic inverse method:Conditional effective transmissivity and hydraulic head fields[J]. Water Resources Research, 32(1):85-92. doi: 10.1029/95WR02869
Zech A, Zehner B, Kolditz O, Attinger, S. 2016. Impact of heterogeneous permeability distribution on the groundwater flow systems of a small sedimentary basin[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 532:90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.030
Zhang Eryong, Tao Zhengping, Wang Xiaoyong, Cui Xudong, Yin Lihe. 2012. A study of vegetation response to groundwater on regional scale in northern Ordos Basin based on structure chart method[J]. Geology in China, 39(3):811-817(in Chinese with English abstract).
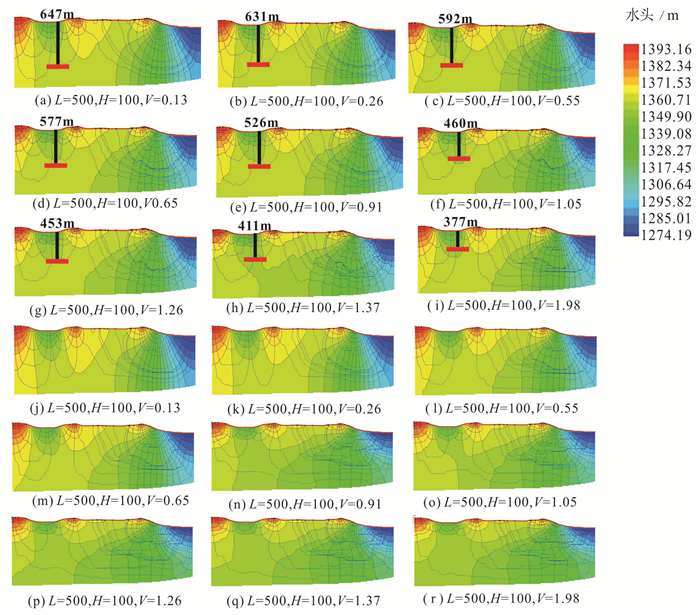
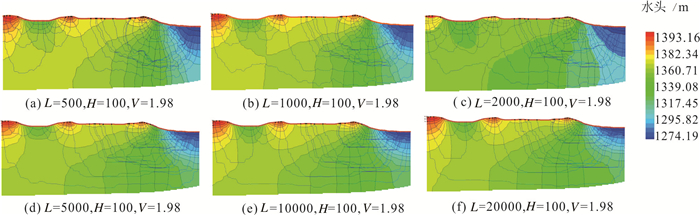
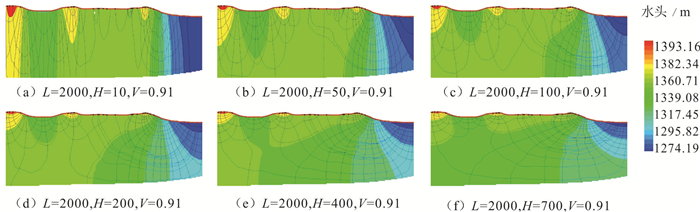
Zhang Jun, Hou Guangcai, Zhao Zhenhong, Yin Lihe, Wang Dong. 2012. Analysis of structural control factors for groundwater flow system based on numerical simulation of profile-Case study of typical northern profile of Ordos Cretaceous Basin[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 32(2):18-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jun, Hou Rongzhe, Yin Lihe, Ma Hongyun, Huang Jinting. 2017. Formation and influencing factors of regional groundwater flow systems[J].Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 44(4):8-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jun, Yin Lihe, Hou Guangcai, Jiang Xiaowei. 2014. A recent review of regional groundwater flow theory——International symposium on regional groundwater flow theory, applications and future development[J]. Northwestern Geology, (3):200-204(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Renquan, Liang Xin, Jin Menggui, Zhou Aiguo, Sun Ronglin. 2005. The trends in contemporary hydrogeology[J]. Hydrogeology& Engineering Geology, 32(1):51-56(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Renquan, Liang Xin, Jin Menggui, Wan Li, Yu Qingchun. 2011.Fundamentals of Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Zhou Yangxiao, Li Wenpeng. 2009. Modeling of regional groundwater flow[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 36(1):1-10(in Chinese with English abstract).
蔡月梅, 王文祥, 张明江, 殷秀兰, 蔡五田, 王瑞久, 李文鹏. 2016.基于环境同位素分析吐鲁番盆地地下水流系统[J].中国地质, 43(4):1439-1445. 陈梦熊, 马凤山. 2002.中国地下水资源与环境[M].北京:地震出版社. 郝治福, 康绍忠. 2006.地下水系统数值模拟的研究现状和发展趋势[J].水利水电科技进展, 26(1):77-81. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsdkjjz200601023 侯光才, 张茂省. 2008.鄂尔多斯盆地地下水勘查研究[M].北京:地质出版社. 梁杏, 张人权, 牛宏, 靳孟贵, 孙蓉琳. 2012.地下水流系统理论与研究方法的发展[J].地质科技情报, 31(5):143-150. 罗杰, 王文科, 段磊, 李英, 张在勇. 2020.银川平原地下水位变化特征及其成因分析[J].西北地质, (1):195-204. 孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽. 2018.哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J].中国地质, 45(6):1128-1141. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180604&flag=1 张二勇, 陶正平, 王晓勇, 崔旭东, 尹立河. 2012.基于植被结构分析法的生态植被与地下水关系研究——以鄂尔多斯盆地内蒙古能源基地为例[J].中国地质, 39(3):811-817. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120323&flag=1 张俊, 侯光才, 赵振宏, 尹立河, 王冬. 2012.基于剖面数值模拟的地下水流系统结构控制因素——以鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地北部典型剖面为例[J].水利水电科技进展, 32(2):18-22. 张俊, 尹立河, 侯光才, 蒋小伟. 2014.区域地下水流理论最新进展——区域地下水流理论、应用与发展国际研讨会综述[J].西北地质, (3):200-204. 张俊, 侯荣哲, 尹立河, 马洪云, 黄金廷. 2017.盆地地下水流系统形成与影响因素分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 44(4):8-14. 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 周爱国, 孙蓉琳. 2005.当代水文地质学发展趋势与对策[J].水文地质工程地质, 32(1):51-56. 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 万力, 于青春. 2011.水文地质学基础[M].北京:地质出版社. 张志远, 蒋小伟, 王俊智, 万力. 2016.基于二维和三维模型的盆地典型剖面流场对比[J].水文地质工程地质, 43(3):1-6. 周仰效, 李文鹏. 2009.区域地下水流模拟[J].水文地质工程地质, 36(1):1-10. -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 张银国,陈建文,龚建明,梁杰,廖晶,王建强,杨长清,赵青芳,孙晶,杨传胜,雷宝华,袁勇. 青岛海洋地质研究所45年来海域油气资源调查进展. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(03): 1-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱清波,王存智,靳国栋,赵希林,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿构造混杂岩露头解剖及其对华南新元古代洋盆演化的启示. 地质通报. 2022(Z1): 388-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 谭满堂,龙文国,魏运许,邓新,田洋,王晶,金巍,徐大良,徐扬,黄皓. 湘东北仓溪岩群锆石U-Pb年龄及新元古代弧盆系演化. 华南地质. 2022(01): 120-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾庆友,林忠良,谢芳军,吴忠如,潘世语. 江西石坞金矿玄武岩地球化学特征及构造意义. 有色金属(矿山部分). 2021(04): 92-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱清波,靳国栋,高天山. 赣东北樟树墩蛇绿混杂岩带1:50000专题地质图数据库. 中国地质. 2021(S2): 66-77 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 任雪斌,李学森. 赣东北樟树墩-西湾蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩和玄武岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 四川地质学报. 2020(03): 364-370 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘婷,郑有业,王朋冲,杨伟光,郭统军. 豆荚状铬铁矿床成矿地球化学指标对比和成矿作用讨论. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2019(01): 176-183+194 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘婷,郑有业,郭统军. 大中型豆荚状铬铁矿床地球化学特征研究. 地质科技情报. 2019(02): 217-225 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郑涛,黄德志,崔建军,徐益龙,周炜鉴. 皖南伏川SSZ型蛇绿岩的地球化学特征与构造意义. 矿物学报. 2019(03): 281-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 兰锐,徐梦婧. 中国造山带地幔橄榄岩的研究现状. 内蒙古石油化工. 2018(10): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: