Relationship between Jinshajiang-Honghe strike-slip fault and Cu-Au polymetallic mineralization of alkaline-rich porphyry
-
摘要:研究目的
金沙江—红河富碱斑岩及铜金多金属成矿带展布于青藏高原东南缘,北部产有玉龙超大型铜钼矿床,中部发育北衙超大型金多金属矿床,在南部的金平(铜厂)地区,铜钼(金)多金属成矿亦显现潜力,是中国西南地区最重要的铜金矿集区之一,已成为东特提斯成矿域内的研究热点。
研究方法本文在该富碱岩浆成矿带内长期工作的基础上,结合已有的研究,概述了该带内典型富碱斑岩和矿床特征。
研究结果富碱斑岩总体上以二长花岗斑岩和石英正长斑岩为主,显示富集碱质(K2O+Na2O含量高)、铝、轻稀土元素及亏损重稀土元素和高场强元素的特性,相似的Sr-Nd同位素组成显示源区主要为下地壳物质;同时在野外调查工作的基础上,讨论了区域走滑构造之次一级构造的发育特征及其对本区成岩成矿的制约,并进一步总结了东特提斯成矿域内受控于金沙江—红河区域走滑深大断裂及其次级构造活动的“区域构造-富碱岩浆-铜金多金属”成矿作用。
结论通过上述三地(玉龙、北衙、铜厂)主要矿区内主控岩断裂构造野外特征观察研究,提出金沙江—红河深大断裂的次一级近北西向构造控制了本区富碱岩浆活动及铜金多金属成矿的认识。
-
关键词:
- 富碱斑岩 /
- 构造-岩浆-成矿耦合 /
- 成矿系统 /
- 金沙江-红河走滑断裂 /
- 矿产勘查工程
创新点: 系统梳理了东特提斯成矿域金沙江—红河走滑构造带内典型富碱斑岩和矿床特征;通过野外详实的构造与成岩成矿关系的调查研究,提出研究区金沙江—红河深大断裂的次一级近北西向(或南北向)构造控制了富碱岩浆活动及铜金多金属成矿的认识。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyry Cu-Au polymetallic metallogenic belt, which produces numbers of large-scale Cu-Au deposits including the Yulong at the north, the Beiya in the middle and the Tongchang at the south, for example, has becoming one of the most productive ore clusters and research focus in the east Tethys domain.
MethodsBased on long-term integrated field investigations and published data analysis, we summarized the characteristics of the typical deposits and the alkaline-rich porphyry.
ResultsThe alkaline-rich porphyry mainly consists of monzonitic granite porphyry and quartz syenite porphyry, showing high contents of K2O-Na2O, Al2O3, LREE and deficit in HREE and HFSE. Similar Sr-Nd isotopic composition indicates that the source area is mainly lower crust material. The development characteristics of regional strike-slip structures and their constraints on diagenesis and mineralization in this area are also discussed, and a "regional structure→alkaline-rich magma→Cu-Au polymetallic" mineralization process controlled by the deep Jinshajiang-Honghe strike-slip fault and its secondary structure activities in the east Tethys metallogenic domain is further summarized.
ConclusionsThrough field observation and study on the main faults in the three typical areas, we suggest that the alkaline-rich magma and related Cu-Au mineralization were primarily controlled by the secondary northwestward faults of the regional Jinshajiang-Honghe strike-slip fault.
-
1. 引 言
“云贵煤炭基地”是中国南方的大型煤炭基地,主要分布于云南省中东部——贵州省中西部地区(丁易,2007),受地形限制,普遍存在煤矿与耕地交错分布的情况,随着煤炭产业的发展,引发的环境问题也逐步凸显(丁振华等,2009;Wang et al., 2020;李继华等,2021),在煤矿开采、运输、洗选、燃煤、煤矸石堆存过程中,重金属通过淋滤、废水排放、粉尘沉降等途径进入周边耕地,改变土壤理化性质,使得矿山周边耕地土壤表现出重金属污染特征(庞文品等,2016;吴先亮等,2018;Pan et al., 2021;李强等,2023),造成土壤质量恶化,引发农作物重金属污染,对人体健康造成危害(姚成斌等,2021;宋绵等,2022;欧灵芝等,2023)。
为减少土壤重金属污染对粮食安全、人体健康安全的影响,重金属污染评价及来源分析成为了实现该目标的重要前提(赵家印等,2022)。重金属污染评价的方法包括单因子污染指数法、内梅罗指数法、污染负荷指数法和潜在生态风险指数法等(Joanna et al., 2018);污染来源分析方法包括相关性分析、聚类分析、主成分分析、正定矩阵因子分析(PMF)模型等(薛志斌等,2018;尹芳等,2021;蒋玉莲等,2023)。由于土壤污染来源和污染过程具有复杂性,使得单一的污染评价方法和来源解析方法具有一定的局限性,结果无法满足需求。因此,将多种方法配合使用,可以使各方法得到的结果相互支持印证,提高污染评价和来源解析结果的可靠性和合理性(于旦洋等,2021)。
以云南省东部典型煤矿区土壤为研究对象,开展样品采集和分析工作,定量描述土壤重金属污染情况,通过统计分析、空间分布规律分析、主成分分析以及PMF模型等多种定性定量分析工具,开展重金属污染源识别和定量解析工作。研究成果可为地方政府掌握土壤污染情况,出台合理控制措施提供数据支撑,也可为煤矿区耕地土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析工作提供参考。
2. 材料与方法
2.1 研究区概况
研究区位于云南省东部(图1),为“云贵煤炭基地”主要产煤区域,属南盘江上游,地理坐标为104°15′~104°20′E,25°43′~25°51′N,属于北温带山地季风湿润气候区,河流发育,地形切割剧烈,年平均温度14℃左右,降水丰富,四季温和。区内煤矿集中,土地利用类型以旱地为主,其次为林地、水田等。出露地层主要为二叠系茅口组、梁山组、峨眉山玄武岩、宣威组及三叠系飞仙关组,其中宣威组为区内产煤地层,岩性为含煤碎屑岩;飞仙关组为碎屑岩,早期产铜矿;茅口组为碳酸盐岩,梁山组为黑色碎屑岩,仅在研究区边缘出露。
2.2 样品采集与分析
2.2.1 样品采集
土壤样品采集时,每个采样点周围50~100 m范围内采集4个子样,采样深度为0~20 cm,混合均匀后组合成1件样品,平均采样密度为9点/km2。样品在室内通风处晾干,干燥过程中使用木棒捶打,防止结块,干燥后去除根系、石块等杂质,全部过10目尼龙筛,混合均匀后,采用四分法取样500 g以上,装入牛皮纸袋中密封,送往实验室进一步加工并分析。
2.2.2 分析测试
土壤样品测试单位为中国地质调查局昆明自然资源综合调查中心实验室。pH试样采用去除二氧化碳的新制备蒸馏水溶解,使用上海仪电科学仪器公司pH计(PHS−3C)测定;As试样采用王水消解,使用北京海光仪器有限公司原子荧光光度计(AFS−9800)测定;Hg试样采用王水消解,使用物化探研究所原子荧光分光光度计(XGY−1011A)测定;Cd、Cu、Pb试样采用HF−HNO3−HClO4消解,使用赛默飞世尔公司等离子质谱仪(iCAP QC)测定;Cr试样压片处理,使用德国PANalytical公司X射线荧光光谱仪(AxiosMAX)测定;Ni、Zn试样采用HNO3−HCl−HF−HClO4消解,使用赛默飞世尔公司电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(iCAP 6300)测定。本批次样品共插入60个国家一级标准物质控制分析的准确度,分别计算每种元素,每件标准物质,每次测定值与标准推荐值之间对数差(ΔlgC)控制分析准确度。元素分析方法的检出限、报出率、准确度、精密度等质量指标均满足《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295−2016)要求。
2.3 污染负荷指数
采用污染负荷指数评价土壤重金属污染程度(麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜等,2017),其计算公式为:
CFi=CiSi (1) P=n√CF1×CF2×⋅⋅⋅CFn (2) 式(1)、(2)中,CFi为土壤重金属i污染指数,Ci和Si分别重金属实测值和标准值,标准值(表1)选用云南省土壤背景值(魏复盛等,1990),P为某样点重金属污染负荷指数,n为该样点重金属污染物的个数。
表 1 土壤理化指标参比标准值Table 1. Reference standard value of soil physicochemical index元素
指标土地
类型风险筛选值/(mg/kg) 管制值/(mg/kg) 云南省土壤
背景值/
(mg/kg)pH≤5.5 5.5<pH≤6.5 6.5<pH≤7.5 pH>7.5 pH≤5.5 5.5<pH≤6.5 6.5<pH≤7.5 pH>7.5 As 水田 30 30 25 20 200 150 120 100 18.40 其他 40 40 30 25 Cd 水田 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.5 2.0 3.0 4.0 0.22 其他 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.6 Cr 水田 250 250 300 350 800 850 1000 1300 65.20 其他 150 150 200 250 Cu 果园 150 150 200 200 — — — — 46.30 其他 50 50 100 100 Hg 水田 0.5 0.5 0.6 1.0 2.0 2.5 4.0 6.0 0.06 其他 1.3 1.8 2.4 3.4 Ni 不区分 60 70 100 190 — — — — 42.50 Pb 水田 80 100 140 240 400 500 700 1000 40.60 其他 70 90 120 170 Zn 不区分 200 200 250 300 — — — — 89.70 SOM — — — — — — — — — 3.89 pH — — — — — — — — — 5.70 注:云南省土壤背景值中pH无量纲、SOM单位为%;风险筛选值和管制值源自《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618−2018)。 Pz=m√P1×P2×⋅⋅⋅Pm (3) 式(3)中,Pz为综合污染负荷指数,m为研究区采样点个数。
污染负荷指数法分级标准为P或Pz≤1,为无污染;1<P或Pz≤2,为轻微污染;2<P或Pz≤3为中度污染;P或Pz>3,重度污染。
2.4 潜在生态风险指数
采用Hakanson(1980)提出的潜在生态风险指数法评价土壤重金属的生态风险情况,定量划分重金属潜在生态风险。单一重金属潜在生态风险系数(E)计算公式如下:
Eir=Tir⋅(CidCil) (4) 式(4)中,Eir为给定重金属i的潜在生态风险系数;Cid为重金属i的实测含量;Cil为重金属i的云南省土壤背景值;Tir为重金属i的毒性响应系数。重金属毒性水平顺序为:Hg>Cd>As>Pb=Cu=Ni>Cr>Zn,给出的毒性响应系数为:Hg=40、Cd=30、As=10、Pb=Cu=Ni=5、Zn=1和Cr=2(王昌宇等,2021)。综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)由各单一重金属潜在生态风险系数加和得到。土壤重金属潜在生态风险分级标准见表2。
表 2 土壤重金属潜在生态风险分级标准Table 2. Classification criteria of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soil参数 取值范围 单一潜在生态风险等级 参数 取值范围 综合潜在生态风险等级 E E<40 轻度 RI RI<150 轻度 40≤E<80 中等 150≤RI<300 中等 80≤E<160 强 300≤RI<600 强 160≤E<320 很强 RI≥600 很强 E≥320 极强 2.5 PMF模型
PMF模型是由Paatero and Tapper(1994)提出的基于因子分析技术的一种源解析方法,通过最小二乘法和迭代计算,不断分解受体样本矩阵从而得到最优解(孙锐等,2021),求解过程中对因子载荷和因子得分均作非负约束,使得到的源成分谱和源贡献率具有可解释性和明确的物理意义(Chueinta et al., 2000),计算公式为:
Xij=p∑K=1gikfkj+eij (5) Q=n∑i=1m∑j=1(xij−p∑k=1gikfkjuij)2 (6) Unc=0.1C+MDL/3 (7) 式(5)、(6)和(7)中,Xij为第i个样品第j种元素浓度矩阵;fkj为第k个源第j种重金属浓度矩阵;gik为第k个源对第i个样品的贡献率;eij为残差矩阵;uij为第i个样品第j种重金属的残差矩阵。因子贡献和分布由PMF模型计算得出,Q为最小化目标函数,Unc为第i个样品第j种重金属的不确定度(Reff et al., 2007),C为某点土壤中元素含量,MDL为元素检测方法的检出限。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 土壤理化指标
研究区土壤中As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn、SOM和pH的统计结果见表3。土壤pH平均值为5.39,整体呈酸性,低于云南省土壤背景值。SOM含量平均值是云南省土壤背景值的1.20倍。Cr、Cu、Cd、Ni、Zn和Hg含量平均值和中位数均超过云南省土壤背景值,其含量平均值分别为云南省土壤背景值的3.89、3.60、3.09、1.92、1.62和1.17倍。对比土壤风险筛选值和管制值,除Hg、Pb外,Cd、Cu、Cr、Ni、Zn和As超过风险筛选值的比例分别为94.97%、93.96%、91.35%、79.28%、3.42%和3.22%,仅有部分样点As、Cd含量超过管制值,比例分别为0.20%、1.41%。
表 3 土壤理化指标数理统计Table 3. Mathematical statistics of soil physicochemical indexes元素指标 最大值/
(mg/kg)最小值/
(mg/kg)中位数/
(mg/kg)平均值/
(mg/kg)标准偏差/
(mg/kg)变异系数/
%超云南省土
壤背景值%超风险筛选值/
%超管制值/
%As 556.00 0.88 5.14 10.05 28.16 280.19 9.46 3.22 0.20 Cd 8.75 0.13 0.57 0.68 0.67 98.09 99.60 94.97 1.41 Cr 577.00 123.00 223.00 253.91 95.15 37.47 100.00 91.35 0 Cu 1344.00 42.80 155.00 166.70 124.22 74.52 99.40 93.96 0 Hg 0.77 0.01 0.06 0.07 0.06 91.92 40.85 0 0 Ni 168.00 38.30 80.50 81.49 15.07 18.50 99.60 79.28 0 Pb 66.10 7.71 24.30 25.24 7.54 29.86 3.62 0 0 Zn 250.00 70.90 144.00 145.21 27.75 19.11 98.19 3.42 0 SOM 20.26 0.34 4.24 4.67 23.38 50.10 56.94 — — pH 8.19 3.84 5.10 5.39 0.86 15.95 29.58 — — 注:最大值、最小值、中位数、平均值、标准偏差中pH无量纲;SOM单位为%。 变异系数为标准偏差与平均值的比值,变异系数越大,可能受到人类活动影响越强(刘同等,2022)。从变异系数来看,研究区土壤重金属空间分布为中度至高度变异,其中As、Cd、Hg和Cu变异系数分别为280.19%、98.09%、91.92%和74.52%,空间分异明显。变异系数顺序为As>Cd>Hg>Cu>Cr>Pb>Zn>Ni。
3.2 空间分布特征
使用ArcGIS中反距离权重法对土壤重金属进行插值分析,空间分布如图2所示。As、Cd、Hg的空间分布有较大的相似性,相对高值区主要呈点状分布在后所镇东部、外后所村东南部,与研究区内出露的茅口组、梁山组等地层分布区耦合,Pb的相对高值区部分与As、Cd、Hg一致,其他相对高值区呈点状零散分布在研究区内。Cu的相对高值区主要呈点状分布在外后所村南部至大庆一带,为飞仙关组分布区。Cr、Ni的部分相对高值区分布较相似,在后所镇东部至大庆东部一带,为飞仙关组分布区,Ni的其他相对高值区分布在峨眉山玄武岩分布区。Pb的相对高值区除在碳酸盐岩分布区出现外,还分布在主要运煤道路及村庄周边。Zn的相对高值区主要分布在峨眉山玄武岩和宣威组分布区。整体来看,地质背景对研究区重金属空间分布影响十分明显,这与李丽辉和王宝禄(2008)研究结果一致。前人研究表明,土壤还可能受到农业生产、人类生活、燃煤取暖、煤矿开采和交通运输等影响(李伟等,2022;秦元礼等,2022)。
3.3 土壤重金属污染评价
3.3.1 污染负荷指数评价
研究区污染负荷指数(P)在0.79~4.73,平均值为1.46,空间分布特征见图3。评价结果显示,研究区土壤以轻微污染为主,占91.75%,其次为中度污染和重度污染分别占3.82%、1.01%,无污染仅占3.42%。茅口组和梁山组分布区与中度、重度污染区耦合,对污染负荷指数影响较大。综合污染负荷指数为1.43,整体表现为轻微污染。
3.3.2 潜在生态风险指数评价
研究区土壤单一重金属潜在生态风险系数(Eri)见图4,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn的潜在生态风险系数的平均值分别为5.46、92.68、7.79、18.00、44.74、9.59、3.11和1.62,潜在生态风险较大的元素为Cd,其次为Hg。其中Cd以中等生态风险为主,其次为强生态风险,分别占50.30%、42.25%,轻度生态风险仅占3.22%,很强和极强生态风险分别占2.62%、1.61%。Hg以轻度生态风险为主,其次为中等生态风险,分别占49.70%、43.26%,少量强、很强和极强生态风险,分别占4.63%、2.01%、0.40%。Cu以轻度生态风险为主,少量中等、强生态风险,分别占97.38%、1.01%、1.61%。As、Cr、Ni、Pb、Zn潜在生态风险系数均小于40,生态风险较小。
土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)空间分布情况(图5a)显示,研究区以中等生态风险为主,其次为轻度生态风险,其中中等、轻度、强和很强生态风险比例分别为55.53%、39.84%、3.02%和1.61%。统计8种重金属对RI的贡献率,结果(图5b)显示:As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn的贡献率分别为2.64%、48.97%、4.85%、10.66%、23.90%、6.08%、1.88%和1.01%。其中Cd贡献率最高,其次为Hg。Cd、Hg本身毒性较高,并且在土壤中含量普遍超过风险筛选值,潜在生态风险较高。结合Cd、Hg空间分布来看,研究区边缘的强、很强生态风险区主要受到Cd、Hg影响,与涂春霖等(2023)对滇东典型煤矿区小流域沉积物重金属评价结果基本一致。
3.4 来源解析
3.4.1 相关性分析
相关性分析是判断元素来源的重要方法,元素间相关系数越大,来自于同一污染源的可能性越大。通过表4可知,As–Hg、Cd–Hg和Ni–Zn显著正相关(P>0.01),相关系数分别为0.65、0.52和0.55,说明As–Hg、Cd–Hg、Ni–Zn部分来源一致,对土壤中该元素组合贡献较高。Ni–Cr显著正相关(P>0.01),但相关系数较小,仅为0.45,结合元素空间分布特征,Cr−Ni分布具有一定的相似性和差异性,导致二者相关系数较小。SOM与Pb显著正相关(P>0.01),相关系数为0.41。pH与重金属之间相关系数均比较小。
表 4 土壤理化指标相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of soil physicochemical indexes元素指标 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn SOM pH As 1 Cd 0.29 1 Cr 0.09 0.19 1 Cu −0.10 0.11 0.21 1 Hg 0.65** 0.52** 0.07 −0.08 1 Ni −0.07 0.03 0.45** 0.12 −0.15 1 Pb 0.22 0.30 0.02 −0.09 0.38** −0.25 1 Zn −0.05 0.16 −0.03 0.03 −0.01 0.55** −0.01 1 SOM −0.04 0.13 −0.19 0.01 0.23 −0.28 0.41** 0.08 1 pH 0.17 0.26 0.14 0.04 0.15 −0.12 0.14 −0.05 0.08 1 注:** 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 3.4.2 主成分分析
主成分分析是通过降维的方式,找出几个综合变量代替原有众多变量,使综合变量尽可能代表原来变量的信息,是有效解析土壤重金属来源的方法(杨玲等,2022)。如表5所示,使用最大方差法对成分矩阵进行旋转,提取出5个特征值大于1的主成分,累积贡献率达到86.56%,可以较好地解释原有变量信息。
表 5 土壤重金属主成分分析结果Table 5. Principal component analysis results of heavy metals in soil元素 成分 1 2 3 4 5 As 0.90 −0.08 0.06 −0.03 −0.11 Cd 0.51 0.23 0.08 0.50 0.32 Cr 0.07 −0.01 0.96 0.06 0.13 Cu −0.07 0.00 0.11 −0.06 0.95 Hg 0.86 −0.02 −0.02 0.30 −0.01 Ni −0.07 0.71 0.57 −0.25 0.00 Pb 0.13 −0.09 −0.01 0.91 −0.12 Zn −0.01 0.96 −0.08 0.06 0.02 特征值 1.85 1.48 1.28 1.26 1.06 贡献率/% 23.15 18.49 16.02 15.20 13.20 累积贡献率/% 23.15 41.64 57.66 73.36 86.56 第一主成分中As、Hg和Cd载荷量较大,分别为0.90、0.86和0.51,As、Cd、Hg部分相对高值区空间分布相似,与茅口组、梁山组分布区耦合,其中茅口组为碳酸盐岩,梁山组为黑色页岩,前人研究显示,碳酸盐岩和黑色页岩在风化成土过程中往往导致重金属富集,是重金属空间分布出现相对高值区的重要影响因素(张国涛等,2016;马宏宏等,2020;陈梓杰等,2021)。除相对高值区外,其他区域As、Hg空间分布较为均匀,可能受到广泛均匀的大气沉降影响。前人研究显示,区内煤层受玄武岩影响,煤炭中As含量较高(聂爱国和谢宏,2004),且区内煤炭工业发达,生产过程中需要大量的煤炭作为燃料和原料,燃煤时产生大量含有As、Cd、Hg等重金属的烟气飞灰(郭胜利等,2015),且煤炭运输过程中产生的灰尘、汽车尾气也含有重金属(刘鹏等,2019),这些物质进入大气中,通过沉降作用进入土壤,导致土壤重金属累积。因此推测As、Hg主要受到大气沉降影响,Cd部分受到大气沉降影响。第一主成分为大气沉降源,贡献率为23.15%。
第二主成分中Zn、Ni载荷量较大,分别为0.96、0.71。Ni分布较均匀,空间上相对高值区与飞仙关组和峨眉山玄武岩地层分布区耦合,Zn相对高值区与峨眉山玄武岩和宣威组分布区耦合。研究显示,玄武岩与其发育土壤中的Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn等微量元素间具有较好的继承性(吴月照和潘懋,1993),宣威组物质主要来源于峨眉山玄武岩风化碎屑(Zhang et al., 2010)。因此推测Zn主要受到峨眉山玄武岩影响,Ni部分受峨眉山玄武岩影响。第二主成分为峨眉山玄武岩自然源,贡献率为18.49%。
第三主成分中Cr、Ni载荷量较大,分别为0.96、0.57,Ni在第二、三主成分均有较大载荷。Cr空间分布特征与飞仙关组套合,研究显示,飞仙关组岩石重矿物中有大量碎屑铬尖晶石,物质来源于晚二叠世峨眉山高钛玄武岩,可见土壤中高Cr、Ni含量与岩石中存在的碎屑铬尖晶石有关(肖高强等,2021);Ni、Cr相对高值区分布特征在飞仙关组分布区具有相似性。综合第二主成分分析结果,推测Cr主要受到飞仙关组碎屑岩影响,Ni主要受到飞仙关组碎屑岩和峨眉山玄武岩共同影响。第三主成分为碎屑岩自然源,贡献率为16.02%。
第四主成分中Pb、Cd和Hg载荷量较大,分别为0.91、0.50、0.30,Cd在第一、四主成分均有较大载荷。Pb与Cd、Hg部分相对高值区空间分布相似,均在茅口组、梁山组分布区,除此之外,其它相对高值区与人类生活区和农业活动区较为套合。野外调查发现研究区化肥和农家肥配合施用,农家肥用量较大;生活垃圾和生活污水水集中处理能力还不足。研究显示,肥料(化肥、农家肥)均含有重金属,由于近年对化肥生产严格管控,化肥中重金属含量低于国家肥料相关标准,农家肥成为农田土壤重金属主要来源之一(童文彬等,2020;徐兴阳等,2020),燃煤取暖的煤渣、生活垃圾和生活污水也含有重金属元素(倪琳等,2020;苏辉跃等,2022),生活垃圾受降水淋滤作用,淋滤液汇入地表径流进入土壤,煤渣和生活污水直接倾倒进入土壤。综合第一主成分分析结果,推测Cd、Hg主要受到大气沉降源和农业及生活复合源共同影响,Pb主要受到农业和生活复合源影响。第四主成分为农业与生活复合源,贡献率为15.20%。
第五主成分中Cu载荷量较大,为0.95。Cu在研究区内超过云南省A层土壤算术均值,相对高值区呈点状沿飞仙关组地层分布,附近曾有铜矿开采,野外调查也发现沿飞仙关组地层分布的炼铜废渣,部分可见铜矿物,是导致相对高值区出现的主要原因。研究显示,峨眉山玄武岩中Cu含量较高,风化碎屑为宣威组物质主要来源,玄武岩分布区土壤中Cu受地层控制明显(贺灵等,2021),因此推测Cu主要受到地质背景和早期铜矿开采冶炼影响。第五主成分为早期炼铜废渣与自然复合源,贡献率为13.20%。
3.4.3 PMF模型解析
使用PMF模型进行污染源解析,剔除了可能影响解析结果的异常值(魏迎辉等,2018)。将浓度和不确定度导入PMF模型,信噪比(S/N)大于6,默认为“Strong”,不断调整因子数量,当因子数量为6时,Q值(1797.32)与理论Q值(1829.13)接近,两者间差值小于10%(蒋玉莲等,2023)。选择6因子时,Pb的r2(数据拟合度)为0.54,其他元素r2均大于0.70,其中As、Cd、Cu、Hg达到0.90以上,说明所选因子数量能够较好解释原有数据包含的信息,解析效果较好。
各因子中元素贡献率及浓度见图6。因子1对Cu、Cr、Ni和Zn贡献较大,分别为63.84%、22.56%、12.55%和10.45%,Cu相对高值区主要分布在早期铜矿冶炼场地周边,且在玄武岩和宣威组中含量较高,因此推测因子1为早期炼铜废渣与自然复合源,贡献率为15.92%。
因子2对Cd、Pb和Zn的贡献率较高,分别为67.88%、55.48%和30.71%。因子2中Cd、Pb含量及贡献率均超过其他因子,空间分布特征与农业活动区和人类生活区耦合,受到人类活动影响。徐兴阳等(2020)研究发现昆明烟区不同种类农家肥中Cd含量为0.59~2.40 mg/kg,Pb含量为20.00~36.10 mg/kg;陈其永等(2022)对2000—2018年我国大气重金属沉降通量时空变化特征进行了研究,发现我国大气中Cd、Pb年通量分别为0.48 mg/(m2·a)、23.37 mg/(m2·a),由农家肥输入土壤的重金属年通量高于大气沉降物,考虑该因子对人类生活影响较大的Hg贡献非常低,因此推测因子2为农业源,贡献率为23.20%。
因子3对Cr、Ni的贡献率较高,分别为52.19%、28.88%,研究显示,飞仙关组碎屑岩中大量铬尖晶石为土壤中Cr重要来源(肖高强等,2021),且Cr、Ni空间分布特征在飞仙关组区具有相似性,因此推测因子3为碎屑岩自然源,贡献率为14.40%。
因子4对As的贡献率较高,为80.60%,研究区内煤层受玄武岩影响,煤炭中As含量较高(丁振华等,2009),野外调查走访发现早期炼铜活动和现今工业活动均使用本地煤炭作为燃料,燃烧过程中As被大量释放到大气中,通过沉降作用进入土壤。土壤对砷的吸附主要依靠正电荷与带负电荷的As络阴离子相互作用实现,SOM作为土壤中普遍存在的带负电荷胶体与正电荷反应优先于As络阴离子(翁焕新等,2000),研究区土壤中SOM含量平均值高于云南省土壤背景值,导致As被土壤吸附较少,使得As平均含量低于云南省土壤背景值,因此推测因子4为大气沉降源,贡献率为13.27%。
因子5对Zn、Ni和Cu贡献率较高,分别为45.79%、39.33%和26.31%,研究显示,玄武岩与其发育土壤中的Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn等微量元素间具有较好的继承性(吴月照和潘懋,1993),因此推测因子5为峨眉山玄武岩自然源,贡献率为17.70%。
因子6对Hg、Pb贡献率较高,分别为70.29%、21.52%,Hg、Pb部分相对高值区与茅口组与梁山组分布区耦合,部分相对高值区又与人类生活区耦合。一般认为Hg与化石燃料使用和含汞现代工业产品相关(Qiu et al., 2006;李伟等,2022),研究区内居民取暖、做饭还经常使用煤炉,Hg易挥发,随烟尘飘散(倪琳等,2020),沉降在人类生活区周边。因此推测因子6为生活源,贡献率为15.52%。
对比主成分分析结果来看,两种源解析方法均表明地质背景是研究区土壤重金属主要来源,其次为农业活动和大气沉降。
4. 结 论
(1)土壤pH平均值为5.39,以酸性为主,SOM含量平均值是云南省土壤背景值的1.20倍,Cr、Cu、Cd、Ni、Zn和Hg含量平均值和中位数均超过云南省土壤背景值。除Hg、Pb外,Cd、Cu、Cr、Ni、Zn和As在部分样品中含量超《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618−2018)中风险筛选值,仅有部分样点As、Cd含量超管制值。
(2)污染负荷指数法评价结果显示,研究区土壤重金属主要为轻微污染,占91.75%,其次为中度污染和重度污染分别占3.82%、1.01%,无污染仅占3.42%。研究区综合污染负荷指数为1.43,呈现轻微污染,中度、重度污染区与茅口组和梁山组等地质高背景区耦合,受其影响明显。潜在生态风险指数法评价结果显示,研究区土壤重金属以中等生态风险为主,其次为轻度生态风险,分别占55.53%、39.84%。Cd、Hg为主要生态风险因子。
(3)主成分分析结果显示,研究区土壤重金属来源主要有5种,分别为大气沉降源,峨眉山玄武岩自然源、碎屑岩自然源、农业与生活复合源和早期炼铜废渣与自然复合源。PMF模型解析结果显示,研究区土壤重金属来源主要有6种,分别为大气沉降源、峨眉山玄武岩自然源、碎屑岩自然源、农业源、生活源和早期炼铜废渣与自然复合源。主成分分析与PMF模型解析在结果上趋于一致,即地质背景是研究区土壤重金属主要来源,其次为农业活动和大气沉降,建议加强相关污染土地的监测和管理,减少农家肥不合理施用,强化煤炭工业污染排放监管。
致谢: 衷心感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵意见和云南黄金集团及西部矿业玉龙铜矿的同仁们在野外工作中提供的帮助。 -
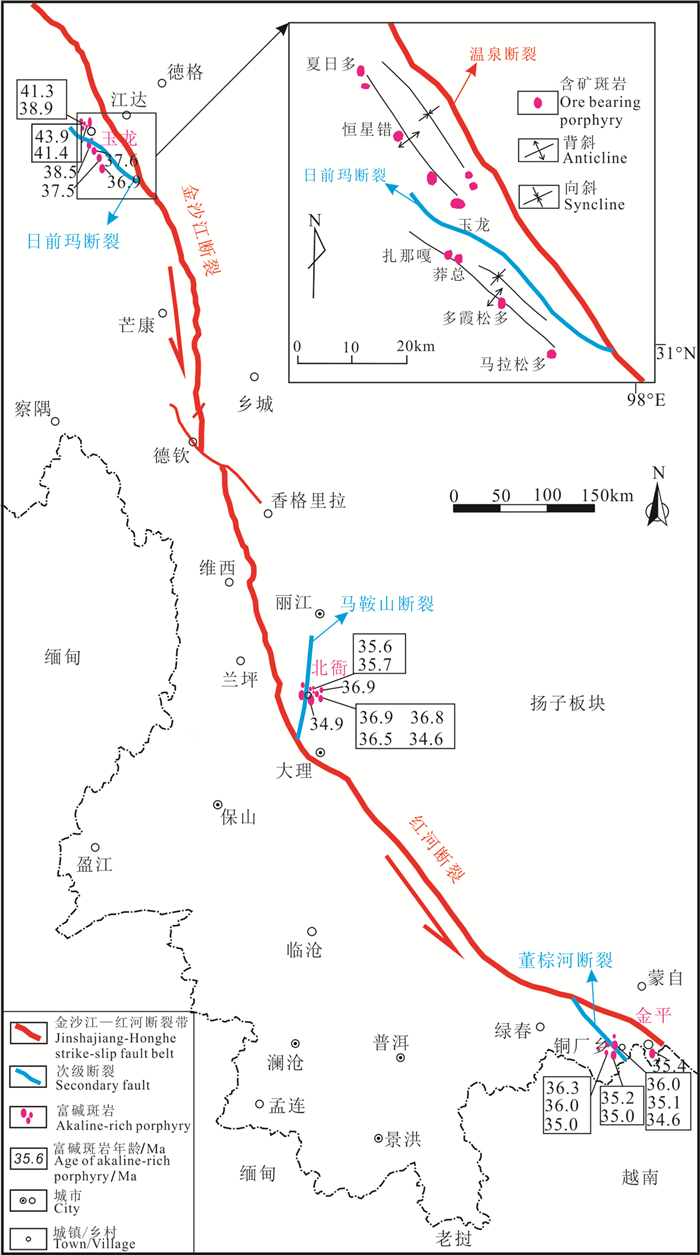
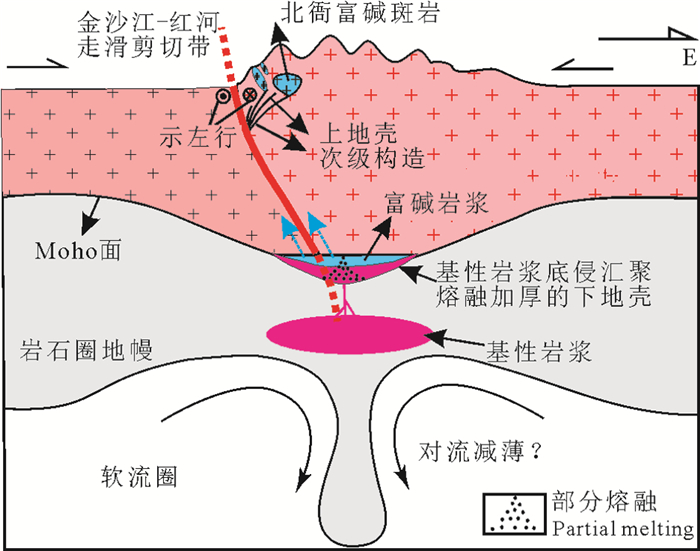
图 1 金沙江—红河富碱斑岩铜金多金属成矿带
表示金沙江—红河走滑断裂带的次级构造控制富碱斑岩的分布(数据来源:Hou et al., 2003; Deng et al., 2014; 王建华,2017;武精凯等,2019)
Figure 1. The Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyry Cu-Au metallogenic belt
Showing the distribution pattern of the alkaline-rich porphyry controlled by the Jinshajiang-Honghe and its secondary faults (Data sources: Hou et al., 2003; Deng et al., 2014; Wang Jianhua, 2017; Wu Jingkai et al., 2019)
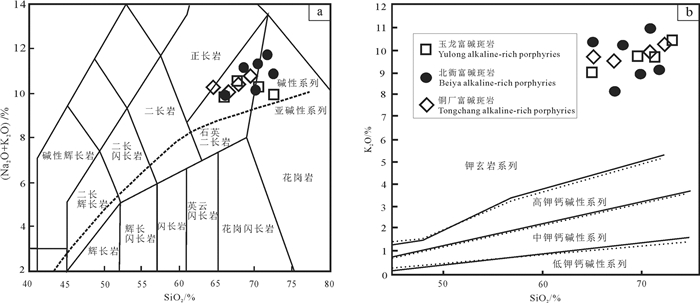
图 2 金沙江—红河富碱斑岩岩石分类图解
a-SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解(底图据Irvine and Baragar, 1971);b-SiO2-K2O图解(底图据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976);数据来源:玉龙(Jiang et al., 2006);北衙(Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2015;王建华,2017);铜厂(胥磊落等,2011)
Figure 2. Variation of the Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyries
a-(K2O+Na2O)-SiO2(after Irvine and Baragar, 1971); b-K2O-SiO2(after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976); Data sources: Yulong (Jiang et al., 2006); Beiya (Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2015; Wang Jianhua, 2017); Tongchang (Xu Leiluo et al., 2011)
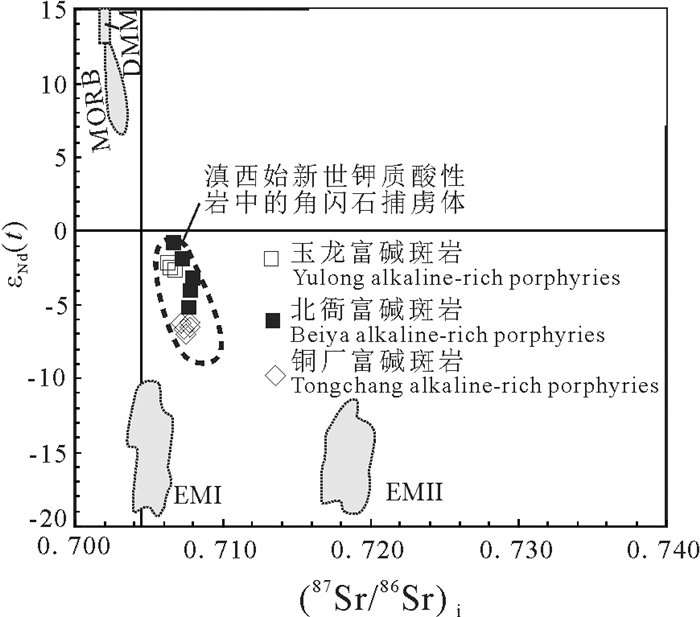
图 3 金沙江—红河富碱斑岩的Sr-Nd同位素组成(据Lu et al., 2013修改)
数据来源:玉龙(Hou et al., 2003; Jiang et al., 2006);北衙(Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2015;王建华,2017;Mao et al., 2017);铜厂(胥磊落等,2011;Xu et al., 2014; 武精凯等,2019)
Figure 3. Sr-Nd isotope compositions of the Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyries (modified from Lu et al., 2013)
Data sources: Yulong (Hou et al., 2003; Jiang et al., 2006); Beiya (Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2015; Wang Jianhua, 2017; Mao et al., 2017); Tongchang (Xu Leiluo et al., 2011; Xu et al., 2014; Wu Jingkai et al., 2019)
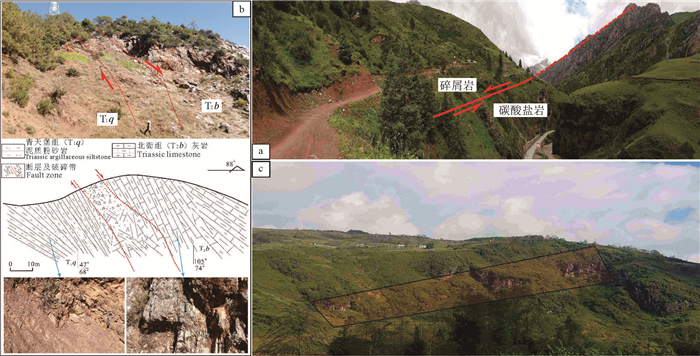
图 4 金沙江—红河走滑断裂带的次一级断裂
a—玉龙矿区南部日前玛张性断裂(观察地点:青泥洞乡南西;镜头方向:321°);b—北衙矿区马鞍山张性断裂(观察地点:焦石硐;镜头方向:55°;王建华,2017);c—铜厂乡南东的张性断裂(观察地点:董棕河村;镜头方向:238°)
Figure 4. Secondary faults of the Jinshajiang-Honghe strike-slip fault
a-The Riqianma extensional fault in the southern area of the Yunlong deposit near Qingnidong town; b-The Maanshan extensional fault in the Jiaoshidong of the Beiya deposit (after Wang Jianhua, 2017); c-The extensional Dongzonghe fault in the southeast of the Tongchang deposit
图 5 受控于金沙江—红河断裂带及其次级构造的富碱岩浆成因演化过程(据Lu et al., 2013;Deng et al., 2015; 王建华等,2016)
Figure 5. Formation of the Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich magma controlled by the regional Jinshajiang-Honghe strike-slip faults and its secondary structures (after Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2015; Wang Jianhua et al., 2016)
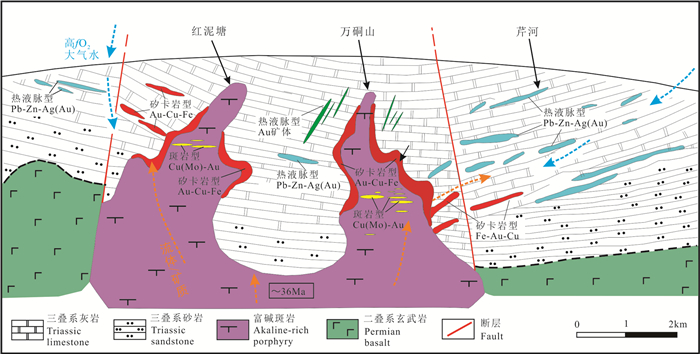
图 6 北衙富碱斑岩金多金属成矿系统示意图(据Li et al., 2016; 王建华,2017)
Figure 6. Sketched map of the ore-forming system in Beiya (after Li et al., 2016; Wang Jianhua, 2017)
表 1 金沙江—红河富碱斑岩铜金多金属成矿带内典型矿床特征
Table 1 Geological characteristics of the typical deposits in the Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyry Cu-Au metallogenic belt

表 2 金沙江—红河带内主要富碱斑岩特征
Table 2 Main characteristics of the Jinshajiang-Honghe alkaline-rich porphyries

-
Adiyaman O, Chorowicz J, Arnaud O N, Gundogdu M N, Gourgaud A. 2001. Late Cenozoic tectonics and volcanism along the North Anatolian fault: New structural and geochemical data[J]. Tectonophysics, 338: 135-165. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00131-7
Bao X S, Yang L Q, He W Y, Gao X. 2018. Importance of magmatic water content and oxidation state for porphyry-style Au mineralization: An example from the giant Beiya Au deposit, SW China[J]. Minerals, 8(10): 1-13.
Bao Xinshang, Yang Liqiang, He Wenyan, Gao Xue, Li Mengmeng. 2019. Constraints of chemical composition of biotite and zircon on crystallization conditions of magma: An example from the Beiya giant Au deposit, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(5): 1447-1462(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.05.08
Bissig T, Cooke D R. 2014. Introduction to the special issue devoted to alkalic porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 109: 819-825. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.109.4.819
Brown M, Solar G S. 1999. The mechanism of ascent and emplacement of granitic magma during transpression: A syntectonic granite paradigm[J]. Tectonophysics, 312: 1-33. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00169-9
Cannell J, Cooke D R, Walshe J L, Stein H. 2005. Geology, mineralization, alteration, and structural evolution of the El Teniente porphyry Cu-Mo deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 100: 979-1003. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.100.5.979
Chen B, Long X P, Wilde S A, Yuan C, Wang Q, Xia X P, Zhang Z F. 2017. Delamination of lithospheric mantle evidenced by Cenozoic potassicrocks in Yunnan, SW China: A contribution to uplift of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 284/285: 709-729. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.05.019
Chen Jianping, Tang Juxing, Cong Yuan, Dong Qingjie, Hao Jinhua. 2009. Geological characteristics and metallogenicmodel in the Yulong porphyry copper deposit, east Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(12): 1887-1900(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.12.007
Chernicoff C J, Richards J P, Zappettini E O. 2002. Crustal lineament control on magmatism and mineralization in northwestern Argentina: Geological, geophysical, and remote sensing evidence[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 21: 127-155. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(02)00087-2
Deng Jun, Hou Zengqian, Mo Xuanxue, Yang Liqiang, Wang Qingfei, Wang C M. 2010. Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 37-42(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.005
Deng Jun, Wang Changming, Li Wenchang, Yang Liqiang, Wang Qingfei. 2014. The situation and enlightenment of the research of the tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1): 52-64(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Santosh M. 2014. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J, Hou Z Q, Jiang C Z, Danyushevsky L. 2015. Geology and genesis of the giant Beiya porphyry-skarn gold deposit, northwestern Yangtze Block, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 457-485. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.015
Deng W M, Huang X, Zhong D L. 1998. Alkali-rich porphyry and its relation with intraplate deformation of north part of Jinsha River belt in western Yunnan, China[J]. Science in China (Series D), 41(3): 297-305. doi: 10.1007/BF02973119
Ebinger C J, Sleep N H. 1998. Cenozoic magmatism throughout east Africa resulting from impact of a single plume[J]. Nature, 395: 788-791. doi: 10.1038/27417
Flower M F J, Hoàng N, Lo C H, Chí C T, Cu'ò'ng N Q, Liu F T, Deng J F, Mo X X. 2013. Potassic magma genesis and the Ailao Shan-Red River fault[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 69: 84-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2012.06.008
Fu Y, Sun X M, Zhou H Y, Lin H, Yang T J. 2016. In-situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology and trace elements analysis of polygenetic titanite from the giant Beiya gold-polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 77: 43-56. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.02.001
Fu Y, Sun X M, Zhou H Y, Lin H, Jiang L Y, Yang T J. 2017. In-situ LA-ICP-MS trace elements analysis of scheelites from the giant Beiya gold-polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province, Southwest China and its metallogenic implications[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 80: 828-837. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.08.030
He W Y, Mo X X, He Z H, White N C, Chen J B, Yang K H, Wang R, Yu X H, Dong G C, Huang X F. 2015. The geology and mineralogy of the Beiyaskarn gold deposit in Yunnan, Southwest China[J]. Economic Geology, 110: 1625-1641. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.6.1625
He W Y, Yang L Q, Campbell M C, Lu Y J, Joël B, Bao X S, Gao X Q, Lu Y G, Xing Y L. 2017. Hydrothermal evolution and ore genesis of the Beiya giant Au polymetallic deposit, western Yunnan, China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 847-862. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.035
He Wenyan. 2014. The Beiya giant gold-polymetallic deposit: magmatism and metallogenic model[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-154(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Zengqian, Ma H W, Zaw K. 2003. The Himalayan Yulong porphyry copper belt: Product of large-scale strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet[J]. Economic Geology, 98: 125-145.
Hou Zengqian, Yang Zhuseng, Xu Wenyi, Mo Xuanxue, Ding Lin, Gao Yongfeng, Dong Fangliu, Li Guangming, Qu Xiaoming, Li Guangming, Zhao Zhidan, Jiang Sihong, Meng Xiangjin, Li Zhenqing, Qin Kezhang, Yang Zhiming. 2006a. Metallogenesis in the Tibetan collisional orogenic belt: I. Mineralization in main collisional orogenic setting[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(4): 337-358(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Zengqian, Pan Guitang, Wang Anjian, Mo Xuanxue, Tian Shihong, Sun Xiaoming, Ding Lin, Wang Erqi, Gao Yongfeng, Xie Yuling, Zeng Pusheng, Qin Kezhang, Xu Jifeng, Qu Xiaoming, Yang Zhiming, Yang Zhuseng, Feng Hongcai, Meng Xiangjin, Li Zhenqing. 2006b. Metallogenesis in the Tibetan collisional orogenic belt: Ⅱ. Mineralization in late-collisional transformation setting[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(5): 521-543(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Zengqian, Zhong Dalai, Deng Wanming. 2004. A tectonic model for porphyry copper-molybdenum-gold metallogenic belts on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Geology in China, 31(1): 1-13(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Z Q, Zhou Y, Wang R, Zheng YC, He W Y, Zhao M, Evans N J, Weinberg RF. 2017. Recycling of metal-fertilized lower continental crust: Origin of non-arc Au-rich porphyry deposits at cratonic edges[J]. Geology, 45: 563-566.
Hou Zengqian. 2010. Metallogenesis of continental collision[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(1): 30-58(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu R Z, Burnard P G, Bi X W, Zhou M F, Peng J T, Su W C, Wu K X. 2004. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion-associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jinshajiang fault belt, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 203(3/4): 305-317.
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal Earth Science, 8: 523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
Jiang H Y, Jiang S Y, Ling H F, Dai B Z. 2006. Low-degree melting of a metasomatized lithospheric mantle for the origin of Cenozoic Yulong monzogranite-porphyry, east Tibet: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 241: 617-633. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.11.023
Jiang Yaohui, Jiang Shanyong, Lin Hongfei, Dai Baozhang. 2006. Petrogenesis of Cu-bearing porphyry associated with continent-continent collisional setting: Evidence from the Yulong porphyry Cu ore-belt, east Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(10): 3109-3122(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Mengqing, Rui Zongyao, Chen Laixian. 1981. Fluid inclusions and mineralization of the Yulong porphyry copper (molybdenum) deposit[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 3: 216-232(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenchang, Pan Guitang, Hou Zengqian, Mo Xuanxue, Wang Liquan. 2010. The Muti-Island-Basin-Collision-Orogenic Metallogenesis and prospecting technologies in "Sanjiang" Region, SW China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-491 (In Chinese).
Li W C, Wang J H, He Z H, Dou S. 2016. Formation of Au-polymetallic ore deposits in alkaline porphyries at Beiya, Yunnan, Southwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.05.003
Liang Huaying, Mo Jihai, Sun Weidong, Zhang Yuquan, Zeng Ti, Huo Guangqian, Charllote A. 2009. Study on geochemical composition and isotope ages of the Malasongduo porphyry associated with Cu-Mo mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 385-392(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin B, Wang L, Tang J, Song Y, Chen Z. 2017. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of ore-bearing porphyries in baomai deposit, Yulong copper belt, Tibet[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 42(9): 1454-1471. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.517
Liu B, Liu H, Zhang C Q, Mao Z H, Zhou Y M, Huang H, He Z H, Su G S. 2015. Geochemistry and geochronology of porphyries from the Beiya gold-polymetallic orefield, western Yunnan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 69: 360-379. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.004
Liu Bingguang, Lu Defu, Cai Xinping. 1999. Study on the Gold Deposits in Yunnan and Sichuan[M]. Beijing: Maritime Press, 1-241 (In Chinese).
Liu Bo. 2014. Diagenetic and Metallogenic Features of Beiya Polymetallic Deposit in Northwest Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-74(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Y J, Kerrich R, Kemp A I S, Mccuaig T C, Hou Z Q, Hart C J R, Li Z X, Cawood P A, Bagas L, Yang Z M, Cliff J, Belousova E A, Jourdan F, Evans N J. 2013. Intercontinental Eocene-Oligocene porohyry Cu mineral system of Yunnan, western Yangtze craton, China: Compositional characteristics, souces, and implications for continental collision metallogeny[J]. Economic Geology, 108: 1541-1576. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.7.1541
Lü Boxi, Duan Jianzhong, Pan Changyun. 1993. Granites and Their Mineralization Specificity in the Sanjiang Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-328(In Chinese).
Ma Hongwen. 1989. On the tectonic environment of magmatism in Yulong porphyry copper belt, eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.1989.mp2001001.x
Mao J W, Zhou Y M, Liu H, Zhang C Q, Fu D G, Liu B. 2017. Metallogenic setting and ore genetic model for the Beiya porphyry-skarn polymetallic Au orefield, western Yunnan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.003
Meng X M, Mao J W, Zhang CQ, Zhang D Y, Liu H. 2018. Melt recharge, fo2-T condition, and metal fertility of felsic magma: Zircon trace element chemistry of Cu-Au porphyries in the Sanjiang orogenic belt, southwest China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 53: 649-663. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0768-y
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58: 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Richards J P. 2003. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposit formation[J]. Economic Geology, 98: 1515-1533. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.8.1515
Richards J P. 2009. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits: Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere[J]. Geology, 37: 247-250.
Rui Zongyao. 1984. Porphyry Cu (Mo) Deposits in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 350(in Chinese).
Sillitoe R H. 2010. Porphyry copper systems[J]. Economic Geology, 105: 3-41. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.1.3
Storti F, Holdsworth R E, Salvini F. 2003. Intraplate strike-slip deformation belts[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 210: 1-14. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.210.01.01
Tong X, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, Zhang S Q, Cousens B, Liu D, Zhang Y, Han M Z, Zhao Y X, Lei S A, Shi Q S, Zhu D C, Sheikh L, Lutfi W. 2019. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Eocene-Oligocene potassic felsic suites in western Yunnan, eastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from petrology, zircon chronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 340/341: 287-315. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.04.023
Wang Jianhua, Li Wenchang, He Zhonghua, Yin Guanghou, Zhou Yunman. 2016. Geological and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic characteristics of the Dashadi porphyry in the Beiya gold polymetallic deposit in western Yunnan and their geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2367-2378 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jianhua, Li Wenchang, Wang Keyong, Yin Guanghou, Wu Song, Jiang Wentao. 2015. The characteristics and evolution of the ore-forming fluids in the Beiya porphyry Au-polymetallic deposit, western Yunnan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3269-3280(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang J H, Yin A, Harrison T M, Grove M, Zhang Y Q, Xie G H. 2001. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188: 123-133. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00315-6
Wang Jianhua. 2017. Alkaline-rich Porphyry Au-polymetallic Metallogeny System in Beiya, Heqin, West Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-130(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xuan, Yang Lin, Deng Jun, Li Huajian, Yu Huazhi, Dong Chaoyi. 2018. Identification of multistage hydrothermal mineralization in the Beiya gold deposit: Evidence from geology, petrography, fluid inclusion, H-O-S isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(5): 1299-1311(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Jingkai, Zhao Zhidan, Yang Yiyun, Lei Hangshan, Miao Zhuang, Liu Dong, Zhu Dicheng, Yu Xuehui. 2019. Petrogenesis and geological implications of the alkali-rich porphyry in southern Ailaoshan-Red River shear zone[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(2): 485-504(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.02.14
Wu Song. 2016. Geochemical characteristics and Genesis of Stratified Pb-Zn-Ag Polymetallic Deposit in the Outer Belt of the Beiya Gold Deposit, Northwest Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-75(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu W B, Liu J L, Zhang L S, Qi Y C, Ling C Y. 2017. Characterizing a middle to upper crustal shear zone: Microstructures, quartz c-axis fabrics, deformation temperatures and flow vorticityanalysis of the northern Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 139: 95-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.026
Xiao Xiaoniu, Yu Xuehui, Mo Xuanxue, Li Yong, Huang Xingkai. 2011. Geochemical characteristics of metallogenesis in the gold-polymetallic deposit in Beiya, western Yunnan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration. 47(2): 170-179(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie Yuling, Hou Zegnqian, Xu Jiuhua, Yang Zhiming, Xu Wenyi, He Jianping. 2005. Evolution of muti-stage fluid and mineralization: Evidence from fluid inclusions in Yulong porphyry copper deposit, east Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(5): 1409-1415(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu L L, Bi X W, Hu R Z, Tang Y Y, Jiang G H, Qi Y Q. 2014. Origin of the ore-forming fluids of the Tongchang porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in the Jinshajiang-Red River alkaline igneous belt, SW China: Constraints from He, Ar and S isotopes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 884-894. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.013
Xu Leiluo, Bi Xianwu, Su Wenchao, Qi Youqiang, Li Liang, Chen Youwei, Dong Shaohua, Tang Yongyong. 2011. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of the quartz syenite porphyry from the Tongchang Porphyry Cu (Mu-Au) deposit in Jinping county, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 697-706(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Shouming. 2007. Mineralization Model of the Beiya Gold Deposit in Northwest Yunnan and Its Relationship with Cenozoic Alkali-rich Porphyry[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-115(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Y, Zhu J J, Hu R Z, Bi X W, Yu H J, Xu L L, Liu B H, Huang M L, Sheng X Y. 2019. Heterogeneous lithospheric mantle beneath the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from Cenozoic high-Mg potassic volcanic rocks in the Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan Cenozoic magmatic belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 180: 1-18.
Xu Zhiqin, Li Haibing, Yang Jingsui. 2006. An orogenic plateau: the orogenic collage and orogenic types of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 1-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.002
Zeng Pusheng, Mo Xuanxue, Yu Xuehui. 2002. Nd, Sr and Pb isotopic characteristics of the alkaline-rich porphyries in western Yunnan and its compression strike-slip setting[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 21(3): 231-241(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang L S, Schärer U. 1999. Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt, China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134(1): 67-85. doi: 10.1007/s004100050469
Zhang Yuquan, Xie Yingwen, Tu Guangzhi. 1987. Preliminary studies of the alkali-rich intrusive rocks in the Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang belt and their bearing on rift tectonics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 3(1): 19-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Fang, Wang Baodi, He Juan, Hao Ming, Wang Peng. 2022.3D visualization modeling and application study of porphyry-skarn gold-copperdeposits in Beiya Area, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 241-252 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou H Y, Sun X M, Fu Y, Lin H, Jiang L Y. 2016. Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of Bi-minerals: Constraints on ore genesis of the Beiya giant porphyry-skarn gold deposit, southwestern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 408-424.
Zhou Y M, Zhang C Q, He Z H, Liu H, Zhou G W, Sun J, Liu B. 2018. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Beiya gold-polymetallic ore deposit, northwestern Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(5): 1841-1861. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13680
Zhou Yunman, Zhang Jialiang, Dong Wenwei, Pu Jiazhong. 2014. Breakthrough of gold ore prospecting to depth of Chang'an gold deposit in southern Ailaoshan metallogenic belt[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 29(2): 185-191(in Chinese with English abstract).
鲍新尚, 杨立强, 和文言, 高雪, 李萌萌. 2019. 黑云母和锆石化学组分对岩浆结晶条件的约束: 以滇西北衙超大型金矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 35(5): 1447-1462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201905009.htm 陈建平, 唐菊兴, 丛源, 董庆吉, 郝金华. 2009. 藏东玉龙斑岩铜矿地质特征及成矿模型[J]. 地质学报, 83(12): 1887-1900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200912007.htm 邓军, 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 杨立强, 王庆飞, 王长明. 2010. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 29(1): 37-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201001006.htm 邓军, 王长明, 李文昌, 杨立强, 王庆飞. 2014. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究态势及启示[J]. 地学前缘, 21(1): 52-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201401008.htm 和文言. 2014. 滇西北衙超大型金多金属矿床岩浆作用与成矿模式[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-154. 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 徐文艺, 莫宣学, 丁林, 高永丰, 董方浏, 李光明, 曲晓明, 李光明, 赵志丹, 江思宏, 孟详金, 李振清, 秦克章, 杨志明. 2006a. 青藏高原碰撞造山带: I. 主碰撞造山成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 25(4): 337-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200802002.htm 侯增谦, 潘桂堂, 王安建, 莫宣学, 田世洪, 孙晓明, 丁林, 王二七, 高永丰, 谢玉玲, 曾普胜, 秦克章, 许继峰, 曲晓明, 杨志明, 杨竹森, 费红彩, 孟祥金, 李振清. 2006b. 青藏高原碰撞造山带: Ⅱ. 晚碰撞转换成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 25(5): 521-543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200606000.htm 侯增谦, 钟大赉, 邓万明. 2004. 青藏高原东缘斑岩铜钼金成矿带的构造模式[J]. 中国地质, 31(1): 1-13. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20040101?st=search 侯增谦. 2010. 大陆碰撞成矿论[J]. 地质学报, 84(1): 30-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201001001.htm 姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 凌洪飞, 戴宝章. 2006. 陆-陆碰撞造山环境下含铜斑岩岩石成因——以藏东玉龙斑岩铜矿带为例[J]. 岩石学报, 27(10): 3109-3122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603019.htm 李萌清, 芮宗瑶, 程莱仙. 1981. 玉龙斑岩铜(钼)矿床的流体包裹体及成矿作用研究[J]. 地质学报, 3: 216-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198103005.htm 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 王立全. 2010. 西南"三江"多岛弧盆-碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-491. 梁华英, 莫济海, 孙卫东, 张玉泉, 曾提, 胡光黔, Charllote A. 2009. 玉龙铜矿带马拉松多斑岩体岩石学及成岩成矿系统年代学分析[J]. 岩石学报, 25(2): 385-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200902012.htm 刘秉光, 陆德富, 蔡新平. 1999. 滇川西部金矿床研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1-241. 刘博. 2014. 滇西北衙金多金属矿床成岩成矿地质特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-74. 吕伯西, 段建中, 潘长云. 1993. 三江地区花岗岩类及其成矿专属性[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-328. 马鸿文. 1989. 论藏东玉龙斑岩铜矿带岩浆活动的构造环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB198901000.htm 芮宗瑶. 1984. 中国斑岩铜(钼)矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 350. 王建华, 李文昌, 和中华, 尹光候, 周云满. 2016. 滇西北衙金矿区大沙地岩体地质特征、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2367-2378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608009.htm 王建华, 李文昌, 王可勇, 尹光候, 吴松, 姜文涛. 2015. 滇西北衙斑岩型金多金属矿床成矿流体特征及其演化[J]. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3269-3280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201511008.htm 王建华. 2017. 滇西鹤庆北衙富碱斑岩金多金属成矿系统研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-130. 王璇, 杨林, 邓军, 李华健, 于华之, 董超一. 2018. 北衙金矿多期热液成矿作用识别: 来自地质、岩相学、流体包裹体和H-O-S同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 34(5): 1299-1311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201805006.htm 吴松. 2016. 滇西北衙金矿外带似层状Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿床地球化学特征及其成因研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-75. 武精凯, 赵志丹, 杨逸云, 雷杭山, 苗壮, 刘栋, 朱弟成, 喻学惠. 2019. 云南哀牢山-红河断裂带南段新生代富碱斑岩岩石成因和地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 35(2): 485-504. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201902014.htm 肖晓牛, 喻学惠, 莫宣学, 李勇, 黄行凯. 2011. 滇西北衙金多金属矿床成矿地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 47(2): 170-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201102006.htm 谢玉玲, 侯增谦, 徐九华, 杨志明, 徐文艺, 何建平. 2005. 藏东玉龙斑岩铜矿床多期流体演化与成矿的流体包裹体证据[J]. 岩石学报, 21(5): 1409-1415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505010.htm 胥磊落, 毕献武, 苏文超, 齐有强, 李亮, 陈佑维, 董少花, 唐永永. 2011. 云南金平铜厂斑岩Cu(Mo-Au)矿床含矿石英正长斑岩地球化学特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 697-706. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201110026.htm 徐受民. 2007. 滇西北衙金矿床的成矿模式及与新生代富碱斑岩的关系[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-115. 许志琴, 李海兵, 杨经绥. 2006. 造山的高原: 青藏高原巨型造山拼贴体和造山类型[J]. 地学前缘, 13(4): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200604001.htm 曾普胜, 莫宣学, 喻学惠. 2002. 滇西富碱斑岩带的Nd、Sr、Pb同位素特征及其挤压走滑背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 21(3): 231-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200203004.htm 张玉泉, 谢应雯, 涂光炽. 1987. 哀牢山-金沙江富碱侵入岩及其与裂谷构造关系初步研究[J]. 岩石学报, 3(1): 19-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB198701002.htm 周放, 王保弟, 贺娟, 郝明, 王鹏. 2022. 云南北衙斑岩-矽卡岩金铜矿床三维可视化建模与应用[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 241-252. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220115?st=search 周云满, 张家良, 董文伟, 普家忠. 2014. 哀牢山南段长安金矿深部找矿新进展[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 29(2): 185-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201402004.htm -
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 金爱芳,殷秀兰,李长青,李文娟,庞菊梅,金晓媚. 张家口地区枯水期地下水水化学特征及其成因机制分析. 环境科学. 2024(02): 826-836 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孟瑞芳,杨会峰,包锡麟,徐步云,李磊,李谨丞. 京津冀平原非常规水资源利用前景分析及其生态环境效应. 中国地质. 2024(01): 221-233 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李晓波,李静. 大汶河流域中下游浅层地下水水化学特征及其影响因素. 环境科学研究. 2024(05): 1015-1026 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 唐辉,何欣琳,郭晓静,马兴瑾,朱家葆. 郑州市城区浅层地下水环境化学特征及成因分析. 河南科学. 2024(08): 1192-1201 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘春燕,刘景涛,朱亮,张玉玺,荆继红,黄冠星,周冰,陈玺,解飞,李备. 高原河谷城市浅层地下水铁锰分布特征、影响因素及其对生态环境的影响——以西宁市为例. 中国地质. 2024(05): 1776-1790 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张博深,李海明,苏思慧,李梦娣,张翠霞. 天津平原地下水水化学特征与碳酸盐风化碳汇特征的时空演变. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文). 2024(05): 1016-1028 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. Jing-jie Li,Sheng Lian,Ming-guo Wang,Huai-sheng Zhang,Tao Yang. Hydrochemical characteristics of surface water in Hengduan mountain region of Eastern Tibet and its response to human activities: A case study of Duoqu Basin, Jinsha River. China Geology. 2024(04): 630-641 .  必应学术
必应学术
8. 邹银先,褚学伟,刘埔,段先前,王中美,王益伟. 贵州喀斯特山区地下水化学特征分析. 地质与资源. 2024(06): 846-854+860 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李月,李洋,周盈,黄晓燕. 苏锡常地区深层地下水化学特征及成因探讨. 上海国土资源. 2024(04): 171-178+202 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: