Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area of Western Kunlun, Xinjiang
-
摘要:研究目的
为了进一步了解西昆仑松潘—甘孜陆块西北缘巴颜喀拉弧后盆地的构造演化。
研究方法对西昆仑东缘独尖山地区二云母二长花岗岩进行了岩相学、地球化学、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素测试。
研究结果LA-ICP-MS锆石年代学研究揭示独尖山地区二长花岗岩成岩年龄为(219.9±1.2)~(227.1±1.5)Ma,为晚三叠世花岗岩。岩石主量元素、微量元素和Hf同位素分析结果揭示该二长花岗岩属高钾钙碱性系列,准铝质—弱过铝质,具岛弧和同碰撞花岗岩特征,物质来源具有壳幔物质混合的特点。
结论结合区域大地构造演化,推测独尖山地区在晚三叠世末期处于碰撞后伸展环境,早期洋-陆俯冲阶段形成的岛弧和同碰撞物质通过部分熔融在研究区内形成了后碰撞花岗岩。
创新点:首次获得了西昆仑独尖山地区三叠纪花岗岩的高精度锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素测试结果,探讨了其成因和大地构造背景。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThe study aims to further understand the tectonic evolution of the back-arc basin of Bayankera, the northwestern margin of Songpan-Ganzi block, Western Kunlun.
MethodsIn this paper, the authors present petrographical, lithogeochemical, LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic data for the two-mica monzogranite in Dujianshan.
ResultsLA-ICP-MS zircon geochronology study reveals that the monzogranites in the Dujianshan area crystallized at (219.9±1.2)-(227.1±1.5) Ma, indicative of the Late Triassic plutons. The results of major elements, trace elements and Hf isotope reveal that the monzogranites are metaluminous-weakly peraluminous rocks, belongs to the high potassium calcium alkaline series and exhibit characteristics of island arc and collisional granites. The source rocks of granites were generated from partial melting of a mixture of crust-mantle materials.
ConclusionsCombined with the regional tectonic evolution, it is speculated that the Dujianshan area is in a post collision extension environment at the end of the Late Triassic, and the island arc and syn-collision materials formed in the early ocean continent subduction stage partially melted to form post collision granite in the area.
-
1. 引言
新疆昆仑—阿尔金地区自太古宙以来,经历了长期而复杂的地质演化,区内岩石-构造格局复杂多变(潘裕生,1990;毕华等,1999;姜春发等,2000;李荣社等,2008;校培喜等,2015),尤其是晚古生代—中生代强烈的岩浆活动,为区内成矿提供了丰富的物源及充足的热源(孙海田,2001;董连慧等,2015;冯宝山等,2016;张传林等,2019;李文渊等,2022)。新疆西昆仑独尖山地区地处青藏高原北缘,东西昆仑交界位置,以阿尔金断裂为界,西北为苏巴什—鲸鱼湖混杂岩带,东南为松潘—甘孜陆块,区域上发育黑石北湖—三道河子构造岩浆岩带(吕金刚等,2006),该岩浆岩带内发育大量的花岗岩类(李荣社等,2008),前人对区内出露的主要岩体做过研究,取得了较为丰富的锆石年龄,其中卧龙岗斜长花岗斑岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为(212.5±3.6) Ma❶,三道河子闪长(玢)岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(216.7±2.0) Ma❷,盼水河花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(210.9±2.8) Ma❸(唐名鹰等,2020),从上述年代学数据看,其时代均为晚三叠世。本区为新疆汞锑元素富集区,区内已发现黄羊岭、卧龙岗、硝尔库勒、长山沟等中大型汞、锑矿床,前人通过对上述矿床的研究,认为汞锑矿的形成与早印支期热液活动相关❹❺❻(杨万志等,2005;陈文平等,2009;李文渊等,2011;张友军等,2014;闫磊等,2016)。
为进一步丰富区内构造岩浆岩带数据,深化区内晚古生代—早中生代俯冲-碰撞造山过程的认识,并对该区铜、金、汞、锑等多金属的成矿时代提供依据,本次研究在西昆仑温泉—独尖山一带1∶5万区域地质调查的基础上,对区内琼木孜塔格雪山北侧出露的二云母二长花岗岩体的岩石学、岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素进行研究。
2. 地质背景
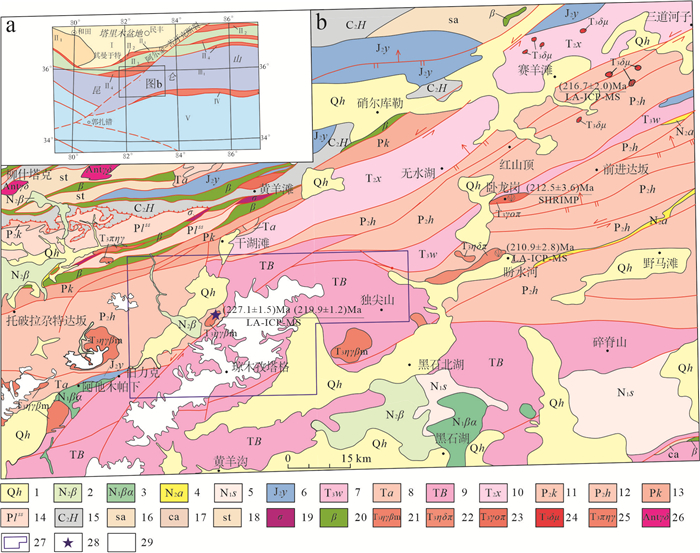
研究区位于青藏高原北缘,东西昆仑结合部位(图 1),其大地构造位置特殊,区内物质组成和构造样式十分复杂,呈现出多层次、多样式、多机制、多阶段的构造演化和变形特点。研究区最早有地质记录的是晚石炭世—早奥陶世花岗闪长岩岩片,其后依次发育了二叠系硫磺达坂砂岩组、二叠系卡拉勒塔什群、中二叠统卡拉孔木组、中二叠统黄羊岭组、三叠系巴颜喀拉山群、中三叠统西长沟组、三叠系阿它木帕下组等地层。零星发育早二叠世辉长辉绿岩、晚三叠世—早侏罗世二长花岗岩-石英闪长岩,其中以晚三叠世侵入岩最为发育。自侏罗纪开始区内进入陆内构造演化阶段,零星发育新近系(玄武)安山岩、火山集块岩,晚更新统玄武岩和第四系冰碛、冲洪积等松散沉积。
![]() 图 1 西昆仑大地构造位置图(a)和独尖山一带区域地质简图(b)❼1—第四系;2—上新统玄武安山岩-火山集块岩建造;3—中新统安山岩建造;4—上新统阿图什组;5—中新统唢纳湖组;6—中侏罗统杨叶组;7—上三叠统卧龙岗组;8—三叠系阿他木帕下组;9—三叠系巴颜喀拉山群;10—中三叠统西长沟组;11—中二叠统卡拉孔木组;12—中二叠统黄羊岭组;13—二叠系卡拉勒塔什群;14—二叠系硫磺达坂砂岩组;15—上石炭统哈拉米兰河群;16—硅质岩岩片;17—碳酸盐岩、复理石岩片;18—浅粒岩夹二云母石英片岩;19—橄榄岩岩片;20—基性—超基性岩片;21—晚三叠世二云二长花岗岩;22—晚三叠世花岗闪长斑岩;23—晚三叠世斜长花岗斑岩;24—晚三叠世闪长玢岩;25—三叠系似斑状二长花岗岩;26—前寒武纪花岗闪长岩;27—研究区范围;28—本次测年样品及岩石地球化学分析样品采样位置;29—冰雪覆盖区;Ⅰ—塔里木陆块;Ⅱ—昆仑造山带;Ⅱ1—昆北微陆块;Ⅱ2—其曼于特—纳赤台结合带;Ⅱ3—昆南微陆块;Ⅱ4—苏巴什—鲸鱼湖结合带;Ⅲ1—松潘—甘孜陆块;Ⅳ—西金乌兰—金沙江结合带;Ⅴ—北羌塘陆块Figure 1. Tectonic location map (a) and regional geological map (b) of Dujianshan, West Kunlun❼1-Quaternary; 2-Basaltic andesite-volcanic agglomerate formation in the Pliocene Series; 3-Mesocene andesite formation; 4-Pliocene Atush Formation; 5-Mesocene Suonahu Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yangye Formation; 7-Upper Triassic Wolonggang Formation; 8-Triassic Atampa Formation; 9-Triassic Bayankera Group; 10-Middle Triassic Xichanggou Formation; 11-Middle Permian Kara Kongmu Formation; 12-Middle Permian Huangyangling Formation; 13-Permian Karaletash Group; 14-Permian sulfur Daban sandstone formation; 15-Hararamani River Group of upper Carboniferous Series; 16-Siliceous rock slices; 17-Carbonate rocks, flysch slices; 18-Leptites interspersed with mica quartz schists; 19-Peridotite slices; 20-Basic-ultrabasic rock slices; 21-Late Triassic Eryuneronite granites; 22-Late Triassic granodiorite porphyries; 23-Late Triassic anorthosite porphyries; 24-Late Triassic diorite porphyrites; 25-Triassic porphyritic monzogranites; 26-Precambrian granodiorites; 27-Scope of study area; 28-Sampling locations of the samples for this dating and petrogeochemical analysis; 29-Snow and ice covered area; Ⅰ-Tarim block; Ⅱ-Kunlun orogenic belt; Ⅱ1-North Kunlun micro-blocks; Ⅱ2-Qimanyute-NaijTal boundary belt; Ⅱ3-South Kunlun Micro-blocks; Ⅱ4-Subashi-Jingyuhu boundary belt; Ⅲ1-Songpan-Ganzi block; Ⅳ-Xijir Ulan-Jinsha River boundary belt; Ⅴ-North Qiangtang block
图 1 西昆仑大地构造位置图(a)和独尖山一带区域地质简图(b)❼1—第四系;2—上新统玄武安山岩-火山集块岩建造;3—中新统安山岩建造;4—上新统阿图什组;5—中新统唢纳湖组;6—中侏罗统杨叶组;7—上三叠统卧龙岗组;8—三叠系阿他木帕下组;9—三叠系巴颜喀拉山群;10—中三叠统西长沟组;11—中二叠统卡拉孔木组;12—中二叠统黄羊岭组;13—二叠系卡拉勒塔什群;14—二叠系硫磺达坂砂岩组;15—上石炭统哈拉米兰河群;16—硅质岩岩片;17—碳酸盐岩、复理石岩片;18—浅粒岩夹二云母石英片岩;19—橄榄岩岩片;20—基性—超基性岩片;21—晚三叠世二云二长花岗岩;22—晚三叠世花岗闪长斑岩;23—晚三叠世斜长花岗斑岩;24—晚三叠世闪长玢岩;25—三叠系似斑状二长花岗岩;26—前寒武纪花岗闪长岩;27—研究区范围;28—本次测年样品及岩石地球化学分析样品采样位置;29—冰雪覆盖区;Ⅰ—塔里木陆块;Ⅱ—昆仑造山带;Ⅱ1—昆北微陆块;Ⅱ2—其曼于特—纳赤台结合带;Ⅱ3—昆南微陆块;Ⅱ4—苏巴什—鲸鱼湖结合带;Ⅲ1—松潘—甘孜陆块;Ⅳ—西金乌兰—金沙江结合带;Ⅴ—北羌塘陆块Figure 1. Tectonic location map (a) and regional geological map (b) of Dujianshan, West Kunlun❼1-Quaternary; 2-Basaltic andesite-volcanic agglomerate formation in the Pliocene Series; 3-Mesocene andesite formation; 4-Pliocene Atush Formation; 5-Mesocene Suonahu Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yangye Formation; 7-Upper Triassic Wolonggang Formation; 8-Triassic Atampa Formation; 9-Triassic Bayankera Group; 10-Middle Triassic Xichanggou Formation; 11-Middle Permian Kara Kongmu Formation; 12-Middle Permian Huangyangling Formation; 13-Permian Karaletash Group; 14-Permian sulfur Daban sandstone formation; 15-Hararamani River Group of upper Carboniferous Series; 16-Siliceous rock slices; 17-Carbonate rocks, flysch slices; 18-Leptites interspersed with mica quartz schists; 19-Peridotite slices; 20-Basic-ultrabasic rock slices; 21-Late Triassic Eryuneronite granites; 22-Late Triassic granodiorite porphyries; 23-Late Triassic anorthosite porphyries; 24-Late Triassic diorite porphyrites; 25-Triassic porphyritic monzogranites; 26-Precambrian granodiorites; 27-Scope of study area; 28-Sampling locations of the samples for this dating and petrogeochemical analysis; 29-Snow and ice covered area; Ⅰ-Tarim block; Ⅱ-Kunlun orogenic belt; Ⅱ1-North Kunlun micro-blocks; Ⅱ2-Qimanyute-NaijTal boundary belt; Ⅱ3-South Kunlun Micro-blocks; Ⅱ4-Subashi-Jingyuhu boundary belt; Ⅲ1-Songpan-Ganzi block; Ⅳ-Xijir Ulan-Jinsha River boundary belt; Ⅴ-North Qiangtang block本次研究的二云母二长花岗岩位于琼木孜塔格雪山北坡,玄武岩火山口以北,呈岩株状产出,平面上呈近椭圆状,岩体与中二叠统黄羊岭组呈侵入接触关系,表现为呈岩脉或岩枝状穿插于围岩裂隙,局部可见不规则棱角状围岩捕掳体,发育热烘烤褪色现象,岩体侵入界线清晰,平面上不规则弯曲,局部沿裂隙灌入围岩,呈不规则状。岩体内发育电气石,长柱状,长度0.5~1 cm,局部形成电气石团块。
二云二长花岗岩呈灰色,花岗结构,块状构造,岩石主要由斜长石、钾长石、黑云母、白云母、石英等组成(图 2)。斜长石含量25%~30%,半自形板状,板长1~3 mm,可见聚片双晶,部分晶粒具强烈的绢云母化。钾长石含量35%~40%,成分以正长石为主,微斜长石含量少,呈半自形—他形板状,长2.5~5 mm,正长石一般无双晶,部分具简单双晶,部分晶粒中心包嵌有较小的斜长石晶粒。黑云母含量6%~7%,棕褐色,鳞片状,片径0.4~3.5 mm,部分鳞片中心包嵌有磷灰石等副矿物。白云母含量3%~4%,无色鳞片状,片径0.5~2.5 mm,常与黑云母共生。石英含量约25%,不规则粒状,粒径1~3 mm,分布于长石晶粒间隙,晶粒波状消光强烈,裂纹发育,裂隙中常充填有次生形成的微粒石英,形成显微脉状。
![]() 图 2 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩野外及镜下特征a—二云母二长花岗岩白云母集合体;b—二云母二长花岗岩中暗色包体;c, d—二云母二长花岗岩镜下特征;Mc—微斜长石;Or—正长石;Ms—白云母;Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Q—石英Figure 2. Photographs and microphotographs of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan areaa-Muscovite aggregates in mica monzogranite; b-Mafic enclaves in mica monzogranite; c, d-Microscopic characteristics of mica monzogranite; Mc-Microcline; Or-Orthoclase; Ms-Muscovite; Bt-Biotite; Pl-Plagioclase; Q-Quartz
图 2 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩野外及镜下特征a—二云母二长花岗岩白云母集合体;b—二云母二长花岗岩中暗色包体;c, d—二云母二长花岗岩镜下特征;Mc—微斜长石;Or—正长石;Ms—白云母;Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Q—石英Figure 2. Photographs and microphotographs of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan areaa-Muscovite aggregates in mica monzogranite; b-Mafic enclaves in mica monzogranite; c, d-Microscopic characteristics of mica monzogranite; Mc-Microcline; Or-Orthoclase; Ms-Muscovite; Bt-Biotite; Pl-Plagioclase; Q-Quartz3. 样品采集及测试方法
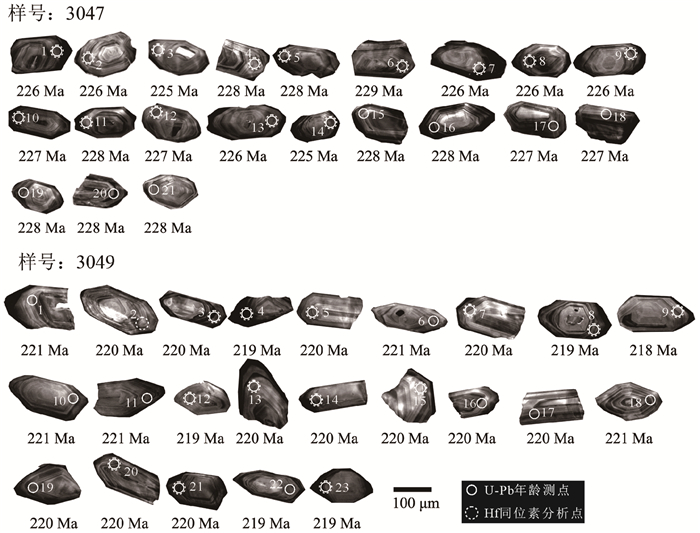
本次在独尖山地区采得2件二云母二长花岗岩同位素年龄样品,样品采样位置地理坐标:3047号为35°40′39″N,82°14′15″E;3049号为:35°40′54″N,82°14′10″E。样品的破碎以及锆石挑选、制靶、阴极发光(CL)图像制备均在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所实验室完成。锆石微区原位U-Pb同位素年龄分析及Hf同位素分析均在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室LA-ICP-MS仪器上用标准测定程序进行,激光剥蚀系统为美国Newwave公司生产的UP193FX型193 nm ArF准分子系统,激光器来自于德国ATL公司,ICP-MS为Agilent 7500a,激光器波长为193 nm,脉冲宽度<4 ns。本次所用束斑直径为25 μm。2件样品均采用锆石标样91500进行外标校正,分析方法及流程见侯可军等(2009)。样品的同位素比值及元素含量计算采用GLITTER_ver4.0程序。锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图的绘制和MSWD的计算用Isoplot3.0程序完成。
Hf同位素分析仪器的运行条件、详细的分析流程见Wu et al.(2006)。本次两件样品试验的91500标样的176Hf/177Hf测定结果是0.282308,该值与目前溶液法获得的值在误差范围内一致。在εHf(t)值计算中,采用Blichert-Toft and Albarède(1997)推荐的球粒陨石值,亏损地幔模式年龄(tDM)计算采用Griffin et al.(2000)的推荐值。
采取的6件主量、微量和稀土元素样品的测试均在河南省岩石矿物测试中心实验室完成,分析结果见表 1。其中主量元素分析在波长色散X荧光光谱仪上完成,分析精度优于10%;微量和稀土元素采用德国Finnigan-MAT公司生产的ELEMENT I(离子质谱仪)测定,微量元素分析精度优于10%,稀土元素分析精度优于5%,分析方法及流程见Qi et al.(2000)。
表 1 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of the two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area
4. 分析结果
4.1 岩石地球化学特征
4.1.1 主量元素特征
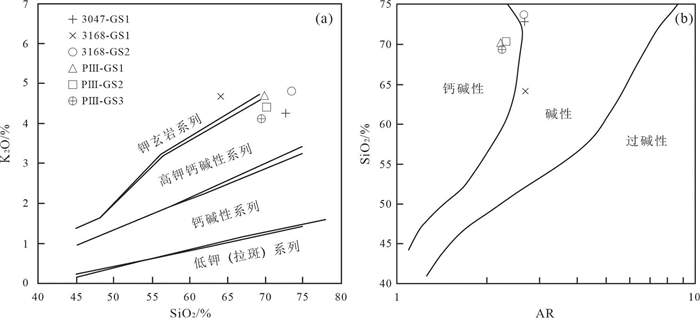
岩石SiO2含量在64.0%~73.5%,平均值为69.9%;Al2O3含量介于13.6%~18.8%,平均值为14.8%;MgO含量介于0.33%~1.26%,平均值为0.71%;CaO、K2O和Na2O含量,含量分别为0.95%~2.48%、4.15%~4.87%和3.00%~4.66%,Na2O/K2O值为0.64~0.98,SiO2-K2O图解显示属高钾钙碱性类型(图 3a)。岩石化学参数σ值为1.95~4.08,AR值为2.21~2.68,在AR-SiO2图解落入碱性—钙碱性区(图 3b);铝饱和指数A/CNK为0.985~1.196,为准铝质—弱过铝质花岗岩类。岩石中DI和SI指数分别变化于80.34~91.82和3.80~10.8,表明岩石经历了一定程度的分异作用。综合主量元素特征分析,岩石属经历一定分异作用的准铝质-弱过铝质高钾钙碱性系列花岗岩。
4.1.2 稀土元素特征
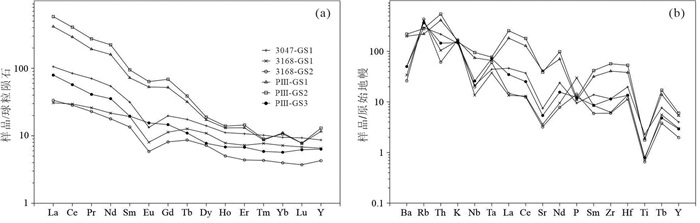
二云母二长花岗岩稀土总量(ΣREE)变化较大,呈现明显的两组,分别为65.05×10-6~165.45×10-6、528.49×10-6~733.3×10-6,前者与平均陆壳稀土总量相当。岩石中重稀土的含量相差不大,为7.19×10-6~32.55×10-6,轻稀土含量相差较大,两组分别为49.88×10-6~149.32×10-6、501.43×10-6~700.77×10-6。其中,轻、重稀土比值(LREE/HREE)亦呈现明显的分组,但均表现为轻稀土富集型,比值分别为4.87~9.92、18.53~21.53,上述岩石表现出不一致的轻稀土富集,表明岩石经过了较强的分异过程。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图表现为向右陡倾斜的模式(图 4a),δEu为0.52~0.91,为弱负铕异常。
4.1.3 微量元素特征
微量元素的原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 4b)显示,微量元素整体呈现从Rb至Ce富集,从P至Yb相对亏损的右倾曲线,其中Nb、Sr、Ti出现强烈亏损,沟谷明显,Rb、La、Ce、Zr、Hf为明显富集,其峰值较高;特征比值中Nb/Ta、Zr/Hf均值分别为11.23、27.46,显示岩石具俯冲带岩浆岩特征,反映地幔与俯冲板片部分熔融产物作用特征。
4.2 锆石U-Pb年龄
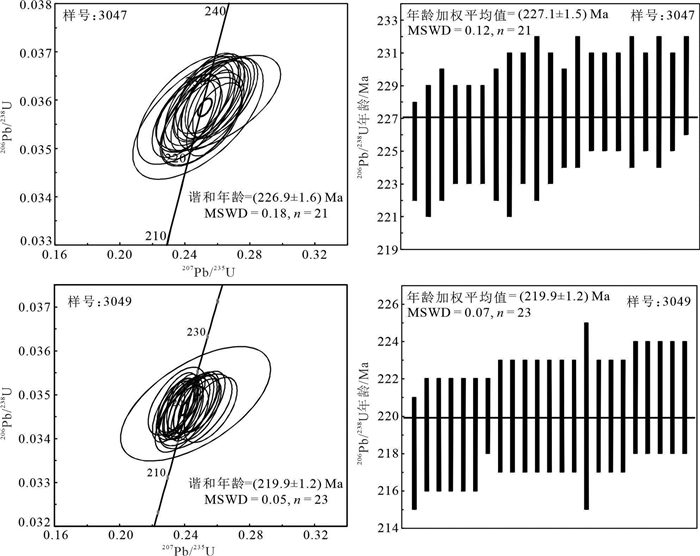
二云母二长花岗岩锆石CL图像(图 5)显示,锆石整体颜色偏暗,多为自形—半自形长柱状,大部分形态较完整,长度变化于100~200 μm,长宽比多为2∶1,多具宽的岩浆振荡环带,个别见残留核,外部无后期变质的增生边。综合以上特征,样品中的锆石应为原岩岩浆成因。
锆石测试点位多选在振荡环带发育部位。锆石U-Pb定年结果(表 2)显示,锆石U含量普遍较低,大多 < 60×10-6,这与锆石整体颜色偏暗相符。大量研究表明,不同成因的锆石具有不同的Th/U比值,本次测试的锆石Th/U比值为0.02~0.34,较一般的岩浆锆石Th/U比值偏低(王海然等,2013),但从锆石形态来看,为典型的岩浆成因锆石,其比值偏低应与初融岩体的特殊性相关。在U-Pb谐和图和年龄频谱上,两件样品所测锆石年龄数据投影均落在谐和线及附近(图 6),其206Pb/238U加权平均年龄分别为(227.1±1.5) Ma(MSWD=0.119)和(219.9±1.2) Ma(MSWD=0.070),表明岩体形成时代为晚三叠世。
表 2 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果Table 2. Results of zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating
4.3 锆石Lu-Hf同位素
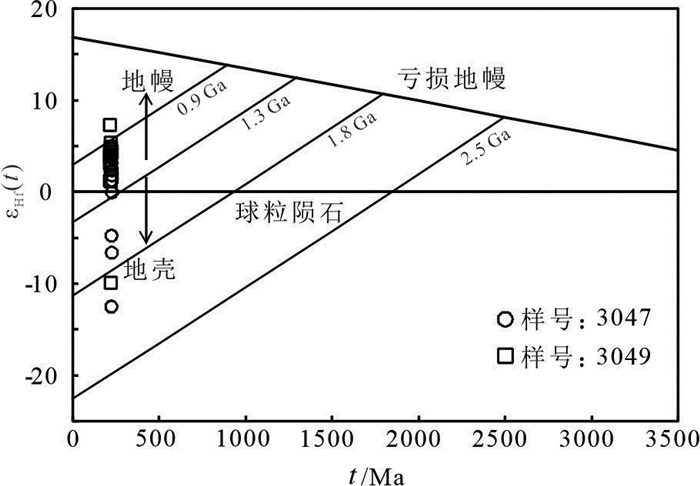
本次对二云母二长花岗岩所取的两件样品,共计28颗测年锆石进行了Lu-Hf同位素分析,结果见表 3。锆石的176Lu/177Hf和176Yb/177Hf比值范围分别为0.00065~0.002504和0.025985~0.101183,其中锆石的176Lu/177Hf值除3件样品外,其余均小于0.002,表明锆石在形成后基本没有受到明显的放射性成因Hf的影响,本次测定的176Hf/177Hf值可以代表其形成时体系的Hf同位素组成。28个测点的176Hf/177Hf值较集中,分布于0.282282~0.282846;其εHf(t)值介于-12.55~7.26,平均值1.74;t2DM年龄为0.79~2.05 Ga,平均值为1.15 Ga。
表 3 锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素组成Table 3. Zircon in-situ Lu-Hf isotopic compositions
5. 讨论
5.1 岩体形成时代
独尖山二云母二长花岗岩位于黑石北湖—三道河子构造岩浆岩带中部偏南,侵位于中二叠统黄羊岭组中,前人研究认为其时代为侏罗纪❼。本次研究采用LA-ICP-MS对该花岗岩进行锆石U-Pb定年,获得锆石206Pb/238U年龄值分别为(227.1±1.5)Ma和(219.9±1.2)Ma,结合锆石阴极发光图像以及锆石Th/U比值,其具有明显的岩浆锆石特征,U-Pb年龄代表了该岩体的侵位时代为晚三叠世,而不是前人认为的侏罗纪❼。
5.2 岩石成因及岩浆源区
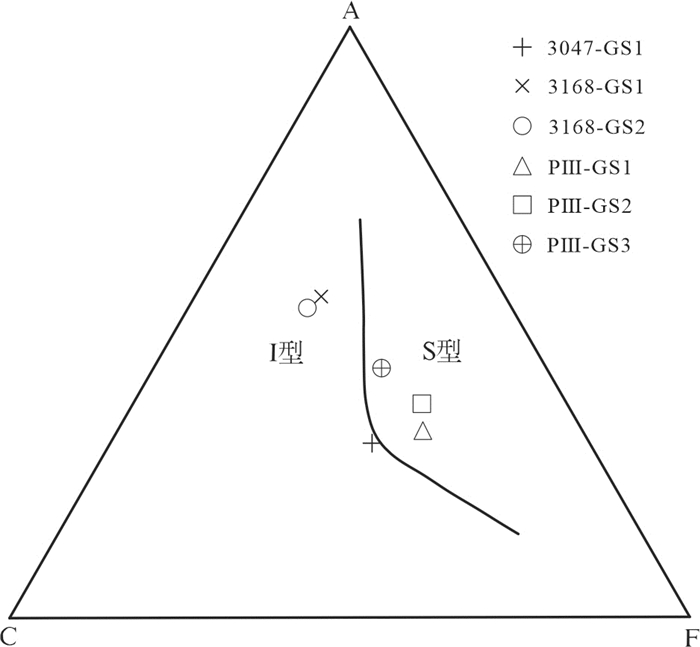
岩石地球化学特征表明,独尖山二云母二长花岗岩属高钾钙碱性系列岩石(图 3a),主量元素A/CNK值(0.985~1.196),表明其为准铝质—弱过铝质花岗岩。根据花岗岩成因系列图解(图 7),样品在S、I型花岗岩中均有分布。
微量元素比值也较好地反映了源区特点,6件样品Rb/Sr值在两个区间分布,分别为0.16~0.22和1.19~4.06,前者介于上地幔值(0.034)与地壳值(0.35)之间,后者远大于地壳值(0.35)的含量比值,Nb/Ta值在两个区间分布,分别为19.48~21.46和5.71~8.39,前者大于地幔值(17.5)含量比值,后者远小于大陆地壳值(11)含量比值,两者比值均显示壳幔物质混合的特点。尤其Nb、Sr、Ti元素的强烈亏损,显示I型花岗岩的特征,但二长花岗岩中较多量的白云母分布,亦显示S型花岗岩的特点。
锆石因具有极低的Lu/Hf值及Hf同位素较好的稳定性,在探讨岩浆起源与演化、示踪岩石源区及壳幔相互作用具有重要的作用(Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997; Griffin et al., 2002; Söderlund et al., 2004)。Peter and Roland(2003)在对岩浆锆石Hf同位素研究时认为,具有较低176Hf/177Hf及εHf(t)值的岩石指示其源区为地壳或经过地壳的混染,而具有较高的176Hf/177Hf及εHf(t)值的岩石则直接来自地幔或由幔源物质分异的新生壳源物质。本次研究获得样品εHf(t)值在-12.55~7.26,样品中锆石Hf同位素组成变化范围达19.81,显示出极大的不均一性,在t-εHf(t)图解中绝大部分数据点在球粒陨石Hf同位素演化线附近及以上的地幔区域(图 8),位于0.9 Ga和1.3 Ga平均演化线之间,二阶段Hf同位素模式年龄为0.79~2.05 Ga,上述数据表明本区二云母二长花岗岩主要物质来源为地幔物质,在岩浆演化过程中,加入了少量古老地壳成分,为壳幔物质混合的产物。
5.3 构造环境及其地球动力学意义
研究区南侧所处的松潘—甘孜陆块晚古生代—中生代经历了古特提斯洋闭合和块体的俯冲消减、拼贴碰撞事件(李荣社等,2008;周玉等,2018;唐名鹰等,2023),区内北侧的巴颜喀拉洋盆向北俯冲消减至早三叠世结束,形成苏巴什—鲸鱼湖蛇绿构造混杂岩带(计文化等, 2004; 温志刚等, 2019)。中三叠世以后,受冈瓦纳大陆与华夏陆块的进一步的挤压,研究区内苏巴什—鲸鱼湖蛇绿构造混杂岩带和其南侧的卡拉勒塔什群岛弧、弧后盆地发生强烈的冲褶变形,岩石圈厚度急剧增加并发生隆起,同时于晚三叠世,在结合带南侧弧后盆地形成后碰撞花岗岩(刘铮, 2015)。
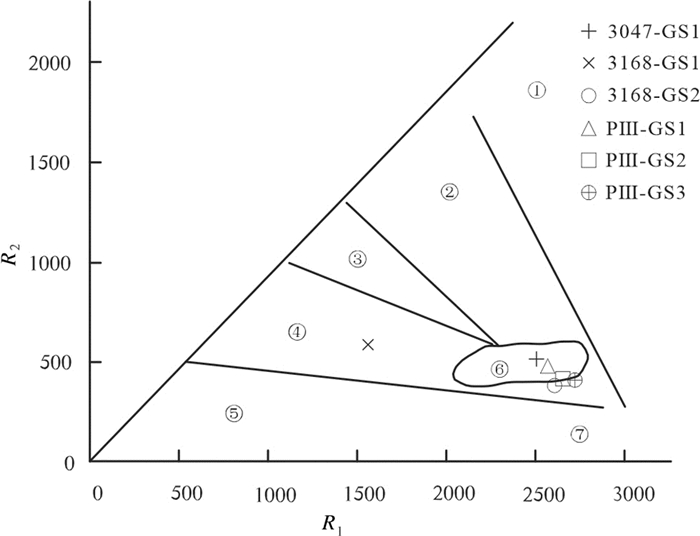
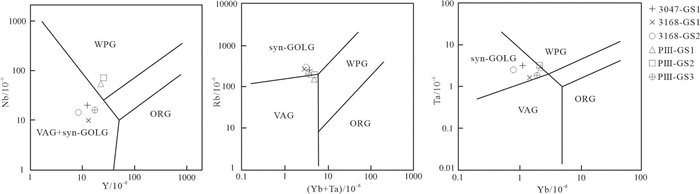
根据常量元素R1-R2构造环境分类图解(图 9),花岗岩投点主要落于同碰撞花岗岩范围内。花岗岩微量元素构造环境的判别图中(图 10),数据投点位于火山弧花岗岩与同碰撞花岗岩交界部位,显示混合花岗岩的特征。花岗岩岩石微量元素蛛网图(图 4b)显示,元素Ba、Nb、Sr、Ti强烈亏损,显示后碰撞花岗岩的岩石特征(Küster and Harms, 1998),岩石稀土和微量元素分析中,样品富集大离子亲石元素Rb、K、La和活泼不相容元素Th,同时特征元素比值中Nb/Ta、Zr/Hf均值显示岩石具消减带岩浆岩特征(Sun and McDonough, 1989),锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析说明幔源物质参与了岩浆活动。上述分析均表明独尖山二云母二长花岗岩具后碰撞花岗岩特征,造成此类情况发生的原因主要为,在区内碰撞造山的后碰撞阶段,随着壳幔相互作用的加强以及强烈的壳幔物质混合,来自于早期洋-陆俯冲阶段形成的岛弧和同碰撞物质参与后碰撞造山活动,于弧后盆地形成大量的混合成因花岗岩(Pearce and Mei, 1989),因而在地球化学性质上常显示岛弧和同碰撞花岗岩的特征。
![]() 图 9 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩主量元素R1-R2图解①—地幔斜长花岗岩;②—破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③—板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④—晚造期花岗岩;⑤—非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥—同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦—造山期后A型花岗岩Figure 9. The pivot elements R1-R2 diagram of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area①-Mantle plagioclase granite; ②-Granite at the edge of the destructive active plate (before the plate collision); ③-Granites in uplift stage after plate collision; ④-Granite of late building period; ⑤-Non-mountainous A-type granite; ⑥-Homophobic (S-type) granite; ⑦-Post-orogenic A-type granite
图 9 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩主量元素R1-R2图解①—地幔斜长花岗岩;②—破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③—板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④—晚造期花岗岩;⑤—非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥—同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦—造山期后A型花岗岩Figure 9. The pivot elements R1-R2 diagram of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area①-Mantle plagioclase granite; ②-Granite at the edge of the destructive active plate (before the plate collision); ③-Granites in uplift stage after plate collision; ④-Granite of late building period; ⑤-Non-mountainous A-type granite; ⑥-Homophobic (S-type) granite; ⑦-Post-orogenic A-type granite![]() 图 10 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩微量元素构造环境判别图解syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩; VAG—火山弧花岗岩; WPG—板内花岗岩; ORG—洋中脊花岗岩Figure 10. Trace element-diagrams for discrimination of structural environment of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan areasyn-COLG-Syn-collision granite; VAG-Volcanic arc granite; WPG-Within-plate granite; ORG-Oceanic ridge granite
图 10 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩微量元素构造环境判别图解syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩; VAG—火山弧花岗岩; WPG—板内花岗岩; ORG—洋中脊花岗岩Figure 10. Trace element-diagrams for discrimination of structural environment of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan areasyn-COLG-Syn-collision granite; VAG-Volcanic arc granite; WPG-Within-plate granite; ORG-Oceanic ridge granite综合以上分析,区内松潘—甘孜地块西北缘在晚三叠世末期属造山晚期的后碰撞构造背景,处于碰撞后伸展环境,早期洋-陆俯冲阶段形成的岛弧和同碰撞物质在结合带南侧独尖山地区侵入形成后碰撞花岗岩。
6. 结论
(1) 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩呈岩株状产出,与中二叠统黄羊岭组呈侵入接触关系,岩石地球化学特征表明,花岗岩属高钾的钙碱性准铝质—弱过铝质系列岩石。岩石微量元素Rb/Sr、Nb/Ta比值特征,显示岩浆具壳幔物质混合的特点。
(2) 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(227.1±1.5)Ma和(219.9±1.2)Ma,表明该岩体形成于晚三叠世。花岗岩锆石具有极大不均一性的εHf(t)值(-12.55~7.26)和偏老的地壳物质年龄(0.79~2.05 Ga),显示幔源物质在岩浆演化过程中加入了少量具较低放射性的古老地壳物质,为幔源岩浆与壳源物质熔融产物混合作用的结果。
(3) 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩岩石特征表明,岩体形成于后碰撞造山环境,岩石具有混合成因花岗岩的特征。综合分析认为,区内松潘—甘孜地块西北缘在晚三叠世末期属造山晚期的后碰撞构造背景,处于碰撞后伸展环境,早期洋-陆俯冲阶段形成的岛弧和同碰撞物质在结合带南侧独尖山地区侵入形成后碰撞花岗岩。
注释
❶新疆地矿局第一区域地质调查大队. 2003. 新疆民丰县昆仑山卧龙岗一带1∶5万区域地质矿产调查报告[R].
❷陕西省区域地质矿产研究院. 2010. 新疆民丰县硝尔库勒一带1∶5万区域地质矿产调查报告[R].
❸山东省第八地质矿产勘查院. 2018. 新疆西昆仑红山顶南一带1∶5万区域地质调查报告[R].
❹新疆地矿局第一区域地质调查大队. 2002. 新疆维吾尔自治区西昆仑尼雅河中上游1∶20万区域化探报告[R].
❺新疆贵源拍卖有限公司. 2008. 新疆民丰县黄羊岭锑矿详查报告[R].
❻乌鲁木齐天和众邦地质勘查有限公司. 2016. 新疆民丰县卧龙岗锑矿普查报告[R].
❼陕西省区域地质调查研究院. 2003. 中华人民共和国1∶25万伯力克幅区域地质调查报告[R].
-
图 1 西昆仑大地构造位置图(a)和独尖山一带区域地质简图(b)❼
1—第四系;2—上新统玄武安山岩-火山集块岩建造;3—中新统安山岩建造;4—上新统阿图什组;5—中新统唢纳湖组;6—中侏罗统杨叶组;7—上三叠统卧龙岗组;8—三叠系阿他木帕下组;9—三叠系巴颜喀拉山群;10—中三叠统西长沟组;11—中二叠统卡拉孔木组;12—中二叠统黄羊岭组;13—二叠系卡拉勒塔什群;14—二叠系硫磺达坂砂岩组;15—上石炭统哈拉米兰河群;16—硅质岩岩片;17—碳酸盐岩、复理石岩片;18—浅粒岩夹二云母石英片岩;19—橄榄岩岩片;20—基性—超基性岩片;21—晚三叠世二云二长花岗岩;22—晚三叠世花岗闪长斑岩;23—晚三叠世斜长花岗斑岩;24—晚三叠世闪长玢岩;25—三叠系似斑状二长花岗岩;26—前寒武纪花岗闪长岩;27—研究区范围;28—本次测年样品及岩石地球化学分析样品采样位置;29—冰雪覆盖区;Ⅰ—塔里木陆块;Ⅱ—昆仑造山带;Ⅱ1—昆北微陆块;Ⅱ2—其曼于特—纳赤台结合带;Ⅱ3—昆南微陆块;Ⅱ4—苏巴什—鲸鱼湖结合带;Ⅲ1—松潘—甘孜陆块;Ⅳ—西金乌兰—金沙江结合带;Ⅴ—北羌塘陆块
Figure 1. Tectonic location map (a) and regional geological map (b) of Dujianshan, West Kunlun❼
1-Quaternary; 2-Basaltic andesite-volcanic agglomerate formation in the Pliocene Series; 3-Mesocene andesite formation; 4-Pliocene Atush Formation; 5-Mesocene Suonahu Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yangye Formation; 7-Upper Triassic Wolonggang Formation; 8-Triassic Atampa Formation; 9-Triassic Bayankera Group; 10-Middle Triassic Xichanggou Formation; 11-Middle Permian Kara Kongmu Formation; 12-Middle Permian Huangyangling Formation; 13-Permian Karaletash Group; 14-Permian sulfur Daban sandstone formation; 15-Hararamani River Group of upper Carboniferous Series; 16-Siliceous rock slices; 17-Carbonate rocks, flysch slices; 18-Leptites interspersed with mica quartz schists; 19-Peridotite slices; 20-Basic-ultrabasic rock slices; 21-Late Triassic Eryuneronite granites; 22-Late Triassic granodiorite porphyries; 23-Late Triassic anorthosite porphyries; 24-Late Triassic diorite porphyrites; 25-Triassic porphyritic monzogranites; 26-Precambrian granodiorites; 27-Scope of study area; 28-Sampling locations of the samples for this dating and petrogeochemical analysis; 29-Snow and ice covered area; Ⅰ-Tarim block; Ⅱ-Kunlun orogenic belt; Ⅱ1-North Kunlun micro-blocks; Ⅱ2-Qimanyute-NaijTal boundary belt; Ⅱ3-South Kunlun Micro-blocks; Ⅱ4-Subashi-Jingyuhu boundary belt; Ⅲ1-Songpan-Ganzi block; Ⅳ-Xijir Ulan-Jinsha River boundary belt; Ⅴ-North Qiangtang block
图 2 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩野外及镜下特征
a—二云母二长花岗岩白云母集合体;b—二云母二长花岗岩中暗色包体;c, d—二云母二长花岗岩镜下特征;Mc—微斜长石;Or—正长石;Ms—白云母;Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Q—石英
Figure 2. Photographs and microphotographs of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area
a-Muscovite aggregates in mica monzogranite; b-Mafic enclaves in mica monzogranite; c, d-Microscopic characteristics of mica monzogranite; Mc-Microcline; Or-Orthoclase; Ms-Muscovite; Bt-Biotite; Pl-Plagioclase; Q-Quartz
图 9 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩主量元素R1-R2图解
①—地幔斜长花岗岩;②—破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③—板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④—晚造期花岗岩;⑤—非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥—同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦—造山期后A型花岗岩
Figure 9. The pivot elements R1-R2 diagram of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area
①-Mantle plagioclase granite; ②-Granite at the edge of the destructive active plate (before the plate collision); ③-Granites in uplift stage after plate collision; ④-Granite of late building period; ⑤-Non-mountainous A-type granite; ⑥-Homophobic (S-type) granite; ⑦-Post-orogenic A-type granite
图 10 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩微量元素构造环境判别图解
syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩; VAG—火山弧花岗岩; WPG—板内花岗岩; ORG—洋中脊花岗岩
Figure 10. Trace element-diagrams for discrimination of structural environment of two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area
syn-COLG-Syn-collision granite; VAG-Volcanic arc granite; WPG-Within-plate granite; ORG-Oceanic ridge granite
表 1 独尖山二云母二长花岗岩主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of the two-mica monzonitic granites in Dujianshan area

表 2 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 2 Results of zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating

表 3 锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素组成
Table 3 Zircon in-situ Lu-Hf isotopic compositions

-
Bi Hua, Wang Zhonggang, Wang Yuanlong, Zhu Xiaoqing. 1999. Tectono-magmatic evolution of the West Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Science in China (Series D), 29(5): 398-406 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Blichert-Toft J, Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148: 243-258. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X
Chen Wenping, Lu Jingang, Han Xiaoming. 2009. Applying ETM+ image data to metallogenic predict for Sb mine in Wolonggang-Huangyangling area[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 27(2): 180-183 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2009.02.017
Dong Lianhui, Liu Dequan, Tang Yanling, Feng Jing, Qu Xun, Li Fengming, Tian Jiangtao, Xu Shiqi. 2015. Five-era metallogenic system of mineral deposits in Xinjiang and its spatial and temporal evolution mode[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(6): 1107-1129 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng Baoshan, Li Boqin, Guo Hongjun, Liu Mingtao, Xue Lanhua, Shi Laohu. 2016. Division and introduction of West Kunlun metallogenic belt[J]. Northwestern Geology, 49(4): 129-135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Tian Yourong. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 481-492 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, Jackson S E, Achterbergh E, O'Reilly S Y, Shee S R. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LA-MC-ICP-MS analyses of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackon S E, Pearson N J, O'Reilly S Y, Xu X S, Zhou X M. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 61(3/4): 237-269.
Ji Wenhua, Han Fanglin, Wang Juchuan, Zhang Junliang. 2004. Composition and geochemistry of the Subashi ophiolitic mélange in the West Kunlun and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(12): 1196-1201 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Chunfa, Wang Zongqi, Li Jintie. 2000. Opening-Closing Tectonics of Central Orogen[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-154 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Küster D, Harms U. 1998. Post-collisional potassic granitoids from the southern and northwestern parts of the Late Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: A review[J]. Lithos, 45(1/4): 177-195.
Li Rongshe, Ji Wenhua, Yang Yongcheng. 2008. Kunlun Mountain and Its Adjacent Area Geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-400 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenyuan, Zhang Zhaowei, Gao Yongbao, Hong Jun, Chen Bo, Zhang Zhibing. 2022. Tectonic transformation of the Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan orogenic belt and related mineralization of critical mineral resources of nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1385-1407 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenyuan, Zhang Zhaowei, Gao Yongbao, Tan Wenjuan, Jiang Hanbing, Guo Zhouping. 2011. Important metallogenic events and tectonic response of Qinling, Qilian and Kunlun orogenic belts[J]. Geology in China, 8(5): 1135-1149 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zheng. 2015. Petrogenesis of Early Mesozoic Granites in Westren Kunlun Orogen and Its Implications for Paleo-Tethys Tectonic Evolution[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lü Jingang, Wang Juchuan, Chu Chunhua, Li Liqun, Liu Rong, Lei Hongmin. 2006. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the Wolonggang monzogranite porphyry in the western segment of the Hoh Xil belt, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(6): 721-724 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pan Yusheng. 1990. Tectonic features and evolution of the Western Kunlun Mountain Region[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 25(3): 224-231 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pearce J A, Mei H. 1988. Volcanic rocks of the 1985 Tibet Geotraverse: Lhasa to Golmud[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 327(1594): 169-201. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1988.0125
Peter D K, Roland M. 2003. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 327- 341. doi: 10.2113/0530327
Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C. 2000. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 51(3): 507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
Söderlund U, Pathcett P J, Verrot J D, Isachsen C E. 2004. The 176Lu decay content determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusion[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219: 311-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3
Sun Haitian. 2001. Metallogenic prospect and target area prediction of large deposit of precious and non-ferrous metals in West Kunlun[C]//Scientific and Technological Achievements of the ninth Five-year Plan of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Geological Society of China: 33-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle compositions and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Tang Mingying, Gao Zhenhua, Dong Zhenkun, Zhai Xiaozhi, Pan Shiyang. 2020. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age and petrogeochemical characteristics of Late Triassic granite porphyry in Panshuihe area, West Kunlum Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 39(2/3): 206-214 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang Mingying, Zhang Yu, Cui Xiaofeng, He Yuliang, Ding Zhengjiang, Dong Zhenkun, Ding Wenjie. 2023. Detrital zircon U-Pb age of Huangyangling Formation in Dujianshan area from West Kunlun, Xinjiang: Implications for tectonic evolution of Tethyan Ocean[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(1): 122-135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Hairan, Zhao Hongge, Qiao Jianxin, Gao Shaohua. 2013. Theory and application of zircon U-Pb isotope dating technique[J]. Geology and Resources, 22(3): 229-232, 242 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wen Zhigang, Hu Chenglin, Wang Hongqiang, Li Wenjun, Nie Zhigang, Wang Jiawei, Du Yao. 2019. Formation age of Subashi ophiolitic in West Kunlun, Xinjiang and its tectonic implication[J]. Northwestern Geology, 52(4): 14-27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, Yang J H, Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 234: 105-126.
Xiao Peixi, Gao Xiaofeng, Kang Lei, Xie Congrui, Xi Rengang, Dong Zengchan, Guo Lei, Yang Zaichao. 2015. New understanding on the time and space framework of strata-rock-structure and the metallogenic geological background of metallogenic belt in western Kunlun-Arkin[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2(2): 48-55 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Lei, Yang Yongfeng, Zhang Weimin, Ma Fucai, Cheng Linqiang, Lu Xiaojun. 2016. Prospecting potential analysis of the Huangyangling-Wolonggang antimony metallogenic belt in Minfeng County, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(9): 1536-1543 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Wanzhi, Zhang Weizhou, Qu Xun. 2005. Geochemical evidence of the relation between the Kuyake fault of east part of west Kunlum Mountains and the Kangxiwar and Altyn Tagh faults[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(4): 316-321 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Chuanlin, Ma Huadong, Zhu Bingyu, Ye Xiantao, Qiu Lin, Zhao Haixiang, Liu Xiaoqiang, Ding Teng, Wang Qian, Hao Xiaoshu. 2019. Tectonic evolution of the Western Kunlun—Karakorum Orogenic Belt and its coupling with the mineralization effect[J]. Geological Review, 65(5): 1077-1102 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Youjun, Duan Huanchun, Jia Qi, Guo Hongjun. 2014. Study on the geological characteristics and sources of ore deposits in Wolonggang, Xinjiang [J]. Mineral Deposits, 33(Z): 63-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Yu, Gong Daxin, Zhou Xiong, Zhou Jiayuan, Yue Xiangyuan. 2018. Petrogeochemistry and zircon geochronology of the Wolonggang granite porphyry in the western segment of the East Kunlun: Implications for tectonic setting of the Hoh Xil-Songpan-Ganzi Block and regional antimony mineralization timing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(10): 1853-1865 (in Chinese with English abstract).
毕华, 王中刚, 王元龙, 朱笑青. 1999. 西昆仑造山带构造-岩浆演化史[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 29(5): 398-406. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199905001.htm 陈文平, 吕金刚, 韩小明. 2009. ETM+影像数据在卧龙岗-黄羊岭一带锑矿找矿中的应用[J]. 新疆地质, 27(2): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200902019.htm 董连慧, 刘德权, 唐延龄, 冯京, 屈迅, 李凤鸣, 田江涛, 徐仕琪. 2015. 试论新疆成矿体系与时空演化模式[J]. 矿床地质, 34(6): 1107-1129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506003.htm 冯宝山, 李博秦, 郭鸿军, 刘铭涛, 薛兰花, 史老虎. 2016. 西昆仑地区矿集区划分及成矿演化[J]. 西北地质, 49(4): 129-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201604014.htm 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 28(4): 481-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200904009.htm 计文化, 韩芳林, 王炬川, 张俊量. 2004. 西昆仑于田南部苏巴什蛇绿混杂岩的组成、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 23(12): 1196-1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200412004.htm 姜春发, 王宗起, 李锦铁. 2000. 中央造山带开合构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-154. 李荣社, 计文化, 杨永成. 2008. 昆仑山及邻区地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-400. 李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 谭文娟, 姜寒冰, 郭周平. 2011. 秦祁昆造山带重要成矿事件与构造响应[J]. 中国地质, 8(5): 1135-1149. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20110502?st=search 李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 洪俊, 陈博, 张志炳. 2022. 昆仑古特提斯构造转换与镍钴锰锂关键矿产成矿作用研究[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1385-1407. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220503?st=search 刘铮. 2015. 西昆仑造山带早中生代花岗岩成因与古特提斯构造演化[D]. 南京: 南京大学. 吕金刚, 王炬川, 禇春华, 李丽群, 刘荣, 雷红民. 2006. 青藏高原可可西里带西段卧龙岗二长花岗斑岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 25(6): 721-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200606011.htm 潘裕生. 1990. 西昆仑山构造特征与演化[J]. 地质科学, 25(3): 224-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199003002.htm 孙海田. 2001. 西昆仑贵金属、有色金属大型矿床成矿远景及靶区预测[C]//中国地质科学院"九五"科技成果汇编, 中国地质学会: 33-34. 唐名鹰, 高振华, 董振昆, 翟孝志, 潘诗洋. 2020. 新疆西昆仑盼水河地区晚三叠世花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 39(2/3): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2020Z1005.htm 唐名鹰, 张宇, 崔霄峰, 何玉良, 丁正江, 董振昆, 丁文洁. 2023. 新疆西昆仑独尖山地区黄羊岭组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及其对特提斯洋构造演化的指示[J]. 地质通报, 42(1): 122-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202301011.htm 王海然, 赵红格, 乔建新, 高少华. 2013. 锆石U-Pb同位素测年原理及应用[J]. 地质与资源, 22(3): 229-232, 242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD201303013.htm 温志刚, 胡成林, 王洪强, 李文军, 聂志刚, 王嘉伟, 杜尧. 2019. 新疆西昆仑苏巴什蛇绿岩形成时代及其构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 52(4): 14-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201904003.htm 校培喜, 高晓峰, 康磊, 谢从瑞, 奚仁刚, 董增产, 过磊, 杨再朝. 2015. 西昆仑-阿尔金成矿带地层-岩石-构造时间隔架及成矿地质背景新认识[J]. 中国地质调查, 2(2): 48-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201502008.htm 闫磊, 杨永锋, 张为民, 马富财, 成林强, 路晓君. 2016. 新疆民丰县卧龙岗-黄羊岭锑成矿带找矿潜力[J]. 地质通报, 35(9): 1536-1543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201609019.htm 杨万志, 张维洲, 屈迅. 2005. 西昆仑山东段库牙克断裂与康西瓦断裂、阿尔金断裂关系的地球化学依据[J]. 地质通报, 24(4): 316-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200504003.htm 张传林, 马华东, 朱炳玉, 叶现韬, 邱林, 赵海香, 刘晓强, 丁腾, 王倩, 郝晓姝. 2019. 西昆仑—喀喇昆仑造山带构造演化及其成矿效应[J]. 地质论评, 65(5): 1077-1102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201905003.htm 张友军, 段焕春, 贾琦, 郭鸿军. 2014. 新疆卧龙岗锑矿地质特征与成矿物质来源研究[J]. 矿床地质, 33(增刊): 63-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2014S1034.htm 周玉, 龚大兴, 周雄, 周家云, 岳相元. 2018. 东昆仑西段卧龙岗花岗斑岩岩石地球化学特征和锆石U-Pb年龄——对可可西里—松潘—甘孜地块构造环境及区域锑成矿时代的限定[J]. 地质通报, 37(10): 1853-1865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201810011.htm -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 何治亮,杨鑫,高键,云露,曹自成,李慧莉,杨佳奇. 特提斯洋与古亚洲洋协同演化控制下的塔里木台盆区油气富集效应. 石油与天然气地质. 2024(03): 637-657 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何国建,胡修棉,楼法生,陈浩鹏,杨晓飞,陈建中,吴春伟,张密椋. 喀喇昆仑北羌塘地体加勒万河地区中——基性岩地球化学与年代学研究. 中国地质. 2024(04): 1422-1440 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 蔡叶蕾 ,武勇 ,秦明宽 ,许强 ,郭强 ,何升 ,林燕 . 塔里木盆地卡拉布拉克地区苏维依组砂岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 世界核地质科学. 2024(06): 1118-1132 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孔会磊,李文渊,任广利,李侃,赵晓健,张江伟. 西昆仑奇台达坂二长花岗岩及其暗色微粒包体对稀有金属伟晶岩形成的指示意义. 岩石学报. 2023(07): 2063-2084 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 鲁浩,刘欢,胡峰,王海波,王超,孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据. 现代地质. 2023(03): 573-585 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: