Geological and mineralization characteristics of Manono–Kitotolo Li−Cs−Ta pegmatite in the Democratic Republic of Congo
-
摘要:研究背景
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩位于刚果(金)中元古代Kibaran稀有金属成矿带,属于锂–铯–钽伟晶岩(LCT),主要由含锂辉石伟晶岩(40%~70%)构成。通过野外地质调查发现:伟晶岩在横向上由外至内依次发育有:花岗细晶岩带(Ⅰ)—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)—锂辉石带(Ⅳ)—石英内核(Ⅴ)。
研究方法通过电子探针(EPMA)法测试,获得伟晶岩中云母、锂辉石、锡石和铌钽铁矿的主量成分,对伟晶岩的分异演化特征、锂矿化、铌钽矿化和锡矿化特征进行了讨论,并对Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的成矿作用进行了分析。
研究结果白云母由外向内Rb、Li和F含量逐渐升高,K/Rb值逐渐降低,锂云母石英带(Ⅴ−1)中产出的锂云母FeO和Rb2O含量相对高于白云母,表明伟晶岩由外向内结晶的分异演化程度较高。
结论锂矿化主要分布在锂辉石伟晶岩(Ⅳ)中,锂辉石粒度呈巨晶—粗粒—中粒变化,主量成分较稳定,但近地表的氧化淋滤作用与黏土化、云英岩化等蚀变作用造成锂元素发生流失;锡矿化分布于Ⅲ—Ⅳ带中,锡石Nb和Ta含量相对较高,属于稀有金属伟晶岩成因,但粗粒锡石主要形成于云英岩化阶段;铌钽矿化分布于Ⅱ—Ⅳ带中,根据元素含量比值显示其为铌铁矿–钽铁矿–锰钽铁矿系列,随着分异作用的进行,铌钽矿物中的钽和锰的含量增加,铌、铁和钛的含量降低,形成富钽、富锰的铌钽铁矿。
创新点:通过伟晶岩地质结构分带和电子探针(EPMA)分析,为Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床提供了新的基础资料和找矿依据。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe Manono–Kitotolo spodumene (40%−70%) pegmatite, one of the lithium−cesium−tantalum pegmatite (LCT) in the world, is located at the Mesoproterozoic Kibaran rare metals metallogenic belt in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The field works revealed that the symbiotic minerals of pegmatite gradually evolved from outside to inside: granite aplite zone(Ⅰ), muscovite−feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ), quartz albitite zone (Ⅲ), spodumene zone (Ⅳ) and quartz kernel (Ⅴ).
MethodsIn this study, the composition of major elements of mica, spodumene, cassiterite and columbite−tantalite are analyzed by Electron probe X−ray micro−analyzer (EPMA) to bring light on Li−Nb−Ta−Sn mineralization and pegmatitic crystallization differentiation.
ResultsThe results show that the content of Rb, Li, and F in muscovite gradually increased from outward (Ⅰ) to inward (Ⅴ), meanwhile the K/Rb gradually decreased. The content of Fe and Rb in lepidolite (V−1) is relatively higher than in muscovite(Ⅱ), which indicating highly fractionated pegmatite inside. Li mineralization mainly occurs in spodumene pegmatite (Ⅳ).
ConclusionsThe grain size of spodumene varies from macro−crystal to coarse grain and medium grain and its principal components keep consistent except Li lost by oxidative leaching, argillation, greisenization and other alterations. Cassiterite with high Nb and Ta is generally formed by greisenization in zone Ⅲ–Ⅳ. Nb−Ta is mineralized in the form of the columbite−tantalite−manganotantalite isomorphism in the zone Ⅱ–Ⅳ, with the development of differentiation, the content of Ta and Mn in minerals increases, while the content of Nb, Fe and Ti decreases and formed Ta−rich and Mn−rich Columbite−tantalite.
-
1. 引 言
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩位于刚果(金)坦噶尼喀省Manono市,地理坐标为27°20′E~27°30′E,7°15′S~7°20′S。该伟晶岩发育大型稀有金属矿床,民采历史悠久,1919—1982年以手工开采锡矿为主,2017年澳大利亚AVZ公司展开了以寻找伟晶岩型锂矿为目标的地质勘查工作,截至2019年5月,探获锂矿石量4.0亿t,氧化锂为660万t(Ferguson et al., 2019),是世界上规模最大、品位最高的未开发伟晶岩型锂矿床。Manono地区以沼泽湿地为主,目前基础地质和矿床地质工作程度较低,Gerards and Ledent(1970)、Cahen et al.(1984)、Kokonyangi et al.(2006)对该矿床所属成矿带的地层、岩浆岩、伟晶岩开展了概略研究;Melcher et al.(2015)通过EPMA对Manono–Kitotolo矿床民采精矿中的铌钽铁矿晶体进行了主量成分分析,但铌钽铁矿产出的具体位置不明;Dewaele et al.(2016)通过EPMA和LA−ICP−MS方法对云母矿物进行了成分分析,主要集中在钠长石化和云英岩化带中。本次研究在前人的研究基础上,通过野外地质调查和室内岩相描述,由电子探针(EPMA)获得Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母、锂辉石、锡石和铌钽铁矿等矿物的主量成分,对伟晶岩的地质和矿化特征进行总结,为Manono–Kitotolo地区开展锂、锡、钽、铌等稀有金属矿产勘查工作提供新的基础资料和理论依据。
2. 区域地质背景
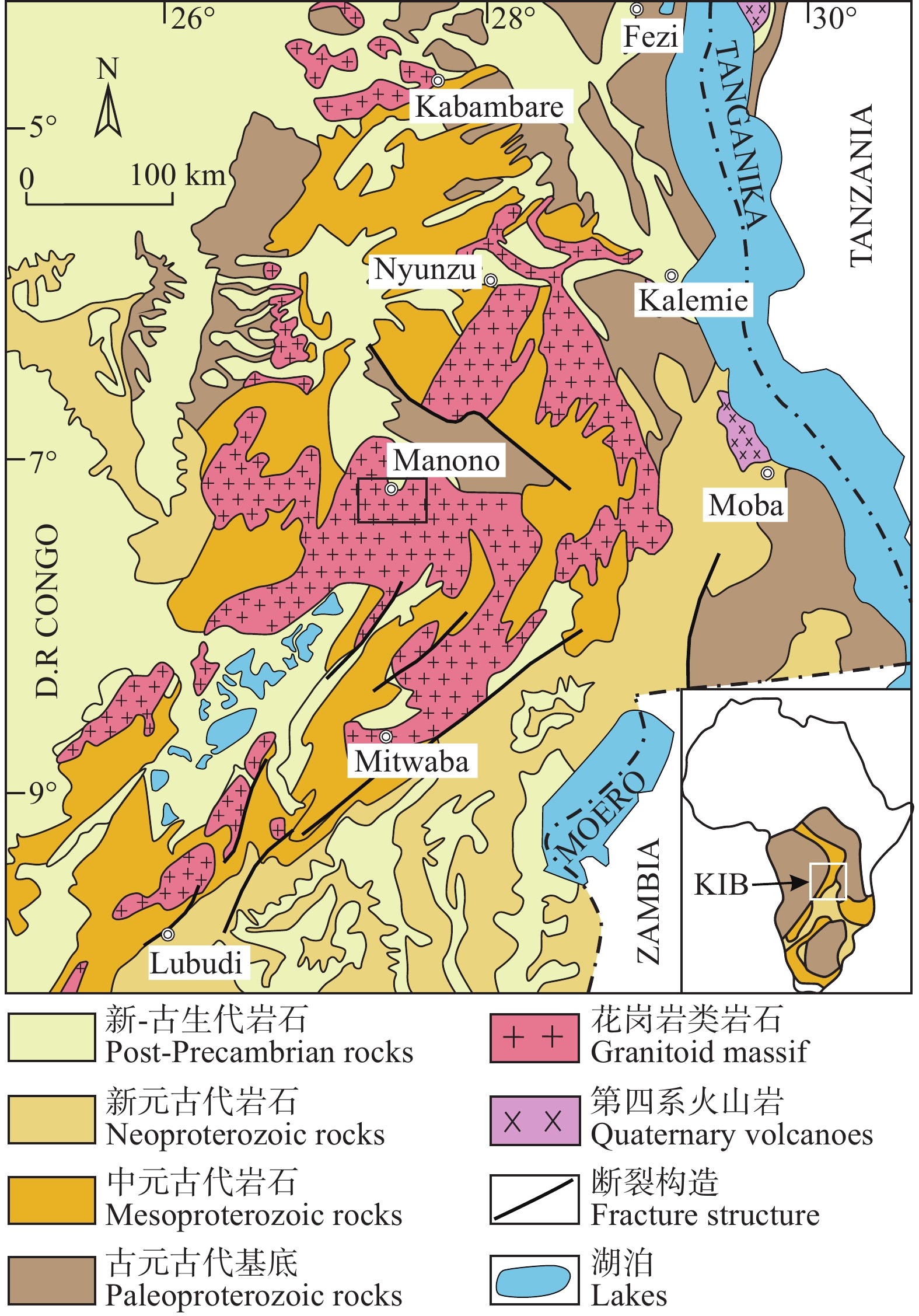
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩位于刚果(金)中元古代Kibaran稀有金属成矿带(KIB),该成矿带是世界上最大的伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床聚集区之一(图1)。Kibaran成矿带主要由厚度大于10 km的中元古代Kibaran超群组成,沉积开始于1420 Ma之前,由绿片岩相−角闪岩相的变质泥岩和石英岩组成,同时被大量岩浆岩侵入(Cahen et al., 1984; Kokonyangi et al., 2006)。
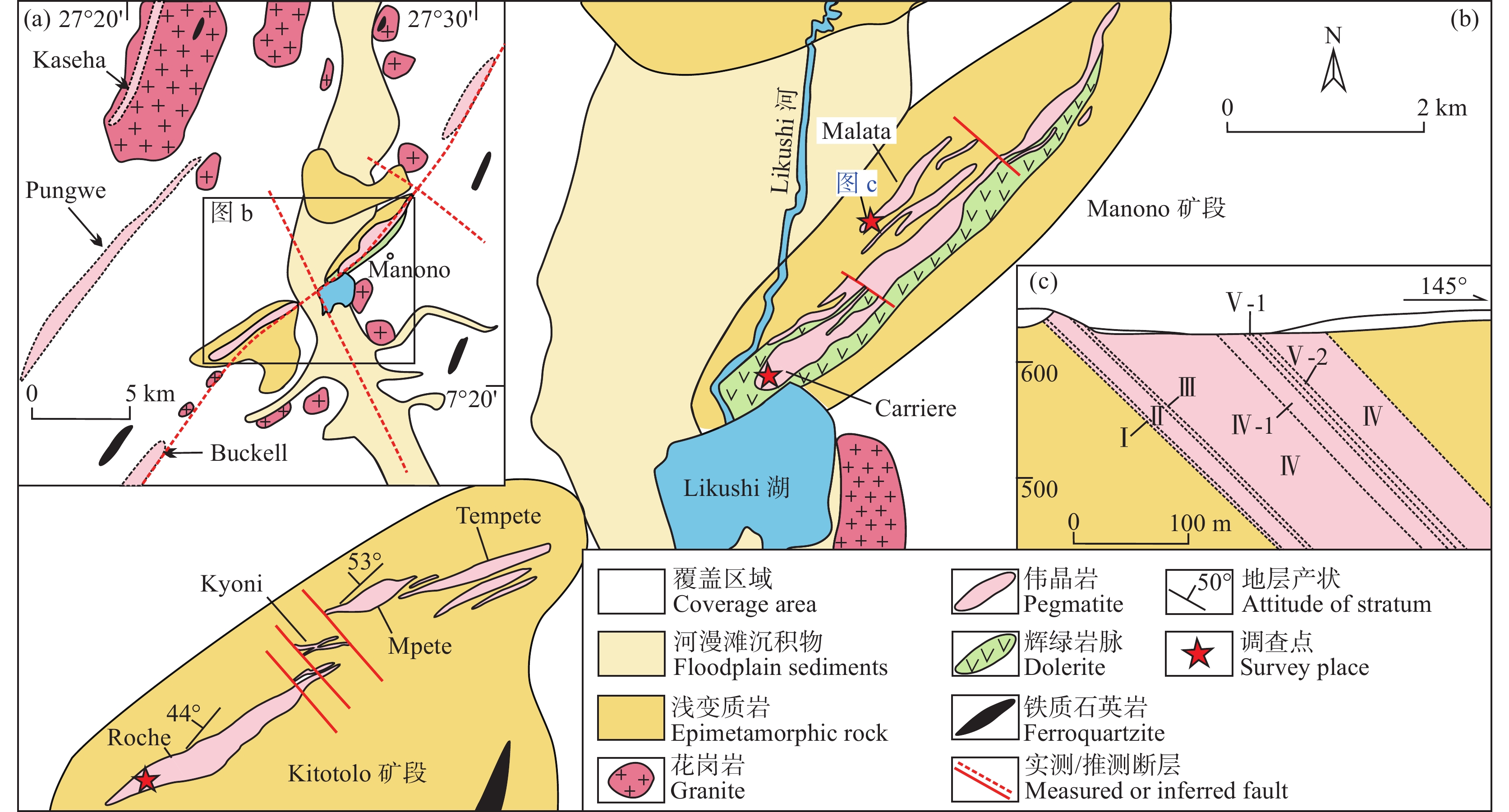
![]() 图 1 Kibaran成矿带区域地质图(据Melcher et al., 2015修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Kibaran metallogenic belt (modified from Melcher et al., 2015)
图 1 Kibaran成矿带区域地质图(据Melcher et al., 2015修改)Figure 1. Regional geological map of Kibaran metallogenic belt (modified from Melcher et al., 2015)Kibaran沉积盆地是Ubendian带左旋平移断裂形成的克拉通内伸展沉积盆地,在中元古代时期主要经历了多次岩浆侵入(G1−G4或GR1−GR5期),形成于1375 Ma的Kibaran造山运动和1.0 Ga的Rodinia超大陆拼合期间(Gerards and Ledent, 1970; Cahen et al., 1984; Kokonyangi et al., 2006; Tack et al., 2010; Dewaelea et al., 2011)。G4期(GR5期)岩浆侵入约(977±18)~(966±21)Ma(Dewaele et al., 2016),岩性特征为淡色偏碱性强过铝质花岗岩,属于后造山期花岗岩(Gerards and Ledent, 1970; Cahen et al., 1984)。Dewaele et al.(2010)研究显示,Kibaran成矿带伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床和石英脉型锡矿床,与最年轻、演化程度最高的G4期(GR5期)花岗岩关系密切。
Manono–Kitotolo矿区出露地层为中元古代Kibaran超群千枚岩、片岩和变质砂岩,地层产状为走向北东30°~60°,倾向北西,地层倾角50°~90°。矿区构造主要为北东和北西向,北东向构造为一背斜褶皱和断裂,北西向构造主要为一系列的断裂,伟晶岩沿着复式背斜轴部的北东向断裂产出(图2a),并受北西向断裂的破坏发生短距离位移。矿区的花岗岩主要分为Lukushi花岗岩、片麻状花岗岩、混合花岗岩、花岗伟晶岩和变辉绿岩等。根据Kokonyangi et al.(2006)的研究显示,Lukushi斑状花岗岩属于高钾过铝质花岗岩,主要矿物由钾长石、斜长石、石英、黑云母组成,被认为是稀有金属成矿的母体花岗岩,但不是伟晶岩母体花岗岩唯一来源,因为伟晶岩熔体还可能来自较深的花岗岩(Dewaele et al., 2016)。变辉绿岩分布于Manono伟晶岩的南东测,与伟晶岩平行分布,在伟晶岩侵位过程中,辉绿岩发生接触变质作用。
![]() 图 2 Manono地区地质简图(a)、Manono–Kitotolo矿区地质图(b)(据Ferguson et al., 2019修改)和Malata伟晶岩脉剖面示意图(c)Figure 2. Geological map of Manono area (a), Manono–Kitotolo mining area (b) (modified from Ferguson et al., 2019), and sectional schematic diagram of Malata pegmatite dike (c)
图 2 Manono地区地质简图(a)、Manono–Kitotolo矿区地质图(b)(据Ferguson et al., 2019修改)和Malata伟晶岩脉剖面示意图(c)Figure 2. Geological map of Manono area (a), Manono–Kitotolo mining area (b) (modified from Ferguson et al., 2019), and sectional schematic diagram of Malata pegmatite dike (c)Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩带走向总长度约15 km,宽约800 m,发育有大型的稀有金属矿床,分为北东部Manono和南西部Kitotolo两个矿段(图2b)。两个矿段都发育有多个单独产出的伟晶岩,伟晶岩产状为走向北东40°~60°,倾向南东,倾角30°~50°,主要沿着构造面侵入围岩中,接触面的走向总体上和区域构造的产状相同。截至2019年5月(Ferguson et al., 2019),Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的矿石量为4亿t,Li2O品位为1.66%,Sn品位为0.075%,Ta品位0.003%。
3. 伟晶岩地质特征
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩属于锂−铯−钽伟晶岩(LCT)(Dewaele et al., 2016; Bradley et al., 2017),主要矿物为石英、钠长石、钾长石、锂辉石、白云母、锂云母等,其次为锡石、铌钽铁矿、石榴子石、电气石等。本次研究对Malata、Carriere和Roche等3个伟晶岩脉开展地质调查,调查结果显示,伟晶岩主体为锂辉石伟晶岩,外部为含白云母长石石英伟晶岩,具有一定的横向分带特征(图2c),由外至内依次发育有花岗细晶岩带(Ⅰ)—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)—锂辉石带(Ⅳ)—石英内核(Ⅴ),但受地表广泛覆盖的影响,分带界线并不清晰,其中Malata伟晶岩脉Ⅰ—Ⅴ结构带的岩石均可见,但厚度较小,Carriere和Roche伟晶岩脉发育Ⅱ—Ⅳ带。
花岗细晶岩带(Ⅰ)主要分布在伟晶岩的边缘,由石英、钾长石、斜长石、白云母、黑云母等组成,少量角闪石、绿柱石、电气石和石榴子石等,粒径1~10 mm。
白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)主要分布于伟晶岩的外侧,厚度不明,由中粗粒的石英、钠长石、钾长石、斜长石、白云母等矿物组成(图3a,图4a),矿物粒度0.2~10 cm,矿物晶形较好,可见细粒石英和钾长石粗晶呈文象和似文象结构(图4b),白云母以片状集合体为主,片径1~5 cm,局部可见少量电气石、铌钽铁矿等矿物,粒度小于5 mm。该类伟晶岩在区域上广泛发育,一般不含矿或矿化弱,并含有5%~10%的电石气,与本区含少量电气石形成鲜明的区别。
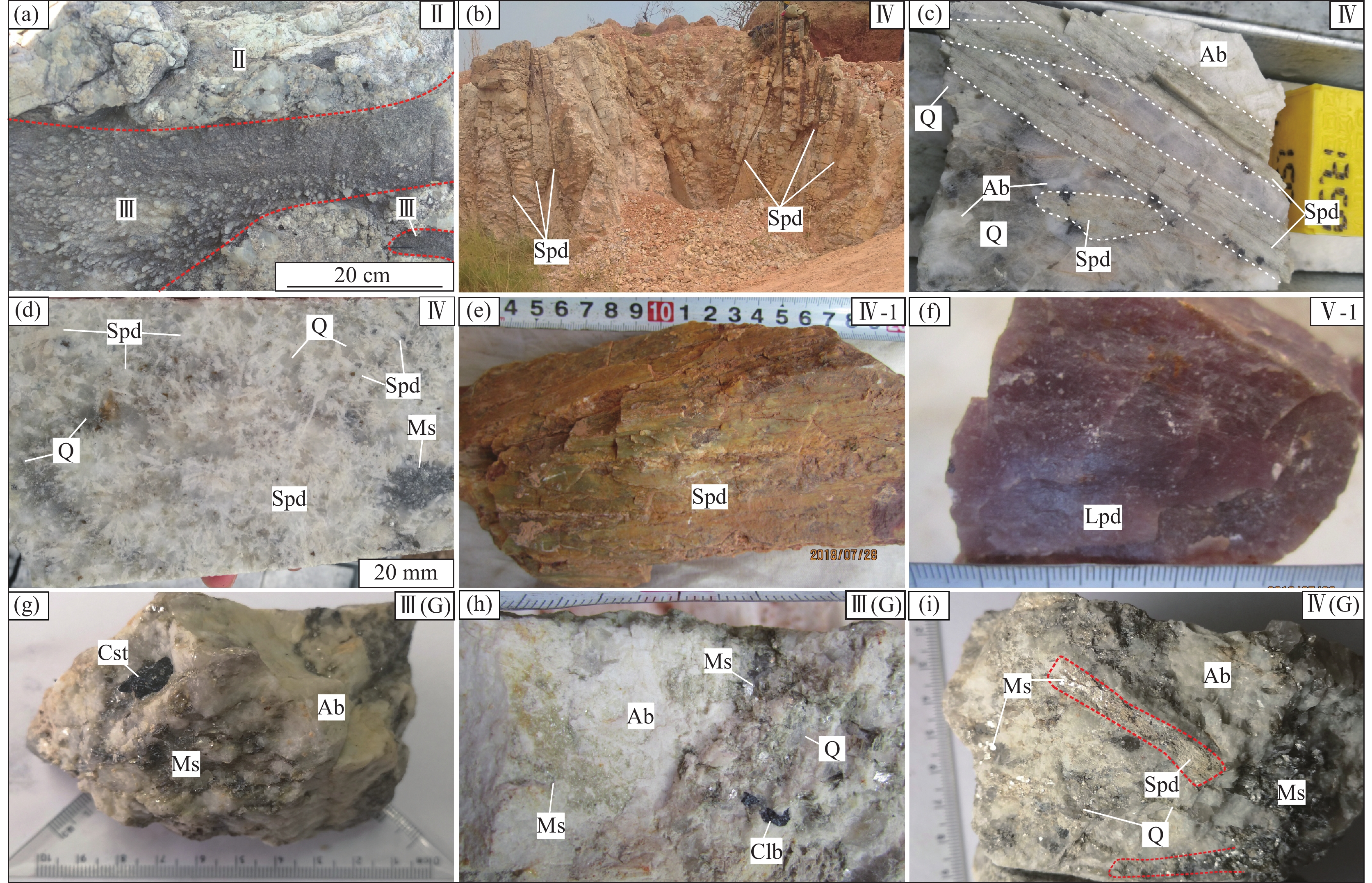
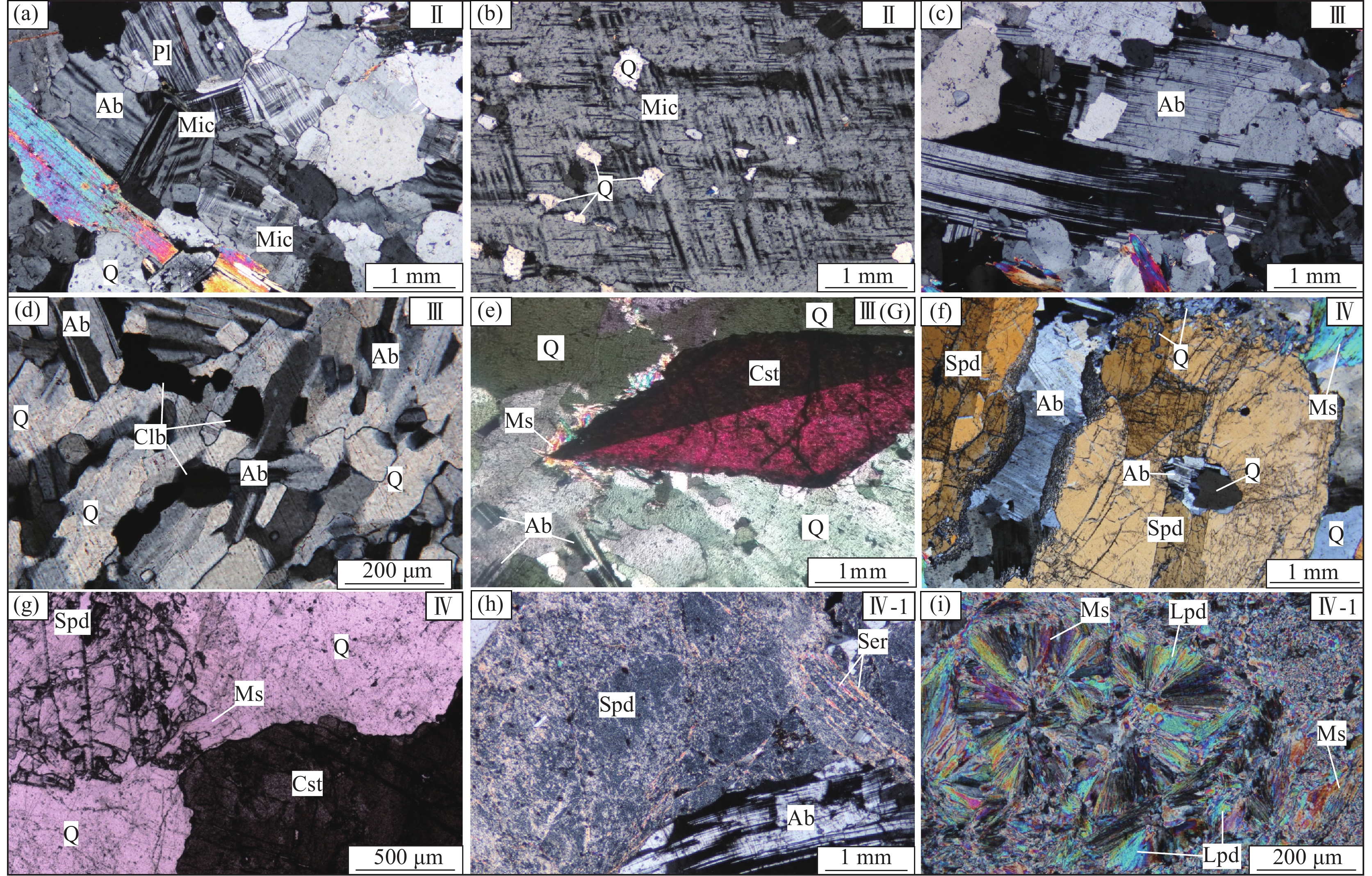
![]() 图 3 Manono−Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石标本照片a—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)穿插于白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅳ带中的长柱状锂辉石巨晶;c—Ⅳ带中的粗粒锂辉石晶体;d—Ⅳ带中的中细粒锂辉石晶体;e—Ⅳ-1带中的蚀变锂辉石晶体;f—Ⅴ-1带中的锂云母;g—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石;h—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的铌钽铁矿;i—云英岩化锂辉石伟晶岩(G/Ⅳ)中锂辉石的交代残余结构;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母Figure 3. Graphs of rock samples in the Manono-Kitotolo pegmatitea–Quartz albite zone (Ⅲ) interspersed with muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Long columnar spodumene giant crystal from zone Ⅳ; c–Coarse spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; d–Medium−fine grained spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; e–Altered spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ−1; f–Lepidolite from zone Ⅴ−1; g–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); h–Coltan in greisenization pegmatite (G); i–Metasomatic relict texture of spodumene from greisenization spodumene pegmatite (G/Ⅳ); Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite-tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite
图 3 Manono−Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石标本照片a—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)穿插于白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅳ带中的长柱状锂辉石巨晶;c—Ⅳ带中的粗粒锂辉石晶体;d—Ⅳ带中的中细粒锂辉石晶体;e—Ⅳ-1带中的蚀变锂辉石晶体;f—Ⅴ-1带中的锂云母;g—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石;h—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的铌钽铁矿;i—云英岩化锂辉石伟晶岩(G/Ⅳ)中锂辉石的交代残余结构;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母Figure 3. Graphs of rock samples in the Manono-Kitotolo pegmatitea–Quartz albite zone (Ⅲ) interspersed with muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Long columnar spodumene giant crystal from zone Ⅳ; c–Coarse spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; d–Medium−fine grained spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; e–Altered spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ−1; f–Lepidolite from zone Ⅴ−1; g–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); h–Coltan in greisenization pegmatite (G); i–Metasomatic relict texture of spodumene from greisenization spodumene pegmatite (G/Ⅳ); Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite-tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite![]() 图 4 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石显微照片a—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅱ带中的细粒石英和粗粒微斜长石呈似文象结构;c—Ⅲ带中的中粒钠长石;d—Ⅲ带中的细粒钠长石和它形铌钽铁矿;e—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石; f—Ⅳ带中锂辉石被细粒的石英、钠长石交代;g—Ⅳ号带中锂辉石与不规则状锡石共生;h—Ⅳ−1带中蚀变锂辉石与中粒钠长石共生;i—Ⅴ−1带中锂云母与白云母共生;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Mic—微斜长石;Pl—斜长石;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母;Ser—绢云母Figure 4. Micrographs of rock samples in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatitea–Muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Fine-grained quartz and coarse-grain microcline is lconographic structure from zoneⅡ; c–Medium albite from zone Ⅲ; d–Fine grained albite and allomorphic columbite-tantalite from zone Ⅲ; e–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); f–Fine quartz and albite metasomatism spodumene from zone Ⅳ; g–Spodumene symbiosis with cassiterite from zone Ⅳ; h–Alteration spodumene symbiosis with medium albite from zone Ⅳ−1; i–Lepidolite symbiosis with Muscovite from zone Ⅴ−1; Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite−tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Mic–Microcline; Pl–Plagioclase; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite; Ser–Sericite
图 4 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石显微照片a—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅱ带中的细粒石英和粗粒微斜长石呈似文象结构;c—Ⅲ带中的中粒钠长石;d—Ⅲ带中的细粒钠长石和它形铌钽铁矿;e—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石; f—Ⅳ带中锂辉石被细粒的石英、钠长石交代;g—Ⅳ号带中锂辉石与不规则状锡石共生;h—Ⅳ−1带中蚀变锂辉石与中粒钠长石共生;i—Ⅴ−1带中锂云母与白云母共生;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Mic—微斜长石;Pl—斜长石;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母;Ser—绢云母Figure 4. Micrographs of rock samples in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatitea–Muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Fine-grained quartz and coarse-grain microcline is lconographic structure from zoneⅡ; c–Medium albite from zone Ⅲ; d–Fine grained albite and allomorphic columbite-tantalite from zone Ⅲ; e–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); f–Fine quartz and albite metasomatism spodumene from zone Ⅳ; g–Spodumene symbiosis with cassiterite from zone Ⅳ; h–Alteration spodumene symbiosis with medium albite from zone Ⅳ−1; i–Lepidolite symbiosis with Muscovite from zone Ⅴ−1; Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite−tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Mic–Microcline; Pl–Plagioclase; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite; Ser–Sericite石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)在伟晶岩中较常见,但厚度较薄,一般1~5 m,呈脉状或不规则状分布(图3a)。岩石由细粒石英、钠长石组成,含少量微斜长石,该带中可见他形细粒铌钽铁矿和少量锡石颗粒。根据野外及镜下特征,钠长石分为两种类型:第一种钠长石呈中粗粒状,与石英、锂辉石等矿物共生,粒径1~15 mm,最大可达10 cm,呈白色自形—半自形产出(图4c);第二种为叶片状、细粒状钠长石,粒径0.1~0.3 mm(图4d),属于晚期钠长石化形成的。铌钽铁矿呈细粒他形结构(图4d),与细粒状的钠长石和石英共生,粒度0.05~2 mm,含量<1%。
锂辉石带(Ⅳ)为Manono–Kitotolo矿区伟晶岩的主要组成,厚度50~300 m,占整个伟晶岩的40%~70%。该带的锂辉石伟晶岩为Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床的主要赋矿岩石,由石英、锂辉石、钠长石、白云母等组成,含钽铌铁矿和锡石,矿物颗粒以粗粒为主,粒径0.5~40 cm。锂辉石伟晶岩可细分为巨锂辉石带、钠长石锂辉石带和石英锂辉石带3类,锂辉石颗粒由巨晶—粗粒—中粒变化。巨锂辉石带目前仅在Malata伟晶岩脉的采坑中有揭露,锂辉石呈长柱状,地表揭露最大粒径3 m×0.2 m(图3b);钠长石锂辉石带占Ⅳ带的70%,主要由钠长石、锂辉石、石英、白云母组成,锂辉石呈长柱状,粒径0.5~30 cm,可见定向排列现象,沿同一生长方向,粒度越大定向排列越明显(图3c),锂辉石的含量10%~25%;石英锂辉石带主要由石英、钠长石、锂辉石和白云母组成,锂辉石呈柱状,粒度0.2~5 cm,密集分布,地表常见梳状、放射状构造(图3d),锂辉石的含量10%~25%。锂辉石带(Ⅳ)中的铌钽铁矿颗粒较大,常呈长板状和半自形粒状,粒度0.5~5 mm,长板状铌钽铁矿长约3~15 mm,厚度0.5~3 mm,锡石呈半自形—他形粒状、不规则状(图4g),粒径0.5~5 mm,铌钽铁矿、锡石一般与锂辉石和钠长石共生。
此外,Malata伟晶岩脉中揭露有蚀变锂辉石带(Ⅳ−1),分布于Ⅳ带与石英内核的接触部位,锂辉石绢云母化、黏土化强烈,矿物结构破化严重,地表呈灰绿色柱状晶体(图3e),粒度0.1~30 cm。镜下特征显示锂辉石呈残留体或交代假象,实际上已成为绢云母、高岭土等矿物的集合体(图4h)。
石英内核(Ⅴ带)以石英为主,其次为锂云母、白云母(图3f),细分为锂云母石英带(Ⅴ−1)和石英带(Ⅴ−2)。锂云母石英带在Malata伟晶岩脉可见,厚度小于1 m。锂云母呈浅紫色,粒度<0.05 mm,局部0.1~0.2 mm,一般与细粒白云母共生,偶见球状、放射状结构(图4i),锂云母蚀变较强烈,以黏土化和绢云母化为主。
伟晶岩中不同结构带的不同矿物组合是由强烈的蚀变引起的,主要蚀变为钠长石化和云英岩化。钠长石化遍及整个伟晶岩体,主要分布于石英钠长岩(Ⅲ带)中,野外可见晚期形成的石英钠长岩脉穿插于Ⅱ、Ⅳ带伟晶岩的边缘(图3a),镜下可见细粒钠长石和石英交代锂辉石晶体(图4f),在Ⅱ带中也常见有细粒状和叶片状钠长石充填在粗粒的碎裂石英中。
在Carriere和Roche伟晶岩脉中发育有较强烈的云英岩化(G带),云英岩化主要分布在石英钠长石带和锂辉石带中。云英岩化伟晶岩中可见中粗粒的锡石(图3g)和板状铌钽铁矿(图3h),锡石呈灰褐色、红褐色,自形—半自形结构,粒径1~5 mm,个别可达2 cm,显微镜下可见双晶特征(图4e),与钠长石、石英及细粒白云母共生(图3g)。 云英岩化锂辉石伟晶岩中可见锂辉石被白云母和细粒石英呈交代残余结构(图3i),但铌钽铁矿未见明显变化。
4. 样品选择及分析方法
本次研究的样品采集自Manono–Kitotolo矿区Malata、Carriere和Roche等3个伟晶岩脉,云母采集自Ⅰ—Ⅴ结构带,锂辉石采集自锂辉石伟晶岩(Ⅳ带),锡石采自云英岩化石英钠长岩(Ⅲ、G带),铌钽铁矿采集自石英钠长岩(Ⅲ带),共采集样品20个,挑选7个具有代表性的样品进行矿物元素组成定量分析(EPMA)。分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心利用JXA−8100电子探针分析仪完成,其加速电压为20 kV,电流1×10−8 A,束斑直径为3~5 μm,分析方式为波谱分析,每个元素数据采集时间 20~40 s。测试使用的标准样品为天然样品和人工合成氧化物,包括透辉石(Si,Kα;Ca,Kα)、硬玉(Na,Kα;Al,Kα)、钾长石(K,Kα)、金红石(Ti,Kα)、石榴石(Fe,Kα)、钙蔷薇辉石(Mn,Kα)、铌金属(Nb,Lα)、钽金属(Ta,Mα)、锡石(Sn,Lα)、萤石(F,Kα)等。数据采用ZAF方法校正。
5. 实验结果
本次研究通过电子探针分析获得Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母的主要组分含量(表1),锂辉石的主要组分含量(表2),锡石和铌钽铁矿的主要组分含量(表3)。
表 1 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母元素组成分析结果Table 1. Analytical data of major composition of mica in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite结构带 矿物 样品号/点位 测试结果/% K/Rb 备注 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO Na2O K2O Rb2O Cs2O F 总量 Ⅰ Ms bgk1-1① 46.72 0.34 34.06 2.49 0.04 0.65 10.64 0.14 bdl 0.85 95.81 69.20 Ms RG16811 47.89 0.03 35.80 — 0.04 1.08 9.37 — — 0.54 100.56 39.71 Ⅱ Ms bgn2-1① 46.11 0.03 36.85 0.82 0.07 0.40 10.41 0.73 0.02 0.34 95.44 12.98 Ms RG5826 46.56 0.03 33.60 — 0.05 0.48 10.66 — — 0.21 100.84 45.17 Ms RG9699 47.53 0.03 33.49 — 0.27 0.54 10.31 — — bdl 99.44 43.69 Ⅳ Ms bgn1-3③ 46.69 bdl 34.90 2.68 0.25 0.53 10.28 0.55 0.02 0.81 95.94 17.02 Ms B34① 46.42 0.05 35.09 2.68 0.34 0.33 10.71 0.71 0.02 0.62 96.40 13.73 Ms RG15992 47.46 0.03 34.73 — 0.30 0.92 9.85 — — 0.56 100.16 15.06 Ms RG16005 46.90 0.04 33.70 — 0.27 0.62 10.32 — — 1.19 100.16 16.30 Ⅳ−1 Ms bgn2-3① 45.62 0.02 38.35 0.05 0.13 0.46 10.45 1.15 bdl 0.00 96.27 8.27 Ms bgn2-3③ 46.15 bdl 36.89 0.08 0.14 0.35 10.62 1.90 bdl 0.63 96.18 5.09 Ⅴ−1 Lpd bgn2-5① 52.57 bdl 24.83 0.10 1.36 0.07 10.20 2.92 0.08 4.44 92.33 3.18 Lpd RG14 55.47 0.01 25.65 0.04 0.39 0.37 9.02 — — 4.05 99.79 5.13 Ⅴ−1 Ms bgn2-5⑤ 46.44 bdl 37.93 0.05 0.07 0.24 9.90 0.75 bdl 0.00 95.38 12.02 Ms bgn2-5② 46.18 bdl 37.92 0.02 0.05 0.21 10.21 1.27 bdl 0.00 95.90 7.32 Ms bgn2-5③ 46.71 0.02 37.89 0.02 bdl 0.17 10.97 0.85 bdl 0.00 96.79 11.75 Ms bgn2-5⑥ 45.33 bdl 37.99 bdl 0.03 0.17 10.06 0.73 0.03 0.00 94.34 12.55 G Ms bgs1-2① 46.82 0.05 32.59 3.57 0.43 0.23 10.61 0.96 bdl 1.43 95.41 10.06 云英岩化 Ms RG16747 58.64 0.04 28.12 — 0.12 0.52 7.96 — — 0.68 101.71 15.85 Ms RG16777 46.44 0.03 34.82 — 0.20 0.66 9.91 — — 1.24 98.91 14.21 Ms RG16958 45.81 0.02 37.40 — 0.16 0.75 10.17 — — 0.61 99.87 14.49 注:RG系列样品的分析结果来自Dewaelea et al.(2016);K/Rb比中的K和Rb含量根据氧化物计算;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母;“bdl”表示低于检出限,“—”表示未检测。 表 2 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中锂辉石元素组成分析结果Table 2. Analytical data of major composition of spodumene in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite样品号/点位 测试结果/% SiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO Na2O K2O CaO Ta2O5 SnO2 总量 bgn1-3① 64.16 27.58 0.48 0.10 0.16 bdl bdl bdl 0.05 92.53 B34③ 63.91 27.54 0.43 0.10 0.14 bdl bdl 0.05 bdl 92.17 B34④ 64.30 27.42 0.19 0.06 0.11 0.02 0.02 bdl bdl 92.12 平均值 64.12 27.51 0.37 0.09 0.14 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.05 92.27 表 3 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中锡石和铌钽铁矿元素组成分析结果Table 3. Analytical data of major composition of cassiterite and columbite-tantalite in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite结构带 矿物 点位 铌钽铁矿和锡石测试结果/% Mn/(Fe+Mn) Ta/(Ta+Nb) SiO2 TiO2 FeO MnO Rb2O Nb2O5 Ta2O5 SnO2 WO3 总量 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1① 0.40 1.62 7.01 8.59 0.40 26.34 52.59 1.00 0.78 99.97 0.55 0.66 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1② 0.41 0.39 6.22 9.82 1.70 28.85 51.38 0.07 0.58 99.42 0.61 0.65 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1③ 0.36 0.24 6.37 10.19 1.45 36.66 43.98 0.27 0.32 99.84 0.61 0.55 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1④ 0.41 1.39 5.93 9.57 1.51 27.64 51.99 0.85 0.32 99.61 0.62 0.66 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1⑤ 0.41 1.87 6.18 8.98 1.56 25.83 52.67 0.99 0.42 98.95 0.59 0.68 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1⑥ 0.34 0.26 6.31 9.89 1.51 36.05 45.27 0.05 0.42 100.1 0.61 0.56 不明 Clb P25 — 0.15 — — — — — 0.08 0.06 — 0.34 0.18 不明 Clb P75 — 0.67 — — — — — 0.31 0.30 — 0.72 0.5 均值 0.39 0.82 6.34 9.51 1.56 30.23 49.65 0.45 0.40 99.65 0.58 0.56 G Cst bgs1-2① 0.62 0.03 0.50 0.05 bdl 1.52 1.93 94.96 bdl 100 0.09 0.57 G Cst bgs1-2② 0.62 0.09 0.25 bdl bdl 0.65 0.7 96.32 bdl 99.06 bdl 0.52 G Cst bgs1-2③ 0.60 0.07 0.08 bdl bdl 0.25 0.43 98.26 bdl 100.1 bdl 0.64 G Cst bgs1-2④ 0.60 0.06 0.25 0.03 bdl 0.56 0.65 94.1 bdl 96.8 0.11 0.54 G Cst bgs1-2⑤ 0.55 0.11 0.71 0.04 bdl 2.38 2.02 93.58 bdl 99.88 0.05 0.47 均值 0.598 0.072 0.36 0.04 bdl 1.072 1.146 95.44 bdl 99.18 0.08 0.55 注:P25、P75分析结果来自Melcher et al.(2015);Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿。 由表1可见,Ⅰ—Ⅴ带的白云母Rb2O含量为0.14%~2.92%,Cs2O含量为0.02%~0.03%,FeO含量为0.02%~3.57%,F含量为0.00%~1.19%。锂云母产出于Ⅴ−1带,Rb2O含量为2.92%,Cs2O含量为0.08%,FeO含量为0.04%~0.10%,F含量为4.05%~4.44%。探针分析结果(表1)显示,Ⅰ—Ⅱ结构带产出的白云母Rb2O含量相对较低,Ⅰ—Ⅳ结构带产出的白云母FeO含量相对较高,同一结构带(Ⅴ−1)产出的锂云母FeO、MnO、Rb2O和F含量相对高于白云母,表明锂云母更富集Fe、Mn、Rb和F元素。此外云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的白云母F含量为0.61%~1.43%,相对高于Ⅰ—Ⅴ带白云母的F含量。
由表2可见,锂辉石主量成分较稳定,杂质较少,SiO2含量为63.91%~64.30%,A12O3含量为27.42%~27.58%,其他组分含量较低,FeO含量为0.19%~0.48%,MnO含量为0.06%~0.10%,Na2O含量为0.11%~0.16%,Ti2O、MgO、K2O含量均低于检出限。
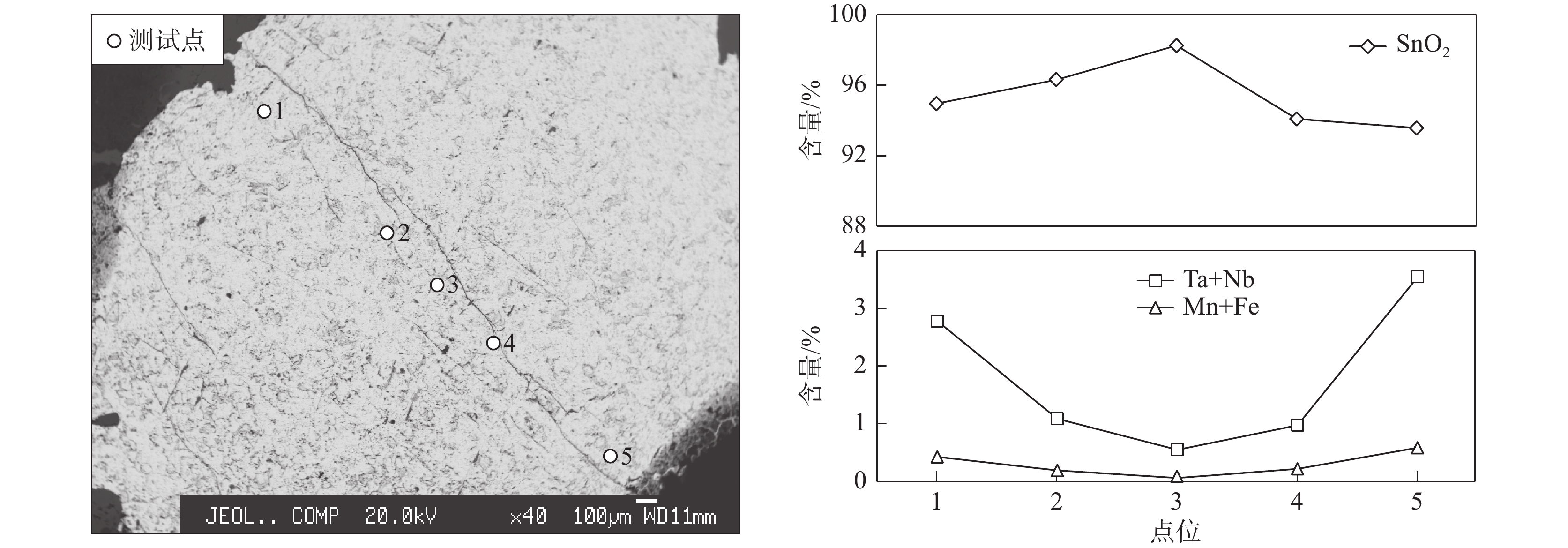
由表3可见,锡石SnO2含量为93.58%~98.26%,Nb2O5含量为0.25%~2.38%;Ta2O5含量为0.43%~2.02%,FeO含量为0.08%~0.71%,MnO含量为0.00%~0.05%;TiO2含量为0.03%~0.11%,锡石晶体中SnO2的含量由中心向两侧逐渐降低,而Nb+Ta和Fe+Mn的含量逐渐升高。
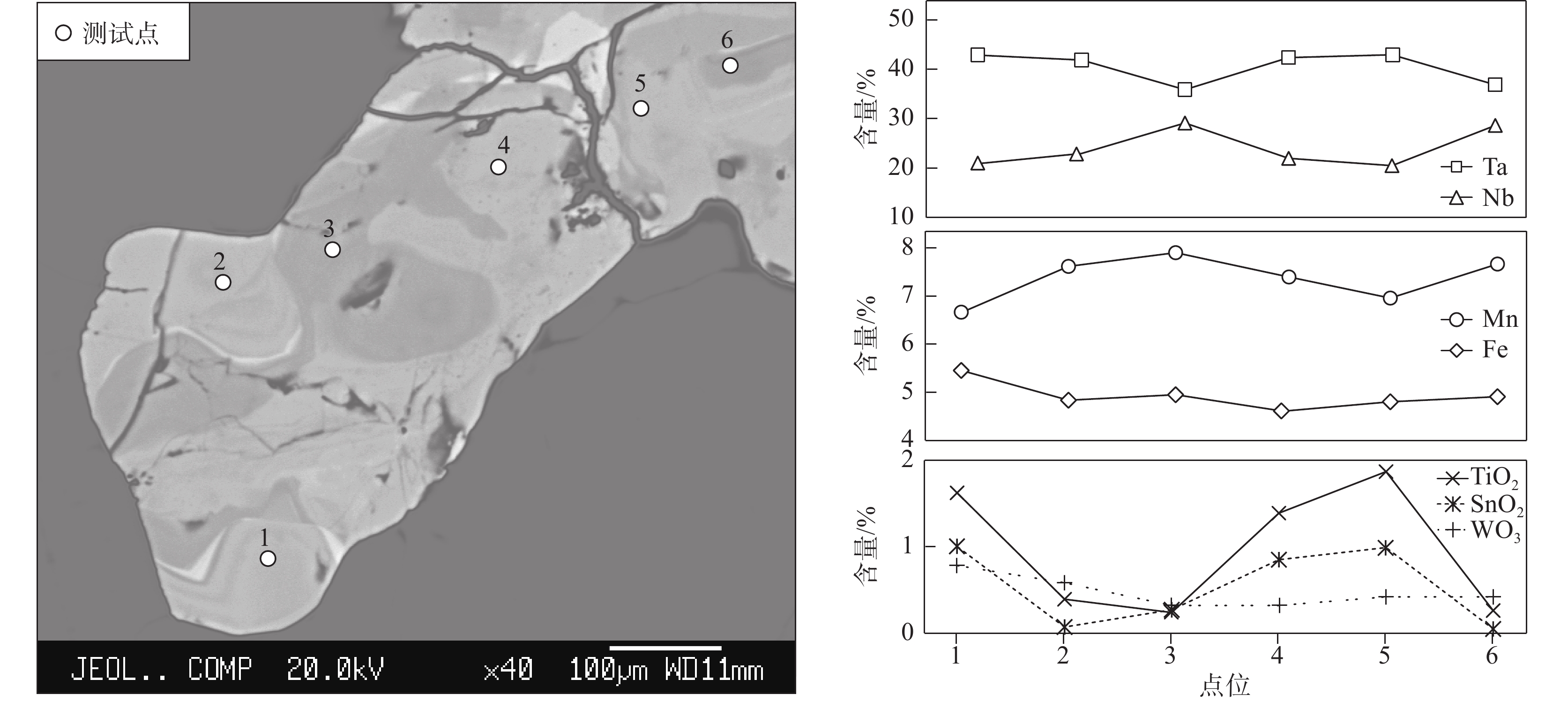
由表3可见,铌钽铁矿Nb2O5含量为25.83%~36.66%,Ta2O5含量为43.98%~52.67%,FeO含量为5.93%~7.01%,MnO含量为8.59%~10.19%,SnO2含量为0.05%~1.00%,WO3含量为0.06%~0.78%,TiO2含量为0.15%~1.87%。通过计算得出的Ta/(Ta+Nb)比值为0.18~0.69,Mn/(Fe+Mn)比值为0.34~0.72,说明Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩产出的铌钽族矿物为铌铁矿–钽铁矿–锰钽铁矿系列。
6. 讨 论
6.1 伟晶岩的分异演化程度
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩与世界上其他伟晶岩相似,产出在围岩时代较老的变质岩区(刘丽君等, 2017; 杨岳清等, 2020),如四川甲基卡和阿勒泰可可托海3号脉伟晶岩(周起凤等, 2013; 王登红等, 2017a)。Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩横向上具有一定的横向分带特征,由外至内发育有花岗细晶岩带(Ⅰ)、白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)、石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)、锂辉石带(Ⅳ)和含锂云母的石英内核(Ⅴ),花岗细晶岩和花岗伟晶岩在绝大多数情况下都是高分异花岗岩的组成部分,是鉴定岩浆高度分异作用的重要岩石学标志(Dill, 2015; 秦克章等, 2019; 肖惠良等, 2023)。
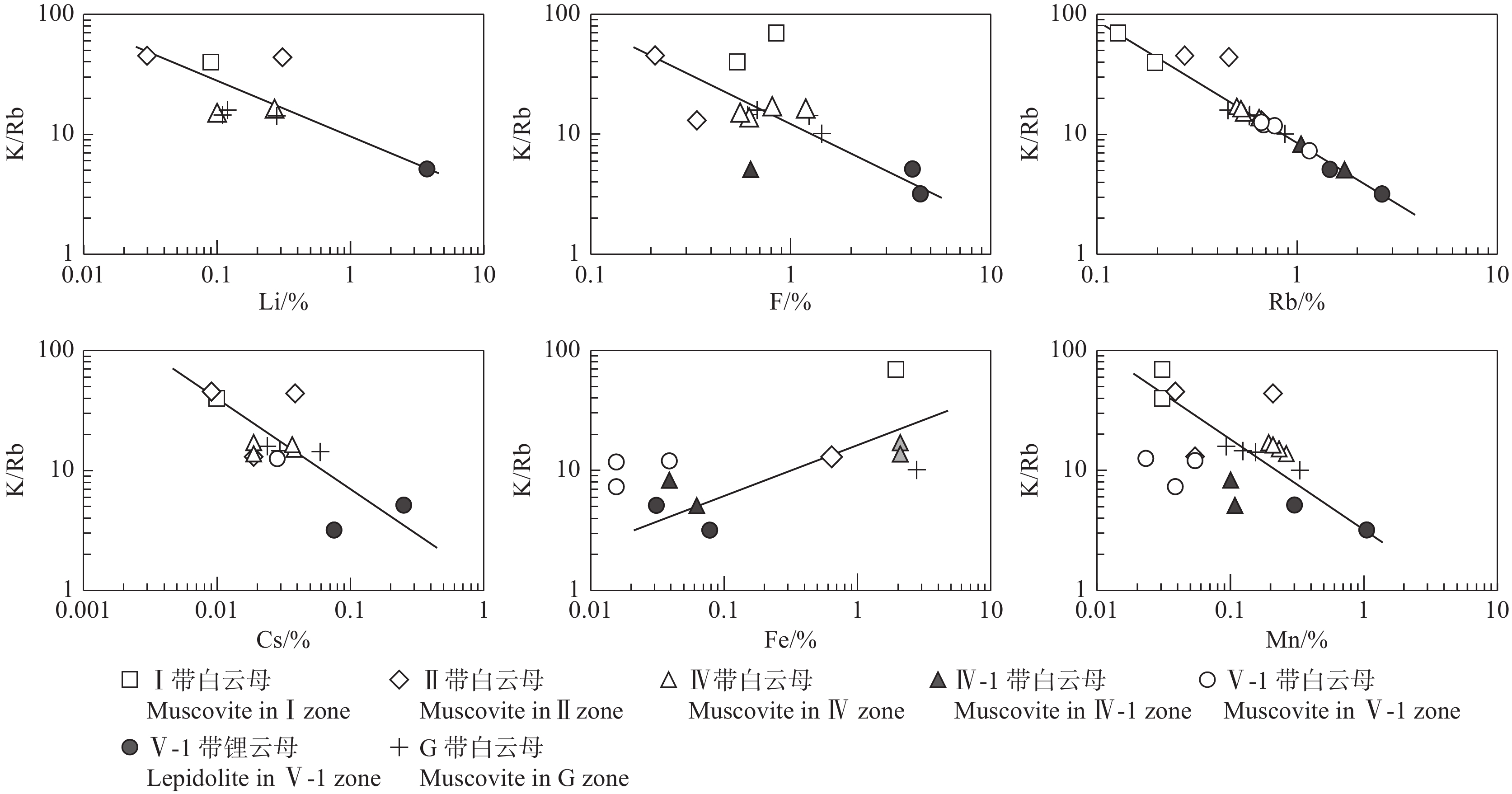
云母为伟晶岩的重要组成矿物和各结构带的贯通性矿物,其物理性质、化学组分及共生关系的研究对伟晶岩的演化过程具有重要指示意义(Vieira et al., 2011; 周起凤等, 2013; 王汝成等, 2019)。Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的云母具有不同的成分分带形式,主要表现为白云母和锂云母呈不规则分带产出,二者主要以共生关系为主(图4i),锂云母是高分异花岗岩最重要的造岩矿物学标志之一(吴福元等, 2017)。伟晶岩中云母的Li、Rb、Cs、F、Ba、Sn、Zn含量和K/Rb值可以反映伟晶岩的演化趋势和分异演化程度(Vieira et al., 2011; 周起凤等, 2013),Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母类矿物在Ⅰ—Ⅴ带的Li、F、Rb和Cs含量逐渐升高,K/Rb值逐渐降低,表明伟晶岩由外向内结晶的分异演化程度较高(图5)。
![]() 图 5 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母的K/Rb vs. Li、F、Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn相关图解(Li数据来源于Dewaele et al., 2016;Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn元素含量根据表1中氧化物的含量换算)Figure 5. K/Rb vs. Li, F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn for micas in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatite (Li data after Dewaele et al., 2016;F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn contents are converted according to the oxide content in Table 1)
图 5 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母的K/Rb vs. Li、F、Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn相关图解(Li数据来源于Dewaele et al., 2016;Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn元素含量根据表1中氧化物的含量换算)Figure 5. K/Rb vs. Li, F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn for micas in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatite (Li data after Dewaele et al., 2016;F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn contents are converted according to the oxide content in Table 1)6.2 锂矿化特征
Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的锂矿化主要发育于含锂辉石伟晶岩(Ⅳ)中,锂辉石与石英、钠长石共生,一般钾长石的含量较少,因此高钠长石和低钾长石的伟晶岩可以作为Manono地区锂矿的找矿标志。在整个伟晶岩发育的过程中,锂的富集与矿化常发生在较晚的阶段,伟晶岩结晶作用与气成热液交代阶段是锂的主要聚集阶段(文春华, 2017),交代作用越强,矿化越强(王盘喜等, 2017)。
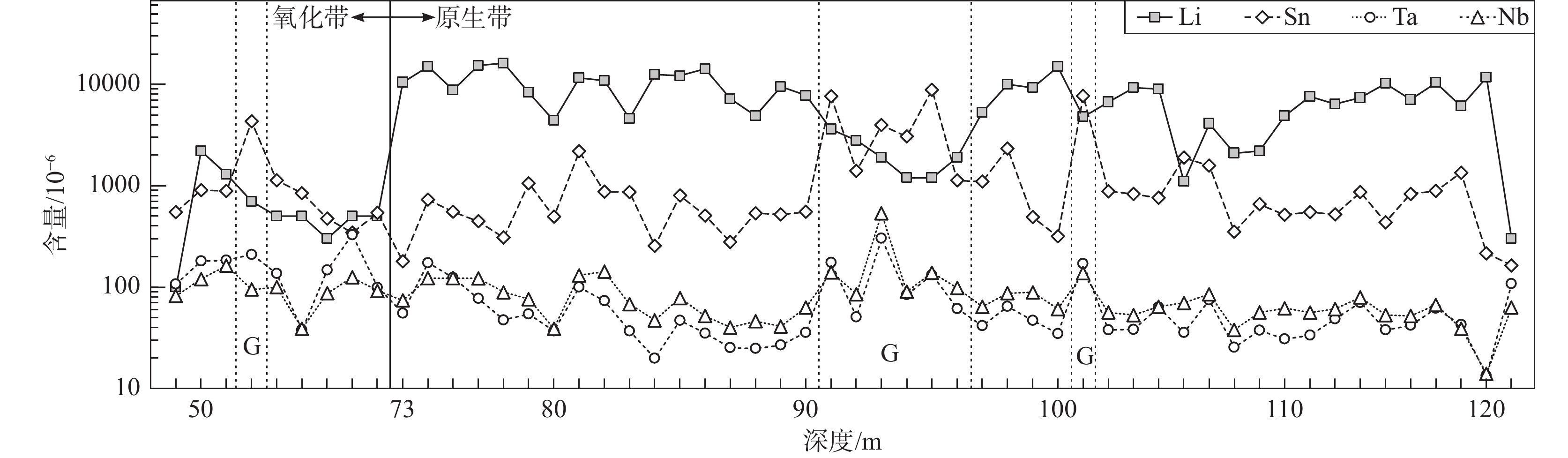
根据锂辉石与Li2O含量的关系显示(Eckhof, 2017; Ferguson et al., 2019),当伟晶岩中的锂辉石含量在20%~30%时,Li含量1.8%~2.0%(Li2O为3.88%~4.64%);锂辉石含量在10%~20%时,Li含量1.0%~1.6%(Li2O为2.15%~3.44%);锂辉石含量在5%~10%时,Li含量约0.60%(Li2O约1.29%)。在Kitotolo矿段中,锂辉石带(Ⅳ)受氧化淋滤的影响,氧化带至地表锂辉石含量<5%,氧化带深度0~70 m,最深可达100 m,根据分析结果显示(Eckhof, 2017),氧化带的Li含量为0%~0.30%(Li2O为0.00%~0.59%),说明在氧化带的风化作用和地下水的淋滤过程中,有可能造成了锂元素的流失。地表氧化带内不同程度的风化伟晶岩和云英岩化伟晶岩(G带)中锂含量明显降低(图6),说明晚期的热液对原生锂辉石进行强烈改造造成了锂的流失,云英岩化对锂辉石的交代造成了锂辉石含量的减低,同时为后期热液活动提供了部分锂(杨岳清等, 2020)。
![]() 图 6 Mpete伟晶岩脉的稀有元素含量变化特征图(数据来源于Eckhof, 2017)Figure 6. Characteristic diagram of rare element content variation of Mpete pegmatite dike (data after Eckhof, 2017)
图 6 Mpete伟晶岩脉的稀有元素含量变化特征图(数据来源于Eckhof, 2017)Figure 6. Characteristic diagram of rare element content variation of Mpete pegmatite dike (data after Eckhof, 2017)6.3 锡矿化特征
粗粒的锡石主要分布在云英岩化伟晶岩中,未蚀变锂辉石伟晶岩中可见少量细粒锡石。探针分析结果显示,锡石的Nb和Ta含量相对较高(图7),WO3含量均低于检出限,属于稀有金属伟晶岩成因的锡石(Tindle and Breaks, 1998),含锡石云英岩化伟晶岩样品的δ18OV-SMOW值+3.5‰,δDV-SMOW值−78.7(Dewaele et al., 2016),为原生岩浆水的典型值。根据富含稀有金属花岗岩(母岩)与伟晶岩之间的连续结晶分异模型(Shearer et al., 1992),锡矿化形成于稀有金属伟晶岩的中晚期。云英岩化伟晶岩中的锡石晶体粒径较大,晶形更完整(图4e),云英岩化形成的锡石中SnO2含量由核部向两侧逐渐减低(图8),说明锡矿化具有多阶段,最早形成伟晶岩的结晶过程中,后期的云英岩化阶段主导锡矿化(Dewaele et al., 2010, 2011)。云英岩化是由富挥发性流体交代围岩的结果(Pirajno, 2010),这些富挥发性的流体是在花岗伟晶岩浆的结晶过程中,由水、其他挥发性物质和不相容元素混合而产生的(Dewaele et al., 2016),因此云英岩化形成的白云母F含量(0.61%~1.43%)高于其他结构带的白云母(0.00%~1.19%)。Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩流体包裹体研究显示(Cryns, 2013; Dewaele et al., 2016),云英岩化样品中发现了熔融包裹体和大量次生低温(120~265℃)流体包裹体,说明该区的云英岩化作用较强。Sn含量与Li、Ta、Nb含量曲线近平行分布,但云英岩化位置(90~96 m)Sn含量发生明显升高(图6),与Li2O含量呈负相关,说明云英岩化对锡矿化具有改造叠加作用,形成高品位、粗粒的锡石,并对锂辉石进行交代造成Li元素的流失。因此,在Manono–Kitotolo矿区,云英岩化是锡矿的重要找矿标志。
![]() 图 8 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中铌钽铁矿的背散射图像和元素含量变化图补丁分带—补丁(浅色)部分Ta/Nb比值改高于深色部分Figure 8. BSE images and the major element composition of columbite−tantalite in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatitePatchy and volatility zonation–The Ta/Nb of the patch (light-colored) was changed to be higher than that of the dark-colored part
图 8 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中铌钽铁矿的背散射图像和元素含量变化图补丁分带—补丁(浅色)部分Ta/Nb比值改高于深色部分Figure 8. BSE images and the major element composition of columbite−tantalite in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatitePatchy and volatility zonation–The Ta/Nb of the patch (light-colored) was changed to be higher than that of the dark-colored part6.4 铌钽矿化特征
根据Manono–Kitotolo稀有矿床中细粒铌钽铁矿主要分布在白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)和石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)中,板状铌钽铁矿主要分布在云英岩化伟晶岩(G)和锂辉石带(Ⅳ)中。
BSE图像显示铌钽铁矿单个晶体呈成分分带特征,主要为补丁分带,其中补丁部分Ta/Nb比值相对较高(图8)。成分分带为交代作用或极度不平衡的条件下形成的(Beurlen et al., 2008),可能与P−T−X条件下的波动有关(Zhang et al., 2004),说明铌钽族矿物主要形成于不稳定的结晶环境。已有研究表明(Tindle and Breaks, 1998),单个铌钽铁矿晶体分带中形成的较早部分为富铌组分,富钽组分形成较晚(图8),即随着分异作用的进行,矿物中的钽和锰的含量增加,铌、铁和钛的含量降低。锂辉石的大量结晶及流体出溶带走大量熔体中的F,导致铌钽族矿物的结晶,且富铌端元的结晶早于富钽端元。Linnen and Keppler(1997)研究显示,在过铝质花岗岩或伟晶岩熔体中富铌端元的溶解度相对低于富钽端元,随伟晶岩分异演化程度加大,Ta/(Ta+Nb)比值升高。在大多数稀有金属花岗岩和花岗伟晶岩中,Mn相对于Fe,Ta相对于Nb的演化是同时发生的,石榴石和电气石的的结晶可以控制Fe、Mn的活动,导致Fe和Mn局部分馏(Zhang et al., 2004),铌锰矿溶解性较差,先结晶,从而富集了残余熔体中的钽,后期形成钽锰矿(Mulja et al., 1996),因此铌钽族矿物呈现由铌铁矿−钽锰矿的演化趋势。
以往的研究表明(陈国建, 2014),钠长石发育的环境对促使Ta2O5和Nb2O5等矿化元素的沉淀、发生成矿作用极为有利,文春华等(2017)认为钠长石化过程是Nb、Ta等稀有金属富集的重要因素。Dewaele et al.(2016)针对Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中铌钽铁矿的岩相学研究,认为铌钽铁矿与后期的钠长石化没有直接关系,本次研究发现,石英钠长岩脉中多处可见铌钽铁矿与细粒钠长石和石英共生(图3h,图4d),由此可见,钠长石化与铌钽铁矿的成矿具有一定的联系,需要进一步研究探索。云英岩化伟晶岩中的锡石Ta+Nb含量由中心向两侧逐渐升高(图7),且云英岩化伟晶岩中可见板状铌钽铁矿,因此云英岩化相关流体对Nb和Ta元素是否有改造富集作用,也有待进一步研究。
6.5 成矿作用分析
根据Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的结构分带和主要矿物特征,推断Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床属于花岗伟晶岩型:从母花岗岩原始岩浆中分离出来的富挥发组分和稀有元素的花岗质熔体,沿母岩体外围地层的构造中侵入,在相对封闭的环境中缓慢冷凝结晶分异成具伟晶结构的岩(矿)体(王登红等, 2017b; 王盘喜等, 2017; 杨岳清等, 2020; 赵如意等, 2024)。稀有金属成矿机制为结晶分异作用和液相不混溶(London, 2018; 秦克章等, 2019),根据富含稀有金属花岗岩(母岩)与伟晶岩之间的连续结晶分异模型,稀有金属结晶顺序为Be→Be−Nb−Ta→Li−Be−Nb−Ta→Li−Cs−Be−Nb−Ta−Sn(Shearer et al., 1992)。Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床中的矿化以锂矿化为主,其次为锡矿化和钽铌矿化,通过年代学的研究显示(Melcher et al., 2015; Dewaele et al., 2016),白云母长石石英伟晶岩(Ⅱ)的白云母40Ar–39Ar年龄为(938.8±5.1)Ma,锂辉石伟晶岩(Ⅳ带)的白云母40Ar–39Ar年龄为(934.0±5.9)Ma,铌钽铁矿(Ⅳ带)的U–Pb年龄为(940.2±5.1)~(947.0±2.8)Ma,云英岩化伟晶岩(Ⅲ带)40Ar–39Ar年龄为(923.83±8.3)Ma,说明钽铌矿化和锂矿化在伟晶岩结晶过程中形成,而云英岩化晚于伟晶岩的形成,稀有金属结晶顺序为Nb−Ta→Li−Nb−Ta→Li−Nb−Ta−Sn→Sn。因此可以将Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床的矿化蚀变分为4个阶段,第一阶段为伟晶岩结晶分异过程中的稀有金属矿化,主要形成锂辉石、铌钽铁矿和少量细粒锡石;第二阶段为钠长石化,主要形成细粒状、糖粒状钠长石和细粒铌钽铁矿;第三阶段为云英岩化,形成粗颗粒的锡石;第四阶段为近地表的黏土化和氧化淋滤作用,造成锂辉石的蚀变和锂元素流失。
7. 结 论
(1)Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩具有一定的横向分带特征,发育有花岗细晶岩带(Ⅰ)—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ)—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)—锂辉石带(Ⅳ)—含锂云母石英内核(Ⅴ),云母类矿物在Ⅰ—Ⅴ带的Li、F、Rb和Cs含量逐渐升高,K/Rb值逐渐降低,表明伟晶岩由外向内结晶的分异演化程度较高。
(2)锂辉石是Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床的最主要的锂矿物,主要分布于锂辉石伟晶岩带(Ⅳ带)中,主量成分较稳定,具有高SiO2、高A12O3的特征,其他组分含量较低,云英岩化和黏土化及氧化带的地下水淋滤作用造成Li2O含量的降低。
(3)锡矿化分布于Ⅲ—Ⅳ带中,锡石Nb和Ta含量相对较高,属于稀有金属伟晶岩成因,后期的云英岩化热液从花岗岩和伟晶岩中溶解锡元素富集成矿,使原先形成的锡石粒度变粗。
(4)铌钽族矿物为铌铁矿–钽铁矿–锰钽铁矿系列,分布于Ⅱ—Ⅳ带中,铌钽铁矿单个晶体呈成分分带特征,说明其形成于不稳定的结晶环境。随着分异作用的进行,铌钽矿物中的钽和锰的含量增加,铌、铁含量降低,形成富钽、富锰的铌钽铁矿。
(5)Manono–Kitotolo稀有金属矿床以锂矿化为主,其次为锡矿化和钽铌矿化,属于花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床,伟晶岩结晶分异过程中发生稀有金属矿化,形成锂辉石、铌钽铁矿和锡石等稀有金属矿物,云英岩化阶段形成粗粒的锡石。
致谢: 本文在野外调查和采样过程中得到了中国地质大学(武汉)蒋少涌教授的现场指导,和澳大利亚AVZ 矿业公司技术总监Greame Johnston先生、中色地科矿产勘查股份有限公司王旭东高级工程师的支持和帮助,成文期间审稿专家和编辑部老师提出了宝贵的修改意见和建议,在此表示衷心的感谢!
-
图 1 Kibaran成矿带区域地质图(据Melcher et al., 2015修改)
Figure 1. Regional geological map of Kibaran metallogenic belt (modified from Melcher et al., 2015)
图 2 Manono地区地质简图(a)、Manono–Kitotolo矿区地质图(b)(据Ferguson et al., 2019修改)和Malata伟晶岩脉剖面示意图(c)
Figure 2. Geological map of Manono area (a), Manono–Kitotolo mining area (b) (modified from Ferguson et al., 2019), and sectional schematic diagram of Malata pegmatite dike (c)
图 3 Manono−Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石标本照片
a—石英钠长石带(Ⅲ)穿插于白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅳ带中的长柱状锂辉石巨晶;c—Ⅳ带中的粗粒锂辉石晶体;d—Ⅳ带中的中细粒锂辉石晶体;e—Ⅳ-1带中的蚀变锂辉石晶体;f—Ⅴ-1带中的锂云母;g—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石;h—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的铌钽铁矿;i—云英岩化锂辉石伟晶岩(G/Ⅳ)中锂辉石的交代残余结构;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母
Figure 3. Graphs of rock samples in the Manono-Kitotolo pegmatite
a–Quartz albite zone (Ⅲ) interspersed with muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Long columnar spodumene giant crystal from zone Ⅳ; c–Coarse spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; d–Medium−fine grained spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ; e–Altered spodumene crystal from zone Ⅳ−1; f–Lepidolite from zone Ⅴ−1; g–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); h–Coltan in greisenization pegmatite (G); i–Metasomatic relict texture of spodumene from greisenization spodumene pegmatite (G/Ⅳ); Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite-tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite
图 4 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩的岩石显微照片
a—白云母长石石英带(Ⅱ);b—Ⅱ带中的细粒石英和粗粒微斜长石呈似文象结构;c—Ⅲ带中的中粒钠长石;d—Ⅲ带中的细粒钠长石和它形铌钽铁矿;e—云英岩化伟晶岩(G)中的粗粒锡石; f—Ⅳ带中锂辉石被细粒的石英、钠长石交代;g—Ⅳ号带中锂辉石与不规则状锡石共生;h—Ⅳ−1带中蚀变锂辉石与中粒钠长石共生;i—Ⅴ−1带中锂云母与白云母共生;Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿;Ab—钠长石;Q—石英;Mic—微斜长石;Pl—斜长石;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母;Ser—绢云母
Figure 4. Micrographs of rock samples in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatite
a–Muscovite feldspar quartz zone (Ⅱ); b–Fine-grained quartz and coarse-grain microcline is lconographic structure from zoneⅡ; c–Medium albite from zone Ⅲ; d–Fine grained albite and allomorphic columbite-tantalite from zone Ⅲ; e–Coarse grain of cassiterite in greisenization pegmatite (G); f–Fine quartz and albite metasomatism spodumene from zone Ⅳ; g–Spodumene symbiosis with cassiterite from zone Ⅳ; h–Alteration spodumene symbiosis with medium albite from zone Ⅳ−1; i–Lepidolite symbiosis with Muscovite from zone Ⅴ−1; Spd–Spodumene; Cst–Cassiterite; Clb–Columbite−tantalite; Ab–Albite; Q–Quartz; Mic–Microcline; Pl–Plagioclase; Ms–Muscovite; Lpd–Lepidolite; Ser–Sericite
图 5 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母的K/Rb vs. Li、F、Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn相关图解(Li数据来源于Dewaele et al., 2016;Rb、Cs、Fe、Mn元素含量根据表1中氧化物的含量换算)
Figure 5. K/Rb vs. Li, F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn for micas in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatite (Li data after Dewaele et al., 2016;F, Rb, Cs, Fe, Mn contents are converted according to the oxide content in Table 1)
图 6 Mpete伟晶岩脉的稀有元素含量变化特征图(数据来源于Eckhof, 2017)
Figure 6. Characteristic diagram of rare element content variation of Mpete pegmatite dike (data after Eckhof, 2017)
图 8 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中铌钽铁矿的背散射图像和元素含量变化图
补丁分带—补丁(浅色)部分Ta/Nb比值改高于深色部分
Figure 8. BSE images and the major element composition of columbite−tantalite in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmatite
Patchy and volatility zonation–The Ta/Nb of the patch (light-colored) was changed to be higher than that of the dark-colored part
表 1 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中云母元素组成分析结果
Table 1 Analytical data of major composition of mica in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite
结构带 矿物 样品号/点位 测试结果/% K/Rb 备注 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO Na2O K2O Rb2O Cs2O F 总量 Ⅰ Ms bgk1-1① 46.72 0.34 34.06 2.49 0.04 0.65 10.64 0.14 bdl 0.85 95.81 69.20 Ms RG16811 47.89 0.03 35.80 — 0.04 1.08 9.37 — — 0.54 100.56 39.71 Ⅱ Ms bgn2-1① 46.11 0.03 36.85 0.82 0.07 0.40 10.41 0.73 0.02 0.34 95.44 12.98 Ms RG5826 46.56 0.03 33.60 — 0.05 0.48 10.66 — — 0.21 100.84 45.17 Ms RG9699 47.53 0.03 33.49 — 0.27 0.54 10.31 — — bdl 99.44 43.69 Ⅳ Ms bgn1-3③ 46.69 bdl 34.90 2.68 0.25 0.53 10.28 0.55 0.02 0.81 95.94 17.02 Ms B34① 46.42 0.05 35.09 2.68 0.34 0.33 10.71 0.71 0.02 0.62 96.40 13.73 Ms RG15992 47.46 0.03 34.73 — 0.30 0.92 9.85 — — 0.56 100.16 15.06 Ms RG16005 46.90 0.04 33.70 — 0.27 0.62 10.32 — — 1.19 100.16 16.30 Ⅳ−1 Ms bgn2-3① 45.62 0.02 38.35 0.05 0.13 0.46 10.45 1.15 bdl 0.00 96.27 8.27 Ms bgn2-3③ 46.15 bdl 36.89 0.08 0.14 0.35 10.62 1.90 bdl 0.63 96.18 5.09 Ⅴ−1 Lpd bgn2-5① 52.57 bdl 24.83 0.10 1.36 0.07 10.20 2.92 0.08 4.44 92.33 3.18 Lpd RG14 55.47 0.01 25.65 0.04 0.39 0.37 9.02 — — 4.05 99.79 5.13 Ⅴ−1 Ms bgn2-5⑤ 46.44 bdl 37.93 0.05 0.07 0.24 9.90 0.75 bdl 0.00 95.38 12.02 Ms bgn2-5② 46.18 bdl 37.92 0.02 0.05 0.21 10.21 1.27 bdl 0.00 95.90 7.32 Ms bgn2-5③ 46.71 0.02 37.89 0.02 bdl 0.17 10.97 0.85 bdl 0.00 96.79 11.75 Ms bgn2-5⑥ 45.33 bdl 37.99 bdl 0.03 0.17 10.06 0.73 0.03 0.00 94.34 12.55 G Ms bgs1-2① 46.82 0.05 32.59 3.57 0.43 0.23 10.61 0.96 bdl 1.43 95.41 10.06 云英岩化 Ms RG16747 58.64 0.04 28.12 — 0.12 0.52 7.96 — — 0.68 101.71 15.85 Ms RG16777 46.44 0.03 34.82 — 0.20 0.66 9.91 — — 1.24 98.91 14.21 Ms RG16958 45.81 0.02 37.40 — 0.16 0.75 10.17 — — 0.61 99.87 14.49 注:RG系列样品的分析结果来自Dewaelea et al.(2016);K/Rb比中的K和Rb含量根据氧化物计算;Ms—白云母;Lpd—锂云母;“bdl”表示低于检出限,“—”表示未检测。 表 2 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中锂辉石元素组成分析结果
Table 2 Analytical data of major composition of spodumene in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite
样品号/点位 测试结果/% SiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO Na2O K2O CaO Ta2O5 SnO2 总量 bgn1-3① 64.16 27.58 0.48 0.10 0.16 bdl bdl bdl 0.05 92.53 B34③ 63.91 27.54 0.43 0.10 0.14 bdl bdl 0.05 bdl 92.17 B34④ 64.30 27.42 0.19 0.06 0.11 0.02 0.02 bdl bdl 92.12 平均值 64.12 27.51 0.37 0.09 0.14 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.05 92.27 表 3 Manono–Kitotolo伟晶岩中锡石和铌钽铁矿元素组成分析结果
Table 3 Analytical data of major composition of cassiterite and columbite-tantalite in the Manono–Kitotolo pegmalite
结构带 矿物 点位 铌钽铁矿和锡石测试结果/% Mn/(Fe+Mn) Ta/(Ta+Nb) SiO2 TiO2 FeO MnO Rb2O Nb2O5 Ta2O5 SnO2 WO3 总量 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1① 0.40 1.62 7.01 8.59 0.40 26.34 52.59 1.00 0.78 99.97 0.55 0.66 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1② 0.41 0.39 6.22 9.82 1.70 28.85 51.38 0.07 0.58 99.42 0.61 0.65 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1③ 0.36 0.24 6.37 10.19 1.45 36.66 43.98 0.27 0.32 99.84 0.61 0.55 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1④ 0.41 1.39 5.93 9.57 1.51 27.64 51.99 0.85 0.32 99.61 0.62 0.66 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1⑤ 0.41 1.87 6.18 8.98 1.56 25.83 52.67 0.99 0.42 98.95 0.59 0.68 Ⅲ Clb bgn1-1⑥ 0.34 0.26 6.31 9.89 1.51 36.05 45.27 0.05 0.42 100.1 0.61 0.56 不明 Clb P25 — 0.15 — — — — — 0.08 0.06 — 0.34 0.18 不明 Clb P75 — 0.67 — — — — — 0.31 0.30 — 0.72 0.5 均值 0.39 0.82 6.34 9.51 1.56 30.23 49.65 0.45 0.40 99.65 0.58 0.56 G Cst bgs1-2① 0.62 0.03 0.50 0.05 bdl 1.52 1.93 94.96 bdl 100 0.09 0.57 G Cst bgs1-2② 0.62 0.09 0.25 bdl bdl 0.65 0.7 96.32 bdl 99.06 bdl 0.52 G Cst bgs1-2③ 0.60 0.07 0.08 bdl bdl 0.25 0.43 98.26 bdl 100.1 bdl 0.64 G Cst bgs1-2④ 0.60 0.06 0.25 0.03 bdl 0.56 0.65 94.1 bdl 96.8 0.11 0.54 G Cst bgs1-2⑤ 0.55 0.11 0.71 0.04 bdl 2.38 2.02 93.58 bdl 99.88 0.05 0.47 均值 0.598 0.072 0.36 0.04 bdl 1.072 1.146 95.44 bdl 99.18 0.08 0.55 注:P25、P75分析结果来自Melcher et al.(2015);Spd—锂辉石;Cst—锡石;Clb—铌钽铁矿。 -
[1] Beurlen H, Da Silva M R R, Thomas R, Soares D R, Olivier P. 2008. Nb–Ta–(Ti–Sn) oxide mineral chemistry as tracer of rare–element granitic pegmatite fractionation in the Borborema Province Northeastern Brazil[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 43: 207−228. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0152-4
[2] Bradley D C, McCauley A D, Stillings L M. 2017. Mineral–Deposit Model for Lithium–Cesium–Tantalum Pegmatites: Chapter O of Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment[R]. Reston, Virginia: U.S. Geological Survey, 1–48.
[3] Cahen L, Delhal J, Vail J R, Bonhomme M, Ledent D. 1984. The Geochronology and Evolution of Africa[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1–512.
[4] Chen Guojian. 2014. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Nanping granitic pegmatite type Ta–Nb deposit, Fujian Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(10): 1550−1561 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Cryns Y. 2013. Petrographical, Mineralogical and Geochemical Study of the Sn, Nb–Ta, Li–Mineralized Pegmatites of Manono–Kitotolo, Katanga (D. R. Congo)[D]. Leuven: Katholieke Universiteit Leuven.
[6] Dewaele S, De Clerq F, Muchez P, Schneider J, Burgess R, Boyce A, Fernandez–Alonso M. 2010. Geology of the cassiterite mineralization in the Rutongo area, Rwanda (Central Africa): Current state of knowledge[J]. Geologica Belgica, 13(1/2): 91−112.
[7] Dewaele S, Henjes–Kunst F, Melcher F, Sitnikova M, Burgess R, Gerdes A, Fernandez–Alonso M, De Clerq F, Muchez P, Lehmann B. 2011. Late Neoproterozoic overprinting of the cassiterite and columbite–tantalite bearing pegmatites of the Gatumba area, Rwanda (Central Africa)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 61: 10−26. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2011.04.004
[8] Dewaele S, Hulsbosch N, Cryns Y, Boyce A, Burgess R, Muchez P. 2016. Geological setting and timing of the world–class Sn Nb–Ta and Li mineralization of Manono–Kitotolo (Katanga, Democratic Republic of Congo)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 373−390. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.004
[9] Dill H G. 2015. Pegmatites and aplites: Their genetic and applied ore geology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 69: 417−561. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.022
[10] Eckhof K. 2017. High–grade Lithium Mineralization Now Drill Confirmed over A Strike Length of 4 km within Three Pegmatites at the Kitotolo Sector, Manono Project, DRC[R]. Perth, Western Australia: AVZ Minerals Limited, 1–29.
[11] Ferguson N, Johnston G, Chen H L, Brans R, Huljich P. 2019. AVZ 2019 Annual Report[R]. Perth, Western Australia: AVZ Minerals Limited, 1–77.
[12] Gerards J, Ledent D L. 1970. Grands traits de la géologie du Rwanda, différents types de roches granitiques et premières données sur les ages de ces roches[J]. Annal es de la Sociéte Géologique de Belgique, 93: 477−489.
[13] Kokonyangi J W, Kampunzu A B, Armstrong R, Yoshida M, Okudaira T, Arima M, Ngulube D A. 2006. The Mesoproterozoic Kibaride belt (Katanga, SE D R Congo)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 46: 1−35. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.01.017
[14] Linnen R L, Keppler H. 1997. Columbite solubility in granitic melts: Consequences for the enrichment and fractionation of Nb and Ta in the earth's crust[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 128: 213−227. doi: 10.1007/s004100050304
[15] Liu Lijun, Wang Denghong, Liu Xifang, Li Jiankang, Dai Hongzhang, Yan Weidong. 2017. The main types, distribution features and present situation of exploration and development for domestic and foreign lithium mine[J]. Geology in China, 44(2): 263−278 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] London D. 2018. Ore–forming processes within granitic pegmatites[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 101: 349−383. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.020
[17] Melcher F, Graupner T, Gäbler H E, Sitnikova M, Henjes–Kunst F, Oberthür T, Gerdes A, Dewaele S, 2015. Tantalum–(niobium–tin) mineralization in African pegmatites and rare metal granites: Constraints from Ta–Nb oxide mineralogy, geochemistry and U–Pb geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 64: 667–719.
[18] Mulja T, Williams–Jones A E, Martin R F, Wood S A. 1996. Compositional variation and structural state of columbite–tantalite in rare–element granitic pegmatites of the Preissac–Lacorne batholith, Quebec, Canada[J]. American Mineralogist, 81: 146−157. doi: 10.2138/am-1996-1-219
[19] Pirajno F. 2010. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems[M]. Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia, 1–1243.
[20] Qin Kezhang, Zhou Qifeng, Tang Dongmei, Wang Chunlong. 2019. Types, internal structural patterns, mineralization and prospects of rare–element pegmatites in East Qinling Mountain in comparison with features of Chinese Altay[J]. Mineral Deposits, 38(5): 970−982 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Shearer C K, Papike J J, Jolliff B L. 1992. Petrogenetic links among granites and pegmatites in the Harney Peak rare–element granite–pegmatite system, Black Hills, South Dakota[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 30: 785−809.
[22] Tack L, Wingate M, DeWaele B, Meert J, Belousova E A, Griffin B, Tahon A, Fernandez–Alonso. 2010. The 1375 Ma “Kibaran event” in Central Africa: Prominent emplacement of bimodal magmatism under extensional regime[J]. Precambrian Research, 180: 63−84. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.022
[23] Tindle A G, Breaks F W. 1998. Oxide minerals of the separation rapids rare element granitic pegmatite group, northwestern Ontario[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 36(2): 609−635.
[24] Vieira R, Roda–Robles E, Pesquera A, Lima A. 2011. Chemical variation and significance of micas from the Fregeneda–Almendra pegmatitic field (Central–Iberian Zone, Spain and Portugal)[J]. American Mineralogist, 96(4): 637−645. doi: 10.2138/am.2011.3584
[25] Wang Denghong, Liu Lijun, Hou Jianglong, Dai Hongzhang, YuYang, Dai Jingjing, Tian Shihong. 2017a. A preliminary review of the application of “Five levels+ Basement” model for Jiajika style rare metal deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(5): 1−17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Wang Denghong, Liu Lijun, Dai Hongzhang, Liu Shanbao, HouJianglong, Wu Xishun. 2017b. Discussion on particularity and prospecting direction of large and superlarge spodumene deposits[J]. Earth Science, 42(12): 2243−2257 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Wang Panxi, Zhu Likuang, Liu Lu, Guo Jungang, Wu Qiushen. 2017. Geological and geochemical characteristics of grainitic pegmatite in Guanpo, Henan Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 4(6): 40−49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Wang Rucheng, Xie Lei, Zhu Zeying, Hu Huan. 2019. Micas: Important indicators of granite–pegmatite–related rare–metal mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(1): 69−75 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.04
[29] Wen Chunhua. 2017. Mineralogical–geochemical characteristics and ore potentiality studies of pegmatite in southern margin of the Mufushan area, Hunan Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(1): 67–74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wu Fuyuan, Liu Xiaochi, Ji Weiqiang, Wang Jiamin, Yang Lei. 2017. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 47(7): 745−765 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Xiao Huiliang, Li Haili, Fan Feipeng, Zeng Zailin, Chen Lezhu, Zhou Yan, Sun Jiandong, Xiao Fan, Chen Xiaoyong, Chen Binfeng. 2023. The mineral prospecting direction of Li−Be−Nb−Ta deposits in East Nanling region[J]. Geology in China, 50(3): 653–676 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Yang Yueqing, Wang Denghong, Liu Shanbao, Liu Lijun, Wang Chenghui, Guo Weiming. 2020. The co–occurrence mechanism of two types of spodumene ore bodies and their prospecting significance in Jiajikan, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(1): 287−302 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Zhang A C, Wang R C, Hu H, Zhang H, Zhu J C, Chen X M. 2004. Chemical evolution of Nb–Ta oxides and zircon from the Koktokay No. 3 granitic pegmatite, Altai, northwestern China[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 68(5): 739−756. doi: 10.1180/0026461046850216
[34] Zhao Ruyi, Wang Denghong, Feng Yonggang, Wang Chenghui, Liang Ting, Li Kaixuan, Dai Hongzhang, Shi Yu, Gao Jinggang. 2024. Characteristics of granitic pegmatite type lithium deposits in different mineralization epochs and its enlightenment for prospecting prediction, China[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 17−41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Zhou Qifeng, Qin Kezhang, Tang Dongmei, Ding Jiangang, Guo Zhenglin. 2013. Mineralogy and significance of micas and feldspars from the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatitic rare–element deposit, Altai[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3004−3022 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 陈国建. 2014. 福建南平花岗伟晶岩型钽铌矿床地质特征与成因[J]. 地质通报, 33(10): 1550−1561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.011 [37] 刘丽君, 王登红, 刘喜方, 李建康, 代鸿章, 闫卫东. 2017. 国内外锂矿主要类型、分布特点及勘查开发现状[J]. 中国地质, 44(2): 263−278. doi: 10.12029/gc20170204 [38] 秦克章, 周起凤, 唐冬梅, 王春龙. 2019. 东秦岭稀有金属伟晶岩的类型、内部结构、矿化及远景—兼与阿尔泰地区对比[J]. 矿床地质, 38(5): 970−982. [39] 王登红, 刘丽君, 侯江龙, 代鸿章, 于扬, 代晶晶, 田世洪. 2017a. 初论甲基卡式稀有金属矿床“五层楼+地下室”勘查模型[J]. 地学前缘, 24(5): 1−17. [40] 王登红, 刘丽君, 代鸿章, 刘善宝, 侯江龙. 吴西顺. 2017b. 试论国内外大型超大型锂辉石矿床特殊性与找矿方向[J]. 地球科学, 42(12): 2243−2257. [41] 王盘喜, 朱黎宽, 刘璐, 郭俊刚, 武秋生. 2017. 河南官坡花岗伟晶岩地质与地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质调查, 4(6): 40−49. [42] 王汝成, 谢磊, 诸泽颖, 胡欢. 2019. 云母: 花岗岩—伟晶岩稀有金属成矿作用的重要标志矿物[J]. 岩石学报, 35(1): 69−75. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.04 [43] 文春华. 2017. 幕阜山南缘地区伟晶岩矿物学、地球化学特征及含矿性分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(1): 67−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.01.008 [44] 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 王佳敏, 杨雷. 2017. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 47(7): 745−765. [45] 肖惠良, 李海立, 范飞鹏, 曾载淋, 陈乐柱, 周延, 孙建东, 肖凡, 陈小勇, 陈斌锋. 2023. 论南岭东段地区锂铍铌钽矿找矿方向[J]. 中国地质, 50(3): 653–676. [46] 杨岳清, 王登红, 刘善宝, 刘丽君, 王成辉, 郭唯明. 2020. 四川甲基卡两类锂辉石矿体共存机制及其找矿意义[J]. 地质学报, 94(1): 287−302. [47] 赵如意, 王登红, 凤永刚, 王成辉, 梁婷, 李凯旋, 代鸿章, 石煜, 高景刚. 2024. 中国不同时代典型花岗伟晶岩型锂矿特征及其对找矿预测的启示[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 17−41. [48] 周起凤, 秦克章, 唐冬梅, 丁建刚, 郭正林. 2013. 阿尔泰可可托海3号脉伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床云母和长石的矿物学研究及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 29(9): 3004−3022.



 下载:
下载: