Geochronology, geochemistry and lithosphere extension of Kafang diabase in Gejiu area, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:研究目的
卡房辉绿岩成因与成岩构造环境的探索对研究个旧地区构造岩浆演化具有重要的科学意义。
研究方法本文基于LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄、全岩地球化学和Sr−Nd−Pb同位素分析等方法研究卡房辉绿岩墙的形成年代、地球化学特征及地质意义。
研究结果锆石U−Pb地质年代学研究表明卡房辉绿岩侵位年龄为77 Ma,年龄为2409 Ma、2616 Ma、290 Ma的继承锆石指示个旧地区存在新太古代和古元古代构造热事件形成的变质基底以及早二叠世的岩浆活动。卡房辉绿岩属于钾玄岩系列,以低硅、高钾、高钛、高镁为特征,富集Rb、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素,具有与洋岛玄武岩相似的稀土和微量元素分布特征。卡房辉绿岩具有较高的初始87Sr/86Sr同位素比值(0.70782~0.70791)和正的εNd(t)值(2.07~2.29);初始铅同位素组成中,(206Pb/204Pb)t=18.286~18.465,(207Pb/204Pb)t=15.668~15.717,(208Pb/204Pb)t=37.763~38.830。Sr−Nd−Pb同位素特征指示卡房辉绿岩岩浆源区具有富集地幔(EM2)特征。
结论卡房辉绿岩成岩机制为在伸展构造背景下,上涌的软流圈地幔底侵富集岩石圈地幔。在岩石圈地幔60~120 km深度,石榴石二辉橄榄岩经过5%~15%的部分熔融,形成了卡房辉绿岩的初始岩浆,在岩浆侵位过程中同化混染下地壳物质并经过较弱的分离结晶作用形成了卡房辉绿岩。
创新点:采用LA−ICP−MS锆石测年、全岩地球化学和Sr−Nd−Pb同位素分析等方法揭示了个旧卡房辉绿岩的形成年代、岩石成因及源区特征。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
ObjictiveThe exploration of the petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Kafang diabase is crucial to know about the tectonomagmatic evolution in Gejiu area.
MethodsBased on LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb age, whole−rock geochemistry and Sr−Nd−Pb isotope analysis, the formation age, geochemical characteristics and geological significance of Kafang diabase dike are studied.
ResultsZircon U−Pb dating shows that the age of Kafang diabase is 77 Ma. Inherited zircon ages (2409 Ma, 2616 Ma, 290 Ma) indicate tectono−thermal related Neoarchean and Paleoproterozoic metamorphic basement and the magmatic activity in Early Permian in Gejiu area. The Kafang diabase belongs to the shoshonite series with the characteristics of low SiO2 content and high K2O, TiO2, MgO contents. In primitive mantle normalized trace elements diagram, these samples show similarities with OIB and enriched in LILEs (such as Rb, K, Sr), depleted in HFSEs (such as Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf). High initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios (0.70782−0.70791), positive εNd(t) values (2.07−2.29) and initial Pb isotopic compositions (206Pb/204Pb=18.286−18.465, 207Pb/204Pb=15.668−15.717, 208Pb/204Pb=37.763−38.830) indicate the enriched mantle (EM2) source.
ConclusionsThe petrogenesis of Kafang diabase is that the upwelling of asthenosphere in an extensional setting induced 5%−15% partial melting of garnet lherzolite at a depth of 60−120 km in the lithospheric mantle. The new−formed magma with characteristics of EM2 consists of the primary magma of the Kafang diabase. During the ascent of magma, contamination of the lower crust occurred accompanied by weak fractional crystallization, and then formed the Kafang diabase.
-
Keywords:
- diabase /
- zircon U−Pb dating /
- geochemistry /
- petrogenesis /
- tectonic setting /
- geological survey engineering /
- Gejiu /
- Yunnan Province
Highlights:The formation age, petrogenesis and source region characteristics of the Kafang diabase in Gejiu area are revealed by the methods of LA–ICP–MS zircon dating, whole-rock geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb isotope analysis.
-
1. 引 言
个旧矿集区位于古特提斯成矿域与滨太平洋成矿域的交汇部位,以盛产锡矿闻名于世。矿区内云英岩—矽卡岩型、层间氧化矿型、产于花岗岩顶部的脉状锡多金属矿床与燕山期花岗岩成矿关系密切(冶金工业部西南冶金地质勘探公司, 1984; Cheng et al., 2010, 2012, 2016; 贾润幸等, 2014; 毛景文等, 2018)。因此,前人研究多集中在花岗岩成矿以及花岗岩成因方面的研究,并取得了一系列的研究成果(莫国培, 2006; 王永磊等, 2007; 徐启东等, 2009; 李肖龙等, 2011; 黄文龙等, 2016)。但是,对于矿区内出露的辉绿岩墙研究程度较低,尤其是缺乏其年代学和同位素证据,制约了我们对个旧杂岩体成因的整体认识。
基性岩脉作为岩石圈伸展作用和构造−岩浆演化的重要标志(Radhakrishna and Mathew, 1996),是起源于软流圈或岩石圈地幔的岩浆在伸展背景下侵位于地壳不同深度的产物,具有重要的构造意义(Weaver and Tamey, 1981; Hoek and Seitz, 1995; 葛小月等, 2003; Hou et al., 2006a, b; Peng et al., 2008; 祁生胜等, 2013)。通过对基性岩脉的研究可以了解地球深部信息和壳幔作用(冯乾文, 2012)以及地表火山作用与深部地幔岩浆活动间的联系(Hooper et al., 2010; Srivastava, 2011)。
古太平洋板块西向俯冲作用导致的弧后伸展作用对了解中国东南部晚中生代的构造演化历史至关重要。最近,笔者在卡房矿段1380开采水平的巷道中发现了一套辉绿岩墙,其成因尚不明确,对其岩石成因和源区特征的探讨对个旧地区的动力学背景研究具有特殊的指示意义,为研究晚白垩世西太平洋构造域伸展构造环境下的岩浆活动提供了重要窗口。本文通过岩石学、LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年代学、全岩主微量元素地球化学和Sr−Nd−Pb同位素地球化学方法探讨卡房辉绿岩岩浆源区特征及成因机制,为晚白垩世西太平洋构造演化提供岩石地球化学制约。
2. 地质背景和样品
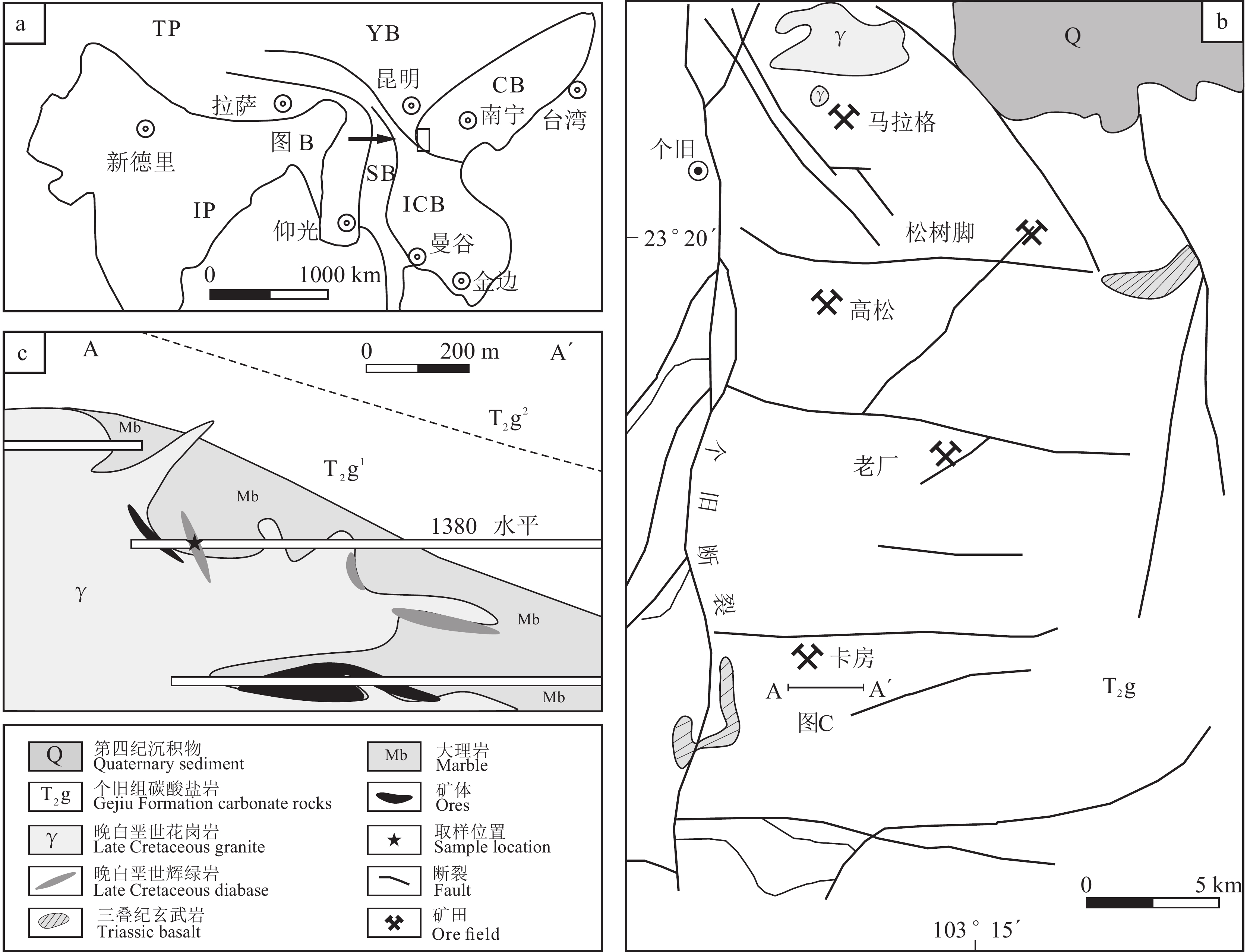
个旧矿区在大地构造上位于印支板块、扬子板块与华夏板块的交汇处附近(图1a)。区内地层以三叠系火山沉积建造为主,其中中三叠统个旧组是以碳酸盐岩为主要的含矿建造。南北向展布的个旧断裂(小江断裂南延部分)为主要的控岩控矿构造,将个旧矿区分为东区和西区两部分,东区次级断裂系统发育,以东西向断裂为主,呈等距分布,是主要的赋矿导矿构造(图1b)。个旧锡铜多金属矿床主要分布于东区,这些矿床由南至北依次为卡房矿段、老厂矿段、高松矿段、松树脚矿段、马拉格矿段。自印支旋回以来,个旧地区构造岩浆活动十分强烈,形成了现在的岩浆岩分布和构造格局(戴福盛, 1990; 李肖龙等, 2011; 赵文君, 2018)。印支期以基性、碱性岩为主的火山、次火山岩广泛分布于矿区南部的新山岩体和北部的麒麟山岩体;燕山期以酸性、碱性侵入岩为主的杂岩体广泛分布于个旧矿区。燕山期晚白垩世岩浆岩主要由花岗岩、二长岩等酸性岩组成,以及少量的辉绿岩、辉长岩、煌斑岩岩脉等,这些侵入体组成复合岩体侵位于地表以下200~1000 m深处,地表仅有少量露头。目前已知的辉绿岩墙有两处,分别分布在老厂矿段东部和卡房矿段(冶金工业部西南冶金地质勘探公司, 1984; 程彦博, 2012),主要侵入到中三叠统碳酸盐岩和砂页岩地层中(图2a),并且与其他基性岩脉(辉长岩)和酸性岩体(二长岩、花岗岩)在时空上密切共生。
![]() 图 1 东南亚地质略图(a),个旧矿区地质简图(b)和卡房剖面及取样位置图(c)TP—塔里木板块;YB—扬子地体;CB—华夏地体;SB—滇缅泰马地体;ICB—印支地体;IP—印度板块Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Southeast Asia (a), geological map of the Gejiu ore district (b) and geological section of diabase in Kafang profile and sample location (c)TP−Tarim Plate; YB−Yangtze Block; CB−Cathaysia Block; SB−Dian−Mian−Tai−Ma Block; ICB−Indochina Block; IP−India Plate
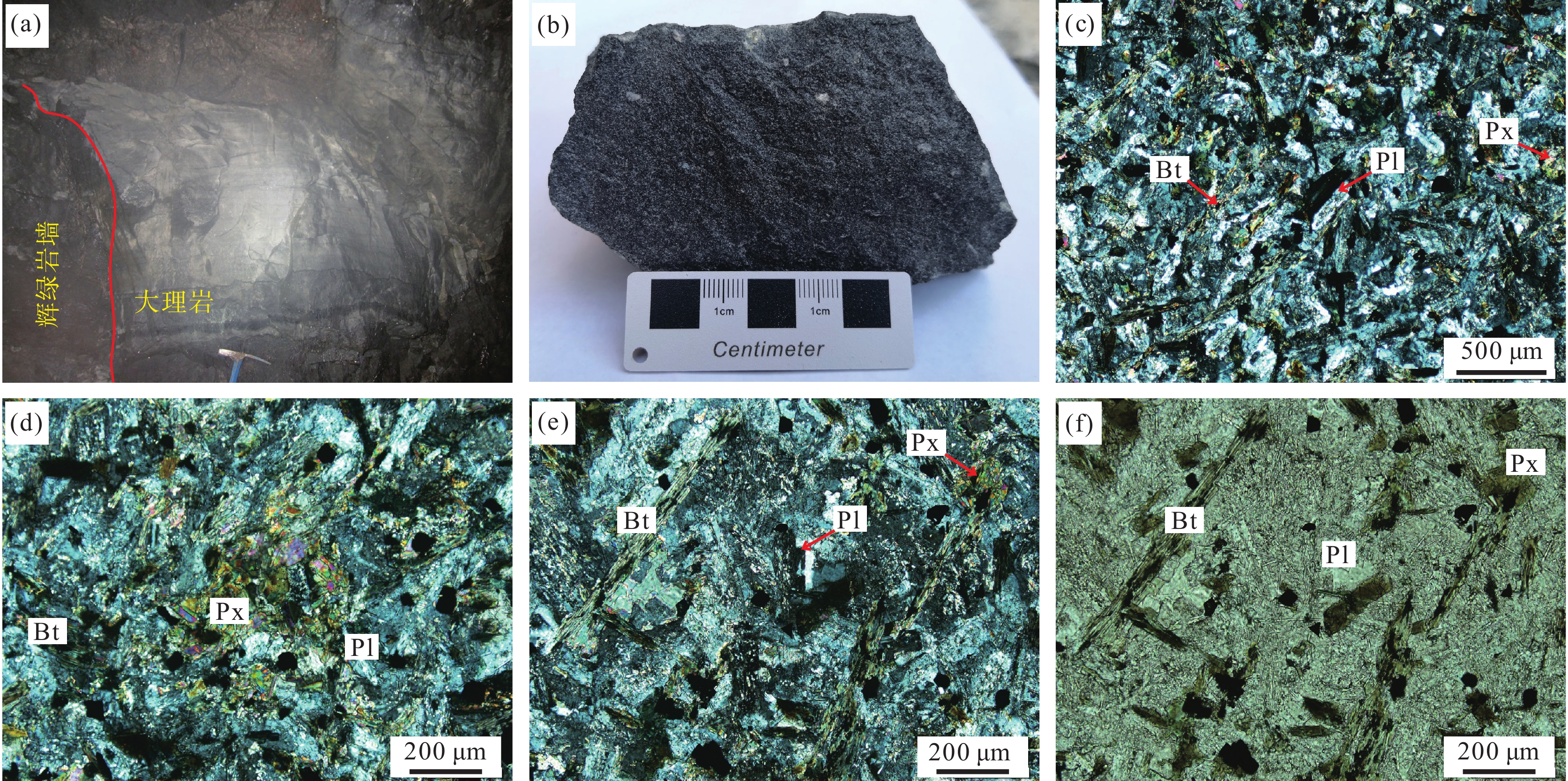
图 1 东南亚地质略图(a),个旧矿区地质简图(b)和卡房剖面及取样位置图(c)TP—塔里木板块;YB—扬子地体;CB—华夏地体;SB—滇缅泰马地体;ICB—印支地体;IP—印度板块Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Southeast Asia (a), geological map of the Gejiu ore district (b) and geological section of diabase in Kafang profile and sample location (c)TP−Tarim Plate; YB−Yangtze Block; CB−Cathaysia Block; SB−Dian−Mian−Tai−Ma Block; ICB−Indochina Block; IP−India Plate![]() 图 2 辉绿岩墙侵入到大理岩中(a),辉绿岩手标本照片(b),正交偏光显微镜下照片(c、d、e),单偏光显微镜下照片(f)Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Px—辉石Figure 2. Diabase intrudes into marble (a), hand specimen of Kafang diabase (b), cross-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (c, d, e), single-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (f)Bt−Biotite; Pl−Plagioclase; Px−Pyroxene
图 2 辉绿岩墙侵入到大理岩中(a),辉绿岩手标本照片(b),正交偏光显微镜下照片(c、d、e),单偏光显微镜下照片(f)Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Px—辉石Figure 2. Diabase intrudes into marble (a), hand specimen of Kafang diabase (b), cross-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (c, d, e), single-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (f)Bt−Biotite; Pl−Plagioclase; Px−Pyroxene卡房辉绿岩大部分隐伏于地下,主要位于花岗岩和个旧组碳酸盐岩的接触带附近,呈陡倾的岩墙状不整合侵入于中三叠统个旧组碳酸盐岩中(图2a)。岩墙宽30~50 cm,岩墙边部发育冷凝边。本次研究在卡房矿段1380水平巷道中共采集辉绿岩样品13件,分别用于锆石U−Pb测年、全岩主微量元素分析和Sr−Nd−Pb同位素分析,取样位置见图1c。辉绿岩样品呈灰绿色,具辉绿结构,致密块状构造(图2b、c)。主要矿物组成为斜长石、辉石以及少量的角闪石和黑云母;次要矿物以磁铁矿、铁钛氧化矿物为主。斜长石含量约为50%,多呈自形—半自形长板状,可见明显双晶结构,矿物边缘发育少量绢云母化蚀变,斜长石以格架状杂乱分布于岩石中;辉石以普通辉石为主,含量约为20%,多呈半自形—他形,辉石发育轻微蚀变,蚀变矿物以透闪石为主;黑云母呈鳞片状,含量约为5%;黑云母以及磁铁矿等暗色矿物充填在斜长石和辉石的粒间空隙中(图2d、e、f)。
3. 分析方法
锆石分选与制靶在河北省区域地质调查所实验室进行。锆石测年在中国科学技术大学重点实验室完成,采用等离子体质谱仪对锆石进行了微区原位U−Pb同位素测定。采用外部锆石年龄标准TEMORA和GJ−1进行U−Pb同位素分馏校正。激光剥蚀以氦气作为剥蚀物质的载体,激光剥蚀束斑直径为32 μm,ICP−MS数据采集选用一个质量峰采集一点的跳峰方式。每测定5~10个样品点测定一组标样(一个标样91500点和一个GJ−1点)。锆石同位素数据处理采用ICPMS DataCal程序(Liu et al., 2010a)和Isoplot程序(Ludwig, 2003)。
全岩元素化学分析测试工作在中矿(天津)岩矿测试实验室进行。主量元素的测试方法为X射线荧光光谱法(XRF),分析误差介于5%~10%;微量元素的分析采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP−MS)分析测试,分析误差优于1.5%。
Sr−Nd同位素的分析测定在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室进行。在Rb−Sr和Sm−Nd同位素分析测定前,粉末状岩石样品首先加入混合同位素示踪剂,然后在混有氢氟酸和硝酸的闷罐中溶解。Rb、Sr、Sm、Nd的分离采用传统的离子交换柱方法,详细分离流程见Yan et al. (2005)。Sr−Nd同位素在VG Axiom质谱仪上测定。质谱测量中Sr同位素分馏用86Sr/88Sr=0.1194校正,Nd同位素分馏用146Nd/144Nd=0.7219校正。采用BCR−2标准样143Nd/144Nd=0.512633±0.000017 (2σ)和87Sr/86Sr=0.705013±0.000019 (2σ)检测分析精度。初始87Sr/86Sr和143Nd/144Nd比值根据锆石U−Pb年龄计算。
Pb同位素测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心进行,准确称取0.1~0.2 g粉末样品于低压密闭溶样罐(PFA)中,用混合酸(HF+HNO3+HClO4)溶解24小时。待样品完全溶解后,蒸干,加入6 mol/L的盐酸转为氯化物蒸干。用1 mL 0.5 mol/L HBr溶解,离心分离,清液加入阴离子交换柱,用0.5 mol/L HBr淋洗杂质,用1 mL 6 mol/L的HCl解析铅于聚四氟乙烯的烧杯中,蒸干备用。同位素分析采用ISOPROBE−T热电离质谱计,用磷酸硅胶将样品点在铼带上,用静态接受方式测量铅同位素比值。实验过程相对湿度为40%,温度为20℃,同位素比值控制误差为2σ。NBS 981校正结果:208Pb/206Pb=2.164940±15,207Pb/206Pb=0.914338±7,204Pb/206Pb=0.0591107±2,全流程本底Pb<100 pg。
4. 分析结果
4.1 锆石U−Pb测年
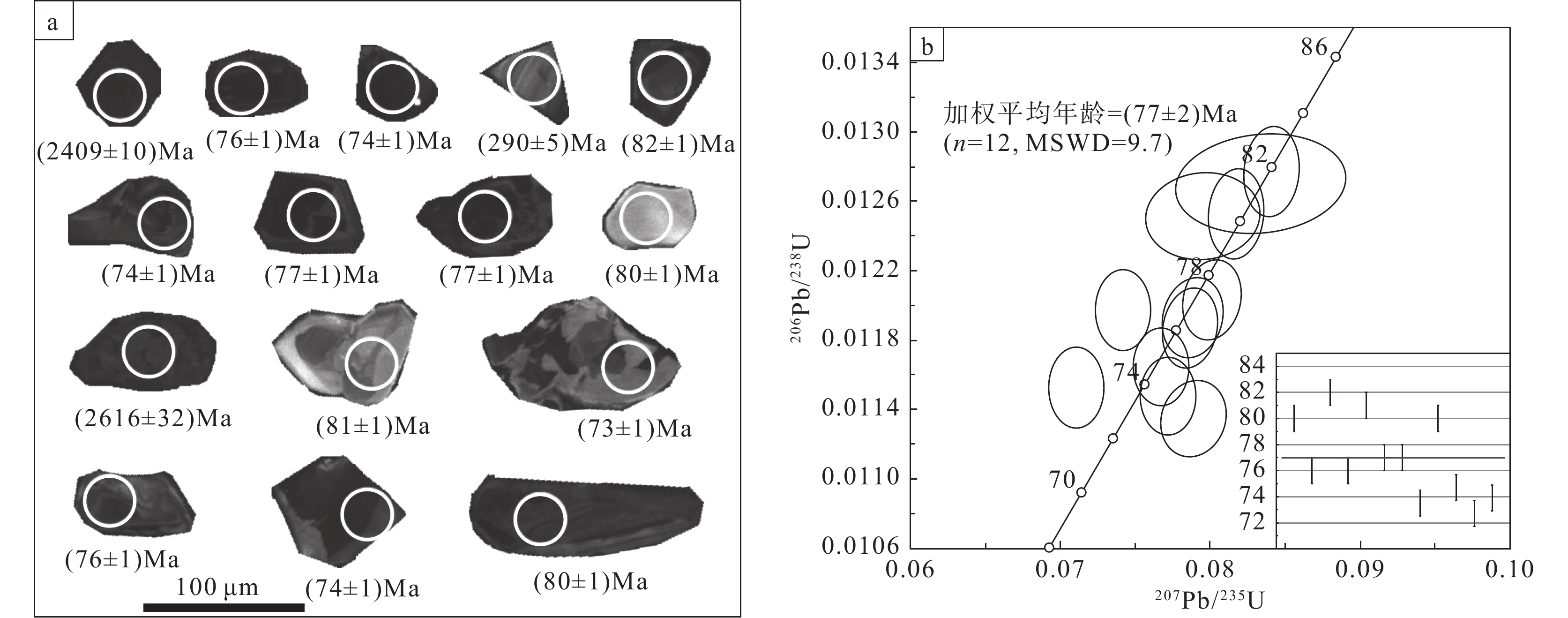
卡房辉绿岩中锆石多呈短柱状,晶形完好,可见少量呈浑圆状的继承锆石。阴极发光图中,锆石颗粒整体呈暗灰色,震荡环带较发育(图3a)。锆石颗粒长30~120 μm,长宽比1∶1~3∶1。本次研究对15个锆石颗粒的15个测点进行分析,分析结果见表1。锆石Th和U含量分别为82×10−6~10637×10−6、98×10−6~5844×10−6,Th/U比值为0.10~2.03,平均值为0.69。其中12个测点为辉绿岩岩浆锆石,锆石的206Pb/238U年龄介于72.7~82.0 Ma,几乎都位于谐和线上,并且集中于77 Ma,表明这些锆石在形成之后其U−Pb体系保持封闭状态,206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为(77±2) Ma(n=12,MSWD=9.7)(图3b)。3个测点为继承锆石,年龄偏大且分散,206Pb/238U年龄分别为2409 Ma、2616 Ma、290 Ma,可能为岩浆捕获的围岩中的继承锆石。
表 1 卡房辉绿岩样品SS13806锆石U−Pb测年数据Table 1. Zircon U−Pb dating data of diabase sample SS13806 in Kafang点号 Th/10−6 U/10−6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 1 573 5844 0.10 0.0473 0.0010 0.0817 0.0012 0.0125 0.0002 80 1 80 1 2 1114 2630 0.42 0.0479 0.0010 0.0788 0.0014 0.0119 0.0002 76 1 77 1 3 114 290 0.39 0.1557 0.0031 10.148 0.1357 0.4723 0.0063 2409 27 2448 12 4 410 1619 0.25 0.0489 0.0012 0.0859 0.0016 0.0127 0.0002 82 1 84 2 5 82 98 0.83 0.0542 0.0034 0.3441 0.0206 0.0461 0.0007 290 5 300 16 6 134 1096 0.12 0.1761 0.0033 8.3755 0.1140 0.3450 0.0045 2616 21 2273 12 7 1088 4868 0.22 0.0481 0.0010 0.0787 0.0012 0.0119 0.0002 76 1 77 1 8 201 408 0.49 0.0476 0.0023 0.0834 0.0038 0.0127 0.0002 81 1 81 4 9 10637 5250 2.03 0.0450 0.0010 0.0743 0.0011 0.0120 0.0002 77 1 73 1 10 5677 4178 1.36 0.0483 0.0010 0.0800 0.0012 0.0120 0.0002 77 1 78 1 11 4314 4061 1.06 0.0488 0.0011 0.0772 0.0012 0.0115 0.0002 74 1 75 1 12 101 267 0.38 0.0461 0.0016 0.0794 0.0025 0.0125 0.0002 80 1 78 2 13 6039 4463 1.35 0.0479 0.0011 0.0768 0.0012 0.0117 0.0002 75 1 75 1 14 2333 2389 0.98 0.0505 0.0012 0.0788 0.0015 0.0113 0.0002 73 1 77 1 15 1052 3382 0.31 0.0448 0.0010 0.0712 0.0012 0.0115 0.0002 74 1 70 1 4.2 主量和微量元素
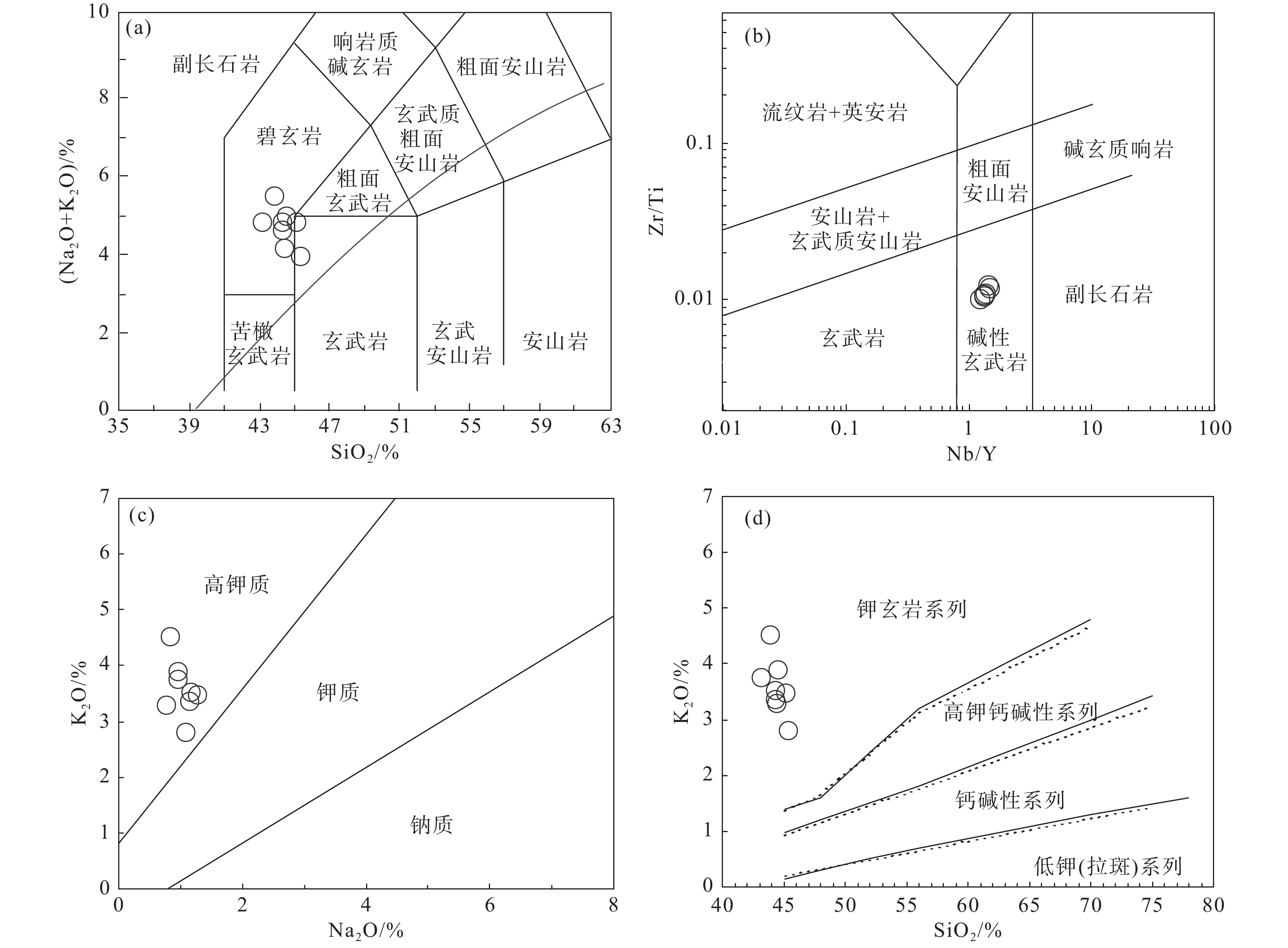
卡房辉绿岩全岩主微量元素分析结果见表2。所采集岩石样品烧失量较低(1.59%~2.26%),指示样品新鲜,后期蚀变作用较弱。卡房辉绿岩具有较低的SiO2含量(43.19%~45.36%)和全碱含量(Na2O+K2O,4.07%~5.35%),较高的K2O(2.81%~4.52%)、TiO2(2.54%~3.15%)、MgO(11.83%~13.19%)含量和Mg#值(64.69~70.60)。在火成岩硅碱(TAS)图中(图4a),大部分样品分布在碧玄岩区域;在Nb/Y−Zr/Ti图解(图4b)中,样品全部落在碱性玄武岩范围内;在Na2O−K2O图解中(图4c),样品全部分布在高钾系列;在SiO2−K2O图解中(图4d),所有样品均分布在钾玄岩系列。
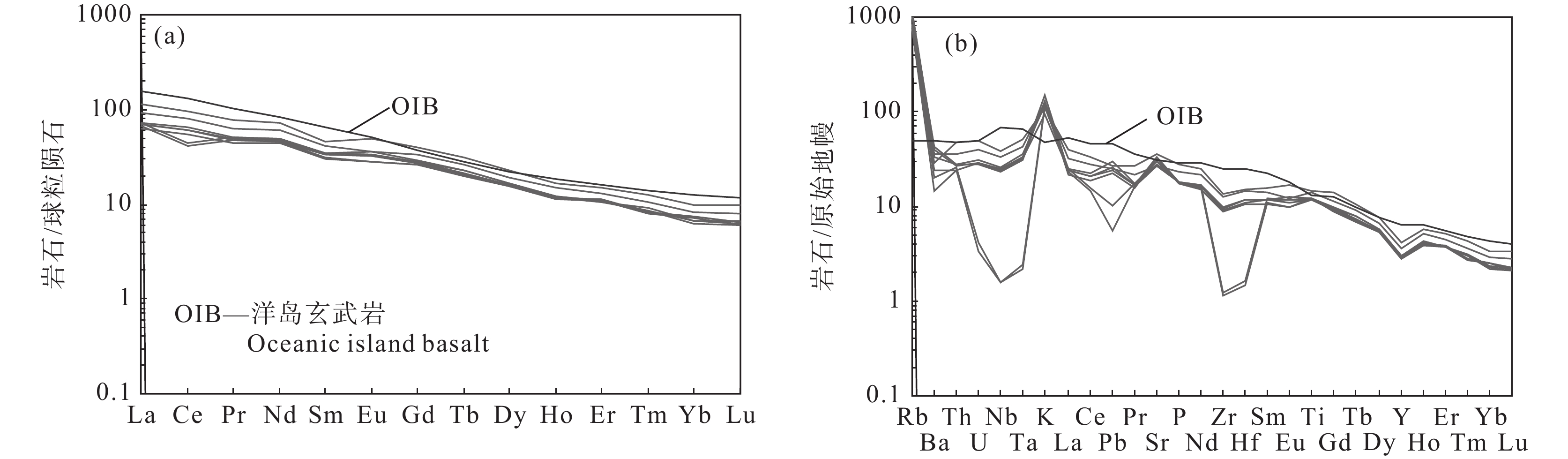
表 2 卡房辉绿岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)含量Table 2. Compositions of whole−rock major (%) and trace elements (10−6) of Kafang diabase分析项目 SS13806 分析项目 SS13806 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 09 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 09 SiO2 43.19 43.87 44.35 44.45 44.32 45.36 45.17 44.56 Nb 23.74 17.98 18.32 26.88 1.13 16.93 1.14 16.31 TiO2 3.05 2.55 2.64 3.15 2.63 2.54 2.63 2.54 Cd 0.30 0.22 0.26 0.27 0.056 0.24 0.053 0.22 Al2O3 12.89 13.16 13.12 13.49 12.93 12.91 12.60 12.72 In 0.29 0.32 0.43 0.91 0.061 0.57 0.047 0.35 TFe2O3 13.53 12.48 12.79 10.12 13.06 11.62 12.73 12.31 Cs 333.4 429.4 339.9 280.7 308.2 256.0 292.2 358.2 MnO 0.170 0.150 0.160 0.150 0.170 0.170 0.190 0.170 Ba 252.8 274.7 299.6 197.9 139.9 169.8 101.5 235.0 MgO 12.94 13.19 11.83 12.27 12.11 12.02 12.18 13.17 La 21.67 16.48 17.38 27.25 17.38 16.52 15.75 14.86 CaO 6.18 6.18 6.93 9.43 7.19 8.95 7.19 6.86 Ce 49.06 37.12 39.30 59.40 27.57 36.91 25.71 33.55 Na2O 0.96 0.83 1.18 0.77 1.15 1.08 1.27 0.96 Pr 6.04 4.64 4.85 7.31 4.87 4.59 4.46 4.25 K2O 3.75 4.52 3.52 3.30 3.36 2.81 3.47 3.89 Nd 28.76 22.22 23.02 33.62 23.01 21.58 21.18 20.73 P2O5 0.50 0.39 0.40 0.60 0.40 0.39 0.40 0.38 Sm 6.29 5.24 5.30 7.01 5.35 5.15 4.78 4.69 LOI 2.26 1.92 1.86 1.80 2.03 1.60 1.59 1.75 Eu 2.05 1.96 2.12 2.82 1.96 1.87 1.64 1.62 Total 99.42 99.24 98.78 99.53 99.35 99.45 99.42 99.31 Gd 6.83 5.68 5.93 8.28 5.68 5.66 5.33 5.40 Li 55.25 58.63 46.99 39.27 14.28 33.77 11.68 45.94 Tb 0.99 0.79 0.85 1.16 0.84 0.79 0.75 0.76 Be 0.54 0.81 0.49 0.43 0.18 0.56 0.15 0.63 Dy 4.91 4.11 4.22 5.69 4.22 4.00 3.99 4.11 Sc 13.79 17.76 14.18 11.48 12.98 12.38 12.61 14.96 Ho 0.83 0.67 0.68 0.93 0.70 0.66 0.64 0.66 V 156.5 151.2 154.7 138.1 11.27 144.1 12.13 142.2 Er 2.17 1.77 1.76 2.46 1.78 1.86 1.79 1.81 Cr 342.2 404.6 394.5 175.0 124.2 380.2 132.1 371.1 Tm 0.27 0.22 0.23 0.32 0.22 0.21 0.20 0.21 Co 38.59 33.53 34.26 20.14 2.55 31.15 3.07 33.55 Yb 1.42 1.13 1.15 1.68 1.06 1.25 1.23 1.25 Ni 159.6 161.1 161.8 96.34 11.29 147.1 14.91 145.0 Lu 0.21 0.16 0.17 0.25 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.16 Cu 117.1 94.72 101.7 80.63 4.84 74.57 4.65 75.75 Hf 4.46 3.59 3.59 4.71 0.51 3.41 0.45 3.28 Zn 115.3 109.1 111.7 104.1 11.14 97.14 12.70 105.8 Ta 1.75 1.37 1.48 2.08 0.09 1.33 0.10 1.29 Ga 12.86 12.97 12.19 14.47 7.64 12.14 6.55 11.12 Pb 1.76 1.72 2.11 1.90 0.72 1.87 0.40 1.58 Rb 705.8 881.6 641.4 667.1 518.3 540.0 477.7 734.4 Bi 0.46 0.29 0.55 0.46 0.053 0.27 0.002 0.14 Sr 570.0 568.9 627.7 743.6 591.5 693.5 566.7 684.2 Th 3.03 2.30 2.32 3.99 2.19 2.02 2.05 2.37 Y 16.15 13.11 13.71 18.72 13.66 12.60 12.96 13.17 U 0.82 0.61 0.66 1.02 0.086 0.61 0.071 0.58 Zr 139.2 106.5 108.6 152.5 13.96 101.1 12.63 97.97 Mg# 65.45 67.68 64.69 70.6 64.75 67.2 65.46 67.94 卡房辉绿岩具有较低的稀土含量(∑REE=87.6×10−6~158.16×10−6),稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解呈右倾式分布(图5a),轻稀土元素相对富集,重稀土元素相对亏损((La/Yb)N=8.53~11.77)。在微量元素原始地幔标准化图解中(图5b),所有样品富集Rb、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素,两个样品具有较大的Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf负异常。稀土元素和微量元素均呈现出与洋岛玄武岩相似的分布特征,仅Rb、K、Sr等活泼元素表现出较大的异常特征。
4.3 Sr−Nd−Pb同位素
卡房辉绿岩全岩Sr−Nd−Pb同位素分析结果见表3和表4。同位素参数按照t=77 Ma进行校正。卡房辉绿岩样品具有较高且一致的初始87Sr/86Sr同位素比值(0.70782~0.70791)和正的εNd(t)值(2.07~2.29)。初始铅同位素组成中,(206Pb/204Pb)t=18.286~18.465,(207Pb/204Pb)t=15.668~15.717,(208Pb/204Pb)t=37.763~38.830。所有样品均分布于北半球参考线的左侧,指示样品含有较高的放射性铅含量。
表 3 卡房辉绿岩Sr−Nd同位素组成Table 3. Sr−Nd isotopic compositions of Kafang diabase样品 年龄/Ma Rb/10−6 Sr/10−6 87Sr/86Sr (87Sr/86Sr)i Sm/10−6 Nd/10−6 143Nd/144Nd (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) SS13806-10 77 478 566 0.71056 0.70791 4.78 21.18 0.51272 0.51266 2.29 SS13806-11 77 734 684 0.71119 0.70782 4.69 20.73 0.51271 0.51265 2.07 表 4 卡房辉绿岩Pb同位素组成Table 4. Pb isotopic compositions of Kafang diabase样品 年龄/Ma 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb (206Pb/204Pb)t (207Pb/204Pb)t (208Pb/204Pb)t Φ μ Th/U SS13806-07 77 18.622±0.003 15.724±0.001 39.212±0.006 18.465 15.717 37.763 0.583 9.68 3.96 SS13806-09 77 18.610±0.007 15.683±0.008 39.254±0.014 18.286 15.668 38.830 0.579 9.61 3.98 注:Φ和μ为源区特征值。 5. 讨 论
5.1 成岩年龄
前人对个旧地区铁镁质岩石的研究较少,仅有少量关于其形成年代的报道。其中,由于受限于分析技术手段,冶金工业部西南冶金地质勘探公司(1984)认为卡房辉绿岩是燕山早期的产物。程彦博(2012)利用LA−ICP−MS方法对老厂铁镁质岩墙和羊坝底煌斑岩中的锆石进行U−Pb测年,获得的年龄分别为82 Ma和77 Ma。张颖等(2013)对个旧西区的贾沙辉长岩进行SIMS锆石U−Pb定年,认为贾沙辉长岩的侵位年代为84 Ma。本次研究所获得的卡房辉绿岩墙岩浆锆石谐和年龄为77 Ma,与前人报道的个旧铁镁质岩石年龄接近。晚白垩世华南板块西部滇东南及桂西北地区广泛发育大规模成岩成矿事件,个旧杂岩体及与花岗岩相关的锡铜多金属成矿系统形成年龄为77~85 Ma,老君山岩体及与花岗岩相关的都龙锡钨多金属成矿系统形成年龄为89~95 Ma,薄竹山岩体及与花岗岩相关的白牛厂银钨锡多金属成矿系统形成年龄为88~91 Ma,广西大厂龙箱盖岩体及锡多金属成矿系统形成年龄为90~100 Ma,广西大明山岩墙群及钨锡多金属成矿系统形成年龄年龄为89~94 Ma(程彦博等, 2008; 陈永清等, 2020)。上述事实表明晚白垩世成岩成矿事件时限为77~100 Ma,卡房辉绿岩的形成时代在此范围内,其岩浆作用属于燕山期晚白垩世岩浆大爆发阶段(Ma et al., 2013),是对华南地区中生代大规模成岩成矿事件的响应。
此外,锆石样品中可见少量继承锆石,继承锆石存在两种类型:一种为浑圆状锆石,锆石年龄为2409 Ma和2616 Ma;另一种为震荡环带较发育的锆石,锆石年龄为290 Ma。这些继承锆石是对个旧地区新太古代、古元古代、晚古生代岩浆和变质事件的响应。年龄结果表明,在290 Ma左右个旧地区存在岩浆作用,与古特提斯分支洋—哀牢山洋东向俯冲至华南板块之下的相关岛弧岩浆作用阶段相吻合(Xu et al., 2007, 2008; Hou et al, 2017)。2409 Ma和2616 Ma的继承锆石呈浑圆状且环带不发育,且具有较低的Th/U比值(0.12~0.39),这些特征暗示其可能为变质锆石(吴浩等,2023)。表明在新太古代—古元古代期间,个旧地区经历了一次较为重要的构造热事件并形成了变质基底,该变质基底构成了扬子板块的雏形(杜远生和童金南, 2008)。除本次研究之外,在扬子板块其他地区也有大量太古宙和古元古代年龄数据报道。例如,湖北崆岭地区高级变质岩和碎屑岩中的残留锆石、碎屑锆石年龄分别为2.0~1.8 Ga、3.8~2.9 Ga(Qiu et al., 2000; 柳小明等, 2005; Zhang et al., 2006a, 2006b; 焦文放等, 2009);湖北京山、湖南宁乡和贵州镇远煌斑岩中捕获锆石年龄2.9~2.5 Ga(Zheng et al., 2004);攀西正长岩中继承锆石年龄2.8~2.7 Ga(刘红英等, 2004);扬子陆块中东部宿松县斜长角闪岩锆石年龄为2.5 Ga(王翔等, 2020)。这些年龄数据表明扬子板块内可能广泛分布太古宙和古元古代变质基底。
新的锆石测年结果表明,卡房辉绿岩形成于晚白垩世。此外,个旧地区还存在新太古代和古元古代由构造热事件形成的变质基底,以及早二叠世的岩浆活动。推测2409 Ma、2616 Ma和290 Ma的锆石可能来源于岩浆同化地壳围岩。
5.2 岩石成因及源区特征
镁铁质岩墙是由幔源玄武质岩浆充填伸展断裂形成的浅层侵入体,其地球化学特征为深入研究深部岩浆过程和地幔源区的组成提供了依据(Halls and Fahrig, 1987)。目前关于OIB型铁镁质岩石成因仍然存在争议,其形成机制可归结为地幔柱或者其他类型的软流圈地幔上涌(Niu et al., 2012; Søager et al., 2013; Buiter and Torsvik, 2014)。从时空分布来看,晚白垩世个旧及相邻区域内不存在地幔柱活动的证据,个旧铁镁质岩墙的形成不可能与地幔柱活动有关,而可能是软流圈地幔上涌导致。晚白垩世铁镁质岩石在个旧地区除卡房辉绿岩外,其他同时代的铁镁质岩石还包括贾沙辉长岩(84 Ma)、老厂铁镁质岩墙(82 Ma)和羊坝底煌斑岩(77 Ma)。张颖等(2013)认为贾沙辉长岩起源于富集地幔较低程度的部分熔融。程彦博(2012)认为老厂铁镁质岩墙和羊坝底煌斑岩来源于富集地幔的部分熔融,并有明显的地壳混染。此外,华南板块西缘亦广泛分布其他晚白垩世铁镁质、超铁镁质岩石。如在黔西南白层地区,陈懋弘等(2009)报道了晚白垩世超基性岩墙(84 Ma)的成因是软流圈上涌导致的富集地幔部分熔融并经历了一定程度的地壳混染。Liu et al. (2010b)报道了贵阳西南鲁容—阴河地区的碱性铁镁质岩墙(85~88 Ma),认为其是由软流圈上涌引起的。广西大厂由花岗斑岩岩墙、闪长玢岩岩墙、次玄武岩岩墙等组成的岩墙群(91 Ma)形成于活动大陆边缘环境(黎应书等, 2011)。赵永贵等(1992)通过地震层析法对滇西深部构造进行对比研究,地震影像表明个旧地区岩石圈地幔相较于外围地区明显减薄,认为这是由软流圈地幔上涌导致的。广泛分布的铁镁质岩墙暗示晚白垩世华南板块西缘可能存在区域性伸展作用,这些铁镁质岩墙可能是由软流圈地幔上涌引起的。
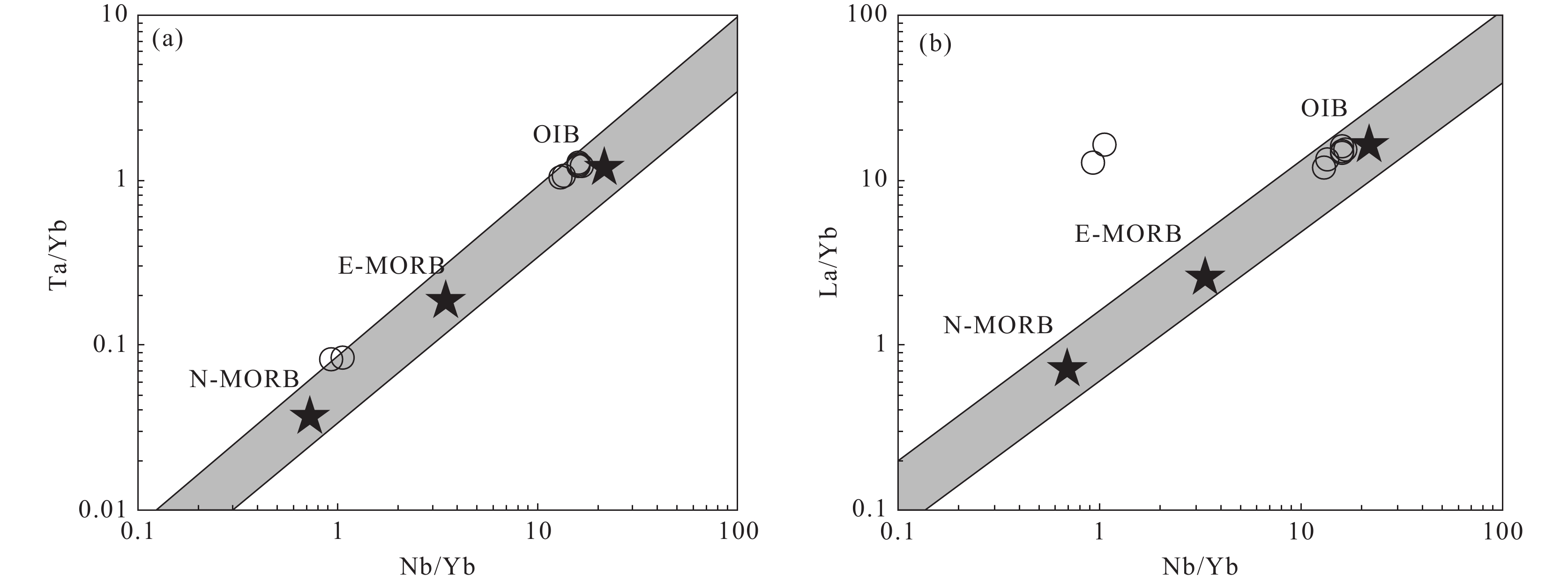
地幔源区以及岩浆后期过程(主要是岩浆侵位过程中的流体作用)对微量元素的影响程度可通过微量元素比值进行区分,受地幔源区控制的元素通常分布在地幔序列(Pearce et and Peate, 1995; 朱永峰等, 2007; 冯志硕等, 2010)。在Nb/Yb−Ta/Yb图解(图6a)和Nb/Yb−La/Yb图解中(图6b),大部分样品落在地幔序列且集中分布于洋岛玄武岩附近,仅有两个样品离群分布,说明这些具有洋岛玄武岩特征的元素主要受控于地幔源区特征。在微量元素原始地幔标准化图解中(图5b),微量元素分布特征与洋岛玄武岩类似,仅Rb、Ba、Nb、Ta、K等活泼元素显示不同程度的异常,这些活动元素的异常可能由后期蚀变作用引起。与洋岛玄武岩相似的地球化学特征暗示卡房辉绿岩可能来自富集地幔源区,软流圈地幔物质上涌导致克拉通边缘岩石圈地幔部分熔融,形成小体积呈分散分布的具洋岛玄武岩特征的玄武质岩浆(Lebedev et al., 2006)。
![]() N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩Figure 6. Nb/Yb−Ta/Yb diagram (a) and Nb/Yb−La/Yb diagram (b) (after Pearce et al., 1995; Feng Zhishuo et al., 2010)N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt
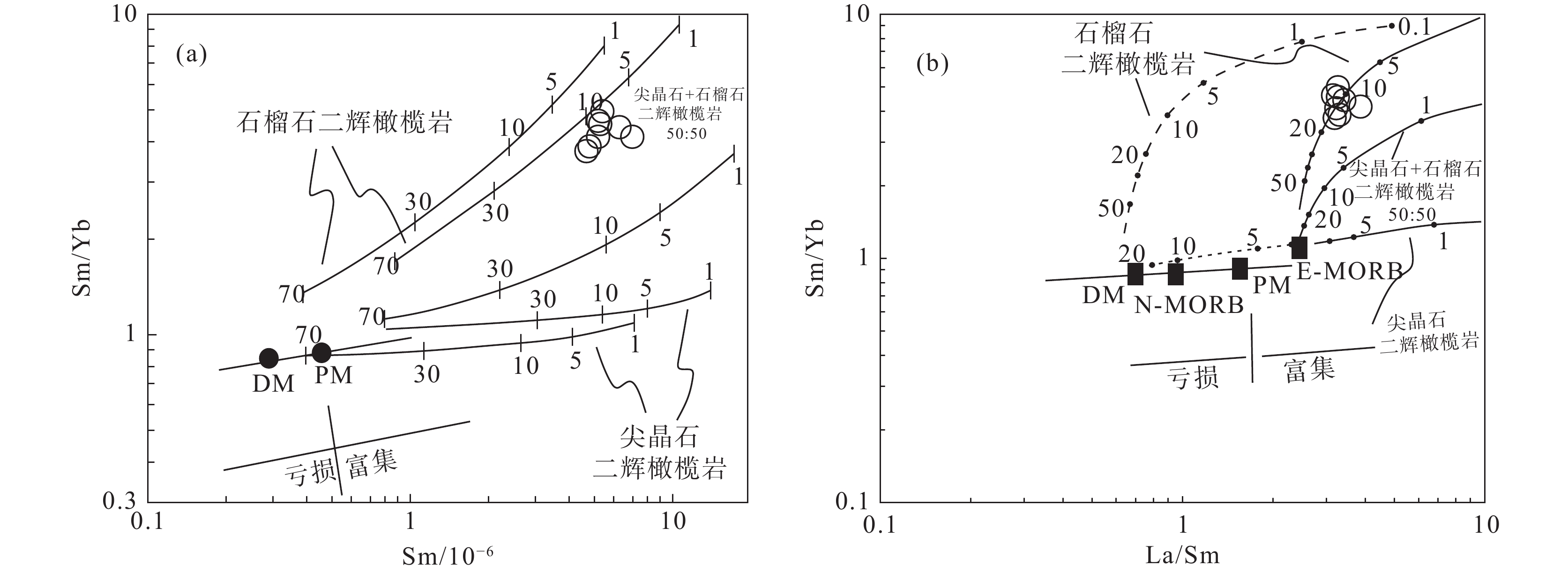
N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩Figure 6. Nb/Yb−Ta/Yb diagram (a) and Nb/Yb−La/Yb diagram (b) (after Pearce et al., 1995; Feng Zhishuo et al., 2010)N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt高场强元素和稀土元素在风化和蚀变过程中具有稳定性,元素含量主要受地幔成分和部分熔融程度的控制。因此,其元素含量和比值可用于判别岩浆源区和确定部分熔融的程度(Staudigel and Hart, 1983; Wang et al., 2007; Zhao and Zhou, 2007; Zhang et al., 2015; 刘浪等, 2020)。La具有比Sm更强的不相容性,在尖晶石或石榴子石地幔部分熔融过程中,La、Sm更倾向于在熔体中富集。Sm相对于Yb的富集主要依赖于熔融过程的残留体中是否存在石榴子石。因此,可通过La、Sm、Yb元素和元素比值研究岩浆源区及部分熔融的程度。在Sm−Sm/Yb图解(图7a)和La/Sm−Sm/Yb图解(图7b)中,样品全部分布在石榴石二辉橄榄岩演化曲线上,指示卡房辉绿岩岩浆源区物质为石榴石二辉橄榄岩,并且部分熔融程度介于5%~15%。
![]() 图 7 Sm−Sm/Yb(a)和La/Sm−Sm/Yb图解(b)(据Aldanmaz et al., 2000)N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;DM—亏损地幔;PM—原始地幔Figure 7. Sm−Sm/Yb (a) and La/Sm−Sm/Yb diagram (b) (after Aldanmaz et al., 2000)N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E-type mid-ocean ridge basalt; DM−Depleted mantle; PM−Primitive mantle
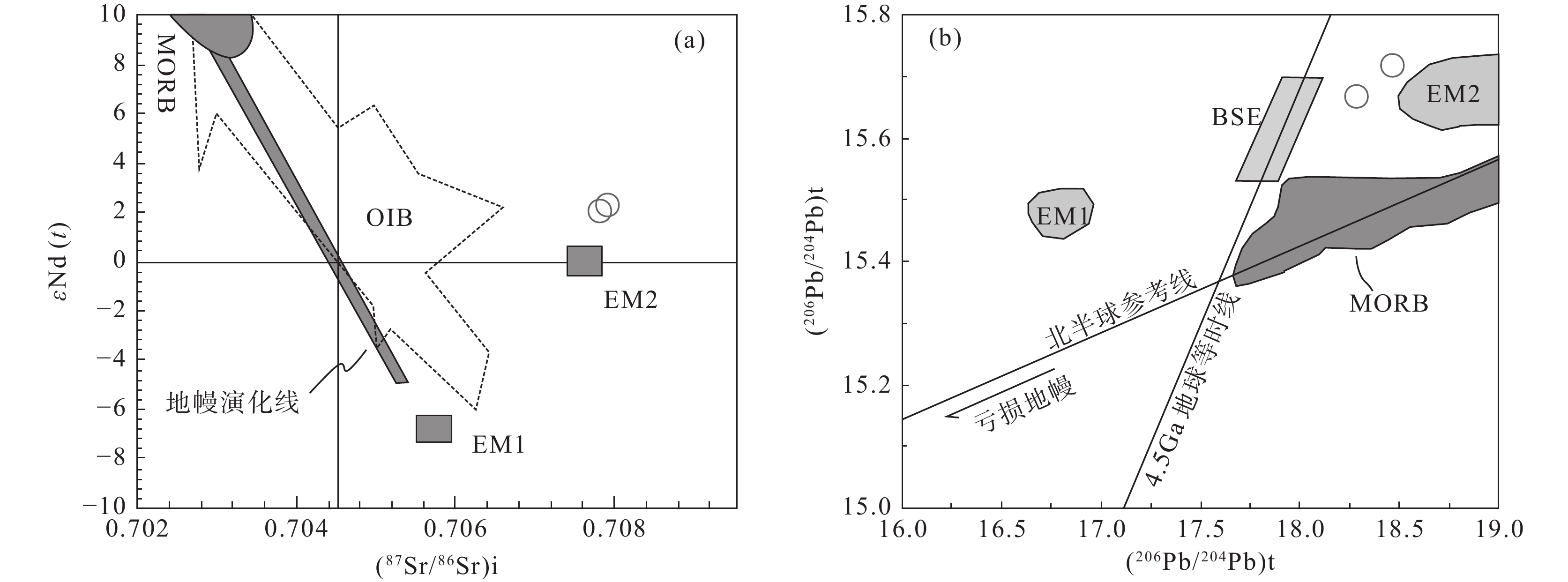
图 7 Sm−Sm/Yb(a)和La/Sm−Sm/Yb图解(b)(据Aldanmaz et al., 2000)N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;DM—亏损地幔;PM—原始地幔Figure 7. Sm−Sm/Yb (a) and La/Sm−Sm/Yb diagram (b) (after Aldanmaz et al., 2000)N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E-type mid-ocean ridge basalt; DM−Depleted mantle; PM−Primitive mantle岩浆体系中岩浆的结晶或分异对同位素的分馏作用影响很小,故而Sr−Nd−Pb同位素可以很好地示踪岩浆物质来源。软流圈地幔在同位素组成上具有亏损地幔特征(低初始87Sr/86Sr值和高εNd(t)值),岩石圈地幔由于长期与对流地幔隔离,并与熔体相互作用,普遍具有富集同位素特征(高初始87Sr/86Sr值和低εNd(t)值)(Zhang et al., 2008)。卡房辉绿岩初始87Sr/86Sr同位素比值(0.70782~0.70791),和εNd(t)值(2.07~2.29)与富集岩石圈地幔相似,在(87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t)图解(图8a)中,岩石样品位于EM2端元附近,指示卡房辉绿岩源区以富集地幔为主。同样,在(206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t图解(图8b)中,样品均位于北半球参考线左侧EM2附近。Sr−Nd−Pb同位素特征暗示卡房辉绿岩岩浆源区具有EM2特征。
![]() 图 8 (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t)图解(a)(据Zimmer et al., 1995)和(206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t图解(b)(据Zindler and Hart, 1986,t=77 Ma;MORB据Zimmer et al., 1995;OIB据White and Duncan, 1995;EM1和EM2据Hart, 1988)MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;EM1—富集1型地幔;EM2—富集2型地幔;BSE—全硅酸盐地球Figure 8. (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t) diagram (a) (after Zimmer et al., 1995) and (206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t diagram (b) (after Zindler and Hart, 1986, t=77 Ma; MORB after Zimmer et al., 1995; OIB after White and Duncan, 1995; EM1 and EM2 after Hart, 1988)MORB−Mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt; EM1−1−type enriched mantle; EM2−2−type enriched mantle; BSE−Bulk silicate earth
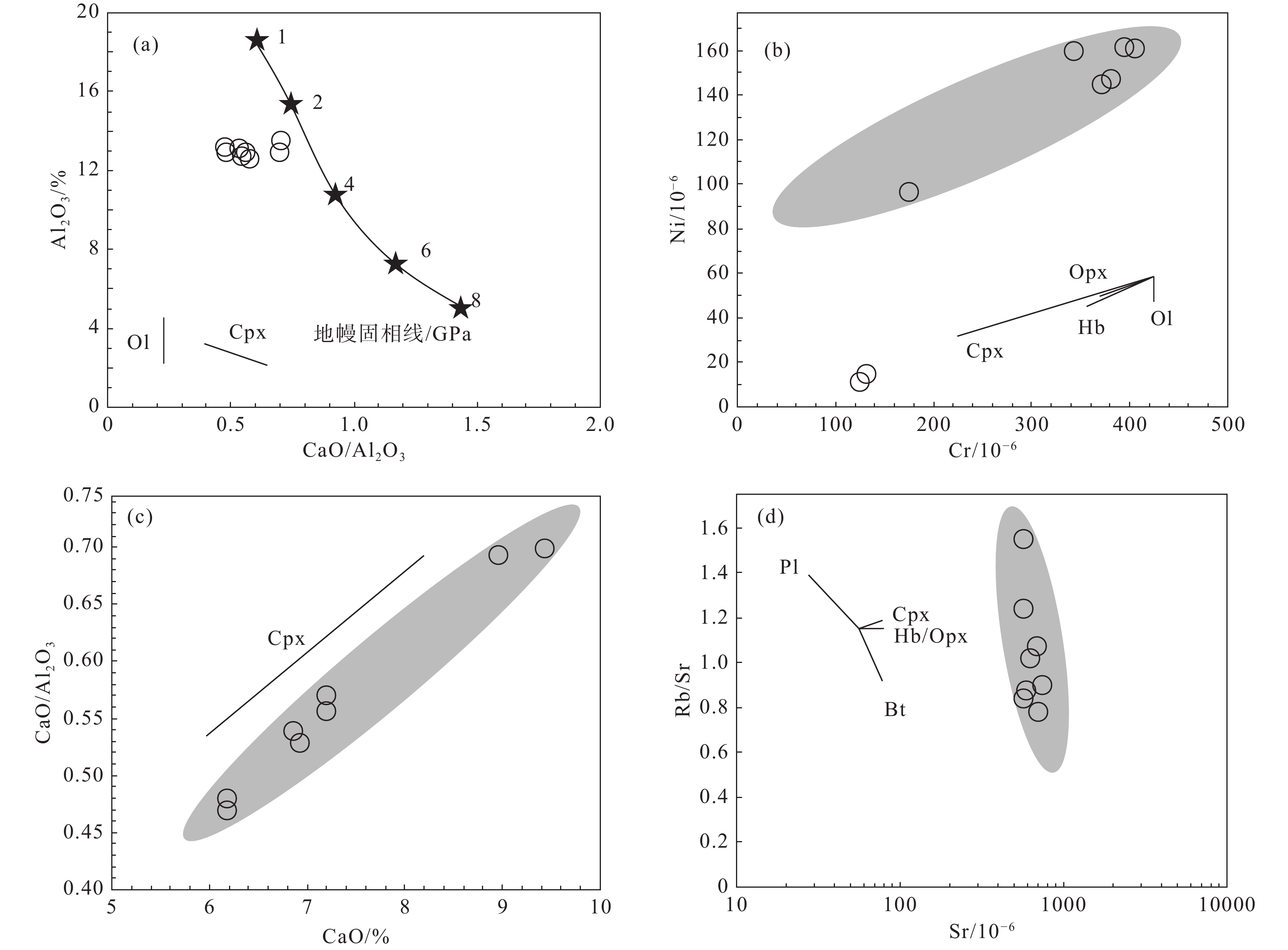
图 8 (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t)图解(a)(据Zimmer et al., 1995)和(206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t图解(b)(据Zindler and Hart, 1986,t=77 Ma;MORB据Zimmer et al., 1995;OIB据White and Duncan, 1995;EM1和EM2据Hart, 1988)MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;EM1—富集1型地幔;EM2—富集2型地幔;BSE—全硅酸盐地球Figure 8. (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t) diagram (a) (after Zimmer et al., 1995) and (206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t diagram (b) (after Zindler and Hart, 1986, t=77 Ma; MORB after Zimmer et al., 1995; OIB after White and Duncan, 1995; EM1 and EM2 after Hart, 1988)MORB−Mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt; EM1−1−type enriched mantle; EM2−2−type enriched mantle; BSE−Bulk silicate earth交代地幔熔融形成的小体积富集熔体具有EM2特征(徐义刚, 1999),EM2成分一般存在于岩石圈地幔中的石榴石相稳定区(韩江伟等, 2009),这与La−Sm−Yb元素体系所指示的岩浆源区特征相一致。大量研究也表明华南地区岩石圈地幔受到过流体或熔体的交代作用(Tatsumoto et al., 1992; 范蔚茗和Menzies, 1992; Xu et al., 2003; Yu et al., 2006)。卡房辉绿岩具有高K2O含量(2.81%~4.52%),富集轻稀土元素和不相容元素,与OIB相似的地球化学特征(杨杰等, 2014)。对碱性玄武岩和金伯利岩中的地幔捕虏体的研究表明交代地幔为OIB的主要源区(Niu et al., 2012)。徐峣等(2019)采用天然地震层析成像方法构建了华南东南部上地幔P波速度结构模型,证实了在软流圈顶部存在低速异常带。在大洋或大陆岩石圈深部普遍存在地幔交代岩脉(如辉石岩、角闪石岩等),表明地幔交代初始熔体(富H2O−CO2硅酸盐熔体)可能起源于地震波低速带。在持续的地幔交代作用下,岩石圈地幔逐渐富集。软流圈地幔上涌导致富集岩石圈地幔部分熔融形成卡房辉绿岩的初始熔体。根据基于实验岩石学所得出的地幔固相线,岩浆分离深度可通过CaO/Al2O3−Al2O3图解进行约束(Herzberg, 1992,1995; Condie, 2003),卡房辉绿岩初始熔体形成深度介于2~4 GPa(60~120 km)(图9a)。
在幔源熔体上升过程中,热的岩浆与冷的地壳围岩之间的热交换将不可避免地导致熔体同化混染地壳物质,岩浆的混染作用主要发生在岩浆侵位结晶之前的地壳深部(李宏博等, 2012)。由于幔源岩浆与地壳物质具有不同的地球化学组成特征,地壳混染作用可以很大程度的改变元素组成特征(DePaolo, 1981),因此可通过元素地球化学特征进行示踪。卡房辉绿岩Nb/Ta比值介于11.5~13.6(平均值为12.7),Zr/Hf比值介于27.5~32.3(平均值为29.8),其Nb/Ta和Zr/Hf比值分别与大陆地壳值接近(大陆地壳Nb/Ta=11,Zr/Hf=33,Taylor and McLennan, 1985),指示形成镁铁质岩墙的岩浆受到了地壳物质混染(Weaver, 1991; Green, 1995; Kalfoun et al., 2002)。这与铁镁质岩浆中捕获的继承锆石所指示岩浆中存在地壳物质的结论一致。地壳具有显著的Nb、Ta负异常(Paces and Bell, 1989; Rudnick and Founain, 1995; Barth et al., 2000),卡房辉绿岩中Nb、Ta具有不同程度的负异常(图5b),同样指示岩浆演化过程中存在壳源物质的混染。此外,卡房辉绿岩还具有如下地球化学特征:低Th/U值(3.3~4.1,两个样品值为25.4,28.9)和Nb/Zr(0.08~0.17)值;Nb/U比值(13.07~29.56,平均值24.75)介于大洋玄武岩(52±15)和陆壳(8)之间(Hofmann, 1997, 2003);较低的Th含量(2.02×10−6~3.99×10−6,通常下地壳相较于上地壳Th亏损明显(Barth et al., 2000))。上述元素地球化学特征均表明卡房辉绿岩岩浆在侵位过程中可能混染了下地壳物质。
卡房辉绿岩具有较高的Mg#值(64.69~70.60),大部分样品Cr(124×10−6~405×10−6)、Ni(96×10−6~161×10−6)含量低于初始岩浆(Mg#=71~83,Cr大于1000×10−6,Ni大于400×10−6; Wilson, 1989),这些特征暗示卡房辉绿岩在形成过程中可能经历了较低的铁镁质矿物(如橄榄石、辉石)的分离结晶作用(刘娇等, 2016)。在分离结晶过程中,熔体中相容元素的浓度可发生急剧变化,因此熔体中Ni、Cr、Sr等元素的浓度可用来指示橄榄石、单斜辉石、斜长石等矿物的分离结晶(Hart and Allegre, 1980)。在Cr−Ni图解(图9b)中,指示在卡房辉绿岩的形成过程中经历了单斜辉石的分离结晶。CaO−CaO/Al2O3图解(图9c)显示单斜辉石的分离结晶。Sr−Rb/Sr图解(图9d)指示黑云母的分离结晶。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解中无Eu负异常特征表明斜长石的分离结晶作用并不明显。在岩石薄片中辉石、黑云母斑晶的存在也支持这一结论,岩石学和地球化学特征表明辉石、黑云母是卡房辉绿岩主要的结晶分异矿物,而斜长石的分离结晶作用较弱。
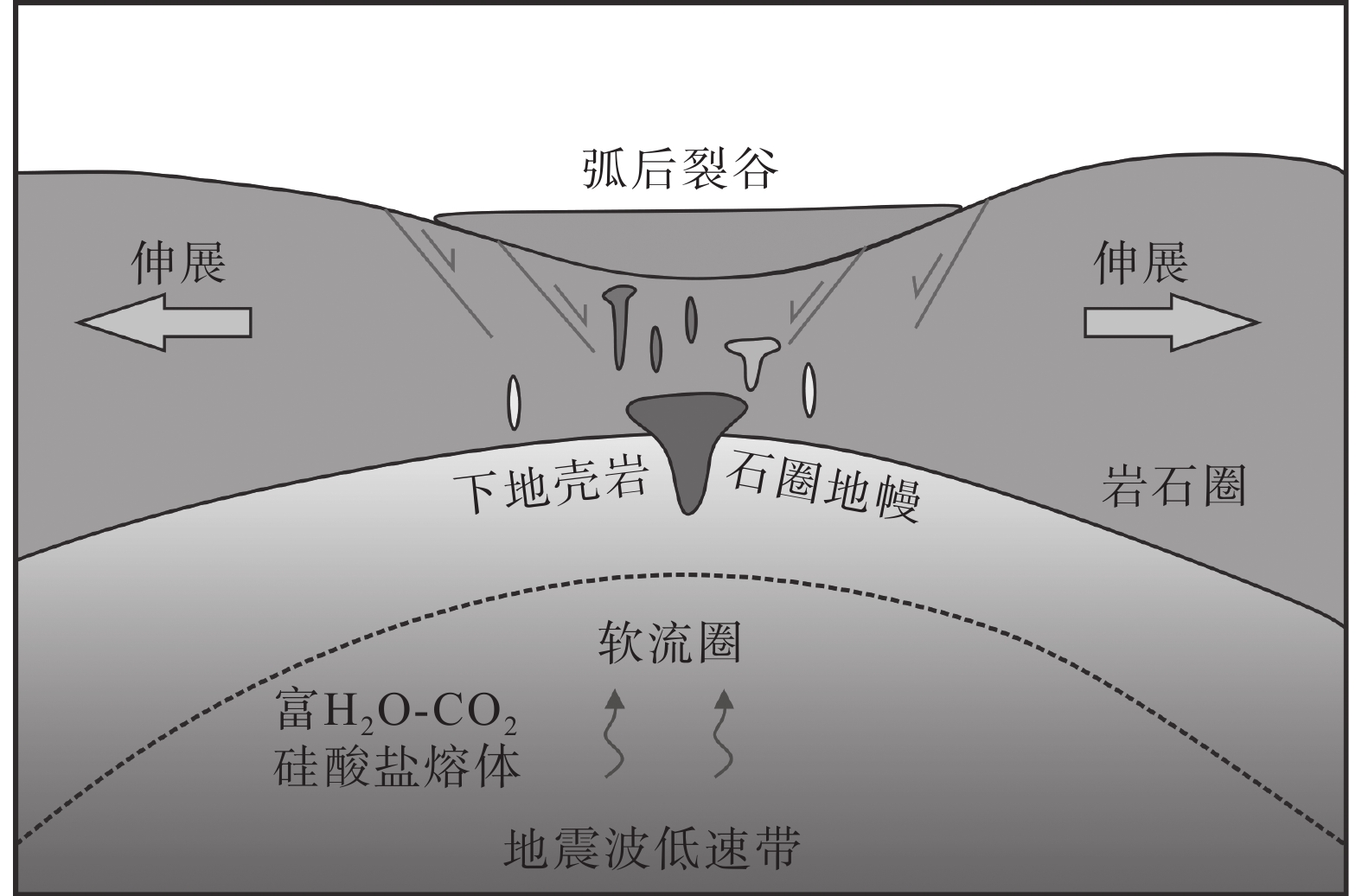
结合岩体特征、岩石地球化学特征和区域构造特征,卡房辉绿岩可能形成于区域伸展背景。在强烈伸展减薄作用下,软流圈地幔上涌底侵富集岩石圈地幔并使其部分熔融形成了卡房辉绿岩的初始岩浆,在岩浆侵位过程中同化混染下地壳物质,经过一定程度的的分离结晶作用后形成了卡房辉绿岩(图10)。
5.3 构造环境
关于个旧地区晚白垩世岩浆杂岩体形成的构造环境存在很多不同的观点。贾润幸等(2014)通过对个旧西区的贾沙二长岩和东区的老卡花岗岩进行地球化学研究,认为晚白垩世个旧地区处于燕山期碰撞造山晚期向造山期后过渡的构造环境。黄文龙等(2016)通过对个旧地区代表性的花岗岩、辉长岩和碱性岩进行锆石U−Pb年代学、全岩地球化学和Hf同位素研究,认为个旧杂岩体形成于燕山期板内伸展构造背景。Cheng et al.(2016)通过对位于云南东南部和越南北东部与Sn−W矿床相关的晚白垩岩浆岩的形成年代进行统计分析,认为这些岩浆作用形成于古太平洋板块向欧亚大陆板块之下俯冲产生的安第斯型活动大陆边缘环境。个旧地区辉绿岩墙多隐伏于地下,目前已揭露的辉绿岩墙分布在卡房矿段和老厂矿段。本文首次以卡房矿段巷道中揭露的辉绿岩为研究对象探讨其形成的构造环境。
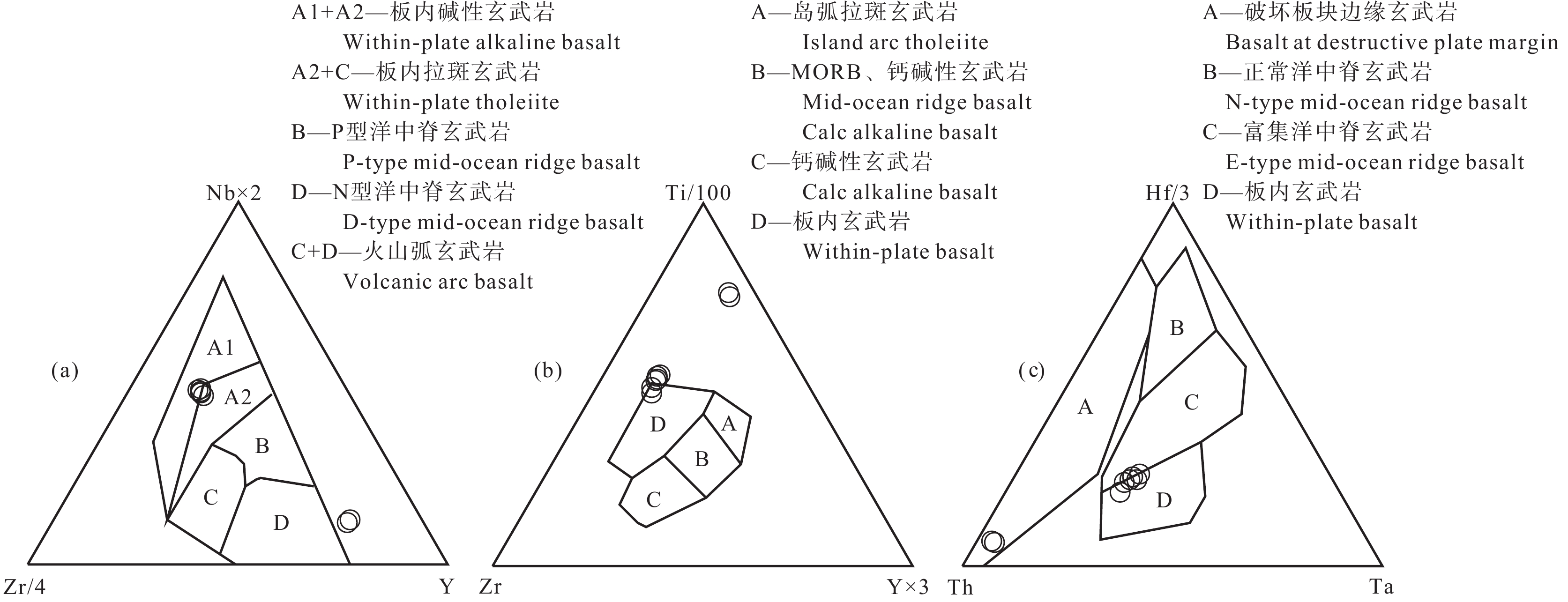
分离结晶和部分熔融等岩浆作用过程对Zr、Y、Nb、Ti等不相容元素的影响较小(Pearce and Cann, 1973; Pearce and Norry, 1979; Mechede, 1986),因此,可通过这些元素鉴别玄武质岩浆形成的构造环境。在Nb−Zr−Y图解(图11a)、Ti−Zr−Y图解(图11b)和Hf−Th−Ta(图11c)图解中,大部分岩石样品均分布在板内玄武岩范围内,暗示卡房辉绿岩的形成可能与伸展作用有关。铁镁质岩墙的形成与岩石圈伸展作用有关,其可在多种大地构造背景下由源自地幔的玄武质岩浆充填张性裂隙形成,一般来说包括3种解释:板内裂谷、坳拉谷、地幔柱热点(葛小月等, 2003; 程彦博, 2012; 祁生胜等, 2013)。个旧地区的铁镁质岩墙侵入于三叠系个旧组中,并且附近无同时期的沉积建造,在区域上分布大量的陆相火山盆地,与地幔柱形成的呈放射状分布的岩墙群明显不同,因此个旧地区的铁镁质岩墙可能与板内裂谷作用有关。
![]() Figure 11. Trace element tectonic discrimination diagrams (after Pearce and Cann, 1973; Wood, 1980; Mechede, 1986)
Figure 11. Trace element tectonic discrimination diagrams (after Pearce and Cann, 1973; Wood, 1980; Mechede, 1986)大量的研究表明,俯冲带镁铁质岩墙可形成于多种动力学背景,如弧后盆地伸展背景(Khan et al., 2007),弧下岩石圈减薄背景(Scarrow et al., 1998)。区域构造演化表明,华南地区早白垩世是弧后扩张和花岗质岩浆活动的鼎盛期,晚白垩世—古近纪则是陆内伸展红盆形成的高峰期(王德滋和舒良树, 2007)。在燕山晚期,个旧所处的右江盆地处于板内演化阶段,盆地内部发生岩石圈减薄、软流圈上涌以及大规模的伸展和拆离,在伸展盆地边缘深大断裂附近出露大量燕山晚期花岗岩和铁镁质岩墙(程彦博, 2012)。在古太平洋板块的低角度俯冲动力学体制下,华南构造体制在135 Ma由挤压转向伸展,中国东部发生大范围弧后伸展作用,形成了大量花岗质岩浆作用和大规模的伸展断陷盆地(李三忠等, 2017)。中国东南部晚白垩世主要处于拉张的构造环境(葛小月等, 2003),表现为沿着一系列大致平行的断裂带形成断陷盆地和伴随的大量A型花岗岩和同期基性岩脉、变质核杂岩以及各种类型的铜金矿床、热液型铀矿。个旧地区基性岩墙与花岗岩共生的岩浆组合指示伸展构造背景,结合卡房辉绿岩的岩体地质特征和地球化学特征,本次研究认为晚白垩世个旧地区处于俯冲带大陆活动边缘形成的伸展构造环境。
6. 结 论
(1)锆石U−Pb定年结果表明卡房辉绿岩年龄为77 Ma。年龄为2409 Ma、2616 Ma、290 Ma的继承锆石指示个旧地区存在新太古代、古元古代的变质基底和早二叠世的岩浆活动。
(2)卡房辉绿岩属于钾玄岩系列,具有低硅、高钾、高镁的特征,富集Rb、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素,稀土和微量元素分布与OIB相似,Sr−Nd−Pb同位素特征指示其源区为富集岩石圈地幔中的石榴石二辉橄榄岩,部分熔融程度介于5%~15%。
(3)卡房辉绿岩起源于富集岩石圈地幔。其成岩机制为在伸展构造背景下,软流圈地幔上涌底侵富集岩石圈地幔并使其部分熔融,形成了卡房辉绿岩的初始岩浆,在岩浆侵位过程中混染了下地壳物质并经过较弱的分离结晶作用最终形成了卡房辉绿岩。
-
图 1 东南亚地质略图(a),个旧矿区地质简图(b)和卡房剖面及取样位置图(c)
TP—塔里木板块;YB—扬子地体;CB—华夏地体;SB—滇缅泰马地体;ICB—印支地体;IP—印度板块
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Southeast Asia (a), geological map of the Gejiu ore district (b) and geological section of diabase in Kafang profile and sample location (c)
TP−Tarim Plate; YB−Yangtze Block; CB−Cathaysia Block; SB−Dian−Mian−Tai−Ma Block; ICB−Indochina Block; IP−India Plate
图 2 辉绿岩墙侵入到大理岩中(a),辉绿岩手标本照片(b),正交偏光显微镜下照片(c、d、e),单偏光显微镜下照片(f)
Bt—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Px—辉石
Figure 2. Diabase intrudes into marble (a), hand specimen of Kafang diabase (b), cross-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (c, d, e), single-polarized light photomicrograph of Kafang diabase (f)
Bt−Biotite; Pl−Plagioclase; Px−Pyroxene
图 6 Nb/Yb−Ta/Yb图解(a)和Nb/Yb−La/Yb图解(b)(据Pearce et al., 1995; 冯志硕等, 2010)
N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩
Figure 6. Nb/Yb−Ta/Yb diagram (a) and Nb/Yb−La/Yb diagram (b) (after Pearce et al., 1995; Feng Zhishuo et al., 2010)
N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt
图 7 Sm−Sm/Yb(a)和La/Sm−Sm/Yb图解(b)(据Aldanmaz et al., 2000)
N−MORB—正常洋中脊玄武岩;E−MORB—富集洋中脊玄武岩;DM—亏损地幔;PM—原始地幔
Figure 7. Sm−Sm/Yb (a) and La/Sm−Sm/Yb diagram (b) (after Aldanmaz et al., 2000)
N−MORB−N−type mid−ocean ridge basalt; E−MORB−E-type mid-ocean ridge basalt; DM−Depleted mantle; PM−Primitive mantle
图 8 (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t)图解(a)(据Zimmer et al., 1995)和(206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t图解(b)(据Zindler and Hart, 1986,t=77 Ma;MORB据Zimmer et al., 1995;OIB据White and Duncan, 1995;EM1和EM2据Hart, 1988)
MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;EM1—富集1型地幔;EM2—富集2型地幔;BSE—全硅酸盐地球
Figure 8. (87Sr/86Sr)i−εNd(t) diagram (a) (after Zimmer et al., 1995) and (206Pb/204Pb)t−(207Pb/204Pb)t diagram (b) (after Zindler and Hart, 1986, t=77 Ma; MORB after Zimmer et al., 1995; OIB after White and Duncan, 1995; EM1 and EM2 after Hart, 1988)
MORB−Mid−ocean ridge basalt; OIB−Oceanic island basalt; EM1−1−type enriched mantle; EM2−2−type enriched mantle; BSE−Bulk silicate earth
图 11 微量元素构造判别图解(据Pearce and Cann, 1973; Wood, 1980; Mechede, 1986)
Figure 11. Trace element tectonic discrimination diagrams (after Pearce and Cann, 1973; Wood, 1980; Mechede, 1986)
表 1 卡房辉绿岩样品SS13806锆石U−Pb测年数据
Table 1 Zircon U−Pb dating data of diabase sample SS13806 in Kafang
点号 Th/10−6 U/10−6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 1 573 5844 0.10 0.0473 0.0010 0.0817 0.0012 0.0125 0.0002 80 1 80 1 2 1114 2630 0.42 0.0479 0.0010 0.0788 0.0014 0.0119 0.0002 76 1 77 1 3 114 290 0.39 0.1557 0.0031 10.148 0.1357 0.4723 0.0063 2409 27 2448 12 4 410 1619 0.25 0.0489 0.0012 0.0859 0.0016 0.0127 0.0002 82 1 84 2 5 82 98 0.83 0.0542 0.0034 0.3441 0.0206 0.0461 0.0007 290 5 300 16 6 134 1096 0.12 0.1761 0.0033 8.3755 0.1140 0.3450 0.0045 2616 21 2273 12 7 1088 4868 0.22 0.0481 0.0010 0.0787 0.0012 0.0119 0.0002 76 1 77 1 8 201 408 0.49 0.0476 0.0023 0.0834 0.0038 0.0127 0.0002 81 1 81 4 9 10637 5250 2.03 0.0450 0.0010 0.0743 0.0011 0.0120 0.0002 77 1 73 1 10 5677 4178 1.36 0.0483 0.0010 0.0800 0.0012 0.0120 0.0002 77 1 78 1 11 4314 4061 1.06 0.0488 0.0011 0.0772 0.0012 0.0115 0.0002 74 1 75 1 12 101 267 0.38 0.0461 0.0016 0.0794 0.0025 0.0125 0.0002 80 1 78 2 13 6039 4463 1.35 0.0479 0.0011 0.0768 0.0012 0.0117 0.0002 75 1 75 1 14 2333 2389 0.98 0.0505 0.0012 0.0788 0.0015 0.0113 0.0002 73 1 77 1 15 1052 3382 0.31 0.0448 0.0010 0.0712 0.0012 0.0115 0.0002 74 1 70 1 表 2 卡房辉绿岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)含量
Table 2 Compositions of whole−rock major (%) and trace elements (10−6) of Kafang diabase
分析项目 SS13806 分析项目 SS13806 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 09 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 09 SiO2 43.19 43.87 44.35 44.45 44.32 45.36 45.17 44.56 Nb 23.74 17.98 18.32 26.88 1.13 16.93 1.14 16.31 TiO2 3.05 2.55 2.64 3.15 2.63 2.54 2.63 2.54 Cd 0.30 0.22 0.26 0.27 0.056 0.24 0.053 0.22 Al2O3 12.89 13.16 13.12 13.49 12.93 12.91 12.60 12.72 In 0.29 0.32 0.43 0.91 0.061 0.57 0.047 0.35 TFe2O3 13.53 12.48 12.79 10.12 13.06 11.62 12.73 12.31 Cs 333.4 429.4 339.9 280.7 308.2 256.0 292.2 358.2 MnO 0.170 0.150 0.160 0.150 0.170 0.170 0.190 0.170 Ba 252.8 274.7 299.6 197.9 139.9 169.8 101.5 235.0 MgO 12.94 13.19 11.83 12.27 12.11 12.02 12.18 13.17 La 21.67 16.48 17.38 27.25 17.38 16.52 15.75 14.86 CaO 6.18 6.18 6.93 9.43 7.19 8.95 7.19 6.86 Ce 49.06 37.12 39.30 59.40 27.57 36.91 25.71 33.55 Na2O 0.96 0.83 1.18 0.77 1.15 1.08 1.27 0.96 Pr 6.04 4.64 4.85 7.31 4.87 4.59 4.46 4.25 K2O 3.75 4.52 3.52 3.30 3.36 2.81 3.47 3.89 Nd 28.76 22.22 23.02 33.62 23.01 21.58 21.18 20.73 P2O5 0.50 0.39 0.40 0.60 0.40 0.39 0.40 0.38 Sm 6.29 5.24 5.30 7.01 5.35 5.15 4.78 4.69 LOI 2.26 1.92 1.86 1.80 2.03 1.60 1.59 1.75 Eu 2.05 1.96 2.12 2.82 1.96 1.87 1.64 1.62 Total 99.42 99.24 98.78 99.53 99.35 99.45 99.42 99.31 Gd 6.83 5.68 5.93 8.28 5.68 5.66 5.33 5.40 Li 55.25 58.63 46.99 39.27 14.28 33.77 11.68 45.94 Tb 0.99 0.79 0.85 1.16 0.84 0.79 0.75 0.76 Be 0.54 0.81 0.49 0.43 0.18 0.56 0.15 0.63 Dy 4.91 4.11 4.22 5.69 4.22 4.00 3.99 4.11 Sc 13.79 17.76 14.18 11.48 12.98 12.38 12.61 14.96 Ho 0.83 0.67 0.68 0.93 0.70 0.66 0.64 0.66 V 156.5 151.2 154.7 138.1 11.27 144.1 12.13 142.2 Er 2.17 1.77 1.76 2.46 1.78 1.86 1.79 1.81 Cr 342.2 404.6 394.5 175.0 124.2 380.2 132.1 371.1 Tm 0.27 0.22 0.23 0.32 0.22 0.21 0.20 0.21 Co 38.59 33.53 34.26 20.14 2.55 31.15 3.07 33.55 Yb 1.42 1.13 1.15 1.68 1.06 1.25 1.23 1.25 Ni 159.6 161.1 161.8 96.34 11.29 147.1 14.91 145.0 Lu 0.21 0.16 0.17 0.25 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.16 Cu 117.1 94.72 101.7 80.63 4.84 74.57 4.65 75.75 Hf 4.46 3.59 3.59 4.71 0.51 3.41 0.45 3.28 Zn 115.3 109.1 111.7 104.1 11.14 97.14 12.70 105.8 Ta 1.75 1.37 1.48 2.08 0.09 1.33 0.10 1.29 Ga 12.86 12.97 12.19 14.47 7.64 12.14 6.55 11.12 Pb 1.76 1.72 2.11 1.90 0.72 1.87 0.40 1.58 Rb 705.8 881.6 641.4 667.1 518.3 540.0 477.7 734.4 Bi 0.46 0.29 0.55 0.46 0.053 0.27 0.002 0.14 Sr 570.0 568.9 627.7 743.6 591.5 693.5 566.7 684.2 Th 3.03 2.30 2.32 3.99 2.19 2.02 2.05 2.37 Y 16.15 13.11 13.71 18.72 13.66 12.60 12.96 13.17 U 0.82 0.61 0.66 1.02 0.086 0.61 0.071 0.58 Zr 139.2 106.5 108.6 152.5 13.96 101.1 12.63 97.97 Mg# 65.45 67.68 64.69 70.6 64.75 67.2 65.46 67.94 表 3 卡房辉绿岩Sr−Nd同位素组成
Table 3 Sr−Nd isotopic compositions of Kafang diabase
样品 年龄/Ma Rb/10−6 Sr/10−6 87Sr/86Sr (87Sr/86Sr)i Sm/10−6 Nd/10−6 143Nd/144Nd (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) SS13806-10 77 478 566 0.71056 0.70791 4.78 21.18 0.51272 0.51266 2.29 SS13806-11 77 734 684 0.71119 0.70782 4.69 20.73 0.51271 0.51265 2.07 表 4 卡房辉绿岩Pb同位素组成
Table 4 Pb isotopic compositions of Kafang diabase
样品 年龄/Ma 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb (206Pb/204Pb)t (207Pb/204Pb)t (208Pb/204Pb)t Φ μ Th/U SS13806-07 77 18.622±0.003 15.724±0.001 39.212±0.006 18.465 15.717 37.763 0.583 9.68 3.96 SS13806-09 77 18.610±0.007 15.683±0.008 39.254±0.014 18.286 15.668 38.830 0.579 9.61 3.98 注:Φ和μ为源区特征值。 -
[1] Aldanmaz E, Pearce J A, Thirlwall M F, Mitchell J G. 2000. Petrogenetic evolution of Late Cenozoic, post−collision volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey[J]. Journal of Volcanology Geothermal Research, 102(1/2): 67−95.
[2] Barth M G, McDonough W F, Rudnick R I. 2000. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 165: 197−213. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00173-4
[3] Buiter S J H, Torsvik T H. 2014. A review of Wilson Cycle plate margins: A role for mantle plumes in continental break−up along sutures?[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 627−653. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.02.007
[4] Chen Maohong, Zhang Wei, Yang Zongxi, Lu Gang, Hou Kejun, Liu Jianhui. 2009. Zircon SHRIMP U−Pb age and Hf isotopic composition of Baiceng ultrabasic dykes in Zhenfeng County, southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(3): 240−250 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chen Yongqing, Chen Shouyu, Huang Jingning, Shang Zhi, Zhao Binbin, Zhang Lina, Wang Zhenyi, Qin Luxue, Yang Rong. 2020. Geodynamic Background−Metallogenic Process−Quantitative Evaluation of Gejiu Super−large Tin−Copper Polymetallic Deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1−206 (in Chinese).
[6] Cheng Yanbo, Mao Jingwen, Chen Maohong, Yang Zongxi, Feng Jiarui, Zhao Haijie. 2008. LA−ICP−MS zircon dating of the alkaline rocks and lamprophyres in Gejiu area and its implications[J]. Geology in China, 35(6): 1138−1149 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Cheng Yanbo. 2012. Spatial−temperal Evolution of the Magmatism and Mineralization in Gejiu Supergiant Sn Polymetallic District and Insights into Several Key Problems[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1−306 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Cheng Y B, Carl S, Mao J W. 2012. Granite, gabbro and mafic microgranular enclaves in the Gejiu area, Yunnan Province, China: A case of two−stage mixing of crust−and mantle−derived magmas[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 164: 659−676. doi: 10.1007/s00410-012-0766-0
[9] Cheng Y B, Mao J W. 2010. Age and geochemistry of granites in Gejiu area, Yunnan Province, SW China: Constraints on their petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos, 120: 258−276. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.013
[10] Cheng Y B, Mao J W, Liu P. 2016. Geodynamic setting of Late Cretaceous Sn−W mineralization in southeastern Yunnan and northeastern Vietnam[J]. Solid Earth Sciences, 1(3): 79−88. doi: 10.1016/j.sesci.2016.12.001
[11] Condie K C. 2003. Incompatible element ratios in oceanic basalts and komatiites, tracking deep mantle sources and continental growth rates with time[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4: 1−28.
[12] Dai Fusheng. 1990. The evolution of two diagenetic series of the Gejiu tin district[J]. Acta Petrologica and Mineralogica, 9(3): 224−233 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] DePaolo D J. 1981. Trace element and isotopic effects of combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 53(2): 189−202. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(81)90153-9
[14] Du Yuansheng, Tong Jinnan. 2008. Introduction to Palaeontology and Historical Geology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1−266 (in Chinese).
[15] Fan Weiming, Menzies M A. 1992. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 320−329 (in Chinese).
[16] Feng Qianwen. 2012. The Late Paleozoic Geodynamical Environment of Central Asia: Evidence from Dark Dykes[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1−182 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Feng Zhishuo, Zhang Zhicheng, Li Jianfeng, Guo Zhaojie. 2010. Geochemistry and geological significance of the Cretaceous OIB−type mafic dykes in Sanweishan, Dunhuang, Gansu Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2): 607−616 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Ge Xiaoyue, Li Xianhua, Zhou Hanwen. 2003. Geochronologic, geochemistry and Sr−Nd isotopes of the Late Cretaceous mafic dike swarms in southern Hainan Island[J]. Geochimica, 32(1): 11−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Green T H. 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust−mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 347−359.
[20] Halls H C, Fahrig W C. 1987. Mafic dike swarms[J]. Geological Society of Canada Special Publication, 34: 57−64.
[21] Han Jiangwei, Xiong Xiaolin, Zhu Zhaoyu. 2009. Geochemistry of Late−Cenozoic basalts from Leiqiong area: The origin of EM2 and the contribution from sub−continental lithosphere mantle[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(12): 3208−3220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Hart S R, Allegre C J. 1980. Trace−element constraints on magma genesis[C]//Hargraves R B, (ed.). Physics of Magmatic Processes. New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 121−159.
[23] Hart S R. 1988. Heterogeneous mantle domains: Signature, genesis and mixing chronologies[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90: 273−296. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90131-8
[24] Herzberg C. 1992. Depth and degree of melting of komatiites[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97: 4521−4540. doi: 10.1029/91JB03066
[25] Herzberg C. 1995. Generation of plume magmas through time: An experimental approach[J]. Chemical Geology, 126: 1−16. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00099-4
[26] Hoek J D, Seitz H M. 1995. Continental mafic dyke swarms as tectonic indicators: An example from the Vestfold Hills, East Antarctica[J]. Precambrian Research, 75(3/4): 121−139.
[27] Hofmann A W. 1997. Mantle geochemistry: The message from oceanic volcanism[J]. Nature, 385: 219−229. doi: 10.1038/385219a0
[28] Hofmann A W. 2003. Sampling Mantle Heterogeneity Through Oceanic Basalts: Isotopes and Trace Elements[M]. Pergamon: Elsevier, 61−101.
[29] Hooper P, Widdowson M, Kelley S. 2010. Tectonic setting and timing of the final Deccan flood basalt eruptions[J]. Geology, 38(9): 839−842. doi: 10.1130/G31072.1
[30] Hou Y L, Zhong Y T, Xu Y G, He B. 2017. The provenance of late Permian karstic bauxite deposits in SW China, constrained by the geochemistry of interbedded clastic rocks, and U−Pb−Hf−O isotopes of detrital zircons[J]. Lithos, 278/281: 240−254. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.013
[31] Hou G T, Liu Y L, Li J H. 2006a. Evidence for ~1.8 Ga extension of the Eastern Block of the North China Craton from SHRIMP U−Pb dating of mafic dyke swarms in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 27(4): 392−401. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.05.001
[32] Hou G T, Wang C C, Li J H, Qian X L. 2006b. Late Paleoproterozoic extension and a paleostress field reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 422: 89−98. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2006.05.008
[33] Huang Wenlong, Xu Jifeng, Chen Jianlin, Huang Feng, Zeng Yunchuan, Pi Qiaohui, Cai Yongfeng, Jiang Xingzhou. 2016. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Gejiu complex in the Yunnan Province, SW China: Petrogenesis and contributions of mantle−derived melts to tin mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2330−2346 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Jia Runxing, Fang Weixuan, Ruan Xueyan. 2014. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic granites in Gejiu Tin deposit, Yunnan setting of the province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 5(2): 257−266 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Jiao Wenfang, Wu Yuanbao, Peng Min, Wang Jing, Yang Saihong. 2009. The oldest basement rock in the Yangtze Craton revealed by zircon U−Pb age and Hf isotope composition[J]. Science in China, 39(7): 972−978 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Kalfoun F, Ionov D, Merlet C. 2002. HFSE residence and Nb/Ta ratios in metasomatised, rutile−bearing mantle peridotites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 199(1/2): 49−65.
[37] Khan T, Murata M, Karim T, Zafar M, Ozawa H. 2007. A Cretaceous dike swarm provides evidence of a spreading axis in the back−arc basin of the Kohistan paleo−island arc, northwestern Himalaya, Pakistan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(2/3): 350−360.
[38] Lebedev S, Meier T, Hilst R D. 2006. Asthenospheric flow and origin of volcanism in the Baikal Rift area[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 249(3/4): 415−424.
[39] Li Hongbo, Zhang Zhaochong, Lü Linsu, Li Yongsheng. 2012. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological significances of the Permian basic dykes in Mianning, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Review, 58(5): 953−964 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Li Sanzhong, Zang Yibo, Wang Pengcheng, Suo Yanhui, Li Xiyao, Liu Xin, Zhou Zaizheng, Liu Xiaoguang, Wang Qian. 2017. Mesozoic tectonic transition in South China and initiation of Palaeo Pacific subduction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(4): 213−225 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Li Xiaolong, Mao Jingwen, Cheng Yanbo. 2011. Petrology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Baishachong and Beipaotai granitic stocks in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Geological Review, 57(6): 837−850 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Li Yingshu, Qin Dexian, Cai Yan, Xie Yang, Chen Nan, Wang Lun, Luo Xi, Yang Xiaoyu, Chen Jiaojiao, He Daqing. 2011. Geological and geochemical features of east dyke and its ore−controlling in Dachang Sn−polymetallic orefield, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(Sup.1): 106−113 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Liu Hongying, Xia Bin, Zhang Yuquan. 2004. Zircon SHRIMP dating ang geological significance of Maomaogou sodic alkaline rock in Huili, Panxi[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49: 1431−1438 (in Chinese).
[44] Liu Jiao, Zhou Yang, Xie Degen, Ji Xingxing, Li Dewei. 2016. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological implications of the lamprophyre in Jianshui, east Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, (6): 1977−1991 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Liu Lang, Liu Demin, Shao Junqi, Ding Guoli, Huang Binbin, Huang Jinshan. 2020. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic evolution of the basaltic trachyandesite in Huize, northeastern Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, 47(3): 678−692 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Liu Xiaoming, Gao Shan, Ling Wenchu, Yuan Honglin, Hu Zhaochu. 2005. Discovery and geological significance of 3.5 Ga detrital zircons in the Yangtze craton[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 15(11): 1334−1337 (in Chinese).
[47] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, Gao C G, Zong K Q, Wang D B. 2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recycling−induced melt−peridotite interactions in the Trans−North China Orogen: U−Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51: 537−571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
[48] Liu S, Su W C, Hu R Z, Feng C X, Gao S, Ian M C, Wang T, Feng G Y, Tao Y, Xia Y. 2010b. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of alkaline ultramafic dykes from southwest Guizhou Province, SW China[J]. Lithos, 114: 253−264. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.08.012
[49] Ludwig K R. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center.
[50] Ma L, Wang Q, Li G X, Wyman D A, Jung G Q, Yang J H, Gou G N, Guo H F. 2013. Early Late Cretaceous (ca. 93 Ma) norites and hornblendites in the Milin area, eastern Gangdese: Lithosphere−asthenosphere interaction during slab rollback and an insight into early Late Cretaceous (ca. 100−80 Ma) magmatic “flare−up” in southern Lhasa (Tibet)[J]. Lithos, 172/173: 17−30. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.03.007
[51] Mao Jingwen, Xie Guiqing, Yuan Shunda, Liu Peng, Meng Xuyang, Zhou Zhenhua, Zheng Wei. 2018. Current research progress and future trends of porphyry−skarn copper and granite−related tin polymetallic deposits in the Circum Pacific metallogenic belts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(9): 2501−2517.
[52] Mechede M. 1986. A method of discriminating between different types of mid−ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb−Zr−Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 56(3/4): 207−218.
[53] Mo Guopei. 2006. Genetic type of granites in Gejiu superlarge tin polymetallic deposit[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 20(4): 413−417 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[54] Niu Y L, Wilson M, Humphreys E R. 2012. A trace element perspective on the source of ocean island basalts (OIB) and fate of subducted ocean crust (SOC) and mantle lithosphere (SML)[J]. Episodes, 35(2): 310−327. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2012/v35i2/002
[55] Paces J B, Bell K. 1989. Non−depleted sub−continental mantle beneath the Superior Province of the Canadian Shield: Nd−Sr isotopic and trace element evidence from mid−continent rift basalts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53: 2023−2035. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90322-0
[56] Peng P, Zhai M G, Ernst R, Guo J H, Liu F, Hu B. 2008. A 1.78 Ga large igneous province in the North China Craton: The Xiong'er volcanic province and the North China dyke swarm[J]. Lithos, 101(3/4): 260−280.
[57] Pearce J A, Cann J R. 1973. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 19(2): 290−300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
[58] Pearce J A, Norry M J. 1979. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 69(1): 33−47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192
[59] Pearce J A, Peate D W. 1995. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 23: 1073−1109.
[60] Qi Shengsheng, Deng Jinfu, Ye Zhanfu, Liu Rong, Wang Guoliang. 2013. LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb dating of Late Devonian diabase dike swarms in Qimantag area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(9): 1385−1393 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[61] Qiu Y M, Gao S, McNaughton N J, Groves D I, Ling W L. 2000. First evidence of ≥3.2 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of South China and its implications for Archean crustal evolution and Phanerozoic tectonics[J]. Geology, 28: 11−14.
[62] Radhakrishna T, Mathew J. 1996. Late Precambrian (850−800 Ma) paleomagnetic pole for the south Indian shield from the Harohalli alkaline dykes Geotectonic: Implications for Gondwana reconstructions[J]. Precambrian Research, 80(1/2): 77−87.
[63] Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. 1995. Nature and composition of the continental crust: A lower crustal perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 33: 267−309. doi: 10.1029/95RG01302
[64] Søager N, Holm P M, Llambías E J. 2013. Payenia volcanic province, southern Mendoza, Argentina: OIB mantle upwelling in a backarc environment[J]. Chemical Geology, 349: 36−53.
[65] Scarrow J H, Leat P T, Wareham C D, Millar I L. 1998. Geochemistry of mafic dykes in the Antarctic Peninsula continental−margin batholith: A record of arc evolution[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 131(2): 289−305.
[66] Southwest Metallurgical Geological Exploration Company. 1984. Geology of Gejiu Tin Deposit[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1−256 (in Chinese).
[67] Srivastava R K. 2011. Dake Swarms: Keys for Geodynamic Interpretation[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 1−603.
[68] Staudigel H, Hart, S R. 1983. Alteration of basaltic glass: Mechanisms and significance for the oceanic crust−seawater budget[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 47: 337−350. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(83)90257-0
[69] Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313−345.
[70] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1−328.
[71] Tatsumoto M, Basu A R, Huang W K, Wang J W, Xie J H. 1992. Sr, Nd, and Pb isotopes of ultramafic xenoliths in volcanic rocks of Eastern China; Enriched components EMⅠ and EMⅡ in subcontinental lithosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 113: 107−128. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(92)90214-G
[72] Wang C Y, Zhou M F, Qi L. 2007. Permian flood basalts and magmatic intrusions in the Jinping (SW China)−Song Da (northern Vietnam) district: Mantle sources, crustal contamination and sulfide segregation[J]. Chemical Geology, 243: 317−343.
[73] Wang Dezi, Shu Liangshu. 2007. On granitic tectono−magmatic assemblages[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 362−370 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[74] Wang Xiang, Ma Changqian, Deng Jialiang, Wu Heng. 2020. Discovery of ~2.5 Ga amphibolite at Liuping Town of Susong County in the mid−eastern region of the Yangtze Block[J]. Geology in China, 47(4): 1262−1263 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[75] Wang Yonglei, Pei Rongfu, Li Jinwen, Wu Junde, Li Li, Wang Haolin. 2007. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of Laochang granite in Gejiu[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(7): 979−985 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[76] Weaver B L, Tamey J. 1981. The Scourie dike suite: Petrogenesis and geochemical nature of the Proterozoic subcontinental mantle[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 78: 175−188. doi: 10.1007/BF00373779
[77] Weaver B L. 1991. The origin of ocean island basalt end−member composition: Trace element and isotopic constrains[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 104(2/4): 381−397.
[78] White W M, Duncan R A. 1995. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Society Island: New evidence for deep mantle recycling. In: Basu A , Hart S R. (eds.). Geochemistry and geochronology of the Society Island: new evidence for deep mantle recycling. Isotope studies of crust−mantle evolution[C]// Geophysics Monograph, 95. AGU, Washington, DC, 1−23.
[79] Wilson M B. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach[M]. London: Unwyn Hyman.
[80] Wood D A. 1980. The application of a Th−Hf−Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British tertiary volcanic province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50: 11−30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
[81] Wu Hao, Xu Zuyang, Yan Weibing, Hao Yujie, Liu Haiyong. 2023. Zircon U–Pb ages and geochemical characteristics of diabase in Nie'erco area, central Tibet: Implication for Neo–Tethyan slab breakoff[J]. Geology in China, 50(6): 1804–1816 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[82] Xu X S, O’Reilly S Y, Griffn W L, Zhou X M. 2003. Enrichment of upper mantle peridotite; Petrological, trace element and isotopic evidence in xenoliths from SE China[J]. Chemical Geology, 198: 163−188. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00004-4
[83] Xu D R, Xia B, Li P C, Chen G H, Ma C, Zhang Y Q. 2007. Protolith natures and U−Pb sensitive high mass−resolution ion microprobe (SHRIMP) zircon ages of the metabasites in Hainan Island, South China: Implications for geodynamic evolution since the Late Precambrian[J]. Island Arc, 16(4): 575−597. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2007.00584.x
[84] Xu D R, Xia B, Bakun−Czubarow N, Bachlinski R, Li P, Chen J, Chen T. 2008. Geochemistry and Sr−Nd isotope systematics of metabasites in the Tunchang area, Hainan Island, South China: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 92(3/4): 361−391.
[85] Xu Qidong, Xia Qinglin, Cheng Qiuming. 2009. Tectono−magmatic evolution related to metallogenic system in Gejiu ore−concentration area, Southeast Yunnan of China[J]. Earth Science, 34(2): 307−311 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[86] Xu Yao, Zhang Yongqian, Yan Jiayong, Xu Zhiwu, Chen Changxin. 2019. Teleseismic P−wave velocity structure of upper mantle beneath the southeastern part of South China and its implications[J]. Geology in China, 46(4): 737−749 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[87] Xu Yigang. 1999. Advances in Chemical Geodynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 159−167 (in Chinese).
[88] Yan Q R, Wang Z Q, Liu S W. 2005. Opening of the Tethys in southwest China and its significance to the breakup of East Gondwanaland in late Paleozoic: Evidence from SHRIMP U−Pb zircon analyses for the Garzê ophiolite block[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50: 256−264. doi: 10.1007/BF02897536
[89] Yang Jie, Pei Xianzhi, Li Ruibao, Li Zuochen, Liu Zhanqing, Pei Lei, Liu Chengjun, Chen Youxin, Chen Guochao, Gao Jingmin. 2014. Geochemical characteristics and geological implications of Haerguole basalt in Buqingshan area on the southern margin of East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geology in China, 41(2): 335−350 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[90] Yu J H, O’Reilly S Y, Zhang M. 2006. Roles of melting and metasomatiam in the formation of the lihtospheric mantle beneath the Leizhou Peninsula, South China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 47: 355−383. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi078
[91] Zhang J W, Dai C G, Huang Z L, Luo T Y, Qian Z K, Zhang Y. 2015. Age and petrogenesis of Anisian magnesian alkali basalts and their genetic association with the Kafang stratiform Cu deposit in the Gejiu supergiant tin−polymetallic district, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Review, 69: 403−416. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.011
[92] Zhang S B, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Zhao Z F, Gao S, Wu F Y. 2006a. Zircon isotope evidence for ≥3.5 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 146: 16−34. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.002
[93] Zhang S B, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Zhao Z F, Gao S, Wu F Y. 2006b. Zircon U−Pb age and Hf isotope evidence for 3.8 Ga crustal remnant and episodic reworking of Archean crust in South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 252: 56−71. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2006.09.027
[94] Zhang X H, Zhang H F, Tang Y J, Wilde S A, Hu Z C. 2008. Geochemistry of Permian bimodal volcanic rocks from Central Inner Mongolia, North China: Implication for tectonic setting and Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Chemical Geology, 249: 262−281. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.01.005
[95] Zhang Ying, Huang ZhilongL, Luo Taiyi, Qian Zhikuan, Zhang Jiawei, Sun Jianbo. 2013. The geochemistry and SIMS U−Pb zircon dating of the Jiasha gabbric−monzonitic intrusion in Gejiu district, Yunnan Province[J]. Geochimica, 42(6): 523−543 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[96] Zhao J H, Zhou M F. 2007. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district (Sichuan Province, SW China): Implications for subduction−related metasomatism in the upper mantle[J]. Precambrian Research, 152: 27−47. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.002
[97] Zhao Wenjun. 2018. Genesis and understanding of the Jiasha complex in Gejiu, Yunman Province[J]. Energy and Environment, 6: 55−58 (in Chinese).
[98] Zhao Yonggui, Zhong Dalai, Liu Jianhua, Wu Hua, Liu Futian. 1992. Fundamentals of geological interpretation for seismic tomography and its application to studying of west Yunnan’s deep structure[J]. Scientin Geologica Sinica, (2): 105−113 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[99] Zheng J, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y, Lu F X, Wang C Y, Zhang M, Wang F Z, Li H M. 2004. 3.6 Ga lower crust in central China: New evidence on the assembly of the North China craton[J]. Geology, 32: 229−232.
[100] Zhu Yongfeng, Xu Xin, Wei Shaoni, Song Biao, Guo Xuan. 2007. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of OIB−like pillow basalts in western Mts. of Karamay city (western Junggar), NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7): 1739−1748 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[101] Zimmer M, Kroner A, Jochum K P, Reischmann T, Todt W. 1995. The Gabal Gerf complex: A Precambrian N−MORB ophiolite in the Nubian Shield, NE Africa[J]. Chemical Geology, 123: 29−51. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00018-H
[102] Zindler A, Hart S R. 1986. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 14: 493−571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[103] 陈懋弘, 章伟, 杨宗喜, 陆刚, 侯可军, 刘建辉. 2009. 黔西南白层超基性岩墙锆石 SHRIMP U−Pb 锆石年龄和 Hf 同位素组成研究[J]. 矿床地质, 28(3): 240−250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.03.002 [104] 陈永清, 陈守余, 黄静宁, 尚志, 赵彬彬, 张丽娜, 王振义, 覃璐雪, 杨融. 2020. 个旧超大型锡铜多金属矿床成矿地质背景过程定量评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1−206. [105] 程彦博, 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 杨宗喜, 冯佳睿, 赵海杰. 2008. 云南个旧锡矿田碱性岩和煌斑岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 35(6): 1138−1149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.06.011 [106] 程彦博. 2012. 个旧超大型锡多金属矿区成岩成矿时空演化及一些关键问题探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1−306. [107] 戴福盛. 1990. 个旧锡矿区两个成岩系列的演化[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 9(3): 224−233. [108] 杜远生, 童金南. 2008. 古生物地史学概论[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1−266. [109] 范蔚茗, Menzies M A. 1992. 中国新生代火山岩年代学与地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 320−329. [110] 冯乾文. 2012. 中亚地区古生代晚期地球动力学环境—来自暗色岩墙的证据[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 1−182. [111] 冯志硕, 张志诚, 李建锋, 郭召杰. 2010. 敦煌三危山地区白至纪OIB型基性岩墙的特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 26(2): 607−616. [112] 葛小月, 李献华, 周汉文. 2003. 琼南晚白垩世基性岩墙群的年代学、元素地球化学和Sr−Nd同位素研究[J]. 地球化学, 32(1): 11−20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.01.002 [113] 韩江伟, 熊小林, 朱照宇. 2009. 雷琼地区晚新生代玄武岩地球化学: EM2成分来源及大陆岩石圈地慢的贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 25(12): 3209−3220. [114] 黄文龙, 许继峰, 陈建林, 黄丰, 曾云川, 皮桥辉, 蔡永丰, 蒋兴洲. 2016. 云南个旧杂岩体年代学与地球化学: 岩石成因和幔源岩浆对锡成矿贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2330−2346. [115] 贾润幸, 方维萱, 隗雪燕. 2014. 云南个旧锡矿花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 5(2): 257−266. [116] 焦文放, 吴元保, 彭敏, 汪晶, 杨赛红. 2009. 扬子板块最古老岩石的锆石U−Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 39(7): 972−978. [117] 李宏博, 张招崇, 吕林素, 李永生. 2012. 四川冕宁基性岩墙的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 58(5): 953−964. [118] 李三忠, 臧艺博, 王鹏程, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 刘鑫, 周在征, 刘晓光, 王倩. 2017. 华南中生代构造转换和古太平洋俯冲启动[J]. 地学前缘, 24(4): 213−225. [119] 李肖龙, 毛景文, 程彦博. 2011. 云南个旧白沙冲和北炮台花岗岩岩石学、地球化学研究及成因探讨[J]. 地质论评, 57(6): 837−850. [120] 黎应书, 秦德先, 蔡燕, 谢阳, 陈楠, 王伦, 罗曦, 杨晓宇, 陈姣姣, 贺大庆. 2011. 广西大厂锡多金属矿田东岩墙地质地球化学特征及其控矿作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(增刊 1): 106−113. [121] 刘红英, 夏斌, 张玉泉. 2004. 攀西会理猫猫沟钠质碱性岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 49: 1431−1438. [122] 刘娇, 周洋, 谢德根, 纪星星, 李德威. 2016. 云南建水煌斑岩年代学和地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 中国地质, (6): 1977−1991. [123] 刘浪, 刘德民, 邵俊琦, 丁国立, 黄彬彬, 黄锦山. 2020. 云南会泽地区玄武粗安岩年代学、地球化学及构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 47(3): 678−692. doi: 10.12029/gc20200309 [124] 柳小明, 高山, 凌文黎, 袁洪林, 胡兆初. 2005. 扬子克拉通35亿年碎屑锆石的发现及其地质意义[J]. 自然科学进展, 15(11): 1334−1337. [125] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 袁顺达, 刘鹏, 孟旭阳, 周振华, 郑伟. 2018. 环太平洋成矿带斑岩−矽卡岩型铜矿和与花岗岩有关的锡多金属矿研究现状与展望[J]. 岩石学报, 34(9): 2501−2517. [126] 莫国培. 2006. 个旧超大型锡多金属矿区花岗岩成因类型[J]. 矿产与地质, 20(4): 413−417. [127] 祁生胜, 邓晋福, 叶占福, 刘荣, 王国良. 2013. 青海祁漫塔格地区晚泥盆世辉绿岩墙群LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 32(9): 1385−1393. [128] 王德滋, 舒良树. 2007. 花岗岩构造岩浆组合[J]. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 362−370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.006 [129] 王翔, 马昌前, 邓佳良, 吴衡. 2020. 扬子陆块中东部宿松县柳坪镇发现~2.5 Ga斜长角闪岩[J]. 中国地质, 47(4): 1262−1263. [130] 王永磊, 裴荣富, 李进文, 武俊德, 李莉, 王浩琳. 2007. 个旧老厂矿田花岗岩地球化学特征及其形成构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 81(7): 979−985. [131] 吴浩, 徐祖阳, 严维兵, 郝宇杰, 刘海永. 2023. 西藏中部聂尔错地区辉绿岩锆石U–Pb年龄与地球化学特征:对新特提斯洋板片断离的指示[J]. 中国地质, 50(6): 1804–1816. [132] 徐启东, 夏庆霖, 成秋明. 2009. 云南个旧矿集区区域构造−岩浆演化与锡铜多金属成矿系统[J]. 地球科学, 34(2): 307−311. [133] 徐峣, 张永谦, 严加永, 徐志伍, 陈昌昕. 2019. 华南东南部上地幔远震P波速度结构及意义[J]. 中国地质, 46(4): 737−749. [134] 徐义刚. 1999. 化学地球动力学进展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 159−167. [135] 杨杰, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 李佐臣, 刘战庆, 裴磊, 刘成军, 陈有炘, 陈国超, 高景民. 2014. 东昆仑南缘布青山地区哈尔郭勒玄武岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 41(2): 335−350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.003 [136] 冶金工业部西南冶金地质勘探公司. 1984. 个旧锡矿地质[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1−256. [137] 张颖, 黄智龙, 罗泰义, 钱志宽, 张嘉玮, 孙建博. 2013. 云南个旧西区贾沙辉长−二长岩体SIMS锆石U−Pb定年及地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 42(6): 523−543. [138] 赵文君. 2018. 云南个旧贾沙岩浆岩认识及成因类型[J]. 能源与环境, 6: 55−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2018.01.027 [139] 赵永贵, 钟大赍, 刘建华, 吴华, 刘福田. 1992. 地震层析地质解释原理及其在滇西深部构造研究中的应用[J]. 地质科学, (2): 105−113. [140] 朱永峰, 徐新, 魏少妮, 宋彪, 郭玻. 2007. 西准噶尔克拉玛依OIB型枕状玄武岩地球化学及其地质意义研究[J]. 岩石学报, 23(7): 1739−1748. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.07.019 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 方维萱,郭玉乾,李天成. 滇东地区裂谷盆地内火山—侵入岩序列与金属成矿. 地质学报. 2024(06): 1776-1802 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 方维萱,郭玉乾,贾润幸,童祥,马振飞. 论云南个旧锡铜钨三稀金属矿集区叠加成矿系统与垂向构造岩相学结构的关系. 地质力学学报. 2021(04): 557-584 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: