Geological landform and structure formation model of the Paleogene Ochirbat salt diapir in the western Kuqa, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
库车前陆冲断带西部古近系奥奇克盐底辟是中国最典型的盐底辟构造,可作为盐构造研究的天然实验室。本文在前人研究的基础上,通过详细的野外填图,同时辅以遥感解译、地震解释和合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)技术,探讨了奥奇克盐底辟盐喀斯特地貌特征,并分析了其形成机制及流变模式。奥奇克盐底辟表面盐喀斯特构造发育,在风化面上可见大量的溶洞、溶蚀冲沟构造,在新鲜面上可见梳状溶痕、微型峰丛等构造样式,此外,溶蚀坍塌等机械侵蚀构造也是本区常见的盐喀斯特构造类型。奥奇克盐底辟在形成过程中受逆冲断层、盐上地层的剥蚀作用、差异负载作用及盐岩自身的浮力作用的控制,共经历了逆冲盐底辟、侵蚀盐底辟、主动盐底辟和被动盐底辟4个主要阶段。盐岩喷出地表后,在重力作用下由核部向四周流动形成盐冰川,季节性河流的存在限制了盐底辟向东侧、东北侧及北侧传播,导致盐底辟呈现单侧增生的流变模式。
Abstract:As the Paleogene Ochirbat salt diapir in the western Kuqa foreland thrust belt is the most typical salt diapir structure in China, it can serves as a natural laboratory for the study of salt structure. Based on previous researches, the methods of field mapping, seismic interpretation, remote sensing images interpretation and InSAR (interferometric synthetic aperture radar) technique were used to analyse the salt karst landform characteristics, formation mechanism and rheological model of the Ochirbat salt diapir. The salt karst landforms are mainly developed on the surface of the salt diapir. Karst caves and gullies can be seen on the weathering surface of the diapir, while rillen karrens and miniature karst peak cluster can be seen on the fresh surface. Further more, collapse structures belonging to salt karst landforms can also be regularly seen in the diapir. The formation of the salt diapir was controlled by many factors, including the thrust fault, the erosion of the overburden, the differential loading and buoyancy, and the evolution process of the diapir can be divided into 4 main stages, including thrust piercement, erosion piercement, active piercement and passive piercement stages. It is summarized that after coming out from the underground, the salt flowed from the core to the periphery of the diapir under the gravity, forming salt glacier, and the seasonal river restricted the salt spreading to east, northeast and north directions, resulting in the asymmetric rheological model of the diapir.
-
1. 引言
祁连山位于华北板块西南缘,与秦岭、昆仑一起构成中国大陆内部巨型的中央造山带,是中国大陆主要造山带之一。北祁连造山带雄踞于河西走廊之南,成为青藏高原的东北界,东南与西秦岭相连,西北被阿尔金山截断(葛肖虹等,1999;杨永春等,2019;图 1a)。前人通过大量岩石学、沉积等研究对北祁连洋盆的俯冲极向做过研究,主要形成了双向俯冲(肖序常等,1978;王荃等,1981;左国朝等,1987;吴才来等,2010)、向北俯冲(许志琴等,1994;夏林圻等, 1996, 1998;张建新等, 1997, 1998;夏林圻等,2016)、向南俯冲(宋述光,1997;刘传周等,2005),目前尚无统一的认识。已有研究表明,通过花岗岩类地球化学特征及同位素年代学的研究可以提供有关其形成的大地构造背景信息,可以作为地质构造示踪剂(徐卫东等,2007;秦海鹏,2012)。目前,在北祁连山造山带毛藏寺、银硐梁、大野口等多处发现有埃达克岩或埃达克质岩石,这类岩石为区域构造背景研究提供了依据,本文试图利用车路沟岩体对北祁连构造演化进行研究。
研究区位于北祁连造山带西段,区内广泛发育寒武系黑茨沟组裂谷火山岩(王晓伟等,2018)、奥陶系阴沟群和扣门子组岛弧-弧后扩张脊型火山岩以及志留系复理石沉积,分布有俯冲混杂岩带,具有典型的沟弧盆体系(夏林圻等,2001),车路沟岩体位于前人所划分的奥陶系岛弧火山岩-沉积岩系中。前人对岩体特征和时代做了一些研究(杨建国等,2003;宋忠宝等,2004;贾群子等,2005),但多围绕其与金成矿作用方面的研究,宋忠宝等(2005)通过对车路沟中英安斑岩进行年代学、地球化学研究,认为车路沟岩体属于碰撞型花岗岩类,形成于碰撞作用晚期。本文通过对车路沟岩体中英云闪长玢岩的岩石学、地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学等方面的研究,分析其岩石成因,揭示其形成时的构造背景,为北祁连造山带构造演化提供约束。
2. 区域地质概况
研究区大地构造位置属北祁连早古生代造山带西段之西端(杨建国等,2003),距离北祁连造山带与阿尔金断裂交汇部位4 km。区域上地层北部有古元古界敦煌岩群零星分布外,以古生界为主,主要有寒武系、奥陶系、志留系,其次为石炭系。区域上侵入岩较为发育,以明芨芨沟岩体、青石峡岩体、青山岩体和车路沟岩体为主,分布范围较大,多呈岩株状分布,展布方向和区域构造线方向基本一致,多呈北西、北西西向。
车路沟岩体位于北祁连造山带西段,紧邻阿尔金走滑断裂南侧,出露面积较大(图 1b),自阴凹大泉至照壁山一带广泛分布,多侵入于奥陶系扣门子组中,岩体被断裂构造破坏严重,形态呈不规则块状,呈岩基状东西向条带状分布,边界明显的受控于断裂构造(夏林圻等,2001),多与地层呈断层接触,接触部位具明显的片理化,反映岩体的形成与板块俯冲、碰撞和造山带上不同的块体之间的构造作用密切相关(吴才来等,2010)。
![]() 图 1 车路沟一带地质简图1—第四系冲、洪积物;2—二叠系砂岩;3—石炭系砂岩;4—志留系复理石建造;5—奥陶系扣门子组火山岩系;6—奥陶系中堡群火山-碎屑岩系;7—奥陶系阴沟群火山岩系;8—石英二长闪长岩;9—英云闪长玢岩;10—闪长玢岩;11—实测断裂构造;12—同位素测年样品采样位置;13—岩石全分析样品采样位置Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Chelugou pluton1- Quaternary; 2- Permian sandstone; 3- Carboniferous sandstone; 4- Silurian flysch formation; 5- Volcanic rocks of Ordovician Koumenzi Formation; 6- Volcanic clastic rocks of Ordovician Zhongbu Group; 7- Volcanic rocks of Ordovician Yingou Group; 8- Quartz monzodiorite; 9- Quartz mica dioritic porphyry; 10-Diorite porphyry; 11-Fault; 12-Sampling position for isotope dating; 13- Sampling position for rock analysis
图 1 车路沟一带地质简图1—第四系冲、洪积物;2—二叠系砂岩;3—石炭系砂岩;4—志留系复理石建造;5—奥陶系扣门子组火山岩系;6—奥陶系中堡群火山-碎屑岩系;7—奥陶系阴沟群火山岩系;8—石英二长闪长岩;9—英云闪长玢岩;10—闪长玢岩;11—实测断裂构造;12—同位素测年样品采样位置;13—岩石全分析样品采样位置Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Chelugou pluton1- Quaternary; 2- Permian sandstone; 3- Carboniferous sandstone; 4- Silurian flysch formation; 5- Volcanic rocks of Ordovician Koumenzi Formation; 6- Volcanic clastic rocks of Ordovician Zhongbu Group; 7- Volcanic rocks of Ordovician Yingou Group; 8- Quartz monzodiorite; 9- Quartz mica dioritic porphyry; 10-Diorite porphyry; 11-Fault; 12-Sampling position for isotope dating; 13- Sampling position for rock analysis3. 岩石学特征
车路沟岩体主要由英云闪长玢岩、闪长玢岩组成,局部为石英闪长玢岩、英云闪长岩等,岩体与地层接触部位产出车路沟金矿、昌马金矿等多个金矿床。主要岩石特征如下:
英云闪长玢岩,灰白色,斑状结构,基质微粒花岗结构,块状构造。斑晶主要是斜长石和角闪石(10%~15%),粒径0.25~1.90 mm。斜长石为自形—半自形晶板条状,角闪石多为长柱状,斜长石具高岭土化、绿帘石化。基质成分由长石、角闪石、石英和不透明矿物组成,粒径小于0.10 mm(图 2a,b)。
闪长玢岩,浅灰黑色,斑状结构,显微粒状半自形柱状粒状结构,块状构造。斑晶为角闪石及少量斜长石,大小一般1~5 mm,星散状分布,含量15%~20%。基质为斜长石、石英、角闪石,大小一般0.1~0.2 mm,少0.02~0.1 mm(细),部分0.2~0.3 mm(细),杂乱分布。具绢云母化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化(图 2c,d)。
4. 样品采集及分析方法
本次工作分别在岩体的不同地方采集了4件新鲜的岩石样品,做了岩石地球化学全分析,所采岩石类型均为英云闪长玢岩,样品重量均大于2 kg,利用玛瑙球磨机研磨至200目进行分析,样品加工由河北省区域地质调查研究所实验室承担,样品的加工过程均是在无污染设备中进行。在岩体西部二家台一带采集了新鲜英云闪长玢岩岩石样品1件,样品重量为11.3 kg,以挑选锆石进行U-Pb同位素测年。
锆石分选、制靶、透反射光拍照和阴极发光拍照均在廊坊诚信地质服务有限公司完成。锆石的激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)原位U-Pb定年在中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心自然资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室完成。激光剥蚀系统为GeoLas Pro,ICP-MS为Agilent 7700x。激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度。对分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算)采用软件Glitter 4.4完成,详细仪器参数和测试过程参见李艳广等(2015)。采用锆石标准91500作为标样进行同位素分馏校正。对于与分析时间有关的U-Th-Pb同位素比值漂移,利用91500的变化采用线性内插的方式进行了校正。锆石样品的U-Pb年龄谐和图绘制和年龄权重平均计算均采用Isoplot Exver 3完成。
5. 分析结果
5.1 地球化学特征
从表 1可知,岩石中SiO2含量60.37% ~66.73%,平均63.75%,Al2O3含量15.65%~16.45%,平均16.01%,Na2O/K2O值7.47~9.96,平均8.38,Na2O高于K2O数倍,P2O5含量SiO2呈反比,与表明其源于贫钾的玄武质岩石(张旗等,2002),为I型花岗岩,里特曼指数(σ43)1.28~2.22,为低钾富钠钙碱性花岗岩,A/CNK为0.90~1.00,平均0.93,为准铝质,且经CIPW标准矿物计算出现刚玉,说明具有活动大陆边缘环境I-S过渡型花岗岩的特征(秦海鹏,2012)。MgO含量1.78~3.95,平均2.63;分异指数DI大于59.55,分异程度中等略高。
表 1 车路沟岩体主量元素(%)、微量元素(10-6)分析结果Table 1. Analytical results of major elements (%) and trace elements (10-6) of the Chelugou rock mass
从微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中可以看出(图 3、表 1),大离子亲石元素(LILE)富集Ba、Sr、Hf,高场强元素(HFSE)明显贫Nb、Ti、Yb,相对富集Zr。稀土总量33.40×10-6~39.27×10-6,平均35.99×10-6,远低于中性岩稀土总量196×10-6和花岗岩稀土总量290×10-6。LREE/HREE值3.95~6.51,轻稀土元素较富集,HREE含量较低,平均6.01×10-6,Y含量7.46×10-6~13.44×10-6,Yb含量0.58×10-6~1.36×10-6,(La/Yb)N值2.87~6.29(表 1),稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分配曲线为右倾型(图 3),轻、重稀土元素分异明显,δEu值1.23~1.49,Eu呈正异常,说明岩浆源区无残留斜长石。稀土元素特征与埃达克岩亏损重稀土、低Y、Yb及正铕异常的特征相符(Defant et al., 1990)。
5.2 U-Pb年代学特征
锆石多呈长柱状或菱形柱体,为典型的锆石晶体形状,多呈自形、半截状,锆石具有明显的震荡环带,部分锆石内部有继承核存在,生长纹路清晰,为典型的岩浆锆石(图 4),本次利用LA ICP-MS对锆石进行了测试,锆石Th/U比值0.07~1.73,平均0.57,具岩浆锆石的特征(表 2)。测试结果中,共有12个测试点具有谐和年龄,表面年龄分为2组(图 5),第一组有5个点,表面年龄406.2~422.9 Ma,获得加权平均年龄(416.6±9.5)M a,MSWD =1.7;第二组有7个点,表面年龄457.7~465 Ma,获得加权平均年龄(462.1±3.8)Ma,MSWD=0.15。第二组年龄应是岩浆侵位结晶年龄,第一组年龄可能反映了后期的岩浆热事件。
表 2 车路沟岩体中LA ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测年结果Table 2. Zircon LA ICP-MS U-Pb isotopic data of the Chelugou pluton
5.3 年代学讨论
宋忠宝等(2005)在车路沟岩体中采集英安斑岩同位素样品进行了U-Pb同位素年龄为(427.7±4.5)Ma,本次工作在开展区内地质调查过程中,结合薄片鉴定认为,前人所认为的英安斑岩即为车路沟岩体中的闪长玢岩,贾群子等(2007)在岩体西部二家台沟采集英云闪长玢岩进行了单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄测定,获得加权平均年龄为(445.6±3.2)Ma,认为该年龄是锆石的结晶年龄,接近岩体的形成年龄。
结合前人测试结果,笔者认为车路沟岩体可能为复式岩体或者岩浆演化经历了较长的时间,岩体中两种岩性整体为同源岩浆演化,岩体演化早期阶段为英云闪长玢岩为主,伴随有中酸性—中性岩浆的分异,后期演化为闪长玢岩。因此,该岩体就位时间为(462.1±3.8)Ma,为中奥陶世。
6. 讨论
埃达克岩是一套具有特定地球化学特征的钙碱性中酸性喷出/侵入岩(Defant et al., 1990),具有高SiO2(≥56%)、高铝(Al2O3≥15%)、富钠(Na2O>K2O)、高Sr(>400×10-6)、低Y(<18×10-6)和Yb(<1.9×10-6)以及不明显的Eu异常等地球化学特征。车路沟岩体SiO2含量为60.37% ~66.31%,Al2O3含量15.72%~16.45%,Na2O含量4.86%~6.19%,K2O含量0.62%~0.72%,Na2O/K2O为7.47~9.96,Sr含量299.52×10-6~525.85×10-6,Y含量7.46×10-6~13.44×10-6,Yb含量0.58×10-6~1.36×10-6,Sr/Y值为30.90~70.48。该岩体轻稀土富集,轻重稀土分馏明显,亏损高场强元素,同时在Y-Sr/Y图解中(图 6a)全部落入埃达克岩区域。上述特征表明,车路沟岩体与典型埃达克岩的特征一致(Defant et al., 1990, 2002;毛启贵等, 2010;Zheng et al., 2018)。
埃达克岩最早被认为是由于年轻的俯冲大洋板片在榴辉岩相下熔融形成火山岩和侵入岩(Defant et al., 1990),随着研究的深入,越来越多与埃达克岩相似地球化学属性的岩石被发现。目前对埃达克岩的成因模式主要有以下4种:(1)俯冲洋壳的部分熔融,随后与上覆楔形地幔橄榄岩发生反应形成埃达克岩(Defant et al., 1990, 2002;Kay,1993;Martin et al., 2005;Wang et al., 2007, 2008a;Tang et al., 2010;毛启贵等, 2010;Zheng et al., 2018);(2)含水玄武质岩浆高/低压条件下发生结晶分异作用(Castillo et al., 1999, 2012;Macpherson et al., 2006);(3)受玄武质岩浆底侵作用或俯冲大陆地壳发生部分熔融产物(Wang et al., 2008b;Lai et al., 2013);(4)增厚下地壳拆沉作用导致部分熔融产生的流体和地幔橄榄岩相互作用形成的高Mg#埃达克岩(Rudnick et al., 1995;Wareham et al., 1997;Chung et al., 2003;Gao et al., 2004;Wang et al., 2006;朱涛等,2014;王楠等,2016)。
车路沟岩体岩石地球化学研究表明,K2O含量0.62%~0.72%,Na2O/K2O值7.47~9.96,与洋壳特征相似,其岩石类型为富Na2O的钙碱性岩浆,这与俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克岩一致(Defant et al., 2002)。岩体具较高的Cr(27.30 × 10-6~70.79 × 10-6)、Ni(27.01×10-6~46.65×10-6)及Mg#值(52.24~59.79),应该是板片俯冲熔融产生的埃达克岩浆与地幔楔相互作用导致MgO加入的结果。车路沟岩体以较低的Nb(1.92×10-6~2.15×10-6)含量与洋岛玄武岩(>20×10-6)Nb值存在明显的差异,反映其并非含水玄武质岩浆结晶分异而成。俯冲大陆地壳发生部分熔融产生的埃达克岩,具有明显的富钾特征(K2O>Na2O),较高的Th含量、Th/U、Th/Ba和Rb/Ba比值,以及Sr的弱异常。车路沟岩体具富钠特征(Na2O>K2O),具有较低的Th含量(0.68 × 10-6~1.57×10-6),以及较低的Th/Ba(0.001~0.004)和Rb/Ba(0.02~0.04)比值和较高的Sr含量(299.52 ×10-6~525.85×10-6),可与俯冲大陆地壳发生部分熔融产生的埃达克岩相区别。拆沉下地壳熔融产生的埃达克岩浆在上升过程中与地幔橄榄岩发生反应从而获得较高的Mg#,拆沉下地壳来源的埃达克岩通常含有壳源继承锆石,而本次研究中锆石结构均一,没有继承性锆石。因此,车路沟岩体应为俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克岩,而非其他成因的埃达克岩。
地球化学特征表明车路沟岩体源于贫钾的玄武质岩石,通过A/MF-C/MF图解对岩浆成因进行了判别,所有数据均落入基性岩的部分熔融(图 6b),推测岩浆来源与新生基性火山岩的部分熔融有关(Zhang et al., 2017),这一点,在野外地质分布特征中也可以分辨,岩体大部分侵入于奥陶系扣门子组弧后扩张型火山岩中,但未见到志留纪复理石建造中有侵入特征,说明其形成与俯冲作用有关。车路沟岩体δEu变化范围为1.10~1.49,平均1.285,表明在岩浆分离结晶过程中斜长石不占据元素总分配系数的主导地位,岩浆中应残留石榴子石或者角闪石。前人研究认为,岩浆源区中以角闪石为残留相时,形成的熔体具轻微上凹的HREE配分模式,且Y/Yb比值一般接近10;当源区中以石榴子石为残留相时,形成的熔体具有倾斜的HREE配分模式同时其Y/Yb比值明显大于10(Rollinson, 1993; 高永丰等,2003)。车路沟岩体Y/Yb比值为9.91~12.90,平均为11.34,稀土配分模式显示(图 3),其为基本向右倾斜的HREE配分模式,表明岩浆岩区残留相以石榴子石为主,由此推测车路沟埃达克岩体来源于基性玄武质岩浆的部分熔融。
在(Y+Nb)-Rb和Y-Nb构造判别图上(图 7),车路沟岩体分别落入火山弧花岗岩(VAG)和火山弧+同碰撞花岗岩(VAG+Sny+COLG)区域内,反映出与火山弧花岗岩的亲缘性。同时,岩体Nb、Ti的负异常其形成于俯冲背景下,Cr、Ni正异常代表有地幔物质的参与。由此推测,车路沟岩体可能是俯冲板片流体交代地幔楔诱发地壳富含石榴石相的基性玄武岩质岩石部分熔融,并在上升过程中混染了火山弧物质所形成的埃达克岩。
区域构造研究表明,北祁连从古元古代中期开始,大陆岩石圈拉伸、减薄,并发生裂谷化(左国朝等,1987;夏林圻等, 1996, 2000;葛肖虹等,1999); 至新元古代,裂谷作用进一步加强,发育以双峰式火山岩为特征的大陆裂谷火山作用;到晚寒武世,最终发生大陆裂解和分离,形成北祁连早古生代洋盆,于奥陶纪北祁连洋盆进入俯冲消减和弧后盆地协同演化阶段,发育大量岛弧和弧后盆地火山岩(左国朝等,1987;夏林圻等, 1991, 1996;葛肖虹等,1999;张旗等,2000;Xia et al., 2003;曾建元等,2007;夏小洪等,2010;Song et al., 2013),至445~424 Ma,洋盆闭合进入陆内碰撞和深俯冲过程(Xia et al., 2003;吴才来等,2006;Zhang et al., 2007)。夏林圻等认为,北祁连加里东造山带是在前寒武纪基底之上发生拉张(679~574 Ma), 至寒武纪末期到早奥陶世(522~495 Ma)形成洋盆,奥陶纪(469~445 Ma)自南西向北东往华北大陆板块之下俯冲,大洋板块持续俯冲致使洋盆闭合(445~428 Ma)。
前人在北祁连造山带中段毛藏寺、北祁连东段银硐梁、北祁连走廊南山北坡大野口均发现了埃达克岩,上述埃达克岩体同位素年龄集中在446~455.8 Ma,均为北祁连早古生代沟弧盆构造环境的产物(王金荣等,2006;赵辛敏等,2018;唐卓等,2018)。本文获得的车路沟岩体的结晶年龄为(462.1±3.8)Ma,与前人研究认为祁连洋向北俯冲的时间吻合,说明车路沟岩体是在奥陶纪祁连洋自南西往北东持续向华北板块之下俯冲过程中形成的。
如前文所述,车路沟岩体具埃达克岩特征,是奥陶纪时期与祁连洋持续向华北板块俯冲作用有关的俯冲洋壳部分熔融和壳幔岩浆混合成因的花岗岩。
7. 结论
(1)车路沟岩体为准铝质低钾钙碱性系列,具有富硅、富铝、富钠、高Mg#、高Sr、高Sr/Y和低HREE、低Y、低Yb的特征,具典型埃达克岩的地球化学特征。
(2)车路沟岩体中英云闪长玢岩的锆石LA -ICP-MS U-Pb测年结果表明,其结晶年龄为(462.1±3.8)Ma,属中奥陶世。
(3)根据岩石学、岩石地球化学研究,结合前人区域构造研究成果,推测车路沟岩体为奥陶纪祁连洋持续向华北板块俯冲,诱使俯冲洋壳部分熔融形成的埃达克岩。
-
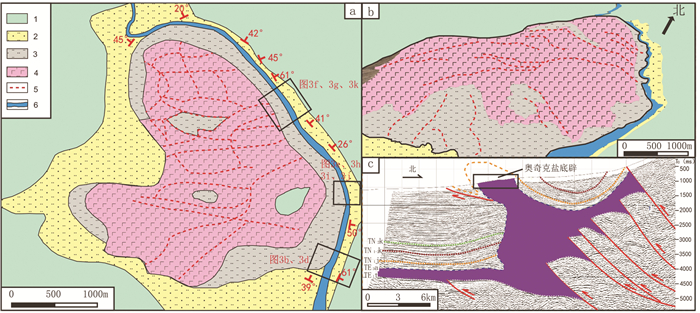
图 2 奥奇克盐底辟变形样式图
a—奥奇克盐底辟野外地质填图(据王会萍,2011修改);b—奥奇克盐底辟三维遥感解译图;c—过奥奇克盐底辟南北向地震剖面解释图(剖面位置见图 1);1—中新统康村组砾岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩、粉砂岩;2—中新统吉迪克组砂岩、粉砂岩;3—渐新统阿瓦特组含岩泥岩、泥质、膏盐;4—渐新统阿瓦特组表面析出的盐岩;5—岩底辟表面冲沟;6—干河道
Figure 2. Deformation pattern of the Ochirbat salt diapir
a-Field mapping of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir (modified from Wang Huiping, 2011); b-3D remote sensing interpretation image of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir; c-Interpretation of a N-S direction seismic profile across the Ochirbat Salt Diapir (the position of the seismic profile is shown in Fig 1). 1-Miocene Kangcun Formation conglometrate, gravel-bearing sandstone, sandstone and siltstone; 2-Miocene Jidique Formation sandstone and siltstone; 3- Oligocene Awat Formation salt- bearing mudstone and gypsum salt; 4- Oligocene Awat Formation salt rock on the surface; 5-Surfacegully of salt diapir; 6-Dry channel
图 3 奥奇克盐底辟野外相关照片
a—奥奇克盐底辟整体形态照片(据李丽, 2008修改);b—奥奇克盐底辟东南缘野外照片,展示了盐底辟和东部围岩的界线,盐上地层可见明显的向斜构造;c—奥奇克盐底辟南部盐上地层变形特征,可见冲断构造和背斜构造;d—奥奇克盐底辟东南缘野外照片,展示了盐底辟和南部围岩的界线;e—奥奇克盐底辟东缘野外照片,河流限制了盐底辟的边界,盐上地层掀斜构造明显;f—奥奇克盐底辟东部盐上吉迪克组和康村组地层界线;g—奥奇克盐底辟东北缘边界,地形较陡峭,新鲜的盐岩大量出露地表;h—奥奇克盐底辟东缘盐岩流动构造,盐岩表面冲沟发育;i—奥奇克盐底辟表面的微型峰丛构造;j—奥奇克盐底辟表面的梳状溶痕构造;k—奥奇克盐底辟正在发生的溶蚀坍塌构造.图b、d、e、f、g、h、i、j、k的位置可见图 2a
Figure 3. Photos of the Ochirbat salt diapir in the field
a-Panorama of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir(modified from the reference Li, 2008); b-Field photo of the southeastern edge of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir, showing the boundary between the diapir and the eastern surrounding rocks.Syncline structure can seen in the surrounding rocks. c Deformation characteristics of the overburden of salt to the south of the diapir. Thrust fault and anticline structure can be seen in this photo. d Field photo of the southeastern edge of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir, showing the boundary between the diapir and the southern surrounding rocks. e Field photo of the eastern edge of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir. The river limits the boundary of the diapir and tilting structure can be seen in the overburden. f Boundary of the Jidike Formation and Kangcun Formation of the overburden on the eastern edge of the diapir. g Field photo showing the northeastern edge of the diapir. The topography is relative steep and fresh salt can be seen in the surface.h Flowing structure in the eastern edge of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir, and gullies can be seen on the weathering surface of the diapir. i rillenkarren structure on the fresh surface of the diapir. k collapse structure which is happening in the Ochirbat Salt Diapir. The position of the photoes b, d, e, f, g, h, I, j, k can be seen in Fig 2a
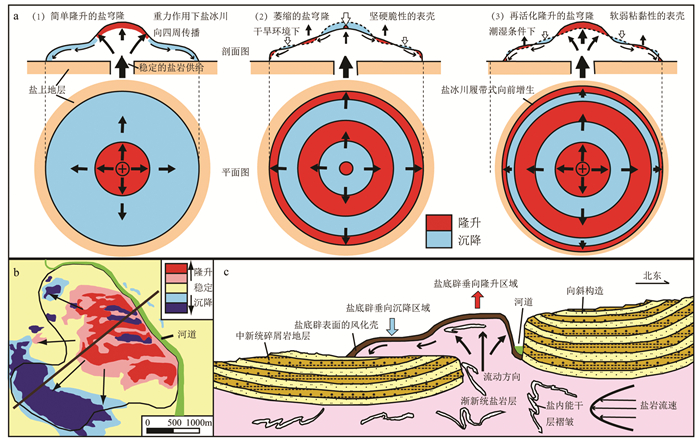
图 4 奥奇克盐底辟流变模式图
a—InSAR图像与盐底辟流变剖面对应关系模型(据Aftabi et al., 2010修改);b—奥奇克盐底辟2003年6月—2010年10月间平均垂向变化;c—奥奇克盐底辟流变剖面(剖面位置可见图 4b)
Figure 4. Rheological model of the Ochirbat salt diapir
a-Model of the corresponding relationship between the InSAR images and rheological profiles of diapirs(modified from Aftabi et al., 2010). bAverage vertical change of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir from 2003.6 to 2010.10. c-Rheological profile of the Ochirbat Salt Diapir (the position of the profile can be seen in Fig 4b)
-
Aftabi P, Roustaie M, Alsop G I, Talbot C J. 2010. InSAR mapping and modelling of an active Iranian salt extrusion[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 167(1):155-170. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-165
Baikpour S, Zulauf G, Dehghani M, Bahroudi A. 2010. InSAR maps and time series observations of surface displacements of rock salt extruded near Garmsar, northern Iran[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 167(1):171-181. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492009-058
Barnhart W D, Lohman R B. 2012. Regional trends in active diapirism revealed by mountain range-scale InSAR time series[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(8):89-106. doi: 10.1029/2012GL051255
Bruthans J, Asadi N, Filippi M, Vilhelm Z, Zare M. 2007. A study of erosion rates on salt diapir surfaces in the Zagros Mountains, SE Iran[J]. Environmental Geology, 53(5):1079-1089. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0734-6
Chen Shuping, Tang Liangjie, Jia Chengzhao, Pi Xuejun, Xie Huiwen. 2004. Salt tectonics in the western Kuqa depression and its relation to oil and gas distribution[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 25(1):30-34, 39(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20949519
Cheng Xiaodao, Li Jianghai, Cheng Haiyan, Deng gang. 2013. Typical surface salt structure and deformation characteristics in western Kuqa depression, Tarim basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 34(2):189-192(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XJSD201302016.htm
Colón C, Webb A A G, Lasserre C, Doin M P, Baudoin P F. 2016. The variety of subaerial active salt deformations in the Kuqa foldthrust belt (China) constrained by InSAR[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 450:83-95. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=b9a224c13a403f0184d59620d0874bd4
Davison I, Alsop I, Blundell D. 1996. Salt tectonics:Some aspects of deformation mechanics[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 100(1):1-10. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.100.01.01
Frumkin A. 1994. Hydrology and denudation rates of halite karst[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 162(1-2):171-189. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(94)90010-8
Frumkin A. 1994. Morphology and development of salt caves[J]. National Speleological Society Bulletin, 56:82-95. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/266160224_Morphology_and_development_of_salt_caves
Frumkin A. 1996. Structure of northern Mount Sedom salt diapir(Israel) from cave evidence and surface morphology[J]. Israel Journal of Earth Sciences, 45(2):73-80. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/266209704_Structure_of_northern_Mount_Sedom_salt_diapir_Israel_from_cave_evidence_and_surface_morphology
Frumkin A. 1998. Salt cave cross-sections and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Geomorphology, 23(2/4):183-191. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169555X98000026
Huang Shaoying, Wang Yueran, Wei Hongxing. 2009. Characteristics of salt structures and its evolution in Kuqa depression, Tarim basin[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 33(1):117-123(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DGYK200901016&dbcode=CJFD&year=2009&dflag=pdfdown
Jackson M P A, Vendeville B C. 1994. Regional extension as a geologic trigger for diapirism[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 106(1):57-73. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1994)106<0057:REAAGT>2.3.CO;2
Jiří Bruthans, Filippi M, Zare M, Churackova Zdenka, Asadi N, Fuchs M, Adamovic Jiri. 2010. Evolution of salt diapir and karst morphology during the last glacial cycle:Effects of sea-level oscillation, diapir and regional uplift, and erosion (Persian Gulf, Iran)[J]. Geomorphology, 121(3):291-304. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=60c613c62f0dc5e57b8e9a778b06fd87
Johnson K S. 1997. Evaporite karst in the United States[J]. Carbonates & Evaporites, 12(1):2-14.
Li J, Webb A A G, Mao X, Eckhoff I, Colon C, Zhang K, Wang H, Li A, He D. 2014. Active surface salt structures of the western Kuqa fold-thrust belt, northwestern China[J]. Geosphere, 10(6):1219-1234. doi: 10.1130/GES01021.1
Li Li. 2008. Research and development conception of salt dome geological relics in Wensu area, Xinjiang[D]. Chang'an University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Yanyou, Qi Jiafu. 2012. Salt-related contractional structure and its main controlling factors of Kelasu structural zone in Kuqa depression:Insights from Physical and numerical experiments[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 47(3):607-617(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S187770581201137X
Lucha P, Cardona F, Gutiérrez F, Guerrero J. 2008. Natural and human-induced dissolution and subsidence processes in the salt outcrop of the Cardona Diapir (NE Spain)[J]. Environmental Geology, 53(5):1023-1035. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0729-3
Neng Yuan, Qi Jiafu, Xie Huiwen, Li Yong, Lei Ganglin, Wu Chao. 2012. Structural characteristics of northern margin of Kuqa depression, Tarim basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(9):1510-1519(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201209014.htm
Qi Jiafu, Lei Ganglin, Li Minggang, Gu Yongxing. 2009. Analysis of structure model and formation mechanism of Kelasu structure zone, Kuqa depression[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 33(1):49-56(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200901008.htm
Qi Jiafu, Li Yong, Wu Chao, Yang Shujiang. 2013. The interpretation models and discussion on the contractive structure deformation of Kuqa depression, Tarim basin[J]. Geology in China, 40(1):106-120(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201301009.htm
Rosen P A, Hensley S, Joughin I R, Li F K, Madsen S N, Rodriguez E, Goldstein R M. 2000. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 88(3):333-382. doi: 10.1109/5.838084
Sesiano J. 2006. Evolution actuelle des phénomènes karstiques dans la Cordillera de la Sal (Atacama, Nord Chili)[J]. Karstologia, 47:49-54. http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=2125521
Talbot C J, Pohjola V. 2009. Subaerial salt extrusions in Iran as analogues of ice sheets, streams and glaciers[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 97(1/4):155-183. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825209001469
Tang Liangjie, Yu Yixin, Yang Wenjing, Peng Gengxin, Lei Ganglin, Jin Wenzheng. 2006. Internal deformation features of detachment layers in the front of the Kuqa foreland fold-thrust belt[J]. Geology in China, 33(5):944-951(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285351201_Internal_deformation_features_of_detachment_layers_in_the_front_of_the_Kuqa_foreland_fold-thrust_belt
Tang Liangjie, Yu Yixin, Yang Wenjing, Peng Gengxin, Lei Ganglin, Ma Yujie. 2007. Paleo-uplifts and salt structures and their influence on hydrocarbon accumulations in the Kuqa depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(2):145-150(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200702001.htm
Tang Pengcheng, Wang Xin, Xie Huiwen, Lei Ganglin, Huang Shaoying. 2010. The Quele area of the Kuqa depression, Tarim basin, NW China:Cenozoic salt structures, evolution and controlling factors[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(12):1735-1745(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201012003.htm
Wang Honghao, Li Jianghai, Li Weibo, Huang Shaoying, Neng Yuan. 2016. Deformation behavior of underground salt rock in Kuqa Kelasu tectonic zone[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 23(4):20-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98573X/201604/669728007.html
Wang Huiping. 2011. Ochirbat salt diapiric structure and hydrocarbon accumulation in the canyon of Xinjiang Wensu county[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science & Technology, 31(1):59-63(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201101014.htm
Wang Xin, Tang Pengcheng, Xie Huiwen, Lei Ganglin, Huang Shaoying. 2009. Cenozoic salt structures and evolution in the western Kuqa depression, Tarim basin, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(1):57-65(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200901009.htm
Wang Zhaoming, Wang Tingdong, Xiao Zhongyao, Xu Zhiming, Li Mei, Lin Feng. 2002. Migration and accumulation of natural gas in Kela-2 gas field[J]. The Chinese Science Bulletin, z1:103-108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb-e2002Z1015
Warren J K. 2006. Evaporites:sediments, resources and hydrocarbons[M]. Springer Science & Business Media.
Weinberger R, Waldmann N, Frumkin A, Gardosh M, Wdowinski S. 2006. Quaternary rise of the sedom diapir, Dead Sea basin[J]. Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, 401:33-51. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229392715_Quaternary_rise_of_the_Sedom_Diapir_Dead_Sea_Basin
Wu Guanghui, Wang Zhaoming, Liu Yukui, Zhang Baoshou. 2004. Kinematics characteristics of the Kuqa depression in the Tarim basin[J]. Geological Review, 50(5):476-483(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200405005.htm
Wu Zhenyun, Yin Hongwei, Wang Xin, Xu Shijin. 2015. The structural features and formation mechanism of exposed salt diapirs in the front of fold-thrust belt, western Kuqa depression[J]. Journal of Nanjing University, (3):612-625(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ201503018.htm
Yin Hongwei, Wang Zhe, Wang Xin, Wu Zhenyun. 2011. Characteristics and mechanics of Cenozoic salt-related structures in Kuqa foreland Basins:Insights from physical modeling and discussion[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 17(2):308-317(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288265154_Characteristics_and_mechanics_of_Cenozoic_salt-related_structures_in_Kuqa_foreland_basins_Insights_from_physical_modeling_and_discussion
Yu Yixin, Tang Liangjie, Li Jingchang, Yang Wenjing, Jin Wenzheng, Peng Gengxin, Lei Ganglin, Wan Guimei. 2006. Influence of basement f aults on the development of salt structures in the kuga foreland fold-and-Thrust belt in the Northern Tarim basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(3):330-336(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200603003.htm
Zebker H A, Goldstein R M. 1986. Topographic mapping from interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 91(B5):4993-4999. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB05p04993
Zhao Mengjun, Lu Xuesong, Zhuo Qingong, Li Yong, Song Yan, Lei Ganglin, Wang Yuan. 2015. Characteristics and distribution law of hydrocarbon accumulation in Kuqa foreland basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(4):395-404(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/282275987_Characteristics_and_distribution_law_of_hydrocarbon_accumulation_in_Kuqa_foreland_basin
Zhao Mengjun, Wang Zhaoming, Zhang Shuichang, Wang Qinghua, Song Yan, Liu Shaobo, Qin Shengfei. 2005. Accumulation and features of natural gas in the Kuqa foreland basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica. 79(3):414-422(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2005.tb00907.x
陈书平, 汤良杰, 贾承造, 皮学军, 谢会文. 2004.库车坳陷西段盐构造及其与油气的关系[J].石油学报, 25(1):30-34, 39. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2004.01.006 程小岛, 李江海, 程海艳, 邓罡. 2013.库车坳陷西部地表典型盐构造样式及变形特征[J].新疆石油地质, 34(2):189-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201302016.htm 黄少英, 王月然, 魏红兴. 2009.塔里木盆地库车坳陷盐构造特征及形成演化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 33(1):117-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.015 李丽. 2008.新疆温宿地区的盐丘地质遗迹研究及开发构想[D].长安大学. 李艳友, 漆家福. 2012.库车坳陷克拉苏构造带分层收缩构造变形及其主控因素[J].地质科学, 47(3):607-617 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2012.03.003 能源, 漆家福, 谢会文, 李勇, 雷刚林, 吴超. 2012.塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部边缘构造特征[J].地质通报, 31(9):1510-1519. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.09.014 漆家福, 雷刚林, 李明刚, 谷永兴. 2009.库车坳陷克拉苏构造带的结构模型及其形成机制[J].大地构造与成矿学, 33(1):49-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.007 漆家福, 李勇, 吴超, 杨书江. 2013.塔里木盆地库车坳陷收缩构造变形模型若干问题的讨论[J].中国地质, 40(1):106-120. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130107&flag=1 汤良杰, 余一欣, 杨文静, 彭更新, 雷刚林, 金文正. 2006.库车前陆褶皱冲断带前缘滑脱层内部变形特征[J].中国地质, 33(5):944-951. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.05.002 汤良杰, 余一欣, 杨文静, 彭更新, 雷刚林, 马玉杰. 2007.库车坳陷古隆起与盐构造特征及控油气作用[J].地质学报, 81(2):145-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200702001.htm 唐鹏程, 汪新, 谢会文, 雷刚林, 黄少英. 2010.库车坳陷却勒地区新生代盐构造特征, 演化及变形控制因素[J].地质学报, 84(12):1735-1745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201012003.htm 汪新, 唐鹏程, 谢会文, 雷刚林, 黄少英. 2009.库车坳陷西段新生代盐构造特征及演化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 33(1):57-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.008 王洪浩, 李江海, 李维波, 黄少英, 能源. 2016.库车克拉苏构造带地下盐岩变形特征分析[J].特种油气藏, 23(4):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.04.004 王会萍. 2011.新疆温宿峡谷盐底辟构造与油气聚集[J].西安科技大学学报, 31(1):59-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2011.01.012 王招明, 王廷栋, 肖中尧, 徐志明, 李梅, 林峰. 2002.克拉2气田天然气的运移和聚集[J].科学通报, z1:103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2002S1015.htm 邬光辉, 王招明, 刘玉魁, 张宝收. 2004.塔里木盆地库车坳陷盐构造运动学特征[J].地质论评, 50(5):476-483. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.05.005 吴珍云, 尹宏伟, 汪新, 徐士进. 2015.库车坳陷西段褶皱-冲断带前缘盐底辟构造特征及形成机制[J].南京大学学报(自然科学), (3):612-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ201503018.htm 尹宏伟, 王哲, 汪新, 吴珍云. 2011.库车前陆盆地新生代盐构造特征及形成机制:物理模拟和讨论[J].高校地质学报, 17(2):308-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.02.016 余一欣, 汤良杰, 李京昌, 杨文静, 金文正, 彭更新, 雷刚林, 万桂梅. 2006.库车前陆褶皱-冲断带基底断裂对盐构造形成的影响[J].地质学报, 80(3):330-336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.03.003 赵孟军, 鲁雪松, 卓勤功, 李勇, 宋岩, 雷刚林, 王媛. 2015.库车前陆盆地油气成藏特征与分布规律[J].石油学报, 36(4):395-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201504001.htm 赵孟军, 王招明, 张水昌, 王清华, 宋岩, 柳少波, 秦胜飞. 2005.库车前陆盆地天然气成藏过程及聚集特征[J].地质学报, 79(3):414-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200503023.htm -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 计波,李向民,黄博涛,王磊,王国强. 南祁连党河南山地区拐杖山岩群玄武岩年代学、地球化学及其构造环境. 中国地质. 2024(03): 965-977 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 杨彦,黄增保,郭小刚,许延龙,颜华. 北祁连榆树沟山金矿区花岗闪长斑岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义. 黄金科学技术. 2024(03): 387-399 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李平,高晓峰,吕鹏瑞,朱小辉,陈隽璐. 祁连山–柴北缘地区岩浆活动的时空分布、成因演变及构造岩浆演化. 西北地质. 2023(04): 283-317 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 白斌,俞胜,刘杰,边成辉,戴霜. 甘肃党河南山地区美丽沟岩体地球化学特征、锆石年代学及地质意义. 矿物学报. 2021(02): 181-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨镇熙,丁书宏,张晶,樊新祥,孔维琼,赵吉昌,荆德龙. 北山造山带早泥盆世埃达克岩的发现及地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志. 2021(02): 185-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘建宏,叶得金,齐瑞荣,贾志磊,王海琦. 甘肃省地矿局“十三五”期间地质勘查进展与成果. 甘肃地质. 2021(02): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: