Zirzon U-Pb age and petrogenisis of plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi, Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia and its collision orogeny
-
摘要:
内蒙古克什克腾旗长岭子斜长花岗斑岩位于大兴安岭锡林浩特增生杂岩带内。本文对长岭子斜长花岗斑岩进行了主微量元素地球化学以及锆石U-Pb年代学和Lu-Hf同位素研究。长岭子斜长花岗斑岩锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(248.1±4.7)Ma,是早三叠世岩浆活动的产物;继承锆石除外,样品中锆石具有正的εHf(t)值(5.78~12.41),二阶段模式年龄TDM2分别为914~488 Ma。长岭子斜长花岗斑岩具有较高的SiO2、Na2O和Al2O3含量以及较低的Fe2O3、MgO和CaO含量,属于偏铝质-过铝质的低钾-钙碱性系列I型花岗岩,富集Rb、K、U、Th、Pb、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nd、Ta、Ti等高场强元素。同时,斜长花岗斑岩具有高Sr低Y以及高Sr/Y比等特点,具有典型的埃达克质岩石特征,形成于加厚下地壳的部分熔融。综合上述地球化学特征,本文认为长岭子斜长花岗斑岩来源于加厚新生下地壳的部分熔融,表明早三叠世兴蒙地区并非岛弧的环境,而是处于碰撞造山环境,古亚洲洋在该时期已经闭合。
Abstract:The Changlingzi plagiogranite porphyry is located in the Xilinhot Late Paleozoic Accretion Complex within the Da Hinggan Mountains. This study is focused on the zircon U -Pb isotopic geochronology, Hf isotopic composition analysis and geochemistry of the Changlingzi plagiogranite porphyry. Zircon crystals from the plagiogranite porphyry yielded weighted average 206Pb/238U age of (248.1±4.7)Ma. The zircons from this porphyry have positive εHf(t) values from 5.78 to 12.41, with TDM2(Hf) ages from 914 to 488Ma. The plagiogranite porphyry has high content of SiO2, Na2O and Al2O3, and low content of TiO2, MgO and CaO, showing a metaluminous-peraluminouslow-K to calc-alkaline affinity, with LREE enrichment and HREE depletion, suggesting I-type granite. In addition, the plagiogranite porphyry has high Sr and low Y values as well as high Sr/Y ratios (74.5~103.4), indicating that the plagiogranite porphyry belongs to adakite. It is suggested that the plagiogranite porphyry was formed by partial melting of the thickened newborn lower crust. And in Early Triassic, Xing' an-Mongolian orogenic belt was in a collisionorogeny tectonic setting, indicating that the Paleo-Asian Ocean had been closed in this period.
-
1. 引言
能源与环境问题一直是困扰世界各国可持续发展的重大问题,进入21世纪,节能减排、开发新能源和走可持续发展道路受到越来越多的关注(刘凯等,2017)。地球是个巨大的热库,其内核(地核)的温度高达约6000℃(汪集旸等,2012)。地核与地表巨大的温差使得地球在不断地向外(大气层)散发着热量,同时地壳内部放射性衰变热、势能转换热、摩擦热等也在不断生成与供给(Clauser,2005)。而在当前的技术经济和地质环境条件下,可以从地壳表面下一定深度内科学、合理地开发出来的地下岩石中的地热能量和地热流体中的热能量及其伴生的有用组分被称之为地热资源(孔维臻,2013)。地热资源是一种极具竞争力的清洁可再生能源,很大程度上可以缓解因大量使用化石能源所造成严重的空气污染问题(马伟斌等,2016),按其成因和产出条件可分为水热型和干热岩型,利用方式分为直接利用和发电两种。
断裂构造对地热田分布具有直接的控制作用(苗可等,2012),因为它是地热水主要储存和运移通道,要掌握地热水的赋存特征,必须掌握断裂的产状及展布特征。江西省会昌县坝背地区地处武夷山和南岭余脉地带,受太平洋构造域的制约,晚侏罗世发生大规模岩浆侵入和火山喷发(燕山期),早白垩世晚期以后发生了强烈的伸展作用,强烈的地壳运动形成密集的断裂构造,成为地下热源导热构造带,并在断裂带附近形成地热异常区。区内有分布于会昌盆地东侧大富足岩体内的河草坑铀矿田和桂坑岩体中的铀矿化(蔡煜琦等,1997),说明区内具有放射性衰变热的持续供给来源。
地下的热作用能明显改变岩石的地球物理性质,构造带、地热田的生储盖等不同部位均具有较明显的电性差异(Wright et al., 1985),地热区电阻率的空间分布不仅受围岩性质的影响,还与勘探对象——热水的分布直接有关(切列缅斯基,1982)。总体上,随着温度的升高,电阻率在不断的降低,可见在地热田勘查中,低阻体成为最重要的寻找目标,由于它的直接指示作用和地热田不同部位电性差异明显,电法和电磁法也就成为地热资源勘探中最直接有效的方法技术(曾昭发等,2012)。直流电测深法、高密度电法、激发极化法、瞬变电磁法等都不乏成功的范例,而CSAMT更是因为其抗干扰能力强、探测深度大、横向分辨率高、受高阻层屏蔽作用影响小等优点,越来越多地被应用到地热勘查中(周仕新,2013)。为了查明会昌县坝背勘查区各断裂构造的产状、规模及深部变化特征,为寻找地热水钻孔布置提供依据,遵循从已知到未知,由浅至深的勘探原则,项目组首先在已知温泉位置布置3条高密度试验测线,确定地球物理方法在该测区的有效性和导水断层的形态、主要物性参数等,接着在已知温泉位置以南布置4条高密度测线,然后在高密度电阻率法资料初步解释成果的基础上再施工CSAMT。
2. 地质概况
会昌县坝背区域上地处武夷山和南岭余脉地带,属低山丘陵地区,地势由西南向东北倾斜,境内峰峦起伏。勘查区最高点在南部海拔标高约389.9 m,最低点海拔标高约190 m,最大相对高差近200 m。工作区及周边地球物理工作程度低,未开展过系统的地球物理工作。区域地质概况详细论述如下(图 1)。
2.1 地层
勘查区内地层岩性特征由新到老分别为第四系(Qh1),上白垩统周田组(K2z)、茅店组(K2m2),下白垩统鸡笼嶂组(K1j)、震旦系桃溪岩组(Pt32 - 3 tx)。其中Qh1主要分布在河水两岸及山间沟谷附近,成因类型为冲积作用,岩性具有二元结构,上部为黄褐色、褐色亚黏土、亚砂土,厚度1.0~2.5m;下部为砂砾石层,砾石成分为石英砂岩,粒径一般2~4 cm,大者达10 cm,结构松散,厚度1.5~3.5 m,总厚度2.5~ 6.0 m。K2z大面积出露勘查区内,为紫红色中厚层状钙质粉砂岩夹薄层细砂岩,下部为紫红色细粒石英砂岩,厚度170~450 m。K2m2大面积出露勘查区西侧,为紫红色巨厚层状砾岩夹钙质粉砂岩、泥岩及粗砂岩,砾石成分以晶屑凝灰岩为主,厚度300~ 800 m。K1j出露于勘查区东北侧,为杂色流纹质熔结凝灰岩,厚度大于200 m。Pt32-3tx小面积出露勘查区北东角,为勘查区褶皱基底,岩性主要为杂色黑云斜长变粒岩、石英片岩,厚度大于400m。这些地层的成分与结构特征无疑为地热水的存储提供了良好条件。
2.2 岩浆岩
勘查区出露岩浆岩来自两个不同时期,出露面积都较大。一是分布于勘查区北东角印支期晚三叠世罗珊序列(T3γt)黑云母、二云母花岗岩;二是分布于勘查区南东角加里东期早志留世汤湖序列(S1gnγ-ξγ)二长、正长花岗岩。
2.3 地质构造
本区的区域大地构造单元在加里东期为中南武夷山褶皱带(江西省区域地质志,1984),之后受太平洋构造域的制约,晚侏罗世发生大规模岩浆侵入和火山喷发(燕山期),在武夷山隆起地带形成一系列的NE、NNE向火山岩盆地,到早白垩世晚期以后,受太平洋板块北北西向左行走滑影响,发生了强烈的伸展作用,盆地由坳陷转为断陷,沉积了巨厚的红色碎屑岩系,不整合地叠覆于火山岩盆地之上。
2.4 地球物理特征
周田组为紫红色中厚层状钙质粉砂岩夹薄层细砂岩,紫红色细粒石英砂岩其视电阻率小于200 Ω·m。茅店组为紫红色巨厚层状砾岩夹钙质粉砂岩、泥岩及粗砂岩,砾石成分以晶屑凝灰岩为主其视电阻率为300~400 Ω·m。鸡笼嶂组为杂色流纹质熔结凝灰岩其视电阻率400~600 Ω·m。震旦系桃溪岩组,为勘查区褶皱基底,岩性主要为杂色黑云斜长变粒岩、石英片岩,其视电阻率大于800 Ω·m。断裂破碎带多系充水,其电阻率相对围岩较低,在视电阻率断面图上多呈现低阻特征,异常等值线密集或扭曲。这就为电法探测断裂破碎带提供了物性条件。
3. 数据采集及处理
3.1 测网布置
勘探区地球物理测线的布置安排在地表调查后,根据地表地质调查情况来确定地球物理测线的起止点。因勘探区内及相邻勘探区均没开展过地球物理工作,进一步了解地球物理方法在该测区的有效性和导水断层的形态、主要物性参数等,为勘查区地球物理参数的设置和地球物理资料的解释工作提供依据,在勘探区外已知的车心出露点布设一条高密度电阻率测量线,编号为S1线,测线长度为0.3 km。由于车心热水泉出露点走向长约50 m,方位为北东10°左右,S1线施工完后视电阻率断面图反映不够明显,因此在S1线南约240 m处布置了长750 m的S2线,方位角为69°;在与车心热水泉出露点走向斜交处布置了长590 m的S3线,方位角为344°,同时将S1线延长到750 m,受地形限制其方位角调整为93°,3条测线极距均为10 m。然后根据地表地质调查情况在勘探区内共布置4条高密度测线,线距500 m,极距10 m。由北向南分别为G1线、G2线、G3线和G4线,每条测线长约1.65 km,方位角为102°。G1测线东侧遇有陡坎、悬崖等障碍物影响布线,因此,实际布线时G1测线往南偏移150 m左右(图 1)。
在高密度电阻率法资料的初步解释成果的基础上,确定在勘探范围内重点勘探区开展可控源音频大地电磁测深工作,由于在勘探区中部有一由西南-北东走向的220 kV的高压电线,对可控源音频大地电磁测深的野外测量数据采集数据质量会有一定的影响,故勘探区内根据实际情况布置了5条可控源音频大地电磁测深测线,测线由南向北、由西向东分别为K1线、K2线、K3线、K4线、K5线。线距在300~500 m,长度在300~840 m,点距30 m,方位角为92°。K2线、K4线、K5线基本上与高密度电阻率法测线重合(图 1)。
3.2 数据采集
高密度电阻率法使用的仪器是重庆奔腾数控技术研究所生产的WDJD-3型和WGMD-1型高密度电阻率测量系统。在试验线S1线布置了两个排列同时用高密度电阻率法α1排列装置和α2排列装置进行测量,经对资料的分析认为采用高密度电阻率法α1排列装置进行测量效果更佳,因而决定高密度电阻率测量工作采用α1排列装置(图 2),电极距10 m,60根电极,排列长度590 m。
CSAMT投入的仪器设备为加拿大凤凰公司的V8网络化多功能电法仪,为保证工作质量,在测量之前标定了仪器和磁棒,并进行了一致性测试,测试结果均符合规范要求。CSAMT测点点距30 m,频率范围1~9600 Hz,有效探测深度大于2.0 km。采集方式为标量模式,接收端和发射端工作示意图如图 3。本项目布设了2个场源,一号场源极距为1316 m,最小收发距为9810 m,在第一天工作结束后,发现频率在100 Hz左右进入近场并且数据信躁比大,于是对发射场源进行了调整,并通过增大收发距,加大供电极距,增大供电电流来保证数据质量。最终选定二号场源位置,极距为2079 m,最小收发距为13269 m,最大供电电流17A。
本次可控源音频大地电磁法测量水平方向电场(MN)平行于场源(AB),水平磁场垂直于场源布设。共设计55个频点,工作频带为1~9600 Hz(表 1),频点间隔均匀分布,高、中频段适度加密。
表 1 CSAMT工作频率Table 1. CSAMT working frequency list
3.3 数据质量评价
本项目共获得高密度电阻率法测量坐标测点261个,质量检查点21个,质量检查点占测点总数7.4%,高密度电阻率法测点数据没有废点,检查点相对均方误差均小于5%,数据质量良好;可控源音频大地电磁测点82个,质量检查点5个,质量检查点占测点总数5.7%,不存在三类点,检查点相对均方误差均小7%,数据质量良好。
3.4 数据处理
高密度电法野外采集的数据传入计算机后,对每个排列所测数据经软件(RES2DINV)进行必要的一些编辑,对个别畸变点进行剔除(图 4)。由于测线地形相差大,因此在进行二维反演时必须进行地形改正,本次计算选用Schwarz-Christoffel变换法作地形改正计算。然后使用有限差分法进行反演得到每个排列的视电阻率断面图,根据反演结果所得的视电阻率断面图,进行破碎带等地质体的初步划分。然后对每个排列所测的数据进行数据拼接得到整条测线的数据,经一系列处理后,得到整条测线的视电阻率断面图。
CSAMT数据处理以测线为单位进行,数据预处理使用的软件为加拿大凤凰公司配套软件CMT Pro Version,通过加载数据;核对点位、极距等信息;查看数据质量来完成预处理过程,最后输出*.AVG文件用于反演。数据反演软件为CSAMT-SW,过程包括:测线记录型文件-(D File)、点位偏差校正*-J*、剔除跳点*-ED*、曲线平滑*-S2*(图 5)、删除近场频点*-WR*、删除坏道数据(重复点数据)*- WC*、静态位移校正、Bostick反演生成*.DMT文件等,最终绘制成图。
4. 电阻率模型分析
高密度视电阻率断面图是以实测数据经数据处理后按点(线)排列方式形成的地表以下不同深度的视电阻率值绘制而成。纵轴为标高,横轴为测点对应距离,剖面方向为102°(图 6、图 7)。通过已收集的钻孔资料可知地下热水是通过岩层裂隙涌向地面的,高密度电阻率法试验S3线就通过了该裂隙带,它在视电阻率断面图上反映为低阻区,据此对全区各线进行解释。鉴于高密度电阻率法的探测深度低于CSAMT,由高密度电阻率法推断的断裂或破碎带在深部的发育和延伸情况还需要CSAMT做进一步的追踪。
CSAMT的主要参数为卡尼亚视电阻率,由实测正交电、磁信号振幅计算而来,与常规电法中视电阻率的意义相同,主要反映勘探体积内岩(矿)石的综合导电性能。图 8为实测数据经处理后按点(线)排列方式形成的地表以下不同深度的卡尼亚视电阻率值绘制而成。纵轴为标高,横轴为测点对应距离,剖面方向为92°。各勘探线CSAMT二维反演电阻率断面图解译如下。
由K1线CSAMT二维反演电阻率断面图(图 8)可看出,剖面内推断的基底起伏大,基底以上地层呈不规则分布。剖面0~480 m,标高-250 m以上;剖面750~840 m,标高240~-50 m为高阻区,推断为白垩纪晚期茅店组砂砾岩。高阻体以下至基底界面区域存在明显的低阻异常带,剖面90~360 m,标高在-396~-550 m、埋深在682~814 m视电阻率值异常低,为低阻异常区,编为1号低阻异常区。剖面660~840 m,标高在-82~-176 m,埋深在396~491 m视电阻率值异常偏小,为低阻异常区,编为2号低阻异常区。剖面120 m附近,标高在230~150 m处视电阻值与两侧差异明显,推测此处有一断裂构造,结合地质资料和G1线高密度视电阻率断面图将该断裂命名为F3,该断裂构造将0~480 m的高阻错断。剖面480 m处两侧电阻率值差异显著,推断该位置有一断裂,结合地质资料和G1线高密度视电阻率断面图(图 7)将该断裂命名为F1,此构造深切至基底。剖面750 m处电阻率差异大且地层错动,推断该处有一断裂构造,此构造深切基底,且造成切割部位发生一定的凹陷,两侧则抬升的现象,结合地质资料和G1线高密度视电阻率断面图将该断裂命名为F4。
K2剖面内推断的基底起伏较小,基底以上地层呈不规则分布。剖面0~480 m处,标高在250~130 m和剖面0~270 m处,标高在-50~-170 m为高阻区,这2个高阻区认为系同一电性层被断裂F3错断所致,推断其高阻区为白垩纪晚期茅店组砂砾岩。剖面180~360 m处,标高在-200~-462 m,埋深在490~758 m视电阻率值异常偏小,存在一明显的低阻异常区,为1号低阻异常区往南的延伸。剖面390 m处电阻率两侧的差异大,延伸深,基底略微凹陷,推断存在一断裂构造,结合G1线高密度视电阻率断面图推断为F4断层往南的延伸。K3剖面内推断的基底起伏大,基底以上地层呈不规则分布;剖面0~240 m处,标高在-292~-584 m,埋深在532~ 826 m视电阻率值异常小,为低阻异常区,同样为1号低阻异常区在该处的表现。剖面120~180m处,标高在160~-220 m为高阻区,推断为白垩系晚期茅店组砂砾岩,该砂砾岩近直立,底部被F3断裂错断。剖面270~300 m处两侧的电阻率差异大,推断该位置存在一断裂构造,构造近乎直立,结合地质资料和G2线高密度视电阻率断面图推测为F4在该处的表现,基底凹陷明显。
K4剖面内推断的基底起伏明显,剖面中部位置基底隆起。剖面0~180 m处,标高120~-800 m和240~300 m处,标高50~-50 m为高阻区,这2个高阻区有错动,推断存在一断裂构造,结合地质资料和G1线高密度视电阻率断面图将该断裂命名为F5。K5剖面内推断的基底起伏平缓,基底以上地层分层明显,各种岩性在横向上分布较均匀,地表至标高-500 m范围内存在三层次高阻,其间夹杂2层厚度50~100 m的低阻区,推断此区域为白垩系茅店组砂砾岩,剖面上部的低阻区编为3号低阻异常区,3号低阻异常区顶、底标高186~131 m,埋深在95~156 m。在剖面中部的低阻区编为4号低阻异常区,4号低阻异常区顶、底标高-82~-316 m,埋深在368~600 m。剖面90~150 m处从表层到基底电性层均有错动,推断该位置存在一断裂构造,结合地质资料和G2线高密度视电阻率断面图将该断裂命名为F5。
5. 解释与讨论
区内断裂主要由一系列北北东或北东及近东西或北西向规模不等的逆冲、斜冲断层和推滑-推覆断裂构造组成,这些密集的(断裂)成为地下热源导热构造带,并在断裂带附近形成地热导常区。通过对电阻率模型的解释获得了测区高阻基底埋深在750~1250 m,基底起伏较大;同时确定了大断层F1、F3、F4、F5的性质和产状(图 8)。F1正断层分布在测区北部边缘,走向为弧形,总体为北西向,倾向为西—西南,倾角73°,断层深切至基底,为测区内导热构造。F3逆断层分布在测区西部,走向为北东向,倾向南东,倾角55°~65°,测区内走向长1800 m。F4正断层分布在测区中东部,走向在G4线— K3线为近南北向,在K3线—K1线为北东向,倾向西—北西,倾角86°,测区内走向长1800 m,深切至基底,为测区内导热构造。F5逆断层分布在测区东部,走向在G4线—G3线为近南北向,在G3线~G1线为北东向,倾向由东转南东,倾角82°,测区内走向长1300 m,深切至基底面。
本区以侵蚀构造低山地形为主,地势上东高西低,植被繁茂,构造裂隙水发育。地下水主要赋存于断裂破碎带和构造裂隙中,富水性极不均一。地下水总体运动方向由南东向北西径流,一部分在车心村的西部(温泉地)排泄于地表,另一部分沿深部构造径流出勘查区。
联合K1、K2、K3剖面图中来看,1号异常区基本上分布在以K1(270 m处)—K2(240 m处)—K3(180 m处)连线为轴线的左右两侧各约100 m范围内,东部为北东向的高阻条带,为F4深大断裂构造的反映。1号异常区在4个低阻异常区内范围最大,长约1000 m,宽约240 m,高约200 m,由南往北的走向特征为北东转向北西,是地热水赋存最为可能的区域,建议在K1线360 m处布设钻孔进行验证,孔深约800 m,满足深大断裂和基底对低阻区的深度控制。
6. 结论
(1)通过高密度和CSAMT电阻率勘测推断出F4、F1构造深切至基底界面,为深大断裂,是温泉主要的导水导热构造。
(2)依据工作区的电性结构特点,厘定了基底的岩性界面,刻画了基底面的起伏情况。
(3)根据CSAMT二维反演的断面图上的低阻异常,圈定了4个低阻异常区,其中1号异常范围最大,为本区含水有利区,亦是寻找地热水的直接依据,建议在K1线360 m处布设钻孔进行验证,孔深约800 m。
(4)验证了高密度和CSAMT电阻率法在坝北区域地热探测中的有效性,为类似地区地热勘查提供了一定的借鉴。
-
图 1 中国东北大地构造简图(a,据陈衍景等, 2012; Chen et al., 2016修改)及黄岗—甘珠尔庙地区地质简图(b,据芮宗瑶等, 1994修改)
Figure 1. Simplified tectonic map of Northeast China (a, modified after Chen et al., 2012, 2016);Sketch geological map of the Huanggang–Ganzhuermiao area (b, modified after Rui et al., 1994)
图 3 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩岩相学特征
a—斜长花岗斑岩手标本照片;b—斜长花岗斑岩中斜长石斑晶发生绢云母化,可见聚片双晶,基质主要为长英质(正交偏光);c—斜长花岗斑岩中正长石斑晶,可见典型的卡式双晶(正交偏光);d—斜长花岗斑岩中正长石斑晶(单偏光);e—斜长花岗斑岩中角闪石斑晶,角闪石被绿帘石交代(正交偏光);f—斜长花岗斑岩中黑云母斑晶(单偏光);Q—石英;Pl—斜长石;Or—正长石;Hb—角闪石;Bi—黑云母
Figure 3. Petrographic characteristics of the plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area
a-Hand specimen photo of the plagiogranite porphyry; b-The feldspar phenocrysts with sericitizationin in plagiogranite porphyry, polysynthetic twin observed in feldspar and the matrix being predominantly felsic (crossed nicols); c-The orthoclase phenocrysts in the plagiogranite porphyry with carlsbad twin observed in orthoclase (crossed nicols); d-The orthoclase phenocrysts in the plagiogranite porphyry (plainlight); e-The hornblende phenocrysts in the plagiogranite porphyry, the hornblende replaced by epidote (crossed nicols); f-The biotite phenocryst in the plagiogranite porphyry (plainlight); Q-Quartz; Pl-Plagioclase; Or-Orthocalse; Hb-Hornblende; Bi-Biotite
图 4 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩SiO2-(Na2O + K2O)图解(a,据Le Maitre, 2002)、A/CNK-A/NK图解(b,据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989)和SiO2-K2O图解(c,据Rickwood, 1989)
Figure 4. SiO2-(Na2O + K2O) (a, after Le Maitre, 2002), ACNKANK (b, after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) and SiO2-K2O (c, after Rickwood, 1989) diagrams for plagiogranite porphyries in Changlingzi area
图 5 长岭子研究区斜长花岗斑岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准化值和原始地幔标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) for plagiogranite porphyries in Changlingzi area (chondrite normalization values and primitive mantle normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
图 7 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩K2O-Na2O图解(据Collins et al., 1982)
Figure 7. K2O-Na2O diagram for plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area (after Collins et al., 1982)
图 8 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩锆石εHf(t)-t图解
(阴影部分代表兴蒙造山带东段中生代花岗岩和辉长岩,虚线框部分代表燕山地区岩浆岩;数据来源:兴蒙造山带东段和燕山地区岩浆岩锆石εHf(t)范围据Yang et al., 2006;中生代火山岩据张超等(2014)和谭皓元等(2017);林西组据朱俊宾等(2017);大石寨组据张健(2012)和作者未发表数据;宝音图群据孙立新等(2013);白垩纪花岗岩据杨奇荻等(2014)、周振华等(2011)和Zhou ZH et al., 2012;侏罗纪花岗岩据杨奇荻等(2014)、刘伟等(2007)和Liu et al., 2009;二叠纪花岗岩据Wang et al., 2017)
Figure 8. Zircon εHf(t)-t diagram for plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area
(The shaded part represents the Mesozoic granites and gabbros in the eastern segment of the Xingmeng orogenic belt, and the dotted section \ represents the magmatic rocks in the Yanshan area)Data sources: Xing'an-Mongolian Orogenic belt and Yanshan area zircon εHf(t) range after Yang et al., 2006; Mesozoic volcanic rocks after Zhang et al., 2014 and Tan et al., 2017; the Linxi Formation after Zhu et al., 2017; the Dashizhai Formation after Zhang, 2012 and the authors'unpublished data; the Baoyintu Group after Sun et al., 2013; Cretaceous granite after Yang et al., 2014 and Zhou et al., 2011, 2012; Jurassic granite after Yang et al., 2012 and Liu et al., 2007, 2009; Permian granite after Wang et al., 2017)
图 9 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩Sr/Y-Y图解(a, 据Martin, 1999)和(La/Yb)N-YbN图解(b, 据Defant et al., 1990)
Figure 9. Sr/Y-Y (a, after Martin, 1999) and (La/Yb)N-YbN (b, after Defant et al., 1990) diagrams of the plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area
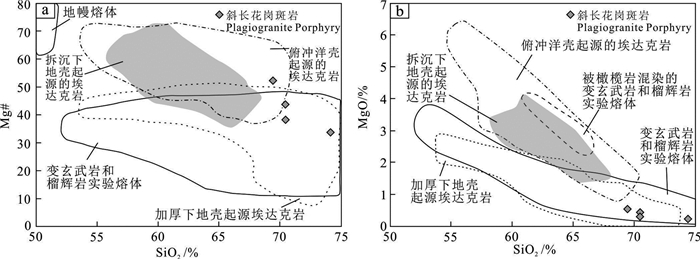
图 10 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩SiO2-Mg#(a)图解和SiO2-MgO图解(b)(据Wang et al., 2006)
Figure 10. SiO2-Mg# (a) diagram and SiO2-MgO diagram (b) for the plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area (after Wang et al., 2006)
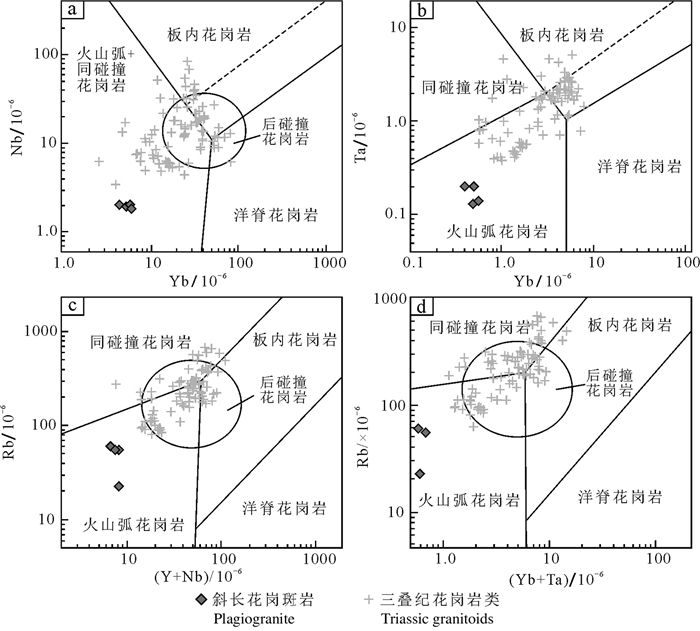
图 11 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩Nb−Y(a), Ta−Yb(b), Rb−(Y+Nb)(c)和Rb−(Yb+Ta)(d)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984, 1996;)
数据来源:三叠纪花岗岩类据李锦轶等, 2007;石玉若等, 2007;张维等, 2010; 叶栩松等, 2011;张万益等, 2012;刘建峰等, 2014; 吴荣泽等, 2015;张海华等, 2015;李晓海等, 2016
Figure 11. Nb−Y (a), Ta−Yb (b), Rb−(Y+Nb) (c) and Rb−(Yb+Ta) (d) diagram (after Pearce et al., 1984, 1996) of plagiogranite porphyries in Changlingzi area
Data sources: Triassic granitoids after Li et al., 2007; Shi et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010; Ye et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015 and Li et al., 2016
表 1 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)分析结果
Table 1 Major (%) and trace(10−6) elements compositions of the plagiogranite porphyries in Changlingzi area

表 2 长岭子斜长花岗斑岩锆石LA−ICP−MS U−Pb定年分析结果
Table 2 LA−ICP−MS Zircon U−Pb analysis for the plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area

表 3 长岭子研究区斜长花岗斑岩锆石Lu−Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Lu−Hf isotope analysis for the plagiogranite porphyry in Changlingzi area

-
Bao Qingzhong, Zhang Changjie, Wu Zhili, Wang Hong, Li Wei, Sang Jiahe, Liu Yongsheng. 2007. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of a Carboniferous quartz-diorite in Baiyingaole area, Inner Mongolia and its implications[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 37(1):15-23(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284025741_SHRIMP_U-Pb_zircon_geochronology_of_a_Carboniferous_quartz-diorite_in_Baiyingaole_area_Inner_Mongolia_and_its_implications?ev=auth_pub
Chen Bin, Chen Changjian, He Jingbo, Liu Ankun. 2013. Origin of Mesozoic high-Mg adakitic rocks from northeastern China:Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(20):1941-1953(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/972012-1254
Chen Bin, Jahn B M, Tian Wei. 2009. Evolution of the Solonker suture zone:Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic ratios and whole-rock Nd-Sr isotope compositions of subduction- and collision-related magmas and forearc sediments[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3):245-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.007
Chen Bin, Jahn B M, Wilde S, Xu Bei. 2000. Two contrasting paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia, China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 328(1):157-182. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001827
Chen Bin, Ma Xinghua, Liu Ankun, Muhetaer Zhari. 2009. Zircon U-Pb ages of the Xilinhot metamorphic complex and blueschist, and implications for tectonic evolution of the Solonker suture[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(12):3123-3129(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200912004.htm
Chen Yanjing, Zhai Mingguo, Jiang Shaoyong. 2009. Significant achievements and open issues in study of orogenesis and metallogenesis surrounding the North China continent[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11):2695-2726(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/268074684_significant_achievements_and_open_issues_in_study_of_orogenesis_and_metallogenesis_surrounding_the_north_china_continent
Chen Yanjing, Zhang Cheng, Li Nuo, Yang Yongfei, Deng Ke. 2012. Geology of the Mo deposits in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 42(5):1223-1268(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201205002.htm
Chen Yanjing, Zhang Cheng, Wang Pin, Pirajno F, Li Nuo. 2016. The Mo deposits of Northeast China:A powerful indicator of tectonic settings and associated evolutionary trends[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 81(2):602-640. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136816302177
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, Chappell B W. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type Granites with Particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Defant M J, Drummond M S. 1990.Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 347(6294):662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Dobretsov N L, Berzin N A, Buslov M M. 1995. Opening and tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Asian ocean[J]. International Geological Review, 37:335-360 doi: 10.1080/00206819509465407
Ge Mengchun, Zhou Wenxiao, Yu Yang, Sun Junjun, Bao Jianquan, Wang Shihai. 2011. Dissolution and supracrustal rocks dating of Xilin Gol Complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(5):182-195(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105018
Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Zhou Changyong, Rahman A A A. 2005. Emplacement age of the Tahe granite and its constraints on the tectonic nature of the Ergun block in the northern part of the Da Hinggan Range[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(18):2097-2105. doi: 10.1360/982005-207
Goolaerts A, Mattielli N, Jong J D, Weis D, Scoates J S. 2004. Hf and Lu isotopic reference values for the zircon standard 91500 by MC-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 206(1):1-9 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254104000397
Han Baofu, Kagami H, Li Huimin. 2004. Age and Nd-Sr isotopic geochemistry of the Guangtoushan alkaline granite, Hebei Province, China:Impications for early Mesozoic crust-mantle interaction in North China Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(6):1375-1388(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_acta-petrologica-sinica_thesis/0201252033707.html
Hong Dawei, Wang Shiguang, Xie Xilin, Zhang Jisheng, Wang Tao. 2003. Correlation between continental crustal growth and the supercontinental cycle:Evidence from the granites with positive εNd in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(2):203-209(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912003001342
Hong Dawei, Wang Shiguang, Xie Xilin, Zhang Jisheng. 2000. Genesis of positive ε(Nd, t) granitoids in the Da Hinggan Mts.-Mongolia Orogenic Belt and growth continental crust[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 7(2):441-456(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dxqy200002016.htm
Huang Jiqing, Chen Bingwei. 1987. The Evolution of the Tethys in China and Adjacent Regions[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Jahn B M, Wu Fuyuan, Hong Dawei. 2000. Important crustal growth in the Phanerozoic:Isotopic evidence of granitoids from eas-tcentral Asia[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 109(1):5-20. doi: 10.1007/BF02719146
Jahn B M. 2004. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and growth of the continental crust in the Phanerozoic[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 226(1):73-100. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.226.01.05
Jian Ping, Liu Dunyi, Kröner A, Windley B F, Shi Yuruo, Zhang Fuqin, Shi Guanghai, Miao Laicheng, Zhang Wei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Liqiao, Ren Jishun. 2008. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China:Implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 101(3):233-259. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493707001508
Jian Ping, Liu Dunyi, Kroner A, Windley B F, Shi Yuruo, Zhang Wei, Zhang Fuqin, Miao Liangcheng, Zhang Liqiao, Tomurhuu D. 2010. Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc-trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia[J]. Lithos, 118(1/2):169-190. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493710001349
Jian Ping, Zhang Qi, Liu Dunyi, Jin Weijun, Jia Xiuqin, Qian Qing. 2005. SHRIMP dating and geological significance of Late Achaean high-Mg diorite(sanukite) and hornblende-granite at Guyang of Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrololica Sinica, 21(1):151-157(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501016.htm
Le Maitre R W. 2002.Igneous Rocks:A Classification and Glossary of Terms[M]. Cambridge U. K.:Cambridge University Press.
Li Jinyi, Gao Liming, Sun Guihua, Li Yaping, Wang Yanbin. 2007. Shuangjingzi middle Triassic syn-collisional crust-derived granite in the east Inner Mongolia and its constraint on the timing of collision between Siberian and Sino-Korean paleo-plates[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3):565-582(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279908280_Shuangjingzi_middle_Triassic_syn-collisional_crust-derived_granite_in_the_east_Inner_Mongolia_and_its_constraint_on_the_timing_of_collision_between_Siberian_and_Sino-Korean_paleo-plates?ev=auth_pub
Li Nnuo, Chen Yanjing, Ulrich T, Lai Yong. 2012a. Fluid inclusion study of the Wunugetu Cu-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 47(5):467-481. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0384-1
Li Nuo, Chen Yanjing, Pirajno F, Gong Hujun, Mao Shidong, Ni Zhiyong. 2012b. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, trace element and Hf isotope geochemistry of the Heyu granite batholith, eastern Qinling, central China:Implications for Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution[J]. Lithos, 142-143(6):34-47. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493712000722
Liu Jianfeng, Chi Xiaoguo, Zhao Zhi, Hu Zhaochu, Chen Junqiang. 2013. Zircon U-Pb age and petrogenetic discussion on Jianshetun adakite in Balinyouqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3):827-839(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201303008.htm
Liu Jianfeng, Chi Xiaoguo, Zhao Zhi, Zhang Xingzhou, Ma Zhihong, Wang Tiefu, Hu Zhaochu. 2011. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of Early Permian Baya'ertuhushuo Gabbro in South Great Xing'an Range[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(1):116-129. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00384.x
Liu Jianfeng, Li Jinyi, Chi Xiaoguo, Qu Junfeng, Hu Zhaochu, Fang Shu, Zhang Zhong. 2013. A late-Carboniferous to early early-Permian subduction-accretion complex in Daqing pasture, southeastern Inner Mongolia:Evidence of northward subduction beneath the Siberian paleoplate southern margin[J]. Lithos, 177(2):285-296. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493713002211
Liu Jianfeng, Li Jinyi, Chi Xiaoguo, Qu Junfeng, Hu Zhaochu, Guo Chunli. 2014. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of the Early Triassic Granite Belt of Southeastern Inner Mongolia and its tectonic setting[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(9):1677-1690(in Chinese with English abstract). http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/docdown/docdownload.aspx?filename=DZXE201409005&dbcode=CJFD&year=2014&dflag=pdfdown
Liu Jianfeng. 2009. Late Paleozoic Magmatism and its Constraints on Regional Tectonic Evolution in Linxi-Dongwuqi Area, Inner Mongolia[D]. Changchun: Jilin University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jianming, Zhang Rui, Zhang Qingzhou. 2004. The regional metallogeny of Da Hinggan Ling, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(1):269-277(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/302500005_The_regional_metallogeny_of_Da_Hinggan_Ling_China
Liu Jun, Wu Guang, Li Yuan, Zhu Mingtian, Zhong Wei. 2012. Re-Os sulfide (chalcopyrite, pyrite and molybdenite) systematics and fluid inclusion study of the Duobaoshan porphyry Cu (Mo) deposit, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49(3):300-312. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912011004330
Liu Shuwen, Lü Yongjun, Feng Yonggang, Zhang Chen, Tian Wei, Yan Quanren, Liu Xiaoming. 2007. Geology and Zircon U-Pb isotoic chronology of Dantazi Complex, Northern Hebei Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3):484-497(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703012.htm
Liu Yongjiang, Li Weiming, Feng Zhiqiang, Wen Quanbo, Neubauer F, Liang Chenyue. 2017. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 43:123-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.013
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Martin H. 1999. Adakitic magmas:modern analogues of Archaean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 46(3):411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
Mu Baolei, Yan Guohan. 1992. Geochemistry of Triassic alkaline or subalkaline igneous complexes in the Yan-Liao area and their significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 66(2):108-122(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284581802_Geochemistry_of_Triassic_alkaline_or_subalkaline_igneous_complexes_in_the_Yan-Liao_area_and_their_significance
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discriminastion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. J.Petrol., 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Peng Peng, Zhai Mingguo. 2002. Two major Precambrian geological events of North China Block(NCB):Characteristics and propery[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 17(6):818-825(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313641457_Two_major_Precambrian_geological_events_of_North_China_block_NCB_Characteristics_and_property
Peng Yuqiong, Ji Chunhua, Xin Yulian. 2002. Petrology and geochronology of the Paleo-Jilin-Heilongjiang Orogenic Belt in the adjacent areas of China, Russia and Korea[J]. Geology and Resources, 11(2):65-75(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90360B/2002002/6723688.html
Peter C. Rickwood. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Qi Jinping, Chen Yanjing, Franco F. 2005. Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of the epithermal deposits in the Northeast China[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 25(2):47-59(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284800731_Geological_characteristics_and_tectonic_setting_of_the_epithermal_deposits_in_northeast_China
Ren Jishun, Chen Tingyu, Niu Baogui. 1990. Tectonics Evolution of the Continental Lithosphere and Metallogeny in Eastern China and Adjacent Areas[M]. Beijing:Science Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rui Zongyao. 1994.Geology of Nonferrous Metallic Deposits in the Northern Margin of the North China Landmass and its Adjacent Area[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 364:299-307 doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Shao Ji'an. 1991. Crust Evolution in the Middle Part of the Northern Margin of Sino-Korean Plate[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shao Ji'an, Tang Kedong. 1995. Terranes in Northeast China and Evolution of Northeast Asia Continental Margin[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press (in Chinese).
Shao Ji'an, He Guoqi, Tang Kedong. 2015. The evolution of Permian continental crust in northern part of North China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):47-55(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94579X/20151/663727495.html
Shi Yuruo, Liu Cui, Deng Jinfu, Jian Ping. 2014. Geochronological frame of granitoids from Central Inner Mongolia and its tectonomagmatic evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11):3155-3171(in Chinese with English abstract). http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=663234862
Shi Yuruo, Liu Dunyi, Miao Laicheng, Zhang Fuqin, Jian Ping, Zhang Wei, Hou Kejun, Xu Junyu. 2010. Devonian A-type granitic magmatism on the northern margin of the North China Craton:SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and Hf-isotopes of the Hongshan granite at Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 17(4):632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.11.011
Shi Yuruo, Liu Dunyi, Zhang Qi, Jian Ping, Zhang Fuqin, Miao Laicheng, Zhang Lvqiao. 2007. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of Triassic A-type granites in Sonid Zuoqi, central Inner Mongolia, China and its tectonic implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(2):183-189(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279549609_SHRIMP_U-Pb_zircon_dating_of_Triassic_A-type_granites_in_Sonid_Zuoqi_Central_Inner_Mongolia_China_and_its_tectonic_implications
Shu Qihai, Lai Yong, Wei Liangmin, Sun Yi, Wang Chao. 2011. Fluid inclusion study of the Baiyinnuo'er Zn-Pb deposit, south segment of the Great Xing'an Mountain, northeastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(5):1467-1482(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201105020.htm
Sláma J, Košler J, Condon D J. 2008. Plešovice zircon-A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 249(1-2):1-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
Sui Zhenmin, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Zhang Jiheng, Xu Xuechun, Cheng Ruiyu. 2006. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic characteristics and their implications of the Early granits in the northeastern Da Hinggan Mts., northeastern China[C]//National Symposium on Petrology and Geodynamics(in Chinese).
Sun S S, McDonough W E. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42: 313-345.
Tang Kedong. 1990. Tectonic development of Paleozoic fold belts at the north margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonics, 9(2):249-260. doi: 10.1029/TC009i002p00249
Tian Wei, Chen Bin, Liu Chaoqun, Zhang Huafeng. 2007. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic composition of the Xiaozhangjiakou ultramafic pluton in norther Hebei[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3):583-590(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/qk/94579X/20073/25485319.0.html
Vervoort J D, Patchett P J. 1996. Behavior of hafnium and neodymium isotopes in the crust:Constraints from Precambrian crustally derived granites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(19):3717-3733. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00201-3
Wang Fang, Chen Fukun, Hou Zhenhui, Peng Peng, Zhai Mingguo. 2009. Zircon ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic composition of late Paleozoic granitoids in the Chongli-Chicheng area, northern margin of the North China Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11):3057-3074(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Qi. 1991. Skarn and its Prospective Evaluation of Baiyinnuoer Pb-Zn Deposit, Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: Peking University(in Chinese).
Wang Qiang, Xu Jifeng, Jian Ping, Bao Zhiwei, Zhao Zhenhuan, Li Chaofeng, Xiong Xiaolin, Ma Jinlong. 2006. Petrogenesis of Adakitic Porphyries in an Extensional Tectonic Setting, Dexing, South China:Implications for the Genesis of Porphyry Copper Mineralization[J]. Journal of Petrology, 47(1):119-144. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi070
Wang Qiang, Xu Jifeng, Zhao Zhenhua. 2001. The summary and commention research on a new kind of igneous rock-Adakite[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 16(2):201-208(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.adearth.ac.cn/EN/abstract/abstract1328.shtml
Wang Quan. 1991. Plate Tectonics between Cathaysia and Angaraland in China[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yanyang, Xu Bei, Cheng Shengdong, Liao Wen, Shao Jun, Wang Yan. 2014. Zircon U-Pb dating of the mafic lava from Wudaoshimen, Hexigten, Inner Mongolia and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7):2055-2062(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/297439171_Zircon_U-Pb_dating_of_the_mafic_lava_from_Wudaoshimen_Hexigten_Inner_Mongolia_and_its_geological_significance
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao Wenjiao, Kroner A, Badarch G. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164:31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Wu Fuyuan, Cao Lin. 1999. Some important problems of geology in Northeastern Asia[J]. World Geology, 30(7):2055-2062(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288260999_Some_important_problems_of_geology_in_northeastern_Asia
Wu Fuyuan, Jahn B M, Wilde S, Sun Deyou. 2000. Phanerozoic crustal growth:U-Pb and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 328(1/2):89-113. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001797
Wu Fuyuan, Li Xianhua, Zheng Yongfei, Gao Shan. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematic and their application in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):185-220(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1492671
Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Ge Wenchun, Zhang Yanbin, Grant M L, Wilde S, Jahn B M. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Lin Qiang. 1999. Petrogenesis of the Phanerozoic granites and crustal growth in Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2):181-189(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1471776
Wu Fuyuan, Yang Yueheng, Xie Liewen, Yang Jinhui, Xu Ping. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 234(1/2):105-126. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254106002452
Wu Guana, Sun Fengyue, Zhao Caisheng, Li Zhitong, Zhao Ailin, Pang Qingbang, Li Guangyuan. 2005. Discoverry of the Early Paleozoic post-collisional granites in northern margin of the Erguna massif and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(23):2733-2743. doi: 10.1007/BF02899644
Wu Guang, Chen Yuchuan, Chen Yanjing, Zeng Qingtao. 2012. Zircon U-Pb ages of the metamorphic supracrustal rocks of the Xinghuadukou Group and granitic complexes in the Argun massif of the northern Great Hinggan Range, NE China, and their tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49(3):214-233. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912011004937
Xiao Wenjiao, Windley B F, Hao Jie, Zhai Mingguo. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 22(6):1-20. doi: 10.1029/2002TC001484/abstract
Xiao Wenjiao, Windley B F, Huang Baochun, Han Chunming, Yuan Chao, Chen Hui, Sun Mengru, Sun Shiru. 2009. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids:Implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6):1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0407-z
Xu Bei, Zhao Pan, Bao Qingzhong, Zhou Yongheng, Wang Yanyang, Luo Zhiwen. 2014. Preliminary study on the pre-Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing-meng Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7):1841-1857(in Chinese with English abstract). http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=661910910
Yan Guohan, Cai Jianhui, Ren Kangxu, He Guoqi, Mu Baolei, Xu Baoliang, Li Fengtang, Yang Bin. 2007. Intraplate extensional magmatism of North China Craton and break-up of three supercontinents and their deep dynamics[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(2):161-174(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200702002.htm
Yang Jinhui, Wu Fuyuan, Shao Ji'an, Wilde S A, Xie Liewen, Liu Xiaoming. 2006. Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan Fold and Thrust Belt, North China[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 246(3):336-352.
Yuan Hongli, Gao Shan, Liu Xiaoming, Li Huiming, Gunther D, Wu Fuyuan. 2004. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3):353-370 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
Zhai Degao, Liu Jiajun, Wang Jianping, Yang Yongqiang, Zhang Hongyu, Wang Xilong, Zhang Qibin, Wang Gongwen, Liu Zhenjiang. 2014. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, and whole-rock geochemistry of the Hashitu molybdenum deposit and host granitoids, Inner Mongolia, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79(2):144-160. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_rock-mineral-analysis_thesis/0201216533806.html
Zhai Mingguo, Peng Peng. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11):2665-2682(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200711002.htm
Zhang Qi, Jin Weijun, Xiong Xiaolin, Li Chengdong, Wang Yuanlong. 2009. Characteristics and implication of O-type adakite in China during different geological periods[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(3):432-447(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DGYK200903018&dbcode=CJFD&year=2009&dflag=pdfdown
Zhang Qi, Qian Qing, Wang Erqi, Wang Yan, Zhao Taiping, Hao Jie, Guo Guangjun. 2001. An east China plateau in mid-late Yanshanian period:Implication from adakites[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(2):248-255(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200102015.htm
Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Xiong Xiaolin. 2008. Adakite and Granite:Challenge and Opportunity[M]. Beijing:China Land Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Qi, Xu Jifeng, Wang Yan, Xiao Long, Liu Hongtao, Wang Yuanlong. 2004. Diversity of adakite[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(z2):959-965(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-zqyd2004z2019.htm
Zhang Quanhong, Zhao Yue, Liu Jianmin, Hu Jianmin, Song Biao, Liu Jian, Wu Hai. 2010. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic magmatism in the northern margin of the North China Block:A preliminary view[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 29(6):824-842(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281629857_Geochronology_geochemistry_and_tectonic_setting_of_the_Late_Paleozoic-Early_Mesozoic_magmatism_in_the_northern_margin_of_the_North_China_block_A_preliminary_review
Zhang Shuanhong, Zhao Yue, Kröner A, Liu Xiaoming, Xie Liewen, Chen Fukun. 2008. Early Permian plutons from the northern North China Block:constraints on continental arc evolution and convergent margin magmatism related to the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6):1441-1467. http://www.springerlink.com/content/w44l4010tv5600n7/
Zhang Shuanhong, Zhao Yue, Song Biao, Hu Jianmin, Liu Shuwen, Yang Yueheng, Chen Fukun, Liu Xiaoming, Liu Jian. 2009. Contrasting Late Carboniferous and Late Permian-Middle Triassic intrusive suites from the northern margin of the North China craton:Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121(1/2):181-200. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0128&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F00206814.2017.1377121&key=10.1130%2FB26157.1
Zhang Shuanhong, Zhao Yue, Song Biao, Yang Zhenyu, Hu Jianmin, Wu Hai. 2007. Carboniferous granitic plutons from the northern margin of the North China block:Implications for a late Paleozoic active continental margin[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(2):451-463. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492005-190
Zhou Zhenhua, Mao Jingwen, Lyckberg P. 2012. Geochronology and isotopic geochemistry of the A-type granites from the Huanggang Sn-Fe deposit, southern Great Hinggan Range, NE China:Implication for their origin and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49(3):272-286. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912012000570
Zhu Xuefeng, Chen Yanjing, Wang Pin, Zhang Cheng, Cai Yunlong, Deng Ke, Xu Qiangwei, Li Kaiyue. 2018. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Hf isotopes of the causative porphyry from the Bilihe porphyry gold deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(5):199-134(in Chinese with English abstract).
鲍庆中, 张长捷, 吴之理, 王宏, 李伟, 桑家和, 刘永生. 2007.内蒙古白音高勒地区石炭纪石英闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 37(1):15-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200701002.htm 陈斌, 陈长健, 贺敬博, 刘安坤. 2013.华北东部中生代高镁埃达克质岩浆的起源:岩石学和Nd-Sr-Os同位素证据[J].科学通报, 58(20):1941-1953. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201320009.htm 陈斌, 马星华, 刘安坤, 木合塔尔.扎日. 2009.锡林浩特杂岩和蓝片岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其对索仑缝合带演化的意义[J].岩石学报, 25(12):3123-3129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200912004.htm 陈衍景, 翟明国, 蒋少涌. 2009.华北大陆边缘造山过程与成矿研究的重要进展和问题[J].岩石学报, 25(11):3-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911003.htm 陈衍景, 张成, 李诺, 杨永飞, 邓轲. 2012.中国东北钼矿床地质[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(5):1223-1268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201205002.htm 葛梦春, 周文孝, 于洋, 孙俊俊, 鲍建泉, 王世海. 2011.内蒙古锡林郭勒杂岩解体及表壳岩系年代确定[J].地学前缘, 18(5):182-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201105017.htm 韩宝福, 加加美宽雄, 李惠民. 2004.河北平泉光头山碱性花岗岩的时代、Nd-Sr同位素特征及其对华北早中生代壳幔相互作用的意义[J].岩石学报, 20(6):1375-1388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200406006.htm 洪大卫, 王式洸, 谢锡林, 张季生, 王涛. 2003.从中亚正εNd值花岗岩看超大陆演化和大陆地壳生长的关系[J].地质学报, 77(2):203-209. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.02.008 洪大卫, 王式洸, 谢锡林, 张季生. 2000.兴蒙造山带正ε(Nd, t)值花岗岩的成因和大陆地壳生长[J].地学前缘, 7(2):441-456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.02.012 黄汲清, 陈炳蔚. 1987.中国及邻区特提斯海的演化[M].北京:地质出版社. 简平, 张旗, 刘敦一, 金维浚, 贾秀勤, 钱青. 2005.内蒙古固阳晚太古代赞岐岩(sanukite)-角闪花岗岩的SHRIMP定年及其意义[J].岩石学报, 21(01):153-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501016.htm 李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 李亚萍, 王彦斌. 2007.内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞的约束[J].岩石学报, 23(3):565-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703006.htm 刘建峰, 迟效国, 赵芝, 胡兆初, 陈军强. 2013.内蒙古巴林右旗建设屯埃达克岩锆石U-Pb年龄及成因讨论[J].岩石学报, 29(3):827-839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303008.htm 刘建峰, 李锦轶, 迟效国, 曲军峰, 胡兆初, 郭春丽. 2014.内蒙古东南部早三叠世花岗岩带岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境[J].地质学报, 88(9):1677-1690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201409005.htm 刘建峰. 2009.内蒙古林西-东乌旗地区晚古生代岩浆作用及其对区域构造演化的制约[D].长春吉林大学. 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲. 2004.大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J].地学前缘, 11(1):269-277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.024 刘树文, 吕勇军, 凤永刚, 张臣, 田伟, 闫全人, 柳小明. 2007.冀北单塔子杂岩的地质学和锆石U-Pb年代学[J].高校地质学报, 13(03):484-497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.017 牟保磊, 阎国翰. 1992.燕辽三叠纪碱性偏碱性杂岩体地球化学特征及意义[J].地质学报, 66(2):108-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199202001.htm 彭澎, 翟明国. 2002.华北陆块前寒武纪两次重大地质事件的特征和性质[J].地球科学进展, 17(06):818-825. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.06.004 彭玉鲸, 纪春华, 辛玉莲. 2002.中俄朝毗邻地区古吉黑造山带岩石及年代记录[J].地质与资源, 11(2):65-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2002.02.001 祁进平, 陈衍景, Franco F. 2005.东北地区浅成低温热液矿床的地质特征和构造背景[J].矿物岩石, 25(2):47-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2005.02.009 任纪舜, 陈廷愚, 牛宝贵. 1990.中国东部及邻区大陆岩石圈的构造演化与成矿[M].北京:科学出版社. 芮宗瑶. 1994.华北陆块北缘及邻区有色金属矿床地质[M].北京:地质出版社. 邵济安, 何国琦, 唐克东. 2015.华北北部二叠纪陆壳演化[J].岩石学报, 31(1):47-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201501003.htm 邵济安, 唐克东. 1995.中国东北地体与东北亚大陆边缘演化[M].北京:地震出版社. 邵济安. 1991.中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M].北京:北京大学出版社. 施光海, 刘敦一, 张福勤, 简平, 苗来成, 石玉若, 陶华. 2003.中国内蒙古锡林郭勒杂岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及意义[J].科学通报, 48(20):2187-2192. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.20.017 石玉若, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 简平. 2014.内蒙古中部花岗质岩类年代学格架及该区构造岩浆演化讨论[J].岩石学报, 30(11):3155-3171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411005.htm 石玉若, 刘敦一, 张旗, 简平, 张福勤, 苗来成, 张履桥. 2007.内蒙古中部苏尼特左旗地区三叠纪A型花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其区域构造意义[J].地质通报, 26(2):69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200702008.htm 舒启海, 赖勇, 魏良民, 孙艺, 王潮. 2011.大兴安岭南段白音诺尔铅锌矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 27(5):1467-1482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105020.htm 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 张吉衡, 徐学纯, 程瑞玉. 2006.大兴安岭东北部地区早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[C]//全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会. 田伟, 陈斌, 刘超群, 张华峰. 2007.冀北小张家口超基性岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 23(3):57-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703007.htm 王芳, 陈福坤, 侯振辉, 彭澎, 翟明国. 2009.华北陆块北缘崇礼-赤城地区晚古生代花岗岩类的锆石年龄和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 25(11):3057-3074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911035.htm 王琦. 1991.内蒙古白音诺铅锌多金属矿床矽卡岩及其含矿性研究[D].北京: 北京大学. 王强, 许继锋, 赵振华. 2001.一种新的火成岩-埃达克岩的研究综述[J].地球科学进展, 16(2):201-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.02.010 王荃. 1991.中国华夏与安加拉古陆间的板块构造[M].北京:北京大学出版社. 王炎阳, 徐备, 程胜东, 廖闻, 邵军, 汪岩. 2014.内蒙古克什克腾旗五道石门基性火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 30(7):2055-2062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407018.htm 吴福元, 曹林. 1999.东北亚地区的若干重要基础地质问题[J].世界地质, 18(2):1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ902.001.htm 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 23(2):185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm 吴福元, 林强, 江博明. 1997.中国北方造山带造山后花岗岩的同位素特点与地壳生长意义[J].科学通报, 42(20):2188-2192. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.20.017 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 1999.东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J].岩石学报, 15(2):181-189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB902.003.htm 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 徐备, 陈斌. 1997.内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J].中国科学(D辑), 27(3):227-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199703005.htm 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 周永恒, 王炎阳, 罗志文. 2014.兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J].岩石学报, 30(7):1841-1857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407001.htm 阎国翰, 蔡剑辉, 任康绪, 何国琦, 牟保磊, 许保良, 李凤棠, 杨斌. 2007.华北克拉通板内拉张性岩浆作用与三个超大陆裂解及深部地球动力学[J].高校地质学报, 13(2):161-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.003 阎国翰, 牟保磊, 许保良, 何国琦, 谭林坤, 赵晖, 何中甫, 张任祜, 乔广生. 2000.燕辽-阴山三叠纪碱性侵入岩年代学和Sr, Nd, Pb同位素特征及意义[J].中国科学, 30(4):383-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200004005.htm 翟明国, 彭澎. 2007.华北克拉通古元古代构造事件[J].岩石学报, 23(11):2665-2682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.001 张旗, 金惟俊, 熊小林, 李承东, 王元龙. 2009.中国不同时代O型埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 33(3):432-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.015 张旗, 钱青, 王二七, 王焰, 赵太平, 郝杰, 郭光军. 2001.燕山中晚期的中国东部高原:埃达克岩的启示[J].地质科学, 36(2):248-255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.02.014 张旗, 王焰, 熊小林. 2008.埃达克岩和花岗岩:挑战与机遇[M].北京:中国大地出版社. 张旗, 许继峰, 王焰, 肖龙, 刘红涛, 王元龙. 2004.埃达克岩的多样性[J].地质通报, 23(z2):959-965. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2004Z2019.htm 张拴宏, 赵越, 刘建民, 胡健民, 宋彪, 刘健, 吴海. 2010.华北地块北缘晚古生代-早中生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 29(6):824-842. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.017 郑永飞. 2004.新元古代岩浆活动与全球变化[J].科学通报, 48(16):1705-1720。 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200316000.htm 朱雪峰, 陈衍景, 王玭, 张成, 蔡云龙, 邓轲, 许强伟, 李凯月. 2018.内蒙古毕力赫斑岩型金矿成矿岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素研究[J].地学前缘, 25(5):125-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201805009.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 陆露,钱程,赵珍. 辽西凌源河坎子碱性杂岩体的成因. 地球科学. 2023(10): 3671-3688 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 胡鹏,段明,熊金莲,曾威,刘行,闫国强,魏佳林. 内蒙古西乌旗沙尔哈达晚侏罗世A型花岗岩:地球化学特征、岩石成因与动力学背景. 地质通报. 2022(08): 1394-1408 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘建峰,李锦轶,赵硕,张进,郑荣国,张文龙,吕前露,郑培玺. 中亚造山带东南部晚古生代-早中生代地壳增生和古亚洲洋演化:来自内蒙古东南部林西-东乌旗地区岩浆岩的证据. 岩石学报. 2022(08): 2181-2215 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张士贞,李奋其,刘函,李俊,苟正彬,秦雅东. 中拉萨地块亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩:班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲板片断离的岩浆作用响应. 地质通报. 2021(11): 1852-1864 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: