Chronology and geochemistry of Mogutu granite in Inner Mongolia and its effect of crustal extension and thinning
-
摘要:
莫古吐花岗岩体位于大兴安岭南段黄岗梁-甘珠尔庙锡多金属成矿带西南端,其岩性主要以黑云母钾长花岗岩为主。文章通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及岩石地球化学研究分析,探讨莫古吐花岗岩的成因类型、岩浆源区及成岩构造背景。锆石U-Pb年代学研究表明,莫古吐岩体形成于148.8~152.7 Ma,属晚侏罗世岩浆产物。岩石学及地球化学特征显示,莫古吐花岗岩属于碱性-弱过铝质系列,具有富SiO2(73.64%~80.86%),富K2O(2.6%~6.0%),贫Al2O3(10.57%~13.88%)的特点,富集Rb、U、Th等大离子亲石元素,亏损P、Ti、Ba、Sr等元素,稀土配分型式呈燕式分布,δEu值为0.10~0.27,负Eu异常明显,锆石饱和温度较高,为795~911℃,属于高演化A型花岗岩。结合年代学、地球化学数据及前人研究成果,认为莫古吐花岗岩体的岩浆源区较浅,成岩物质主要以壳源物质为主,岩体形成于地壳伸展-减薄的构造环境中,与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋构造体制的关系更为密切。
Abstract:The Mogutu granite pluton is emplaced in the southwest Huanggangliang to Ganzhuermiao tin-polymetal metallogenic belt in Southern Da Hinggan Mountains, which is mainly composed of biotite moyite. The genetic type, magmatic source region and diagenetic tectonic setting of the Mogutugranite were studied by U-Pb dating of zircon in LA-ICP-MS and petrogeochemical analysis. Zircon LA-ICP-MS dating of the biotite moyite yields a concordant age of 148.8-152.7Ma, which means that the Mogutu granite pluton was formed in Late Jurassic. The Mogutu granites is characterized by weak peraluminous and alkaline, high content of SiO2 (73.64%-80.86%), K2O(2.6%-6.0%), but low content of Al2O3 (10.57%-13.88%), depletion in P、Ti、Ba、Sr, and enrichment Rb、U、Th. The chondrite-normalized patterns of REE are in seagull forms, with strong negative Eu anomalies, with 0.10 to 0.27 of δEu, and higher zircon saturation temperatures(795-911℃), which indicates that the Mogutu pluton is similar to A-type granite. Therefore, the Moguto granites shows highly fractionated A -type granite affinity. Based on the previous research results, it is inferred that the depth of magma source of Mogutu granite pluton is shallow, the magmatic substance was derived from the crust, and the granite pluton was emplaced in the tectonic setting of crustal extension and thinning more likely related to the closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk tectonic belt.
-
1. 引言
在资源枯竭、经济发展和环境保护的三重压力下,寻找并开发利用新型清洁能源是关系国计民生和社会可持续发展的紧迫任务。推动绿色发展,构建清洁、安全、高效的能源体系已成为时代的要求。地热资源作为清洁能源的重要组成部分被寄予厚望。
天津市地热资源条件优越,地热开发利用水平一直处于全国前列。天津地热勘查研究工作开始于20世纪70年代,李四光同志主导的天津地热会战掀起了全国地热勘查研究的第一个春天,并发现了新近系和奥陶系两个热储。80年代以来,在市政府和原地矿部的支持以及联合国开发计划署的援助下,地热勘查开始向深部基岩热储发展,先后完成王兰庄、山岭子、塘沽地区三个地热田的勘查工作。自此之后,天津的地热研究与开发工作一直处于中国前列。先后发现地热田8个,已发现两大类6个热储,即孔隙型热储(新近系明化镇组、馆陶组热储和古近系东营组)和裂隙溶隙型热储(奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储),3000 m以浅年可开采地热流体为7606×104 m3。其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段热储是天津地热开发的主力储层。随着开发强度不断增大,部分地区开采潜力已达极限(天津地热勘查开发设计院, 2000;Wang, 2008;王继革等,2013)。
随着钻探技术的不断进步和清洁能源需求的持续增长,向地球深部进军,探测深部地热资源、开辟深部热储第二空间、增加可开采资源量,成为保障天津地区地热可持续开发的有效途径之一。为此,2017年以来,中国地质调查局在天津东丽湖地区部署了深部地热探测工作,并在主力储层下部探获雾迷山组二段高产能新储层。本文主要介绍天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储探测和高产能地热井参数研究取得的新成果、新进展。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 地热地质背景
天津市地处Ⅰ级构造单元华北地台北缘,以宁河—宝坻断裂为界分为北部山区和南部平原区。其中,南部平原区属Ⅱ级构造单元华北断坳区,是中、新生代断陷、坳陷盆地。区内Ⅲ级构造单元包括一隆两坳即沧县隆起、冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷。隆起和坳陷及其间分布的诸多Ⅳ级构造单元凸起、凹陷的延伸方向和较大断裂的走向均呈北北东(NNE)向,形成雁行式相间排列的构造格局(陈墨香, 1988)(图 1)。
宝坻—宁河断裂以南为天津南部平原区,总面积8700 km2,地热资源条件优越。发育有王兰庄、山岭子、滨海、武清、潘庄—芦台、宁河—汉沽、万家码头和周良庄等8个地热田,年可开采地热流体7606×104 m3(图 2)。各地热田均位于华北断坳范围内,地面均为第四系松散沉积物覆盖,厚度可达数百米。其下是巨厚的新生界陆相碎屑岩沉积,是一套半胶结的砂岩和泥岩地层,沉积厚度在沧县隆起相对较薄,在冀中坳陷和黄骅坳陷沉积较厚,最大厚度可达近万米。在新生界的巨大不整合覆盖之下,主要是古生界和中上元古界的基底地层,在坳陷中还有局部中生界分布。区内地热资源主要赋存于两大类6个储层中:一类为孔隙型热储,包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组和古近系东营组热储;一类为裂隙溶隙型热储,包括奥陶系、寒武系和蓟县系雾迷山组热储(张百鸣等, 2006; Wang, 2008)(图 3)。
东丽湖地区位于天津市东部,隶属于天津市东丽区,位于Ⅳ级构造单元潘庄凸起上,发育有著名的山岭子地热田。依据研究区内地热井的钻探资料,揭露的地层从新到老为:新生界(第四系和新近系)、古生界(奥陶系和寒武系)、中新元古界(青白口系和蓟县系)(表 1)。区内已发现新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、奥陶系和蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段4个热储。其中,雾迷山组三、四段为当前主力储层,沧县隆起上钻孔揭露顶板埋深为1752~2016 m,揭露厚度为480~1032 m,单井出水量为70~120 m3/h,最大可达204 m3/h,出水温度为88~102℃,孔隙度1%~5.8%,渗透率5.52×10-14 m2,水化学类型为Cl · HCO3·SO4-Na或Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na型,总矿化度为1670~2200 mg/L,总硬度为120~240 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值为7.3~8.4(林黎等, 2007; 王继革等, 2013)。从区域地质资料看(高昌,2003;赵苏民等, 2006),区内雾迷山组厚度约3500 m,岩石组合为一套富镁碳酸盐岩,岩性主要为白云岩。燧石条带白云岩、硅质白云岩夹2~5层棕红、紫红色泥岩和页岩,可作为雾迷山组三、四段和一、二段的分界线。从岩性组合的相似性可以推测,雾迷山组一、二段可作为未来深部热储探测的重要方向,也是本次研究的重点。
表 1 天津东丽湖地区综合地层简表Table 1. The simplified table of geological strata in Donglihu area, Tianjin
2.2 开发利用现状
天津地热资源开发利用水平在全国居于较高地位,也是全国中低温地热直接利用规模最大的城市,是全国第一批“中国温泉之都”。自20世纪30年代以来,经过80多年的发展,天津地热资源开发利用从浅到深、从无序到有序、从粗放到精细,逐渐形成了规模化、产业化,在中国地热勘查开发利用史上具有举足轻重的作用。截至2017年,天津市共有地热开采井466眼,年开采总量为5181.08×104 m3,其中,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段约占开采总量的54%。地热资源主要应用于供暖、洗浴、理疗、旅游、养殖等。其中,供暖是最主要的利用方式,占年总开采量的81.5%。建有地热供暖小区及公建项目496个,全市地热供暖总面积达3500×104 m2,占全市集中供暖面积的8%,是中国利用水热型地热资源供暖规模最大的城市。
东丽湖地区现有地热井34眼。其中,新近系明化镇组4眼,新近系馆陶组2眼,奥陶系3眼,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段25眼。年开采地热流体约395.44×104 m3,采用梯级、综合利用和群井联动回灌的开发模式,达到资源的优化配置和实时调控,地热利用率和回灌率达到95%以上,实现了资源的统一规划、统一开发和统一管理。地热资源广泛应用于供暖、温泉洗浴、养生理疗、康乐旅游、矿泉水开发等领域,建有东丽湖温泉旅游度假区,在发展温泉旅游产业,促进地区经济发展,保护生态环境方面取得了显著的成效。2008年12月25日和2011年12月30日,分别被中国矿业联合会和国土资源部命名为“中国温泉之乡”。
3. 深部热储探测方法
本次研究主要基于地质综合分析,采用地球物理探测、地热钻探、地球物理测井和热储试验相结合的方法开展探测研究。
3.1 地球物理探测
为满足深部储层探测需要,本次地球物理探测的主要目标确定为5 km以浅地层的结构探测,为地热钻探提供依据。由于探测深度大,且存在高压线、铁路等城市干扰源,本次地球物理探测采用了二维地震和时频电磁相结合的勘查方法,其中,时频电磁方法首次应用到地热勘查领域。时频电磁方法是通过大功率人工场源激发信号,测量研究区测线的电磁场分量,分析频率域信号的振幅和相位特征,来获得介质的地电参数(电阻率和极化率),把信号转换到时间域,建立高分辨的电法勘探的时间断面。较传统电磁方法,在应对强电磁干扰方面具有一定的优势(Dong et al., 2008; 周印明等, 2013, 2015)。
本次工作部署时频电磁法完成测线4条,剖面24.4 km,点距200 m,物理点128个;二维地震完成剖面3条,8.25 km,测点254个(图 4)。
地球物理探测结果初步揭示了天津东丽湖地区雾迷山组二段的分布。从TFEM-1测线地质剖面解译图(图 5)可以看出,F1沧东断裂西侧,电阻率异常特征从上至下依次为“低—高—低—高—次高—高”,表层低阻和浅层高、低阻分别是第四系、新近系明化镇组与馆陶组地层响应特征,电阻率过渡连续,无明显的错断。第二套高阻层为寒武系(Є) 与青白口系(Qb)的反映,深部的次高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组4段(Jxw4)的反映,深部的高阻为蓟县系雾迷山组2、3段(Jxw2-3)的反映。蓟县系雾迷山组四段埋深2300~3000 m,下部发育雾迷山组二段和三段地层,埋深在3000 m以下。因缺乏雾迷山组二、三段电性参数,不易进一步细分。从二维地震DZ01剖面解释图(图 6)可以看出,区内4000 m以浅揭示的地层分别为第四系、新近系明化镇组、新近系馆陶组、寒武系、青白口系和蓟县系雾迷山组。新近系馆陶组底界以上主要标准反射界面清晰可辨,以下反射界面呈断续分布。推测第四系底界埋深341~363 m;新近系明化镇组底界埋深1123~1160 m,馆陶组底界埋深1347~1500 m;寒武系张夏组底界埋深1758~2033 m,馒头组底界埋深1786~2113 m,昌平组底界埋深1856~2164 m;青白口系底界埋深2196~2444 m;蓟县系雾迷山组四段底界埋深2802~3004 m,三段底界二段顶界埋深3552~3726 m。4000 m探测深度范围内未揭示蓟县系雾迷山组底界。
3.2 地热科学钻探
在天津东丽湖部署地热科学钻探CGSD-01井,目标层位为蓟县系雾迷山组二段。2017年11月20日开钻,2018年11月19日完钻。成井深度4051.68 m,3715 m进入雾迷山组二段储层,是当时天津最深的地热井。
该井井身结构为三开直井。其中,护壁段(0~76 m)采用Ф660.4 mm冲击钻钻头施工,下入Ф508 mm×8.0 mm无缝套管,总长度为74.42 m。一开井段(76~1469.53 m)采用Ф444.5 mm牙轮钻头钻进,入Ф339.7 mm×J55钢级套管,长度1469.84 m。二开井段(1469.53~2262.75 m)采用Ф311.2 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф244.5 mm×10.03 mm N80钢级套管,长度866.60 m,与一开套管重叠68.12 m。三开井段(2262.75~4051.68 m)采用Ф215.9 mm牙轮钻头钻进,下入Ф177.8 mm×9.19 mm N80钢级套管,长度1939.96 m,其中实管长度为1747.23 m,花管长度为192.73 m,与二开套管重叠151.03 m。钻进过程中,开展了岩屑和岩心采集工作。1500 m以浅每5 m捞取岩屑一次,1500 m以深每2 m捞取岩屑一次,全井共计捞取岩屑样1873个。500~4051.68 m井段采取定深分段采取岩心,累计取心37回次,进尺161.25 m,长度140.78 m,采取率85%。
3.3 地球物理测井
钻井过程中,对地热井开展了综合地球物理测井工作,主要包括温度测井、压力测井、井径测井、井斜测井、视电阻率测井、双感应测井、自然电位测井、自然伽马测井、声波测井、伽马-伽马测井和流体流量测井11项。
3.4 热储试验
钻探完成后,为获取蓟县系雾迷山组二段新储层热储参数,对地热井开展了3个落程的稳定流降压抽水试验。其中,大落程试验历时62 h,涌水量130.2 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间39.5 h;中落程试验历时24 h,涌水量94.5 m3/h,水温度稳定在100℃,稳定时间16.5 h;小落程试验历时16 h,涌水量43.9 m3/h,水温度稳定在98℃,稳定时间8 h(图 7)。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1 热储结构特征
综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇地层包括:第四系、新近系、寒武系、青白口系及蓟县系。钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储(表 2)。
表 2 天津东丽湖CGSD-01井钻遇地层表Table 2. Geological stratum of well CGSD-01 in the Tianjin
本次研究在地热井中实现雾迷山组四、三、二段精细划分,自上而下叙述如下。
雾迷山组四段(Jxw4):深度段为2258~2896 m,地层厚度638 m。上部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶白云岩,偶见少量深灰色厚层角砾状白云岩、灰白色硅质白云岩等;下部岩性主要为浅灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩交互;底部主要发育灰黑色白云质泥岩夹细晶白云岩、泥晶白云岩、硅质白云岩。受原始沉积及沉积后多期次构造与岩溶作用等影响,雾迷山组四段白云岩层系整体较破碎,钻井岩心中裂隙和溶蚀孔洞极其发育,为地热水提供了良好的储集空间。
雾迷山组三段(Jxw3):深度段为2896~3715 m,地层厚度819 m。上部岩性主要为深灰色细晶白云岩与灰黑色泥晶白云岩、泥质白云岩、白云质泥岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组三段上部的GR值较雾迷山组四段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也表现出类似特征;雾迷山组三段测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率值,下部整体较上部好(图 8);下部岩性主要发育浅灰—灰黑色细晶白云岩夹灰黑色泥晶—泥质白云岩、灰质泥晶白云岩及白云质泥岩;底部以发育一套紫红色泥质白云岩夹浅灰色细晶白云岩为典型特征,厚度约73 m,裂隙不发育,具有隔水—弱透水性质,作为与下伏雾迷山组二段的分界。
雾迷山组二段(Jxw2)深度段为3715~4051 m,地层厚度336 m,未钻穿。与上覆雾迷山组三段相比,雾迷山组二段的岩性及电测特征存在明显的差别(图 8)。岩性特征上,雾迷山组二段上部主要发育浅灰色细晶白云岩夹浅灰色粉晶白云岩、灰黑色泥质白云岩,之上为雾迷山组三段底部紫红色泥质白云岩作为两者明显分界;雾迷山组二段下部主要为浅灰色粉晶白云岩与灰黑色泥质白云岩交互。电测曲线上,雾迷山组二段上部的GR值、自然电位值(SP)较雾迷山组三段底部低为特征,测井解释的泥质含量值也体现出类似特征;雾迷山组二段上部的深侧向、浅侧向电阻率较雾迷山组三段底部高为特征。雾迷山组二段内部,自下而上,GR值、自然电位值(SP)、深侧向电阻率、浅侧向电阻率及测井解释的泥质含量呈逐渐变小趋势;声波时差呈逐渐变大趋势,测井资料解释的孔隙度和渗透率呈逐渐变大趋势,指示雾迷山组二段上部的热储层较下部更为发育。
4.2 温度特征
2018年11月19日对CGSD-01井开展了稳态测温。从测温曲线(图 9)可以看出,CGSD-01井底温度105℃。井温总体呈凸型曲线特征,体现了储盖层热传导机制为总体传导型、层间对流型。总体地温梯度2.4℃/100 m。其中,0~400 m第四纪地层地温梯度最高,可达8℃/100 m;400~2300 m新近系与寒武系盖层地温梯度次之,为2.4℃/100 m;2300~3500 m雾迷山组三、四段主力储层受对流作用影响,地温梯度最小,为0.83℃/100 m;3500 m以下雾迷山组二段储层地温梯度为1.7℃/100 m,对流作用较主力储层稍弱。
岩石热物性分析表明,雾迷山组二段岩石热导率在4.33~7.96 W/(m · K)(10个样品,表 3),平均值5.66 W/(m·K),略高于雾迷山组三四段平均值4.37 W/(m·K)。
表 3 CGSD-01井雾迷山组二段热储热导率测试值Table 3. Thermal conductivity test results of Wumishan Formation section 2 in well CGSD-01
4.3 热储参数
热储参数计算主要依据降压抽水试验计算。由于地热水密度与温度具有相关性,造成观测水位不能真实地反映地热井实际水位的变化,这种现象称之为“井筒效应”。资料整理过程中,以储层中部温度102.6℃作为储层温度对试验观测数据进行校准。校正后,做出的动水位埋深曲线如图 10。
采用Dupuit公式与W.Sihart公式对试验数据进行分析计算CGSD-01井的热储参数。本次抽水试验目标热储层为蓟县系雾迷山组二段,厚度336.68 m(未穿透),根据测井数据显示,裂隙厚度为123.1 m。根据降压抽水试验数据及相关校正,地热井基本参数见表 4。计算结果见表 5。依据降压抽水试验计算结果,取三个落程试验平均值可以得出,CGSD-01井单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d。
表 4 CGSD-01井热储参数计算基本参数Table 4. Reservoir parameters of well CGSD-01 表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
4.4 水化学特征
抽水试验过程中,采集样品对雾迷山组二段地热水进行了水化学、同位素和气体成分分析。
水化学分析表明,雾迷山组二段地热水水化学类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1770.0 mg/L,总硬度124.6 mg/L(以CaCO3计),pH值7.63。
结垢性和腐蚀性表明,地热水不生成碳酸钙垢,不生成硫酸钙垢,不生成硅酸盐垢,对管道及利用设施具有中等腐蚀性。
气体组分测试表明,溶解气体中以氮气和甲烷为主,分别占气体组分含量的66%和27%,还有少量乙烷、丙烷、异丁烷和异戊烷,指示储层处于还原环境。
同位素分析表明,地热水δD为-72‰~-72.7‰,δ18O为9.3‰~-9.5‰,δ13C为-3‰~-3.6‰,87Sr/86Sr为0.7113~0.7114。综合水化学和同位素特征,初步推断雾迷山组二段地热水来源于大气降水,主要发生混合、阳离子交替吸附、碳酸盐岩溶解、硫酸盐还原等作用,且未达到平衡。
4.5 开发利用潜力分析与建议
从区域地质背景和地层沉积序列看,雾迷山二段热储在潘庄凸起区全区均有分布,分布面积约604 km2,依据CGSD-01地热参数井信息,对潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量进行保守估算。年可开采热资源量按照100 a富水段可回收热量的0.01% 进行保守估算,其热量每年折合标煤250万t,初步估计可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
为了提高地热资源利用率,本文建议推广地热利用集约节约新技术,采用地热梯级利用联合水源热泵、地板辐射采暖、群井联动、地热与燃气或太阳能等多能源结合技术,降低尾水排放温度,实现地热资源利用最大化。
5. 结论
(1) 综合全井段地球物理测井、岩心与岩屑及区域地热地质等资料,CGSD-01井钻遇主要储层5个,主要包括新近系明化镇组、馆陶组2个砂岩热储,寒武系昌平组灰岩热储,蓟县系雾迷山组三四段和一二段白云岩热储。
(2) 雾迷山组二段上部单位涌水量1.53 m3/h · m,渗透系数0.40 m/d,导水系数48.69 m2/d,岩石热导率5.66 W/(m · K),地热水类型为Cl · SO4 · HCO3-Na型,矿化度1.7 g/L,热储参数与潘庄凸起三、四段热储相近。
(3) CGSD-01井降压抽水试验结果表明,蓟县系雾迷山组二段单井最大涌水量可达130 m3/h,出水温度100 ℃,单井可满足约30万m2建筑物供暖需求;初步估计潘庄凸起雾迷山组二段热储热量可满足供暖面积6114×104 m2。
(4) 从区域地层沉积规律看,天津地区深部雾迷山组一段、杨庄组、高于庄组,厚度大、岩溶发育,与雾迷山组四、三、二段性质相似,均具有成为高产能新储层的可能性,加强深部地热探测研究意义重大。
致谢: 野外地质工作得到北京矿产地质研究院蒋斌斌、管育春等工程师的大力支持和帮助;测试工作得到合肥工业大学矿床成因与勘查技术研究中心矿物微区分析实验室汪方跃老师的热情帮助;审稿专家给论文提出了许多建设性的意见,特此感谢! -
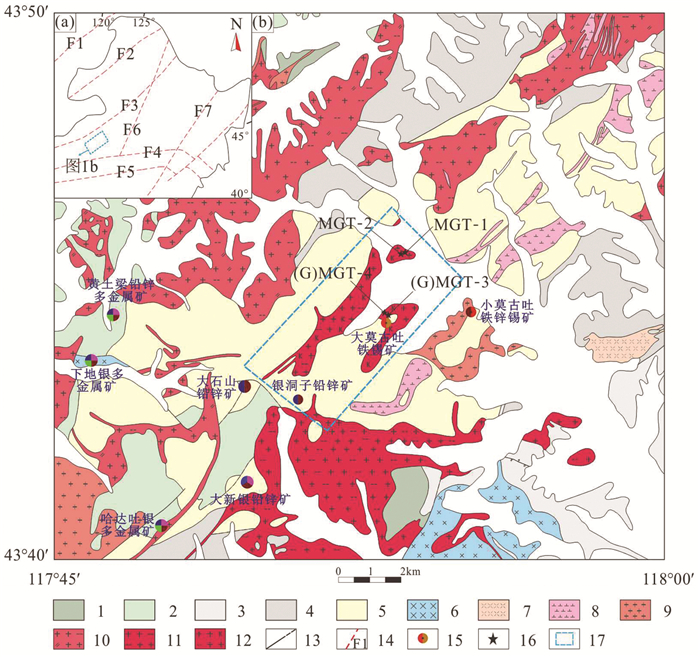
图 1 中国东北区域构造单元划分(a,据Wu et al., 2011)、莫古吐地区区域地质图(b,据项目组内部资料修编)
1—满克头鄂博组晶屑凝灰岩、凝灰质角砾岩;2—新民组粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂砾岩;3—林西组粉砂岩、板岩;4—哲斯组变质粉砂岩、钙质砂岩、大理岩、硅质岩、粉砂质板岩;5—大石寨组安山岩、细碧岩;6—辉长岩;7—流纹斑岩;8—闪长岩;9—花岗斑岩;10—黑云母二长花岗岩;11—黑云母花岗岩;12—黑云母钾长花岗岩;13—整合接触;14—断裂及编号(F1—蒙古—鄂霍茨克断裂;F2—德尔布干断裂;F3—贺根山断裂;F4—西拉木伦断裂;F5—康保—赤峰断裂;F6—嫩江八里罕断裂;F7—佳木斯—伊通断裂);15—金属矿床;16—采样位置;17—研究区
Figure 1. Tectonic subdivisions of northeastern China(a, after Wu et al., 2011); Regional geological map of the Mogutu area (b, after internal materials)
1- Crystal tuff and tuffaceous breccia of the Manketouerbo Formation; 2- Siltstone, fine sandstone and glutenite of the Xinmin Formation; 3- Siltstone and slate of the Linxi Formation; 4- Metamorphic siltstone, calcareous sandstone, marble, siliceous and silty slate of the Zhesi Formation; 5- Andesite and spilite of the Dashizhai Formation; 6- Gabbro; 7- Rhyolite porphyry; 8- Diorite; 9- Granite porphyry; 10- Biotite adamellite; 11- Biotite- granite; 12- Biotite moyite; 13- Conformity; 14- Fracture and No. (F1- Mongolia Okhotsk fracture; F2- Deerbugan fracture; F3- Hegenshan fracture; F4 − Xilamulun fracture; F5- Kangbao- Chifeng fracture; F6- Nengjiang- Balihan fracture; F7-Jiamusi—Yitong fracture); 15-Ore deposit; 16-Sampling position; 17-Researched area
图 3 莫古吐花岗岩显微镜下照片
a—浅肉红色黑云母钾长花岗岩正交偏光镜下照片(+);b—灰白色黑云母钾长花岗岩正交偏光镜下照片(+);c—正长石的卡氏双晶(+);d—微斜长石交代溶蚀斜长石及斜长石发育卡钠复合双晶(+);e—绢云母呈斜长石假象发育(+);f—黑云母绿泥石化,并析出磁铁矿(−);Qz—石英;Bi—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Kf—钾长石;Pth—条纹长石;Mt—磁铁矿;Ser—绢云母化;(+)—正交偏光;(−)—单偏光
Figure 3. Microphotographs of Mogutu granite
a- Yellowish pink biotite moyite; b- Gray biotite moyite; c- Carlsbad twin law of orthoclase; d- Plagioclase was absorbed by the microcline and carlsbadal bite compound twin of plagioclase; e- Sericite appears to develop in the illusion of plagioclase; f- Magnetite precipitation of biotite mainly results from epidotization; Qz-Quartz; Bi-Bitite; Pl-Plagioclase; Kf-K-feldspar; Pth-Perthite; Mt-Magnetite; Ser-Sericitization; (−)-Plane polarization; (+)-Orthogonal polarization
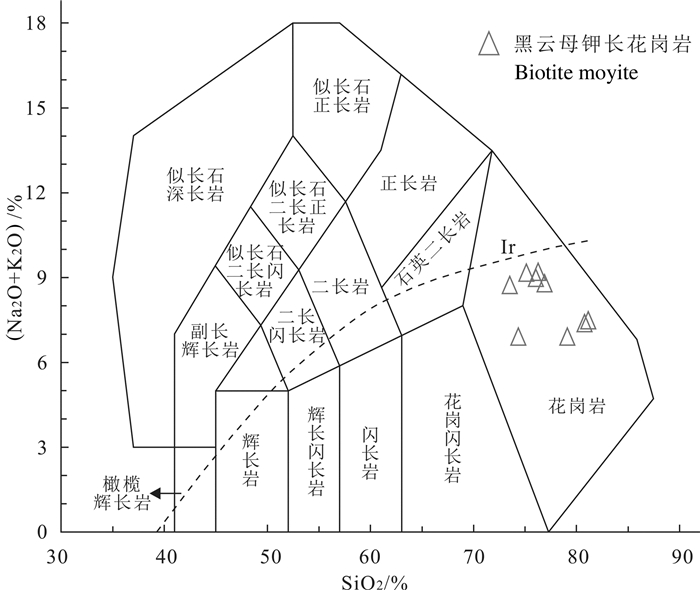
图 6 莫古吐花岗岩TAS分类图解(据Middlemost, 1994)
Figure 6. TAS diagram of the Mogutu granite(after Middlemost, 1994)
图 7 莫古吐花岗岩SiO2−AR岩石系列判别图(据Rickwood, 1989)和A/CNK−ANK图解(据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989)
Figure 7. SiO2−AR discriminant diagram (after Rickwood, 1989) and A/CNK−ANK Diagram (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) of the granite
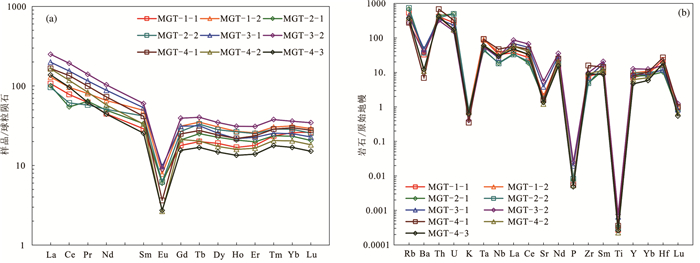
图 8 莫古吐花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石分布型式图(a)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蜘蛛图(b)
(标准化数据据文献Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)
Figure 8. Chondrite-normalized REE pattern(a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram(b)of the Mogutu granite
(chondrite and primitive mantle normalized values after reference Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)
图 9 莫古吐花岗岩Rb−Sr−Ba图解(据Müller and Groves, 2001)
Figure 9. Rb−Sr−Ba triangular diagram of the Mogutu granite (after Müller and Groves, 2001)
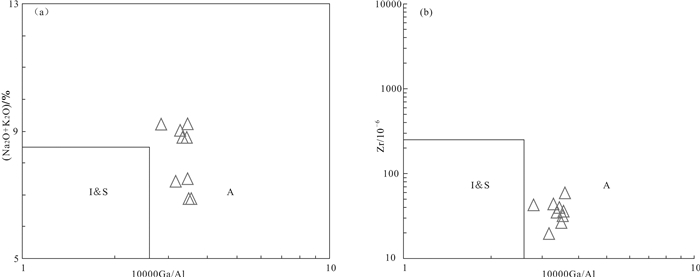
图 10 104×Ga/Al−(Na2O+K2O)图解(a)与104×Ga/Al−Zr图解(b)(底图据Joseph et al., 1987)
Figure 10. 104×Ga/Al−(Na2O+K2O) diagram(a) and 104×Ga/Al−Zr diagram of the Mogutu granite(b)(after Joseph et al., 1987)
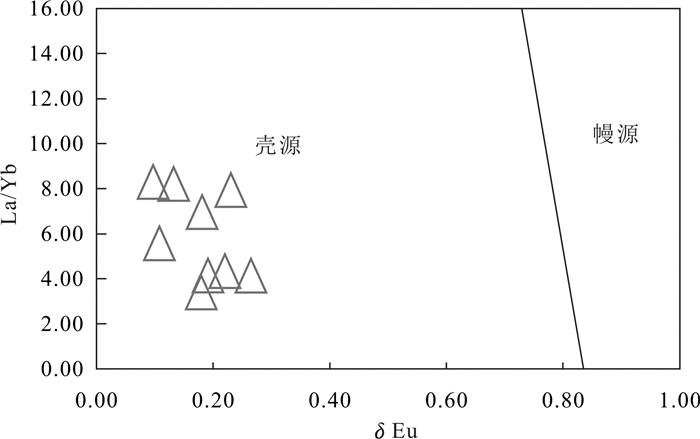
图 11 莫古吐花岗岩δEu−La/Yb图解(底图据文献Joseph et al., 1987)
Figure 11. δEu−La/Yb diagram of the Mogutu granite (after reference Joseph et al., 1987)
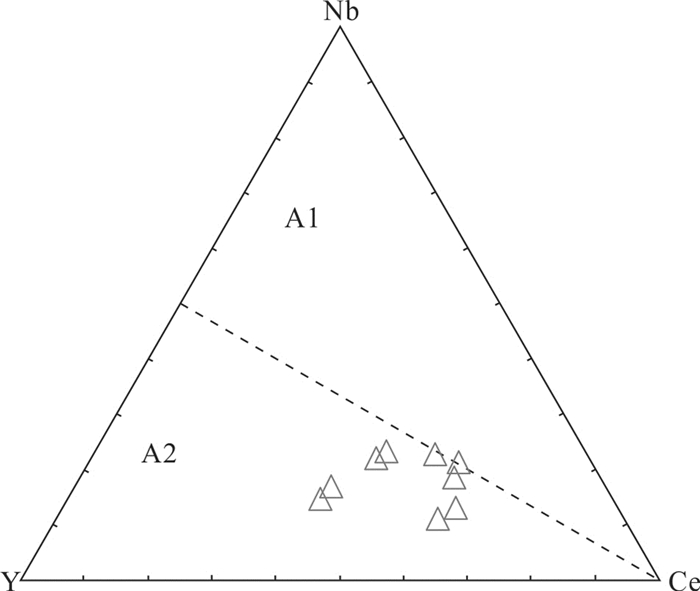
图 12 莫古吐花岗岩Nb−Ce−Y构造环境判别图解(底图据文献Pearce et al., 1984)
A1—非造山花岗岩;A2—造山后花岗岩
Figure 12. Nb−Ce−Y discrimination diagram of tectonic setting of the Mogutu granite(after reference Pearce et al., 1984)
A1-anorogenic granite; A2-post-orogenic granite
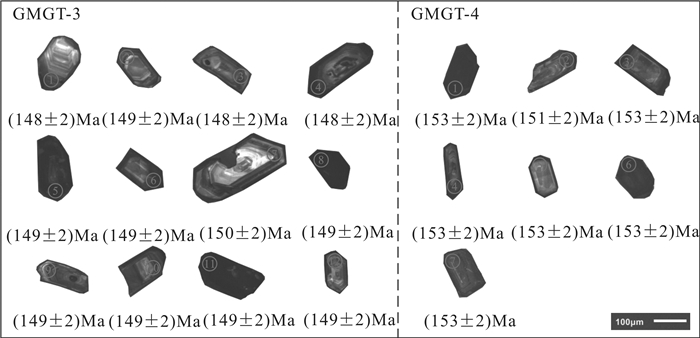
表 1 莫古吐花岗岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb分析数据
Table 1 LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb age of the Mogutu granite

表 2 莫古吐花岗岩体主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)组成
Table 2 Major element (%) and trace element (10−6) composition of the Mogutu granite

-
Cai Jianhui, Yan Guohan, Xu Baoliang, Wang Guanyu, Mu Baolei, Zhao Yongchao. 2006. The late Mesozoic alkaline intrusive rocks at the east foot of the Taihang-Da Hinggan Mountains:Lithogeochemical characteristics and their implication[J]. Acta Geoscientice Sinica, 27(5):447-459(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chappell B W, White A J R. 1974. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 8(2):173-174.
Chen Zhiguang, Zhang Lianchang, Wu Huaying, Wang Bo, Zeng Qindong. 2008. Geochemistry study and tectonic background of A style host granite in Nianzigou molybdenum doposit in Xilamulun molybdenum metallogenic belt, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4):257-267(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200804027.htm
Cheng Xiyin, Zhu Xinyou, Liu Zi. 2017. Magmatic evolution and tin polymetallic mineralization of Yanshenian highly fractionated granite in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36:142-142(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dill H G. 2015. Pegmatites and aplites:Their genetic and applied ore geology[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 69:417-561. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.022
Eby G N. 1990. The A-type granitoids:A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 26(1):115-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002449379090043Z
Eby G N. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 20(7):641. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Fan W M, Guo F, Wang Y J, Lin G. 2003. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 121(1):115-135. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80016058827
Gao Fei, Liu Yongjiang, Wen Quanbo, Li Weimin, Feng Zhiqiang, Fan Wenliang, Tan Chao. 2018. Zircon U-Pb ages and its geological implication of Mesozoic granites in Tuquan-Keerqin Youyizhongqi region[J]. Journal of Jinlin University(Earth Science Edition), 48(3):769-783(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/329307248_Zircon_U-Pb_Ages_and_Its_Geological_Implication_of_Mesozoic_Granites_in_Tuquan-Keerqin_Youyizhongqi_Region
Gao Yuan, Zheng Changqing, Yao Wengui, Wang Hao, Li Juan, Shi Lu, Cui Fanghua, Gao Feng, Zhang Xingxing. 2013. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Luotuobozi pluton in the Haduohe area in the Northern Daxing'anling[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(9):1293-1310(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201309008
Gu Yuchao, Chen Renyi, Jia Bin, Yu Chantao, Ju Nan. 2017. Zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the syenogranite from the Bianjiadayuan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit of Mongolia and its tectonic implications[J]. Geology in China, 44(1):101-117(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201701009.htm
Guo F, Li H X, Fan W M, Li J Y, Zhao L, Huang M W, Xu W L. 2015. Early Jurassic subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Ocean in NE China:Petrologic and geochemical evidence from the Tumen mafic intrusive complex[J]. Lithos, 224-225:46-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.02.014
Harris N B W, Inger S. 1992. Trace element modelling of pelite-derived granites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 110(1):46-56. doi: 10.1007/BF00310881
Hoskin P W O, Black L P. 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4):423-439. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x
Huang Shiqi, Dong Shuwen, Zhang Fuqin, Miao Laicheng, Zhu Mingshuai. 2014. Tectonic deformation and dynamic characteristics of the middle-part of the Mongolia-Okhotsk Collisional Belt, Mongolia[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(4):415-424(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98325A/201404/662004045.html
Jai Xiaohui, Wang Qiang, Tang Gongjian. 2009. A-type granites:Research progress and implication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(3):465-480(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200903020.htm
Jiang Sihong, Nie Fengjun, Liu Yifei, Yun Fei. 2010. Sulfur and lead isotopic compositionas of Bairendaba and Weilasituo silver-polymetallic deposits, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral and Deposits, 29(1):101-112(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/main/zcps.aspx?c=1&id=33117129
Joseph B. Whalen, Kenneth L. 1987. Currie, Bruce W. Chappell. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 95(4):407-419. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0102&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F00206814.2017.1377121&key=10.1007%2FBF00402202
King P L, Chappell B W, Allen C M, White A J R. 2001. Are A-type granites the high-temperature felsic granites? Evidence from fractionated granites of the Wangrah Suite[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 48(4):501-514. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00881.x
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, Allen C M. 1997. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
Li Jintie, Mo Shenguo, He Zhengjun, Sun Guihua, Chen Wen. 2004. The timing of crustal sinistral strike-slip movement in the northern Great Khing'an ranges and its constraint on reconstruction of the crustal tectonic evolution of NE China and adjacent areas since the Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3):157-168(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY200403022.htm
Li Pengchuan, Liu Zhengdong, Li Shichao, Xu Zhongyuan, Li Gang, Guan Qingbin.2016.Geochronology, geochemistry, zircon Hf isotopic characteristics and tectonic setting of Hudugeshaorong Pluton in Balinyouqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science, 41(12):1995-2007(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201612003.htm
Lin Qiang, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Cao Lin. 2004. Geochemistry of Mesozoic granites in Da Hinggan Ling ranges[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3):403-412(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279699322_Geochemistry_of_Mesozoic_granites_in_Da_Hinggan_Ling_rangs
Liu Chanshi, Chen Xiaoming, Chen Peiron, Wang Rucheng, Hu Huan. 2003. Subdivision, discrimination criteria and genesis for A-type rock suites[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 9(4):573-591(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_geological-journal-china-universities_thesis/0201253567896.html
Liu Jianming, Zhang Rui, Zhang Qinzhou. 2004. The Regional Metallogeny of Da Hinggan Ling, China[J]. Earth Science Frontires, 11(1):269-277(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/302500005_The_regional_metallogeny_of_Da_Hinggan_Ling_China
Liu Zhi, Lü Xinbiao, Mei Wei. 2012. Discussion on metallogenic material source of Huanggang Sn-Fe Deposit——Evidence from O -S-Pb isotopic compositions[J]. Mineral Deposits, (S1):583-584(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zhi, Lü Xinbiao, Mei Wei. 2013. The isotopic composition of S-Pb-O of Huanggang Sn-Fe Deposit, Inner Mongolia:Implications for the ore-forming material source[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 33(3):30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283380720_Sulfur-lead-oxygen_isotope_compositions_of_the_huanggang_skarn_Fe-Sn_deposit_Inner_Mongolia_Implications_for_the_sources_of_ore-forming_materials
Loiselle M C and Wones DR. 1979. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr., 11:468. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10019593683
Long Zhou, Lai Lin, Zhang Xuebin, Zhangmingyang, Zhou Changhong. 2017. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the A-type granites in Sunite Youqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 53(6):1115-1128(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201706007.htm
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Mao Jingwen, Zhou Zhenhua, Wu Guang, Jiang Sihong, Liu Chenglin, Li Houmin, Ouyang Hegen, Liu Jun.2013. Metallogenic regularity and minerogenetic series of ore deposits in Inner Mongolia and adjacent areas[J]. Mineral Deposits, 32(4):715-729(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285350451_Metallogenic_regularity_and_minerogenetic_series_of_ore_deposits_in_Inner_Mongolia_and_adjacent_areas
Mao Jingweng, Xie Guiqing, Zhang Zuoheng, Li Xiaofeng, Wang Yitian, Zhangchangqing, Li Yongfeng. 2005. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1):169-188(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/282053876_Mesozoic_large-scale_metallogenic_pulses_in_North_China_and_Corresponding_geodynamic_setting
Mao Jingweng, Zhang Zuoheng, Yu Jinjie, Wang Yitian, Niu Baogui. 2003. Geodynamic settings of large-scale metallogenic pulses in Mesozoic in North China and its adjacent areas:Enlightenment from mineralization age about metal deposits[J]. Science in China, 33(4):289-299(in Chinese with English abstract).
Meng Q R. 2003. What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract?[J]. Tectonophysics, 369(3/4):155-174. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195103001951
Middlemost E A K. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 37(3/4):215-224. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012825294900299
Müller D, Groves D I. 2001. Potassic igneous rocks and associated gold-copper mineralization[J]. Mineral Resource Reviews, 56(2/3):265-266.
Ouyang H G, Mao J W, Santosh M, Zhou J, Zhou Z Z, Wu Y, Hou L. 2013. Geodynamic setting of Mesozoic magmatism in NE China and surrounding regions:Perspectives from spatio-temporal distribution patterns of ore deposits[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 78(12):222-236. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912013003593
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jour. Petrol., 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Peng Qingsong, Zhang Zhiqiang, Zhu Xinyou, Huang Xingkai, Xuqiao. 2017. U-Pb age of zircon mineral in Huaganzigou pluton and its geological significance in central and southern part of the Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Mineral Exploration, 8(6):927-936(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201706003.htm
Ren Yaowu. 1995. Analysis of regional ore-controlling factors of tin-copper polymetallic ore deposit in the southeast margin of Da Hinggan Ling[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 14(1):33-34(in Chinese with English abstract).
Rickwood P C. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Shao J A, Liu F T, Chen H. 2000. Seismic tomography of the northest Pacific and its geodynamic implications[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 11(1):46-49.
Shao Ji'an, Liu Futian, Chen Hui, Han Qingjun. 2001. Relationship between Mesozoic Magmatism and Subduction in Da Hinggan-Yanshan Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(1):56-63(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86253X/20011/1001445410.html
Shao Ji'an, Mu Baolei, Zhu Huizhong, Zhang Lüqiao. 2010. Material source and tectonic settings of the Mesozoic mineralization of the Da Hinggan Mts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(3):649-656(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1472509
Shao Ji'an, Zhang Lüqiao, Mu Baolei. 2015. Magmatism in the Mesozoic extending orogenic process of Da Hinggan MTS[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(4):339-346(in Chinese with English abstract). http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10008463139
She Hongquan, Li Jinwen, Xiang Anping, Guan Jidong, Yang Xuncheng, Zhang Dequan, Tan Gang, Zhang Bin. 2012. U-Pb ages of the zircons from primary rocks in middle-northern Daxinganlin and its implications to geotectonic evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2):217-240(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Tapani Rämö O, Mclemore V T, Hamilton M A, Kosunen P J, Heizler M, Haapala I. 2003. Intermittent 1630-1220 Ma magmatism in central Mazatzal province:New geochronologic piercing points and some tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 31(4):335-338. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0335:IMMICM>2.0.CO;2
Wang Chunnv, Wang Quanming, Yu Xiaofei, Han Zhenzhe. 2016. Metallognetic characteristics of tin and ore-serach prospect in the southern part of Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geology and Exploration, 52(2):220-227(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, Ying J F, Zhang Y T, Wu F Y, Zhu R X. 2006. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China):Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 251(1):179-198.
Wang Jingbin, Wang Yuwang, Wang Lijuan. 2005. Tin-polymetallic metallogenic series in the southern part of Da Hinggan mountains China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 41(6):15-20(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200506002.htm
Wang Lijuan, Hidehiko Shimazaki, Wang Jingbin, Wang Yuwang. 2001. Ore-forming fluid and Mineralization of Huanggang Sn-Fe Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Science in China:Earth Science, 31(7):553-562(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285832551_Ore-forming_fluid_and_mineralization_of_Huangguangliang_skarn_Fe-Sn_deposit
Wang T, Zheng Y D, Zhang J J, Zeng L S, Donskaya T, Guo Lei, Li J B. 2011. Pattern and kinematic polarity of Late Mesozoic extension in continental NE Asia:Perspectives from metamorphic core complexes[J]. Tectonics, 30(6).
Wang Yanbin, Han Juan, Li Jianbo, OuYang Zhixia, Tong Ying, Hou Kejun. 2010. Age, petrogenesis and geological significance of the deformed granitoids in the Louzidian metamorphic core complex, southern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia:Evidence from zircon U-Pb dates and Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 29(6):763-778(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSKW201006013.htm
Wang Yang. 2009. Geochemistry of the Baicha A-type granite in Beijing Municipality:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(1):13-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
Waston E B, Harrison T M. 1983. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, Zhang Y B, Grant M L, Wilde S A, Jahn B M. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H, Jahn B M, Wilde S. 2002. A-type granites in northeastern China:Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 187(1/2):143-173.
Wu Fuyuan, Li Xianhua, Yang Jinhui, Zheng Yongfei. 2007. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6):1217-1238(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279707410_Discussion_on_the_petrogenesis_of_granites
Wu Fuyuan, Liu Xiaochi, Ji Weiqiang, Wang Jiamin, Yang Lei. 2017. Highly fractionated granites:Recognition and research[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 47(7):745-765(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Baoliang, Yan Guohan, Zhang Chen, Li Zhitong, He Zhongfu. 1989. Petrological subdivision and source material of A-type granites[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 5(3):113-124(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Bei Fuping, Meng En, Tang Jie, Xu Meijun, Wang wei. 2012. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China:Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock assocaitions[J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 29(2):339-353(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Qidi, Guo Lei, Wang Tao, Zeng Tao, Zhang Lei, Tong Ying, Shi Xingjun, Zhang Jianjun. 2014. Geochronology, origin, sources and tectonic settings of Late Mesozoic two-stage granites in the Ganzhuermiao region, central and southern Da Hinggan Range, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7):1961-1981(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291495722_Geochronology_origin_sources_and_tectonic_settings_of_Late_Mesozoic_two-stage_granites_in_the_Ganzhuermiao_region_central_and_southern_Da_Hinggan_Range_NE_China
Ying J F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, Wang F. 2010. Geochronological framework of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China, and their geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39(6):786-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.035
Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Qin K Z, Fan H G, Chu S X, Wang Y B, Zhou L L. 2013. Types, characteristics, and time-space distribution of molybdenum deposits in China[J]. International Geology Review, 55(11):1311-1358. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.774195
Zeng Q D, Sun Y, Chu S X, Duan X X, Liu J M. 2015. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Dongshanwan porphyry Mo-W deposit, Northeast China:Implications for the Late Jurassic tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97:472-485. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.027
Zeng Q, Liu J, Zhang Z. 2010. Re-Os geochronology of porphyry molybdenum deposit in south segment of Da Hinggan Mountains, Northeast China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 21(4):392-401. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0102-4
Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, Wu F Y, Yang J H, Wilde S A, Li M. 2010. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 276(3):144-165.
Zhang Qi, Jin Weijun, Li Chengdong, Wang Yuanlong. 2009. Yanshanian large-scale magmatism and lithosphere thinning in Eastern China:Relation to large igneous Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(2):21-51(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200902003.htm
Zhang Qi, Ran Hao, Li Chengdong. 2012. A-type granite:What is the essence?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(4):621-626(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201204015.htm
Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Li Chengdong, Wang Yuanlong, Jin Weijun, Jia Xiuqin. 2006. Granite classification on the Sr and Yb contents and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(9):2249-2269(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1473353
Zhang Qi, Wang Yuanlong, Jin Weijun, Jia Xiuqin, Li Chengdong. 2008. Criteria for the recognition of pre-, syn- and post-orogenic granitic rocks[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(1):1-18(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200801002.htm
Zhang Qi. 2013. Is the Mesozoic magmatism in eastern China related to the westward subduction of the Pacific plate?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(1):113-128(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285504847_Is_the_Mesozoic_magmatism_in_Eastern_China_related_to_the_Westward_subduction_of_the_Pacific_Plate
Zhang Qi. 2013. The criteria and discrimination for A-type granites:A reply to the question put forward by Wang Yang and some other persons for "A-type granite:What is essence?"[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(2):267-274(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201302014.htm
Zhang Xuebing. 2017. Pb-Zn Polymetallic Deposits Metallogenic Series and Prospecting Direction of the West Slope of Southern Great Xing'an Range[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Xinyou, Zhang Zhimei, Fu Xu, Li Baiyang, Wang Yanli, Jiao Shoutao, Sun Yalin. 2016. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Weilasito Sn-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 43(1):188-208(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/311433623_Geological_and_geochemical_characteristics_of_the_Weilasito_Sn-Zn_deposit_Inner_Mongolia
蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 许保良, 王关玉, 牟保磊, 赵永超. 2006.太行山-大兴安岭东麓晚中生代碱性侵入岩岩石地球化学特征及其意义[J].地球学报, 27(5):447-459. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.007 陈志广, 张连昌, 吴华英, 万博, 曾庆栋. 2008.内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带碾子沟钼矿A型花岗岩地球化学和构造背景[J].岩石学报, 24(4):257-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200804027.htm 程细音, 祝新友, 刘孜. 2017.内蒙古赤峰燕山晚期高演化花岗岩岩浆演化与锡多金属成矿[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36:142-142. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201704001120.htm 高飞, 刘永江, 温泉波, 李伟民, 冯志强, 范文亮, 汤超. 2018.内蒙古突泉-科尔沁右翼中旗地区中生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(3):769-783. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201803012.htm 高源, 郑常青, 姚文贵, 王浩, 李娟, 施璐, 崔芳华, 高峰, 张行行. 2013.大兴安岭北段哈多河地区骆驼脖子岩体地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学[J].地质学报, 87(9):1293-1310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201309008.htm 顾玉超, 陈仁义, 贾斌, 宋万兵, 余昌涛, 鞠楠. 2017.内蒙古边家大院铅锌银矿床深部正长花岗岩年代学与形成环境研究[J].中国地质, 44(1):101-117. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170108&flag=1 黄始琪, 董树文, 张福勤, 苗来成, 朱明帅. 2014.蒙古-鄂霍茨克构造带中段构造变形及动力学特征[J].地球学报, 35(4):415-424. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201404004.htm 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建. 2009. A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 33(3):465-480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.017 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 云飞. 2010.内蒙古拜仁达坝及维拉斯托银多金属矿床的硫和铅同位素研究[J].矿床地质, 29(1):101-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.010 李锦轶, 莫申国, 和政军, 孙桂华, 陈文. 2004.大兴安岭北段地壳左行走滑运动的时代及其对中国东北及邻区中生代以来地壳构造演化重建的制约[J].地学前缘, 11(3):157-168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.017 李鹏川, 刘正宏, 李世超, 徐仲元, 李刚, 关庆彬. 2016.内蒙古巴林右旗胡都格绍荣岩体的年代学、地球化学、Hf同位素特征及构造背景[J].地球科学, 41(12):1995-2007. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201612003.htm 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 孙德有, 曹林. 2004.大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J].岩石学报, 20(3):403-412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200403004.htm 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 王汝成, 胡欢. 2003. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J].高校地质学报, 9(4):573-591. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.04.011 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲. 2004.大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J].地学前缘, 11(1):269-277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.024 刘智, 吕新彪, 梅微. 2012.内蒙黄岗铁锡矿床物质来源探讨——来自O-Pb-S同位素的证据[J].矿床地质, (S1):583-584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2012S1295.htm 刘智, 吕新彪, 梅微. 2013.内蒙古黄岗矽卡岩型铁锡矿床S-Pb-O同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的指示[J].矿物岩石, 33(3):30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2013.03.006 龙舟, 来林, 张学斌, 张明洋, 周长红. 2017.内蒙古苏尼特右旗白垩纪A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].地质与勘探, 53(6):1115-1128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2017.06.007 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 李晓峰, 王义天, 张长青, 李永峰. 2005.中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背[J].岩石学报, 21(1):169-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501018.htm 毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 王义天, 牛宝贵. 2003.华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学背景:从金属矿床年龄精测得到启示[J].中国科学:地球科学, 33(4):289-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304000.htm 毛景文, 周振华, 武广, 江思宏, 刘成林, 李厚民, 欧阳荷根, 刘军. 2013.内蒙古及邻区矿床成矿规律与成矿系列[J].矿床地质, 32(4):715-729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.04.006 彭青松, 张志强, 祝新友, 黄行凯, 徐巧. 2017.大兴安岭中南段桦杆子沟岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].矿产勘查, 8(6):927-936. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2017.06.003 任耀武. 1995.大兴安岭东南缘锡铜多金属矿床区域控矿因素分析[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 14(1):33-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH501.011.htm 邵济安, 刘福田, 陈辉, 韩庆军. 2001.大兴安岭-燕山晚中生代岩浆活动与俯冲作用关系[J].地质学报, 75(1):56-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.01.006 邵济安, 牟保磊, 朱慧忠, 张履桥. 2010.大兴安岭中南段中生代成矿物质的深部来源与背景[J].岩石学报, 26(3):649-656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201003001.htm 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊. 2015.大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J].地学前缘, 6(4):339-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY199904025.htm 佘宏全, 李进文, 向安平, 关继东, 杨勋城, 张德全, 谭刚, 张斌. 2012.大兴安岭中北段原岩锆石U-Pb测年及其与区域构造演化关系[J].岩石学报, 28(2):217-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202019.htm 汪洋. 2009.北京白查A型花岗岩的地球化学特征及其成因与构造指示意义[J].岩石学报, 25(1):13-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200901003.htm 王春女, 王全明, 于晓飞, 韩振哲. 2016.大兴安岭南段锡矿成矿特征及找矿前景[J].地质与勘探, 52(2):220-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201602003.htm 王京彬, 王玉往, 王莉娟. 2005.大兴安岭南段锡多金属成矿系列[J].地质与勘探, 41(6):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2005.06.003 王莉娟, 岛崎英彦, 王京彬, 王玉往. 2001.黄岗梁矽卡岩型铁锡矿床成矿流体及成矿作用[J].中国科学:地球科学, 31(7):553-562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200107003.htm 王彦斌, 韩娟, 李建波, 欧阳志侠, 童英, 候可军. 2010.内蒙赤峰楼子店拆离断层带下盘变形花岗质岩石的时代、成因及其地质意义——锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 29(6):763-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.013 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 郑永飞. 2007.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 23(6):1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 王佳敏, 杨雷. 2017.高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J].中国科学:地球科学, 47(7):745-765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201707001.htm 许保良, 阎国翰, 张臣, 李之彤, 何中甫. 1998. A型花岗岩的岩石学亚类及其物质来源[J].地学前缘, 5(3):113-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1998.03.011 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 孟恩, 唐杰, 徐美君, 王伟. 2012.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 29(2):339-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302002.htm 杨奇荻, 郭磊, 王涛, 曾涛, 张磊, 童英, 史兴俊, 张建军. 2014.大兴安岭中南段甘珠尔庙地区晚中生代两期花岗岩的时代、成因、物源及其构造背景[J].岩石学报, 30(7):1961-1981. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407011.htm 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 王元龙. 2009.中国东部燕山期大规模岩浆活动与岩石圈减薄:与大火成岩省的关系[J].地学前缘, 16(2):21-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.002 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东. 2012. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 31(4):621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.014 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 贾秀勤. 2006.花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 22(9):2249-2269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609000.htm 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 贾秀勤, 李承东. 2008.造山前、造山和造山后花岗岩的识别[J].地质通报, 27(1):1-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.01.001 张旗. 2013. A型花岗岩的标志和判别——兼答汪洋等对"A型花岗岩的实质是什么"的质疑[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 32(2):267-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.02.014 张旗. 2013.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 32(1):113-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.010 张雪冰. 2017.大兴安岭南段西坡铅锌多金属矿床成矿系列与找矿方向[D].吉林大学. 祝新友, 张志辉, 付旭, 李柏阳, 王艳丽, 焦守涛, 孙雅琳. 2016.内蒙古赤峰维拉斯托大型锡多金属矿的地质地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 43(1):188-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.014 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 何沛欣. 广东省粤中断裂型碳酸盐岩地热水的水文地球化学研究——以马星-隔陂地热系统为例. 广东化工. 2024(05): 67-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王君照,李胜涛,岳冬冬,张秋霞,李菊红,崔俊艳,杨骊. 基于GIS与GOCAD的天津双窑凸起构造区热储三维地质建模. 科学技术与工程. 2023(14): 5887-5902 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程正璞,雷鸣,李戍,连晟,魏强. 天津东丽湖深部岩溶热储时频电磁法探测及有利区预测. 华北地质. 2023(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 岳冬冬,贾小丰,张秋霞,冯昭龙,李胜涛. 天津山岭子地热田蓟县系雾迷山组热储流体同位素特征及其指示意义. 华北地质. 2023(02): 45-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘杰,宋美钰,胥博文,阮传侠,石峰. 天津市馆陶组地热流体可采量计算方法及适宜性分区研究. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1655-1666 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 杨吉龙,汪大明,牛文超,相振群,刘洋,赵泽霖,程先钰. 天津地热资源开发利用前景及存在问题. 华北地质. 2022(03): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王婷灏,汪新伟,毛翔,罗璐,高楠安,刘慧盈,吴陈冰洁. 沧县隆起北部地区地热资源特征及开发潜力. 中国地质. 2022(06): 1747-1764 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: