Boundary definition of Wufeng Formation and Longmaxi Formation in well DD1 and sedimentary environment evolution of Northeastern Yunnan
-
摘要:
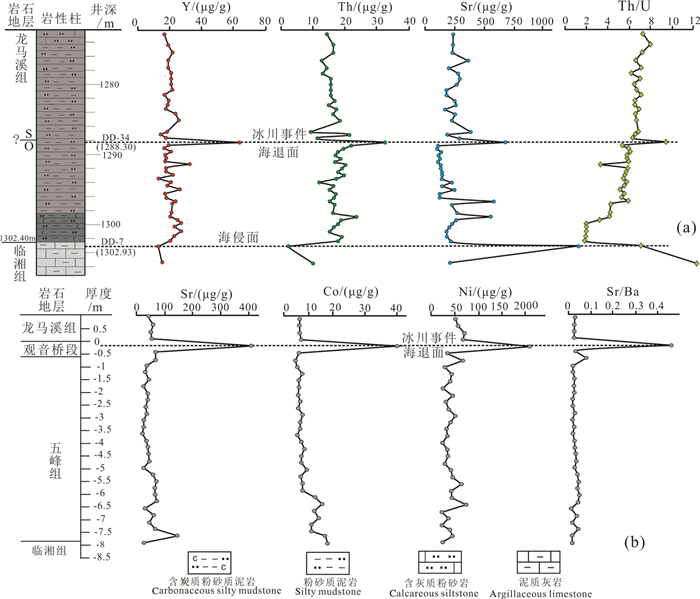
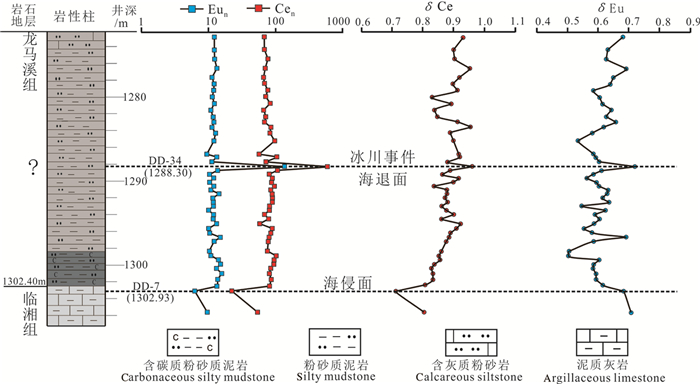
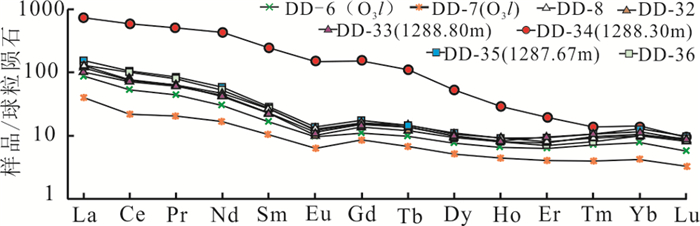
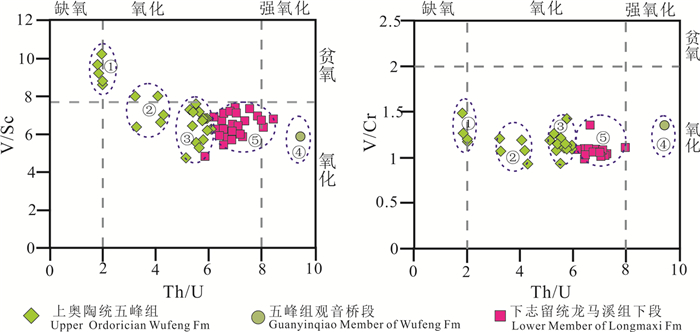
DD1井上奥陶统临湘组泥灰岩之上发育大套粉砂质泥岩,笔石化石缺乏,也未发现观音桥段含赫南特贝灰岩标志层,O-S界线通过生物地层和岩石地层方法难以确定。微量、稀土元素分析表明,粉砂质泥岩中部(1288.3 m)的Th、Sr、Y、Th/U以及Cen、Eun、δCe、δEu曲线均呈现尖锐的异常峰,该处∑REE含量显著高于上下地层,REE分布曲线右倾斜率更大。将DD1井与扬子地区其他O-S界线剖面的元素地球化学特征进行对比分析,可判断DD1井存在五峰组观音桥段,该标志层的厚度也小于1 m。微量元素地球化学氧化-还原判别图还表明,五峰期-龙马溪期早期沉积水介质主要处于弱氧化环境,观音桥期氧化性达到最强;根据沉积学标志分析,O-S之交沉积相演变过程为:潮下→潮间→潮上→潮间,在观音桥期水体最浅,为潮上带沉积。
Abstract:Although the Upper Ordovician Linxiang Formation marl in DD1 well is covered with thick silty mudstone, there is a lack of graptolite fossil, and no Hirnantia limestone marker stratum of the Guanyinqiao Member. Therefore, it is difficult to determine the boundary between Ordovician System and Silurian System by biostratigraphic and petrostratigraphic methods. The analysis of trace elements and REE of silty mudstone in the well DD1 shows that Th, Sr, Y, Th/U, Cen, Eun, δCe and δEu curves at the middle part of silty mudstone (1288.3m) present sharp abnormal peaks with significantly higher ΣREE content of silty mudstone (1288.3m) than its upper and lower silty mudstone and great right slope of the REE distribution curve. By comparing the elemental geochemistry characteristics of the well DD1 with other O-S boundary in the Yangtze Region, it can be concluded that there exists Guanyinqiao Member of Wufeng Formation in the well DD1, and the thickness of this marker layer is also less than 1 m. The geochemical redox discriminant graph shows that the sedimentary water medium mainly was in weak oxidation environment from the Wufeng period to the early Longmaxi period, and its oxidation was the strongest in the Guanyinqiao period. According to the analysis of sedimentary markers, the evolution process of the sedimentary facies at the O-S transition is as follows:subtidal → intertidal → supertidal → intertidal; in the Guanyinqiao period, the water was the shallowest, and there existed supertidal deposits.
-
致谢: 本文在古生物鉴定方面得到了中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所詹仁斌研究员和樊隽轩研究员的帮助,成文过程中与中国地质调查局成都地质调查中心刘伟高工、陆俊泽工程师进行有益的讨论,审稿专家也提出了宝贵的意见,在此一并表示感谢!
-
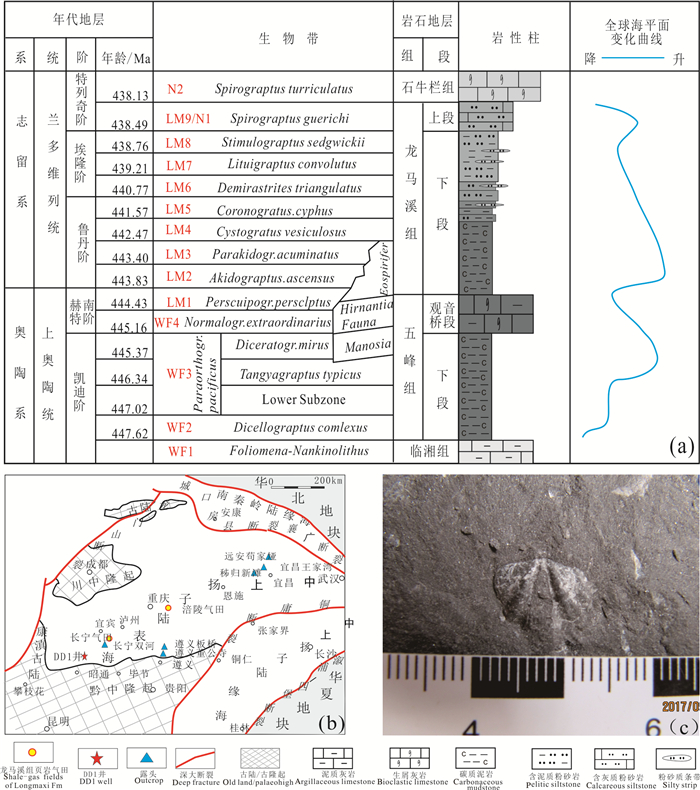
图 1 DD1井地质背景图
a—中上扬子地区奥陶系-志留系界线附近年代地层、岩石地层及生物地层划分(据陈旭等, 1987, 2017; 聂海宽等, 2011;略有修改);b—中上扬子晚奥陶世赫南特期(五峰期)DD1井所处古地理与大地构造背景(据戎嘉余等, 1987;牟传龙等, 2011;略有修改);c—DD1井龙马溪组中部(井深1205.5 m处)粉-细砂岩中的腕足化石
Figure 1. Geological map of the well DD1
a-division of chronostratigraphy, lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy near the Ordovician-Silurian boundary in the upper and middle Yangtze plate (modified from Chen Xu et al., 1987, 2017; Nie Haikuan et al., 2011); b-paleogeography and geotectonic setting of DD1 well in Hirnantian (Wufeng period) in the middle and upper Yangtze plate (modified from Rong Jiayu et al., 1987, Mou Chuanlong et al., 2011); c-brachiopod fossils from siltstone in the middle of Longmaxi Formation (1205.5 m) of DD1 well
图 2 奥陶系—志留系界线附近敏感微量元素地球化学异常分布曲线对比图
a—滇东北DD1井;b—湖北省远安县苟家垭剖面(据王传尚等, 2002)
Figure 2. Sensitive trace elements curves near Ordovician-Silurian boundary
a-DD1 well in Northwest Yunnan; b-Goujiaya section, Yuan'an County, Hubei Province(after Wang Chuanshang et al., 2002)
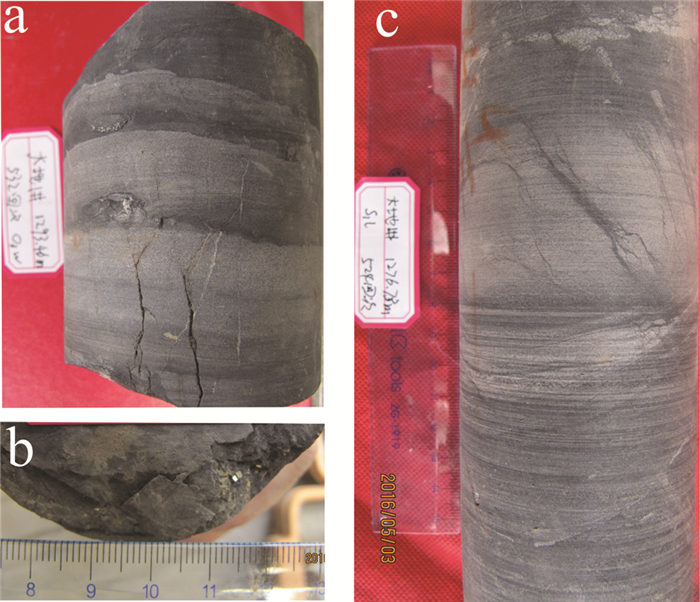
图 6 DD1井奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组下段发育的沉积标志
a—波状层理、脉状层理,五峰组下段,1293.46 m;b—菱形自形黄铁矿,五峰组下段,1291.51m;c—透镜状层理、粉砂质条带,龙马溪组下段底部,1276.78 m
Figure 6. Sedimentological markers from Wufeng Formation to Lower Member of Longmaxi Formation in the well DD1
a- Wavy bedding, vein bedding, Lower member of Wufeng Formation, 1293.46 m; b- Rhombic euhedral pyrite, Lower member of Wufeng Formation, 1291.51m; c- Lenticular bedding and silty belt, the bottom of Lower Longmaxi Formation, 1276.78 m
表 1 DD1井部分代表性样品主量、微量和稀土元素含量及比值(主量元素单位为%;其他元素为μg/g)
Table 1 Contents and ratios of trace elements, REE(μg/g) and major elements(%)in some samples of well DD1

-
Algeo T J, Maynard J B. 2004. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems[J]. Chemical Geology, 206:289-318. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.009
Chen Xiaohong, Wang Xiaofeng. 1999. Multiple stratigraphic subdivision and sea level changes of the early Paleozoic in Yangtze Gorges area[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 15(3):1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HNKC199903000.htm
Chen X, Rong J Y, Mitchell C E, Harper D A T, Fan J X, Zhan R B, Zhang Y D, Li R Y, Wang Y. 2000. Late Ordovician to earliest Silurian graptolite and brachiopod biozonation from the Yangtze region, South China, with a global correlation[J]. Geological Magazine, 137:623-650. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800004702
Chen Xu, Fan junxuan, Wang Wenhui, Wang Hongyan, Nie Haikuan, Shi Xuewen, Wen zhidong, Chen Dongyang, Li Wenjie. 2017. Stage-progressive distribution pattern of the Lungmachi black graptolitic shales from Guizhou to Chongqing, Central China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 60:1133-1146(in Chinese).
Fan junxuan, Melchin M J, Chen Xu, Wang Yi, Zhang Yuandong, Chen Qing, Chi Zhaoli, Chen Feng. 2011. Biostratigraphy and geography of the Ordovician-Silurian Lungmachi black shales in South China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 54:1854-1863(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4301-3
Fang Yiting, Bian Lizeng, Yu Jianhua, Feng Hongzhen. 1993. Sedimentary environment pattern of Yangtz palte in Wufeng age of Late Ordovician[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 11(3):7-12(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199303001.htm
Feng Hongzhen, Erdtmann B D, Wang Haifeng. 2000. Anomaly of whole-rock Ce and sea level variation in Early Paleozoic in the upper Yangtze plate[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 30(1):66-72(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG200003011.htm
Feng Weiming, Zhao Zhan, Li Rong, Yu Qian, Ye Dingnan. 2020. Geological characteristics of shale gas of the Wufeng Fm -Longmaxi Fm in DD1 well in Northeast Yunnan and their exploration significances[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(4):17-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao Li, Wang Zongxiu, Liang Mingliang, Zhang Linyan, Li Huijun, Li Chunlin, Gao Wanli. 2019. Material composition and hydrocarbon potentialof the shale of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in northwestern Hunan[J]. Geology in China, 46(2):407-418(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201902018.htm
Guo Xusheng, Hu Dongfeng, Wen Zhidong, Liu Ruobing. 2014. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity in marine shale gas in the Lower Paleozoic of Sichuan Basin and its periphery:A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation of Jiaoshiba area[J]. Geology in China, 41(3):893-901(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DIZI201403016.htm
Goodfellow W D, Nowlan G S, McCracken A D, Lenz A C. 1992. Geochemical anomalies near the Ordovician-Silurian boundary, northern Yukon Territory, Canada[J]. Historical Biology, 6:1-23. doi: 10.1080/10292389209380415
He Jianglin, Liu Wei, Yang Ping, Yu Qian, Wang Jian, Wang Zhengjiang, Lu Junze, Qin Chuan. 2017. Genetic conditions of the shale gas and delineation of the favourable areas in the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation on the southwestern margin of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 37(3):50-58(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201703006.htm
Jones B, Manning D A C. 1994. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 111:111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
Kimura H, Watanabe Y. 2001.Ocean anoxia at the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary[J].Geology, 29:995-998. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0995:OAATPC>2.0.CO;2
Li Shuangjian, Xiao Kaihua, Wo Yujin, Long Shengxiang, Cai Liguo. 2008. REE geochemical characteristics and their geological signification in Silurian, west of Hunan Province and north of Guizhou Province[J]. Geoscience, 22(2):273-280(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200802014.htm
Lin Jiashan, Liu Jianqing, Feng Weiming, Jing Xiaoyan. 2014. Organic geochemical signatures and palaeo-environmental implications for the source rocks from the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northern Guizhou[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 34(2):79-85(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_sedimentary-geology-tethyan_thesis/0201252083262.html
Ma Yongsheng, Cai Xunyu, Zhao Peirong. 2018. China's shale gas exploration and development:Understanding and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(4):561-574(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S187638041830065X
Melchin M J, Mitchell C E, Holmden C, Štorch P. 2013. Environmental changes in the Late Ordovician-early Silurian:Review and new insights from black shales and nitrogen isotopes[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 125(11/12):1635-1670. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013GSAB..125.1635M
Mou Chuanlong, Zhou Kenken, Liang Wei, Ge Xiangying. 2011. Early Paleozoic sedimentary environment of hydrocarbon source rocks in the Middle-Upper Yangtze region and petroleum and gas exploration[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 85(4):526-532(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95080X/201104/38280138.html
Mu Enzhi, Zhu Zhaoling, Chen Junyuan, Rong Jiayu. 1983. Silurian in Shuanghe Section, Changning County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 7(3):208-215(in Chinese).
Munnecke A, Calner M, Harper D, Servais T. 2010. Ordovician and Silurian sea-water chemistry, sea level, and climate:A synopsis[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 296(4):389-413. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103308390.html
Nie Haikuan, Jin Zhijun, Ma Xin, Liu Zhongbao, Lin Tuo, Yang Zhenheng. 2017. Graptolites zone and sedimentary characteristics of Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 38(2):160-174(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYXB201702004.htm
Pi Xuejun, Liu Chuxiong, Chen Ying, Sun Zuoyu, Hao Weicheng. 2007. Discussion on chemo-stratigraphic characteristics of boundary bed between the top part of the Ordovician and the basal part of the Silurian at Dawangou Section, Keping, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 43(2):183-189(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/296184133_Discussion_on_chemo-stratigraphic_characteristics_of_boundary_bed_between_the_top_part_of_the_ordovician_and_the_basal_part_of_the_Silurian_at_Dawangou_Section_Keping_Xinjiang
Rong Jiayu, Chen Xu, Wang Yi, Zhan Renbin, Liu Jianbo, Huang Bing, Tang Peng, Wu Rongchang, Wang Guangxu. 2011.Northward expansion of Central Guizhou oldland through the Ordovician and Silurian transition:Evidence and implications[J]. Sci. Sin. Terrae, 41:1407-14151(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/zd-2011-41-10-1407
Rong Jiayu, Chen Xu, Zhan Renbin, Fan Junxuan, Wang Yi, Zhang Yuandong, Li Yue, Huang Bing, Wu Rongchang, Wang Guangxu. 2010. New observation on Ordovician-Silurian boundary strata of Southern Tongzi County, Northern Guizhou, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 34(4):337-348(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283466272_New_observation_on_Ordovician-Silurian_boundary_strata_of_southern_Tongzi_county_northern_Guizhou_Southwest_China
Sugitani K, Yamashita F, Nagaoka T, Yamamoto K, Minamie M, Mimura K, Suzuki K. 2006. Geochemistry and sedimentary petrology of Archean clastic sedimentary rocks at Mt. Goldsworthy, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia:Evidence for the early evolution of continental crust and hydrothermal alteration[J]. Precambrian Research, 147:124-147. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.02.006
Underwood C J, Deynoux M, Ghienne J F. 1998. High palaeolatitude(Hodh, Mauritania) recovery of graptolite faunas after the Hirnantian (end Ordovician) extinction event[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 142:91-105. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(98)00070-4
Wang K, Orth C J. 1993. The great latest Ordovician extinction on the South China Plate:Chemostratigraphic studies of the Ordovician-Silurian boundary interval on the Yangtze Platform[J]. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 104:61-79. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(93)90120-8
Wang Chuanshang, Chen Xiaohong, Wang Xiaofeng. 2002. Late Ordovician chemical anomaly and the environmental changes across the Ordovician-Silurian Boundary in Yangtze Gorges[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 26(4):272-279(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303286151_Late_Ordovician_chemical_anomaly_and_the_environmental_changes_across_the_Ordovician-Silurian_boundary_in_Yangtz_Gorges
Wang Yuman, Dong Dazhong, Huang Jinliang, LI Xinjing, Wang Shufang.2016. Guanyinqiao Member lithofacies of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation around the Sichuan Basin and the significance to shale gas plays, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 43(1):42-50(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_petroleum-exploration-development_thesis/0201218119171.html
Wang Yuman, Li Xinjing, Dong Dazhong, Zhang Chenchen, Wang Shufang. 2017. Main factors controlling the sedimentation of high-quality shale in Wufeng-Longmaxi Fm, Upper Yangtze region[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 37(4):9-20(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352854017301250
Wang Zhengjiang, Yu Qian, Yang Ping, Liu Wei, Yang Fei, Liu Jiahong, Xong Guoqing, He Jianglin, Deng Qi. 2018. The main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment and exploration prospect areas in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou border areas, southwestern China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 38(3):1-15(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201803001.htm
Wignall P B, Twitchett R J. 1996. Oceanic anoxia and the end Permian mass extinction[J]. Science, 272:1155-1158. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5265.1155
Yan Detian, Chen Daizhao, Wang Zao, Wang Jianguo. 2009. Geochemical changes across the Ordovician-Silurian transition on the yangtze platform, South China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, (Ser. D), 39(3):38-54(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ed200901005
Yan D T, Wang H, Fu Q, Chen Z H, He J, Gao Z. 2015. Geochemical characteristics in the Longmaxi Formation (Early Silurian) of South China:Implications for organic matter accumulation[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 65:290-301. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817215001440
Yang R, He S, Hu Q H, Hu D F, Yi J Z. 2016.Paleo-ocean redox environments of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng and the first member in Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formations in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 53(4) 426-440. doi: 10.1139/cjes-2015-0210
Yang Ping, Wang Zhengjiang, Yu Qian, Liu Wei, Liu Jiahong, Xiong Guoqing, He Jianglin, Yang Fei. 2019. An resources potential analysis of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale gas in the southwestern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 46(3):601-614(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201903012.htm
Zhan Renbin, Liu Jianbo, Percival I G, Jin Jisuo, Li Guipeng. 2010. Biodiversification of Late Ordovician Hirnantia Fauna on the Upper Yangtze Platform, South China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 40(9):1154-1163(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG201012007.htm
Zhang T S, Kershaw S, Wan Y, Lan G Z. 2000.Geochemical and facies evidence for palaeoenvironmental change during the Late Ordovician Hirnantian glaciation in South Sichuan Province, China[J]. Glob Planet Change, 24:133-152. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(99)00063-6
陈孝红, 汪啸风.1999.长江三峡地区早古生代多重地层划分与海平面升降事件[J].华南地质与矿产, 15(3):1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC199903000.htm 陈旭, 樊隽轩, 王文卉, 王红岩, 聂海宽, 石学文, 文治东, 陈冬阳, 李文杰.2017.黔渝地区志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的阶段性渐进展布模式[J].中国科学:地球科学, 47(6):720-732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201706005.htm 樊隽轩, Michael J.Melchin, 陈旭, 王怿, 张元动, 陈清, 迟昭利, 陈峰.2012.华南奥陶-志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的生物地层学[J].中国科学:地球科学, 42(1):130-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201201015.htm 方一亭, 边立曾, 俞剑华, 冯洪真.1993.晚奥陶世五峰期扬子板块沉积模式[J].沉积学报, 11(3):7-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199303001.htm 冯洪真, Bernd-D.Erdtmann, 王海峰. 2000.上扬子区早古生代全岩Ce异常与海平面长缓变化[J].中国科学:地球科学, 30(1):66-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200001009.htm 冯伟明, 赵瞻, 李嵘, 余谦, 叶定南. 2020.滇东北DD1井五峰-龙马溪组页岩气地质特征及其勘探启示[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 40(4):17-24. 高莉, 王宗秀, 梁明亮, 张林炎, 李会军, 李春麟, 高万里. 2019.湘西北地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩物质组成特征与页岩气潜力分析[J].中国地质, 46(2):407-418. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190217&flag=1 何江林, 刘伟, 杨平, 余谦, 王剑, 汪正江, 陆俊泽, 秦川. 2017.四川盆地西南缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气形成条件与有利区优选[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 37(3):50-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2017.03.006 郭旭升, 胡东风, 文治东, 刘若冰. 2014.四川盆地及周缘下古生界海相页岩气富集高产主控因素——以焦石坝地区五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J].中国地质, 41(3):893-901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.03.016 李双建, 肖开华, 沃玉进, 龙胜祥, 蔡立国. 2008.湘西、黔北地区志留系稀土元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].现代地质, 22(2):273-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.02.014 林家善, 刘建清, 冯伟明, 景小燕. 2014.黔北下志留统龙马溪组烃源岩有机地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 34(2):79-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201402012.htm 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 2018.中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J].石油勘探与开发, 45(4):561-574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804004.htm 穆恩之, 朱兆玲, 陈均远, 戎嘉余.1983.四川长宁双河的志留系[J].地层学杂志, 7(3):208-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198303005.htm 牟传龙, 周恳恳, 梁薇, 葛祥英. 2011.中上扬子地区早古生代烃源岩沉积环境与油气勘探[J].地质学报, 85(4):526-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201104009.htm 聂海宽, 金之钧, 马鑫, 刘忠宝, 林拓, 杨振恒.2017.四川盆地及邻区上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组底部笔石带及沉积特征[J].石油学报, 38(2):160-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201702004.htm 皮学军, 刘楚雄, 陈颖, 孙作玉, 郝维城. 2007.新疆柯坪大湾沟奥陶系顶部-志留系底部化学地层特征讨论[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 43(2):183-189. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2007.02.006 戎嘉余, 陈旭, 王怿, 詹仁斌, 刘建波, 黄冰, 唐鹏, 吴荣昌, 王光旭. 2011.奥陶-志留纪之交黔中古陆的变迁:证据与启示[J].中国科学:地球科学, 41(10):1407-1415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201110003.htm 戎嘉余, 陈旭, 詹仁斌, 樊隽轩, 王怿, 张元动, 李越, 黄冰, 吴荣昌, 王光旭. 2010.贵州桐梓县境南部奥陶系-志留系界线地层新认识[J].地层学杂志, 34(4):337-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201004002.htm 王传尚, 陈孝红, 汪啸风. 2002.峡区晚奥陶世地球化学异常与奥陶系-志留系之交环境变迁[J].地层学杂志, 26(4):272-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2002.04.006 王玉满, 董大忠, 黄金亮, 李新景, 王淑芳. 2016.四川盆地及周边上奥陶统五峰组观音桥段岩相特征及对页岩气选区意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 43(1):42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201601006.htm 王玉满, 李新景, 董大忠, 张晨晨, 王淑芳. 2017.上扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组优质页岩沉积主控因素[J].天然气工业, 37(4):9-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201704004.htm 汪正江, 余谦, 杨平, 刘伟, 杨菲, 刘家洪, 熊国庆, 何江林, 邓奇. 2018.川滇黔邻区龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素与勘探方向[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 38(3):1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2018.03.001 严德天, 陈代钊, 王清晨, 汪建国. 2009.扬子地区奥陶系-志留系界线附近地球化学研究[J].中国科学:地球科学, 39(3):285-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200903005.htm 杨平, 汪正江, 余谦, 刘伟, 刘家洪, 熊国庆, 何江林, 杨菲.2019.四川盆地西南缘五峰-龙马溪组页岩气资源潜力分析[J].中国地质, 46(3):601-614. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190311&flag=1 詹仁斌, 刘建波, Ian G. Percival, 靳吉锁, 李贵鹏. 2010.华南上扬子区晚奥陶世赫南特贝动物群的时空演变[J].中国科学:地球科学, 40(9):1154-1163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201009007.htm



 下载:
下载: