Brittleness characteristics and influencing factors of marine shale of Niutitang Formation in Xuefeng region: A case study of Well XZD−1
-
摘要:研究目的
开展页岩储层脆性评价对页岩气勘探开发中的有利层段优选具有重要意义。
研究方法基于矿物组成、地球物理测井、岩石力学实验与裂缝发育程度等基础资料,采用矿物组分法与基于地球物理测井的岩石力学参数法对雪峰地区牛蹄塘组海相页岩的脆性特征进行分析与评价,并以此探讨页岩脆性的影响因素。
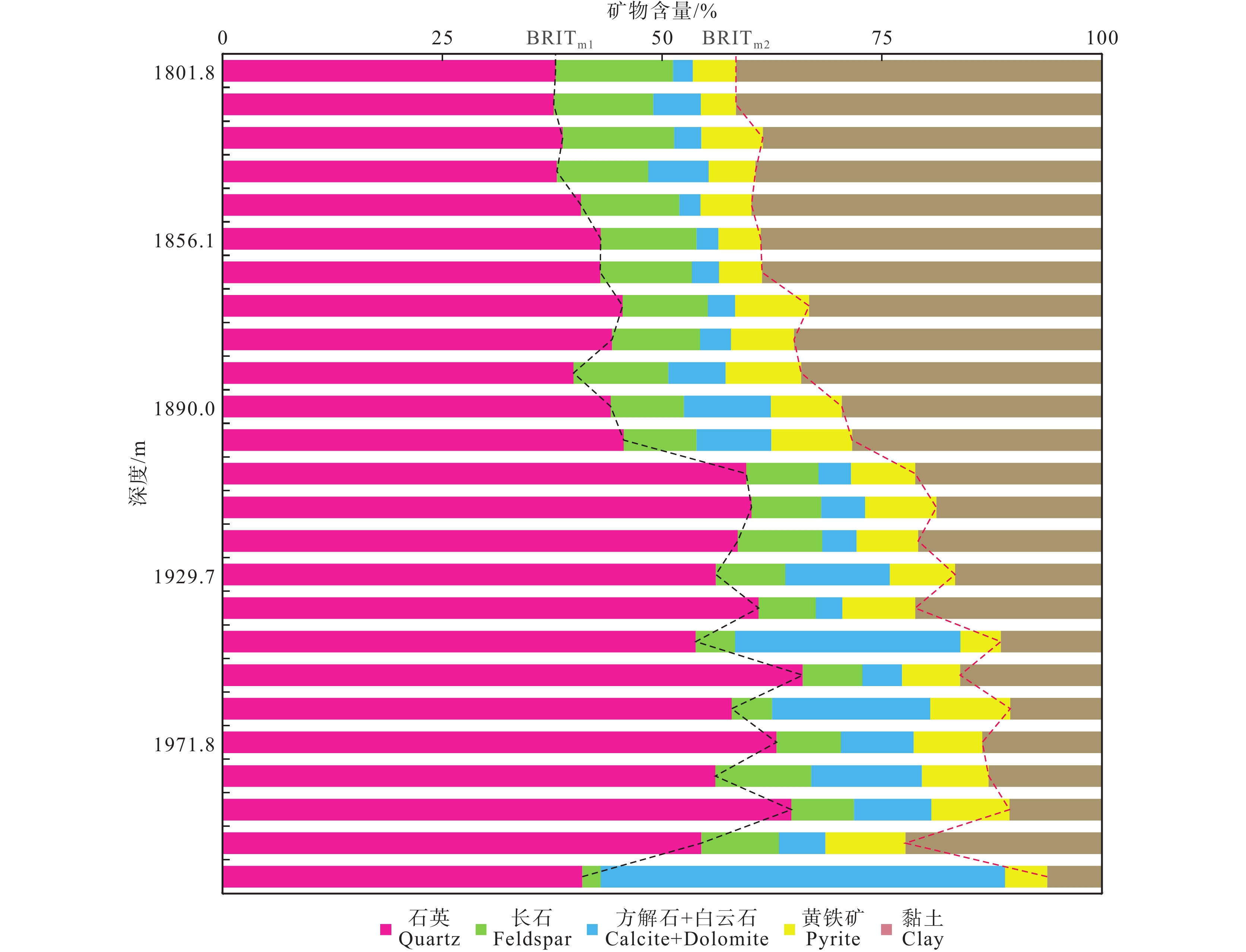
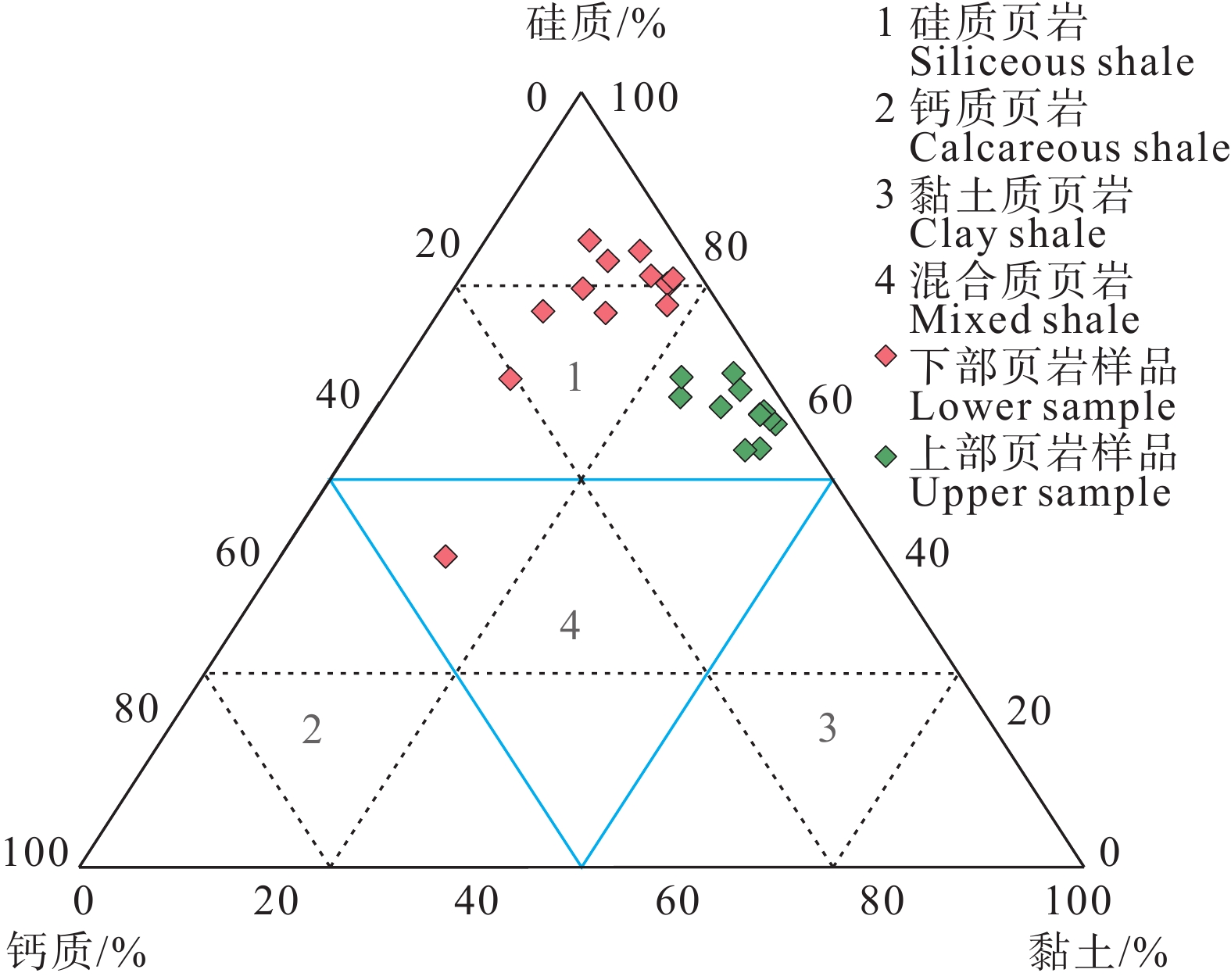
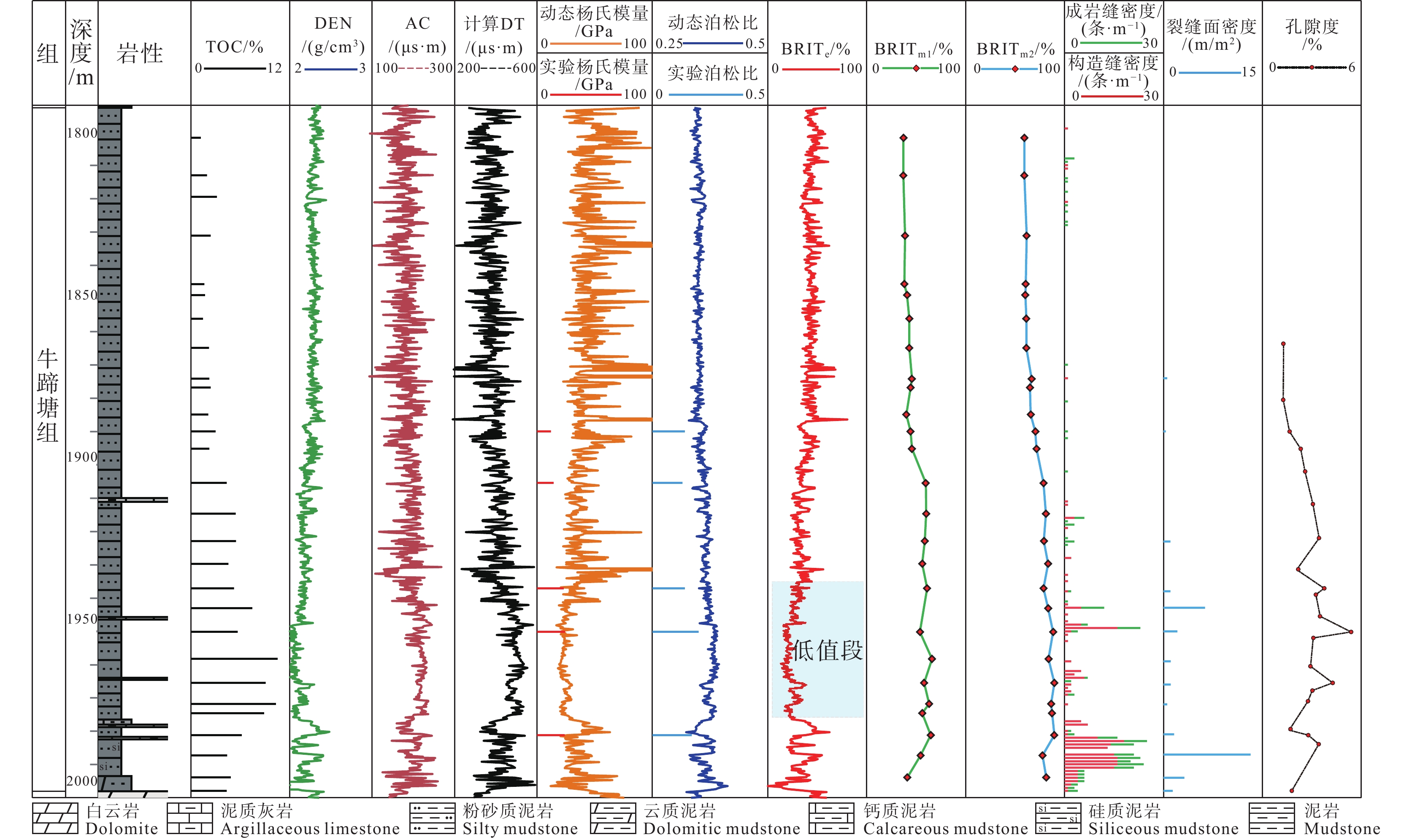
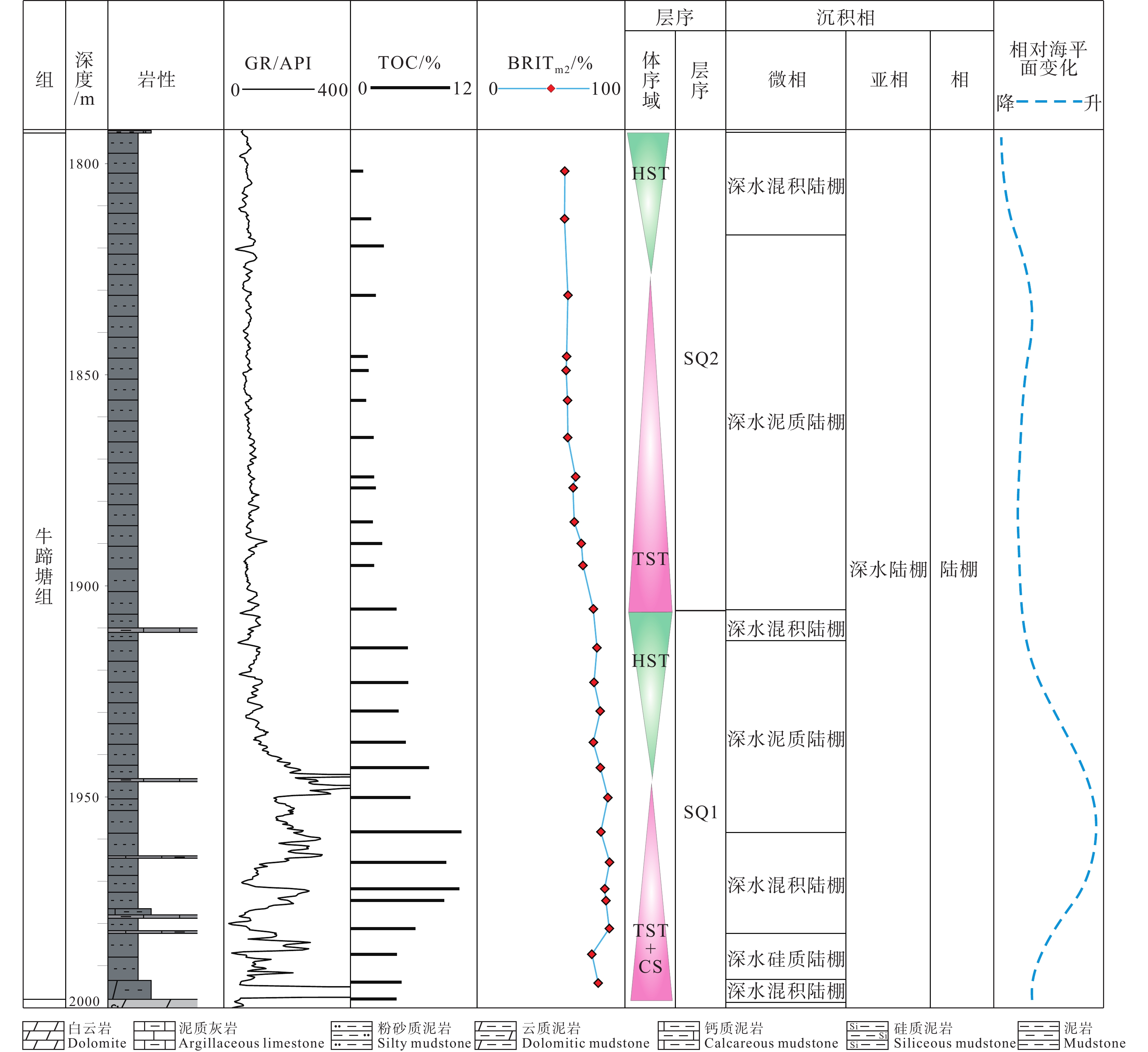
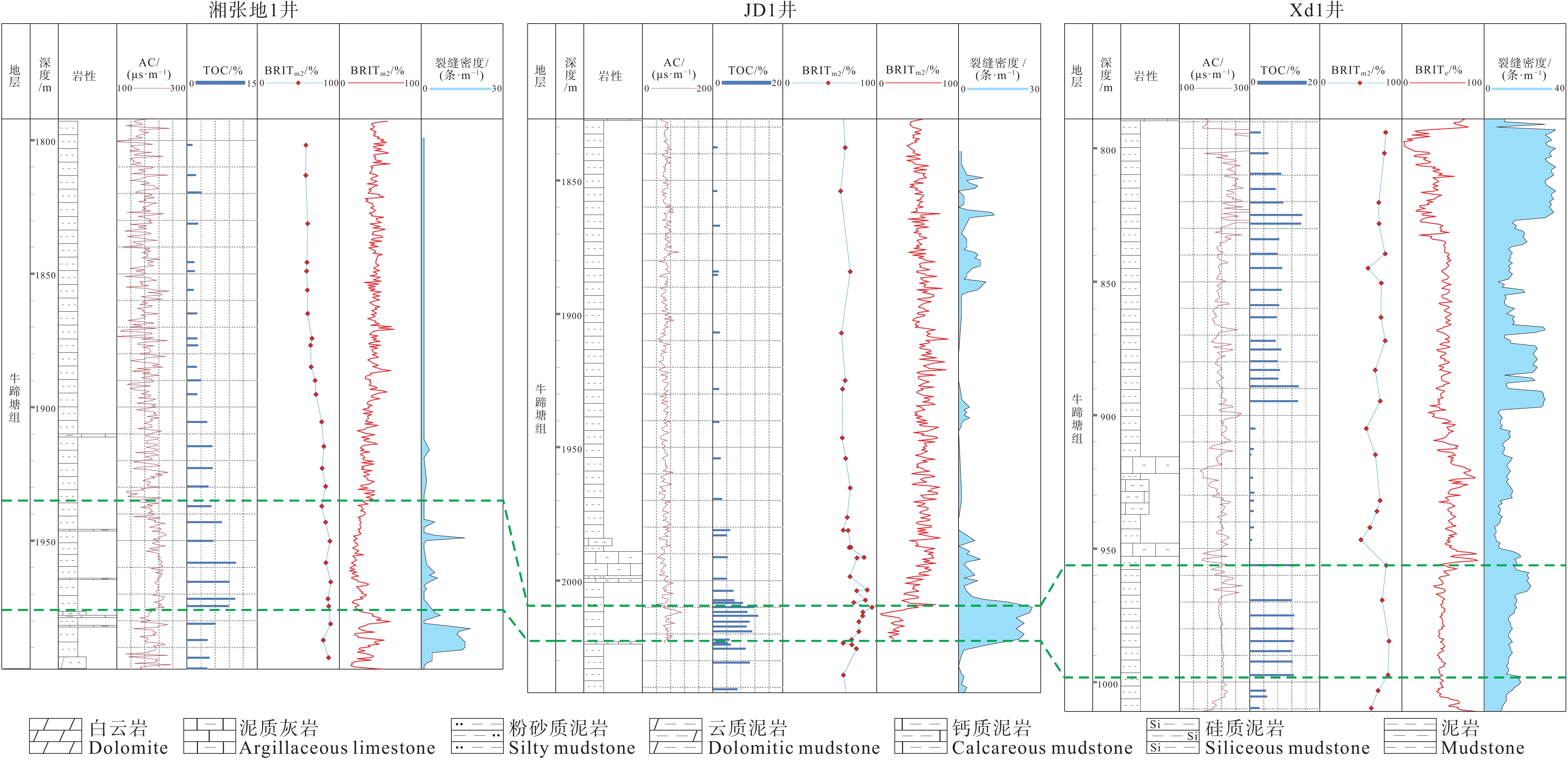
研究结果基于石英、长石、黄铁矿和碳酸盐含量的脆性矿物组分法对该区牛蹄塘组页岩脆性的评价最为适用,以区内湘张地1井为例,页岩脆性指数为59.2%~93.8%,平均值74.4%,受沉积环境、成岩演化、埋深、构造作用等因素共同影响。
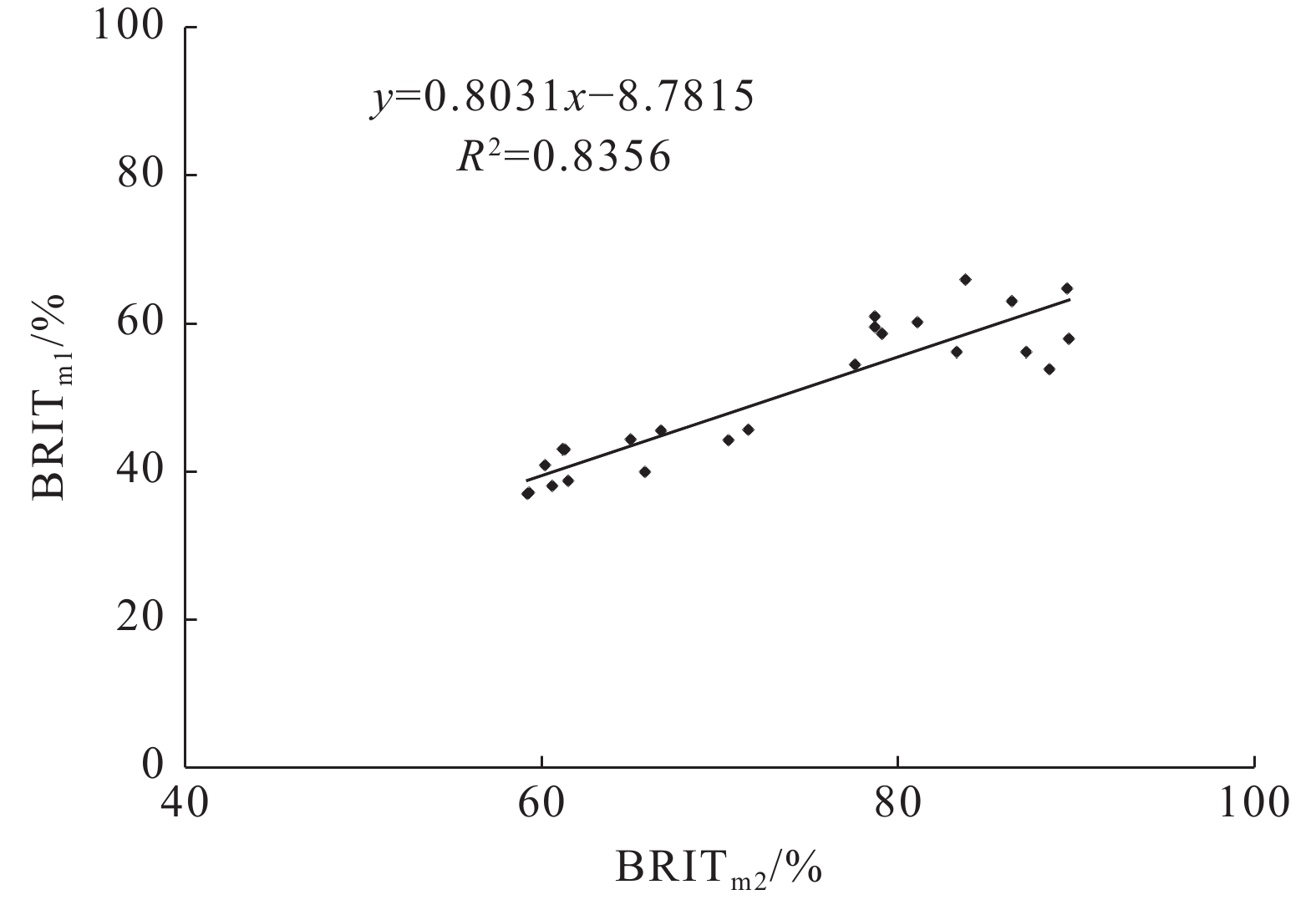
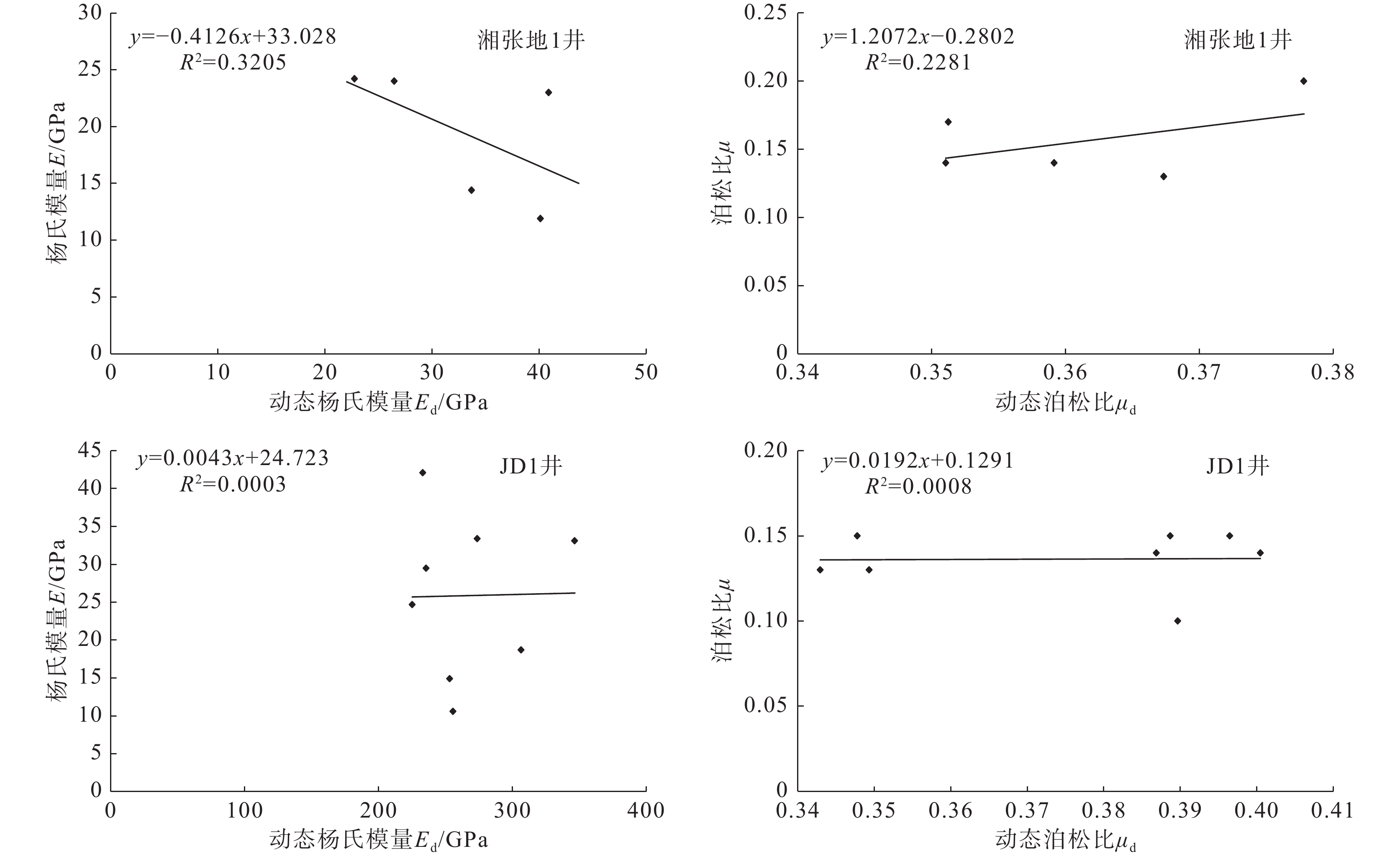
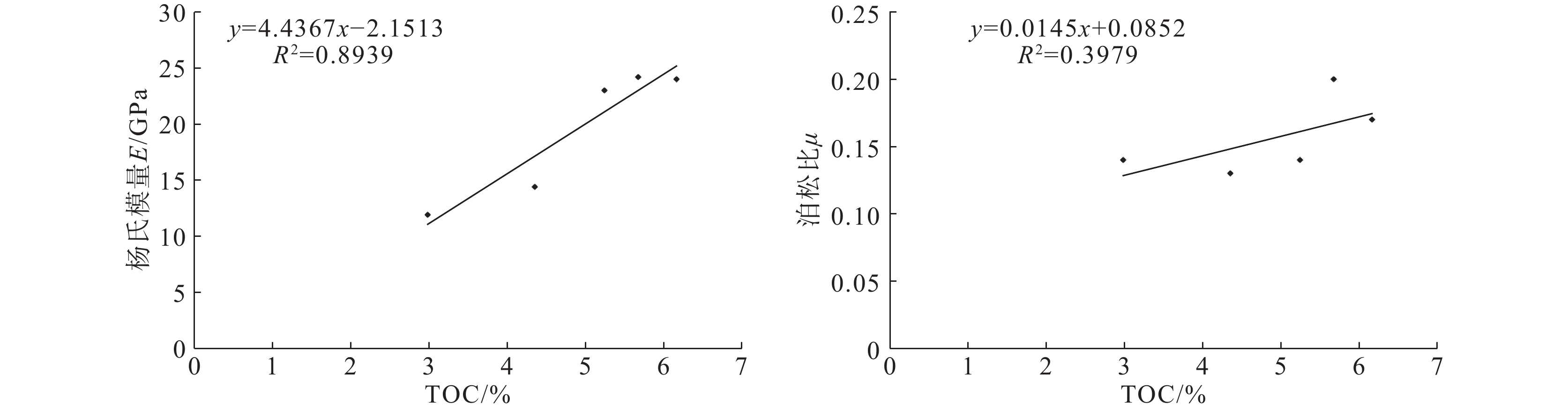
结论稳定的深水陆棚−盆地相沉积环境与晚成岩演化阶段决定牛蹄塘组页岩脆性整体较高,该环境下生物成因的硅质、黄铁矿等脆性矿物较为富集,并受沉积时水体深度变化影响自下而上呈现先升高后降低、整体逐渐降低的含量变化趋势,导致页岩脆性及天然裂缝发育程度具有相似的纵向变化规律,三者之间相辅相成;同时,此类脆性矿物与有机质含量具有良好的正相关关系,其对页岩脆性的贡献远大于有机质本身对塑性的加成。此外,岩石力学参数与脆性指数之间的相关性表明,杨氏模量在该区牛蹄塘组页岩脆性评价中的权重高于泊松比。
创新点:(1)采用多方法有效性综合分析,优选出适用于牛蹄塘组页岩的脆性评价方法,明确了深水陆棚−盆地相沉积环境与晚成岩演化阶段是牛蹄塘组页岩脆性整体较高的主控因素;(2)通过梳理脆性指数、岩石力学参数与TOC三者之间关系,厘定生物成因脆性矿物与有机质含量对页岩脆性的贡献,明确了不同岩石力学参数在脆性评价中的权重。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe brittleness evaluation of shale reservoir is of great significance for determining the favorable stratigraphic zone in shale gas exploration and development.
MethodsBased on the basic data of mineral composition, geophysical logging, rock mechanics experiment and fracture development characteristics of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Xuefeng region, the brittleness characteristics of Niutitang Formation shale are comprehensively analyzed and evaluated by mineral composition and rock mechanics parameter based on geophysical logging, and the influencing factors of shale brittleness are discussed.
ResultsThe results indicate that the brittle mineral composition based on the contents of quartz, feldspar, pyrite and carbonate is the most suitable method to evaluate the brittleness of Niutitang Formation shale in this region. Taking Well XZD−1 in this area as an example, the brittleness index of Niutitang Formation shale is 59.2%−93.8%, with an average value of 74.4%, which is influenced by sedimentary environment, diagenetic evolution, burial depth, tectonism and other factors.
ConclusionThe stable deep−water shelf basin facies sedimentary environment and late diagenetic evolution stage determine that the overall brittleness of Niutitang Formation shale in Xuefeng region is relatively high. In this sedimentary environment, biogenic brittle minerals such as siliceous and pyrite are more abundant. The content of brittle minerals is affected by the change in water depth during sedimentation, showing a trend of increasing first and then decreasing from bottom to top, gradually decreasing overall. This leads to a similar vertical variation law in shale brittleness and the development of natural fractures, and the three complement each other. Meanwhile, such brittle minerals have a good positive correlation with organic matter content, and their contribution to shale brittleness is much greater than that of organic matter to shale plasticity. In addition, the correlation between rock mechanics parameters and brittleness index indicates that the Young's modulus plays a more important role in the evaluation of Niutitang Formation shale brittleness in this area than the Poisson's ratio.
Highlights:(1) The brittleness evaluation method suitable for the Niutitang Formation shale is selected by comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of various methods, and it is clarified that the deep-water shelf basin facies sedimentary environment and late diagenetic evolution stage are the main controlling factors for the overall high brittleness of the Niutitang Formation shale. (2) By sorting out the relationship among brittleness index, rock mechanics parameters and TOC, the contribution of biogenic brittle minerals and organic matter content to shale brittleness is determined, and the weight of different rock mechanics parameters in brittleness evaluation is clarified.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
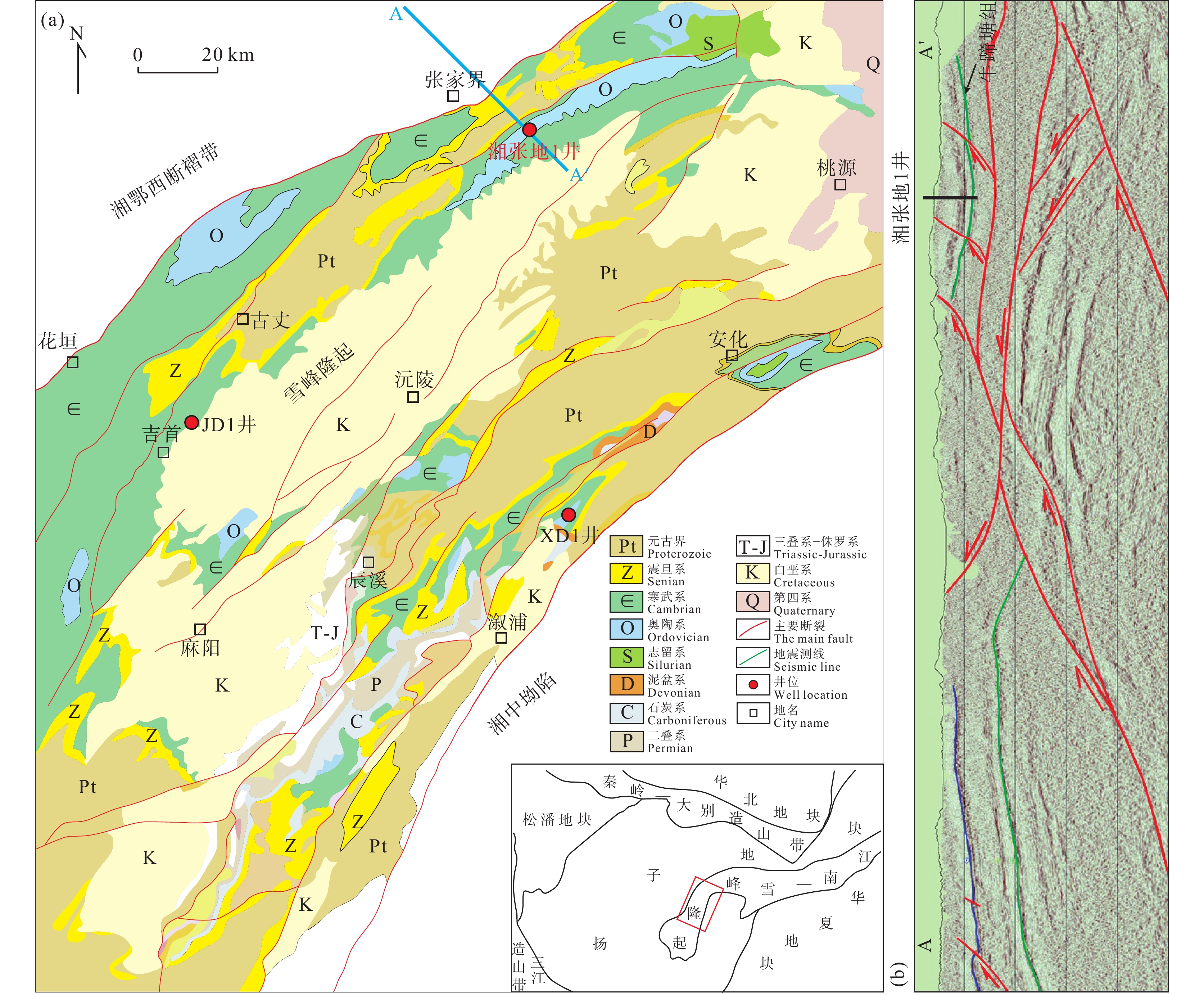
湘中坳陷作为南方复杂构造区页岩气勘探的热点地区之一,也是中国油气勘探久攻未克的地区。前期在湘中地区北部的涟源凹陷泥盆系和石炭系获得了页岩气突破和发现,证实了湘中地区上古生界页岩气资源丰富。但对湘中地区南部的邵阳凹陷调查程度较为薄弱,针对邵阳凹陷二叠系仅开展了少量基础地质调查工作,页岩气资源潜力评价方面的工作尤为欠缺。本次研究依托邵阳湘邵地1井(XSD1井)钻探工程建立了邵阳凹陷二叠系地层层序序列,揭示了主要含气页岩层系的分布特征,获取了含气性评价参数,对湘中地区二叠系页岩气勘探开发和重新评价湘中坳陷页岩气资源潜力具有重要的现实意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心在收集分析区域地质相关资料的基础上,结合邵阳凹陷短陂桥向斜的煤田浅钻、非震物探等资料开展页岩气地质综合评价,采用页岩埋深500~4500 m,页岩有机碳含量≥1.0%,页岩厚度≥15 m,页岩有机质热演化程度1.0%~3.5%的评价参数在短陂桥向斜区优选页岩气远景区,论证部署了1口小口径页岩气地质调查井—XSD1井,湖南煤田地质勘查有限公司组织实施钻探(图 1a)。该井采样全井段取心钻井工艺,测井选取PSJ-2数字测井系统,录井采用SK-2000G气测录井,钻获二叠系大隆组156.05 m(暗色硅质页岩、钙质泥岩94.48 m),龙潭组349.95 m(暗色泥岩216.93 m,粉砂质泥岩36.9 m),对这两套层系共采集暗色泥岩样品33件,进行解析气含量测定分析,落实了含气性评价参数。
3. 结果(Results)
本次样品分析工作由武汉地质调查中心古生物与生命-环境协同演化重点实验室完成,采用YSQ-IIIA岩石解析气测定仪(燃烧法)对含气段岩心共计33件样品进行分析。该井钻获二叠系大隆组厚度156.05 m,为一套硅质岩、硅质页岩、炭质钙质泥岩地层。其中在井深842~930.2 m硅质页岩、钙质泥岩段,气测全烃值从1.06%上升至16.54%,甲烷值从1.01%上升至14.04%,13件大隆组硅质页岩现场解析总含气量为1.29~9.97 m3/t,平均4.85 m3/t。实现了湘中坳陷二叠系页岩气新发现,有效拓展了华南地区大隆组勘探范围。
钻获龙潭组厚度349.95 m,上段为一套细砂岩、粉砂岩夹泥岩潮坪相沉积地层,下段为一套炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹薄层细砂岩泻湖相沉积地层。在井深1013.4~1048 m泥岩与粉砂岩互层段气测全烃值最高可达19.87%,甲烷值最高为16.94%,7件泥岩与粉砂岩样品现场解析总含气量0.57~3.42 m3/t,平均1.78 m3/t;井深1088.10~1199.75 m泥岩夹泥质粉砂岩含气层111.6 m,气测全烃值最高可达28.2%,甲烷值最高为23.6%,13件泥岩、粉砂质泥岩样品现场解析总含气量0.90~4.55 m3/t,平均2.01 m3/t(图 1b),首次查明了湘中坳陷二叠系龙潭组非常规油气分布特点。
通过区域地质背景分析,并结合煤田区域地质资料,本研究认为滑脱断裂(F9)上下盘具有不同的页岩气聚集条件。滑脱断裂之上由一系列的同向逆断层形成的逆冲推覆体,地层变形强烈,且裂缝发育,导致页岩气保存条件变差。滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,地层平缓,不发育次级通天断裂,与下盘地层形成反向遮挡,易形成封闭,保存条件良好(图 1c)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)二叠系大隆组岩性以硅质岩、硅质页岩为主,夹少量灰岩。主要含气段存在于上段硅质页岩段,厚88.2 m,含气量平均为4.85 m3/t,含气性优越,资源潜力大。
(2)二叠系龙潭组上段以致密砂岩气为主,含气量平均为1.78 m3/t;下段以页岩气为主,泥岩厚达177.47 m,含气量平均为2.01 m3/t,具有泥岩厚度大,含气性好等特征。
(3)保存条件是页岩气富集关键,构造改造弱的封闭演化环境有利于页岩气保存,研究区滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,易形成封闭,保存条件良好。
(4)湘邵地1井在二叠系大隆组和龙潭组获得良好的页岩气显示,证实了湘中地区二叠系具有良好的页岩气资源潜力,对湘中地区页岩气资源潜力评价具有重要意义。
5. 基金项目(Fund support)
本文为中国地质调查局项目“中扬子地区油气页岩气调查评价”(DD20221659)资助的成果。
-
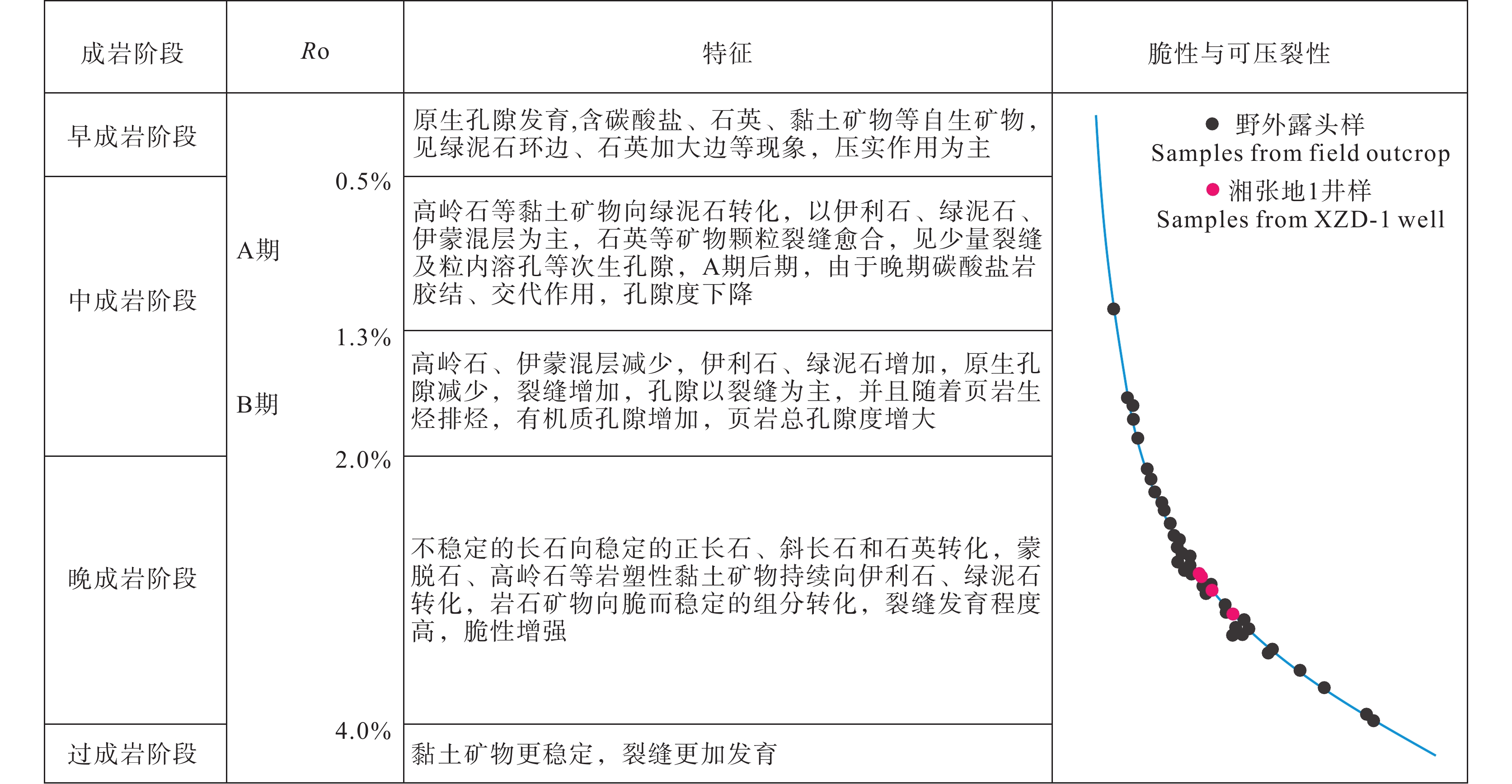
图 9 雪峰地区牛蹄塘组页岩成岩演化阶段特征(据吴晶晶等,2018修改)
Figure 9. Characteristics of diagenetic evolution stages of Niutitang Formation shale in Xuefeng region (modified from Wu Jingjing et al., 2018)
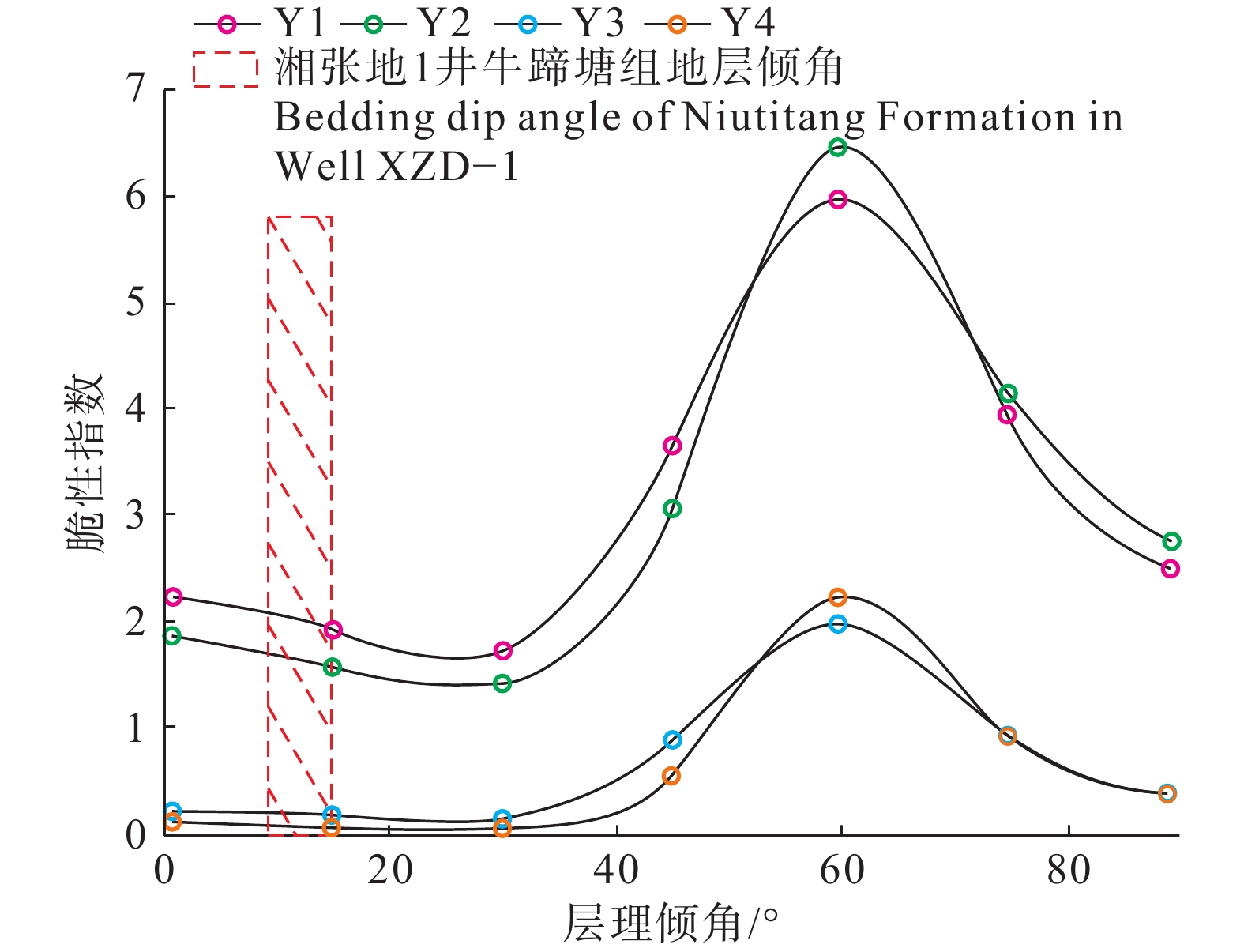
图 10 页岩不同层理倾角与脆性指数关系(据张军等,2017修改)
Figure 10. Relationship between different bedding dip angles and brittleness index of shale (modified from Zhang Jun et al., 2017)
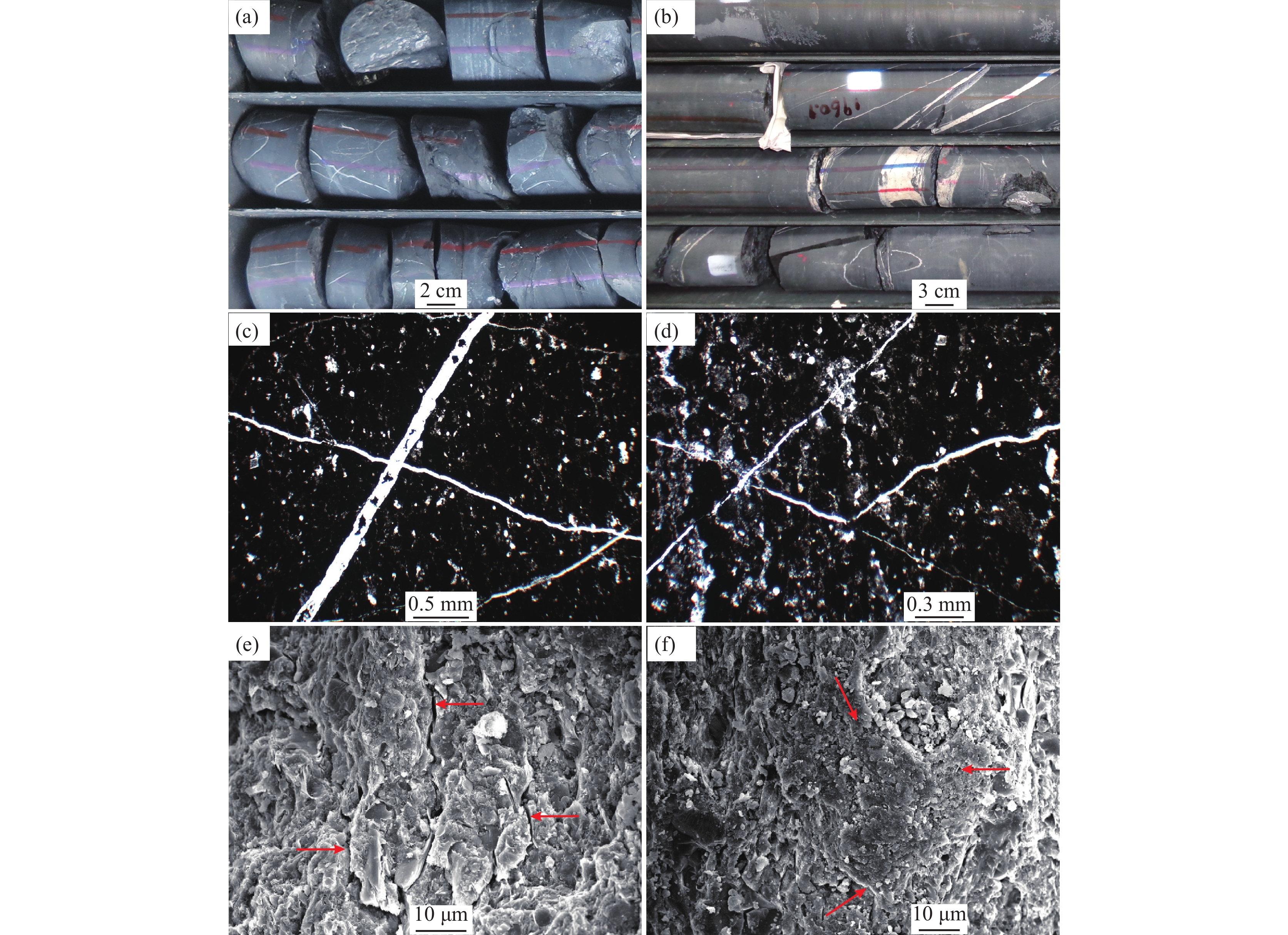
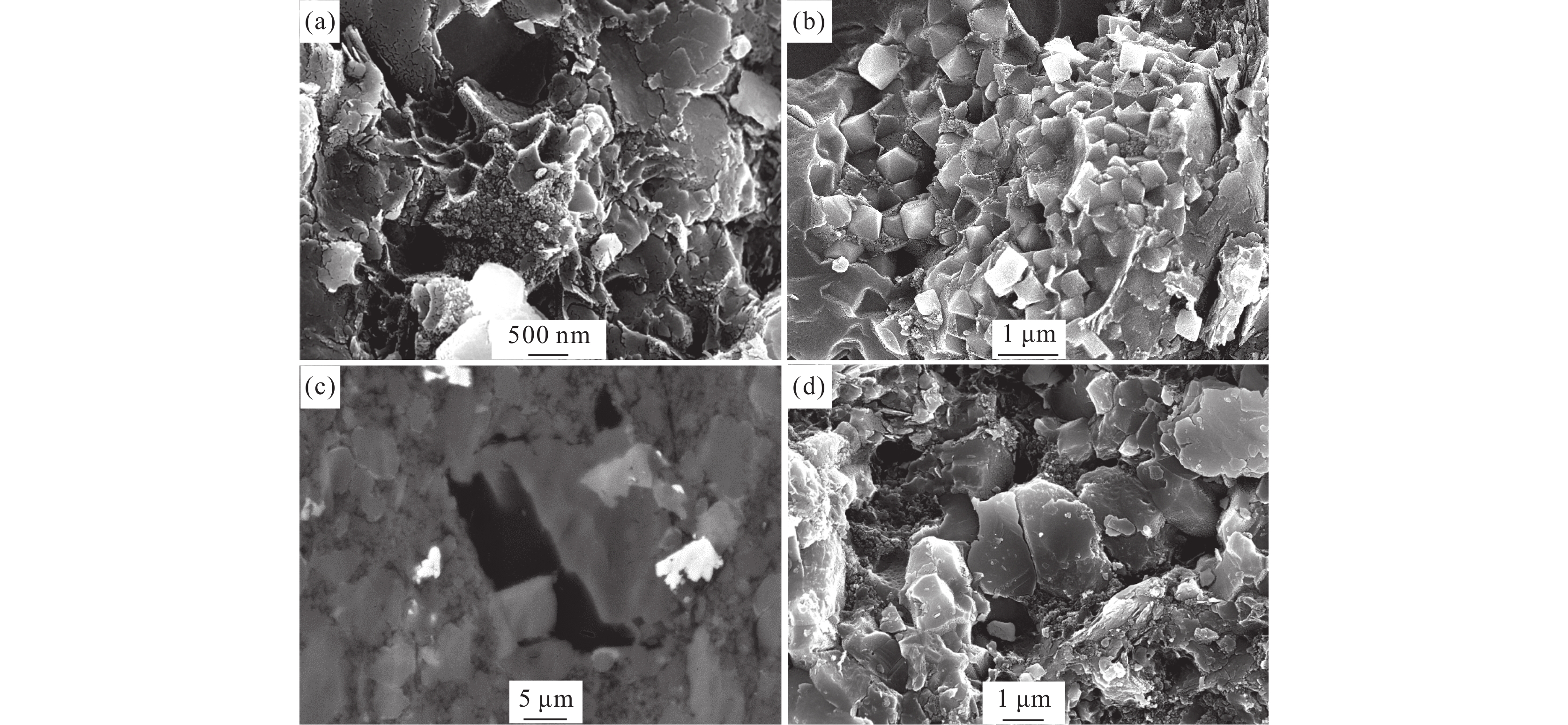
图 11 牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝与孔隙发育特征
a—高角度与低角度构造裂缝,1990.2 m;b—高角度构造裂缝与低角度成岩缝,1960.0 m;c、d—岩心裂缝发育段对应的微裂缝,1990.3 m;e—扫描电镜下的微米级裂缝,1905.5 m;f—裂缝发育带内的微裂缝与微孔隙,1974.6 m
Figure 11. Development characteristics of fractures and pores in Niutitang Formation shale
a−High angle and low angle structural fractures, 1990.2 m; b−High angle structural fractures and low angle diagenetic fractures,1960.0 m; c,d−Microfractures corresponding to the fracture development section of the core,1990.3 m; e−Micrometer fractures under FE−SEM,1905.5 m; f−Micro−fractures and micro−pores in the fracture development zone, 1974.6 m
图 13 有机质与自生石英、长石、黄铁矿等矿物共生
a—有机质与石英交互共生,1905.5 m;b—有机质与黄铁矿共生,1943.1 m;c—有机质与碳酸盐矿物共生,1965.5 m;d—有机质与石英、长石、黄铁矿、伊利石共生,1937.1 m
Figure 13. Organic matter coexists with authigenic quartz, feldspar and pyrite
a−Organic matter coexists with authigenic quartz, 1905.5 m; b−Organic matter coexists with pyrite, 1943.1 m; c−Organic matter coexists with carbonate minerals, 1965.5 m; d−Organic matter coexists with quartz, feldspar, pyrite and illite, 1937.1 m
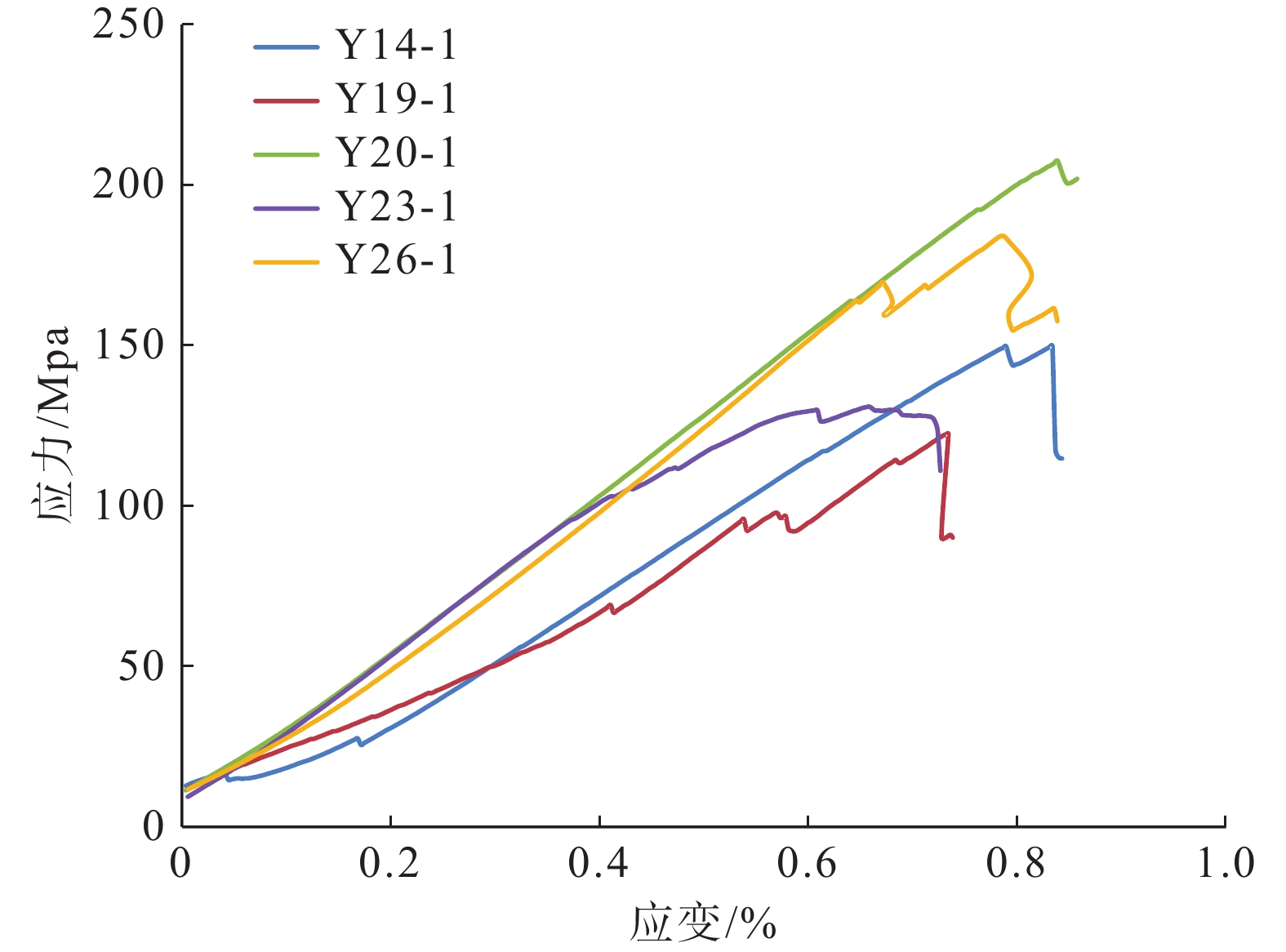
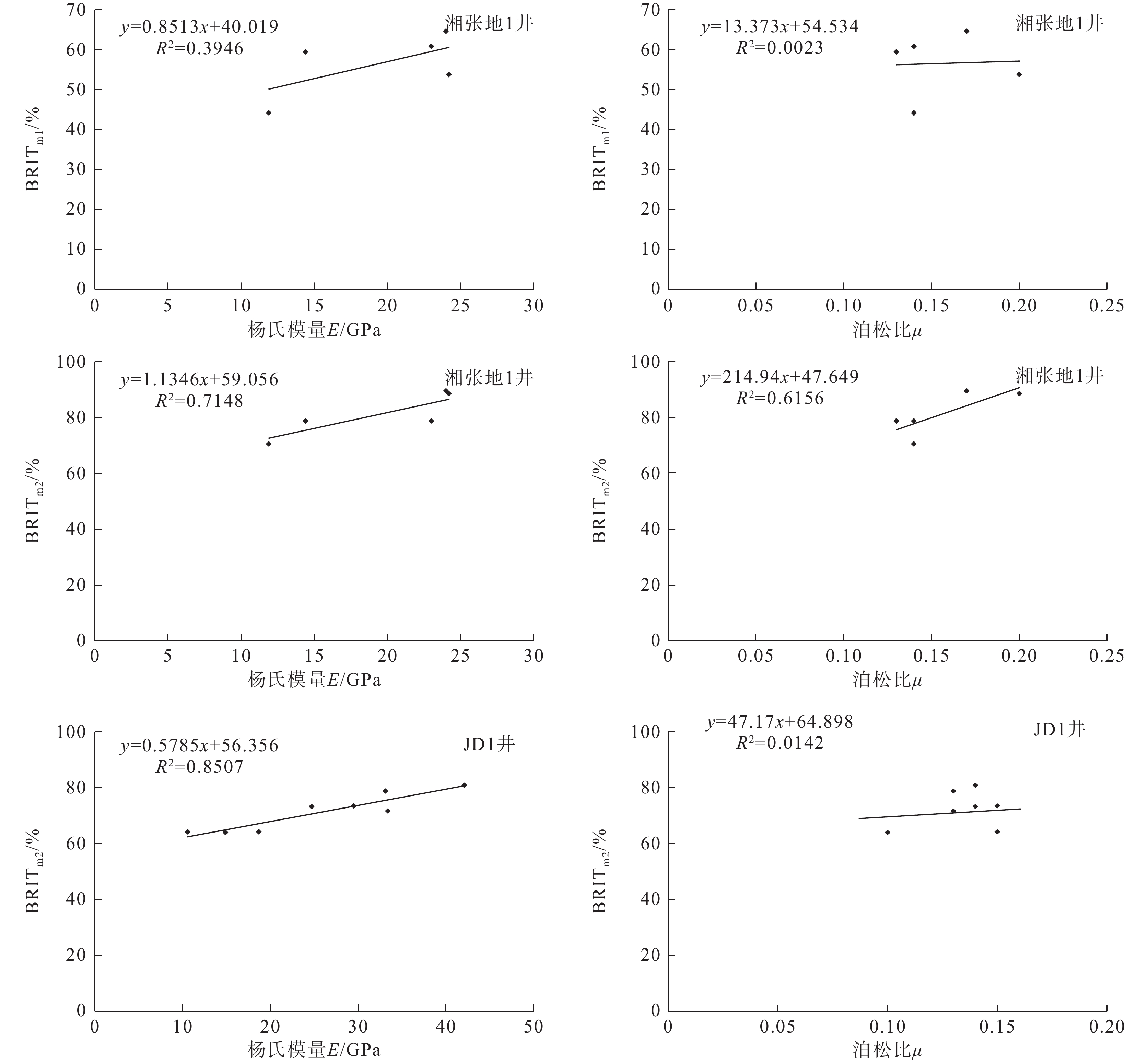
表 1 岩石单轴压缩实验力学参数
Table 1 Mechanical parameters of rock uniaxial compression test
样号 样品深度/m 所属位置 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 抗压强度/MPa Y14-1 1890.0 上部页岩段 11.9 0.14 143.7 Y19-1 1905.0 上部页岩段 14.4 0.13 120.1 Y20-1 1937.1 下部页岩段 23.0 0.14 169.7 Y23-1 1950.2 下部页岩段 24.2 0.20 115.2 Y26-1 1981.2 下部页岩段 24.0 0.17 178.8 -
[1] Bai Daoyuan, Tang Fenpei, Li Bin, Zeng Guangqian, Li Yinmin, Jiang Wen. 2022. Summary of main mineralization events in Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 151−180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Bowker K A. 2007. Barnett shale gas production, Fort Worth Basin: Issues and discussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 91(4): 523−533. doi: 10.1306/06190606018
[3] Deng Dafei, Mei Lianfu, Shen Chuanbo, Liu Zhaoqian, Tang Jiguang, Fan Yuanfang. 2014. Major factors of accumulation and destruction mechanisms of marine strata related hydrocarbon in the northern margin of the Jiangnan−Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(5): 1466−1477 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Diao Haiyan. 2013. Rock mechanical properties and brittleness evaluation of shale reservoir[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3300−3306 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Fang Dazhi, Zeng Hui, Wang Ning, Zhang Yong. 2015. Study on high production factors of high−pressure shale gas from Haynesville shale gas development data[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 37(2): 58−62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fu Yongqiang, Ma Faming, Zeng Lixin, She Chaoyi, Chen Yan. 2011. Key techniques of experimental evaluation in the fracturing treatment for shale gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 31(4): 51−54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Ge Hongkui, Chen Yu, Lin Yingsong. 2001. Microscopic mechanism of difference between static and dynamic elastic parameters of rock[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China (Edition of Natural Science), 25(4): 34−36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Gong L, Wang J, Gao S, Fu X F, Liu B, Miao F B, Zhou X P, Meng Q K. 2021. Characterization, controlling factors and evolution of fracture effectiveness in shale oil reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 203: 108655. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108655
[9] He Jianhua, Ding Wenlong, Wang Zhe, Lan Baofeng, Zhao Jinli, Zhao Dong. 2015. Main controlling factors of fracture network formation of volume fracturing in shale reservoirs and its evaluation method[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(4): 108−118 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Hou Zhenkun, Yang Chunhe, Wei Xiang, Wang Lei, Wei Yuanlong, Xu Feng, Wang Hu. 2016. Experimental study on the brittle characteristics of Longmaxi Formation shale[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 41(5): 1188−1196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Huang Yanran, Xiao Zhenghui, Jiao Peng, Qin Mingyan, Yu Ye, Wang Xikai, Cao Taotao. 2018. Comparison of factors for shale gas accumulation in Niutitang formation wells in northwestern Hunan and its implications[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 49(9): 2240−2248 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Jarvie D M, Hill R J, Ruble T E, Pollastro R. 2007. Unconventional shale−gas systems: The Mississippian Barnett Shale of north−central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale−gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 91(4): 475−499.
[13] Li Qinghui, Chen Mian, Fred P W, Jin Yan, Li Zhimeng. 2012. Influences of engineering factors on shale gas productivity: A case study from the Haynesville shale gas reservoir in North America[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 32(4): 54−59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Liu An, Li Xubing, Wang Chuanshang, Wei Kai, Wang Baozhong. 2013. Analysis of geochemical feature and sediment environment for hydrocarbon source rocks of Cambrian in west Hunan−Hubei Area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(6): 1122−1132 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Mei Lianfu, Deng Dafei, Shen Chuanbo, Liu Zhaoqian. 2012. Tectonic dynamics and marine hydrocarbon accumulation of Jiangnan−Xuefeng uplift[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 31(5): 85−93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Miao Fengbin, Peng Zhongqin, Wang Chuanshang, Yue Yong, Wang Zongxin. 2019. Gas−bearing capacity and controlling factors of Niutitang Formation Shale in Well XZD−1, western margin of Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Earth Science, 44(11): 3662−3677 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Miao Fengbin, Peng Zhongqin, Wang Zongxin, Yu Yuning, Ma Yong, Sui Zhiheng. 2020. Development characteristics and major controlling factors of shale fracture in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, western margin of Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 39(2): 31−42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Peng Zhongqin, Tian Wei, Miao Fengbin, Wang Baozhong, Wang Chuanshang. 2019. Geological features and favorable area prediction of shale gas in Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation of Xuefeng ancient uplift and its periphery[J]. Earth Science, 44(10): 3512−3528 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Pu Boling, Dong Dazhong, Wang Fengqin, Wang Yuman, Huang Jinliang. 2020. The effect of sedimentary facies on Longmaxi shale gas in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 47(1): 111−120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Rickman R, Mullen M, Petre J, Grieser W V, Kundert D P. 2008. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale [C]// SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, USA.
[21] Shi Xian, Cheng Yuanfang, Jiang Shu, Cai Dongsheng, Zhang Tao. 2014. Experimental study of microstructure and rock properties of shale samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 33(S2): 3439−3445 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Tang Ying, Xing Yun, Li Lezhong, Zhang Binhai, Jiang Shixin. 2012. Influence factors and evaluation methods of the gas shale fracability[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 356−363 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Wang Chuanshang, Zeng Xiongwei, Li Xubing, Liu An, Bai Yunshan. 2013. The classification and correlation of the Cambrian strata in western Xuefeng Mountain area[J]. Geology in China, 40(2): 439−448 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Wang Ruyue, Gong Dajian, Ding Wenlong, Leng Jigao, Yin Shuai, Wang Xinghua, Sun Yaxiong. 2016. Brittleness evaluation of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in the Upper Yangtze region: A case study in the Cengong block, Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1): 87−95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Wang Yuman, Wang Shufang, Dong Dazhong, Li, Xinjing, Huang Jinliang, Zhang Chenchen, Guan Quanzhong. 2016. Lithofacies characterization of Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, southern Sichuan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1): 119−133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Wu Jingjing, Zhang Shaohe, Cao Han, Sun Pinghe. 2018. Fracability evaluation of shale gas reservoir in Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, northwestern Hunan[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 49(5): 1160−1168 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Wu Yue, Fan Tailiang, Jiang Shu, Li Yifan, Zhang Junpeng, Ding Huaiyu. 2015. Mineralogy and brittleness features of the shale in the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation and the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 22(4): 59−63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Xia Zunyi, Ma Haiyang, Fang Kun. 2019. Rock mechanical properties and fracability of continental shale in Zhanhua Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 41(1): 134−141 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Xu Ganchuan, Zhong Guanghai, Xie Bing, Huang Tianjun. 2014. Petrophysical experiment−based logging evaluation method of shale brittleness[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(12): 38−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Yuan Junliang, Deng Jingen, Zhang Dingyu, Li Dahua, Yan Wei, Chen Chaogang, Cheng Lijun, Chen Zijian. 2013. Fracability evaluation of shale−gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(3): 523−527 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Zeng Yijin, Chen Zuo, Bian Xiaobing. 2016. Breakthrough in stagedfracturing technology for deep shale gas reservoirs in SE Sichuan basin and its implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 36(1): 61−67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Zhang Chenchen, Wang Yuman, Dong Dazhong, Guan Quanzhong. 2016. Brittleness characteristics of Wufeng−Longmaxi shale in Changning region, Southern Sichuan, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27(9): 1629−1639 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Zhang Jun, Ai Chi, Li Yuwei, Zeng Jia, Qiu Dezhi. 2017. Brittleness evaluation index based on energy variation in the whole process of rock failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 36(6): 1326−1340 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Zhao Pei, Li Xianqing, Sun Jie, Lai Shouning, Fu Tongyang, Su Guiping, Tian Xingwang. 2014. Study on mineral composition and brittleness characteristics of shale gas reservoirs from the Lower Paleozoic in the Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 28(2): 396−403 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Zhao Wenzhi, Li Jianzhong, Yang Tao, Wang Shufang, Huang Jinliang. 2016. Geological difference and its significance of marine shale gases in South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 43(4): 499−510 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Zhong Cheng, Qin Qirong, Zhou Jiling, Hu Dongfeng, Wei Zhihong. 2018. Brittleness evaluation of organic−rich shale in Longmaxi Formation in Dingshan Area, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(4): 167−174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] 柏道远, 唐分配, 李彬, 曾广乾, 李银敏, 姜文. 2022. 湖南省成矿地质事件纲要[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 151−180. [38] 邓大飞, 梅廉夫, 沈传波, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 凡元芳. 2014. 江南—雪峰隆起北缘海相油气富集主控因素和破坏机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(5): 1466−1477. [39] 刁海燕. 2013. 泥页岩储层岩石力学特性及脆性评价[J]. 岩石学报, 29(9): 3300−3306. [40] 房大志, 曾辉, 王宁, 张勇. 2015. 从Haynesville页岩气开发数据研究高压页岩气高产因素[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 37(2): 58−62. [41] 付永强, 马发明, 曾立新, 佘朝毅, 陈艳. 2011. 页岩气藏储层压裂实验评价关键技术[J]. 天然气工业, 31(4): 51−54. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.04.012 [42] 葛洪魁, 陈颙, 林英松. 2001. 岩石动态与静态弹性参数差别的微观机理[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 25(4): 34−36. [43] 何建华, 丁文龙, 王哲, 蓝宝锋, 赵金利, 赵冬. 2015. 页岩储层体积压裂缝网形成的主控因素及评价方法[J]. 地质科技情报, 34(4): 108−118. [44] 侯振坤, 杨春和, 魏翔, 王磊, 魏元龙, 徐峰, 汪虎. 2016. 龙马溪组页岩脆性特征试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 41(5): 1188−1196. [45] 黄俨然, 肖正辉, 焦鹏, 秦明阳, 余烨, 王玺凯, 曹涛涛. 2018. 湘西北牛蹄塘组探井页岩气富集要素的对比和启示[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 49(9): 2240−2248. [46] 李庆辉, 陈勉, Fred P Wang, 金衍, 李志猛. 2012. 工程因素对页岩气产量的影响—以北美Haynesville页岩气藏为例[J]. 天然气工业, 32(4): 54−59. [47] 刘安, 李旭兵, 王传尚, 危凯, 王保忠. 2013. 湘鄂西寒武系烃源岩地球化学特征与沉积环境分析[J]. 沉积学报, 31(6): 1122−1132. [48] 梅廉夫, 邓大飞, 沈传波, 刘昭茜. 2012. 江南—雪峰隆起构造动力学与海相油气成藏演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 31(5): 85−93. [49] 苗凤彬, 彭中勤, 汪宗欣, 于玉宁, 马勇, 隋志恒. 2020. 雪峰隆起西缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 39(2): 31−42. [50] 苗凤彬, 彭中勤, 王传尚, 岳勇, 汪宗欣. 2019. 雪峰隆起西缘湘张地1井牛蹄塘组页岩含气性特征及控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 44(11): 3662−3677. [51] 彭中勤, 田巍, 苗凤彬, 王保忠, 王传尚. 2019. 雪峰古隆起边缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏地质特征及有利区预测[J]. 地球科学, 44(10): 3512−3528. [52] 蒲泊伶, 董大忠, 王凤琴, 王玉满, 黄金亮. 2020. 沉积相带对川南龙马溪组页岩气富集的影响[J]. 中国地质, 47(1): 111−120. doi: 10.12029/gc20200109 [53] 时贤, 程远方, 蒋恕, 蔡东升, 张涛. 2014. 页岩微观结构及岩石力学特征实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 33(S2): 3439−3445. [54] 唐颖, 邢云, 李乐忠, 张滨海, 蒋时馨. 2012. 页岩储层可压裂性影响因素及评价方法[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 356−363. [55] 王传尚, 曾雄伟, 李旭兵, 刘安, 白云山. 2013. 雪峰山西侧地区寒武系地层划分与对比[J]. 中国地质, 40(2): 439−448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.008 [56] 王濡岳, 龚大建, 丁文龙, 冷济高, 尹帅, 王兴华, 孙雅雄. 2016. 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩储层脆性评价: 以贵州岑巩区块为例[J]. 地学前缘, 23(1): 87−95. [57] 王玉满, 王淑芳, 董大忠, 李新景, 黄金亮, 张晨晨, 管全中. 2016. 川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩岩相表征[J]. 地学前缘, 23(1): 119−133. [58] 吴晶晶, 张绍和, 曹函, 孙平贺. 2018. 湘西北下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气储层可压裂性评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 49(5): 1160−1168. [59] 伍岳, 樊太亮, 蒋恕, 李一凡, 张俊鹏, 丁怀宇. 2015. 四川盆地南缘上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩矿物组成与脆性特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 22(4): 59−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.04.011 [60] 夏遵义, 马海洋, 房堃. 2019. 渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷陆相页岩储层岩石力学特征及可压裂性研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 41(1): 134−141. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901134 [61] 徐赣川, 钟光海, 谢冰, 黄天俊. 2014. 基于岩石物理实验的页岩脆性测井评价方法[J]. 天然气工业, 34(12): 38−45. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.12.005 [62] 袁俊亮, 邓金根, 张定宇, 李大华, 闫伟, 陈朝刚, 程礼军, 陈子剑. 2013. 页岩气储层可压裂性评价技术[J]. 石油学报, 34(3): 523−527. doi: 10.7623/syxb201303015 [63] 曾义金, 陈作, 卞晓冰. 2016. 川东南深层页岩气分段压裂技术的突破与认识[J]. 天然气工业, 36(1): 61−67. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.01.007 [64] 张晨晨, 王玉满, 董大忠, 管全中. 2016. 川南长宁地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩脆性特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 27(9): 1629−1639. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.09.1629 [65] 张军, 艾池, 李玉伟, 曾佳, 仇德智. 2017. 基于岩石破坏全过程能量演化的脆性评价指数[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 36(6): 1326−1340. [66] 赵佩, 李贤庆, 孙杰, 赖守宁, 付铜洋, 苏桂萍, 田兴旺. 2014. 川南地区下古生界页岩气储层矿物组成与脆性特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 28(2): 396−403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.02.018 [67] 赵文智, 李建忠, 杨涛, 王淑芳, 黄金亮. 2016. 中国南方海相页岩气成藏差异性比较与意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 43(4): 499−510. doi: 10.11698/PED.2016.04.01 [68] 钟城, 秦启荣, 周吉羚, 胡东风, 魏志红. 2018. 川东南丁山地区龙马溪组富有机质页岩脆性评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 37(4): 167−174.




 下载:
下载: