The first large-sized graphite deposit in Tibet: geology of the Qingguo graphite deposit and U-Pb age of its ore-bearing pluton
-
摘要:
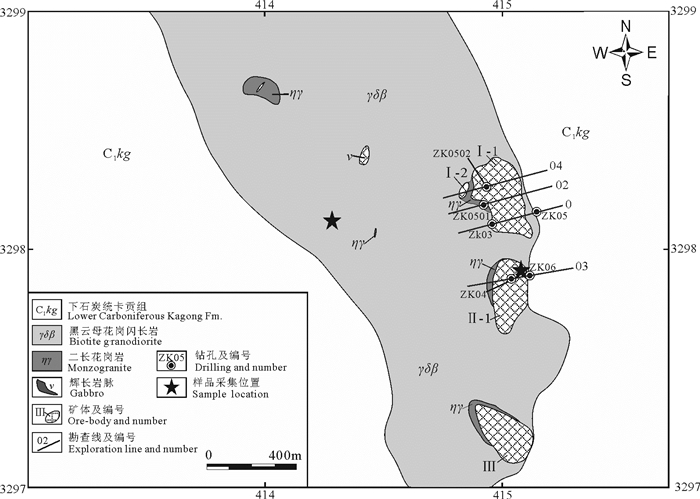
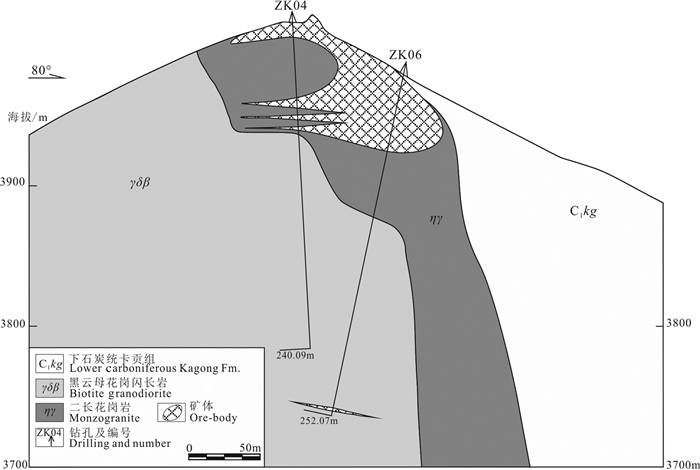
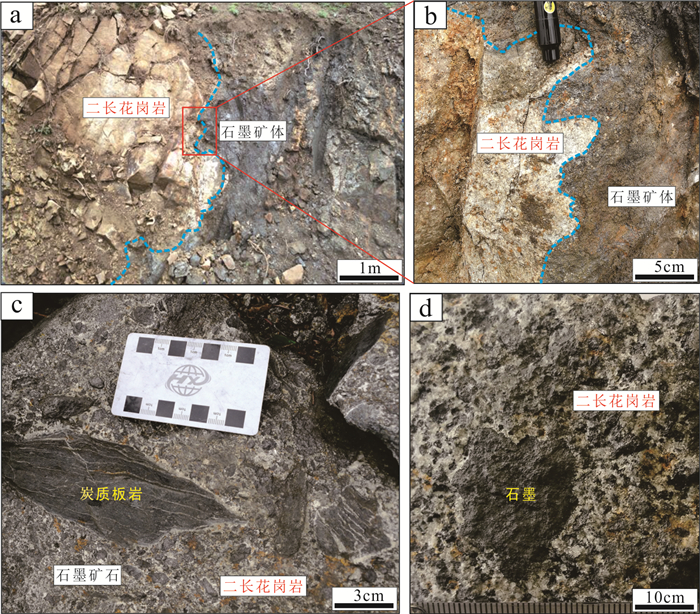
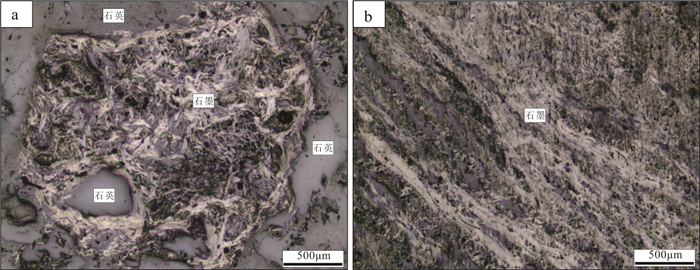
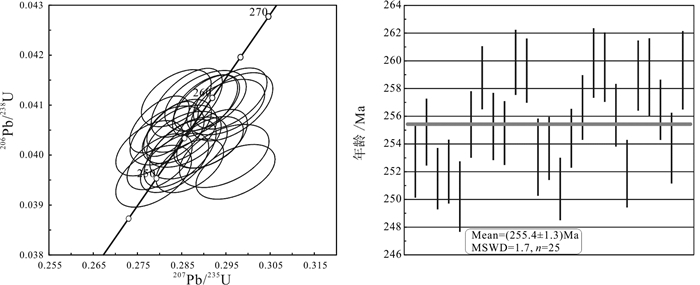
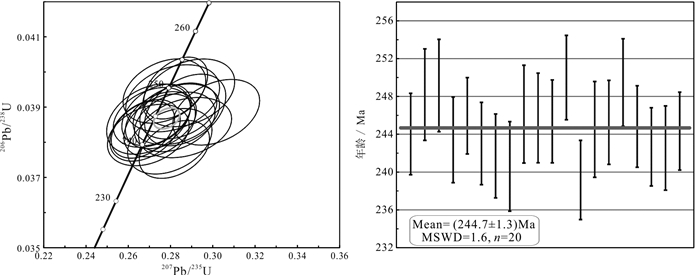
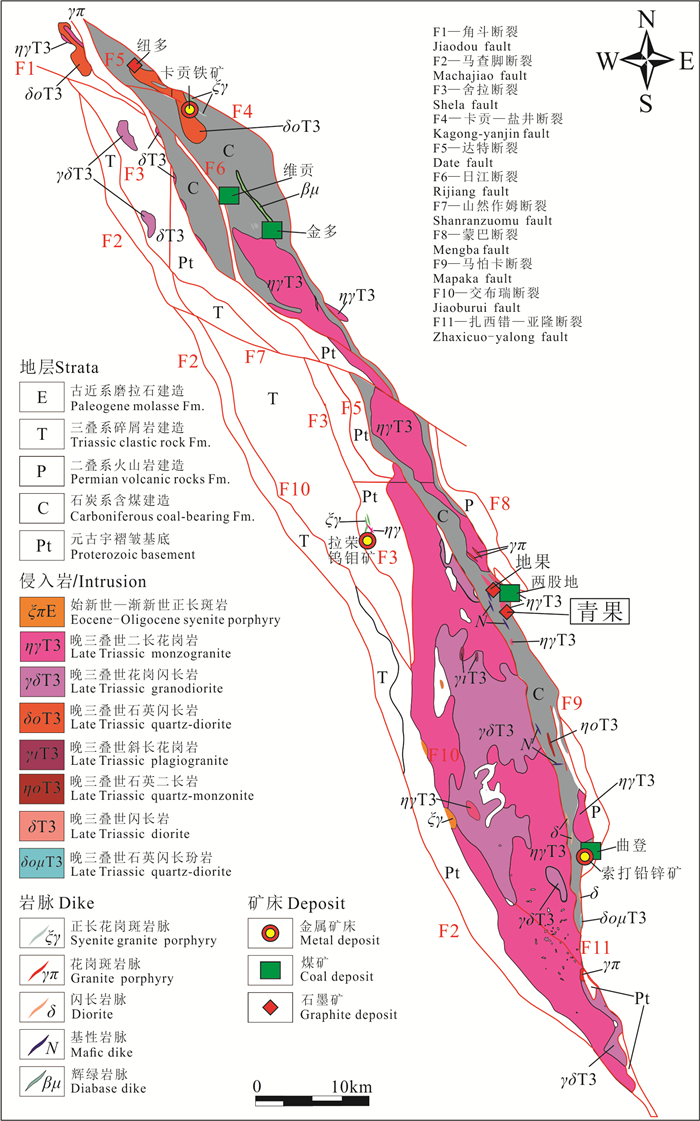
中国石墨矿产资源丰富,已有的勘查和研究成果多集中于中部、东部地区,而西藏地区石墨矿资源现状及找矿潜力并不清晰。随着矿产勘查工作的投入,在三江地区探获了西藏首例大型石墨矿床——青果石墨矿床。估算结果表明,青果石墨矿床资源量为106.94万t固定碳矿物量(333+334),平均品位8.40%。文章通过详细的野外地质调查及钻孔地质编录,查明青果矿床的基本地质特征;利用锆石U-Pb年代学分析,厘定其含矿岩体的成岩时代,并结合碳同位素组成,探究矿床成因及成矿时代。研究表明,青果矿床石墨主要呈球状、不规则粒状产于二长花岗岩中,矿体呈板状、不规则状,是二长花岗岩捕掳下石炭统卡贡组含煤地层在岩浆热液作用下重结晶的产物。含矿二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(244.7±1.3)Ma,形成于中三叠世,代表了含矿岩浆活动的时限,也近似代表石墨成矿时代。区域上多个石墨矿床/点的发现,表明西藏三江地区具备较好的晶质石墨矿找矿潜力。
Abstract:China is rich in graphite mineral resources, and the existing exploration and research results are mostly concentrated in the central and eastern regions. However, the present situation and prospecting potential of graphite mineral resources in Tibet are not clear. With the investment of mineral exploration work, the first large graphite deposit in the Sanjiang area of Tibet was discovered, namely the Qingguo graphite deposit. Its resource is 1.0694 million tons of fixed carbon minerals (indicated and inferred) at average grade of 8.40%. Through detailed field geological survey and borehole geological logging, the basic geological characteristics of the deposit have been clarified. The emplacement age of the ore-bearing pluton was determined by zircon U-Pb geochronology. Combined with the carbon isotopic composition, the genesis and metallogenic age of the deposit were studied. Orebodies in the deposits are hosted in a monzogranite pluton as thick tabular and irregular shape, and graphite is present as ball or irregular rains. These ore-bodies might be formed as the product of recrystallization during the magmatic hydrothermal activity when the coal-bearing strata of the Lower Carboniferous Kagong Formation were captured by monzogranite magma. The U-Pb age of ore-bearing monzogranite yielding (244.7±1.3)Ma indicates its emplacement during Middle Triassic, which represents the magmatic age and metallogenic age. The discovery of many graphite deposits and prospects in Tibet indicate that there is good exploration potential of graphite resources, especially in the Sanjiang area.
-
Keywords:
- graphite deposit /
- mineral characteristics /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- mineral exploration engineering /
- Qingguo /
- Tibet
-
致谢: 感谢西藏地勘局曾庆高高级工程师、西洛朗杰高级工程师的悉心指导;感谢自然资源部沉积盆地与油气重点实验室对实验测试的帮助;感谢匿名审稿专家提出的宝贵审改意见。
-
表 1 西藏青果石墨矿床花岗闪长岩、二长花岗岩锆石测年结果
Table 1 U-Pb dating data of granodiorite and monzogranite in the Qingguo graphite deposit, Tibet

表 2 西藏石墨矿床地质信息一览
Table 2 Geological information of these graphite deposits in Tibet

-
Ai Jiang, Lü Xinbiao, Li Zuowu, Wu Yalun. 2018. A super-large graphite deposit discovered in granite rocks at Huangyangshan, Xinjiang, China[J]. China Geology, 1: 164-166. doi: 10.31035/cg2018016
Baiju K R, Satish-Kumar M, Kagi H, Nambiar C G, Ravisankar M. 2005. Mineralogical characterization of graphite deposits from Thodupuzha-Kanjirappally Belt, Madurai granulite block, Southern India[J]. Gondwana Research, 8(2): 223-230. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)71120-5
Bai Jianke, Chen Juanlu, Peng Suxia. 2018. Geochronology and geochemistry of ore-bearing intrusions from Huangyangshan magmatic hydrothermal graphite deposit in Qitai County, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(8): 2327-2340 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cai Wenchun, Zeng Zhongcheng, Song Shuguang, Li Jingchen, Wu Hao, Chen Yan. 2020. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Xianghe crystalline graphite deposit in Shangnan County of Shaanxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 53(3): 220-232(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yanjing, Liu Congqiang, Chen Huayong, Zhang Zengjie, Li Chao. 2000. Carbon isotope geochemistry of graphite deposits and ore-bearing khondalite series in North China: Implications f or several geoscientific problems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(2): 233-244(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng Jun, Ge Liangsheng, Yang Liqiang. 2013. Tectonic dynamic system and compound orogeny: Additionally discussing the temporal-spatial evolution of Sanjiang orogeny, Southwest China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1099-1114(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dun Jun, Zhang Jing, Wang Qinfei. 2018. Research advances of composite metallogenic system and deep driving mechanism in the Tethys, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(5): 1229-1238(in Chinese with English abstract).
Fan Bingliang, Bai Tao, Feng Dexing, Zhang Tingting, Tang Yong, Zhang Liwen, Liang Hongyan. 2018. Zircon U-Pb age and genesis of Niuduo biotite mon-zogranite in east Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(7): 1226-1235(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZQYD201807007.htm
Guo Na, Chen Jianping, Tang Juxing. 2008. Remote sensing information extraction of mineralizing anomaly in the Dongdashan arean of Eastern Tibet[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 44(4): 69-73(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200804012.htm
Katz M B. 1987. Graphite deposits of Sri Lanka: A consequence of granulite facies metamorphism[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 22: 18-25. doi: 10.1007/BF00204238
Lei Weiyan, Shi Guanghai, Liu Yinxin. 2013. Research progress on trace element characteristics of zircons of different origins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(4): 273-284(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Chao, Wang Denghong, Zhao Hong, Pei Haoxiang, Li Xinwein, Zhou Limin, Du Andao, Qu Wenjun. 2015. Minerogenetic regularity of graphite deposits in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(6): 1223-1236(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506011.htm
Li Chao, Wang Denghong, Zhou Limin, Zhao Hong, Li Xinwei, Qu Wenjun. 2017. Study on the Re-Os isotope composition of graphite from the Lutang graphite deposit in Hunan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 36(3): 297-304(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Kaiyue, Chen Yanjing, Yu Zhenbing, Tang Shuhao, Chen Weiyu. 2018. Carbon isotope compositions and geochemical characteristics of the Zhangshe graphite deposit of the Jingshan Group, Jiaobei[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(5): 19-33(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Siyuan, Sun Li, Meng Fanlei, Zhang Jidan, Li Yunguo. 2016. Resource potential prediction of the Yunshan graphite deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Geology, 40(2): 288-292(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201602016.htm
Lin Bin, Chen Yuchuan, Tang Juxing, Wang Qin, Song Yang, Yang Chao, Wang Wenlei, He Wen, Zhang Lejun. 2017b. 40Ar/39Ar and Rb-Sr ages of the Tiegelongnan porphyry Cu-(Au) deposit in the Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt of Tibet, China: Implication for generation of super-large deposit[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(2): 602-616. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13120
Lin Bin, Wang Liqiang, Tang Juxing, Tang Juxing, Song Yang, Zhou Xin, Liu Zhibo, Gao Yiming, Tang Xiao Qiang, Xu Ruige, Chen Zaojun. 2017. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of ore-bearing porphyries in Baomai deposit, Yulong Copper Belt, Tibet[J]. Earth Science, 42(9): 1454-1471(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201709002.htm
Lin Bin, Wang Liqiang, Tang Juxing, Song Yang, Cao Huawen, Baker M J, Zhang Lejun, Zhou Xin. 2018. Geology, geochronology, geochemical characteristics and origin of Baomai porphyry Cu (Mo) deposit, Yulong Belt, Tibet[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 186-204. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.10.025
Lin Bin, Tang Juxing, Chen Yuchuan Michael Baker, Song Yang, Yang Huanhuan, Wang Qin, He Wen, Liu Zhibo. 2019. Geology and geochronology of Naruo large porphyry-breccia Cu deposit in the Duolong district, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 66: 168-182. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.07.009
Lin Bin, Tang Juxing, Chen Yuchuan, Song Yang, Greg Hall, Wang Qin, Yang Chao, Fang Xiang, Duan Jilin, Yang Huanhuan, Liu Zhibo, Wang Yiyun, Feng Jun. 2017a. Geochronology and genesis of the Tiegelongnan porphyry-epithermal Cu(Au) deposit in Tibet: Evidence from U-Pb, Re-Os dating and Hf, S, H-O isotopes[J]. Resource Geology, 67(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1111/rge.12113
Liu Jun, zhu Xiangping, Li Wenchang, Wang Baodi, Dong Yu, Yang Fucheng, Yang Houbin, Wu Jianghua. 2019. Molybdenite Re-Os dating of the Larong porphyry W-Mo deposit in eastern Tibet and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(7): 1708-1719. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXE201907011.htm
Liu Yongsheng, Hu Zaochu, Zong Keqing, Gao Changgui, Gao Shan, Xu Juan, Chen Haihong. 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55: 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Liu Songbai, Yang Meizhen, Wu Hongen, Zhao Wenping, Zhang Lianlian. 2011. Metallogenic model of graphite deposit from Sujiquan, Eastern Junggaer[J]. Xijiang Geology, 29(2): 178-182. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201102013.htm
Lu Yaozu, Shi Guocheng. 2016. Geological characteristics and genersis analysis of graphite deposit in South Mountain of Datonggou region, Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Qinghai University (Natural Science), 34(2): 53-59(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201602010.htm
Ludwig K R. 2012. User's manual for isoplot 3.75: A geochronological tool kit for Microsoft Excel: Berkeley, Berkeley Geochronology Center, 1-70.
Ma Xudong, Zhong Yan, Chen Yali, Qu Xiaoming. 2019. The graphite mineralized controlled by the sedimentary process of the Khondalite series, western north China craton[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(6): 1155-1168(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Yubo, Xing Shuwen, Xiao Keyan, Yu Cheng, Tang Chen, Ding Jianhua, Zhang Yong, Ma Lukuo. 2016. Geological metallogenic characteristics and mineral resource potential of the Au-Ag-Cu-Mo metallogenic belt in Eastern Jilin-Heilongjiang Provinces[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(7): 1281-1297(in Chinese with English abstract).
Martín-Méndez, Iván y Boixereu, Ester y Villaseca González, Carlos. 2016. Mineralogical and isotopic characterization of graphite deposits from the Anatectic complex of Toledo, central Spain[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 51 (5): 575-590. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0625-9
Mo Rujue, Liu Shaobin, Huang Cuirong, Zhang Guangrong, Tan Guanmin, Wang Baoxian, Xiao Xiangzhang. 1989. Geology of China Graphite Deposit[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 1-290 (in Chinese).
Sun Li, Xu Cuiping, Xiao Keyan, Zhu Yusheng, Yan Lingya. 2018. Geological characteristics, metallogenic regularities and the exploration of graphite deposits in China[J]. China Geology, 3: 425-434.
Tang Juxing, Zhang Li, Li Zhijun, Chen Jianping, Huang Wei, Wang Qian. 2006a. Porphyry copper deposit controlled by structural nose trap: Yulong porphyry copper deposit in eastern Tibet[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(6): 652-662 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200606001.htm
Tang Juxing, Zhong Kanghui, Liu Zhaochang, Li Zhijun, Dong Shuyi, Zhang Li. 2006b. Intracontinent orogen and metallogenesis in Himalayan Epoch: Changdu large composite basin, Eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9): 1364-1376(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/282766815_Intracontinent_orogen_and_metallogenesis_in_Himalayan_epoch_Changdu_large_composite_basin_eastern_Tibet
Tang Juxing. 2019. Mineral resources base investigation and research status of the Tibet Plateau and its adjacent major metallogenic belts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(3): 617-624(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.03.01
Xiao Keyan, Sun Li, Li Siyuan, Huang An. 2016. Geological characteristics and mineralization potential of graphite resource in China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 37(5): 607-614(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/316599452_Geological_characteristics_and_mineralization_potential_of_graphite_resource_in_China
Xin Junqiang, Shui Yingdong, Shao Ji, Chen Xuejun, 2017. Geological characteristics and potential analysis of graphite deposits in Xixi Te Guole of Qinghai[J]. Journal of Qinghai University (Natural Science), 35(2): 60-66(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201702011.htm
Xin Junqiang, Yang Yanjing, Zhao Shenghui, Lei Yanjun, He Huhu. 2015. Geological characteristics and ore genesis of east Hongshui River graphite deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Qinghai University(Natural Science), 33(6): 81-84(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201506014.htm
Xu Xinwen, Duan Jianhua, Lu Yaozu, Bai Qiang, Xu Jiaqiu. 2019. Geological characteristics and availiability evaluation of graphite deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Metal Mine, (1): 125-140(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JSKS201901025.htm
Yan Lingya, Gao Shuxue, Sun Li, Chen Zhengguo, Jiao Lixiang, Sun Li, Liu Yanfei, Zhou Wen. 2018a. Metallogenic characteristics and metallogenic zoning of graphite deposits in China[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 421-440 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201803002.htm
Yan Lingya, Gao Shuxue, Sun Li, Chen Zhengguo, Jiao Lixiang, Zhou Wen, Liu Yanfei, Sun Jixiu. 2018b. Metallogenic characteristics and metallogenic factors of regional metamorphic graphite deposit in China[J]. China Non-metallic Mining Industry, (3): 21-24, 28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LGFK201803010.htm
Zhang Guoxin, Hu Aiqin, Zhang Hongbin, Zhang Qianfeng, Shen Youlin. 1996. Carbon isotopic evidence for the origin of the spherical graphite in a granite-hosted granphite deposit, Sujiquan, Xinjiang, China[J]. Geochemica, 25(4): 379-386(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX604.009.htm
Zhang Sujiang, Cui Wei, Zhang Yanwen, Han Jian, Shang Lei. 2018. Summarize on the graphite mineral resources and their distribution at home and abroad[J]. China Mining Magazine, 27(10): 8-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201810002.htm
Zhong Kanghui, Tang Juxing, Liu Zhaochang, Kou Linlin, Dong Shuyi, Li Zhijun, Zhou Huiwen. 2006. Mesozoic-Cenozoic intracontinental rifting of Changdu-Simao tectonic zone in east margin of Qinhai-Tibet, WS China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9): 1295-1311(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291841839_Mesozoic_-_Cenozoic_intracontinental_rifting_of_Changdu_-_Simao_Tectonic_Zone_in_east_margin_of_Qinghai_-_Tibet_WS_China
白建科, 陈隽璐, 彭素霞. 2018. 新疆奇台县黄羊山岩浆热液型石墨矿床含矿岩体年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 34(8): 2327-2340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201808009.htm 蔡文春, 曾忠诚, 宋曙光, 李景晨, 吴昊, 陈艳. 2020. 陕西商南湘河晶质石墨矿床地质特征与成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 53(3): 220-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202003022.htm 陈衍景, 刘丛强, 陈华勇, 张增杰, 李超. 2000. 中国北方石墨矿床及赋矿孔达岩系碳同位素特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 16(2): 233-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200002012.htm 邓军, 葛良胜, 杨立强. 2013. 构造动力体制与复合造山作用——兼论三江复合造山带时空演化[J]. 岩石学报, 29(4): 1099-1114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201304001.htm 邓军, 张静, 王庆飞. 2018. 中国西南特提斯典型复合成矿系统及其深部驱动机制研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 34(5): 1229-1238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201805001.htm 樊炳良, 白涛, 冯德新, 张婷婷, 汤勇, 张力文, 梁宏岩. 2018. 藏东纽多黑云母二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及成因[J]. 地质通报, 37(7): 1226-1235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201807007.htm 郭娜, 陈建平, 唐菊兴. 2008. 藏东东达山地区遥感找矿地质异常提取方法研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 44(4): 69-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200804012.htm 雷玮琰, 施光海, 刘迎新. 2013. 不同成因锆石的微量元素特征研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 20(4): 273-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304028.htm 李超, 王登红, 赵鸿, 裴浩翔, 李欣尉, 周利敏, 杜安道, 屈文俊. 2015. 中国石墨矿床成矿规律概要[J]. 矿床地质, 34(6): 1223-1236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506011.htm 李超, 王登红, 周利敏, 赵鸿, 李欣尉, 屈文俊. 2017. 湖南鲁塘石墨矿Re-Os同位素研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 36(3): 297-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201703013.htm 李凯月, 陈衍景, 佘振兵, 汤好书, 陈威宇. 2018. 胶北荆山群张舍石墨矿碳同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 25(5): 19-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201805003.htm 李思远, 孙莉, 孟凡磊, 张寄丹, 李云国. 2016. 黑龙江云山石墨矿床资源潜力预测[J]. 地质学刊, 40(2): 288-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.02.288 林彬, 王立强, 唐菊兴, 宋扬, 周新, 刘治博, 高一鸣, 唐晓倩, 徐瑞阁, 陈早军. 2017. 西藏玉龙铜矿带包买矿床含矿斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 地球科学, 42(9): 1454-1471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201709002.htm 刘松柏, 杨梅珍, 吴洪恩, 赵文平, 张练练. 2011. 新疆苏吉泉球状石墨矿床成矿模式[J]. 新疆地质, 29(2): 178-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2011.02.012 刘俊, 祝向平, 李文昌, 王保弟, 董宇, 杨富成, 杨后斌, 吴江华. 2019. 藏东拉荣斑岩钨钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 93(7): 1708-1719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.07.011 路耀祖, 石国成. 2016. 青海大通沟南山石墨矿床地质特征及其成因分析[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版) 34, (2): 53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201602010.htm 马旭东, 钟焱, 陈雅丽, 曲晓明. 2019. 华北克拉通孔兹岩带内孔兹岩系沉积过程对石墨矿床成矿的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(6): 1155-1168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201906007.htm . 马玉波, 邢树文, 肖克炎, 于城, 唐臣, 丁建华, 张勇, 马路阔. 2016. 吉黑东部Au-Ag-Cu-Mo-石墨成矿带主要地质成矿特征及潜力分析[J]. 地质学报, 90(7): 1281-1297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.07.003 莫如爵, 刘绍斌, 黄翠蓉, 张光荣, 谭冠民, 王宝娴, 肖祥章. 1989. 中国石墨矿床地质[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1-290. 唐菊兴, 张丽, 李志军, 陈建平, 黄卫, 王乾. 2006a. 西藏玉龙铜矿床——鼻状构造圈闭控制的特大型矿床[J]. 矿床地质, 25(6): 652-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200606001.htm 唐菊兴, 钟康惠, 刘肇昌, 李志军, 董树义, 张丽. 2006b. 藏东缘昌都大型复合盆地喜马拉雅期陆内造山与成矿作用[J]. 地质学报, 80(9): 1364-1376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609012.htm 唐菊兴. 2019. 青藏高原及邻区重要成矿带矿产资源基地调查与研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 35(3): 617-624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201903001.htm 肖克炎, 孙莉, 李思远, 黄安. 2016. 我国石墨矿产地质特征及资源潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 37(5): 607-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201605009.htm 辛军强, 水应东, 邵继, 陈学俊. 2017. 青海细细特郭勒地区石墨矿床地质特征及潜力分析[J]. 青海大学学报, 35(2): 60-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201702011.htm 辛军强, 杨延景, 赵生辉, 雷延军, 何虎虎. 2015. 青海洪水河东地区石墨矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版) 33(6): 81-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201506014.htm 徐新文, 段建华, 路耀祖, 白强, 徐加球. 2019. 青海省石墨矿地质特征及可利用性评价[J]. 金属矿山, (1): 125-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201901025.htm 颜玲亚, 高树学, 陈正国, 焦丽香, 孙莉, 刘艳飞, 周雯. 2018a. 中国石墨矿成矿特征及成矿区带划分[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 421-440. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180301&flag=1 颜玲亚, 高树学, 孙莉, 陈正国, 焦丽香, 周雯, 刘艳飞, 孙即秀. 2018b. 我国区域变质型石墨矿成矿特征及成矿要素[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, (3): 21-24, 28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LGFK201803010.htm 张国新, 胡霭琴, 张鸿斌, 张前锋, 申佑林. 1996. 新疆苏吉泉石墨矿床成因的碳同位素证据[J]. 地球化学, 25(4): 379-386. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.04.010 张苏江, 崔立伟, 张彦文, 韩健, 尚磊. 2018. 国内外石墨矿产资源及其分布概述[J]. 中国矿业, 27(10): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201810002.htm 钟康惠, 唐菊兴, 刘肇昌, 寇林林, 董树义, 李志军, 周慧文. 2006. 青藏东缘昌都-思茅构造带中新生代陆内裂谷作用[J]. 地质学报, 80(9): 1295-1311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.007



 下载:
下载: