Geology, ore-forming fluid and metallogenic age of orogenic gold deposits in the Northern Qaidam
-
摘要:
柴达木盆地北缘是一条著名的超高压变质带,带内矿产资源丰富。造山带金矿广泛分布于柴北缘带内,本文着重对柴北缘金矿的地质特征、成矿流体的温度和同位素及成矿时代进行研究。结果显示:柴北缘造山型金矿主要赋存在中元古界、寒武系和奥陶系变质岩发育的剪切带中,且多数矿体的展布与NW向的构造相关。大多数金矿成矿温度呈双峰态分布,少部分呈单峰态分布,显示受到多期流体作用。成矿流体的δ18OH2O-SMOW(-1.7‰~10.31‰)和δDV-SMOW(-113.8‰~-41.6‰)指示其变质流体受到岩浆水及大气水等共同作用。含金硫化物(黄铁和方铅矿)的δ34S为0.5‰~11‰,主要集中在5‰~9‰,206Pb/204Pb为18.238~19.296,207Pb/204Pb为15.547~15.773,208Pb/204Pb为37.918~38.978,指示了成矿物质来源于地幔-上地壳,且一定程度上都受到了岩浆作用的影响。构造演化与成矿时代显示柴北缘发生了426~376 Ma、357~330 Ma和288~246 Ma三次金成矿事件。
Abstract:The northern margin of Qaidam Basin is a well-known ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt with abundant mineral resources. The orogenic gold deposits are widely distributed in the northern Qaidam. This paper focuses on the study of the geological characteristics, temperature and isotopes of ore-forming fluids of the gold deposits in northern Qaidam. The results show that the orogenic gold deposits are mainly distributed in the shear zones of the Mesoproterozoic, Cambrian and Ordovician metamorphic rocks, and most ore bodies is related to the NW-trending structures. Besides, the mineralization temperature of most gold deposits is bimodal, and only a few gold deposits exhibit monomodal in temperature, indicating that multi-phase fluids were involved in the mineralization process. The δ18OH2O-SMOW (-1.7‰-10.31‰) and δDV-SMOW(-113.8‰﹣-41.6‰) of the ore-forming fluid indicate that the metamorphic fluid is influenced by magmatic water and atmospheric water. The δ34S of gold-containing sulfides (pyrite and galena) ranges from 0.5‰ to 11‰, mainly in the range of 5‰ to 9‰, 206Pb/204Pb from 18.238 to 19.296, 207Pb/204Pb from 15.547 to 15.773, and 208Pb/204Pb from 37.918 to 38.978, which indicates that the ore-forming materials are derived from the mantle-upper crust, and are affected by magmatism to some extent. The tectonic evolution and metallogenic ages reveal that three gold metallogenic events occurred in the northern Qaidam during 426-376 Ma、357-330 Ma and 288-246 Ma.
-
1. 引言
造山型金矿床作为重要的金矿床类型,其占世界黄金资源的30%以上(Groves et al., 1988)。造山带中形成的造山型金矿床主要位于由挤压或走滑变形中应力相对低的区域,如次级断裂构造中(McCuaig et al., 1988)。大多数造山型金矿床是在绿片岩相变质条件下形成的(Goldfarb et al., 2001, 2015; Deng and Wang, 2016)。造山型金矿的成矿流体和金的来源是至今尚未解决的问题(卢焕章等, 2018)。一般认为成矿流体中的Au(HS)2-络合物是金元素运输及富集的载体(McCuaig et al., 1988)。金成矿流体来源多样,包括:(1)岩石变质作用(Groves et al., 2003); (2)含碳沉积物(Large et al., 2011); (3)岩浆热液(Tomkins et al., 2013); (4)海水(Chang et al., 2008); (5)变质脱水(Phillips and Powell, 2009, 2010)。事实上各个时代的大多数造山型金矿床的成矿流体具有盐度低(≤10%NaCleqv),高碳(CO2 + CH4含量为5%~30%),低Cl和高S含量等特征(卢焕章等, 2018)。而造山型金矿床成矿流体的一致性,说明它们可能来自相同或者是多阶段形成的热液流体(卢焕章, 1991;卢焕章和池国祥, 1995)。此外,造山型金矿的成矿时代也是其研究的热点,争论的焦点主要在于是形成于变质峰期前(Phillips and Powell, 2009, 2010;Tomkins, 2010)还是变质峰期与峰期后(Groves et al., 1998;Goldfarb et al., 2005)。前者主要认为造山带在抬升剥蚀过程中,变质峰期与地壳的深度有关,即越深则达到峰期的时间越晚,且也可能受到之后变质作用的叠加,从而表现出成矿时代比围岩变质时期晚(Phillips and Powell, 2010)。后者则基于造山型金矿的成矿时代统计(Knight et al., 1993, 2000;Dziggel et al., 2010;Kolb et al., 2015),并结合变质时代、蚀变特征、穿切关系等。同时,前人研究发现这些造山型金矿的成矿峰期与陆壳增生速率的峰期和超大陆拼合峰期吻合较好(Goldfarb et al., 2001)。
造山型金矿床也是中国重要的黄金来源,广泛分布于天山造山带(Chen et al., 2012),哀牢山构造带(Zhang et al., 2018),华北克拉通北缘(Hart et al., 2002)和中国西北的造山带(Mao et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2009;李猛等,2020)。柴达木盆地北缘(简称柴北缘)造山带是中国西北部的重要的造山带之一,含有一系列Au、Cu、Pb和Zn矿床(Zhang et al., 2009)。本区是中国重要的金成矿带,目前发现9个金矿床,金矿化点十余处,远景资源量在300 t以上。前人研究认为这些金矿与造山作用密切相关,但缺乏系统性总结,从而限制了我们对柴北缘造山型金矿的理解。本文在前人研究和最新地质资料的基础上,对柴北缘造山型金矿进行初步探讨,希望能够对柴北缘造山型金矿的找矿工作有所启迪。
2. 地质背景
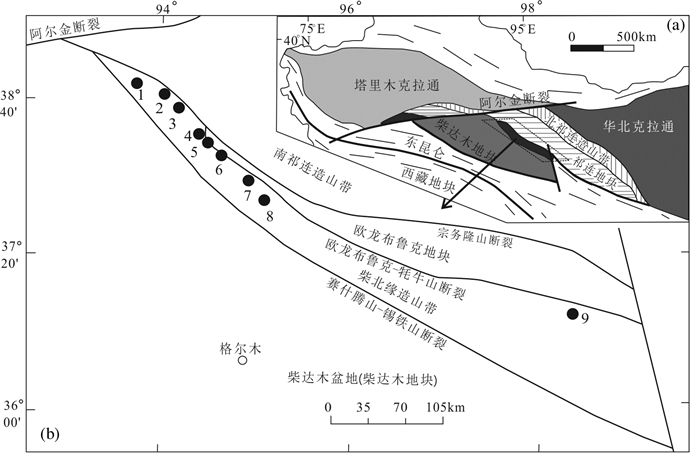
柴北缘造山带整体走向为西北-东南,长约900 km,宽25~160 km(图 1)。北邻祁连造山带,南接柴达木地块(柴达木盆地)(Song et al., 2014; 蔡鹏捷等,2019)。欧龙布鲁克—牦牛山断裂将柴北缘从欧龙布鲁克地块向北分离(Chen et al., 2009)。在其西北端,造山带被阿尔金断裂切割(Wittlinger et al., 1998)。前人研究表明,柴达木盆地北部在早奥陶世发生俯冲,与祁连地块的碰撞发生在晚奥陶世到中泥盆世(Yang, 2002; 蔡鹏捷等, 2018)。
![]() 1—胜利沟金矿;2—野骆驼泉金矿;3—千枚岭金矿;4—红柳沟金矿;5—青龙沟金矿;6—滩间山金矿;7—鱼卡金矿;8—双口山金矿;9—赛坝沟金矿Figure 1. Schematic map showing the major tectonic units in northwest China (a, modified from Song et al., 2013) and simplified map showing the tectonic framework of the northern Qaidam(b, modified from Zhang et al., 2009)1-Shengligou gold deposit; 2-Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 3-Qianmeiling gold deposit; 4-Hongliugou gold deposit; 5-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 6-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 7-Yuka gold deposit; 8-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 9-Saibagou gold deposit
1—胜利沟金矿;2—野骆驼泉金矿;3—千枚岭金矿;4—红柳沟金矿;5—青龙沟金矿;6—滩间山金矿;7—鱼卡金矿;8—双口山金矿;9—赛坝沟金矿Figure 1. Schematic map showing the major tectonic units in northwest China (a, modified from Song et al., 2013) and simplified map showing the tectonic framework of the northern Qaidam(b, modified from Zhang et al., 2009)1-Shengligou gold deposit; 2-Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 3-Qianmeiling gold deposit; 4-Hongliugou gold deposit; 5-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 6-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 7-Yuka gold deposit; 8-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 9-Saibagou gold deposit柴北缘的主要岩石地层单位包括古元古界达肯大板岩群、中—新元古界鱼卡河岩群、滩间山岩群和下古生界弧相关的火山和沉积岩(Zhang et al., 2017a, b)。柴北缘作为著名的超高压变质带,前人通过对高压/超高压变质岩(榴辉岩和片麻岩)和花岗岩的地质年代学和地球化学研究,建立了一个大陆碰撞造山带从早期海底俯冲(>440 Ma)、大陆俯冲和碰撞(440~ 420 Ma)、俯冲板块的剥露(420~390 Ma)和最终造山带崩塌(390~360 Ma)的演化模型(Song et al., 2014;张建新等, 2015;Zhang et al., 2017a, b)。
3. 柴北缘造山型金矿床地质概况
俯冲相关增生造山作用的成矿模型预测,柴北缘有利于造山型成矿(Goldfarb et al., 2001, 2015; Deng and Wang, 2016)。柴北缘造山带已发现大量的造山型金矿床,包括胜利沟、野骆驼泉、千枚岭、红柳沟、青龙沟、滩间山、赛坝沟、鱼卡和双口山,以蚀变岩型和石英脉型为主(国家辉, 1998;张德军, 2001, 2005, 2007a, 2007b;Zhang et al., 2009;范贤斌, 2017;孟和, 2017;蔡鹏捷等, 2018)。
柴北缘造山型金矿的地质特征见表 1。总体上,柴北缘的造山带金矿体主要赋存于中元古界、寒武系和奥陶系低品位变质岩发育的剪切带中(Deng and Wang, 2016)。其中胜利沟、野骆驼泉、千枚岭、红柳沟、鱼卡和双口山金矿主要产于寒武—奥陶系滩间山群,青龙沟和滩间山金矿产于中元古界万洞沟群,赛坝沟金矿的赋矿围岩为中粗粒花岗闪长岩-英云闪长岩。基本上所有金矿的围岩蚀变包括硅化、绿泥石化、绢云母化,部分还有碳酸盐化(千枚岭、红柳沟、滩间山、鱼卡、双口山),黄铁绢英岩化(赛坝沟金矿)。多数金矿体的展布与NW向的韧性剪切或断层破碎带相关,少数还与次级构造有关(野骆驼泉、千枚岭、青龙沟、滩间山、双口山)。矿石构造大部分为浸染状、细脉浸染状,部分可见团块状矿石(滩间山和鱼卡)。这些金矿的元素组合均表现为Au-As。
Table 1. Geological characteristics of the orogenic gold deposits in Northern Qaidam
4. 金矿成矿温度特征
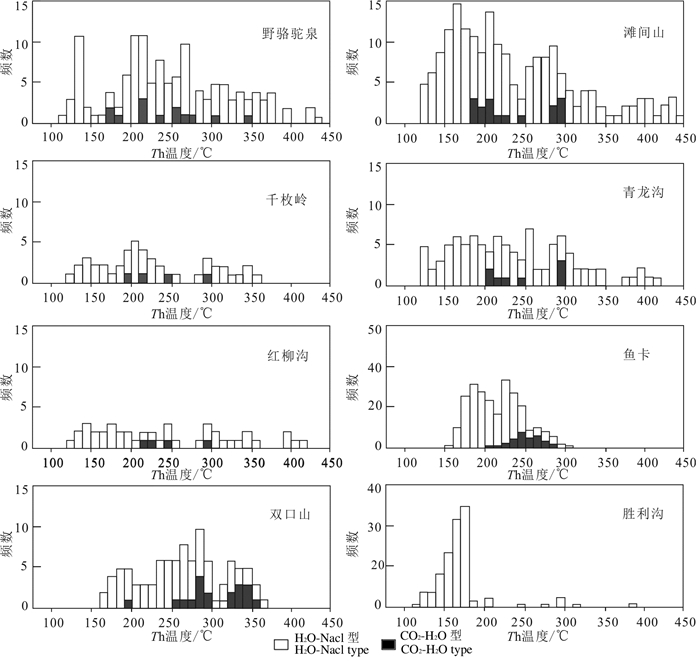
对柴北缘造山型金矿与成矿相关的流体包裹体均一温度、冰点、盐度等进行统计(表 2,图 2):野骆驼泉(CO2-H2O型:峰值177~261℃和270~341℃,盐度为1.6%~8.9%;H2O-NaCl型:119~437℃,冰点为-7.8~-0.9℃,盐度为1.6%~11.4%)(张德全等, 2001)、滩间山(CO2-H2O型:峰值在186~250℃和280~296℃,盐度为1.4%~7.9%;H2O-NaCl型:121~ 449℃,冰点为-7.0~-0.9℃,盐度为1.6%~10.5%) (张德全等, 2001)、千枚岭(CO2-H2O型:峰值191~ 243℃,299℃,盐度为2.4%~7.3%;H2O-NaCl型:124~358℃,冰点-6.9~-1.5℃,盐度为2.6%~10.3%) (张德全等, 2001)、青龙沟(CO2- H2O型:200~ 245℃,293~299℃,盐度为1.8%~8.3%;H2O-NaCl型:129~418℃,冰点为-6.0~-0.7℃,盐度为1.2%~ 9.2%)(张德全等, 2001)、红柳沟(CO2-H2O型:213~ 245℃,295℃,盐度为2.4%~8.1%;H2O-NaCl型:129~420℃,冰点为- 5.9~- 1.2℃,盐度为2.1% ~ 9.1%)(张德全等, 2001)、鱼卡(CO2-H2O型:193~ 249℃;H2O- NaCl型:188~285℃,冰点为- 7.5~-0.7℃,盐度为1.22%~11.10%)(范贤斌, 2017;蔡鹏捷, 2018)、双口山(CO2-H2O型:252~290℃,320~ 358℃;H2O-NaCl型:161~365.6℃,冰点为-5.6~ -3.0℃,盐度为1.91%~14.25%)(孟和, 2017)、胜利沟(H2O- NaCl型:120~209℃,206~385℃,冰点为-9.7~-1.8℃,盐度为3.06%~13.62%)(黄亚, 2013)。
Table 2. Temperature measurement data of fluid inclusions of orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (datas from Zhang et al., 2001; Huang, 2013; Fan, 2017; Meng, 2017; Cai et al., 2018)
![]() Figure 2. Histogram showing homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (after Zhang et al., 2001; Huang, 2013; Fan, 2017; Meng, 2017; Cai et al., 2018c)
Figure 2. Histogram showing homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (after Zhang et al., 2001; Huang, 2013; Fan, 2017; Meng, 2017; Cai et al., 2018c)不难看出,成矿流体的均一在各个矿床之间存在一定的差异。这种差异应该是与成矿作用时的压力-温度不同有关,也与围岩的组成有关。但这些矿床的成矿温度还是在200~400℃,仅有几十度的差别,均在造山型金矿的成矿温度(卢焕章等, 2018)。大部分矿床(点) 中呈双峰态分布, 只有少部分矿床(点)中呈单峰态分布。张德全(2007)对柴北缘—东昆仑金矿流体包裹体研究认为,这可能与不同造山时期的成矿作用有关,且对应了低盐度的H2O-CO2-NaCl-CH4(晚加里东碰撞造山期)和H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4(晚华力西—印支碰撞造山期)两种不同的成矿流体。
一般认为金成矿具有多个成矿阶段, 从早期的高温阶段到后期的低温阶段(卢焕章等, 2018)。金矿化主要包含了4个阶段:①乳白色石英黄铁矿阶段;②含金石英黄铁矿阶段;③含金多金属硫化物石英阶段;④碳酸盐阶段(卢焕章等, 2018)。前人对柴北缘造山型金矿流体包裹体的研究主要针对与金矿的成矿流体相关第二和第三阶段。对柴北缘造山型金矿的流体包裹体显微观察,均发现有富CO2型、含CO2水溶液型(CO2-H2O型)和水溶液型(H2O-NaCl型) 三类,这与典型的造山型金矿中流体包裹体类型是一致的(Groves et al., 1998; Kerrich et al., 2000; Hagemann and Cassidy, 2000; 陈衍景等, 2007)。
5. 金成矿流体与物质来源
5.1 氢、氧同位素特征
利用与成矿相关的氢、氧同位素,能够有效地揭示成矿流体的来源,区分其来源岩浆水、变质水或大气降水,从而有助于判别流体的演化轨迹和矿床成因(杨利亚等, 2013)。造山型金矿的成矿流体往往经历了长距离迁移,其氢、氧同位素组成除了反映源区性质之外,可能表征沿着流体通道的水/岩反应、源区和围岩或后期流体的混合特征(Ridley and Diamond, 2000; Beaudoin and Pitre, 2005; 蔡鹏捷, 2019)。
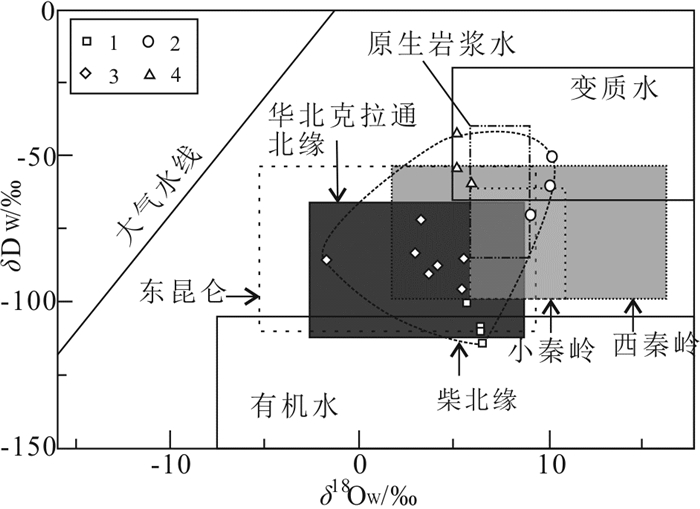
柴北缘造山型金矿成矿流体中δ18OH2O-SNOW = -1.7‰ ~ 10.31‰和δDV- SMOW = -113.8 ‰~ -41.6 ‰ (表 3,图 3),其中滩间山金矿δ18OH2O-SNOW = 9.15‰ ~ 10.31‰,δDV-SMOW=-69.9‰ ~ -50‰;青龙沟金矿δ18OH2O - SNOW =- 1.7‰ ~ 5.5‰,δDV- SMOW=- 95.1‰ ~ -71.4‰;鱼卡金矿δ18OH2O-SNOW =5.2‰ ~ 6.01‰,δDV-SMOW=-58.5‰ ~-41.6‰;双口山金矿δ18OH2O-SNOW = 5.75‰ ~ 6.45‰,δDV-SMOW=-113.8‰ ~ -99.8‰。柴北缘这些金矿的H-O同位素特征,是无法用单一大气水或原生岩浆水的参与解释,只有是在复杂的造山过程中变质流体受到岩浆水及大气水等共同作用所导致。从图 3也可见,整个柴北缘金矿的H-O同位素基本上也与华北克拉通北缘、小秦岭、西秦岭、东昆仑等造山带中的造山型金矿范围重叠。
表 3 柴北缘造山型金矿H-O同位素Table 3. δ18O and δD values of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam
![]() 图 3 柴北缘造山型金矿δD与δ18Owater比值图(底图据Deng and Wang, 2016)1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—青龙沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿Figure 3. δD (‰) vs. δ18Owater (‰) diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Deng and Wang, 2016)1-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3- Qinglonggou gold deposit; 4-Yuka gold deposit
图 3 柴北缘造山型金矿δD与δ18Owater比值图(底图据Deng and Wang, 2016)1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—青龙沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿Figure 3. δD (‰) vs. δ18Owater (‰) diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Deng and Wang, 2016)1-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3- Qinglonggou gold deposit; 4-Yuka gold deposit5.2 硫、铅同位素特征
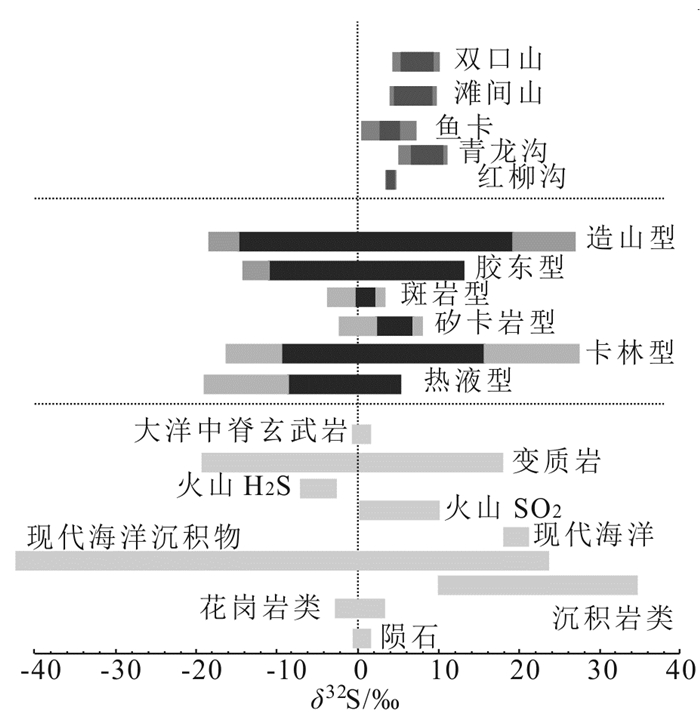
硫化物的硫同位素组成对于追踪成矿物质来源和约束成矿过程是非常有效的(Hodkiewicz et al., 2009)。柴北缘金矿中含金黄铁矿的δ34S在0.5‰~ 11‰,主要集中在5‰~9‰(表 4,图 4),其中滩间山金矿δ34S为5.31‰~8.54‰;青龙沟金矿δ34S为5.0‰ ~11.0‰;鱼卡金矿δ34S为0.5‰~7.4‰;双口山金矿δ34S为6.0‰ ~10.0‰;红柳沟金矿δ34S为3.9‰ ~4.4‰。总体柴北缘金矿黄铁矿的δ34S与金矿类型进行对比,主要落在造山型金矿和卡林型金矿范围内,源区特征主要落在变质岩类型的范围内(图 4),推测成矿流体在上升过程中与通道围岩发生水-岩作用而产生的混合硫,总体上指示了带内的金矿应属于造山型金矿。
表 4 柴北缘造山型金矿S同位素特征Table 4. Analytical results of S isotope of the orogenic gold deposits in Northern Qaidam
![]() 图 4 柴北缘造山型金矿与其他类型S同位素对比(据Deng and Wang, 2016修改)Figure 4. Comparison of S isotopes between orogenic gold deposits in the northern margin of Qaidam and other types of gold deposits
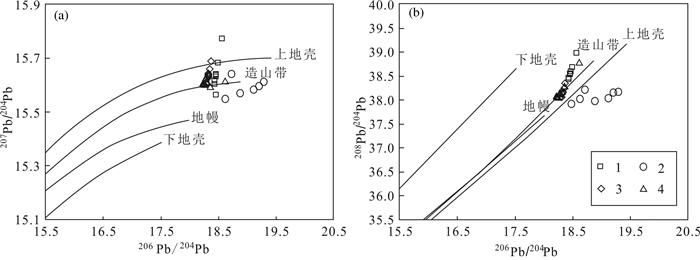
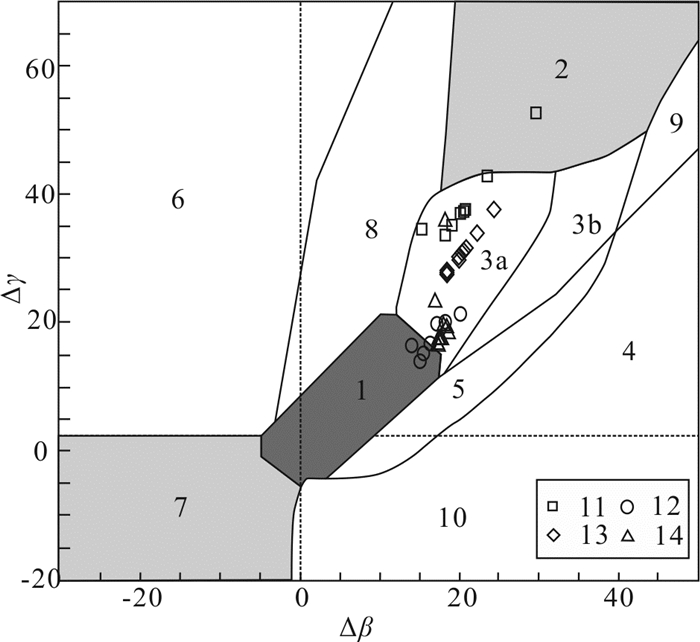
图 4 柴北缘造山型金矿与其他类型S同位素对比(据Deng and Wang, 2016修改)Figure 4. Comparison of S isotopes between orogenic gold deposits in the northern margin of Qaidam and other types of gold deposits矿石的铅同位素同样是一类对成矿来源的有效示踪工具(Doe and Stacey, 1974; Zartman and Doe, 1981)。柴北缘金矿中黄铁矿或共生方铅矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.238~19.296,207Pb/204Pb为15.547~ 15.773,208Pb/204Pb为37.918~38.978,∆β为14.15~ 29.79,∆γ为11.95~51.92(表 5)。其中胜利沟金矿中方铅矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.300~18.374,207Pb/204Pb为15.602~15.688,208Pb/204Pb为38.054~38.346,∆β为14.15~20.28,∆γ为11.95~18.38(表 5);滩间山金矿中黄铁矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.476~19.296,207Pb/204Pb为15.547~15.641,208Pb/204Pb为37.918~38.211,∆β为18.55~24.41,∆γ为28.66~36.42(表 5);鱼卡金矿中黄铁矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.238~18.62,207Pb/204Pb为15.59~ 15.618,208Pb/204Pb为38.039~38.775,∆β为16.96~ 18.78,∆γ为15.29~34.82(表 5);双口山金矿中方铅矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.437~18.567,207Pb/204Pb为15.617~ 15.773,208Pb/204Pb为38.466~38.978,∆β为15.33~ 29.79,∆γ为32.26~51.92,黄铁矿的206Pb/204Pb为18.435~18.460,207Pb/204Pb为15.604~15.634,208Pb/204Pb为38.431~38.531,∆β为18.24~20.91,∆γ为26.03~ 30.10(表 5)。柴北缘金矿含金矿物的Pb同位素投点可见主要落在了上地壳和造山带演化线之间(图 5),这些Pb同位素特征说明柴北缘金矿的成矿物质大多来源于地幔—上地壳的混合作用(图 6),且一定程度上受到了岩浆作用的影响,也指示了其应该与造山作用相关。
表 5 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素特征Table 5. Pb-isotpic compositions and characteristic parameters of orgen gold deposits in the northern Qaidam
![]() 图 5 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素构造图解(底图据Zartman and Doe, 1981)1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—胜利沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿Figure 5. Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)
图 5 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素构造图解(底图据Zartman and Doe, 1981)1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—胜利沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿Figure 5. Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)![]() 图 6 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素Δβ-Δγ图解(底图据朱炳泉等, 1998)1—地幔源Pb; 2—上地壳源Pb; 3—上地壳与地幔混合的俯冲带Pb (3a—岩浆作用; 3b—沉积作用); 4—化学沉积型Pb; 5—海底热水作用Pb; 6—中深变质作用Pb; 7—深变质下地壳Pb; 8—造山带Pb; 9—古老页岩上地壳Pb; 10—退变质作用Pb;11—双口山金矿;12—滩间山金矿;13—胜利沟金矿;14—鱼卡金矿Figure 6. Pb isotope Δβ-Δγ diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zhu et al., 1998)1- mantle lead; 2-upper crust lead; 3- subduction zone lead mixed with upper crust and mantle(3a -magmatism; 3b- deposition); 4- chemical deposition lead; 5- submarine hot water lead; 6-mesometamorphism lead; 7- katametamorphism lower crust lead; 8-orogenic belt lead; 9- ancient shale upper crust lead; 10- retrograde metamorphism lead; 11-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 12-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 13-Shengligou gold deposit; 14-Yuka gold deposit
图 6 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素Δβ-Δγ图解(底图据朱炳泉等, 1998)1—地幔源Pb; 2—上地壳源Pb; 3—上地壳与地幔混合的俯冲带Pb (3a—岩浆作用; 3b—沉积作用); 4—化学沉积型Pb; 5—海底热水作用Pb; 6—中深变质作用Pb; 7—深变质下地壳Pb; 8—造山带Pb; 9—古老页岩上地壳Pb; 10—退变质作用Pb;11—双口山金矿;12—滩间山金矿;13—胜利沟金矿;14—鱼卡金矿Figure 6. Pb isotope Δβ-Δγ diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zhu et al., 1998)1- mantle lead; 2-upper crust lead; 3- subduction zone lead mixed with upper crust and mantle(3a -magmatism; 3b- deposition); 4- chemical deposition lead; 5- submarine hot water lead; 6-mesometamorphism lead; 7- katametamorphism lower crust lead; 8-orogenic belt lead; 9- ancient shale upper crust lead; 10- retrograde metamorphism lead; 11-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 12-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 13-Shengligou gold deposit; 14-Yuka gold deposit6. 柴北缘造山型金成矿时代
前人对柴北缘构造带中的金矿相关的成岩成矿时代进行了厘定(表 6):野骆驼泉金矿成矿时代为(246.0±3.0)Ma(张德全等, 2005);青龙沟金矿成矿时代为(409.4±2.3)Ma(张德全等, 2005)、(410.3± 5.8)Ma(张德全等, 2005)、274.6 Ma(林文山等, 2006);滩间山金矿成矿时代为409.4 Ma(张德全等., 2001)、401 Ma(张德全等, 2001)、(394±6)Ma (Li, 2011)、385.8 Ma(崔艳合等, 2000)、(356±2.8) Ma(贾群子等, 2013)、(350.4 ± 3.2)Ma(张博文, 2010)、(344.7±2)Ma(李世金, 2011)、(344±2.2)Ma(张博文, 2010)、(330±24.3)Ma(张德全等, 2001)、(288.9±7.3)Ma(崔艳合等, 2000)、(289.6±6)Ma(崔艳合等, 2000)、288 Ma(Zhang et al., 2009)、(284.04±2.95)Ma(张德全等, 2005)、284 Ma(张德全等, 2005)、(275.9 ± 7.2)Ma(崔艳合等, 2000)、(268.94 ± 4.31)Ma(崔艳合等, 2000)、268.9 Ma (Zhang et al., 2009)、209 Ma(国家辉, 1998);鱼卡金矿成矿时代为(376.9±4.0)Ma、(387.5±7.2)Ma(范贤斌, 2017);双口山金矿成矿时代为(357.7±5.28)Ma (孟和, 2017);赛坝沟金矿成矿时代为(425.5±2.1) Ma(丰成友等, 2002)、(426±2)Ma(张德全等, 2005)、(210±3)Ma(丰成友等, 2002)。上述成矿时代指示了柴北缘造带中的金矿大多与复合造山过程有关。
表 6 柴北缘造山型金矿相关成岩与成矿时间Table 6. Diagenetic and metallogenic ages of orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam
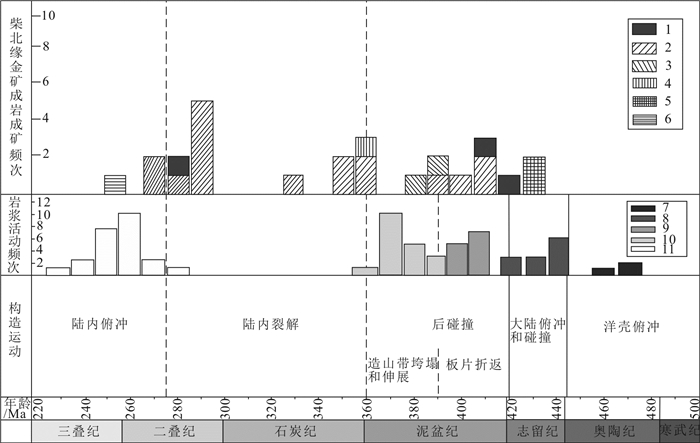
将柴北缘金矿成矿时期与岩浆活动和构造运动分期进行对比(图 7),综合前人研究,可见寒武—奥陶纪时期,柴北缘的洋盆逐渐关闭,洋壳俯冲导致岛弧火山岩(滩间山岩群)的形成,洋壳俯冲结束后,柴达木地块与欧龙布鲁克微陆块开始碰撞,形成了加里东期的柴北缘碰撞造山带(赵志新,2018),造山期后的一系列岩浆活动奠定了柴北缘造山型金矿形成的基础(张德全等, 2001, 2005;Zhang et al., 2009)。整个柴北缘造山型金矿的成矿期主要集中在426~376 Ma、357~330 Ma和288~246 Ma三个时期。第一个成矿期与区域的加里东期碰撞造山过程相关,第二成矿期与陆内裂解的岩浆活动有关,第三成矿期则与晚华力西—印支期造山过程有关。其中加里东晚期,柴达木陆块向祁连陆块的俯冲由正向俯冲变成斜向俯冲,导致区域上形成了一条右行剪切走滑构造带,同时柴北缘这种应力的转变也进一步促进了岩浆活动的加剧及地层的褶皱变形,从而导致成矿热液流体沿原有构造体系发生叠加富集(丰成友等, 2002; 张德全等, 2005)。从时间上,不难看出,第一时期是属于柴北缘超高压变质峰期之后,该期矿床成矿时代的差异应该是所处不同位置及成矿深度导致。第二成矿期属于柴北缘碰撞造山后地壳增厚后减薄时期,岩浆活动对金矿的进一步富化。第三成矿期则是古特提斯洋的开合导致该区新的造山活动,热液与岩浆新的叠加作用。事实上,一般认为挤压或者从伸展到挤压的转换阶段,才是造山型金矿最有利的形成时期(王庆飞等,2019)。柴北缘大部分的造山型金矿都属于一次造山作用的产物,而带内滩间山、青龙沟、塞巴沟等经历了两期以上,其中滩间山金矿的三期复合成矿作用可能是导致其成为柴北缘最大金矿的原因。
![]() 图 7 柴北缘构造事件、岩浆活动与金矿成矿时代耦合图(据赵志新,2018修改)1—青龙沟金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—鱼卡金矿;4—双口山金矿;5—赛坝沟金矿;6—野骆驼泉金矿;7—镁质钙性-钙碱性花岗岩;8—钙碱性花岗岩;9—钙碱-碱钙性花岗岩;10—钙碱花岗岩、拉斑质基性岩;11—碱性花岗岩Figure 7. Coupling diagram showing tectonic event, magmatic activity and metallogenic age of gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Zhao Zhixin, 2018)1-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3-Yuka gold deposit; 4-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 5-Saibagou gold deposit; 6- Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 7-Magnesian calc alkaline granite; 8-Calc alkaline granite; 9-Calc alkaline- alkali calcium granite; 10-Calc alkaline granite, tholeiitic basic rock; 11-Alkaline granite
图 7 柴北缘构造事件、岩浆活动与金矿成矿时代耦合图(据赵志新,2018修改)1—青龙沟金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—鱼卡金矿;4—双口山金矿;5—赛坝沟金矿;6—野骆驼泉金矿;7—镁质钙性-钙碱性花岗岩;8—钙碱性花岗岩;9—钙碱-碱钙性花岗岩;10—钙碱花岗岩、拉斑质基性岩;11—碱性花岗岩Figure 7. Coupling diagram showing tectonic event, magmatic activity and metallogenic age of gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Zhao Zhixin, 2018)1-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3-Yuka gold deposit; 4-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 5-Saibagou gold deposit; 6- Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 7-Magnesian calc alkaline granite; 8-Calc alkaline granite; 9-Calc alkaline- alkali calcium granite; 10-Calc alkaline granite, tholeiitic basic rock; 11-Alkaline granite7. 结论
(1) 柴北缘造山型金矿主要赋存在中元古代、寒武系和奥陶系低品位变质岩发育的剪切带中,且多数矿体的展布与NW向的构造相关。
(2) 柴北缘造山型金矿大部分矿床(点) 成矿温度呈双峰态分布, 只有少部分矿床(点)中呈单峰态分布,指示了受到多期流体作用。
(3) 柴北缘造山型金矿的成矿流体中δ18OH2O-SMOW=-1.7‰ ~ 10.31‰和δDV-SMOW = -113.8 ‰ ~ -41.6 ‰,指示其变质流体受到岩浆水及大气水等共同作用。含金硫化物(黄铁和方铅矿)的δ34S在0.5‰ ~11‰,主要集中在5‰ ~9‰,206Pb/204Pb为18.238~19.296,207Pb/204Pb为15.547~15.773,208Pb/204Pb为37.918~38.978,指示了成矿物质来源于地幔-上地壳,且一定程度上都受到了岩浆作用的影响。
(4)柴北缘的复合造山运动导致造山型金矿存在(426~376)Ma、(357~330)Ma和(288~246)Ma三个成矿期。
-
图 1 中国西北部主要构造单元示意图(a,据Song et al., 2013修改)及柴北缘构造格局与造山型金矿床空间位置图(b,据Zhang et al., 2009修改)
1—胜利沟金矿;2—野骆驼泉金矿;3—千枚岭金矿;4—红柳沟金矿;5—青龙沟金矿;6—滩间山金矿;7—鱼卡金矿;8—双口山金矿;9—赛坝沟金矿
Figure 1. Schematic map showing the major tectonic units in northwest China (a, modified from Song et al., 2013) and simplified map showing the tectonic framework of the northern Qaidam(b, modified from Zhang et al., 2009)
1-Shengligou gold deposit; 2-Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 3-Qianmeiling gold deposit; 4-Hongliugou gold deposit; 5-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 6-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 7-Yuka gold deposit; 8-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 9-Saibagou gold deposit
图 2 柴北缘造山型金矿流体包裹体均一温度(Th)直方图(据张德全等, 2001;黄亚,2013;范贤斌, 2017;孟和, 2017;蔡鹏捷等, 2018)
Figure 2. Histogram showing homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (after Zhang et al., 2001; Huang, 2013; Fan, 2017; Meng, 2017; Cai et al., 2018c)
图 3 柴北缘造山型金矿δD与δ18Owater比值图(底图据Deng and Wang, 2016)
1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—青龙沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿
Figure 3. δD (‰) vs. δ18Owater (‰) diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Deng and Wang, 2016)
1-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3- Qinglonggou gold deposit; 4-Yuka gold deposit
图 4 柴北缘造山型金矿与其他类型S同位素对比(据Deng and Wang, 2016修改)
Figure 4. Comparison of S isotopes between orogenic gold deposits in the northern margin of Qaidam and other types of gold deposits
图 5 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素构造图解(底图据Zartman and Doe, 1981)
1—双口山金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—胜利沟金矿;4—鱼卡金矿
Figure 5. Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)
Pb isotope diagrams of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zartman and Doe, 1981)
图 6 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素Δβ-Δγ图解(底图据朱炳泉等, 1998)
1—地幔源Pb; 2—上地壳源Pb; 3—上地壳与地幔混合的俯冲带Pb (3a—岩浆作用; 3b—沉积作用); 4—化学沉积型Pb; 5—海底热水作用Pb; 6—中深变质作用Pb; 7—深变质下地壳Pb; 8—造山带Pb; 9—古老页岩上地壳Pb; 10—退变质作用Pb;11—双口山金矿;12—滩间山金矿;13—胜利沟金矿;14—鱼卡金矿
Figure 6. Pb isotope Δβ-Δγ diagram of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (basic diagram modified from Zhu et al., 1998)
1- mantle lead; 2-upper crust lead; 3- subduction zone lead mixed with upper crust and mantle(3a -magmatism; 3b- deposition); 4- chemical deposition lead; 5- submarine hot water lead; 6-mesometamorphism lead; 7- katametamorphism lower crust lead; 8-orogenic belt lead; 9- ancient shale upper crust lead; 10- retrograde metamorphism lead; 11-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 12-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 13-Shengligou gold deposit; 14-Yuka gold deposit
图 7 柴北缘构造事件、岩浆活动与金矿成矿时代耦合图(据赵志新,2018修改)
1—青龙沟金矿;2—滩间山金矿;3—鱼卡金矿;4—双口山金矿;5—赛坝沟金矿;6—野骆驼泉金矿;7—镁质钙性-钙碱性花岗岩;8—钙碱性花岗岩;9—钙碱-碱钙性花岗岩;10—钙碱花岗岩、拉斑质基性岩;11—碱性花岗岩
Figure 7. Coupling diagram showing tectonic event, magmatic activity and metallogenic age of gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (modified from Zhao Zhixin, 2018)
1-Qinglonggou gold deposit; 2-Tanjianshan gold deposit; 3-Yuka gold deposit; 4-Shuangkoushan gold deposit; 5-Saibagou gold deposit; 6- Yeluotuoquan gold deposit; 7-Magnesian calc alkaline granite; 8-Calc alkaline granite; 9-Calc alkaline- alkali calcium granite; 10-Calc alkaline granite, tholeiitic basic rock; 11-Alkaline granite
表 1 柴北缘地质特征简表(据张德全等, 2001, 2005, 2007修改)
Table 1 Geological characteristics of the orogenic gold deposits in Northern Qaidam

表 2 柴北缘造山型金矿流体包裹体显微测温数据(据张德全等, 2001;黄亚,2013;范贤斌, 2017;孟和, 2017;蔡鹏捷等, 2018)
Table 2 Temperature measurement data of fluid inclusions of orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam (datas from Zhang et al., 2001; Huang, 2013; Fan, 2017; Meng, 2017; Cai et al., 2018)

表 3 柴北缘造山型金矿H-O同位素
Table 3 δ18O and δD values of the orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam

表 4 柴北缘造山型金矿S同位素特征
Table 4 Analytical results of S isotope of the orogenic gold deposits in Northern Qaidam

表 5 柴北缘造山型金矿Pb同位素特征
Table 5 Pb-isotpic compositions and characteristic parameters of orgen gold deposits in the northern Qaidam

表 6 柴北缘造山型金矿相关成岩与成矿时间
Table 6 Diagenetic and metallogenic ages of orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam

-
Beaudoin G, Pitre D. 2005. Stable isotope geochemistry of the Archean Val-d'Or (Canada) orogenic gold vein field[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 40(1): 59-75. doi: 10.1007/s00126-005-0474-z
Cai Pengjie, Xu Rongke, Zheng Youye, Fan Xianbin, Ma Chao, Bai Jie, Chen Xin, Yu Junzhen. 2018. Exploration guided by study on ore-forming fluid inclusions——a case study of Yuka orogenic gold deposit in north margin of Qaidam basin[J]. Contributions to Geolgoy and Mineral Resources Research, 33(4): 651-660(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZZK201804021.htm
Cai Pengjie, Zheng Youye, Lu Lihui, Chen Xin, Yin Yueming, Hou Weidong, Hang, Xu Rongke. 2019. Trace elements characteristics of pyrites in Tanjianshan gold deposit, Northern Qaidam, China: Implications for multiple gold mineralizing events[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 29(10): 2381-2393(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/337656214_Trace_elements_characteristics_of_pyrites_in_Tanjianshan_gold_deposit_Northern_Qaidam_China_Implications_for_multiple_gold_mineralizing_events
Chang Zhaoshan, Large R R, Maslennikov V. 2008. Sulfur isotopes in sediment-hosted orogenic gold deposits: Evidence for an early timing and a seawater sulfur source[J]. Geology, 36(12): 971. doi: 10.1130/G25001A.1
Chen Huayong, Chen Yanjing, Baker M. 2012. Isotopic geochemistry of the Sawayaerdun orogenic-type gold deposit, Tianshan, northwest China: Implications for ore genesis and mineral exploration[J]. Chemical Geology, 310-311(3): 1-11. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254112001519
Chen Danling, Liu Lenox, Sun Youwen, Liou Juhn. 2009. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3): 259-272.
Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Fan Hongrui, Pirajno F, Lai Yong, Su Wenchao. 2007. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2085-2108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1470537
Chui Yanhe, Zhang Dequan, Li Daxin, Gu Guangxian, Feng Chenyou. 2000. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Tanjianshan gold deposit, Qinghai province[J]. Mineral Deposit, 19(3): 211-222(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200003002.htm
Deng Jun, Wang Qingfei. 2016. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
Doe B R, Stacey J S. 1974. The application of lead isotope of the problem of ore genesis and ore prospect evolution[J]. Economic Geology, 69: 724-789. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80012995796
Dziggel A, Poujol M, Otto A, Kisters A FM, Trieloff M, Schwarz W H, Meyer M. 2010. New U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar ages from the northern margin of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa: Implications for the formation of Mesoarchaean gold deposits[J]. Precambrian Research, 179(1/4): 206-220. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926810000811
Fan Xianbin. 2017. A Discussion on Genesis of Yuqia Gold Deposit in Da Chaidan of Qinghai Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-78(in Chinese with English abstract).
Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. 2001. Orogenic gold and geologic time: A global synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 18(1/2): 1-75. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136801000166
Goldfarb R J, Baker T, Dubé B, Groves D I, Gosselin P. 2005. Distribution, character, and genesis of gold deposits in metamorphic belts[C]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson, J F H, Goldfarb J (eds.). Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Society of Economic Geologists, Littleton, Colorado, USA, 407-450.
Goldfarb R J, Groves D I. 2015. Orogenic gold: Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time[J]. Lithos, 233: 2-26. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.011
Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebremariam M, Hagemann S G, Robertdl F. 1998. Orogenic gold deposits: A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1/5): 7-27.
Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Robert F C, Hart J R. 2003. Gold deposits in metamorphic belts: Overview of current understanding, outstanding problems, future research, and exploration significance[J]. Economic Geology, 98: 1-29. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80015919027
Guo Jiahui, Chen Shuwang. 1998. Origin of the ore-forming matter of Tanjianshan gold field, Qinhai Province[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 7(3): 189-204(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD803.003.htm
Guo Jiahui. 1998. Characteristics of magmatite and its relation to gold mineralization of Tanjianshan gold field[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 7(2): 96-103(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD802.002.htm
Hagemann S G, Cassidy K F. 2000. Archean orogenic lode Au deposits[J]. Reviews in Economic Geology, 13: 9-68.
Hart C J, Goldfarb R J, Qiu Y, Snee L, Miller L D, Miller M L. 2002. Gold deposits of the northern margin of the North China Craton: Multiple Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic mineralizing events[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3/4): 326-351. doi: 10.1007/s00126-001-0239-2
He Lingxiong, Fan Zhaoxiong. 2006. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Hongliugou gold deposit in Dachaidan, Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 20(2): 36-42(in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=KCYD200601007&dbcode=CJFD&year=2006&dflag=pdfdown
Huang Ya. 2013. Geological Characteristics and Mineralization of Shengligou Gold Deposit, Qinhai Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 1-89(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hodkiewicz P F, Groves D I, Davidson G J, Weinberg R F, Hagemanm S G. 2009. Influence of structural setting on sulphur isotopes in Archean orogenic gold deposits, Eastern Goldfields Province, Yilgarn, Western Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 44(2): 129-150. doi: 10.1007/s00126-008-0211-5
Jia Qunzi, Du Yuliang, Zhao Ziji, Song Zhongbao, Quan Shoucun, Chen Bo, Kong Huilei, Li Yazhi, Li Jinchao, Chen Xiangyang, Zhang Yulian. 2013. Zircon LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of the plagiogranite porphyry from Tanjianshan gold ore district in north margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 32(1): 87-93(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201301018.htm
Kerrich R, Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Garwin S, Jia Y F. 2000. The characteristics origins and geodynamic settings of supergiant gold metallogenic province[J]. Science in China (Series D), 43(supp.): 1-68(in Chinese).
Knight J T, Groves D I, Ridley J R. 1993. The Coolgardie goldfied, Western Australia: District-scale controls on an Archaean Gold Camp in an amphibolite facies terrane[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 28(6): 436-456. doi: 10.1007/BF02431601
Knight J T, Ridley J R, Groves D I. 2000. The Archean amphibolite facies Coolgardie goldfield, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Nature, controls, and gold field-scale patterns of hydrothermal wall-rock alteration[J]. Economic Geology, 95(1): 49-84. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.1.49
Kolb J, Dziggel A, Bagas L. 2015. Hypozonal Lode gold deposits: A genetic concept based on a review of the new consort, Renco, Hutti, Hira Buddini, Navachab, Nevoria and the granites deposits[J]. Precambrian Research, 262: 20-44. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.02.022
Large R R, Bull S W, Maslennikov V V A. 2011. Carbonaceous sedimentary source-rock model for Carlin-type and orogenic gold deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 106(3): 331-358. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.106.3.331
Li Shijin. 2011. Geogdynamic Evolution of Qilian Orogenic Belt and Metallogenesis of Endogenous Metals[D]. Changchun: Jinlin University, 1-204(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Meng, Hu Chaobing, Zha Xianfeng, Gao Xiaofeng, Ren Guangli, Li Ting, Yao Zhiliang. 2020. On the discovery and prospecting significance of the Baozigou gold deposit in the western part of East Kunlun, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 53(3): 169-174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Wenshan, Fan Zhaoxiong, He Lingxiong. 2006. Geological characteristics, ore indicators and orientation of Qinglonggou gold deposit, Dachaidan, Qinghai[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 20 (2): 122-127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200602004.htm
Lu Huangzhang. 1991. Fluid inclusion studies of some Archean gold deposits[J]. Acta Nineralogical Sinica, 11(4): 289-297(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199104000.htm
Lu Huangzhang, Chi Guoxiang. 1995. Geochemical characteristics of fluids in shear zones and their significance for mineral exploration[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, 15(1): 9-22. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX501.001.htm
Lu Huangzhang, Chi Guoxiang, Zhu Xiaoqing, Guha J, Archambault G, Wang Zhonggang. 2018. Geological characteristics and ore forming fluids of orogenic gold deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogeni, 42(2): 244-265 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DGYK201802005&dbcode=CJFD&year=2018&dflag=pdfdown
Mao Jingwen, Zhang Zuoheng, Yang Jianmin, Zhang Zhaochong. 2000. The Hanshan gold deposit in the Caledonian North Qilian orogenic belt, NW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 35(1): 63-71. doi: 10.1007/PL00002969
Meng He. 2017. The Genesis Study of South of Shuangkoushan Silver-Lead-Gold Deposit, Qinghai Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-89(in Chinese with English abstract).
McCuaig T C, Kerrich R. 1998. P-T-t-deformation-fluid characteristics of lode gold deposits: Evidence from alteration systematic[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 12(6): 381-453. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136898800024
Ridley J R, Diamond LW. 2000. Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models//Hagemann S G, Brown P E (eds.). Gold in 2000: Reviews in Economic Geology. SEG Reviews, 13: 141-162.
Song Shuguang, Niu Yaoling, Su Li, Xia Xiaohong, 2013. Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 23: 1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004
Song Shuguang, Niu Yaoling, Su Li, Zhang Cong, Zhang Lifei. 2014. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling: The example of the north Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 129: 59-84. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010
Tong Haikui, Zhang Shungui, Xu Guowu, Huang Yinbao. 2009. Characteristic and gensis of ductile-shear zone related gold deposits in Saibagou of Wulan county[J]. Northwestern Geology, 42(1): 88-94(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200901012.htm
Tomkins A G. 2010. Windows of metamorphic sulfur liber-ation in the crust: Implications for gold deposit genesis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(11): 3246-3259. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.03.003
Tomkins A G. 2013. A biogeochemical influence on the secular distribution of orogenic gold[J]. Economic Geology, 108(2): 193-197. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.2.193
Phillips G N, Powell R. 2009. Formation of gold deposits: Review and evaluation of the continuum model[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 94(1/4): 1-21. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825209000348
Phillips G N, Powell R. 2010. Formation of gold deposits: a metamorphic devolatilization model[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28(6): 689-718. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2010.00887.x
Wei Zhanhao, Du Shengpeng, Wang Jian, Zhang Yanjun, Zhang Yuting, Chen Changxin, Bai Yina. 2015. Evolution characteristics of fluid and genesis of Qinglonggou gold deposit in Qinghai[J]. Global Geology, 34(4): 951-960(in Chinese with English abstract). http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/docdown/docdownload.aspx?filename=SJDZ201504007&dbcode=CJFD&year=2015&dflag=pdfdown
Wittlinger G, Tapponnier P, Poupinet G, Jiang M. 1998. Tomographic evidence for localized lithospheric shear along the Altyn Tagh fault[J]. Science, 282: 74-76. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5386.74
Yang Liya, Yang Liqiang, Yuan Wanming, Zhang Chuang, Zhao Kai, Yu Haijun. 2013. Origin and evolution of ore fluid for orogenic gold traced by D-O isotopes: A case from the Jiapigou gold belt, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 4025-4035(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201311031.htm
Yang Jingsui. 2002. Early Paleozoic North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt on the Northeastern Tibetan plateau and a paired subduction model[J]. Terra Nova, 14: 397-404. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00438.x
Zartman R E, Doe B R. 1981. Plumbotectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 75: 135-162. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(81)90213-4
Zeng Dong. 2013. Prospecting Potential for Yeluotuoquan Gold Deposit in Qinhai Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-40(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Bowen. 2010. Study on Metalliferous Deposits Mineralization in Southern Qilian Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province[D]. Changchun: Jinlin University, 1-192.
Zhang Dequan, Feng Chengyou, Li Daxin, Xu Wenyi, She Hongquan, Dong Yingjun, Chui Yanghe. 2001. Orogenic gold deposits in the north Qaidam and East Kunlun Orogen, West China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 20(2): 137-146(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200102005.htm
Zhang Dequan, Dang Xingyan, She Hongquan, Li Daxin, Feng Chengyou, Li Jinwen. 2005. Ar-Ar dating of orogenic gold deposits in northern margin of Qaidam and East Kunlun mountains and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(2): 87-98(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200502001
Zhang Dequan, Zhang Hui, Feng Chengyou, She Hongquan, Li Jinwen, Li Daxin. 2007a. Fluid inclusions in orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam margin-East Kunlun region[J]. Geology in China, 34(5): 843-854(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200705011.htm
Zhang Dequan, Wang Fuchun, She Hongquan, Feng Chengyou, Li Daxin, Li Jinwen. 2007b. Three-order ore-controlling structural system of orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam margin-East Kunlun region[J]. Geology in China, 34(1): 92-100(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200701013.htm
Zhang Dequan, She Hongquan, Feng Chengyou, Li Daxin, Li Jinwen. 2009. Geology, age, and fluid inclusions of the Tanjianshan gold deposit, western China: Two orogenies and two gold mineralizing events[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1): 250-263. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136809000638
Zhang Yaoyao, Zhang Da, Wu Ganguo, Di Yongjun, Li Xingjian, Bu Xingchen, Liu Jun. 2018. Origin of the Daping gold deposit in the Ailaoshan metallogenic belt, SW China: Insights from geology, isotope geochemistry and geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 96: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.009
Zhang Long, Chen Renxu, Zheng Yongfei, Li Wancai, Hu Zhaochu, Yang Yueheg, Tang Haolan. 2016. The tectonic transition from oceanic subduction to continental subduction: Zirconological constraints from two types of eclogites in the North Qaidam Orogen, Northern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 244: 122-139. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.12.003
Zhang Long, Chen Renxu, Zheng Yongfei, Hu Zhaochu, Xu Lijuan. 2017b. Whole-rock and zircon geochemical distinction between oceanic- and continental-type eclogites in the North Qaidam Orogen, Northern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 44: 67-88. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.10.021
Zhang Jianxin, Yu Shenyao, Li Yunshuai, Yu Xinxin, Lin Yihui, Mao Xiaohong. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of proto-tethyan ocean: Early paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam Orogenic System[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31 (12): 3531-3554 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_acta-petrologica-sinica_thesis/0201252016521.html
Zhang Yanjun. 2017. Study on the Metallogenesis of Endogenous Metallic Deposits in Tanjianshan Area in Qinghai Province[D]. Changchun: Jinlin University, 1-182(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Zhixin. 2018. Paleozoic Tectono-Magmatic Evolution and Its Control on Lead-Zinc Mineralization in Xitieshan, North Qaidam[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-184(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Bingquan, Li Xianhua, Dai Tongmo, Chen Yuwei, Fan Sikun, Gui Xuntang, Wang Huifen. 1998. Isotopes System Theory and Its Application in Earth Science——On the Evolution of the Continental Crust and Mantle[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 216-235 (in Chinese).
Zhu Xiaohui, Chen Ddanlin, Liu Liang, Zhao Jiao, Zhang Le. 2014. Geochronology, geochemistry and significance of the Early Paleozoic back-arc type ophiolite in Lüliangshan area, North Qaidam[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30: 822-834 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94579X/20143/49499595.html
蔡鹏捷, 许荣科, 郑有业, 范贤斌, 马超, 白杰, 陈鑫, 俞军真. 2018. 基于成矿流体包裹体的勘探——以柴北缘鱼卡造山型金矿为例[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 33(4): 651-660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201804021.htm 蔡鹏捷, 郑有业, 鲁立辉, 陈鑫, 殷悦铭, 侯维东, 韩登辉, 许荣科. 2019. 柴北缘滩间山金矿黄铁矿微量元素特征: 指示多阶段金矿化事件[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 29(10): 2381-2393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201910019.htm 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, Pirajno F, 赖勇, 苏文超, 张辉. 2007. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2085-2108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.009 崔艳合, 张德全, 李大新, 顾光先, 丰成友. 2000. 青海滩间山金矿床地质地球化学及成因机制[J]. 矿床地质, 19(3): 211-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2000.03.003 范贤斌. 2017. 青海省大柴旦镇鱼卡金矿成因探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-78. 国家辉, 陈树旺. 1998. 滩间山金矿田成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 贵金属地质, 7(3): 29-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD803.003.htm 国家辉. 1998. 滩间山金矿田岩浆岩特征及其与金矿化关系[J]. 贵金属地质, 7 (2): 96-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD802.002.htm 贺领兄, 范照雄. 2006. 青海省大柴旦红柳沟金矿床的地质特征及其成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质. 20(2): 36-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200601007.htm 贾群子, 杜玉良, 赵子基, 宋忠宝, 全守村, 陈博, 孔会磊, 栗亚芝, 李金超, 陈向阳, 张雨莲. 2013. 柴达木盆地北缘滩间山金矿区斜长花岗斑岩锆石LA-MC-ICPMS测年及其岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 32(1): 87-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201301018.htm 李猛, 胡朝斌, 查显锋, 高晓峰, 任广利, 李婷, 姚志亮. 2020. 东昆仑西段新疆阿确墩地区豹子沟金矿的发现及其找矿意义[J]. 西北地质, 53(3): 169-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202003014.htm 李世金. 2011. 祁连造山带地球动力学演化与内生金属矿产成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-204. 林文山, 范照雄, 贺领兄. 2006. 青海省大柴旦青龙沟金矿床地质特征、找矿标志和找矿方向[J]. 矿产与地质, 20 (2): 122-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2006.02.005 卢焕章. 1991. 从包裹体研究探索太古代一些金矿的成矿机理[J]. 矿物学报, 11(4): 289-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199104000.htm 卢焕章, 池国祥. 1995. 剪切带中流体地球化学特征及其找矿意义[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 15(1): 9-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX501.001.htm 卢焕章, 池国祥, 朱笑青, Guha J, Archambault G, 王中刚. 2018. 造山型金矿的地质特征和成矿流体[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 42(2): 244-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201802005.htm 孟和. 2017. 青海省大柴旦双口山南银铅金矿床成因研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-78. 童海奎, 张顺桂, 许国武, 黄银宝. 2009. 乌兰县赛坝沟韧性剪切带型金矿特征及成因[J]. 西北地质, 42(1): 88-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2009.01.009 王庆飞, 邓军, 赵鹤森, 杨林, 马麒镒, 李华健. 2019. 造山型金矿研究进展: 兼论中国造山型金成矿作用[J]. 地球科学, 44(6): 2155-2186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201906029.htm 魏占浩, 杜生鹏, 王键, 张延军, 张宇婷, 陈昌昕, 白宜娜. 2015. 青海青龙沟金矿成矿流体演化特征及矿床成因研究[J]. 世界地质, 34(4): 951-960. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.04.007 杨利亚, 杨立强, 袁万明, 张闯, 赵凯, 于海军. 2013. 造山型金矿成矿流体来源与演化的氢-氧同位素示踪: 夹皮沟金矿带例析[J]. 岩石学报, 29(11): 4025-4035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311031.htm 曾东. 2013. 青海省野骆驼泉金矿找矿前景浅析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-40. 张博文. 2010. 青海南祁连造山带内生金属矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-192. 张德全, 丰成友, 李大新, 徐文艺, 阎升好, 佘宏全, 董英君, 崔艳合. 2001. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区的造山型金矿床[J]. 矿床地质, 20(2): 137-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.02.006 张德全, 党兴彦, 佘宏全, 李大新, 丰成友, 李进文. 2005. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区造山型金矿床的Ar-Ar测年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 24(2): 87-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.02.001 张德全, 张慧, 丰成友, 佘宏全, 李进文, 李大新. 2007a. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区造山型金矿床的流体包裹体研究[J]. 中国地质, 34 (5): 843-854. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070512&flag=1 张德全, 王富春, 佘宏全, 丰成友, 李大新, 李进文. 2007b. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区造山型金矿床的三级控矿构造系统[J]. 中国地质, 34(1): 92-100. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070114&flag=1 张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红. 2015. 原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合: 阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用[J]. 岩石学报, 31(12): 3531-3554. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201512003.htm 张延军. 2017. 青海省滩间山地区内生金属矿产成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-182. 赵志新. 2018. 柴北缘锡铁山地区古生代构造岩浆演化与铅锌成矿控制[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-184. 朱炳泉, 李献华, 戴橦谟, 陈毓蔚, 范嗣昆, 桂训唐, 王慧芬. 1998. 地球科学中同位素体系理论与应用——兼论中国大陆壳幔演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 216-235. -
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 俞军真,郑有业,王永才,王建国,马波,贾翠霞,张琳琳. 柴北缘青龙沟金矿床闪长玢岩锆石年代学、黄铁矿原位硫同位素和微量元素特征及找矿启示. 黄金. 2024(11): 9-17+136 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 甄世民,查钟健,王大钊,刘家军,庞振山,程志中,薛建玲,王江,白海军,李阳,陈超. 河北张宣地区中山沟金矿成矿流体特征及其对侵入岩型碲金矿床的限定. 中国地质. 2023(02): 605-621 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 赵呈祥,薛春纪,赵晓波,李鹏,刘洋涛,李君阳,赵伟策,李健. 柴北缘造山带滩间山金矿田多期侵入岩年代学及其地质意义. 地质与勘探. 2023(03): 591-607 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张灵桧. 柴达木盆地西北缘交通社金矿地质特征及找矿前景. 中国锰业. 2023(04): 83-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王进寿,潘彤,薛万文,李鹏,安永尉,田永革,雷晓清,余福承. 青海省柴北缘成矿带区域成矿规律综述. 矿床地质. 2022(05): 917-938 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 徐永利,郑有业,许荣科,严康,左恒斌. 基于成矿元素复杂度的地球化学数据处理方法在找矿实践中的应用——以柴北缘造山带绿梁山地区为例. 黄金. 2022(11): 25-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 唐名鹰,何宗围,朱德全,张宇,高振华,董振昆,李小东. 柴北缘赛坝沟金矿床硫、铅同位素组成:对成矿物质来源的指示. 矿床地质. 2021(01): 117-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 童海奎,龙灵利,马永胜,仓索南尖措,吴鸿梅. 青海大柴旦镇尕日力根砾岩型金矿成矿特征研究. 矿产勘查. 2021(03): 534-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李顺庭,龙灵利,王宁. 韧性剪切带型金矿研究进展. 矿产勘查. 2021(04): 802-813 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: