Discovery of Paleo-volcanic edifice and determination of its eruptive circles of Emeishan basalt in Zhaojue-Meigu Area, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
四川昭觉—美姑地区峨眉山玄武岩古火山机构的发现及其喷发旋回的确定提要:野外地质调查发现,扬子西缘昭觉—美姑一带存在多处峨眉山玄武岩组古火山机构,为研究其火山喷发旋回与方式提供了良好窗口。古火山机构的岩石类型主要由巨厚玄武岩以及少量的火山碎屑岩和火山碎屑熔岩组成,且均具火山颈爆发相、溢流相和火山洼地相堆积构造特征。系统的地质剖面研究表明,峨眉山玄武岩组存在3次快速喷发亚旋回及25个火山韵律,亚旋回之间不存在火山间歇期。其中,第一亚旋回和第三亚旋回的喷发方式均以爆发相与溢流相为主,而第二亚旋回则以溢流相为主。峨眉山玄武岩组古火山机构的系统厘定和研究,揭示了峨眉山大火成岩省的火山喷发方式和旋回韵律特征,为研究与峨眉山玄武岩组相关的成矿成藏作用提供了重要地层资料。
Abstract:The geological survey revealed that several paleo-volcanic edifices related to Emeishan basalt were identified in the Zhaojue-Meigu area on the western margin of Yangtze Block, which provides an excellent window for studying their eruption cycles and modes. The rock types of paleo-volcanic edifices are mainly composed of thick basalts, small amounts of pyroclastic rocks and volcanic clastic lavas. They have the characteristics of explosive facies, lava overflow facies and volcanic depression facies. Systematic geological profile suggest that there are three rapid eruption cycles (without any interval) and 25 volcanic rhythms during the formation of the Emeishan basalt Formation. Among them, the eruption patterns of the first and third cycles are dominated by the explosive facies and lava overflow facies, while the second cycle is dominated by the overflow phase. The systematic confirmation and study of the paleo-volcanic edifices reveal the volcanic eruption pattern and cycle rhythm characteristics of Emeishan large igneous province, which provides important data for the further study of the Wupo copper deposits in the western margin of Yangtze Block.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
甘肃省高台县大青山地区地处阿拉善地块龙首山基底杂岩带,位于酒东盆地马营凹陷东段山前沉积盆地北缘(图 1a)。区内主要出露有古元古界—新太古界龙首山岩群、中元古界蓟县系墩子沟群、海西期侵入岩、侏罗系龙凤山组和白垩系庙沟组(图 1b)。
为实现研究区金属资源和油气资源的综合调查,中国地质调查局发展研究中心联合甘肃省地调院、探矿工程所、吉林大学在前期“甘肃省高台县臭泥墩—西小口子地区三幅1∶5万矿产远景调查”项目基础上,通过开展专题地质填图、矿产综合信息预测、智能找矿预测等工作,部署实施钻孔ZK1201,以期实现找矿突破。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
利用研究区地质调查、磁法、激电测深、化探数据和无人机影像等资料,开展综合信息解译。采用卷积和孪生网络神经网络模型对区内典型金属矿床成矿作用特征标志、油气赋矿层位进行深度学习,提出工程验证建议。钻探验证所采用钻机为汽车钻,整机包括车底盘、动力系统、液压系统、操控系统等。
3. 结果(Results)
在综合研究和智能预测的基础上,布设的ZK1201孔在钻穿早二叠世花岗闪长岩(图 1c)后,钻遇地层,续钻至393.8 m后终孔(图 1c)。此次工作共钻遇中侏罗统龙凤山组地层220 m,共发现14层油层(总厚145 m,单层最大厚度28 m,最小厚度1.4 m)。钻孔含油性由上部砾岩(油斑级以下)向下部砂岩(富含油或饱含油)逐渐增多,其中高角度裂缝普遍见可流动原油(图 1d~g)。经国家地质实验测试中心分析,原油中饱和烃、芳烃含量分别占32.4%和34.6%,为高品质轻质原油。原油中正构烷烃分布完整,主峰碳数、奇偶优势及甾烷和藿烷分布都指示其陆相烃源岩来源。
野外地质调查发现,白垩系庙沟组近水平发育,与下伏侏罗系龙凤山组呈角度不整合接触。庙沟组主要由厚层暗色泥岩组成,并发育薄层暗色粉砂质泥岩,可能为区域烃源岩层。初步判断成熟的烃源岩排出的油气沿角度不整合运移至侏罗系砂砾岩和砂岩储层后,被逆冲推覆花岗岩体封闭,形成构造-岩性油气藏(图 1h)。
研究发现区域内沉积盆地最南缘边界处在祁连山北缘断裂之下,最北缘处在龙首山断裂的下盘,南北跨度约80 km。区域内沉积地层较厚,其中侏罗系龙凤山组厚约2100 m,白垩系庙沟组厚约900 m,说明研究区具有较大的成藏潜力。此次油气藏的发现,预示着大青山地区具有完整的油气成藏系统,显示出良好油气勘探前景。建议进一步加强油气基础地质调查研究工作。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)在大青山地区花岗岩逆冲推覆体之下的中生代沉积地层中发现原油,所发现的高品质轻质原油,具陆相烃源岩来源特征。
(2)研究区具有良好的油气勘探前景,建议进一步加强油气地质调查研究工作。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
感谢甘肃省地质调查院董国强,北京探矿工程研究所渠洪杰、谭春亮以及国家实验测试中心沈斌在野外工作和样品测试过程中的协助。
-
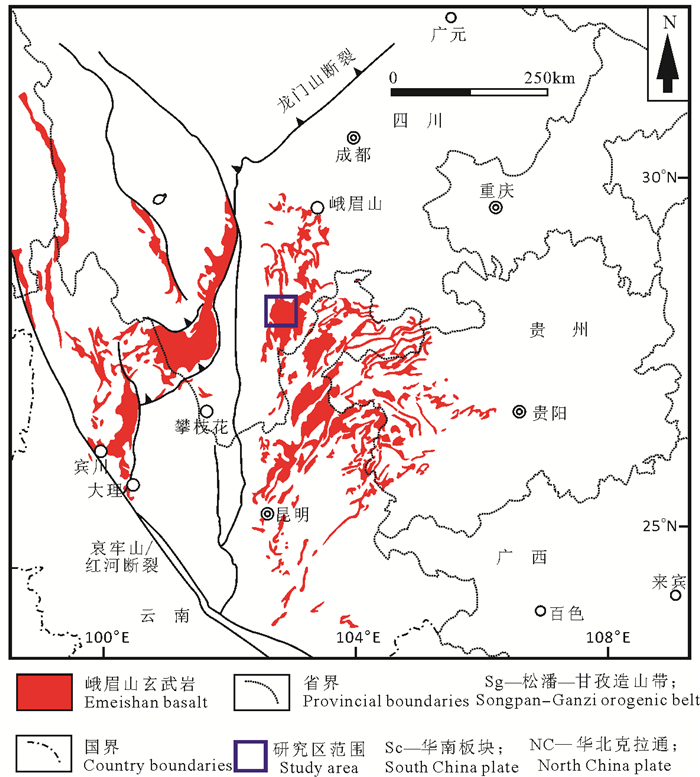
图 1 峨眉山玄武岩分布示意图及研究区位置(据Ali et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2010修改)
Figure 1. Schematic map showing the distribution of the Emeishan basalts and the studied area (modified from Ali et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2010)
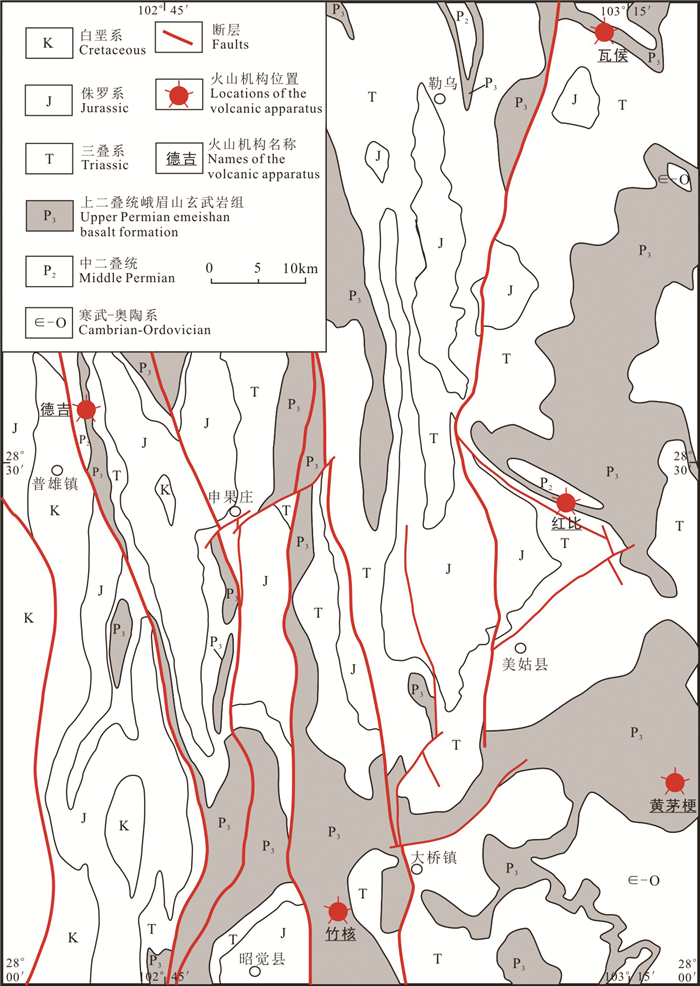
图 3 第一喷发亚旋回古火山机构岩石的野外特征
a—瓦侯火山集块岩露头;b—瓦侯火山集块岩中的灰岩集块和石英砂岩集块;c—竹核火山集块岩棱角状灰岩集块;d—竹核火山集块岩熔蚀港湾状的灰岩集块;e—德吉火山集块岩中玄武岩集块;f—黄茅梗火山集块岩中浑圆状的灰岩集块和次棱状的玄武岩集块
Figure 3. Field photographs of ancient volcanic apparatus rocks in the first eruptive cycle
a-Wahou volcanic agglomerate outcrop; b-Limestone and Quartz sandstone aggregates in the Wahou volcanic aggregates; c-Zhouhe nuclear volcanic aggregates and angular limestone aggregates; d-Zhouher volcanic aggregates and melting embayment limestone aggregates; e-Deji basalt aggregates in volcanic aggregates; f-Round limestone aggregates and subangular basalt aggregates in the Huangmaogeng volcanic aggregates
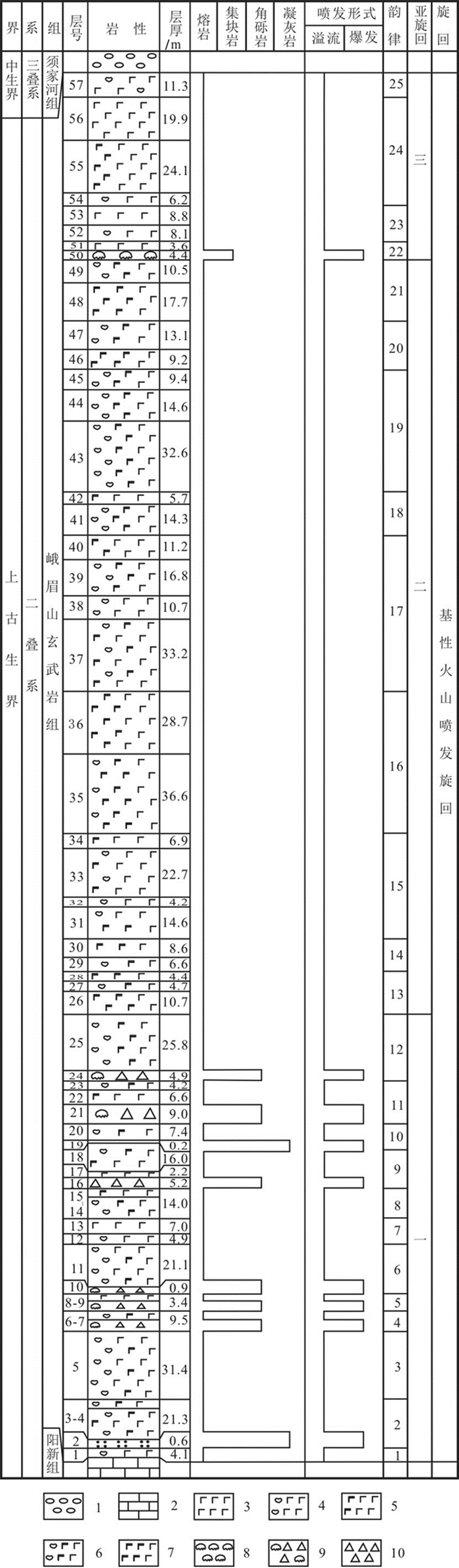
图 5 峨眉山玄武岩喷发韵律旋回划分
1—砾岩;2—灰岩;3—块状玄武岩;4—杏仁状玄武岩;5—斑状玄武岩;6—杏仁斑状玄武岩;7—多斑状玄武岩;8—玄武质集块岩;9—玄武质含集块角砾岩;10—玄武质火山角砾岩
Figure 5. Division of the eruption rhythm and cycle for the Emeishan basalt
1-Conglomerate; 2-Limestone; 3-Aphyric Basalt; 4-Amygdaloidal basalt; 5-Porphyritic basalt; 6-Amygdaloidal-phyric basalt; 7-Polyporphyric basalt; 8-Basaltic agglomerate; 9-Basaltic agglomerated breccia; 10-Basaltic volcanic breccia
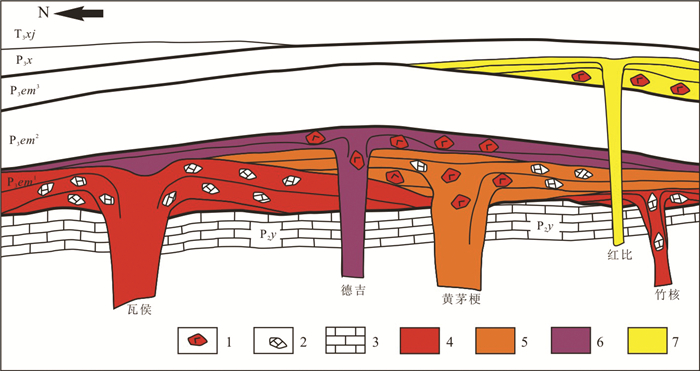
表 1 本文厘定的火山机构的地理位置和岩石学信息
Table 1 Information on the position and petrology of the identified volcanic apparatus in this study

-
Ali J R, Fitton J G, Herzberg C. 2010. Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the mantle-plume up-doming hypothesis[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, London, 167: 953-959. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492009-129
Bagherpour B, Bucher H, Yuan D X, Leu M, Zhang C, Shen S Z. 2018. Early Wuchiapingian (Lopingian, late Permian) drowning event in the South China block suggests a late eruptive phase of Emeishan large igneous Province[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 169: 119-132. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.07.013
Campbell I H, Griffiths R W. 1990. Implications of mantle plume structure for the evolution of flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 99: 79-93. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(90)90072-6
Day M O, Ramezani J, Bowring S A, Sadler P M, Erwin D H, Abdala F, Rubidge B S. 2015. When and how did the terrestrial mid-Permian mass extinction occur? Evidence from the tetrapod record of the Karoo Basin, South Africa[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 282, 20150834. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.0834
Deng Min, Hou Mingcai, Zhang Benjian, Li Xiuhua. 2014. Favorable reservoir analysis of Emeishan basalt in Zhougongshan area of southwest Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 41(2): 378-386 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fan Weiming, Wang Yuejun, Peng Touping, Miao Laicheng, Guo Feng. 2004. Ar-Ar and U-Pb geochronology of Late Paleozoic basalts in western Guangxi and its constraints on the eruption age of Emeishan basalt magmatism[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(18): 1892-1900 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-18-1892
Feng Renwei, Wang Xingzhi, Zhang Fan, Yang Yueming, Li Yuegang, Pang Yanjun, Zhang Ruoxiang. 2008. The study on reservoir property and characteristics of the Emeishan basalts of Zhougongshan and its neighbour area in the Southwest Sichuan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 26(6): 912-924 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/cjxb200806003
Gao Xuezhen. 2014. Study on metallogenic model of basalt copper deposits in mount Emei[J]. Sichuan Nonferrous Metals, (2): 26-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ACJS201402008.htm
Green G W. 2008. Volcanic stratigraphical architecture of the East Mendip Silurian Inlier, Somerset, UK[J]. Proceedings of the Geologists' Association, 119: 339-350. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7878(08)80310-0
He B, Xu Y G, Wang Y M, Luo Z Y. 2006. Sedimentation and lithofacies paleogeography in southwestern China before and after the emeishan flood volcanism: New insights into surface response to mantle plume activity[J]. The Journal of Geology, 114: 117-132. doi: 10.1086/498103
He Bin, Xu Yigang, Xiaolong, Wang Kangming, Sha Shaoli. 2003. Generation and spatial distribution of the Emeishan large igneous province: New evidence from stratigraphic records[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(2): 194-202 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291852047_Generation_and_spatial_distribution_of_the_Emeishan_Large_Igneous_Province_New_evidence_from_stratigraphic_records
Huang H, Du Y S, Yang J H, Zhou L, Hu L S, Huang H W, Huang Z Q. 2014. Origin of Permian basalts and clastic rocks in Napo, Southwest China: Implications for the erosion and eruption of the Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Lithos, 208/209: 324-338. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.022
Huang H, Cawood P A, Hou M C, Yang J H, Ni S J, Du Y S, Yan Z K, Wang J. 2016. Silicic ash beds bracket Emeishan Large Igneous province to < 1 m. y. at~260 Ma[J]. Lithos, 264: 17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.013
Huang H, Hou M C, Qing H R, Zhou L, Yang J H, Du Y S, Tian J C, Ni S J, Xiong F H. 2019. The contribution of the Emeishan large igneous province to the strontium isotope evolution of the Capitanian seawater[J]. International Geology Review, 1-13. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2019.1571448
Liu Baojun, Xu Xiaosong. 1994. Atlas of Lithofacies and Paleogeography in South of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Lu Jianlin, Zuo Zongxin, Shi Zheng, Dong Xia, Wu Qingjie, Song Xiaobo. 2019. Characteristics of Permian volcanism in the western Sichuan Basin and its natural gas exploration potential[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 39(2): 46-53 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352854019300889
Lu Jiren, Zhang Guangdi, Zhang Chengxin, Gu Guangxian, Liu Yushu, Huang Yuneng. 1988. A genetic model for layered intrusions and vanadic titanomanetite deposits in Panzhihua-Xichang area[J]. Mineral Deposits, 7 (2): 3-11 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198802001.htm
Ma Xinhua, Yang Yu, Zhangjian, Xie Jirong. 2019. A major discovery in Permian volcanic rock gas reservoir exploration in the Sichuan Basin and its implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 39(2): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352854019300774?utm_source=TrendMD&utm_medium=cpc
Pearce T H. 1971. Short distance fluvial rounding of volcanic detritus[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 41: 1069-1072. http://archives.datapages.com/data/sepm/journals/v38-41/data/041/041004/1069.htm
Sun Y D, Lai X L, Wignall P B, Widdowson M, Ali J R, Jiang H S, Wang W, Yan C B, Bond D P, Védrine S. 2010. Dating the onset and nature of the Middle Permian Emeishan large igneous province eruptions in SW China using conodont biostratigraphy and its bearing on mantle plume uplift models[J]. Lithos, 119: 20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.05.012
Shellnutt J G. 2014. The Emeishan large igneous province: A synthesis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 5: 369-394. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.07.003
Thompson G M, Ali J R, Song X Y, Jolley D W. 2001. Emeishan basalts, SW China: Reappraisal of the formation's type area stratigraphy and a discussion of its significance as a large igneous province[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 158: 593-599. doi: 10.1144/jgs.158.4.593
Valentine G A, Cortés J A. 2013. Time and space variations in magmatic and phreatomagmatic eruptive processes at Easy Chair (Lunar Crater Volcanic Field, Nevada, USA)[J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 75: 752. doi: 10.1007/s00445-013-0752-z
Wignall P B, Sun Y D, Bond D P G, Izon G, Newton R J, Védrine S, Widdowson M, Ali J R, Lai X L. 2009. Volcanism, mass extinction, and carbon isotope fluctuations in the Middle Permian of China[J]. Science, 324: 1179-1182. doi: 10.1126/science.1171956
Wang Weifeng, Gao Bin, Wei Pingsheng, Pan Jianguo, Li Fei, Yi Zejun. 2012. Research of volcanic reservoir characters and hydrocarbon accumulation models[J]. Progress in Geophys., 27(6): 2478-2491 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201206023.htm
Wang Yan, Wang Kun, Xing Changming, Wei Bo, Dong Huan, Cao Yonghua. 2017. Metallogenic diversity related to the Late Middle Permian Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(3): 405-418 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201703004.htm
Wen L, Li Y, Yi H Y, Liu X, Zhang B J, Qiu Y C, Zhou G, Zhang X H. 2019. Lithofacies and reservoir characteristics of Permian volcanic rocks in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, . 39(2): 17-27 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352854019300890?utm_source=TrendMD&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=Natural_Gas_Industry_B_TrendMD_1
Xiao L, Xu Y G, Mei H J, Zheng Y F, He B, Pirajno F. 2004. Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province, SW China: Implications for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 228: 525-546. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.002
Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, Wu G Y. 2001. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 58: 145-168. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00055-X
Xu Y G, He B, Chung S L. 2004. Geologic, geochemical and geophysical consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood-basalt province[J]. Geology, 32(10): 917. doi: 10.1130/G20602.1
Xu Y G, Chung S L, Shao H, He B. 2010. Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, southwest China: Petrogenesis and their link with the end-Guadalupian biological crisis[J]. Lithos, 119: 47-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.04.013
Xu Yigang, Zhong Yuting, Wei Xun, Chen Jun, Liu Haiquan, Xie Wei, Luo Zhenyu, Li Hongyan, He Bin, Huang Xialong, Wang Yan, Chen Yun. 2017. Permian Mantle Plumes and Earth's Surface System Evolution[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(3): 359-373 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang J, Cawood P A, Du Y, Condon D J, Yan J, Liu J, Huang Y, Yuan D. 2018. Early Wuchiapingian cooling linked to Emeishan basaltic weathering[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 492: 102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.04.004
Yu S Y, Song X Y, Chen L M, Li X B. 2014. Postdated melting of subcontinental lithospheric mantle by the Emeishan mantle plume: Evidence from the Anyi intrusion, Yunnan, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 57: 560-573. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.08.006
Zheng L D, Yang Z Y, Tong Y B, Yuan W. 2010. Magnetostratigraphic constraints on two-stage eruptions of the Emeishan continental flood basalts[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 11, Q12014.
Zhong Y T, He B, Mundil R, Xu Y G. 2014. CA-TIMS zircon U-Pb dating of felsic ignimbrite from the Binchuan section: Implications for the termination age of Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Lithos, 204: 14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.005
Zhou M F, Malpas J, Song X Y, Robinson P T, Sun M, Kennedy A K, Lesher C M, Keays R R. 2002. A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196: 113-122. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00608-2
Zhou M F, Zhao J H, Qi L, Su W, Hu R. 2006. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of Permian mafic rocks in the Funing area, SW China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 151: 1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00410-005-0030-y
邓敏, 侯明才, 张本健, 李秀华. 2014. 川西南部周公山地区峨眉山玄武岩有利储层分析[J]. 中国地质, 41(2): 378-386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.006 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 彭头平, 苗来成, 郭峰. 2004. 桂西晚古生代玄武岩Ar-Ar和U-Pb年代学及其对峨眉山玄武岩省喷发时代的约束[J]. 科学通报, 49(18): 1892-1900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.18.013 冯仁蔚, 王兴志, 张帆, 杨跃明, 李跃纲, 庞艳君, 张若祥. 2008. 四川西南部周公山及邻区"峨眉山玄武岩"特征及储集性能研究[J]. 沉积学报, 26(6): 912-924. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200806005.htm 高学震. 2014. 峨眉山玄武岩铜矿成矿模式研究[J]. 四川有色金属, (2): 26-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ACJS201402008.htm 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 王康明, 沙绍礼. 2003. 峨眉山大火成岩省的形成机制及空间展布: 来自沉积地层学的新证据[J]. 地质学报, 77(2): 194-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200302012.htm 刘宝珺, 许效松. 1994. 中国南方岩相古地理图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 卢记仁, 张光弟, 张承信, 顾光先, 刘玉书, 黄与能. 1988. 攀西层状岩体及钒钛磁铁矿床成因模式[J]. 矿床地质, 7(2): 3-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198802001.htm 陆建林, 左宗鑫, 师政, 董霞, 吴清杰, 宋晓波. 2019. 四川盆地西部二叠系火山作用特征与天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 39(2): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201902009.htm 马新华, 杨雨, 张健, 谢继容. 2019. 四川盆地二叠系火山碎屑岩气藏勘探重大发现及其启示[J]. 天然气工业, 39(2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201902002.htm 王伟锋, 高斌, 卫平生, 潘建国, 李飞, 易泽军. 2012. 火山岩储层特征与油气成藏模式研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 27(6): 2478-2491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201206023.htm 王焰, 王坤, 邢长明, 魏博, 董欢, 曹永华. 2017. 二叠纪峨眉山地幔柱岩浆成矿作用的多样性[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(3): 405-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201703004.htm 徐义刚, 钟玉婷, 位荀, 陈军, 刘海泉, 颉炜, 罗震宇, 李洪颜, 何斌, 黄小龙, 王焰, 陈赟. 2017. 二叠纪地幔柱与地表系统演变[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(3)359-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201703001.htm




 下载:
下载: