Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of early Cretaceous Yaocun A-type granite in the Lower Yangtze region
-
摘要:
姚村岩体位于下扬子江南造山带东北端,主要由中心相的中粗粒正长花岗岩和边缘相的细粒似斑状正长花岗岩组成。本文对该岩体进行了详细的锆石U-Pb年代学、主量元素、微量元素以及Nd-Hf同位素研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年表明姚村岩体的形成年龄为(127.6±1.4)Ma,为燕山晚期岩浆活动的产物。岩石地球化学研究表明姚村岩体属于A型花岗岩,具高硅、富铁,锆饱和温度高、轻重稀土分馏明显、富集Rb、Th、U、K、Pb等元素而亏损Ba、Nb、Sr和Ti等元素、铕负异常显著(Eu/Eu*=0.22~0.46)的特点。姚村岩体的全岩εNd(t)值与锆石εHf(t)值分别变化于-6.2~-5.7和-13.9~-5.0,两阶段Nd和Hf同位素模式年龄分别为TDM2(Nd)=1439~1532 Ma和TDM2(Hf)=1508~2062 Ma,Nd同位素的模式年龄重叠于Hf同位素模式年龄。结合区域地质研究成果认为,姚村岩体可能于早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲作用之后伸展-拉伸环境下,由中元古代地壳重熔而成。
Abstract:The Yaocun pluton in Southern Anhui Province, lithologically consisting mainly of medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite in its centre and fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite on its margin, is outcropped around the northeastern Jiangnan orogeny of the Lower Yangtze region. This paper reports detailed study results of its the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, major elements, trace elements, whole-rock Nd isotopic compositions and zircon Hf isotopic compositions. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages show that the Yaocun pluton, as the product of magmatic activity in the late Yanshanian period, was emplaced at 127.6±1.4Ma. The studies of petrography and geochemistry of this rock indicate that it is A-type granite, and is characterized by rich silica, high iron, high zircon saturation temperatures, enrichment of Rb, Th, U, K and Pb, depletion of Ba, Nb, Sr and Ti, and significant negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu*=0.22-0.46). Its εNd(t) and εHf(t) values range from -6.2 to -5.7 and from -13.9 to -5.0 respectively, and the calculated two-stage model ages (TDM2) of Nd and Hf isotopes from 1439 Ma to 1532 Ma and from 1508 Ma to 2062 Ma respectively. Combined with the results of regional geological research, it is suggested that the Yaocun pluton might be formed by the Mesoproterozoic crust remelting under extension-tension environment after the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate during the Early Cretaceous.
-
1. 引言
下扬子地区包括长江中下游和江南造山带两个构造单元(图 1a),以广泛发育燕山期岩浆作用为特点。对其中长江中下游地区的研究表明,岩浆事件主要可分为4期:第一期为145~135 Ma,包括发育在断隆区的高钾钙碱性闪长岩类,一般具有埃达克岩特征;第二期为135~128 Ma,以发育在断凹区的橄榄安粗岩系火山岩和双峰式火山岩为主;第三期为127~123 Ma,主要为A型花岗岩;第四期为109~101 Ma,以宁镇地区的中酸性侵入岩为主(毛景文等,2004;周涛发等,2008;闫峻等,2012;薛怀民等,2013;关俊朋等,2015;薛怀民等,2016;王继强等,2017;王存智等,2018;陈俊等,2018)。
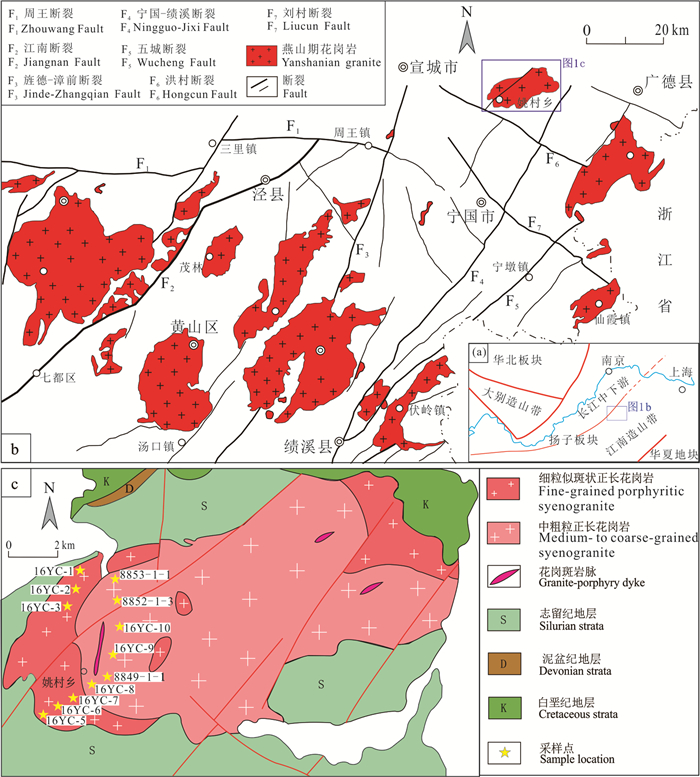
![]() 图 1 大地构造位置图(a)、区域构造略图(b,据陈芳等,2014修改)及岩体地质简图(c)Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Lower Yangtze region showing the location of the studied area(a); tectonic sketch map of the studied area(b, after Chen Fang et al., 2014); and geological sketch map of the Yaocun pluton(c)
图 1 大地构造位置图(a)、区域构造略图(b,据陈芳等,2014修改)及岩体地质简图(c)Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Lower Yangtze region showing the location of the studied area(a); tectonic sketch map of the studied area(b, after Chen Fang et al., 2014); and geological sketch map of the Yaocun pluton(c)江南造山带的燕山期岩浆岩分布更加广泛,近年来大量的高精度年代学资料显示,皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆活动可分为两期:分别为152~137 Ma和136~122 Ma(Wu et al., 2012; 闫峻等,2017)。早期以花岗闪长岩为主,属于高钾钙碱性系列I型花岗岩(薛怀民等,2009;周翔等,2012;Wu et al., 2012;周洁等,2013);晚期以正长花岗岩为主,少量二长花岗岩,多数具有A型花岗岩的特征(薛怀民等,2009;Wu et al., 2012;Zhou et al., 2013;陈芳等,2014; 高冉等,2017)。
但是,目前对于皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆岩的研究多集中在皖南山区,对于北东段的工作明显偏弱,特别是关于姚村岩体的研究,仅有一个较为可靠的年代学资料(Wu et al., 2012)。本次工作对姚村岩体开展了详细的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、全岩主量和微量稀土元素、Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素组成的研究工作,以深入探讨姚村岩体的岩石成因类型、物质来源及构造环境。
2. 地质背景及岩体地质特征
下扬子地区位于扬子板块东部,其北和西北部以襄樊—广济断裂、郯庐断裂为界与大别造山带相邻,南以江绍断裂为界与华夏地块相接。通常以江南断裂为界,下扬子地区又可分为北西的长江中下游地区(沿江带)和南东的皖南江南造山带(江南带)两个构造单元(闫峻等,2017)(图 1a)。
姚村岩体位于皖南江南造山带北东段,地理位置处于安徽省郎溪县西南部的姚村乡。研究区内NE向断裂发育,并被少量NW向断裂所切。燕山期岩浆侵入活动强烈,多以中大型岩基或者复式岩体出露,如太平—黄山岩体、九华山岩体、刘村岩体及姚村岩体等(图 1b)。
姚村岩体呈北东向椭圆状侵入于志留系砂泥岩中(图 1c),出露面积约107 km2。岩体与围岩界线清晰,接触面呈波状或锯齿状,均外倾。接触带热变质作用强烈,形成宽500~1000 m角岩带。岩体边部局部发育宽窄不等的冷凝边,并偶见角岩化的砂岩捕虏体。姚村岩体主要由中心相的中粗粒正长花岗岩和边缘相的细粒似斑状正长花岗岩组成,两者呈渐变过渡关系,晚期还有细粒花岗岩侵入。
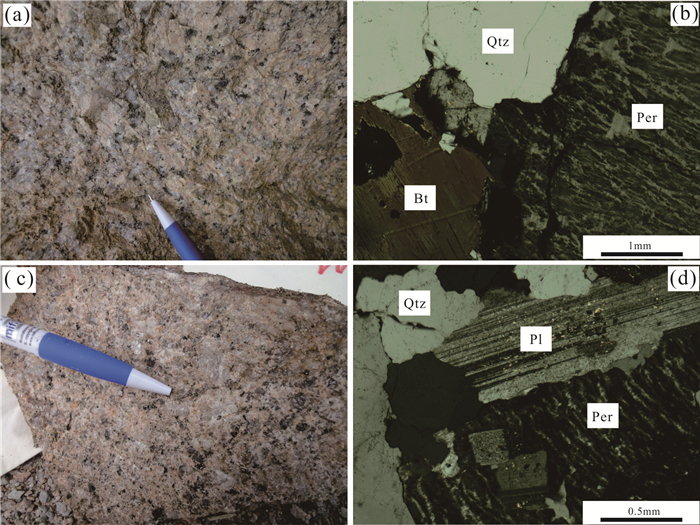
中粗粒正长花岗岩呈浅灰-肉红色,块状构造,中粗粒花岗结构(图 2a),局部呈似斑状。主要矿物成分为石英(30%~35%),斜长石(10%~15%,可见聚片双晶),条纹长石(45%~55%),黑云母(2%~5%)(图 2b)。副矿物有锆石、磷灰石、褐帘石等。
细粒似斑状正长花岗岩呈肉红—浅肉红色,块状构造,似斑状结构(图 2c)。斑晶以石英为主,次为钾长石。基质呈细粒结构,由条纹长石(45%~50%)、石英(25%~35%)、斜长石(10%~20%)及少量黑云母(2%~5%)组成(图 2d)。副矿物有锆石、磷灰石等。
3. 分析测试方法
全岩粉末样处理及锆石挑选工作在河北省廊坊辰昌岩矿检测技术服务有限公司进行,锆石制靶及阴极发光(CL)照相在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。
全岩主量和微量元素分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成,其中主量元素采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测定(仪器型号:PE300D),并采用等离子光谱和化学法测定进行互检。微量元素和稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)测定(型号:PW4400),同时分析2个国家标样(GSR3和GSR5)和3个平行样以保证分析结果的准确度,分析精度相对误差符合行业标准。
全岩Sr-Nd同位素在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。根据微量元素中Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd含量称取适量样品于Teflon闷罐中,加入87Rb-84Sr和149Sm-150Nd混合稀释剂并用HF、HNO3和HClO4充分溶解后用离子交换树脂分离出Rb、Sr、Sm和Nd,在ISOPROBE-T热电离质谱仪(TIMS)上测试。整个分析流程实验本底为:Rb、Sr < 100×10-12;Sm、Nd < 50×10-12。
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,锆石定年分析所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀所用斑束直径为25 μm,频率为10 Hz,能量密度约为2.5 J/cm2,以He为载气。LA-MC-ICP-MS激光剥蚀采用单点剥蚀的方法,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M127为外标进行校正。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal程序(Liu et al., 2008, 2010),锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot3.0程序获得(Ludwig, 2003)。详细参数及实验测试过程参见侯可军等(2009)。
锆石Hf同位素分析测试工作在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室完成。该项分析是在锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年的基础上,参照锆石CL图像,选择在原年龄测点位置或附近进行,所用仪器为New-wave UP193激光剥蚀系统及其相连接的Thermo Neptune Plus多接收等离子体质谱仪,以He作为载气,分析中使用的激光束斑直径为44 μm,频率为8 Hz,剥蚀时间为26 s,采用MT作为外部标样,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282530±0.000030。εHf(t) 计算采用的176Lu的衰变常数为1.865×10-11(Scherer et al., 2001),球粒陨石176Hf/177Hf=0.282772,176Lu/177Hf=0.0332(Blichert,1997)。亏损地幔Hf模式年龄(TDM1)采用176Hf/177Hf= 0.283251,176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Vervoot & Blichert-Toft,1999),二阶段Hf模式年龄(TDM2)采用平均大陆壳176Lu/177Hf=0.015计算(Griffin et al., 2002)。
4. 分析结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
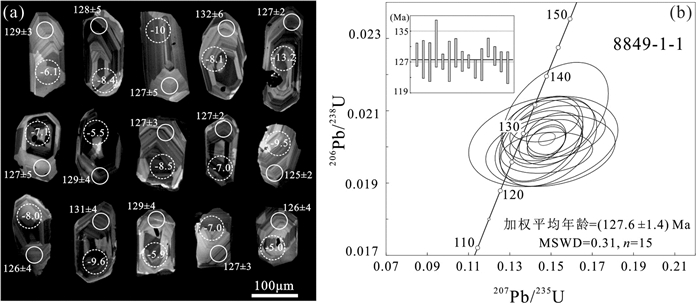
对姚村岩体中的中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)进行了锆石U-Pb年代学研究。样品中锆石呈无色和淡黄色,形态为柱状,长100~120 μm,宽50~60 μm,长宽比一般在2∶1左右。在锆石阴极发光图像(CL)上(图 3a),所有锆石均发育清晰的震荡环带,显示岩浆锆石的特点。对样品进行了24个点的锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析,定年数据列于表 1。
![]() 图 3 姚村岩体代表性锆石CL图像(a)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)(实线小圈为锆石U-Pb同位素分析点,虚线大圈为Hf同位素分析点)Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons(a) and U-Pb Concordia diagrams of samples(b) from the YaocunA-type granitic pluton. Small solid circles are spots for U-Pb isotope analyses, and big dashed circles are spots for Hf isotope analyses表 1 姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb geochronology results in the Yaocun coarse-grained syenogranite
图 3 姚村岩体代表性锆石CL图像(a)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)(实线小圈为锆石U-Pb同位素分析点,虚线大圈为Hf同位素分析点)Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons(a) and U-Pb Concordia diagrams of samples(b) from the YaocunA-type granitic pluton. Small solid circles are spots for U-Pb isotope analyses, and big dashed circles are spots for Hf isotope analyses表 1 姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb geochronology results in the Yaocun coarse-grained syenogranite
这些锆石中Pb含量较低,变化于2×10-6~10× 10-6,Th含量介于58×10-6~306×10-6,U含量介于89×10-6~372×10-6。Th/U比值为0.60~1.06,均大于0.40,属典型的岩浆成因锆石(Wu and Zheng, 2004)。从测试结果看,样品206Pb/238U表面年龄都较为集中,24个点全部集中在125~135 Ma。但部分点(如1、2、3、4、5、12、13、19、22)207Pb/206Pb年龄与206Pb/238U相差太大,谐和度小于90%,除掉这9个不谐和的数据点外,其他15个点的分析数据在谐和曲线上成群分布(图 3b),206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(127.6 ±1.4)Ma(n=15,MSWD=0.31),代表了姚村岩体的形成时代,属早白垩世岩浆活动的产物。
4.2 全岩地球化学特征
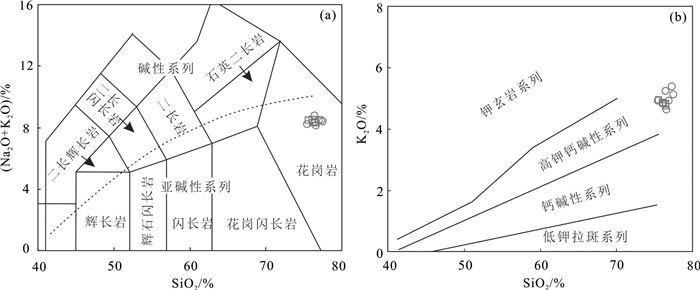
对姚村岩体细粒似斑状正长花岗岩和中粗粒正长花岗岩进行了全岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析,结果列于表 2。姚村岩体均具有较高的SiO2(75.46%~77.55%)和全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量(8.11%~8.75%),较低的TiO2(0.08%~0.22%)、CaO(0.23%~ 0.65%)、MgO(0.07% ~0.29%)和P2O5(0.01% ~ 0.04%)含量。在TAS分类图解中(图 4a),所有样品全部投入花岗岩区域内,属于亚碱性系列。在SiO2-K2O图解中(图 4b),全部落入高钾钙碱性系列。Al2O3含量为11.85%~12.83%(平均12.42%),铝碱比(A/NK)介于1.08~1.18,铝过饱和度(A/CNK)为1.0~1.1,属弱过铝质岩石。
表 2 姚村岩体全岩主量元素(%)、稀土元素和微量元素含量(10-6)Table 2. The content of main elements (%), rare earth elements and trace elements(10-6) of the Yaocun pluton
![]() 图 4 姚村岩体TAS分类图解(a)(据Middlemost, 1994)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Peccerillo et al., 1976)(圆形为中粗粒正长花岗岩,正方形为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 4. Alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and SiO2-K2O diagram(b, after Peccerillo et al., 1976) of the Yaocun pluton(The circle represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the square represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
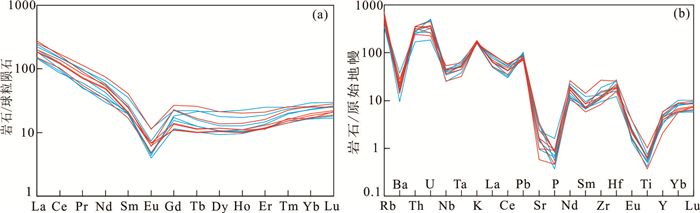
图 4 姚村岩体TAS分类图解(a)(据Middlemost, 1994)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Peccerillo et al., 1976)(圆形为中粗粒正长花岗岩,正方形为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 4. Alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and SiO2-K2O diagram(b, after Peccerillo et al., 1976) of the Yaocun pluton(The circle represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the square represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)姚村岩体REE总量为125×10-6~241×10-6,在球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素分布图上(图 5a),姚村岩体轻重稀土分馏明显,表现为LREE富集的右倾分布型式,轻重稀土明显分馏,(La/Yb)N=6.40~10.74(平均值为9.46),并且显示强烈的Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.22~0.46)。在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上(图 5b),所有样品具有明显的Rb、U、Th、K、Pb、Nd、Zr、Hf正异常,显著的Ba、Nb、Ta、Sr、P、Ti负异常。
![]() 图 5 姚村岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔的标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(红线为中粗粒正长花岗岩,蓝线为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution diagram of Yaocun pluton (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider (b) Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element date(b) for samples of the Yaocun pluton.(Normalizing values are from Sun & McDonough 1989). (The red line represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the blue line represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
图 5 姚村岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔的标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(红线为中粗粒正长花岗岩,蓝线为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution diagram of Yaocun pluton (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider (b) Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element date(b) for samples of the Yaocun pluton.(Normalizing values are from Sun & McDonough 1989). (The red line represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the blue line represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)4.3 全岩Sr-Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素特征
姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩全岩Sr、Nd同位素测试结果列于表 3。结果显示,姚村岩体具有均一的Sr、Nd同位素组成,87Sr/86Sr初始比值介于0.7098~0.7101,143Nd/144Nd值介于0.512207~0.512253,εNd(t)值变化于-6.2~-5.7,二阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2介于1493~1532 Ma。
表 3 姚村岩体全岩Sr-Nd同位素测试结果Table 3. Sr-Nd isotope compositions of representative samples from the Yaocun pluton
姚村岩体中的中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)锆石Hf同位素分析结果列于表 4。这些岩浆锆石具有相对均一的Hf同位素组成,176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf比值范围较大,分别变化于0.000949~0.001992和0.282303~0.282552,176Hf/177Hf初始比值介于0.282299~0.282548,εHf(t)值介于-13.9 ~ -5,TDM1介于1004~1364 Ma.,TDM2介于1508~2062 Ma。
表 4 姚村岩体(8849-1-1)锆石Hf同位素组成Table 4. Hf isotopic compositions of zircon grains from the Yaocun pluton determined by LA-MC-ICP-MS
5. 讨论
5.1 姚村岩体的成岩年龄
对于姚村岩体的成岩年龄,前人Rb-Sr法曾测得127 Ma的年龄结果(章邦栋,1989),Wu et al.(2012)也获得正长花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb年龄为(127.2±1.9)Ma。本次获得的姚村岩体似斑状正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)锆石U-Pb年龄为(127.6±1.4)Ma,与前人结果在误差范围内一致,代表了姚村岩体的成岩时代。因此,姚村岩体属于皖南江南造山带燕山期岩浆活动的晚阶段,和带内其他A型花岗岩的侵入时代一致。
5.2 岩石类型
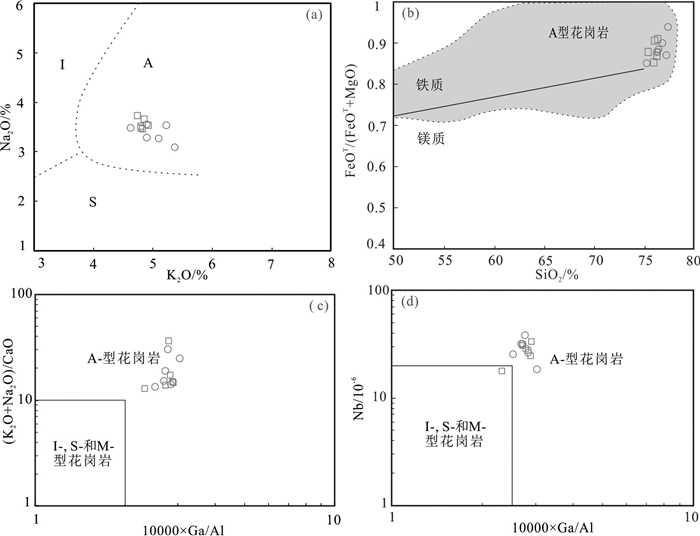
根据不同的源岩性质一般将花岗岩被分为I型、S型、M型(Whalen et al., 1987; Bonin, 2007)。而A型花岗岩最先由Loiselle和Wones(1979)提出,用来定义一类碱性(Alkaline)、无水(Anhydrous)、非造山(Anorogenic)的花岗岩,具有特殊的地球化学特征(Loiselle & Wones, 1979)。
姚村岩体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量(8.11%~8.75%)、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)比值(0.84~0.92)、高场强元素和稀土元素含量,同时具有较低的Ba、Sr、Ti和Eu含量,这些地球化学特征与典型的A型花岗岩类似(Loiselle & Wones, 1979; Whalen et al., 1987; Bonin, 2007; Frost & Frost, 2008)。在前人提出的花岗岩类型判别图解中(图 6),包括Na2O-K2O图解(图 6a,据Collins et al., 1982)、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)-SiO2图解(图 6b,据Frost & Frost, 2011)、(Na2O + K2O)/CaO-1000×Ga/Al和Nb-1000×Ga/Al图解(图 6c和图 6d,据Whalen et al., 1987),除个别样品点外,姚村岩体基本落入A型花岗岩范围内。
![]() 图 6 姚村A型花岗岩判别图解(底图a据Collins et al., 1982;底图b据Frost and Frost, 2011; 底图c和d据Whalen et al., 1987)(图例同图 4)Figure 6. Chemical discrimination diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton: (a) Na2O vs. K2O; (b) FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) vs.SiO2; (c) (K2O+Na2O) /CaO vs. 10, 000 Ga; (d) Nb vs. 10, 000 Ga (a after Collins et al., 1982; b after Frost and Frost, 2011; c and d after Whalen et al., 1987). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 6 姚村A型花岗岩判别图解(底图a据Collins et al., 1982;底图b据Frost and Frost, 2011; 底图c和d据Whalen et al., 1987)(图例同图 4)Figure 6. Chemical discrimination diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton: (a) Na2O vs. K2O; (b) FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) vs.SiO2; (c) (K2O+Na2O) /CaO vs. 10, 000 Ga; (d) Nb vs. 10, 000 Ga (a after Collins et al., 1982; b after Frost and Frost, 2011; c and d after Whalen et al., 1987). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4另外,根据Watson and Harrison(2005)提出的锆饱和温度计,计算得到的姚村岩体成岩温度为785 ~ 899℃(平均827℃),指示姚村岩体形成温度较高,与典型A型花岗岩类似,而明显高于一般的I型和S型花岗岩的锆石饱和温度(< 800℃)。因此,姚村岩体为A型花岗岩。
5.3 岩石成因及源区性质
尽管A型花岗岩一般认为形成于伸展的构造环境,但是对其成因过程还存在不同认识,主要有两种模式:(1)幔源玄武质岩浆的结晶分异,并伴随或不伴随地壳混染(Loiselle & Wones, 1979; Turner et al., 1992;Mushkin et al., 2003; Bonin, 2007);(2)特殊地壳原岩的部分熔融(Collins et al., 1982; Whalen et al., 1987; Creaser et al., 1991)。
通常由幔源玄武质岩浆结晶分异而成的A型花岗岩一般会和大规模基性岩共生(Turner et al., 1992),并具有亏损的同位素组成(Kemp and Hawkesworth, 2005)。宣城地区暂未发现与第三阶段岩浆作用同时期的基性岩浆岩。同时,姚村岩体εNd(t)值变化于-6.2~ -5.7,εHf(t)值介于-13.9 ~ -5,具有较为富集的同位素组成,据此推断,姚村岩体不是由幔源玄武质岩浆结晶分异而来,其主体上应为壳源岩浆岩。
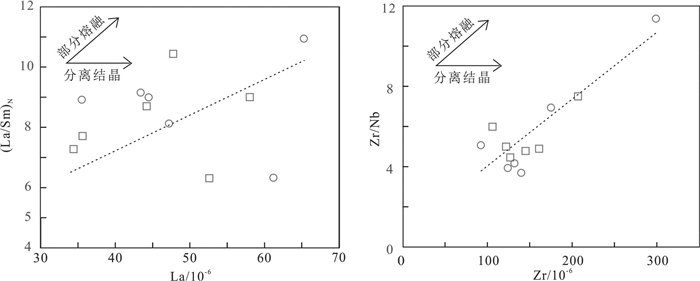
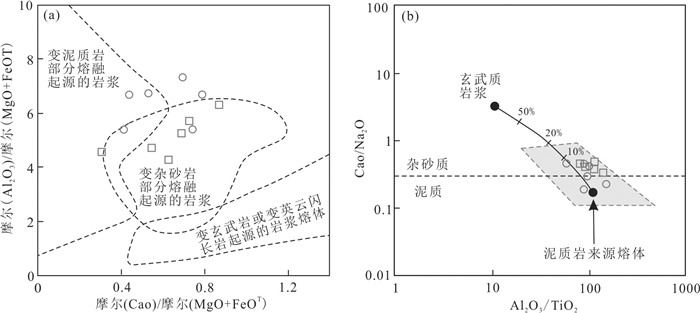
(La/Sm)N对La以及Zr/Nb对Zr的正相关表明部分熔融可能是控制姚村岩体成因的主要岩浆过程(图 7)。在花岗岩源岩判别图解中,姚村岩体投影于变泥质和变杂砂岩的部分熔融产生的熔体区域内(图 8a),并且排除镁铁质组分的混入(图 8b),表明姚村岩体地球化学特征继承其原岩。
![]() 图 8 姚村岩体源岩判别图解:(a)摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT)-摩尔CaO/(MgO+FeOT)图解(据Altherr et al., 2000); (b)Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O图解(据Sylvester., 1998)(图例同图 4)Figure 8. (a) Molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT) vs. CaO/(MgO + FeOT) and (b) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton (a after Altherr et al., 2000 and b after Sylvester., 1998). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 8 姚村岩体源岩判别图解:(a)摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT)-摩尔CaO/(MgO+FeOT)图解(据Altherr et al., 2000); (b)Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O图解(据Sylvester., 1998)(图例同图 4)Figure 8. (a) Molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT) vs. CaO/(MgO + FeOT) and (b) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton (a after Altherr et al., 2000 and b after Sylvester., 1998). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4下扬子陆块具有“一盖两底”的格局,新太古代—新元古代崆岭群—董岭岩群为“江北型”基底,中新元古代双桥山群—溪口岩群(上溪群)为“江南型”基底(常印佛和董树文等,1996)。姚村正长花岗岩相比于崆岭群灰色片麻岩(Xing et al., 1994;凌文黎等,1998;Ma et al., 2000)及董岭岩群角闪岩(Xing et al., 1994)具有相对较高的Nd同位素。同时锆石Hf同位素显示,崆岭群TTG片麻岩和董岭岩群中锆石Hf同位素组成远比姚村正长花岗岩的锆石Hf同位素要富集(Zhang et al., 2006;Guo et al., 2014;Zhang et al., 2015;Chen et al., 2016),表明以崆岭群和董岭岩群所代表的古老地壳不是岩浆源区。
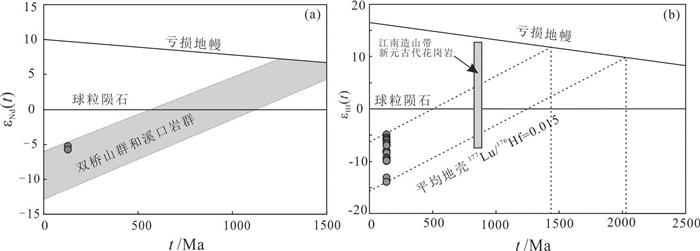
姚村岩体样品的Nd模式年龄(TDM2=1493~1532 Ma)及锆石Hf模式年龄(TDM2=1508~2062 Ma)表明原岩为中元古代时期物质。在t-εHf(t)图解中,姚村正长花岗岩的εNd(t)值落于双桥山群和溪口岩群的Nd同位素演化线范围内(图 9a),同样在t-εHf(t)图解中,由中元古代地壳部分熔融而成的新元古代花岗岩的Hf同位素演化线范围全部覆盖姚村岩体的εNd(t)值(图 9b)。以上同位素特征表明姚村岩体为这些中元古代地壳物质在约127 Ma时期重熔的产物。
![]() 图 9 姚村岩体全岩εNd(t)-t图解(a, 双桥山群和溪口岩群全岩Nd同位素据Chen & Jahn, 1998)和锆石εHf(t)-t图解(b,新元古代花岗岩锆石Hf同位素据Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013)Figure 9. εNd(t) vs. t diagram (a, after Chen & Jahn, 1998) and εHf(t) vs. t diagram (b, after Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013) of the Yaocun pluton
图 9 姚村岩体全岩εNd(t)-t图解(a, 双桥山群和溪口岩群全岩Nd同位素据Chen & Jahn, 1998)和锆石εHf(t)-t图解(b,新元古代花岗岩锆石Hf同位素据Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013)Figure 9. εNd(t) vs. t diagram (a, after Chen & Jahn, 1998) and εHf(t) vs. t diagram (b, after Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013) of the Yaocun pluton5.4 构造环境
对于华南东部燕山期构造背景,曾存在逆冲推覆成因(Hsü et al., 1988)、岩石圈伸展与软流圈地幔上涌(Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2003)、中生代开始的整个中国东海岸裂谷(Gilder et al., 1991)以及华南中生代地幔柱上升(Deng et al., 2004)等多种不同认识,但目前绝大多数学者已认可古太平洋板块对欧亚板块的俯冲消减作用才是形成华南东南部燕山期花岗质岩石-火山岩的根本动力学机制(Zhou & Li, 2000;Zhou et al., 2006;Li & Li, 2007;Sun et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2011; He & Xu, 2012; Li et al., 2012; 吕庆田等,2019)。
虽然俯冲作用的精细过程还存在多种观点,但对于华南东部(140~125 Ma)的岩浆活动,一般认为形成于伸展的构造环境(Li, 2000; Wang et al, 2003; Zhou et al., 2013; 邢光福等, 2017),皖南江南造山带晚期阶段136~122 Ma的岩浆活动也受控于此构造背景之下(闫峻等,2017)。
姚村A型花岗岩的侵位时代在127 Ma左右,邻区其他A型花岗岩,如刘村岩体(132 Ma,陈芳等,2014)、九华山岩体(130~131 Ma,Wu et al., 2012)、黄山岩体(125~127 Ma,薛怀民等,2009)、伏岭岩体(124 Ma,Zhou et al., 2013)、牯牛降岩体(130 Ma,谢建成等,2012)、铜山岩体(129 Ma, Jiang et al., 2011)、杨梅湾岩体(135 Ma, Yang et al., 2012)、白菊花尖岩体(126 Ma, Wong et al., 2009)、大茅山(126~ 122 Ma, Jiang et al., 2011)、三清山(132~130 Ma, Sun et al., 2015)、灵山岩体(134~132 Ma,Wang et al., 2018)等,年龄均集中在135~124 Ma。
广泛出露的A型花岗岩充分说明此时本区处于弧后的伸展环境(薛怀民等,2009;张舒等,2009;Wu et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2013; 陈芳等,2014;高冉等,2017)。从侏罗纪到白垩纪,随着板片俯冲角度增加,弧后延伸作用逐渐增强(Zhou et al., 2006)。后续的软流圈上涌导致了陆下岩石圈地慢的熔融,产生了大量的玄武质岩浆底侵至下地壳(Zhou & Li, 2000)。玄武质岩浆的底侵为中元古代基底沉积岩的大范围部分熔融提供了热源,从而产生了A型花岗质岩浆。
6. 结论
(1)姚村岩体形成年龄为(127.6 ±1.4)Ma,属早白垩世岩浆作用的产物,对应于皖南江南造山带第二阶段岩浆活动。
(2)姚村岩体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)比值、高场强元素和稀土元素含量,同时具有较低的Ba、Sr、Ti和Eu含量以及较高的锆石饱和温度,表明姚村岩体为A型花岗岩。
(3)全岩Sr-Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素特征指示姚村岩体为下扬子中元古代地壳物质部分熔融的产物,形成于早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲作用之后弧后拉伸环境下。
-
图 1 大地构造位置图(a)、区域构造略图(b,据陈芳等,2014修改)及岩体地质简图(c)
Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Lower Yangtze region showing the location of the studied area(a); tectonic sketch map of the studied area(b, after Chen Fang et al., 2014); and geological sketch map of the Yaocun pluton(c)
图 3 姚村岩体代表性锆石CL图像(a)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)
(实线小圈为锆石U-Pb同位素分析点,虚线大圈为Hf同位素分析点)
Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons(a) and U-Pb Concordia diagrams of samples(b) from the Yaocun
A-type granitic pluton. Small solid circles are spots for U-Pb isotope analyses, and big dashed circles are spots for Hf isotope analyses
图 4 姚村岩体TAS分类图解(a)(据Middlemost, 1994)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Peccerillo et al., 1976)(圆形为中粗粒正长花岗岩,正方形为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)
Figure 4. Alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and SiO2-K2O diagram(b, after Peccerillo et al., 1976) of the Yaocun pluton
(The circle represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the square represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
图 5 姚村岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)
(球粒陨石和原始地幔的标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(红线为中粗粒正长花岗岩,蓝线为细粒似斑状正长花岗岩)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution diagram of Yaocun pluton (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider (b) Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element date(b) for samples of the Yaocun pluton.
(Normalizing values are from Sun & McDonough 1989). (The red line represents medium-to coarse-grained syenogranite, and the blue line represents fine-grained porphyritic syenogranite.)
图 6 姚村A型花岗岩判别图解(底图a据Collins et al., 1982;底图b据Frost and Frost, 2011; 底图c和d据Whalen et al., 1987)(图例同图 4)
Figure 6. Chemical discrimination diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton: (a) Na2O vs. K2O; (b) FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) vs.SiO2; (c) (K2O+Na2O) /CaO vs. 10, 000 Ga; (d) Nb vs. 10, 000 Ga (a after Collins et al., 1982; b after Frost and Frost, 2011; c and d after Whalen et al., 1987). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 8 姚村岩体源岩判别图解:(a)摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT)-摩尔CaO/(MgO+FeOT)图解(据Altherr et al., 2000); (b)Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O图解(据Sylvester., 1998)(图例同图 4)
Figure 8. (a) Molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT) vs. CaO/(MgO + FeOT) and (b) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagrams of the Yaocun A-type granitic pluton (a after Altherr et al., 2000 and b after Sylvester., 1998). Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4
图 9 姚村岩体全岩εNd(t)-t图解(a, 双桥山群和溪口岩群全岩Nd同位素据Chen & Jahn, 1998)和锆石εHf(t)-t图解(b,新元古代花岗岩锆石Hf同位素据Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013)
Figure 9. εNd(t) vs. t diagram (a, after Chen & Jahn, 1998) and εHf(t) vs. t diagram (b, after Zhang & Zheng, 2013; Wang et al., 2013) of the Yaocun pluton
表 1 姚村岩体中粗粒正长花岗岩(8849-1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb geochronology results in the Yaocun coarse-grained syenogranite

表 2 姚村岩体全岩主量元素(%)、稀土元素和微量元素含量(10-6)
Table 2 The content of main elements (%), rare earth elements and trace elements(10-6) of the Yaocun pluton

表 3 姚村岩体全岩Sr-Nd同位素测试结果
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotope compositions of representative samples from the Yaocun pluton

表 4 姚村岩体(8849-1-1)锆石Hf同位素组成
Table 4 Hf isotopic compositions of zircon grains from the Yaocun pluton determined by LA-MC-ICP-MS

-
Altherr R, Holl A, Hegner E, Langer C, Kreuzer H. 2000. High-potassium, calcalkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides, northern Vosges (France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 50: 51-73. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00052-3
Blichert-Toft J, Albarede F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planet Science Letter, 148(1/2): 243-258.
Bonin B. 2007. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 97, 1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007
Chang Yinfo, Dong Shuwen. 1996. On tectonics of "poly-basement withone cover" in middle-lower Yangtze craton China[J]. Volcanology and Mineral Resources, 17(1/2): 1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ1996Z1000.htm
Chen C H, Lee C Y, Shinjo R. 2008. Was there Jurassic paleo-Pacific subduction in South China? Constraints from 40Ar/39Ar dating, elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Mesozoic basalts[J]. Lithos, 106(1-2): 83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.06.009
Chen Fang, Wang Denghong, Du Jianguo, Xu Wei, Hu Haifeng, Wang Keyou, Yu Youlin, Tang Jinlai. 2014. Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Liucun monzogranite in ningguo, Anhui Provinceand and their geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(5): 869-882 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201405005.htm
Chen Jun, Wang Hui, Wang Lijuan, Guan Junpeng. 2018. Petrogenesis of Jinniu rock mass in Chuzhou area: Melting of delaminated lower crust or mixing of crust and mantle[J]. Geology in China, 45(1): 110-128(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201801011.htm
Chen Z H, Xing G F. 2016. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopic evidence for a coherent Paleoproterozoic basement beneath the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 279: 81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.04.002
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, Chappell B W. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80, 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J. 1991. A-type granites revisited: Assessment of residual source model[J]. Geology, 19: 163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0163:ATGRAO>2.3.CO;2
Deng J F, Mo X X, Zhao H L, Wu Z X, Luo Z H, Su S G. 2004. A newmodel for the dynamic evolution of Chinese lithosphere: 'continental roots-plume tectonics'[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 65 (3/4): 223-275. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825203001065
Frost B R, Frost C D. 2008. A geochemical classification for feldspathic igneous rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 49: 1955-1969. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egn054
Frost C D, Frost B R. 2011. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids: their compositional variability and modes of origin[J]. Journal of Petrology 52, 39-53. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egq070
Gao Ran, Yan Jun, Li Quanzhong, Liu Xiaoqiang, Wang Sinuo. 2017. Petrogenesis of Tanshan Pluton in the Southern Anhui Province: Chronological and geochemical constraints[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 23(2): 227-243 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GXDX201702005.htm
Gilder S A, Keller G R, Luo M, Goodell P C. 1991. Eastern Asia and the Western Pacific timing and spatial distribution of rifting in China[J]. Tectonophysics, 197(2-4): 225-243. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(91)90043-R
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. 2002. Zircon geochemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous conplexes[J]. Lithos, 61: 237-269. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
Guan Junpeng, Weii Fubiao, Sun Guoxi, Huang Jianping, Wang Lijuan. 2015. Zircon U-Pb dating of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the middle section of Ningzhen district and their metallogenic implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(2): 344-354 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201502015.htm
Guo J L, Gao S, Wu Y S. 2014.3.45 Ga granitic gneisses from the Yangtze Craton, South China: Implications for Early Archean crustal growth[J]. Precambrian Resiearch, 242, 82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.018
Chen J F, Jahn B M. 1998. Crust evolution of southeastem China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 284(1/2): 101-133. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195197001868
He Z Y, Xu X S. 2012. Petrogenesis of the Late Yanshanian mantle-derived intrusions in southeastern China: Response to the geodynamics of paleo-Pacific plate subduction[J]. Chemical Geology, 328: 208-221. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.09.014
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Tian Yourong. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 481-492 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009GeCAS..73R.552H
Hsü K J, Sun S, Li J L, Chen H H, Pen H P, Sengor A M C. 1988. Mesozoic overthrust tectonics in south China[J]. Geology, 16(5): 418-421. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0418:MOTISC>2.3.CO;2
Jiang Y H, Zhao P, Zhou Q, Liao S Y, Jin G D. 2011. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Early Cretaceous SandA-type granites in the northwest of the Gan-Hang rift, SE China[J]. Lithos, 121, 55-73. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.10.001
Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J. 2005. Granitic perspectives on the generation and secular evolution of the continental crust[C]//Rudnick R J (ed. ). Treatise on Geochemistry. Pergamon, Oxford, 1-64.
Li X H. 2000. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18 (3): 293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
Li Z X, Li X H. 2007. Formation of the 1300 km wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 35(2): 179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
Li Z X, Li X H, Chung S L, Lo C H, Xu X S and Li W X. 2012. Magmatic switch on and switch off along the South China continental margin since the Permian: Transition from an Andean type to a Western Pacific type plate boundary[J]. Tectonophysics, 532/535: 271-290. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.02.011
Ling Wenli, Gao Shan, Zheng Haifei, Zhou Lian, Zhao Zubin. 1998. An Sm-Nd isotopic dating study of the Archean Kongling complex in the Huangling area of the Yangtze craton[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin (Chinese Version), 43(1): 86-89 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1998-43-1-86
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, Wang D B. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51: 537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
Liu Y S, Hu ZC, Gao S, Chen H L. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257: 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Loiselle M C, Wones D R. 1979. Characteristics of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 11(7): 468. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10019593683
Ludwig K R. 2003. Isoplot/EX Version 2.49: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 1a: 1-56.
Lü Qingtian, Meng Guixiang, Yan Jiayong, Zhang Kun, Zhao Jinhua, Gong Xuejing. 2019. Multi-scale exploration of mineral system: Concept and progress-A case study in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt[J]. Geology in China, 46(4): 673-689(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201904002.htm
Ma C, Ehlers C, Xu C, et al. 2000. The roots of Ac Dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terrane: constraints from geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotope systematics[J]. Precambrian Research, 102: 279-301. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00069-3
Mao Jingwen, Holly S, Du Andao, Zhou Taofa, Mei Yanxiong, Li Yongfeng, Zang Wenshuan, Li Jinwen. 2004. Molybdenite Re-Os precise dating for molybdenite from Cu-Au-Mo deposits in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Belt and its implications for mineralizatotn[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1): 121-131 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXE200401014.htm
Middlemost, E A K. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 37: 215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Mushkin A, Navon O, Halicz L, Hartmann G and Stein M. 2003. The petrogenesis of A-type magmas from the Amram Massif, southernIsrael[J]. Journal of Petrology, 44(5): 815-832. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.815
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. 1976. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58: 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Scherer E, Munker C and Mezger K. 2001. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock[J]. Science, 293: 683-687. doi: 10.1126/science.1061372
Sun F J, Xu X S, Zou H B, Xia Y. 2015. Petrogenesis and magmatic evolution of ~130 Ma A-type granites in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 98, 209-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.018
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Sanders A D, Norry M J (ed. ). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42: 313-345.
Sun W D, Ding X, Hu Y H, Li X H. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533-542. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021
Sylvester P J. 1998. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 45(1-4): 29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
Xing F M, Xu X, Li Z C, 1994. Discovery of the Early Proterozoic basement in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River and its significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2: 135-139. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXTW199402010.htm
Turner S P, Foden J D, Morrison R S. 1992. Derivation of some Atype magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma: An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J]. Lithos, 28, 151-179. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(92)90029-X
Vervoort J D, Blichert-Toft J. 1999. Evolution of the depleted mantle: Hf isotope evidence from juvenile rocks through time[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(3/4): 533-556.
Wang Cunzhi, Huang Zhizhong, Zhao Xilin, Chu Pingli, Huang Wencheng, Song Shiming, Chen Zhihong. 2018. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous acid volcanic rocks at Shuidong Area, Xuancheng City in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 37(5): 697-715 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSKW201805001.htm
Wang C Z, Zhao X L, Huang Z Z, Xing G F, Wang L X. 2018. Early Cretaceous Extensional tectonism related petrology of the Gan Hang Belt SE China: Lingshan A type granite at ca. 130 Ma[J]. Geological Journal, 53(6): 2487-2506. doi: 10.1002/gj.3083
Wang F Y, Ling M X, Ding X, Hu Y H, Zhou J B, Yang X Y, Liang H Y, Fan W M, Sun W D. 2011. Mesozoic large magmatic events and mineralization in SE China: Oblique subduction of the Pacific plate[J]. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 704-726. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2010.503736
Wang Jiqiang, Sun Weian, Yuan Feng, Shang Shigui, Zhou Taofa, Zhong Fuming, Zhang Ruofei. 2017. Geological characteristics, rock-forming epoch and genesis of the Danizhuang Cu deposit in Luzong basin[J]. Geology in China, 44(1): 86-100(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201701008.htm
Wang X L, Zhou J C, Wan Y S, Kitajima K, Wang D, Bonamici C, Qiu J S, Sun T. 2013. Magmatic evolution and crustal recycling for Neoproterozoic strongly peraluminous granitoids from southern China: Hf and O isotopes in zircon[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 366 (2): 71-82.
Wang Y J, Fan W M, Guo F, Peng T P, Li C W. 2003. Geochemistry of Mesozoic mafic rocks adjacent to the Chenzhou Linwu fault, South China: Implications for the lithospheric boundary between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks[J]. International Geology Review, 45 (3): 263-286. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.45.3.263
Watson E B, Harrison T M. 2005. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth[J]. Science, 308 (5723): 841-844. doi: 10.1126/science.1110873
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95: 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Wong J, Sun M, Xing G F, Li X H, Zhao G C, Wong K, Yuan C, Xia X P, Li L M. & Wu FY. 2009. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of the Baijuhuajian metaluminous A-type granite: extension at 125-100 Ma and its tectonic significance for South China[J]. Lithos, 112: 289-305. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.03.009
Wu F Y, Ji W Q, Sun D H. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesozoic granites in southern Anhui Province, China[J]. Lithos, 150: 6-25 doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.020
Wu Y B and Zheng Y F. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constranints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49: 1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
Xie Jiancheng, Chen Si, Rong Wei, Li Quanzhong, Yang Xiaoyong, Sun Weidong. 2012. Geochronolgy, geochemistry and tectonic significance of Guniujiang A-type granite in Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(12): 4007-4020.
Xing Guangfu, Hong Wentao, Zhang Xuehui, Zhao Xilin, Ban Yizhong, Xiao Fan. 2017. Yanshanian granitic magmatisms and their mineralizations in East China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33 (5): 1571-1590 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue Huaimin. 2016. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of volcanism in the Liyang volcanic basin on the southeastern margin of the Middle-Lower Yangtze region[J]. Geochimica, 45(3): 213-234 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201603001.htm
Xue Huaimin, Ma Fang, Guan Haiyan, Wang Yipeng. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks in Huaining basin incomparison with other basins in the middle-lower Yangtze region[J]. Geology in China, 40(3): 694-714 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201303/46331692.html
Xue Huaimin, Wang Yinggeng, Ma Fang, Wang Cheng, Wang Deen, Zuo Yanlong. 2009. The Huangshan A-type granites with tetrad REE: constraints on Mesozoiclithospheric thinning of the southeastern Yangtze craton?[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(2), 247-259 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Jun, Hou Tianjie, Wang Aiguo, Wang Deen, Zhang Dingyuan, Weng Wangfei, Liu Jianmin, Liu Xiaoqiang, Li Quanzhong. 2017. Comparative study of genesis of earlier-stage metallogenic granite and later-stage barren granite in the south Anhui Province[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 47(11): 1269-1291.
Yan Jun, Peng Ge, Liu Jianmin, Li Quanzhong, Chen Zhihong, Shi Lei, Liu Xiaoqiang, Jiang Zizhao. 2012. Petrogenesis of granites from Fanchang district, the Lower Yangtze region: Zircon geochronology and Hf-O isotopes constrains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 3209-3227 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210014.htm
Yang S Y, Jiang S Y, Zhao K D, Jiang Y H, Ling H F, Luo L. 2012. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significance of two Early Cretaceous A-type granites in the Gan-Hang Belt, Southeast China[J]. Lithos, 150: 155-70. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.01.028
Zhang Bangtong, Zhai Jianping, Ling Hongfei. 1989. The geological and geochemical characteristcs of the mixed crust-mantle derivation type uranium-bearing granitoids in the lower Yangzi fault depression zone[J]. Uranium Geology, 5(3): 134-143 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198903001.htm
Zhang S B, He Q, Zheng Y F. 2015. Geochronological and geochemical evidence for the nature of the Dongling Complex in South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 256: 17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.10.013
Zhang S B, Zheng Y F. 2013. Formation and evolution of Precambrian continental lithosphere in South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(7): 1241-1260.
Zhang S B, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Zhao Z F, Gao S, Wu F Y. 2006. Zircon isotope evidence for ≥ 3.5 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 146: 16-34. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.002
Zhou J, Jiang Y H, Xing G F, Zeng Y, Ge W Y. 2013. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Cretaceous A-type granites from the NE Jiangnan Orogen, SE China[J]. International Geology Review, 55: 1359-1383. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.774199
Zhou Jie, Jiang Yaohui, Zeng Yong, Ge Weiya. 2013. Zircon U-Pb age and Sr, Nd, Hf isotope geochemistry of Jingde pluton ineastern Jiangnan orogen, South China[J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1379-1391 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201305004.htm
Zhou Taofa, Fan Yu, Yuan Feng. 2008. Advanees on petrogesnis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1665-1678 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Xiang, Yu Xinqi, Yang Heming, Wang Deen, Du Yudiao, Ke Hongbiao. 2012. Petrogenesis and geochronology of the high Ba-Sr Kaobeijian granodiorite porphyry, Jixi County, south Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10): 3403-3417 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou X M, Li W X. 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 326 (3-4): 269-287. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00120-7
Zhou X M, Sun T, Shen W Z, Shu L S. 2006. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 29(1): 26-33. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i1/004
常印佛, 董树文. 1996. 论中-下扬子"一盖多底"格局与演化[J]. 火山地质与矿产, 17(1/2): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ1996Z1000.htm 陈芳, 王登红, 杜建国, 许卫, 胡海风, 王克友, 余有林, 汤金来. 2014. 安徽宁国刘村二长花岗岩地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 88(5): 869-882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201405005.htm 陈俊, 王辉, 王丽娟, 关俊朋. 2018. 滁州地区金牛侵入体的岩石成因: 拆沉下地壳熔融还是壳幔混合[J]. 中国地质, 45(1): 110-128. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180110&flag=1 高冉, 闫峻, 李全忠, 刘晓强, 王思诺. 2017. 皖南谭山岩体成因: 年代学和地球化学制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 23(2): 227-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201702005.htm 关俊朋, 韦福彪, 孙国曦, 黄建平, 王丽娟. 2015. 宁镇中段中酸性侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其成岩成矿指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(2): 344-354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2015.02.014 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICPMS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 28(4): 481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 凌文黎, 高山, 郑海飞, 周炼, 赵祖斌. 1998. 扬子克拉通黄陵地区崆岭杂岩Sm-Nd同位素地质年代学研究[J]. 科学通报, 43(1): 86-89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.01.022 吕庆田, 孟贵祥, 严加永, 张昆, 赵金花, 龚雪婧. 2019. 成矿系统的多尺度探测: 概念与进展——以长江中下游成矿带为例[J]. 中国地质, 46(4): 673-689. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190401&flag=1 毛景文, Holly S, 杜安道, 周涛发, 梅燕雄, 李永峰, 藏文栓, 李进文. 2004. 长江中下游地区铜金(钼)矿Re-Os年龄测定及其对成矿作用的指示[J]. 地质学报, 78(1): 121-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200401014.htm 王存智, 黄志忠, 赵希林, 褚平利, 黄文成, 宋世明, 陈志洪. 2018. 长江中下游宣城水东地区早白垩世酸性火山岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 37(5): 697-715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2018.05.001 王继强, 孙维安, 袁峰, 尚世贵, 周涛发, 钟富明, 张若飞. 2017. 庐枞盆地大倪庄铜矿床地质特征、成岩时代及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 44(1): 86-100. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170107&flag=1 谢建成, 陈思, 荣伟, 李全忠, 杨晓勇, 孙卫东. 2012. 安徽牯牛降A型花岗岩的年代学、地球化学和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 28(12): 4007-4020. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201212017.htm 邢光福, 洪文涛, 张雪辉, 赵希林, 班宜忠, 肖凡. 2017. 华东地区燕山期花岗质岩浆与成矿作用关系研究[J]. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1571-1590. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201705014.htm 薛怀民. 2016. 长江中下游火山岩带东南缘溧阳盆地火山作用的年代学、地球化学及岩浆成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 45(3): 213-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2016.03.001 薛怀民, 马芳, 关海燕, 王一鹏. 2013. 怀宁盆地火山岩的年代学、地球化学及与长江中下游其他火山岩盆地的对比[J]. 中国地质, 40(3): 694-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.03.004 薛怀民, 汪应庚, 马芳, 汪诚, 王德恩, 左延龙, 2009. 高度演化的黄山A型花岗岩: 对扬子克拉通东南部中生代岩石圈减薄的约束?[J]. 地质学报, 83(2), 247-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200902011.htm 闫峻, 后田结, 王爱国, 王德恩, 张定源, 翁望飞, 刘建敏, 刘晓强, 李全忠. 2017. 皖南中生代早期成矿和晚期非成矿花岗岩成因对比[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 47(11): 1269-1291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201711002.htm 闫峻, 彭戈, 刘建敏, 李全忠, 陈志洪, 史磊, 刘晓强, 姜子朝. 2012. 下扬子繁昌地区花岗岩成因: 锆石年代学和Hf-O同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 28(10): 3209-3227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210014.htm 章邦桐, 翟建平, 凌洪飞. 1989. 扬子断陷带中壳幔混源型产铀花岗岩的地质地球化学特征[J]. 铀矿地质, 5(3): 134-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ198903001.htm 周洁, 姜耀辉, 曾勇, 葛伟亚. 2013. 江南造山带东段旌德岩体锆石LA-ICPMS年龄和Nd-Sr-Hf同位素地球化学[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1379-1391. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.004 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰. 2008. 长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿作用研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1665-1678. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201602001.htm 周翔, 余心起, 杨赫鸣, 王德恩, 杜玉雕, 柯宏飙. 2012. 皖南绩溪县靠背尖高Ba-Sr花岗闪长斑岩年代学及其成因[J]. 岩石学报, 28(10): 3403-3417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210027.htm -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 郑伟,陈天虎,杜建国,陈芳,丁宁,张舒. 皖南伏岭A型花岗岩的成因——地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu—Hf同位素特征. 地质论评. 2024(01): 189-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王存智,朱清波,靳国栋,褚平利,刘凯. “皖南高原”的发现及其演化史初探——来自皖南及其邻区燕山期两期花岗岩的证据. 地质通报. 2024(Z1): 390-400 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张洪文,平先权,黄伟,刘金业,高博,艾磊,王刚,孙艳秋. 黑龙江伊春地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境探讨. 地质与资源. 2024(03): 280-290 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱永胜,李超,刘群,江志,郑荥,郭君. 皖南姚村A型花岗岩磷灰石特征及其对成岩成矿的指示. 华东地质. 2024(03): 302-317 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙辉,左延龙,王昭文,檀荣华. 皖南地区萤石矿控矿因素及成矿规律研究. 安徽地质. 2024(04): 300-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王朝,李阳,陶威,沈仕豪,邓佳良,王耀,储东如. 下扬子地区汤口断裂带构造特征、期次及动力学探讨. 地质科学. 2023(03): 764-784 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 豆保娜,王安东,丁宁,陶继华,万建军. 安徽省岩浆岩放射性生热率特征研究. 岩石矿物学杂志. 2022(03): 609-627 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 高玲,闫峻,李全忠,谢建成. 皖南姚村岩体花岗岩风化壳稀土元素赋存特征. 地质论评. 2022(05): 1820-1838 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张小胖,张军,罗贤冬,卢逢亮. 皖南姚村岩体稀有金属元素地球化学特征及找矿前景探讨. 能源技术与管理. 2021(03): 19-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘欣,伍月,金珊合. 皖浙赣交界莲花山岩体U-Pb锆石年龄及其地质意义. 地质与资源. 2021(06): 666-674+682 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: