Fragmentation law of carbonate rocks under different confining pressure in Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Gaoyang geothermal field, Xiong'an New Area
-
摘要:研究目的
雄安新区高阳地热田D34钻孔为中国地质调查局中国地质科学院于2020年钻获的华北盆地最高温地热井,井口温度达123.4℃,出水量为94.5 m3/h,为使温度如此高的地热井的地热开发利用程度最大化,开展压裂增产是其重要举措。因此,为获取相关参数,以制定最优的压裂增产方案,本次研究拟厘清储层岩石在不同围压下的破碎规律。
研究方法本文在前人研究的基础上,以D34井钻获的深部高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩为研究对象,开展了常规三轴抗压及抗拉实验。
研究结果实验结果表明:(1)高于庄组碳酸盐岩拉伸强度特征与压缩强度特征相近,且表现出明显的压缩破坏特征。随着围岩压力的增加,抗压强度具有典型的二次增高特征。(2)抗压强度及裂隙展布形态随深度变化呈现出差异性,其中均匀发育的多裂缝和单一主缝为主要形式扩展。在20 MPa、40 MPa围压下,屈服强度分别与弹性模量、泊松比协同变化。(3)储层不同深度拉伸裂隙的扩展方式有所差异,较浅部拉伸裂隙主要以小幅度多级扩展为主,而较深部岩石则表现出均匀扩展态势。
结论结合抗压和抗拉实验结果,认为热储高于庄组压裂增产效果较好,且储层浅部形成复杂压裂网络的可能性高于深部储层,但总体脆性指数分布差异较小,故认为无需对储层不同深度采取不同的压裂施工方案。
创新点:首次识别并揭示了雄安新区高阳地热田深部第二热储空间高于庄组碳酸盐岩天然裂缝形态及在不同围压下的破碎规律。
Abstract:The paper is the result of geothermal geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveD34 well of Gaoyang geothermal field in Xiong'an New Area is the highest temperature geothermal well in North China Basin drilled by Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences and China Geological Survey in 2020. The wellhead temperature is 123.4℃, and the water output is 94.5 m3/h. Obviously, such high temperature corresponds with a relatively low flow. In order to provide important theoretical support for fracturing stimulation, this study intends to clarify the fragmentation law of reservoir carbonate rock under different confining pressures.
MethodsBased on previous studies, this paper takes the deep Gaoyuzhuang Formation reservoir carbonate rocks drilled from D34 well as the research object, and carries out conventional triaxial compression and tensile experiments.
ResultsThe experimental results show that: (1) The tensile strength characteristics of the reservoir carbonate rock in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation are similar with that of compressive strength, and shows obvious compression failure features. With the increase of the surrounding rock pressure, the compressive strength shows a typical secondary increase. (2) The compressive strength and the distribution of the fractures show differences with the depth. Among them, the uniformly developed multiple fractures and single main fractures are the main forms of expansion. Under the confining pressure of 20 MPa and 40 MPa, the yield strength changes synergistically with the Young's Modulus and Poisson's Ratio, respectively. (3) The expansion methods of tensile fractures are different with different depth. The shallower tensile fractures mainly expand with small amplitude and multi-stage expansion, while the deeper rocks show a uniform expansion trend.
ConclusionsCombined with the result of conventional triaxial compression and tensile experiments, it is concluded that the possibility of forming a complex fracturing network in the shallow part of the reservoir is higher than that in the deep part, but the overall brittleness index is less different, so there is no need to adopt different construction plans for different depths of the reservoir.
-
1. 引言
近年来,人口增长和工业发展增加了对能源的需求,化石燃料燃烧引起的气候变化、全球变暖等问题导致几乎所有的国家将能源结构向地热能、太阳能、风能和生物质能等可再生能源调整,地热能的开发利用在许多国家持续增长(汪集旸和孙占学,2001;Goldstein et al., 2009)。地热资源作为一种清洁可再生能源,在中国分布广泛、储量丰富,因此,在供暖、供热、制冷、温室等行业有着广阔的应用前景(郑克棪,2009;蔺文静等,2013;魏帅超等,2023)。设立雄安新区是以习近平总书记为核心的党中央根据新时代的国家发展需要做出的重大决策,要建设蓝绿交融、水天一色的生态友好城市,必须做好大气污染防治工作(庞忠和等, 2014)。冬季是华北地区雾霾频发的时期,清洁供暖是从源头上治理雾霾的关键一环。雄安新区位于华北平原冀中坳陷中部,水热型地热资源丰富,是中国中东部地区地热资源开发利用条件最好的地区(王贵玲等,2017a;马峰,2019;Wang et al., 2020)。目前,雄安新区雄县利用地热供暖满足了县城90 %以上的供热需求,年替代标准煤9万t,实现CO2减排22.5万t,创建了地热利用的“雄县模式”,已支撑地热供暖形成产业,替代了燃煤,缓解了该地区的雾霾(王贵玲,2017b;庞忠和等,2017)。
雄安新区共分布有牛驼镇地热田、容城地热田和高阳地热田北部三个碳酸盐岩地热田。其中,牛驼镇地热田和容城地热田具有多年开发研究历史,而高阳地热田的开发时间较晚,研究程度较低(陈墨香等,1982;周瑞良等,1989)。2017年党中央和国务院决定设立雄安新区以来,自然资源部中国地质调查局在该区部署实施了一系列的地热资源勘查研究工作,推动了华北地区中高温地热资源的开发利用研究。其中,中国地质调查局中国地质科学院于2020年在雄安新区高阳地热田部署的D34钻孔成功揭露了高于庄组热储,该井完钻深度4507 m,井口温度达123.4 ℃,为华北盆地最高温地热井,可用于地热发电。该井出水量为94.5 m3/h,但前人研究表明雄安新区高于庄组热储最大水量超过170 m3/h(王贵玲等,2018)。此外,目前已查明高于庄组热储特征,认为其热储温度高、流体流量大、岩溶裂隙较发育、含水层占比高、热储发育面积广等特点,是除雾迷山组热储以外的另一主力热储(王贵玲等,2018;王思琪等,2021;邢一飞等,2022)。因此,压裂增产是提高高于庄组地热开发利用率的重要举措之一。
岩石强度是岩石抵抗外力破坏的能力(赵秀娟等,2012),其对设计压裂增产方案具有重要意义(曾立新,1999)。因此,在开展压裂增产实验之前,需要厘清储层岩石在不同围压下的破碎规律。本次研究对雄安新区高阳地热田高于庄组储层碳酸盐岩开展了不同围压下的常规三轴压缩实验和抗拉实验,收集了相关力学参数,通过应力-应变曲线及位移-负荷特征,结合强度特征,阐明高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩在不同围压下的破坏损伤规律,以为压裂增产方案的制订提供重要的参考,最终服务于地热的开发利用,实现对高于庄组地热资源利用的最大化,使产研成果转化的效果达到最佳。
2. 试验
2.1 试样的选取与制备
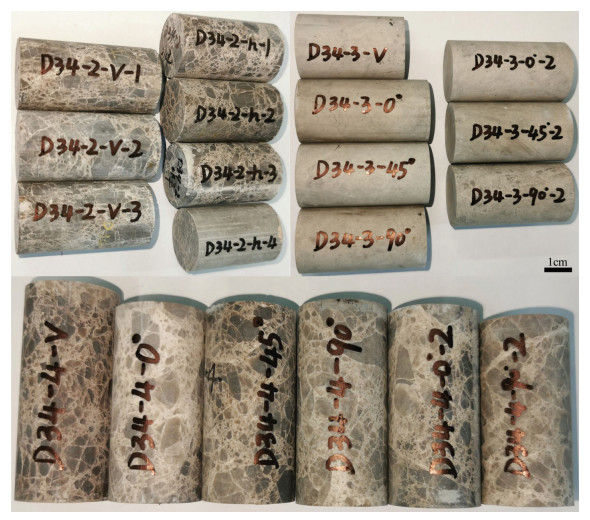
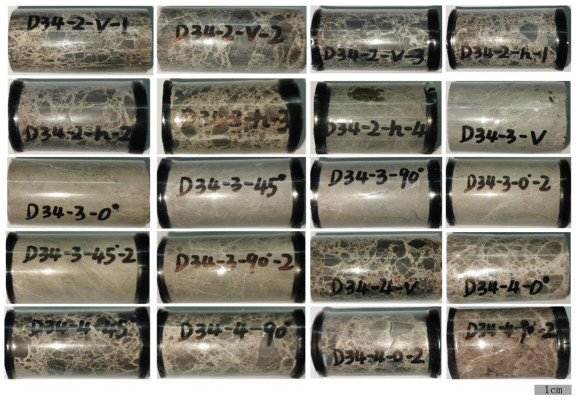
本次实验研究所用岩心D34-2、D34-3和D34-4为取自雄安新区高阳地热田D34井热储高于庄组不同深度的碳酸盐岩,样品埋深分布在4195~4506 m。其中,D34-2和D34-4白云岩样品具有隐爆后被石英胶结的特征,D34-3为未受热液活动改造的灰色泥晶白云岩,其矿物组成见表 1。通过岩心切割机和双面磨光机对所获得的3块岩心样品进行加工,共制成20件试样(图 1)。20件试样的具体参数见表 2。
表 1 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩全岩及黏土矿物X-射线衍射定量分析结果Table 1. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis results of whole rock and clay minerals of reservoir carbonate rock in D34 well, Gaoyuzhuang Formation 表 2 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩单、三轴抗压强度实验结果及相关计算参数Table 2. Experimental results and calculated parameter of uniaxial and triaxial compressive strength of reservoir carbonate rock in D34 well, Gaoyuzhuang Formation
表 2 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩单、三轴抗压强度实验结果及相关计算参数Table 2. Experimental results and calculated parameter of uniaxial and triaxial compressive strength of reservoir carbonate rock in D34 well, Gaoyuzhuang Formation
2.2 试验设备及方法
2.2.1 抗压强度实验
本次研究开展了不同围压下单轴及三轴强度试验,三轴抗压测试分6级进行,围压分别为0 MPa、10 MPa、20 MPa、30 MPa、40 MPa及50 MPa,所用设备如图 2所示,实验破坏前照片见图 3。主要实验过程为:首先将加工好的岩样放入高压釜内;打开计算机数据采集系统,调好程序;三轴试验时,通过高压泵施加围压到一定值,然后开启液压机给试样加轴向载荷,由数据采集系统记录加载过程中岩样的应力和应变,直至岩样产生破坏,停止加载,加载速率为0.02~0.04 mm/min;待实验结束,由计算机数据采集系统绘出应力-应变曲线,保存文件或由打印机打印输出。
2.2.2 抗拉强度实验
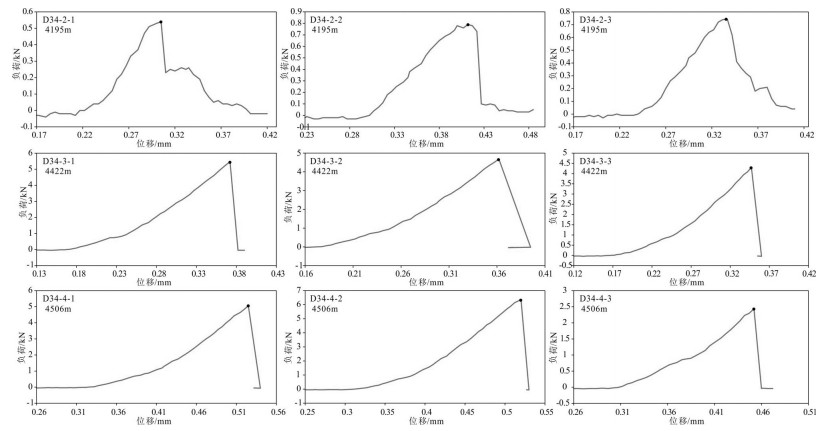
本次研究采用间接试验方法确定拉伸强度,所用设备如图 4所示,即在压机压盘之间对岩石圆柱体施加径向压力,使试件在加载平面内以拉伸破裂的方式发生破坏,该法又称巴西实验。实验过程如下:将加工好的标准岩柱切成如图 4所示薄片,将两根垫条沿加载基线固定在试件两端,然后放到压机上均匀加载,加载速率为1 mm/min,直至试件破坏(图 4),记录破坏载荷。
3. 试验结果及数据分析
3.1 抗压强度实验分析
3.1.1 应力-应变曲线特征
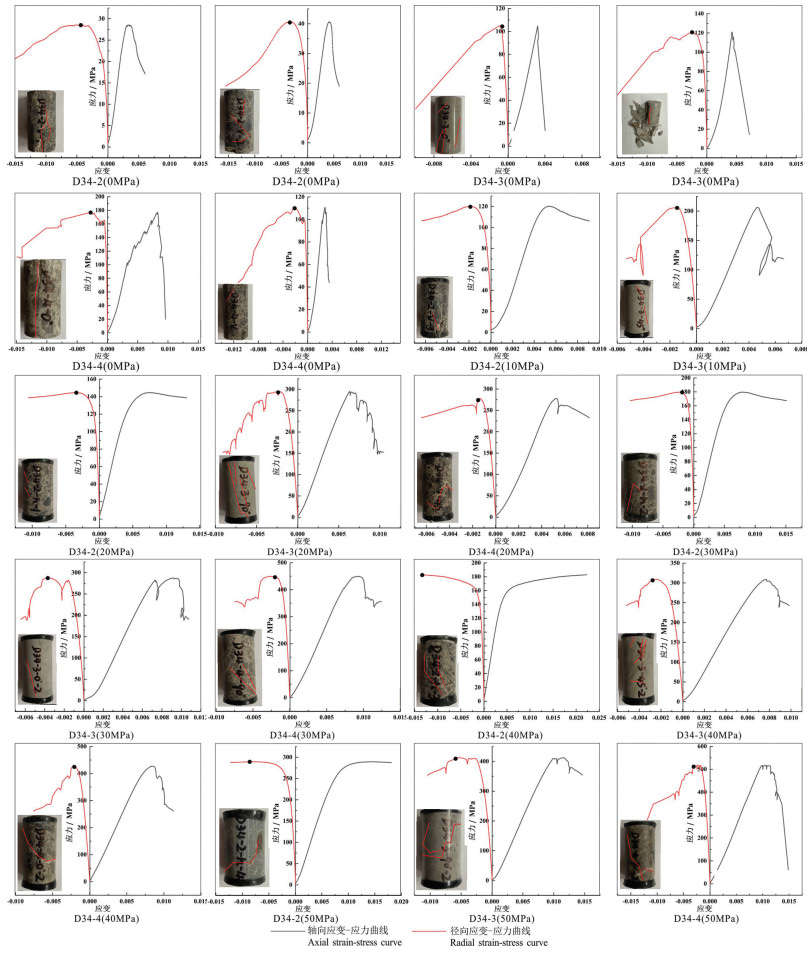
应力-应变曲线表征了岩石不同受力情况下的变形特征,是分析岩石力学破坏的基础依据,因此,对于特殊赋存环境下地层岩石的应力-应变曲线特征进行分析是非常有意义的(席道瑛和徐松林,2016)。高于庄组储层不同深度碳酸盐岩在三轴压缩应力作用下的应力-应变全程曲线特征如图 5所示,分别分析了在0 MPa、10 MPa、20 MPa、30 MPa、40 MPa和50 MPa不同围压下碳酸盐岩的轴向应变和径向应变。
(1)由图 5可知,在一定范围内,不同围压下,大部分样品应力-应变曲线在达到峰值应力后迅速跌落,破坏突然并伴有清脆响声。随后进入峰后残余变形阶段,岩石承载能力随变形增加而迅速跌落,但未降至0 MPa,说明破坏后的碳酸盐岩仍有微量的抗压能力。
(2)除D34-2样品外,各试件均在峰后产生较大径向应变,表明在环向应变控制下,岩石内应变缓慢释放,能够使得岩石稳定破碎。另外,大部分岩样在达到峰值强度后轴向应力迅速跌落,而仅有少量试件在峰后进入残余阶段,具有一定的残余强度,表现出较强的脆性破坏特征。同时说明,在50 MPa围压下储层碳酸盐岩不足以由脆性向塑性转化。碳酸盐岩的弹性阶段随初始围压的增大而增长,峰值强度和屈服强度随初始围压的增大而显著增强,在试验过程中表现出明显的围压效应。
(3)在不同围压下,除D34-2样品表现出明显的塑性破坏特征外,D34-3和D34-4均呈现为脆性破坏特征。说明储层浅部以塑性破坏为主,而深部则为脆性破坏。
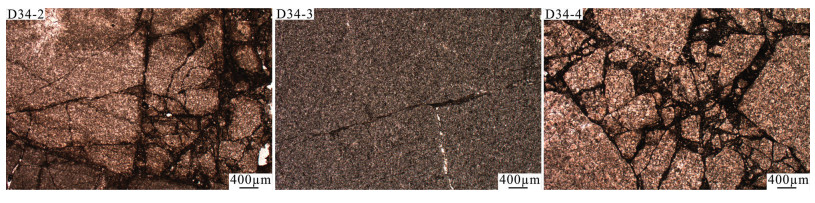
(4)三件样品的压缩屈服强度随着围岩压力的增大而增大,这种趋势D34-3和D34-4样品变化幅度大。且相同围压下,D34-3和D34-4屈服强度均比D34-2大。将压裂后外部宏观裂隙形态进行描绘,发现D34-3岩石的裂隙形态为多裂隙密布发展,而D34-2和D34-4岩样裂隙形态呈现单主裂隙。因D34-3和D34-4岩样屈服强度相近,认为裂隙发育形态不同可能是岩石本身的结构构造特征差异导致的,如前述,D34-2和D34-4白云岩样品有隐爆后被石英胶结的特征,D34-3为未受热液活动改造的灰色泥晶白云岩,且通过显微岩相学的观察发现,D34-2和D34-4样品天然裂隙较为发育,而D34-3天然裂隙发育情况较差(图 6)。此外,三件样品全岩矿物含量分析结果(表 1)表明,储层不同深度碳酸盐岩的矿物组成及成分较为一致,均为石英和白云石,且黏土矿物相对含量差别也不大,即热储碳酸盐矿物分布较为均匀。因此,尽管天然裂缝的发育情况有所差别,但并不是决定屈服强度的重要因素,针对此特征,认为可简化压裂方案,无需针对储层不同深度设计不同的压裂方案。
3.1.2 屈服强度特征
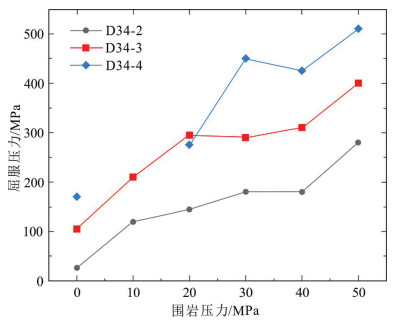
此外,本次研究还提取了三件样品在不同围压下的屈服强度变化曲线,进行定量分析如图 7所示。
分析发现,整体上,随着围岩压力的增大,储层不同深度碳酸盐岩屈服强度表现出先快速增大,后增大速度减缓,后又快速增大的变化趋势。其中,D34-3和D34-4在围岩压力时强度较为接近,但围岩压力超过20 MPa时,D34-4样品屈服强度发生了快速增长。整体上,20 MPa和40 MPa围岩压力是两个变化趋势转换的压力,该变化趋势与普通碳酸盐岩变化趋势有一定差别,表现出典型的二次增高的趋势。
3.1.3 弹性模量和泊松比
弹性模量和泊松比是岩石的重要力学参数,其变化会影响裂缝几何形状和渗透率(岳喜伟等,2014;郭亮亮,2016),因此本次研究在获得这两个参数的同时,列出了高于庄组储层碳酸盐岩在不同围压下弹性模量和泊松比的变化规律。
其中,弹性模量通过以下公式计算获得:

(1) 式中,E—弹性模量,MPa;△σa—轴向应力增量;△εa—轴向应变增量。
岩石泊松比的计算公式为:

(2) 式中,ν—岩石泊松比;△εa—轴向应变增量;△εr—径向应变增量。
弹性模量和泊松比的实验结果见表 1。不同围压下的弹性模量和泊松比变化趋势见图 8。
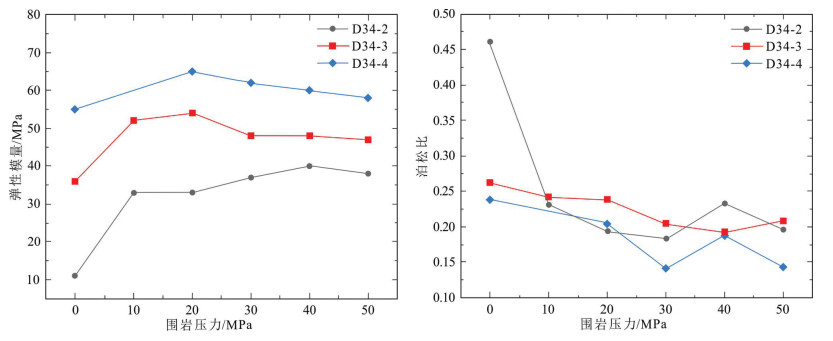
由图 8可知,随着围岩压力的增大,弹性模量先呈增加趋势,然后趋近于平衡。且弹性模量中D34-4 > D34-3 > D34-2,说明随着储层深度的增加,弹性模量有增加的趋势。三件样品强度在围岩20 MPa时,弹性模量发生明显变化,这与屈服强度的变化是一致的,而在40 MPa时弹性模量却未发生明显变化。泊松比的变化三者较为接近,在40 MPa表现出明显的波动。因此,可以认为在20 MPa围压时屈服强度的变化与引起弹性模量变化的因素相关,而在40 MPa时屈服强度的变化与引起泊松比变化的因素相关。因此,高温热储碳酸盐岩表现出自身力学的特性。
3.1.4 脆性指数
岩石的脆性指数是由泊松比和弹性模量共同决定的,是反映压裂效果的重要参数(Rickman et al., 2008)。本次研究在实验获得的弹性模量和泊松比值(表 1)的基础上,根据Rickman et al. (2008)提出的方法,计算了高于庄组热储层碳酸盐岩的脆性指数,所用公式如下:

(3) 
(4) 
(5) 式中,YM-BRIT—基于弹性模量的脆性计算值;YMS_C—弹性模量值;PR_BRIT—基于泊松比的脆性计算值;PR_C—泊松比值;BRIT—脆性指数。
计算结果见表 2。三件样品D34-2,D34-3和D34-4的脆性指数平均值分别为63.93、52.98和57.07,脆性指数越大,压裂效果越好。高于庄组碳酸盐岩整体压裂效果较好,储层浅部的压裂效果更优于深部,即随着深度的增加,压裂效果会降低,但总体脆性指数分布差异较小,故认为无需对储层不同深度采取不同的压裂施工方案。
3.2 抗拉特征
本次实验按下列公式计算岩石抗拉强度:

(6) 式中σt—岩石抗拉强度,Mpa;P —试件破坏荷载,N;D —试件直径,mm;h—试件厚度,mm。
表 3 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩抗拉实验结果Table 3. Tensile test results of the reservoir carbonate rock in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation of D34 well
结合图 9发现,D34-2岩石的抗拉强度在三件岩样中为最低,D34-3和D34-4抗拉强度较为接近,且岩石破碎过程中张拉特性和压缩特性变化趋势相同,说明随着储层深度的增加,抗拉强度呈增加趋势,但当深度增加到一定程度后,抗拉强度变化不大,且随着深度增大,张拉特性和压缩特性变化趋势也相同。由于D34-2样品深度最浅,表现出脆性指数较大,在拉伸破坏过程中,应力表现出缓慢锯齿状变化,说明该类岩石单次破坏范围小,以小结构单元破坏为主。而D34-3和D34-4岩石样品较D34-2深度较深,拉伸破坏曲线较为平滑,裂隙扩展形式为均匀破碎形式。说明储层浅部拉伸破坏以小结构单元破坏为主,而储层深部拉伸破坏以均匀破碎为主。
4. 结论
(1)高于庄组碳酸盐岩拉伸强度特征与压缩强度特征相近,且表现出明显的压缩破坏特征。随着围岩压力的增加,抗压强度具有典型的二次增高特征。
(2)抗压强度及裂隙展布形态随深度变化呈现出差异性,其中均匀发育的多裂缝和单一主缝为主要形式扩展。在20 MPa、40 MPa围压下,屈服强度分别与弹性模量、泊松比协同变化。
(3)储层不同深度拉伸裂隙的扩展方式有所差异,较浅部拉伸裂隙主要以小幅度多级扩展为主,而较深部岩石则表现出均匀扩展态势。
(4)储层浅部形成复杂压裂网络的可能性高于深部储层,但总体脆性指数分布差异较小,故认为无需对储层不同深度采取不同的压裂施工方案。
-
表 1 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩全岩及黏土矿物X-射线衍射定量分析结果
Table 1 Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis results of whole rock and clay minerals of reservoir carbonate rock in D34 well, Gaoyuzhuang Formation

表 2 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩单、三轴抗压强度实验结果及相关计算参数
Table 2 Experimental results and calculated parameter of uniaxial and triaxial compressive strength of reservoir carbonate rock in D34 well, Gaoyuzhuang Formation

表 3 D34井高于庄组热储碳酸盐岩抗拉实验结果
Table 3 Tensile test results of the reservoir carbonate rock in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation of D34 well

-
Chen Moxiang, Huang Geshan, Zhang Wenren, Zhang Rongyan, Liu Bingyi. 1982. The temperature distribution pattern and the utilization of geothermal water at Niutuozhen basement protrusion of central Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, (3): 239-252 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Goldstein B A, Hill A J, Long A, Budd A R, Holgate F, Malavazos M. 2009. Hot rock geothermal energy plays in Australia[R]. Proceedings, Thirty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California.
Guo Liangliang. 2016. Test and Model Research of Hydraulic Fracturing and Reservoir Damage Evolution in Enhanced Geothermal System[D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli, Wang Guiling. 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 40(1): 312-321 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Feng, Wang Guiling, Wei Shuaichao, Sun Zhanxue. 2019. Summary of hot research topics in geothermal exploration in 2018[J]. Science & Technology Review, 37(1): 134-143 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pang Zhonghe, Huang Shaopeng, Hu Shengbiao, Zhao Ping, He Lijuan. 2014. Geothermal studies in China: Progress and prospects 1995-2014[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 49(3): 719-727 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pang Zhonghe, Kong Yanlong, Pang Jumei, Hu Shengbiao, Wang Jiyang. 2017. Geothermal resources and development in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 32(11): 1224-1230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rickman R, Mullen M, Petre E, Grieser B, Kundert D. 2008. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Colorado: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 121-129.
Wang Jiyang, Sun Zhanxue. 2001. Magical Geothermal[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Lin Wenjing, Liu Feng, Zhu Xi, Liu Yanguang, Li Jun. 2017a. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tijian-Hebei region[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1074-1085 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Liang Jiyun, Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli. 2017b. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(4): 449-459 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Li Jun, Wu Aimin, Zhang Wei, Hu Qiuyue. 2018. A study of the thermal storage characteristics of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, a new layer system if thermal reservoir in Rongcheng uplift area, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 39(5): 533-541 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Wanli Wang, Wei Zhang, Feng Ma, Feng Liu. 2020. The status quo and prospect of geothermal resources exploration and development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China[J]. China Geology, 3: 173-181. doi: 10.31035/cg2020013
Wang Siqi, Zhang Baojian, Ma Yan, Li Yanyan, Xing Yifei, Yuan Wenzhen, Li Jun, Gao Jun, Zhao Tian. 2021. Heat accumulation mechanism of deep ancient buried hill in the Northeast of Gaoyang geothermal field, Xiong'an New Area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(3): 12-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Shuaichao, Zhang Wei, Fu Yong, Liu Feng, Wang Guiling, Yuan Ruoxi, Yan Xiaoxue, Liao Yuzhong. 2023. Distribution characteristics and resource potential evaluation of lithium in geothermal water in China[J]. Geology in China, doi: 10.12029/20230214001(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xi Daoying, Xu Songlin. 2016. Petrophysics and Constitutive Theory[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xing Yifei, Wang Huiqun, Li Jie, Teng Yanguo, Zhang Baojian, Li Yanyan, Wang Guiling. 2022. Chemical field of geothermal water in Xiong'an New Area and analysis of influencing factors[J]. Geology in China, 49(6): 1711-1722 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yue Xiwei, Dai Junsheng, Wang Ke. 2014. Influence of rock mechanics parameters on development of fracture[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 20(4): 372-378 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Lixin. 1999. Laboratory test methods study of deep rock physical mechanics[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 5: 1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Xiujuan, Zhang Xujiao, Li Zongmin, Wu Zhonghai, Ye Peisheng, Sun Dongsheng, Lü Yong. 2012. The engineering mechanical properties of the rock mass along the Dali-Ruili railway, western Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31: 366-373 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Keyan. 2009. Strategic Development of Geothermal Energy[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Ruiliang, Liu Qisheng, Zhang Jing, Yang Liqiang. 1989. The geothermal features and exploitive prospects of the geothermal field of salient type of bed rock of Niutuozhen in the fault basin of north China[C]//Bulletin of the 562 Comprehensive Geological Brigade Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, (7/8): 21-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈墨香, 黄歌山, 张文仁, 张容燕, 刘炳义. 1982. 冀中牛驼镇凸起地温场的特点及地下热水的开发利用[J]. 地质科学, (3): 239-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198203000.htm 郭亮亮. 2016. 增强型地热系统水力压裂和储层损伤演化的试验及模型研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学. 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 王贵玲. 2013. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 40(1): 312-321. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20130121?st=search 马峰, 王贵玲, 魏帅超, 孙占学. 2019. 2018地热勘探开发热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 37(1): 134-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201901016.htm 庞忠和, 黄少鹏, 胡圣标, 赵平, 何丽娟. 2014. 中国地热研究的进展与展望(1995-2014)[J]. 地质科学, 49(3): 719-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201403002.htm 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 庞菊梅, 胡圣标, 汪集旸. 2017. 雄安新区地热资源与开发利用研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 32(11): 1224-1230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202107025.htm 汪集旸, 孙占学. 2001. 神奇的地热[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社. 王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 刘峰, 朱喜, 刘彦广, 李郡. 2017a. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1074-1085. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20170603?st=search 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽. 2017b. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 38(4): 449-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704002.htm 王贵玲, 李郡, 吴爱民, 张薇, 胡秋韵. 2018. 河北容城凸起区热储新层系-高于庄组热储特征研究[J]. 地球学报, 39(5): 533-541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805003.htm 王思琪, 张保建, 马岩, 李燕燕, 邢一飞, 袁文真, 李郡, 高俊, 赵甜. 2021. 雄安新区高阳地热田东北部深部古潜山聚热机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 40(3): 12-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103002.htm 魏帅超, 张薇, 付勇, 刘峰, 原若溪, 闫晓雪, 廖煜钟, 王贵玲. 2023. 我国地热水中锂元素分布特征及资源开发利用[J]. 中国地质, dio: 10.12029/20230214001. doi: 10.12029/20230214001 席道瑛, 徐松林. 2016. 岩石物理学与本构理论[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社. 邢一飞, 王慧群, 李捷, 滕彦国, 张保健, 李燕燕, 王贵玲. 2022. 雄安新区地热水的化学场特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质, 49(6): 1711-1722. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220601?st=search 岳喜伟, 戴俊生, 王珂. 2014. 岩石力学参数对裂缝发育程度的影响[J]. 地质力学学报, 20(4): 372-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201404005.htm 曾立新. 1999. 深层岩石力学性质的试验方法[J]. 地质力学学报, 5: 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX901.010.htm 赵秀娟, 张绪教, 李宗敏, 吴中海, 叶培盛, 孙东生, 吕勇. 2012. 滇西大理至瑞丽铁路沿线岩石力学参数的测定及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 31: 366-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2012Z1020.htm 郑克棪. 2009. 地热能的战略开发[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 周瑞良, 刘琦胜, 张晶, 杨力强. 1989. 华北断陷盆地牛驼镇基岩高凸起型热田地质特征及其开发前景[C]. 中国地质科学院562综合大队集刊, (7/8): 21-36. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李红岩,高小荣,任小庆,孙彩霞,卢星辰,许勇. 雄安新区三维地热地质模型方法研究. 地质与资源. 2024(02): 222-229+236 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱思雨,曹佳文,丰成君,王继明,孟静,戚帮申,张鹏. 河北高阳低凸起深部热储层回灌注水诱发断层失稳危险性探讨. 地质力学学报. 2023(02): 220-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨睿月,黄中伟,温海涛,丛日超,胡晓丽,马峰. 雄安新区深部地热储层水力喷射酸化压裂技术. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版). 2023(12): 1277-1287 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 韩博,夏雨波,马震,王小丹,郭旭,林良俊,裴艳东. 雄安新区工程地质层组划分、三维地质结构构建及其在城市规划建设中的应用. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1903-1918 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 邢一飞,王慧群,李捷,滕彦国,张保健,李燕燕,王贵玲. 雄安新区地热水的化学场特征及影响因素分析. 中国地质. 2022(06): 1711-1722 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: