Property and source of the ore–forming fluids and genesis of the Sidaogou scheelite deposit in the eastern Yanbian area, Jilin Province
-
摘要:研究目的
四道沟钨矿床位于延边东部Au–Cu–W矿集区,是具代表性的石英脉型白钨矿矿床。本文通过该矿床的成矿流体性质、来源及矿床成因研究,以提升东北地区石英脉型白钨矿矿床的成矿理论认识,并为该类型白钨矿进一步找矿提供理论支撑。
研究方法本文开展了主成矿阶段含白钨矿–石英脉流体包裹体岩相学、显微测温和激光拉曼光谱分析,并配合C–H–O同位素和白钨矿稀土元素分析。
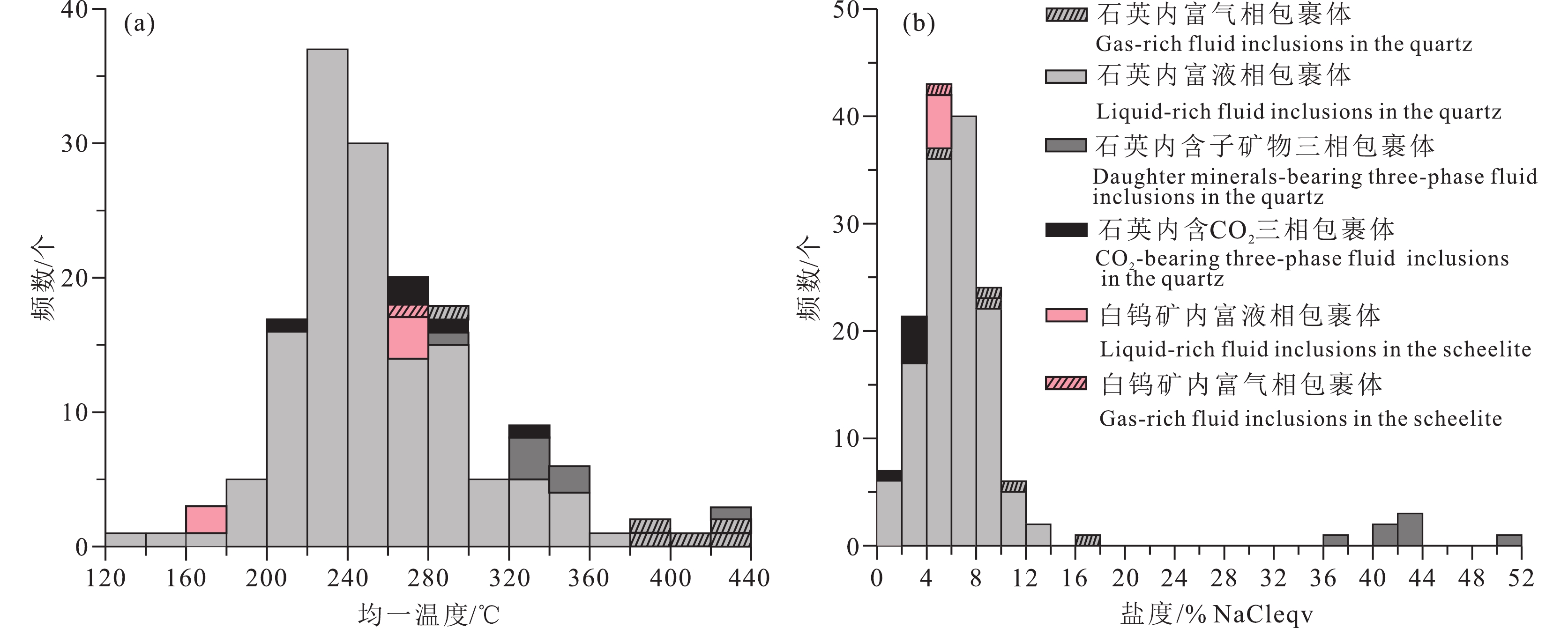
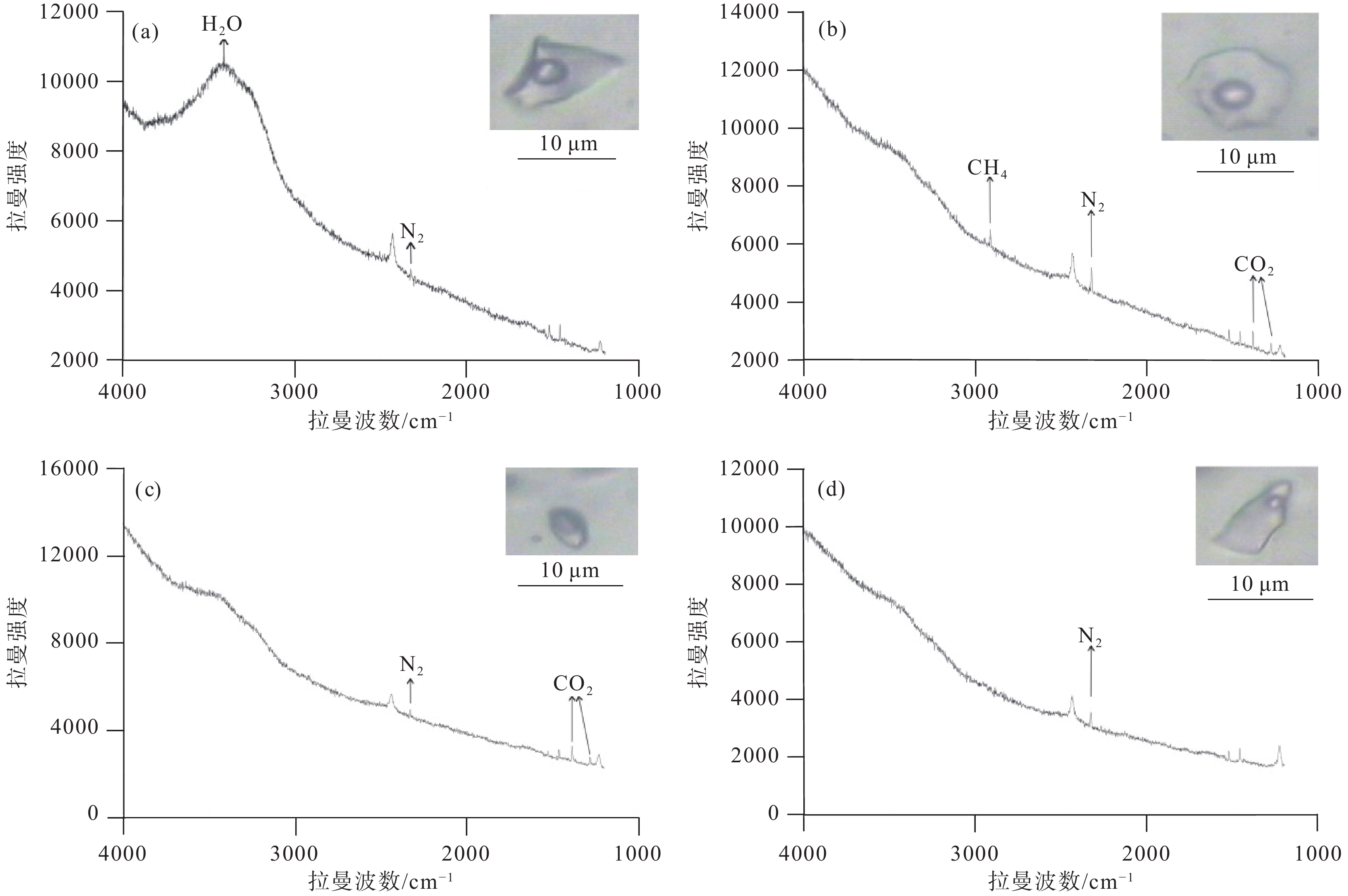
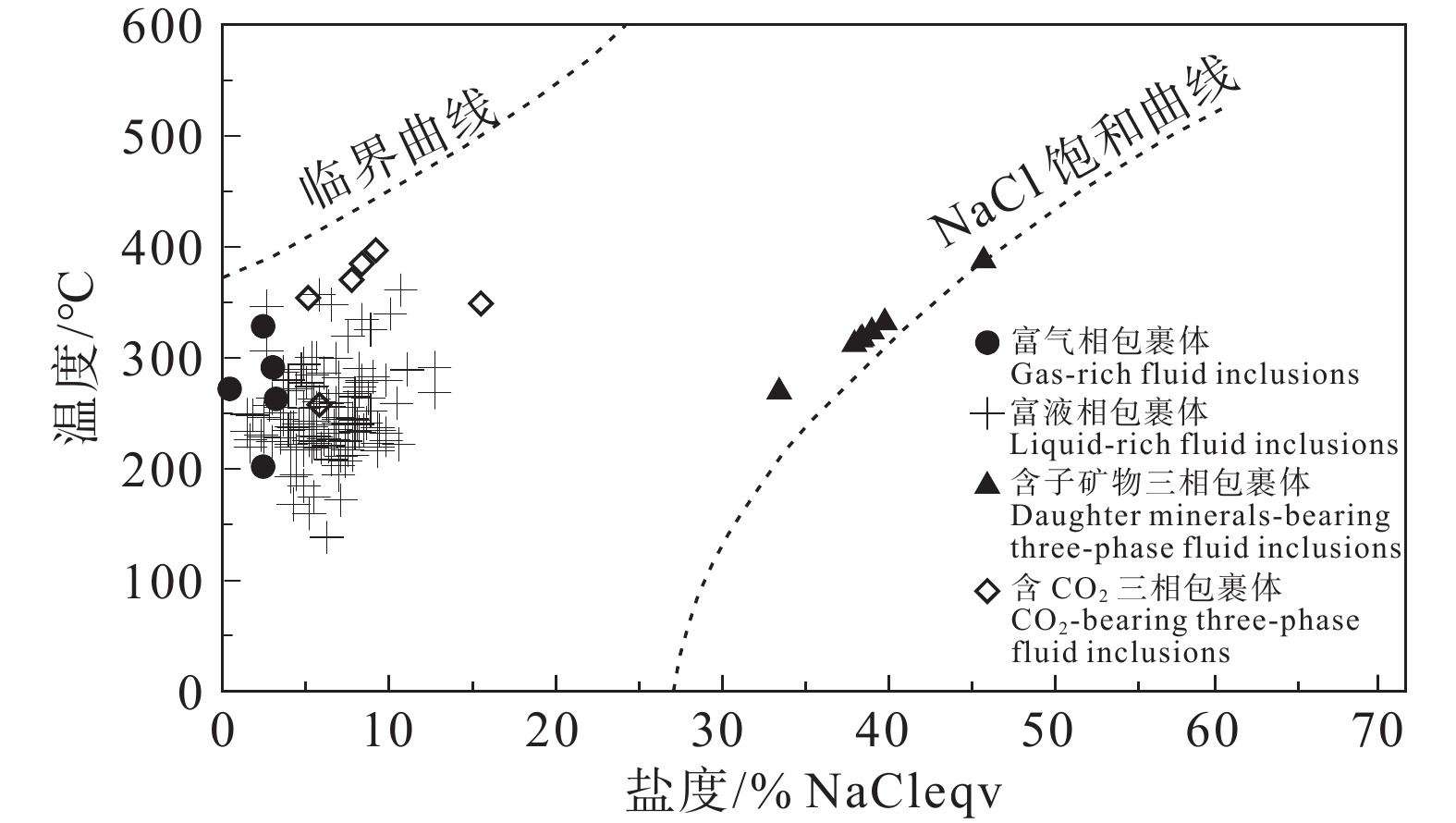
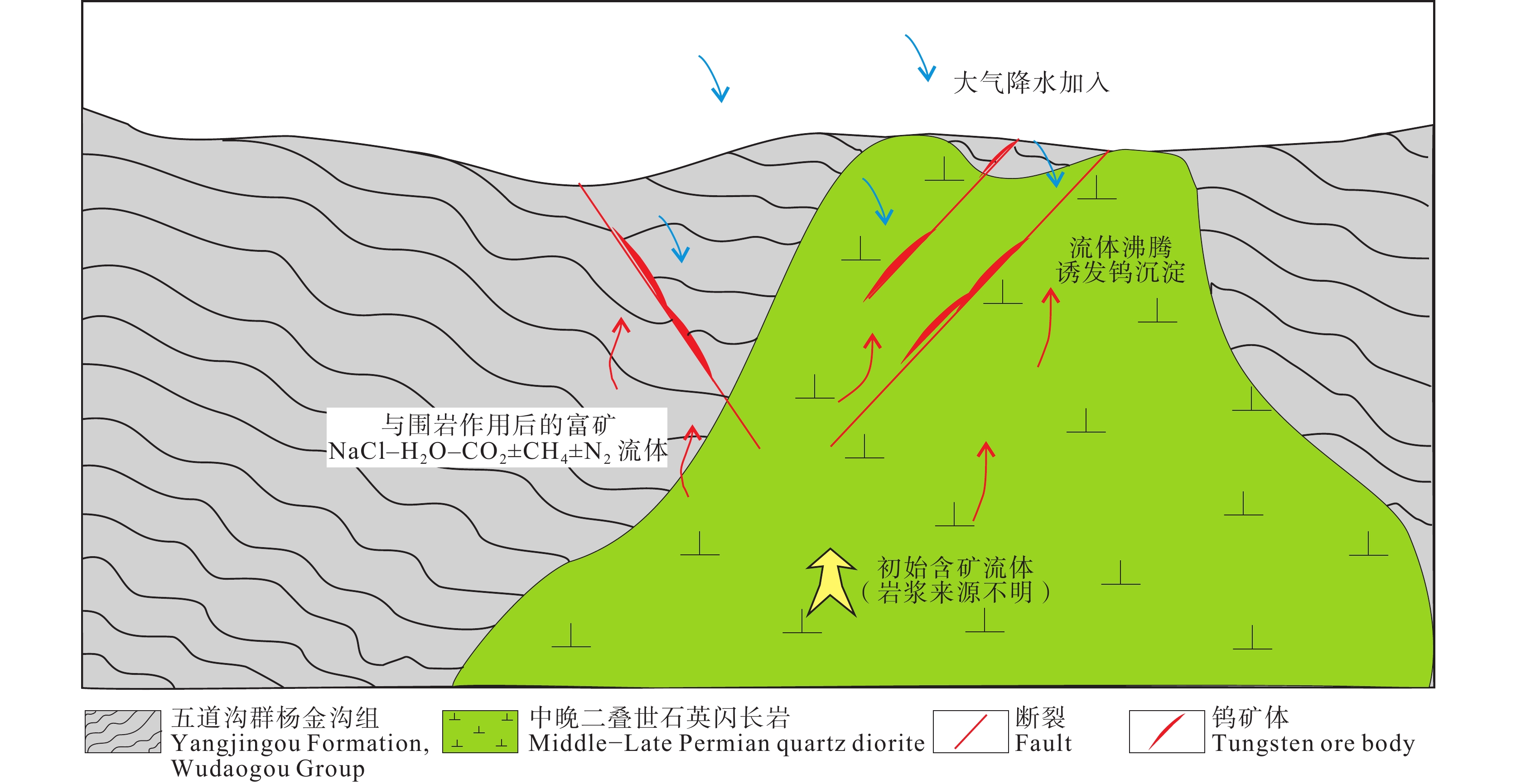
研究结果流体包裹体岩相学及显微测温相关研究结果显示,主成矿阶段石英中同时分布有富气相、富液相、含石盐子矿物三相以及含CO2三相等类型原生水溶液包裹体,这些不同类型流体包裹体的均一温度大体一致,应属于沸腾流体包裹体。富气端元流体包裹体的最低均一温度为283℃,基本代表了成矿温度。激光拉曼光谱分析结果显示,成矿流体中气相成分以H2O和CO2为主,还有少量N2和CH4。四道沟白钨矿呈现出“驼峰式”的稀土元素配分型式以及弱的负δEu异常。
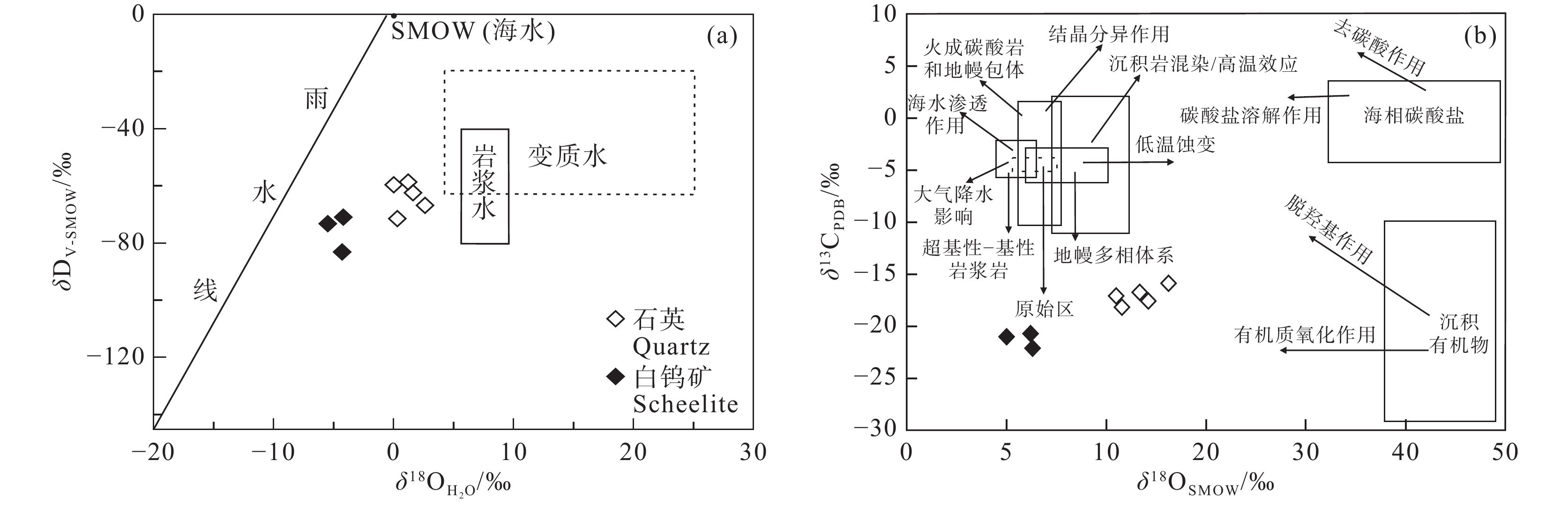
结论四道沟钨矿床的成矿流体为氧化性的、高中温的NaCl–H2O–CO2±CH4±N2的流体。C–H–O同位素分析结果表明,成矿流体主要为岩浆水,还有少量大气降水的加入,而流体中的碳主要来源于五道沟群变质沉积岩系的有机物氧化作用。四道沟钨矿床为中温岩浆热液型钨矿床,流体沸腾作用是白钨矿大规模沉淀的主要机制。
创新点:采用白钨矿流体包裹体与稀土元素相关分析,确定成矿流体性质和成矿机制。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveSidaogou deposit is located in the Au–Cu–W ore concentrated area of the eastern Yanbian, and is a typical quartz vein type scheelite deposit. This paper studied the property and source of the ore–forming fluids and genesis of the deposit, to promote the understanding of the quartz vein type scheelite deposit in NE China and further prospecting.
MethodsThis paper presents the petrographic observation, microtemperature measurement and Laser Roman spectral analysis of the fluid inclusion, C–H–O isotope analysis and rare earth element compositions for the Sidaogou scheelite–quartz veins.
ResultsPetrographic observation indicates that the liquid–rich, daughter minerals–bearing, gas–rich, and CO2–bearing inclusions coexisted in the quartz, and all the types of fluid inclusions have similar homogenization temperatures, which indicate that they belong to boiling fluid inclusions. The lowest homogenization temperature of the gas–rich fluid inclusion (283℃) represents the ore−forming temperature. Laser Raman spectral analysis indicates that the gas phases in the fluid inclusions include H2O and CO2, as well as minor CH4 and N2. Scheelite grains yield “hump” type REE patterns with weak negative δEu anomalies.
ConclusionsThe results indicate that the ore–forming fluids of the Sidaogou scheelite deposit are oxidizing NaCl–H2O–CO2±CH4±N2 fluids with high–medium temperature. C–H–O isotopic data indicate that the ore–forming fluids were mainly derived from magmatic water, mixed with a little bit of meteoric water, and the carbonaceous material resulted from oxidation of organic material in the sedimentary rocks from the Wudaogou Group. Therefore, Sidaogou scheelite deposit belongs to mesothermal vein type scheelite deposit, and the fluid boiling induced the precipitation of scheelite.
Highlights:The fluid inclusions and rare earth element compositions of scheelite were analyzed to determine the nature of ore–forming fluids and metallogenetic mechanism.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
湘中坳陷作为南方复杂构造区页岩气勘探的热点地区之一,也是中国油气勘探久攻未克的地区。前期在湘中地区北部的涟源凹陷泥盆系和石炭系获得了页岩气突破和发现,证实了湘中地区上古生界页岩气资源丰富。但对湘中地区南部的邵阳凹陷调查程度较为薄弱,针对邵阳凹陷二叠系仅开展了少量基础地质调查工作,页岩气资源潜力评价方面的工作尤为欠缺。本次研究依托邵阳湘邵地1井(XSD1井)钻探工程建立了邵阳凹陷二叠系地层层序序列,揭示了主要含气页岩层系的分布特征,获取了含气性评价参数,对湘中地区二叠系页岩气勘探开发和重新评价湘中坳陷页岩气资源潜力具有重要的现实意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心在收集分析区域地质相关资料的基础上,结合邵阳凹陷短陂桥向斜的煤田浅钻、非震物探等资料开展页岩气地质综合评价,采用页岩埋深500~4500 m,页岩有机碳含量≥1.0%,页岩厚度≥15 m,页岩有机质热演化程度1.0%~3.5%的评价参数在短陂桥向斜区优选页岩气远景区,论证部署了1口小口径页岩气地质调查井—XSD1井,湖南煤田地质勘查有限公司组织实施钻探(图 1a)。该井采样全井段取心钻井工艺,测井选取PSJ-2数字测井系统,录井采用SK-2000G气测录井,钻获二叠系大隆组156.05 m(暗色硅质页岩、钙质泥岩94.48 m),龙潭组349.95 m(暗色泥岩216.93 m,粉砂质泥岩36.9 m),对这两套层系共采集暗色泥岩样品33件,进行解析气含量测定分析,落实了含气性评价参数。
3. 结果(Results)
本次样品分析工作由武汉地质调查中心古生物与生命-环境协同演化重点实验室完成,采用YSQ-IIIA岩石解析气测定仪(燃烧法)对含气段岩心共计33件样品进行分析。该井钻获二叠系大隆组厚度156.05 m,为一套硅质岩、硅质页岩、炭质钙质泥岩地层。其中在井深842~930.2 m硅质页岩、钙质泥岩段,气测全烃值从1.06%上升至16.54%,甲烷值从1.01%上升至14.04%,13件大隆组硅质页岩现场解析总含气量为1.29~9.97 m3/t,平均4.85 m3/t。实现了湘中坳陷二叠系页岩气新发现,有效拓展了华南地区大隆组勘探范围。
钻获龙潭组厚度349.95 m,上段为一套细砂岩、粉砂岩夹泥岩潮坪相沉积地层,下段为一套炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹薄层细砂岩泻湖相沉积地层。在井深1013.4~1048 m泥岩与粉砂岩互层段气测全烃值最高可达19.87%,甲烷值最高为16.94%,7件泥岩与粉砂岩样品现场解析总含气量0.57~3.42 m3/t,平均1.78 m3/t;井深1088.10~1199.75 m泥岩夹泥质粉砂岩含气层111.6 m,气测全烃值最高可达28.2%,甲烷值最高为23.6%,13件泥岩、粉砂质泥岩样品现场解析总含气量0.90~4.55 m3/t,平均2.01 m3/t(图 1b),首次查明了湘中坳陷二叠系龙潭组非常规油气分布特点。
通过区域地质背景分析,并结合煤田区域地质资料,本研究认为滑脱断裂(F9)上下盘具有不同的页岩气聚集条件。滑脱断裂之上由一系列的同向逆断层形成的逆冲推覆体,地层变形强烈,且裂缝发育,导致页岩气保存条件变差。滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,地层平缓,不发育次级通天断裂,与下盘地层形成反向遮挡,易形成封闭,保存条件良好(图 1c)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)二叠系大隆组岩性以硅质岩、硅质页岩为主,夹少量灰岩。主要含气段存在于上段硅质页岩段,厚88.2 m,含气量平均为4.85 m3/t,含气性优越,资源潜力大。
(2)二叠系龙潭组上段以致密砂岩气为主,含气量平均为1.78 m3/t;下段以页岩气为主,泥岩厚达177.47 m,含气量平均为2.01 m3/t,具有泥岩厚度大,含气性好等特征。
(3)保存条件是页岩气富集关键,构造改造弱的封闭演化环境有利于页岩气保存,研究区滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,易形成封闭,保存条件良好。
(4)湘邵地1井在二叠系大隆组和龙潭组获得良好的页岩气显示,证实了湘中地区二叠系具有良好的页岩气资源潜力,对湘中地区页岩气资源潜力评价具有重要意义。
5. 基金项目(Fund support)
本文为中国地质调查局项目“中扬子地区油气页岩气调查评价”(DD20221659)资助的成果。
-
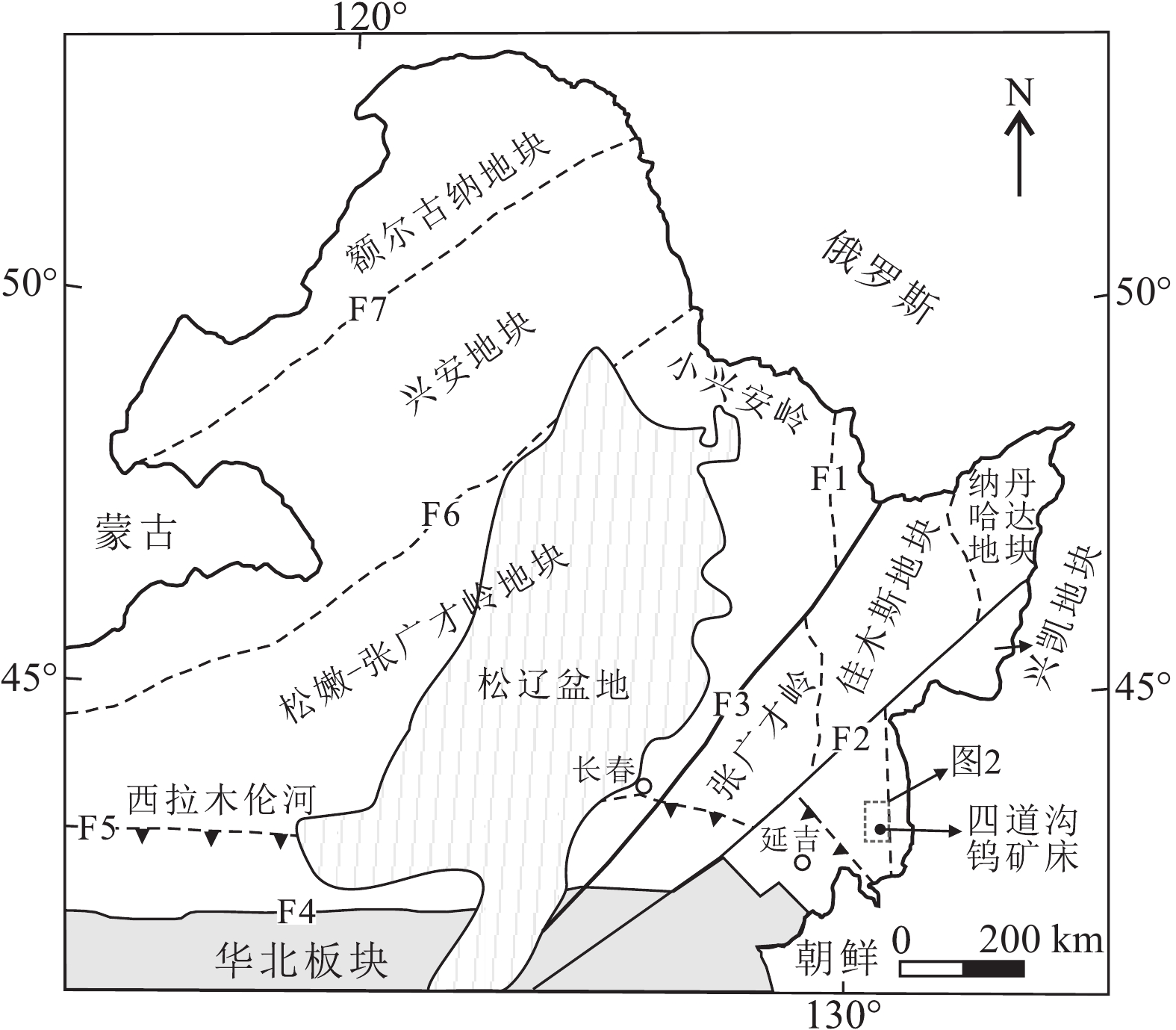
图 1 东北地区构造划分及延边东部地区构造位置(据Wu et al., 2011修改)
F1—牡丹江断裂;F2—敦化—密山断裂;F3—伊通—依兰断裂;F4—赤峰—开原—海龙—富尔河—龙井县白金断裂;F5—西拉木伦—长春—汪清—珲春缝合带;F6—贺根山—黑河断裂;F7—塔源—喜桂图断裂
Figure 1. Tectonic division of the NE China and tectonic location of the eastern Yanbian area (modified from Wu et al., 2011)
F1–Mudanjiang fault; F2–Dunhua–Mishan fault; F3–Yitong–Yilan fault; F4–Chifeng–Kaiyuan–Hailong–Fuerhe–Baijin fault; F5–Xar Moron River–Changchun–Wangqing–Hunchun suture zone; F6–Hegenshan–Heihe fault; F7–Tayuan–Xiguitu fault
图 4 四道沟白钨矿矿石手标本照片(a)及显微镜下照片(b、c、d)
a—含团块状白钨矿石英脉矿石;b—单偏光镜下石英脉矿石内的白钨矿半自形集合体;c、d—含矿石英闪长岩体发育的磁黄铁矿化;Qtz—石英;Sch—白钨矿;Po—磁黄铁矿
Figure 4. Photographs (a) and micrographs (b, c, d) of the Sidaogou scheelite ores
a–Massive scheelit–quartz vein ores; b–Scheelite aggregates in the quartz vein under a plane polarizedlight; c, d–Pyrrhotite mineralization within the ore-hosting quartz diorite; Qtz–Quartz; Sch–Scheelite; Po–Pyrrhotite
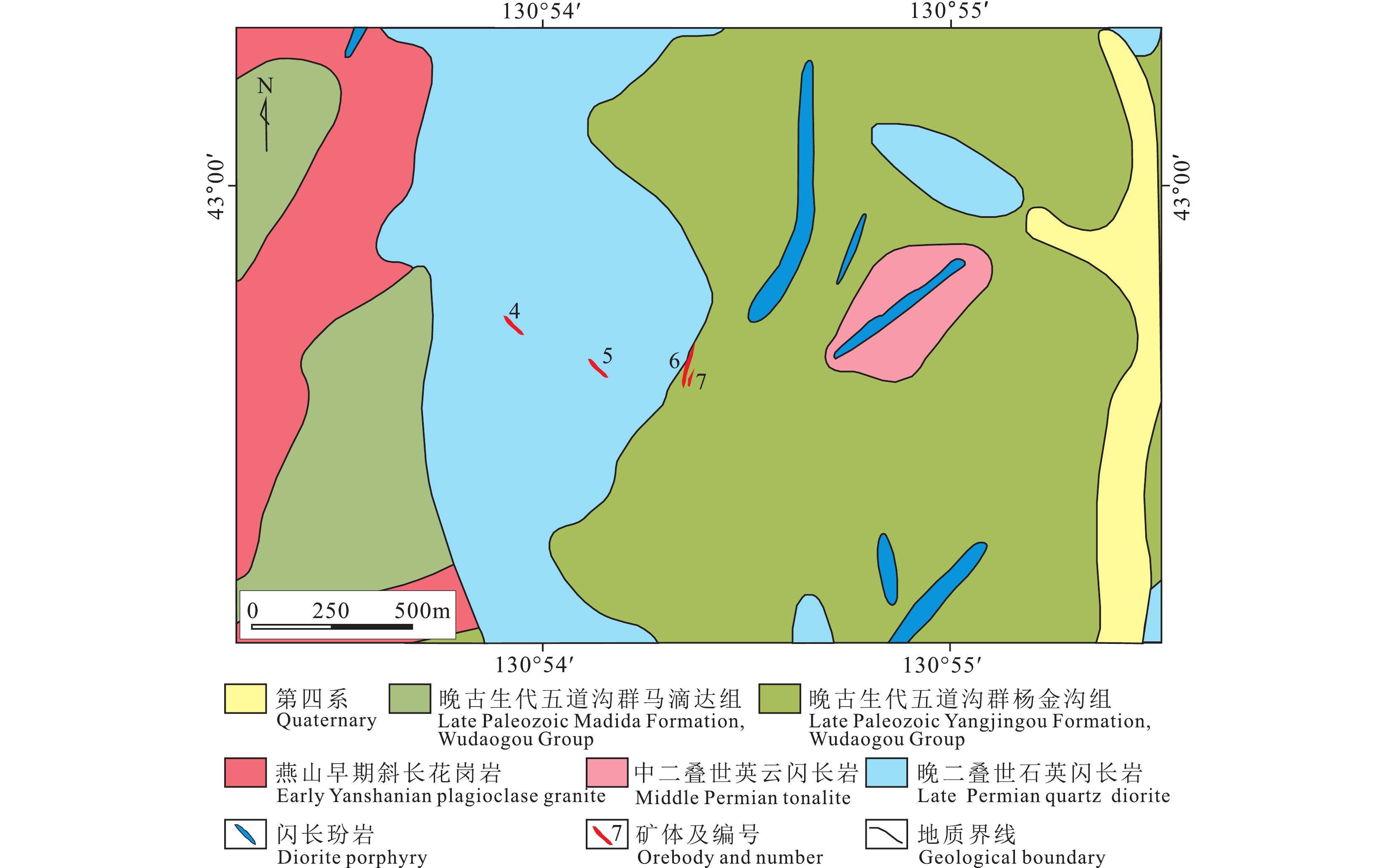
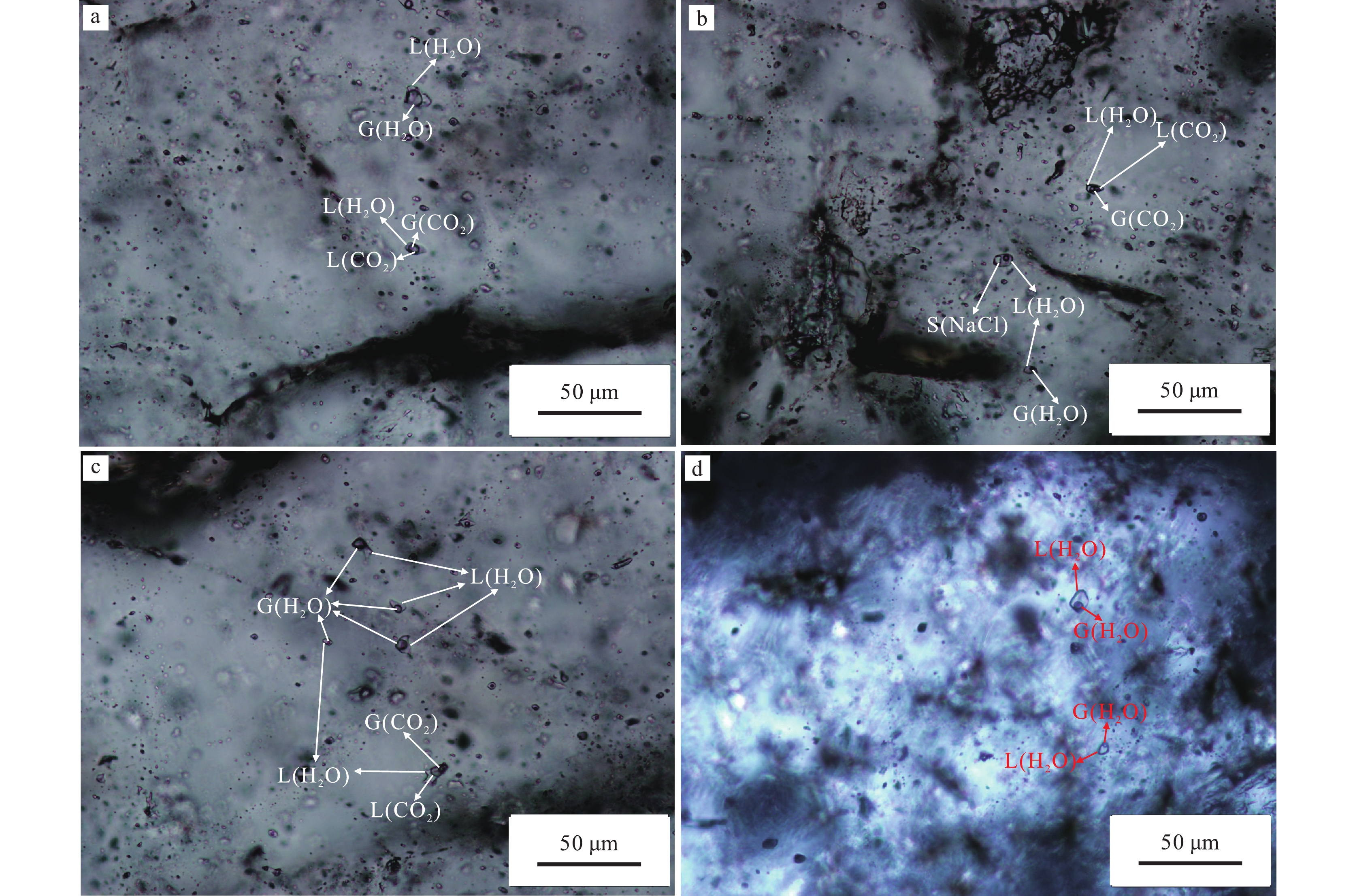
图 5 四道沟钨矿床流体包裹体显微照片
a—石英中含有富气相及含CO2三相包裹体;b—石英中富液相、含石盐子矿物三相包裹体及含CO2三相包裹体共生;c—石英中富液相、含CO2三相包裹体及富气相包裹体共生;d—白钨矿内富液相包裹体
Figure 5. Micrographs of the fluid inclusions in the Sidaogou scheelite deposit
a–Gas–rich fluid inclusions and CO2–bearing three–phase fluid inclusions within the quartz; b–Liquid–rich fluid inclusions and daughter minerals–bearing three–phase fluid inclusions within the quartz; c–Liquid–rich fluid inclusions, CO2–bearing three–phase fluid inclusions, and gas–rich fluid inclusions within the quartz; d–Liquid–rich fluid inclusions within the scheelite grains
图 8 四道沟钨矿床δ18OH2O–δDV−SMOW(a,底图据Taylor, 1974)与δ18OSMOW–δ13CPDB图解(b,据Ray et al., 1999;Hoefs, 2009)
Figure 8. Diagrams of δ18OH2O–δDV−SMOW (a, after Taylor, 1974) and δ18OSMOW–δ13CPDB (b, after Ray et al., 1999; Hoefs, 2009)
图 9 四道沟钨矿床白钨矿球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(标准化数据值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 9. Chondrite–normalized REE patterns of the scheelite in the Sidaogou deposit (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
表 1 四道沟钨矿样品特征
Table 1 Characteristics of the Sidaogou scheelite deposit
样品类型 成矿阶段 采样位置 测试手段 测试对象 样品数量 样品特征 石英−粗粒
白钨矿矿石早期石英−粗粒
白钨矿阶段5号钨矿体
地表探槽流体包裹体岩相学及显微测温 石英和白钨矿 2件 含粗粒团块状白钨矿的石英脉 激光拉曼光谱分析 石英 2件 含粗粒团块状白钨矿的石英脉 C–H–O同位素 白钨矿 3件 粗粒、团块状白钨矿 石英 5件 含粗粒团块状白钨矿的石英脉 ICP–MS稀土元素 白钨矿 3件 粗粒、团块状白钨矿 表 2 四道沟钨矿床石英和白钨矿中流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 2 Microthermometric results of fluid inclusions within the quartz and scheelite of the Sidaogou scheelite deposit
样品号 成矿
阶段测试
矿物包裹体类型
(测试数量)冰点温度/
℃子晶溶解
温度/℃气泡消失
温度/℃CO2初熔
温度/℃CO2笼合物
熔化温度/℃CO2部分
均一温度/℃完全均一
温度/℃最终均
一方式s−2 石英−
粗粒
白钨矿
阶段石英 富液相(40) −5.7~−0.8 138~357 液相 s-3 石英 富液相(86) −10.0~−0.8 194~361 液相 富气相(6) −13.0~−4 283~435 气相 含子矿物三相(7) 280~423 273~362 294~423 液相,
子晶最终
融化为主含CO2三相(5) −69.8~−59.4 8~10 17~29 202~329 液相 白钨矿 富液相(5) −3.3~−2.5 160~278 液相 富气相(1) −4 284 气相 表 3 四道沟钨矿床C–H–O同位素分析结果
Table 3 C–H–O isotopic data of the Sidaogou scheelite deposit
编号 样品类型 δ13CV-PDB/‰ δDV-SMOW/‰ δ18OV-SMOW/‰ δ18OH2O/‰ S-1 白钨矿 −20.7 −83.2 6.2 −4.26 S-2 白钨矿 −22.1 −71.0 6.3 −4.16 S-3 白钨矿 −21.0 −73.3 5.0 −5.46 S-4 石英脉 −17.9 −71.5 10.8 0.34 S-5 石英脉 −17.3 −62.5 12.1 1.64 S-6 石英脉 −15.6 −66.9 13.1 2.64 S-7 石英脉 −16.8 −59.7 10.5 0.04 S-8 石英脉 −16.4 −58.7 11.7 1.24 表 4 四道沟钨矿床白钨矿稀土元素组成(10−6)
Table 4 Rare earth element compositions (10−6) of scheelite grains in the Sidaogou scheelite deposit
样品 SDG-1 SDG-2 SDG-3 La 1.79 1.78 1.76 Ce 7.94 7.96 7.58 Pr 1.69 1.68 1.76 Nd 12 12.1 11.8 Sm 7.28 7.35 7.52 Eu 2.78 2.82 2.92 Gd 16 16 16.1 Tb 3.7 3.78 3.84 Dy 32.1 32.8 32.8 Ho 7.54 7.74 7.72 Er 19.4 19.9 20 Tm 2.4 2.46 2.37 Yb 9.91 10.1 9.74 Lu 1.09 1.1 1.06 Y 214 214 210 ΣREE 125.62 127.57 126.97 LREE 33.48 33.69 33.34 HREE 92.14 93.88 93.63 LREE/HREE 0.36 0.36 0.36 (La/Yb)N 0.12 0.12 0.12 δEu 0.76 0.77 0.79 δCe 0.96 0.97 0.9 表 5 延边东部Au–Cu–W矿集区钨矿床地质特征对比
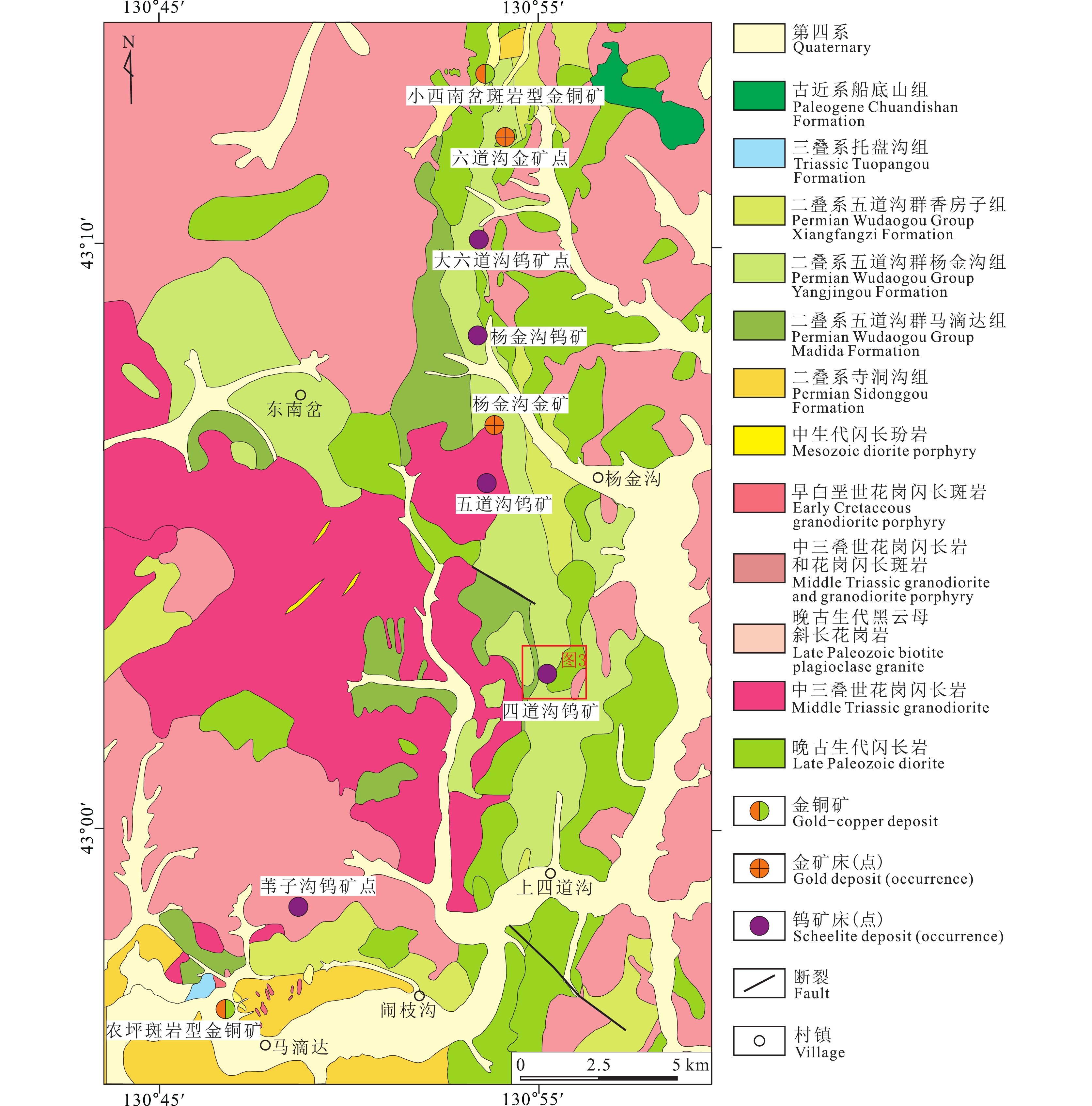
Table 5 Comparison of the geological characteristics in the scheelite deposits of the Au–Cu–W ore concentrated area of the eastern Yanbian
矿床名称 四道沟钨矿床 五道沟钨矿床 杨金沟钨矿床 赋矿地层 五道沟群杨金沟组 成矿相关岩体 晚二叠世石英闪长岩(I型) 中二叠世花岗闪长岩(I型) 晚二叠世英云闪长岩(I型) 控矿构造 NW向和NNE向断裂构造 岩体和围岩中的NW向断裂构造 NW、NWW向断裂或五道沟群中、上段的层间破碎带 矿体特征 沿石英闪长岩与五道沟群变质岩系接触带附近NW向和NNE向断裂呈石英细脉带状,矿体少,厚度小、品位高 沿花岗闪长岩体中的NW向断裂呈单脉状,矿体数量少,单脉厚度大、品位高 呈细脉、网脉状沿五道沟群中、上段的NW、NWW向断裂或层间破碎带分布,矿体数量多、厚度小、品位相对较低 金属矿物 白钨矿为主,少量磁黄铁矿 白钨矿为主,少量黄铁矿、辉钼矿、毒砂、磁黄铁矿、黄铜矿 以白钨矿为主,少量毒砂、磁黄铁矿、黄铁矿、黄铜矿等,偶见辉钼矿、铁闪锌矿 围岩蚀变 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、绿泥石化 硅化、钠长石化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、黑云母化和白云母化 硅化、钠长石化、黑云母化、白云母化及碳酸盐化 矿床成因 热液脉型矿床 资料来源 本文 陈聪等, 2015 任云生等, 2010 -
[1] Cao Huahua. 2010. Chronology and Geochemistry of Late Hercynian Gabbro and Diorite in Hunchun Area[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Chen C, Ren Y S, Zhao H L, Zou X T, Yang Q, Hu Z C. 2014. Permian age of the Wudaogou Group in eastern Yanbian: Detrital zircon U–Pb constraints on the closure of the Palaeo–Asian Ocean in Northeast China[J]. International Geology Review, 56(14): 1754−1768. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.956348
[3] Chen C, Ren Y S, Zhao H L, Yang Q, Zou X T. 2015. The whole–rock geochemical composition of the Wudaogou Group in Eastern Yanbian, NE China–New clues to its relationship with the gold and tungsten mineralization and the evolution of the Paleo–Asian Ocean[J]. Resource Geology, 65(3): 232−248. doi: 10.1111/rge.12068
[4] Chen C, Ren Y S, Zhao H L, Yang Q, Shang Q Q. 2017. Age, tectonic setting, and metallogenic implication of Phanerozoic granitic magmatism at the eastern margin of the Xing’an–Mongolian Orogenic Belt, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 144: 368−383. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.012
[5] Chen Cong. 2017. Late Paleozoic–Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution and Regional Metallogenic Regularity of the Eastern Yanbian Area, NE China[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Chen Cong, Ren Yunsheng, Zhao Hualei, Yang Qun, Zou Xintong, Hou Kejun, Jiang Guohao. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry and metallogenic significance of Wudaogou granodiorite intrusion in Eastern Yanbian, NE China[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 46(8): 2962−2973 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Fu Changliang. 2009. The Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Granitoid from Xiaoxi'nancha in Hunchu Area, Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Ghaderi M, Palin J M, Campbell I H, Sylvester P J. 1999. Rare earth element systematics in scheelite from hydrothermal gold deposits in the Kalgoorlie–Norseman region, western Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 94(3): 423−437. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.94.3.423
[9] Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. 1988. Freezing point depression of NaCl–KCl–H2O[J]. Economic Geology, 83(1): 197−202. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197
[10] Hao Yujie, Ren Yunsheng, Zhao Hualei, Zou Xintong, Chen Cong, Hou Zhaoshuo, Qu Wenjun. 2013. Re–Os isotopic dating of the molybdenite from the Cuihongshan W–Mo polymetallic deposit in Heilongjiang Province and Its geological significance[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 43(6): 1840−1851 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] He Peng, Yan Guangsheng, Zhu Xinyou, Zhang Zhongyi, Wang Yanli, Cheng Xiyin, Li Yongsheng, Zhen Shimin, Du Zezhong, Jia Delong, Gong Xiaodong. 2013. Fluid inclusion study of the Saishitang Cu deposit in Qinghai[J]. China Geology, 40(2): 580−594 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Hoefs J. 2009. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, Sixth Ed. Springer–Verlag[M]. Berlin: Heidelberg, 130–135.
[13] Li Dongjin. 1997. Lithostratigraphy of Jilin Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1–388 (in Chinese).
[14] Li Kekun, Wang Chunlian, Chen Xinli, Wang Guixiang, Shang Pengqiang, Zhang Qingsong, Liu Zengzheng, Han Zhikun, Yan Xiaobo, Jiang Jiyong. 2023. Characteristics of trace and rare earth elements of fluorite ore in Shaowu area, Fujian Province and its indication to ore-forming materials[J]. Geology in China, 50(3): 806–817 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Liu Hanbin, Jin Guishan, Li Junjie, Han Juan, Zhang Jianfeng, Zhangjia, Zhong Fangwen, Guo Dongqiao. 2013. Determination of stable isotope composition in uranium geological samples[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 30(3): 174−180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Lu Huanzhang, Fan Hongrui, Ni Pei. 2004. Fluid Inclusion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1–487(in Chinese).
[17] Mao Yin. 2012. Study on Stable Isotope, Fluid Inclusions and Mineralization of Saishitang Cu–polymetallic Deposit, Qinghai Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 1–67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Meng Qingli, Zhou Yongchang, Chai Sheli. 2001. The Porphyry and Hydrothermal Lode Gold and Copper Deposits in Eastern Yanbian Region of China[M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1–163 (in Chinese).
[19] Qin Zhengwei, Fu Jianming, Xing Guangfu, Cheng Shunbo, Lu Youyue, Zhu Yingxue. 2022. The petrogenetic differences of the Middle–Late Jurassic W-, Sn-, Pb-Zn-Cu-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, South China[J]. Geology in China, 49(2): 518–539 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Ray J S, Ramesh R, Pande K. 1999. Carbon isotopes in Kerguelen plume derived carbonatites: Evidence for recycled inorganic carbon[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 170(3): 205−214. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00112-0
[21] Ren Yunsheng, Junan, Zhao Hualei, Wang Hui, Lu Xiuquan, Wu Changzhi. 2011. Geological characteristics and fluid inclusions of Wudaogou lode scheelite deposit in Eastern Yanbian, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 6(41): 1763−1744 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Ren Yunsheng, Zhao Hualei, Lei En, Wang Hui, Ju Nan, Wu Changzhi. 2010. Trace element and rare earth element geochemistry of the scheelite and ore genesis of the Yangjingou large scheelite deposit in Yanbian area, northeastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(12): 3720−3726 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Roedder E. 1984. Fluid inclusions: Reviews in mineralogy[J]. Mineralogical Society of America, 12: 1−646.
[24] Shao Jielian. 1990. Mineralogy of Gold Ore Exploration[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1–158 (in Chinese).
[25] Sheng Jifu, Chen Zhenghui, Liu Lijun, Ying Rujuan, Huang Fan, Wang Denghong, Wang Jiahuan, Zeng Le. 2015. Outline of metallogeny of tungsten deposits in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(6): 1038−1050 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Sterner S, Michael H, Donald L, Bodnar R J. 1988. Synthetic fluid inclusions. V. Solubility relations in the system NaCl–KCl–H2O under vapor–saturated conditions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(5): 989−1005. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90254-2
[27] Sun Fengyue, Wang Li, Huo Liang, Wang Keyong. 2008. Fluid inclusion study on Wulaga gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province and implications for ore genesis[J]. China Geology, 35(6): 1267−1273 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313–345.
[29] Taylor H P. 1974. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 69(6): 843−883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843
[30] Touret J. 1977. The Significance of Fluid Inclusions in Metamorphic Rocks[M]. Springer Netherlands, 203–227.
[31] Wang Mingyan, Jia Muxin, Xiao Yiwu, Sun Chuan Rao, Li Yanfeng, Jin Jianwen. 2014. Current status and sustainable development strategies of tungsten resources in China[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 4(2): 76−81 (in Chinese).
[32] Wang Zhigang. 2012. Study on Metallogenesis of Mesozoic Endogenetic Metal Deposits in the Eastern Part of Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–181 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wu F Y, Jahn B M, Wilde S, Sun D Y. 2000. Phanerozoic crustal growth: U–Pb and Sr–Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 328(1): 89−113.
[34] Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, Zhang Y B, Grant M L, Wilde S A, Jahn B M. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1−30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
[35] Xiong Dexin, Sun Xiaoming, Shi Guiyong, Wang Shengwei, Gao Jianfeng, Xue Ting. 2006. Trace elements, rare earth elements (REE) and Nd–Sr isotopic compositions in scheelites and their implications for the mineralization in Daping gold mine in Yunnan province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 733−741 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Zhang Chao. 2014. The Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Yanbian Area in the Eastern Segment of Northern Margin of the North China Block[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Zhang Dongliang, Peng Jiantang, Fu Yazhou, Peng Guangxiong. 2012. Rare–earth element geochemistry in Ca–bearing minerals from the Xianghuapu tungsten deposit, Hunan Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 65−74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhang Wenhuai, Chen Ziying. 1993. Fluid Inclusion Geology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1–255 (in Chinese).
[39] Zhao Hualei. 2014. Ore Genesis and Geodynamic Settings of Tungsten Deposits in Eastern Jilin and Heilongjiang Provinces[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1–139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Zhao Hualei, Ren Yunsheng, Junan, Wang Hui, Hou Kejun. 2011. Geochronology and geochemistry of metallogenic intrusion in Baishilazi tungsten deposit of Eastern Yanbian Area, Northeast China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(60): 1726−1736 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] 曹花花. 2010. 珲春地区晚海西期辉长岩–闪长岩的形成时代和地球化学[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–44. [42] 陈聪. 2017. 延边东部晚古生代—中生代构造演化与区域成矿规律[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–202. [43] 陈聪, 任云生, 赵华雷, 杨群, 邹欣桐, 侯可军, 蒋国豪. 2015. 延边东部五道沟花岗闪长岩体的年代学与地球化学特征及其成矿意义[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 46(8): 2962−2973. [44] 付长亮. 2009. 珲春小西南岔地区花岗岩类的时代、地球化学特征与成因[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–61. [45] 郝宇杰, 任云生, 赵华雷, 邹欣桐, 陈聪, 侯召硕, 屈文俊. 2013. 黑龙江省翠宏山钨钼多金属矿床辉钼矿Re–Os同位素定年及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(自然科学版), 43(6): 1840−1851. [46] 何鹏, 严光生, 祝新友, 张忠义, 王艳丽, 程细音, 李永胜, 甄世民, 杜泽忠, 贾德龙, 巩小栋. 2013. 青海赛什塘铜矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 中国地质, 40(2): 580−594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.021 [47] 李东津. 1997. 吉林省岩石地层[M]. 北京: 中国地质大学出版社, 1–388. [48] 栗克坤, 王春连, 陈新立, 王桂香, 商朋强, 张青松, 刘增政, 韩志坤, 闫晓博, 蒋济勇. 2023. 福建邵武地区萤石矿微量、稀土元素特征及对成矿物质指示[J]. 中国地质, 50(3): 806–817. [49] 刘汉彬, 金贵善, 李军杰, 韩娟, 张建锋, 张佳, 钟芳文, 郭东侨. 2013. 铀矿地质样品的稳定同位素组成测试方法[J]. 世界核地质科学, 30(3): 174−180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2013.03.009 [50] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培. 2004. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1–487. [51] 毛寅. 2012. 青海省赛什塘铜多金属矿床稳定同位素、流体包裹体及成矿作用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 1–67. [52] 孟庆丽, 周永昶, 柴社立. 2001. 中国延边东部斑岩–热液脉型铜金矿床[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1–163. [53] 秦拯纬, 付建明, 邢光福, 程顺波, 卢友月, 祝颖雪. 2022. 南岭成矿带中—晚侏罗世成钨、成锡、成铅锌(铜)花岗岩的差异性研究[J]. 中国地质, 49(2): 518–539. [54] 任云生, 鞠楠, 赵华雷, 王辉, 卢秀全, 吴昌志. 2011. 延边东部五道沟脉型白钨矿矿床地质特征及流体包裹体[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(6): 1736−1744. [55] 任云生, 赵华雷, 雷恩, 王辉, 鞠楠, 吴昌志. 2010. 延边杨金沟大型钨矿床白钨矿的微量和稀土元素地球化学特征及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 26(12): 3720−3726. [56] 邵洁涟. 1990. 金矿找矿矿物学[M]. 北京: 中国地质大学出版社, 1–158. [57] 盛继福, 陈郑辉, 刘丽君, 应立娟, 黄凡, 王登红, 王家欢, 曾乐. 2015. 中国钨矿成矿规律概要[J]. 地质学报, 89(6): 1038−1050. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.004 [58] 孙丰月, 王力, 霍亮, 王可勇. 2008. 黑龙江乌拉嘎大型金矿床流体包裹体特征及矿床成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 35(6): 1267−1273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.06.022 [59] 王明燕, 贾木欣, 肖仪武, 孙传尧, 李艳峰, 金建文. 2014. 中国钨矿资源现状及可持续发展对策[J]. 有色金属工程, 4(2): 76−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2014.02.018 [60] 汪志刚. 2012. 吉林东部中生代内生金属矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–181. [61] 熊德信, 孙晓明, 石贵勇, 王生伟, 高建峰, 薛婷. 2006. 云南大坪金矿白钨矿微量元素、稀土元素和Sr–Nd同位素组成特征及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 733−741. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.03.023 [62] 张超. 2014. 华北板块北缘东段延边地区中生代构造演化[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–137. [63] 张东亮, 彭建堂, 符亚洲, 彭光雄. 2012. 湖南香花铺钨矿床含钙矿物的稀土元素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 28(1): 65−74. [64] 张文淮, 陈紫英. 1993. 流体包裹体地质学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1–255. [65] 赵华雷. 2014. 吉黑东部钨矿成因及成矿地球动力学背景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1–139. [66] 赵华雷, 任云生, 鞠楠, 王辉, 侯可军. 2011. 延边白石砬子钨矿床成矿岩体的年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(自然科学版), 41(6): 1726−1736.




 下载:
下载: