-
摘要:
淮河流域人均水资源量为475 m3,不足全国人均水资源量(2100 m3)的1/4,且地下水质量较差,水资源供需矛盾突出,严重制约区域社会经济高质量发展。本研究以水循环理论为指导,利用多期地下水资源调查数据,分析了淮河流域地下水资源量、影响因素及可持续开发利用潜力。分析结果显示:淮河流域水循环过程主要受人工开采影响,导致地下水位持续下降,有效蒸发减弱;淮河流域地下水天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a;流域地下水质量总体一般,平原区孔隙水中Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比不足30%,与历史数据对比,水质呈劣化趋势;流域浅层地下水开采潜力呈现南部大于北部、山区大于平原的特征。淮河流域内,江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区浅层地下水开采潜力较大;豫东、鲁西南局部地区浅层地下水已超采,无开发利用潜力;其余地区浅层地下水盈余量较小。研究结果为区域地下水资源科学开发利用提供了地学依据。
Abstract:The per capita water resources of Huaihe River Basin are 475 cubic meters, which is less than one quarter of the national per capita water resources (2100 m3), and the quality of groundwater is poor. The contradiction between supply and demand of water resources is prominent, which seriously restricts the high-quality development of regional social economy. Based on the theory of water cycle, the study analyzes the groundwater resources, influencing factors, sustainable development and utilization potential in Huaihe River Basin by using the data of multi-stage groundwater resources survey. The results as follows: (1) The water circulation process in Huaihe River Basin is mainly affected by artificial mining, which leads to the continuous decline of groundwater level and the weakening of effective evaporation; The natural resources of groundwater in Huaihe River Basin are 32.697 billion m3 per year; (2) The quality of groundwater in the basin is generally average, and the proportion of Type Ⅰ-Ⅲ water in pore groundwater is less than 30%; At the same time, the water quality is deteriorating compared with the historical data; (3) The exploitation potential characteristics of shallow groundwater in the basin can be summarized as the south is greater than the north and the mountain area is greater than the plain; Jiangsu and Anhui is relatively larger in the Huaihe River Basin; On the contrary, the shallow groundwater in some areas of Eastern Henan and southwestern Shandong has been over exploited and has no potential for development and utilization; Finally, the surplus of shallow groundwater in other areas is small; (4) The results provide a geological basis for the scientific development and utilization of regional groundwater resources.
-
1. 引言
淮河流域是中国中东部地区重要的商品粮主产区及能源资源供应区,流域内交错叠加了淮河生态经济区、山东半岛蓝色经济区、长江三角洲一体化发展区等重要国家战略规划,地理位置极其重要。1970年代以前淮河流域地下水长期处于自然因素主导的补排平衡状态,70年代中后期人工开采量增大,世纪之交达到巅峰并持续了十多年(葛伟亚,2007)。长期过量开采造成了诸多环境地质问题:地下水位持续下降、地面沉降、水质劣化(文冬光等,2012;陆徐荣等,2014),据2020年统计资料,流域浅层地下水位强下降区面积超过30000 km2。过量开采地下水造成的环境地质问题制约着区域社会经济发展,需要深入、持续开展地下水资源评价与开发利用潜力研究,为流域经济可持续发展提供地质数据支撑及解决方案。
流域地下水资源评价及研究工作在欧美起步较早,1930年代美国已经陆续开展了流域尺度地下水资源研究工作,德国中南部开展了持续的地下水要素评价、监测、示踪研究工作。20世纪中叶,以海河流域及淮河流域北部地区为首的流域地下水资源相关研究逐步开展。淮河流域已开展3次地下水资源评价工作,基本查明了不同时序、动态要素制约下的阶段性地下水资源禀赋。基于供水安全目的的流域尺度地下水化学特征调查开展多次,基本查明了流域地下水分布特征及水质现状❶(张炎斋和吴培任,2005;水艳和张炎斋,2009)。针对地下水开采引发的环境地质问题专项调查开展多次,如地面沉降调查、劣质水区地方病环境地质问题调查、苏北沿海环境地质问题综合调查等,阶段性查明流域环境地质问题,并建立了部分水文要素监测设施(陶月赞和岳文君,2003)。总之,淮河流域地下水相关调查及研究积累了大量的数据及成果,为区域水资源可持续开发利用提供了相当丰硕的参考依据,但也存在一定的讨论空间:一是更高生态约束条件下的地下水资源评价和开发潜力研究尚需深入开展工作;二是地下水资源动态平衡特征需要进一步研究。本文数据基于“沙颍河-涡河流域水文地质调查”项目,在第二次全国地下水资源评价数据基础上,利用区内20年来开展的1∶5万水文地质调查成果、蚌埠和郑州水文试验站试验成果、2019年以来的流域专项水文试验成果,校核更新了流域水文地质参数,重点参考2019、2020年水均衡要素数据,在流域新的生态约束条件下开了淮河流域地下水资源特征和开发潜力研究。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 范围
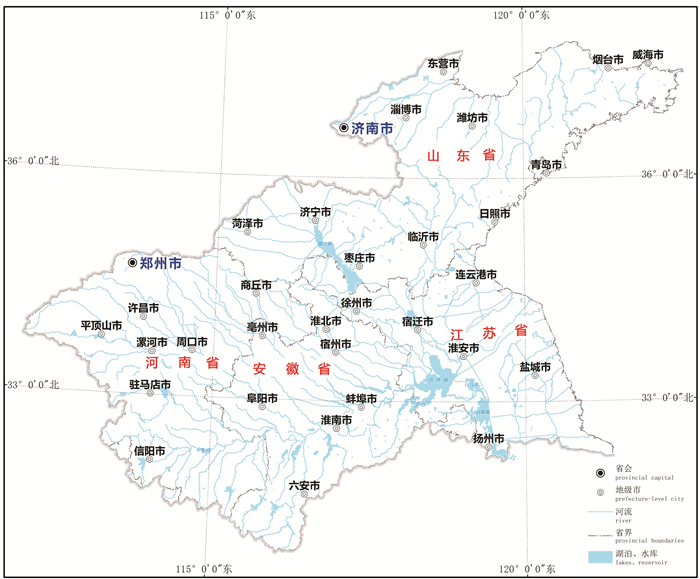
淮河流域(包括山东半岛)位于111°55′~122°45′E、30°55′~38°05′N,面积约33万km2,流域主要覆盖河南、安徽、江苏、山东四省(图 1)。
2.2 降水特征
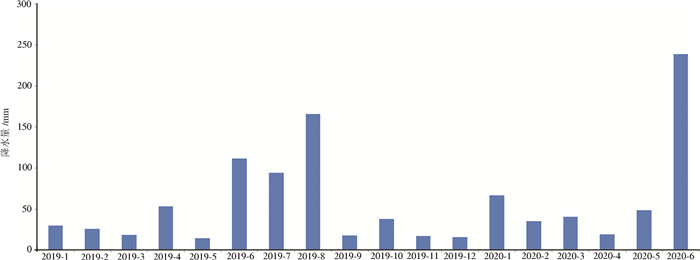
淮河流域处于中国南北气候过渡带,流域内多年平均降水量600~1400 mm,空间上降水量由南向北递减。降雨量的年际、年内分布极不均匀,差异较大,汛期(6—9月)降水占全年降水的50%~70%(图 2)。
2.3 含水系统
淮河流域地下水主要分为松散岩类孔隙水、碳酸盐岩类裂隙岩溶水和基岩裂隙水3种类型。其中分布最广的为松散岩类孔隙水,其次为岩溶水和基岩裂隙水,但有供水意义的主要为孔隙水和岩溶水。
平原区松散岩类孔隙水在区内分布最为广泛,按其埋藏深度可分为浅层地下水和深层地下水。在流域内平原区地表下30~55 m,区域上广泛分布有一层14~20 m厚的黏性土层,因此,传统上大致以地表下50 m为界限,将埋深小于和大于50 m的松散岩类孔隙含水层组分别划分为浅层含水岩组和深层含水岩组(葛伟亚,2006)。
淮河流域上游地区地下水基本是由西北流向东南,南部西部则由西向东流。北部岗状平原区浅层孔隙地下水水位埋深一般大于6 m;北部低缓平原区地下水水位埋深大部分为2~4 m;南部地下水水位埋深大部分小于2 m。浅层孔隙地下水水位主要受降水和蒸发及地表水影响,水位变幅一般为1.5~2.5 m。淮河流域深层地下水整体流向为从山前向平原径流,整体水位稳定,受季节影响较小,在阜阳—太和、亳州等地形成地下水位降落漏斗,江苏省盐城市附近深层地下水位呈逐年上升趋势。
3. 研究方法及数据来源
3.1 评价方法
山区采用径流模数法进行地下水资源评价,平原区采用均衡法进行评价。平原区地下水以孔隙水为主要评价本体。流域内承压孔隙水补给条件艰苛,深层承压孔隙地下水年龄均在25 ka以上(龚建师,2005),目前生态约束条件下,认为该层地下水为不可更新地下水,未做资源评价。
地下水质量评价依据《地下水质量标准》(GB/T14848-2017), 采用单因子综合评价法,对35项常规无机化学指标进行评价。
地下水开采潜力评价参照《地下水潜力评价技术要求》(GWI-D4)开展相关评价,潜力表征参数为开采潜力系数,该系数为可采量与现状开采量的比值,系数≥1.4,表示潜力大,1.2~1.4表示潜力较大,1.0~1.2,表示潜力较小,系数<1.0表示无潜力。
3.2 数据来源
以第二次地下水资源评价数据为基础,汇总域内2000年以来开展的120余幅1∶5万水文地质调查工作成果、城市地质调查成果,参考域内两个水文试验站相关试验成果,结合“沙颍河—涡河流域水文地质调查”项目野外实验,校核更新了流域的降雨入渗系数、含水层导水系数、山丘区地下水径流模数、山前侧向补给系数、弹性释水系数、渠系入渗系数等水文地质参数。
通过收集气象部门数据,汇总更新了流域降水、蒸发数据。
通过收集水利公报数据,结合野外典型断面校核实测数据,融合汇总了流域水文参数及地下水资源开发利用数据。
4. 结果与分析
4.1 水循环要素演变
4.1.1 降水补给要素变化
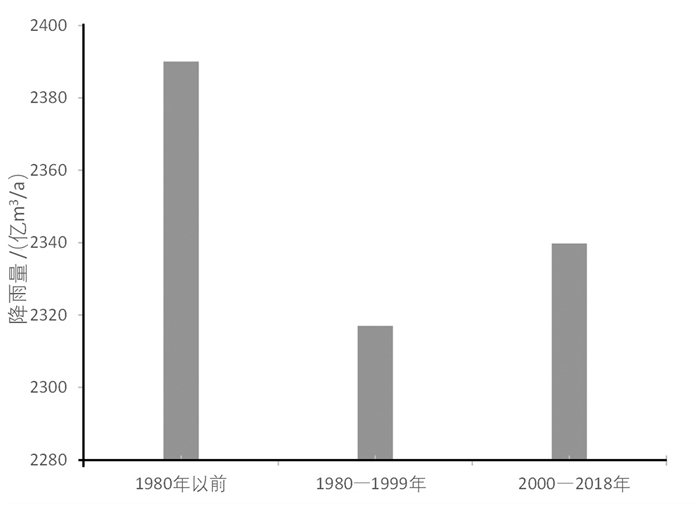
降雨量按照多年平均降雨量统计,统计结果如图 3所示。结果显示,不同阶段淮河流域多年平均降雨量差异不大,1980年以前为2390亿m3/a,1980—1999年为2317亿m3/a,2000—2018年为2339.8亿m3/a。
4.1.2 蒸散发排泄要素变化
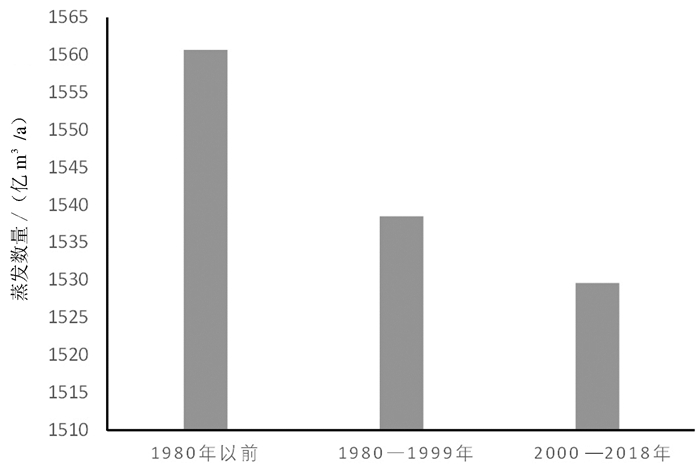
2000年以前的蒸散发量按《淮河流域水污染治理与水资源可持续利用》中给出的蒸散发量进行统计,2000—2018年蒸散发量按照降雨量、产流、入渗、其他排泄量等进行计算(吴祖成,2016;薛阳等,2017)。淮河流域多年平均蒸散发量变化如图 4所示。1980年以前,流域多年平均蒸散发量1560.67亿m3/a,1980—1999年多年平均蒸散发量1538.49亿m3/a,2000—2018年多年平均蒸散发量为1529.6亿m3/a。数值差异不大,但呈持续微弱下降趋势。
4.1.3 人工开采要素变化
淮河流域开发利用地下水历史较早,以开采平原区浅层地下水用于农业灌溉为主。建国初期,只有少量的土井开采地下水用作农灌和居民生活,工业用水开采地下水很少。
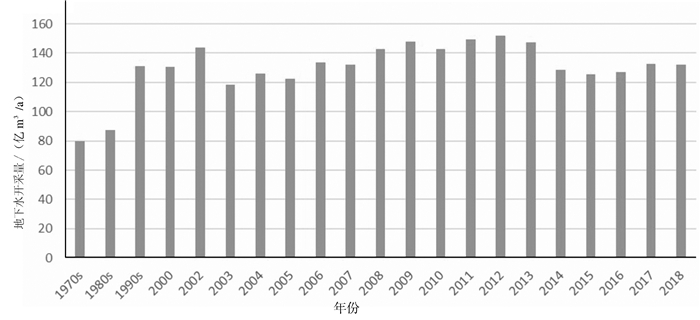
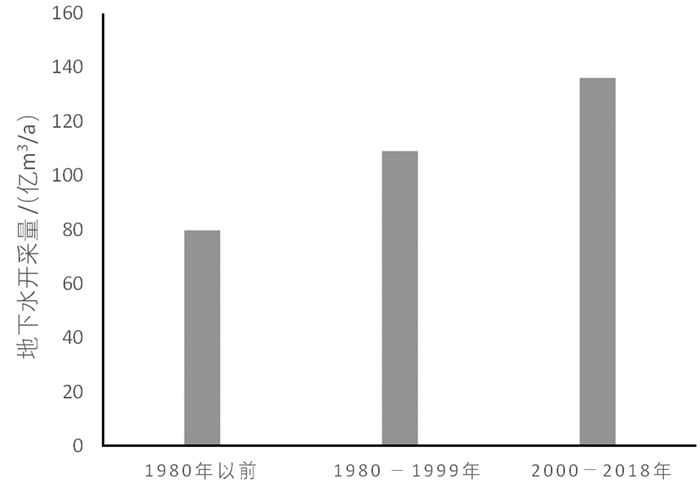
从淮河流域开采量历史变化(图 5)可以看出,30多年来地下水开采量增长迅速。20世纪70年代地下水开采量约79.81亿m3/a,80年代地下水开采量约87.28亿m3/a,90年代地下水开采量约为131.28亿m3/a,到了2000—2004年年均地下水开采量增加到138.03亿m3/a。70年代、80年代开采量变化不大,到了90年代跨越式增长,2000—2018年开采量呈波动稳定状态。通过上述数据,结合流域社会经济发展阶段,以及2000年加大治淮力度等时间节点,可以把淮河流域人工开采地下水历史划为3个典型阶段,即1980年以前,1980—1999年,2000—2018年3个阶段(图 6)。
4.1.4 地下水位变化
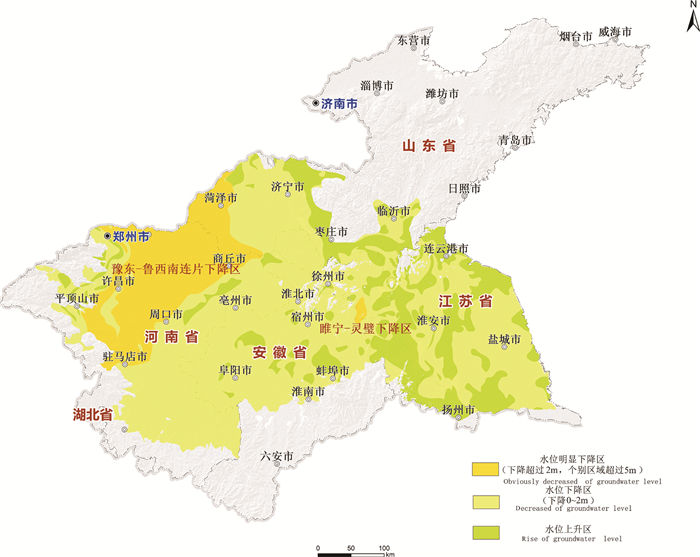
淮河流域地下水循环条件演化的主导因素为人工开采,在流域内人工开采最严重的为豫东平原、鲁西南地区、皖北平原、苏北平原。据2005年及2020年流域地下水位统测数据,淮河流域浅层地下水水位大部分呈下降趋势,15年来浅层地下水明显下降区面积达3.2万km2。
4.2 地下水资源状况
4.2.1 地下水资源评价分区
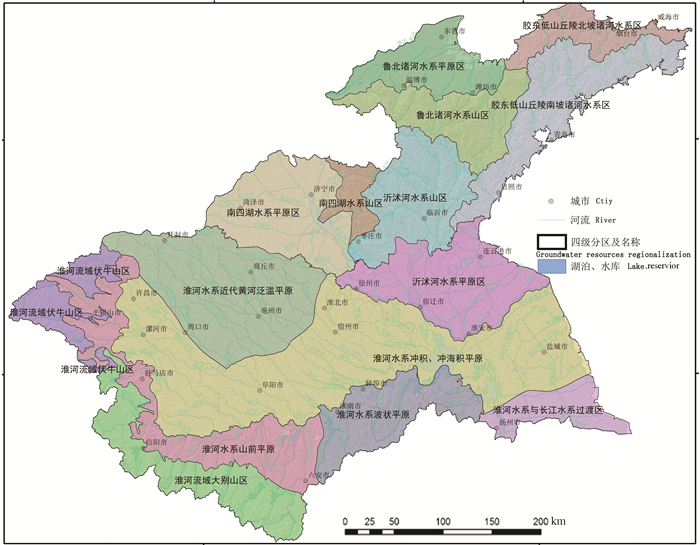
根据统一性、系统性、层次性、继承性原则,结合淮河流域特殊的地理、气象、地质地貌背景,有针对性的对淮河流域进行地下水资源分区。淮河流域可划分为1个一级分区、3个二级分区、6个三级分区、15个四级分区(表 1、图 8)。
表 1 淮河流域水文地质单元划分表Table 1. Hydrogeological unit division of Huaihe River Basin
4.2.2 地下水资源及空间分布
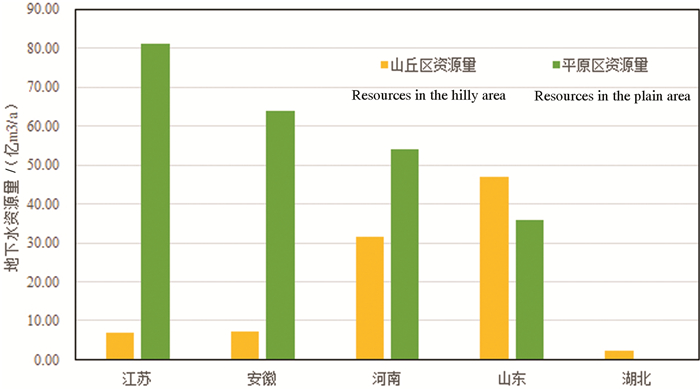
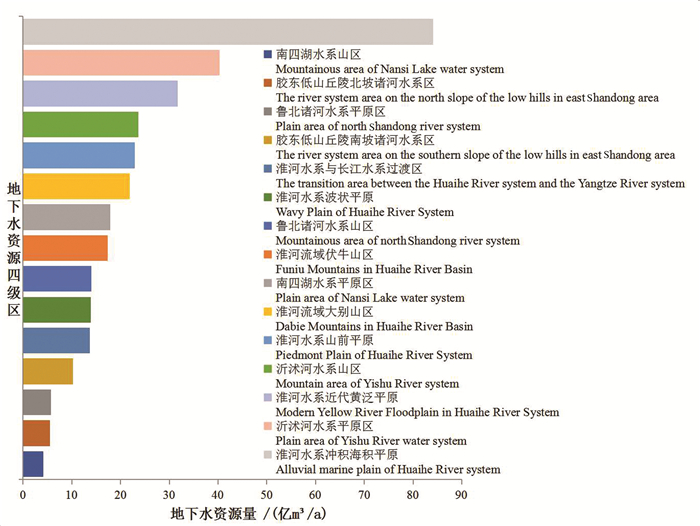
流域浅层天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,其中平原区天然资源量为234.8502亿m3/a,山丘区天然资源量为94.6929亿m3/a,山丘和平原区重复计算量为2.5775亿m3/a。按地下水四级区统计,南四湖水系平原天然资源量为17.91亿m3/a;淮河水系近代黄泛平原区天然资源量为31.68亿m3/a;南四湖水系山区天然资源量为4.11亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系平原区天然资源量为5.69亿m3/a;沂沭河水系平原区天然资源量为40.31亿m3/a;沂沭河水系山区天然资源量为23.61亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵南坡诸河水系区天然资源量为10.20亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵北坡诸河水系区天然资源量为5.56亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系山区天然资源量为14.00亿m3/a;淮河水系波状平原天然资源量为13.86亿m3/a;淮河水系与长江水系过渡区天然资源量为13.73亿m3/a;黄淮冲积、海积平原天然资源量为84.10亿m3/a;淮河流域大别山区天然资源量为21.89亿m3/a;淮河水系山前平原天然资源量为22.89亿m3/a;淮河流域伏牛山区天然资源量为17.41亿m3/a。按省统计,山东天然资源量为82.515亿m3/a;河南天然资源量为83.203亿m3/a;安徽天然资源量为71.134亿m3/a;江苏天然资源量为87.755亿m3/a,湖北浅层水天然资源量为2.359亿m3/a(图 9、图 10)。
4.3 地下水质量现状
利用2019年国家地下水监测工程780个测孔测试数据及2019年区域460组水化学测试数据,基于35个常规无机化学指标,开展流域主要平原地区地下水质量评价。结果显示,淮河流域地下水质量总体一般,浅层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比6.7%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比93.3%,深层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比8.5%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比91.5%。浅层地下水和深层地下水主要影响因子均为铁、锰、硬度等指标,淮北平原、苏北局部地区、豫东鲁西南局部地区深层地下水砷、氟超标严重。
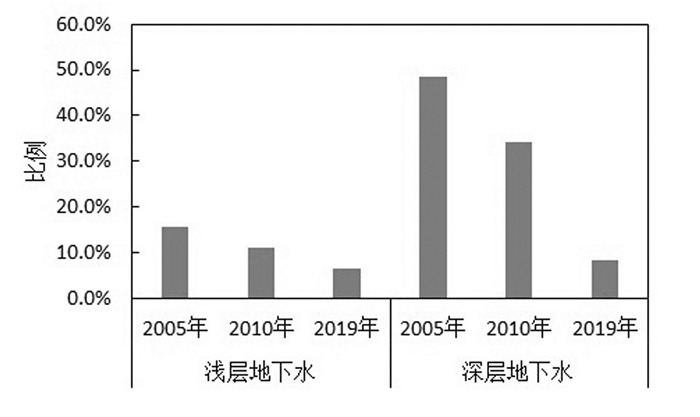
与2005、2010年淮河流域地下水质量评价结果对比,现状浅层地下水质量在经历了2005—2010年显著恶化后,近年在地表水质量总体好转的情况下,仍在趋于恶化,总体超标水比例增加了4.3%,但Ⅴ类水降低了6.2%(图 11)。
深层水超标率从2005年的51.6%到2010年65.9%,近年呈现出显著恶化趋势,2019年超标水比例已上升25.6%,达2005—2010年恶化趋势的1.8倍,且Ⅳ、Ⅴ均呈大幅上升趋势。
4.4 地下水开采潜力
采用开采潜力系数法进行区域地下水开采潜力评价。由于区域深层地下水在新的生态约束条件下无可利用资源量,故现状深层地下水开采区均为无潜力区。
浅层地下水(含基岩裂隙水)开采潜力总体上南部大于北部,山区-平原复合行政区大于纯平原行政区。其中江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区、河南南部地区浅层地下水开采潜力较大,豫东地区、山东大部分地区开采潜力小,郑州、开封、许昌、漯河、商丘、周口、济宁、淄博、菏泽超采严重,已无潜力(表 2)。
表 2 浅层地下水开采潜力状况(108m3/a)Table 2. Exploitation potential of shallow groundwater (108 m3/a)
5. 讨论与建议
淮河流域人均水资源量为475 m3,不足全国人均水资源量(2012年,2100 m3)的1/4,加上水质劣化,使得水资源供需矛盾更加突出。南水北调中线工程对豫东供水、东线工程对苏皖鲁供水一定程度缓解了域内缺水问题,但在新时期高质量发展导向的生态约束条件下,水资源供需形势仍然严峻。且一定程度的人工干预水资源配置造成了水文要素异化反馈,亟待开展相关科学研究。为进一步缓解淮河流域水资源供需矛盾,优化水资源配置问题,提出以下建议:
(1)深入开展流域尺度地下水地表水一体化调查研究,逐步寻求科学途径,解决流域水资源配置现状。目前,流域内重地表水配置、轻地下水参与,如2001—2019年,地表水利用率达65.2%,地下水利用率为53.1%,应合理配置不同时空条件下的地表水、地下水利用占比。
(2)开展劣质水区地下水资源系统调查,提出基于水质安全的可持续供水建议。淮河流域地下水质量问题是困扰流域浅层地下水开发的主要问题,部分地区高氟、高砷、高碘地下水造成的地方病在区内仍有发生,2019年测试数据显示豫东皖北苏北等地浅层地下水样本氟化物含量超标占比26.22%,碘化物超标占比20.64%,豫东皖北苏北等地深层水样本氟化物含量超标率27.92%,碘化物超标47.17%。安全供水需求导向的水资源调查工作需要深入开展。
(3)南水北调东线工程、引江济淮工程在改善北方缺水地区水资源利用问题的同时,也造成了沿线部分受水区水位不稳定变化,由此引起一定生态响应,如土壤盐渍化、水质变化等,需要加强沿线受水影响区水文要素监测工作,为水资源配置精细化管理、生态响应科学问题研究提供支撑。
6. 结论
(1)受人工开采持续增大影响,流域地下水循环特征发生变化,浅层地下水位持续下降,豫东、鲁西南地区2005年以来浅层地下水位下降5 m以上面积超过30000 km2。浅层地下水位下降导致有效蒸发强度变弱,蒸发量持续下降,多年平均有效蒸发强度从2000年前的1538.49 mm降至近期的1529.6 mm。
(2)淮河流域浅层地下水天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,人均171.19亿m3/a,地下水资源相对一般。
(3)淮河流域平原地区地下水总体一般,浅层、深层孔隙水Ⅴ类水占比分别达47.7%、44.9%;与2005年、2010年历史数据相比,水质呈劣化趋势,2019年测试数据显示区域地下水中高氟水、高碘水占比仍在20%以上,深层地下水碘化物超标近半。
(4)浅层地下水开发盈余量总体南多北少、山区多平原少;江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区总体开采潜力大,可采系数均在1.0以上,最大达103.92×108 m3/a,豫东、鲁西南地区开采潜力小,部分地市如漯河、周口、菏泽等地超采严重,已无潜力。
注释
❶叶念军,葛伟亚,龚建师,杨则东,左正金,陆徐荣,徐建国,王献坤,杨小双,彭玉怀,王付军,赵华荣,刘红樱,朱恒华,陆华,杨佩明,徐华,陈秀其,杨磊,程生平,周锴锷,邢怀学,穆倩,朱春芳,陈鸿汉,李炳华. 2012. 淮河流域环境地质调查报告[R]. 南京:中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心.
-
表 1 淮河流域水文地质单元划分表
Table 1 Hydrogeological unit division of Huaihe River Basin

表 2 浅层地下水开采潜力状况(108m3/a)
Table 2 Exploitation potential of shallow groundwater (108 m3/a)

-
Ge Weiya, Ye Nianjun, Gong Jianshi, Yu Junjie, Zuo Zhengjin, Yang Zedong, Huang Jingjun. 2006. The Quaternary aquifer division and character analysis of plain in Huaihe River basin[J]. Resources Survey and Environment, 27(4): 268-276(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ge Weiya, Ye Nianjun, Gong Jianshi, Zuo Zhengjin, Yang Zedong, Lu Xurong. 2007. Rational development and utilization of groundwater resource in the plain of Huaihe Basin[J]. Groundwater, 29(5): 37-40(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU200705013.htm
Gong Jianshi, Ye Nianjun, Gu Weizu, Ha Chengyou, Chen Lezhu, Ge Yawei, Yu Junjie. 2005. A brief analysis of hydrogeochemistry in Huaibei Plain[C]//Collected papers of Groundwater resource research (2005), 646-651(in Chinese).
Jiang Yuehua, Lin Liangjun, Chen Lide, Ni Huayong, Ge Weiya, Cheng Hangxin, Zhai Gangyi, Wang Guiling, Ban Yizhong, Li Yuan, Lei Mingtang, Tan Chengxuan, Su Jingwen, Zhou Quanping, Zhang Taili, Li Yun, Liu Hongying, Peng Ke, Wang Hanmei. 2017. Research on conditions of resources and environment and major geological problems in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1045-1061(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706002.htm
Lu Xurong, Lei Yang, Hua Lu, Gu Xiaoxi. 2014. A tentative discussion on the control factors of Iodine content in phreatic water in Huaihe River Plains of Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Geoscienlica Sinica, 35(2): 211-216(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shui Yan, Zhang Yanzhai. 2009. Investigation and analysis of groundwater quality in Huaibei typical area of Huaihe River Basin[J]. Harnessing the Huaihe River, (12): 13-14(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tao Yuezan, Yue Wenjun. 2003. Problems and suggestions on dynamic monitoring of groundwater in Huaihe River Basin of Anhui Province[J]. Harnessing the Huaihe River, (10): 17-18(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wen Dongguang, Lin Liangjun, Sun Jichao, Zhang Zhaoji, Jiang Yuehua, Ye Nianjun, Fei Yuhong, Qian Yong, Gong Jianshi, Zhou Xun, ZhangYuxi. 2012. Groundwater quality and contamination assessmentin, the main plains of Eastern China[J]. Earth Science, 37(2): 220-228(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201202002
Wu Zucheng. 2016. Application of analytical-equilibrium method in groundwater source Area of Henan Plain in Huaihe River Basin[J]. Ground Water, 38(1): 42-44(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue Yang, Jin Xiaomei, Zhu Xiaoqian. 2017. Variation of evapotranspiration of Ningxia Yellow River economiczone and the validation using water budget method[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 44(3): 27-32(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201703005.htm
Zhang Yanzhai, Wu Peiren. 2005. Water quality investigation and analysis of shallow groundwater in the plain area of Huaihe River Basin[J]. Harnessing the Huaihe River, (12): 8-9(in Chinese with English abstract).
葛伟亚, 叶念军, 龚建师, 于俊杰, 左正金, 杨则东, 黄敬军. 2006. 淮河流域平原区第四系含水层划分及特征分析[J]. 资源调查与环境, 27(4): 268-276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2006.04.004 葛伟亚, 叶念军, 龚建师, 左正金, 杨则东, 陆徐荣. 2007. 淮河流域平原区地下水资源合理开发利用模式研究[J]. 地下水, 29(5): 37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2007.05.012 龚建师, 叶念军, 顾慰祖, 哈承佑, 陈乐柱, 葛伟亚, 于俊杰. 2005. 淮北平原水文地球化学简析[C]//2005年全国地下水资源与环境学术研讨会, 646-651. 姜月华, 林良俊, 陈立德, 倪化勇, 葛伟亚, 成杭新, 翟刚毅, 王贵玲, 班宜忠, 李媛, 雷明堂, 谭成轩, 苏晶文, 周权平, 张泰丽, 李云, 刘红樱, 彭柯, 王寒梅. 2017. 长江经济带资源环境条件与重大地质问题[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1045-1061. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170601&flag=1 陆徐荣, 杨磊, 陆华, 谷小溪. 2014. 江苏平原地区(淮河流域)潜水碘含量控制因素探讨[J]. 地球学报, 35(2): 211-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201402015.htm 水艳, 张炎斋. 2009. 淮河流域淮北典型地区地下水质量调查分析[J]. 治淮, (12): 13-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9243.2009.12.007 陶月赞, 岳文君. 2003. 安徽省淮河流域地下水动态监测存在的问题与改进建议[J]. 治淮, (10): 17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9243.2003.10.011 文冬光, 林良俊, 孙继朝, 张兆吉, 姜月华, 叶念军, 费宇红, 钱永, 龚建师, 周迅, 张玉玺. 2012. 中国东部主要平原地下水质量与污染评价[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 37(2): 220-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201202005.htm 吴祖成. 2016. 解析-均衡法在淮河流域河南平原地下水水源地中的应用[J]. 地下水, 38(1): 42-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.01.013 薛阳, 金晓媚, 朱晓倩. 2017. 宁夏沿黄经济区蒸散量变化特征及水均衡方法验证[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 44(3): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201703005.htm 张炎斋, 吴培任. 2005. 淮河流域平原区浅层地下水水质调查分析[J]. 治淮, (12): 8-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9243.2005.12.004 -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 曹先树,王浩,吴晨晨,曹炎煦,顾雨田. 淮河流域及山东半岛地下水超采原因与管理对策. 水利水电科技进展. 2024(05): 65-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 高瑜,张华,武贵华,杨帆,康晓莉,周俊蓉,武红梅,刘海峰. 云南省新一轮地下水资源评价成果. 中国岩溶. 2024(06): 1248-1260 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑志伟,何刚,张世玉,蒋怀印,符艺文. GRA-解耦模型新型城镇化与生态安全关联评估. 河北环境工程学院学报. 2023(04): 58-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱春芳,龚建师,陶小虎,檀梦皎,周锴锷,王赫生,李亮,叶永红. 淮河流域浅层地下水水化学特征10年对比分析及其环境变迁意义. 华东地质. 2023(03): 282-291 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张胜武,黄超群,李小胜,刘海猛. 淮河生态经济带水生态文明发展水平的时空格局演变及收敛性研究. 长江流域资源与环境. 2023(10): 2158-2172 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王赫生,龚建师,陶小虎,赵贵章,郭鹏哲,周锴锷,焦团理,檀梦皎,朱春芳,许乃政,李亮,叶永红. 淮北平原浅层地下水多年动态变化及监测统测评估. 中国地质. 2022(06): 1778-1791 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: