Quantitative evaluation of shale brittleness based on statistics: Taking shale of Niutitang formation in western Hubei as an example
-
摘要:研究目的
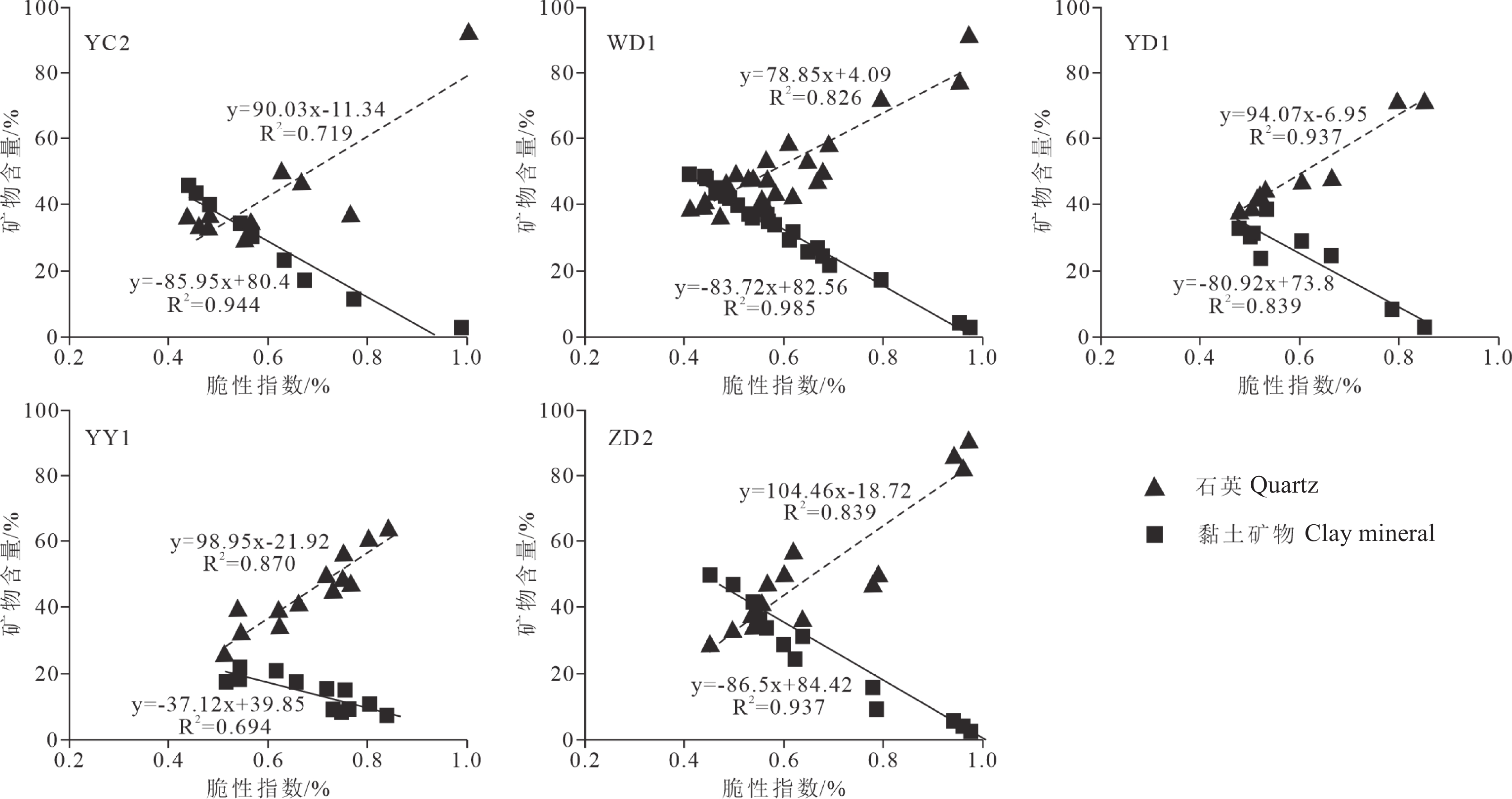
页岩储层的脆性是反映页岩气储集层压裂品质的参数之一,对压裂难易程度和压裂缝网形态有着重要的影响。
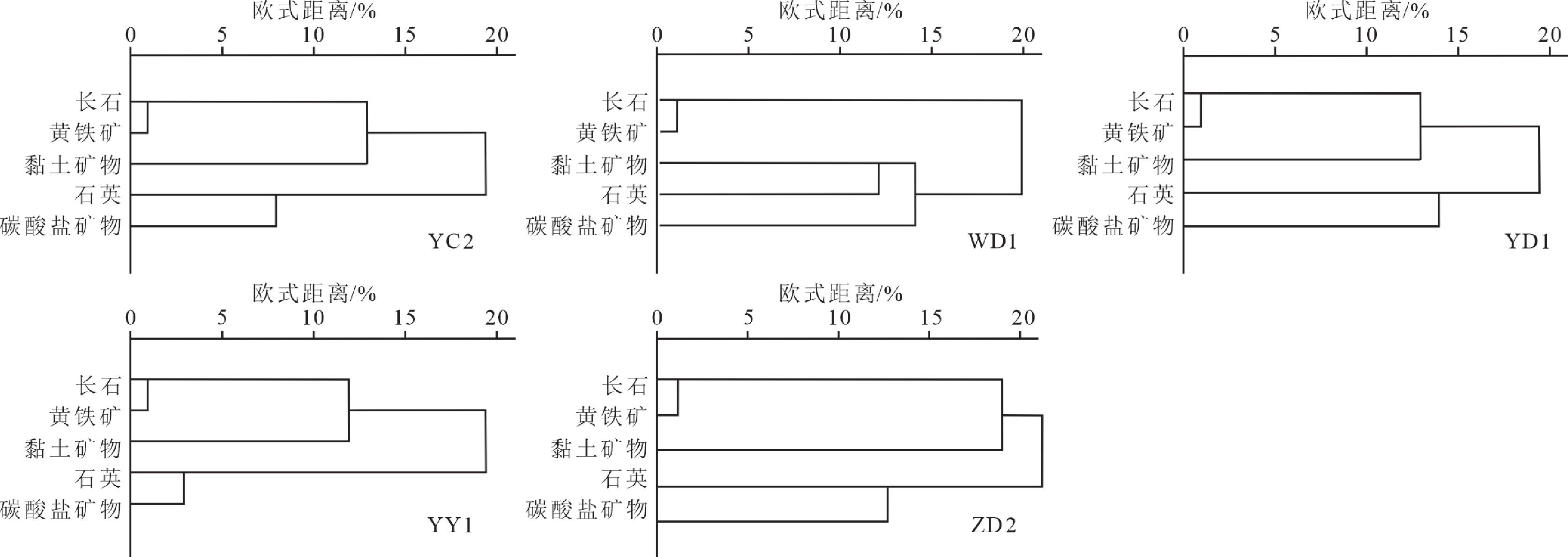
研究方法为准确评价鄂西地区牛蹄塘组页岩储层脆性特征,对鄂西黄陵背斜南翼五口钻井进行了系统采样和全岩矿物及黏土含量测试、主微量元素含量测试、声学力学联测实验等分析测试,利用聚类分析和主成分分析法对页岩脆性进行了定量评价。
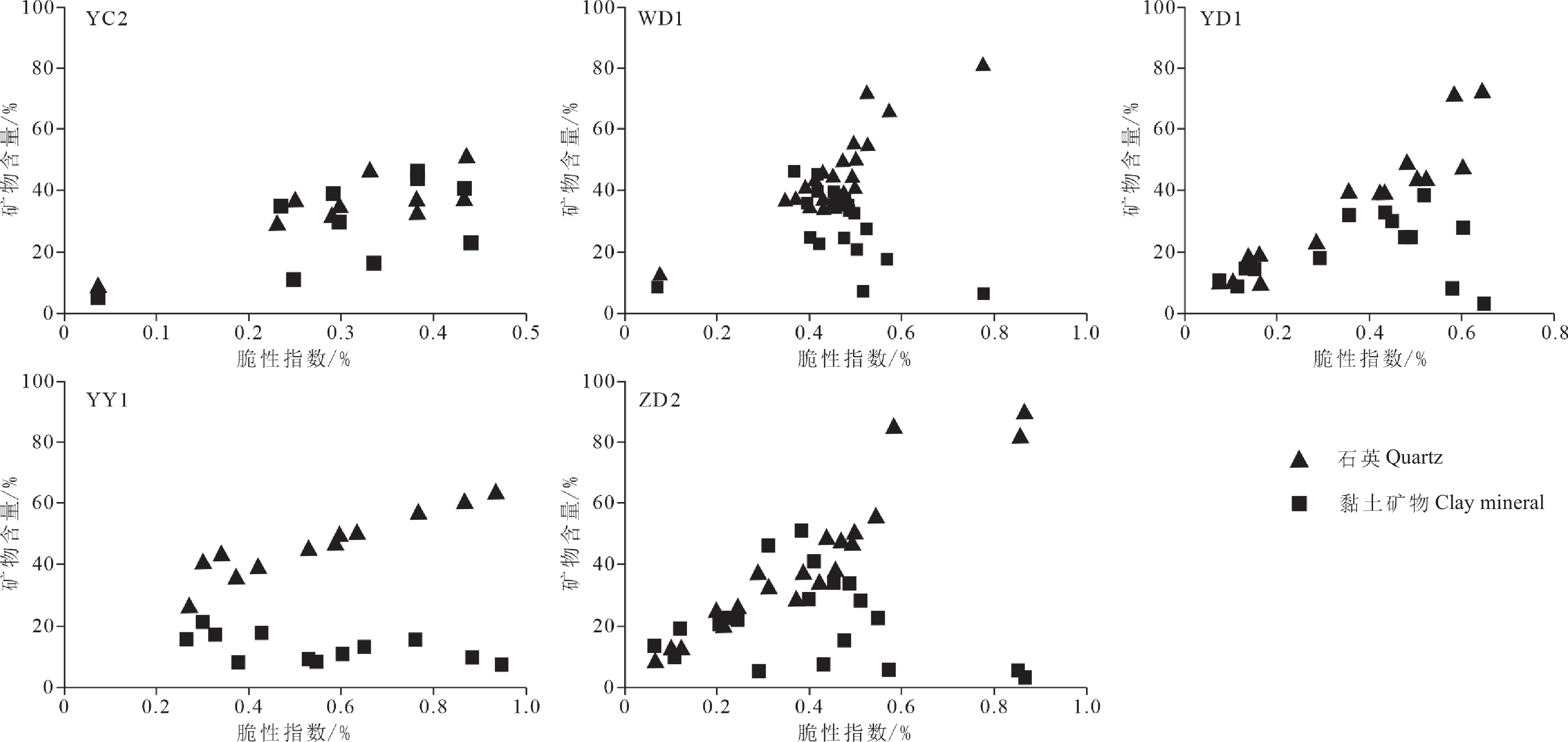
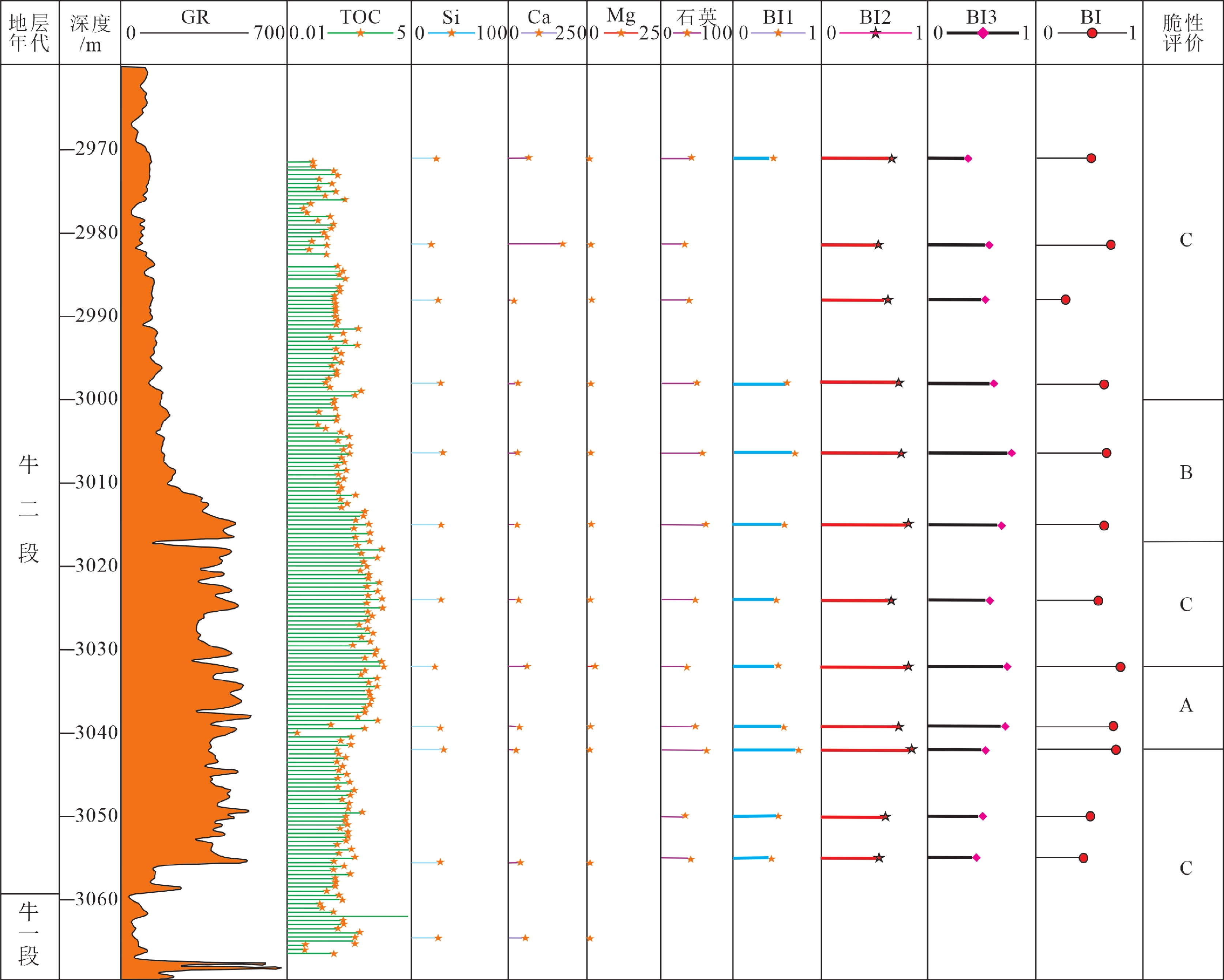
研究结果矿物与岩石脆性密切相关,利用聚类分析方法可以定量表征泥页岩中有效脆性矿物成分和非有效脆性矿物成分;利用主成分分析法建立了基于岩石力学、矿物组分和元素成分的脆性指数综合定量评价公式,克服单一方法的局限性,形成鄂西地区牛蹄塘组页岩层段的脆性指数剖面。
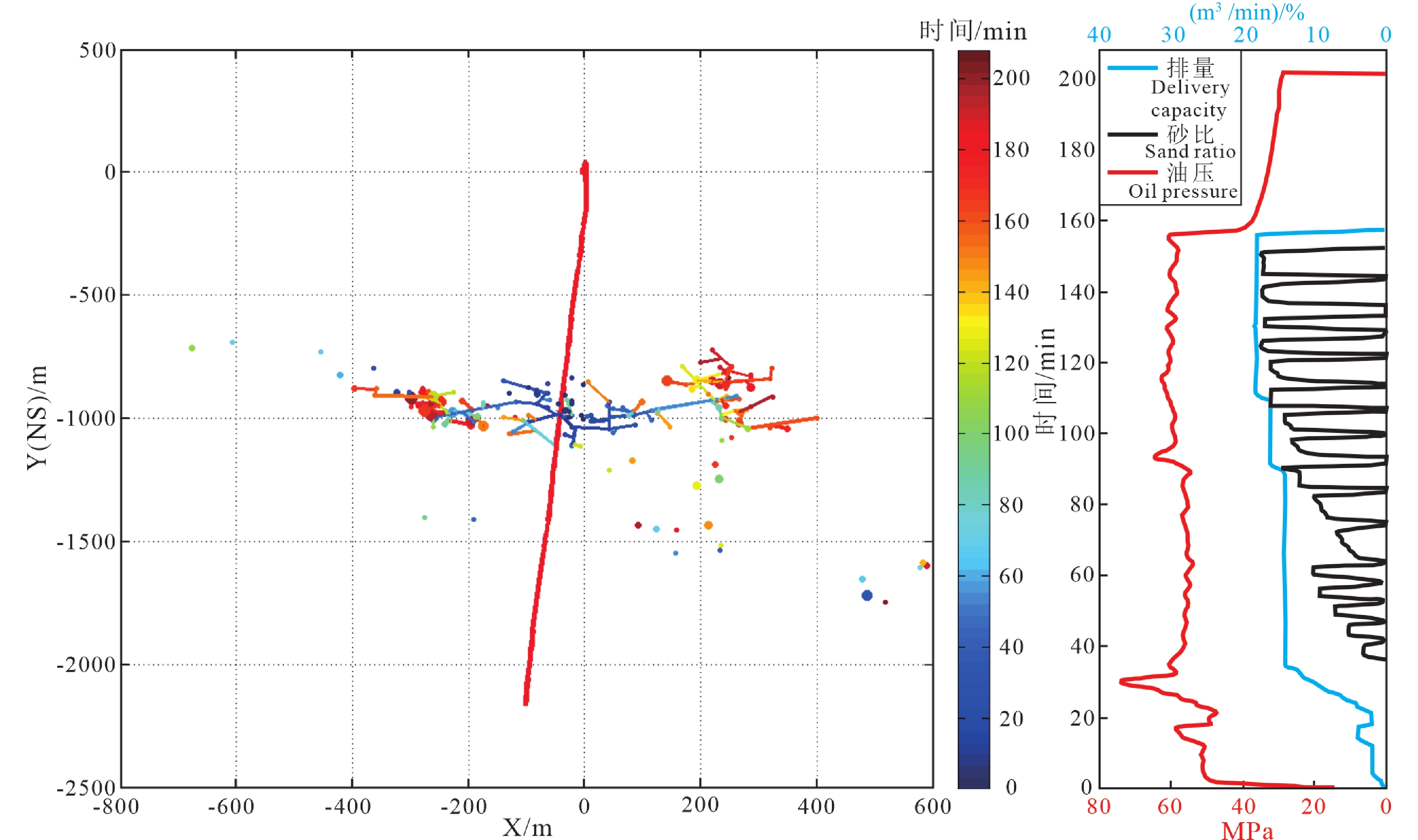
结论微地震监测及压裂施工结果显示,新建立的脆性指数剖面能准确指示页岩的高脆性层段,与压裂结果吻合较好。
创新点:克服单一方法的局限性,利用多种地质因素数学模型建立脆性指数模型;对页岩脆性进行定量评价并在实践中检验。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThe brittleness of shale reservoir is one of the parameters reflecting the fracturing quality of shale gas reservoir, which has an important influence on the degree of difficulty of fracturing and the shape of fracture network.
MethodsIn order to accurately evaluate the brittleness characteristics of Niutitang Formation shale reservoir in western Hubei, systematic sampling, whole rock mineral and clay content test, main and trace element content test, acoustic mechanics joint test and other analytical tests were carried out on five wells in the south wing of Huangling anticline in western Hubei. The quantitative evaluation of shale brittleness was carried out by cluster analysis and principal component analysis.
ResultsThere is a close relationship between minerals and rock brittleness, and the cluster analysis method can quantitatively characterize the effective brittle mineral composition and non−effective brittle mineral composition in shale; The comprehensive quantitative evaluation formula of brittleness index based on rock mechanics, mineral composition and element composition is established by using principal component analysis method, which overcomes the limitation of single method and forms the brittleness index profile of Niutitang Formation shale section in Western Hubei.
ConclusionsThe results of microseismic monitoring and fracturing show that the newly established brittle index profile can accurately indicate the high brittle layer of shale, and the fracturing effect is good.
Highlights:Overcoming the limitation of a single method, a brittleness index model is established by using a variety of geological factor mathematical models. The shale brittleness is quantitatively evaluated and tested in practice.
-
-
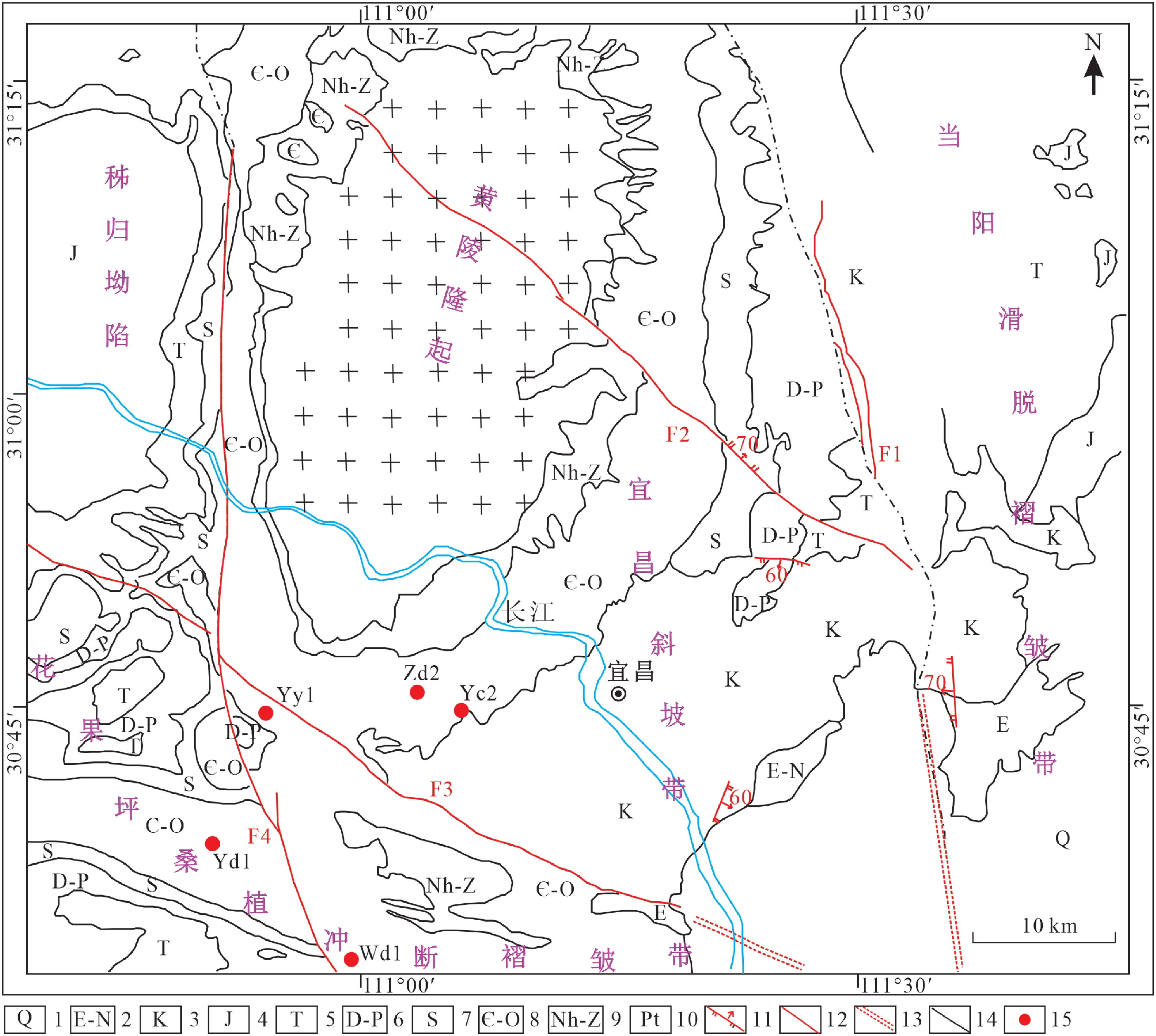
图 1 鄂西黄陵背斜周边地质略图(据陈孝红等, 2018修改)
1—第四系;2—古近系—新近系;3—白垩系;4—侏罗系;5—三叠系;6—泥盆系—二叠系;7—志留系;8—寒武系—奥陶系;9—南华系—震旦系;10—新元古代花岗岩;11—向斜轴线;12—正断层;13—性质不明断层;14—构造单元边界;15—取样钻井
Figure 1. Structural outline of the Huangling anticline in western Hubei and surrounding areas (modified from Chen Xiaohong et al., 2018)
1–Quaternary; 2–Paleogene–Neogene; 3–Cretaceous; 4–Jurassic; 5–Triassic; 6–Devonian–Permian; 7–Silurian; 8–Cambrian–Ordovician; 9–Nanhua–Sinian; 10–Neoproterozoic granite; 11–Syncline axis; 12–Normal fault; 13–Unknown fault; 14–Tectonic unit boundary; 15–Sampling wells
表 1 鄂西地区部分页岩样品矿物组分
Table 1 Mineral compositions of the shale samples in western Hubei
井名 矿物组分体积分数/% 采样深度/m 样品数量 石英 长石 碳酸盐矿物 黄铁矿 黏土矿物 YY1 (26~64)/45.38 (11~23)/17.62 (8~31)/18 (3~7)/4.9 (8~21)/13.92 2936~3064 13 YC2 (29.6~92.1)/43.22 (0~7.3)/4.17 (7.9~40)/16.33 (0~8.8)/6.0 (0~42.9)/28.31 2440~2490 10 YD1 (38.6~71.8)/49.71 (5.6~16)/8.49 (6.3~16)/10.18 (2.2~9.2)/5.99 (3.1~39.2)/25.07 1061~1182 9 ZD2 (29.3~90.6)/52.6 (0~13.3)/5.87 (2.2~22.9)/11.28 (0~7.6)/3.7 (2.9~50.4)/25.36 700~835 13 WD1 (36.4~90.9)/50.28 (0~9.9)/7.34 (0~16.5)/5.46 (0~5.5)/2.2 (2.9~48.9)/33.52 670~1315 25 注:表中矿物组分表示:(最小值~最大值)/平均值。 表 2 鄂西地区部分页岩样品元素含量
Table 2 Element compositions of the shale samples in western Hubei
井名 元素含量/% Si Ca Mg K Al YY1 (20.41~33.42)/28.12 (1.62~17.20)/4.79 (0.46~2.58)/1.07 (1.44~3.01)/2.09 (3.48~9.16)/5.74 YC2 (18.48~39.05)/24.48 (2.66~17.32)/8.89 (0.56~2.45)/1.8 (0~3.62)/2.48 (0.16~9.26)/6.98 YD1 (18.11~29.03)/24.58 (2.09~9.03)/4.34 (0.54~2.52)/1.51 (1.1~2.8)/2.06 (3.67~8.14)/6.37 ZD2 (21.17~36.67)/28.73 (1.21~14.83)/7 (0.51~2.32)/1.77 (1.12~3.22)/2.44 (2.05~9.83)/6.68 WD1 (3.99~33.92)/26.56 (0.26~25.47)/4.64 (0.42~10.46)/2.09 (0.15~3.5)/1.97 (1.02~11.26)/7.22 注:采样深度和样品数量、及元素含量表示方法见表1。 表 3 解释的总方差
Table 3 Total variance explained
成分 初始特征值 提取平方和载入 合计 方差% 累积% 合计 方差% 累积% 1 1.375 45.843 45.843 1.375 45.843 45.843 2 1.317 43.896 89.739 1.317 43.896 89.739 3 0.308 10.261 100 -
[1] Chen Xiaohong, Wang Chuanshang, Liu An, Luo Shengyuan, Li Hai, Wei Kai. 2017. The discovery of the shale gas in the Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation of Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(1): 188−189 (in Chinese).
[2] Chen Xiaohong, Wei Kai, Zhang Baoming, Li Peijun, Li Hai, Liu An, Luo Shengyuan. 2018. Main geological factors controlling shale gas reservior in the Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation in Yichang of Hubei Province as well as its and enrichment patterns[J]. Geology in China, 45(2): 207−226 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Cong Ping, Yan Jianping, Jing Cui, Zhang Jiahao, Tang Mingjun, Wang Jun, Geng Bin, Wang Min, Chao Jing. 2021. Logging evaluation and distribution characteristics of fracturing grade in shale gas reservoir: a case study from Wufeng Formation and Longmaxi Formation in X area, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic reservoirs, 33(3): 177−188 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Dashtian H, Jafari G R, Sahimi M. 2011. Scaling, multifractality, and long–range correlations in well log data of largescale porous media[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 390(11): 2096−2111. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.01.010
[5] Ge M N, Chen K, Chen X L, Wang C, Bao S J. 2020. The influence factors of gas–bearing and geological characteristics of Niutitang Formation shale in the southern margin of Xuefeng Mountain ancient uplift: A case of Well Huangdi 1[J]. China Geology, 3(4): 533−544. doi: 10.31035/cg2020072
[6] He Xiang, Li Qun. 2020. Quantitative definition and evaluation of brittle minerals in shale based on statistics: taking shale of Wufeng–Longmaxi Formationin Sichuan Basin and its peripheral area as an Example[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 35(2): 42−49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] He Xiaoqun. 2004. Multivariate Statistical Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Renmin University Press (in Chinese).
[8] Jarvie D M, Hill R, Jruble T E. 2007. Unconventional shale gas systems the Mississippian Bamett Shale of northcentral Texas as one model for thermogenic shale gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 91(4): 475−499. doi: 10.1306/12190606068
[9] Jin X C, Shah S N, Roegiers J C. 2015. Fracability evaluation in shale reservoirs: An integrated petrophysics and geomechanics approach[J]. SPE Journal, 20(3): 518−526. doi: 10.2118/168589-PA
[10] Lai Fuqiang, Luo Han, Gong Dajian, Xia Weixu, Li Fei. 2018. New evaluation model for brittle index of shale reservoir: A case study of Niutitang formation shale reservoir in Guizhou province[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 33(6): 2358−2367 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Li Haohan, Song Teng, Chen Ke, Lin Tuo, Jin Chunshuang, Meng Fanyang, Wang Peng, Zhang Yanlin. 2017. The discovery of shale gas from Sinian Formation at ZD–2 well in western Hubei[J]. Geology in China, 44(4): 812−813 (in Chinese).
[12] Niu Qiang, Zeng Jianhui, Wang Xin, Zhou Kaifu, Li Xiangfeng, Sun Peng. 2014. Application of X–ray element logging to shale brittleness evaluation in Shengli oil & field[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 21(1): 24−27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Qin Xiaoyan, Wang Zhenliang, Yu Hongyan, Cheng Hao, Lei Yuhong, Luo Xiaorong, Zhang Lixia, Jiang Chengfu, Gao Chao. 2016. Geophysical well logging in brittleness evaluation based on rock mechanics characteristic: A case study from the member 7 shale of Yanchang Formation in southeast Ordos Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 31(2): 762−769 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Rickman R, Mullen M, Petre, E. 2008. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: all shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale[R]. SPE115258.
[15] Sun Honghua, Jiang Weizhai, Meng Qingfeng, Fan Wei, Xu Hao, Zhang Mingyang, Zhao Yan, Wang Candanting. 2020. Method of accurately evaluating the brittleness of marine shale by elementary composition[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 31(3): 1−7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Sun Jianmeng, Han Zhilei, Qin Ruibai, Zhang Jinyan. 2015. Log evaluation method of fracturing performance in tight gas reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(1): 74−80 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Tang Ying, Xing Yun, Li Lezhong, Zhang Binhai, Jiang Shixin. 2012. Influence factors and evaluation methods of the gas fracability[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 356−363 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Wang Jianbo, Feng Minggang, Yan Wei, Liu Shuai. 2016. Influence factors and evaluation methods for shale reservoir fracability in Jiaoshiba Area[J]. Fault Block Oil & Gas Field, 23(2): 216−220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Wang Ruyue, Gong Dajian, Ding Wenlong, Leng Jigao, Yin Shuai, Wang Xinghua, Sun Yaxiong. 2016. Brittleness evaluation of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in the Upper Yangtze region: A case study in the Cengong block, Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1): 87−95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Wang Shengjian, Ren Shoumai, Zhou Zhi, Wu Liyan, Guo Tianxu, Liu Yimin, Hou Qidong. 2020. Discussion on petrophysical evaluation of shale gas reservoir in the second Member of Sinian Doushantuo Formation in Western Hubei Province, South China[J]. Geology in China, 47(1): 133−143 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Wen Tao, Zhang Xin, Sun Jinshan, Jia Yongsheng, Lang Min, Jia Wenjun, Li Decheng, Sun Lixia, Tang Mingjun. 2020. Brittle evaluation based on energy evolution at pre–peak and post–peak stage[J]. Earth Science, 46(9): 3385−3396 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Pan X P, Zhang G Z, Chen J J. 2020. The construction of shale rock physics model and brittleness prediction for high porosity shale gas bearing reservoir[J]. Petroleum Science, 17: 658−670. doi: 10.1007/s12182-020-00432-2
[23] Xue Wei. 2001. Statistical Analysis and Application of SPSS[M]. Beijing: China People's Publishing House (in Chinese).
[24] Zhai Gangyi, Bao Shujing, Wang Yufang, Chen Ke, Wang Shengjian, Zhou Zhi, Song Teng, Li Haohao. 2017. Reservoir accumulation model at the edge of palaeohigh and significant discovery of shale gas in Yichang area, Hubei province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(4): 441−447 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Zhai Gangyi, Wang Yufang, Liu Guoheng, Lu Yongchao, He Sheng, Zhou Zhi, Li Juan, Zhang Yunxiao. 2020. Accumulation model of the Sinian–Cambrian shale gas in western Hubei Province, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(5): 696−713 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Zhai Wenbao, Li Jun, Zhou Yingcao, Liu Gonghui, Huang Tao, Song Xuefeng. 2018. New evaluation method of shale reservoir fracability based on logging data[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 30(3): 112−123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Zhang Wentong, Dong Wei. 2013. Advanced Course of SPSS Statistical Analysis[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press (in Chinese).
[28] 陈孝红, 王传尚, 刘安, 罗胜元, 李海, 危凯. 2017. 湖北宜昌地区寒武系水井沱组探获页岩气[J]. 中国地质, 44(1): 188−189. doi: 10.12029/gc20170113 [29] 陈孝红, 危凯, 张保民, 李培军, 李海, 刘安, 罗胜元. 2018. 湖北宜昌寒武系水井沱组页岩气藏主控地质因素和富集模式[J]. 中国地质, 45(2): 207−226. doi: 10.12029/gc20180201 [30] 丛平, 闫建平, 井翠, 张家浩, 唐洪明, 王军, 耿斌, 王敏, 晁静. 2021. 页岩气储层可压裂性级别测井评价及展布特征—以川南X地区五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 33(3): 177−188. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210319 [31] 何翔, 李群. 2020. 基于统计学页岩脆性矿物定量界定及评价—以四川盆地及其周缘五峰—龙马溪组页岩为例[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 35(2): 42−49. [32] 何晓群. 2004. 多元统计分析[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社. [33] 赖富强, 罗涵, 龚大建, 夏炜旭, 李飞. 2018. 一种新的页岩气储层脆性指数评价模型研究—以贵州下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩储层为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 33(6): 2358−2367. [34] 李浩涵, 宋腾, 陈科, 林拓, 金春爽, 孟凡洋, 王鹏, 张焱林. 2017. 鄂西地区(秭地2井)震旦纪地层发现页岩气[J]. 中国地质, 44(4): 812−813. [35] 牛强, 曾溅辉, 王鑫, 周开富, 李向峰, 孙鹏. 2014. X射线元素录井技术在胜利油区泥页岩脆性评价中的应用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 21(1): 24−27. [36] 秦晓艳, 王震亮, 于红岩, 程昊, 雷裕红, 罗晓容, 张丽霞, 姜呈馥, 高潮. 2016. 基于岩石力学特征的陆相泥页岩脆性地球物理测井评价—以鄂尔多斯盆地东南部下寺湾地区延长组长7段为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 31(2): 762−769. [37] 孙红华, 姜维寨, 孟庆峰, 范伟, 徐皓, 张明扬, 赵岩, 王灿丹婷. 2020. 利用元素成分准确评价海相页岩脆性的方法[J]. 录井工程, 31(3): 1−7. [38] 孙建孟, 韩志磊, 秦瑞宝, 张晋言. 2015. 致密气储层可压裂性测井评价方法[J]. 石油学报, 36(1): 74−80. [39] 唐颖, 邢云, 李乐忠, 张滨海, 蒋时馨. 2012. 页岩储层可压裂性影响因素及评价方法[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 356−363. [40] 王建波, 冯明刚, 严伟, 刘帅. 2016. 焦石坝地区页岩储层可压裂性影响因素及计算方法[J]. 断块油气田, 23(2): 216−220. [41] 王濡岳, 龚大建, 丁文龙, 冷济高, 尹帅, 王兴华, 孙雅雄. 2016. 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩储层脆性评价—以贵州岑巩区块为例[J]. 地学前缘, 23(1): 87−95. [42] 王胜建, 任收麦, 周志, 吴丽艳, 郭天旭, 刘一珉, 侯啓东. 2020. 鄂西地区震旦系陡山沱组二段页岩气储层测井评价初探[J]. 中国地质, 47(1): 133−143. [43] 温韬, 张馨, 孙金山, 贾永胜, 郎珉, 贾文君, 李德成, 孙莉霞, 唐辉明. 2020. 基于峰前和峰后能量演化特征的岩石脆性评价[J]. 地球科学, 46(9): 3385−3396. [44] 薛薇. 2001. 统计分析与SPSS的应用[M]. 北京: 中国人民出版社. [45] 翟刚毅, 包书景, 王玉芳, 陈科, 王胜建, 周志, 宋腾, 李浩涵. 2017. 古隆起边缘成藏模式与湖北宜昌页岩气重大发现[J]. 地球学报, 38(4): 441−447. [46] 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 刘国恒, 陆永潮, 何生, 周志, 李娟, 张云枭. 2020. 鄂西地区震旦系–寒武系页岩气成藏模式[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(5): 696−713. [47] 翟文宝, 李军, 周英操, 柳贡慧, 黄涛, 宋学锋. 2018. 基于测井资料的页岩储层可压裂性评价新方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 30(3): 112−123. [48] 张文彤, 董伟. 2013. SPSS 统计分析高级教程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社.



 下载:
下载: